

MLA 9th Edition Formatting
A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Formatting your paper in MLA style can feel like a pretty daunting task . In this post, we’ll show you exactly how to set up your paper for MLA (9th edition), as quickly and easily as possible. We’ll also share our popular free MLA template , to help you fast-track your writing.
Overview: MLA 9th Edition Formatting
- Structure and layout
- General page setup
- The opening section
- The main body
- Works cited (reference list)
- Free MLA 9 template
MLA Structure and Layout
Let’s start by looking at the overall structure of a typical student paper formatted for MLA 9th edition, before diving into the details of each section. For the most part, MLA papers follow a standardised structure, consisting of the following parts:
The opening section : While MLA doesn’t require a dedicated title page (unlike APA ), it does require an opening section that details some important information about yourself, your university and the paper itself.
The main body : The main body begins directly after the opening section on the first page. This is the “heart” of your paper and there are a very specific requirements regarding how you present and format this content.
The appendix (or appendices): While using an appendix in a student paper is relatively uncommon, you’ll place this section directly after the main body section, if required by your university.
The “Works Cited” list : This section is equivalent to what we’d usually call a references page and it’s where you’ll detail all the reference information corresponding to the in-text citations in the main body of your paper.
These four sections form the standard structure and order of a student paper using MLA 9th edition. As we mentioned, not all sections are always required , so be sure to double check what your university expects from you before submitting. Also, it’s always a good idea to ask your university if they have any style requirements in addition to the standard MLA specification.
Now that we’ve got a big-picture view of the typical paper structure, let’s look at the specific formatting requirements for each of these sections.
Generic Page Setup
Before you jump into writing up your paper, you’ll first need to set up your document to align with MLA’s generic page requirements. Alternatively, you can download our MLA paper template (which comes fully preformatted).
MLA 9th edition requires a 1-inch margin on all sides , for all pages. That said, if you’re writing a dissertation, thesis or any document that will ultimately be printed and bound, your university will likely require a larger left margin to accommodate for physical binding.
Fonts & sizing
MLA does not require that you use any specific font, but we do recommend sticking to the tried and tested , well-accepted fonts. For example, you might consider using one of the following:
- Sans serif fonts : Calibri (11), Arial (11), or Lucida Sans Unicode (10)
- Serif fonts : Times New Roman (12), Georgia (11), or Computer Modern (10)
Whichever font you opt for, be sure to use it consistently throughout your paper . Don’t chop and change, or use different fonts for different parts of the document (e.g., different fonts for the body text and the headings). Also, keep in mind that while MLA does not have a specific font requirement, your university may have its own preference or requirement. So, be sure to check with them beforehand regarding any additional specifications they may have.
In general, all text throughout your document needs to be left-aligned and should not be justified (i.e., leave an uneven right edge). You might consider using a different alignment for section headings, but in general, it’s best to keep things simple .
Line spacing
MLA 9th edition requires double line spacing throughout the document . There should also be no extra space before and after paragraphs . This applies to all sections of the paper, including the “Works Cited” page (more on this later).
Page header
Last but not least, you’ll need to set up a running header for your document. This should contain your last name, followed by the page number. Both of these should be positioned in the top right corner of all pages (even the first page). On a related note, there’s no need for you to include any footer content unless your university specifically requests it.
Now that we’ve looked at the generic formatting considerations, let’s dive into the specific requirements for each section of your paper.
The Opening Section
While MLA-formatted papers typically don’t require a title page, there are very specific requirements regarding the opening section of the first page .
Here’s how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition.
- On the first line, write your full name (flush left)
- On a new line, write your professor or instructor’s full name
- On a new line, write the course code and course name
- On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
- On a new line, write the full title of your paper , centre-aligned and using title case (consider using a title case converter if you’re not familiar with this)
- On a new line, begin your body content
All of the above should be in plain, unformatted font – in other words, you don’t need to apply any boldfacing, underlining , etc. That said, you should use italics whenever you’re writing out the titles of other works (for example, titles of books or articles).
To make it all a little more tangible, below is an example of a first page formatted according to the MLA specifications that we just covered.

The Main Body
While the formatting requirements for the body section are relatively light for MLA (at least when compared to APA ), there are still quite a few important things to pay attention to. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
Each of your paragraphs needs to start on a new line , and the first sentence of each paragraph requires a half-inch indent (while the rest of the paragraph is flush left aligned). Note that each paragraph simply starts on a new line and doesn’t require an additional blank line.
MLA 9th edition is fairly flexible in terms of heading formatting. There is no specified formatting, so you can decide what works best for you. However, there are still a few basic rules you need to follow:
- All your headings should be written in title case – never use all caps
- There should be no period following a heading
- Each heading level needs to be uniquely formatted and easily distinguishable from other levels (for example, a distinct difference in terms of boldfacing, underlining or italicisation)
- You can have as many heading levels as you need, but each level must have at least two instances
Abbreviations
When using abbreviations, you’ll need to make sure that you’re using the MLA version of the abbreviation . Below we’ve listed a few common ones you should be aware of:
- Appendix: app.
- Circa: c. or ca.
- Chapter: ch.
- Column: col.
- Definition: def.
- Department: dept.
- Example: e.g.
- Edition: ed.
- Figure: fig.
- Foreword: fwd.
- That is: i.e.
- Journal: jour.
- Library: lib.
- Manuscript(s): MS
- Number: no.
- Quoted in: qtd. in
- Revised: rev.
- Section: sec. or sect.
- Series: ser.
- Translation: trans.
- Version: vers.
- Variant: var.
- Volume: vol.
If you’re interested, you can find a more comprehensive list here . Alternatively, if you have access to the MLA 9th edition handbook, you can find the full list in the first appendix.

In-text citations
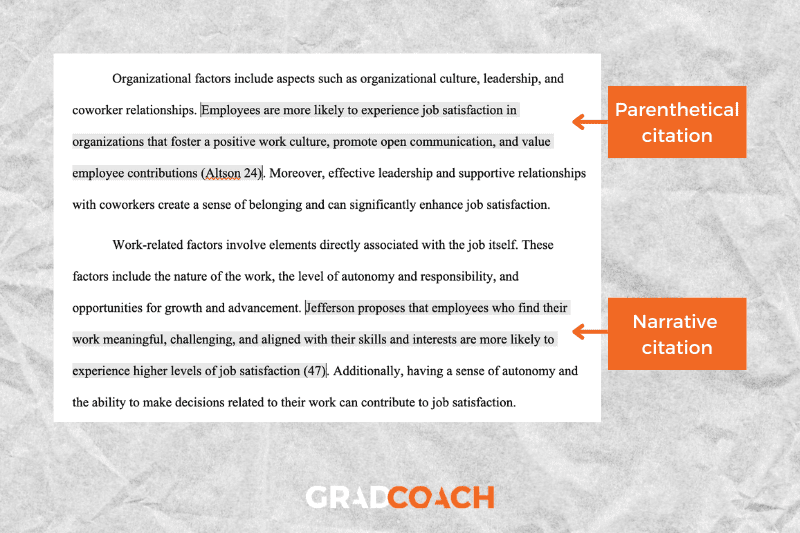
MLA 9 has a very specific set of requirements regarding how to cite your sources within the body of your paper. Here are some of the most important things to help you get started with MLA citations.
Author-page number system: in-text citations consist of (at a minimum) the lead author’s last name, followed by the page number of the paragraph you are citing. There is no comma between the two components (only a space).
Types of citations: MLA allows two types of in-text citations: parenthetical and narrative . Parenthetical citations feature the author and page number in parentheses (brackets) at the end of the respective sentence. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen 13).
Narrative citations, on the other hand, weave the author’s name into the flow of the sentence and then present the publication date in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Here’s an example:
Jansen states that MLA 9th edition is easy for students to grasp if they visit the Grad Coach blog (13).
In general, it’s a good idea to utilise a mix of both in your writing. Narrative citations are particularly useful when you want to highlight or contrast authors or their viewpoints, while parenthetical citations are useful when you want to strengthen your own academic voice. In other words, both formats have their respective strengths and weaknesses, so try to use citation format strategically in your writing.
Quotations: when quoting text verbatim from a source, there is no need to do anything differently in terms of the citation itself, but do remember to wrap the verbatim text in quotation marks. Here’s an example:
Jansen proposes that MLA 9th edition is “easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog” (13).
Multiple authors: when citing resources that were authored by three or more people, you only need to list the lead author, followed by “et al.”. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen et al. 13).
Below are a few more examples from our free MLA template .
Please keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list of all the MLA 9th edition citation-related requirements – just a shortlist of the most commonly relevant ones. If you’d like to learn more, consult the MLA handbook .
The Works Cited (Reference List)
The final section that you’ll need to pay close attention to is the “Works Cited” page, which should contain a list of reference information for all the sources cited in the body of the paper. Again, MLA has a quite a meaty set of specifications regarding the content and formatting of this list, but we’ll cover the basics here to get your started on the right foot.
Basic setup
Your reference list needs to start on a new page and should be titled “Works Cited”. The title should be unformatted and centred . The reference list should then start on the next line. As with the rest of your document, you should use double line spacing throughout.
When it comes to the reference list itself, you’ll need to keep the following in mind:
- All the sources that you cited in the body of your document should feature in the reference list. Make sure that every citation is accounted for .
- The references should be ordered alphabetically , according to the lead author’s last name .
- The exact information required within each entry depends on the type of content being referenced (e.g., a journal article, web page, etc.)
- Components that may need to feature (other than the author) include the title of the source, the title of the container, other contributors, the article version or number, the publisher, the publication date, and the location.
- All references should be left-aligned and should use a hanging indent – i.e., the second line of any given reference (if it has one) should be indented a half inch.
We have to stress that these are just the basics. MLA 9th edition requires that your references be structured and formatted in a very specific way , depending on the type of resource. If you plan to draft your reference list manually, it’s important to consult your university’s style guide or the MLA manual itself. This leads us to our next point…
In general, it’s a bad idea to write your reference list manually . Given the incredibly high level of intricacy involved, it’s highly likely that you’ll make mistakes if you try to craft this section yourself. A better solution is to use (free) reference management software such as Mendeley or Zotero . Either of these will take care of the formatting and content for you, and they’ll do a much more accurate job of it too.
If you’re not familiar with any sort of reference management software, be sure to check out our easy-to-follow Mendeley explainer video below.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve provided a primer covering how to format your paper according to MLA 9th edition. To recap, we’ve looked at the following:
- The structure and layout
- The general page setup
- The “Works Cited” page (reference list)
Remember to always check your university’s style guide to familiarise yourself with any additional requirements they may. Also, if your university has specified anything that contrasts what we’ve discussed here, please do follow their guidance .
If you need any help formatting your paper for MLA 9, take a look at our “done for you” language editing and proofreading service . Simply send us your document and we’ll take care of all the MLA formatting intracies on your behalf.
Very well recounted!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Line Spacing & Margins
Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper.
Leave 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and each side.
Indent the first line of each paragraph half an inch from the left margin.
Quotes longer than 4 lines should be written as a block of text a half an inch from the left margin.
Heading and Title
An MLA research paper does not need a title page, but your instructor may require one. If no instructions are given, follow the MLA guidelines below:
Type the following one inch from the top of the first page, flush with the left margin (double spacing throughout).
Your Instructor's Name
Course Number or Name
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange
Indent the next line and begin typing your text.
Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The page numbers will be one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. If your instructor prefers no page number on the first page, begin numbering from 2 on the second page.
Sample Papers from MLA
There are sample papers available in the MLA Style Center. Check them out to see the correct formatting.
Styling Headings and Subheadings
According to the MLA Style Center website, writers should avoid using headings in shorter papers. If you are writing a longer research paper, you may want to include headings and subheadings to help organize the sections of your paper. Advice from the MLA Style Center :
"Levels
The paper or chapter title is the first level of heading, and it must be the most prominent.
Headings should be styled in descending order of prominence. After the first level, the other headings are subheadings—that is, they are subordinate. Font styling and size are used to signal prominence. In general, a boldface, larger font indicates prominence; a smaller font, italics, and lack of bold can be used to signal subordination. For readability, don’t go overboard: avoid using all capital letters for headings (in some cases, small capitals may be acceptable):
Heading Level 1
Heading Level 2
Heading Level 3
Note that word-processing software often has built-in heading styles.
Consistency
Consistency in the styling of headings and subheadings is key to signaling to readers the structure of a research project. That is, each level 1 heading should appear in the same style and size, as should each level 2 heading, and so on. Generally, avoid numbers and letters to designate heads unless you are working in a discipline where doing so is conventional. Note that a heading labeled “1” requires a subsequent heading labeled “2,” and a heading labeled “a” requires a subsequent heading labeled “b.”
In a project that is not professionally designed and published, headings should be flush with the left margin, to avoid confusion with block quotations. (The exception is the paper or chapter title, which is centered in MLA style.)
For readability, it is helpful to include a line space above and below a heading, as shown in this post.
No internal heading level should have only one instance. For example, if you have one level 1 heading, you need to have a second level 1 heading. (The exceptions are the paper or chapter title and the headings for notes and the list of works cited.) You should also generally have text under each heading.
Capitalization
Capitalize headings like the titles of works, as explained in section 1.2 of the MLA Handbook.
The shorter, the better."
Modern Language Association. "How Do I Style Headings and Subheadings in a Research Paper?" MLA Style Center., 13 December 2018, style.mla.org/styling-headings-and-subheadings .
MLA Style Paper Template
- MLA 9th Edition Paper Template This template was created and saved as a Word template for Microsoft Word 2016. The process for saving and using the template is the same for the instructions given above for 2013.
You can save a personal template in Microsoft Word (IRSC students, download Office for free, see a librarian if you need help). Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style paper. Microsoft Word will allow you to save personal templates. Once you have the template opened in Word
Click "Save as"
Give the file a name
Under "Save as type", select Word Template

Then when you open Word, you will be able to choose a template rather than a blank document. You might have to select Personal to find your template.

Sample MLA Paper

How to Use the MLA Style Template
Formatting Group Project Papers
For a research paper written collaboratively by several students, such as for a group project, create a title page instead of listing all authors in the header on page 1 of the essay. On the title page, list each student's full name, placing one name on each double-spaced line. After the final student name, enter the professor's name. After the professor's name, give the course name. The last line of the heading will be the date in 5 August 2021 format. Press Enter a few times to move down the page then give the paper title, centered.

- << Previous: Citing Poetry
- Next: Formatting Your Works Cited List >>
- Last Updated: Jul 22, 2024 4:57 PM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla
Using MLA Format

Document Sources
Works cited quick guide.
Learn how to use the MLA format template.
Digital Citation Tool
Build citations with our interactive template.
In-Text Citations
Get help with in-text citations.
Endnotes and Footnotes
Read our guide about using notes in MLA style.

Set Up Your Paper
Setting up a research paper.
Get our guidelines for setting up academic research papers.
Formatting Captions
Learn how to format captions.
Sample Papers
Read sample papers written in MLA style.
Annotated Bibliographies
Learn how to set up an annotated bibliography.

