Jayendra's Cloud Certification Blog
Google cloud – mountkirk games case study.
Mountkirk Games makes online, session-based, multiplayer games for mobile platforms. They have recently started expanding to other platforms after successfully migrating their on-premises environments to Google Cloud. Their most recent endeavor is to create a retro-style first-person shooter (FPS) game that allows hundreds of simultaneous players to join a geo-specific digital arena from multiple platforms and locations. A real-time digital banner will display a global leaderboard of all the top players across every active arena.

Solution Concept
Mountkirk Games is building a new multiplayer game that they expect to be very popular. They plan to deploy the game’s backend on Google Kubernetes Engine so they can scale rapidly and use Google’s global load balancer to route players to the closest regional game arenas. In order to keep the global leader board in sync, they plan to use a multi-region Spanner cluster.
So the key here is the company wants to deploy the new game to Google Kubernetes Engine exposed globally using a Global Load Balancer and configured to scale rapidly and bring it closer to the users. Backend DB would be managed using a multi-region Cloud Spanner cluster.
Executive Statement
Our last game was the first time we used Google Cloud, and it was a tremendous success. We were able to analyze player behavior and game telemetry in ways that we never could before. This success allowed us to bet on a full migration to the cloud and to start building all-new games using cloud-native design principles. Our new game is our most ambitious to date and will open up doors for us to support more gaming platforms beyond mobile. Latency is our top priority, although cost management is the next most important challenge. As with our first cloud-based game, we have grown to expect the cloud to enable advanced analytics capabilities so we can rapidly iterate on our deployments of bug fixes and new functionality.
So the key points here are the company has moved to Google Cloud with great success and wants to build new games in the cloud. Key priorities are high performance, low latency, cost, advanced analytics, quick deployment, and time-to-market cycles.
Business Requirements
Support multiple gaming platforms.
Support multiple regions.
- Can be handled using a Global HTTP load balancer with GKE in each region.
- Can be handled using multi-region Cloud Spanner
- Other multi-regional services like Cloud Storage , Cloud Datastore, Cloud Pub/Sub , BigQuery can be used.
Support rapid iteration of game features.
- Can be handled using Deployment Manager and IaaC services like Terraform to automate infrastructure provisioning
- Cloud Build + Cloud Deploy/Spinnaker can be used for rapid continuous integration and deployment
Minimize latency
- can be reduced using a Global HTTP load balancer, which would route the user to the closest region
- using multi-regional resources like Cloud Spanner would also help reduce latency
Optimize for dynamic scaling
- can be done using GKE Cluster Autoscaler and Horizontal Pod Autoscaling to dynamically scale the nodes and applications as per the demand
- Cloud Spanner can be scaled dynamically
Use managed services and pooled resources.
- Using GKE , with Global Load Balancer for computing and Cloud Spanner would help cover the application stack using managed services
Minimize costs.
- Using minimal resources and enabling auto-scaling as per the demand would help minimize costs
Existing Technical Environment
The existing environment was recently migrated to Google Cloud, and five games came across using lift-and-shift virtual machine migrations, with a few minor exceptions. Each new game exists in an isolated Google Cloud project nested below a folder that maintains most of the permissions and network policies. Legacy games with low traffic have been consolidated into a single project. There are also separate environments for development and testing.
Key points here are the resource hierarchy exists with a project for each new game under a folder to control access using Service Control Permissions. Also, some of the small games would be hosted in a single project. There are also different environments for development, testing, and production.
Technical Requirements
Dynamically scale based on game activity.
Publish scoring data on a near-real-time global leaderboard.
- can be handled using Pub/Sub for capturing data and Cloud DataFlow for processing the data on the fly i.e real time
Store game activity logs in structured files for future analysis.
- can be handled using Cloud Storage to store logs for future analysis
- analysis can be handled using BigQuery either loading the data or using federated data source
- data can also be stored directly using BigQuery as it would provide a low-cost data storage (as compared to Bigtable) for analytics
- another advantage of BigQuery over Bigtable in this case its multi-regional, meeting the global footprint and latency requirements
Use GPU processing to render graphics server-side for multi-platform support.
- Support eventual migration of legacy games to this new platform.
