- Climate Essay Topics Topics: 260
- Global Warming Paper Topics Topics: 184
- Deforestation Paper Topics Topics: 60
- Air Pollution Essay Topics Topics: 119
- Pollution Research Topics Topics: 236
- Biodiversity Paper Topics Topics: 58
- Recycling Topics Topics: 123
- Earthquake Essay Topics Topics: 107
- Renewable Energy Paper Topics Topics: 118
- Alternative Energy Paper Topics Topics: 92
- Dump Research Topics Topics: 47
- Ecosystem Essay Topics Topics: 71
- Hurricane Research Topics Topics: 139
- Environment Research Topics Topics: 490
- Environmental Issues Research Topics Topics: 111

317 Climate Change Essay Topics
Looking for fresh and original climate change titles for your assignment? Look no further! Check out this list of excellent climate change topics for essays, research papers, and presentations. Need some additional inspiration? Click on the links to access helpful climate change essay samples!
🏆 Best Essay Topics on Climate Change
📚 catchy climate change essay topics, 👍 good climate change research topics & essay examples, 🎓 most interesting climate change research titles, 🌶️ hot climate change topics for research, 💡 simple climate change essay ideas, ✍️ climate change essay topics for college, ❓ climate change research paper questions, ✅ climate change topics for presentation, 🔎 current climate change topics for research, ⭐ climate change research topics: our list’s benefits.
- The Problem of Global Warming and Ways of Its Solution
- Environmental Health Theory and Climate Change
- Climate Change and Future Generations
- Global Warming is Not a Myth
- Investing in Climate Change vs. Space Exploration
- Global Warming and Ozone Depletion
- Climate Change Impacts
- Climate Change Impacts on Oceans The consequences of climate change on seawater have had harmful impacts, including irreversible damage to the water’s natural environment and ecological system.
- Tree Planting and Climate Change Climate change has serious effects on the environment and the existence of living organisms.Tree planting is an effective strategy of ameliorating climate change.
- Food Security: The Impact of Climate Change Since climate change affects the natural world, it is evident that it poses particular challenges for food security in the future.
- Climate Change: The Impact of Technology The most evident effect of technology on climate change is the possibility of finding new solutions to climate change problems.
- Extreme Weather and Global Warming The Global warming is a bad phenomenon that is causing to see level raise, change weather pattern, and create alteration in animal life.
- The Problem of Climate Change in the 21st Century Climate change is among the top threats facing the world in the 21st century, and it deserves prioritization when planning how to move the country and the globe forward.
- Solving the Climate Change Crisis by Using Renewable Energy Sources Climate change has caused extreme changes in temperature and weather patterns on planet Earth, thus threatening the lives of living organisms.
- Climate Change: Concept and Theories Climate change has become a concern of scientists rather recently. There are numerous theories as to the reasons for this process, but there are still no particular answers.
- Climate Change and Corporate Responsibility The problem of climate change is not new, but it becomes more and more crucial nowadays. The first changes in climate were observed during the industrial period, from the 1750s.
- Climate Change in Africa and How to Address It According to environmental scientists, Africa is exposed to the effects of climatic alterations subject to its elevated levels of poverty, and dependence on rain-fed farming.
- Social Issue: Climate Change The topic of climate change was chosen to learn more in the modern sense about the phenomenon that most people have heard about for decades.
- How Climate Changes Affect Coastal Areas Natural disasters and hazards caused by climate change are especially the cases during modern times, as the number of toxic substances and polluting elements is increasing every year.
- Al Gore’s Speech on Global Warming Using two essential constituents of a subtle rhetoric analysis for speech or text, the paper scrutinizes Al Gore’s speech on global warming.
- How Global Warming Affects Wildlife Global warming is a matter of great concern since it affects humans and wildlife directly, and this issue should be addressed appropriately.
- Electric Vehicles and Their Impact on Climate Change Internal combustion engine vehicles (ICEV) that have dominated the market over the recent decades are now giving way to electric vehicles (EV) experiencing rapid growth.
- Impact of Climate Change on Property Development and Management This essay will focus on the BBC article, COP26 promises could limit global warming to 1.8C, with a specific focus on the impact of climate change on property development.
- Climate Change From the Anthropological Perspective The adaptive nature of the anthropological development of humanity explains the contemporary global problems, and climate change may be assessed from the human adaptation perspective.
- Global Warming: Myth or Reality? Global warming can be described as a progressive increase in the earth’s temperature as a result of a trap to greenhouse gases within its atmosphere.
- Global Warming With an Emphasis on the Arctic This paper presents the impact of global warming with a focus on the Arctic region. It also provides key solutions that can be implemented to reduce its effects.
- Philosophers’ Theories on Climate Change The paper demonstrates two philosophers’ theories on climate change, namely Laura Westra and Graham Long. The thoughts and ideas are evaluated by using a hypothetical situation.
- Climate Change in Terms of Project Management The primary aim of the following paper is to define the notion of climate change in terms of project management, risk management, and business communication.
- Energy Crisis and Climate Change The global community needs to adopt an energy efficient behavior and invest in the exploration of sustainable energy resources.
- Security and Climate Change Climate change has been happening at an unprecedented rate over the last decade to become a major global concern.
- Climate Change and Global Warming Global warming is a subject that has elicited a heated debate for a long time. This debate is commonplace among scholars and policy makers.
- Climate Change: A Global Concern The phenomenon of climate change has attracted a notable amount of attention, the early 1990s being the point at which the phenomenon in question became a worldwide concern.
- Solubility of Carbon Dioxide Related to Climate Change The solubility of carbon dioxide is directly related to climate change because oceans absorb excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Devastating Effects of Global Warming The incapacitating consequences of a changing climate have resulted in significant distress among vulnerable populations as they face various challenges.
- Climate Change and Environmental Anxiety Individuals must develop a strategy to be able to resist climate change. In addition, there is a need for a global plan to restrain the influence of global warming.
- The Controversies of Climate Change This paper discusses the issue of climate change by considering the arguments presented by both the proponents and opponents based on ethical principles and sources of moral value.
- The Effect of Global Warming and the Future Global warming effects are the social and environmental changes brought-about by the increase in global temperatures.
- Climate Change as an Ethical Issue Although global warming is a hotly debated topic, some groups claim that the issue is not as acute as it is presented.
- Water Scarcity as Effect of Climate Change Climate change is the cause of variability in the water cycle, which also reduces the predictability of water availability, demand, and quality, aggravating water scarcity.
- Air Pollution Crisis and Climate Change in China Air pollution is a serious problem in many countries, including China. The main source of air pollutants is fumes from burning fuels in industries or vehicles.
- Fast Fashion and Its Impacts on Global Warming Fast fashion contributes to this change in weather conditions due to its improper disposal, leading to the release of emissions into the atmosphere, thus causing global warming.
- The Health Impacts of Climate Change in China Although climate change could not directly affect the Chinese population’s health, climate change interference could increase the number of respiratory system diseases, etc.
- The Impact of Climate Change on Inflectional Diseases This paper will examine the increasing spread of infectious diseases as one of the effects of climate change, as well as current and possible measures to overcome it.
- Car Emissions and Global Warming The emissions problem that is caused by the excessive use of cars is an issue that affects most of the modern world and needs to be addressed as soon as possible to prevent further adverse impact.
- Global Warming Challenges Solving in General Electric Environmental solutions that favor the growth of the company rather than social responsibility drive the decisions and policies of the company.
- Climate Change, Human Activities and Remedies Human beings are the worst enemies of the environment. The Kyoto Protocol and the concept of green buildings are the two major interventions to climatic change and global warming.
- Car Emission Effects on Global Warming Car emissions are expected to aid policy makers in national governments, automobile manufacturers, fuel industry CEOs and city planners.
- Effects of Global Warming: Essay Example According to environmentalists and other nature conservatives, Africa would be the worst hit continent by the effects of global warming despite emitting less greenhouse gases.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation Creating a planning model for climate change and environmental degradation requires a comprehensive approach that considers multiple factors.
- The Climate Change Impact on Sea Levels and Coastal Zones This paper summarizes the effects of climate change on seawater levels and subsequent effects on the coastal zones.
- Global Warming and Business Ethics Business ethics is significant in promoting effective industrial activities that promote environmental conservation and reduce global warming.
- Global Warming Effects on the Environment and Animals Global warming is a threat to the survival and well-being of human and animal life. This discussion aims to provide the effects of the current global warming threats.
- Climate Change and Accessibility to Safe Water The paper discusses climate change’s effect on water accessibility, providing graphs on water scarcity and freshwater use and resources.
- The Global Impact of Climate Change Into Our Homes and Families A home is a significant part of someone’s life. That’s why it is always considered as part of basic needs. They give people a sense of belonging and security.
- “The Basics of Climate Change” Blog The author of “The Basics of Climate Change” reveals the main concepts about the balance between the input and output of energy on Earth that directly relate to the climate.
- Global Warming, Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Global warming refers to an increase in the Earth’s average temperature that is characterized by rising global surface temperatures and the accumulation of pollutants in the atmosphere.
- Human Impact on the Environment Leading to Climate Change An elevated amount of greenhouse gases results in the retention of solar energy in the low levels of the atmosphere, which in turn brings to the melting of glaciers.
- It’s Not My Fault: Global Warming and Moral Responsibility The work of the American professor of ethical sciences Sinnott-Armstrong approaches the phenomenon of global warming in terms of individual and collective responsibility.
- Journal and Newspaper Collection on Global Warming This paper comments on Journal/ newspaper article on global warming from major newspapers and journals around the world
- Climate Change and Its Potential Impact on Agriculture and Food Supply The global food supply chain has been greatly affected by the impact of global climate change. There are, however, benefits as well as drawbacks to crop production.
- The Issue of Unstoppable Global Warming and Its Effects Drought levels shall increase if the temperatures remain high, evaporation shall increase too, mostly at summer and fall, could worsen famine, and the danger of wildfires.
- Climate Change and Social Responsibility in the UAE The UAE is rapidly developing for several decades already, which has a positive influence on the well-being of the population.
- Climate Changes Impact on Agriculture and Livestock The project evaluates the influences of climate changes on agriculture and livestock in different areas in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- Climate Change and Its Evidence The review of common claims about global warming made it possible to say that in spite of some skeptical opinions, it might be really happening.
- Climate Change: When Nature Is in Agony The issue of climate changes not new; it has already been on the agenda of the world ecologists in 1990s, and in 2010s, the issue seems to have gained a new significance.
- Climate Change and International Trade The relationship between climate change and international trade has been on a great verge of developing a new critical issue. This was so evident at the Conference of Parties Climate Conference.
- Climate Change and Fall of the Western Roman Empire The authors researched the relevant literature about why the Empire failed and how climate change was connected to the decline.
- Questions on Information Revolution and Global Warming The information revolution characterizes the period of change propelled by the development of computer technology. Technological advancements impact people’s lives.
- The Climate Change Issue in the Political Agenda One of the significant challenges modern societies have in combating the harmful impacts of climate change is the political agenda, which obscures the more comprehensive picture.
- Climate Change: The Negative Effects Climate change impacts the world through weather changes. Extreme weather events are becoming more common and more severe. Climate change is also causing the ocean to acidify.
- Climate Change Threats to Global Hospitality Industry Climate change is a growing threat to the global hospitality industry, and humanity must take action to mitigate its impact.
- Climate Change and Resource Scarcity The paper states that Sustainable Development Goal 13, Climate Action, is the United Nations’ goal to take urgent action to combat climate change.
- Climate Change as a Global Problem One of the global problems of our time is global warming. This problem is relevant not in any particular country but all over the world.
- Is the Threat of Global Warming Real? Increases in Earth’s average temperature over an extended period are called global warming. Greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere have recently increased.
- Climate Change Threats in Public Perception Diverse social, economic, ecological, and geopolitical variables that operate on multiple scales contribute to different levels of human vulnerability to climate change threats.
- How Climate Change Impacts Aviation The issue of climate change and its impact on the aviation industry has been a developing story lately due to the two-way relationship between them.
- The Key to Addressing Climate Change in Modern Business Globalisation, industrialisation, and rise of global corporations promoted the increased topicality of the climate change topic and its transformation into a shared problem.
- Overpopulation, Climate Change, and Security Issues This research paper examines such social and environmental issues as overpopulation, urbanization, climate change, food security, and air pollution.
- Climate Change as a Healthcare Priority Human-caused climate change significantly impacts the ecological situation and many areas of human life, such as health care.
- Climate Change: Nature Communications Climate change is one of the main concerns in contemporary global society. This subject is an issue of great contention, with different sides disagreeing.
- Global Warming: Understanding Causes of Event Global warming is a phenomenon characterized by the gradual increase of the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere.
- Climate Change and Its Impact on the Weather Climate change is a serious issue nowadays, considering that it is bound to affect my generation and the next ones.
- Climate Change: Impact on Lemurs Climate change and other environmental issues severely impact the lifestyle and behaviors of lemurs. High temperatures make lemurs spend more time on the ground.
- The Effect of Climate Change on Weather Climate change is resulting in weather extremes that are affecting millions of people around the world in recent times.
- Climate Change: Impact on Extreme Weather Events The article summarizes the scientific paper on the impact of climate change on extreme weather events worldwide.
- Climate Change: Causes, Dynamics, and Effects It is crucial to provide a description of the problem of the climate crisis, its causes and effects, and possible prevention measures.
- Ethical, Moral, and Christian Views on Climate Change Strategies Climate change strategies pose ethical, moral, and religious concerns that influence people to bring change and conserve the environment.
- The History of Climate Change and Global Warming Issue The paper states that the history of climate change and the solutions communities opted for are critical to tackling the current global warming issue.
- Greenpeace’s Climate Change Article Review The article What Are the Solutions to Climate Change by Greenpeace explains the ways climate change can be resolved while using comprehensive terms and being concise.
- Worldwide Effects of Global Warming The article conveys Trenberth’s message about the far-reaching implications of global warming on climate and the urgent need for collective action to address its consequences.
- Climate Change and Health: Public Health Human activity influences the environment in various ways, from climate change acceleration to the increasing deforestation that can cause another global pandemic.
- Climate Change and Global Warming Awareness If people continue to have misconceptions about global warming, climate change will negatively impact weather, food security, and biodiversity.
- Global Warming and Climate Change and Their Impact on Humans Climate change and global warming are significant issues with negative impacts on all aspects of human life; for example, they disrupt the food web, hurting humans and wildlife.
- Earth Day and the Climate Change Agenda This research paper examines the social significance and ecological value of Earth Day in the face of the climate change agenda.
- The Earth Day and Climate Change Climate change remains a relevant topic despite over fifty years of efforts since the establishment of Earth Day in 1970.
- Desertification and Climate Change Desertification can be prevented by holistic and planned grazing. This transformation can lead to better outcomes in the fight against climate change.
- Importance of Climate Change Issue Decision The situation of climate change is the central issue of the 21st century, and its solution is a turning point in history.
- Climate Changes Effects on the North and South Pole Global climate change has led to major problems in the North and South Pole ecosystems, with many animals losing their homes and even becoming endangered.
- Climate Change and Creation of Earth Day Climate change enables communities to create environmental initiatives, industries to update their manufacturing, and politicians to influence the problem through their campaigns.
- Climate Change Mitigation Strategies and Animals The thesis of the article is clear and identifies two main points, which are the problem that the global discussion does not propose sufficient methods to solve the issue.
- The Climate Change: Project Topic Exploration Climate change is an environmental problem that relates to an increase in the Earth’s average surface temperature.
- Analysis of Climate Change Ethical Issues Climate change is a major problem in contemporary society, evidenced by issues such as global warming that have affected and continue to wreck societal norms around the world.
- “The Impact of Climate Change Mitigation Strategies on Animal Welfare” by Shields and Orme-Evans The paper states that for animal welfare to improve, climate change mitigation strategies should encompass systematic changes in the industry.
- Climate Change from Different Perspectives The climate change situation has two types of responses, with one camp making deliberate efforts to minimize the impact of climate change and others ignoring the issue altogether.
- Climate Change: The Impact on North America As the analysis of climate change patterns reveals, the North American continent is on the verge of profound environmental changes resulting from global warming.
- The Impacts of Climate Change Mitigation Strategies on Animal Welfare The article by Shields and Orme-Evans focuses on the problem of climate change from the aspect of greenhouse emissions from farm animals and their contribution to global warming.
- How Climate Change Influenced Global Migration Migration and conflict have become the most important reasons causing researchers’ interest in climate change.
- Climate Change and Crop Production This paper aims to discuss how climate change affects crop production in Latin American, Central American, and Eastern African regions.
- Global Warming and Crop Production in Africa Many people are aware of the current and future negative effects of global warming. Global warming will cause severe reductions in the crop in Africa, particularly in Ethiopia.
- Carbon Markets and Climate Change Many climatological concepts predict a rise in worldwide average temperature over the succeeding few decades centered on tripling atmospheric carbon oxide levels.
- Solar Activity as a Cause of Climate Change Climate change is not solely the result of human activity because solar activity also impacts the Earth’s climate in a significant manner.
- How Human Activities Cause Climate Change Scientists and various leaders globally have seriously debated the causes of climate change. This essay involves a discussion of how human activities cause climate change.
- Climate Change: Risks and Consequences Climate change has long been one of the global environmental challenges humanity has faced. A slow but steady rise in surface temperatures is a sustainable trend.
- Carbon Dioxide Factor in Climate Change Increasing atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide have a profound effect on global warming, and in turn, it affects the total temperature of the Earth.
- Climate Change: The Role of Scientific and Technological Progress This paper serves as a starting point when looking at climate change and the effects of scientific and technological progress.
- Consequences of Global Warming Although the opinions about the causes of climate change are diverse, the effects of human activities and natural elements are similar and lead to global warming.
- Climate Change and Modern Indigenous Treaties in Northern Canada The purpose of this paper is to answer the following question: how does climate change affect aboriginal culture, food gathering, and Canadian government policy?
- Water Scarcity Due to Climate Change This paper focuses on the adverse impact that water scarcity has brought today with the view that water is the most valuable element in running critical processes.
- Ascertaining Scientific Truth on Climate Change Human activities impact the environment. The consequences of anthropological actions reverberate across all aspects of the Earth’s habitat.
- Climate Change Prevention Improvements This paper aims to examine the principal indicators in achieving improvements in climate change prevention and the current results of programs.
- Discussion of Impact of Climate Change in Society Modern scholars and environmentalists acknowledge that climate change is a major challenge affecting the global society today.
- The UN Climate Change Conference: Indigenous Concerns During the UN Climate Change Conference, it was clear that indigenous environmental defenders have a particular stake in the outcomes of climate change global negotiations.
- Climate Change Prediction for the Caribbean Climate change can be defined as the global spectacle of climate alteration described by the earth’s natural climate variations due to human activities.
- Climate Change: Canada’s Environment Policy The essay argues that Canada is a major contributor to climate change and its environmental policies are inadequate in resolving the environmental problems.
- Researching the Interactions between Climate Change and Plankton Communities This paper is aimed at examining the interactions between climate change and plankton communities, focusing on the abundance, distribution, and structure of the species.
- Climate Change in “The Parable of the Sower” by Butler Butler’s “The Parable of The Sower” is a post-apocalyptic knowledge literature novel that addresses climate modification and socioeconomic inequalities.
- Social Challenges of Climate Change Climate change is among the most pressing global issues, and it is not easy to find a solution that will work for everyone.
- Global Warming: “Hopeful Lessons From the Battle to Save Rainforests” The “Hopeful lessons from the battle to save rainforests” video proposes several solutions to deforestation and global warming.
- Climate Change: Factors and Future Climate change and global warming have been stressed since the early 20th century, and different environmental corps and governments have communicated several mitigation techniques.
- Climate Change and Global Health Climate change is among the most discussed topics in various fields, as it has overarching effects on many aspects of human life.
- Global Warming Effects on Earth Global warming presents a considerable threat by having an enormous influence on humanity’s social, economic, and physical state.
- The Affect of Climate Change on the Social and Environmental Determinants of Health There is a lack of sufficient awareness in society about how climate change affects health although it significantly influences its environmental determinants.
- Climate Change in Environmentally Vulnerable Countries The repercussions of climate change are global in character and unprecedented in size, ranging from changing weather patterns to sea level rise.
- Climate Change and the Media Biases This essay’s purpose is to address the media bias concerning the rising global warming and climate change, referring to news articles made by scientists and various scholars.
- The Future of Coal Plants Regarding Climate Change The use of coal plants to provide energy has been at the center of the growth of many economies of the world. However, coal is associated with the emission of greenhouse gasses.
- Global Warming and Economics Discussion The article discusses that at the international level, the carbon tax is not always conducive to climate change regulation.
- Climate Change and Food Production Cycle In order to address the problem of climate change in relation to the overproduction of food, a more responsible attitude toward its consumption.
- Global Warming: The Importance of Addressing the Climate Crisis The paper states that global warming has many consequences. Multiple scientific discoveries emphasize the importance of addressing the climate crisis urgently.
- Examining the Potential of Digital Earth Services in Connection to Global Warming In this work, the primary characteristics of global warming will be discussed with the implementation of digital Earth tools, examining the data from these sources.
- Climate Change and Carbon Dioxide Emissions Climate change is in large part caused by human action, and the continued industrial development of the world can be accredited to exacerbating the problem further than ever.
- Climate Change Reflection in Law System The paper states that climate change in the coming decade will be crucial to achieving global goals set on the governmental and international levels.
- The Impact of Climate Change on the United States Climate change is a serious issue faced by the United States, and it has various effects, including in the spheres of economy, animal habitat, and health of the population.
- The Science Behind Climate Change Regardless of how strong the natural change to the climate system was, it could not have led to the temperature increase seen over the past semicentenary.
- Oil Spills and How They Are Related to Climate Change The paper states that oil spills are destructive to ecosystems. Oil spills and climate change are two deeply interrelated environmental phenomena.
- Greenhouse Effect as a Cause of Global Warming The report serves an informative function and is designed to explore the nature of global warming through the greenhouse effect.
- Causes of Climate Change and Ways to Reduce It Despite the effects, investing in green energy, increasing vegetation cover, and conducting public education are some measures that can be taken to reduce climate change.
- Solar Energy in China and Its Influence on Climate Change The influence of solar energy on climate change has impacted production, the advancement of solar energy has impacted climate change in the geography of China.
- Natural Climate Solutions for Climate Change in China The crisis in China gives rise to several significant environmental problems, including air pollution, land degradation, deforestation, and poor water quality.
- International Climate Change Law and National Acts The growing number of countries involved in the fight against environmental problems is seen as a positive step. As a justification, the scope of emission coverage is considered.
- Harmful Impact of Climate Change Climate change is one of the most notable environmental problems that humanity is facing today and defines it as ‘long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns’.
- Global Warming in Relation to Human Population Size The density of the world population in the future is a crucial component of climate policy to safeguard the vulnerable future generation.
- Anthropogenic Influence on Climate Change Throughout History The objective of this paper is to discuss the anthropogenic influence on climate change through history and adaptations during the glaciation period.
- Climate Change, Its Causes and Implications The purpose of this paper is to present the causes and implications of climate change and to elaborate on the current climate change policies.
- Climate Change and Tesla’s Electric Cars The paper discusses environmental sustainability. Using Tesla company electric vehicles is the best decision for tackling the climate change problem.
- Disasters Caused by Climate Change This paper focuses on several recent natural disasters caused by climate change – simultaneous fires in Russia and floods in Pakistan.
- Climate Change and Mitigation Approaches The issue of climate change may appear to be extremely controversial. The reason behind that is the fact that environmental changes have both dependence and influence on humanity.
- Impacts of Climate Change on Electricity Demand in China Fan et al.’s “Impacts of climate change on electricity demand in China” article forecasts the potential effects on the electricity demand under three climate change scenarios.
- Tree Planting Ameliorating Climate Change Environmentalists and policymakers have been designing strategies to ameliorate climate change in a sustainable manner.
- Impacts of Climate Change on Agriculture and Food This paper will examine four aspects of climate change: variation in the rainfall pattern, water levels, drought, temperature, and heatwaves.
- The Truth Behind Climate Change The real solution of the problem of climate change could be to decarbonize the global energy system that is 80% fossil fuel, but it is significant in scale.
- “Climate Change Facts and Effect on Economy” by Amadeo Kimberly Amadeo attempts to address one of the ecological issues, namely global warming, and introduces the article Climate Change Facts and Effect on Economy.
- Web-Based Organizational Discourses: Climate Change This paper pertains to the investigation of argumentation formation within the process of interaction with organizations holding similar and opposite opinions and viewpoints.
- Discussing Climate Change: Randy Johnson In this work, I will describe an interview with an expert meteorologist Randy Johnson, and provide information necessary to understand his background and experience.
- How Human Behavior Promotes Climate Change Uncontrolled reproduction is one of several behaviors promoting climate change. It increases the size of the population and changes its distribution.
- The Impact of Global Climate Change on Health The following paper will investigate two health concerns associated with climate change in the U.S., Australia, and Vietnam
- Environmental Issues: Problems of Climate Change The paper states that climate change poses a threat to the planet in various forms, including vital impacts on health, food, water, and air.
- Iron Fertilization: Solving Global Warming The discussion in this paper considers some of the international as well as maritime laws that deal with the application of iron fertilization as a method of mitigating global warming.
- How Car Emissions Affect Global Warming
- The Catholic Response to the Climate Change
- Climate Change: Dangers and Prevention
- Correlation of “Climate Change” and Public Health
- The Problem of Climate Change in South Florida
- Climate Change as a Public Health Issue
- Economic Model for Global Warming
- Religion and Politics: Pope Francis and Climate Change
- How Climate Change Increases the Risk of Hurricanes
- Global Warming From a Social Studies Perspective
- The Effect of Climate Change on the Environment
- Climate Change: El Niño Oscillation Phenomenon (ENSO)
- Climate and Social Change in Global Warming Crisis
- Capitalism, Climate Change, and Globalization
- The Importance of Addressing Climate Change
- Impact of Climate Change on Early Societies
- Modern Environmental Issues: Climate Change
- Global Warming and Climate Change
- Climate Change: The Leading Cause of Global Warming
- Climate Change: Causes and Consequences, and the Issue of Social Collapse
- Canada: The First Victim of Global Climate Change
- Sustainable Development: The Climate Change Issues
- Climate Change Skepticism in Relation to Global Warming
- The Issue of Global Warming in the Community
- Climate Change as a Challenge to Australia
- Global Warming: Do Human Activities Threaten to Change Climate?
- Global Warming and Mitigation Strategies
- Global Warming: Is It Caused by Nature or Mankind?
- Controversy About Global Warming: Skepticism and Reality
- Global Warming and Other Ecology Issues
- Global Warming: Harmful Impact on the Polar Bears
- Global Warming: Issue Analysis
- Oil and Gas Industry Response to Global Warming
- Global Warming: Causes and Solutions
- The Kyoto Protocol: First Framework for Fighting Global Warming
- Global Warming: Causes, Factors and Effects
- Global Warming as Not a New-Fangled Issue
- The Global Warming Crisis and Ways of its Solution
- Global Warming: Causes and Consequences
- Women’s Activism Sources Around Climate Change
- Weather and Climate Change: Physical Equations
- Climate Change and Impact on Human Health
- Ecofeminism: Women Against Climate Change
- Health Issues Caused by Climate Change
- Respiratory Diseases Caused by Climate Change
- Global Warming and Its Various Consequences
- Climate Change Factors and Impacts on Blue Crab Populations
- Global Warming Leads Climate Change
- Climate Change Impacts Florida’s Biodiversity
- The Paris Accord: Macroeconomics and Global Warming
- Climate Change and Related Issues in Canada
- Climate Change as Political Leaders’ Primary Concern
- Virtue Ethics: Altering Testimony on Global Warming
- Climate Change Initiative in Canada
- Impact of Climate Change on Intermodal Transportation
- Global Warming and Its Health Implications
- Global Warming and Its Threats: Debates
- Remote Sensing Applications to Climate Change
- Climate Change and Human Heath
- The Issue of Global Warming
- Napa Valley Wine Industry and Climate Change
- Climate Change Policies and Regulation
- Climate Change Affecting Global Public Health
- Global Warming Problems due to Economic Growth
- Global Warming and the Free Rider Problem
- Trump Presidency: Immigration and Climate Change
- Iron Seeding Oceans: Global Warming Solution
- Biodiversity, Global Warming, Environmental Conservation
- Climate Change as a Threat to Pension Fund
- Climate Change: Changing Patterns of Malaria
- The Problem of Global Warming and Its Effects
- Global Climate Change and Health Concerns
- British Petroleum’s Risks due to Climate Changes
- Paris Agreement: Climate Change Deal
- Global Warming as a Humanity’s Fault
- Impact of Climate Change on Vector-Borne Diseases: Focus on Malaria
- Understanding Climate Change: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
- Multinational Corporations and Climate Change
- Humans Contribution to Global Climate Change
- Global Warming: Impacts and Consequences on Ecology and Society
- Global Warming: Car Emissions Effects
- Environmental Studies of Global Warming: Cause and Mitigation
- EPA’s Role in Enforcing US Environmental Policies
- Global Warming Causes and Impacts
- Environmental Studies: The Global Warming Holocaust
- The Issue of Global Climate Change and the Use of Global Ethic
- Global Warming Crisis: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
- Causes and Effects of Global Warming on the Environment
- What Natural Forces Have Caused Climate Change?
- What Problems Are Involved with Establishing an International Climate Change Regime?
- What Role Has Human Activity Played in Causing Climate Change?
- What Does the World Say About Climate Change?
- What Are the Five Main Effects of Climate Change?
- What Is Climate Change and How Is It Changing?
- What Is Climate Change in Simple Words?
- How Does Climate Change Affect Human Life?
- Why Is Climate Change Important?
- How Does Climate Change Affect Society?
- What Are Some of the Signs of Climate Change?
- What Are the Impacts of Climate Change?
- What Is the Main Ways of Solving Climate Change Issue?
- What Are Some Examples of Climate Change?
- How Does Climate Change Affect Our Human Rights?
- What Can Students Do to Help Climate Change?
- How Can We Reduce the Impact of Climate Change?
- When Did Climate Change Become an Issue?
- Can Climate Change Be Stopped?
- Where Is Climate Change the Worst?
- Why Is Climate Change a Global Challenge?
- How Many Years Do We Have to Save the Planet From Climate Change?
- How Many Years Until Climate Change Is Irreversible?
- What American State Is Safest From Climate Change?
- Where Should People Live to Avoid Climate Change?
- What Countries Will Be the Least Affected by Climate Change?
- Who Will Benefit From Climate Change?
- What Is China Doing About Climate Change?
- Which Country Is the Biggest Contributor to Climate Change?
- What Is the Most Effective Solution to Climate Change?
- Climate Change-Related Health Risks
- Climate Change Threats to Ecosystems and Species
- How Deforestation Leads to Climate Change
- Costs and Benefits of Climate Change Mitigation Strategies
- The Feasibility and Challenges of Renewable Energy Transition
- The Politics of Climate Change: Cooperation and Disagreements
- How Climate Change Affects Agriculture and Food Production
- Climate Change, Migration, and Environmental Refugees
- The Connection Between Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events
- The Effectiveness of Climate Messaging and Public Perception
- How Climate Models Help Predicting Future Climate Scenarios
- What Are the Social Justice Dimensions of Climate Change?
- Best Personal Carbon Footprint Reduction Strategies
- The Impact of Climate Change on Freshwater Availability
- Strategies to Cope with Changing Climate Conditions
- The Role of Urban Planning in Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
- How Indigenous Knowledge Can Help Understand Climate Change
- The Adverse Effect of Climate Change on Polar Regions and Indigenous Peoples
- The Consequences of Climate Change and Ocean Acidification for Marine Ecosystems
- The Relationship between Environmental Changes and International Security
Here’s what makes our list of topics stand out:
| All the topics are available to you at no cost! | |
| Our fresh essay titles will inspire great writing. | |
| Check them out to get even more ideas. | |
| Our list features plenty of topics to choose from. |
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 317 Climate Change Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/climate-change-essay-topics/
"317 Climate Change Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/climate-change-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '317 Climate Change Essay Topics'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "317 Climate Change Essay Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/climate-change-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "317 Climate Change Essay Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/climate-change-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "317 Climate Change Essay Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/climate-change-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Climate Change were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on June 20, 2024 .
337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples
You will notice that there are many climate change research topics you can discuss. Our team has prepared this compilation of 185 ideas that you can use in your work.
📝 Key Points to Use to Write an Outstanding Climate Change Essay
🏆 best climate change title ideas & essay examples, 🥇 most interesting climate change topics to write about, 🎓 simple & easy research titles about climate change, 👍 good research topics about climate change, 🔍 interesting topics to write about climate change, ⭐ good essay topics on climate change, ❓ climate change essay questions.
A climate change essay is familiar to most students who learn biology, ecology, and politics. In order to write a great essay on climate change, you need to explore the topic in great detail and show your understanding of it.
This article will provide you with some key points that you could use in your paper to make it engaging and compelling.
First of all, explore the factors contributing to climate change. Most people know that climate change is associated with pollution, but it is essential to examine the bigger picture. Consider the following questions:
- What is the mechanism by which climate change occurs?
- How do the activities of large corporations contribute to climate change?
- Why is the issue of deforestation essential to climate change?
- How do people’s daily activities promote climate change?
Secondly, you can focus on solutions to the problems outlined above.
Climate change essay topics often provide recommendations on how individuals and corporations could reduce their environmental impact. These questions may help to guide you through this section:
- How can large corporations decrease the influence of their operations on the environment?
- Can you think of any examples of corporations who have successfully decreased their environmental footprint?
- What steps can people take to reduce pollution and waste as part of their daily routine?
- Do you believe that trends such as reforestation and renewable energy will help to stop climate change? Why or why not?
- Can climate change be reversed at all, or is it an inescapable trend?
In connection with these topics, you could also discuss various government policies to address climate change. Over the past decades, many countries enacted laws to reduce environmental damage. There are plenty of ideas that you could address here:
- What are some famous national policies for environmental protection?
- Are laws and regulations effective in protecting the environment? Why or why not?
- How do environmentally-friendly policies affect individuals and businesses?
- Are there any climate change graphs that show the effectiveness of national policies for reducing environmental damage?
- How could government policies on climate change be improved?
Despite the fact that there is definite proof of climate change, the concept is opposed by certain politicians, business persons, and even scientists.
You could address the opposition to climate change in your essay and consider the following:
- Why do some people think that climate change is not real?
- What is the ultimate proof of climate change?
- Why is it beneficial for politicians and business persons to argue against climate change?
- Do you think that climate change is a real issue? Why or why not?
The impact of ecological damage on people, animals, and plants is the focus of most essay titles on global warming and climate change. Indeed, describing climate change effects in detail could earn you some extra marks. Use scholarly resources to research these climate change essay questions:
- How has climate change impacted wildlife already?
