Scope and Delimitations in Research
Delimitations are the boundaries that the researcher sets in a research study, deciding what to include and what to exclude. They help to narrow down the study and make it more manageable and relevant to the research goal.
Updated on October 19, 2022

All scientific research has boundaries, whether or not the authors clearly explain them. Your study's scope and delimitations are the sections where you define the broader parameters and boundaries of your research.
The scope details what your study will explore, such as the target population, extent, or study duration. Delimitations are factors and variables not included in the study.
Scope and delimitations are not methodological shortcomings; they're always under your control. Discussing these is essential because doing so shows that your project is manageable and scientifically sound.
This article covers:
- What's meant by “scope” and “delimitations”
- Why these are integral components of every study
- How and where to actually write about scope and delimitations in your manuscript
- Examples of scope and delimitations from published studies

What is the scope in a research paper?
Simply put, the scope is the domain of your research. It describes the extent to which the research question will be explored in your study.
Articulating your study's scope early on helps you make your research question focused and realistic.
It also helps decide what data you need to collect (and, therefore, what data collection tools you need to design). Getting this right is vital for both academic articles and funding applications.
What are delimitations in a research paper?
Delimitations are those factors or aspects of the research area that you'll exclude from your research. The scope and delimitations of the study are intimately linked.
Essentially, delimitations form a more detailed and narrowed-down formulation of the scope in terms of exclusion. The delimitations explain what was (intentionally) not considered within the given piece of research.
Scope and delimitations examples
Use the following examples provided by our expert PhD editors as a reference when coming up with your own scope and delimitations.
Scope example
Your research question is, “What is the impact of bullying on the mental health of adolescents?” This topic, on its own, doesn't say much about what's being investigated.
The scope, for example, could encompass:
- Variables: “bullying” (dependent variable), “mental health” (independent variable), and ways of defining or measuring them
- Bullying type: Both face-to-face and cyberbullying
- Target population: Adolescents aged 12–17
- Geographical coverage: France or only one specific town in France
Delimitations example
Look back at the previous example.
Exploring the adverse effects of bullying on adolescents' mental health is a preliminary delimitation. This one was chosen from among many possible research questions (e.g., the impact of bullying on suicide rates, or children or adults).
Delimiting factors could include:
- Research design : Mixed-methods research, including thematic analysis of semi-structured interviews and statistical analysis of a survey
- Timeframe : Data collection to run for 3 months
- Population size : 100 survey participants; 15 interviewees
- Recruitment of participants : Quota sampling (aiming for specific portions of men, women, ethnic minority students etc.)
We can see that every choice you make in planning and conducting your research inevitably excludes other possible options.
What's the difference between limitations and delimitations?
Delimitations and limitations are entirely different, although they often get mixed up. These are the main differences:
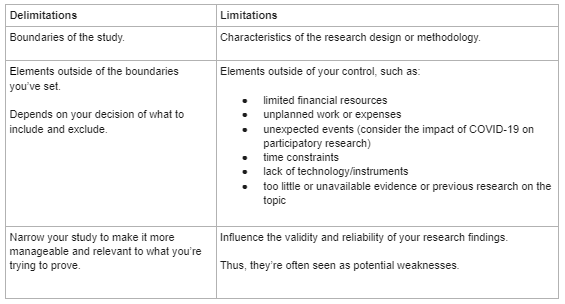
This chart explains the difference between delimitations and limitations. Delimitations are the boundaries of the study while the limitations are the characteristics of the research design or methodology.
Delimitations encompass the elements outside of the boundaries you've set and depends on your decision of what yo include and exclude. On the flip side, limitations are the elements outside of your control, such as:
- limited financial resources
- unplanned work or expenses
- unexpected events (for example, the COVID-19 pandemic)
- time constraints
- lack of technology/instruments
- unavailable evidence or previous research on the topic
Delimitations involve narrowing your study to make it more manageable and relevant to what you're trying to prove. Limitations influence the validity and reliability of your research findings. Limitations are seen as potential weaknesses in your research.
Example of the differences
To clarify these differences, go back to the limitations of the earlier example.
Limitations could comprise:
- Sample size : Not large enough to provide generalizable conclusions.
- Sampling approach : Non-probability sampling has increased bias risk. For instance, the researchers might not manage to capture the experiences of ethnic minority students.
- Methodological pitfalls : Research participants from an urban area (Paris) are likely to be more advantaged than students in rural areas. A study exploring the latter's experiences will probably yield very different findings.
Where do you write the scope and delimitations, and why?