Reference Architecture

Refer to Mobile Gaming Analysis Telemetry solution
Mountkirk Games References
- Google Cloud – Mountkrik Games
2 thoughts on “ Google Cloud – Mountkirk Games Case Study ”
This needs to be re-visited. The use case now talks about using GKE in solution concept.
Mountkirk has been updated – working on the same.
Comments are closed.
SALE on Practice Exams and Courses! For Extra 20% Off Use Coupon RNPAUG4. Click here!

GCP – How To Work on MountKirk Games Case Study
What is ‘MountKirk games’ ?
‘MountKirk games’ is a fictitious company name used as a case study in Google Cloud platform (GCP). The company develops mobile games for its global user base. It aims to leverage on high scalability, continuous deployment, real-time analytics, minimum latency features offered in GCP for their future multiplayer game releases.
Why this case study is important?
MountKirk games is one of the case studies included in the Google Professional Cloud Architect (PCA) certification examination. We can expect maximum of 10 questions based on any two case studies listed in the examination guide.
For tips, resources and more helpful information on PCA exam, please read my blog – Six steps to Google Professional Cloud Architect Certification Blog
How to approach the solution ?
The solution approach consists of simple four steps method as mentioned in my previous blog in detail.
- Identify GCP products or services based on company requirements.
- Identify the knowledge gaps and do the relevant readings.
- Refer the industry best practices guidelines.
- Draw the solution diagram and discuss it with colleagues.
Company overview
Mountkirk Games makes online, session-based, multiplayer games for mobile platforms. They have recently started expanding to other platforms after successfully migrating their on-premises environments to Google Cloud. Their most recent endeavor is to create a retro-style first-person shooter (FPS) game that allows hundreds of simultaneous players to join a geo-specific digital arena from multiple platforms and locations. A real-time digital banner will display a global leaderboard of all the top players across every active arena.
Solution concept
The company is building a new multiplayer game that they expect to be very popular. They plan to deploy the game’s backend on Google Kubernetes Engine so they can scale rapidly and use Google’s global load balancer to route players to the closest regional game arenas. In order to keep the global leader board in sync, they plan to use a multi-region Spanner cluster (gaming database).
Existing technical environment
The existing environment was recently migrated to Google Cloud, and five games came across using lift-and-shift virtual machine migrations, with a few minor exceptions. Each new game exists in an isolated Google Cloud project nested below a folder that maintains most of the permissions (IAM) and network policies. Legacy games with low traffic have been consolidated into a single project. There are also separate environments for development and testing.
Business requirements
- Support multiple gaming platforms and multiple regions.
- Minimize latency.
- Support rapid iteration of game features.
- Optimize for dynamic scaling.
- Use managed services and pooled resources.
- Minimize costs
Products/services Identified
- Integration via Cloud Pub/Sub to ingest real-time event messages sent from a large number of mobile apps.
- Multi-regional GKE clusters with auto-scaling feature enabled for scalable environments based on user gaming activity.
- CI-CD pipeline using Cloud Repository, Jenkin builds, Docker, Container registry, Terraform tools.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) along with Global Load Balancer provides content closer and faster to users with reduced latency within service level objective limits.
Technical requirements
- Dynamically scale based on game activity.
- Publish scoring data on a near real-time global leaderboard.
- Store game activity logs in structured files for future analysis.
- Use GPU processing to render graphics server-side for multi-platform support.
- Support eventual migration of legacy games to this new platform.
- Kubernetes Engine provides dynamic scalability feature to grow in size in case of higher traffic.
- Memorystore is in-memory database on cloud provides rapid access to scoring data on global leaderboards.
- Google Cloud Storage is the recommended place to store large files like game activity logs for future processing.
- Cloud Dataflow transforms the JSON event into structured, schema-based data.
- BigQuery – all gaming data is loaded into the BigQuery analytics engine.
Executive statement
Our last game was the first time we used Google Cloud, and it was a tremendous success. We were able to analyze player behavior and game telemetry in ways that we never could before. This success allowed us to bet on a full migration to the cloud and to start building all-new games using cloud-native design principles.
Our new game is our most ambitious to date and will open up doors for us to support more gaming platforms beyond mobile. Latency is our top priority, although cost management is the next most important challenge. As with our first cloud-based game, we have grown to expect the cloud to enable advanced analytics capabilities so we can rapidly iterate on our deployments of bug fixes and new functionality.