- If climate change advances at the same pace, what will be the consequences for people?
- Besides climate change, what are the impacts of water and air pollution? What does the recent United Nations’ report on climate change say about its effects?
- In your opinion, could climate change lead to the end of life on Earth? Why or why not?
Covering at least some of the points discussed in this post will help you write an excellent climate change paper! Don’t forget to search our website for more useful materials, including a climate change essay outline, sample papers, and much more!
- Climate Change – Problems and Solutions It is important to avoid cutting trees and reduce the utilization of energy to protect the environment. Many organizations have been developed to enhance innovation and technology in the innovation of eco-friendly machines.
- Causes and Effects of Climate Changes Climate change is the transformation in the distribution patterns of weather or changes in average weather conditions of a place or the whole world over long periods.
- Global Warming as Serious Threat to Humanity One of the most critical aspects of global warming is the inability of populations to predict, manage, and decrease natural disruptions due to their inconsistency and poor cooperation between available resources.
- Is Climate Change a Real Threat? Climate change is a threat, but its impact is not as critical as wrong political decisions, poor social support, and unstable economics.
- Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions The agreement across the board is that human activities such as emissions of the greenhouse gases have contributed to global warming.
- Climate Change – Global Warming For instance, in the last one century, scientists have directly linked the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere with the increase in temperature of the earth.
- Climate Change Causes and Predictions These changes are as a result of the changes in the factors which determine the amount of sunlight that gets to the earth surface.
- The Role of Technology in Climate Change The latter is people’s addiction, obsession, and ingenuity when it comes to technology, which was the main cause of climate change and will be the primary solution to it as well.
- Climate Change and Its Impacts on the UAE Currently, the rise in temperature in the Arctic is contributing to the melting of the ice sheets. The long-range weather forecast indicates that the majority of the coastal areas in the UAE are at the […]
- Climate Change: Human Impact on the Environment This paper is an in-depth exploration of the effects that human activities have had on the environment, and the way the same is captured in the movie, The Eleventh Hour.
- Transportation Impact on Climate Change It is apparent that the number of motor vehicles in the world is increasing by the day, and this translates to an increase in the amount of pollutants produced by the transportation industry annually.
- The Impact of Climate Change on Food Security Currently, the world is beginning to encounter the effects of the continuous warming of the Earth. Some of the heat must be reflected in space to ensure that there is a temperature balance in the […]
- Climate Change Impacts on Ocean Life The destruction of the ozone layer has led to the exposure of the earth to harmful radiation from the sun. The rising temperatures in the oceans hinder the upward flow of nutrients from the seabed […]
- Global Warming and Human Impact: Pros and Cons These points include the movement of gases in the atmosphere as a result of certain human activities, the increase of the temperature because of greenhouse gas emissions, and the rise of the oceans’ level that […]
- Climate Change and Role of Government He considers that the forest’s preservation is vital, as it is the wellspring of our human well-being. As such, the legislature can pass policies that would contribute to safeguarding our nation’s well-being, but they do […]
- Climate Change Definition and Description The wind patterns, the temperature and the amount of rainfall are used to determine the changes in temperature. Usually, the atmosphere changes in a way that the energy of the sun absorbed by the atmosphere […]
- Research Driven Critique: Steven Maher and Climate Change The ravaging effects of Covid-19 must not distract the world from the impending ramifications of severe environmental and climatic events that shaped the lives of a significant portion of the population in the past year.
- How Aviation Impacts Climate Change A measurement of the earth’s radiation budget imbalance brought on by changes in the quantities of gases and aerosols or cloudiness is known as radiative forcing.
- Tourism and Climate Change Problem There are a number of factors that propelled the growth of tourism and these factors include the improvement of the standards of living in many developed nations, good work polices allowing more time for vacations […]
- Climate Change’s Impact on Crop Production I will address the inefficiencies of water use in our food production systems, food waste, and the impact of temperature on crop yield.
- Climate Change: The Day After Tomorrow In the beginning of the film “The Day After Tomorrow”, the main character, Professor Jack Hall, is trying to warn the world of the drastic consequences of a changing climate being caused by the polluting […]
- Climate Change: Causes, Impact on People and the Environment Climate change is the alteration of the normal climatic conditions in the earth, and it occurs over some time. In as much as there are arguments based around the subject, it is mainly caused by […]
- Maize Production and Climate Change in South Africa Maize farming covers 58% of the crop area in South Africa and 60% of this is in drier areas of the country.
- Neolithic Revolution and Climate Change At the primary stage of the evolution of human civilization, the rise of agriculture in the later part of stone age, also known as the Neolithic Revolution, was ultimately necessary to keep pace with the […]
- “Climate Change: Turning Up the Heat” by Barrie Pittock The researcher stresses that people should try to minimize the negative effects of climate change in order to enable humanity to adapt to the changing environment in a more effective way.
- Global Perspectives in the Climate Change Strategy It is required to provide an overview of those programs and schemes of actions that were used in the local, federal and global policies of the countries of the world to combat air pollution.
- Climate Change as a Global Security Threat It is important to stress that agriculture problems can become real for the USA as well since numerous draughts and natural disasters negatively affect this branch of the US economy.
- Climate Change, Development and Disaster Risk Reduction However, the increased cases of droughts, storms, and very high rainfalls in different places are indicative of the culmination of the effects of climate change, and major disasters are yet to follow in the future.
- Anthropogenic Climate Change Since anthropogenic climate change occurs due to the cumulative effect of greenhouse gases, it is imperative that climatologists focus on both immediate and long term interventions to avert future crises of global warming that seem […]
- Wildfires and Impact of Climate Change Climate change has played a significant role in raise the likelihood and size of wildfires around the world. Climate change causes more moisture to evaporate from the earth, drying up the soil and making vegetation […]
- Rainforests of Victoria: Potential Effects of Climate Change The results of the research by Brooke in the year 2005 was examined to establish the actual impacts of climate change on the East Gippsland forest, especially for the fern specie.
- Climate Change and Renewable Energy Options The existence of various classes of world economies in the rural setting and the rise of the middle class economies has put more pressure on environmental services that are highly demanded and the use of […]
- Saving the Forest and Climate Changes The greenhouse gases from such emissions play a key role in the depletion of the most essential ozone layer, thereby increasing the solar heating effect on the adjacent Earth’s surface as well as the rate […]
- Climate Change: Mitigation Strategies To address the latter views, the current essay will show that the temperature issue exists and poses a serious threat to the planet.
- Global Warming and Effects Within 50 Years Global warming by few Scientists is often known as “climate change” the reason being is that according to the global warming is not the warming of earth it basically is the misbalance in climate.
- Energy Conservation for Solving Climate Change Problem The United States Environmental Protection Agency reports that of all the ways energy is used in America, about 39% is used to generate electricity.
- The Three Myths of Climate Change In the video, Linda Mortsch debunks three fundamental misconceptions people have regarding climate change and sets the record straight that the phenomenon is happening now, affects everyone, and is not easy to adapt.
- The Climate Change Articles Comparison In a broader sense, both articles address the concept of sustainability and the means of reinforcing its significance in the context of modern global society to prevent further deterioration of the environment from happening.
- Climate Change: The Key Issues An analysis of world literature indicates the emergence in recent years of a number of scientific publications on the medical and environmental consequences of global climate change.
- Global Warming: Causes and Consequences Other definitions of global warming are “the increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s near-surface air and oceans since the mid-twentieth century and its projected continuation”.
- Technological and Policy Solutions to Prevent Climate Change Scientists and researchers across the globe are talking about the alarming rates of temperature increase, which threaten the integrity of the polar ice caps.
- The Key Drivers of Climate Change The use of fossil fuel in building cooling and heating, transportation, and in the manufacture of goods leads to an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere.
- Ways to Reduce Global Warming The objectives of this report are to identify the causes of global warming, to highlight the expected effects of global warming and to identify ways of reducing global warming.
- The Straw Man Fallacy in the Topic of Climate Change The straw man fallacy is a type of logical fallacy whereby one person misrepresents their opponent’s question or argument to make it easier to respond.
- Desert, Glaciers, and Climate Change When the wind blows in a relatively flat area with no vegetation, this wind moves loose and fine particles to erode a vast area of the landscape continuously in a process called deflation.
- Evidence of Climate Change The primary reason for the matter is the melting of ice sheets, which adds water to the ocean. The Republic of Maldives is already starting to feel the effects of global sea-level rise now.
- Weather Abnormalities and Climate Change One of the crucial signs of climate change is the rise of the sea level. Thus, the problem of climate change is a threat to water security and needs resolution.
- Technology Influence on Climate Change Undoubtedly, global warming is a portrayal of climate change in the modern world and hence the need for appropriate interventions to foster the sustainability of the environment.
- Climate Change’s Negative Impact on Biodiversity This essay’s primary objective is to trace and evaluate the impact of climate change on biological diversity through the lens of transformations in the marine and forest ecosystems and evaluation of the agricultural sector both […]
- Climate Change Impact on Bangladesh Today, there are a lot of scientists from the fields of ecology and meteorology who are monitoring the changes of climate in various regions of the world.
- The Role of Science and Technology in International Relations Regarding Climate Change This paper examines the role of science and technology as it has been used to address the challenge of climate change, which is one of the major issues affecting the global societies today.
- Climate Change: Is Capitalism the Problem or the Solution? This means that capitalism, which is the ability to produce wealth lies in the solution and also the causes of the current global climatic governance.
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Tourism in Coastal Areas It is hereby recommended that governments have a huge role to play in mitigating the negative effects of climate change on coastal towns.
- The Negative Effects of Climate Change in Cities This is exemplified by the seasonal hurricanes in the USA and the surrounding regions, the hurricanes of which have destroyed houses and roads in the past.
- Biology of Climate Change There is sufficient evidence that recent climate change is a result of human activities.”Warming of the climate system is unequivocal; as is now evident from observations of increases in global average air and ocean temperatures, […]
- Impact of Food Waste on Climate Change In conclusion, I believe that some of the measures that can be taken to prevent food waste are calculating the population and their needs.
- Climate Change and Resource Sustainability in Balkan: How Quickly the Impact is Happening In addition, regarding the relief of the Balkans, their territory is dominated by a large number of mountains and hills, especially in the west, among which the northern boundary extends to the Julian Alps and […]
- Climate Change: Renewable Energy Sources Climate change is the biggest threat to humanity, and deforestation and “oil dependency” only exacerbate the situation and rapidly kill people. Therefore it is important to invest in the development of renewable energy sources.
- Climate Change and the Allegory of the Cave Plato’s allegory of the cave reflects well our current relationship with the environment and ways to find a better way to live in the world and live with it.
- Climate Change, Economy, and Environment Central to the sociological approach to climate change is studying the relationship between the economy and the environment. Another critical area of sociologists ‘ attention is the relationship between inequality and the environment.
- Terrorism, Corruption, and Climate Change as Threats Therefore, threats affecting countries around the globe include terrorism, corruption, and climate change that can be mitigated through integrated counter-terror mechanisms, severe punishment for dishonest practices, and creating awareness of safe practices.
- Climate Change’s Impact on Hendra Virus Transmission to humans occurs once people are exposed to an infected horse’s body fluids, excretions, and tissues. Land clearing in giant fruit bats’ habitats has exacerbated food shortages due to climate change, which has led […]
- Global Climate Change and Environmental Conservation There may be a significantly lesser possibility that skeptics will acknowledge the facts and implications of climate change, which may result in a lower desire on their part to adopt adaptation. The climate of Minnesota […]
- Beef Production’s Impact on Climate Change This industry is detrimental to the state of the planet and, in the long term, can lead to irreversible consequences. It is important to monitor the possible consequences and reduce the consumption of beef.
- Cities and Climate Change: Articles Summary The exponential population growth in the United States of America and the energy demands put the nation in a dilemma. Climate change challenges are experienced as a result of an increase in greenhouse gas emissions […]
- The Impact of Climate Change on Vulnerable Human Populations The fact that the rise in temperatures caused by the greenhouse effect is a threat to humans development has focused global attention on the “emissions generated from the combustion” of fossil fuels.
- Food Waste Management: Impact on Sustainability and Climate Change How effective is composting food waste in enhancing sustainability and reducing the effects of climate change? The following key terms are used to identify and scrutinize references and study materials.”Food waste” and sustain* “Food waste” […]
- Protecting the Environment Against Climate Change The destruction of the ozone layer, which helps in filtering the excessive ray of light and heat from the sun, expose people to some skin cancer and causes drought.
- The Global Warming Problem and Solution Therefore, it is essential to make radical decisions, first of all, to reduce the use of fossil fuels such as oil, carbon, and natural gas. One of the ways of struggle is to protest in […]
- Climate Change and Immigration Issues Due to its extensive coverage of the aspects of climate migration, the article will be significant to the research process in acquiring a better understanding of the effects of climate change on different people from […]
- Global Warming: Speculation and Biased Information For example, people or organizations that deny the extent or existence of global warming may finance the creation and dissemination of incorrect information.
- Impacts of Climate Change on Ocean The development of phytoplankton is sensitive to the temperature of the ocean. Some marine life is leaving the ocean due to the rising water temperature.
- Impact of Climate Change on the Mining Sector After studying the necessary information on the topic of sustainability and Sustainability reports, the organization was allocated one of the activities that it performs to maintain it.
- Climate Change: Historical Background and Social Values The Presidential and Congress elections in the US were usually accompanied by the increased interest in the issue of climate change in the 2010s.
- Communities and Climate Change Article by Kehoe In the article, he describes the stringent living conditions of the First Nations communities and estimates the dangers of climate change for these remote areas.
- Discussion: Reverting Climate Change Undertaking some of these activities requires a lot of finances that have seen governments setting aside funds to help in the budgeting and planning of the institutions.
- Was Climate Change Affecting Species? It was used because it helps establish the significance of the research topic and describes the specific effects of climate change on species.
- Climate Change Attitudes and Counteractions The argument is constructed around the assumption that the deteriorating conditions of climate will soon become one of the main reasons why many people decide to migrate to other places.
- How Climate Change Could Impact the Global Economy In “This is How Climate Change Could Affect the World Economy,” Natalie Marchand draws attention to the fact that over the next 30 years, global GDP will shrink by up to 18% if global temperatures […]
- Effective Policy Sets to Curb Climate Change A low population and economic growth significantly reduce climate change while reducing deforestation and methane gas, further slowing climate change. The world should adopt this model and effectively increase renewable use to fight climate change.
- Climate Change: Social-Ecological Systems Framework One of the ways to understand and assess the technogenic impact on various ecological systems is to apply the Social-Ecological Systems Framework.
- The Climate Change Mitigation Issues Indeed, from the utilitarian perspective, the current state of affairs is beneficial only for the small percentage of the world population that mostly resides in developed countries.
- The Dangers of Global Warming: Environmental and Economic Collapse Global warming is caused by the so-called ‘Greenhouse effect’, when gases in Earth’s atmosphere, such as water vapor or methane, let the Sun’s light enter the planet but keep some of its heat in.
- Aviation, Climate Change, and Better Engine Designs: Reducing CO2 Emissions The presence of increasing levels of CO2 and other oxides led to the deterioration of the ozone layer. More clients and partners in the industry were becoming aware and willing to pursue the issue of […]
- Climate Change as a Problem for Businesses and How to Manage It Additionally, some businesses are directly contributing to climate change due to a lack of measures that will minimise the emission of carbon.
- Climate Change and Disease-Carrying Insects In order to prevent the spreading of the viruses through insects, the governments should implement policies against the emissions which contribute to the growth of the insects’ populations.
- Aspects of Global Warming Global warming refers to the steadily increasing temperature of the Earth, while climate change is how global warming changes the weather and climate of the planet.
- David Lammy on Climate Change and Racial Justice However, Lammy argues that people of color living in the global south and urban areas are the ones who are most affected by the climate emergency.
- Moral Aspects of Climate Change Addresses However, these approaches are anthropocentric because they intend to alleviate the level of human destruction to the environment, but place human beings and their economic development at the center of all initiatives.
- Feminism: A Road Map to Overcoming COVID-19 and Climate Change By exposing how individuals relate to one another as humans, institutions, and organizations, feminism aids in the identification of these frequent dimensions of suffering.
- Global Warming: Moral and Political Challenge That is, if the politicians were to advocate the preservation of the environment, they would encourage businesses completely to adopt alternative methods and careful usage of resources.
- Climate Change: Inconsistencies in Reporting An alternative route that may be taken is to engage in honest debates about the issue, which will reduce alarmism and defeatism.
- Climate Change: The Chornobyl Nuclear Accident Also, I want to investigate the reasons behind the decision of the USSR government to conceal the truth and not let people save their lives.
- “World on the Edge”: Managing the Causes of Climate Change Brown’s main idea is to show the possibility of an extremely unfortunate outcome in the future as a result of the development of local agricultural problems – China, Iran, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, and others – […]
- Gendering Climate Change: Geographical Insights In the given article, the author discusses the implications of climate change on gender and social relations and encourages scholars and activists to think critically and engage in debates on a global scale.
- Climate Change and Its Consequences for Oklahoma This concept can be defined as a rise in the Earth’s temperature due to anthropogenic activity, resulting in alteration of usual weather in various parts of the planet.
- Climate Change Impacts in Sub-Saharan Africa This is why I believe it is necessary to conduct careful, thorough research on why climate change is a threat to our planet and how to stop it.
- Climate Change: Global Warming Intensity Average temperatures on Earth are rising faster than at any time in the past 2,000 years, and the last five of them have been the hottest in the history of meteorological observations since 1850.
- The Negative Results of Climate Change Climate change refers to the rise of the sea due to hot oceans expanding and the melting of ice sheets and glaciers.
- Addressing Climate Change: The Collective Action Problem While all the nations agree that climate change is a source of substantial harm to the economy, the environment, and public health, not all countries have similar incentives for addressing the problem. Addressing the problem […]
- Health Issues on the Climate Change However, the mortality rate of air pollution in the United States is relatively low compared to the rest of the world.
- Collective Climate Change Responsibility The fact is that individuals are not the most critical contributors to the climate crisis, and while ditching the plastic straw might feel good on a personal level, it will not solve the situation.
- Climate Change and Challenges in Miami, Florida The issue of poor environment maintenance in Miami, Florida, has led to climate change, resulting in sea-level rise, an increase of flood levels, and droughts, and warmer temperatures in the area.
- Global Warming and Climate Change The author shows the tragedy of the situation with climate change by the example of birds that arrived too early from the South, as the buds begin to bloom, although it is still icy.
- Climate Change as Systemic Risk of Globalization However, the integration became more complex and rapid over the years, making it systemic due to the higher number of internal connections.
- Impact of Climate Change on Increased Wildfires Over the past decades, America has experienced the most severe fires in its history regarding the coverage of affected areas and the cost of damage.
- Creating a Policy Briefing Book: Climate Change in China After that, a necessary step included the evaluation of the data gathered and the development of a summary that perfectly demonstrated the crucial points of this complication.
- Natural Climate Solutions for Climate Change in China The social system and its response to climate change are directly related to the well-being, economic status, and quality of life of the population.
- Climate Change and Limiting the Fuel-Powered Transportation When considering the options for limiting the extent of the usage of fuel-powered vehicles, one should pay attention to the use of personal vehicles and the propensity among most citizens to prefer diesel cars as […]
- Climate Change Laboratory Report To determine the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causing global warming in the next ten decades, if the estimated rate of deforestation is maintained.
- Climate Change and Stabilization Wages The more the annual road activity indicates that more cars traversed throughout a fiscal year, the higher the size of the annual fuel consumption. The Carbon Capture and Storage technology can also reduce carbon emissions […]
- UK Climate Change Act 2008 The aim of the UK is to balance the levels of greenhouse gases to circumvent the perilous issue of climate change, as well as make it probable for people to acclimatize to an inevitable climate […]
- Sustainability, Climate Change Impact on Supply Chains & Circular Economy With recycling, reusing of materials, and collecting waste, industries help to fight ecological issues, which are the cause of climate change by saving nature’s integrity.
- Climate Change Indicators and Media Interference There is no certainty in the bright future for the Earth in the long-term perspective considering the devastating aftereffects that the phenomenon might bring. The indicators are essential to evaluate the scale of the growing […]
- Climate Change: Sustainability Development and Environmental Law The media significantly contributes to the creation of awareness, thus the importance of integrating the role of the news press with sustainability practices.
- How Climate Change Affects Conflict and Peace The review looks at various works from different years on the environment, connections to conflict, and the impact of climate change.
- Toyota Corporation: The Effects of Climate Change on the Word’s Automobile Sector Considering the broad nature of the sector, the study has taken into account the case of Toyota Motor Corporation which is one of the firms operating within the sector.
- The Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture However, the move to introduce foreign species of grass such as Bermuda grass in the region while maintaining the native grass has been faced by challenges related to the fiscal importance of the production.
- Health and Climate Change Climate change, which is a universal problem, is thought to have devastating effects on human and animal health. However, the precise health effects are not known.
- The Issue of Climate Change The only confirmed facts are the impact of one’s culture and community on willingness to participate in environmental projects, and some people can refuse to join, thereby demonstrating their individuality.
- Climate Change as a Battle of Generation Z These issues have attracted the attention of the generation who they have identified climate change as the most challenging problem the world is facing today.
- Climate Change and Health in Nunavut, Canada Then, the authors tend to use strict and formal language while delivering their findings and ideas, which, again, is due to the scholarly character of the article. Thus, the article seems to have a good […]
- Climate Change: Anticipating Drastic Consequences Modern scientists focus on the problem of the climate change because of expecting the dramatic consequences of the process in the future.
- The Analysis of Process of Climate Change Dietz is the head of the Division of Nutrition and Physical Activity at the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.
- The Way Climate Change Affects the Planet It can help analyze past events such as the Pleistocene ice ages, but the current climate change does not fit the criteria. It demonstrates how slower the change was when compared to the current climate […]
- Polar Bear Decline: Climate Change From Pole to Pole In comparison to 2005 where five of the populations were stable, it shows that there was a decline in stability of polar bear population.
- Preparing for the Impacts of Climate Change The three areas of interest that this report discusses are the impacts of climate change on social, economic and environmental fronts which are the key areas that have created a lot of debate and discussion […]
- Climate Change and Threat to Animals In the coming years, the increase in the global temperatures will make many living populations less able to adapt to the emergent conditions or to migrate to other regions that are suitable for their survival.
- Strategy for Garnering Effective Action on Climate Change Mitigation The approach should be participatory in that every member of the community is aware of ways that leads to climate change in order to take the necessary precaution measures. Many member nations have failed to […]
- Impact of Global Climate Change on Malaria There will be a comparison of the intensity of the changes to the magnitude of the impacts on malaria endemicity proposed within the future scenarios of the climate.
- Climate Change Economics: A Review of Greenstone and Oliver’s Analysis The article by Greenstone and Oliver indicates that the problem of global warming is one of the most perilous disasters whose effects are seen in low agricultural output, poor economic wellbeing of people, and high […]
- Pygmy-Possum Burramys Parvus: The Effects of Climate Change The study will be guided by the following research question: In what ways will the predicted loss of snow cover due to climate change influence the density and habitat use of the mountain pygmy-possum populations […]
- Climate Change and the Occurrence of Infectious Diseases This paper seeks to explore the nature of two vector-borne diseases, malaria, and dengue fever, in regards to the characteristics that would make them prone to effects of climate change, and to highlight some of […]
- Links Between Methane, Plants, and Climate Change According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, it is the anthropogenic activities that has increased the load of greenhouse gases since the mid-20th century that has resulted in global warming. It is only the […]
- United Nations Climate Change Conference In the Kyoto protocol, members agreed that nations needed to reduce the carbon emissions to levels that could not threaten the planet’s livelihoods.
- The Involve of Black People in the Seeking of Climate Change Whereas some researchers use the magnitude of pollution release as opposed to closeness to a hazardous site to define exposure, others utilize the dispersion of pollutants model to comprehend the link between exposure and population.
- Climate Change Dynamics: Are We Ready for the Future? One of the critical challenges of preparedness for future environmental changes is the uncertainty of how the climate system will change in several decades.
- How Climate Change Impacts Ocean Temperature and Marine Life The ocean’s surface consumes the excess heat from the air, which leads to significant issues in all of the planet’s ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Plan for Abu Dhabi City, UAE Abu Dhabi is the capital city of the UAE and the Abu Dhabi Emirate and is located on a triangular island in the Persian Gulf.
- Climate Change in Communication Moreover, environmental reporting is not accurate and useful since profits influence and political interference affect the attainment of truthful, objective, and fair facts that would promote efficiency in newsrooms on environmental reporting.
- Global Pollution and Climate Change Both of these works address the topic of Global pollution, Global warming, and Climate change, which are relevant to the current situation in the world.
- Climate Change Is a Scientific Fallacy Even in the worst-case scenario whereby the earth gives in and fails to support human activities, there can always be a way out.
- Climate Change: Change Up Your Approach People are becoming aware of the relevance of things and different aspects of their life, which is a positive trend. However, the share of this kind of energy will be reduced dramatically which is favorable […]
- Climate Change: The Broken Ozone Layer It explains the effects of climate change and the adaptation methods used. Vulnerability is basically the level of exposure and weakness of an aspect with regard to climate change.
- Climate Change and Economic Growth The graph displays the levels of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and the years before our time with the number 0 being the year 1950.
- Tropic of Chaos: Climate Change and the New Geography of Violence The point of confluence in the cattle raids in East Africa and the planting of opium in the poor communities is the struggle to beat the effects of climatic changes.
- Personal Insight: Climate Change To my mind, economic implications are one of the most concerning because the economy is one of the pillars of modern society.
- A Shift From Climate Change Awareness Under New President Such statements raised concerns among American journalists and general population about the future of the organization as one of the main forces who advocated for the safe and healthy environment of Americans and the global […]
- Human Influence on Climate Change Climate changes are dangerous because they influence all the living creatures in the world. Thus, it is hard to overestimate the threat for humankind the climate changes represent.
- Environmental Studies: Climate Changes Ozone hole is related to forest loss in that the hole is caused by reaction of different chemicals that are found in the atmosphere and some of these gases, for example, the carbon dioxide gas […]
- Global Warming: Negative Effects to the Environment The effect was the greening of the environment and its transformation into habitable zones for humans The second system has been a consequence of the first, storage.
- Global Warming Problem Overview: Significantly Changing the Climate Patterns The government is not in a position to come up with specific costs that are attached to the extent of environmental pollution neither are the polluters aware about the costs that are attached to the […]
- Global Change Biology in Terms of Global Warming A risk assessment method showed that the current population could persist for at least 2000 years at hatchling sex ratios of up to 75% male.
- The Politics of Climate Change, Saving the Environment In the first article, the author expresses his concern with the problem of data utilization on climate change and negative consequences arising from this.
- Global Warming Issues Review and Environmental Sustainability Whether it is the melt down of Arctic ice, the damage of the Ozone layer, extra pollution in developing countries; all sums up to one thing in common and that is global warming.
- Starbucks: Corporate Social Responsibility and Global Climate Change Then in the 90s and onwards to the 21st century, Starbucks coffee can be seen almost anywhere and in places where one least expects to see a Starbucks store.
- Global Warming: Ways to Help End Global Warming An innovative understanding of global warming has included it in the agenda of firms and governments. 5 trillion dollars are shouldering the responsibility of collecting and distributing information on the firms’ exposure to carbon emission-related […]
- Biofuels and Climate Change Developed countries are in the forefront to promote biofuels as a solution to the oil crisis and to a broader sense, the food crisis.
- The Influence of Global Warming and Pollution on the Environment This essay is going to address global warming from a psychological point of view with an emphasis on the psychological and social reasons that make it important to tackle this problem which is threatening the […]
- How Global Warming Has an Effect on Wildlife? According to one of the most detailed ecological studies of climate change, global warming is already directly affecting the lives of animals and plants living in various habitats across the world.
- Climate Change Risks in South Eastern Australia
- The Politics and Economics of International Action on Climate Change
- Climate Change: Influence on Lifestyle in the Future
- Climate Change During Socialism and Capitalistic Epochs
- Climate Change and Public Health Policies
- Climate Changes: Cause and Effect
- World Trade as the Adjustment Mechanism of Agriculture to Climate Change by Julia & Duchin
- Chad Frischmann: The Young Minds Solving Climate Change
- Public Health Education on Climate Change Effects
- Research Plan “Climate Change”
- Diets and Climate Change
- The Role of Human Activities on the Climate Change
- Climate Change Factors and Countermeasures
- Climate Change Effects on Population Health
- Climate Change: Who Is at Fault?
- Climate Change: Reducing Industrial Air Pollution
- Global Climate Change and Biological Implications
- Global Warming, Its Consequences and Prevention
- Climate Change and Risks for Business in Australia
- Climate Change Solutions for Australia
- Climate Change, Industrial Ecology and Environmental Chemistry
- “Climate Change May Destroy Alaskan Towns” Video
- Climate Change Effects on Kenya’s Tea Industry
- Environmental Perils: Climate Change Issue
- Technologically Produced Emissions Impact on Climate Change
- Climate Change and American National Security
- Climate Change, Air Pollution, Soil Degradation
- Climate Change in Canada
- International Climate Change Agreements
- Polar Transformations as a Global Warming Issue
- Moral Obligations to Climate Change and Animal Life
- Technology’s Impact on Climate Change
- Climate Change in Abu Dhabi
- Global Warming and Climate Change: Fighting and Solutions
- Climate Change Debates and Scientific Opinion
- Earth’s Geologic History and Global Climate Change
- CO2 Emission and Climate Change Misconceptions
- Geoengineering as a Possible Response to Climate Change
- Global Warming: People Impact on the Environment
- Climate Change Probability and Predictions
- Climate Changes and Human Population Distribution
- Climate Change as International Issue
- Climate Change for Australian Magpie-Lark Birds
- Climate Change Effects on Ocean Acidification
- Climate Change Governance: Concepts and Theories
- Climate Change Impacts on the Aviation Industry
- Climate Change Management and Risk Governance
- United Nation and Climate Change
- Human Rights and Climate Change Policy-Making
- Climate Change: Anthropological Concepts and Perspectives
- Climate Change Impacts on Business in Bangladesh
- Pollution & Climate Change as Environmental Risks
- Climate Change: Nicholas Stern and Ross Garnaut Views
- Challenges Facing Humanity: Technology and Climate Change
- Climate Change Potential Consequences
- Climate Change in United Kingdom
- Climate Change From International Relations Perspective
- Climate Change and International Collaboration
- International Security and Climate Change
- Climate Change Effects on World Economy
- Global Warming and Climate Change
- Responsible Factors for Climate Change
- Organisational Sustainability and Climate Change Strategy
- The Effect of Science on Climate Change
- Vulnerability of World Countries to Climate Change
- Anthropogenic Climate Change
- The Implementation of MOOCs on Climate Change
- The Climate Change and the Asset-Based Community Development
- Global Warming and Its Effects on the Environment
- Climate Change Research Studies
- Environmental Issue – Climate Change
- Climate Change Negative Health Impacts
- Early Climate Change Science
- Climate Change and Corporate World
- Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) in Reducing the Effects of Climate Change
- Climate Change Affecting Coral Triangle Turtles
- Introduction to Climate Change: Major Threats and the Means to Avoid Them
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Indigenous Peoples
- Asian Drivers of Global Change
- The Causes and Effects of Climate Change in the US
- Metholdogy for Economic Discourse Analysis in Climate Change
- The Impact of Climate Change on New Hampshire Business
- Climate Change Effects on an Individual’s Life in the Future
- The Role of Behavioural Economics in Energy and Climate Policy
- The Economic Cost of Climate Change Effects
- Climate Change: Floods in Queensland Australia
- Impact of Climate Change and Solutions
- Climate Change and Its Global Implications in Hospitality and Tourism
- Climate Change Needs Human Behavior Change
- Negative Impacts of Climate Change in the Urban Areas and Possible Strategies to Address Them
- Climate Changes: Snowpack
- The United Nation’s Response to Climate Change
- Critical Review: “Food’s Footprint: Agriculture and Climate Change” by Jennifer Burney
- Global Warming: Justing Gillis Discussing Studies on Climate Change
- Economics and Human Induced Climate Change
- Business & Climate Change
- Global Warming Causes and Unfavorable Climatic Changes
- Spin, Science and Climate Change
- Climate Change, Coming Home: Global Warming’s Effects on Populations
- Social Concepts and Climate Change
- Climate Change and Human Health
- Climate Change: The Complex Issue of Global Warming
- Climate Changes: Human Activities and Global Warming
- Public Awareness of Climate Changes and Carbon Footprints
- Climate Change: Impact of Carbon Emissions to the Atmosphere
- Problems of Climate Change
- Solving the Climate Change Crisis Through Development of Renewable Energy
- Climate Change Is the Biggest Challenge in the World That Affects the Flexibility of Individual Specie
- Climate Changes
- Climate Change Definition and Causes
- Climate Change: Nearing a Mini Ice Age
- Global Warming Outcomes and Sea-Level Changes
- Climate Change: Causes and Effects
- China Climate Change
- Protecting Forests to Prevent Climate Change
- Climate Change in Saudi Arabia and Miami
- Effects of Global Warming on the Environment
- Threat to Biodiversity Is Just as Important as Climate Change
- Does Climate Change Affect Entrepreneurs?
- Does Climate Change Information Affect Stated Risks of Pine Beetle Impacts on Forests
- Does Energy Consumption Contribute to Climate Change?
- Does Forced Solidarity Hinder Adaptation to Climate Change?
- Does Risk Communication Really Decrease Cooperation in Climate Change Mitigation?
- Does Risk Perception Limit the Climate Change Mitigation Behaviors?
- What Are the Differences Between Climate Change and Global Warming?
- What Are the Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture in North East Central Europe?
- What Are the Policy Challenges That National Governments Face in Addressing Climate Change?
- What Are the Primary Causes of Climate Change?
- What Are the Risks of Climate Change and Global Warming?
- What Does Climate Change Mean for Agriculture in Developing Countries?
- What Drives the International Transfer of Climate Change Mitigation Technologies?
- What Economic Impacts Are Expected to Result From Climate Change?
- What Motivates Farmers’ Adaptation to Climate Change?
- What Natural Forces Have Caused Climate Change?
- What Problems Are Involved With Establishing an International Climate Change?
- What Role Has Human Activity Played in Causing Climate Change?
- Which Incentives Does Regulation Give to Adapt Network Infrastructure to Climate Change?
- Why Climate Change Affects Us?
- Why Does Climate Change Present Potential Dangers for the African Continent?
- Why Economic Analysis Supports Strong Action on Climate Change?
- Why Should People Care For the Perceived Event of Climate Change?
- Why the Climate Change Debate Has Not Created More Cleantech Funds in Sweden?
- Why Worry About Climate Change?
- Will African Agriculture Survive Climate Change?
- Will Carbon Tax Mitigate the Effects of Climate Change?
- Will Climate Change Affect Agriculture?
- Will Climate Change Cause Enormous Social Costs for Poor Asian Cities?
- Will Religion and Faith Be the Answer to Climate Change?
- Flood Essay Topics
- Ecosystem Essay Topics
- Atmosphere Questions
- Extinction Research Topics
- Desert Research Ideas
- Greenhouse Gases Research Ideas
- Recycling Research Ideas
- Water Issues Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/
"337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
List: 15 essential reads for the climate crisis
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

