
18 Descriptive Research Examples
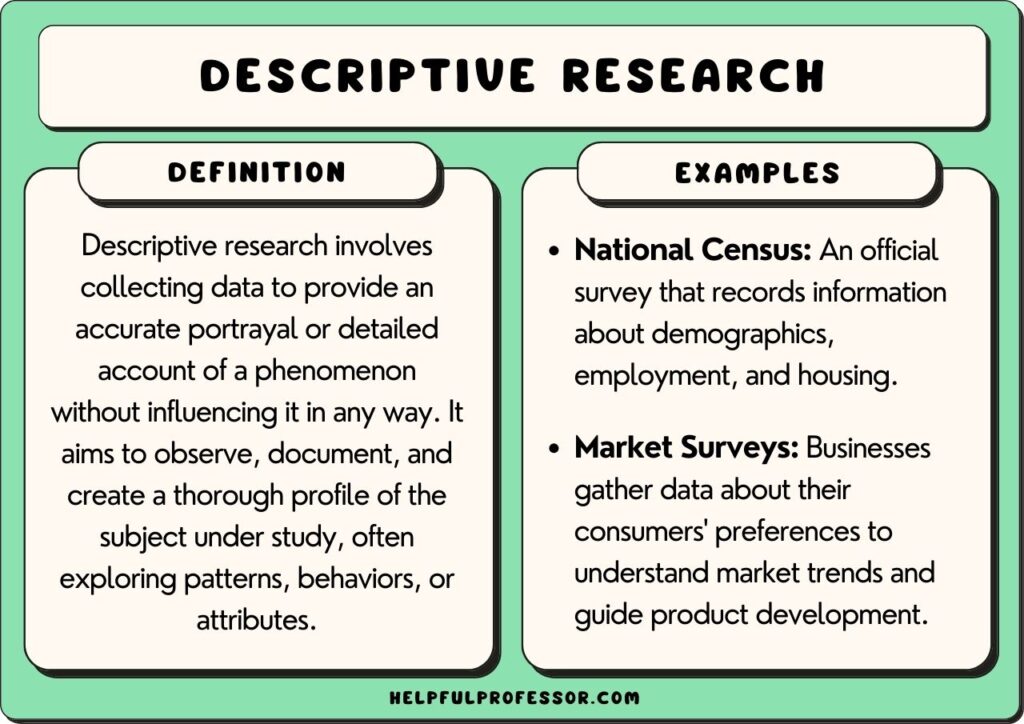
Descriptive research involves gathering data to provide a detailed account or depiction of a phenomenon without manipulating variables or conducting experiments.
A scholarly definition is:
“Descriptive research is defined as a research approach that describes the characteristics of the population, sample or phenomenon studied. This method focuses more on the “what” rather than the “why” of the research subject.” (Matanda, 2022, p. 63)
The key feature of descriptive research is that it merely describes phenomena and does not attempt to manipulate variables nor determine cause and effect .
To determine cause and effect , a researcher would need to use an alternate methodology, such as experimental research design .
Common approaches to descriptive research include:
- Cross-sectional research : A cross-sectional study gathers data on a population at a specific time to get descriptive data that could include categories (e.g. age or income brackets) to get a better understanding of the makeup of a population.
- Longitudinal research : Longitudinal studies return to a population to collect data at several different points in time, allowing for description of changes in categories over time. However, as it’s descriptive, it cannot infer cause and effect (Erickson, 2017).
Methods that could be used include:
- Surveys: For example, sending out a census survey to be completed at the exact same date and time by everyone in a population.
- Case Study : For example, an in-depth description of a specific person or group of people to gain in-depth qualitative information that can describe a phenomenon but cannot be generalized to other cases.
- Observational Method : For example, a researcher taking field notes in an ethnographic study. (Siedlecki, 2020)
Descriptive Research Examples
1. Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (Psychology): Researchers analyze various behavior patterns, cognitive skills, and social interaction abilities specific to children with Autism Spectrum Disorder to comprehensively describe the disorder’s symptom spectrum. This detailed description classifies it as descriptive research, rather than analytical or experimental, as it merely records what is observed without altering any variables or trying to establish causality.
2. Consumer Purchase Decision Process in E-commerce Marketplaces (Marketing): By documenting and describing all the factors that influence consumer decisions on online marketplaces, researchers don’t attempt to predict future behavior or establish causes—just describe observed behavior—making it descriptive research.
3. Impacts of Climate Change on Agricultural Practices (Environmental Studies): Descriptive research is seen as scientists outline how climate changes influence various agricultural practices by observing and then meticulously categorizing the impacts on crop variability, farming seasons, and pest infestations without manipulating any variables in real-time.
4. Work Environment and Employee Performance (Human Resources Management): A study of this nature, describing the correlation between various workplace elements and employee performance, falls under descriptive research as it merely narrates the observed patterns without altering any conditions or testing hypotheses.
5. Factors Influencing Student Performance (Education): Researchers describe various factors affecting students’ academic performance, such as studying techniques, parental involvement, and peer influence. The study is categorized as descriptive research because its principal aim is to depict facts as they stand without trying to infer causal relationships.
6. Technological Advances in Healthcare (Healthcare): This research describes and categorizes different technological advances (such as telemedicine, AI-enabled tools, digital collaboration) in healthcare without testing or modifying any parameters, making it an example of descriptive research.
7. Urbanization and Biodiversity Loss (Ecology): By describing the impact of rapid urban expansion on biodiversity loss, this study serves as a descriptive research example. It observes the ongoing situation without manipulating it, offering a comprehensive depiction of the existing scenario rather than investigating the cause-effect relationship.
8. Architectural Styles across Centuries (Art History): A study documenting and describing various architectural styles throughout centuries essentially represents descriptive research. It aims to narrate and categorize facts without exploring the underlying reasons or predicting future trends.
9. Media Usage Patterns among Teenagers (Sociology): When researchers document and describe the media consumption habits among teenagers, they are performing a descriptive research study. Their main intention is to observe and report the prevailing trends rather than establish causes or predict future behaviors.
10. Dietary Habits and Lifestyle Diseases (Nutrition Science): By describing the dietary patterns of different population groups and correlating them with the prevalence of lifestyle diseases, researchers perform descriptive research. They merely describe observed connections without altering any diet plans or lifestyles.
11. Shifts in Global Energy Consumption (Environmental Economics): When researchers describe the global patterns of energy consumption and how they’ve shifted over the years, they conduct descriptive research. The focus is on recording and portraying the current state without attempting to infer causes or predict the future.
12. Literacy and Employment Rates in Rural Areas (Sociology): A study aims at describing the literacy rates in rural areas and correlating it with employment levels. It falls under descriptive research because it maps the scenario without manipulating parameters or proving a hypothesis.
13. Women Representation in Tech Industry (Gender Studies): A detailed description of the presence and roles of women across various sectors of the tech industry is a typical case of descriptive research. It merely observes and records the status quo without establishing causality or making predictions.
14. Impact of Urban Green Spaces on Mental Health (Environmental Psychology): When researchers document and describe the influence of green urban spaces on residents’ mental health, they are undertaking descriptive research. They seek purely to understand the current state rather than exploring cause-effect relationships.
15. Trends in Smartphone usage among Elderly (Gerontology): Research describing how the elderly population utilizes smartphones, including popular features and challenges encountered, serves as descriptive research. Researcher’s aim is merely to capture what is happening without manipulating variables or posing predictions.
16. Shifts in Voter Preferences (Political Science): A study describing the shift in voter preferences during a particular electoral cycle is descriptive research. It simply records the preferences revealed without drawing causal inferences or suggesting future voting patterns.
17. Understanding Trust in Autonomous Vehicles (Transportation Psychology): This comprises research describing public attitudes and trust levels when it comes to autonomous vehicles. By merely depicting observed sentiments, without engineering any situations or offering predictions, it’s considered descriptive research.
18. The Impact of Social Media on Body Image (Psychology): Descriptive research to outline the experiences and perceptions of individuals relating to body image in the era of social media. Observing these elements without altering any variables qualifies it as descriptive research.
Descriptive vs Experimental Research
Descriptive research merely observes, records, and presents the actual state of affairs without manipulating any variables, while experimental research involves deliberately changing one or more variables to determine their effect on a particular outcome.
De Vaus (2001) succinctly explains that descriptive studies find out what is going on , but experimental research finds out why it’s going on /
Simple definitions are below:
- Descriptive research is primarily about describing the characteristics or behaviors in a population, often through surveys or observational methods. It provides rich detail about a specific phenomenon but does not allow for conclusive causal statements; however, it can offer essential leads or ideas for further experimental research (Ivey, 2016).
- Experimental research , often conducted in controlled environments, aims to establish causal relationships by manipulating one or more independent variables and observing the effects on dependent variables (Devi, 2017; Mukherjee, 2019).
Experimental designs often involve a control group and random assignment . While it can provide compelling evidence for cause and effect, its artificial setting might not perfectly mirror real-worldly conditions, potentially affecting the generalizability of its findings.
These two types of research are complementary, with descriptive studies often leading to hypotheses that are then tested experimentally (Devi, 2017; Zhao et al., 2021).
Benefits and Limitations of Descriptive Research
Descriptive research offers several benefits: it allows researchers to gather a vast amount of data and present a complete picture of the situation or phenomenon under study, even within large groups or over long time periods.
It’s also flexible in terms of the variety of methods used, such as surveys, observations, and case studies, and it can be instrumental in identifying patterns or trends and generating hypotheses (Erickson, 2017).
However, it also has its limitations.
The primary drawback is that it can’t establish cause-effect relationships, as no variables are manipulated. This lack of control over variables also opens up possibilities for bias, as researchers might inadvertently influence responses during data collection (De Vaus, 2001).
Additionally, the findings of descriptive research are often not generalizable since they are heavily reliant on the chosen sample’s characteristics.
See More Types of Research Design Here
De Vaus, D. A. (2001). Research Design in Social Research . SAGE Publications.
Devi, P. S. (2017). Research Methodology: A Handbook for Beginners . Notion Press.
Erickson, G. S. (2017). Descriptive research design. In New Methods of Market Research and Analysis (pp. 51-77). Edward Elgar Publishing.
Gresham, B. B. (2016). Concepts of Evidence-based Practice for the Physical Therapist Assistant . F.A. Davis Company.
Ivey, J. (2016). Is descriptive research worth doing?. Pediatric nursing , 42 (4), 189. ( Source )
Krishnaswamy, K. N., Sivakumar, A. I., & Mathirajan, M. (2009). Management Research Methodology: Integration of Principles, Methods and Techniques . Pearson Education.
Matanda, E. (2022). Research Methods and Statistics for Cross-Cutting Research: Handbook for Multidisciplinary Research . Langaa RPCIG.
Monsen, E. R., & Van Horn, L. (2007). Research: Successful Approaches . American Dietetic Association.
Mukherjee, S. P. (2019). A Guide to Research Methodology: An Overview of Research Problems, Tasks and Methods . CRC Press.
Siedlecki, S. L. (2020). Understanding descriptive research designs and methods. Clinical Nurse Specialist , 34 (1), 8-12. ( Source )
Zhao, P., Ross, K., Li, P., & Dennis, B. (2021). Making Sense of Social Research Methodology: A Student and Practitioner Centered Approach . SAGE Publications.

Dave Cornell (PhD)
Dr. Cornell has worked in education for more than 20 years. His work has involved designing teacher certification for Trinity College in London and in-service training for state governments in the United States. He has trained kindergarten teachers in 8 countries and helped businessmen and women open baby centers and kindergartens in 3 countries.
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Social Learning Theory Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 10 Latent Learning Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 13 Sociocultural Theory Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 21 Experiential Learning Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Social Learning Theory Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 10 Latent Learning Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 13 Sociocultural Theory Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 21 Experiential Learning Examples
1 thought on “18 Descriptive Research Examples”
Very nice, educative article. I appreciate the efforts.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
Analytical Research: What is it, Importance + Examples

Finding knowledge is a loose translation of the word “research.” It’s a systematic and scientific way of researching a particular subject. As a result, research is a form of scientific investigation that seeks to learn more. Analytical research is one of them.
Any kind of research is a way to learn new things. In this research, data and other pertinent information about a project are assembled; after the information is gathered and assessed, the sources are used to support a notion or prove a hypothesis.
An individual can successfully draw out minor facts to make more significant conclusions about the subject matter by using critical thinking abilities (a technique of thinking that entails identifying a claim or assumption and determining whether it is accurate or untrue).
What is analytical research?
This particular kind of research calls for using critical thinking abilities and assessing data and information pertinent to the project at hand.
Determines the causal connections between two or more variables. The analytical study aims to identify the causes and mechanisms underlying the trade deficit’s movement throughout a given period.
It is used by various professionals, including psychologists, doctors, and students, to identify the most pertinent material during investigations. One learns crucial information from analytical research that helps them contribute fresh concepts to the work they are producing.
Some researchers perform it to uncover information that supports ongoing research to strengthen the validity of their findings. Other scholars engage in analytical research to generate fresh perspectives on the subject.
Various approaches to performing research include literary analysis, Gap analysis , general public surveys, clinical trials, and meta-analysis.
Importance of analytical research
The goal of analytical research is to develop new ideas that are more believable by combining numerous minute details.
The analytical investigation is what explains why a claim should be trusted. Finding out why something occurs is complex. You need to be able to evaluate information critically and think critically.
This kind of information aids in proving the validity of a theory or supporting a hypothesis. It assists in recognizing a claim and determining whether it is true.
Analytical kind of research is valuable to many people, including students, psychologists, marketers, and others. It aids in determining which advertising initiatives within a firm perform best. In the meantime, medical research and research design determine how well a particular treatment does.
Thus, analytical research can help people achieve their goals while saving lives and money.
Methods of Conducting Analytical Research
Analytical research is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information to make inferences and reach conclusions. Depending on the purpose of the research and the data you have access to, you can conduct analytical research using a variety of methods. Here are a few typical approaches:
Quantitative research
Numerical data are gathered and analyzed using this method. Statistical methods are then used to analyze the information, which is often collected using surveys, experiments, or pre-existing datasets. Results from quantitative research can be measured, compared, and generalized numerically.
Qualitative research
In contrast to quantitative research, qualitative research focuses on collecting non-numerical information. It gathers detailed information using techniques like interviews, focus groups, observations, or content research. Understanding social phenomena, exploring experiences, and revealing underlying meanings and motivations are all goals of qualitative research.
Mixed methods research
This strategy combines quantitative and qualitative methodologies to grasp a research problem thoroughly. Mixed methods research often entails gathering and evaluating both numerical and non-numerical data, integrating the results, and offering a more comprehensive viewpoint on the research issue.
Experimental research
Experimental research is frequently employed in scientific trials and investigations to establish causal links between variables. This approach entails modifying variables in a controlled environment to identify cause-and-effect connections. Researchers randomly divide volunteers into several groups, provide various interventions or treatments, and track the results.
Observational research
With this approach, behaviors or occurrences are observed and methodically recorded without any outside interference or variable data manipulation . Both controlled surroundings and naturalistic settings can be used for observational research . It offers useful insights into behaviors that occur in the actual world and enables researchers to explore events as they naturally occur.
Case study research
This approach entails thorough research of a single case or a small group of related cases. Case-control studies frequently include a variety of information sources, including observations, records, and interviews. They offer rich, in-depth insights and are particularly helpful for researching complex phenomena in practical settings.
Secondary data analysis
Examining secondary information is time and money-efficient, enabling researchers to explore new research issues or confirm prior findings. With this approach, researchers examine previously gathered information for a different reason. Information from earlier cohort studies, accessible databases, or corporate documents may be included in this.
Content analysis
Content research is frequently employed in social sciences, media observational studies, and cross-sectional studies. This approach systematically examines the content of texts, including media, speeches, and written documents. Themes, patterns, or keywords are found and categorized by researchers to make inferences about the content.
Depending on your research objectives, the resources at your disposal, and the type of data you wish to analyze, selecting the most appropriate approach or combination of methodologies is crucial to conducting analytical research.
Examples of analytical research
Analytical research takes a unique measurement. Instead, you would consider the causes and changes to the trade imbalance. Detailed statistics and statistical checks help guarantee that the results are significant.
For example, it can look into why the value of the Japanese Yen has decreased. This is so that an analytical study can consider “how” and “why” questions.
Another example is that someone might conduct analytical research to identify a study’s gap. It presents a fresh perspective on your data. Therefore, it aids in supporting or refuting notions.
Descriptive vs analytical research
Here are the key differences between descriptive research and analytical research:
The study of cause and effect makes extensive use of analytical research. It benefits from numerous academic disciplines, including marketing, health, and psychology, because it offers more conclusive information for addressing research issues.
QuestionPro offers solutions for every issue and industry, making it more than just survey software. For handling data, we also have systems like our InsightsHub research library.
You may make crucial decisions quickly while using QuestionPro to understand your clients and other study subjects better. Make use of the possibilities of the enterprise-grade research suite right away!
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 8 Data Trends to Understand the Future of Data
May 30, 2024

Top 12 Interactive Presentation Software to Engage Your User
May 29, 2024

Trend Report: Guide for Market Dynamics & Strategic Analysis

Cannabis Industry Business Intelligence: Impact on Research
May 28, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what , where , when , and how questions , but not why questions.
A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables . Unlike in experimental research , the researcher does not control or manipulate any of the variables, but only observes and measures them.
Table of contents
When to use a descriptive research design, descriptive research methods.
Descriptive research is an appropriate choice when the research aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, and categories.
It is useful when not much is known yet about the topic or problem. Before you can research why something happens, you need to understand how, when, and where it happens.
- How has the London housing market changed over the past 20 years?
- Do customers of company X prefer product Y or product Z?
- What are the main genetic, behavioural, and morphological differences between European wildcats and domestic cats?
- What are the most popular online news sources among under-18s?
- How prevalent is disease A in population B?
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research , though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable .
Survey research allows you to gather large volumes of data that can be analysed for frequencies, averages, and patterns. Common uses of surveys include:
- Describing the demographics of a country or region
- Gauging public opinion on political and social topics
- Evaluating satisfaction with a company’s products or an organisation’s services
Observations
Observations allow you to gather data on behaviours and phenomena without having to rely on the honesty and accuracy of respondents. This method is often used by psychological, social, and market researchers to understand how people act in real-life situations.
Observation of physical entities and phenomena is also an important part of research in the natural sciences. Before you can develop testable hypotheses , models, or theories, it’s necessary to observe and systematically describe the subject under investigation.
Case studies
A case study can be used to describe the characteristics of a specific subject (such as a person, group, event, or organisation). Instead of gathering a large volume of data to identify patterns across time or location, case studies gather detailed data to identify the characteristics of a narrowly defined subject.
Rather than aiming to describe generalisable facts, case studies often focus on unusual or interesting cases that challenge assumptions, add complexity, or reveal something new about a research problem .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 31 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/descriptive-research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, correlational research | guide, design & examples, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods.
Critical Writing 101
Descriptive vs analytical vs critical writing.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | April 2017
Across the thousands of students we work with , descriptive writing (as opposed to critical or analytical writing) is an incredibly pervasive problem . In fact, it’s probably the biggest killer of marks in dissertations, theses and research papers . So, in this post, we’ll explain the difference between descriptive and analytical writing in straightforward terms, along with plenty of practical examples.
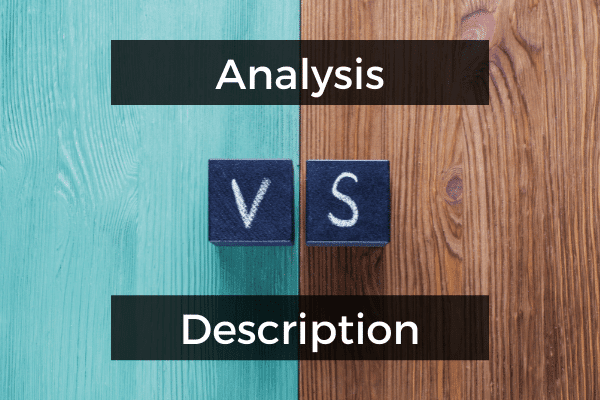
Descriptive vs Analytical Writing
Writing critically is one of the most important skills you’ll need to master for your academic journey, but what exactly does this mean?
Well, when it comes to writing, at least for academic purposes, there are two main types – descriptive writing and critical writing. Critical writing is also sometimes referred to as analytical writing, so we’ll use these two terms interchangeably.
To understand what constitutes critical (or analytical) writing, it’s useful to compare it against its opposite, descriptive writing. At the most basic level, descriptive writing merely communicates the “ what ”, “ where ”, “ when ” or “ who ”. In other words, it describes a thing, place, time or person. It doesn’t consider anything beyond that or explore the situation’s impact, importance or meaning. Here’s an example of a descriptive sentence:
“Yesterday, the president unexpectedly fired the minister of finance.”
As you can see, this sentence just states what happened, when it happened and who was involved. Classic descriptive writing.
Contrasted to this, critical writing takes things a step further and unveils the “ so what? ” – in other words, it explains the impact or consequence of a given situation. Let’s stick with the same event and look at an example of analytical writing:
“The president’s unexpected firing of the well-respected finance minister had an immediate negative impact on investor confidence. This led to a sharp decrease in the value of the local currency, especially against the US dollar. This devaluation means that all dollar-based imports are now expected to rise in cost, thereby raising the cost of living for citizens, and reducing disposable income.”
As you can see in this example, the descriptive version only tells us what happened (the president fired the finance minister), whereas the critical version goes on to discuss some of the impacts of the president’s actions.

Ideally, critical writing should always link back to the broader objectives of the paper or project, explaining what each thing or event means in relation to those objectives. In a dissertation or thesis, this would involve linking the discussion back to the research aims, objectives and research questions – in other words, the golden thread .
Sounds a bit fluffy and conceptual? Let’s look at an example:
If your research aims involved understanding how the local environment impacts demand for specialty imported vegetables, you would need to explain how the devaluation of the local currency means that the imported vegetables would become more expensive relative to locally farmed options. This in turn would likely have a negative impact on sales, as consumers would turn to cheaper local alternatives.
As you can see, critical (or analytical) writing goes beyond just describing (that’s what descriptive writing covers) and instead focuses on the meaning of things, events or situations, especially in relation to the core research aims and questions.
Need a helping hand?
But wait, there’s more.
This “ what vs so what” distinction is important in understanding the difference between description and analysis, but it is not the only difference – the differences go deeper than this. The table below explains some other key differences between descriptive and analytical writing.
Should I avoid descriptive writing altogether?
Not quite. For the most part, you’ll need some descriptive writing to lay the foundation for the critical, analytical writing. In other words, you’ll usually need to state the “what” before you can discuss the “so what”. Therefore, description is simply unavoidable and in fact quite essential , but you do want to keep it to a minimum and focus your word count on the analytical side of things.
As you write, a good rule of thumb is to identify every what (in other words, every descriptive point you make) and then check whether it is accompanied by a so what (in other words, a critical conclusion regarding its meaning or impact).
Of course, this won’t always be necessary as some conclusions are fairly obvious and go without saying. But, this basic practice should help you minimise description, maximise analysis, and most importantly, earn you marks!
Let’s recap.
So, the key takeaways for this post are as follows:
- Descriptive writing focuses on the what , while critical/analytical writing focuses on the so what .
- Analytical writing should link the discussion back to the research aims, objectives or research questions (the golden thread).
- Some amount of description will always be needed, but aim to minimise description and maximise analysis to earn higher marks.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

19 Comments
Thank you so much. This was helpful and a switch from the bad writing habits to the good habits.
Great to hear that, Sarah. Glad you found it useful!
I am currently working on my Masters Thesis and found this extremely informative and helpful. Thank you kindly.
I’m currently a University student and this is so helpful. Thank you.
It really helped me to get the exact meaning of analytical writing. Differences between the two explains it well
Thank you! this was very useful
With much appreciation, I say thank you. Your explanations are down to earth. It has been helpful.
Very helpful towards my theses journey! Many thanks 👍
very helpful
very helpful indeed
Thanks Derek for the useful coaching
Thank you for sharing this. I was stuck on descriptive now I can do my corrections. Thank you.
I was struggling to differentiate between descriptive and analytical writing. I googled and found this as it is so helpful. Thank you for sharing.
I am glad to see this differences of descriptive against analytical writing. This is going to improve my masters dissertation
Thanks in deed. It was helpful
Thank you so much. I’m now better informed
Busy with MBA in South Africa, this is very helpful as most of the writing requires one to expound on the topics. thanks for this, it’s a salvation from watching the blinking cursor for hours while figuring out what to write to hit the 5000 word target 😂
It’s been fantastic and enriching. Thanks a lot, GRAD COACH.
Wonderful explanation of descriptive vs analytic writing with examples. This is going to be greatly helpful for me as I am writing my thesis at the moment. Thank you Grad Coach. I follow your YouTube videos and subscribed and liked every time I watch one.
Very useful piece. thanks
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Descriptive Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods

One of the components of research is getting enough information about the research problem—the what, how, when and where answers, which is why descriptive research is an important type of research. It is very useful when conducting research whose aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, correlations, and categories.
This research method takes a problem with little to no relevant information and gives it a befitting description using qualitative and quantitative research method s. Descriptive research aims to accurately describe a research problem.
In the subsequent sections, we will be explaining what descriptive research means, its types, examples, and data collection methods.
What is Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is a type of research that describes a population, situation, or phenomenon that is being studied. It focuses on answering the how, what, when, and where questions If a research problem, rather than the why.
This is mainly because it is important to have a proper understanding of what a research problem is about before investigating why it exists in the first place.
For example, an investor considering an investment in the ever-changing Amsterdam housing market needs to understand what the current state of the market is, how it changes (increasing or decreasing), and when it changes (time of the year) before asking for the why. This is where descriptive research comes in.
What Are The Types of Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is classified into different types according to the kind of approach that is used in conducting descriptive research. The different types of descriptive research are highlighted below:
- Descriptive-survey
Descriptive survey research uses surveys to gather data about varying subjects. This data aims to know the extent to which different conditions can be obtained among these subjects.
For example, a researcher wants to determine the qualification of employed professionals in Maryland. He uses a survey as his research instrument , and each item on the survey related to qualifications is subjected to a Yes/No answer.
This way, the researcher can describe the qualifications possessed by the employed demographics of this community.
- Descriptive-normative survey
This is an extension of the descriptive survey, with the addition being the normative element. In the descriptive-normative survey, the results of the study should be compared with the norm.
For example, an organization that wishes to test the skills of its employees by a team may have them take a skills test. The skills tests are the evaluation tool in this case, and the result of this test is compared with the norm of each role.
If the score of the team is one standard deviation above the mean, it is very satisfactory, if within the mean, satisfactory, and one standard deviation below the mean is unsatisfactory.
- Descriptive-status
This is a quantitative description technique that seeks to answer questions about real-life situations. For example, a researcher researching the income of the employees in a company, and the relationship with their performance.
A survey will be carried out to gather enough data about the income of the employees, then their performance will be evaluated and compared to their income. This will help determine whether a higher income means better performance and low income means lower performance or vice versa.
- Descriptive-analysis
The descriptive-analysis method of research describes a subject by further analyzing it, which in this case involves dividing it into 2 parts. For example, the HR personnel of a company that wishes to analyze the job role of each employee of the company may divide the employees into the people that work at the Headquarters in the US and those that work from Oslo, Norway office.
A questionnaire is devised to analyze the job role of employees with similar salaries and who work in similar positions.
- Descriptive classification
This method is employed in biological sciences for the classification of plants and animals. A researcher who wishes to classify the sea animals into different species will collect samples from various search stations, then classify them accordingly.
- Descriptive-comparative
In descriptive-comparative research, the researcher considers 2 variables that are not manipulated, and establish a formal procedure to conclude that one is better than the other. For example, an examination body wants to determine the better method of conducting tests between paper-based and computer-based tests.
A random sample of potential participants of the test may be asked to use the 2 different methods, and factors like failure rates, time factors, and others will be evaluated to arrive at the best method.
- Correlative Survey
Correlative surveys are used to determine whether the relationship between 2 variables is positive, negative, or neutral. That is, if 2 variables say X and Y are directly proportional, inversely proportional or are not related to each other.
Examples of Descriptive Research
There are different examples of descriptive research, that may be highlighted from its types, uses, and applications. However, we will be restricting ourselves to only 3 distinct examples in this article.
- Comparing Student Performance:
An academic institution may wish 2 compare the performance of its junior high school students in English language and Mathematics. This may be used to classify students based on 2 major groups, with one group going ahead to study while courses, while the other study courses in the Arts & Humanities field.
Students who are more proficient in mathematics will be encouraged to go into STEM and vice versa. Institutions may also use this data to identify students’ weak points and work on ways to assist them.
- Scientific Classification
During the major scientific classification of plants, animals, and periodic table elements, the characteristics and components of each subject are evaluated and used to determine how they are classified.
For example, living things may be classified into kingdom Plantae or kingdom animal is depending on their nature. Further classification may group animals into mammals, pieces, vertebrae, invertebrae, etc.
All these classifications are made a result of descriptive research which describes what they are.
- Human Behavior
When studying human behaviour based on a factor or event, the researcher observes the characteristics, behaviour, and reaction, then use it to conclude. A company willing to sell to its target market needs to first study the behaviour of the market.
This may be done by observing how its target reacts to a competitor’s product, then use it to determine their behaviour.
What are the Characteristics of Descriptive Research?
The characteristics of descriptive research can be highlighted from its definition, applications, data collection methods, and examples. Some characteristics of descriptive research are:
- Quantitativeness
Descriptive research uses a quantitative research method by collecting quantifiable information to be used for statistical analysis of the population sample. This is very common when dealing with research in the physical sciences.
- Qualitativeness
It can also be carried out using the qualitative research method, to properly describe the research problem. This is because descriptive research is more explanatory than exploratory or experimental.
- Uncontrolled variables
In descriptive research, researchers cannot control the variables like they do in experimental research.
- The basis for further research
The results of descriptive research can be further analyzed and used in other research methods. It can also inform the next line of research, including the research method that should be used.
This is because it provides basic information about the research problem, which may give birth to other questions like why a particular thing is the way it is.
Why Use Descriptive Research Design?
Descriptive research can be used to investigate the background of a research problem and get the required information needed to carry out further research. It is used in multiple ways by different organizations, and especially when getting the required information about their target audience.
- Define subject characteristics :
It is used to determine the characteristics of the subjects, including their traits, behaviour, opinion, etc. This information may be gathered with the use of surveys, which are shared with the respondents who in this case, are the research subjects.
For example, a survey evaluating the number of hours millennials in a community spends on the internet weekly, will help a service provider make informed business decisions regarding the market potential of the community.
- Measure Data Trends
It helps to measure the changes in data over some time through statistical methods. Consider the case of individuals who want to invest in stock markets, so they evaluate the changes in prices of the available stocks to make a decision investment decision.
Brokerage companies are however the ones who carry out the descriptive research process, while individuals can view the data trends and make decisions.
Descriptive research is also used to compare how different demographics respond to certain variables. For example, an organization may study how people with different income levels react to the launch of a new Apple phone.
This kind of research may take a survey that will help determine which group of individuals are purchasing the new Apple phone. Do the low-income earners also purchase the phone, or only the high-income earners do?
Further research using another technique will explain why low-income earners are purchasing the phone even though they can barely afford it. This will help inform strategies that will lure other low-income earners and increase company sales.
- Validate existing conditions
When you are not sure about the validity of an existing condition, you can use descriptive research to ascertain the underlying patterns of the research object. This is because descriptive research methods make an in-depth analysis of each variable before making conclusions.
- Conducted Overtime
Descriptive research is conducted over some time to ascertain the changes observed at each point in time. The higher the number of times it is conducted, the more authentic the conclusion will be.
What are the Disadvantages of Descriptive Research?
- Response and Non-response Bias
Respondents may either decide not to respond to questions or give incorrect responses if they feel the questions are too confidential. When researchers use observational methods, respondents may also decide to behave in a particular manner because they feel they are being watched.
- The researcher may decide to influence the result of the research due to personal opinion or bias towards a particular subject. For example, a stockbroker who also has a business of his own may try to lure investors into investing in his own company by manipulating results.
- A case-study or sample taken from a large population is not representative of the whole population.
- Limited scope:The scope of descriptive research is limited to the what of research, with no information on why thereby limiting the scope of the research.
What are the Data Collection Methods in Descriptive Research?
There are 3 main data collection methods in descriptive research, namely; observational method, case study method, and survey research.
1. Observational Method
The observational method allows researchers to collect data based on their view of the behaviour and characteristics of the respondent, with the respondents themselves not directly having an input. It is often used in market research, psychology, and some other social science research to understand human behaviour.
It is also an important aspect of physical scientific research, with it being one of the most effective methods of conducting descriptive research . This process can be said to be either quantitative or qualitative.
Quantitative observation involved the objective collection of numerical data , whose results can be analyzed using numerical and statistical methods.
Qualitative observation, on the other hand, involves the monitoring of characteristics and not the measurement of numbers. The researcher makes his observation from a distance, records it, and is used to inform conclusions.
2. Case Study Method
A case study is a sample group (an individual, a group of people, organizations, events, etc.) whose characteristics are used to describe the characteristics of a larger group in which the case study is a subgroup. The information gathered from investigating a case study may be generalized to serve the larger group.
This generalization, may, however, be risky because case studies are not sufficient to make accurate predictions about larger groups. Case studies are a poor case of generalization.
3. Survey Research
This is a very popular data collection method in research designs. In survey research, researchers create a survey or questionnaire and distribute it to respondents who give answers.
Generally, it is used to obtain quick information directly from the primary source and also conducting rigorous quantitative and qualitative research. In some cases, survey research uses a blend of both qualitative and quantitative strategies.
Survey research can be carried out both online and offline using the following methods
- Online Surveys: This is a cheap method of carrying out surveys and getting enough responses. It can be carried out using Formplus, an online survey builder. Formplus has amazing tools and features that will help increase response rates.
- Offline Surveys: This includes paper forms, mobile offline forms , and SMS-based forms.
What Are The Differences Between Descriptive and Correlational Research?
Before going into the differences between descriptive and correlation research, we need to have a proper understanding of what correlation research is about. Therefore, we will be giving a summary of the correlation research below.
Correlational research is a type of descriptive research, which is used to measure the relationship between 2 variables, with the researcher having no control over them. It aims to find whether there is; positive correlation (both variables change in the same direction), negative correlation (the variables change in the opposite direction), or zero correlation (there is no relationship between the variables).
Correlational research may be used in 2 situations;
(i) when trying to find out if there is a relationship between two variables, and
(ii) when a causal relationship is suspected between two variables, but it is impractical or unethical to conduct experimental research that manipulates one of the variables.
Below are some of the differences between correlational and descriptive research:
- Definitions :
Descriptive research aims is a type of research that provides an in-depth understanding of the study population, while correlational research is the type of research that measures the relationship between 2 variables.
- Characteristics :
Descriptive research provides descriptive data explaining what the research subject is about, while correlation research explores the relationship between data and not their description.
- Predictions :
Predictions cannot be made in descriptive research while correlation research accommodates the possibility of making predictions.
Descriptive Research vs. Causal Research
Descriptive research and causal research are both research methodologies, however, one focuses on a subject’s behaviors while the latter focuses on a relationship’s cause-and-effect. To buttress the above point, descriptive research aims to describe and document the characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena of a particular or specific population or situation.
It focuses on providing an accurate and detailed account of an already existing state of affairs between variables. Descriptive research answers the questions of “what,” “where,” “when,” and “how” without attempting to establish any causal relationships or explain any underlying factors that might have caused the behavior.
Causal research, on the other hand, seeks to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It aims to point out the factors that influence or cause a particular result or behavior. Causal research involves manipulating variables, controlling conditions or a subgroup, and observing the resulting effects. The primary objective of causal research is to establish a cause-effect relationship and provide insights into why certain phenomena happen the way they do.
Descriptive Research vs. Analytical Research
Descriptive research provides a detailed and comprehensive account of a specific situation or phenomenon. It focuses on describing and summarizing data without making inferences or attempting to explain underlying factors or the cause of the factor.
It is primarily concerned with providing an accurate and objective representation of the subject of research. While analytical research goes beyond the description of the phenomena and seeks to analyze and interpret data to discover if there are patterns, relationships, or any underlying factors.
It examines the data critically, applies statistical techniques or other analytical methods, and draws conclusions based on the discovery. Analytical research also aims to explore the relationships between variables and understand the underlying mechanisms or processes involved.
Descriptive Research vs. Exploratory Research
Descriptive research is a research method that focuses on providing a detailed and accurate account of a specific situation, group, or phenomenon. This type of research describes the characteristics, behaviors, or relationships within the given context without looking for an underlying cause.
Descriptive research typically involves collecting and analyzing quantitative or qualitative data to generate descriptive statistics or narratives. Exploratory research differs from descriptive research because it aims to explore and gain firsthand insights or knowledge into a relatively unexplored or poorly understood topic.
It focuses on generating ideas, hypotheses, or theories rather than providing definitive answers. Exploratory research is often conducted at the early stages of a research project to gather preliminary information and identify key variables or factors for further investigation. It involves open-ended interviews, observations, or small-scale surveys to gather qualitative data.
Read More – Exploratory Research: What are its Method & Examples?
Descriptive Research vs. Experimental Research
Descriptive research aims to describe and document the characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena of a particular population or situation. It focuses on providing an accurate and detailed account of the existing state of affairs.
Descriptive research typically involves collecting data through surveys, observations, or existing records and analyzing the data to generate descriptive statistics or narratives. It does not involve manipulating variables or establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
Experimental research, on the other hand, involves manipulating variables and controlling conditions to investigate cause-and-effect relationships. It aims to establish causal relationships by introducing an intervention or treatment and observing the resulting effects.
Experimental research typically involves randomly assigning participants to different groups, such as control and experimental groups, and measuring the outcomes. It allows researchers to control for confounding variables and draw causal conclusions.
Related – Experimental vs Non-Experimental Research: 15 Key Differences
Descriptive Research vs. Explanatory Research
Descriptive research focuses on providing a detailed and accurate account of a specific situation, group, or phenomenon. It aims to describe the characteristics, behaviors, or relationships within the given context.
Descriptive research is primarily concerned with providing an objective representation of the subject of study without explaining underlying causes or mechanisms. Explanatory research seeks to explain the relationships between variables and uncover the underlying causes or mechanisms.
It goes beyond description and aims to understand the reasons or factors that influence a particular outcome or behavior. Explanatory research involves analyzing data, conducting statistical analyses, and developing theories or models to explain the observed relationships.
Descriptive Research vs. Inferential Research
Descriptive research focuses on describing and summarizing data without making inferences or generalizations beyond the specific sample or population being studied. It aims to provide an accurate and objective representation of the subject of study.
Descriptive research typically involves analyzing data to generate descriptive statistics, such as means, frequencies, or percentages, to describe the characteristics or behaviors observed.
Inferential research, however, involves making inferences or generalizations about a larger population based on a smaller sample.
It aims to draw conclusions about the population characteristics or relationships by analyzing the sample data. Inferential research uses statistical techniques to estimate population parameters, test hypotheses, and determine the level of confidence or significance in the findings.
Related – Inferential Statistics: Definition, Types + Examples
Conclusion
The uniqueness of descriptive research partly lies in its ability to explore both quantitative and qualitative research methods. Therefore, when conducting descriptive research, researchers have the opportunity to use a wide variety of techniques that aids the research process.
Descriptive research explores research problems in-depth, beyond the surface level thereby giving a detailed description of the research subject. That way, it can aid further research in the field, including other research methods .
It is also very useful in solving real-life problems in various fields of social science, physical science, and education.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- descriptive research
- descriptive research method
- example of descriptive research
- types of descriptive research
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Cross-Sectional Studies: Types, Pros, Cons & Uses
In this article, we’ll look at what cross-sectional studies are, how it applies to your research and how to use Formplus to collect...

Type I vs Type II Errors: Causes, Examples & Prevention
This article will discuss the two different types of errors in hypothesis testing and how you can prevent them from occurring in your research
Acceptance Sampling: Meaning, Examples, When to Use
In this post, we will discuss extensively what acceptance sampling is and when it is applied.
Extrapolation in Statistical Research: Definition, Examples, Types, Applications
In this article we’ll look at the different types and characteristics of extrapolation, plus how it contrasts to interpolation.
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..

What is Descriptive Research and How is it Used?

Introduction
What does descriptive research mean, why would you use a descriptive research design, what are the characteristics of descriptive research, examples of descriptive research, what are the data collection methods in descriptive research, how do you analyze descriptive research data, ensuring validity and reliability in the findings.
Conducting descriptive research offers researchers a way to present phenomena as they naturally occur. Rooted in an open-ended and non-experimental nature, this type of research focuses on portraying the details of specific phenomena or contexts, helping readers gain a clearer understanding of topics of interest.
From businesses gauging customer satisfaction to educators assessing classroom dynamics, the data collected from descriptive research provides invaluable insights across various fields.
This article aims to illuminate the essence, utility, characteristics, and methods associated with descriptive research, guiding those who wish to harness its potential in their respective domains.

At its core, descriptive research refers to a systematic approach used by researchers to collect, analyze, and present data about real-life phenomena to describe it in its natural context. It primarily aims to describe what exists, based on empirical observations .
Unlike experimental research, where variables are manipulated to observe outcomes, descriptive research deals with the "as-is" scenario to facilitate further research by providing a framework or new insights on which continuing studies can build.
Definition of descriptive research
Descriptive research is defined as a research method that observes and describes the characteristics of a particular group, situation, or phenomenon.
The goal is not to establish cause and effect relationships but rather to provide a detailed account of the situation.
The difference between descriptive and exploratory research
While both descriptive and exploratory research seek to provide insights into a topic or phenomenon, they differ in their focus. Exploratory research is more about investigating a topic to develop preliminary insights or to identify potential areas of interest.
In contrast, descriptive research offers detailed accounts and descriptions of the observed phenomenon, seeking to paint a full picture of what's happening.
The evolution of descriptive research in academia
Historically, descriptive research has played a foundational role in numerous academic disciplines. Anthropologists, for instance, used this approach to document cultures and societies. Psychologists have employed it to capture behaviors, emotions, and reactions.
Over time, the method has evolved, incorporating technological advancements and adapting to contemporary needs, yet its essence remains rooted in describing a phenomenon or setting as it is.
Descriptive research serves as a cornerstone in the research landscape for its ability to provide a detailed snapshot of life. Its unique qualities and methods make it an invaluable method for various research purposes. Here's why:
Benefits of obtaining a clear picture
Descriptive research captures the present state of phenomena, offering researchers a detailed reflection of situations. This unaltered representation is crucial for sectors like marketing, where understanding current consumer behavior can shape future strategies.
Facilitating data interpretation
Given its straightforward nature, descriptive research can provide data that's easier to interpret, both for researchers and their audiences. Rather than analyzing complex statistical relationships among variables, researchers present detailed descriptions of their qualitative observations . Researchers can engage in in depth analysis relating to their research question , but audiences can also draw insights from their own interpretations or reflections on potential underlying patterns.
Enhancing the clarity of the research problem
By presenting things as they are, descriptive research can help elucidate ambiguous research questions. A well-executed descriptive study can shine light on overlooked aspects of a problem, paving the way for further investigative research.
Addressing practical problems
In real-world scenarios, it's not always feasible to manipulate variables or set up controlled experiments. For instance, in social sciences, understanding cultural norms without interference is paramount. Descriptive research allows for such non-intrusive insights, ensuring genuine understanding.
Building a foundation for future research
Often, descriptive studies act as stepping stones for more complex research endeavors. By establishing baseline data and highlighting patterns, they create a platform upon which more intricate hypotheses can be built and tested in subsequent studies.
Descriptive research is distinguished by a set of hallmark characteristics that set it apart from other research methodologies . Recognizing these features can help researchers effectively design, implement , and interpret descriptive studies.
Specificity in the research question
As with all research, descriptive research starts with a well-defined research question aiming to detail a particular phenomenon. The specificity ensures that the study remains focused on gathering relevant data without unnecessary deviations.
Focus on the present situation
While some research methods aim to predict future trends or uncover historical truths, descriptive research is predominantly concerned with the present. It seeks to capture the current state of affairs, such as understanding today's consumer habits or documenting a newly observed phenomenon.
Standardized and structured methodology
To ensure credibility and consistency in results, descriptive research often employs standardized methods. Whether it's using a fixed set of survey questions or adhering to specific observation protocols, this structured approach ensures that data is collected uniformly, making it easier to compare and analyze.
Non-manipulative approach in observation
One of the standout features of descriptive research is its non-invasive nature. Researchers observe and document without influencing the research subject or the environment. This passive stance ensures that the data gathered is a genuine reflection of the phenomenon under study.
Replicability and consistency in results
Due to its structured methodology, findings from descriptive research can often be replicated in different settings or with different samples. This consistency adds to the credibility of the results, reinforcing the validity of the insights drawn from the study.
Analyze data quickly and efficiently with ATLAS.ti
Download a free trial to see how you can make sense of complex qualitative data.
Numerous fields and sectors conduct descriptive research for its versatile and detailed nature. Through its focus on presenting things as they naturally occur, it provides insights into a myriad of scenarios. Here are some tangible examples from diverse domains:
Conducting market research
Businesses often turn to data analysis through descriptive research to understand the demographics of their target market. For instance, a company launching a new product might survey potential customers to understand their age, gender, income level, and purchasing habits, offering valuable data for targeted marketing strategies.
Evaluating employee behaviors
Organizations rely on descriptive research designs to assess the behavior and attitudes of their employees. By conducting observations or surveys , companies can gather data on workplace satisfaction, collaboration patterns, or the impact of a new office layout on productivity.
Understanding consumer preferences
Brands aiming to understand their consumers' likes and dislikes often use descriptive research. By observing shopping behaviors or conducting product feedback surveys , they can gauge preferences and adjust their offerings accordingly.
Documenting historical patterns
Historians and anthropologists employ descriptive research to identify patterns through analysis of events or cultural practices. For instance, a historian might detail the daily life in a particular era, while an anthropologist might document rituals and ceremonies of a specific tribe.
Assessing student performance
Educational researchers can utilize descriptive studies to understand the effectiveness of teaching methodologies. By observing classrooms or surveying students, they can measure data trends and gauge the impact of a new teaching technique or curriculum on student engagement and performance.
Descriptive research methods aim to authentically represent situations and phenomena. These techniques ensure the collection of comprehensive and reliable data about the subject of interest.
The most appropriate descriptive research method depends on the research question and resources available for your research study.
Surveys and questionnaires
One of the most familiar tools in the researcher's arsenal, surveys and questionnaires offer a structured means of collecting data from a vast audience. Through carefully designed questions, researchers can obtain standardized responses that lend themselves to straightforward comparison and analysis in quantitative and qualitative research .
Survey research can manifest in various formats, from face-to-face interactions and telephone conversations to digital platforms. While surveys can reach a broad audience and generate quantitative data ripe for statistical analysis, they also come with the challenge of potential biases in design and rely heavily on respondent honesty.
Observations and case studies
Direct or participant observation is a method wherein researchers actively watch and document behaviors or events. A researcher might, for instance, observe the dynamics within a classroom or the behaviors of shoppers in a market setting.
Case studies provide an even deeper dive, focusing on a thorough analysis of a specific individual, group, or event. These methods present the advantage of capturing real-time, detailed data, but they might also be time-intensive and can sometimes introduce observer bias .
Interviews and focus groups
Interviews , whether they follow a structured script or flow more organically, are a powerful means to extract detailed insights directly from participants. On the other hand, focus groups gather multiple participants for discussions, aiming to gather diverse and collective opinions on a particular topic or product.
These methods offer the benefit of deep insights and adaptability in data collection . However, they necessitate skilled interviewers, and focus group settings might see individual opinions being influenced by group dynamics.
Document and content analysis
Here, instead of generating new data, researchers examine existing documents or content . This can range from studying historical records and newspapers to analyzing media content or literature.
Analyzing existing content offers the advantage of accessibility and can provide insights over longer time frames. However, the reliability and relevance of the content are paramount, and researchers must approach this method with a discerning eye.
Descriptive research data, rich in details and insights, necessitates meticulous analysis to derive meaningful conclusions. The analysis process transforms raw data into structured findings that can be communicated and acted upon.
Qualitative content analysis
For data collected through interviews , focus groups , observations , or open-ended survey questions , qualitative content analysis is a popular choice. This involves examining non-numerical data to identify patterns, themes, or categories.
By coding responses or observations , researchers can identify recurring elements, making it easier to comprehend larger data sets and draw insights.
Using descriptive statistics
When dealing with quantitative data from surveys or experiments, descriptive statistics are invaluable. Measures such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and frequency distributions help summarize data sets, providing a snapshot of the overall patterns.
Graphical representations like histograms, pie charts, or bar graphs can further help in visualizing these statistics.
Coding and categorizing the data
Both qualitative and quantitative data often require coding. Coding involves assigning labels to specific responses or behaviors to group similar segments of data. This categorization aids in identifying patterns, especially in vast data sets.
For instance, responses to open-ended questions in a survey can be coded based on keywords or sentiments, allowing for a more structured analysis.
Visual representation through graphs and charts
Visual aids like graphs, charts, and plots can simplify complex data, making it more accessible and understandable. Whether it's showcasing frequency distributions through histograms or mapping out relationships with networks, visual representations can elucidate trends and patterns effectively.
In the realm of research , the credibility of findings is paramount. Without trustworthiness in the results, even the most meticulously gathered data can lose its value. Two cornerstones that bolster the credibility of research outcomes are validity and reliability .
Validity: Measuring the right thing
Validity addresses the accuracy of the research. It seeks to answer the question: Is the research genuinely measuring what it aims to measure? In descriptive research, where the objective is to paint an authentic picture of the current state of affairs, ensuring validity is crucial.
For instance, if a study aims to understand consumer preferences for a product category, the questions posed should genuinely reflect those preferences and not veer into unrelated territories. Multiple forms of validity, including content, criterion, and construct validity, can be examined to ensure that the research instruments and processes are aligned with the research goals.
Reliability: Consistency in findings
Reliability, on the other hand, pertains to the consistency of the research findings. When a study demonstrates reliability, this suggests that others could repeat the study and the outcomes would remain consistent across repetitions.
In descriptive research, factors like the clarity of survey questions , the training of observers , and the standardization of interview protocols play a role in enhancing reliability. Techniques such as test-retest and internal consistency measurements can be employed to assess and improve reliability.

Make your research happen with ATLAS.ti
Analyze descriptive research with our powerful data analysis interface. Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti.