Get Writing and Teaching Tips
Ask the mla.
Browse answers and ask MLA editors questions.
Writing Tips
Improve your writing with these suggestions.
Teaching Resources and Advice
Get teaching advice, lesson plans, and activities.
Test your knowledge with these fun quizzes.
Recent questions from Ask the MLA
When do i capitalize the first letter of a quotation.
Whether you capitalize the first letter of a quotation depends on how the quotation fits into your sentence. Capitalize the first letter of a quotation,… Read More
How do I cite quotations from different pages of a work?
This post explains how to cite quotations from different pages of a work. Read More
How do I cite a playlist?
Cite a playlist by following the MLA template of core elements. In the Title of Container element, include the name of the playlist surrounded in… Read More
How do I alphabetize Irish surnames in the works-cited list?
This post explains how to alphabetize Irish surnames Read More
How do I alphabetize a works-cited-list entry that begins with a hashtag or another symbol?
The MLA recommends that writers should “ignore symbols when alphabetizing” (“How”). This includes hashtags. Thus, if an entry begins with a hashtag or another symbol,… Read More
How do I cite a work accessed through Wayback Machine ?
Wayback Machine is an archive of websites that lives on the Internet Archive ’s site, so you would treat the Internet Archive as the container of… Read More
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What Is the MLA Format for an Essay?

4-minute read
- 12th October 2023
When writing academic essays, adhering to the proper formatting guidelines is crucial. One of the most widely used styles for academic writing is the Modern Language Association (MLA) format. However, MLA is more than just providing in-text citations and a Works Cited page . If you’re curious, read on.
Today’s post will explore:
● What MLA format is.
● Why it is important.
● How to correctly format essays in MLA style .
What Is MLA Format?
MLA format is a set of guidelines established by the Modern Language Association for writing and documenting research papers, essays, and scholarly articles. These guidelines provide a standardized way to structure and format academic writing, making it easier for readers to understand and engage with the content.
Why Is MLA Format Important?
MLA format serves several important purposes in academic writing:
1. Clarity and Readability
Thanks to its standardized layout and citation style, MLA ensures your essay is easy to read and comprehend.
2. Academic Integrity
Properly citing sources demonstrates academic integrity by giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism .
3. Consistency
MLA provides a consistent and uniform structure for essays, making it easier for readers and instructors to navigate your work.
4. Publication Standards
Many academic journals and publishers require submissions to follow MLA guidelines, making it crucial for researchers and authors.
How to Format Your Essay in MLA Style
Now, let’s go through step-by-step instructions to help you correctly format your essay.
1. Margins and Page Layout
● Go to the Page Layout settings in your word processor and set one-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
● Set the text to be left-aligned.
● Choose a legible 12-point font (e.g., Times New Roman or Arial).
2. Create a Title Page
● Include your name, instructor’s name, course title, and the date in the upper left-hand corner.
● Center the title of your essay, using standard capitalization (no bold, italics, or underlining).
3. Insert Header and Page Numbers
● Create a header in the upper right-hand corner with your last name and page number (e.g., Jones 1).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
4. Use Proper Line Spacing
● Use double-spacing throughout the entire essay, including the Works Cited page.
5. In-Text Citations
● Cite sources within your essay using parenthetical citations (author’s last name and page number).
Example: We have no time to appreciate the finer things in life (Toldo 201)
● Include a Works Cited page with full bibliographic details for all cited sources.
● Ensure that in-text citations correspond to entries in the Works Cited page.
6. Works Cited Page
● You must start the list with the title Works Cited.
● List all sources used in alphabetical order by the author’s last name.
● Follow a specific format for different types of sources (books, journal articles, websites, etc.).
MLA format is essential to academic writing, ensuring clarity, consistency, and proper citation of sources. As MLA is a widely used style, you’ll have a few essays during your undergraduate years that will require you to adhere to its standards. You can confidently format your essays in MLA style, impressing your professors and maintaining academic integrity by following our guidelines in this post.
We strongly recommend proofreading your essay once it’s finished. Proofreading can be challenging, so we recommend asking our proofreading experts to review your writing . They’ll ensure perfect grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Additionally, they can check that your essay adheres to MLA standards. Consider submitting a 500-word document for free!
Happy learning and happy writing!
1. Is MLA the same as APA or Chicago Turabian?
No! MLA formatting is different from other referencing styles such as APA and Chicago Turabian. If you’re used to using APA or Chicago, you’ll have to familiarize yourself with MLA.
2. Will failing to adhere to MLA affect my essay’s grade?
If your essay is required to be in MLA format, it must adhere to the standards. You can expect the professor to deduct marks for failing to adhere to MLA.
3. Can I write References or Reference List instead of Works Cited?
The title for the list of references must be Works Cited. Again, you could lose marks for deviating from the required title.
4. How will I know if my essay needs to be in MLA?
The essay rubric will usually state the required referencing style. Otherwise, we recommend checking with your professor.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
TAFT COLLEGE
MLA Style Guide, 9th Edition: Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Other contributors
- Publication date
- Optional Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Editor(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- Works Cited Practice
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper.
Leave 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and each side.
Indent the first line of each paragraph half an inch from the left margin.
Quotes longer than 4 lines should be written as a block of text a half an inch from the left margin.
Heading and Title
An MLA research paper does not need a title page, but your instructor may require one. If no instructions are given, follow the MLA guidelines below:
Type the following one inch from the top of the first page, flush with the left margin (double spacing throughout).
Your Instructor's Name
Course Number or Name
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange
Indent the next line and begin typing your text.
Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The page numbers will be one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. If your instructor prefers no page number on the first page, begin numbering from 2 on the second page.
Formatting first page MLA MS Word using a MAC
Formatting first page mla goggle.dox, formatting first page mla ms word using pc, mla format setup in word 2013.
The links below provide step by step instructions on setting up your paper using MLA Style guidelines.
- Formatting Your Paper using MS Word - PC
- Formatting Your Paper using MS Word - MAC
Sample MLA Paper
- MLA Research Paper Template Properly formatted MLA Style research paper. Download and save to your computer so that you will always have the correct format for writing.

There are three sample papers available in the MLA Style Center. Check them out to see the correct formatting.
- << Previous: How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Next: Formatting Your Works Cited List >>
- Last Updated: Mar 24, 2022 5:10 PM
- URL: https://lib.taftcollege.edu/c.php?g=628017
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format
MLA Format: Everything You Need to Know Here
Welcome to an overview of “What is MLA Format?” in relation to paper formatting. You’ll find in-depth guidelines, examples, and visual samples to help you easily format your paper. This guide does not serve as a reference for MLA citation format.
For help determining the proper structure for citing, refer to the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here is another informative site which may help with further understanding of MLA citation format.
Guidelines for Formatting a Paper in MLA
- Use white 8 ½ x 11” paper.
- Make 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and sides.
- The first word in every paragraph should be indented one half inch.
- Indent set-off or block quotations one half inch from the left margin.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read, such as Times New Roman. Make sure that italics look different from the regular typeface.
- Use 12-point size.
- Double space the entire research paper, even the Works Cited page.
- Leave one space after periods and other punctuation marks, unless your instructor tells you to leave two spaces.
These guidelines come from the MLA Style Center’s web page “Formatting a Research Paper.”
MLA Guide Overview
There are various sections in this guide. Each section provides an in-depth overview of the different components to keep in mind when developing an MLA paper.
This guide includes the following sections:
- Format background
- General paper formatting
- MLA heading format & title page instructions
- Running head & page numbers
- Paraphrases
- Abbreviations
- Numbers (includes the use of numbers in MLA outline format)
- Images, tables, and musical scores
- MLA works cited format
- MLA citation format (for in-depth citation rules visit this MLA citation guide or MLA in-text citation guide)
- Edits & proofreading
If you need more guidance, a website like EasyBib.com usually has guides and tools to help you out. There’s also resources on other styles, like our guide on “ APA reference page ”, otherwise known as a “References” page.
MLA Format Background
The Modern Language Association (MLA) is an organization responsible for developing MLA format. It was developed as a means for researchers, students, and scholars in the literature and language fields to uniformly format their papers and assignments. This uniform, or consistent, method to developing a paper or assignment allows for easy reading. Today, MLA is not only used in literature and language subject areas; many others have adopted it as well.
The Modern Language Association released the 9th and most current edition of their MLA Handbook in April 2021. The Handbook provides thorough instructions on citing, as well as guidelines for submitting work that adheres to the Modern Language Association’s rules and standards. Although we’re not affiliated with the MLA, our citation specialists bring you this thoughtful and informative guide on the format.
Looking for information about previous editions to the Handbook ? Want to learn more about the origin of “What is MLA format?” Click here to learn about the previous editions to the Handbook .
Actually, are you looking for help on using another style? See how to cite an APA journal , learn to create an APA book citation , and more!
Formatting the Header in MLA
To create a header for your first page, follow these steps:
- Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin.
- Type your name, your instructor’s name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
- Double space once more and center the title. Do NOT underline, bold, or type the title in all capital letters. Only italicize words that would normally be italicized in the text. Example: Character Development in The Great Gatsby
- Do not place a period after the title or after any headings
- Double space between the title and first lines of the text

General Paper Formatting
Paper choice.
While many professors, instructors, and publications allow electronic submission, some prefer printed, hard copies of papers. This section focuses on the type of paper to use for printed submission.
If you choose to print your paper, use white paper only. Do not use ivory, off-white, or any other shades or colors.
Choose a standard, high quality paper to print your project on. Do not use cardstock. It is not necessary to use resum é paper. Use typical, high quality printer or copy paper.
When it comes to size, 8 ½-by-11-inch paper is the recommended size. If you’d like to use a different size, ask your teacher prior to submission.
Use One-Inch Margins in MLA
Use one-inch margins around the entire page. The running head should be the only item seen in the one inch margin (see below for more on running heads).
Most word processing programs automatically default to using one inch margins. Check the page settings section of the program to locate the margin size.
Indenting Paragraphs in MLA
Indent the first word in every paragraph. Sentences should begin one half inch from the left margin.
It is not necessary to manually measure half an inch. Use the “tab” button on the keyboard to create a half inch space.
Double Space Paragraphs in MLA
MLA research paper format requires that the entire research paper or MLA format essay includes double-spaced lines. Double-spaced lines should be found in between the written body of the work, in the heading, and also on the MLA reference page.
While it may seem tempting to place a few extra lines between the heading, title, and beginning of the paper, lines should all be double spaced.
Font and Font Size in MLA
In an MLA paper, it is acceptable to use any font type that is easy to read. Many source types, such as books and articles, use fonts that are easy to read, so if you’re seeking an appropriate font style, look at other sources for guidance. Two of the most commonly used fonts are Arial and Times New Roman.
It is important for the reader to be able to distinguish the difference between italicized and regular font, so if you choose a font style different than Arial or Times New Roman, make sure the difference between the two type styles is evident.
The use of a 12-point font size is recommended as this is the default size for many word processing programs. It is acceptable to use another standard size, such as 11-point or 11.5-point.
Some professors or instructors will provide guidance on how to secure hard copies of projects. If your instructor does not provide you with any expectations or guidance, a simple staple in the top left corner should suffice. If a stapler is not available, some instructors allow paper or binder clips.
Do not fold the top left corner down to secure the pages together. The page could easily unfold, causing a mess of papers. While binders and plastic holders are cute, in reality, they add bulk to a professor or instructor who may like to take the papers home for grading purposes. Keep the binding simple and clean. Staples work best, and binder and paper clips are the next best option.
As always, follow any instructions your professor or teacher may provide. The guidelines found here are simply recommendations.
MLA Heading & Title Page Instructions
The web page “Formatting a Research Paper” gives two options when it comes to creating the header for your project:
- An MLA format heading can be placed at the top of the first page
- A title page can grace the front of the assignment. If you choose to create a title page, keep in mind that there aren’t any official title page or cover page guidelines in MLA format. See more information below.
If choosing option one, creating an MLA heading, you’ll need to include four main components:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The name and number of the course or class
- The assignment’s due date
The first item typed on the paper should be your full name.
- Position your name one inch from the top and left margins of the page.
- Add a double space beneath your name, and type the name of your instructor.
- Below the professor or instructor’s name should be a double space, followed by the name of the course, class, or section number (if available).
- Below it, include another double space and add the assignment’s due date (Day Month Year).
Here’s an example:

The assignment’s title should be placed below the due date, after a double space. Align the title so it sits in the center of the MLA format paper. The title should be written in standard lettering, without underlines, bold font, italicized font, or any quotation marks. Only include italics or quotation marks if your title includes the title of another source.
Here is an example of an MLA header for an MLA format essay, paper, or assignment:
Neal E. Bibdarsh
Professor Haujeemoto
English 201
The Trials and Tribulations of Lincoln’s Reciting of “The Gettysburg Address”
*Note: The quotation marks here are around the title of a speech included in the paper’s title.
Most research papers use a standard MLA format heading, like the one seen above. If your instructor requires you to create a standalone title page, ask him or her for specifications. MLA does not have specific instructions for developing an MLA title page. We recommend you use an MLA header for your project.
If your teacher or professor requires a standalone title page, but has not provided any guidance or specifications, here are a few suggestions from EasyBib.com and this MLA guide :
- Center and double space all of the text on your page.
- Place the name of your school at the top of the page.
- Skip down to about the center of the page and type the title of your paper. Do not bold the title, italicize the entire title, place quotation marks around it, or type the title out in capital letters.
- Use italics for the titles of any sources in the title of your paper. Example: An Analysis of Mythical Creatures in Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
- first letter of the title
- first letter of the last word
- first letter of any adjectives, adverbs, nouns, pronouns, and verbs
- If your paper has a subtitle, include on the next line below your title.
- Skip down to the bottom third of the page and add your name, the the name of your instructor, the name/number of the course or class, and the assignment’s due date on four separate lines.
- Keep the font size at 12 pt., or a size close to it, to make it look professional.
- Use the same font as the text of the paper. The Modern Language Association recommends any font that is easy to read and has a clear distinction between italics and standard font. Times New Roman and Arial are recommended, but many other fonts work as well.
- Include a page number in the top right corner of the paper. For more information on how to style page numbers, check out the next section, “Running Head and Page Numbers.”
- We do not recommend adding any images or cover art to the title page.
Click additional information about essays to see an example of a formatted header.
You can either create a title page using the EasyBib Title Page creator or omit the title page completely and use a header.
Running Head & Page Numbers in MLA
A running head is a brief heading that is placed in the top right corner of every page in a project. The Modern Language Association Style Center (online) states that the running head consists of:
- Last name of the paper’s author
- Page number
General tips to keep in mind:
- The running head is placed in the upper right-hand corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin of the page.
- Type your last name before the page number.
- The last name and page number should be separated by a single space.
- Do not place the word “page” or use an abbreviation, such as p. or pg., before the page number.
- Quite often, the running head begins on the second page, but your instructor may ask you to include the running head on the first page of the assignment. As always, if your instructor provides you with specific directions, follow his or her guidelines.