We — Ayana Elizabeth Johnson and Katharine Wilkinson — are climate experts who focus on solutions, leadership and building community.
We are a natural and a social scientist, a Northerner and a Southerner. We’re also both lifelong interdisciplinarians in love with words and the cofounders of The All We Can Save Project , in support of women climate leaders.
Our collaboration has led us to read widely and deeply about the climate crisis that’s facing humanity. Here are 15 of our favorite writings on climate — this eclectic list contains books, essays, a newsletter, a scientific paper, even legislation and they’re all ones we wholeheartedly recommend.
All We Can Save: Truth, Courage, and Solutions for the Climate Crisis coedited by Ayana Elizabeth Johnson and Katharine Wilkinson
We had the honor of editing this collection of 41 essays, 17 poems, quotes and original illustrations — so naturally we love it! But you don’t have to take our word for it. As Rolling Stone said : “Taken together, the breadth of their voices forms a mosaic that honors the complexity of the climate crisis like few, if any, books on the topic have done yet. … The book is a feast of ideas and perspectives, setting a big table for the climate movement, declaring all are welcome.” All We Can Save nourished, educated and transformed us as we shaped its pages, and we can’t wait for it to do the same for you.
Ghost Fishing: An Eco-justice Poetry Anthology edited by Melissa Tuckey
We count ourselves among those who can’t make sense of the climate crisis without the aid of poets, who help us to see more clearly, feel our feelings, catch our breath, and know we’re not alone. This anthology is a magnificent quilt of poems that are made for this moment and all its intersections.
“We Don’t Have to Halt Climate Action to Fight Racism” by Mary Annaïse Heglar
“Climate People,” as she likes to call us, should be grateful that Mary Annaïse Heglar decided a few years back to pick up her pen once more as a writer. All of her essays are necessary reading, but this one is especially so, crafted from Mary’s perspective as a “Black Climate Person.” It’s a powerful articulation of the inextricability of a society that values Black lives and a livable planet for all.
Sacred Instructions: Indigenous Wisdom for Living Spirit-Based Change by Sherri Mitchell — Weh’na Ha’mu Kwasset
Weh’na Ha’mu Kwasset means “she who brings the light,” and Sherri Mitchell does exactly that in this incredible tapestry of a book, which begins with Penawahpskek Nation creation stories and concludes with guidance on what it means to live in a time of prophecy. It is rare that a book so generously shares wisdom, much less wisdom about how we got to where we are, what needs mending, and what a path forward that’s grounded in ancestral ways of knowing and being might look like.
Emergent Strategy: Shaping Change, Changing Worlds by adrienne maree brown
How lucky are we to be contemporaries of adrienne maree brown? Very. This is a book that we come back to time and time again to ground and enliven our work. We love this line from her about oak trees: “Under the earth, always, they reach for each other, they grow such that their roots are intertwined and create a system of strength that is as resilient on a sunny day as it is in a hurricane.” That’s the kind of community we’re trying to nurture.
“Circumstances Affecting the Heat of the Sun’s Rays” by Eunice Newton Foote
Eunice Newton Foote rarely gets the credit she’s due — and she deserves a lot of credit. In fact, we like to think of her as the first climate feminist. In 1856, she connected the dots between carbon dioxide and planetary warming, but science and history forgot (dismissed?) her until recently. This is her original paper, which was published in The American Journal of Science and Arts . Foote was also a signatory to the women’s rights manifesto created at Seneca Falls in 1848, alongside visionaries like Frederick Douglass.
The Drawdown Review by Project Drawdown
Full disclosure: Katharine is The Drawdown Review’ s editor-in-chief and principal writer. But Ayana fully endorses this recommendation — it’s a valuable resource as we charge ahead toward climate solutions. We all need to know what tools are in the toolbox, and The Drawdown Review is the latest compendium of climate solutions that already exist. This publication is beautifully designed, grounded in research, and you can access it for free.
The Green New Deal Resolution by the 116th US Congress
It seems that almost everyone has an opinion about the Green New Deal, but few people have read the actual piece of legislation: House Resolution 109: Recognizing the Duty of the Federal Government to Create a Green New Deal, which was introduced by Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and Sen. Ed Markey. The big secret is that it’s only 14 pages! It makes a clear, compelling and concise case for what comprehensive climate policy should look like in the US. We’d love for everyone to read it so we can all have a more grounded discussion about what we might agree and disagree with and chart a course forward.
“Think This Pandemic Is Bad? We Have Another Crisis Coming” by Rhiana Gunn-Wright
Speaking of policy … this op-ed , penned by Rhiana Gunn-Wright, who is one of the policy leads for the Green New Deal, makes the connections between climate, justice, COVID-19 and our recession as clear as day. She lays out an ironclad case for the the need to address these issues together, and why. As she writes, “We need to design the stimulus not only to help the US economy recover but to also become more resilient to the climate crisis, the next multitrillion-dollar crisis headed our way.”
“How Can We Plan for a Future in California?” by Leah Stokes
In the midst of raging fires and continuing pandemic, UC Santa Barbara Professor Leah Stokes, who’s based in Santa Barbara, lays it plain in her piece : “I don’t want to live in a world where we have to decide which mask to wear for which disaster, but this is the world we are making. And we’ve only started to alter the climate. Imagine what it will be like when we’ve doubled or tripled the warming, as we are on track to do.” As she and others have been pointing out, journalists have been failing to make the critical connection: “What’s happening in California has a name: climate change.”
HEATED by Emily Atkin
This is the reading rec that keeps on giving, literally — it’s a daily newsletter that brings climate accountability journalism right to your inbox. It’s chock full of smarts, spunk, truth-telling and super timely writing that isn’t hemmed in by media overlords. If you’re pissed off about the climate crisis, Emily Atkin made HEATED just for you.
The July 20 2020 Issue of TIME Magazine
This entire issue, titled “One Last Chance”, is dedicated to coverage of climate, and it includes wise words from so many luminaries from politician Stacey Abrams to soil scientist Asmeret Asefaw Berhe , with a lead piece by Time ’s climate journalist Justin Worland. Ayana also has a piece in this issue called “ We Can’t Solve the Climate Crisis Unless Black Lives Matter .” To see all of this collected in one place — insights on topics from oceans to agriculture to politics to activism — was heartening. We hope there’s much more of this to come, from many magazines.
“Wakanda Doesn’t Have Suburbs” by Kendra Pierre Louis
A pop-culture connoisseur and expert storyteller, Kendra Pierre Louis takes up the topic of climate stories in her essay — the good, the bad, and the ugly. The good, she explains, are all too rare, and that’s a big problem because stories are powerful. Black Panther may be our best story of living thoughtfully and well on this planet, not least thanks to an absence of carbon-spewing suburbs. It’s going to take much better narratives, and many more of them, if humans are to, as she puts it, “repair our relationship with the Earth and re-envision our societies in ways that are not just in keeping with our ecosystems but also make our lives better.” !
“We Need Courage, Not Hope, to Face Climate Change” by Kate Marvel PhD
This piece by NASA climate scientist Kate Marvel is, as the kids say, a whole mood. Hope is not enough, hope is often passive, and that won’t get us where we need to go. Pretty much everyone who works on climate is constantly being asked what gives us hope — how presumptuous to assume we have it! But what we do have is courage. In spades. As Marvel writes in this poetic piece: “We need courage, not hope. Grief, after all, is the cost of being alive. We are all fated to live lives shot through with sadness, and are not worth less for it. Courage is the resolve to do well without the assurance of a happy ending.”
Truth, Courage, and Solutions for the Climate Crisis
Admittedly, this last recommendation isn’t something to read, but to watch and listen to. This playlist of TED Talks by women climate leaders (who were all contributors to our anthology All We Can Save — read about it above) will inspire you, deepen your understanding, connect the dots and help you find where you might fit into the heaps of climate work that needs doing. It includes poignant talks by Colette Pichon Battle and Christine Nieves Rodriguez , which are respectively about communities in Louisiana and Puerto Rico recovering from hurricanes and rebuilding resilience and which broke our hearts open. We were so moved we invited them to adapt their talks into essays for All We Can Save . Christine’s piece — “Community is Our Best Chance” — is the final essay in the book and the note we want to end on here. It’s not about what each of us can do as individuals to address the climate crisis; it’s about what we can do together . Building community around solutions is the most important thing.
Watch Ayana Elizabeth Johnson’s TED Talk here:
Watch Katharine Wilkinson’s TED Talk here:

About the authors
Ayana Elizabeth Johnson PhD is a marine biologist, policy expert and Brooklyn native. She is founder of the nonprofit think tank Urban Ocean Lab, founder and CEO of the consultancy Ocean Collectiv and cocreator and cohost of the Spotify/Gimlet podcast How to Save a Planet. She coedited the anthology All We Can Save and cofounded The All We Can Save Project in support of women climate leaders. Her mission is to build community around climate solutions. Find her @ayanaeliza.
Katharine Wilkinson PhD is an author, strategist, teacher and one of 15 “women who will save the world,” according to Time magazine. Her writings on climate include The Drawdown Review, the New York Times bestseller Drawdown and Between God & Green. She is coeditor of All We Can Save and co founder of The All We Can Save Project, in support of women climate leaders. Wilkinson is a former Rhodes Scholar. Find her @DrKWilkinson.
- ayana elizabeth johnson
- climate change
- katharine wilkinson
- reading list
- society and culture
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

6 ways to give that aren't about money

A smart way to handle anxiety -- courtesy of soccer great Lionel Messi

How do top athletes get into the zone? By getting uncomfortable

6 things people do around the world to slow down

Creating a contract -- yes, a contract! -- could help you get what you want from your relationship

Could your life story use an update? Here’s how to do it

6 tips to help you be a better human now

How to have better conversations on social media (really!)

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

9 youth climate activists from around the world share their book and podcast picks

How to talk honestly to kids about climate change -- and still give them hope

Here's how your climate-related choices are contagious (in a good way!)

Jane Fonda: Why women are at the forefront of climate solutions
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Climate change articles from across Nature Portfolio
Climate change refers to a statistically defined change in the average and/or variability of the climate system, this includes the atmosphere, the water cycle, the land surface, ice and the living components of Earth. The definition does not usually require the causes of change to be attributed, for example to human activity, but there are exceptions.

The greenhouse gas cost of irrigation as adaptation
Energy use from on-farm pumping only captures two-thirds of US greenhouse gas emissions from irrigation.
- Bonnie M. McGill
Urban flooding is intensified by outdated design guidelines and a lack of a systems approach
Despite substantial investments in urban stormwater management systems around the world, cities are experiencing soaring impacts that are inconsistent with assumed levels of flood protection. This suggests that there are flaws in existing stormwater design methods and guidelines, which currently do not properly account for the complexity of flood flows in urban landscapes and their interactions with infrastructure and with natural and artificial water bodies.
- Valeriy Y. Ivanov
- Vinh Ngoc Tran
- Daniel B. Wright
Spatial heterogeneity in post-fire vegetation productivity recovery and its drivers
A global analysis of post-fire vegetation productivity recovery reveals that the recovery time shows spatial variations across vegetation types and regions. The dominant factors that influence the recovery time in the majority of the global burned area are the post-fire climate conditions, such as soil moisture, vapour pressure deficit and air temperature.
Related Subjects
- Attribution
- Climate and Earth system modelling
- Climate-change impacts
- Climate-change mitigation
- Projection and prediction
Latest Research and Reviews
Unaddressed non-energy use in the chemical industry can undermine fossil fuels phase-out
The chemical sector is both hard-to-abate and hard-to-defossilize. This study shows how limiting the availability of alternative carbon feedstocks impacts climate goals and efforts to phase out fossil fuels.
- Marianne Zanon-Zotin
- Luiz Bernardo Baptista
- Roberto Schaeffer
Summer heat wave in 2022 led to rapid warming of permafrost in the central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
- Xiaofan Zhu
- Weiying Liu
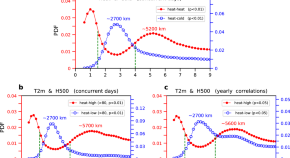
Sketching the spatial disparities in heatwave trends by changing atmospheric teleconnections in the Northern Hemisphere
This study uses complex networks to identify atmospheric teleconnections driving summer heatwaves in the Northern Hemisphere. The results show that changes in certain teleconnections drive the spatial differences in heatwave variability and trends.
- Fenying Cai
- Caihong Liu
- Jürgen Kurths
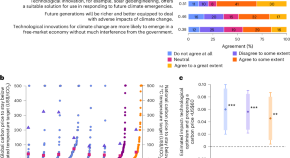
Technology-minded climate delegates support less stringent climate policies
Within high-level conferences devoted to climate or sustainability action, differences in views can lead to differences in policy. This study surveyed how delegates at COP24 perceived the efficacy of technology and climate targets.
- Maximilian Nicolaus Burger
- Donia Mahabadi
- Björn Vollan
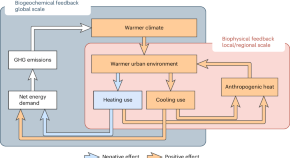
Elevated urban energy risks due to climate-driven biophysical feedbacks
Climate change affects the energy demand for heating and cooling in cities, which in turn leads to additional urban warming. Here, the authors show that when including such two-way biophysical feedbacks, the cooling (heating) energy demand more than doubles (is halved) under high emissions.
- Xinchang ‘Cathy’ Li
- Yiwen Zhang
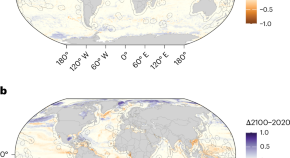
Fisheries track the future redistribution of marine species
The authors consider environmental niche models for the current and future distribution of fishing fleets and gear from 82 countries. Despite overall redistribution of fleets to the poles, they show that most nations—particularly tropical ones—may struggle to track expected fish stock shifts.
- Leonardo Cruz
- Maria Pennino
- Priscila Lopes
News and Comment

Academics say flying to meetings harms the climate — but they carry on
A survey at one of the biggest UK research universities finds that staff often end up flying to meetings despite a preference to avoid air travel.
- Alix Soliman
Heat wave attribution assessment using deep learning
- Fernando Chirigati

How we slashed our lab’s carbon footprint
Jane Kilcoyne and colleagues took action after calculating that their biotoxin chemistry lab produced 4000 kilograms of waste per year, none of which was recyled.
Atmospheric water vapour as a potential water source and its impact on energy systems
Atmospheric water vapour, an abundant yet underutilized resource, may hold potential as a new water source but is held back by its high enthalpy of condensation. This property also contributes to a negative feedback loop between cooling systems and greenhouse gases, accelerating global warming.
- Fredrik Edström
- Per Dahlbäck

Ancient DNA debunks Rapa Nui ‘ecological suicide’ theory
Study refutes claim that mismanagement of natural resources led to population crash — plus a tiny wasp that’s been found in an unexpected place.
- Benjamin Thompson
- Nick Petrić Howe
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Global Warming