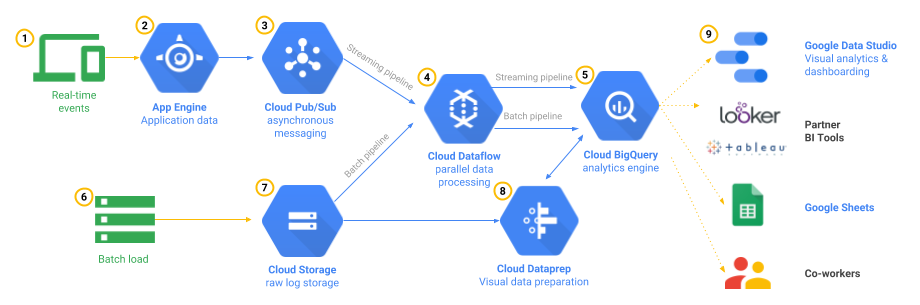
Proposed Solution Diagram
Based on the above requirements, we find that the central theme of the case study is ‘To provide Global gaming platform with scalability, low latency, high analytics capability’.
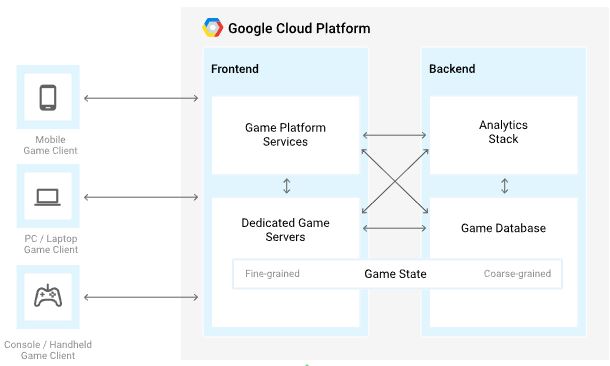
Solution Description
The frontend components of the gaming architecture include:
- Game platform services that provide extra-game functionality.
- Dedicated game servers that host the game.
The backend components of the gaming architecture include:
- Game state, persisted in the system of record and stored in the game database like Cloud Spanner.
- An analytics stack that stores and queries analytics and gameplay events.
In the gaming world, millions of mobile devices send the real-time event messages simultaneously. These events are ingested at scale with Cloud Pub/Sub. The Dataflow pipelines transform JSON event into structured, schema-based data for storing in BigQuery data warehouse for further analytics.
Cloud Storage is used to store large files like historical game activity logs from cloud logging for batch processing. The Dataflow pipelines processes the batch load before storing in BigQuery engine for analytics. Cloud Dataprep is a tool to visually exploring, cleaning and preparing structured and unstructured data for analysis.
Google Data Studio is a data visualisation tool which allows to create and share interactive gaming leaderboards using data in BigQuery. Other data visualization tools such as Looker, Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel are capable of directly running the BigQuery queries within them.
Further Reading – TerramEarth case study solution. Blog
Sample Case Questions
- MountKirk Games needs to build out their streaming data analytics pipeline to feed from their game backend application. What GCP services in which order will achieve this?
- The gaming company wants to set up a real-time analytics platform for their new game. The new platform must meet their technical requirements. Which combinations of Google Cloud Technology will meet all of their requirements?
- Mountkirk Games has deployed their new backend on Google Cloud Platform (GCP). You want to create a thorough testing process for new versions of the backend before they are released to the public. You want the testing environment to scale in an economical way. How should you design the process?
- MountKirk Games uses Kubernetes and Google Kubernetes Engine and wants to Use GPU processing to render graphics server-side. But GPUs are expensive so they are planning to use preemptible GPU nodes. What do they have to perform for the above solution?
Checkout 200+ practice exam questions here – Google Professional Cloud Architect Certification – Practice Exam
Hope you find this case study solution useful for PCA certification examination preparation.
Written exclusively for ReviewNPrep.com – By Manoj P. (Connect with me on LinkedIn ).
References:
- Building a Mobile Gaming Analytics Platform
- visual paradigm
Manoj Patil
Thanks for reading. You can get more technology news, promos and free content in our popular email newsletter. Over 50,000 people subscribe. Enter your email now and join us.
Search Here
Recent blogs.