Before adding this information manually onto every single page, check to see if the word processor you’re using has the capability to automatically add this information for you. Try looking in the settings area where page numbers or headers can be added or modified.
Google Docs: Adding a header
- Go to the menu section “Insert.”
- Select “Page numbers” and select the option that places the page number in the upper-right corner.
- A page number will appear; your cursor will blink next to it.
- Move your cursor to the left of the page number.
- Type your last name. Add a space between your name and the page number.
- You should now have a properly formatted header on every page!
Microsoft Word Document: Adding a header
- Double-click in the space at the top of the page (where the page number is).
- OR Go to the “Insert” menu, select “Header,” and select “Edit Header.”
- Type your last name next to page number. If it isn’t already right-aligned, go to the “Home” menu and right-align your name.
Quotations in MLA
Quotes are added into assignments to help defend an argument, prove a point, add emphasis, or simply liven up a project.
Quotes should not take up the majority of your paper or assignment. Quotes should be sprinkled sparingly throughout, and quotes longer than 4 lines should be formatted as MLA block quotes . Use direct quotes from outside sources to enhance and expand on your own writing and ideas.
Words from quotes belong to the individual who spoke or wrote them, so it is essential to credit that individual’s work. Credit him or her by adding what is called an “in-text citation” into the body of the project.
There are three ways to add quotes: 1. With the author’s name in the sentence (a citation in prose).
Dan Gutman shares a glimpse into the overall plot by stating, “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman is the author of the book that this quote is pulled from.
2. Without the author’s name in the sentence (a parenthetical citation).
The main character’s confusing experience is realized and explained when he states “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (Gutman 5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman’s name isn’t included in the sentence. It’s included in the parentheses at the end of the sentence. This is an example of a proper MLA style citation in the body of a project.
3. In a block quote, which is used when a large quote, of 4 lines or more, is added into a project.
Using footnotes and endnotes
The Modern Language Association generally promotes the use of references as described in the sections above, but footnotes and endnotes are also acceptable forms of references to use in your paper.
Footnotes and endnotes are helpful to use in a variety of circumstances. Here are a few scenarios when it may seem appropriate to use this type of referencing:
- When you are referring to a number of various sources, by various authors, in a section of your paper. In this situation, it is a good idea to use a footnote or endnote to share information for parenthetical references. This will encourage the reader to stay focused on the text of the research paper, instead of having to read through all of the reference information.
- When you are sharing additional information that doesn’t quite fit into the scope of the paper, but is beneficial for the reader. These types of footnotes and endnotes are helpful when explaining translations, adding background information, or sharing counterexamples to research.
To include a footnote or endnote, add a superscript number at the end of the sentence the footnote or endnote refers to. They can be included mid-sentence if necessary, but be sure to add it after any punctuation, such as commas or periods. Find a location that doesn’t distract the reader from the content and flow of the paper.
Within the text example:
Numerous well-known children’s books include characters from a wide range of races and ethnicities, thus promoting diversity and multiculturalism.¹
At the bottom of the page (footnote) or at the end of the section (endnote):
¹See Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez. While Parr’s work features characters of various colors, such as pink or blue, children easily correlate it with individuals of different races and ethnicities.
On the last page of the assignment, the writer includes the full references for the books by Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez.
For more on block quotes and a further, detailed explanation on the use of quotes, including MLA footnotes, refer to our MLA In-Text Citation and Parenthetical Citations Guide. In this guide you’ll find further information including directions for the use of quotes without an author, page numbers, and how to properly credit work from electronic sources.
For guides on citations in another style, check out APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation .
Paraphrases in MLA
Paraphrases are created when text or speech from another source are added into a project, but the writer chooses to summarize them and weave in his or her own writing and writing style.
Even though the writer modifies the information from another source, it is still necessary to credit the source using proper format ( Handbook 98). Paraphrased information uses the same MLA reference format as stated in the section directly above this one.
Here is an acceptable paraphrase:
Original text:
“Stay hungry. Stay foolish.” Steve Jobs
Paraphrase:
Steve Jobs encouraged students at Stanford to continue with their determination, drive, and ambitious behavior. They should never be simply satisfied with the status quo. They should continue to push themselves despite possible obstacles and failures.
To develop a well-written paraphrase, follow these simple, step-by-step instructions.
- Find a phrase, sentence, paragraph, or section of original text you’d like to turn into a paraphrase.
- Read the text carefully and make sure you fully comprehend its meaning. A writer can only develop a well-written paraphrase if the information has been fully grasped and understood. If you’re having difficulty understanding the information, take a few minutes to read up on tricky words and background information. If all else fails, ask a friend to see if they’re able to make sense of the concepts.
- After analyzing and completely understanding the original text, put it to the side. Take a moment to think about what you’ve read and connect the idea to your own assignment.
- Now that the information is completely understood, take a moment to rewrite what you’ve read, in your own words and writing style. Do not simply substitute words in the original text with synonyms. That’s plagiarism! Show off and demonstrate your ability to process the original information, connect it to the content in your paper, and write it in your own individual and unique writing style.
- Include an in-text reference next to the paraphrase. All paraphrases include references, similar to direct quotes. See the “Quotations” section of this guide to learn how to properly attribute your paraphrased information.
- Give yourself a pat on the back! Paraphrasing is an important part of the research and writing process.
Wondering if it’s better to quote or paraphrase?
An essential part of the research process involves adding direct quotes and paraphrases into projects. Direct quotes provide word-for-word evidence and allow writers to use another author’s eloquent words and language in their own projects. When it comes to paraphrases, writers are able to take a block of text and shrink the scope of it into the their papers. Paper writers can also use paraphrases to demonstrate their ability to analyze and reiterate information in a meaningful and relevant way.
If you’re wondering which one is better to consistently use, quotes or paraphrases, there’s a clear winner. Paraphrases come out on top. Sure, direct quotes are incredibly beneficial, but copying and pasting too many of these into a project can cause a reader to lose sight of the writer’s own voice. Mixing your own voice with another author’s too much can make for choppy and disjointed reading.
The ultimate goal of a research project is to have your voice and research merged together as one. Paraphrases allow just that. When you combine information from outside sources with your own writing style, it demonstrates your ability as a researcher to showcase your understanding and analyzation of a topic.
Remember, whether you’re adding direct quotes or paraphrases into a project, both types of additions need references. References are placed after the quotes and paraphrases, and also at the end of an assignment.
If you’re looking for additional help with your punctuation or grammar, check out the EasyBib plagiarism checker !
Using Abbreviations in MLA
Abbreviations are commonly used in many source types including websites, blog posts, books, and journal articles. It is acceptable to use abbreviations in all of these sources.
When it comes to school and research assignments, however, the MLA Handbook states that abbreviations should be used rarely in the prose of your paper (293). Spelling out abbreviations into their full words and meanings is recommended. This ensures understanding and avoids any confusion from your reader.
There are times when you may feel it is perfectly acceptable to use an abbreviation rather than its typed out counterpart in a paper. If you do abbreviate, be sure you are using commonly accepted abbreviations, which you can find in the dictionary. You can also review Appendix 1 in the MLA Handbook .
General Abbreviation Tips
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus can be abbreviated to HIV, not H.I.V.
- United States should be US, not U.S.
- Digital video disc should be DVD, not D.V.D.
- For lower case abbreviations, it is acceptable to include periods between the letters.
- The abbreviation, “For example” = e.g.
- If there is a mix of lower case and upper case letters, do not use periods if the majority of the letters are upper case. Examples include PhD and EdD
Abbreviating Months
Type out entire month names when being used in the body of a research paper or assignment.
She rented out the beach house from May through September
When it comes to references, MLA bibliography format requires months longer than four letters to be abbreviated.
- July = July
- November = Nov.
Other abbreviations that are perfectly acceptable to use in a bibliography (not the body of a project) include:
- p. or pp. for page and page numbers
- ch. for chapter
- ed. for edition
- trans. for translation or translated
- vol. for volume
- no. for number
- rev. for revised
Again, these abbreviations should only be used in the final page(s) of a project, the MLA Works Cited list. They should not be used in the body of a project.
For more information on bibliographies, see our MLA format Works Cited List page.
Abbreviating Publishers
One of the quirkiest things about this particular style is how publisher names are structured on the final page of references. Certain words are abbreviated, some words are omitted, and other words are written in full.
Words describing what type of business the publisher is are omitted from the works cited. Here’s a breakdown of the words that should be excluded:
- Co. (Company)
- Corp. (Corporation)
- Inc. (Incorporated)
- Ltd. (Limited)
- The (when at the beginning of the name)
If a publisher’s name contains the words “University” and “Press” (or the equivalent in another language), the words should be abbreviated to the letters “U” and “P” in your citation. But if only one of the words appears, it should be written out normally.
Here are a few examples:
- University of Delaware
- U College of London P
All other words related to the names of publishers should be written out in full.
Abbreviating Titles
Certain classical and biblical works are abbreviated in a bibliography, but also in any parenthetical references in the text.
The official handbook provides a lengthy list, spanning over multiple pages, of the preferred abbreviations to use for classical and biblical works ( Handbook 295-301), but here’s a quick snapshot of some of the commonly used ones:
Hebrew Bible or Old Testament = OT
- Deut. = Deuteronomy
- Gen. = Genesis
- Lev. = Leviticus
- Num. = Numbers
- Ps. = Psalms
New Testament = NT
- 1 Cor. = 1 Corinthians
- Jas. = James
- Matt. = Matthew
Shakespeare:
- Ado = Much Ado about Nothing
- 3H6 = Henry VI, Part 3
- JC = Julius Caesar
- Mac. = Macbeth
- MND = A Midsummer Night’s Dream
- Oth. = Othello
- Rom. = Romeo and Juliet
Again, the titles above are allowed to be abbreviated both in references in parentheses in the body of a project and also on the final page of references. If you’re wondering why, it’s because they’re cited often and it’s unnecessary to type out the entire title names.
Formatting Numbers in MLA
Use of numerals.
If the project calls for frequent use of numbers (such as a scientific study or statistics), use numerals that precede measurements.
- 247 milligrams
Other items to keep in mind:
In divisions, use numbers, ex: In page 5 of the study
Arabic Numbers
When including a number in a paper, spell out the number if it can be written as one word (such as six ) or two words (such as sixty-two ). For fractions, decimals, or longer numbers, type them out using digits. For larger numbers, write the number itself ( Handbook 82-84).
- twenty-seven
- one hundred
If the number comes before a unit of measurement or label, type the number using digits.
- 8 tablespoons
- 3 July 2018
- 25 King Street
More on Numbers
Starting a sentence with a number is generally frowned upon. Try modifying the sentence so that the number, or number word, is found elsewhere.
Instead of:
225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Use this sentence:
A total of 225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
If modifying the sentence is not possible or does not work well with the flow of the assignment or paper, type out the written number:
Two hundred twenty five children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Do not include any ISBN numbers in your paper.
Outline Format
The Modern Language Association does not have any requirements regarding the structure of an outline. If your teacher asks you to create an MLA outline, we recommend using roman numerals, capital and lowercase letters, and numbers.
Here is an example of a recommended outline structure:

In addition to outlines, use roman numerals for suffixes.
- King George IV
Using Images, Tables, & Musical Scores in MLA
Photographs, data sets, tables, graphs, and other images are often added into projects or papers to promote or aid understanding. They provide meaningful visuals for the reader. If the illustration or visual image does not enhance the quality of the paper, do not include it in the project.
Tables and illustrations should be placed as close as possible to the text that they most closely refer to.
For an image to be significant and easily identifiable, place it as close as possible to the text in the project where it is discussed.
It is not acceptable to simply place an image in a project without including identifiable information. All images must include information about its origin.
Here are the directions to properly attribute an image:
- Assign an Arabic number. The image closest to the beginning of the project should be labeled as Fig. 1. The next image in the project should be Fig. 2. and so on.
- Provide a caption. The caption should be a brief explanation or the title of the contents of the image. Place the caption directly next to the label.
- Immediately following the caption, it is acceptable to include attribution information. If the image is not discussed further in the rest of the paper or project, it is acceptable to include the MLA bibliography format citation below the image and omit it from the bibliography or MLA format works cited page.
In the text of the project or paper where the figure is discussed, include the label in parentheses to ensure the reader knows where to find the figure in your paper.
In the text:
Sarah’s tattoo design was filled with two of her favorite flowers: lilies and daffodils along a thinly curved vine (fig. 1).
Image formatting:
(Image Would Be Here) Fig. 1. Sarah’s Tattoo. barneyWILLIAMSable, Deviant Art , 2011, barneywilliamsable.deviantart.com/art/Sarah-s-Tattoo-design-193048938.
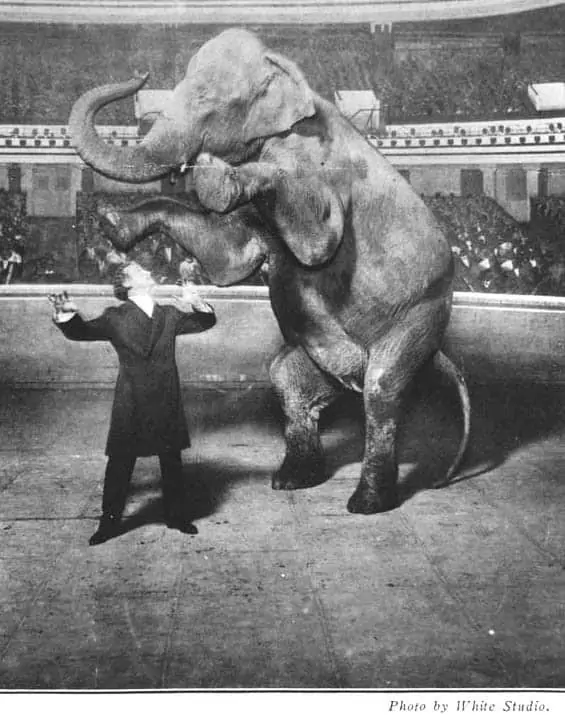

Fig. 1. White Studio. “Houdini and Jennie, the Elephant, Performing at the Hippodrome, New York.” Library of Congress , www.loc.gov/item/96518833/.
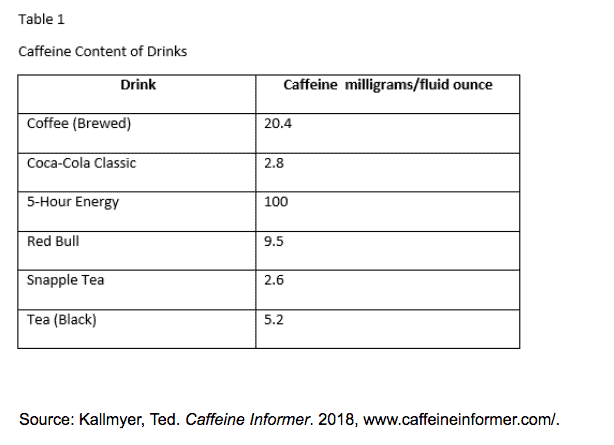
When adding a table or data set into a project, it is formatted a little differently. Above the data set, include the label “Table” with an Arabic numeral, and title it. The table number and title should be located flush left and on separate lines. The first table seen in the project is labeled as Table 1. The second table in the project is Table 2, and so on. The table’s title should be written in title case form (the first letter of each word is capitalized, except for small, insignificant words).
Underneath the table, provide the source and any notes. Notes should be labeled with a letter, rather than a numeral, so the reader is able to differentiate between the notes of the text and the notes of the table.
International Scholars from India Enrolled at Yale University a
| Year | India | South Korea |
| 2012-2013 | 191 | 126 |
| 2013-2014 | 200 | 123 |
| 2014-2015 | 197 | 116 |
| 2015-2016 | 210 | 120 |
Source: “International Scholars Academic Year 2015-2016.” Yale University , Office of International Students and Scholars, yale.app.box.com/v/scholar-2015-2016. a. The numbers reflect students who are enrolled full-time.
The information included above and below any images or table should be double spaced, similar to the rest of the project or paper.
Musical Scores
Musical scores need to be labeled as well. When including a musical score in a project, label musical scores with “Ex.” which is short for example. This label should be placed below the musical score. Next to the abbreviation “Ex.”, assign the score an Arabic numeral. The first musical score in the project should be labeled as Ex. 1. The second musical score found in an assignment should be labeled as Ex. 2., and so on.
If possible, provide a caption after to the label. If the caption below the sheet music includes enough information about the source, it is not necessary to include the full reference at the end of the assignment.
Here is an example of a possible label and caption:
Ex. 4. Scott Joplin, The Entertainer, piano, C major.
Another example:

Here’s more on tables and illustrations.
Using Lists in MLA
It’s appropriate to add lists into an MLA format essay as long as the proper rules are followed.
Lists created using MLA essay format look different than a grocery list or any other type of vertical listing of items. Items in a list are included in your prose, rather than the traditional vertical style.
Often, you will use a colon between the introductory sentence and the list. But you should not include a colon if the first item in the list is part of the sentence.
List Example #1
Here is an example of how a list may look incorporated into the prose of a research project or assignment:
William Shakespeare wrote numerous plays, many of which were considered tragedies: Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear .
List Example #2 Here is an example of how a list may look in a research project or assignment when the list is part of the introductory sentence:
Many of William Shakespeare’s were tragedies. Some of his most popular tragedies include Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear.
MLA Works Cited Format
EasyBib.com has a full, comprehensive guide to creating a proper works cited MLA format , but here are a few items to keep in mind when developing this portion of a project:
- The list of citations should be the very last page of a research project or essay.
- The top of the page should include the running head and the page number.
- All entries should be placed in alphabetical order by the first item in the MLA format citation.
- The entire page should be double spaced.
For more detailed information, make sure to check out the EasyBib guide to MLA format Works Cited pages.
MLA Citation Format
The majority of this guide focuses on MLA formatting in regards to MLA paper format rules and guidelines. If you’re seeking information related to the proper formatting of an MLA citation, refer to our individual pages and posts on various types of citations.
If you’re simply looking for the general structure for full references, which are found on the final pages of projects, here’s the proper order:
Author’s Last name, Author’s First name. “Title of Source.”* Title of Container , Names of other contributors along with their specific roles, version of the source (if it differs from the original or is unique), any key numbers associated with the source that aren’t dates (such as journal issue numbers or volume numbers), Name of the Publisher, publication date, location (such as the URL or page numbers).
*Note: A title may be in italics instead of quotation marks, depending of the type of source. The general rule is that works that are self-contained (like books, journals, or television shows) are formatted in italics. Works that are part of a larger work (like articles, chapters, or specific episodes) are formatting in quotation marks.
MLA Format Citing FAQs:
“What in the world are containers?”
Containers are what hold the source. If you’re creating a reference for a chapter in a book, the title of the chapter is the title of the source , and the container is the title of the book . The book holds the chapter, so it’s the container. If you’re searching for how to cite a website, here’s a tip: the title of the source is the name of the individual page and the title of the container is the name of the full website.
“This seems like a lot of information for a reference. Is it all necessary?”
The short answer is “No!” When citing, only include the components that help the reader locate the exact same source themselves.
It isn’t necessary to go digging for items such as numbers, version types, or names of other individuals or contributors associated with the source if they aren’t applicable. If you think it’s beneficial for the reader, then include it.
Related to citations, here are helpful pages on:
- MLA citation website format
- Citing a book
- Citing a journal
- What is a DOI ?
- More on PDFs
If you’re looking for an MLA citation generator, head to the EasyBib homepage. Our formatter will help you create citations quickly and easily!
Need APA, too? There are also EasyBib tools and an APA citation website reference guide to help you learn the basics.
Edits and Proofreading
Editing and proofreading your assignment prior to submission is an incredibly important step in the research process. Editing involves checking the paper for the following items:
- Spelling : Are all words spelled correctly? Review all proper names, places, and other unique words to ensure correct spelling. When finished, run the project through a spell checker. Many word processing programs, such as Microsoft Word and Google Drive, provide a free spell checking feature. While spell checks are beneficial, they do not always spot every mistake, so make sure you take the time to read through the assignment carefully. If you’re still not sure if your project contains proper spelling, ask a friend to read through it. They may find a mistake you missed!
- Grammar : Check your assignment to make sure you’ve included proper word usage. There are numerous grammar checkers available to review your project prior to submission. Again, take the time to review any recommendations from these programs prior to accepting the suggestions and revisions.
- Punctuation : Check to make sure the end of every sentence has an ending punctuation mark. Also make sure commas, hyphens, colons, and other punctuation marks are placed in the appropriate places.
- Attribution : Do all quotes and paraphrases include a citation? Did you create an in-text citation for each individual piece of information?
Smart idea: running your paper through a paper checker before you turn it in. EasyBib Plus offers a checker that scans for grammar errors and unintentional plagiarism.
Check out our MLA sample papers . Also, check out the EasyBib MLA Annotated Bibliography Guide.
Don’t forget to use the EasyBib citation generator to develop your Modern Language Association style references.EasyBib.com also has helpful guides on APA format and more styles . Lastly, stay up-to-date on what’s coming by following our EasyBib Twitter account.
Works Cited
“Formatting a Research Paper.” The MLA Style Center , Modern Language Association of America, style.mla.org/formatting-papers/.
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. You can find her here on Twitter. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The works-cited list provides the reader full information so that a reader can locate the source for further use.
Basic formatting
The works-cited list appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes if they are present.
Page margins
All margins (top, bottom, left, and right) should be set at 1 inch.
Running head
Write the running head in the top right of the page at 0.5 inch from the top. Use the running head “Surname Page #.”
The font should be clear enough to read. For example, Times New Roman font set to 12 points.
Formatting entries
Entries should be double-spaced, including a double-space between the heading and the first entry. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Formatting the title
The title should be “Works Cited.” Center the title. Do not bold, italicize, or underline the title. If you cite only one source in the list, the title should be “Work Cited.” If you include sources that you only consulted and didn’t cite directly, the title should be changed accordingly to “Works Cited and Consulted.”
Arranging works cited
Works-cited-list entries are arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name (or the editor’s last name for entire edited collections). Double-space all entries. Begin each entry flush with the left margin. If any entry runs over more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin (sometimes called a hanging indent).
Example works cited
Damasio, Antonio. The Feeling of What Happens: Body, Emotion and the Making of Consciousness . Vintage, 2000.
Hill, R. T. “Legitimizing Colonial Privilege: Native Americans at a Quincentenary of Discourse.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 16, no. 1, 1996, pp. 92–100.
MacDonald, Shauna M. “Performance as Critical Posthuman Pedagogy.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 34, no. 2, 2014, pp. 164–81.
Zilio, M. “Canada Will Not Move Embassy to Jerusalem, Federal Government Says.” The Globe and Mail . 7 Sept. 2017, www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/canada-will-not-move-embassy-to-jerusalem-federal-government-says/article37219576/ .
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed in the text. It is styled in two ways: a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when directly quoting text from the source being cited. When including a page number, do not include a comma or any other punctuation mark between the author’s surname and the page number.
Parenthetical citations usually add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Sometimes they include a page number or other locator. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
The spiritual geography of the landscape is explained (Cooper).
If you want to cite a chapter number, a scene, or a line number, follow the abbreviation guidelines below:
When including a more specific locator number rather than a page number, place a comma between the author’s surname and the label.
(Cooper, ch. 2).
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for sources with different numbers or types of authors:
Use only the surname of the author in parenthetical citations. If you want to add a page number (or another indicator of the place in a work), add it after the author’s surname without any punctuation between the surname and the page number.
(Abraham 7).
Two authors
Add only the surnames of the authors. Use “and” to separate the two authors.
(Langmuir and Einstein).
Three or more authors
Add only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
(Low et al.).
Corporate author
Shorten the organization name wherever possible, excluding any initial articles and using the shortest noun phrase (e.g., shorten Literary Society of Tamil Culture to Literary Society).
(Literary Society).
If there is no author for the source, use the source title in place of the author’s surname.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them is shortened to Fantastic Beasts .
( Fantastic Beasts 160).
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Mla format papers: step-by-step tips for formatting research essays in mla style.
Jerz > Writing > Academic [ Argument | Title | Thesis | Blueprint | Pro/Con | Quoting | MLA Format ]
(View a Google Doc template for an MLA Style paper .)
0.1) If you’ve been asked to submit a paper in MLA style, your instructor is asking you to format the page and present the content in a specific way. Just as football referees dress a certain way, and Japanese chefs cook a certain way, writers in certain disciplines follow a certain set of conventions. This document will show you how to format an essay in MLA style.
0.2) If, instead of questions about putting the final formatting touches on your essay, you have questions about what to write, see instead my handouts on writing a short research paper , coming up with a good thesis statement , and using quotations in the body of your paper .

- Document Settings (1 inch margins; double spaced; 12-point)
- Page Header (name and page number, upper right of every page)
- Title Block (assignment info and an informative title)
- Citations (no comma between the author and page number; commas and periods go outside of inline quotes)
- Works Cited List (lots of tricky details! sort alphabetically by author, not by the order the quotes appear in your paper)
For the most complete information, check your campus library or writing center for the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 8th ed.

MLA Style Format (First Page)

How to format the Works Cited page of an MLA style paper.

1. Document Settings
Your word processor comes with default settings (margin, line height, paragraph spacing, and typeface) that will likely need adjustment. For MLA style, you need:
| all around (double-space the whole paper, including title block and Works Cited list) after the title, between paragraphs, or between bibliography items typeface (usually ) | |
| (Jump directly to instructions for adjusting MS-Word settings in or ; or, skip ahead to .) | |
1.1 Adjusting Document Settings in MS-Word (Windows)
My copy of Microsoft Word for Windows defaults to
- 1-inch margins all around
- 1.15 line height
- 10pt spacing between paragraphs
- Calibri 11-point typeface.
Changing to MLA Style (Windows)
- The default margins in my test run were fine, but if you need to change them: Page Layout -> Margins -> Normal (1-inch all around)
- The default line height is too low. Change it to 2.0. Home -> Line Spacing -> 2.0. (You could try fudging it to 1.9 or 2.1 to meet a page count, but any more than that and your instructor may notice.)
- The MS-Word default adds extra space after paragraphs.(MLA Style instead requires you to signal paragraph breaks by indenting the first line.) CTRL-A (select all your text) Home -> Line Spacing -> Remove Space After Paragraph
- Change the typeface to Times New Roman 12-point. Home -> Font Face Selector (change to Times New Roman) Home -> Font Size Selector (change to 12)
1.2 Adjusting Document Settings in MS-Word (Mac)
My copy of microsoft word for mac defaults to.
- 1.25 inch left and right margins, 1 inch top and bottom
- 1.0 line height
- no extra spacing after paragraphs
- Cambria 12-point typeface
Changing to MLA style (Mac)
- In my test run, the left and right margins are too big. To change them: Layout -> Margins -> Normal (1-inch all around)
- The default line height is too low. Change it to 2.0. Home -> Line Spacing -> 2.0
- My Mac copy of MS-Word does not add extra spaces after paragraphs. If yours does: Home -> Line Spacing -> Line Spacing Options… (a new window will pop up) Don’t add space between paragraphs of the same style (check this box) -> OK
- The 12-point Cambria will probably be fine, but to change the typeface: Home -> Font Face Selector (change to Times New Roman) Home -> Font Size Selector (change to 12)
2. Page Header
In the top right of every page, use your word processor’s “Page Header” function add an automatic page number and your surname.
2.1 Adding the Page Header in MS-Word (Windows)
- Insert -> Page Number -> Top of Page -> (choose the right-justified “Plain Number” option)
- The cursor will jump automatically to the right place for you to t ype your surname .
- Click anywhere in the body of the paper to exit the header area.
2.2 Adding the Page Header in MS-Word (Mac)
- Insert (in the top menu) -> Page Numbers… -> (Set “Position” to “Top of Page (header)” and “Alignment” to “Right”)
- Click just to the left of the new page number, and type your surname .
- On my test document, my name was too far over to the left; grab the triangular tab adjuster just above your name, and drag it a notch to the right .
3. Title Block
In the upper left corner, type your name, your instructor’s name, the course number and section, and today’s date. Centered on the next line, type an informative title that actually informs the reader of your main point (not just “English Paper” or “A Comparison between Hamlet and Macbeth”).

- Like all the other text in an MLA style paper, the title block is double-spaced .
- The title is in the same font as the rest of the paper — it is not boldface, or enlarged.
- There is no extra space above or below the title.
- A truly informative title will include the general topic, and your precise opinion on that topic. (So, if you pan to compare Hamlet and Macbeth, your title should state the unique point you want to make about Hamlet and Macbeth. Reuse part of your thesis statement.)
4. Citations
This handout presumes you already know why you should cite your sources (to establish your authority, to introduce persuasive evidence, to avoid plagiarism , etc.).
To fully cite a source requires two stages. The first happens in the body of your paper (the “in-text citation”) and the second happens on a separate page at the end of your paper (see “Works Cited List,” below.)
4.1 Citing a Block Quote (more than three lines)

- Long quotes can start to look like filler. Only use a block quote if you have a very good reason to include the whole passage. (You can usually make your point with a shorter quote.)
- Place the parenthetical citation (the author’s name and the page number) after the period . (This is different from inline quotes, below.)
- There is no comma between the author’s name and the page number.
- If the quotation runs across more than one page: (Wordsworth-Fuller 20-21) or (Wordsworth-Fuller 420-21).
- Skip wordy introductions such as, “In his informative guide The Amazing Writing Book , published by Elizabeth Mount College in 2010, the noted composition expert Maxwell Wordsworth-Fuller describes the importance of citations in MLA style papers.” Cutting the filler leaves more room to develop your own original ideas. (See “ Integrating Quotations .”)
4.2 Citing an Inline Quotation
When the passage you want to quote is less than three lines long, use inline style. Here we have two brief passages, taken from the same page of the same source, so we can handle both with a single parenthetical citation.

- The parenthetical citation appears outside the quoted material.
- The period that ends the sentence comes after the close parenthesis . (This is different from block quotes, above.)
- In this example, we have changed the first word a little, lowercasing it in order to fit it into our own sentence. To let the reader know what we changed, we put [] around it.
- Again, note the absence of a full sentence that explains who Wordsworth-Fuller is and where the quote comes from. All that info will be in the Works Cited list, so we leave it out of the body of the paper.
4.3 Citing a Paraphrase
Let’s imagine we want to reference Wordsworth-Fuller’s general idea about citation as a way to establish credibility, but we don’t need to include any of the technical details. We can save space, and make it much easier on our reader, if we paraphrase:

- Use paraphrasing for variety, or to make a passing reference without taking up much space.
- If we use an author’s idea, rephrased in our own words, we must still cite the idea.
Tips for avoiding common errors in MLA citations.
5. Works Cited List
A research paper isn’t a research paper unless you end with full bibliographical details on every source you cited. This part can be tedious and tricky; leave yourself plenty of time to do it.