- Updated on
- Apr 27, 2024

Being able to write an essay is an integral part of mastering any language. Essays form an integral part of many academic and scholastic exams like the SAT, and UPSC amongst many others. It is a crucial evaluative part of English proficiency tests as well like IELTS, TOEFL, etc. Major essays are meant to emphasize public issues of concern that can have significant consequences on the world. To understand the concept of Global Warming and its causes and effects, we must first examine the many factors that influence the planet’s temperature and what this implies for the world’s future. Here’s an unbiased look at the essay on Global Warming and other essential related topics.
Short Essay on Global Warming and Climate Change?
Since the industrial and scientific revolutions, Earth’s resources have been gradually depleted. Furthermore, the start of the world’s population’s exponential expansion is particularly hard on the environment. Simply put, as the population’s need for consumption grows, so does the use of natural resources , as well as the waste generated by that consumption.
Climate change has been one of the most significant long-term consequences of this. Climate change is more than just the rise or fall of global temperatures; it also affects rain cycles, wind patterns, cyclone frequencies, sea levels, and other factors. It has an impact on all major life groupings on the planet.
Also Read: Essay on Yoga Day
Also Read: Speech on Yoga Day
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth’s average surface temperature over the past century, primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by people burning fossil fuels . The greenhouse gases consist of methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and chlorofluorocarbons. The weather prediction has been becoming more complex with every passing year, with seasons more indistinguishable, and the general temperatures hotter.
The number of hurricanes, cyclones, droughts, floods, etc., has risen steadily since the onset of the 21st century. The supervillain behind all these changes is Global Warming. The name is quite self-explanatory; it means the rise in the temperature of the Earth.
Also Read: What is a Natural Disaster?
What are the Causes of Global Warming?
According to recent studies, many scientists believe the following are the primary four causes of global warming:
- Deforestation
- Greenhouse emissions
- Carbon emissions per capita
Extreme global warming is causing natural disasters , which can be seen all around us. One of the causes of global warming is the extreme release of greenhouse gases that become trapped on the earth’s surface, causing the temperature to rise. Similarly, volcanoes contribute to global warming by spewing excessive CO2 into the atmosphere.
The increase in population is one of the major causes of Global Warming. This increase in population also leads to increased air pollution . Automobiles emit a lot of CO2, which remains in the atmosphere. This increase in population is also causing deforestation, which contributes to global warming.
The earth’s surface emits energy into the atmosphere in the form of heat, keeping the balance with the incoming energy. Global warming depletes the ozone layer, bringing about the end of the world. There is a clear indication that increased global warming will result in the extinction of all life on Earth’s surface.
Also Read: Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation, and Wildlife Resources
Solutions for Global Warming
Of course, industries and multinational conglomerates emit more carbon than the average citizen. Nonetheless, activism and community effort are the only viable ways to slow the worsening effects of global warming. Furthermore, at the state or government level, world leaders must develop concrete plans and step-by-step programmes to ensure that no further harm is done to the environment in general.
Although we are almost too late to slow the rate of global warming, finding the right solution is critical. Everyone, from individuals to governments, must work together to find a solution to Global Warming. Some of the factors to consider are pollution control, population growth, and the use of natural resources.
One very important contribution you can make is to reduce your use of plastic. Plastic is the primary cause of global warming, and recycling it takes years. Another factor to consider is deforestation, which will aid in the control of global warming. More tree planting should be encouraged to green the environment. Certain rules should also govern industrialization. Building industries in green zones that affect plants and species should be prohibited.
Also Read: Essay on Pollution
Effects of Global Warming
Global warming is a real problem that many people want to disprove to gain political advantage. However, as global citizens, we must ensure that only the truth is presented in the media.
This decade has seen a significant impact from global warming. The two most common phenomena observed are glacier retreat and arctic shrinkage. Glaciers are rapidly melting. These are clear manifestations of climate change.
Another significant effect of global warming is the rise in sea level. Flooding is occurring in low-lying areas as a result of sea-level rise. Many countries have experienced extreme weather conditions. Every year, we have unusually heavy rain, extreme heat and cold, wildfires, and other natural disasters.
Similarly, as global warming continues, marine life is being severely impacted. This is causing the extinction of marine species as well as other problems. Furthermore, changes are expected in coral reefs, which will face extinction in the coming years. These effects will intensify in the coming years, effectively halting species expansion. Furthermore, humans will eventually feel the negative effects of Global Warming.
Also Read: Concept of Sustainable Development
Sample Essays on Global Warming
Here are some sample essays on Global Warming:
Essay on Global Warming Paragraph in 100 – 150 words
Global Warming is caused by the increase of carbon dioxide levels in the earth’s atmosphere and is a result of human activities that have been causing harm to our environment for the past few centuries now. Global Warming is something that can’t be ignored and steps have to be taken to tackle the situation globally. The average temperature is constantly rising by 1.5 degrees Celsius over the last few years.
The best method to prevent future damage to the earth, cutting down more forests should be banned and Afforestation should be encouraged. Start by planting trees near your homes and offices, participate in events, and teach the importance of planting trees. It is impossible to undo the damage but it is possible to stop further harm.
Also Read: Social Forestry
Essay on Global Warming in 250 Words
Over a long period, it is observed that the temperature of the earth is increasing. This affected wildlife, animals, humans, and every living organism on earth. Glaciers have been melting, and many countries have started water shortages, flooding, and erosion and all this is because of global warming.
No one can be blamed for global warming except for humans. Human activities such as gases released from power plants, transportation, and deforestation have increased gases such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere. The main question is how can we control the current situation and build a better world for future generations. It starts with little steps by every individual.
Start using cloth bags made from sustainable materials for all shopping purposes, instead of using high-watt lights use energy-efficient bulbs, switch off the electricity, don’t waste water, abolish deforestation and encourage planting more trees. Shift the use of energy from petroleum or other fossil fuels to wind and solar energy. Instead of throwing out the old clothes donate them to someone so that it is recycled.
Donate old books, don’t waste paper. Above all, spread awareness about global warming. Every little thing a person does towards saving the earth will contribute in big or small amounts. We must learn that 1% effort is better than no effort. Pledge to take care of Mother Nature and speak up about global warming.
Also Read: Types of Water Pollution
Essay on Global Warming in 500 Words
Global warming isn’t a prediction, it is happening! A person denying it or unaware of it is in the most simple terms complicit. Do we have another planet to live on? Unfortunately, we have been bestowed with this one planet only that can sustain life yet over the years we have turned a blind eye to the plight it is in. Global warming is not an abstract concept but a global phenomenon occurring ever so slowly even at this moment. Global Warming is a phenomenon that is occurring every minute resulting in a gradual increase in the Earth’s overall climate. Brought about by greenhouse gases that trap the solar radiation in the atmosphere, global warming can change the entire map of the earth, displacing areas, flooding many countries, and destroying multiple lifeforms. Extreme weather is a direct consequence of global warming but it is not an exhaustive consequence. There are virtually limitless effects of global warming which are all harmful to life on earth. The sea level is increasing by 0.12 inches per year worldwide. This is happening because of the melting of polar ice caps because of global warming. This has increased the frequency of floods in many lowland areas and has caused damage to coral reefs. The Arctic is one of the worst-hit areas affected by global warming. Air quality has been adversely affected and the acidity of the seawater has also increased causing severe damage to marine life forms. Severe natural disasters are brought about by global warming which has had dire effects on life and property. As long as mankind produces greenhouse gases, global warming will continue to accelerate. The consequences are felt at a much smaller scale which will increase to become drastic shortly. The power to save the day lies in the hands of humans, the need is to seize the day. Energy consumption should be reduced on an individual basis. Fuel-efficient cars and other electronics should be encouraged to reduce the wastage of energy sources. This will also improve air quality and reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Global warming is an evil that can only be defeated when fought together. It is better late than never. If we all take steps today, we will have a much brighter future tomorrow. Global warming is the bane of our existence and various policies have come up worldwide to fight it but that is not enough. The actual difference is made when we work at an individual level to fight it. Understanding its import now is crucial before it becomes an irrevocable mistake. Exterminating global warming is of utmost importance and each one of us is as responsible for it as the next.
Also Read: Essay on Library: 100, 200 and 250 Words
Essay on Global Warming UPSC
Always hear about global warming everywhere, but do we know what it is? The evil of the worst form, global warming is a phenomenon that can affect life more fatally. Global warming refers to the increase in the earth’s temperature as a result of various human activities. The planet is gradually getting hotter and threatening the existence of lifeforms on it. Despite being relentlessly studied and researched, global warming for the majority of the population remains an abstract concept of science. It is this concept that over the years has culminated in making global warming a stark reality and not a concept covered in books. Global warming is not caused by one sole reason that can be curbed. Multifarious factors cause global warming most of which are a part of an individual’s daily existence. Burning of fuels for cooking, in vehicles, and for other conventional uses, a large amount of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, and methane amongst many others is produced which accelerates global warming. Rampant deforestation also results in global warming as lesser green cover results in an increased presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which is a greenhouse gas. Finding a solution to global warming is of immediate importance. Global warming is a phenomenon that has to be fought unitedly. Planting more trees can be the first step that can be taken toward warding off the severe consequences of global warming. Increasing the green cover will result in regulating the carbon cycle. There should be a shift from using nonrenewable energy to renewable energy such as wind or solar energy which causes less pollution and thereby hinder the acceleration of global warming. Reducing energy needs at an individual level and not wasting energy in any form is the most important step to be taken against global warming. The warning bells are tolling to awaken us from the deep slumber of complacency we have slipped into. Humans can fight against nature and it is high time we acknowledged that. With all our scientific progress and technological inventions, fighting off the negative effects of global warming is implausible. We have to remember that we do not inherit the earth from our ancestors but borrow it from our future generations and the responsibility lies on our shoulders to bequeath them a healthy planet for life to exist.
Also Read: Essay on Disaster Management
Climate Change and Global Warming Essay
Global Warming and Climate Change are two sides of the same coin. Both are interrelated with each other and are two issues of major concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases released such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere cause Global Warming which leads to climate change. Black holes have started to form in the ozone layer that protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays.
Human activities have created climate change and global warming. Industrial waste and fumes are the major contributors to global warming.
Another factor affecting is the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation and also one of the reasons for climate change. Global warming has resulted in shrinking mountain glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic and causing climate change. Switching from the use of fossil fuels to energy sources like wind and solar.
When buying any electronic appliance buy the best quality with energy savings stars. Don’t waste water and encourage rainwater harvesting in your community.
Also Read: Essay on Air Pollution
Tips to Write an Essay
Writing an effective essay needs skills that few people possess and even fewer know how to implement. While writing an essay can be an assiduous task that can be unnerving at times, some key pointers can be inculcated to draft a successful essay. These involve focusing on the structure of the essay, planning it out well, and emphasizing crucial details.
Mentioned below are some pointers that can help you write better structure and more thoughtful essays that will get across to your readers:
- Prepare an outline for the essay to ensure continuity and relevance and no break in the structure of the essay
- Decide on a thesis statement that will form the basis of your essay. It will be the point of your essay and help readers understand your contention
- Follow the structure of an introduction, a detailed body followed by a conclusion so that the readers can comprehend the essay in a particular manner without any dissonance.
- Make your beginning catchy and include solutions in your conclusion to make the essay insightful and lucrative to read
- Reread before putting it out and add your flair to the essay to make it more personal and thereby unique and intriguing for readers
Also Read: I Love My India Essay: 100 and 500+ Words in English for School Students
Ans. Both natural and man-made factors contribute to global warming. The natural one also contains methane gas, volcanic eruptions, and greenhouse gases. Deforestation, mining, livestock raising, burning fossil fuels, and other man-made causes are next.
Ans. The government and the general public can work together to stop global warming. Trees must be planted more often, and deforestation must be prohibited. Auto usage needs to be curbed, and recycling needs to be promoted.
Ans. Switching to renewable energy sources , adopting sustainable farming, transportation, and energy methods, and conserving water and other natural resources.
Relevant Blogs
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Digvijay Singh
Having 2+ years of experience in educational content writing, withholding a Bachelor's in Physical Education and Sports Science and a strong interest in writing educational content for students enrolled in domestic and foreign study abroad programmes. I believe in offering a distinct viewpoint to the table, to help students deal with the complexities of both domestic and foreign educational systems. Through engaging storytelling and insightful analysis, I aim to inspire my readers to embark on their educational journeys, whether abroad or at home, and to make the most of every learning opportunity that comes their way.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
This was really a good essay on global warming… There has been used many unic words..and I really liked it!!!Seriously I had been looking for a essay about Global warming just like this…
Thank you for the comment!
I want to learn how to write essay writing so I joined this page.This page is very useful for everyone.
Hi, we are glad that we could help you to write essays. We have a beginner’s guide to write essays ( https://leverageedu.com/blog/essay-writing/ ) and we think this might help you.
It is not good , to have global warming in our earth .So we all have to afforestation program on all the world.
thank you so much
Very educative , helpful and it is really going to strength my English knowledge to structure my essay in future
Thank you for the comment, please follow our newsletter to get more insights on studying abroad and exams!
Global warming is the increase in 𝓽𝓱𝓮 ᴀᴠᴇʀᴀɢᴇ ᴛᴇᴍᴘᴇʀᴀᴛᴜʀᴇs ᴏғ ᴇᴀʀᴛʜ🌎 ᴀᴛᴍᴏsᴘʜᴇʀᴇ

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
The Center for Global Studies
Climate change argumentation.
Carmen Vanderhoof, Curriculum and Instruction, College of Education, Penn State
Carmen Vanderhoof is a doctoral candidate in Science Education at Penn State. Her research employs multimodal discourse analysis of elementary students engaged in a collaborative engineering design challenge in order to examine students’ decision-making practices. Prior to resuming graduate studies, she was a secondary science teacher and conducted molecular biology research.
- Subject(s): Earth Science
- Topic: Climate Change and Sustainability
- Grade/Level: 9-12 (can be adapted to grades 6-8)
- Objectives: Students will be able to write a scientific argument using evidence and reasoning to support claims. Students will also be able to reflect on the weaknesses in their own arguments in order to improve their argument and then respond to other arguments.
- Suggested Time Allotment: 4-5 hours (extra time for extension)
This lesson is derived from Dr. Peter Buckland’s sustainability presentation for the Center for Global Studies . Dr. Peter Buckland, a Penn State alumnus, is a postdoctoral fellow for the Sustainability Institute. He has drawn together many resources for teaching about climate change, sustainability, and other environmental issues.
While there are many resources for teaching about climate change and sustainability, it may be tough to figure out where to start. There are massive amounts of data available to the general public and students need help searching for good sources of evidence. Prior to launching into a search, it would be worthwhile figuring out what the students already know about climate change, where they learned it, and how they feel about efforts to reduce our carbon footprint. There are many options for eliciting prior knowledge, including taking online quizzes, whole-class discussion, or drawing concept maps. For this initial step, it is important that students feel comfortable to share, without engaging in disagreements. The main idea is to increase students’ understanding about global warming, rather than focus on the potential controversial nature of this topic.
A major goal of this unit is to engage students in co-constructing evidence-based explanations through individual writing, sharing, re-writing, group discussion, and whole group reflection. The argumentation format presented here contains claims supported by evidence and reasoning (Claims Evidence Reasoning – CER). Argumentation in this sense is different from how the word “argument” is used in everyday language. Argumentation is a collaborative process towards an end goal, rather than a competition to win (Duschl & Osborne, 2002). Scientific argumentation is the process of negotiating and communicating findings through a series of claims supported by evidence from various sources along with a rationale or reasoning linking the claim with the evidence. For students, making the link between claim and evidence can be the most difficult part of the process.
Where does the evidence come from?
Evidence and data are often used synonymously, but there is a difference. Evidence is “the representation of data in a form that undergirds an argument that works to answer the original question” (Hand et al., 2009, p. 129). This explains why even though scientists may use the same data to draw explanations from, the final product may take different forms depending on which parts of the data were used and how. For example, in a court case experts from opposing sides may use the same data to persuade the jury to reach different conclusions. Another way to explain this distinction to students is “the story built from the data that leads to a claim is the evidence” (Hand et al., 2009, p. 129). Evidence can come from many sources – results from controlled experiments, measurements, books, articles, websites, personal observations, etc. It is important to discuss with students the issue of the source’s reliability and accuracy. When using data freely available online, ask yourself: Who conducted the study? Who funded the research? Where was it published or presented?
What is a claim and how do I find it?
A scientific claim is a statement that answers a question or an inference based on information, rather than just personal opinion.
How can I connect the claim(s) with the evidence?
That’s where the justification or reasoning comes in. This portion of the argument explains why the evidence is relevant to the claim or how the evidence supports the claim.

Implementation
Learning context and connecting to state standards.
This interdisciplinary unit can be used in an earth science class or adapted to environmental science, chemistry, or physics. The key to adapting the lesson is guiding students to sources of data that fit the discipline they are studying.
For earth science , students can explain the difference between climate and weather, describe the factors associated with global climate change, and explore a variety of data sources to draw their evidence from. Pennsylvania Academic Standards for earth and space science (secondary): 3.3.12.A1, 3.3.12.A6, 3.3.10.A7.
For environmental science , students can analyze the costs and benefits of pollution control measures. Pennsylvania Academic Standards for Environment and Ecology (secondary): 4.5.12.C.
For chemistry and physics , students can explain the function of greenhouse gases, construct a model of the greenhouse effect, and model energy flow through the atmosphere. Pennsylvania Academic Standards for Physical Sciences (secondary): 3.2.10.B6.
New Generation Science Standards (NGSS) Connections
Human impacts and global climate change are directly addressed in the NGSS. Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCI): HS-ESS3-3, HS-ESS3-4, HS-ESS3-5, HS-ESS3-6.
Lesson 1: Introduction to climate change
- What are greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect? (sample answer: greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane contribute to overall heating of the atmosphere; these gases trap heat just like the glass in a greenhouse or in a car)
- What is the difference between weather and climate? (sample answer: weather is the daily temperature and precipitation measurements, while climate is a much longer pattern over multiple years)
Drawing of the greenhouse effect – as individuals or in pairs, have students look up the greenhouse effect and draw a diagram to represent it; share out with the class
- Optional: figure out students’ beliefs about global warming using the Yale Six Americas Survey (students answer a series of questions and at the end they are given one of the following categories: alarmed, concerned, cautious, disengaged, doubtful, dismissive).
Lesson 2: Searching for and evaluating evidence
- Compare different data sources and assess their credibility
- Temperature
- Precipitation
- Storm surge
- Ask the students to think about what types of claims they can make about climate change using the data they found (Sample claims: human activity is causing global warming or sea-level rise in the next fifty years will affect coastal cities like Amsterdam, Hong Kong, or New Orleans).
Lesson 3: Writing an argument using evidence
- Claim – an inference or a statement that answers a question
- Evidence – an outside source of information that supports the claim, often drawn from selected data
- Reasoning – the justification/support for the claim; what connects the evidence with the claim
- Extending arguments – have students exchange papers and notice the strengths of the other arguments they are reading (can do multiple cycles of reading); ask students to go back to their original argument and expand it with more evidence and/or more justification for why the evidence supports the claim
- Anticipate Rebuttals – ask students to think and write about any weaknesses in their own argument
Lesson 4: Argumentation discussion
- rebuttal – challenges a component of someone’s argument – for example, a challenge to the evidence used in the original argument
- counterargument – a whole new argument that challenges the original argument
- respect group members and their ideas
- wait for group members to finish their turns before speaking
- be mindful of your own contributions to the discussion (try not to take over the whole discussion so others can contribute too; conversely, if you didn’t already talk, find a way to bring in a new argument, expand on an existing argument, or challenge another argument)
- Debate/discussion – In table groups have students share their arguments and practice rebuttals and counterarguments
- Whole-group reflection – ask students to share key points from their discussion
Lesson 5: Argumentation in action case study
Mumbai, india case study.
Rishi is a thirteen year old boy who attends the Gayak Rafi Nagar Urdu Municipal school in Mumbai. There is a massive landfill called Deonar right across from his school. Every day 4,000 tons of waste are piled on top of the existing garbage spanning 132 hectares (roughly half a square mile). Rishi ventures out to the landfill after school to look for materials that he can later trade for a little bit of extra money to help his family. He feels lucky that he gets to go to school during the day; others are not so lucky. One of his friends, Aamir, had to stop going to school and work full time after his dad got injured. They often meet to chat while they dig through the garbage with sticks. Occasionally, they find books in okay shape, which aren’t worth anything in trade, but to them they are valuable.
One day Rishi was out to the market with his mom and saw the sky darken with a heavy smoke that blocked out the sun. They both hurried home and found out there was a state of emergency and the schools closed for two days. It took many days to put out the fire at Deonar. He heard his dad say that the fire was so bad that it could be seen from space. He wonders what it would be like to see Mumbai from up there. Some days he wishes the government would close down Deonar and clean it up. Other days he wonders what would happen to all the people that depend on it to live if the city shuts down Deonar.
Mumbai is one of the coastal cities that are considered vulnerable with increasing global temperature and sea level rise. The urban poor are most affected by climate change. Their shelter could be wiped out by a tropical storm and rebuilding would be very difficult.
Write a letter to a public official who may be able to influence policy in Mumbai.
What would you recommend they do? Should they close Deonar? What can they do to reduce air pollution in the city and prepare for possible storms? Remember to use evidence in your argument.
If students want to read the articles that inspired the case study direct them to: http://unhabitat.org/urban-themes/climate-change/
http://www.bloomberg.com/slideshow/2012-07-06/top-20-cities-with-billions-at-risk-from-climate-change.html#slide16
http://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-07-26/smelly-dumps-drive-away-affordable-homes-in-land-starved-mumbai
http://www.cnn.com/2016/02/05/asia/mumbai-giant-garbage-dump-fire/
Resources:
- Lines of Evidence video from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine http://nas-sites.org/americasclimatechoices/videos-multimedia/climate-change-lines-of-evidence-videos/
- Climate Literacy and Energy Awareness Network (CLEAN)
- Climate maps from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- Sources of data from NASA
- Explore the original source of the Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences (PNAS) study
Differentiated Instruction
- For visual learners – use diagrams, encourage students to map out their arguments prior to writing them
- For auditory learners – use the lines of evidence video
- For ESL students – provide them with a variety of greenhouse gases diagrams, allow for a more flexible argument format and focus on general meaning-making – ex. using arrows to connect their sources of evidence to claims
- For advanced learners – ask them to search through larger data sets and make comparisons between data from different sources; they can also research environmental policies and why they stalled out in congress
- For learners that need more support – print out excerpts from articles; pinpoint the main ideas to help with the research; help students connect their evidence with their claims; consider allowing students to work in pairs to accomplish the writing task
Argument write-up – check that students’ arguments contain claims supported by evidence and reasoning and that they thought about possible weaknesses in their own arguments.
Case study letter – check that students included evidence in their letter.
References:
Duschl, R. A., & Osborne, J. (2002). Supporting and promoting argumentation discourse in science education.
Hand, B. et al. (2009) Negotiating Science: The Critical Role of Argumentation in Student Inquiry. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann.
McNeill, K. L., & Krajcik, J. (2012). Claim, evidence and reasoning: Supporting grade 5 – 8 students in constructing scientific explanations. New York, NY: Pearson Allyn & Bacon.
Sawyer, R. K. (Ed.). (2014). The Cambridge handbook of the learning sciences. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
https://www3.epa.gov/climatechange/kids/basics/today/greenhouse-gases.html
http://unhabitat.org/urban-themes/climate-change/

MIT Global Change
Search form, responding to the climate threat: essays on humanity’s greatest challenge, abstract/summary:.
Authors' Summary: This book demonstrates how robust and evolving science can be relevant to public discourse about climate policy. Fighting climate change is the ultimate societal challenge, and the difficulty is not just in the wrenching adjustments required to cut greenhouse emissions and to respond to change already under way. A second and equally important difficulty is ensuring widespread public understanding of the natural and social science. This understanding is essential for an effective risk management strategy at a planetary scale. The scientific, economic, and policy aspects of climate change are already a challenge to communicate, without factoring in the distractions and deflections from organized programs of misinformation and denial.
Here, four scholars, each with decades of research on the climate threat, take on the task of explaining our current understanding of the climate threat and what can be done about it, in lay language—importantly, without losing critical aspects of the natural and social science. In a series of essays, published during the 2020 presidential election, the COVID pandemic, and through the fall of 2021, they explain the essential components of the challenge, countering the forces of distrust of the science and opposition to a vigorous national response.
Each of the essays provides an opportunity to learn about a particular aspect of climate science and policy within the complex context of current events. The overall volume is more than the sum of its individual articles. Proceeding each essay is an explanation of the context in which it was written, followed by observation of what has happened since its first publication. In addition to its discussion of topical issues in modern climate science, the book also explores science communication to a broad audience. Its authors are not only scientists – they are also teachers, using current events to teach when people are listening. For preserving Earth’s planetary life support system, science and teaching are essential. Advancing both is an unending task.
- Book/Chapter
Yohe, G., H. Jacoby, R. Richels and B. Santer
Abstract/Summary:
Posted to public: .
- Share full article

The Science of Climate Change Explained: Facts, Evidence and Proof
Definitive answers to the big questions.
Credit... Photo Illustration by Andrea D'Aquino
Supported by
By Julia Rosen
Ms. Rosen is a journalist with a Ph.D. in geology. Her research involved studying ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica to understand past climate changes.
- Published April 19, 2021 Updated Nov. 6, 2021
The science of climate change is more solid and widely agreed upon than you might think. But the scope of the topic, as well as rampant disinformation, can make it hard to separate fact from fiction. Here, we’ve done our best to present you with not only the most accurate scientific information, but also an explanation of how we know it.
How do we know climate change is really happening?
- How much agreement is there among scientists about climate change?
- Do we really only have 150 years of climate data? How is that enough to tell us about centuries of change?
- How do we know climate change is caused by humans?
- Since greenhouse gases occur naturally, how do we know they’re causing Earth’s temperature to rise?
- Why should we be worried that the planet has warmed 2°F since the 1800s?
- Is climate change a part of the planet’s natural warming and cooling cycles?
- How do we know global warming is not because of the sun or volcanoes?
- How can winters and certain places be getting colder if the planet is warming?
- Wildfires and bad weather have always happened. How do we know there’s a connection to climate change?
- How bad are the effects of climate change going to be?
- What will it cost to do something about climate change, versus doing nothing?
Climate change is often cast as a prediction made by complicated computer models. But the scientific basis for climate change is much broader, and models are actually only one part of it (and, for what it’s worth, they’re surprisingly accurate ).
For more than a century , scientists have understood the basic physics behind why greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide cause warming. These gases make up just a small fraction of the atmosphere but exert outsized control on Earth’s climate by trapping some of the planet’s heat before it escapes into space. This greenhouse effect is important: It’s why a planet so far from the sun has liquid water and life!
However, during the Industrial Revolution, people started burning coal and other fossil fuels to power factories, smelters and steam engines, which added more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Ever since, human activities have been heating the planet.

Where it was cooler or warmer in 2020 compared with the middle of the 20th century

Global average temperature compared with the middle of the 20th century
+0.75°C
–0.25°

30 billion metric tons
Carbon dioxide emitted worldwide 1850-2017
Rest of world
Other developed
European Union
Developed economies
Other countries
United States

E.U. and U.K.

We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures
Kashif abbass.
1 School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094 People’s Republic of China
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim
2 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Chemical Pollution Control and Resources Reuse, School of Environmental and Biological Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Xiaolingwei 200, Nanjing, 210094 People’s Republic of China
Huaming Song
Muntasir murshed.
3 School of Business and Economics, North South University, Dhaka, 1229 Bangladesh
4 Department of Journalism, Media and Communications, Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Haider Mahmood
5 Department of Finance, College of Business Administration, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, 173, Alkharj, 11942 Saudi Arabia
Ijaz Younis
Associated data.
Data sources and relevant links are provided in the paper to access data.
Climate change is a long-lasting change in the weather arrays across tropics to polls. It is a global threat that has embarked on to put stress on various sectors. This study is aimed to conceptually engineer how climate variability is deteriorating the sustainability of diverse sectors worldwide. Specifically, the agricultural sector’s vulnerability is a globally concerning scenario, as sufficient production and food supplies are threatened due to irreversible weather fluctuations. In turn, it is challenging the global feeding patterns, particularly in countries with agriculture as an integral part of their economy and total productivity. Climate change has also put the integrity and survival of many species at stake due to shifts in optimum temperature ranges, thereby accelerating biodiversity loss by progressively changing the ecosystem structures. Climate variations increase the likelihood of particular food and waterborne and vector-borne diseases, and a recent example is a coronavirus pandemic. Climate change also accelerates the enigma of antimicrobial resistance, another threat to human health due to the increasing incidence of resistant pathogenic infections. Besides, the global tourism industry is devastated as climate change impacts unfavorable tourism spots. The methodology investigates hypothetical scenarios of climate variability and attempts to describe the quality of evidence to facilitate readers’ careful, critical engagement. Secondary data is used to identify sustainability issues such as environmental, social, and economic viability. To better understand the problem, gathered the information in this report from various media outlets, research agencies, policy papers, newspapers, and other sources. This review is a sectorial assessment of climate change mitigation and adaptation approaches worldwide in the aforementioned sectors and the associated economic costs. According to the findings, government involvement is necessary for the country’s long-term development through strict accountability of resources and regulations implemented in the past to generate cutting-edge climate policy. Therefore, mitigating the impacts of climate change must be of the utmost importance, and hence, this global threat requires global commitment to address its dreadful implications to ensure global sustenance.
Introduction
Worldwide observed and anticipated climatic changes for the twenty-first century and global warming are significant global changes that have been encountered during the past 65 years. Climate change (CC) is an inter-governmental complex challenge globally with its influence over various components of the ecological, environmental, socio-political, and socio-economic disciplines (Adger et al. 2005 ; Leal Filho et al. 2021 ; Feliciano et al. 2022 ). Climate change involves heightened temperatures across numerous worlds (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ; Schuurmans 2021 ; Weisheimer and Palmer 2005 ; Yadav et al. 2015 ). With the onset of the industrial revolution, the problem of earth climate was amplified manifold (Leppänen et al. 2014 ). It is reported that the immediate attention and due steps might increase the probability of overcoming its devastating impacts. It is not plausible to interpret the exact consequences of climate change (CC) on a sectoral basis (Izaguirre et al. 2021 ; Jurgilevich et al. 2017 ), which is evident by the emerging level of recognition plus the inclusion of climatic uncertainties at both local and national level of policymaking (Ayers et al. 2014 ).
Climate change is characterized based on the comprehensive long-haul temperature and precipitation trends and other components such as pressure and humidity level in the surrounding environment. Besides, the irregular weather patterns, retreating of global ice sheets, and the corresponding elevated sea level rise are among the most renowned international and domestic effects of climate change (Lipczynska-Kochany 2018 ; Michel et al. 2021 ; Murshed and Dao 2020 ). Before the industrial revolution, natural sources, including volcanoes, forest fires, and seismic activities, were regarded as the distinct sources of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as CO 2 , CH 4 , N 2 O, and H 2 O into the atmosphere (Murshed et al. 2020 ; Hussain et al. 2020 ; Sovacool et al. 2021 ; Usman and Balsalobre-Lorente 2022 ; Murshed 2022 ). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) struck a major agreement to tackle climate change and accelerate and intensify the actions and investments required for a sustainable low-carbon future at Conference of the Parties (COP-21) in Paris on December 12, 2015. The Paris Agreement expands on the Convention by bringing all nations together for the first time in a single cause to undertake ambitious measures to prevent climate change and adapt to its impacts, with increased funding to assist developing countries in doing so. As so, it marks a turning point in the global climate fight. The core goal of the Paris Agreement is to improve the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping the global temperature rise this century well below 2 °C over pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5° C (Sharma et al. 2020 ; Sharif et al. 2020 ; Chien et al. 2021 .
Furthermore, the agreement aspires to strengthen nations’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and align financing flows with low GHG emissions and climate-resilient paths (Shahbaz et al. 2019 ; Anwar et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2022a ). To achieve these lofty goals, adequate financial resources must be mobilized and provided, as well as a new technology framework and expanded capacity building, allowing developing countries and the most vulnerable countries to act under their respective national objectives. The agreement also establishes a more transparent action and support mechanism. All Parties are required by the Paris Agreement to do their best through “nationally determined contributions” (NDCs) and to strengthen these efforts in the coming years (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2020 ). It includes obligations that all Parties regularly report on their emissions and implementation activities. A global stock-take will be conducted every five years to review collective progress toward the agreement’s goal and inform the Parties’ future individual actions. The Paris Agreement became available for signature on April 22, 2016, Earth Day, at the United Nations Headquarters in New York. On November 4, 2016, it went into effect 30 days after the so-called double threshold was met (ratification by 55 nations accounting for at least 55% of world emissions). More countries have ratified and continue to ratify the agreement since then, bringing 125 Parties in early 2017. To fully operationalize the Paris Agreement, a work program was initiated in Paris to define mechanisms, processes, and recommendations on a wide range of concerns (Murshed et al. 2021 ). Since 2016, Parties have collaborated in subsidiary bodies (APA, SBSTA, and SBI) and numerous formed entities. The Conference of the Parties functioning as the meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA) convened for the first time in November 2016 in Marrakesh in conjunction with COP22 and made its first two resolutions. The work plan is scheduled to be finished by 2018. Some mitigation and adaptation strategies to reduce the emission in the prospective of Paris agreement are following firstly, a long-term goal of keeping the increase in global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels, secondly, to aim to limit the rise to 1.5 °C, since this would significantly reduce risks and the impacts of climate change, thirdly, on the need for global emissions to peak as soon as possible, recognizing that this will take longer for developing countries, lastly, to undertake rapid reductions after that under the best available science, to achieve a balance between emissions and removals in the second half of the century. On the other side, some adaptation strategies are; strengthening societies’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and to continue & expand international assistance for developing nations’ adaptation.
However, anthropogenic activities are currently regarded as most accountable for CC (Murshed et al. 2022 ). Apart from the industrial revolution, other anthropogenic activities include excessive agricultural operations, which further involve the high use of fuel-based mechanization, burning of agricultural residues, burning fossil fuels, deforestation, national and domestic transportation sectors, etc. (Huang et al. 2016 ). Consequently, these anthropogenic activities lead to climatic catastrophes, damaging local and global infrastructure, human health, and total productivity. Energy consumption has mounted GHGs levels concerning warming temperatures as most of the energy production in developing countries comes from fossil fuels (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2022 ; Usman et al. 2022b ; Abbass et al. 2021a ; Ishikawa-Ishiwata and Furuya 2022 ).
This review aims to highlight the effects of climate change in a socio-scientific aspect by analyzing the existing literature on various sectorial pieces of evidence globally that influence the environment. Although this review provides a thorough examination of climate change and its severe affected sectors that pose a grave danger for global agriculture, biodiversity, health, economy, forestry, and tourism, and to purpose some practical prophylactic measures and mitigation strategies to be adapted as sound substitutes to survive from climate change (CC) impacts. The societal implications of irregular weather patterns and other effects of climate changes are discussed in detail. Some numerous sustainable mitigation measures and adaptation practices and techniques at the global level are discussed in this review with an in-depth focus on its economic, social, and environmental aspects. Methods of data collection section are included in the supplementary information.
Review methodology
Related study and its objectives.
Today, we live an ordinary life in the beautiful digital, globalized world where climate change has a decisive role. What happens in one country has a massive influence on geographically far apart countries, which points to the current crisis known as COVID-19 (Sarkar et al. 2021 ). The most dangerous disease like COVID-19 has affected the world’s climate changes and economic conditions (Abbass et al. 2022 ; Pirasteh-Anosheh et al. 2021 ). The purpose of the present study is to review the status of research on the subject, which is based on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures” by systematically reviewing past published and unpublished research work. Furthermore, the current study seeks to comment on research on the same topic and suggest future research on the same topic. Specifically, the present study aims: The first one is, organize publications to make them easy and quick to find. Secondly, to explore issues in this area, propose an outline of research for future work. The third aim of the study is to synthesize the previous literature on climate change, various sectors, and their mitigation measurement. Lastly , classify the articles according to the different methods and procedures that have been adopted.
Review methodology for reviewers
This review-based article followed systematic literature review techniques that have proved the literature review as a rigorous framework (Benita 2021 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ). Moreover, we illustrate in Fig. 1 the search method that we have started for this research. First, finalized the research theme to search literature (Cooper et al. 2018 ). Second, used numerous research databases to search related articles and download from the database (Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus Index Journals, Emerald, Elsevier Science Direct, Springer, and Sciverse). We focused on various articles, with research articles, feedback pieces, short notes, debates, and review articles published in scholarly journals. Reports used to search for multiple keywords such as “Climate Change,” “Mitigation and Adaptation,” “Department of Agriculture and Human Health,” “Department of Biodiversity and Forestry,” etc.; in summary, keyword list and full text have been made. Initially, the search for keywords yielded a large amount of literature.