It can be surprisingly empowering to realize you're restricted when conducting scholarly research. But this realization also makes writing up your research easier to grasp and makes it easier to see its limits and the expectations placed on it. Properly revealing this information serves your field and the greater scientific community.
Openly (but briefly) acknowledge the scope and delimitations of your study early on. The Abstract and Introduction sections are good places to set the parameters of your paper.
Next, discuss the scope and delimitations in greater detail in the Methods section. You'll need to do this to justify your methodological approach and data collection instruments, as well as analyses
At this point, spell out why these delimitations were set. What alternative options did you consider? Why did you reject alternatives? What could your study not address?
Let's say you're gathering data that can be derived from different but related experiments. You must convince the reader that the one you selected best suits your research question.
Finally, a solid paper will return to the scope and delimitations in the Findings or Discussion section. Doing so helps readers contextualize and interpret findings because the study's scope and methods influence the results.
For instance, agricultural field experiments carried out under irrigated conditions yield different results from experiments carried out without irrigation.
Being transparent about the scope and any outstanding issues increases your research's credibility and objectivity. It helps other researchers replicate your study and advance scientific understanding of the same topic (e.g., by adopting a different approach).
How do you write the scope and delimitations?
Define the scope and delimitations of your study before collecting data. This is critical. This step should be part of your research project planning.
Answering the following questions will help you address your scope and delimitations clearly and convincingly.
- What are your study's aims and objectives?
- Why did you carry out the study?
- What was the exact topic under investigation?
- Which factors and variables were included? And state why specific variables were omitted from the research scope.
- Who or what did the study explore? What was the target population?
- What was the study's location (geographical area) or setting (e.g., laboratory)?
- What was the timeframe within which you collected your data ?
- Consider a study exploring the differences between identical twins who were raised together versus identical twins who weren't. The data collection might span 5, 10, or more years.
- A study exploring a new immigration policy will cover the period since the policy came into effect and the present moment.
- How was the research conducted (research design)?
- Experimental research, qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods research, literature review, etc.
- What data collection tools and analysis techniques were used? e.g., If you chose quantitative methods, which statistical analysis techniques and software did you use?
- What did you find?
- What did you conclude?
Useful vocabulary for scope and delimitations
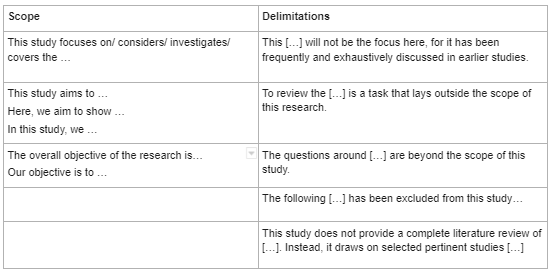
When explaining both the scope and delimitations, it's important to use the proper language to clearly state each.
For the scope , use the following language:
- This study focuses on/considers/investigates/covers the following:
- This study aims to . . . / Here, we aim to show . . . / In this study, we . . .
- The overall objective of the research is . . . / Our objective is to . . .
When stating the delimitations, use the following language:
- This [ . . . ] will not be the focus, for it has been frequently and exhaustively discusses in earlier studies.
- To review the [ . . . ] is a task that lies outside the scope of this study.
- The following [ . . . ] has been excluded from this study . . .
- This study does not provide a complete literature review of [ . . . ]. Instead, it draws on selected pertinent studies [ . . . ]
Analysis of a published scope
In one example, Simione and Gnagnarella (2020) compared the psychological and behavioral impact of COVID-19 on Italy's health workers and general population.
Here's a breakdown of the study's scope into smaller chunks and discussion of what works and why.
Also notable is that this study's delimitations include references to:
- Recruitment of participants: Convenience sampling
- Demographic characteristics of study participants: Age, sex, etc.
- Measurements methods: E.g., the death anxiety scale of the Existential Concerns Questionnaire (ECQ; van Bruggen et al., 2017) etc.
- Data analysis tool: The statistical software R
Analysis of published scope and delimitations
Scope of the study : Johnsson et al. (2019) explored the effect of in-hospital physiotherapy on postoperative physical capacity, physical activity, and lung function in patients who underwent lung cancer surgery.
The delimitations narrowed down the scope as follows:
Refine your scope, delimitations, and scientific English
English ability shouldn't limit how clear and impactful your research can be. Expert AJE editors are available to assess your science and polish your academic writing. See AJE services here .