- Privacy Policy

Home » Descriptive Analytics – Methods, Tools and Examples
Descriptive Analytics – Methods, Tools and Examples
Table of Contents

Descriptive Analytics
Definition:
Descriptive analytics focused on describing or summarizing raw data and making it interpretable. This type of analytics provides insight into what has happened in the past. It involves the analysis of historical data to identify patterns, trends, and insights. Descriptive analytics often uses visualization tools to represent the data in a way that is easy to interpret.
Descriptive Analytics in Research
Descriptive analytics plays a crucial role in research, helping investigators understand and describe the data collected in their studies. Here’s how descriptive analytics is typically used in a research setting:
- Descriptive Statistics: In research, descriptive analytics often takes the form of descriptive statistics . This includes calculating measures of central tendency (like mean, median, and mode), measures of dispersion (like range, variance, and standard deviation), and measures of frequency (like count, percent, and frequency). These calculations help researchers summarize and understand their data.
- Visualizing Data: Descriptive analytics also involves creating visual representations of data to better understand and communicate research findings . This might involve creating bar graphs, line graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, box plots, and other visualizations.
- Exploratory Data Analysis: Before conducting any formal statistical tests, researchers often conduct an exploratory data analysis, which is a form of descriptive analytics. This might involve looking at distributions of variables, checking for outliers, and exploring relationships between variables.
- Initial Findings: Descriptive analytics are often reported in the results section of a research study to provide readers with an overview of the data. For example, a researcher might report average scores, demographic breakdowns, or the percentage of participants who endorsed each response on a survey.
- Establishing Patterns and Relationships: Descriptive analytics helps in identifying patterns, trends, or relationships in the data, which can guide subsequent analysis or future research. For instance, researchers might look at the correlation between variables as a part of descriptive analytics.
Descriptive Analytics Techniques
Descriptive analytics involves a variety of techniques to summarize, interpret, and visualize historical data. Some commonly used techniques include:
Statistical Analysis
This includes basic statistical methods like mean, median, mode (central tendency), standard deviation, variance (dispersion), correlation, and regression (relationships between variables).
Data Aggregation
It is the process of compiling and summarizing data to obtain a general perspective. It can involve methods like sum, count, average, min, max, etc., often applied to a group of data.
Data Mining
This involves analyzing large volumes of data to discover patterns, trends, and insights. Techniques used in data mining can include clustering (grouping similar data), classification (assigning data into categories), association rules (finding relationships between variables), and anomaly detection (identifying outliers).
Data Visualization
This involves presenting data in a graphical or pictorial format to provide clear and easy understanding of the data patterns, trends, and insights. Common data visualization methods include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, histograms, and more complex forms like heat maps and interactive dashboards.
This involves organizing data into informational summaries to monitor how different areas of a business are performing. Reports can be generated manually or automatically and can be presented in tables, graphs, or dashboards.
Cross-tabulation (or Pivot Tables)
It involves displaying the relationship between two or more variables in a tabular form. It can provide a deeper understanding of the data by allowing comparisons and revealing patterns and correlations that may not be readily apparent in raw data.
Descriptive Modeling
Some techniques use complex algorithms to interpret data. Examples include decision tree analysis, which provides a graphical representation of decision-making situations, and neural networks, which are used to identify correlations and patterns in large data sets.
Descriptive Analytics Tools
Some common Descriptive Analytics Tools are as follows:
Excel: Microsoft Excel is a widely used tool that can be used for simple descriptive analytics. It has powerful statistical and data visualization capabilities. Pivot tables are a particularly useful feature for summarizing and analyzing large data sets.
Tableau: Tableau is a data visualization tool that is used to represent data in a graphical or pictorial format. It can handle large data sets and allows for real-time data analysis.
Power BI: Power BI, another product from Microsoft, is a business analytics tool that provides interactive visualizations with self-service business intelligence capabilities.
QlikView: QlikView is a data visualization and discovery tool. It allows users to analyze data and use this data to support decision-making.
SAS: SAS is a software suite that can mine, alter, manage and retrieve data from a variety of sources and perform statistical analysis on it.
SPSS: SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) is a software package used for statistical analysis. It’s widely used in social sciences research but also in other industries.
Google Analytics: For web data, Google Analytics is a popular tool. It allows businesses to analyze in-depth detail about the visitors on their website, providing valuable insights that can help shape the success strategy of a business.
R and Python: Both are programming languages that have robust capabilities for statistical analysis and data visualization. With packages like pandas, matplotlib, seaborn in Python and ggplot2, dplyr in R, these languages are powerful tools for descriptive analytics.
Looker: Looker is a modern data platform that can take data from any database and let you start exploring and visualizing.
When to use Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics forms the base of the data analysis workflow and is typically the first step in understanding your business or organization’s data. Here are some situations when you might use descriptive analytics:
Understanding Past Behavior: Descriptive analytics is essential for understanding what has happened in the past. If you need to understand past sales trends, customer behavior, or operational performance, descriptive analytics is the tool you’d use.
Reporting Key Metrics: Descriptive analytics is used to establish and report key performance indicators (KPIs). It can help in tracking and presenting these KPIs in dashboards or regular reports.
Identifying Patterns and Trends: If you need to identify patterns or trends in your data, descriptive analytics can provide these insights. This might include identifying seasonality in sales data, understanding peak operational times, or spotting trends in customer behavior.
Informing Business Decisions: The insights provided by descriptive analytics can inform business strategy and decision-making. By understanding what has happened in the past, you can make more informed decisions about what steps to take in the future.
Benchmarking Performance: Descriptive analytics can be used to compare current performance against historical data. This can be used for benchmarking and setting performance goals.
Auditing and Regulatory Compliance: In sectors where compliance and auditing are essential, descriptive analytics can provide the necessary data and trends over specific periods.
Initial Data Exploration: When you first acquire a dataset, descriptive analytics is useful to understand the structure of the data, the relationships between variables, and any apparent anomalies or outliers.
Examples of Descriptive Analytics
Examples of Descriptive Analytics are as follows:
Retail Industry: A retail company might use descriptive analytics to analyze sales data from the past year. They could break down sales by month to identify any seasonality trends. For example, they might find that sales increase in November and December due to holiday shopping. They could also break down sales by product to identify which items are the most popular. This analysis could inform their purchasing and stocking decisions for the next year. Additionally, data on customer demographics could be analyzed to understand who their primary customers are, guiding their marketing strategies.
Healthcare Industry: In healthcare, descriptive analytics could be used to analyze patient data over time. For instance, a hospital might analyze data on patient admissions to identify trends in admission rates. They might find that admissions for certain conditions are higher at certain times of the year. This could help them allocate resources more effectively. Also, analyzing patient outcomes data can help identify the most effective treatments or highlight areas where improvement is needed.
Finance Industry: A financial firm might use descriptive analytics to analyze historical market data. They could look at trends in stock prices, trading volume, or economic indicators to inform their investment decisions. For example, analyzing the price-earnings ratios of stocks in a certain sector over time could reveal patterns that suggest whether the sector is currently overvalued or undervalued. Similarly, credit card companies can analyze transaction data to detect any unusual patterns, which could be signs of fraud.
Advantages of Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics plays a vital role in the world of data analysis, providing numerous advantages:
- Understanding the Past: Descriptive analytics provides an understanding of what has happened in the past, offering valuable context for future decision-making.
- Data Summarization: Descriptive analytics is used to simplify and summarize complex datasets, which can make the information more understandable and accessible.
- Identifying Patterns and Trends: With descriptive analytics, organizations can identify patterns, trends, and correlations in their data, which can provide valuable insights.
- Inform Decision-Making: The insights generated through descriptive analytics can inform strategic decisions and help organizations to react more quickly to events or changes in behavior.
- Basis for Further Analysis: Descriptive analytics lays the groundwork for further analytical activities. It’s the first necessary step before moving on to more advanced forms of analytics like predictive analytics (forecasting future events) or prescriptive analytics (advising on possible outcomes).
- Performance Evaluation: It allows organizations to evaluate their performance by comparing current results with past results, enabling them to see where improvements have been made and where further improvements can be targeted.
- Enhanced Reporting and Dashboards: Through the use of visualization techniques, descriptive analytics can improve the quality of reports and dashboards, making the data more understandable and easier to interpret for stakeholders at all levels of the organization.
- Immediate Value: Unlike some other types of analytics, descriptive analytics can provide immediate insights, as it doesn’t require complex models or deep analytical capabilities to provide value.
Disadvantages of Descriptive Analytics
While descriptive analytics offers numerous benefits, it also has certain limitations or disadvantages. Here are a few to consider:
- Limited to Past Data: Descriptive analytics primarily deals with historical data and provides insights about past events. It does not predict future events or trends and can’t help you understand possible future outcomes on its own.
- Lack of Deep Insights: While descriptive analytics helps in identifying what happened, it does not answer why it happened. For deeper insights, you would need to use diagnostic analytics, which analyzes data to understand the root cause of a particular outcome.
- Can Be Misleading: If not properly executed, descriptive analytics can sometimes lead to incorrect conclusions. For example, correlation does not imply causation, but descriptive analytics might tempt one to make such an inference.
- Data Quality Issues: The accuracy and usefulness of descriptive analytics are heavily reliant on the quality of the underlying data. If the data is incomplete, incorrect, or biased, the results of the descriptive analytics will be too.
- Over-reliance on Descriptive Analytics: Businesses may rely too much on descriptive analytics and not enough on predictive and prescriptive analytics. While understanding past and present data is important, it’s equally vital to forecast future trends and make data-driven decisions based on those predictions.
- Doesn’t Provide Actionable Insights: Descriptive analytics is used to interpret historical data and identify patterns and trends, but it doesn’t provide recommendations or courses of action. For that, prescriptive analytics is needed.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Digital Ethnography – Types, Methods and Examples

Predictive Analytics – Techniques, Tools and...

Big Data Analytics -Types, Tools and Methods

Diagnostic Analytics – Methods, Tools and...

Blockchain Research – Methods, Types and Examples

Social Network Analysis – Types, Tools and...
Child Care and Early Education Research Connections
Descriptive research studies.
Descriptive research is a type of research that is used to describe the characteristics of a population. It collects data that are used to answer a wide range of what, when, and how questions pertaining to a particular population or group. For example, descriptive studies might be used to answer questions such as: What percentage of Head Start teachers have a bachelor's degree or higher? What is the average reading ability of 5-year-olds when they first enter kindergarten? What kinds of math activities are used in early childhood programs? When do children first receive regular child care from someone other than their parents? When are children with developmental disabilities first diagnosed and when do they first receive services? What factors do programs consider when making decisions about the type of assessments that will be used to assess the skills of the children in their programs? How do the types of services children receive from their early childhood program change as children age?
Descriptive research does not answer questions about why a certain phenomenon occurs or what the causes are. Answers to such questions are best obtained from randomized and quasi-experimental studies . However, data from descriptive studies can be used to examine the relationships (correlations) among variables. While the findings from correlational analyses are not evidence of causality, they can help to distinguish variables that may be important in explaining a phenomenon from those that are not. Thus, descriptive research is often used to generate hypotheses that should be tested using more rigorous designs.
A variety of data collection methods may be used alone or in combination to answer the types of questions guiding descriptive research. Some of the more common methods include surveys, interviews, observations, case studies, and portfolios. The data collected through these methods can be either quantitative or qualitative. Quantitative data are typically analyzed and presenting using descriptive statistics . Using quantitative data, researchers may describe the characteristics of a sample or population in terms of percentages (e.g., percentage of population that belong to different racial/ethnic groups, percentage of low-income families that receive different government services) or averages (e.g., average household income, average scores of reading, mathematics and language assessments). Quantitative data, such as narrative data collected as part of a case study, may be used to organize, classify, and used to identify patterns of behaviors, attitudes, and other characteristics of groups.
Descriptive studies have an important role in early care and education research. Studies such as the National Survey of Early Care and Education and the National Household Education Surveys Program have greatly increased our knowledge of the supply of and demand for child care in the U.S. The Head Start Family and Child Experiences Survey and the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study Program have provided researchers, policy makers and practitioners with rich information about school readiness skills of children in the U.S.
Each of the methods used to collect descriptive data have their own strengths and limitations. The following are some of the strengths and limitations of descriptive research studies in general.
Study participants are questioned or observed in a natural setting (e.g., their homes, child care or educational settings).
Study data can be used to identify the prevalence of particular problems and the need for new or additional services to address these problems.
Descriptive research may identify areas in need of additional research and relationships between variables that require future study. Descriptive research is often referred to as "hypothesis generating research."
Depending on the data collection method used, descriptive studies can generate rich datasets on large and diverse samples.
Limitations:
Descriptive studies cannot be used to establish cause and effect relationships.
Respondents may not be truthful when answering survey questions or may give socially desirable responses.
The choice and wording of questions on a questionnaire may influence the descriptive findings.
Depending on the type and size of sample, the findings may not be generalizable or produce an accurate description of the population of interest.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Descriptive Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Descriptive research: what it is and how to use it.
8 min read Understanding the who, what and where of a situation or target group is an essential part of effective research and making informed business decisions.
For example you might want to understand what percentage of CEOs have a bachelor’s degree or higher. Or you might want to understand what percentage of low income families receive government support – or what kind of support they receive.
Descriptive research is what will be used in these types of studies.
In this guide we’ll look through the main issues relating to descriptive research to give you a better understanding of what it is, and how and why you can use it.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research is a research method used to try and determine the characteristics of a population or particular phenomenon.
Using descriptive research you can identify patterns in the characteristics of a group to essentially establish everything you need to understand apart from why something has happened.
Market researchers use descriptive research for a range of commercial purposes to guide key decisions.
For example you could use descriptive research to understand fashion trends in a given city when planning your clothing collection for the year. Using descriptive research you can conduct in depth analysis on the demographic makeup of your target area and use the data analysis to establish buying patterns.
Conducting descriptive research wouldn’t, however, tell you why shoppers are buying a particular type of fashion item.
Descriptive research design
Descriptive research design uses a range of both qualitative research and quantitative data (although quantitative research is the primary research method) to gather information to make accurate predictions about a particular problem or hypothesis.
As a survey method, descriptive research designs will help researchers identify characteristics in their target market or particular population.
These characteristics in the population sample can be identified, observed and measured to guide decisions.
Descriptive research characteristics
While there are a number of descriptive research methods you can deploy for data collection, descriptive research does have a number of predictable characteristics.
Here are a few of the things to consider:
Measure data trends with statistical outcomes
Descriptive research is often popular for survey research because it generates answers in a statistical form, which makes it easy for researchers to carry out a simple statistical analysis to interpret what the data is saying.
Descriptive research design is ideal for further research
Because the data collection for descriptive research produces statistical outcomes, it can also be used as secondary data for another research study.
Plus, the data collected from descriptive research can be subjected to other types of data analysis .
Uncontrolled variables
A key component of the descriptive research method is that it uses random variables that are not controlled by the researchers. This is because descriptive research aims to understand the natural behavior of the research subject.
It’s carried out in a natural environment
Descriptive research is often carried out in a natural environment. This is because researchers aim to gather data in a natural setting to avoid swaying respondents.
Data can be gathered using survey questions or online surveys.
For example, if you want to understand the fashion trends we mentioned earlier, you would set up a study in which a researcher observes people in the respondent’s natural environment to understand their habits and preferences.
Descriptive research allows for cross sectional study
Because of the nature of descriptive research design and the randomness of the sample group being observed, descriptive research is ideal for cross sectional studies – essentially the demographics of the group can vary widely and your aim is to gain insights from within the group.
This can be highly beneficial when you’re looking to understand the behaviors or preferences of a wider population.
Descriptive research advantages
There are many advantages to using descriptive research, some of them include:
Cost effectiveness
Because the elements needed for descriptive research design are not specific or highly targeted (and occur within the respondent’s natural environment) this type of study is relatively cheap to carry out.
Multiple types of data can be collected
A big advantage of this research type, is that you can use it to collect both quantitative and qualitative data. This means you can use the stats gathered to easily identify underlying patterns in your respondents’ behavior.
Descriptive research disadvantages
Potential reliability issues.
When conducting descriptive research it’s important that the initial survey questions are properly formulated.
If not, it could make the answers unreliable and risk the credibility of your study.
Potential limitations
As we’ve mentioned, descriptive research design is ideal for understanding the what, who or where of a situation or phenomenon.
However, it can’t help you understand the cause or effect of the behavior. This means you’ll need to conduct further research to get a more complete picture of a situation.
Descriptive research methods
Because descriptive research methods include a range of quantitative and qualitative research, there are several research methods you can use.
Use case studies
Case studies in descriptive research involve conducting in-depth and detailed studies in which researchers get a specific person or case to answer questions.
Case studies shouldn’t be used to generate results, rather it should be used to build or establish hypothesis that you can expand into further market research .
For example you could gather detailed data about a specific business phenomenon, and then use this deeper understanding of that specific case.
Use observational methods
This type of study uses qualitative observations to understand human behavior within a particular group.
By understanding how the different demographics respond within your sample you can identify patterns and trends.
As an observational method, descriptive research will not tell you the cause of any particular behaviors, but that could be established with further research.
Use survey research
Surveys are one of the most cost effective ways to gather descriptive data.
An online survey or questionnaire can be used in descriptive studies to gather quantitative information about a particular problem.
Survey research is ideal if you’re using descriptive research as your primary research.
Descriptive research examples
Descriptive research is used for a number of commercial purposes or when organizations need to understand the behaviors or opinions of a population.
One of the biggest examples of descriptive research that is used in every democratic country, is during elections.
Using descriptive research, researchers will use surveys to understand who voters are more likely to choose out of the parties or candidates available.
Using the data provided, researchers can analyze the data to understand what the election result will be.
In a commercial setting, retailers often use descriptive research to figure out trends in shopping and buying decisions.
By gathering information on the habits of shoppers, retailers can get a better understanding of the purchases being made.
Another example that is widely used around the world, is the national census that takes place to understand the population.
The research will provide a more accurate picture of a population’s demographic makeup and help to understand changes over time in areas like population age, health and education level.
Where Qualtrics helps with descriptive research
Whatever type of research you want to carry out, there’s a survey type that will work.
Qualtrics can help you determine the appropriate method and ensure you design a study that will deliver the insights you need.
Our experts can help you with your market research needs , ensuring you get the most out of Qualtrics market research software to design, launch and analyze your data to guide better, more accurate decisions for your organization.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Clin Res
- v.10(1); Jan-Mar 2019
Study designs: Part 2 – Descriptive studies
Rakesh aggarwal.
Department of Gastroenterology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
Priya Ranganathan
1 Department of Anaesthesiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
One of the first steps in planning a research study is the choice of study design. The available study designs are divided broadly into two types – observational and interventional. Of the various observational study designs, the descriptive design is the simplest. It allows the researcher to study and describe the distribution of one or more variables, without regard to any causal or other hypotheses. This article discusses the subtypes of descriptive study design, and their strengths and limitations.
INTRODUCTION
In our previous article in this series,[ 1 ] we introduced the concept of “study designs”– as “the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research question.” Study designs are primarily of two types – observational and interventional, with the former being loosely divided into “descriptive” and “analytical.” In this article, we discuss the descriptive study designs.
WHAT IS A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY?
A descriptive study is one that is designed to describe the distribution of one or more variables, without regard to any causal or other hypothesis.
TYPES OF DESCRIPTIVE STUDIES
Descriptive studies can be of several types, namely, case reports, case series, cross-sectional studies, and ecological studies. In the first three of these, data are collected on individuals, whereas the last one uses aggregated data for groups.
Case reports and case series
A case report refers to the description of a patient with an unusual disease or with simultaneous occurrence of more than one condition. A case series is similar, except that it is an aggregation of multiple (often only a few) similar cases. Many case reports and case series are anecdotal and of limited value. However, some of these bring to the fore a hitherto unrecognized disease and play an important role in advancing medical science. For instance, HIV/AIDS was first recognized through a case report of disseminated Kaposi's sarcoma in a young homosexual man,[ 2 ] and a case series of such men with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia.[ 3 ]
In other cases, description of a chance observation may open an entirely new line of investigation. Some examples include: fatal disseminated Bacillus Calmette–Guérin infection in a baby born to a mother taking infliximab for Crohn's disease suggesting that adminstration of infliximab may bring about reactivation of tuberculosis,[ 4 ] progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy following natalizumab treatment – describing a new adverse effect of drugs that target cell adhesion molecule α4-integrin,[ 5 ] and demonstration of a tumor caused by invasive transformed cancer cells from a colonizing tapeworm in an HIV-infected person.[ 6 ]
Cross-sectional studies
Studies with a cross-sectional study design involve the collection of information on the presence or level of one or more variables of interest (health-related characteristic), whether exposure (e.g., a risk factor) or outcome (e.g., a disease) as they exist in a defined population at one particular time. If these data are analyzed only to determine the distribution of one or more variables, these are “descriptive.” However, often, in a cross-sectional study, the investigator also assesses the relationship between the presence of an exposure and that of an outcome. Such cross-sectional studies are referred to as “analytical” and will be discussed in the next article in this series.
Cross-sectional studies can be thought of as providing a “snapshot” of the frequency and characteristics of a disease in a population at a particular point in time. These are very good for measuring the prevalence of a disease or of a risk factor in a population. Thus, these are very helpful in assessing the disease burden and healthcare needs.
Let us look at a study that was aimed to assess the prevalence of myopia among Indian children.[ 7 ] In this study, trained health workers visited schools in Delhi and tested visual acuity in all children studying in classes 1–9. Of the 9884 children screened, 1297 (13.1%) had myopia (defined as spherical refractive error of −0.50 diopters (D) or worse in either or both eyes), and the mean myopic error was −1.86 ± 1.4 D. Furthermore, overall, 322 (3.3%), 247 (2.5%) and 3 children had mild, moderate, and severe visual impairment, respectively. These parts of the study looked at the prevalence and degree of myopia or of visual impairment, and did not assess the relationship of one variable with another or test a causative hypothesis – these qualify as a descriptive cross-sectional study. These data would be helpful to a health planner to assess the need for a school eye health program, and to know the proportion of children in her jurisdiction who would need corrective glasses.
The authors did, subsequently in the paper, look at the relationship of myopia (an outcome) with children's age, gender, socioeconomic status, type of school, mother's education, etc. (each of which qualifies as an exposure). Those parts of the paper look at the relationship between different variables and thus qualify as having “analytical” cross-sectional design.
Sometimes, cross-sectional studies are repeated after a time interval in the same population (using the same subjects as were included in the initial study, or a fresh sample) to identify temporal trends in the occurrence of one or more variables, and to determine the incidence of a disease (i.e., number of new cases) or its natural history. Indeed, the investigators in the myopia study above visited the same children and reassessed them a year later. This separate follow-up study[ 8 ] showed that “new” myopia had developed in 3.4% of children (incidence rate), with a mean change of −1.09 ± 0.55 D. Among those with myopia at the time of the initial survey, 49.2% showed progression of myopia with a mean change of −0.27 ± 0.42 D.
Cross-sectional studies are usually simple to do and inexpensive. Furthermore, these usually do not pose much of a challenge from an ethics viewpoint.
However, this design does carry a risk of bias, i.e., the results of the study may not represent the true situation in the population. This could arise from either selection bias or measurement bias. The former relates to differences between the population and the sample studied. The myopia study included only those children who attended school, and the prevalence of myopia could have been different in those did not attend school (e.g., those with severe myopia may not be able to see the blackboard and hence may have been more likely to drop out of school). The measurement bias in this study would relate to the accuracy of measurement and the cutoff used. If the investigators had used a cutoff of −0.25 D (instead of −0.50 D) to define myopia, the prevalence would have been higher. Furthermore, if the measurements were not done accurately, some cases with myopia could have been missed, or vice versa, affecting the study results.
Ecological studies
Ecological (also sometimes called as correlational) study design involves looking for association between an exposure and an outcome across populations rather than in individuals. For instance, a study in the United States found a relation between household firearm ownership in various states and the firearm death rates during the period 2007–2010.[ 9 ] Thus, in this study, the unit of assessment was a state and not an individual.
These studies are convenient to do since the data have often already been collected and are available from a reliable source. This design is particularly useful when the differences in exposure between individuals within a group are much smaller than the differences in exposure between groups. For instance, the intake of particular food items is likely to vary less between people in a particular group but can vary widely across groups, for example, people living in different countries.
However, the ecological study design has some important limitations.First, an association between exposure and outcome at the group level may not be true at the individual level (a phenomenon also referred to as “ecological fallacy”).[ 10 ] Second, the association may be related to a third factor which in turn is related to both the exposure and the outcome, the so-called “confounding”. For instance, an ecological association between higher income level and greater cardiovascular mortality across countries may be related to a higher prevalence of obesity. Third, migration of people between regions with different exposure levels may also introduce an error. A fourth consideration may be the use of differing definitions for exposure, outcome or both in different populations.
Descriptive studies, irrespective of the subtype, are often very easy to conduct. For case reports, case series, and ecological studies, the data are already available. For cross-sectional studies, these can be easily collected (usually in one encounter). Thus, these study designs are often inexpensive, quick and do not need too much effort. Furthermore, these studies often do not face serious ethics scrutiny, except if the information sought to be collected is of confidential nature (e.g., sexual practices, substance use, etc.).
Descriptive studies are useful for estimating the burden of disease (e.g., prevalence or incidence) in a population. This information is useful for resource planning. For instance, information on prevalence of cataract in a city may help the government decide on the appropriate number of ophthalmologic facilities. Data from descriptive studies done in different populations or done at different times in the same population may help identify geographic variation and temporal change in the frequency of disease. This may help generate hypotheses regarding the cause of the disease, which can then be verified using another, more complex design.
DISADVANTAGES
As with other study designs, descriptive studies have their own pitfalls. Case reports and case-series refer to a solitary patient or to only a few cases, who may represent a chance occurrence. Hence, conclusions based on these run the risk of being non-representative, and hence unreliable. In cross-sectional studies, the validity of results is highly dependent on whether the study sample is well representative of the population proposed to be studied, and whether all the individual measurements were made using an accurate and identical tool, or not. If the information on a variable cannot be obtained accurately, for instance in a study where the participants are asked about socially unacceptable (e.g., promiscuity) or illegal (e.g., substance use) behavior, the results are unlikely to be reliable.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

Descriptive vs. Analytical Research in Sociology: A Comparative Study

Table of Contents
When we delve into the world of research, particularly in fields like patterns of social relationships , social interaction, and culture.">sociology , we encounter a myriad of methods designed to uncover the layers of human society and behavior. Two of the most fundamental research methods are descriptive and analytical research . Each plays a crucial role in understanding our world, but they do so in distinctly different ways. So, what exactly are these methods, and how do they compare when applied in the realm of social studies? Let’s embark on a comparative journey to understand these methodologies better.
Understanding Descriptive Research
Descriptive research is akin to the meticulous work of an artist attempting to capture the intricate details of a landscape. It aims to accurately describe the characteristics of a particular population or phenomenon. By painting a picture of the ‘what’ aspect, this method helps researchers to understand the prevalence of certain attributes, behaviors, or issues within a group.