- Unlocking Career Success with a Simple Resume Template
- Mastering E-commerce PPC Management: 12 Tips for Success
- Why Prototype Testing is Key to Reducing Risks and Boosting Success
- 10 Best College Search Websites for High School Students for 2024
- Use These ChatGPT Prompts To Land Your Dream Job
- Understanding the Role: A Comprehensive Guide to the Registered Behavior Technician (RBT) Job Description
- Market Your Online Course Like a Pro: 7 Expert Tips

Our Marketplace for your Next Certification

Popular Tags
- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
- Certification
Professional Cloud Architect
Certification exam guide
A Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Architect enables organizations to leverage Google Cloud technologies. Through an understanding of cloud architecture and Google technology, this individual designs, develops, and manages robust, secure, scalable, highly available, and dynamic solutions to drive business objectives. The Cloud Architect should be proficient in all aspects of enterprise cloud strategy, solution design, and architectural best practices. The Cloud Architect should also be experienced in software development methodologies and approaches including multi-tiered distributed applications which span multicloud or hybrid environments.
Case studies
During the exam for the Cloud Architect Certification, some of the questions may refer you to a case study that describes a fictitious business and solution concept. These case studies are intended to provide additional context to help you choose your answers. Review the case studies that may be used in the exam.
EHR Healthcare
Helicopter Racing League
Mountkirk Games
TerramEarth
Section 1: Designing and planning a cloud solution architecture (~24% of the exam)
1.1 Designing a solution infrastructure that meets business requirements. Considerations include:
● Business use cases and product strategy
● Cost optimization
● Supporting the application design
● Integration with external systems
● Movement of data
● Design decision trade-offs
● Build, buy, modify, or deprecate
● Success measurements (e.g., key performance indicators [KPI], return on investment [ROI], metrics)
● Compliance and observability
1.2 Designing a solution infrastructure that meets technical requirements. Considerations include:
● High availability and failover design
● Elasticity of cloud resources with respect to quotas and limits
● Scalability to meet growth requirements
● Performance and latency
1.3 Designing network, storage, and compute resources. Considerations include:
● Integration with on-premises/multicloud environments
● Cloud-native networking (VPC, peering, firewalls, container networking)
● Choosing data processing technologies
● Choosing appropriate storage types (e.g., object, file, databases)
● Choosing compute resources (e.g., preemptible, custom machine type, specialized workload)
● Mapping compute needs to platform products
1.4 Creating a migration plan (i.e., documents and architectural diagrams). Considerations include:
● Integrating solutions with existing systems
● Migrating systems and data to support the solution
● Software license mapping
● Network planning
● Testing and proofs of concept
● Dependency management planning
1.5 Envisioning future solution improvements. Considerations include:
● Cloud and technology improvements
● Evolution of business needs
● Evangelism and advocacy
Section 2: Managing and provisioning a solution infrastructure (~15% of the exam)
2.1 Configuring network topologies. Considerations include:
● Extending to on-premises environments (hybrid networking)
● Extending to a multicloud environment that may include Google Cloud to Google Cloud communication
● Security protection (e.g. intrusion protection, access control, firewalls)
2.2 Configuring individual storage systems. Considerations include:
● Data storage allocation
● Data processing/compute provisioning
● Security and access management
● Network configuration for data transfer and latency
● Data retention and data life cycle management
● Data growth planning
2.3 Configuring compute systems. Considerations include:
● Compute resource provisioning
● Compute volatility configuration (preemptible vs. standard)
● Network configuration for compute resources (Google Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, serverless networking)
● Infrastructure orchestration, resource configuration, and patch management
● Container orchestration
Section 3: Designing for security and compliance (~18% of the exam)
3.1 Designing for security. Considerations include:
● Identity and access management (IAM)
● Resource hierarchy (organizations, folders, projects)
● Data security (key management, encryption, secret management)
● Separation of duties (SoD)
● Security controls (e.g., auditing, VPC Service Controls, context aware access, organization policy)
● Managing customer-managed encryption keys with Cloud Key Management Service
● Remote access
3.2 Designing for compliance. Considerations include:
● Legislation (e.g., health record privacy, children’s privacy, data privacy, and ownership)