Methodology search for finalized articles for investigations.
Source : constructed by authors
Since 2020, it has been impossible to review all the articles found; some restrictions have been set for the literature exhibition. The study searched 95 articles on a different database mentioned above based on the nature of the study. It excluded 40 irrelevant papers due to copied from a previous search after readings tiles, abstract and full pieces. The criteria for inclusion were: (i) articles focused on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures,” and (ii) the search key terms related to study requirements. The complete procedure yielded 55 articles for our study. We repeat our search on the “Web of Science and Google Scholars” database to enhance the search results and check the referenced articles.
In this study, 55 articles are reviewed systematically and analyzed for research topics and other aspects, such as the methods, contexts, and theories used in these studies. Furthermore, this study analyzes closely related areas to provide unique research opportunities in the future. The study also discussed future direction opportunities and research questions by understanding the research findings climate changes and other affected sectors. The reviewed paper framework analysis process is outlined in Fig. 2 .

Framework of the analysis Process.
Natural disasters and climate change’s socio-economic consequences
Natural and environmental disasters can be highly variable from year to year; some years pass with very few deaths before a significant disaster event claims many lives (Symanski et al. 2021 ). Approximately 60,000 people globally died from natural disasters each year on average over the past decade (Ritchie and Roser 2014 ; Wiranata and Simbolon 2021 ). So, according to the report, around 0.1% of global deaths. Annual variability in the number and share of deaths from natural disasters in recent decades are shown in Fig. 3 . The number of fatalities can be meager—sometimes less than 10,000, and as few as 0.01% of all deaths. But shock events have a devastating impact: the 1983–1985 famine and drought in Ethiopia; the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami; Cyclone Nargis, which struck Myanmar in 2008; and the 2010 Port-au-Prince earthquake in Haiti and now recent example is COVID-19 pandemic (Erman et al. 2021 ). These events pushed global disaster deaths to over 200,000—more than 0.4% of deaths in these years. Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are. Historical evidence shows that earlier disaster detection, more robust infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response programmers have substantially reduced disaster deaths worldwide. Low-income is also the most vulnerable to disasters; improving living conditions, facilities, and response services in these areas would be critical in reducing natural disaster deaths in the coming decades.

Global deaths from natural disasters, 1978 to 2020.
Source EMDAT ( 2020 )
The interior regions of the continent are likely to be impacted by rising temperatures (Dimri et al. 2018 ; Goes et al. 2020 ; Mannig et al. 2018 ; Schuurmans 2021 ). Weather patterns change due to the shortage of natural resources (water), increase in glacier melting, and rising mercury are likely to cause extinction to many planted species (Gampe et al. 2016 ; Mihiretu et al. 2021 ; Shaffril et al. 2018 ).On the other hand, the coastal ecosystem is on the verge of devastation (Perera et al. 2018 ; Phillips 2018 ). The temperature rises, insect disease outbreaks, health-related problems, and seasonal and lifestyle changes are persistent, with a strong probability of these patterns continuing in the future (Abbass et al. 2021c ; Hussain et al. 2018 ). At the global level, a shortage of good infrastructure and insufficient adaptive capacity are hammering the most (IPCC 2013 ). In addition to the above concerns, a lack of environmental education and knowledge, outdated consumer behavior, a scarcity of incentives, a lack of legislation, and the government’s lack of commitment to climate change contribute to the general public’s concerns. By 2050, a 2 to 3% rise in mercury and a drastic shift in rainfall patterns may have serious consequences (Huang et al. 2022 ; Gorst et al. 2018 ). Natural and environmental calamities caused huge losses globally, such as decreased agriculture outputs, rehabilitation of the system, and rebuilding necessary technologies (Ali and Erenstein 2017 ; Ramankutty et al. 2018 ; Yu et al. 2021 ) (Table (Table1). 1 ). Furthermore, in the last 3 or 4 years, the world has been plagued by smog-related eye and skin diseases, as well as a rise in road accidents due to poor visibility.
Main natural danger statistics for 1985–2020 at the global level
| Key natural hazards statistics from 1978 to 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | 1978 change | 2018 | Absolute change | Relative |
| Drought | 63 | 0 | − 63 | − 100% |
| Earthquake | 25,162 | 4,321 | − 20,841 | − 83% |
| Extreme temperature | 150 | 536 | + 386 | + 257% |
| Extreme weather | 3676 | 1,666 | − 2,010 | − 55% |
| Flood | 5,897 | 2,869 | − 3,028 | − 51% |
| Landslide | 86 | 275 | + 189 | + 220% |
| Mass movement | 50 | 17 | − 33 | − 66% |
| Volcanic activity | 268 | 878 | + 610 | + 228% |
| Wildfire | 2 | 247 | + 245 | + 12,250% |
| All − natural disasters | 35,036 | 10,809 | − 24,227 | − 69% |
Source: EM-DAT ( 2020 )
Climate change and agriculture
Global agriculture is the ultimate sector responsible for 30–40% of all greenhouse emissions, which makes it a leading industry predominantly contributing to climate warming and significantly impacted by it (Grieg; Mishra et al. 2021 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Thornton and Lipper 2014 ). Numerous agro-environmental and climatic factors that have a dominant influence on agriculture productivity (Pautasso et al. 2012 ) are significantly impacted in response to precipitation extremes including floods, forest fires, and droughts (Huang 2004 ). Besides, the immense dependency on exhaustible resources also fuels the fire and leads global agriculture to become prone to devastation. Godfray et al. ( 2010 ) mentioned that decline in agriculture challenges the farmer’s quality of life and thus a significant factor to poverty as the food and water supplies are critically impacted by CC (Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Rosenzweig et al. 2014 ). As an essential part of the economic systems, especially in developing countries, agricultural systems affect the overall economy and potentially the well-being of households (Schlenker and Roberts 2009 ). According to the report published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, i.e., CH 4, CO 2 , and N 2 O, are increased in the air to extraordinary levels over the last few centuries (Usman and Makhdum 2021 ; Stocker et al. 2013 ). Climate change is the composite outcome of two different factors. The first is the natural causes, and the second is the anthropogenic actions (Karami 2012 ). It is also forecasted that the world may experience a typical rise in temperature stretching from 1 to 3.7 °C at the end of this century (Pachauri et al. 2014 ). The world’s crop production is also highly vulnerable to these global temperature-changing trends as raised temperatures will pose severe negative impacts on crop growth (Reidsma et al. 2009 ). Some of the recent modeling about the fate of global agriculture is briefly described below.
Decline in cereal productivity
Crop productivity will also be affected dramatically in the next few decades due to variations in integral abiotic factors such as temperature, solar radiation, precipitation, and CO 2 . These all factors are included in various regulatory instruments like progress and growth, weather-tempted changes, pest invasions (Cammell and Knight 1992 ), accompanying disease snags (Fand et al. 2012 ), water supplies (Panda et al. 2003 ), high prices of agro-products in world’s agriculture industry, and preeminent quantity of fertilizer consumption. Lobell and field ( 2007 ) claimed that from 1962 to 2002, wheat crop output had condensed significantly due to rising temperatures. Therefore, during 1980–2011, the common wheat productivity trends endorsed extreme temperature events confirmed by Gourdji et al. ( 2013 ) around South Asia, South America, and Central Asia. Various other studies (Asseng, Cao, Zhang, and Ludwig 2009 ; Asseng et al. 2013 ; García et al. 2015 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ) also proved that wheat output is negatively affected by the rising temperatures and also caused adverse effects on biomass productivity (Calderini et al. 1999 ; Sadras and Slafer 2012 ). Hereafter, the rice crop is also influenced by the high temperatures at night. These difficulties will worsen because the temperature will be rising further in the future owing to CC (Tebaldi et al. 2006 ). Another research conducted in China revealed that a 4.6% of rice production per 1 °C has happened connected with the advancement in night temperatures (Tao et al. 2006 ). Moreover, the average night temperature growth also affected rice indicia cultivar’s output pragmatically during 25 years in the Philippines (Peng et al. 2004 ). It is anticipated that the increase in world average temperature will also cause a substantial reduction in yield (Hatfield et al. 2011 ; Lobell and Gourdji 2012 ). In the southern hemisphere, Parry et al. ( 2007 ) noted a rise of 1–4 °C in average daily temperatures at the end of spring season unti the middle of summers, and this raised temperature reduced crop output by cutting down the time length for phenophases eventually reduce the yield (Hatfield and Prueger 2015 ; R. Ortiz 2008 ). Also, world climate models have recommended that humid and subtropical regions expect to be plentiful prey to the upcoming heat strokes (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ). Grain production is the amalgamation of two constituents: the average weight and the grain output/m 2 , however, in crop production. Crop output is mainly accredited to the grain quantity (Araus et al. 2008 ; Gambín and Borrás 2010 ). In the times of grain set, yield resources are mainly strewn between hitherto defined components, i.e., grain usual weight and grain output, which presents a trade-off between them (Gambín and Borrás 2010 ) beside disparities in per grain integration (B. L. Gambín et al. 2006 ). In addition to this, the maize crop is also susceptible to raised temperatures, principally in the flowering stage (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). In reality, the lower grain number is associated with insufficient acclimatization due to intense photosynthesis and higher respiration and the high-temperature effect on the reproduction phenomena (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). During the flowering phase, maize visible to heat (30–36 °C) seemed less anthesis-silking intermissions (Edreira et al. 2011 ). Another research by Dupuis and Dumas ( 1990 ) proved that a drop in spikelet when directly visible to high temperatures above 35 °C in vitro pollination. Abnormalities in kernel number claimed by Vega et al. ( 2001 ) is related to conceded plant development during a flowering phase that is linked with the active ear growth phase and categorized as a critical phase for approximation of kernel number during silking (Otegui and Bonhomme 1998 ).
The retort of rice output to high temperature presents disparities in flowering patterns, and seed set lessens and lessens grain weight (Qasim et al. 2020 ; Qasim, Hammad, Maqsood, Tariq, & Chawla). During the daytime, heat directly impacts flowers which lessens the thesis period and quickens the earlier peak flowering (Tao et al. 2006 ). Antagonistic effect of higher daytime temperature d on pollen sprouting proposed seed set decay, whereas, seed set was lengthily reduced than could be explicated by pollen growing at high temperatures 40◦C (Matsui et al. 2001 ).
The decline in wheat output is linked with higher temperatures, confirmed in numerous studies (Semenov 2009 ; Stone and Nicolas 1994 ). High temperatures fast-track the arrangements of plant expansion (Blum et al. 2001 ), diminution photosynthetic process (Salvucci and Crafts‐Brandner 2004 ), and also considerably affect the reproductive operations (Farooq et al. 2011 ).
The destructive impacts of CC induced weather extremes to deteriorate the integrity of crops (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ), e.g., Spartan cold and extreme fog cause falling and discoloration of betel leaves (Rosenzweig et al. 2001 ), giving them a somehow reddish appearance, squeezing of lemon leaves (Pautasso et al. 2012 ), as well as root rot of pineapple, have reported (Vedwan and Rhoades 2001 ). Henceforth, in tackling the disruptive effects of CC, several short-term and long-term management approaches are the crucial need of time (Fig. 4 ). Moreover, various studies (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ; Patz et al. 2005 ; Pautasso et al. 2012 ) have demonstrated adapting trends such as ameliorating crop diversity can yield better adaptability towards CC.

Schematic description of potential impacts of climate change on the agriculture sector and the appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures to overcome its impact.
Climate change impacts on biodiversity
Global biodiversity is among the severe victims of CC because it is the fastest emerging cause of species loss. Studies demonstrated that the massive scale species dynamics are considerably associated with diverse climatic events (Abraham and Chain 1988 ; Manes et al. 2021 ; A. M. D. Ortiz et al. 2021 ). Both the pace and magnitude of CC are altering the compatible habitat ranges for living entities of marine, freshwater, and terrestrial regions. Alterations in general climate regimes influence the integrity of ecosystems in numerous ways, such as variation in the relative abundance of species, range shifts, changes in activity timing, and microhabitat use (Bates et al. 2014 ). The geographic distribution of any species often depends upon its ability to tolerate environmental stresses, biological interactions, and dispersal constraints. Hence, instead of the CC, the local species must only accept, adapt, move, or face extinction (Berg et al. 2010 ). So, the best performer species have a better survival capacity for adjusting to new ecosystems or a decreased perseverance to survive where they are already situated (Bates et al. 2014 ). An important aspect here is the inadequate habitat connectivity and access to microclimates, also crucial in raising the exposure to climate warming and extreme heatwave episodes. For example, the carbon sequestration rates are undergoing fluctuations due to climate-driven expansion in the range of global mangroves (Cavanaugh et al. 2014 ).
Similarly, the loss of kelp-forest ecosystems in various regions and its occupancy by the seaweed turfs has set the track for elevated herbivory by the high influx of tropical fish populations. Not only this, the increased water temperatures have exacerbated the conditions far away from the physiological tolerance level of the kelp communities (Vergés et al. 2016 ; Wernberg et al. 2016 ). Another pertinent danger is the devastation of keystone species, which even has more pervasive effects on the entire communities in that habitat (Zarnetske et al. 2012 ). It is particularly important as CC does not specify specific populations or communities. Eventually, this CC-induced redistribution of species may deteriorate carbon storage and the net ecosystem productivity (Weed et al. 2013 ). Among the typical disruptions, the prominent ones include impacts on marine and terrestrial productivity, marine community assembly, and the extended invasion of toxic cyanobacteria bloom (Fossheim et al. 2015 ).
The CC-impacted species extinction is widely reported in the literature (Beesley et al. 2019 ; Urban 2015 ), and the predictions of demise until the twenty-first century are dreadful (Abbass et al. 2019 ; Pereira et al. 2013 ). In a few cases, northward shifting of species may not be formidable as it allows mountain-dwelling species to find optimum climates. However, the migrant species may be trapped in isolated and incompatible habitats due to losing topography and range (Dullinger et al. 2012 ). For example, a study indicated that the American pika has been extirpated or intensely diminished in some regions, primarily attributed to the CC-impacted extinction or at least local extirpation (Stewart et al. 2015 ). Besides, the anticipation of persistent responses to the impacts of CC often requires data records of several decades to rigorously analyze the critical pre and post CC patterns at species and ecosystem levels (Manes et al. 2021 ; Testa et al. 2018 ).
Nonetheless, the availability of such long-term data records is rare; hence, attempts are needed to focus on these profound aspects. Biodiversity is also vulnerable to the other associated impacts of CC, such as rising temperatures, droughts, and certain invasive pest species. For instance, a study revealed the changes in the composition of plankton communities attributed to rising temperatures. Henceforth, alterations in such aquatic producer communities, i.e., diatoms and calcareous plants, can ultimately lead to variation in the recycling of biological carbon. Moreover, such changes are characterized as a potential contributor to CO 2 differences between the Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods (Kohfeld et al. 2005 ).
Climate change implications on human health
It is an understood corporality that human health is a significant victim of CC (Costello et al. 2009 ). According to the WHO, CC might be responsible for 250,000 additional deaths per year during 2030–2050 (Watts et al. 2015 ). These deaths are attributed to extreme weather-induced mortality and morbidity and the global expansion of vector-borne diseases (Lemery et al. 2021; Yang and Usman 2021 ; Meierrieks 2021 ; UNEP 2017 ). Here, some of the emerging health issues pertinent to this global problem are briefly described.
Climate change and antimicrobial resistance with corresponding economic costs
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an up-surging complex global health challenge (Garner et al. 2019 ; Lemery et al. 2021 ). Health professionals across the globe are extremely worried due to this phenomenon that has critical potential to reverse almost all the progress that has been achieved so far in the health discipline (Gosling and Arnell 2016 ). A massive amount of antibiotics is produced by many pharmaceutical industries worldwide, and the pathogenic microorganisms are gradually developing resistance to them, which can be comprehended how strongly this aspect can shake the foundations of national and global economies (UNEP 2017 ). This statement is supported by the fact that AMR is not developing in a particular region or country. Instead, it is flourishing in every continent of the world (WHO 2018 ). This plague is heavily pushing humanity to the post-antibiotic era, in which currently antibiotic-susceptible pathogens will once again lead to certain endemics and pandemics after being resistant(WHO 2018 ). Undesirably, if this statement would become a factuality, there might emerge certain risks in undertaking sophisticated interventions such as chemotherapy, joint replacement cases, and organ transplantation (Su et al. 2018 ). Presently, the amplification of drug resistance cases has made common illnesses like pneumonia, post-surgical infections, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, etc., too difficult and costly to be treated or cure well (WHO 2018 ). From a simple example, it can be assumed how easily antibiotic-resistant strains can be transmitted from one person to another and ultimately travel across the boundaries (Berendonk et al. 2015 ). Talking about the second- and third-generation classes of antibiotics, e.g., most renowned generations of cephalosporin antibiotics that are more expensive, broad-spectrum, more toxic, and usually require more extended periods whenever prescribed to patients (Lemery et al. 2021 ; Pärnänen et al. 2019 ). This scenario has also revealed that the abundance of resistant strains of pathogens was also higher in the Southern part (WHO 2018 ). As southern parts are generally warmer than their counterparts, it is evident from this example how CC-induced global warming can augment the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains within the biosphere, eventually putting additional economic burden in the face of developing new and costlier antibiotics. The ARG exchange to susceptible bacteria through one of the potential mechanisms, transformation, transduction, and conjugation; Selection pressure can be caused by certain antibiotics, metals or pesticides, etc., as shown in Fig. 5 .

A typical interaction between the susceptible and resistant strains.
Source: Elsayed et al. ( 2021 ); Karkman et al. ( 2018 )
Certain studies highlighted that conventional urban wastewater treatment plants are typical hotspots where most bacterial strains exchange genetic material through horizontal gene transfer (Fig. 5 ). Although at present, the extent of risks associated with the antibiotic resistance found in wastewater is complicated; environmental scientists and engineers have particular concerns about the potential impacts of these antibiotic resistance genes on human health (Ashbolt 2015 ). At most undesirable and worst case, these antibiotic-resistant genes containing bacteria can make their way to enter into the environment (Pruden et al. 2013 ), irrigation water used for crops and public water supplies and ultimately become a part of food chains and food webs (Ma et al. 2019 ; D. Wu et al. 2019 ). This problem has been reported manifold in several countries (Hendriksen et al. 2019 ), where wastewater as a means of irrigated water is quite common.
Climate change and vector borne-diseases
Temperature is a fundamental factor for the sustenance of living entities regardless of an ecosystem. So, a specific living being, especially a pathogen, requires a sophisticated temperature range to exist on earth. The second essential component of CC is precipitation, which also impacts numerous infectious agents’ transport and dissemination patterns. Global rising temperature is a significant cause of many species extinction. On the one hand, this changing environmental temperature may be causing species extinction, and on the other, this warming temperature might favor the thriving of some new organisms. Here, it was evident that some pathogens may also upraise once non-evident or reported (Patz et al. 2000 ). This concept can be exemplified through certain pathogenic strains of microorganisms that how the likelihood of various diseases increases in response to climate warming-induced environmental changes (Table (Table2 2 ).
Examples of how various environmental changes affect various infectious diseases in humans
| Environmental modifications | Potential diseases | The causative organisms and pathway of effect |
|---|---|---|
| Construction of canals, dams, irrigation pathways | Schistosomiasis | Snail host locale, human contact |
| Malaria | Upbringing places for mosquitoes | |
| Helminthiases | Larval contact due to moist soil | |
| River blindness | Blackfly upbringing | |
| Agro-strengthening | Malaria | Crop pesticides |
| Venezuelan hemorrhagic fever | Rodent abundance, contact | |
| Suburbanization | Cholera | deprived hygiene, asepsis; augmented water municipal assembling pollution |
| Dengue | Water-gathering rubbishes Aedes aegypti mosquito upbringing sites | |
| Cutaneous leishmaniasis | PSandfly vectors | |
| Deforestation and new tenancy | Malaria | Upbringing sites and trajectories, migration of vulnerable people |
| Oropouche | upsurge contact, upbringing of directions | |
| Visceral leishmaniasis | Recurrent contact with sandfly vectors | |
| Agriculture | Lyme disease | Tick hosts, outside revelation |
| Ocean heating | Red tide | Poisonous algal blooms |
Source: Aron and Patz ( 2001 )
A recent example is an outburst of coronavirus (COVID-19) in the Republic of China, causing pneumonia and severe acute respiratory complications (Cui et al. 2021 ; Song et al. 2021 ). The large family of viruses is harbored in numerous animals, bats, and snakes in particular (livescience.com) with the subsequent transfer into human beings. Hence, it is worth noting that the thriving of numerous vectors involved in spreading various diseases is influenced by Climate change (Ogden 2018 ; Santos et al. 2021 ).
Psychological impacts of climate change
Climate change (CC) is responsible for the rapid dissemination and exaggeration of certain epidemics and pandemics. In addition to the vast apparent impacts of climate change on health, forestry, agriculture, etc., it may also have psychological implications on vulnerable societies. It can be exemplified through the recent outburst of (COVID-19) in various countries around the world (Pal 2021 ). Besides, the victims of this viral infection have made healthy beings scarier and terrified. In the wake of such epidemics, people with common colds or fever are also frightened and must pass specific regulatory protocols. Living in such situations continuously terrifies the public and makes the stress familiar, which eventually makes them psychologically weak (npr.org).
CC boosts the extent of anxiety, distress, and other issues in public, pushing them to develop various mental-related problems. Besides, frequent exposure to extreme climatic catastrophes such as geological disasters also imprints post-traumatic disorder, and their ubiquitous occurrence paves the way to developing chronic psychological dysfunction. Moreover, repetitive listening from media also causes an increase in the person’s stress level (Association 2020 ). Similarly, communities living in flood-prone areas constantly live in extreme fear of drowning and die by floods. In addition to human lives, the flood-induced destruction of physical infrastructure is a specific reason for putting pressure on these communities (Ogden 2018 ). For instance, Ogden ( 2018 ) comprehensively denoted that Katrina’s Hurricane augmented the mental health issues in the victim communities.
Climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Forests are the global regulators of the world’s climate (FAO 2018 ) and have an indispensable role in regulating global carbon and nitrogen cycles (Rehman et al. 2021 ; Reichstein and Carvalhais 2019 ). Hence, disturbances in forest ecology affect the micro and macro-climates (Ellison et al. 2017 ). Climate warming, in return, has profound impacts on the growth and productivity of transboundary forests by influencing the temperature and precipitation patterns, etc. As CC induces specific changes in the typical structure and functions of ecosystems (Zhang et al. 2017 ) as well impacts forest health, climate change also has several devastating consequences such as forest fires, droughts, pest outbreaks (EPA 2018 ), and last but not the least is the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities. The rising frequency and intensity of another CC product, i.e., droughts, pose plenty of challenges to the well-being of global forests (Diffenbaugh et al. 2017 ), which is further projected to increase soon (Hartmann et al. 2018 ; Lehner et al. 2017 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ). Hence, CC induces storms, with more significant impacts also put extra pressure on the survival of the global forests (Martínez-Alvarado et al. 2018 ), significantly since their influences are augmented during higher winter precipitations with corresponding wetter soils causing weak root anchorage of trees (Brázdil et al. 2018 ). Surging temperature regimes causes alterations in usual precipitation patterns, which is a significant hurdle for the survival of temperate forests (Allen et al. 2010 ; Flannigan et al. 2013 ), letting them encounter severe stress and disturbances which adversely affects the local tree species (Hubbart et al. 2016 ; Millar and Stephenson 2015 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ).
Climate change impacts on forest-dependent communities
Forests are the fundamental livelihood resource for about 1.6 billion people worldwide; out of them, 350 million are distinguished with relatively higher reliance (Bank 2008 ). Agro-forestry-dependent communities comprise 1.2 billion, and 60 million indigenous people solely rely on forests and their products to sustain their lives (Sunderlin et al. 2005 ). For example, in the entire African continent, more than 2/3rd of inhabitants depend on forest resources and woodlands for their alimonies, e.g., food, fuelwood and grazing (Wasiq and Ahmad 2004 ). The livings of these people are more intensely affected by the climatic disruptions making their lives harder (Brown et al. 2014 ). On the one hand, forest communities are incredibly vulnerable to CC due to their livelihoods, cultural and spiritual ties as well as socio-ecological connections, and on the other, they are not familiar with the term “climate change.” (Rahman and Alam 2016 ). Among the destructive impacts of temperature and rainfall, disruption of the agroforestry crops with resultant downscale growth and yield (Macchi et al. 2008 ). Cruz ( 2015 ) ascribed that forest-dependent smallholder farmers in the Philippines face the enigma of delayed fruiting, more severe damages by insect and pest incidences due to unfavorable temperature regimes, and changed rainfall patterns.
Among these series of challenges to forest communities, their well-being is also distinctly vulnerable to CC. Though the detailed climate change impacts on human health have been comprehensively mentioned in the previous section, some studies have listed a few more devastating effects on the prosperity of forest-dependent communities. For instance, the Himalayan people have been experiencing frequent skin-borne diseases such as malaria and other skin diseases due to increasing mosquitoes, wild boar as well, and new wasps species, particularly in higher altitudes that were almost non-existent before last 5–10 years (Xu et al. 2008 ). Similarly, people living at high altitudes in Bangladesh have experienced frequent mosquito-borne calamities (Fardous; Sharma 2012 ). In addition, the pace of other waterborne diseases such as infectious diarrhea, cholera, pathogenic induced abdominal complications and dengue has also been boosted in other distinguished regions of Bangladesh (Cell 2009 ; Gunter et al. 2008 ).
Pest outbreak
Upscaling hotter climate may positively affect the mobile organisms with shorter generation times because they can scurry from harsh conditions than the immobile species (Fettig et al. 2013 ; Schoene and Bernier 2012 ) and are also relatively more capable of adapting to new environments (Jactel et al. 2019 ). It reveals that insects adapt quickly to global warming due to their mobility advantages. Due to past outbreaks, the trees (forests) are relatively more susceptible victims (Kurz et al. 2008 ). Before CC, the influence of factors mentioned earlier, i.e., droughts and storms, was existent and made the forests susceptible to insect pest interventions; however, the global forests remain steadfast, assiduous, and green (Jactel et al. 2019 ). The typical reasons could be the insect herbivores were regulated by several tree defenses and pressures of predation (Wilkinson and Sherratt 2016 ). As climate greatly influences these phenomena, the global forests cannot be so sedulous against such challenges (Jactel et al. 2019 ). Table Table3 3 demonstrates some of the particular considerations with practical examples that are essential while mitigating the impacts of CC in the forestry sector.
Essential considerations while mitigating the climate change impacts on the forestry sector
| Attributes | Description | Forestry example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purposefulness | Autonomous | Includes continuing application of prevailing information and techniques in retort to experienced climate change | Thin to reduce drought stress; construct breaks in vegetation to Stop feast of wildfires, vermin, and ailments |
| Timing | Preemptive | Necessitates interactive change to diminish future injury, jeopardy, and weakness, often through planning, observing, growing consciousness, structure partnerships, and ornamental erudition or investigation | Ensure forest property against potential future losses; transition to species or stand erections that are better reformed to predictable future conditions; trial with new forestry organization practices |
| Scope | Incremental | Involves making small changes in present circumstances to circumvent disturbances and ongoing to chase the same purposes | Condense rotation pauses to decrease the likelihood of harm to storm Events, differentiate classes to blowout jeopardy; thin to lessening compactness and defenselessness of jungle stands to tension |
| Goal | Opposition | Shield or defend from alteration; take procedures to reservation constancy and battle change | Generate refugia for rare classes; defend woodlands from austere fire and wind uproar; alter forest construction to reduce harshness or extent of wind and ice impairment; establish breaks in vegetation to dampen the spread of vermin, ailments, and wildfire |
Source : Fischer ( 2019 )
Climate change impacts on tourism
Tourism is a commercial activity that has roots in multi-dimensions and an efficient tool with adequate job generation potential, revenue creation, earning of spectacular foreign exchange, enhancement in cross-cultural promulgation and cooperation, a business tool for entrepreneurs and eventually for the country’s national development (Arshad et al. 2018 ; Scott 2021 ). Among a plethora of other disciplines, the tourism industry is also a distinct victim of climate warming (Gössling et al. 2012 ; Hall et al. 2015 ) as the climate is among the essential resources that enable tourism in particular regions as most preferred locations. Different places at different times of the year attract tourists both within and across the countries depending upon the feasibility and compatibility of particular weather patterns. Hence, the massive variations in these weather patterns resulting from CC will eventually lead to monumental challenges to the local economy in that specific area’s particular and national economy (Bujosa et al. 2015 ). For instance, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report demonstrated that the global tourism industry had faced a considerable decline in the duration of ski season, including the loss of some ski areas and the dramatic shifts in tourist destinations’ climate warming.
Furthermore, different studies (Neuvonen et al. 2015 ; Scott et al. 2004 ) indicated that various currently perfect tourist spots, e.g., coastal areas, splendid islands, and ski resorts, will suffer consequences of CC. It is also worth noting that the quality and potential of administrative management potential to cope with the influence of CC on the tourism industry is of crucial significance, which renders specific strengths of resiliency to numerous destinations to withstand against it (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). Similarly, in the partial or complete absence of adequate socio-economic and socio-political capital, the high-demanding tourist sites scurry towards the verge of vulnerability. The susceptibility of tourism is based on different components such as the extent of exposure, sensitivity, life-supporting sectors, and capacity assessment factors (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). It is obvious corporality that sectors such as health, food, ecosystems, human habitat, infrastructure, water availability, and the accessibility of a particular region are prone to CC. Henceforth, the sensitivity of these critical sectors to CC and, in return, the adaptive measures are a hallmark in determining the composite vulnerability of climate warming (Ionescu et al. 2009 ).
Moreover, the dependence on imported food items, poor hygienic conditions, and inadequate health professionals are dominant aspects affecting the local terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity. Meanwhile, the greater dependency on ecosystem services and its products also makes a destination more fragile to become a prey of CC (Rizvi et al. 2015 ). Some significant non-climatic factors are important indicators of a particular ecosystem’s typical health and functioning, e.g., resource richness and abundance portray the picture of ecosystem stability. Similarly, the species abundance is also a productive tool that ensures that the ecosystem has a higher buffering capacity, which is terrific in terms of resiliency (Roscher et al. 2013 ).
Climate change impacts on the economic sector
Climate plays a significant role in overall productivity and economic growth. Due to its increasingly global existence and its effect on economic growth, CC has become one of the major concerns of both local and international environmental policymakers (Ferreira et al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Abbass et al. 2021b ; Lamperti et al. 2021 ). The adverse effects of CC on the overall productivity factor of the agricultural sector are therefore significant for understanding the creation of local adaptation policies and the composition of productive climate policy contracts. Previous studies on CC in the world have already forecasted its effects on the agricultural sector. Researchers have found that global CC will impact the agricultural sector in different world regions. The study of the impacts of CC on various agrarian activities in other demographic areas and the development of relative strategies to respond to effects has become a focal point for researchers (Chandioet al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Mosavi et al. 2020 ).
With the rapid growth of global warming since the 1980s, the temperature has started increasing globally, which resulted in the incredible transformation of rain and evaporation in the countries. The agricultural development of many countries has been reliant, delicate, and susceptible to CC for a long time, and it is on the development of agriculture total factor productivity (ATFP) influence different crops and yields of farmers (Alhassan 2021 ; Wu 2020 ).
Food security and natural disasters are increasing rapidly in the world. Several major climatic/natural disasters have impacted local crop production in the countries concerned. The effects of these natural disasters have been poorly controlled by the development of the economies and populations and may affect human life as well. One example is China, which is among the world’s most affected countries, vulnerable to natural disasters due to its large population, harsh environmental conditions, rapid CC, low environmental stability, and disaster power. According to the January 2016 statistical survey, China experienced an economic loss of 298.3 billion Yuan, and about 137 million Chinese people were severely affected by various natural disasters (Xie et al. 2018 ).
Mitigation and adaptation strategies of climate changes
Adaptation and mitigation are the crucial factors to address the response to CC (Jahanzad et al. 2020 ). Researchers define mitigation on climate changes, and on the other hand, adaptation directly impacts climate changes like floods. To some extent, mitigation reduces or moderates greenhouse gas emission, and it becomes a critical issue both economically and environmentally (Botzen et al. 2021 ; Jahanzad et al. 2020 ; Kongsager 2018 ; Smit et al. 2000 ; Vale et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2021 ; Verheyen 2005 ).
Researchers have deep concern about the adaptation and mitigation methodologies in sectoral and geographical contexts. Agriculture, industry, forestry, transport, and land use are the main sectors to adapt and mitigate policies(Kärkkäinen et al. 2020 ; Waheed et al. 2021 ). Adaptation and mitigation require particular concern both at the national and international levels. The world has faced a significant problem of climate change in the last decades, and adaptation to these effects is compulsory for economic and social development. To adapt and mitigate against CC, one should develop policies and strategies at the international level (Hussain et al. 2020 ). Figure 6 depicts the list of current studies on sectoral impacts of CC with adaptation and mitigation measures globally.

