

The History of Homework: Why Was it Invented and Who Was Behind It?
- By Emily Summers
- February 14, 2020
Homework is long-standing education staple, one that many students hate with a fiery passion. We can’t really blame them, especially if it’s a primary source of stress that can result in headaches, exhaustion, and lack of sleep.
It’s not uncommon for students, parents, and even some teachers to complain about bringing assignments home. Yet, for millions of children around the world, homework is still a huge part of their daily lives as students — even if it continues to be one of their biggest causes of stress and unrest.
It makes one wonder, who in their right mind would invent such a thing as homework?
Who Invented Homework?
Pliny the younger: when in ancient rome, horace mann: the father of modern homework, the history of homework in america, 1900s: anti-homework sentiment & homework bans, 1930: homework as child labor, early-to-mid 20th century: homework and the progressive era, the cold war: homework starts heating up, 1980s: homework in a nation at risk, early 21 st century, state of homework today: why is it being questioned, should students get homework pros of cons of bringing school work home.

Online, there are many articles that point to Roberto Nevilis as the first educator to give his students homework. He created it as a way to punish his lazy students and ensure that they fully learned their lessons. However, these pieces of information mostly come from obscure educational blogs or forum websites with questionable claims. No credible news source or website has ever mentioned the name Roberto Nevilis as the person who invented homework . In fact, it’s possible that Nevilis never even existed.
As we’re not entirely sure who to credit for creating the bane of students’ existence and the reasons why homework was invented, we can use a few historical trivia to help narrow down our search.
Mentions of the term “homework” date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger , an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches. But some would argue that the assignment wasn’t exactly the type of written work that students have to do at home nowadays. Only introverted individuals with a fear of public speaking would find it difficult and stressful.
It’s also safe to argue that since homework is an integral part of education, it’s probable that it has existed since the dawn of learning, like a beacon of light to all those helpless and lost (or to cast darkness on those who despise it). This means that Romans, Enlightenment philosophers, and Middle Age monks all read, memorized, and sang pieces well before homework was given any definition. It’s harder to play the blame game this way unless you want to point your finger at Horace Mann.
In the 19 th century, Horace Mann , a politician and educational reformer had a strong interest in the compulsory public education system of Germany as a newly unified nation-state. Pupils attending the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given mandatory assignments that they needed to complete at home during their own time. This requirement emphasized the state’s power over individuals at a time when nationalists such as Johann Gottlieb Fichte were rallying support for a unified German state. Basically, the state used homework as an element of power play.
Despite its political origins, the system of bringing school assignments home spread across Europe and eventually found their way to Horace Mann, who was in Prussia at that time. He brought the system home with him to America where homework became a daily activity in the lives of students.
Despite homework being a near-universal part of the American educational experience today, it hasn’t always been universally accepted. Take a look at its turbulent history in America.
In 1901, just a few decades after Horace Mann introduced the concept to Americans, homework was banned in the Pacific state of California . The ban affected students younger than 15 years old and stayed in effect until 1917.
Around the same time, prominent publications such as The New York Times and Ladies’ Home Journal published statements from medical professionals and parents who stated that homework was detrimental to children’s health.
In 1930, the American Child Health Association declared homework as a type of child labor . Since laws against child labor had been passed recently during that time, the proclamation painted homework as unacceptable educational practice, making everyone wonder why homework was invented in the first place.
However, it’s keen to note that one of the reasons why homework was so frowned upon was because children were needed to help out with household chores (a.k.a. a less intensive and more socially acceptable form of child labor).
During the progressive education reforms of the late 19 th and early 20 th centuries, educators started looking for ways to make homework assignments more personal and relevant to the interests of individual students. Maybe this was how immortal essay topics such as “What I Want to Be When I Grow Up” and “What I Did During My Summer Vacation” were born.
After World War II, the Cold War heated up rivalries between the U.S. and Russia. Sputnik 1’s launch in 1957 intensified the competition between Americans and Russians – including their youth.
Education authorities in the U.S. decided that implementing rigorous homework to American students of all ages was the best way to ensure that they were always one step ahead of their Russian counterparts, especially in the competitive fields of Math and Science.
In 1986, the U.S. Department of Education’s pamphlet, “What Works,” included homework as one of the effective strategies to boost the quality of education. This came three years after the National Commission on Excellence in Education published “ Nation at Risk: The Imperative for Educational Reform .” The landmark report lambasted the state of America’s schools, calling for reforms to right the alarming direction that public education was headed.
Today, many educators, students, parents, and other concerned citizens have once again started questioning why homework was invented and if it’s still valuable.
Homework now is facing major backlash around the world. With more than 60% of high school and college students seeking counselling for conditions such as clinical depression and anxiety, all of which are brought about by school, it’s safe to say that American students are more stressed out than they should be.
After sitting through hours at school, they leave only to start on a mountain pile of homework. Not only does it take up a large chunk of time that they can otherwise spend on their hobbies and interests, it also stops them from getting enough sleep. This can lead to students experiencing physical health problems, a lack of balance in their lives, and alienation from their peers and society in general.
Is homework important and necessary ? Or is it doing more harm than good? Here some key advantages and disadvantages to consider.
- It encourages the discipline of practice
Using the same formula or memorizing the same information over and over can be difficult and boring, but it reinforces the practice of discipline. To master a skill, repetition is often needed. By completing homework every night, specifically with difficult subjects, the concepts become easier to understand, helping students polish their skills and achieve their life goals.
- It teaches students to manage their time
Homework goes beyond just completing tasks. It encourages children to develop their skills in time management as schedules need to be organized to ensure that all tasks can be completed within the day.
- It provides more time for students to complete their learning process
The time allotted for each subject in school is often limited to 1 hour or less per day. That’s not enough time for students to grasp the material and core concepts of each subject. By creating specific homework assignments, it becomes possible for students to make up for the deficiencies in time.
- It discourages creative endeavors
If a student spends 3-5 hours a day on homework, those are 3-5 hours that they can’t use to pursue creative passions. Students might like to read leisurely or take up new hobbies but homework takes away their time from painting, learning an instrument, or developing new skills.
- Homework is typically geared toward benchmarks
Teachers often assign homework to improve students’ test scores. Although this can result in positive outcomes such as better study habits, the fact is that when students feel tired, they won’t likely absorb as much information. Their stress levels will go up and they’ll feel the curriculum burnout.
- No evidence that homework creates improvements
Research shows that homework doesn’t improve academic performance ; it can even make it worse. Homework creates a negative attitude towards schooling and education, making students dread going to their classes. If they don’t like attending their lessons, they will be unmotivated to listen to the discussions.
With all of the struggles that students face each day due to homework, it’s puzzling to understand why it was even invented. However, whether you think it’s helpful or not, just because the concept has survived for centuries doesn’t mean that it has to stay within the educational system.
Not all students care about the history of homework, but they all do care about the future of their educational pursuits. Maybe one day, homework will be fully removed from the curriculum of schools all over the world but until that day comes, students will have to burn the midnight oil to pass their requirements on time and hopefully achieve their own versions of success.
About the Author
Emily summers.