● Commercial (e.g., sensitive data such as credit card information handling, personally identifiable information [PII])
● Industry certifications (e.g., SOC 2)
● Audits (including logs)
Section 4: Analyzing and optimizing technical and business processes (~18% of the exam)
4.1 Analyzing and defining technical processes. Considerations include:
● Software development life cycle (SDLC)
● Continuous integration / continuous deployment
● Troubleshooting / root cause analysis best practices
● Testing and validation of software and infrastructure
● Service catalog and provisioning
● Business continuity and disaster recovery
4.2 Analyzing and defining business processes. Considerations include:
● Stakeholder management (e.g. influencing and facilitation)
● Change management
● Team assessment / skills readiness
● Decision-making processes
● Customer success management
● Cost optimization / resource optimization (capex / opex)
4.3 Developing procedures to ensure reliability of solutions in production (e.g., chaos engineering, penetration testing)
Section 5: Managing implementation (~11% of the exam)
5.1 Advising development/operation teams to ensure successful deployment of the solution. Considerations include:
● Application development
● API best practices
● Testing frameworks (load/unit/integration)
● Data and system migration and management tooling
5.2 Interacting with Google Cloud programmatically. Considerations include:
● Google Cloud Shell
● Google Cloud SDK (gcloud, gsutil and bq)
● Cloud Emulators (e.g. Cloud Bigtable, Datastore, Spanner, Pub/Sub, Firestore)
Section 6: Ensuring solution and operations reliability (~14% of the exam)
6.1 Monitoring/logging/profiling/alerting solution
6.2 Deployment and release management
6.3 Assisting with the support of deployed solutions
6.4 Evaluating quality control measures
Take the next step
Tell us what you’re solving for. A Google Cloud expert will help you find the best solution.
- Work with a trusted partner Find a partner
- Start using Google Cloud Try it free
- Continue browsing See all products
- Start using Google Cloud Go to console
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings
This is my solution design/implementation for the Mountkirk Games sample case study provided by Google ( https://cloud.google.com/certification/guides/cloud-architect/casestudy-mountkirkgames-rev2 ) - solution may be different due upgrade of Google Cloud Platform.
fdicarlo/GCP_MountkirkGames
Folders and files.
| Name | Name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Commits | ||||
Repository files navigation
Architecture implementation Technical implementation
Sample case study: Mountkirk Games
Mountkirk Games makes online, session-based, multiplayer games for mobile platforms. They build all of their games using some server-side integration. Historically, they have used cloud providers to lease physical servers.
Due to the unexpected popularity of some of their games, they have had problems scaling their global audience, application servers, MySQL databases, and analytics tools.
Their current model is to write game statistics to files and send them through an ETL tool that loads them into a centralized MySQL database for reporting.
1. Solution concept
Mountkirk Games is building a new game, which they expect to be very popular. They plan to deploy the game’s backend on Compute Engine so they can capture streaming metrics, run intensive analytics, and take advantage of its autoscaling server environment and integrate with a managed NoSQL database.
2. Business requirements
- Increase to a global footprint
- Improve uptime—downtime is loss of players
- Increase efficiency of the cloud resources we use
- Reduce latency to all customers
3. Technical requirements
Requirements for game backend platform.
- Dynamically scale up or down based on game activity
- Connect to a transactional database service to manage user profiles and game state
- Store game activity in a timeseries database service for future analysis
- As the system scales, ensure that data is not lost due to processing backlogs
- Run hardened Linux distro
Requirements for game analytics platform
- Process incoming data on the fly directly from the game servers
- Process data that arrives late because of slow mobile networks
- Allow queries to access at least 10 TB of historical data
- Process files that are regularly uploaded by users’ mobile devices
4. Executive statement
Our last successful game did not scale well with our previous cloud provider, resulting in lower user adoption and affecting the game’s reputation. Our investors want more key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the speed and stability of the game, as well as other metrics that provide deeper insight into usage patterns so we can adapt the game to target users. Additionally, our current technology stack cannot provide the scale we need, so we want to replace MySQL and move to an environment that provides autoscaling and low latency load balancing and frees us up from managing physical servers.