Key Features of Descriptive Research
- Snapshot in time: It often involves studying a single point or period, providing a snapshot rather than a motion picture.
- Surveys and observations : Common tools include surveys , observations, and case studies .
- Quantitative data: It leans heavily on quantitative data to present findings in numerical format.
- No hypothesis testing: Unlike other research types, it doesn’t typically involve hypothesis testing.
When to Use Descriptive Research
- Establishing a baseline : When there’s a need to set a reference point for future studies or track changes over time.
- Exploratory purposes: When little is known about a topic and there’s a need to gather initial information that could inform future research.
- Policy-making: When organizations or government bodies need factual data to inform decisions and policies.
Exploring Analytical Research
On the flip side, analytical research steps beyond mere description to explore the ‘why’ and ‘how’. It’s like a detective piecing together clues to not just recount events, but to understand the relationships and causations behind them. Analytical researchers critically evaluate information to draw conclusions and generalizations that extend beyond the immediate data.
Key Characteristics of Analytical Research
- Critical evaluation: It involves a deep analysis of the available information to form judgments.
- Qualitative and quantitative data: Uses both numerical data and non-numerical data for a more comprehensive analysis.
- Hypothesis-driven: This method often starts with a hypothesis that the research is designed to test.
- Seeking patterns: Aims to identify patterns, relationships, and causations.
When to Opt for Analytical Research
- Understanding complexities: When the research question is complex and requires understanding the interplay of various factors.
- Building upon previous research: When expanding on existing knowledge or challenging prevailing theories.
- Recommendations for action: When research is aimed at providing actionable insights or solutions to problems.
Comparing Descriptive and Analytical Research in Real-World Scenarios
Imagine a sociologist aiming to tackle a pressing social issue, such as the dynamics of homelessness in urban areas. Descriptive research would enable them to establish the scale and scope of homelessness, identifying key demographics and patterns. Analytical research, however, would take these findings and probe deeper into the causes, examining the social, economic, and political factors that contribute to the situation and what can be done to alleviate it.
Advantages and Limitations
Each research type has its own set of strengths and weaknesses. Descriptive research is powerful for mapping out the landscape but may fall short in explaining the underlying reasons for observed phenomena. Analytical research, with its depth, can provide those explanations, but it may be more time-consuming and complex to conduct.
Choosing the Right Approach
Deciding between descriptive and analytical research often comes down to the specific objectives of the study. It’s not uncommon for researchers to employ both methods within the same broader research project to maximize their understanding of a topic.
In conclusion, descriptive and analytical research are two sides of the same coin, offering different lenses through which we can view and interpret the intricacies of social phenomena. By understanding their distinctions and applications, researchers can better design studies that yield rich, actionable insights into the fabric of society.
What do you think? Could a blend of both descriptive and analytical research provide a more holistic understanding of social issues? Are there situations where one method is clearly preferable over the other?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Research Methodologies & Methods
1 Logic of Inquiry in Social Research
- A Science of Society
- Comte’s Ideas on the Nature of Sociology
- Observation in Social Sciences
- Logical Understanding of Social Reality
2 Empirical Approach
- Empirical Approach
- Rules of Data Collection
- Cultural Relativism
- Problems Encountered in Data Collection
- Difference between Common Sense and Science
- What is Ethical?
- What is Normal?
- Understanding the Data Collected
- Managing Diversities in Social Research
- Problematising the Object of Study
- Conclusion: Return to Good Old Empirical Approach
3 Diverse Logic of Theory Building
- Concern with Theory in Sociology
- Concepts: Basic Elements of Theories
- Why Do We Need Theory?
- Hypothesis Description and Experimentation
- Controlled Experiment
- Designing an Experiment
- How to Test a Hypothesis
- Sensitivity to Alternative Explanations
- Rival Hypothesis Construction
- The Use and Scope of Social Science Theory
- Theory Building and Researcher’s Values
4 Theoretical Analysis
- Premises of Evolutionary and Functional Theories
- Critique of Evolutionary and Functional Theories
- Turning away from Functionalism
- What after Functionalism
- Post-modernism
- Trends other than Post-modernism
5 Issues of Epistemology
- Some Major Concerns of Epistemology
- Rationalism
- Phenomenology: Bracketing Experience
6 Philosophy of Social Science
- Foundations of Science
- Science, Modernity, and Sociology
- Rethinking Science
- Crisis in Foundation
7 Positivism and its Critique
- Heroic Science and Origin of Positivism
- Early Positivism
- Consolidation of Positivism
- Critiques of Positivism
8 Hermeneutics
- Methodological Disputes in the Social Sciences
- Tracing the History of Hermeneutics
- Hermeneutics and Sociology
- Philosophical Hermeneutics
- The Hermeneutics of Suspicion
- Phenomenology and Hermeneutics
9 Comparative Method
- Relationship with Common Sense; Interrogating Ideological Location
- The Historical Context
- Elements of the Comparative Approach
10 Feminist Approach
- Features of the Feminist Method
- Feminist Methods adopt the Reflexive Stance
- Feminist Discourse in India
11 Participatory Method
- Delineation of Key Features
12 Types of Research
- Basic and Applied Research
- Descriptive and Analytical Research
- Empirical and Exploratory Research
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- Explanatory (Causal) and Longitudinal Research
- Experimental and Evaluative Research
- Participatory Action Research
13 Methods of Research
- Evolutionary Method
- Comparative Method
- Historical Method
- Personal Documents
14 Elements of Research Design
- Structuring the Research Process
15 Sampling Methods and Estimation of Sample Size
- Classification of Sampling Methods
- Sample Size
16 Measures of Central Tendency
- Relationship between Mean, Mode, and Median
- Choosing a Measure of Central Tendency
17 Measures of Dispersion and Variability
- The Variance
- The Standard Deviation
- Coefficient of Variation
18 Statistical Inference- Tests of Hypothesis
- Statistical Inference
- Tests of Significance
19 Correlation and Regression
- Correlation
- Method of Calculating Correlation of Ungrouped Data
- Method Of Calculating Correlation Of Grouped Data
20 Survey Method
- Rationale of Survey Research Method
- History of Survey Research
- Defining Survey Research
- Sampling and Survey Techniques
- Operationalising Survey Research Tools
- Advantages and Weaknesses of Survey Research
21 Survey Design
- Preliminary Considerations
- Stages / Phases in Survey Research
- Formulation of Research Question
- Survey Research Designs
- Sampling Design
22 Survey Instrumentation
- Techniques/Instruments for Data Collection
- Questionnaire Construction
- Issues in Designing a Survey Instrument
23 Survey Execution and Data Analysis
- Problems and Issues in Executing Survey Research
- Data Analysis
- Ethical Issues in Survey Research
24 Field Research – I
- History of Field Research
- Ethnography
- Theme Selection
- Gaining Entry in the Field
- Key Informants
- Participant Observation
25 Field Research – II
- Interview its Types and Process
- Feminist and Postmodernist Perspectives on Interviewing
- Narrative Analysis
- Interpretation
- Case Study and its Types
- Life Histories
- Oral History
- PRA and RRA Techniques
26 Reliability, Validity and Triangulation
- Concepts of Reliability and Validity
- Three Types of “Reliability”
- Working Towards Reliability
- Procedural Validity
- Field Research as a Validity Check
- Method Appropriate Criteria
- Triangulation
- Ethical Considerations in Qualitative Research
27 Qualitative Data Formatting and Processing
- Qualitative Data Processing and Analysis
- Description
- Classification
- Making Connections
- Theoretical Coding
- Qualitative Content Analysis
28 Writing up Qualitative Data
- Problems of Writing Up
- Grasp and Then Render
- “Writing Down” and “Writing Up”
- Write Early
- Writing Styles
- First Draft
29 Using Internet and Word Processor
- What is Internet and How Does it Work?
- Internet Services
- Searching on the Web: Search Engines
- Accessing and Using Online Information
- Online Journals and Texts
- Statistical Reference Sites
- Data Sources
- Uses of E-mail Services in Research
30 Using SPSS for Data Analysis Contents
- Introduction
- Starting and Exiting SPSS
- Creating a Data File
- Univariate Analysis
- Bivariate Analysis
31 Using SPSS in Report Writing
- Why to Use SPSS
- Working with SPSS Output
- Copying SPSS Output to MS Word Document
32 Tabulation and Graphic Presentation- Case Studies
- Structure for Presentation of Research Findings
- Data Presentation: Editing, Coding, and Transcribing
- Case Studies
- Qualitative Data Analysis and Presentation through Software
- Types of ICT used for Research
33 Guidelines to Research Project Assignment
- Overview of Research Methodologies and Methods (MSO 002)
- Research Project Objectives
- Preparation for Research Project
- Stages of the Research Project
- Supervision During the Research Project
- Submission of Research Project
- Methodology for Evaluating Research Project
Share on Mastodon

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 3: Developing a Research Question
3.2 Exploration, Description, Explanation
As you can see, there is much to think about and many decisions to be made as you begin to define your research question and your research project. Something else you will need to consider in the early stages is whether your research will be exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory. Each of these types of research has a different aim or purpose, consequently, how you design your research project will be determined in part by this decision. In the following paragraphs we will look at these three types of research.
Exploratory research
Researchers conducting exploratory research are typically at the early stages of examining their topics. These sorts of projects are usually conducted when a researcher wants to test the feasibility of conducting a more extensive study; he or she wants to figure out the lay of the land with respect to the particular topic. Perhaps very little prior research has been conducted on this subject. If this is the case, a researcher may wish to do some exploratory work to learn what method to use in collecting data, how best to approach research participants, or even what sorts of questions are reasonable to ask. A researcher wanting to simply satisfy his or her own curiosity about a topic could also conduct exploratory research. Conducting exploratory research on a topic is often a necessary first step, both to satisfy researcher curiosity about the subject and to better understand the phenomenon and the research participants in order to design a larger, subsequent study. See Table 2.1 for examples.
Descriptive research
Sometimes the goal of research is to describe or define a particular phenomenon. In this case, descriptive research would be an appropriate strategy. A descriptive may, for example, aim to describe a pattern. For example, researchers often collect information to describe something for the benefit of the general public. Market researchers rely on descriptive research to tell them what consumers think of their products. In fact, descriptive research has many useful applications, and you probably rely on findings from descriptive research without even being aware that that is what you are doing. See Table 3.1 for examples.
Explanatory research
The third type of research, explanatory research, seeks to answer “why” questions. In this case, the researcher is trying to identify the causes and effects of whatever phenomenon is being studied. An explanatory study of college students’ addictions to their electronic gadgets, for example, might aim to understand why students become addicted. Does it have anything to do with their family histories? Does it have anything to do with their other extracurricular hobbies and activities? Does it have anything to do with the people with whom they spend their time? An explanatory study could answer these kinds of questions. See Table 3.1 for examples.
Table 3.1 Exploratory, descriptive and explanatory research differences (Adapted from Adjei, n.d.).
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Descriptive Analytics? 5 Examples

- 09 Nov 2021
Data analytics is a valuable tool for businesses aiming to increase revenue, improve products, and retain customers. According to research by global management consulting firm McKinsey & Company, companies that use data analytics are 23 times more likely to outperform competitors in terms of new customer acquisition than non-data-driven companies. They were also nine times more likely to surpass them in measures of customer loyalty and 19 times more likely to achieve above-average profitability.
Data analytics can be broken into four key types :
- Descriptive, which answers the question, “What happened?”
- Diagnostic , which answers the question, “Why did this happen?”
- Predictive , which answers the question, “What might happen in the future?”
- Prescriptive , which answers the question, “What should we do next?”
Each type of data analysis can help you reach specific goals and be used in tandem to create a full picture of data that informs your organization’s strategy formulation and decision-making.
Descriptive analytics can be leveraged on its own or act as a foundation for the other three analytics types. If you’re new to the field of business analytics, descriptive analytics is an accessible and rewarding place to start.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Descriptive Analytics?
Descriptive analytics is the process of using current and historical data to identify trends and relationships. It’s sometimes called the simplest form of data analysis because it describes trends and relationships but doesn’t dig deeper.
Descriptive analytics is relatively accessible and likely something your organization uses daily. Basic statistical software, such as Microsoft Excel or data visualization tools , such as Google Charts and Tableau, can help parse data, identify trends and relationships between variables, and visually display information.
Descriptive analytics is especially useful for communicating change over time and uses trends as a springboard for further analysis to drive decision-making .
Here are five examples of descriptive analytics in action to apply at your organization.
Related: 5 Business Analytics Skills for Professionals
5 Examples of Descriptive Analytics
1. traffic and engagement reports.
One example of descriptive analytics is reporting. If your organization tracks engagement in the form of social media analytics or web traffic, you’re already using descriptive analytics.
These reports are created by taking raw data—generated when users interact with your website, advertisements, or social media content—and using it to compare current metrics to historical metrics and visualize trends.
For example, you may be responsible for reporting on which media channels drive the most traffic to the product page of your company’s website. Using descriptive analytics, you can analyze the page’s traffic data to determine the number of users from each source. You may decide to take it one step further and compare traffic source data to historical data from the same sources. This can enable you to update your team on movement; for instance, highlighting that traffic from paid advertisements increased 20 percent year over year.
The three other analytics types can then be used to determine why traffic from each source increased or decreased over time, if trends are predicted to continue, and what your team’s best course of action is moving forward.
2. Financial Statement Analysis
Another example of descriptive analytics that may be familiar to you is financial statement analysis. Financial statements are periodic reports that detail financial information about a business and, together, give a holistic view of a company’s financial health.
There are several types of financial statements, including the balance sheet , income statement , cash flow statement , and statement of shareholders’ equity. Each caters to a specific audience and conveys different information about a company’s finances.
Financial statement analysis can be done in three primary ways: vertical, horizontal, and ratio.
Vertical analysis involves reading a statement from top to bottom and comparing each item to those above and below it. This helps determine relationships between variables. For instance, if each line item is a percentage of the total, comparing them can provide insight into which are taking up larger and smaller percentages of the whole.
Horizontal analysis involves reading a statement from left to right and comparing each item to itself from a previous period. This type of analysis determines change over time.
Finally, ratio analysis involves comparing one section of a report to another based on their relationships to the whole. This directly compares items across periods, as well as your company’s ratios to the industry’s to gauge whether yours is over- or underperforming.
Each of these financial statement analysis methods are examples of descriptive analytics, as they provide information about trends and relationships between variables based on current and historical data.

3. Demand Trends
Descriptive analytics can also be used to identify trends in customer preference and behavior and make assumptions about the demand for specific products or services.
Streaming provider Netflix’s trend identification provides an excellent use case for descriptive analytics. Netflix’s team—which has a track record of being heavily data-driven—gathers data on users’ in-platform behavior. They analyze this data to determine which TV series and movies are trending at any given time and list trending titles in a section of the platform’s home screen.
Not only does this data allow Netflix users to see what’s popular—and thus, what they might enjoy watching—but it allows the Netflix team to know which types of media, themes, and actors are especially favored at a certain time. This can drive decision-making about future original content creation, contracts with existing production companies, marketing, and retargeting campaigns.
4. Aggregated Survey Results
Descriptive analytics is also useful in market research. When it comes time to glean insights from survey and focus group data, descriptive analytics can help identify relationships between variables and trends.
For instance, you may conduct a survey and identify that as respondents’ age increases, so does their likelihood to purchase your product. If you’ve conducted this survey multiple times over several years, descriptive analytics can tell you if this age-purchase correlation has always existed or if it was something that only occurred this year.
Insights like this can pave the way for diagnostic analytics to explain why certain factors are correlated. You can then leverage predictive and prescriptive analytics to plan future product improvements or marketing campaigns based on those trends.
Related: What Is Marketing Analytics?
5. Progress to Goals
Finally, descriptive analytics can be applied to track progress to goals. Reporting on progress toward key performance indicators (KPIs) can help your team understand if efforts are on track or if adjustments need to be made.
For example, if your organization aims to reach 500,000 monthly unique page views, you can use traffic data to communicate how you’re tracking toward it. Perhaps halfway through the month, you’re at 200,000 unique page views. This would be underperforming because you’d like to be halfway to your goal at that point—at 250,000 unique page views. This descriptive analysis of your team’s progress can allow further analysis to examine what can be done differently to improve traffic numbers and get back on track to hit your KPI.

Using Data to Identify Relationships and Trends
“Never before has so much data about so many different things been collected and stored every second of every day,” says Harvard Business School Professor Jan Hammond in the online course Business Analytics . “In this world of big data, data literacy —the ability to analyze, interpret, and even question data—is an increasingly valuable skill.”
Leveraging descriptive analytics to communicate change based on current and historical data and as a foundation for diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics has the potential to take you and your organization far.
Do you want to become a data-driven professional? Explore our eight-week Business Analytics course and our three-course Credential of Readiness (CORe) program to deepen your analytical skills and apply them to real-world business problems.

About the Author

Descriptive Research: Methods And Examples
A research project always begins with selecting a topic. The next step is for researchers to identify the specific areas…

A research project always begins with selecting a topic. The next step is for researchers to identify the specific areas of interest. After that, they tackle the key component of any research problem: how to gather enough quality information. If we opt for a descriptive research design we have to ask the correct questions to access the right information.
For instance, researchers may choose to focus on why people invest in cryptocurrency, knowing how dynamic the market is rather than asking why the market is so shaky. These are completely different questions that require different research approaches. Adopting the descriptive method can help capitalize on trends the information reveals. Descriptive research examples show the thorough research involved in such a study.
Get to know more about descriptive research design .
Descriptive Research Meaning
Features of descriptive research design, types of descriptive research, descriptive research methods, applications of descriptive research, descriptive research examples.
A descriptive method of research is one that describes the characteristics of a phenomenon, situation or population. It uses quantitative and qualitative approaches to describe problems with little relevant information. Descriptive research accurately describes a research problem without asking why a particular event happened. By researching market patterns, the descriptive method answers how patterns change, what caused the change and when the change occurred, instead of dwelling on why the change happened.
Descriptive research refers to questions, study design and analysis of data conducted on a particular topic. It is a strictly observational research methodology with no influence on variables. Some distinctive features of descriptive research are:
- It’s a research method that collects quantifiable information for statistical analysis of a sample. It’s a quantitative market research tool that can analyze the nature of a demographic
- In a descriptive method of research , the nature of research study variables is determined with observation, without influence from the researcher
- Descriptive research is cross-sectional and different sections of a group can be studied
- The analyzed data is collected and serves as information for other search techniques. In this way, a descriptive research design becomes the basis of further research
To understand the descriptive research meaning , data collection methods, examples and application, we need a deeper understanding of its features.
Different ways of approaching the descriptive method help break it down further. Let’s look at the different types of descriptive research :
Descriptive Survey
Descriptive normative survey, descriptive status.
This type of research quantitatively describes real-life situations. For example, to understand the relation between wages and performance, research on employee salaries and their respective performances can be conducted.
Descriptive Analysis
This technique analyzes a subject further. Once the relation between wages and performance has been established, an organization can further analyze employee performance by researching the output of those who work from an office with those who work from home.
Descriptive Classification
Descriptive classification is mainly used in the field of biological science. It helps researchers classify species once they have studied the data collected from different search stations.
Descriptive Comparative
Comparing two variables can show if one is better than the other. Doing this through tests or surveys can reveal all the advantages and disadvantages associated with the two. For example, this technique can be used to find out if paper ballots are better than electronic voting devices.
Correlative Survey
The researcher has to effectively interpret the area of the problem and then decide the appropriate technique of descriptive research design .
A researcher can choose one of the following methods to solve research problems and meet research goals:
Observational Method
With this method, a researcher observes the behaviors, mannerisms and characteristics of the participants. It is widely used in psychology and market research and does not require the participants to be involved directly. It’s an effective method and can be both qualitative and quantitative for the sheer volume and variety of data that is generated.
Survey Research
It’s a popular method of data collection in research. It follows the principle of obtaining information quickly and directly from the main source. The idea is to use rigorous qualitative and quantitative research methods and ask crucial questions essential to the business for the short and long term.
Case Study Method
Case studies tend to fall short in situations where researchers are dealing with highly diverse people or conditions. Surveys and observations are carried out effectively but the time of execution significantly differs between the two.
There are multiple applications of descriptive research design but executives must learn that it’s crucial to clearly define the research goals first. Here’s how organizations use descriptive research to meet their objectives:
- As a tool to analyze participants : It’s important to understand the behaviors, traits and patterns of the participants to draw a conclusion about them. Close-ended questions can reveal their opinions and attitudes. Descriptive research can help understand the participant and assist in making strategic business decisions
- Designed to measure data trends : It’s a statistically capable research design that, over time, allows organizations to measure data trends. A survey can reveal unfavorable scenarios and give an organization the time to fix unprofitable moves
- Scope of comparison: Surveys and research can allow an organization to compare two products across different groups. This can provide a detailed comparison of the products and an opportunity for the organization to capitalize on a large demographic
- Conducting research at any time: An analysis can be conducted at any time and any number of variables can be evaluated. It helps to ascertain differences and similarities
Descriptive research is widely used due to its non-invasive nature. Quantitative observations allow in-depth analysis and a chance to validate any existing condition.
There are several different descriptive research examples that highlight the types, applications and uses of this research method. Let’s look at a few:
- Before launching a new line of gym wear, an organization chose more than one descriptive method to gather vital information. Their objective was to find the kind of gym clothes people like wearing and the ones they would like to see in the market. The organization chose to conduct a survey by recording responses in gyms, sports shops and yoga centers. As a second method, they chose to observe members of different gyms and fitness institutions. They collected volumes of vital data such as color and design preferences and the amount of money they’re willing to spend on it .
- To get a good idea of people’s tastes and expectations, an organization conducted a survey by offering a new flavor of the sauce and recorded people’s responses by gathering data from store owners. This let them understand how people reacted, whether they found the product reasonably priced, whether it served its purpose and their overall general preferences. Based on this, the brand tweaked its core marketing strategies and made the product widely acceptable .
Descriptive research can be used by an organization to understand the spending patterns of customers as well as by a psychologist who has to deal with mentally ill patients. In both these professions, the individuals will require thorough analyses of their subjects and large amounts of crucial data to develop a plan of action.
Every method of descriptive research can provide information that is diverse, thorough and varied. This supports future research and hypotheses. But although they can be quick, cheap and easy to conduct in the participants’ natural environment, descriptive research design can be limited by the kind of information it provides, especially with case studies. Trying to generalize a larger population based on the data gathered from a smaller sample size can be futile. Similarly, a researcher can unknowingly influence the outcome of a research project due to their personal opinions and biases. In any case, a manager has to be prepared to collect important information in substantial quantities and have a balanced approach to prevent influencing the result.
Harappa’s Thinking Critically program harnesses the power of information to strengthen decision-making skills. It’s a growth-driven course for young professionals and managers who want to be focused on their strategies, outperform targets and step up to assume the role of leader in their organizations. It’s for any professional who wants to lay a foundation for a successful career and business owners who’re looking to take their organizations to new heights.
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics such as Main Objectives of Research , Examples of Experimental Research , Methods Of Ethnographic Research , and How To Use Blended Learning to upgrade your knowledge and skills.

Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
- Open access
- Published: 27 May 2024
Association between gut microbiota and anxiety disorders: a bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study
- Jianbing Li 1 ,
- Changhe Fan 1 ,
- Jiaqi Wang 2 ,
- Bulang Tang 2 ,
- Jiafan Cao 2 ,
- Xianzhe Hu 2 ,
- Xuan Zhao 2 &
- Caiqin Feng 1
BMC Psychiatry volume 24 , Article number: 398 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
144 Accesses
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
There are many articles reporting that the component of intestinal microbiota implies a link to anxiety disorders (AD), and the brain-gut axis is also a hot topic in current research. However, the specific relevance between gut microbiota and AD is uncertain. We aimed to investigate causal relationship between gut microbiota and AD by using bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR).
Genetic instrumental variable (IV) for the gut microbiota were obtained from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) involving 18,340 participants. Summary data for AD were derived from the GWAS and included 158,565 cases and 300,995 controls. We applied the inverse variance weighted (IVW) method as the main analysis. Cochran’s Q values was computed to evaluate the heterogeneity among IVs. Sensitivity analyses including intercept of MR-Egger method and MR-PRESSO analysis were used to test the horizontal pleiotropy.
We discovered 9 potential connections between bacterial traits on genus level and AD. Utilizing the IVW method, we identified 5 bacterial genera that exhibited a direct correlation with the risk of AD: genus Eubacteriumbrachygroup , genus Coprococcus3 , genus Enterorhabdus , genus Oxalobacter , genus Ruminiclostridium6 . Additionally, we found 4 bacterial genera that exhibited a negative association with AD: genus Blautia , genus Butyricicoccus , genus Erysipelotrichaceae-UCG003 and genus Parasutterella . The associations were confirmed by the sensitivity analyses.
Our study found a causal relation between parts of the gut microbiota and AD. Further randomized controlled trials are crucial to elucidate the positive effects of probiotics on AD and their particular protection systems.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Anxiety disorders (AD), being the prevailing mental disorders, have a substantial impact on individuals and society alike [ 1 ]. The core features of AD contain indiscriminate anxiety and fear or elusion of persistent and debilitating threats, resulting in substantial medical costs and a burdensome morbidity burden [ 1 , 2 ]. As one of the most popular mental illnesses among young individuals, AD are also the earliest-onset mental disorders [ 3 ]. Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a significant surge in the occurrence of AD among children, adolescents, and young adults globally [ 4 ]. First-line treatments for AD include medication and psychotherapy [ 5 ]. However, medication treatments carry certain side effects and risks, such as dependence, cognitive impairment, and an increased risk of heart disease [ 6 ]. The majority of individuals suffering from AD lack access to efficacious treatment options, leaving them vulnerable to relapse [ 7 , 8 ].
Many studies have shown that the occurrence of AD is related to changes in intestinal flora [ 9 , 10 ]. In social anxiety disorder (SAD), there was an increase in the relative abundance of Anaeromassillibacillus and Gordonibacter genera, whereas healthy controls exhibited an enrichment of Parasuterella [ 11 ]. Another article found a reduction in Eubacterium rectale and Fecalibacterium , as well as an increase in Escherichia , Shigella , Fusobacterium , and Ruminococcus in patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) [ 12 ]. In addition, there are numerous documents demonstrating an association between the gut microbiota and mental illness, and the modulation of the gut microbiota on the gut-brain axis has garnered significant attention, such as an elevation of Enterobacteriaceae and Desulfovibrio , and a reduction of Faecalibacterium in patients with AD [ 10 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. In the aforementioned section, it was observed that the evidence exhibits complexities and disparities, as well as some contradictory results, potentially stemming from various confounding factors among different studies.
The previous studies examining the connection between gut microbiota and AD have predominantly relied on cross-sectional designs, which limits the ability to establish a causal relationship between these associations. Therefore, unraveling the causal mechanisms behind gut microbiota-derived AD not only enhances our understanding of their pathogenesis but also provides valuable guidance for implementing microbiota-directed interventions in clinical settings to address AD. Previous Mendelian randomization (MR) studies have primarily focused on investigating the causal relationship between oral microbiota abundance and AD, or between gut microbiota and other psychiatric disorders. A systematic MR study specifically examining the causal relationship between gut microbiota and AD is still lacking in the current literature. In light of this, it is imperative to unravel the causal link between the gut microbiota and AD.
MR is a statistical approach that infers a causal relationship with exposure to a result. It leverages genetic variations linked to the exposure as a proxy for the exposure itself, enabling the assessment of the association between the exposure and the outcome [ 18 ]. Due to the highly effective findings of large-scale genome-wide association study (GWAS) at the gut microbiota and disease level, MR analysis has been abroad used in many scenarios, such as between the oral microbiome and AD, relations between genetically determined metabolites and anxiety symptoms [ 19 , 20 ]. However, there are no specific studies on the causal relationship between gut microbiota and AD. In this research, we applied a bidirectional two-sample MR method to investigate causal relationship between the gut microbiota and AD.
Materials and methods
The assumptions and study design of mr.
MR is a methodology employed to assess causal associations between variables. In order to ensure the validity of MR analysis, 3 fundamental assumptions must be met: (i) the instrumental variable (IV) exhibits a strong link to the exposure factor, (ii) the IV remains unaffected by potential confounding factors., and (iii) the IV influences the result factor solely via the exposure factor [ 21 ]. By applying strict selection criteria, appropriate SNPs were selected as IV for conducting MR analysis on two independent samples. The main aim was to examine the causal relationship between gut microbiota and AD. Furthermore, this study adhered to the guidelines outlined in the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology-Mendelian Randomization (STROBE-MR) framework [ 22 ] (Fig. 1 ).
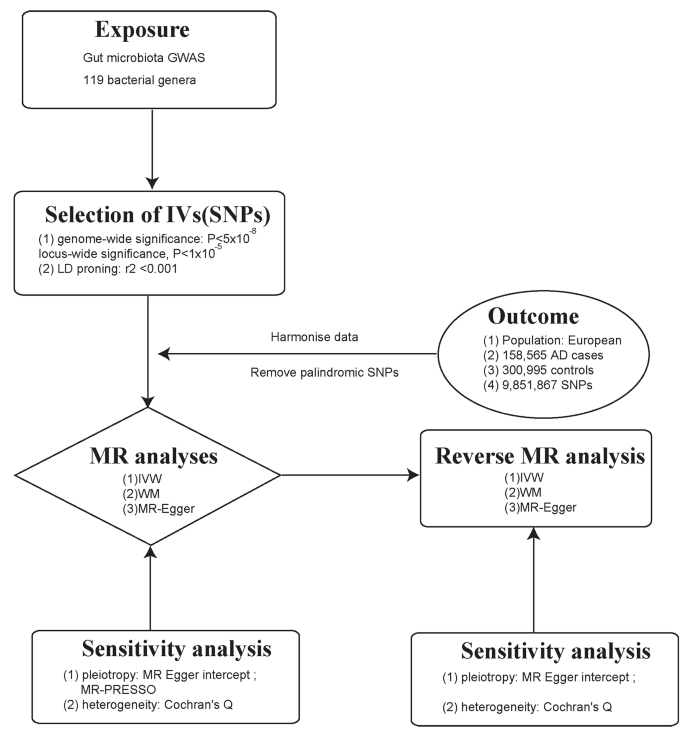
A flowchart illustrating the MR analysis process for the association between gut microbiota and AD
Data sources
The data on gut microbiota GWAS used in this study were obtained from an overall meta-analysis conducted by the MiBioGen consortium. The meta-analysis comprised a total of 18,340 individuals from 24 different groups. The alliance combines human whole-genome genotyping with fecal 16 S rRNA sequencing data to perform thorough research and analysis. The large-scale, multi-ethnic genome-wide meta-analysis provided valuable insights into the genetic influences on the gut microbiome composition [ 23 ]. The GWAS data on the gut microbiome can be integrated into MR studies to explore the causal relationship between genetic variations in the gut microbiome and phenotypic traits, providing valuable insights into the role of the microbiome in human health and disease.
As for the data on genetic variants linked to AD, they were sourced from the Medical Research Council Integrative Epidemiology Unit (MRC-IEU) consortium. The cases were defined as individuals who had sought medical attention for symptoms of nervousness, anxiety, or depression. The study population consisted of individuals of European descent, comprising both males and females, and the data were sourced from the year 2018. The dataset included a total of 158,565 cases and 300,995 controls. The diagnosis was based on self-report questionnaires. Detailed information regarding the data origins for this MR study can be found in Table 1 [ 24 , 25 ].
Selection of IV
The GWAS data of exposure contained a total of 5 taxonomic levels for 211 bacterial groups. The genus level is the smallest and most specific classification level. To accurately identify each pathogenic bacterial group, we focused our analysis only on the genus level, specifically examining 131 bacterial classifications. After excluding 12 unknown groups, a total of 119 bacterial genera were included in the study.
To fulfill the demands of MR studies, our initial step involved the SNPs that exhibited an intense association with the exposure factors. However, when employing a stringent threshold of ( P < 5 × 10 − 8 ), we obtained a limited number of IVs. Consequently, we adjusted the threshold to ( P < 1 × 10 − 5 ) to ensure the inclusion of more IVs, thereby enabling robust and reliable results. For the selection of IVs associated with AD in the reverse MR analysis, a heightened level of stringency was implemented by applying a P -value threshold of P < 5 × 10 − 8 .
We utilized the F-statistic to further evaluate the instrument strength. The F-statistic was determined using the formula: F = β 2 / SE 2 . This statistic provided an assessment of the overall instrument strength [ 26 ] (Fig. 2 ). An F-statistic exceeding 10 was considered indicative of an intense conjunction between the IV and the exposure. Besides P -value threshold, the F statistic in our analysis would provide additional information on the instrument strength beyond P -value.
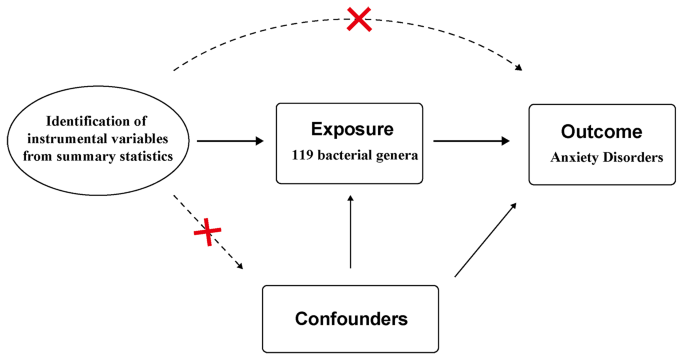
Assumptions in MR studies: a brief overview
Statistical analysis
The primary methodology employed in MR analysis is the inverse variance weighting (IVW) method. This approach utilizes a meta-analysis technique to combine the Wald estimates connected to individual single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), providing comprehensive estimate of the collective impact of gut microbiota on AD. A crucial assumption in MR is the absence of horizontal pleiotropy, where the IV has a direct impact on the outcome variable solely through the exposure factor, without any influence from through alternative pathways. When this assumption is satisfied, the IVW method can provide estimates that are consistent and estimates [ 27 ]. In cases where a causal relationship ( P < 0.05) is established by the IVW method, two alternative approaches, namely MR-Egger and the weighted median approach, are utilized to supplement an enrich the IVW results. The MR-Egger method relaxes the assumption of a zero intercept, and it can estimate causal effects, even pleiotropy was presented in IVs. The intercept in the MR-Egger method can indicate the extent of horizontal pleiotropy [ 27 ]. These additional methods provide valuable insights and strengthen the overall analysis by considering potential biases and alternative causal pathways.
The weighted median method can return unbiased causal estimate when only 50% of SNPs are valid [ 28 ]. In this study, we employed a significance threshold of P < 0.05 to determine statistical significance, and the assessment of causality was expressed through odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). In instances where causal relationships were established, unidentified taxa were excluded, and additional sensitivity analyses were performed to guarantee the stability of the consequences. The false discovery rate (FDR) is utilized to control for multiple testing and reduce the likelihood of false positive findings. All of the aforementioned analyses were performed utilizing the TwoSampleMR package (version 0.5.7) in R (version 4.3.0), providing a robust and standardized approach to MR analysis.
According to the criteria for IV selection, a total of 1,531 SNPs were identified and selected as IV associated with gut microbiota. The F-statistics for these IVs all exceed 10, suggesting that the estimated coefficients are improbable to be influenced by the bias caused by weak instruments. Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 provides detailed information about the selected IVs. None of the SNPs were involved in more than one of the association results in Fig. 3 .
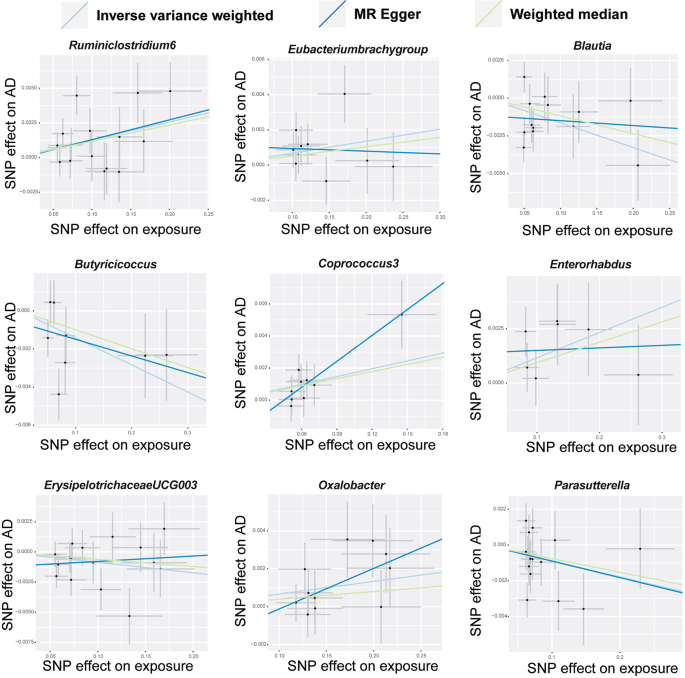
The scatter plots depict the causal relationship between gut microbiota and AD
The majority of gut microbiota showed no significant correlation with AD. However, using the IVW method, we identified 9 bacterial features that were significantly associated with the risk of AD on genus level (Supplementary Table 3 ). We used 3 methods, IVW, weighted median and MR-Egger, and defined P < 0.05 for IVW method screening as a positive result.
Among them, 4 bacterial genera are negatively correlated with AD, indicating that a higher genetically predicted a lower risk of for AD (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table 4 ). They are: genus Blautia (OR = 0.9838, 95% CI, 0.9725–0.9952, P = 0.0056), genus Butyricicoccus (OR = 0.9859, 95% CI, 0.9739–0.9981, P = 0.0233), genus ErysipelotrichaceaeUCG003 (OR = 0.9914, 95% CI, 0.9833–0.9995, P = 0.0381) and genus Parasutterella (OR = 0.9911, 95% CI, 0.9823–0.9999, P = 0.0478). Supplementary Table 4 shows the completed data. In sensitivity analysis, MR-Egger, weighted median demonstrated consistent results, except for genus ErysipelotrichaceaeUCG003 , where the MR-Egger trend was in the contrary direction compared to IVW and weighted median.
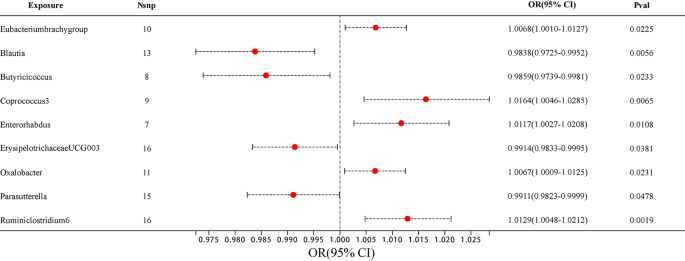
The forest plot illustrates the connections between 9 bacterial genus traits and the likelihood of developing AD
Another 5 bacterial genera showed a positive correlation with AD, genus Eubacteriumbrachygroup (OR = 1.0068, 95% CI, 1.0010–1.0127, P = 0.0225), genus Coprococcus3 (OR = 1.0164, 95% CI, 1.0046–1.0285, P = 0.0065), genus Enterorhabdus (OR = 1.0117, 95% CI, 1.0027–1.0208, P = 0.0108), genus Oxalobacter (OR = 1.0067, 95% CI, 1.0009–1.0125, P = 0.0231) and genus Ruminiclostridium6 (OR = 1.0129, 95% CI, 1.0048–1.0212, P = 0.0019) (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table 4 ). In the MR-Egger method, the trends of genus Eubacteriumbrachygroup are different from those of the IVW and WM methods.
In horizontal pleiotropy analysis, we used the MR-Egger method and found P -value of the MR-intercept were all greater than 0.05. In addition, further MR PRESSO analysis was conducted, ruling out the existence of horizontal pleiotropy ( P > 0.05) (Supplementary Tables 5 and 6 ). To assess the heterogeneity of gut microbiome IVs, we employed Cochran’s Q test statistics, which revealed no heterogeneity among the gut microbiome IVs ( P > 0.05) (Supplementary Table 7 ).
Reverse MR analyses were conducted to examine the links between the 9 bacterial genera and AD. No significant statistical relationship was observed using the IVW method: genus Eubacteriumbrachygroup (OR = 1.4058, 95% CI, 0.4060–4.8674, P = 0.5909), genus Blautia (OR = 0.9453, 95% CI, 0.5572–1.6038, P = 0.8348), genus Butyricicoccus (OR = 0.9834, 95% CI, 0.5704–1.6952, P = 0.9518), genus Coprococcus3 (OR = 0.8886, 95% CI, 0.5040–1.5667, P = 0.6831), genus Enterorhabdus (OR = 1.0383, 95% CI, 0.4168–2.5868, P = 0.9356), genus ErysipelotrichaceaeUCG003 (OR = 0.6593, 95% CI, 0.3556–1.2221, P = 0.1858), genus Oxalobacter (OR = 1.2849, 95% CI, 0.4021–4.1051, P = 0.6724), genus Parasutterella (OR = 0.7245, 95% CI, 0.3713–1.4136, P = 0.3447), genus Ruminiclostridium6 (OR = 0.7095, 95% CI, 0.3825–1.3162, P = 0.2764) (Supplementary Tables 8 and 9 ).
In the context of this study, we used two-sample MR studies to discover the link between AD and gut microbiota. Among the 9 bacterial genus we found, 4 bacteria were negatively correlated with AD and may have a positive effect on AD, and the other 5 bacteria were positively correlated with the occurrence of AD and may promote the development of AD.
Blautia stercoris MRx0006 has been shown to alleviate social dysfunctions, monotonous behaviors, and anxiety-like behaviors relevant to autism disorders in a mouse model. MRx0006 administration at the microbial level, as observed by Paromita Sen et al., resulted in a reduction in the abundance of Alistipes putredinis, which likely underlie the observed increase in expressions of oxytocin, arginine vasopressin, and their receptors, ultimately leading to improved behavioral outcomes [ 29 ]. Butyricicoccus was also inversely associated with AD in a cross-sectional study, which is consistent with our findings [ 12 ]. Approximately 70% of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) exhibit comorbid symptoms of anxiety, and the findings from a published article confirming the decreased relative abundance of ErysipelotrichaceaeUCG003 in ASD patients further support our research results indicating a negative correlation between ErysipelotrichaceaeUCG003 and AD [ 30 ]. In a study examining SAD, the control group exhibited higher levels of the positive bacteria Parasutterella compared to the anxiety group. The term “psychobiotics” has been coined to refer to these microbes that are associated with improved mood [ 11 ]. However, in a study by Yi Zhang et al., a psychological stress model was established in C57BL/6J mice, followed by fecal microbiota transplantation using samples from stressed (S) and non-stressed (NS) mice. The results showed an increased abundance of Parasutterella in S mice and mechanistic analysis suggested its potential involvement in negative regulation of metabolism. Despite this controversial finding, our study utilized MR to reveal a negative association between Parasutterella and anxiety disorders. However, further experimental investigations are required to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms [ 31 ].
Five bacterial genera positively linked to anxiety may indicate that they exacerbate anxiety, but they were less reported. In a study in which consuming prebiotics altered the microbiota of healthy adults, the prebiotics reduced Eubacteriumbrachygroup but did not significantly change biomarkers of stress or mental health symptoms [ 32 ]. In previous studies on AD cases, it has been found that individuals with AD have lower levels of Coprococcus [ 33 ]. However, in our study, we observed an increasing trend in Coprococcus3 , despite belonging to the same genus. This suggests that even within the same genus, the impact of different genus may vary. In contrast to our findings, Enterorhabdus exhibited a declining pattern in a mouse model of anxiety and depression induced by social defeat [ 34 ]. This observation highlights the influence of various factors on alterations in gut microbiota, which may diverge across different species.
Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that our study has certain limitations. First, the results of this analysis are limited to European populations and may not be generalizable to other populations. Secondly, we observed that the adjusted P -values remained relatively large after multiple test adjustment. The reduced statistical power resulting from the limited sample size may also constrain our ability to detect significant associations between variables. Finally, proving the direct impact of sample types on the outcomes is challenging. However, the selection of sample types is often constrained by the availability of suitable genetic instruments and relevant data sources. The dataset we utilized does not provide specific information on the dietary habits of the individuals or their other medical conditions. Therefore, further examination and validation are needed in the future.
In summary, utilizing large-scale GWAS analysis, MR studies have disclosed a causal relationship between gut microbiota and AD. Among these, 4 bacterial genera exhibited a negative correlation, while 5 bacteria genera showed a positive correlation with AD. However, further exploration of the mechanisms linking gut microbiota to AD requires the establishment of larger GWAS databases. Several gut bacteria have been identified to reduce the occurrence of anxiety, offering promising prospects for the treatment and precaution of AD. Subsequent research should prioritize the exploration of the underlying mechanisms and the development of targeted interventions based on these findings.
Data availability
The raw data analyzed during the current study were available in public databases including IEU database(ukb-b-6991) and MiBioGen database(https://mibiogen.gcc.rug.nl). The code and data related to this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Anxiety disorders
- Mendelian randomization
Instrumental variable(s)
Genome-wide association study
Medical Research Council Integrative Epidemiology Unit
Inverse variance weighting
Social anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder
Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology-Mendelian Randomization
Single nucleotide polymorphism(s)
Odds ratios
Confidence intervals
Autism spectrum disorder
Major depressive disorder
Penninx BW, Pine DS, Holmes EA, et al. Anxiety disorders[J] Lancet. 2021;397:914–27.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bandelow B, Michaelis S. Epidemiology of anxiety disorders in the 21st century[J]. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2015;17:327–35.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Warner EN, Ammerman RT, Glauser TA, et al. Developmental epidemiology of pediatric anxiety disorders[J]. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2023;32:511–30.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fortuna LR, Brown IC, Lewis Woods GG, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on anxiety disorders in Youth: coping with stress, worry, and recovering from a Pandemic[J]. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2023;32:531–42.
Wehry AM, Beesdo-Baum K, Hennelly MM, et al. Assessment and treatment of anxiety disorders in children and adolescents[J]. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17:52.
Szuhany KL, Simon NM. Anxiety disorders: a review[J]. JAMA. 2022;328:2431–45.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Uher R. The global impact of anxiety disorders[J]. Lancet Psychiatry. 2023;10:239–40.
Scholten W, Ten Have M, Van Geel C, et al. Recurrence of anxiety disorders and its predictors in the general population[J]. Psychol Med. 2023;53:1334–42.
Yang B, Wei J, Ju P, et al. Effects of regulating intestinal microbiota on anxiety symptoms: a systematic review[J]. Gen Psychiatr. 2019;32:e100056.
Simpson CA, Diaz-Arteche C, Eliby D, et al. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression - a systematic review[J]. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;83:101943.
Butler MI, Bastiaanssen TFS, Long-Smith C, et al. The gut microbiome in social anxiety disorder: evidence of altered composition and function[J]. Translational Psychiatry. 2023;13:95.
Jiang HY, Zhang X, Yu ZH, et al. Altered gut microbiota profile in patients with generalized anxiety disorder[J]. J Psychiatr Res. 2018;104:130–6.
Socała K, Doboszewska U, Szopa A, et al. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders[J]. Pharmacol Res. 2021;172:105840.
Nikolova VL, Smith MRB, Hall LJ, et al. Perturbations in gut microbiota composition in psychiatric disorders: a review and meta-analysis[J]. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:1343–54.
Generoso JS, Giridharan VV, Lee J, et al. The role of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric disorders[J]. Braz J Psychiatry. 2021;43:293–305.
Mörkl S, Butler MI, Holl A, et al. Probiotics and the microbiota-gut-brain axis: focus on psychiatry[J]. Curr Nutr Rep. 2020;9:171–82.
Needham BD, Funabashi M, Adame MD, et al. A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice[J]. Nature. 2022;602:647–53.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Emdin CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S. Mendelian Randomization[J] JAMA. 2017;318:1925–6.
Li C, Chen Y, Wen Y, et al. A genetic association study reveals the relationship between the oral microbiome and anxiety and depression symptoms[J]. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:960756.
Xiao G, He Q, Liu L, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: a two-sample mendelian randomization study[J]. J Transl Med. 2022;20:475.
Xie L, Zhao H, Chen W. Relationship between gut microbiota and thyroid function: a two-sample mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1240752.
Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BR, et al. Strengthening the reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology using mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR Statement[J]. JAMA. 2021;326:1614–21.
Kurilshikov A, Medina-Gomez C, Bacigalupe R, et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition[J]. Nat Genet. 2021;53:156–65.
Lyall DM, Inskip HM, Mackay D, et al. Low birth weight and features of neuroticism and mood disorder in 83 545 participants of the UK Biobank cohort[J]. BJPsych Open. 2016;2:38–44.
Smith DJ, Nicholl BI, Cullen B, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of probable major depression and bipolar disorder within UK biobank: cross-sectional study of 172,751 participants[J]. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e75362.
Burgess S, Thompson SG. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in mendelian randomization studies[J]. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40:755–64.
Burgess S, Butterworth A, Thompson SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data[J]. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37:658–65.
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some Invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator[J]. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40:304–14.
Sen P, Sherwin E, Sandhu K, et al. The live biotherapeutic Blautia stercoris MRx0006 attenuates social deficits, repetitive behaviour, and anxiety-like behaviour in a mouse model relevant to autism[J]. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;106:115–26.
Chen Y-C, Lin H-Y, Chien Y, et al. Altered gut microbiota correlates with behavioral problems but not gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with autism[J]. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;106:161–78.
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wu J, et al. Implications of gut microbiota dysbiosis and fecal metabolite changes in psychologically stressed mice[J]. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1124454.
Mysonhimer AR, Cannavale CN, Bailey MA, et al. Prebiotic consumption alters Microbiota but not biological markers of stress and inflammation or mental health symptoms in healthy adults: a randomized, controlled, crossover trial[J]. J Nutr. 2023;153:1283–96.
Chen YH, Bai J, Wu D, et al. Association between fecal microbiota and generalized anxiety disorder: severity and early treatment response[J]. J Affect Disord. 2019;259:56–66.
Zou R, Tian P, Xu M, et al. Psychobiotics as a novel strategy for alleviating anxiety and depression[J]. J Funct Foods. 2021;86:104718.
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the hospital action teams, staff, and participants from the participating hospitals for their valuable support in data collection. Additionally, we extend our appreciation to our collaborators for their assistance throughout the process.
Program of Guangzhou Science and Technology Program Project (No. 202102010115) and Guangdong Yiyang Healthcare Charity Foundation (No. JZ2022001-3).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychiatry, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, Guangzhou, 510317, PR China
Jianbing Li, Changhe Fan & Caiqin Feng
School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, 510006, China
Jiaqi Wang, Bulang Tang, Jiafan Cao, Xianzhe Hu & Xuan Zhao
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CQF designed the research framework. JBL is responsible for data and analysis methods determination as well as manuscript writing. CHF assisted in conducting the literature review. JQW was responsible for manuscript writing. BLT and JFC performed the data statistical analysis. XZH and XZ were responsible for critical revisions.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Caiqin Feng .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, supplementary material 4, supplementary material 5, supplementary material 6, supplementary material 7, supplementary material 8, supplementary material 9, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Li, J., Fan, C., Wang, J. et al. Association between gut microbiota and anxiety disorders: a bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study. BMC Psychiatry 24 , 398 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05824-x
Download citation
Received : 23 December 2023
Accepted : 09 May 2024
Published : 27 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-024-05824-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Gut microbiota
- Single nucleotide polymorphism
BMC Psychiatry
ISSN: 1471-244X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 28 May 2024
Parental experiences of caring for preterm infants in the neonatal intensive care unit, Limpopo Province: a descriptive qualitative study exploring the cultural determinants
- Madimetja J. Nyaloko 1 ,
- Welma Lubbe 1 ,
- Salaminah S. Moloko-Phiri 1 &
- Khumoetsile D. Shopo 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 669 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
40 Accesses
Metrics details
Parent-infant interaction is highly recommended during the preterm infant hospitalisation period in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). Integrating culturally sensitive healthcare during hospitalisation of preterm infants is critical for positive health outcomes. However, there is still a paucity of evidence on parental experience regarding cultural practices that can be integrated into preterm infant care in the NICU. The study explored and described the cultural determinants of parents that can be integrated into the care of preterm infants in the NICU.
A descriptive qualitative research design was followed where twenty ( n =20) parents of preterm infants were purposively selected. The study was conducted in the NICU in Limpopo using in-depth individual interviews. Taguette software and a thematic analysis framework were used to analyse the data. The COREQ guidelines and checklist were employed to ensure reporting standardisation.
Four themes emerged from the thematic analysis: 1) Lived experienced by parents of preterm infants, 2) Interactions with healthcare professionals, 3) Cultural practices concerning preterm infant care, and 4) Indigenous healthcare practices for preterm infants.
Conclusions
The study emphasised a need for healthcare professionals to understand the challenges parents of preterm infants face in NICU care. Furthermore, healthcare professionals should know indigenous healthcare practices to ensure relevant, culturally sensitive care.
Peer Review reports
Introduction and background
Parenting is an intricate process involving the upbringing and caring for a child from infancy to adulthood through promoting and supporting the child’s physical, emotional, social, and intellectual development [ 1 ]. This process becomes challenging, particularly when it involves preterm infants admitted to the hospital [ 2 ]. The birth of a preterm infant can be an epoch-making, evocative, and occasionally devastating parental experience [ 3 ]. A preterm infant is defined as a child born before the 37 th week of pregnancy is completed [ 4 ]. Annually, approximately 15 million preterm births are documented out of 160 million live births, accounting for an 11.5% global preterm birth rate [ 5 ]. Between 2010 and 2020, more than 60% of global preterm births occurred in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa [ 5 ]. One in every seven infants in South Africa was born before their due date and required NICU admission [ 5 ].
The NICU is typically a foreign and intimidating environment for parents, due to the need for continuous monitoring and medical intervention for infants who are fragile and sick. Parents can experience stress, guilt, anxiety, and sadness due to the infant's uncertain health prognosis [ 6 ]. The active involvement of parents in preterm infant care activities in the NICU is crucial for infant developmental outcomes [ 7 ]. Healthcare professionals should comprehend the parental experience of caring for a preterm infant in the NICU to address parental needs and enhance parent-infant interaction and attachment [ 8 ]. This interaction may in turn increase parental satisfaction, thus promoting more appropriate parent-infant interaction, including attachment and bonding [ 9 ].
Although parent-infant interaction is beneficial, cultural variables need to be acknowledged. Parenting is deeply rooted in a culture characterized by ideologies concerning how an individual should act, feel and think as an in-group member [ 10 ]. Therefore, the parental involvement and parent-infant interaction might be disrupted if the parental cultural practice is not considered. Cultural practices influence the parents' infant care approach [ 11 , 12 ]. The values and ideals of culture are conveyed to the next generation through child-rearing practices, which implies that cultures are contextually sensitive parenting guidelines [ 13 ].
Parents of preterm infants in Limpopo Province, South Africa, come from various cultural backgrounds, which may influence how they understand and react to the care provided to their preterm infant in the NICU. Various childrearing practices associated with culture influence the health of preterm infants [ 14 ]. These practices include massaging the baby, applying oil to the eyes and ears, burping the baby, applying black carbon to the eyes, and trimming the nails. Parental involvement in preterm infant care in the NICU may also be influenced by culture [ 15 ]. The cultural views and ideas of healthcare professionals can potentially affect the standard of care offered to preterm infants and their parents in the NICU. These cultural views and ideas are health beliefs that explain the cause of illness, its prevention or treatment methods, and the appropriate individuals who should participate in the healing process [ 16 ].
Healthcare professionals who have a comprehensive understanding of the parental cultural determinants can facilitate the nurturing and promoting of adequate parental-infant care and interaction, which is the foundation for developing preterm infants [ 17 ]. Lack of support from healthcare professionals regarding the cultural aspects of parent-infant interaction may negate parents' cultural practices, and increase negative perceptions and dissatisfaction with the healthcare service provided in the NICU [ 17 ]. Consequently, this may result in a lack of parental awareness or responsiveness to the infant, associated with delayed infant cognitive development and multiple behavioural problems [ 18 ].
Despite the recognition of the importance of parental involvement in NICU care and the documented emotional challenges experienced by parents, there is a gap in the literature regarding the specific experiences and cultural practices of parents caring for preterm infants which can be integrated in NICU in settings, such as Limpopo Province in South Africa. The province has seen a significant increase in the number of newborn babies weighing under 2,500 grams in recent years [ 19 ]. The study aimed to explore and describe the cultural determinants of parents that can be integrated into the care of preterm infants admitted to the NICU in Limpopo Province to ensure culturally sensitive care. This study is unique due to its focus on South Africa, specifically Limpopo Province, which is the centre of cultural practices due to its rurality. The main research question was: 'What are the cultural determinants which influence the parental experience that can be integrated into the care of preterm infants in the NICU in Limpopo Province?
The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) checklist was followed to ensure standardisation in reporting the study type, design, execution, analysis, and results [ 20 ].