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
- Privacy Policy

Home » Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and Examples
Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Scope of the Research
Scope of research refers to the range of topics, areas, and subjects that a research project intends to cover. It is the extent and limitations of the study, defining what is included and excluded in the research.
The scope of a research project depends on various factors, such as the research questions , objectives , methodology, and available resources. It is essential to define the scope of the research project clearly to avoid confusion and ensure that the study addresses the intended research questions.
How to Write Scope of the Research
Writing the scope of the research involves identifying the specific boundaries and limitations of the study. Here are some steps you can follow to write a clear and concise scope of the research:
- Identify the research question: Start by identifying the specific question that you want to answer through your research . This will help you focus your research and define the scope more clearly.
- Define the objectives: Once you have identified the research question, define the objectives of your study. What specific goals do you want to achieve through your research?
- Determine the population and sample: Identify the population or group of people that you will be studying, as well as the sample size and selection criteria. This will help you narrow down the scope of your research and ensure that your findings are applicable to the intended audience.
- Identify the variables: Determine the variables that will be measured or analyzed in your research. This could include demographic variables, independent variables , dependent variables , or any other relevant factors.
- Define the timeframe: Determine the timeframe for your study, including the start and end date, as well as any specific time intervals that will be measured.
- Determine the geographical scope: If your research is location-specific, define the geographical scope of your study. This could include specific regions, cities, or neighborhoods that you will be focusing on.
- Outline the limitations: Finally, outline any limitations or constraints of your research, such as time, resources, or access to data. This will help readers understand the scope and applicability of your research findings.
Examples of the Scope of the Research
Some Examples of the Scope of the Research are as follows:
Title : “Investigating the impact of artificial intelligence on job automation in the IT industry”
Scope of Research:
This study aims to explore the impact of artificial intelligence on job automation in the IT industry. The research will involve a qualitative analysis of job postings, identifying tasks that can be automated using AI. The study will also assess the potential implications of job automation on the workforce, including job displacement, job creation, and changes in job requirements.
Title : “Developing a machine learning model for predicting cyberattacks on corporate networks”
This study will develop a machine learning model for predicting cyberattacks on corporate networks. The research will involve collecting and analyzing network traffic data, identifying patterns and trends that are indicative of cyberattacks. The study aims to build an accurate and reliable predictive model that can help organizations identify and prevent cyberattacks before they occur.
Title: “Assessing the usability of a mobile app for managing personal finances”
This study will assess the usability of a mobile app for managing personal finances. The research will involve conducting a usability test with a group of participants, evaluating the app’s ease of use, efficiency, and user satisfaction. The study aims to identify areas of the app that need improvement, and to provide recommendations for enhancing its usability and user experience.
Title : “Exploring the effects of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction among college students”
This study aims to investigate the impact of mindfulness meditation on reducing stress levels among college students. The research will involve a randomized controlled trial with two groups: a treatment group that receives mindfulness meditation training and a control group that receives no intervention. The study will examine changes in stress levels, as measured by self-report questionnaires, before and after the intervention.
Title: “Investigating the impact of social media on body image dissatisfaction among young adults”
This study will explore the relationship between social media use and body image dissatisfaction among young adults. The research will involve a cross-sectional survey of participants aged 18-25, assessing their social media use, body image perceptions, and self-esteem. The study aims to identify any correlations between social media use and body image dissatisfaction, and to determine if certain social media platforms or types of content are particularly harmful.
When to Write Scope of the Research
Here is a guide on When to Write the Scope of the Research:
- Before starting your research project, it’s important to clearly define the scope of your study. This will help you stay focused on your research question and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- The scope of the research should be determined by the research question or problem statement. It should outline what you intend to investigate and what you will not be investigating.
- The scope should also take into consideration any limitations of the study, such as time, resources, or access to data. This will help you realistically plan and execute your research.
- Writing the scope of the research early in the research process can also help you refine your research question and identify any gaps in the existing literature that your study can address.
- It’s important to revisit the scope of the research throughout the research process to ensure that you stay on track and make any necessary adjustments.
- The scope of the research should be clearly communicated in the research proposal or study protocol to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the research objectives and limitations.
- The scope of the research should also be reflected in the research design, methods, and analysis plan. This will ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner that is aligned with the research objectives.
- The scope of the research should be written in a clear and concise manner, using language that is accessible to all stakeholders, including those who may not be familiar with the research topic or methodology.
- When writing the scope of the research, it’s important to be transparent about any assumptions or biases that may influence the research findings. This will help ensure that the research is conducted in an ethical and responsible manner.
- The scope of the research should be reviewed and approved by the research supervisor, committee members, or other relevant stakeholders. This will ensure that the research is feasible, relevant, and contributes to the field of study.
- Finally, the scope of the research should be clearly stated in the research report or dissertation to provide context for the research findings and conclusions. This will help readers understand the significance of the research and its contribution to the field of study.
Purpose of Scope of the Research
Purposes of Scope of the Research are as follows:
- Defines the boundaries and extent of the study.
- Determines the specific objectives and research questions to be addressed.
- Provides direction and focus for the research.
- Helps to identify the relevant theories, concepts, and variables to be studied.
- Enables the researcher to select the appropriate research methodology and techniques.
- Allows for the allocation of resources (time, money, personnel) to the research.
- Establishes the criteria for the selection of the sample and data collection methods.
- Facilitates the interpretation and generalization of the results.
- Ensures the ethical considerations and constraints are addressed.
- Provides a framework for the presentation and dissemination of the research findings.
Advantages of Scope of the Research
Here are some advantages of having a well-defined scope of research:
- Provides clarity and focus: Defining the scope of research helps to provide clarity and focus to the study. This ensures that the research stays on track and does not deviate from its intended purpose.
- Helps to manage resources: Knowing the scope of research allows researchers to allocate resources effectively. This includes managing time, budget, and personnel required to conduct the study.
- Improves the quality of research: A well-defined scope of research helps to ensure that the study is designed to achieve specific objectives. This helps to improve the quality of the research by reducing the likelihood of errors or bias.
- Facilitates communication: A clear scope of research enables researchers to communicate the goals and objectives of the study to stakeholders, such as funding agencies or participants. This facilitates understanding and enhances cooperation.
- Enables replication : A well-defined scope of research makes it easier to replicate the study in the future. This allows other researchers to validate the findings and build upon them, leading to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Increases the relevance of research: Defining the scope of research helps to ensure that the study is relevant to the problem or issue being investigated. This increases the likelihood that the findings will be useful and applicable to real-world situations.
- Reduces the risk of scope creep : Scope creep occurs when the research expands beyond the original scope, leading to an increase in the time, cost, and resources required to complete the study. A clear definition of the scope of research helps to reduce the risk of scope creep by establishing boundaries and limitations.
- Enhances the credibility of research: A well-defined scope of research helps to enhance the credibility of the study by ensuring that it is designed to achieve specific objectives and answer specific research questions. This makes it easier for others to assess the validity and reliability of the study.
- Provides a framework for decision-making : A clear scope of research provides a framework for decision-making throughout the research process. This includes decisions related to data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
Scope of the Research Vs Scope of the Project
| Scope of Research | Scope of Project |
|---|---|
| A focused and specific implementation of a solution | Focused and specific implementation of a solution |
| Seeks to explore and discover new information and knowledge | Aims to solve a problem or address a specific need |
| Can be theoretical or practical in nature | Generally practical, with tangible deliverables |
| May involve data collection, analysis, and interpretation | Involves planning, execution, and monitoring of tasks and activities |
| Usually conducted over a longer period of time | Has a defined timeline and milestones |
| May result in publications, reports, or academic degrees | Results in a product, service, or outcome that meets the project objectives |
| Can have implications beyond the specific project or application | Has a direct impact on the stakeholders and users involved in the project |