How to format the “Works Cited” list of an MLA style paper.
- MS-Word Wind: Insert -> Page Break -> New Page.
- MS-Word Mac: Document Elements -> Break -> Page.
- Title your new page: Works Cited MLA style calls for no extra spaces above or below the page title; no special formatting.
5.1. How to Create an Individual Works Cited Entry
Exactly what goes into each item in your bibliography depends on what kind of item it is. The general format is as follows:
Author. Title of Source. Container, contributors, version, volume and issue, publisher, date, location.
Exactly how that basic format gets turned into a Works Cited entry depends on the source.
Here’s the basic format for any book:

- Gibaldi, Joseph, and George Spelvin.
- Gibaldi, Joseph, Alan Smithee, and George Spelvin.
- GIbaldi, Joseph et al.
- The italicized phrase “ et al. ” is an abbreviation for the Latin “et alia,” meaning “and others.”
- The “ al. ” is short for a longer word, so we mark the abbreviation with a period.
- The “ et” is not an abbreviation, so it doesn’t get a period.
- Place periods after the author’s name, after the title of the book, and at the end of the entry.
- The title of the book is italicized .
- The publisher is the name of the organization responsible for publishing the book. In this example it’s the Modern Language Association. It might instead be Project Gutenberg, the US Department of Agriculture, or the World Health Organization,
Basic Format for Any Academic Article
Author. “Title of Article in Quotation Marks.” Title of Journal in Italics, volume #, issue #, YEAR, pp. [pages of article]. Italicized Name of Database.

Let’s break that example down.
The author Margaret Kantz wrote the article “Helping Students Use Textual Sources Persuasively.” That article doesn’t exist on its own floating in space; it was published by a journal called College English, in the 52nd year of publication, in the first issue of its 52nd volume, in the year 1990, the article started on page 74 and ran through page 91. The student found this article while searching the database Academic Search Elite .
Every academic article has a specific title, and is published in a journal with a different title. (Online citation generators often get this wrong, and will often repeat the same title twice.)
What is this “volume 52, number 1”?
If College English were a TV series, then “volume” would be which season, and “number” would be the episode number. The title of the article would be the equivalent of a scene within that episode.
The title of the database, Academic Search Elite , is like the title of the streaming service you’d need to sign into. If you were talking about your favorite TV show and you told me it was on Netflix, or Disney+, I could find it. But if you told me “It’s on my MacBook” or “It’s on my Samsung phone,” that wouldn’t help me to find it.
| . It’s not the name of a database; it’s a tool researchers use to access databases, but different schools can access different databases through different subscription plans | |
| If you tell me that I can find your favorite TV show “on a MacBook,” that’s too vague. Just because I own a MacBook doesn’t automatically grant me access to all the streaming services you access on your MacBook. In a similar way, telling me you found a source on “ ” is too vague. | |
| “ ” or “ | |
| This is like telling me your favorite TV show is on Netflix or Disney+. It tells me the specific name of the database I need to access in order to find the article you found. | |
Basic Format for Any Web Page

In the above example, reporter Camila Domonoske filed a news story called “Students Have ‘Dismaying’ Inability To Tell Fake News From Real, Study Finds,” that aired on a news program called The Two-Way , which is published by National Public Radio, and the story aired Nov 23, 2016.
In MLS Style, the full URL is optional. Really long URLs with long strings of numbers in them are often generated for specific users, so someone else who visits that same URL will often get an error message.
You might shorten the URL to “npr.org,” because it would be a simple matter to use a search engine to find the actual story.
Other Citation Examples
What if your source doesn’t fit any of my examples?
You might be trying to cite something that doesn’t fit the above pattern, like a social media post, a video game, a work of art, an email from a relative, a billboard, or something else. It’s just not practical for me to try to include an example of every single thing it’s possible to cite.
The MLA citation format is designed to be flexible, so that it works for forms of media that haven’t been invented yet.
See Purdue OWL’s handouts for how to create a bibliography entry for a book , an article in a periodical (such as a journal or newspaper), or an electronic source (such as an email, web page or a YouTube clip). See also this list of other common sources (such as a personal interview or a movie).
5.2. How to Organize Your Works Cited list
Sort the entries alphabetically by the author ‘s last name.
- If the author is an organization (such as a government agency or non-profit foundation), alphabetize according to the name of the organization .
- If you are citing a painting, or a composer, then obviously “author” has to be interpreted a little loosely.
- Unless your instructor ask you to organize your Works Cited list differently, everything should be alphabetized together, in a single list. MLA does not require that you separate works of different kinds, or that you cite works in the order that they appeared in your paper, or that you write annotations to go along with each item.
- Use double-spaced line height. (in my copy of Word, I select the text and choose Format -> Paragraph -> Line spacing -> Double -> OK.)
- Use hanging indent paragraph format. (In my copy of word, I select the text then choose Format -> Paragraph -> Indentation -> Special -> Hanging Indent.)
29 May 2011 — new document posted, replacing outdated handout written in 1999. 06 Jun 2011 — expanded section on organizing the Works Cited list, since several readers asked for clarification. 07 Jun 2011 — reorganized for emphasis 19 Apr 2012 — added numbers to more subheads 24 Mar 2014 — added details on Works Cited paragraph formatting. 02 Oct 2016 — updated with MLA 8th Edition details. 30 Nov 2016 — added annotated Works Cited sample image. 07 Sep 2020 — updated section 5.1
| If your college instructor wants you to cite every fact or opinion you find in an outside source, how do you make room for your own opinion? Paraphrase, quote selectively, and avoid summary. –Dennis G. Jerz (Jerz’s Literacy Weblog) Choose a form, fill it out, and push the button… you will get an individual entry for a “Works Cited” page, which you may then copy and paste into your word processor. My “BibBuilder” is more like a guide than a full-fledged utility, but you may nevertheless find it helpful. Find everything you need to know about formatting a paper, name, number, quotations, works cited, and more in MLA format! |
571 thoughts on “ MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Tips for Formatting Research Essays in MLA Style ”
This guide to formatting MLA style papers is incredibly detailed and helpful! It’s great to have step-by-step instructions for setting up everything from margins to citations correctly. Thanks for sharing—this will definitely make writing research papers in MLA format much easier!
The information was very helpful
Pingback: Academic Argument: an evidence-based defense of a non-obvious position on a complex issue. | Jerz's Literacy Weblog (est. 1999)
Thanks for sharing such an informative post with us.
fantastic information
Thanks for info!
hello i am nate sedmack i am here to kill all the furries for what they did to gavin born
I’m learning more writing a paper
it was very informational and helped me a lot
Pingback: Flipped Classes: Omit Housekeeping Mechanics from Recorded Lectures to Lengthen Their Shelf-life | Jerz's Literacy Weblog
Curious how you would Cite this webpage? haha…
awesome reminders
what about if when your using a quote and there is no name just anonomus
Honestly, I’d say find another way to make your point. An anonymous saying like “A stitch in time saves nine” won’t help you demonstrate your ability to write the kind of scholarly paper that MLA is designed for. Certainly investigate the quote to find out whether it maybe comes from Shakespeare or some other source that you can quote. I might identify the example I used as “English proverb,” but since I won’t be marking your paper, you really should check with your instructor.
This article..thing is the only reason I am passing my online college class. Especially the citation builder. Thank you!
I would Like You To Give Simple Instructions Not Complicated Ones , and Include also how much Papers Should be worked on.
Khalid, if there is any particular detail you are confused about, please let me know what question you have and perhaps I can help. There is no specific answer to how much a paper should be worked on. It depends on what grade you want to earn, how much time you have, whether your instructor is willing to meet with you before the due date, whether your instructor will give you the chance to revise your work, and many other factors.
hahahah xD me too same
How do I cite a photo that I found online?
Is it a historical photograph or a photograph published in a book that someone scanned and posted on line, is it a photograph of something like a sculpture? Is your paper focused on the work of the photographer, the makeup artist who prepared the model, the digital image enhancer who altered the image, the model? There is no single correct way to cite a photograph, because there are many different reasons to cite a photograph. Your instructor would be able to give you more specific advice. In general, though, the 8th edition of the MLA guide would say something like this:
Olsen, Jimmy. “Superman Rescues Boy Scouts from Lava Pit.” Photograph. The Daily Planet . July 22, 1956.
If you found the picture on a blog or a Flickr gallery, adjust the citation accordingly. If you found the image as the result of a Google search for something, you might very well end up finding a page that re-uses someone else’s picture without appropriately giving credit. There are many variables. Talk to your instructor, who will be the one grading your work, and will therefore be the right person to advise you on what to do.
is the text or what you wrote supposed to be centered in the page or to the left margin
Left margin.
Pingback: New Graphic for MLA Style Paper Handout | Jerz's Literacy Weblog
cool it was helpful
Pingback: Business Question of the day! Thursday, March 10, 2016 | thebuzinessbreakdown
I think you should include online resource citation instructions
Click on “Citing” at the top of the page. One of the options on the other end of that link is how to cite a web page.
Pingback: How To Put Double Space On Microsoft Works – Information
which writing style (MLA, APA) have more importance for students of social sciences, media sciences and business?
It depends on the instructor or editor who’s calling the shots. http://subjectguides.library.american.edu/c.php?g=175008&p=1154150
Very informative. It helped introduce my tired old mind to the MLA format. So, I can better help coach and prepare my wife for her English course. Thank you very much.
Pingback: For Future Reference: MLA Formatting | wr115fisette
Pingback: For Future Reference: MLA Formatting | wr115mhcc
I’m using a book title and author as my paper heading. How is that formatted?
I would tell my own students that a book title and the name of an author is not a good paper title, and I would ask them to write a title that catches the reader’s attention, identifies the topic, and identifies what position the paper is going to take on the topic. But if you are not my student, then I’m not the person who will be evaluating your paper. MLA style puts the book title in italics. Other than that, I really don’t have any advice for you.
Thank you very much for this useful information. As a freshman in highschool, my biology teacher asked for me to write an essay in mLA format about evolution. I had no clue what mLA format was,so I searched it up and it brought me here. In middle school I never wrote an essay in this format before,but I feel very confident to type my first mLA essay and I’m excited to do so! (Right after I finish my draft >.<) thank you very much! (⌒▽⌒)✌
This wasn’t helpful at all
Shavez, what were you looking for? This page is about formatting a paper you have already written. The first section includes links to pages about how to write essays.
u a real nigga dennis
really dude my collies and I would prefer that you didn’t use any profane language due to younger children that may be reading this
thank u i got an A 97 percent
this was very helpful i got an A 95 percent
hi my name is Jessie i have to writ a 2 pages Essay about MLA can someone help me
Dennis, what lends itself to science in the APA system? And what lends itself to the Humanities with the MLA? TIA.
As compared to MLA papers, APA papers tend to be shorter, and divided up into sections. Authors who use APA style tend to publish more frequently, because their knowledge goes out of date more quickly; so the date is prominent in APA citations, and page numbers are rare.
By contrast, people who use MLA style tend to write longer essays that aren’t divided up into standard sections like “procedure” and “conclusions.” Humanities scholarship generally doesn’t go out of date quickly. Instead of conducting experiments, humanists read and write a lot of longer essays and books, re-interpreting and quoting passages from them. MLA style makes the page numbers prominent, so that other scholars can easily find and re-read those same passages for themselves, and further the work of scholarship as it is conducted in the humanities.
Thanks for the reply. What do you mean by ” MLA style tend to write longer essays that aren’t divided up into standard sections like “procedure” and “conclusions.”? Are we not suppose to use conclusions in MLA format? In my English class, we use MLA with conclusions, but what do you mean by “procedure” and “conclusions”? I understand each instructor is different but is it right to use conclusions in an MLA paper…or am I getting confused?
Typically papers written in MLA style DO have a conclusion, but it would not be set off in a separate section under the subheading “Conclusion.” MLA papers tend NOT to follow a standard, particular structure. Papers written in the sciences DO have a fairly rigid set of sections, with separate subheadings. But it’s best for you to talk to your teacher about the specifics of any asisgnment.
Ok, thanks. I just wanted to ask and clarify it. Also, doesn’t the word “humanist” means something else entirely? The Humanist term today implies ‘human’ and is often used for atheists, for example… or am I wrong?
I used the term “humanist” to mean “a person who studies the culture of humans,” without intending the more specific meaning you mention. At my school, the humanities division includes theologians.
seems easy enough
We get asked often about what “format” the college application essay should be in. Although not generally… http://t.co/v1TTNxtE4e
Pingback: Academic paper style guide research | Screenin' Culture
When using MLA format, do you list the book title, the title of the article or both?
For guidance on citing individual sources, see the link in item 4, above. This page is about formatting the paper once you’ve already written it.
I wrote a paper and it looks just like your example. I followed everything to the “t” and my professor says that my header is indented and my paragraphs are double indented and the page numbers are in wrong format. What can I do?
Winston, I suggest you talk to your professor. I have been teaching from thiis handout for years, and when a student makes a formatting error on a rough draft, I just ask them to fix it for the revision. But your instructor is the one who designed the assignment and who evaluates your submissions, so he or she is the person to approach with questions.
I agree. .let me ask you this. Are your headers indented?
The screenshot was taken from a page that I created following the instructions for using MS-Word with a MacBook Pro. I followed the instructions that are on the page. But surely your instructor gave you guidelines, in a handout or an assigned textbook, which is why I encourage you to have this conversation with your instructor. Whether your instructor does or does not agree with the information on this page really doesn’t matter, since your instructor created the assignment and evaluates it according to his or her own criteria. I suggest you let your your teacher know you are confused about what you did wrong, and ask for an opportunity to make minor formatting changes to a paper that, we hope, met all the major criteria.
How do you add footnotes to an MLA style paper?
Most word processors will have an Insert -> Footnote or Insert -> Note (footnote or endnote) option. Most short college papers don’t need footnotes. (They aren’t for documenting sources — use an in-text citation and a Works Cited list instead.) I suggest you talk to your instructor about whether you really do need to use a footnote.
RT @DennisJerz: MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Instructions for Writing Research Essays #mlastyle http://t.co/B6pGb3Pkeh
Thank you so much!! I love the Bib builder!!
I’m glad to hear you found it helpful!
Dear Dr. Jerz,
I am writing to request permission to link your webpage, “MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Instructions for Writing Research Essays” to our website.
Marie Walcroft Librarian Lansdale School of Business
I am glad you found this page helpful. Yes, you are welcome to include a link and a brief extract.
Can you put what information is supposed to be in each paragraph???
Emma, I’m afraid I don’t understand the question. I feel like you’ve asked me what emotions are supposed to be in each verse of a song, or what colors are supposed to be in a painting. The many different kinds of songs or paintings are all created for different reasons; likewise, paragraphs are assigned, written, and read for a whole range of different reasons, so there’s no answer that covers all possible cases.
that was beautiful
I really find this useful (especially fudging the line spacing to 2.1). Good job!
Im in middle school and I have to do this. I have never heard of MLA Format and this helped ALOT. Thanks so much! Hopefully I get a good grade on this paper!
“@pretti_slimm: @Thyler_Jonzy http://t.co/QIf00vlgws try this site looks helpful”I just found a sample paper on Google
Pingback: MLA Format Papers: Step-by-step Instructions for Writing Research Essays - My Blog
Pingback: Freshman English Composition Resources
Is the Table of Contents double spaced – MLA?
i think you should add an explanation about page header. that was what i was looking for
See item 2 from the table of contents: http://jerz.setonhill.edu/writing/academic1/mla-style-papers/#page-header
when you say page numbers (Wordworth-Fuller 20), are you referring to the page number within the MLA document or the page number the text appears on within the authors works?
In this case, your paper would be referring to something you found on page 20 of the text by Wordsworth-Fuller.
With your delicate information about to write MLA format essay in right way will lead me to successful college year.
Thank you for useful information about how to write MLA format essay. Before my college year I didn’t know there were many different forms of essay. When my professor asked me to write MLA format I had no idea how to write it, but with your delicate information I think I will survive my college year. Thank you again.
I’m glad to know you found this page helpful. Most instructors will be happy to help if you stop by during their office hours, and if your prof is too busy for that most universities will have a writing center where you can get help at any stage of any assignment involving writing.
Thank you for valuable information. Before my college year in America I didn’t know what MLA Format was, but with this delicate information I will survive my college year.
Pingback: How to Write a Successful Research Paper with MLA | Critical Approaches to the American Renaissance
That means the quote is from page 20 of the book or article written by Wordsworth-Fuller.
Very good information, I really needed this incite on research paper formats. It has such thorough details and that make it so much easier to understand.
How do you in text cite a website? I didnt really see much about that.
I think you should add an explanation about page numbers. That was what I was looking for, but I couldn’t find the significant area.
Section 2 explains how to put page numbers in the header, and section 4 discusses page numbers in citations.
read it… it’s there.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > Writing an Essay in MLA Format
Writing an Essay in MLA Format
Knowing how to write a Modern Language Association—or MLA—essay is an essential part of making it through school these days. Be warned, however, that daunting little tasks await around every corner—whether it’s knowing where to set your margins, how to edit a header, the right way to format a heading, and beyond!