The study applied a qualitative research design following a descriptive approach [ 21 ]. In-depth individual interviews were used to explore and describe the experiences of parents of preterm infants admitted to the NICU in Limpopo Province through a cultural determinant lens.
The current study was conducted in the NICU of a tertiary hospital in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Limpopo Province was selected based on two grounds: 1) Cultural practices are more evident in rural villages than in semi-urban or urban settings [ 22 ], 84.2% of the study population live in rural areas [ 23 ]; and 2) one in every seven infants is born before its due date in South Africa [ 5 ], the Limpopo Province accounts for high preterm birth rates [ 19 ].
Participants and sample
The population comprised mothers of a preterm infant admitted to the NICU. For this study, a parent was defined as the mother of a preterm infant in the NICU. Purposive sampling was used to select twenty ( n =20) participants from the NICU in a tertiary hospital [ 24 ]. The inclusion criteria required that 1) the participant be the parent of a preterm infant; 2) the parent had a preterm infant in the NICU for a minimum of two weeks (As set out by the researcher, the contextually relevant time for an immersive experience was two weeks); 3) the parent be able to speak either Sepedi, Xitsonga, Tshivenda, or English (the common local languages). Mothers of preterm infants who were in critical condition were excluded. There were no refusals to participate. The sample size was determined based on data saturation, which was reached with n =20 participants [ 25 ].
Recruitment
The first author (Ph.D.) and an independent person recruited the participants face-to-face by distributing recruitment material such as flyers and asynchronously by displaying posters on the noticeboards in the selected hospital's NICU and a place where the mother lodge in the hospital. Recruitment was conducted after ethical approvals and permission from the hospital were granted. Participants who expressed interest in the study notified the first author through a phone call, SMS, or WhatsApp text message. The first author then contacted the potential participants to provide detailed information regarding the study aim and data collection method, including audio recordings of interviews, confidentiality agreements, written informed consent, and voluntary participation. Potential participants who showed interest were given an informed consent form and a minimum of 48 hours to consult and inform their partners or family members. The first author was accessible telephonically for any clarity-seeking questions. The first author contacted the agreed participants to schedule the hospital-based interviews on the agreed-upon dates. All consented mothers participated and there were no withdrawals.
Data collection
The interview guide was developed for this current study in English, and translated to local languages (Sepedi, Xitsonga, and Tshivenda) by assistant researchers who are fluent with these respective languages. Three bilingual speakers (Sepedi, Xitsonga, and Tshivenda) checked the translations from English to these local languages for accuracy, which was endorsed. Furthermore, the interview schedule was piloted with two participants to assess its effectiveness and suitability (See supplementary document 1). Pilot study was instrumental in refining the interview guide and ensuring that it would yield the desired data during the primary study. The in-depth interview began with an open-ended question, as shown in Table 1 below.
The data was collected between August and September 2022. In-depth individual interviews were conducted by the first author and assistant researcher using Sepedi, Xitsonga, Tshivenda, or English in a private room in the hospital to ensure confidentiality. COVID-19 precautionary measures were followed to protect the health and safety of participants and interviewers. Furniture was wiped with a 70% based-alcohol solution before and after each interview, chairs were spaced 1.5 meters apart to ensure adequate social distance and researchers and participants sanitised their hands before entering and exiting the room. Participants and the interviewer wore a surgical facial mask covering the nose and mouth throughout the interview.
The first author served as the lead interviewer, the assistant researcher functioned as a support system in case of a language barrier. The interviews were conducted in the participant's preferred language (Sepedi, Xitsonga, Tshivenda, or English). The interviewer used probing questions to encourage the participants to elaborate, and all other questions arose from the dialogue. The duration of each interview was between 45 and 65 minutes.
With the participants' permission, two audio recording devices were used to record each interview, whereby one served as a backup in case the main one defaulted. During each interview, the first author compiled field notes regarding the context, non-communication cues, and impressions to complement the recorded audio. Data collection continued until no new data emerged, whereby data saturation was declared. All the interviews were conducted at the hospital.
After data collection, the first author and assistant researchers transcribed the data verbatim, including field notes in English. The researchers' subjective experiences regarding the explored phenomenon were described to avoid influencing data analysis: a process termed bracketing [ 26 ]. Three bilingual speakers (Sepedi, Xitsonga, and Tshivenda) checked the translations to English transcriptions for accuracy against the audio recordings. Additionally, two transcripts (10% of the sample) were back translated, and accuracy was verified by an independent co-coder and two co-authors [SSM, KDS]. No substantial linguistic issues were identified during the translation process.
Data analysis
Giorgi's data analysis method [ 27 , 28 ] was applied to comprehend the essence of the experiences of parents of preterm infants in the NICU. The data analysis process constituted five steps: understanding raw data, constructing a constituent profile, forming a theme index, merging participants' theme indexes, and searching the thematic index to develop interpretive themes.
Trustworthiness
The four criteria of Lincoln and Guba [ 29 ] were applied to establish the trustworthiness of the current study. Credibility was established by member checking with 10% of the sample ( n =2) by sending the transcript and developed themes. The supervisors (experts) conducted a confirmability audit of the study project by checking and rechecking the collected raw-, coded- and interpreted data to affirm neutrality. Additionally, the study followed a rigorous descriptive qualitative method and underwent a peer review process that confirmed the consistency of the data, and the findings ensured dependability, while data saturation and a detailed description of the methodology ensured transferability.
Demographic data
Twenty ( n =20) mothers of preterm infants admitted to the NICU in a tertiary hospital participated in this study. The participants’ ages ranged from 18 to 39 years, with the majority being between 18 and 25. The majority of parents had three children. Regarding education, nine participants had a secondary-level education, and 11 had a tertiary education. Of the 20 participants, nine were unemployed, two were self-employed, one was fully employed, one was employed part-time, and seven were students (Refer to Table 2 ).
Emerging themes and sub-themes
Four main themes emerged from the data analysis. These were: lived experienced by parents of preterm infants, interactions with healthcare professionals, cultural practices concerning preterm infant care, and indigenous healthcare practices for preterm infants. These themes, supported by sub-themes, are outlined in Table 3 .
Theme 1 lived experienced by parents of preterm infants
The current study's first theme emerged as the lived experienced by parents of preterm infants. Parents experienced considerable challenges while caring for the preterm infants in the NICU. Lived difficulties experiences by parents are further explored through the sub-themes: stress and exhaustion, and longing for home.
Sub-theme 1.1 stress and exhaustion
Participants felt an overwhelming sense of exhaustion and stress, as they cared for their infants in the NICU. Participant responses revealed a pervasive fear of the unknown, coupled with emotional turmoil and physical strain. The uncertainty surrounding the health of their infants exacerbates their distress, leading to heightened anxiety and feelings of helplessness. This emotional burden is compounded by the challenges of navigating complex medical information and coping with unexpected health complications. Participants expressed shock, describing the unexpected event of preterm birth and the overwhelming emotions following the delivery of a preterm infant.
One participant reported:
We are always scared when we go to see babies because we don't know what it is, especially when you leave the baby without the tube; you think she may vomit when you are not around, and the next thing you will be receiving a call saying your baby is no more. (P1, 18-year-old)
Participant 1's expression of fear illustrates the constant apprehension experienced by mothers in the NICU, highlighting the emotional strain of anticipating potential emergencies and adverse outcomes. Another participant indicated the overwhelming uncertainty faced by the mothers upon entering the NICU, emphasizing the need for clear communication and reassurance from healthcare providers. The following quote supports the participant’s experience:
What if they tell me the situation is like this when I enter there? Honestly speaking, it frightens us. We just wish that it didn't ring so that when you get there, they tell you that they needed you so and so . (P2, 25-year-old)
Another participant highlighted the shock and fear induced by the sight of an extremely premature infant, illustrating the emotional toll of witnessing their vulnerability.
This baby, she was too small, like it was the first time seeing a small child like this. I once saw premature, but it was not like this, this one was so small, so I was scared. (P4, 24-year-old)
Another participant described her emotional response to distressing news about her baby's health which underscores the profound impact of medical uncertainties on maternal well-being, emphasizing the need for sensitive communication and support.
When they told me that my baby was like this and this, I even cried. (P10, 39-year-old)
Additionally, other participant’s narrative reflected the overwhelming fear and uncertainty experienced by mothers in the NICU, highlighting the emotional toll of constantly anticipating adverse outcomes and navigating complex medical situations. The following quotes reflect the participants’ experiences:
What I'm dealing with, because I was very broken and did not know what it is, will the baby survive, what will she do, what's going to happen. The answer is not right, as, for us, we are always afraid, we don't know what it is when you are here. (P17, 23-year-old)
Sub-theme 1.2 longing for home
The emotional strain and challenges faced by mothers while caring for their infants in the hospital setting evoke a profound yearning for the sense of security, comfort and belonging that home provides. The participants described their experience of not getting enough rest and sleep while caring for their preterm infant in the NICU which would not happen if they were home. Contributing factors include the time required to visit the NICU for the infant’s care routine, time spent walking from the mother's lodge to the NICU and back, and the separation of mother and infant.
The participant reflected on the contrast between hospital practices and what would have been done if she were at home:
Yes, here in the hospital, they want you to bathe the baby like this while at home they want you to do this and this or at home, you would do this when you see him doing that. It's things I want to know. (P5, 38-year-old)
This quote encapsulates the longing for the familiar routines and comforts of home amidst the unfamiliarity of hospital protocols. It highlights the sense of control and autonomy associated with home, where individuals adhere to their own customs and practices, as opposed to the regulated environment of the hospital. Another participant reminisces about cultural practices that would have been observed in her home environment:
Yeah, like mostly, like back at home, in our culture, we believe that a baby less than a month old must be bathed by the mother or grandmother... If I was at home, I will be feeding her with soft porridge without giving her any medications because this medication makes her defecate twice a day or so and this makes her lose weight. (P7, 32-year-old)
This excerpt emphasises the role of cultural traditions and familial support in shaping caregiving practices. It underlines the interconnectedness between home and cultural identity, where adherence to traditional customs provides a sense of security and belonging, particularly in the context of new-born care. Furthermore, another participant described the traditional approach to newborn care back home:
No, after birth when I come home, we don’t bathe the baby right away, we dampen the cloth in lukewarm water and just wipe the baby where he is dirty. We wash the head because the hair traps a lot of dirty things (blood and birth secretions), we avoid the full bath so that we don’t expose the baby to flu. (P18, 20-year-old)
Other participants compared hospital feeding methods with traditional practices at home. The participants reported that:
Here we feed the baby with breast milk using pipes (NG tubes and syringes) but at home, we do a light and very soft porridge. (P16, 38-year-old)
This comparison highlights the adaptation to different environments and the longing for familiar routines. It shows how home serves as a sanctuary where individuals adhere to their preferred methods of infant care, reinforcing the notion of home as a place of comfort and familiarity. Other participants expressed a longing for the comforts of home and the familiar routines:
So, the first challenge is that we wake up. We only sleep two hours. Most of the time we spend on the way, we do not have time to rest. Like when you are going that way, you may find that you are going for a long time in the baby’s room. When you are coming here, and you try to sleep, time is gone, you must go back. (P14, 39-year-old)
This statement reflects the desire for a sense of normalcy and routine amidst the challenges of hospitalisation. It highlights the idea that home represents a heaven of rest and recuperation, where individuals can adhere to their preferred practices and routines, particularly during significant life events such as childrearing.
Theme 2 interactions with healthcare professionals
In this study, interaction is perceived as communication and involvement in preterm infant care among healthcare professionals and parents of preterm infants in the NICU. The sub-themes included NICU care, communication, and healthcare professional attitudes.
Sub-theme 2.1 care in NICU
This sub-theme concerns how healthcare professionals cared for preterm infants and their parents in the NICU. Some indicated that they received adequate care from nurses and doctors in the NICU.
One participant indicated that:
The doctors are mostly here; they used to come only to check and update [us] about the baby's condition. The people who take part mostly are the nurses. Okay, looking at the ICU there is no problems, all is right. (P02, 25-year-old)
A similar view was echoed by another participant who stated:
Yes, they help me take care of the baby, and the doctors are nearby if there is something the doctor and nurses can help with. (P13, 22-year-old)
Another participant shared that she had only seen good things and is at peace with the care that she is receiving in the NICU:
In [N]ICU I have not seen any bad things; I only noticed the good things. My baby was in troubles, but she is not well, nurses are checking her every time so does the doctors. So up to so far, I never had any problems with nurses and doctors. I am at peace. (P18, 20-year-old)
However, one participant expressed dissatisfaction with the care she received in the NICU. The following quote confirms this:
They end up swearing at us and to be treated this way, been shouted, it ends up affecting our minds since I already have a problem with my baby’s condition. (P12, 28-year-old)
The participants’ responses highlight that they experienced positive and negative care while looking after their preterm infants in NICU; it appears that they appreciated the care, although some were unhappy.
Sub-theme 2.2 communication in NICU
Nearly all parents mentioned the importance of healthcare professionals practising effective communication as clinicians. In this context, communication is the exchange of information between parents of preterm infants and healthcare professionals in the NICU. The parents indicated that they had experienced satisfactory communication with healthcare professionals while caring for their preterm infant in the NICU. This includes comprehensive explanations; for instance, the doctor offered information regarding the baby's weight decrease in terms that parents could comprehend, giving them relief. The following quotes support the experience:
Yes, is not it that when we come here, we are under stress? So, if we want to say sister (nurse), may I ask, how is my baby doing? She can answer me; if she does not know, she must go and ask or tell me that I do not know about this one. I can ask someone who knows, like have good communication. (P17, 23-year-old)
Yes, the same doctor that I ask him regarding the baby’s weight loss. He explained to me well and now I understand, am free because the weight is no longer 0.8 kg, it is now around 1.0 kg. The support is good because when you ask something they quickly actioned it, so there is support. (P18, 20-year-old)
The above participants highlighted the importance of efficient communication in interactions between parents and healthcare professionals in the NICU and its positive effects on parents’ experiences and well-being. Nevertheless, other participants expressed dissatisfaction with the communication they received from the healthcare professionals in the NICU. One of the cited reasons for their dissatisfaction was that healthcare professionals discussed the infant's condition in a language the parents did not understand.
One participant mentioned that:
They asked me if I knew why my baby went to the theatre? What is the reason he came here? I said yes; I just heard them saying it is the authority which I do not know what they meant. (P06, 23-year-old)
Similarly, other participants expressed disappointment that healthcare professionals were not informing them about the interventions/procedures before implementation. The following quotes support the parental disappointment:
We do want to know because when we arrive in the ward, we just see that intravenous lines were inserted, and blood sample were collected, and we also see that the infant was pricked several times on the extremities hence do not even know where the samples are taken to. (P16, 38-year-old)
It is the same as when he was in high care because after labour, my baby was sent to high care, and the next morning he was in ICU without informing me. (P19, 23-year-old)
Moreover, another participant mentioned feeling confused because of the conflicting communication from healthcare professionals. The following quote supports this confusion:
The other one enters tells you the baby should change sides and give you reasons. When you tell them one said I should not change sides, they end up swearing at us end up confusing us. (P12, 28-year-old)
Participants highlighted the negative impact that poor communication could have on their experience in the NICU, as well as the significance of simple and consistent communication with healthcare professionals. They expressed a desire for precise, reliable information to understand what was happening to their preterm infants and to feel more involved in the care of their infants.
Sub-theme 2.3 attitude of healthcare professionals in NICU
The participants in the study expressed dissatisfaction with the attitudes of healthcare professionals in the NICU, as illustrated by the two quotes below:
When you go to the nurse and tell her that the tube is disconnected from the baby and the secretions are coming out through the nose, so the response will be like, what do you want me to do because your baby did that (mother rolling the eyes)? (P01, 18-year-old)
Okay there was this nurse who was on a night shift yesterday and she was busy with files, and when we wanted to ask her to collect some of the things for us, and she would say to us that we must go collect those things for ourselves because she is busy. So, when we got there to collect for ourselves, we found another nurse who asked us as to where our nurse is because we should not be doing this for ourselves. So, when we called her, she showed to me that she does not like her job. (P08, 31-year-old)
Another participant further mentioned that:
There is a nurse that seemed to have an advanced age, whenever we ask her to assist our babies, or asking some supplies to help our babies she is rude. She once told me that [my] babies are ugly such like me. (P20, 19-year-old)
More so, some mothers lamented the lack of communication from the nurses. For example
Their communication is not good because they hide things from us, sometimes you will find that they had taken your baby’s blood and not tell you about the results or what the results implies, and even when you ask the nurses, they would tell you that they are doing what they have been instructed to do. Sometimes you also find your baby inserted with drip, and when you ask, they do not say or explain the reason for all of these. (P08, 31-year-old)
Even though other participants expressed their dissatisfaction regarding the attitude of the healthcare professionals, other participants felt the opposite. One participant mentioned that she had a satisfactory relationship with the healthcare professionals expressed in the quote:
I am pleased with how the hospital is providing her with milk, yes, I am happy they help. (P12, 28-year-old)
Similarly, another participant added that she has only observed good things concerning the level of service provided to her infant:
In [N]ICU I haven’t seen any bad things; I only noticed the good things. (P18, 20-year-old)
Most parents expressed satisfaction with the level of support provided by the healthcare professionals in the NICU. The participants describe the support as encouraging and helping them to understand that challenges are a normal part of the process, as indicated by the below quotes:
Yes, their support is good. It is the kind of support that encourages you to understand that things like this are there and there are these kinds of challenges. (P07, 32-year-old)
Additionally, another participant alluded that:
The support from the nurses is very good, each one of them know me because I have been here for a long time. When they arrive, they call and ask how is the baby [doing]? Initially it was scary because my baby was the smallest one in the unit, and I was new but now am used to the nurses and the unit. (P18, 20-year-old)
Theme 3 cultural practice concerning preterm infant care
The third main theme was the cultural practices concerning preterm infant care. This study's concepts associated with this theme include practices and behaviours conducted after childbirth. This includes the infant naming practice, infant access restrictions, family involvement, and religious practice observance.
Sub-theme 3.1 infant naming by senior family members
Participants indicated that they adhere to the cultural practices of naming the preterm infant after birth. These cultural practices include understanding who is responsible for naming the infant, introducing the infant to the ancestors, and the meaning associated with the name given. The quotes show that senior family members, particularly grandmothers, are responsible for naming the infant and performing ancestral veneration to introduce the infant to the ancestors after birth.
One participant shared that:
If the granny [was] still alive, she [would be] the right [person] to appoint my parent to name the infant. (P02, 25-year-old)
Another participant supported the preceding statement by stating:
Well, when I call them at home regarding the name, my grandmother would want her name to be passed down to the child. (P08, 31-year-old)
The above data highlight that the grandmothers are responsible for naming the infants. This is because naming a preterm infant in Limpopo Province is culturally associated with the practice of ancestral communication, which grandmothers perform. Furthermore, one participant indicated that the infants are named based on various events in life. The following quotation illustrates this:
Because they used a dead person's name, so they are informing the owner of the name that there is someone who will use it. (P02, 25-year-old)
The above quote highlights the belief that a preterm infant is given the name of a deceased person to keep their memory alive and to ensure the continuation of a family legacy. Also, ancestral communication rituals should be performed to inform the name's owner. In addition, another participant indicated that infant naming is culturally essential and that a misnamed infant will continuously cry. The following quotation evidences this belief:
They do that; for example, they can call a baby by name like Sara, and if the baby stops crying, it means that is the name she wanted. And these things happen because they can call her by her name; the baby then stops crying and is healed instantly. (P01, 18-year-old)
The above data suggest that naming a preterm infant may positively affect the infant’s health and well-being when culturally informed. The beliefs and practices related to naming a preterm infant reflect the cultural values and traditions of the parents, which are essential considerations in providing culturally sensitive care in the NICU.
Sub-theme 3.2 infant access restrictions
Participants indicated that everyone is not permitted access to the room where the preterm infant is kept. Access restrictions include funeral attendees, pregnant women and individuals who recently engaged in sexual activities. The following section further explores how participants perceived these restricted individuals as harmful to the infant through a cultural lens based on their experiences during preterm infant care. A common experience for many participants was that individuals who participated in funeral services should perform cultural rituals with ashes and some aloes when entering, as illustrated in the following quotes.
They [those attended the funeral] enter the baby's room, they bath the baby with aloe and ashes a little bit and even on the joints so that she must never get sick. (P01, 18-year-old)
Usually, when they are from a funeral, they take ashes, apply them to the baby and make her swallow a bit of it so that they do not suppress her. (P02, 25-year-old)
An additional participant concurred with the preceding participants and elaborated that:
According to culture all babies from newborn to a child aged 6 to 7, when one person at home goes to the funeral, when that person comes back home takes ashes and rub it on the tummies of all these age group so that none of them can get suppressed or have negative auras. (P20, 19-year-old)
The data highlight the cultural belief that there are diseases and negative auras that can be acquired from funeral services and that precautionary measures must be taken to prevent the spread of these harmful elements to the preterm infant. In addition to the precautionary measures highlighted above, other participants explained that people who attend funerals should be isolated from the infant for some period before regaining access to the infant's room, as illustrated by the two quotes below:
I am staying with my grandmother, but if they are from the funeral, it means only I will nurse the baby. They will take seven days without entering the baby's room. (P04, 24-year-old)
She [person attended the funeral] must stay there for seven days before she returns, and after that, she can come back and help me with the baby. (P11, 27-year-old)
The above quotes indicate that isolating individuals who attended the funeral service for seven days will allow the acquired diseases and negative auras from the funeral to clear up and minimize the chances of transmission to the infant. Pregnant women were the second restriction. The following quotes illustrate beliefs and practices surrounding the presence and interactions of preterm infants and pregnant women:
Traditionally, we think she will suppress the baby. If a pregnant person carries the baby, she will delay the baby's growth. You find that at around six months, the baby is still unable to sit, so they believe it is because a pregnant person carried the baby. She is not supposed to enter the baby's room until the baby gets out. (P02, 25-year-old)
Another participant said:
If someone is pregnant, she is not supposed to hold a baby in such a way that the legs of the baby are on [her-pregnant woman] abdomen because we believe that if the baby's legs are stepping on top of the pregnant person's abdomen, the baby won't walk until the pregnant woman give birth, she will wait for the unborn baby to be born before she can walk. (P01, 18-year-old)
The first quote highlights the complete restriction of pregnant women from gaining access to the infant due to the negative impact (slow growth) that she can have on the infant. However, the second quote indicated that a pregnant woman can be granted access to the infant’s room and can even carry the infant, although with precautions not to allow the infant’s leg to come in contact with the abdomen. Through this analysis, it becomes clear that cultural beliefs and practices play a substantial role in shaping the experiences of pregnant women and their interaction with preterm infants. The final restriction was holding the infant after sexual intercourse. Most participants revealed a common belief that sexual intercourse could lead to the transfer of a negative aura to the infant. The following quote exemplifies this belief:
When the cord has not yet fallen, my grandmother is the only person who is allowed to enter because she has passed that stage of sexual intercourse. The rest of them are not allowed because we are trying to avoid negative aura to be passed on to the child, and if that happen, he will cry a lot. So, no one is allowed except my grandmother. (P08, 31-year-old)
Other participants stated, in support of the preceding statement:
They [siblings] might be coming from their partners and you would find that they were intimate in a way, so their energies will affect the baby negatively. (P09, 30-year-old)
Because they [grandmothers] do not have sexual intercourse anymore and they have experience. Culturally, it is believed that people who had sexual intercourse had negative aura. (P16, 38-year-old)
The data suggest that the role of grandmothers in caring for preterm infants is essential and safe as they are free of negative energies due to their age, experience, and abstinence from sexual intercourse. Furthermore, the data highlights that individuals who engage in sexual intercourse bring negative auras to the baby and are, therefore, not allowed to be in close proximity to the newborn. This cultural practice aims to ensure the well-being and health of the preterm infant by avoiding contact with individuals who have recently engaged in sexual intercourse.
Sub-theme 3.3 family involvement
Cultural practices concerning preterm infant care restrict infant access and allow family members to assist in caring for the infant. The following quotations illustrate participants' experience regarding family involvement while caring for the infant.
One participant stated that:
When I am here, the nurses help me, which is the same when you are at home. There is no difference. (P11, 27-year-old)
Another participant expressed a similar view:
It is very important because when you get help as a new mom you also get time to rest, in my family they would bathe the infant and massage you. (P12, 28-year-old)
In support of the above participants, another participant added that:
At home it is better because we have people who are assisting us, and we have time to rest (P16, 38-year-old)
The conclusion that can be drawn from these findings is that the involvement of family members in caring for the infant enabled the mothers to rest rather than continuously caring for the infant alone, which may be exhausting.
Sub-theme 3.4 religious practices observance/beliefs
In context of this study, most parents were religious and observed religious practices in terms of prayer and using ditaelo (church prescriptions - the church practices believed to be effective in curing the patient and preventing misfortune). This is connected to the belief that their infants would be protected from illness and be healthy, parents would be strengthened, and healthcare professionals would be granted wisdom to care for the infants. Most parents prayed to God for their preterm infant to get better and be healed. The following quotes illustrate this:
I just thought my baby is going to die but because God is present, I prayed I got baby boy. Now I thank God because of my faith and even the doctors had confidence that the baby will be okay. (P18, 20-year-old)
I pray every time I go to the ward for God to give her life and when I leave, I do not know what they will do to her, to not be affected when a lot of activities are done to her body. (P02, 25-year-old) Furthermore, parents also prayed for themselves and drew strength from their spiritual anchor to overcome the challenges they experienced while caring for their preterm infant in the NICU.
I have a way of overcoming my fears and sadness through prayer so that I can be able to receive strength . (P11, 27-year-old)
Other participants also highlighted this. For example, one participant indicated that:
When I am down, I pray for 2 minutes and ask God for strength. Then after, I feel okay. (P02, 25-year-old)
Moreover, participants did not only pray for themselves and their infants but also for healthcare professionals to have wisdom while caring for their infants. The following quotes demonstrate this intercession:
I believe that is the reason I prayed, because evil spirits can block the doctors view for them not see anything. (P12, 28-year-old)
Until now I just pray to God to give wisdom to doctors so that they treat my baby well then, I can go home. (P18, 20-year-old)
Lastly, one participant believed that prayer is more effective when performed in person, in the presence of others, rather than done alone. The participant stated that:
I prefer that when I pray, I must be there with two or more people because the prayer becomes more powerful when you are many. (P11, 27-year-old)
These findings highlights that the communal aspect of religious practices is vital for some individuals and that they believe that the power of prayer is amplified when performed with others. The quotes in this analysis indicate that the participants view prayer as connecting with a higher power, seeking strength, wisdom, and healing for themselves and the preterm infant in their care. Another aspect of religious practice, observance/practice called ditaelo , was also used to protect their infants from evil spirits and heal them.
Theme 4 indigenous healthcare practices for preterm infants
The final theme from the data analysis was “indigenous healthcare practices for preterm infants,” which parents described as the beliefs, knowledge, and habits about health passed down from generation to generation in a specific community. This theme is further explored through the following four subthemes.
Sub-theme 4.1 cultural practices used for cleaning the umbilical cord
Most participants believed that the indigenous care method for the umbilical cord is a vital cultural practice related to preterm infant care. Although the participants used surgical spirit in the NICU, they expressed the practices of using various herbal formulations that they would like to incorporate in the NICU during umbilical cord care. The following quotes reflect this.