About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing...

Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Project – Definition, Writing Guide and...

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
Scope and Delimitations – Explained & Example
- By DiscoverPhDs
- October 2, 2020

What Is Scope and Delimitation in Research?
The scope and delimitations of a thesis, dissertation or research paper define the topic and boundaries of the research problem to be investigated.
The scope details how in-depth your study is to explore the research question and the parameters in which it will operate in relation to the population and timeframe.
The delimitations of a study are the factors and variables not to be included in the investigation. In other words, they are the boundaries the researcher sets in terms of study duration, population size and type of participants, etc.
Difference Between Delimitations and Limitations
Delimitations refer to the boundaries of the research study, based on the researcher’s decision of what to include and what to exclude. They narrow your study to make it more manageable and relevant to what you are trying to prove.
Limitations relate to the validity and reliability of the study. They are characteristics of the research design or methodology that are out of your control but influence your research findings. Because of this, they determine the internal and external validity of your study and are considered potential weaknesses.
In other words, limitations are what the researcher cannot do (elements outside of their control) and delimitations are what the researcher will not do (elements outside of the boundaries they have set). Both are important because they help to put the research findings into context, and although they explain how the study is limited, they increase the credibility and validity of a research project.
Guidelines on How to Write a Scope
A good scope statement will answer the following six questions:

- Why – the general aims and objectives (purpose) of the research.
- What – the subject to be investigated, and the included variables.
- Where – the location or setting of the study, i.e. where the data will be gathered and to which entity the data will belong.
- When – the timeframe within which the data is to be collected.
- Who – the subject matter of the study and the population from which they will be selected. This population needs to be large enough to be able to make generalisations.
- How – how the research is to be conducted, including a description of the research design (e.g. whether it is experimental research, qualitative research or a case study), methodology, research tools and analysis techniques.
To make things as clear as possible, you should also state why specific variables were omitted from the research scope, and whether this was because it was a delimitation or a limitation. You should also explain why they could not be overcome with standard research methods backed up by scientific evidence.
How to Start Writing Your Study Scope
Use the below prompts as an effective way to start writing your scope:
- This study is to focus on…
- This study covers the…
- This study aims to…
Guidelines on How to Write Delimitations
Since the delimitation parameters are within the researcher’s control, readers need to know why they were set, what alternative options were available, and why these alternatives were rejected. For example, if you are collecting data that can be derived from three different but similar experiments, the reader needs to understand how and why you decided to select the one you have.
Your reasons should always be linked back to your research question, as all delimitations should result from trying to make your study more relevant to your scope. Therefore, the scope and delimitations are usually considered together when writing a paper.
How to Start Writing Your Study Delimitations
Use the below prompts as an effective way to start writing your study delimitations:
- This study does not cover…
- This study is limited to…
- The following has been excluded from this study…
Examples of Delimitation in Research
Examples of delimitations include:
- research objectives,
- research questions,
- research variables,
- target populations,
- statistical analysis techniques .
Examples of Limitations in Research
Examples of limitations include:
- Issues with sample and selection,
- Insufficient sample size, population traits or specific participants for statistical significance,
- Lack of previous research studies on the topic which has allowed for further analysis,
- Limitations in the technology/instruments used to collect your data,
- Limited financial resources and/or funding constraints.

Learn about defining your workspace, having a list of daily tasks and using technology to stay connected, all whilst working from home as a research student.

Find out the differences between a Literature Review and an Annotated Bibliography, whey they should be used and how to write them.

This post gives you the best questions to ask at a PhD interview, to help you work out if your potential supervisor and lab is a good fit for you.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

Do you need to have published papers to do a PhD? The simple answer is no but it could benefit your application if you can.

Learning how to effectively collaborate with others is an important skill for anyone in academia to develop.

Dr Rowe gained his PhD in the fields of Chemistry and Biological Sciences from the University of East Anglia in 2018. He is now a project coordinator for Norwich Science Festival and also for Pint of Science in Norwich.

Dr Thirlaway gained his PhD in immunology from the University of Nottingham in 2018. He is now a Science Communicator at the Natural History Museum, London.
Join Thousands of Students

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Scope and Limitation of the Study This study focused on the Effects of Mentoring Program on Adversity Quotient® of Selected Freshmen College Students of First Asia Institute of Technology and Humanities during the Second Semester of Academic Year 2008 - 2009. The respondents of the study were composed of 181 randomly
Abstract. Social research is an endeavour that, most times, gives researchers the needed freedom and independence to inquire into issues they observe to be problematic or need understanding....
This article explores the importance of recognizing limitations and discusses how to write them effectively. By interpreting limitations in research and considering prevalent examples, we aim to reframe the perception from shameful mistakes to respectable revelations.
the limitations of your study in a way that anticipates and blunts reviewers’ criticisms of your work and demonstrates that you are a knowledgeable, adept researcher in your field. Address your study’s limitations in a concise paragraph near the end of the Discussion section.
This article covers: What's meant by “scope” and “delimitations”. Why these are integral components of every study. How and where to actually write about scope and delimitations in your manuscript. Examples of scope and delimitations from published studies.
The scope of the research should be clearly communicated in the research proposal or study protocol to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the research objectives and limitations. The scope of the research should also be reflected in the research design, methods, and analysis plan.
The scope and delimitations of a thesis, dissertation or paper define the topic and boundaries of a research problem - learn how to form them.
Scope and Limitation Sample Thesis PDF - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the challenges of writing a thesis, particularly defining the scope and limitations.
Scope and Limitation Thesis Sample PDF - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
This document discusses the scope and limitations of research for a thesis. It explains that the scope outlines the boundaries of what will and won't be investigated and provides context for the study.