While we can’t write your paper for you, this guide can certainly help you understand the proper MLA format for your essay. Keep reading to learn about writing an MLA-format paper with some tips for making sure it’s done right the first time.

Get the most out of your documents with Word
Elevate your writing and collaborate with others - anywhere, anytime
What is an MLA-format essay? It’s not uncommon for associations and organizations to follow a standard format and writing style. The Associated Press (AP) and University of Chicago styles are most common in professional settings. News outlets typically prefer the AP style, while businesses and creative agencies will choose the Chicago style. Academia, on the other hand, traditionally follows APA and MLA styles. APA (not the same as AP style) comes from the American Psychological Association and is used in scholarly articles. An MLA-format essay fits the established style for citing references and formatting essays established by the Modern Language Association.
Required elements of an MLA-format paper. MLA is the preferred style when writing an essay in high school and most college settings. As with other writing styles, there are specific characteristics and items an MLA-format paper needs to include to fit the bill of the style. Every MLA-format essay must include the following:
- One-inch margins
- Double-spaced text
- Easy-to-read font (typically Times New Roman) in size 12
- New paragraphs indented 0.5 inches
- Italicized media titles (books, magazines, etc.), no underlining
- Page numbers in the header 0.5 inches from the top of the page
- Oxford comma
- Center-justified title
- Headings and subheadings
- Clearly labeled and titled tables and figures
- Parenthetical citations
In addition to the listed elements above, every MLA essay must include a Works Cited. MLA format doesn’t require a title page, but it also doesn’t deem them unnecessary, so it’s up to your professor whether you’ll need one or not. One way to take the edge off the process of writing this type of essay is to use a free template or a handy built-in tool that helps you build bibliographies and more.

Tips for meeting MLA formatting guidelines. It’s said that the devil is in the details, and it’s never truer than when it comes to MLA-format essays. The following tips are areas to pay attention to when writing your essay:
- Set your margins. Your software might be set to one-inch margins, double-spaced text, and 0.5-inch indentations by default—but you can save yourself the trouble (and a headache) later in the writing process by adjusting them before you get started. Of course, one of the best parts about using a computer to write your essay is that you can always make adjustments later.
- Straighten out your headings . One area students might miss with MLA formatting is with the title, headings, and subheadings. It’s normal to want to use bold or italicized typeface on your titles and headings to make them stand out from the rest of the text. MLA style specifically calls for them to match the rest of the text without any alterations aside from title case. A centered or left-justified heading will stand out enough from the rest of your text that it needn’t any additional adjustments.
- Understand subheadings. While primary headings aren’t to receive any special formatting, subheadings will be changed to set them apart from their headings. For example, if your heading is about mammals, you might have subheadings about land and water mammals. You can further organize your water mammals subheading into types of whales and dolphins. Using subheadings helps to organize your writing and makes it easier to consume as a reader.
- Know how to cite your work. The information you’re presenting in your essay didn’t mysteriously appear from out of the ether. You need to give credit where it’s due when writing an MLA-format paper, so you’re giving credit to the original author of your sources. You can also improve your writing credibility and avoid plagiarism. Plagiarism is one of the biggest academic offenses a student can commit and could lead to expulsion in some cases. Properly citing your work with parenthetical citations and quoting authors when necessary will help to keep you covered.
When it comes down to it, practice makes perfect. The more essays you write, the better you’ll become at writing and meeting the expectations of MLA style. Before you know it, MLA format will be second nature, and everything will fall into place.
Still having a hard time visualizing what an MLA essay looks like? Check out a sample paper so you can see first-hand how they’re formatted!
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

How to write a plot twist in your story
When executed carefully, a plot twist has the power to shock and dazzle your reader. Learn how you can incorporate one into your writing.

What's the difference between a memoir and an autobiography?
Explore the differences between memoirs, autobiographies, and biographies.

When to use 'while' vs. 'whilst'
“While” and “whilst” are usually interchangeable, but not always. See how they differ and learn how to use them effectively.

What is touch typing (and why is it important)?
Learn about the benefits of touch typing and how it can help you type faster and more accurately.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories
MLA Style Essay Made Easy: Walkthrough of MLA Formatting
Table of contents
- 1 Understanding MLA Format
- 2.1 Margins & Font
- 2.2 Title Page Requirements
- 2.3 Page Numbering & Headers
- 2.4 Proper Spacing & Indentation
- 3.1 General Guidelines for MLA Citations
- 3.2 The Author Page Citation Format Rule
- 3.3 Standard Citation Format For Print Sources
- 3.4 Citing a Work by Multiple Authors in MLA
- 3.5 MLA Guidelines for Print Sources With Unknown Authors
- 3.6 Citing Works With the Same Last Names
- 3.7 Citing Multiple Works by the Same Author in MLA
- 3.8 Citing Multivolume Works in MLA
- 3.9 Citing the Bible
- 3.10 Citing Indirect Sources
- 3.11 Citing Electronic Sources
- 4.1 Proper MLA Formatting of Quotations
- 4.2 Brief Quotations
- 4.3 Long Quotations
- 4.4 Adding or Omitting Words in Quotes
- 5.1 Works Cited Entries in MLA 9th Edition Style
- 5.2 Books and e-Books
- 5.3 Journal Articles
- 5.4 Websites & Online Sources
- 5.5 Films & Multimedia
- 5.6 Interviews & Personal Communication
- 6 Bibliographic & Content Notes
- 7.1 Specific MLA Abbreviations
- 8 Formatting Numbers in MLA
- 9 Lists in MLA
- 10 MLA Formatting Takeaway
The MLA format is the most common type of formatting used for academic papers. Every student in the US should become familiar with this format for the research papers and essays they submit. It should be referred to when citing sources and formatting papers in literature, language, and the arts. This format is crucial for understanding the guidelines of citation. It can also help students present their work in an organized and straightforward manner. Throughout this formatting guide, we’ll explore the key areas of how to write in MLA format effectively.