Latest Mountkirk Games Case Study (2024) - Google Cloud (GCP) Architect
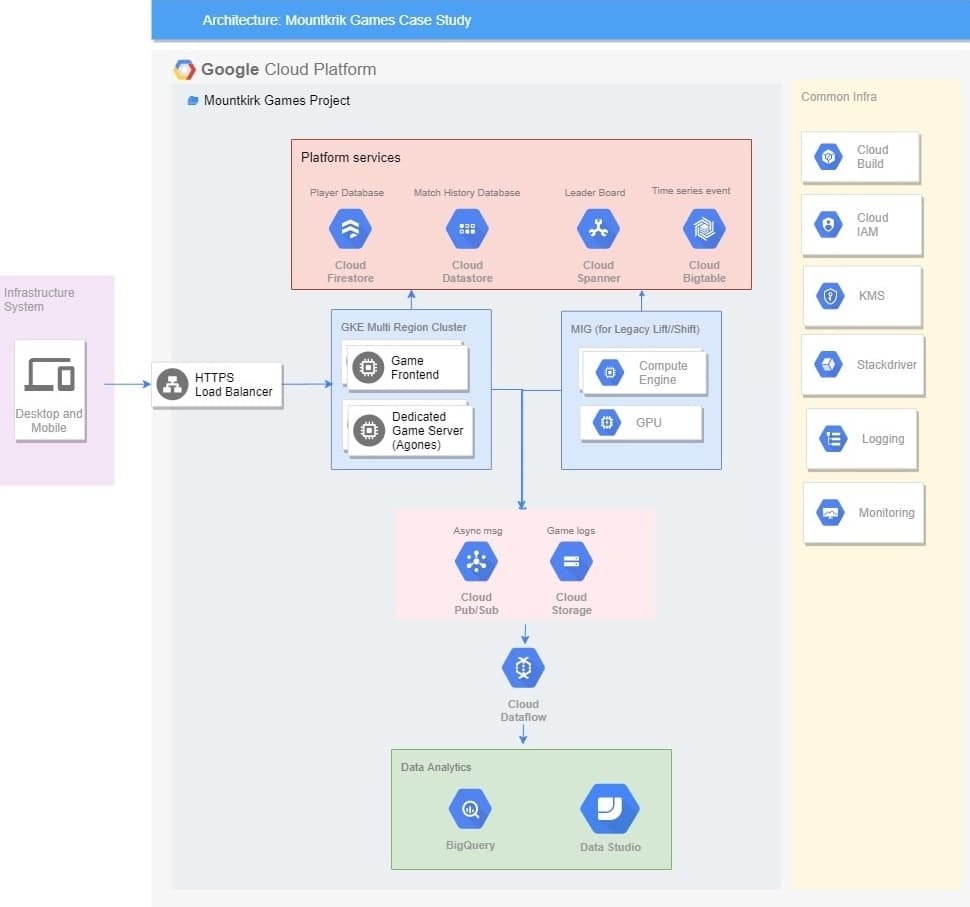
Possible architecture solution.
- Kubernetes + Agones (Gaming Server) : For multiplayer gaming
- Cloud Storage : Store game activity logs in organised files for later analysis in the cloud.
- Batch : Cloud Storage > Dataflow > BigQuery
- Streaming : Pub/Sub > Dataflow > BigQuery
- Common infra : Cloud build, KMS, IAM, Logger etc
Reference Architecture Solution diagram
There will be multiple possbile solutions for this use case, to understand the implementation better we have give reference architcture which is one of possible solution Below reference architecture depicts different aspect of Gaming Analytics cloud Platform solution like gaming server on GKE, Batch and stream pipleine and common cross cutting infrastructure components :
Recommendation for Top Popular Post :

Unlimited Access
Exam professional cloud architect topic 6 question 6 discussion.
For this question, refer to the Mountkirk Games case study. Which managed storage option meets Mountkirk's technical requirement for storing game activity in a time series database service?
- A. Cloud Bigtable
- B. Cloud Spanner
- C. BigQuery
- D. Cloud Datastore
anirban7172
Jabrrj68w02ond1, burner_1984, get it certification.
Unlock free, top-quality video courses on ExamTopics with a simple registration. Elevate your learning journey with our expertly curated content. Register now to access a diverse range of educational resources designed for your success. Start learning today with ExamTopics!
Log in to ExamTopics
Report comment.