Sectoral impacts of climate change with adaptation and mitigation measures.
Conclusion and future perspectives
Specific socio-agricultural, socio-economic, and physical systems are the cornerstone of psychological well-being, and the alteration in these systems by CC will have disastrous impacts. Climate variability, alongside other anthropogenic and natural stressors, influences human and environmental health sustainability. Food security is another concerning scenario that may lead to compromised food quality, higher food prices, and inadequate food distribution systems. Global forests are challenged by different climatic factors such as storms, droughts, flash floods, and intense precipitation. On the other hand, their anthropogenic wiping is aggrandizing their existence. Undoubtedly, the vulnerability scale of the world’s regions differs; however, appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures can aid the decision-making bodies in developing effective policies to tackle its impacts. Presently, modern life on earth has tailored to consistent climatic patterns, and accordingly, adapting to such considerable variations is of paramount importance. Because the faster changes in climate will make it harder to survive and adjust, this globally-raising enigma calls for immediate attention at every scale ranging from elementary community level to international level. Still, much effort, research, and dedication are required, which is the most critical time. Some policy implications can help us to mitigate the consequences of climate change, especially the most affected sectors like the agriculture sector;
Warming might lengthen the season in frost-prone growing regions (temperate and arctic zones), allowing for longer-maturing seasonal cultivars with better yields (Pfadenhauer 2020 ; Bonacci 2019 ). Extending the planting season may allow additional crops each year; when warming leads to frequent warmer months highs over critical thresholds, a split season with a brief summer fallow may be conceivable for short-period crops such as wheat barley, cereals, and many other vegetable crops. The capacity to prolong the planting season in tropical and subtropical places where the harvest season is constrained by precipitation or agriculture farming occurs after the year may be more limited and dependent on how precipitation patterns vary (Wu et al. 2017 ).
The genetic component is comprehensive for many yields, but it is restricted like kiwi fruit for a few. Ali et al. ( 2017 ) investigated how new crops will react to climatic changes (also stated in Mall et al. 2017 ). Hot temperature, drought, insect resistance; salt tolerance; and overall crop production and product quality increases would all be advantageous (Akkari 2016 ). Genetic mapping and engineering can introduce a greater spectrum of features. The adoption of genetically altered cultivars has been slowed, particularly in the early forecasts owing to the complexity in ensuring features are expediently expressed throughout the entire plant, customer concerns, economic profitability, and regulatory impediments (Wirehn 2018 ; Davidson et al. 2016 ).
To get the full benefit of the CO 2 would certainly require additional nitrogen and other fertilizers. Nitrogen not consumed by the plants may be excreted into groundwater, discharged into water surface, or emitted from the land, soil nitrous oxide when large doses of fertilizer are sprayed. Increased nitrogen levels in groundwater sources have been related to human chronic illnesses and impact marine ecosystems. Cultivation, grain drying, and other field activities have all been examined in depth in the studies (Barua et al. 2018 ).
- The technological and socio-economic adaptation
The policy consequence of the causative conclusion is that as a source of alternative energy, biofuel production is one of the routes that explain oil price volatility separate from international macroeconomic factors. Even though biofuel production has just begun in a few sample nations, there is still a tremendous worldwide need for feedstock to satisfy industrial expansion in China and the USA, which explains the food price relationship to the global oil price. Essentially, oil-exporting countries may create incentives in their economies to increase food production. It may accomplish by giving farmers financing, seedlings, fertilizers, and farming equipment. Because of the declining global oil price and, as a result, their earnings from oil export, oil-producing nations may be unable to subsidize food imports even in the near term. As a result, these countries can boost the agricultural value chain for export. It may be accomplished through R&D and adding value to their food products to increase income by correcting exchange rate misalignment and adverse trade terms. These nations may also diversify their economies away from oil, as dependence on oil exports alone is no longer economically viable given the extreme volatility of global oil prices. Finally, resource-rich and oil-exporting countries can convert to non-food renewable energy sources such as solar, hydro, coal, wind, wave, and tidal energy. By doing so, both world food and oil supplies would be maintained rather than harmed.
IRENA’s modeling work shows that, if a comprehensive policy framework is in place, efforts toward decarbonizing the energy future will benefit economic activity, jobs (outweighing losses in the fossil fuel industry), and welfare. Countries with weak domestic supply chains and a large reliance on fossil fuel income, in particular, must undertake structural reforms to capitalize on the opportunities inherent in the energy transition. Governments continue to give major policy assistance to extract fossil fuels, including tax incentives, financing, direct infrastructure expenditures, exemptions from environmental regulations, and other measures. The majority of major oil and gas producing countries intend to increase output. Some countries intend to cut coal output, while others plan to maintain or expand it. While some nations are beginning to explore and execute policies aimed at a just and equitable transition away from fossil fuel production, these efforts have yet to impact major producing countries’ plans and goals. Verifiable and comparable data on fossil fuel output and assistance from governments and industries are critical to closing the production gap. Governments could increase openness by declaring their production intentions in their climate obligations under the Paris Agreement.
It is firmly believed that achieving the Paris Agreement commitments is doubtlful without undergoing renewable energy transition across the globe (Murshed 2020 ; Zhao et al. 2022 ). Policy instruments play the most important role in determining the degree of investment in renewable energy technology. This study examines the efficacy of various policy strategies in the renewable energy industry of multiple nations. Although its impact is more visible in established renewable energy markets, a renewable portfolio standard is also a useful policy instrument. The cost of producing renewable energy is still greater than other traditional energy sources. Furthermore, government incentives in the R&D sector can foster innovation in this field, resulting in cost reductions in the renewable energy industry. These nations may export their technologies and share their policy experiences by forming networks among their renewable energy-focused organizations. All policy measures aim to reduce production costs while increasing the proportion of renewables to a country’s energy system. Meanwhile, long-term contracts with renewable energy providers, government commitment and control, and the establishment of long-term goals can assist developing nations in deploying renewable energy technology in their energy sector.
Author contribution
KA: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Study design, Formal analysis, Visualization, Revised draft, Writing-review, and editing. MZQ: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Writing-review, and editing. HS: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, literature review, Revised drapt, and writing review and editing. MM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. HM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. IY: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, literature review, and writing review and editing.
Availability of data and material
Declarations.
Not applicable.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Kashif Abbass, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@ssabbafihsak .
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim, Email: moc.kooltuo@888misaqnahseez .
Huaming Song, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@gnimauh .
Muntasir Murshed, Email: [email protected] .
Haider Mahmood, Email: moc.liamtoh@doomhamrediah .
Ijaz Younis, Email: nc.ude.tsujn@sinuoyzaji .
- Abbass K, Begum H, Alam ASA, Awang AH, Abdelsalam MK, Egdair IMM, Wahid R (2022) Fresh Insight through a Keynesian Theory Approach to Investigate the Economic Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Pakistan. Sustain 14(3):1054
- Abbass K, Niazi AAK, Qazi TF, Basit A, Song H (2021a) The aftermath of COVID-19 pandemic period: barriers in implementation of social distancing at workplace. Library Hi Tech
- Abbass K, Song H, Khan F, Begum H, Asif M (2021b) Fresh insight through the VAR approach to investigate the effects of fiscal policy on environmental pollution in Pakistan. Environ Scie Poll Res 1–14 [ PubMed ]
- Abbass K, Song H, Shah SM, Aziz B. Determinants of Stock Return for Non-Financial Sector: Evidence from Energy Sector of Pakistan. J Bus Fin Aff. 2019; 8 (370):2167–0234. [ Google Scholar ]
- Abbass K, Tanveer A, Huaming S, Khatiya AA (2021c) Impact of financial resources utilization on firm performance: a case of SMEs working in Pakistan
- Abraham E, Chain E. An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. 1940. Rev Infect Dis. 1988; 10 (4):677. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adger WN, Arnell NW, Tompkins EL. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Glob Environ Chang. 2005; 15 (2):77–86. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2004.12.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akkari C, Bryant CR. The co-construction approach as approach to developing adaptation strategies in the face of climate change and variability: A conceptual framework. Agricultural Research. 2016; 5 (2):162–173. doi: 10.1007/s40003-016-0208-8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alhassan H (2021) The effect of agricultural total factor productivity on environmental degradation in sub-Saharan Africa. Sci Afr 12:e00740
- Ali A, Erenstein O. Assessing farmer use of climate change adaptation practices and impacts on food security and poverty in Pakistan. Clim Risk Manag. 2017; 16 :183–194. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2016.12.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen CD, Macalady AK, Chenchouni H, Bachelet D, McDowell N, Vennetier M, Hogg ET. A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For Ecol Manag. 2010; 259 (4):660–684. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anwar A, Sinha A, Sharif A, Siddique M, Irshad S, Anwar W, Malik S (2021) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy consumption, financial development, and CO2 emissions: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Dev Sust. 10.1007/s10668-021-01716-2
- Araus JL, Slafer GA, Royo C, Serret MD. Breeding for yield potential and stress adaptation in cereals. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2008; 27 (6):377–412. doi: 10.1080/07352680802467736. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aron JL, Patz J (2001) Ecosystem change and public health: a global perspective: JHU Press
- Arshad MI, Iqbal MA, Shahbaz M. Pakistan tourism industry and challenges: a review. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research. 2018; 23 (2):121–132. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2017.1410192. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashbolt NJ. Microbial contamination of drinking water and human health from community water systems. Current Environmental Health Reports. 2015; 2 (1):95–106. doi: 10.1007/s40572-014-0037-5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Asseng S, Cao W, Zhang W, Ludwig F (2009) Crop physiology, modelling and climate change: impact and adaptation strategies. Crop Physiol 511–543
- Asseng S, Ewert F, Rosenzweig C, Jones JW, Hatfield JL, Ruane AC, Cammarano D. Uncertainty in simulating wheat yields under climate change. Nat Clim Chang. 2013; 3 (9):827–832. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1916. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Association A (2020) Climate change is threatening mental health, American Psychological Association, “Kirsten Weir, . from < https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/07-08/climate-change >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ayers J, Huq S, Wright H, Faisal A, Hussain S. Mainstreaming climate change adaptation into development in Bangladesh. Clim Dev. 2014; 6 :293–305. doi: 10.1080/17565529.2014.977761. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Sinha A, Adedoyin FF (2020) Consequences of COVID-19 on the social isolation of the Chinese economy: accounting for the role of reduction in carbon emissions. Air Qual Atmos Health 13(12):1439–1451
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Ibáñez-Luzón L, Usman M, Shahbaz M. The environmental Kuznets curve, based on the economic complexity, and the pollution haven hypothesis in PIIGS countries. Renew Energy. 2022; 185 :1441–1455. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.059. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bank W (2008) Forests sourcebook: practical guidance for sustaining forests in development cooperation: World Bank
- Barua S, Valenzuela E (2018) Climate change impacts on global agricultural trade patterns: evidence from the past 50 years. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Sustainable Development (pp. 26–28)
- Bates AE, Pecl GT, Frusher S, Hobday AJ, Wernberg T, Smale DA, Colwell RK. Defining and observing stages of climate-mediated range shifts in marine systems. Glob Environ Chang. 2014; 26 :27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.03.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Battisti DS, Naylor RL. Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science. 2009; 323 (5911):240–244. doi: 10.1126/science.1164363. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beesley L, Close PG, Gwinn DC, Long M, Moroz M, Koster WM, Storer T. Flow-mediated movement of freshwater catfish, Tandanus bostocki, in a regulated semi-urban river, to inform environmental water releases. Ecol Freshw Fish. 2019; 28 (3):434–445. doi: 10.1111/eff.12466. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Benita F (2021) Human mobility behavior in COVID-19: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 70:102916 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Berendonk TU, Manaia CM, Merlin C, Fatta-Kassinos D, Cytryn E, Walsh F, Pons M-N. Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015; 13 (5):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3439. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berg MP, Kiers ET, Driessen G, Van DerHEIJDEN M, Kooi BW, Kuenen F, Ellers J. Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence in a changing world. Glob Change Biol. 2010; 16 (2):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02014.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blum A, Klueva N, Nguyen H. Wheat cellular thermotolerance is related to yield under heat stress. Euphytica. 2001; 117 (2):117–123. doi: 10.1023/A:1004083305905. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bonacci O. Air temperature and precipitation analyses on a small Mediterranean island: the case of the remote island of Lastovo (Adriatic Sea, Croatia) Acta Hydrotechnica. 2019; 32 (57):135–150. doi: 10.15292/acta.hydro.2019.10. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Botzen W, Duijndam S, van Beukering P (2021) Lessons for climate policy from behavioral biases towards COVID-19 and climate change risks. World Dev 137:105214 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Brázdil R, Stucki P, Szabó P, Řezníčková L, Dolák L, Dobrovolný P, Suchánková S. Windstorms and forest disturbances in the Czech Lands: 1801–2015. Agric for Meteorol. 2018; 250 :47–63. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown HCP, Smit B, Somorin OA, Sonwa DJ, Nkem JN. Climate change and forest communities: prospects for building institutional adaptive capacity in the Congo Basin forests. Ambio. 2014; 43 (6):759–769. doi: 10.1007/s13280-014-0493-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bujosa A, Riera A, Torres CM. Valuing tourism demand attributes to guide climate change adaptation measures efficiently: the case of the Spanish domestic travel market. Tour Manage. 2015; 47 :233–239. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2014.09.023. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Calderini D, Abeledo L, Savin R, Slafer GA. Effect of temperature and carpel size during pre-anthesis on potential grain weight in wheat. J Agric Sci. 1999; 132 (4):453–459. doi: 10.1017/S0021859699006504. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cammell M, Knight J. Effects of climatic change on the population dynamics of crop pests. Adv Ecol Res. 1992; 22 :117–162. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60135-X. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cavanaugh KC, Kellner JR, Forde AJ, Gruner DS, Parker JD, Rodriguez W, Feller IC. Poleward expansion of mangroves is a threshold response to decreased frequency of extreme cold events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014; 111 (2):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315800111. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cell CC (2009) Climate change and health impacts in Bangladesh. Clima Chang Cell DoE MoEF
- Chandio AA, Jiang Y, Rehman A, Rauf A (2020) Short and long-run impacts of climate change on agriculture: an empirical evidence from China. Int J Clim Chang Strat Manag
- Chaudhary P, Rai S, Wangdi S, Mao A, Rehman N, Chettri S, Bawa KS (2011) Consistency of local perceptions of climate change in the Kangchenjunga Himalaya landscape. Curr Sci 504–513
- Chien F, Anwar A, Hsu CC, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Sinha A (2021) The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol Soc 65:101587
- Cooper C, Booth A, Varley-Campbell J, Britten N, Garside R. Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018; 18 (1):1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen A, Ball S, Bell S, Bellamy R, Kett M. Managing the health effects of climate change: lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. The Lancet. 2009; 373 (9676):1693–1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cruz DLA (2015) Mother Figured. University of Chicago Press. Retrieved from, 10.7208/9780226315072
- Cui W, Ouyang T, Qiu Y, Cui D (2021) Literature Review of the Implications of Exercise Rehabilitation Strategies for SARS Patients on the Recovery of COVID-19 Patients. Paper presented at the Healthcare [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Davidson D. Gaps in agricultural climate adaptation research. Nat Clim Chang. 2016; 6 (5):433–435. doi: 10.1038/nclimate3007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Diffenbaugh NS, Singh D, Mankin JS, Horton DE, Swain DL, Touma D, Tsiang M. Quantifying the influence of global warming on unprecedented extreme climate events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017; 114 (19):4881–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618082114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dimri A, Kumar D, Choudhary A, Maharana P. Future changes over the Himalayas: mean temperature. Global Planet Change. 2018; 162 :235–251. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.01.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dullinger S, Gattringer A, Thuiller W, Moser D, Zimmermann N, Guisan A. Extinction debt of high-mountain plants under twenty-first-century climate change. Nat Clim Chang: Nature Publishing Group; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dupuis I, Dumas C. Influence of temperature stress on in vitro fertilization and heat shock protein synthesis in maize (Zea mays L.) reproductive tissues. Plant Physiol. 1990; 94 (2):665–670. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.665. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Otegui ME. Heat stress in temperate and tropical maize hybrids: a novel approach for assessing sources of kernel loss in field conditions. Field Crop Res. 2013; 142 :58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2012.11.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Carpici EB, Sammarro D, Otegui M. Heat stress effects around flowering on kernel set of temperate and tropical maize hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2011; 123 (2):62–73. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.04.015. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellison D, Morris CE, Locatelli B, Sheil D, Cohen J, Murdiyarso D, Pokorny J. Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world. Glob Environ Chang. 2017; 43 :51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2017.01.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elsayed ZM, Eldehna WM, Abdel-Aziz MM, El Hassab MA, Elkaeed EB, Al-Warhi T, Mohammed ER. Development of novel isatin–nicotinohydrazide hybrids with potent activity against susceptible/resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis and bronchitis causing–bacteria. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021; 36 (1):384–393. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1868450. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- EM-DAT (2020) EMDAT: OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database, Université catholique de Louvain – Brussels – Belgium. from http://www.emdat.be
- EPA U (2018) United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA Year in Review
- Erman A, De Vries Robbe SA, Thies SF, Kabir K, Maruo M (2021) Gender Dimensions of Disaster Risk and Resilience
- Fand BB, Kamble AL, Kumar M. Will climate change pose serious threat to crop pest management: a critical review. Int J Sci Res Publ. 2012; 2 (11):1–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- FAO (2018).The State of the World’s Forests 2018 - Forest Pathways to Sustainable Development.
- Fardous S Perception of climate change in Kaptai National Park. Rural Livelihoods and Protected Landscape: Co-Management in the Wetlands and Forests of Bangladesh, 186–204
- Farooq M, Bramley H, Palta JA, Siddique KH. Heat stress in wheat during reproductive and grain-filling phases. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2011; 30 (6):491–507. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.615687. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feliciano D, Recha J, Ambaw G, MacSween K, Solomon D, Wollenberg E (2022) Assessment of agricultural emissions, climate change mitigation and adaptation practices in Ethiopia. Clim Policy 1–18
- Ferreira JJ, Fernandes CI, Ferreira FA (2020) Technology transfer, climate change mitigation, and environmental patent impact on sustainability and economic growth: a comparison of European countries. Technol Forecast Soc Change 150:119770
- Fettig CJ, Reid ML, Bentz BJ, Sevanto S, Spittlehouse DL, Wang T. Changing climates, changing forests: a western North American perspective. J Forest. 2013; 111 (3):214–228. doi: 10.5849/jof.12-085. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fischer AP. Characterizing behavioral adaptation to climate change in temperate forests. Landsc Urban Plan. 2019; 188 :72–79. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.09.024. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flannigan M, Cantin AS, De Groot WJ, Wotton M, Newbery A, Gowman LM. Global wildland fire season severity in the 21st century. For Ecol Manage. 2013; 294 :54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.10.022. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fossheim M, Primicerio R, Johannesen E, Ingvaldsen RB, Aschan MM, Dolgov AV. Recent warming leads to a rapid borealization of fish communities in the Arctic. Nat Clim Chang. 2015; 5 (7):673–677. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2647. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Füssel HM, Hildén M (2014) How is uncertainty addressed in the knowledge base for national adaptation planning? Adapting to an Uncertain Climate (pp. 41–66): Springer
- Gambín BL, Borrás L, Otegui ME. Source–sink relations and kernel weight differences in maize temperate hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2006; 95 (2–3):316–326. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2005.04.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gambín B, Borrás L. Resource distribution and the trade-off between seed number and seed weight: a comparison across crop species. Annals of Applied Biology. 2010; 156 (1):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00367.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gampe D, Nikulin G, Ludwig R. Using an ensemble of regional climate models to assess climate change impacts on water scarcity in European river basins. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 573 :1503–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.053. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- García GA, Dreccer MF, Miralles DJ, Serrago RA. High night temperatures during grain number determination reduce wheat and barley grain yield: a field study. Glob Change Biol. 2015; 21 (11):4153–4164. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13009. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garner E, Inyang M, Garvey E, Parks J, Glover C, Grimaldi A, Edwards MA. Impact of blending for direct potable reuse on premise plumbing microbial ecology and regrowth of opportunistic pathogens and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Water Res. 2019; 151 :75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.003. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gleditsch NP (2021) This time is different! Or is it? NeoMalthusians and environmental optimists in the age of climate change. J Peace Res 0022343320969785
- Godfray HCJ, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Toulmin C. Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science. 2010; 327 (5967):812–818. doi: 10.1126/science.1185383. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goes S, Hasterok D, Schutt DL, Klöcking M (2020) Continental lithospheric temperatures: A review. Phys Earth Planet Inter 106509
- Gorst A, Dehlavi A, Groom B. Crop productivity and adaptation to climate change in Pakistan. Environ Dev Econ. 2018; 23 (6):679–701. doi: 10.1017/S1355770X18000232. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gosling SN, Arnell NW. A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Clim Change. 2016; 134 (3):371–385. doi: 10.1007/s10584-013-0853-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM, Ceron J-P, Dubois G. Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Ann Tour Res. 2012; 39 (1):36–58. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2011.11.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gourdji SM, Sibley AM, Lobell DB. Global crop exposure to critical high temperatures in the reproductive period: historical trends and future projections. Environ Res Lett. 2013; 8 (2):024041. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024041. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grieg E Responsible Consumption and Production
- Gunter BG, Rahman A, Rahman A (2008) How Vulnerable are Bangladesh’s Indigenous People to Climate Change? Bangladesh Development Research Center (BDRC)
- Hall CM, Amelung B, Cohen S, Eijgelaar E, Gössling S, Higham J, Scott D. On climate change skepticism and denial in tourism. J Sustain Tour. 2015; 23 (1):4–25. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2014.953544. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hartmann H, Moura CF, Anderegg WR, Ruehr NK, Salmon Y, Allen CD, Galbraith D. Research frontiers for improving our understanding of drought-induced tree and forest mortality. New Phytol. 2018; 218 (1):15–28. doi: 10.1111/nph.15048. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Prueger JH. Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather and Climate Extremes. 2015; 10 :4–10. doi: 10.1016/j.wace.2015.08.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Boote KJ, Kimball B, Ziska L, Izaurralde RC, Ort D, Wolfe D. Climate impacts on agriculture: implications for crop production. Agron J. 2011; 103 (2):351–370. doi: 10.2134/agronj2010.0303. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hendriksen RS, Munk P, Njage P, Van Bunnik B, McNally L, Lukjancenko O, Kjeldgaard J. Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat Commun. 2019; 10 (1):1124. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08853-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang S (2004) Global trade patterns in fruits and vegetables. USDA-ERS Agriculture and Trade Report No. WRS-04–06
- Huang W, Gao Q-X, Cao G-L, Ma Z-Y, Zhang W-D, Chao Q-C. Effect of urban symbiosis development in China on GHG emissions reduction. Adv Clim Chang Res. 2016; 7 (4):247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2016.12.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M, Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: Is there any difference between E-7 (developing) and G-7 (developed) countries? Tech Soc 68:101853
- Hubbart JA, Guyette R, Muzika R-M. More than drought: precipitation variance, excessive wetness, pathogens and the future of the western edge of the eastern deciduous forest. Sci Total Environ. 2016; 566 :463–467. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.108. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Butt AR, Uzma F, Ahmed R, Irshad S, Rehman A, Yousaf B. A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess. 2020; 192 (1):48. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7956-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ahmed R, Uzma F, Ali MU, Butt AR. Regional and sectoral assessment on climate-change in Pakistan: social norms and indigenous perceptions on climate-change adaptation and mitigation in relation to global context. J Clean Prod. 2018; 200 :791–808. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.272. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Intergov. Panel Clim Chang 33 from 10.1017/CBO9781107415324
- Ionescu C, Klein RJ, Hinkel J, Kumar KK, Klein R. Towards a formal framework of vulnerability to climate change. Environ Model Assess. 2009; 14 (1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/s10666-008-9179-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. Clim Chang Phys Sci Basis Contrib Work Gr I Fifth Assess Rep
- Ishikawa-Ishiwata Y, Furuya J (2022) Economic evaluation and climate change adaptation measures for rice production in vietnam using a supply and demand model: special emphasis on the Mekong River Delta region in Vietnam. In Interlocal Adaptations to Climate Change in East and Southeast Asia (pp. 45–53). Springer, Cham
- Izaguirre C, Losada I, Camus P, Vigh J, Stenek V. Climate change risk to global port operations. Nat Clim Chang. 2021; 11 (1):14–20. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-00937-z. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jactel H, Koricheva J, Castagneyrol B (2019) Responses of forest insect pests to climate change: not so simple. Current opinion in insect science [ PubMed ]
- Jahanzad E, Holtz BA, Zuber CA, Doll D, Brewer KM, Hogan S, Gaudin AC. Orchard recycling improves climate change adaptation and mitigation potential of almond production systems. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (3):e0229588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229588. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jurgilevich A, Räsänen A, Groundstroem F, Juhola S. A systematic review of dynamics in climate risk and vulnerability assessments. Environ Res Lett. 2017; 12 (1):013002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa5508. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karami E (2012) Climate change, resilience and poverty in the developing world. Paper presented at the Culture, Politics and Climate change conference
- Kärkkäinen L, Lehtonen H, Helin J, Lintunen J, Peltonen-Sainio P, Regina K, . . . Packalen T (2020) Evaluation of policy instruments for supporting greenhouse gas mitigation efforts in agricultural and urban land use. Land Use Policy 99:104991
- Karkman A, Do TT, Walsh F, Virta MP. Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol. 2018; 26 (3):220–228. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.09.005. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohfeld KE, Le Quéré C, Harrison SP, Anderson RF. Role of marine biology in glacial-interglacial CO2 cycles. Science. 2005; 308 (5718):74–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1105375. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kongsager R. Linking climate change adaptation and mitigation: a review with evidence from the land-use sectors. Land. 2018; 7 (4):158. doi: 10.3390/land7040158. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kurz WA, Dymond C, Stinson G, Rampley G, Neilson E, Carroll A, Safranyik L. Mountain pine beetle and forest carbon feedback to climate change. Nature. 2008; 452 (7190):987. doi: 10.1038/nature06777. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamperti F, Bosetti V, Roventini A, Tavoni M, Treibich T (2021) Three green financial policies to address climate risks. J Financial Stab 54:100875
- Leal Filho W, Azeiteiro UM, Balogun AL, Setti AFF, Mucova SA, Ayal D, . . . Oguge NO (2021) The influence of ecosystems services depletion to climate change adaptation efforts in Africa. Sci Total Environ 146414 [ PubMed ]
- Lehner F, Coats S, Stocker TF, Pendergrass AG, Sanderson BM, Raible CC, Smerdon JE. Projected drought risk in 1.5 C and 2 C warmer climates. Geophys Res Lett. 2017; 44 (14):7419–7428. doi: 10.1002/2017GL074117. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemery J, Knowlton K, Sorensen C (2021) Global climate change and human health: from science to practice: John Wiley & Sons
- Leppänen S, Saikkonen L, Ollikainen M (2014) Impact of Climate Change on cereal grain production in Russia: Mimeo
- Lipczynska-Kochany E. Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: a review. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 640 :1548–1565. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.376. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- livescience.com. New coronavirus may have ‘jumped’ to humans from snakes, study finds, live science,. from < https://www.livescience.com/new-coronavirus-origin-snakes.html > accessed on Jan 2020
- Lobell DB, Field CB. Global scale climate–crop yield relationships and the impacts of recent warming. Environ Res Lett. 2007; 2 (1):014002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/2/1/014002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lobell DB, Gourdji SM. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012; 160 (4):1686–1697. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208298. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma L, Li B, Zhang T. New insights into antibiotic resistome in drinking water and management perspectives: a metagenomic based study of small-sized microbes. Water Res. 2019; 152 :191–201. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.069. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Macchi M, Oviedo G, Gotheil S, Cross K, Boedhihartono A, Wolfangel C, Howell M (2008) Indigenous and traditional peoples and climate change. International Union for the Conservation of Nature, Gland, Suiza
- Mall RK, Gupta A, Sonkar G (2017) Effect of climate change on agricultural crops. In Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (pp. 23–46). Elsevier
- Manes S, Costello MJ, Beckett H, Debnath A, Devenish-Nelson E, Grey KA, . . . Krause C (2021) Endemism increases species’ climate change risk in areas of global biodiversity importance. Biol Conserv 257:109070
- Mannig B, Pollinger F, Gafurov A, Vorogushyn S, Unger-Shayesteh K (2018) Impacts of climate change in Central Asia Encyclopedia of the Anthropocene (pp. 195–203): Elsevier
- Martínez-Alvarado O, Gray SL, Hart NC, Clark PA, Hodges K, Roberts MJ. Increased wind risk from sting-jet windstorms with climate change. Environ Res Lett. 2018; 13 (4):044002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aaae3a. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matsui T, Omasa K, Horie T. The difference in sterility due to high temperatures during the flowering period among japonica-rice varieties. Plant Production Science. 2001; 4 (2):90–93. doi: 10.1626/pps.4.90. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meierrieks D (2021) Weather shocks, climate change and human health. World Dev 138:105228
- Michel D, Eriksson M, Klimes M (2021) Climate change and (in) security in transboundary river basins Handbook of Security and the Environment: Edward Elgar Publishing
- Mihiretu A, Okoyo EN, Lemma T. Awareness of climate change and its associated risks jointly explain context-specific adaptation in the Arid-tropics. Northeast Ethiopia SN Social Sciences. 2021; 1 (2):1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Millar CI, Stephenson NL. Temperate forest health in an era of emerging megadisturbance. Science. 2015; 349 (6250):823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa9933. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mishra A, Bruno E, Zilberman D (2021) Compound natural and human disasters: Managing drought and COVID-19 to sustain global agriculture and food sectors. Sci Total Environ 754:142210 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mosavi SH, Soltani S, Khalilian S (2020) Coping with climate change in agriculture: Evidence from Hamadan-Bahar plain in Iran. Agric Water Manag 241:106332
- Murshed M (2020) An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36254–36281. 10.1007/s11356-020-09497-3 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Murshed M. Pathways to clean cooking fuel transition in low and middle income Sub-Saharan African countries: the relevance of improving energy use efficiency. Sustainable Production and Consumption. 2022; 30 :396–412. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Dao NTT. Revisiting the CO2 emission-induced EKC hypothesis in South Asia: the role of Export Quality Improvement. GeoJournal. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s10708-020-10270-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Abbass K, Rashid S. Modelling renewable energy adoption across south Asian economies: Empirical evidence from Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Int J Finan Eco. 2021; 26 (4):5425–5450. doi: 10.1002/ijfe.2073. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Elheddad M, Ahmed R. Value addition in the services sector and its heterogeneous impacts on CO2 emissions: revisiting the EKC hypothesis for the OPEC using panel spatial estimation techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (31):38951–38973. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09593-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Al-Tal R, Mahmood H, Elheddad M, Ahmed R (2022) Can intra-regional trade, renewable energy use, foreign direct investments, and economic growth reduce ecological footprints in South Asia? Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy. 10.1080/15567249.2022.2038730
- Neuvonen M, Sievänen T, Fronzek S, Lahtinen I, Veijalainen N, Carter TR. Vulnerability of cross-country skiing to climate change in Finland–an interactive mapping tool. J Outdoor Recreat Tour. 2015; 11 :64–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jort.2015.06.010. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- npr.org. Please Help Me.’ What people in China are saying about the outbreak on social media, npr.org, . from < https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/01/24/799000379/please-help-me-what-people-in-china-are-saying-about-the-outbreak-on-social-medi >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ogden LE. Climate change, pathogens, and people: the challenges of monitoring a moving target. Bioscience. 2018; 68 (10):733–739. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biy101. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz AMD, Outhwaite CL, Dalin C, Newbold T. A review of the interactions between biodiversity, agriculture, climate change, and international trade: research and policy priorities. One Earth. 2021; 4 (1):88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2020.12.008. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz R. Crop genetic engineering under global climate change. Ann Arid Zone. 2008; 47 (3):343. [ Google Scholar ]
- Otegui MAE, Bonhomme R. Grain yield components in maize: I. Ear growth and kernel set. Field Crop Res. 1998; 56 (3):247–256. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(97)00093-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pachauri RK, Allen MR, Barros VR, Broome J, Cramer W, Christ R, . . . Dasgupta P (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Ipcc
- Pal JK. Visualizing the knowledge outburst in global research on COVID-19. Scientometrics. 2021; 126 (5):4173–4193. doi: 10.1007/s11192-021-03912-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panda R, Behera S, Kashyap P. Effective management of irrigation water for wheat under stressed conditions. Agric Water Manag. 2003; 63 (1):37–56. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3774(03)00099-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pärnänen KM, Narciso-da-Rocha C, Kneis D, Berendonk TU, Cacace D, Do TT, Jaeger T. Antibiotic resistance in European wastewater treatment plants mirrors the pattern of clinical antibiotic resistance prevalence. Sci Adv. 2019; 5 (3):eaau9124. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau9124. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parry M, Parry ML, Canziani O, Palutikof J, Van der Linden P, Hanson C (2007) Climate change 2007-impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: Working group II contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC (Vol. 4): Cambridge University Press
- Patz JA, Campbell-Lendrum D, Holloway T, Foley JA. Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature. 2005; 438 (7066):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nature04188. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patz JA, Graczyk TK, Geller N, Vittor AY. Effects of environmental change on emerging parasitic diseases. Int J Parasitol. 2000; 30 (12–13):1395–1405. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00141-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pautasso M, Döring TF, Garbelotto M, Pellis L, Jeger MJ. Impacts of climate change on plant diseases—opinions and trends. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2012; 133 (1):295–313. doi: 10.1007/s10658-012-9936-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong X, Cassman KG. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004; 101 (27):9971–9975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403720101. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller GN, Jongman R, Scholes RJ, Cardoso A. Essential biodiversity variables. Science. 2013; 339 (6117):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.1229931. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perera K, De Silva K, Amarasinghe M. Potential impact of predicted sea level rise on carbon sink function of mangrove ecosystems with special reference to Negombo estuary, Sri Lanka. Global Planet Change. 2018; 161 :162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.12.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pfadenhauer JS, Klötzli FA (2020) Zonal Vegetation of the Subtropical (Warm–Temperate) Zone with Winter Rain. In Global Vegetation (pp. 455–514). Springer, Cham
- Phillips JD. Environmental gradients and complexity in coastal landscape response to sea level rise. CATENA. 2018; 169 :107–118. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.05.036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pirasteh-Anosheh H, Parnian A, Spasiano D, Race M, Ashraf M (2021) Haloculture: A system to mitigate the negative impacts of pandemics on the environment, society and economy, emphasizing COVID-19. Environ Res 111228 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Pruden A, Larsson DJ, Amézquita A, Collignon P, Brandt KK, Graham DW, Snape JR. Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ Health Perspect. 2013; 121 (8):878–885. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1206446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Abbas F, Saeed S, Bakhat HF, Nasim W, Fahad S. The potential applications of picotechnology in biomedical and environmental sciences. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (1):133–142. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06554-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Maqsood F, Tariq T, Chawla MS Climate Change Implication on Cereal Crop Productivity
- Rahman M, Alam K. Forest dependent indigenous communities’ perception and adaptation to climate change through local knowledge in the protected area—a Bangladesh case study. Climate. 2016; 4 (1):12. doi: 10.3390/cli4010012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramankutty N, Mehrabi Z, Waha K, Jarvis L, Kremen C, Herrero M, Rieseberg LH. Trends in global agricultural land use: implications for environmental health and food security. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2018; 69 :789–815. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040256. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Irfan M, Traore O, Chandio AA (2021) Towards environmental Sustainability: devolving the influence of carbon dioxide emission to population growth, climate change, Forestry, livestock and crops production in Pakistan. Ecol Indic 125:107460
- Reichstein M, Carvalhais N. Aspects of forest biomass in the Earth system: its role and major unknowns. Surv Geophys. 2019; 40 (4):693–707. doi: 10.1007/s10712-019-09551-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reidsma P, Ewert F, Boogaard H, van Diepen K. Regional crop modelling in Europe: the impact of climatic conditions and farm characteristics on maize yields. Agric Syst. 2009; 100 (1–3):51–60. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2008.12.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchie H, Roser M (2014) Natural disasters. Our World in Data
- Rizvi AR, Baig S, Verdone M. Ecosystems based adaptation: knowledge gaps in making an economic case for investing in nature based solutions for climate change. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN; 2015. p. 48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roscher C, Fergus AJ, Petermann JS, Buchmann N, Schmid B, Schulze E-D. What happens to the sown species if a biodiversity experiment is not weeded? Basic Appl Ecol. 2013; 14 (3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/j.baae.2013.01.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Elliott J, Deryng D, Ruane AC, Müller C, Arneth A, Khabarov N. Assessing agricultural risks of climate change in the 21st century in a global gridded crop model intercomparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014; 111 (9):3268–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222463110. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Iglesius A, Yang XB, Epstein PR, Chivian E (2001) Climate change and extreme weather events-implications for food production, plant diseases, and pests
- Sadras VO, Slafer GA. Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: heritabilities reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crop Res. 2012; 127 :215–224. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.11.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salvucci ME, Crafts-Brandner SJ. Inhibition of photosynthesis by heat stress: the activation state of Rubisco as a limiting factor in photosynthesis. Physiol Plant. 2004; 120 (2):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.0031-9317.2004.0173.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santos WS, Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Garcez LM, Abad-Franch F. Deforestation effects on Attalea palms and their resident Rhodnius, vectors of Chagas disease, in eastern Amazonia. PLoS ONE. 2021; 16 (5):e0252071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252071. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarkar P, Debnath N, Reang D (2021) Coupled human-environment system amid COVID-19 crisis: a conceptual model to understand the nexus. Sci Total Environ 753:141757 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Schlenker W, Roberts MJ. Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to US crop yields under climate change. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009; 106 (37):15594–15598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906865106. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schoene DH, Bernier PY. Adapting forestry and forests to climate change: a challenge to change the paradigm. Forest Policy Econ. 2012; 24 :12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.forpol.2011.04.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schuurmans C (2021) The world heat budget: expected changes Climate Change (pp. 1–15): CRC Press
- Scott D. Sustainable Tourism and the Grand Challenge of Climate Change. Sustainability. 2021; 13 (4):1966. doi: 10.3390/su13041966. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scott D, McBoyle G, Schwartzentruber M. Climate change and the distribution of climatic resources for tourism in North America. Climate Res. 2004; 27 (2):105–117. doi: 10.3354/cr027105. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Semenov MA. Impacts of climate change on wheat in England and Wales. J R Soc Interface. 2009; 6 (33):343–350. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0285. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaffril HAM, Krauss SE, Samsuddin SF. A systematic review on Asian’s farmers’ adaptation practices towards climate change. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 644 :683–695. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.349. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shahbaz M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Sinha A (2019) Foreign direct Investment–CO2 emissions nexus in Middle East and North African countries: Importance of biomass energy consumption. J Clean Product 217:603–614
- Sharif A, Mishra S, Sinha A, Jiao Z, Shahbaz M, Afshan S (2020) The renewable energy consumption-environmental degradation nexus in Top-10 polluted countries: Fresh insights from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Renew Energy 150:670–690
- Sharma R. Impacts on human health of climate and land use change in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region. Mt Res Dev. 2012; 32 (4):480–486. doi: 10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-12-00068.1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P. Examining the impacts of economic and demographic aspects on the ecological footprint in South and Southeast Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020; 27 (29):36970–36982. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09659-3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smit B, Burton I, Klein RJ, Wandel J (2000) An anatomy of adaptation to climate change and variability Societal adaptation to climate variability and change (pp. 223–251): Springer
- Song Y, Fan H, Tang X, Luo Y, Liu P, Chen Y (2021) The effects of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on ischemic stroke and the possible underlying mechanisms. Int J Neurosci 1–20 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Sovacool BK, Griffiths S, Kim J, Bazilian M (2021) Climate change and industrial F-gases: a critical and systematic review of developments, sociotechnical systems and policy options for reducing synthetic greenhouse gas emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 141:110759
- Stewart JA, Perrine JD, Nichols LB, Thorne JH, Millar CI, Goehring KE, Wright DH. Revisiting the past to foretell the future: summer temperature and habitat area predict pika extirpations in California. J Biogeogr. 2015; 42 (5):880–890. doi: 10.1111/jbi.12466. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stocker T, Qin D, Plattner G, Tignor M, Allen S, Boschung J, . . . Midgley P (2013) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Working group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth assessment report: Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1535p
- Stone P, Nicolas M. Wheat cultivars vary widely in their responses of grain yield and quality to short periods of post-anthesis heat stress. Funct Plant Biol. 1994; 21 (6):887–900. doi: 10.1071/PP9940887. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Su H-C, Liu Y-S, Pan C-G, Chen J, He L-Y, Ying G-G. Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community changes in drinking water treatment system: from drinking water source to tap water. Sci Total Environ. 2018; 616 :453–461. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.318. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sunderlin WD, Angelsen A, Belcher B, Burgers P, Nasi R, Santoso L, Wunder S. Livelihoods, forests, and conservation in developing countries: an overview. World Dev. 2005; 33 (9):1383–1402. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2004.10.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Symanski E, Han HA, Han I, McDaniel M, Whitworth KW, McCurdy S, . . . Delclos GL (2021) Responding to natural and industrial disasters: partnerships and lessons learned. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness 1–4 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Tao F, Yokozawa M, Xu Y, Hayashi Y, Zhang Z. Climate changes and trends in phenology and yields of field crops in China, 1981–2000. Agric for Meteorol. 2006; 138 (1–4):82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tebaldi C, Hayhoe K, Arblaster JM, Meehl GA. Going to the extremes. Clim Change. 2006; 79 (3–4):185–211. doi: 10.1007/s10584-006-9051-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Testa G, Koon E, Johannesson L, McKenna G, Anthony T, Klintmalm G, Gunby R (2018) This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as
- Thornton PK, Lipper L (2014) How does climate change alter agricultural strategies to support food security? (Vol. 1340): Intl Food Policy Res Inst
- Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag. 2003; 14 (3):207–222. doi: 10.1111/1467-8551.00375. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNEP (2017) United nations environment programme: frontiers 2017. from https://www.unenvironment.org/news-and-stories/press-release/antimicrobial-resistance - environmental-pollution-among-biggest
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: Can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Ene Policy 162:112780
- Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P. Pollution concern during globalization mode in financially resource-rich countries: Do financial development, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption matter? Rene. Energy. 2022; 183 :90–102. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.067. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Usman M, Jahanger A, Makhdum MSA, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bashir A (2022a) How do financial development, energy consumption, natural resources, and globalization affect Arctic countries’ economic growth and environmental quality? An advanced panel data simulation. Energy 241:122515
- Usman M, Khalid K, Mehdi MA. What determines environmental deficit in Asia? Embossing the role of renewable and non-renewable energy utilization. Renew Energy. 2021; 168 :1165–1176. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.01.012. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Urban MC. Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science. 2015; 348 (6234):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4984. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vale MM, Arias PA, Ortega G, Cardoso M, Oliveira BF, Loyola R, Scarano FR (2021) Climate change and biodiversity in the Atlantic Forest: best climatic models, predicted changes and impacts, and adaptation options The Atlantic Forest (pp. 253–267): Springer
- Vedwan N, Rhoades RE. Climate change in the Western Himalayas of India: a study of local perception and response. Climate Res. 2001; 19 (2):109–117. doi: 10.3354/cr019109. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vega CR, Andrade FH, Sadras VO, Uhart SA, Valentinuz OR. Seed number as a function of growth. A comparative study in soybean, sunflower, and maize. Crop Sci. 2001; 41 (3):748–754. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2001.413748x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vergés A, Doropoulos C, Malcolm HA, Skye M, Garcia-Pizá M, Marzinelli EM, Vila-Concejo A. Long-term empirical evidence of ocean warming leading to tropicalization of fish communities, increased herbivory, and loss of kelp. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016; 113 (48):13791–13796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610725113. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verheyen R (2005) Climate change damage and international law: prevention duties and state responsibility (Vol. 54): Martinus Nijhoff Publishers
- Waheed A, Fischer TB, Khan MI. Climate Change Policy Coherence across Policies, Plans, and Strategies in Pakistan—implications for the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Plan. Environ Manage. 2021; 67 (5):793–810. doi: 10.1007/s00267-021-01449-y. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wasiq M, Ahmad M (2004) Sustaining forests: a development strategy: The World Bank
- Watts N, Adger WN, Agnolucci P, Blackstock J, Byass P, Cai W, Cooper A. Health and climate change: policy responses to protect public health. The Lancet. 2015; 386 (10006):1861–1914. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60854-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weed AS, Ayres MP, Hicke JA. Consequences of climate change for biotic disturbances in North American forests. Ecol Monogr. 2013; 83 (4):441–470. doi: 10.1890/13-0160.1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weisheimer A, Palmer T (2005) Changing frequency of occurrence of extreme seasonal temperatures under global warming. Geophys Res Lett 32(20)
- Wernberg T, Bennett S, Babcock RC, De Bettignies T, Cure K, Depczynski M, Hovey RK. Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science. 2016; 353 (6295):169–172. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8745. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO (2018) WHO, 2018. Antimicrobial resistance
- Wilkinson DM, Sherratt TN. Why is the world green? The interactions of top–down and bottom–up processes in terrestrial vegetation ecology. Plant Ecolog Divers. 2016; 9 (2):127–140. doi: 10.1080/17550874.2016.1178353. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiranata IJ, Simbolon K. Increasing awareness capacity of disaster potential as a support to achieve sustainable development goal (sdg) 13 in lampung province. Jurnal Pir: Power in International Relations. 2021; 5 (2):129–146. doi: 10.22303/pir.5.2.2021.129-146. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiréhn L. Nordic agriculture under climate change: a systematic review of challenges, opportunities and adaptation strategies for crop production. Land Use Policy. 2018; 77 :63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.04.059. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu D, Su Y, Xi H, Chen X, Xie B. Urban and agriculturally influenced water contribute differently to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in a mega-city river network. Water Res. 2019; 158 :11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.010. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu HX (2020) Losing Steam?—An industry origin analysis of China’s productivity slowdown Measuring Economic Growth and Productivity (pp. 137–167): Elsevier
- Wu H, Qian H, Chen J, Huo C. Assessment of agricultural drought vulnerability in the Guanzhong Plain. China Water Resources Management. 2017; 31 (5):1557–1574. doi: 10.1007/s11269-017-1594-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xie W, Huang J, Wang J, Cui Q, Robertson R, Chen K (2018) Climate change impacts on China’s agriculture: the responses from market and trade. China Econ Rev
- Xu J, Sharma R, Fang J, Xu Y. Critical linkages between land-use transition and human health in the Himalayan region. Environ Int. 2008; 34 (2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.08.004. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yadav MK, Singh R, Singh K, Mall R, Patel C, Yadav S, Singh M. Assessment of climate change impact on productivity of different cereal crops in Varanasi. India J Agrometeorol. 2015; 17 (2):179–184. doi: 10.54386/jam.v17i2.1000. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang B, Usman M. Do industrialization, economic growth and globalization processes influence the ecological footprint and healthcare expenditures? Fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for countries with the highest healthcare expenditures. Sust Prod Cons. 2021; 28 :893–910. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yu Z, Razzaq A, Rehman A, Shah A, Jameel K, Mor RS (2021) Disruption in global supply chain and socio-economic shocks: a lesson from COVID-19 for sustainable production and consumption. Oper Manag Res 1–16
- Zarnetske PL, Skelly DK, Urban MC. Biotic multipliers of climate change. Science. 2012; 336 (6088):1516–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.1222732. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang M, Liu N, Harper R, Li Q, Liu K, Wei X, Liu S. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J Hydrol. 2017; 546 :44–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.12.040. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhao J, Sinha A, Inuwa N, Wang Y, Murshed M, Abbasi KR (2022) Does Structural Transformation in Economy Impact Inequality in Renewable Energy Productivity? Implications for Sustainable Development. Renew Energy 189:853–864. 10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.050