I take table salt with that powdered wood soot and apply it [umbilical cord] on the cord every time you bathe the baby until it dries. (P10, 39-year-old)
We took soil from termite mound, chickens’ manure and placed them there for it to fall. (P12, 28-year-old)
Additionally, the same view was echoed by other participants, explaining that:
The herbs will shrink the cord, which will eventually fall off. After that, they will give you herbs to spread over the cord area, which will help the cord to close from inside. I was using the ashes to mix with Vaseline, then spread the mixture over the cord. (P15, 32-year-old)
We clean the cord with surgical spirit. Then we also use the head from the ‘matches’ stick and mix with the mouse poo and crush it down until is a fine powder. Then we apply the fine powder on the cord area. (P20, 19-year-old)
In addition to the various preferred herbal formulations, other participants mentioned that they apply breastmilk on the umbilical cord to increase the rate at which it dries. This is evident in the following quotes:
We do a full bath after two days with warm water, then clean the cord with the spirit, and apply breast milk so that the cord can dry and fall fast. (P18, 20-year-old)
They say we pour breast milk on the cord, like basically the newborn baby we need to apply the breast milk when I wake up in the morning, on the belly button. (P17, 23-year-old)
Furthermore, despite using surgical spirit in the NICU, participants were dissatisfied with its effectiveness. Most mothers felt that the delayed umbilical cord drying, and detachment were caused using surgical spirits.
One participant mentioned:
The way of taking care of children here is different; for instance, the surgical spirit is not so effective in cleaning and making the cord dry. The cord would have fallen by now if I was home. (P05, 38-year-old)
Another participant expressed that:
With home remedies it takes up to three days but with the surgical spirit, it takes seven days. It is fast if you do it traditionally. (P13, 22-year-old)
In support of the above participant, another participant further explained that:
We are staying with elderly people at our homes, so immediately after the baby is born, we start by treating her umbilical cord, which, culturally or religion-wise, is much faster than what we use here at the hospital, because even here at the hospital, they treat the cord by spreading spirit on the cord, but it takes time. (P14, 39-year-old)
Sub-theme 4.2 treatment of dehydration “ phogwana or lebalana ”
Some illnesses experienced by newborns are deemed to be not-for-hospital treatment but require indigenous healthcare practices or treatment. For example, dehydration is an indigenous childhood illness called phogwana, which traditionalists treat through herbal formulations. Other participants were concerned that their infant might suffer from phogwana while admitted to the NICU.
Maybe if I do things the way I am used to doing on the baby, he might recover, or maybe the baby has phogwana, and the doctor thinks it is something they can treat. (P06, 23-year-old)
The following participant echoed a similar notion in support:
When the baby is sick with lebalana, you do not take the baby to the hospital because they do not know how to treat that. You take her to someone. In Tshivenda, we say when the baby has lebalana, they must cut, burn things that came out of it, and then come to the baby… then the baby heals at the same time. (P17, 23-year-old)
Furthermore, participants shared that phogwana needs to be treated by a traditional healer or with traditional medicine. This is evident in the following quote.
If the phogwana is not beating well, there is a traditional medicine that we apply to make sure that it does not affect the baby. (P16, 38-year-old)
Sub-theme 4.3 care of eyes, ears, and nose
The subtheme of "care of eyes, ears, and nose " within the major theme of indigenous healthcare practices for preterm infants is represented by traditional methods of addressing issues related to the eyes, ears, and nose. Most participants reported using breast milk to clean and treat minor ailments of the eyes, ears, and nose.
Most of the time we use breast milk to take care of their eyes, and that even allows them to sleep peacefully, we take few drops of our breast milk and pour them inside his eyes. (P08, 31-year-old)
Another participant added that:
If the eyes are having discharge, we express breast milk inside the eyes and wipes it using the tongue to remove the discharges. (P16, 38-year-old)
In addition to using breast milk for eyes, it was reported to treat blocked nostrils and common flu and clean the umbilical cord, as reflected in the following quotes.
Breast milk works especially when the eyes are white or having the discharges. Same as the nose, when the baby is having a flu, we put few drops of breast milk that is our culture. (P18, 20-year-old)
Participants believe that the non-nutritional use of breast milk as a remedy or treatment for minor ailments of the eyes, sinuses, and ears is effective. This traditional belief may be because breast milk contains antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Sub-theme 4.4 infant bathing practices
The current study further revealed that preterm infant bathing was not only done for hygiene-related reasons but was also seen as serving to stimulate weight, for physical strengthening, and to protect the infant against evil spirits. These reasons are reflected in the following quotes.
Traditionally we bathe her with sehlapišo (traditional medicine) used to bathe infants to stimulate weight gain. (P13, 22-year-old)
Another participant also shared that:
We use leaves from the Baobab tree to bathe the baby; it is a medication. It is responsible for making the baby strong. (P10, 39-year-old)
In addition to herbal medicines that stimulate infant weight, other participants reported using herbal formulations to protect the infant against evil spirits and negative auras. The usage of herbal formulations is evident in the following quotes:
They use mogato (a traditional form of medicine to protect the baby from being suppressed) for bathing her. They put mogato inside the water and then just bath her, more especially if there is someone from the extended family coming to visit. (P02, 25-year-old)
I use the mixture, add it to the water, and bathe the baby to remove the negative spirits and aura, and some is for weight-gaining stimulation because young babies are difficult to hold due to their size. (P14, 39-year-old)
Lastly, other participants also shared the same notion; however, they indicated that this kind of herbal formulation called sehlapišo should not be used on the infant’s head during bathing as it is believed that the infant’s head will grow at an expedited rate should it come in contact with sehlapišo . The following quotes demonstrate this point:
When we use ‘sehlapišo’ for two days, we keep the water and then the next day we dilute it with hot water so that it becomes warm, and then after bathing we rinse him. we only bath his arms and legs because if we bath his head and neck they will grow too as this is used for growing or gaining weight. (P08, 31-year-old)
You do not touch the baby’s head when using ‘sehlapišo’ you only bath him from the neck to his toes, because they say if it happens that you touch the baby’s head while bathing him, [otherwise] the head and face becomes swollen and changes size. (P09, 30-year-old)
This study highlights parents' experiences caring for their preterm infants and the cultural determinants that can be integrated into preterm care to ensure culturally sensitive care. Four major themes and related sub-themes emphasise the importance of healthcare professionals respecting and acknowledging cultural practices, beliefs, and customs relevant to parents of preterm infants admitted to their facilities.
Participants in the current study experienced a range of negative feelings, including shock, fear, and anxiety, concerning the unexpected event of preterm birth, consistent with the literature. For instance, studies conducted in Sweden [ 30 ] and Denmark [ 31 ] reported that the abruptness of preterm birth, combined with the physical environment of the NICU, evokes feelings of shock and overwhelm in parents. Furthermore, the fear and anxiety experienced by the participants in this study while caring for their preterm infant in the NICU corroborate the findings in existing literature [ 32 , 33 ]. Both studies reported that parents often oscillate between hope and fear, particularly regarding their infant's survival and the possible long-term health complications associated with preterm birth. This correlation could be explained by the fact that preterm birth is traumatic and a potential stressor because it occurs mostly under emergency conditions, often threatening both the parents and the infant's well-being.
The current study's findings revealed that most participants acknowledged receiving satisfactory care from the nurses and doctors, as they were regularly present and helpful in tending to the infants' needs. This finding mirrors those of a study which noted that parents appreciate the quality of care provided by healthcare professionals in the NICU [ 34 ]. However, some participants felt that the nurses were often not friendly and mistreated them in the NICU. The findings are similar to the study which reported that some parents were dissatisfied with the care they received, which often stemmed from perceived rude behavior or negligence [ 35 ]. While technical, medical treatment and care are vital, the current data highlight how such care significantly influences parents' experiences in the NICU.
Communication, both in content and manner, is essential in the NICU setting, as it profoundly impacts parental experiences [ 36 ]. In addition, communication was also identified as a critical component in providing quality care to a diverse population concerning incorporating culturally competent care [ 37 ]. The current findings showed that many parents were satisfied with the communication they received from healthcare professionals, particularly when they were given clear explanations about their infants' condition. However, specific communication issues, including using incomprehensible medical jargon, insufficient intervention information, and conflicting advice from different professionals, were pointed out. These issues align with previous research, highlighting the need for improved communication strategies in the NICU to better inform and support parents [ 38 ].
Regarding the attitude of healthcare professionals, our findings revealed a mixed perception among parents. Some parents expressed dissatisfaction with the perceived negative attitudes of healthcare professionals, echoing similar findings by Shields et al. [ 39 ]. Negative attitudes from healthcare professionals can lead to mistrust and increased stress among parents [ 40 ]. Conversely, other parents in our study reported positive attitudes and felt well-supported and valued by the NICU staff. This positive perception aligns with the previous study which suggested that positive interactions with healthcare professionals can improve parental satisfaction [ 41 ]. While the current findings corroborate existing literature, the heightened perception of both positive and negative aspects of care, communication, and attitude might be attributed to cultural diversity in Limpopo Province.
The current study found that naming preterm infants is the domain of senior family members, particularly grandmothers. This finding aligns with previous work which asserted that grandmothers play a crucial role in naming infants and performing associated rituals in African cultures [ 42 ]. This role could be because the naming process is closely related to ancestral communication, which grandmothers frequently facilitate. Furthermore, the study indicates that infants' names often carry important cultural meanings or memorials, reflecting events or individuals in the family's history. The belief in the power of naming to affect an infant's well-being corroborates with the previous study’s assertion that names in most African cultures bear profound significance, carrying the family's hopes, aspirations, and legacies [ 43 ]. Additionally, names help individuals understand who they are and the community to which they belong. Such findings underscore the importance of cultural considerations concerning naming preterm infants in the NICU to promote culturally sensitive care and enhance parents' experiences.
In this study, three cultural restrictions on infant access aimed at safeguarding preterm infants' health were revealed. These restrictions primarily concern those who attended funerals, pregnant women, and people who recently engaged in sexual intercourse. First, funeral attendants: participants believed they could introduce diseases or negative auras to preterm infants, so precautionary measures needed to be taken before access could be granted again. The precautionary measure, which includes isolating funeral attendants for several days and having them wash their hands with aloe and ashes before touching the infant, aligns with a study by McAdoo [ 44 ], which reported similar customs among various African cultures. The use of aloe and ashes might stem from the fact that they contain some antibacterial properties, which may kill or lessen bacteria.
Second, according to our findings, pregnant women were also viewed as potentially harmful to preterm infants. This finding is unique as no other similar study could be located regarding the harm that could be brought by pregnant women. Third, individuals who recently engaged in sexual intercourse were deemed to have negative auras that could harm infants, particularly from parents' perspectives. This restriction echoes findings of previous study which revealed that newborns are isolated from young girls who engage in sexual activities as they can delay umbilical cord falling off [ 45 ]. This finding highlights the need for open dialogue and understanding regarding sexual practices in NICU care.
This study's findings underline the key role of family members in caring for preterm infants, which aligns with previous research in the field. Particularly, participant responses corroborated the evidence of family involvement as crucial to maternal well-being and infant care, as shown in a study conducted in the United States [ 46 ]. The responses reflect an appreciation for the support offered by extended family, primarily in providing mothers with rest and recovery time, mirroring previous findings [ 47 ]. The significance of family engagement in this study can be linked to cultural norms and values in the Limpopo Province and South Africa.
Most South African tribes, particularly indigenous ones, strongly believe in communal assistance and interdependence, particularly at significant life events such as childbirth. This is frequently characterised by extended family members stepping in to aid and support the new mother, allowing her time to relax and heal while contributing to the infant's care. Additionally, the similarity in support between NICU nurses and family members emphasized by participants resonates with the notion of family-centred care advocated by other scholars [ 48 ]. This approach, which suggests that healthcare providers can emulate a sense of familial support, highlights the importance of aligning clinical practices with the socio-cultural context of care.
Most participants expressed a reliance on prayer for the health of their infants, personal strength, and wisdom for healthcare professionals, which aligns with other studies that demonstrated the importance of spiritual beliefs in health outcomes and coping mechanisms [ 49 , 50 , 51 ]. Moreover, the idea of communal prayer being more potent than individual prayer, as pointed out by one participant, echoes classic sociological theory on the collective effervescence and emotional energy generated in communal religious rituals [ 52 ]. This finding accentuates the importance of understanding and integrating spiritual needs and beliefs in the NICU environment.
Interestingly, participants in the current study also invoked ' ditaelo ', or church prescriptions, in protecting and healing their infants. This practice, not extensively documented in the existing literature, appears to be a distinct element of religious observance in this cultural context. It may relate to African traditional healing practices, as discussed in the previous studies which indicated a unique fusion of Christianity and indigenous beliefs [ 53 , 54 ]. This practice underscores the cultural and spiritual complexity surrounding NICU care in the Limpopo Province and calls for further research to better comprehend these practices and their implications for infant care.
The participants’ experiences in the current study regarding umbilical cord care revealed that most parents reported using and believing in traditional cord care practices. These participants further described using ashes, powdered wood soot, breast milk, and soil from termite mounds topically to dry off and heal the umbilical cord. The use of herbs to treat and care for the umbilical cord was not unique to the participants in this study. In Sub-Saharan countries including South Africa [ 45 ], Zambia [ 55 ], Nigeria [ 56 ], Pakistan [ 57 ], and Uganda [ 58 ], the topical application of substances to the umbilical cord to hasten its detachment has been reported. It is important to acknowledge that while these traditional practices hold cultural significance and have been used for generations, their efficacy and safety may differ. In some cases, such practices may carry risks, such as infection or irritation. Healthcare providers should be aware of these cultural practices and engage in open and respectful conversation with families to understand their beliefs and preferences while also providing safe evidence-based care.
Moreover, participants also expressed dissatisfaction with modern procedures, such as surgical spirits, which they perceived as less effective than traditional practices because it makes the cord detach after seven days. This perception echoes the findings of study which revealed that some cultures believe traditional practices provide superior results compared to modern medical care, particularly for infants [ 59 ]. Although the herbal formulation was preferred over modern medical care, it has not been scientifically evaluated and studied; therefore, there is a potential risk of infection and other complications. Further research is needed to understand the scientific functionality of herbal formulations used to treat and dry off the umbilical cord.
This study showed that there are perceptions that certain medical conditions affecting newborns do not necessitate hospital care but rather require indigenous healthcare practices or treatment. For instance, phogwana was mentioned as a condition that needs out-of-hospital treatment by traditionalists. Similarly, this finding supports the previous literature which documented that the treatment of phogwana requires a traditional healer [ 44 , 60 ]. In addition, the literature indicated that the characteristics, prevention, and treatment of phogwana correspond to specific cultural contexts [ 61 ]. Providing medical care for premature infants outside of the hospital, under the guidance of traditionalists, may pose result risks, such as adverse responses to herbal therapy and metabolic poisoning. The immature organs of preterm newborns may have limited ability to efficiently remove metabolites of herbal medicines, which could potentially cause more health complications and death [ 62 ].
Furthermore, regarding the care of eyes, ears, and nose, participants reported using breast milk as a treatment for minor ailments. The belief in the antibacterial effects and healing properties of breast milk in traditional medicine is further substantiated by this finding, aligning with existing literature. These studies reinforce the multifunctional uses of breast milk beyond nutrition, including its application in treating eye infections [ 63 ] and alleviating nasal congestion, among others [ 64 ]. Although the benefits of breast milk are recognised, it is crucial to follow proper hygiene protocols when dealing with it. This includes washing your hands before handling breast milk and using sterile containers and applicators. Neglecting to maintain good hygiene can potentially introduce infections to the ears, nose, and eyes.
The participants in the current study reported that infant bathing was performed with different herbs for several purposes, such as stimulation of weight, warding off the evil spirit, and strengthening and protecting the infant. Herbal formulations used for bathing included sehlapišo , mogato , and baobab tree leaves. This study's findings agree with several studies on the African continent. In Uganda, infants were bathed with kyogero to attract fortunes [ 65 ], and in South Africa [ 44 ], India [ 66 ] and Nigeria [ 67 ], herbal medicine was also used during infant bathing for strengthening and spiritual protection purposes. One possible reason for the similarity could be that all studies reporting indigenous infant bathing were conducted on the African continent, which has overlapping cultural practices. It is clear from this finding that bathing practices are not merely physiologically functional but are often symbolic, serving various socio-cultural purposes and highlighting the intersection of cultural belief and healthcare. Preterm infants are vulnerable to health risks such as hypothermia, skin irritation, and infection due to their underdeveloped thermoregulatory system, delicate skin, and immature immune system [ 68 ]. Ritual bathing, particularly if not performed carefully, has the potential to worsen these health risks. It is recommended that healthcare professionals should ensures measures to guarantee that the ritual bathing environment for preterm newborns is secure, hygienic, and at a suitable temperature to reduce these dangers.
Limitations and strengths of the study
This study explored the cultural determinants of parents that can be incorporated into preterm infant care to ensure culturally sensitive care as part of maternal and childcare routine in the NICU in Limpopo Province. Although the qualitative design was the most appropriate to explore the phenomenon in this study, it limited the study's findings as it was not generalizable. Additionally, the primary investigator’s unconscious biases and perceptions could have influenced data analysis, however bracketing was applied to limit bias. Furthermore, to limit biases, the experts conducted a confirmability audit of the study project by checking and rechecking the collected raw-, coded- and interpreted data. The current study was conducted in a public hospital in Limpopo Province to explore the experiences of parents of preterm infants in the NICU, which may differ substantially from those in private hospitals and other provinces. Therefore, future research is recommended to explore this phenomenon in private hospitals and other provinces in South Africa.
The current study provides an understanding of parents' experiences caring for preterm infants in the NICU. The study offered meaningful insights into indigenous healthcare practices, emphasizing their crucial role in preterm infant care in specific cultural contexts. The cultural determinants included various topics, such as caring for the umbilical cord, treating phogwana , caring for the eyes, ears, and nose, and infant bathing customs. These practices showed a deeply ingrained belief system and a rich cultural heritage that have a meaningful impact on healthcare behaviours. However, these cultural determinants might have both positive and negative implications.
The findings demonstrated a strong reliance on traditional methods and herbal formulations in caring for preterm infants. Parents emphasised the advantages of these practices over current medical procedures, notably in treating disorders not frequently recognised by modern medicine and the care of the umbilical cord. This discontent with contemporary practices, highlights the need for culturally sensitive healthcare which can be conducted by conducting cultural assessments to understand the beliefs, values, and practices of the families in the NICU.
Overall, the findings of this study highlight the profound role of indigenous healthcare practices for preterm infants, reinforcing the need for a culturally sensitive approach in healthcare.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset materials generated and analysed during this study are accessible upon justified request from the corresponding author [MN].
Abbreviations
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
North-West University
Brooks JB. The process of parenting. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Higher Education; 2012.
Muller-Nix C, Ansermet F. Prematurity, risk factors, and protective factors. In: Zeanah CH, editor. Handbook of infant mental health. New York: The Guilford Press; 2009. p. 180–96.
Google Scholar
Shaw RJ, St John N, Lilo EA, Jo B, Benitz W, Stevenson DK, Horwitz SM. Prevention of traumatic stress in mothers with preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2013;132(Suppl 4):e886-94.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). Reproductive health. Preterm birth. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/pretermbirth.htm#:~:text=Preterm%20birth%0is%20when%20a,of%20pregnancy%20have%20been%20completed Accessed 02 December 2022.
WHO (World Health Organization). Preterm birth. 2017; https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/preterm-birth Accessed 18 Feb 2022.
Malakouti J, Jabraeeli M, Valizadeh S, Babapour J. Mother’s experience of having a preterm infant in the neonatal intensive care unit: a phenomenological study. Iran J Crit Care Nurs. 2013;5:172–81.
Pineda R, Bender J, Hall B, Shabosky L, Annecca A, Smith J. Parent participation in the neonatal intensive care unit: predictors and relationships to neuro behavior and developmental outcomes. Early Hum Dev. 2018;117:32–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2017.12.008 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Rihan SH, Mohamadeen LM, Zayadneh SA, Hilal FM, Rashid HA, Azzam NM, Khalaf DJ, Badran EF, Safadi R.R. Parents’ experience of having an infant in the neonatal intensive care unit: a qualitative study. Cureus. 2021;13 Suppl 7:e16747. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.16747 .
Ghadery-Sefat A, Abdeyazdan Z, Badiee Z, Zargham-Boroujeni A. Relationship between parent-infant attachment and parental satisfaction with supportive nursing care. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2016;21(Suppl 1):71–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-9066.174756 .
Bornstein MH. Cultural approaches to parenting. Parenting. 2012;12(Suppl 2–3):212–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2012.683359 .
Sarapat P, Fongkaew W, Jintrawet U, Mesukko J, Ray, L. Perceptions and practices of parents in caring for their hospitalized preterm infants. Pac Rim Int J Nurs Res. 2017;21 Suppl 3: 220–233. Available online: https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/PRIJNR/article/view/78177 Accessed 20 April 2021.
Brooks JL, Holdtich-Davis D, Docherty SL, Theodorou CS. Birthing and parenting a premature infant in a cultural context. Qual Health Res. 2016;26(Suppl 3):387–98. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732315573205 .
Harkness S, Super CM, Moscardino U, Rha JH, Blom MJ, Huitrón B, Johnston C, Sutherland M, Hyun OK, Axia G, Palacios J. Cultural models and developmental agendas: implications for arousal and self-regulation in early infancy. J Dev Processes. 2007;1(Suppl 2):5–39.
Joseph N, Unnikrishnan B, Naik V, Mahantshetti N, Mallapur M, Kotian S, Nelliyanil M. Infant rearing practices in South India: a longitudinal study. J Family Med Prim Care. 2013;2(Suppl 1):37–47. https://doi.org/10.4103/2249-4863.109942 .
Owoo NS, Lambon-Quayefio MP. National health insurance, social influence and antenatal care use in Ghana. Health Econ Rev. 2013;3(Suppl 19):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-1991-3-19 .
Article Google Scholar
Arabiat D, Whitehead L, Al Jabery M, Hamdan-Mansour A, Shaheen A, Abu Sabbah E. Beliefs about illness and treatment decision modelling during ill-health in Arabic families. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2021;14:1755–68. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S311900 .
Steyn E, Poggenpoel M, Myburgh C. Lived experiences of parents of premature babies in the intensive care unit in a private hospital in Johannesburg, South Africa. Curationis. 2017;40(Suppl 1):8. https://doi.org/10.4102/curationis.v40i1.1698 .
Pinderhughes EE, Dodge KA, Bates JE, Pettit GS, Zelli A. Discipline responses: Influences of parents’ socioeconomic status, ethnicity, beliefs about parenting, stress, and cognitive-emotional processes. J Fam Psychol. 2000;14(Suppl 3):380–400. https://doi.org/10.1037//0893-3200.14.3.380 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malwela T, Maputle MS. The preterm birth rate in a resource-stricken rural area of the Limpopo Province South Africa. NRR. 2022;12:67–75. https://doi.org/10.2147/NRR.S33816 .
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(Suppl 6):349–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042 .
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: part 2 - descriptive studies. Perspect Clin Res. 2019;10(1):34–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18 .
Tani Y, Hashimoto S, Ochiai M. What makes rural, traditional, cultures more sustainable? Implications from conservation efforts in mountainous rural communities of Japan. Landsc Res. 2016;41(Suppl 8):892–905. https://doi.org/10.1080/01426397.2016.1184631 .
Stats SA (Statistics South Africa). General Household Survey 2019: statistical release P0318. 2020; http://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/P0318/P03182019.pdf Accessed 1 June 2021.
Edmonds WA, Kennedy TD. An applied guide to research designs: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods. 2nd ed. Los Angeles: Sage Publications; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Boddy CR. Sample size for qualitative research. Qual Market Res. 2016;19 Suppl 4:426–32. https://doi.org/10.1108/qmr-06-2016-0053 .
Vagle MD. Crafting phenomenological research. 3rd ed. Walnut Creek: Left Coast Press Inc; 2014.
Giorgi A. A phenomenological perspective on certain qualitative research methods. J Phenomenol Psychol. 1994;25(Suppl 2):190–220. https://doi.org/10.1163/156916294X00034 .
Schweitzer RPD. Phenomenological research methodology: a guide paper presented at phenomenology seminar for Edith Cowan University. Bunbury: Bunbury; 1998.
Lincoln YS, Guba EG. Naturalistic inquiry. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications; 1985.
Lindberg B, Öhrling K. Experiences of having a prematurely born infant from the perspective of others in Northern Sweden. Int J Circumpolar Health. 2008;67(Suppl 5):461–71. https://doi.org/10.3402/ijch.v67i5.18353 .
Moseholm E, Fetters MD. Early parental coping and children’s behavioural and emotional problems at 6 and 18 months: a Danish cohort study. BMJ Open. 2016;6(Suppl 5):e010347.
Cleveland LM. Parenting in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2008;37(Suppl 6):666–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6909.2008.00288.x .
Holditch-Davis D, Bartlett TR, Blickman AL, Miles MS, Poston DJ. Parental distress and adjustment over time in neonatal intensive care unit. J Dev Behav. 2003;24(Suppl 5):314–22.
Wigert H, Berg M, Hellström AL. Parental presence when their child is in neonatal intensive care. Scand J Caring Sci. 2010;24(Suppl 1):139–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-6712.2009.00697.x .
Franck LS, Cox S, Allen A, Winter I. Parental concern and distress about infant pain. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2004;89(Suppl 1):71F – 75. https://doi.org/10.1136/fn.89.1.F71 .
De Rouck S, Leys M. Information needs of parents of children admitted to a neonatal intensive care unit: a review of the literature (1990–2008). Patient Educ Couns. 2009;76(Suppl 2):159–73.
Shopo KD, Rabie T, Du Preez A, Bester P. Experiences of midwives regarding provision of culturally competent care to women receiving maternal care in South Africa. Midwifery. 2023;116:103527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2022.103527 .
O’Hagan S, Manias E, Elder C, Pill J, Woodward-Kron R, McNamara T, Webb G, McColl G. What counts as effective communication in nursing? Evidence from nurse educators’ and clinicians’ feedback on nurse interactions with simulated patients. J Adv Nurs. 2014;70(Suppl 6):1344–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.12296 .
Shields L, Zhou H, Pratt J, Taylor M. Family-centered care for hospitalized children aged 0–12 years. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10:CD004811.
PubMed Google Scholar
Lindberg B, Axelsson K, Öhrling K. The birth of premature infants: experiences from the fathers’ perspective. J Neonatal Nurs. 2007;13(Suppl 4):142–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnn.2007.05.004 .
Labrie NH, van Veenendaal NR, Ludolph RA, Ket JC, van der Schoor SR, van Kempen AA. Effects of parent-provider communication during infant hospitalization in the NICU on parents: a systematic review with meta-synthesis and narrative synthesis. Patient Educ Counsel. 2021;104(Suppl 7):1526–52.
Mkhize N. African traditions and the social, economic and moral dimensions of fatherhood. In: Richter L.M, Morrell R, editors. Baba: men and fatherhood in South Africa. HSRC Press, California, United States; 2006. 183–198.
McAdoo JL. The roles of African American fathers: an ecological perspective. Fam Soc. 1993;74(Suppl 1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/104438949307400103 .
Clouse K, Malope-Kgokong B, Bor J, Nattey C, Mudau M, Maskew M. The South African National HIV pregnancy cohort: evaluating continuity of care among women living with HIV. BMC Public Health. 2020;20:1662. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09679-1 .
Shopo KD, Rabie T, Du Preez A, Bester P. Experiences of women receiving maternal care regarding cultural practices in selected public hospitals in the North West Province, South Africa. Int J Afr Nursing Sci. 2024;20:100680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2024.100680 .
Craig JW, Glick C, Phillips R, Hall SL, Smith J, Browne J. Recommendations for involving the family in developmental care of the NICU baby. J Perinatol. 2015;35 Suppl S1:S5–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2015.142 .
Mabaso MHL, Ndaba T, Mkhize-Kwitshana ZL. Overview of maternal, neonatal and child deaths in South Africa: challenges, opportunities, progress and future prospects. Int J MCH AIDS. 2014;2(Suppl 2):182–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kuo DZ, Houtrow AJ, Arango P, Kuhlthau KA, Simmons JM, Neff JM. Family-centered care: current applications and future directions in pediatric health care. Matern Child Health J. 2012;16(Suppl 2):297–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-011-0751-7 .
Willemse S, Smeets W, Van Leeuwen E, Nielen-Rosier T, Janssen L, Foudraine N. Spiritual care in the intensive care unit: an integrative literature research. J Crit Care. 2020;57:55–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.01.026 .
Koenig HG. Religion, spirituality, and health: the research and clinical implications. ISRN Psychiatry. 2012;2012:1–33. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/278730 .
Pargament KI. The psychology of religion and coping: theory, research, practice. New York: The Guilford Press; 1997.
Durkheim E, Fields KE. The elementary forms of religious life. New York: Free Press; 1995.
Mbiti JS. African religions & philosophy. 2nd rev. and enl. Edition. Heinemann: Oxford: Portsmouth, N.H., United Kingdom; 1990.
Ngubane H. Body and mind in Zulu medicine: an ethnography of health and disease in Nyuswa-Zulu thought and practice. London, New York: Academic Press; 1977.
Herlihy JM, Shaikh A, Mazimba A, Gagne N, Grogan C, Mpamba C, et al. Local perceptions, cultural beliefs and practices that shape umbilical cord care: a qualitative study in Southern Province, Zambia. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(Suppl 11):e79191. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079191 .