COMMENTS
Mountkirk Games is building a new multiplayer game that they expect to be very popular. They plan to deploy the game's backend on Google Kubernetes Engine so they can scale rapidly and use Google's global load balancer to route players to the closest regional game arenas. In order to keep the global leader board in sync, they plan to use a
Solution Concept. Mountkirk Games is building a new multiplayer game that they expect to be very popular. They plan to deploy the game's backend on Google Kubernetes Engine so they can scale rapidly and use Google's global load balancer to route players to the closest regional game arenas. In order to keep the global leader board in sync ...
What is 'MountKirk games' ? 'MountKirk games' is a fictitious company name used as a case study in Google Cloud platform (GCP). The company develops mobile games for its global user base. It aims to leverage on high scalability, continuous deployment, real-time analytics, minimum latency features offered in GCP for their future ...
Case studies. During the exam for the Cloud Architect Certification, some of the questions may refer you to a case study that describes a fictitious business and solution concept. ... Mountkirk Games. TerramEarth. Register now Register now Section 1: Designing and planning a cloud solution architecture (~24% of the exam) 1.1 Designing a ...
Mountkirk Games makes online, session-based, multiplayer games for mobile platforms. They build all of their games using some server-side integration. Historically, they have used cloud providers to lease physical servers. Due to the unexpected popularity of some of their games, they have had ...
Hello everyone, welcome back to my channel, The Cloud Pilot. In this video, I'm going to share my proposed solution architecture for the Mountkirk Games case...
This case study has been around for a while and was recently modified on May 1, 2021 to coincide with the latest version of the Architect certificate exam. Let's discuss understand and analyze this case study Company overview. Maker of online, session-based, multiplayer games for mobile devices.
Join this channel to get access to perks:https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCL8vwy2jhEtQrC-Rx6qzCZg/join
Case Study Review: Mountkirk Games. Sep 20. Written By Iman Ghanizada. Credit goes to Indro Bhattacharyafor this series of case study posts. As most of you know by now, the Google PCA (Professional Cloud Architect) exam was revamped on May 1st, 2021. With the new version of the exam, and having cleared it myself last month, I noticed some ...
Solutioning Mountkirk Games for Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect exam. Case study: https://cloud.google.com/certification/guides/cloud-architect/cas...
Hello there, As GCP has revised the version of Professional Certified Architect exam, now the case studies have changed as well. Following are the new ones, While Mountkirk and TerramEarth were previously there as well, the problem statement has completely changed. If anyone has come across any solutions to these new case studies, please share.
GCP Certified Architect - Mountkirk Case Study Learn with flashcards, games and more — for free. ... Mountkirk Case Study Learn with flashcards, games and more — for free. ... Mountkirk Games wants to minimize latency and ensure high availability. Which Google Cloud service offers global distribution and strong consistency?
Actual exam question from Google's Professional Cloud Architect. Question #: 6. Topic #: 6. [All Professional Cloud Architect Questions] For this question, refer to the Mountkirk Games case study. Which managed storage option meets Mountkirk's technical requirement for storing game activity in a time series database service?
#GoogleCloud #CloudArchitect #MountkirkGames #CloudComputing #GCP #ExamPrep #MountkirkGamesCaseStudy #BigQuery #KubernetesEngine #ComputeEngine #cloudstor...
Question: 5 For this question, refer to the Mountkirk Games case study Mountkirk Games needs to create a repeatable and configurable mechanism for deploying isolated application environments. Developers and testers can access each other's environments and resources, but they cannot access staging or production resources. The staging environment needs access to some services from production.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Mountkirk Games makes online, session-based, multiplayer games for the most popular mobile platforms. They build all of their games using some server-side integration. Historically, they have used cloud providers to lease physical servers. Due to the unexpected popularity of some of their games, they have had problems scaling ...
Learning for GCP professional cloud architect requires to study Mountkirk Games case study, use case got updated since 01.05.2021, which is really long and ...
Which two steps should be part of their migration plan? (Choose two.) A. Evaluate the impact of migrating their current batch ETL code to Cloud Dataflow. B. Write a schema migration plan to denormalize data for better performance in BigQuery. For this question, refer to the Mountkirk Games case study.
Question: 5 For this question, refer to the Mountkirk Games case study Mountkirk Games needs to create a repeatable and configurable mechanism for deploying isolated application environments. Developers and testers can access each other's environments and resources, but they cannot access staging or production resources. The staging environment needs access to some services from production.