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
- Climatic variation since the last glaciation
- The greenhouse effect
- Radiative forcing
- Water vapour
- Carbon dioxide
- Surface-level ozone and other compounds
- Nitrous oxides and fluorinated gases
- Land-use change
- Stratospheric ozone depletion
- Volcanic aerosols
- Variations in solar output
- Variations in Earth’s orbit
- Water vapour feedback
- Cloud feedbacks
- Ice albedo feedback
- Carbon cycle feedbacks
- Modern observations
- Prehistorical climate records
- Theoretical climate models
- Patterns of warming
- Precipitation patterns
- Regional predictions
- Ice melt and sea level rise
- Ocean circulation changes
- Tropical cyclones
- Environmental consequences of global warming
- Socioeconomic consequences of global warming

How does global warming work?
Where does global warming occur in the atmosphere, why is global warming a social problem, where does global warming affect polar bears.

global warming
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- U.S. Department of Transportation - Global Warming: A Science Overview
- NOAA Climate.gov - Climate Change: Global Temperature
- Natural Resources Defense Council - Global Warming 101
- American Institute of Physics - The discovery of global warming
- LiveScience - Causes of Global Warming
- global warming - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- global warming - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

Human activity affects global surface temperatures by changing Earth ’s radiative balance—the “give and take” between what comes in during the day and what Earth emits at night. Increases in greenhouse gases —i.e., trace gases such as carbon dioxide and methane that absorb heat energy emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiate it back—generated by industry and transportation cause the atmosphere to retain more heat, which increases temperatures and alters precipitation patterns.
Global warming, the phenomenon of increasing average air temperatures near Earth’s surface over the past one to two centuries, happens mostly in the troposphere , the lowest level of the atmosphere, which extends from Earth’s surface up to a height of 6–11 miles. This layer contains most of Earth’s clouds and is where living things and their habitats and weather primarily occur.
Continued global warming is expected to impact everything from energy use to water availability to crop productivity throughout the world. Poor countries and communities with limited abilities to adapt to these changes are expected to suffer disproportionately. Global warming is already being associated with increases in the incidence of severe and extreme weather, heavy flooding , and wildfires —phenomena that threaten homes, dams, transportation networks, and other facets of human infrastructure. Learn more about how the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report, released in 2021, describes the social impacts of global warming.
Polar bears live in the Arctic , where they use the region’s ice floes as they hunt seals and other marine mammals . Temperature increases related to global warming have been the most pronounced at the poles, where they often make the difference between frozen and melted ice. Polar bears rely on small gaps in the ice to hunt their prey. As these gaps widen because of continued melting, prey capture has become more challenging for these animals.
Recent News
global warming , the phenomenon of increasing average air temperatures near the surface of Earth over the past one to two centuries. Climate scientists have since the mid-20th century gathered detailed observations of various weather phenomena (such as temperatures, precipitation , and storms) and of related influences on climate (such as ocean currents and the atmosphere’s chemical composition). These data indicate that Earth’s climate has changed over almost every conceivable timescale since the beginning of geologic time and that human activities since at least the beginning of the Industrial Revolution have a growing influence over the pace and extent of present-day climate change .
Giving voice to a growing conviction of most of the scientific community , the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was formed in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). The IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), published in 2021, noted that the best estimate of the increase in global average surface temperature between 1850 and 2019 was 1.07 °C (1.9 °F). An IPCC special report produced in 2018 noted that human beings and their activities have been responsible for a worldwide average temperature increase between 0.8 and 1.2 °C (1.4 and 2.2 °F) since preindustrial times, and most of the warming over the second half of the 20th century could be attributed to human activities.
AR6 produced a series of global climate predictions based on modeling five greenhouse gas emission scenarios that accounted for future emissions, mitigation (severity reduction) measures, and uncertainties in the model projections. Some of the main uncertainties include the precise role of feedback processes and the impacts of industrial pollutants known as aerosols , which may offset some warming. The lowest-emissions scenario, which assumed steep cuts in greenhouse gas emissions beginning in 2015, predicted that the global mean surface temperature would increase between 1.0 and 1.8 °C (1.8 and 3.2 °F) by 2100 relative to the 1850–1900 average. This range stood in stark contrast to the highest-emissions scenario, which predicted that the mean surface temperature would rise between 3.3 and 5.7 °C (5.9 and 10.2 °F) by 2100 based on the assumption that greenhouse gas emissions would continue to increase throughout the 21st century. The intermediate-emissions scenario, which assumed that emissions would stabilize by 2050 before declining gradually, projected an increase of between 2.1 and 3.5 °C (3.8 and 6.3 °F) by 2100.
Many climate scientists agree that significant societal, economic, and ecological damage would result if the global average temperature rose by more than 2 °C (3.6 °F) in such a short time. Such damage would include increased extinction of many plant and animal species, shifts in patterns of agriculture , and rising sea levels. By 2015 all but a few national governments had begun the process of instituting carbon reduction plans as part of the Paris Agreement , a treaty designed to help countries keep global warming to 1.5 °C (2.7 °F) above preindustrial levels in order to avoid the worst of the predicted effects. Whereas authors of the 2018 special report noted that should carbon emissions continue at their present rate, the increase in average near-surface air temperature would reach 1.5 °C sometime between 2030 and 2052, authors of the AR6 report suggested that this threshold would be reached by 2041 at the latest.

The AR6 report also noted that the global average sea level had risen by some 20 cm (7.9 inches) between 1901 and 2018 and that sea level rose faster in the second half of the 20th century than in the first half. It also predicted, again depending on a wide range of scenarios, that the global average sea level would rise by different amounts by 2100 relative to the 1995–2014 average. Under the report’s lowest-emission scenario, sea level would rise by 28–55 cm (11–21.7 inches), whereas, under the intermediate emissions scenario, sea level would rise by 44–76 cm (17.3–29.9 inches). The highest-emissions scenario suggested that sea level would rise by 63–101 cm (24.8–39.8 inches) by 2100.

The scenarios referred to above depend mainly on future concentrations of certain trace gases, called greenhouse gases , that have been injected into the lower atmosphere in increasing amounts through the burning of fossil fuels for industry, transportation , and residential uses. Modern global warming is the result of an increase in magnitude of the so-called greenhouse effect , a warming of Earth’s surface and lower atmosphere caused by the presence of water vapour , carbon dioxide , methane , nitrous oxides , and other greenhouse gases. In 2014 the IPCC first reported that concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides in the atmosphere surpassed those found in ice cores dating back 800,000 years.

Of all these gases, carbon dioxide is the most important, both for its role in the greenhouse effect and for its role in the human economy. It has been estimated that, at the beginning of the industrial age in the mid-18th century, carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere were roughly 280 parts per million (ppm). By the end of 2022 they had risen to 419 ppm, and, if fossil fuels continue to be burned at current rates, they are projected to reach 550 ppm by the mid-21st century—essentially, a doubling of carbon dioxide concentrations in 300 years.