Understanding MLA Format
Every new high school student asks, “ What is MLA format? “. The Modern Language Association format provides guidelines for formatting styles and citations that students can use for academic writing. It’s mainly used for subjects in humanities and liberal arts. Students must use this type of formatting when writing research papers for languages, literacy studies, visual arts, media studies, and similar courses. Scientific research doesn’t require students to write a paper in MLA format.
The MLA format for papers has been introduced previously. A group of teachers and like-minded students founded the Modern Language Association in 1883. This group’s mission was to promote the studies of language and literature. They developed the original MLA formatting guide to provide a basic outline of how to cover research papers. These MLA paper formatting guidelines were used to help students create organized research papers.
Of course, things have changed a lot since 1883. The MLA Handbook has kept up with the times. It has undergone several revisions and updates throughout the years. The most recent update was in 2021, when the 9th edition of the handbook was released. The MLA 9 essay format edition included valuable information for the modern student, such as citing digital sources. Now, students can also access digital tools for formatting, like the MLA citation generator and other online resources.
Throughout the years, there has been consistency with the MLA Handbook. Its purpose is to provide guidelines for students who must properly format your papers in MLA format and credit sources. Using this format helps students ensure that the presentation of their work is accurate and consistent.
Basic MLA Formatting Guidelines
There are specific criteria every MLA format essay must include. This section will cover some essential MLA formatting rules that every student should become familiar with. These rules are set so that every MLA paper has a consistent layout. They ensure good readability and organization.
Margins & Font
A student should never submit a research paper covered in a font from the top corner to the bottom. Every paper must have a 1-inch margin. The margins for MLA writing format should be on every side of the paper ( one inch from the top, bottom, left, and right ).
Always follow your professor’s instructions for font style and size. If no instructions are stated, the general MLA format font size rule is to use Times New Roman 12-point. You may use a different professional-looking font if your professor has approved it.
Title Page Requirements
The correct MLA format doesn’t require students to craft a title page. Instead of a separate page, students should present the following information in the top left corner of the first page before the first MLA header:
- Student’s name
- Professor’s name
- Course name
This information should always be stated above the paper’s title when writing in MLA format. The title must be entered on the following line. Always ensure the essay title is centered, uses title case-sized font, and double-spacing.
Page Numbering & Headers
The MLA formatting instructions also require students to use the ‘running head’ rule to number their pages. Each separate page of the essay in MLA format will be numbered. The page number will appear in the upper right-hand corner, with the student’s last name in front of it. The first page of the MLA paper should look similar to this:
Campbell- 1
Proper Spacing & Indentation
The MLA format paper should always be double-spaced. The double space leaves room for the professor to add notes. Students also need to use a 1/2-inch indent from the left margin for the first sentence of every paragraph.
In-Text Citations
With every research paper, students must cite their sources using in-text citations. This is how credit can be given to the original author. It’s also a good indicator of where the facts and research came from. The MLA format requirements state that students must use specific guidelines for citing sources.
General Guidelines for MLA Citations
A general citation can be used for print or digital. It will include the author’s last name and page numbers that contain the information. You will only need to reference the page number if you mention the author’s name in the sentence with your citing information.
The Author Page Citation Format Rule
The author page citation format is a simplified version of a general MLA citation. For this one, students only need to state the author’s last name and the page number where the information can be found. The author page citation will look like this:
Standard Citation Format For Print Sources
The MLA formatted paper guidelines are for citing sources from a book or print media. The in-text citation should include the author’s name and the page number with the information. It should also include the book title, edition (if specified), publisher, and year of publication. Here is an example of a standard citation for print.
Last Name, First Name, Book Title, Publisher, Year, Page (or page range)
Citing a Work by Multiple Authors in MLA
Sometimes, a student needs to cite sources that more than one author wrote. How you cite the source will depend on how many authors are included in the work. You can have both names and the page number if there are only two authors. Here is an example:
Barnes and Roth, 37
It’s essential to avoid using too many commas when citing sources. If three or more authors write the work being cited, you will only include some of their names. Instead, you will mention the first author’s last name followed by “et al”. It should look like this:
Barnes et al, 37
MLA Guidelines for Print Sources With Unknown Authors
There may be occasions where a student needs to cite sources that have unknown authors. For these situations, put the title of the work being referenced and the page number. The citation should look like this:
Title Work, 37
Citing Works With the Same Last Names
The MLA format has a very specific rule for citing text written by multiple authors with the same last name. With this type of work, mention the title and the edition number (if applicable) after the last name. Don’t forget to mention the page number as well. Here is an example of what it should look like:
Barnes, Title Work, 3rd ed., 37
Citing Multiple Works by the Same Author in MLA
Occasionally, students may need to reference multiple works from the same author. Each piece of work should have its citation. However, students can group them by using the word ‘and’. Here is an example:
(Barnes, Title Work 37) and (Barnes, Text Example 58)
Citing Multivolume Works in MLA
If an author has several volumes of a title piece, you must include the volume number in your citation. This is very easy to do. All that is required is to put the volume number between the author’s name and the page number. It should look like this:
Barnes vol 3 37
Citing the Bible
Citing a passage from the bible is slightly different than other pieces of work. In this citation, the student won’t give credit to an author. Instead, they will mention the verse, chapter, and page. For example:
Matthew 5:3-10
Citing Indirect Sources
According to the MLA Handbook, students should always use material from the source. But, sometimes, this isn’t possible. An indirect quote or indirect source is when you receive the information secondhand. For this type of citation, students should always use “qtd. in” along with the source they read. It should look similar to this:
qtd. in Roth 59
Citing Electronic Sources
When researching papers online, students must provide relevant information about the URL they used. An electronic source citing MLA format should include the following information:
- Author’s name
- Article title
- Website’s name
- Date of access
Here is an example of how to make a webpage citation when citing online sources for essays:
Barnes, Title Work, Webpage Name, 20 October 2023, www.examplesite.com/example123
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Quoting and paraphrasing are common in academic writing. Proper quoting citations with the MLA format is imperative because it helps students avoid plagiarism. If a student needs to reference another person’s idea, they should always use quotes, check PapersOwl if you have any doubts. Quotes can help students incorporate the outside information into their work. The MLA Handbook has specific guidelines for using quotes in academic papers.
Proper MLA Formatting of Quotations
Everyone must follow proper formatting rules to avoid plagiarism when writing a paper in MLA format. Luckily, these rules aren’t complicated. The quote should always have a parenthesis at the end that includes the author’s last name and the page number. Another way that’s acceptable to format a quote is if the author’s name and page number are used in the sentence before the quote. Here are two examples of quotation formatting that can be used:
- “This is an example quote.” (Barnes, 37)
- According to Barnes on page 37, this is how you use quotation marks. “Example quote placed here.”
Brief Quotations
A brief quote usually consists of less than three lines of text. The best way to format these quotes is to integrate the author’s name in the sentence leading up to the quote, followed by the exact quote in quotation marks. It should look similar to this sample MLA format:
According to Barnes, “There are many different quotes that can be acceptable to use in academic writing. Students should always use quotes to avoid plagiarism.”
Long Quotations
A long quote will contain three or more lines of text. The formatting for these quotes is different from a brief quote. Students will need to separate the quote from the rest of the paper. After a sentence leading up to the quote, it should begin on the following line (double-spaced). Always indent the quote one inch from the left margin.
Students can approach this quote with a parenthesis at the end of an introductory sentence. Always use the style that works best with the research paper being presented.
The long quotation should look similar to this:
“Every good research paper should include relevant quotes from an author or other professionals. This gives the reader more insight into the topic being discussed. It also helps the student avoid plagiarism when they want to share another person’s idea to support their research topic.”
(Barnes, 37)
Adding or Omitting Words in Quotes
Students may need to add or omit words in the quote for their MLA paper. Extra words may need to be added to a quote to help the reader better understand what the quote is referencing. When adding words to a quote, always add brackets to show that they are separate from the original statement. Here is an example of how and when to add words to a quote:
Original quote: “The new workspace should help them stay productive.”
Quote with added words: “The new workspace should help them [shop employees] stay productive.”
Omitting words could be necessary if the student needs to shorten the text for block quotations. They can keep the quote brief and to the point by omitting words. In this situation, nothing is done to show words have been removed. Quotes should be as original as possible. Only remove words if they add no value to the text. Here is an example of when it’s appropriate to remove words from a quote:
Original quote: “It’s easier to access online games using a mobile app on your smartphone.”
Quote with omitted words: “It’s easier to access games using an app on your smartphone.”
The example above shows that the quote’s message is read similarly to the omitted words. Removing the text doesn’t change the tone or message of the quote. Never omit words if the quote reads differently. For example, removing the phrase “mobile app” from the original quote above would completely change what’s being said.
MLA Works Cited Page Guidelines for Different Types of Sources
The works cited page is used as a reference list. Students will provide all the sources they used to get information for their MLA-style essay. This list aims to help readers locate the sources to verify the information. It proves the students didn’t make up any information shared in their essays.
A proper MLA format for the works cited page will include every resource used during the research process. This will include:
- Newspaper articles
- Magazine articles
Every MLA research paper should contain cited sources in a specific order. This will be further explained in the sections below.
Works Cited Entries in MLA 9th Edition Style
According to the most recent edition of the MLA format for an essay, the cited page should contain a list of sources alphabetically. All authors should be listed from A to Z. For sources with unknown authors, students can use the title to determine where it belongs.
The MLA format requires all sources listed on the cited page to be double-spaced. A hanging indent must be used for each new source added to the list.
Books and e-Books
A specific MLA citation format can be used for referencing information from books and e-books. Every book citation should include the following information in this order:
- Author’s name (last name first- i.e., Barnes, Michael)
- Publication Date
- Book Format (print or e-book)
Here are a few citation examples for books and e-books:
- Hill, Nathan. Wellness: A Novel. Bond Street Books. 2023. Print.
- Sokunbi, Bola. Clever Girl Finance: Ditch Debt, Save Money, and Build Real Wealth. Wiley. 2019. E-Book.
- Harris, Jillian and Wesszer, Tori. Fraiche Food, Fuller Hearts. Penguin Canada. 2023. Print.
Students can also simplify this process using a b ook citation generator or other online resources.
Journal Articles
Journal works are frequently referenced in students’ papers. All of the required information must be included when a journal or magazine article is mentioned on the cited list using the MLA research paper format. Every journal article reference should contain the following parenthetical citations in order:
- Author’s last name and first initial ( i.e. Barnes, M )
- Article title: Subtitle (if applicable) in quotation marks
- Journal name
- Volume & issue
- DOI (digital object identifier) for online journals
The following examples show how journal articles should be mentioned on the cited page.
With subtitle: Jones, T. “The Importance of Citing Sources: A Beginner’s Guide To The Cited Page”. Teacher’s Journal Deluxe. Vol 12, no. 3. May, 2017. pp 30-33.
Without subtitle: Barnes, M. “How Professors Want You To Cite Sources”. Academic Journal. Vol 9, no. 11. Sept., 2020. pp 14-15.
Students can also use this format to cite a newspaper , magazines, and other print articles.
Websites & Online Sources
Students can now access more information online to help them research their essays. Sources online are acceptable as long as the web page is cited using the MLA paper format. When finding online resources, it’s common to come across recycled information. Always use the source to make your cited page as credible as possible. The best type of online sources to use are .gov and .org websites. Using .com/.ca/.co websites is acceptable if it’s a credible source or brand (i.e., www.nationalgeographic.com or www.forbes.com). Try to avoid citing blogs or social media posts unless you are directly quoting the person posting from the account.
According to the MLA format guidelines, the following information should be stated in order when you make web page citationa for every research paper:
- Author’s Name (if available)
- Source Title
- Website Title
Here is an MLA format example of how an online source should be cited in the MLA footnotes.
Barnes, Michael. “How To Cite Sources”. Proper Formatting Online, 10 May 2023, www.examplesite.com/how-to-cite-sources .
Films & Multimedia
Since students should use the MLA essay format on art subjects, there may be times when they need to generate citations from Video . This is very common in media studies. When referencing film, always include the following information in order:
- Director’s name
- Production Company
- Year of release
- Format of the source used ( i.e., DVD, Blu-ray, digital )
Here are a couple of examples of how to reference a film on the cited page:
- Craven, Wes, director. Scream. Miramax. 1996. DVD.
- Gerwig, Greta, director. Barbie. Warners Bros. 2023. Google TV.
Students may also reference multimedia posted online, such as YouTube videos. The creator’s name may not be available when referencing an online video. In this situation, it’s acceptable to cite their username. The following information should be cited in order when referencing an online video.
- Creator’s name or username
- Video title (in quotation marks)
- Platform or website name
- Channel (if applicable)
- The date the video was posted
Here is an example of how to generate citations from video through online multimedia:
Warner Bros Entertainment. “Singin’ in the Rain | Good Mornin'”. YouTube. 2022. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pyMU8O2B2Vs
A similar format can be used for works cited from podcasts, radio shows, and other online video and audio media.
Interviews & Personal Communication
Certain projects will require students to conduct personal interviews. It’s still necessary to cite sources when using information from interviews. A student can also directly quote their interview subject in the research paper. There are several ways that students can interview people for research. This includes:
- Online chat
Personal interviews and communications are an efficient way to get valuable insight and real information on a topic. Citing these communications is also very easy. Mention the interviewee’s name (last name, first name) followed by the type of communication and the date of contact. Students can also add any other relevant information that could be useful to the reader ( i.e., business name, occupation, etc. ). Here is an example of how a personal interview can be cited:
Richards, Blake. Email Interview. 19 October, 2022.
Forte, Johan. Optometrist. Personal interview. 15 April 2023.
In the second example, the interviewee’s occupation was relevant to the communications. The student provides this information using the MLA format for the research paper to help the reader understand why the quote is relevant to the subject.
Bibliographic & Content Notes
An MLA paper should provide as much information as possible. Bibliographic and content notes are excellent tools. They are a great addition to academic papers because they provide more information on the sources that were used for research. The works cited page should contain basic information about the sources. However, the bibliographic and content notes allow students to provide detailed information on these sources. It’s common for the notes to contain more analyses, context, and commentaries on the topic.
Sometimes, a student wants to provide information about a source that isn’t directly related to the essay’s main topic. For example, they may have read an online article that inspired their idea for the research project. They can cite this source in the content notes and explain why it was important for their piece. They may also want to provide more context about their ideas or experiences that were useful to the research paper.
For example, a student may cite a chapter in a book that was directly related to information stated in their paper. However, much information was shared in the book that helped craft the essay. In the bibliographic notes, students can provide more context about the content. They can also include notes that will give the reader more insight into how the source relates to the essay’s main topic.
Overall, the main goal of using bibliographic and content notes is to ensure readers thoroughly understand the information. Students can provide their thoughts and crucial information when this section is used effectively. An excellent bibliographic page can also help students establish credibility with their research.
Common MLA Abbreviations
Using abbreviations in-text citations is common because it concisely presents the information. The MLA style cited page should be easy to read. Abbreviations help save space and list the information in a presentable format.
The abbreviations most commonly used in the MLA format are ‘et al.’, ‘vol’, and ‘p’.
- “Et al.” is an abbreviation for et al Ia. This phrase is used to indicate that there were multiple authors credited to the source. Instead of naming each individual, only the first author’s name will be listed, followed by et al.
- “Vol.” is an abbreviation for volume. This is about the volume number of the book, journal, magazine, or other source used.
- “P.” is the abbreviation for page. When one page is listed, it will look like this: p. 12. If a page range is listed, then the abbreviation ‘pp’ will be used, such as pp. 12-18.
Specific MLA Abbreviations
There are MLA abbreviations that are used for specific citations. These are specialized abbreviations that should only be used for certain situations.
“Ibid” is an abbreviation for ibidem. Students may have to use this abbreviation to list multiple citations from the same source. For example, there could be various page numbers that a student needs to cite from one book. In this case, the citation should look like this:
First citation: Barnes 15
Second citation: Ibid 73
“N.d.” is another specific abbreviation. This one should only be used if a publication date is unavailable. Here is an example of how to use the n.d. abbreviation properly:
Barnes, Michael. Example Book. Example Publisher. N.d. Print.
Formatting Numbers in MLA
There are formatting rules for using numbers in research essays and in-text citations. All small numbers (one through nine) should be spelled out. Some examples include one chapter, two cups of sugar, or seven days late.
Once numbers reach the double digits, students should use the Arabic numeral format. Any number above 10 should be printed like this: 11, 12, 13, 14, etc.
The number should always be in Arabic numerals when it comes to measurements, ages, dates, and units. For example: 5 pounds, 15 minutes, 60%, 32 degrees, etc. The Arabic numeral format should also be used when there is a series of numbers, such as 4 children, 8 teenagers, 13 adults, 6 seniors.
Large numbers should be written out. This includes any number separated by commas, like fifty thousand, three million, or a billion.
Sentences that contain mixed numbers will use both numeral and print. It’s essential to remain consistent with how these sentences are worded. Here is a good example: 6 four-year-olds, 8 five-year-olds, 10 six-year-olds, and 4 seven-year-olds attended the birthday party.
Lists in MLA
Students must avoid cramming too much information in one section using the MLA format for paragraphs. MLA recommends lists as a practical way to organize information in essays. Students can use bullet lists or numbered lists. Specific guidelines should be followed to ensure the lists are being used accurately.
Bulleted lists present a list of items in no particular order on separate lines. The list states each item individually, making it easier to read. Here is an example of how a bulleted list could be used:
Recipe Ingredients
- 1 cup sugar
- 1/2 tsp salt
- 2 cups flour
- 1/2 cup softened butter
Numbered lists are used to present items or information in consecutive order when students write a paper in MLA format. They are commonly to use for directions to be followed. Here is an example of using a numbered list:
- Preheat the oven to 350 degrees F.
- Mix all wet ingredients together.
- In a separate bowl, mix dry ingredients together.
MLA Formatting Takeaway
The MLA style paper is used for academic papers by students in the US. This format is an excellent way to ensure every written paper has been cited correctly. Students must use parenthetical citations to avoid plagiarism when presenting research. Using the MLA formatting for research papers correctly ensures that every essay submitted is presented in a clear and understandable writing style.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Format an Essay
Last Updated: July 29, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Carrie Adkins, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano . Carrie Adkins is the cofounder of NursingClio, an open access, peer-reviewed, collaborative blog that connects historical scholarship to current issues in gender and medicine. She completed her PhD in American History at the University of Oregon in 2013. While completing her PhD, she earned numerous competitive research grants, teaching fellowships, and writing awards. There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 92,802 times.
You’re opening your laptop to write an essay, knowing exactly what you want to write, but then it hits you: you don’t know how to format it! Using the correct format when writing an essay can help your paper look polished and professional while earning you full credit. In this article, we'll teach you the basics of formatting an essay according to three common styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago Style.
Setting Up Your Document

- If you can’t find information on the style guide you should be following, talk to your instructor after class to discuss the assignment or send them a quick email with your questions.
- If your instructor lets you pick the format of your essay, opt for the style that matches your course or degree best: MLA is best for English and humanities; APA is typically for education, psychology, and sciences; Chicago Style is common for business, history, and fine arts.

- Most word processors default to 1 inch (2.5 cm) margins.

- Do not change the font size, style, or color throughout your essay.

- Change the spacing on Google Docs by clicking on Format , and then selecting “Line spacing.”
- Click on Layout in Microsoft Word, and then click the arrow at the bottom left of the “paragraph” section.

- Using the page number function will create consecutive numbering.
- When using Chicago Style, don’t include a page number on your title page. The first page after the title page should be numbered starting at 2. [5] X Research source
- In APA format, a running heading may be required in the left-hand header. This is a maximum of 50 characters that’s the full or abbreviated version of your essay’s title. [6] X Research source

- For APA formatting, place the title in bold at the center of the page 3 to 4 lines down from the top. Insert one double-spaced line under the title and type your name. Under your name, in separate centered lines, type out the name of your school, course, instructor, and assignment due date. [8] X Research source
- For Chicago Style, set your cursor ⅓ of the way down the page, then type your title. In the very center of your page, put your name. Move your cursor ⅔ down the page, then write your course number, followed by your instructor’s name and paper due date on separate, double-spaced lines. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Double-space the heading like the rest of your paper.
Writing the Essay Body

- Use standard capitalization rules for your title.
- Do not underline, italicize, or put quotation marks around your title, unless you include other titles of referred texts.

- A good hook might include a quote, statistic, or rhetorical question.
- For example, you might write, “Every day in the United States, accidents caused by distracted drivers kill 9 people and injure more than 1,000 others.”

- "Action must be taken to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving, including enacting laws against texting while driving, educating the public about the risks, and giving strong punishments to offenders."
- "Although passing and enforcing new laws can be challenging, the best way to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving is to enact a law against texting, educate the public about the new law, and levy strong penalties."

- Use transitions between paragraphs so your paper flows well. For example, say, “In addition to,” “Similarly,” or “On the other hand.” [16] X Research source

- A statement of impact might be, "Every day that distracted driving goes unaddressed, another 9 families must plan a funeral."
- A call to action might read, “Fewer distracted driving accidents are possible, but only if every driver keeps their focus on the road.”
Using References

- In MLA format, citations should include the author’s last name and the page number where you found the information. If the author's name appears in the sentence, use just the page number. [18] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- For APA format, include the author’s last name and the publication year. If the author’s name appears in the sentence, use just the year. [19] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- If you don’t use parenthetical or internal citations, your instructor may accuse you of plagiarizing.

- At the bottom of the page, include the source’s information from your bibliography page next to the footnote number. [20] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Each footnote should be numbered consecutively.

- If you’re using MLA format, this page will be titled “Works Cited.”
- In APA and Chicago Style, title the page “References.”