Abhulimhen-Iyoha B, Ibadin M. Determinants of cord care practices among mothers in Benin city, Edo State Nigeria. Niger J Clin Pract. 2012;15(Suppl 2):210–3. https://doi.org/10.4103/1119-3077.97320 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Khan GN, Memon ZA, Bhutta ZA. A cross sectional study of newborn care practices in Gilgit Pakistan. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2013;6(Suppl 1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.3233/NPM-1364712 .
Byaruhanga RN, Nsungwa-Sabiiti J, Kiguli J, Balyeku A, Nsabagasani X, Peterson S. Hurdles and opportunities for newborn care in rural Uganda. Midwifery. 2011;27(Suppl 6):775–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2010.02.005 .
Ozioma EOJ, Chinwe OAN. Herbal medicines in African traditional medicine. Herb Med. 2019;10:191–214. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.80348 .
Shai-Mahoko SN. The Role of indigenous healers in disease prevention and health promotion among black South Africans: a case study of the North West Province. Thesis, doctor of philosophy, University of South Africa, South Africa. 1997; https://uir.unisa.ac.za/handle/10500/17721 Accessed 20 June 2023.
Kay MA. Fallen fontanelle: culture-bound or cross-cultural? Med Anthropol. 1993;15(Suppl 2):137–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/01459740.1993.9966086 .
Adama EA, Sundin D, Bayes S. Sociocultural practices affecting the care of preterm infants in the Ghanaian community. J Transcult Nurs. 2021;32(Suppl 5):458–65.
Baynham JT, Moorman MA, Donnellan C, Cevallos V, Keenan JD. Antibacterial effect of human milk for common causes of paediatric conjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013;97:377–439. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2012-302833 .
Karcz K, Walkowiak M, Makuch J, Olejnik I, Królak-Olejnik B. Non-nutritional use of human milk part 1: a survey of the use of breast milk as a therapy for mucosal infections of various types in Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(Suppl 10):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101715 .
Kayom VO, Kakuru A, Kiguli S. Newborn care practices among mother-infant dyads in urban Uganda. Int J Pediatr. 2015;2015:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/815938 .
Owns AM, Mengue Eyi S, Van Andel T. Traditional medicine, and childcare in Western Africa: mothers’ knowledge, folk illnesses, and patterns of healthcare-seeking behaviour. PLoS One. 2014;9(Suppl 8):e105972. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105972 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
John ME, Nsemo AD, John EE, Opiah MM, Robinson-Bassey GC, Yagba J. Indigenous child care beliefs and practices in the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria: implications for health care. Int J Health Res. 2015;5(Suppl 11):235–47.
Oranges T, Dini V, Romanelli M. Skin physiology of the neonate and infant: clinical implications. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2015;4 Suppl 10:587–95. https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2015.0642 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their gratitude to all the parents of preterm infants who participated in this study and the assistant researchers who assisted in collecting the data.
Open access funding provided by North-West University. This manuscript was extracted from a funded research project by the NWU postgraduate bursary and Faculty of Health Sciences bursary (Funding code/number: not applicable).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
NuMIQ Research Focus Area, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
Madimetja J. Nyaloko, Welma Lubbe, Salaminah S. Moloko-Phiri & Khumoetsile D. Shopo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.N. conceptualised and developed the research protocol, conducted research (gathered, analysed, interpreted, and managed the data), and wrote the initial draft. W.L., S.S.M., and K.D.S. supervised the research and provided inputs and guidance for the research protocol development, data collection, analysis, and interpretations. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Madimetja J. Nyaloko .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The current study was executed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by North-West University Health Research Ethical committee [NWU-00267-21-S1]. Limpopo Province [LP-2021-08-027] granted permission to conduct the study through the National Health Research Database website. The management of the tertiary hospital granted goodwill permission for the study to be undertaken in their NICU. All the parents of preterm infants who participated in the study provided written informed consent. Participants were informed that participation in the study was voluntary and that they could withdraw anytime without penalty.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1. , rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nyaloko, M.J., Lubbe, W., Moloko-Phiri, S.S. et al. Parental experiences of caring for preterm infants in the neonatal intensive care unit, Limpopo Province: a descriptive qualitative study exploring the cultural determinants. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 669 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11117-6
Download citation
Received : 11 October 2023
Accepted : 17 May 2024
Published : 28 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11117-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Parental experiences
- Preterm infant
- Neonatal intensive care unit
- Descriptive
- Cultural determinants
- Healthcare professionals
- Culturally sensitive care
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
CRO Platform
Test your insights. Run experiments. Win. Or learn. And then win.
eCommerce Customer Analytics Platform
Acquisition matters. But retention matters more. Understand, monitor & nurture the best customers.
- Case Studies
- Ebooks, Tools, Templates
- Digital Marketing Glossary
- eCommerce Growth Stories
- eCommerce Growth Show
- Help & Technical Documentation
CRO Guide > Chapter 3.1
Qualitative Research: Definition, Methodology, Limitation & Examples
Qualitative research is a method focused on understanding human behavior and experiences through non-numerical data. Examples of qualitative research include:
- One-on-one interviews,
- Focus groups, Ethnographic research,
- Case studies,
- Record keeping,
- Qualitative observations
In this article, we’ll provide tips and tricks on how to use qualitative research to better understand your audience through real world examples and improve your ROI. We’ll also learn the difference between qualitative and quantitative data.
Table of Contents
Marketers often seek to understand their customers deeply. Qualitative research methods such as face-to-face interviews, focus groups, and qualitative observations can provide valuable insights into your products, your market, and your customers’ opinions and motivations. Understanding these nuances can significantly enhance marketing strategies and overall customer satisfaction.
What is Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication. This method focuses on the “why” rather than the “what” people think about you. Thus, qualitative research seeks to uncover the underlying motivations, attitudes, and beliefs that drive people’s actions.
Let’s say you have an online shop catering to a general audience. You do a demographic analysis and you find out that most of your customers are male. Naturally, you will want to find out why women are not buying from you. And that’s what qualitative research will help you find out.
In the case of your online shop, qualitative research would involve reaching out to female non-customers through methods such as in-depth interviews or focus groups. These interactions provide a platform for women to express their thoughts, feelings, and concerns regarding your products or brand. Through qualitative analysis, you can uncover valuable insights into factors such as product preferences, user experience, brand perception, and barriers to purchase.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research methods are designed in a manner that helps reveal the behavior and perception of a target audience regarding a particular topic.
The most frequently used qualitative analysis methods are one-on-one interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, case study research, record keeping, and qualitative observation.
1. One-on-one interviews
Conducting one-on-one interviews is one of the most common qualitative research methods. One of the advantages of this method is that it provides a great opportunity to gather precise data about what people think and their motivations.
Spending time talking to customers not only helps marketers understand who their clients are, but also helps with customer care: clients love hearing from brands. This strengthens the relationship between a brand and its clients and paves the way for customer testimonials.
- A company might conduct interviews to understand why a product failed to meet sales expectations.
- A researcher might use interviews to gather personal stories about experiences with healthcare.
These interviews can be performed face-to-face or on the phone and usually last between half an hour to over two hours.
When a one-on-one interview is conducted face-to-face, it also gives the marketer the opportunity to read the body language of the respondent and match the responses.
2. Focus groups
Focus groups gather a small number of people to discuss and provide feedback on a particular subject. The ideal size of a focus group is usually between five and eight participants. The size of focus groups should reflect the participants’ familiarity with the topic. For less important topics or when participants have little experience, a group of 10 can be effective. For more critical topics or when participants are more knowledgeable, a smaller group of five to six is preferable for deeper discussions.
The main goal of a focus group is to find answers to the “why”, “what”, and “how” questions. This method is highly effective in exploring people’s feelings and ideas in a social setting, where group dynamics can bring out insights that might not emerge in one-on-one situations.
- A focus group could be used to test reactions to a new product concept.
- Marketers might use focus groups to see how different demographic groups react to an advertising campaign.
One advantage that focus groups have is that the marketer doesn’t necessarily have to interact with the group in person. Nowadays focus groups can be sent as online qualitative surveys on various devices.
Focus groups are an expensive option compared to the other qualitative research methods, which is why they are typically used to explain complex processes.
3. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is the most in-depth observational method that studies individuals in their naturally occurring environment.
This method aims at understanding the cultures, challenges, motivations, and settings that occur.
- A study of workplace culture within a tech startup.
- Observational research in a remote village to understand local traditions.
Ethnographic research requires the marketer to adapt to the target audiences’ environments (a different organization, a different city, or even a remote location), which is why geographical constraints can be an issue while collecting data.
This type of research can last from a few days to a few years. It’s challenging and time-consuming and solely depends on the expertise of the marketer to be able to analyze, observe, and infer the data.
4. Case study research
The case study method has grown into a valuable qualitative research method. This type of research method is usually used in education or social sciences. It involves a comprehensive examination of a single instance or event, providing detailed insights into complex issues in real-life contexts.
- Analyzing a single school’s innovative teaching method.
- A detailed study of a patient’s medical treatment over several years.
Case study research may seem difficult to operate, but it’s actually one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding of the data collection methods and inferring the data.
5. Record keeping
Record keeping is similar to going to the library: you go over books or any other reference material to collect relevant data. This method uses already existing reliable documents and similar sources of information as a data source.
- Historical research using old newspapers and letters.
- A study on policy changes over the years by examining government records.
This method is useful for constructing a historical context around a research topic or verifying other findings with documented evidence.
6. Qualitative observation
Qualitative observation is a method that uses subjective methodologies to gather systematic information or data. This method deals with the five major sensory organs and their functioning, sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing.
- Sight : Observing the way customers visually interact with product displays in a store to understand their browsing behaviors and preferences.
- Smell : Noting reactions of consumers to different scents in a fragrance shop to study the impact of olfactory elements on product preference.
- Touch : Watching how individuals interact with different materials in a clothing store to assess the importance of texture in fabric selection.
- Taste : Evaluating reactions of participants in a taste test to identify flavor profiles that appeal to different demographic groups.
- Hearing : Documenting responses to changes in background music within a retail environment to determine its effect on shopping behavior and mood.
Below we are also providing real-life examples of qualitative research that demonstrate practical applications across various contexts:
Qualitative Research Real World Examples
Let’s explore some examples of how qualitative research can be applied in different contexts.
1. Online grocery shop with a predominantly male audience
Method used: one-on-one interviews.
Let’s go back to one of the previous examples. You have an online grocery shop. By nature, it addresses a general audience, but after you do a demographic analysis you find out that most of your customers are male.
One good method to determine why women are not buying from you is to hold one-on-one interviews with potential customers in the category.
Interviewing a sample of potential female customers should reveal why they don’t find your store appealing. The reasons could range from not stocking enough products for women to perhaps the store’s emphasis on heavy-duty tools and automotive products, for example. These insights can guide adjustments in inventory and marketing strategies.
2. Software company launching a new product
Method used: focus groups.
Focus groups are great for establishing product-market fit.
Let’s assume you are a software company that wants to launch a new product and you hold a focus group with 12 people. Although getting their feedback regarding users’ experience with the product is a good thing, this sample is too small to define how the entire market will react to your product.
So what you can do instead is holding multiple focus groups in 20 different geographic regions. Each region should be hosting a group of 12 for each market segment; you can even segment your audience based on age. This would be a better way to establish credibility in the feedback you receive.
3. Alan Pushkin’s “God’s Choice: The Total World of a Fundamentalist Christian School”
Method used: ethnographic research.
Moving from a fictional example to a real-life one, let’s analyze Alan Peshkin’s 1986 book “God’s Choice: The Total World of a Fundamentalist Christian School”.
Peshkin studied the culture of Bethany Baptist Academy by interviewing the students, parents, teachers, and members of the community alike, and spending eighteen months observing them to provide a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of Christian schooling as an alternative to public education.
The study highlights the school’s unified purpose, rigorous academic environment, and strong community support while also pointing out its lack of cultural diversity and openness to differing viewpoints. These insights are crucial for understanding how such educational settings operate and what they offer to students.
Even after discovering all this, Peshkin still presented the school in a positive light and stated that public schools have much to learn from such schools.
Peshkin’s in-depth research represents a qualitative study that uses observations and unstructured interviews, without any assumptions or hypotheses. He utilizes descriptive or non-quantifiable data on Bethany Baptist Academy specifically, without attempting to generalize the findings to other Christian schools.
4. Understanding buyers’ trends
Method used: record keeping.
Another way marketers can use quality research is to understand buyers’ trends. To do this, marketers need to look at historical data for both their company and their industry and identify where buyers are purchasing items in higher volumes.
For example, electronics distributors know that the holiday season is a peak market for sales while life insurance agents find that spring and summer wedding months are good seasons for targeting new clients.
5. Determining products/services missing from the market
Conducting your own research isn’t always necessary. If there are significant breakthroughs in your industry, you can use industry data and adapt it to your marketing needs.
The influx of hacking and hijacking of cloud-based information has made Internet security a topic of many industry reports lately. A software company could use these reports to better understand the problems its clients are facing.
As a result, the company can provide solutions prospects already know they need.
Real-time Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Benchmark Report
See where your business stands compared to 1,000+ e-stores in different industries.
Qualitative Research Approaches
Once the marketer has decided that their research questions will provide data that is qualitative in nature, the next step is to choose the appropriate qualitative approach.
The approach chosen will take into account the purpose of the research, the role of the researcher, the data collected, the method of data analysis , and how the results will be presented. The most common approaches include:
- Narrative : This method focuses on individual life stories to understand personal experiences and journeys. It examines how people structure their stories and the themes within them to explore human existence. For example, a narrative study might look at cancer survivors to understand their resilience and coping strategies.
- Phenomenology : attempts to understand or explain life experiences or phenomena; It aims to reveal the depth of human consciousness and perception, such as by studying the daily lives of those with chronic illnesses.
- Grounded theory : investigates the process, action, or interaction with the goal of developing a theory “grounded” in observations and empirical data.
- Ethnography : describes and interprets an ethnic, cultural, or social group;
- Case study : examines episodic events in a definable framework, develops in-depth analyses of single or multiple cases, and generally explains “how”. An example might be studying a community health program to evaluate its success and impact.
How to Analyze Qualitative Data
Analyzing qualitative data involves interpreting non-numerical data to uncover patterns, themes, and deeper insights. This process is typically more subjective and requires a systematic approach to ensure reliability and validity.
1. Data Collection
Ensure that your data collection methods (e.g., interviews, focus groups, observations) are well-documented and comprehensive. This step is crucial because the quality and depth of the data collected will significantly influence the analysis.
2. Data Preparation
Once collected, the data needs to be organized. Transcribe audio and video recordings, and gather all notes and documents. Ensure that all data is anonymized to protect participant confidentiality where necessary.
3. Familiarization
Immerse yourself in the data by reading through the materials multiple times. This helps you get a general sense of the information and begin identifying patterns or recurring themes.
Develop a coding system to tag data with labels that summarize and account for each piece of information. Codes can be words, phrases, or acronyms that represent how these segments relate to your research questions.
- Descriptive Coding : Summarize the primary topic of the data.
- In Vivo Coding : Use language and terms used by the participants themselves.
- Process Coding : Use gerunds (“-ing” words) to label the processes at play.
- Emotion Coding : Identify and record the emotions conveyed or experienced.
5. Thematic Development
Group codes into themes that represent larger patterns in the data. These themes should relate directly to the research questions and form a coherent narrative about the findings.
6. Interpreting the Data
Interpret the data by constructing a logical narrative. This involves piecing together the themes to explain larger insights about the data. Link the results back to your research objectives and existing literature to bolster your interpretations.
7. Validation
Check the reliability and validity of your findings by reviewing if the interpretations are supported by the data. This may involve revisiting the data multiple times or discussing the findings with colleagues or participants for validation.
8. Reporting
Finally, present the findings in a clear and organized manner. Use direct quotes and detailed descriptions to illustrate the themes and insights. The report should communicate the narrative you’ve built from your data, clearly linking your findings to your research questions.
Limitations of qualitative research
The disadvantages of qualitative research are quite unique. The techniques of the data collector and their own unique observations can alter the information in subtle ways. That being said, these are the qualitative research’s limitations:
1. It’s a time-consuming process
The main drawback of qualitative study is that the process is time-consuming. Another problem is that the interpretations are limited. Personal experience and knowledge influence observations and conclusions.
Thus, qualitative research might take several weeks or months. Also, since this process delves into personal interaction for data collection, discussions often tend to deviate from the main issue to be studied.
2. You can’t verify the results of qualitative research
Because qualitative research is open-ended, participants have more control over the content of the data collected. So the marketer is not able to verify the results objectively against the scenarios stated by the respondents. For example, in a focus group discussing a new product, participants might express their feelings about the design and functionality. However, these opinions are influenced by individual tastes and experiences, making it difficult to ascertain a universally applicable conclusion from these discussions.
3. It’s a labor-intensive approach
Qualitative research requires a labor-intensive analysis process such as categorization, recording, etc. Similarly, qualitative research requires well-experienced marketers to obtain the needed data from a group of respondents.
4. It’s difficult to investigate causality
Qualitative research requires thoughtful planning to ensure the obtained results are accurate. There is no way to analyze qualitative data mathematically. This type of research is based more on opinion and judgment rather than results. Because all qualitative studies are unique they are difficult to replicate.
5. Qualitative research is not statistically representative
Because qualitative research is a perspective-based method of research, the responses given are not measured.
Comparisons can be made and this can lead toward duplication, but for the most part, quantitative data is required for circumstances that need statistical representation and that is not part of the qualitative research process.
While doing a qualitative study, it’s important to cross-reference the data obtained with the quantitative data. By continuously surveying prospects and customers marketers can build a stronger database of useful information.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
Image source
Quantitative and qualitative research are two distinct methodologies used in the field of market research, each offering unique insights and approaches to understanding consumer behavior and preferences.
As we already defined, qualitative analysis seeks to explore the deeper meanings, perceptions, and motivations behind human behavior through non-numerical data. On the other hand, quantitative research focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and statistical relationships.
Let’s explore their key differences:
Nature of Data:
- Quantitative research : Involves numerical data that can be measured and analyzed statistically.
- Qualitative research : Focuses on non-numerical data, such as words, images, and observations, to capture subjective experiences and meanings.
Research Questions:
- Quantitative research : Typically addresses questions related to “how many,” “how much,” or “to what extent,” aiming to quantify relationships and patterns.
- Qualitative research: Explores questions related to “why” and “how,” aiming to understand the underlying motivations, beliefs, and perceptions of individuals.
Data Collection Methods:
- Quantitative research : Relies on structured surveys, experiments, or observations with predefined variables and measures.
- Qualitative research : Utilizes open-ended interviews, focus groups, participant observations, and textual analysis to gather rich, contextually nuanced data.
Analysis Techniques:
- Quantitative research: Involves statistical analysis to identify correlations, associations, or differences between variables.
- Qualitative research: Employs thematic analysis, coding, and interpretation to uncover patterns, themes, and insights within qualitative data.
Do Conversion Rate Optimization the Right way.
Explore helps you make the most out of your CRO efforts through advanced A/B testing, surveys, advanced segmentation and optimised customer journeys.
If you haven’t subscribed yet to our newsletter, now is your chance!
Like what you’re reading?
Join the informed ecommerce crowd.
We will never bug you with irrelevant info.
By clicking the Button, you confirm that you agree with our Terms and Conditions .
Continue your Conversion Rate Optimization Journey
- Last modified: January 3, 2023
- Conversion Rate Optimization , User Research
Valentin Radu
We’re a team of people that want to empower marketers around the world to create marketing campaigns that matter to consumers in a smart way. Meet us at the intersection of creativity, integrity, and development, and let us show you how to optimize your marketing.
Our Software
- > Book a Demo
- > Partner Program
- > Affiliate Program
- Blog Sitemap
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy & Security
- Cookies Policy
- REVEAL Terms and Conditions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Descriptive research classifies, describes, compares, and measures data. Meanwhile, analytical research focuses on cause and effect. For example, take numbers on the changing trade deficits between the United States and the rest of the world in 2015-2018. This is descriptive research.
Benefits of Descriptive Research: Limitations of Descriptive Research: Rich Data: Provides a comprehensive and detailed profile of the subject or issue through rich data, offering a thorough understanding (Gresham, 2016). Lack of Control: Cannot control variables or external factors, potentially influencing the accuracy and reliability of the data. Basis for Further Research: Helps to identify ...
As discussed earlier, common research methods for descriptive research include surveys, case studies, observational studies, cross-sectional studies, and longitudinal studies. Design your study: Plan the details of your study, including the sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis plan.
Descriptive research methods. Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research, though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable.. Surveys. Survey research allows you to gather large volumes of data that can be analyzed for frequencies, averages ...
Descriptive research is a methodological approach that seeks to depict the characteristics of a phenomenon or subject under investigation. In scientific inquiry, it serves as a foundational tool for researchers aiming to observe, record, and analyze the intricate details of a particular topic. This method provides a rich and detailed account ...
Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive research are: Quantitative research: It is a quantitative research method that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis of the population sample. It is a popular market research tool that allows us to collect and describe the demographic segment's nature.
Another example is that someone might conduct analytical research to identify a study's gap. It presents a fresh perspective on your data. Therefore, it aids in supporting or refuting notions. Descriptive vs analytical research. Here are the key differences between descriptive research and analytical research:
16. Approaching Descriptive Analysis: Summary Descriptive analysis is a valuable research tool. It can contribute to a wide range of studies, both descriptive and causal in nature. When approaching descriptive work, researchers should endeavor to first recognize a phenomenon of interest.
Descriptive research methods. Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research, though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable.. Surveys. Survey research allows you to gather large volumes of data that can be analysed for frequencies, averages ...
For example, suppose you are a website beta testing an app feature. In that case, descriptive research invites users to try the feature, tracking their behavior and then asking their opinions. Can be applied to many research methods and areas. Examples include healthcare, SaaS, psychology, political studies, education, and pop culture.
Descriptive writing focuses on the what, while critical/analytical writing focuses on the so what. Analytical writing should link the discussion back to the research aims, objectives or research questions (the golden thread). Some amount of description will always be needed, but aim to minimise description and maximise analysis to earn higher ...
Some characteristics of descriptive research are: Quantitativeness. Descriptive research uses a quantitative research method by collecting quantifiable information to be used for statistical analysis of the population sample. This is very common when dealing with research in the physical sciences. Qualitativeness.
You can also create a mixed methods research design that has elements of both. Descriptive research vs experimental research. Descriptive research gathers data without controlling any variables, while experimental research manipulates and controls variables to determine cause and effect.
Definition of descriptive research. Descriptive research is defined as a research method that observes and describes the characteristics of a particular group, situation, or phenomenon. The goal is not to establish cause and effect relationships but rather to provide a detailed account of the situation.
Descriptive Analytics. Definition: Descriptive analytics focused on describing or summarizing raw data and making it interpretable. This type of analytics provides insight into what has happened in the past. It involves the analysis of historical data to identify patterns, trends, and insights. Descriptive analytics often uses visualization ...
Descriptive employs observation and surveys; analytical uses statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. Descriptive aims to identify patterns or trends, while analytical aims to establish causation. Descriptive research is often qualitative, whereas analytical can be both qualitative and quantitative.
Descriptive research is a type of research that is used to describe the characteristics of a population. It collects data that are used to answer a wide range of what, when, and how questions pertaining to a particular population or group. For example, descriptive studies might be used to answer questions such as: What percentage of Head Start ...
Descriptive analysis identifies patterns in data to answer questions about who, what, where, when, and to what extent. This guide describes how to more effectively approach, conduct, and communicate quantitative descriptive analysis. The primary audience for this guide includes members of the research community who conduct and publish both ...
Descriptive research design. Descriptive research design uses a range of both qualitative research and quantitative data (although quantitative research is the primary research method) to gather information to make accurate predictions about a particular problem or hypothesis. As a survey method, descriptive research designs will help ...
INTRODUCTION. In our previous article in this series, [ 1] we introduced the concept of "study designs"- as "the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research question.". Study designs are primarily of two types - observational and interventional, with the former being ...
In this particular book, we present descriptive-interpretive qualitative research by Robert Elliott and Ladislav Timulak. This generic approach is the culmination of many years of method development and research by these authors, who were pioneers in introducing qualitative research to the psycho-therapy field.
Descriptive research would enable them to establish the scale and scope of homelessness, identifying key demographics and patterns. Analytical research, however, would take these findings and probe deeper into the causes, examining the social, economic, and political factors that contribute to the situation and what can be done to alleviate it.
In fact, descriptive research has many useful applications, and you probably rely on findings from descriptive research without even being aware that that is what you are doing. See Table 3.1 for examples. Explanatory research. The third type of research, explanatory research, seeks to answer "why" questions.
5 Examples of Descriptive Analytics. 1. Traffic and Engagement Reports. One example of descriptive analytics is reporting. If your organization tracks engagement in the form of social media analytics or web traffic, you're already using descriptive analytics. These reports are created by taking raw data—generated when users interact with ...
Descriptive research is widely used due to its non-invasive nature. Quantitative observations allow in-depth analysis and a chance to validate any existing condition. Descriptive Research Examples . There are several different descriptive research examples that highlight the types, applications and uses of this research method. Let's look at ...
Descriptive research is a research method used to try and determine the characteristics of a population or particular phenomenon. Discover the world's research 25+ million members
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
There are many articles reporting that the component of intestinal microbiota implies a link to anxiety disorders (AD), and the brain-gut axis is also a hot topic in current research. However, the specific relevance between gut microbiota and AD is uncertain. We aimed to investigate causal relationship between gut microbiota and AD by using bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR).
A descriptive qualitative research design was followed where twenty (n=20) parents of preterm infants were purposively selected. The study was conducted in the NICU in Limpopo using in-depth individual interviews. Taguette software and a thematic analysis framework were used to analyse the data.
Qualitative research is a method focused on understanding human behavior and experiences through non-numerical data. Examples of qualitative research include: One-on-one interviews, Focus groups, Ethnographic research, Case studies, Record keeping, Qualitative observations. In this article, we'll provide tips and tricks on how to use ...