A vigorous debate is in progress over the extent and seriousness of rising surface temperatures, the effects of past and future warming on human life, and the need for action to reduce future warming and deal with its consequences. This article provides an overview of the scientific background related to the subject of global warming. It considers the causes of rising near-surface air temperatures, the influencing factors, the process of climate research and forecasting, and the possible ecological and social impacts of rising temperatures. For an overview of the public policy developments related to global warming occurring since the mid-20th century, see global warming policy . For a detailed description of Earth’s climate, its processes, and the responses of living things to its changing nature, see climate . For additional background on how Earth’s climate has changed throughout geologic time , see climatic variation and change . For a full description of Earth’s gaseous envelope, within which climate change and global warming occur, see atmosphere .
Newsroom Post
Climate change: a threat to human wellbeing and health of the planet. taking action now can secure our future.
BERLIN, Feb 28 – Human-induced climate change is causing dangerous and widespread disruption in nature and affecting the lives of billions of people around the world, despite efforts to reduce the risks. People and ecosystems least able to cope are being hardest hit, said scientists in the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report, released today.
“This report is a dire warning about the consequences of inaction,” said Hoesung Lee, Chair of the IPCC. “It shows that climate change is a grave and mounting threat to our wellbeing and a healthy planet. Our actions today will shape how people adapt and nature responds to increasing climate risks.”
The world faces unavoidable multiple climate hazards over the next two decades with global warming of 1.5°C (2.7°F). Even temporarily exceeding this warming level will result in additional severe impacts, some of which will be irreversible. Risks for society will increase, including to infrastructure and low-lying coastal settlements.
The Summary for Policymakers of the IPCC Working Group II report, Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability was approved on Sunday, February 27 2022, by 195 member governments of the IPCC, through a virtual approval session that was held over two weeks starting on February 14.
Urgent action required to deal with increasing risks
Increased heatwaves, droughts and floods are already exceeding plants’ and animals’ tolerance thresholds, driving mass mortalities in species such as trees and corals. These weather extremes are occurring simultaneously, causing cascading impacts that are increasingly difficult to manage. They have exposed millions of people to acute food and water insecurity, especially in Africa, Asia, Central and South America, on Small Islands and in the Arctic.
To avoid mounting loss of life, biodiversity and infrastructure, ambitious, accelerated action is required to adapt to climate change, at the same time as making rapid, deep cuts in greenhouse gas emissions. So far, progress on adaptation is uneven and there are increasing gaps between action taken and what is needed to deal with the increasing risks, the new report finds. These gaps are largest among lower-income populations.
The Working Group II report is the second instalment of the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), which will be completed this year.
“This report recognizes the interdependence of climate, biodiversity and people and integrates natural, social and economic sciences more strongly than earlier IPCC assessments,” said Hoesung Lee. “It emphasizes the urgency of immediate and more ambitious action to address climate risks. Half measures are no longer an option.”
Safeguarding and strengthening nature is key to securing a liveable future
There are options to adapt to a changing climate. This report provides new insights into nature’s potential not only to reduce climate risks but also to improve people’s lives.
“Healthy ecosystems are more resilient to climate change and provide life-critical services such as food and clean water”, said IPCC Working Group II Co-Chair Hans-Otto Pörtner. “By restoring degraded ecosystems and effectively and equitably conserving 30 to 50 per cent of Earth’s land, freshwater and ocean habitats, society can benefit from nature’s capacity to absorb and store carbon, and we can accelerate progress towards sustainable development, but adequate finance and political support are essential.”
Scientists point out that climate change interacts with global trends such as unsustainable use of natural resources, growing urbanization, social inequalities, losses and damages from extreme events and a pandemic, jeopardizing future development.
“Our assessment clearly shows that tackling all these different challenges involves everyone – governments, the private sector, civil society – working together to prioritize risk reduction, as well as equity and justice, in decision-making and investment,” said IPCC Working Group II Co-Chair Debra Roberts.
“In this way, different interests, values and world views can be reconciled. By bringing together scientific and technological know-how as well as Indigenous and local knowledge, solutions will be more effective. Failure to achieve climate resilient and sustainable development will result in a sub-optimal future for people and nature.”
Cities: Hotspots of impacts and risks, but also a crucial part of the solution
This report provides a detailed assessment of climate change impacts, risks and adaptation in cities, where more than half the world’s population lives. People’s health, lives and livelihoods, as well as property and critical infrastructure, including energy and transportation systems, are being increasingly adversely affected by hazards from heatwaves, storms, drought and flooding as well as slow-onset changes, including sea level rise.
“Together, growing urbanization and climate change create complex risks, especially for those cities that already experience poorly planned urban growth, high levels of poverty and unemployment, and a lack of basic services,” Debra Roberts said.
“But cities also provide opportunities for climate action – green buildings, reliable supplies of clean water and renewable energy, and sustainable transport systems that connect urban and rural areas can all lead to a more inclusive, fairer society.”
There is increasing evidence of adaptation that has caused unintended consequences, for example destroying nature, putting peoples’ lives at risk or increasing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be avoided by involving everyone in planning, attention to equity and justice, and drawing on Indigenous and local knowledge.
A narrowing window for action
Climate change is a global challenge that requires local solutions and that’s why the Working Group II contribution to the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) provides extensive regional information to enable Climate Resilient Development.
The report clearly states Climate Resilient Development is already challenging at current warming levels. It will become more limited if global warming exceeds 1.5°C (2.7°F). In some regions it will be impossible if global warming exceeds 2°C (3.6°F). This key finding underlines the urgency for climate action, focusing on equity and justice. Adequate funding, technology transfer, political commitment and partnership lead to more effective climate change adaptation and emissions reductions.
“The scientific evidence is unequivocal: climate change is a threat to human wellbeing and the health of the planet. Any further delay in concerted global action will miss a brief and rapidly closing window to secure a liveable future,” said Hans-Otto Pörtner.
For more information, please contact:
IPCC Press Office, Email: [email protected] IPCC Working Group II: Sina Löschke, Komila Nabiyeva: [email protected]
Notes for Editors
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Working Group II report examines the impacts of climate change on nature and people around the globe. It explores future impacts at different levels of warming and the resulting risks and offers options to strengthen nature’s and society’s resilience to ongoing climate change, to fight hunger, poverty, and inequality and keep Earth a place worth living on – for current as well as for future generations.
Working Group II introduces several new components in its latest report: One is a special section on climate change impacts, risks and options to act for cities and settlements by the sea, tropical forests, mountains, biodiversity hotspots, dryland and deserts, the Mediterranean as well as the polar regions. Another is an atlas that will present data and findings on observed and projected climate change impacts and risks from global to regional scales, thus offering even more insights for decision makers.
The Summary for Policymakers of the Working Group II contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) as well as additional materials and information are available at https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/
Note : Originally scheduled for release in September 2021, the report was delayed for several months by the COVID-19 pandemic, as work in the scientific community including the IPCC shifted online. This is the second time that the IPCC has conducted a virtual approval session for one of its reports.
AR6 Working Group II in numbers
270 authors from 67 countries
- 47 – coordinating authors
- 184 – lead authors
- 39 – review editors
- 675 – contributing authors
Over 34,000 cited references
A total of 62,418 expert and government review comments
(First Order Draft 16,348; Second Order Draft 40,293; Final Government Distribution: 5,777)
More information about the Sixth Assessment Report can be found here .
Additional media resources
Assets available after the embargo is lifted on Media Essentials website .
Press conference recording, collection of sound bites from WGII authors, link to presentation slides, B-roll of approval session, link to launch Trello board including press release and video trailer in UN languages, a social media pack.
The website includes outreach materials such as videos about the IPCC and video recordings from outreach events conducted as webinars or live-streamed events.
Most videos published by the IPCC can be found on our YouTube channel. Credit for artwork
About the IPCC
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the UN body for assessing the science related to climate change. It was established by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1988 to provide political leaders with periodic scientific assessments concerning climate change, its implications and risks, as well as to put forward adaptation and mitigation strategies. In the same year the UN General Assembly endorsed the action by the WMO and UNEP in jointly establishing the IPCC. It has 195 member states.
Thousands of people from all over the world contribute to the work of the IPCC. For the assessment reports, IPCC scientists volunteer their time to assess the thousands of scientific papers published each year to provide a comprehensive summary of what is known about the drivers of climate change, its impacts and future risks, and how adaptation and mitigation can reduce those risks.
The IPCC has three working groups: Working Group I , dealing with the physical science basis of climate change; Working Group II , dealing with impacts, adaptation and vulnerability; and Working Group III , dealing with the mitigation of climate change. It also has a Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories that develops methodologies for measuring emissions and removals. As part of the IPCC, a Task Group on Data Support for Climate Change Assessments (TG-Data) provides guidance to the Data Distribution Centre (DDC) on curation, traceability, stability, availability and transparency of data and scenarios related to the reports of the IPCC.
IPCC assessments provide governments, at all levels, with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies. IPCC assessments are a key input into the international negotiations to tackle climate change. IPCC reports are drafted and reviewed in several stages, thus guaranteeing objectivity and transparency. An IPCC assessment report consists of the contributions of the three working groups and a Synthesis Report. The Synthesis Report integrates the findings of the three working group reports and of any special reports prepared in that assessment cycle.
About the Sixth Assessment Cycle
At its 41st Session in February 2015, the IPCC decided to produce a Sixth Assessment Report (AR6). At its 42nd Session in October 2015 it elected a new Bureau that would oversee the work on this report and the Special Reports to be produced in the assessment cycle.
Global Warming of 1.5°C , an IPCC special report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty was launched in October 2018.
Climate Change and Land , an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems was launched in August 2019, and the Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate was released in September 2019.
In May 2019 the IPCC released the 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories , an update to the methodology used by governments to estimate their greenhouse gas emissions and removals.
In August 2021 the IPCC released the Working Group I contribution to the AR6, Climate Change 2021, the Physical Science Basis
The Working Group III contribution to the AR6 is scheduled for early April 2022.
The Synthesis Report of the Sixth Assessment Report will be completed in the second half of 2022.
For more information go to www.ipcc.ch
Related Content
Remarks by the ipcc chair during the press conference to present the working group ii contribution to the sixth assessment report.
Monday, 28 February 2022 Distinguished representatives of the media, WMO Secretary-General Petteri, UNEP Executive Director Andersen, We have just heard …
February 2022
Fifty-fifth session of the ipcc (ipcc-55) and twelfth session of working group ii (wgii-12), february 14, 2022, working group report, ar6 climate change 2022: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability.
Essay: To fix climate anxiety (and also climate change), we first have to fix individualism

- Copy Link URL Copied!

How do you cope? I feel the sorrow, the quiet plea for guidance every time someone asks me this question. As an environmental reporter dedicated to helping people make sense of climate change, I know I should have answers. But the truth is, it took me until now to face my own grief.
My heart keeps breaking whenever I meet yet another child struggling with asthma amid orange, smoke-filled skies. I, too, am reeling from the whiplash of extreme drought and extreme rain , and I’m still haunted by the thought of a mother having to call each of her daughters to say goodbye as the homes around her cave to fire.
Each year, as I reflect on my own reporting on the floods that keep getting worse and the toxic pollution building up in all forms of life , I find myself questioning whether I could ever justify bringing my own children into this world. I agonize over the amount of plastic we can’t avoid using and mourn the monarch butterflies that have vanished. With each new heat record shattered, and each new report declaring a code red for humanity , I can’t help but feel like we’re just counting down the days to our own extinction.
In the face of sea level rise, can we reimagine California’s vanishing coastline?
“Climate anxiety” is the term we now use to describe these feelings, but I must confess, I was perplexed when I first heard these words a few years ago. Anger, frustration, helplessness, exhaustion — these are the emotions I come across more often when getting to know the communities bracing for, or recovering from, the devastation of what they’ve long considered home.
Then a college student asked me about climate anxiety. It came up again on social media, and again in personal essays and polls. This paralyzing dread was suddenly the talk of the town — but it has also, very noticeably, remained absent in some circles.
All this has led me to wonder: What, exactly, is climate anxiety? And how should we cope? At first blush, this anxiety seems rooted in a fear that we’ll never go back to normal, that the future we were once promised is now gone. But who this “normal” is even for (and what we’re actually afraid of losing) speaks to a much more complicated question:
Is this anxiety pointing to a deeper responsibility that we all must face — and ultimately, is this anxiety something we can transcend?
For Jade Sasser, whose research on climate emotions has been grounded by her own experiences as a Black woman, these questions sharpened into focus during a research-methods seminar that she was teaching early last year at UC Riverside.
The class — all female, many from low-income immigrant communities — had been a fairly quiet group all quarter, so Sasser was surprised when the room completely erupted after she broached what she thought would be an academic, somewhat dispassionate discussion about climate change and the future.
Every student was suddenly talking, even yelling, over one another. Thought after thought tumbled out as they shared that not only does the future feel bleak when it comes to the job market, the housing crisis and whether their generation will ever be able to “settle down with kids” — but all this is many times worse when you’re not white, not documented and not born into a college-educated family.
How can they feel hopeful about the future, they asked, when, on top of everything already stacked against them, they also have to worry about wildfires, extreme heat and air pollution getting out of control?
‘It’s almost shameful to want to have children’
‘Climate Anxiety and the Kid Question’ asks: With American society feeling more socially and politically polarized than ever, is it right to bring another person into the world?
“It was literally a collective meltdown unlike anything I had ever experienced,” said Sasser, whose podcast and book, “ Climate Anxiety and the Kid Question, ” were largely inspired by her students that day. “I understood in that moment that you cannot assume someone does not also experience anxiety simply because their way of talking about it may not be the same as yours.”
It doesn’t help, she added, that many people don’t realize what they’re feeling is climate anxiety because the way we talk about it tends to center the experiences of white and more privileged people — people who have been insulated from oppression and have rarely (until now) had to worry about the safety of their own future.
“For a lot of people, climate anxiety looks a certain way: It looks very scared, it looks very sad, and it looks like a person who is ready, willing and able to talk about it,” Sasser said. “But for those who are experiencing many compounding forms of vulnerability at the same time, you can’t just pick out one part of it and say, ‘Oh, this is what’s causing me to feel this way.’”
A brave first step is to acknowledge privilege — and to support, and perhaps even learn, from those who have had to be resilient long before climate change became so overwhelming.
“For me, this work is a matter of survival,” said Kevin J. Patel, who grew up in South L.A. and has been fighting for climate justice since he was 11. He was contemplative, nodding, when I shared what I learned from Sasser, and he gently added that one privilege many communities don’t have is the ability to turn it off. Not everyone can go on a vacation or take a day to recharge, he said. Even having the time to talk about your sadness can be a luxury.
Feeling climate anxiety? These books offer glimmers of hope — and much-needed wisdom
Patel learned at a young age that not all communities get the same level of care. Growing up with hazy air, in a neighborhood hemmed in by the 10 and 110 freeways, Patel almost collapsed one day in front of his sixth-grade class when his heart suddenly started pounding at more than 300 beats per minute.
His parents, farmers from Gujarat, India, rushed Patel to the emergency room and held his hand while everyone around him thought he was dying. After months of hospital visits and procedures, doctors determined that he had developed a severe heart condition in large part due to the smog.
‘For me, this work is a matter of survival.’
— Kevin J. Patel
As he learned to live with an irregular heartbeat, he found joy in his family’s tiny garden and marveled at all the ladybugs that gathered on the tulsi, a special type of basil. He taught his classmates that food came from the ground, not the grocery store, and together, they went on to form an environmental club.
Today, Patel speaks with the hardened wisdom of someone who has experienced much more than the typical 23-year-old. He’s constantly doing something — whether it’s supporting a neighbor, getting water bottle refill stations installed at his school, or turning the idea of a Los Angeles County Youth Climate Commission into reality. For years, he has guided other marginalized youth through OneUpAction , a grassroots environmental group that he built from the ground up.
Even if he doesn’t call it anxiety, he admits he sometimes has trouble focusing, and there’s a tenseness in his body that can be hard to shake off. But he’s usually able to turn it around by talking to his friends or elders, or by reciting his favorite proverb:
They tried to bury us, but they didn’t know we were seeds.
“It’s not about what I need, it’s about what my community needs,” he said. “There is joy in caring for one another. There is joy in coming together to fight for a future that we believe in.”
When talking about climate anxiety, it’s important to differentiate whether you’re assessing these emotions as a mental health condition, or as a cultural phenomenon.
Let’s start with mental health: Polls show climate anxiety is on the rise and that people all around the world are losing sleep over climate change. Organizations like the Climate-Aware Therapist Directory and the American Psychiatric Assn. have put together an increasing number of guides and resources to help more people understand how climate change has affected our emotional well-being.
Poll shows Californians’ climate anxiety is on the rise
Just knowing that climate change is getting worse can trigger serious psychological responses. And the shock and trauma are all the more great if you’ve already had to live through the kinds of disasters that keep the rest of us up at night.
It’s also important to note that social media has magnified our sense of doom. What you see on social media tends to be a particularly intense and cherry-picked version of reality, but studies show that’s exactly how the vast majority of young people are getting their information about climate change: online rather than in school.
But you can’t treat climate anxiety like other forms of anxiety, and here’s where the cultural politics come in: The only way to make climate anxiety go away is to make climate change go away, and given the fraught and deeply systemic underpinnings of climate change, we must also consider this context when it comes to our climate emotions. How we feel is just as much a product of the narratives that have shaped the way we perceive and respond to the world.
“Climate anxiety can’t be limited to just a clinical setting — we have to take it out of the therapy room and look at it through a lens of privilege, and power, and the economic, historical and social structures that are at the root of the problem,” said Sarah Jaquette Ray, whose book “ A Field Guide to Climate Anxiety ” is a call to arms to think more expansively about our despair. “Treating a person’s climate anxiety without challenging these systems only addresses the symptoms, not the causes... and if white or more privileged emotions get the most airtime, and if we don’t see how climate is intersecting with all these other problems, that can result in a greater silencing of the people most impacted.”

Ray, an environmental humanist who chairs the environmental studies program at Cal Poly Humboldt, also emphasized that our distress can actually be a catalyst for much-needed change. These emotions are meant to shake us out of complacency, to sound the alarm to the very real crisis before us. But if we don’t openly talk about climate anxiety as something that is not only normal but also expected, we run the risk of further individualizing the problem. We already have a tendency to shut down and feel alone in our sorrows, which traps us into thinking only about ourselves.
“One huge reason why climate anxiety feels so awful is this feeling of not being able to do anything about it,” Ray said. “But if you actually saw yourself as part of a collective, as interconnected with all these other movements doing meaningful things, you wouldn’t be feeling this despair and loneliness.”
The trick to fixing climate anxiety is to fix individualism, she said. Start small, tap into what you’re already good at, join something bigger than yourself.
And by fixing individualism, as many young activists like Patel have already figured out, we just might have a better shot at fixing climate change.
Let us consider, for a moment, how the words that we use can also limit the way we think about our vulnerability and despair.
Something as simple as the “climate” in “climate anxiety” and how we define “environment” can unintentionally reinforce who we center in the conversation.
“In Nigeria, what we call our environment — it’s not just trees and mountains — it’s also about our food, our jobs, the biodiversity that gives us the life support that we need to thrive every day. That’s what we call our environment; it’s about our people,” said Jennifer Uchendu, who founded SustyVibes , a youth-led sustainability group based in her home country, as well as the Eco-Anxiety in Africa Project , which seeks to validate the emotions and experiences of communities often overlooked in climate conversations. “So if people are being oppressed by the system, it is still linked to our idea of the environment.”
Many of Uchendu’s elders have expressed a lifetime of feeling frustrated and powerless, for example, but she said they didn’t immediately connect these feelings to climate change because “climate anxiety” sounded to them like a new and elite phenomenon.
Editorial: California can make climate polluters pay for the mess they have made of Earth
We hear so often today that climate change is the existential crisis of our time, but that dismisses the trauma and violence to all the people who have been fighting to survive for centuries. Colonization, greed and exploitation are inseparable from climate change, Uchendu said, but we miss these connections when we consider our emotions only through a Western lens.
For Jessa Calderon, a Chumash and Tongva songwriter, these disconnects are ever-present in the concrete-hardened rivers snaking through Los Angeles, and the sour taste of industrialization often singeing the air. In her darkest moments, her heart hurts wondering if her son, Honor, will grow up to know clean water.
Her voice cracked as she recalled a brown bear that had been struck dead on the freeway near the Cajon Pass. As she watched strangers gawk at the limp body and share videos online, she wished she had been able to put the bear to rest and sing him into the spirit world.
“If we don’t see them as our people, then we have no hope for ourselves as a people, because we’re showing that we care about nothing more than ourselves,” she said. “And if we care about nothing more than ourselves, then we’re going to continue to devastate each other and the land.”
It is not too late to turn your climate anxiety into climate empathy. Acknowledging the emotional toll on people beyond yourself can be an opportunity to listen and support one another. Embracing our feelings — and then finding others who also want to turn their fear into action — can be the missing spark to much-needed social and environmental healing.
There is also wisdom to be learned in the songs and traditions of past movements, when people banded together — for civil rights, for women’s suffrage — and found ways to keep hope alive against all odds. And the more we look to the young people still caring for their elders in Nigeria, and to our Indigenous neighbors who continue to sing and love and tend to every living being, the better we might also comprehend the resilience required of all of us in the warming years ahead.
Opinion: Here are the places that could become too hot for humans due to climate change
So how should we cope? For Patel, living with his irregular but unwavering heartbeat, he finds strength in the words of adrienne maree brown, who famously wrote in “ Emergent Strategy ” that in the same way our lives are shaped today by our ancestors, we ourselves are future ancestors. Calderon, who similarly taught her son to leave this Earth better with every passing generation, confided to me that on the days when the sorrow feels too great, she sneaks off to plant native manzanita seeds in neighborhoods stripped of plants and trees.
As I’m reminded of all the love we can still sow for the future, I think of Phoenix Armenta, a longtime climate justice organizer in Oakland who has inspired numerous people, including myself, to take heart in all the times we actually got it right. (Remember acid rain? It was a huge problem, but collective action inspired multiple countries to join forces in the 1980s, and we did what needed to be done.)
“Imagine what kind of world you actually want to live in and start working to make that happen,” said Armenta, who recently made the switch to government planning to help more communities find their voice and determine their own visions for the future.
To grieve the world as we know it is to miss out on opportunities to transform our world for the better. To believe we have nothing left to hope for is a self-fulfilling void. We must find the courage to care, to change, to reimagine the systems that got us into such a devastating crisis in the first place — and we must allow ourselves to dream.
“But it can’t just be my dream, or your dream. It has to be our collective dream,” Armenta said. “I’ve known for a very long time that I can’t save the world, but we can save the world together.”
More to Read

Climate disasters can elicit despair when they go viral. These activists found inspiration
Sept. 12, 2024

Comic: Emerging from environmental dissociation
Sept. 11, 2024

Rosanna Xia is an environment reporter for the Los Angeles Times, where she specializes in stories about the coast and ocean. She was a Pulitzer Prize finalist in 2020 for explanatory reporting, and her award-winning book, “ California Against the Sea ,” has been praised as a poetic and mind-expanding exploration of what we stand to lose in the face of rising water.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Opinion: How farming can turn carbon from a climate threat into an asset
Sept. 14, 2024

Climate & Environment
The air quality in Big Bear suddenly reached hazardous levels this week. What happened?

Yucaipa residents fight back against massive warehouse proposal

California reports a total of eight H5N1 bird flu outbreaks among dairy herds
Sept. 13, 2024

Climate Change: Evidence and Causes: Update 2020 (2020)
Chapter: conclusion, c onclusion.
This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of the recent change is almost certainly due to emissions of greenhouse gases caused by human activities. Further climate change is inevitable; if emissions of greenhouse gases continue unabated, future changes will substantially exceed those that have occurred so far. There remains a range of estimates of the magnitude and regional expression of future change, but increases in the extremes of climate that can adversely affect natural ecosystems and human activities and infrastructure are expected.
Citizens and governments can choose among several options (or a mixture of those options) in response to this information: they can change their pattern of energy production and usage in order to limit emissions of greenhouse gases and hence the magnitude of climate changes; they can wait for changes to occur and accept the losses, damage, and suffering that arise; they can adapt to actual and expected changes as much as possible; or they can seek as yet unproven “geoengineering” solutions to counteract some of the climate changes that would otherwise occur. Each of these options has risks, attractions and costs, and what is actually done may be a mixture of these different options. Different nations and communities will vary in their vulnerability and their capacity to adapt. There is an important debate to be had about choices among these options, to decide what is best for each group or nation, and most importantly for the global population as a whole. The options have to be discussed at a global scale because in many cases those communities that are most vulnerable control few of the emissions, either past or future. Our description of the science of climate change, with both its facts and its uncertainties, is offered as a basis to inform that policy debate.
A CKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The following individuals served as the primary writing team for the 2014 and 2020 editions of this document:
- Eric Wolff FRS, (UK lead), University of Cambridge
- Inez Fung (NAS, US lead), University of California, Berkeley
- Brian Hoskins FRS, Grantham Institute for Climate Change
- John F.B. Mitchell FRS, UK Met Office
- Tim Palmer FRS, University of Oxford
- Benjamin Santer (NAS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- John Shepherd FRS, University of Southampton
- Keith Shine FRS, University of Reading.
- Susan Solomon (NAS), Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Kevin Trenberth, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Walsh, University of Alaska, Fairbanks
- Don Wuebbles, University of Illinois
Staff support for the 2020 revision was provided by Richard Walker, Amanda Purcell, Nancy Huddleston, and Michael Hudson. We offer special thanks to Rebecca Lindsey and NOAA Climate.gov for providing data and figure updates.
The following individuals served as reviewers of the 2014 document in accordance with procedures approved by the Royal Society and the National Academy of Sciences:
- Richard Alley (NAS), Department of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University
- Alec Broers FRS, Former President of the Royal Academy of Engineering
- Harry Elderfield FRS, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Cambridge
- Joanna Haigh FRS, Professor of Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London
- Isaac Held (NAS), NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
- John Kutzbach (NAS), Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin
- Jerry Meehl, Senior Scientist, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Pendry FRS, Imperial College London
- John Pyle FRS, Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge
- Gavin Schmidt, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
- Emily Shuckburgh, British Antarctic Survey
- Gabrielle Walker, Journalist
- Andrew Watson FRS, University of East Anglia
The Support for the 2014 Edition was provided by NAS Endowment Funds. We offer sincere thanks to the Ralph J. and Carol M. Cicerone Endowment for NAS Missions for supporting the production of this 2020 Edition.
F OR FURTHER READING
For more detailed discussion of the topics addressed in this document (including references to the underlying original research), see:
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2019: Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [ https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc ]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), 2019: Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration: A Research Agenda [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/25259 ]
- Royal Society, 2018: Greenhouse gas removal [ https://raeng.org.uk/greenhousegasremoval ]
- U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP), 2018: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume II: Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States [ https://nca2018.globalchange.gov ]
- IPCC, 2018: Global Warming of 1.5°C [ https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15 ]
- USGCRP, 2017: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I: Climate Science Special Reports [ https://science2017.globalchange.gov ]
- NASEM, 2016: Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/21852 ]
- IPCC, 2013: Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Working Group 1. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis [ https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1 ]
- NRC, 2013: Abrupt Impacts of Climate Change: Anticipating Surprises [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18373 ]
- NRC, 2011: Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts Over Decades to Millennia [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12877 ]
- Royal Society 2010: Climate Change: A Summary of the Science [ https://royalsociety.org/topics-policy/publications/2010/climate-change-summary-science ]
- NRC, 2010: America’s Climate Choices: Advancing the Science of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12782 ]
Much of the original data underlying the scientific findings discussed here are available at:
- https://data.ucar.edu/
- https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu
- https://iridl.ldeo.columbia.edu
- https://ess-dive.lbl.gov/
- https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/
- https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
- http://scrippsco2.ucsd.edu
- http://hahana.soest.hawaii.edu/hot/
| was established to advise the United States on scientific and technical issues when President Lincoln signed a Congressional charter in 1863. The National Research Council, the operating arm of the National Academy of Sciences and the National Academy of Engineering, has issued numerous reports on the causes of and potential responses to climate change. Climate change resources from the National Research Council are available at . | |
| is a self-governing Fellowship of many of the world’s most distinguished scientists. Its members are drawn from all areas of science, engineering, and medicine. It is the national academy of science in the UK. The Society’s fundamental purpose, reflected in its founding Charters of the 1660s, is to recognise, promote, and support excellence in science, and to encourage the development and use of science for the benefit of humanity. More information on the Society’s climate change work is available at |

Climate change is one of the defining issues of our time. It is now more certain than ever, based on many lines of evidence, that humans are changing Earth's climate. The Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, with their similar missions to promote the use of science to benefit society and to inform critical policy debates, produced the original Climate Change: Evidence and Causes in 2014. It was written and reviewed by a UK-US team of leading climate scientists. This new edition, prepared by the same author team, has been updated with the most recent climate data and scientific analyses, all of which reinforce our understanding of human-caused climate change.
Scientific information is a vital component for society to make informed decisions about how to reduce the magnitude of climate change and how to adapt to its impacts. This booklet serves as a key reference document for decision makers, policy makers, educators, and others seeking authoritative answers about the current state of climate-change science.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This research paper examines the social significance and ecological value of Earth Day in the face of the climate change agenda. The Earth Day and Climate Change. Climate change remains a relevant topic despite over fifty years of efforts since the establishment of Earth Day in 1970. Desertification and Climate Change.
🏆 Best Climate Change Title Ideas & Essay Examples. Get your 100% original paper on any topic done in as little as 1 hour. Learn More . Climate Change - Problems and Solutions. It is important to avoid cutting trees and reduce the utilization of energy to protect the environment. Many organizations have been developed to enhance innovation ...
Climate Change Sample Essay 250 Words. Climate change represents a pressing global challenge that demands immediate attention and concerted efforts. Human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This results in a greenhouse effect ...
200 Words Essay on Climate Change. The climate of the Earth has changed significantly over time. While some of these changes were brought on by natural events like volcanic eruptions, floods, forest fires, etc., many of the changes were brought on by human activity. The burning of fossil fuels, domesticating livestock, and other human ...
1,000 Word Climate Change Essay. Climate change in the world can be caused by various activities. When climate change occurs; temperatures can increase a dramatically. When temperature rises, many different changes can occur on Earth. For example, it can result in more floods, droughts, or intense rain, as well as more frequent and severe heat ...
Climate Change The world's ecological issues have been studied intensely by scientists in various academic disciplines vigorously for many years and have been greatly accelerated in recent decades. The level of understanding about how natural systems on the planet operate has become immensely sophisticated. Although there are still some issues that remain puzzling, on the whole, scientists ...
Bahçeşehir College is committed to increasing students' awareness of the changing world we live in. This climate change essay competition saw many students submitting well thought out pieces of writing. These essays were marked on their format, creativity, organisation, clarity, unity/development of thought, and grammar/mechanics.
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
Here are 15 of our favorite writings on climate — this eclectic list contains books, essays, a newsletter, a scientific paper, even legislation and they're all ones we wholeheartedly recommend. All We Can Save: Truth, Courage, and Solutions for the Climate Crisis coedited by Ayana Elizabeth Johnson and Katharine Wilkinson.
Climate Explained is a collection of short primers that answer diverse climate change questions, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security. Image 1. Example Climate Explained essays on the Yale Climate ...
RSS Feed. Climate change refers to a statistically defined change in the average and/or variability of the climate system, this includes the atmosphere, the water cycle, the land surface, ice and ...
Climate Change and Global Warming Essay. Global Warming and Climate Change are two sides of the same coin. Both are interrelated with each other and are two issues of major concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases released such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth's atmosphere cause Global Warming which leads to climate ...
Summary. Subject (s): Earth Science. Topic: Climate Change and Sustainability. Grade/Level: 9-12 (can be adapted to grades 6-8) Objectives: Students will be able to write a scientific argument using evidence and reasoning to support claims. Students will also be able to reflect on the weaknesses in their own arguments in order to improve their ...
Top 25 Climate Change Essay Titles. 1. How Climate Change became a False Religion. 2. Why Greta Thunberg Needs to Go Back to School and Stop Whining about Climate Change. 3. Facilitating the Climate Change Hoax: How the Left Uses Social Media to Foster Fear, Panic and Policy Change. 4.
Authors' Summary: This book demonstrates how robust and evolving science can be relevant to public discourse about climate policy. Fighting climate change is the ultimate societal challenge, and the difficulty is not just in the wrenching adjustments required to cut greenhouse emissions and to respond to change already under way. A second and ...
Climate change is impacting ecosystems through changes in mean conditions and in climate variability, coupled with other associated changes such as increased ocean acidification and atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations. It also interacts with other pressures on ecosystems, including degradation, defaunation and fragmentation.
Average global temperatures have increased by 2.2 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1.2 degrees Celsius, since 1880, with the greatest changes happening in the late 20th century. Land areas have warmed more ...
The Economist 's Open Future essay competition asked people between 16 and 25 years old to answer the question: "What fundamental economic and political change, if any, is needed for an effective response to climate change?". Entrants had 1,000 words. (The shortest essay took just two: "Abolish capitalism".)
Abstract. Climate change is a long-lasting change in the weather arrays across tropics to polls. It is a global threat that has embarked on to put stress on various sectors. This study is aimed to conceptually engineer how climate variability is deteriorating the sustainability of diverse sectors worldwide.
Global warming, the phenomenon of rising average air temperatures near Earth's surface over the past 100 to 200 years. Although Earth's climate has been evolving since the dawn of geologic time, human activities since the Industrial Revolution have a growing influence over the pace and extent of climate change.
In 2015, the Paris Agreement, which is legally binding on climate change, has been accepted by approximately 191 countries to limit global warming to below 2, if possible, to 1.5. The countries have committed to achieve this primary goal and minimise global warming. To accomplish this goal requires all parties to put forward their best efforts ...
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The Working Group II report examines the impacts of climate change on nature and people around the globe. It explores future impacts at different levels of warming and the ...
Then a college student asked me about climate anxiety. It came up again on social media, and again in personal essays and polls. This paralyzing dread was suddenly the talk of the town — but it ...
C ONCLUSION. This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of ...