- If you have more than one work from the same author, list alphabetically following the title name for MLA and by earliest to latest publication year for APA and Chicago Style.
- Double-space the references page like the rest of your paper.
- Use a hanging indent of 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) if your citations are longer than one line. Press Tab to indent any lines after the first. [23] X Research source
- Citations should include (when applicable) the author(s)’s name(s), title of the work, publication date and/or year, and page numbers.
- Sites like Grammarly , EasyBib , and MyBib can help generate citations if you get stuck.
Formatting Resources

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-englishcomposition1/chapter/text-mla-document-formatting/
- ↑ https://www.une.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/392149/WE_Formatting-your-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://content.nroc.org/DevelopmentalEnglish/unit10/Foundations/formatting-a-college-essay-mla-style.html
- ↑ https://camosun.libguides.com/Chicago-17thEd/titlePage
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/page-header
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/title-page
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/writing-speaking-resources/mla-8-style-format
- ↑ https://cflibguides.lonestar.edu/chicago/paperformat
- ↑ https://www.uvu.edu/writingcenter/docs/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://www.deanza.edu/faculty/cruzmayra/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://monroecollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=589208&p=4073046
- ↑ https://library.menloschool.org/chicago
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Maansi Richard
May 8, 2019
Did this article help you?
Jan 7, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Storyteller's Sale
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
MLA Format: The Ultimate Guide to Correctly Formatting Your Paper

By Hannah Yang

So you need to create an MLA heading? You’re not alone—MLA format is one of the most common styles you’ll be expected to use when you’re writing a humanities paper, whether you’re a high-school student or a PhD candidate.
Read on to learn what a correct MLA heading looks like and how to create one that works like magic.
What Is an MLA Heading?
How do you format an mla heading, what is an mla header, how do you format an mla header, headings are only the beginning, commonly asked questions about mla headers, final thoughts.
The term “MLA heading” refers to five lines of important information that appear at the top of the first page.
Here are two examples of what an MLA heading could look like:
Hermione Granger
Professor McGonagall
Transfiguration—6th period
18 October 1991
“How to Turn A Matchstick into a Needle”
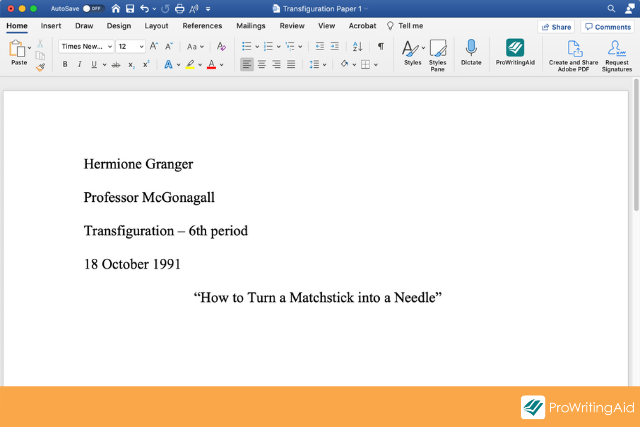
Harry J. Potter
Prof. Remus Lupin
Defense Against the Dark Arts
4 March 1994
“Why I Think My Professor Is a Werewolf”
Why are these headings important? Well, your teacher probably collects hundreds of papers every year. If any identifying information is missing from these assignments, grading and organizing them becomes much more of a challenge.
MLA headings ensure that all key information is presented upfront. With just a glance at the first page, your teacher can easily figure out who wrote this paper, when it was submitted, and which class it was written for.

What Are the Parts of an MLA Heading?
An MLA heading should include:
- Your instructor’s name
- The name of the class
- The date the assignment is due
- The title of your paper
Your instructor may give you specific guidelines about how much detail to include in each line. For example, some teachers may ask you to refer to them by their titles, while others may ask you to use their full names. If you haven’t been given any specific instructions, don’t sweat it—any option is fine as long as it’s clear and consistent.
Follow these formatting rules for your MLA heading:
- Start each piece of information on a separate line
- Don’t use any periods, commas, or other punctuation at the end of the line
- Keep the heading double-spaced, in the same font as the rest of your paper
- Left-align the first four lines (they should start at the 1-inch margin on the left side of your paper)
- Center the title (it should appear in the middle of your paper)
- Make sure your title is in title case
Title case means that major words should be capitalized and minor words should be lowercase. Major words include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, and any word longer than four letters. Minor words include conjunctions, prepositions, and articles.
Tip: Remember that Hermione’s “Society for the Promotion of Elfish Welfare” shortens to S.P.E.W., not S.F.T.P.O.E.W—only the major words are capitalized!

The MLA heading should only appear on the first page of your paper . But wait, you’re not done yet! In the rest of your paper, you need to include something called an MLA header at the top right corner of every page.
Think of the MLA header as a short, simple “You are here” marker that shows the reader where they are in the paper. By looking at the MLA headers, your instructor can easily understand where each page goes and which paper it belongs to.
What Are the Parts of an MLA Header?
The MLA header consists of your last name and page number.
For example, the second page of Hermione Granger’s essays would be labeled “Granger 2”, the third would be labeled “Granger 3”, and so on.
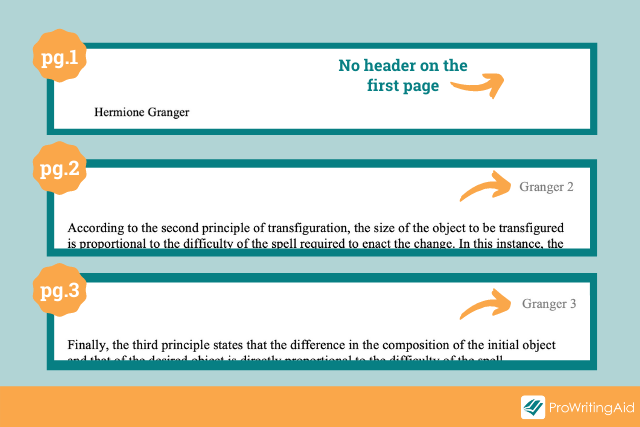
Creating MLA Headers in Microsoft Word
If you’re writing your paper in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Click Insert
- Scroll down to Page Numbers and click on it
- Set the position to “Top of Page (Header)”
- Set the alignment to “Right”
- Make sure there’s no checkmark in the box for “Show number on first page”
- Click on the page number and type your last name before the number
- Set your font and font size to match the rest of your paper, if they don’t already
Creating MLA Headers in Google Docs
If you’re writing your paper in Google Docs, follow these steps:
- Scroll down to Page Numbers and hover over it
- Choose the option that sets your page number in the upper right corner
- Set your font and type size to match the rest of your paper, if they don’t already
Tip: After you create your first MLA header, save a template document for yourself that you can re-use next time, so you don’t have to follow these steps every time you write a paper!
Once you've got your headings sorted, it's time to start writing your paper. While we can't help you edit the content of your essay , ProWritingAid is here to make sure your grammar, spelling, and style is on point.
As well as checking your grammar, ProWritingAid also shows you your progress towards key goals like varied sentence structure, active voice, readability, and more. The target scores are all based on averages for real essays, so you'll always know if you're on track.
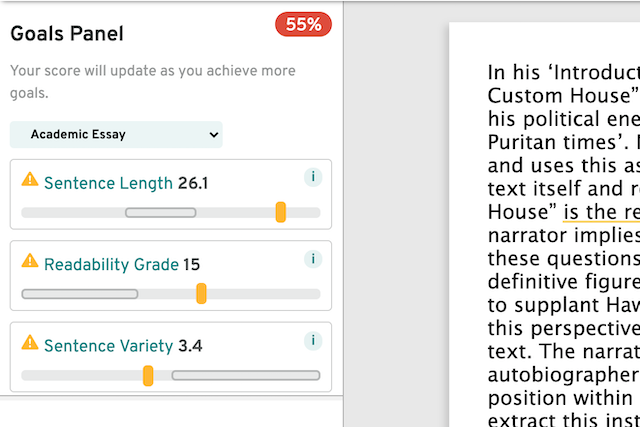
Ready to start receiving feedback before you submit your work?











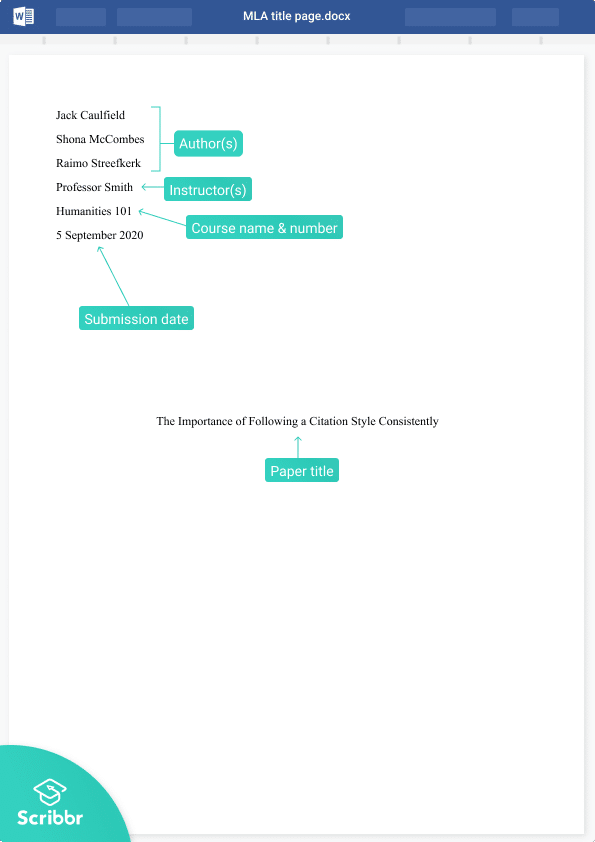
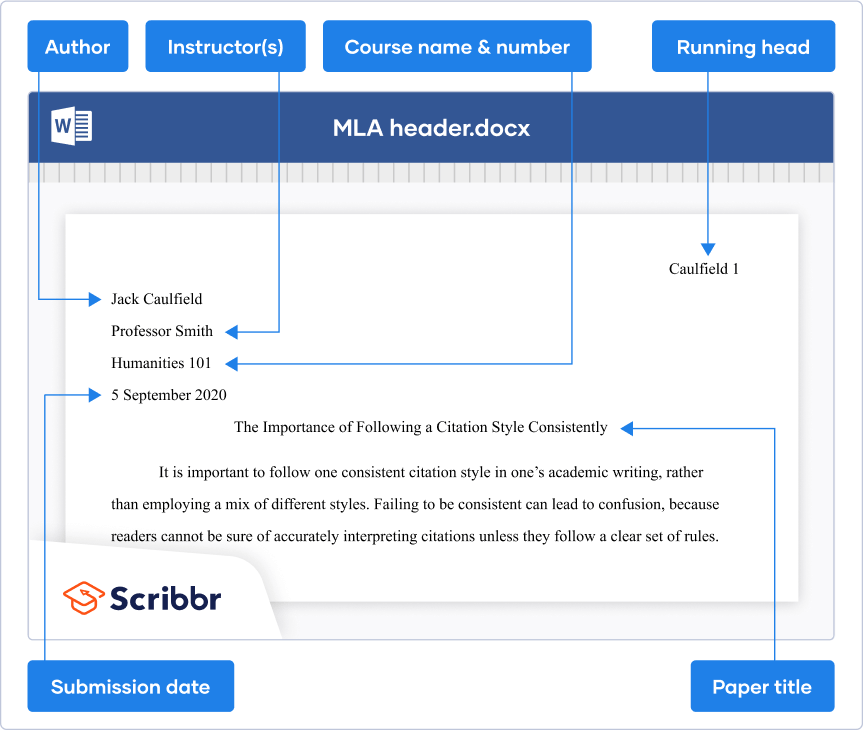



IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper. Double-space the text of your paper and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are each distinct from one another.
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
MLA formatting rules. 1 The sources page is referred to as the works cited page. It appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes. 2 The entire paper is double-spaced, including block quotations and the references on the works cited page. 3 Use block quotes for quotations that are four lines or longer.
General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Works Cited Page. Resources on writing an MLA style works cited page, including citation formats. Basic Format Basic guidelines for formatting the works cited page at the end of an MLA style paper Books
Here's how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition. On the first line, write your full name (flush left) On a new line, write your professor or instructor's full name. On a new line, write the course code and course name. On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style paper. ... create a title page instead of listing all authors in the header on page 1 of the essay. On the title page, list each student's full ...
The nine core elements of MLA citations. 1. Author. Begin each source entry with the name of the author (s) or creator (s). The name of the first author is always inverted (Last name, First name). When a source has two authors, the second author's name is shown in the normal order (First name Last name).
Get started with MLA style. Learn how to document sources, set up your paper, and improve your teaching and writing. Document Sources Works Cited Quick Guide Learn how to use the MLA format template. Digital Citation Tool Build citations with our interactive template. In-Text Citations Get help with in-text citations. Endnotes and Footnotes Read our …
How to Format Your Essay in MLA Style. Now, let's go through step-by-step instructions to help you correctly format your essay. 1. Margins and Page Layout. Go to the Page Layout settings in your word processor and set one-inch margins on all sides of the paper. Set the text to be left-aligned.
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange. Indent the next line and begin typing your text. Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand ...
Formatting the Header in MLA. To create a header for your first page, follow these steps: Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin. Type your name, your instructor's name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
Like all the other text in an MLA style paper, the title block is double-spaced.; The title is in the same font as the rest of the paper — it is not boldface, or enlarged.; There is no extra space above or below the title.; A truly informative title will include the general topic, and your precise opinion on that topic. (So, if you pan to compare Hamlet and Macbeth, your title should state ...
Every MLA-format essay must include the following: One-inch margins. Double-spaced text. Easy-to-read font (typically Times New Roman) in size 12. New paragraphs indented 0.5 inches. Italicized media titles (books, magazines, etc.), no underlining. Page numbers in the header 0.5 inches from the top of the page.
Each separate page of the essay in MLA format will be numbered. The page number will appear in the upper right-hand corner, with the student's last name in front of it. The first page of the MLA paper should look similar to this: Campbell- 1. Proper Spacing & Indentation. The MLA format paper should always be double-spaced.
MLA style is most commonly used to cite sources within the language arts, cultural studies, and other humanities disciplines. This resource, revised according to the 9th edition of the MLA manual published in April 2021, offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, and the Works Cited page.
Use quotation marks around the title if it is part of a larger work (e.g. a chapter of a book, an article in a journal, or a page on a website). All major words in a title are capitalized. The same format is used in the Works Cited list and in the text itself. Place in quotation marks. Italicize.
If your instructor lets you pick the format of your essay, opt for the style that matches your course or degree best: MLA is best for English and humanities; APA is typically for education, psychology, and sciences; Chicago Style is common for business, history, and fine arts. 2. Set your margins to 1 inch (2.5 cm) for all style guides.
Creating MLA Headers in Microsoft Word. If you're writing your paper in Microsoft Word, follow these steps: Click Insert. Scroll down to Page Numbers and click on it. Set the position to "Top of Page (Header)". Set the alignment to "Right". Make sure there's no checkmark in the box for "Show number on first page".
The Modern Language Association uses the MLA Handbook to provide guidelines on MLA Style, which is the citation style you will be using in this class to format your papers and cite your sources.Included on this page are important documents and links that will help you to use MLA properly. New MLA 9 rules state that the citation should NOT include http:\\
APA Style provides specific directions on what information to include in certain kinds of papers. Specifically, if you are conducting and reporting the results of experiments, you should follow APA's journal article reporting standards, or APA Style JARS. JARS ensure that all researchers consistently report the same kinds of information ...
MLA title page format. To create an MLA format title page, list the following on separate lines, left-aligned at the top of the page: Then leave a few blank lines and list the title of the paper, centered and in title case, halfway down the page. All text should be double-spaced and in the same font as the rest of the paper.
This page introduces you to the Modern Language Association (MLA) Style for writing and formatting research papers. To get the most out of this page, you should begin with the introductory material below, which covers what is MLA Style, why it is used, and who should apply this style to their work. Then you are invited to browse through the OWL ...
MLA style. Title. Per the MLA style, a table of contents is not obligatory. Nonetheless, if your professor requires it, this part must be called "Contents" or "Table of Contents" and lined up at the top center area of the page. Formatting. The MLA guide generally uses a simpler approach with fewer formalities regarding the TOC.
This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use. This resource contains a sample MLA paper that adheres to the 2016 updates. To download the MLA sample paper, click this link.
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...