Reasons You Should Learn French Now

10 Careers to Pursue After High School if Youre a People Person

How Summer Camp Fosters Social Skills

6 reasons to read to your child regularly at home

Is the D Important in Pharmacy? Why Pharm.D or RPh Degrees Shouldn’t Matter

How to Email a Professor: Guide on How to Start and End an Email Conversation

Everything You Need to Know About Getting a Post-Secondary Education

Grammar Corner: What’s The Difference Between Analysis vs Analyses?

History Cooperative
The Homework Dilemma: Who Invented Homework?
The inventor of homework may be unknown, but its evolution reflects contributions from educators, philosophers, and students. Homework reinforces learning, fosters discipline, and prepares students for the future, spanning from ancient civilizations to modern education. Ongoing debates probe its balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility, prompting innovative alternatives like project-based and personalized learning. As education evolves, the enigma of homework endures.
Table of Contents
Who Invented Homework?
While historical records don’t provide a definitive answer regarding the inventor of homework in the modern sense, two prominent figures, Roberto Nevelis of Venice and Horace Mann, are often linked to the concept’s early development.
Roberto Nevelis of Venice: A Mythical Innovator?
Roberto Nevelis, a Venetian educator from the 16th century, is frequently credited with the invention of homework. The story goes that Nevelis assigned tasks to his students outside regular classroom hours to reinforce their learning—a practice that aligns with the essence of homework. However, the historical evidence supporting Nevelis as the inventor of homework is rather elusive, leaving room for skepticism.
While Nevelis’s role remains somewhat mythical, his association with homework highlights the early recognition of the concept’s educational value.
Horace Mann: Shaping the American Educational Landscape
Horace Mann, often regarded as the “Father of American Education,” made significant contributions to the American public school system in the 19th century. Though he may not have single-handedly invented homework, his educational reforms played a crucial role in its widespread adoption.
Mann’s vision for education emphasized discipline and rigor, which included assigning tasks to be completed outside of the classroom. While he did not create homework in the traditional sense, his influence on the American education system paved the way for its integration.
The invention of homework was driven by several educational objectives. It aimed to reinforce classroom learning, ensuring knowledge retention and skill development. Homework also served as a means to promote self-discipline and responsibility among students, fostering valuable study habits and time management skills.
Why Was Homework Invented?
The invention of homework was not a random educational practice but rather a deliberate strategy with several essential objectives in mind.
Reinforcing Classroom Learning
Foremost among these objectives was the need to reinforce classroom learning. When students leave the classroom, the goal is for them to retain and apply the knowledge they have acquired during their lessons. Homework emerged as a powerful tool for achieving this goal. It provided students with a structured platform to revisit the day’s lessons, practice what they had learned, and solidify their understanding.
Homework assignments often mirrored classroom activities, allowing students to extend their learning beyond the confines of school hours. Through the repetition of exercises and tasks related to the curriculum, students could deepen their comprehension and mastery of various subjects.
Fostering Self-Discipline and Responsibility
Another significant objective behind the creation of homework was the promotion of self-discipline and responsibility among students. Education has always been about more than just the acquisition of knowledge; it also involves the development of life skills and habits that prepare individuals for future challenges.
By assigning tasks to be completed independently at home, educators aimed to instill valuable study habits and time management skills. Students were expected to take ownership of their learning, manage their time effectively, and meet deadlines—a set of skills that have enduring relevance in contemporary education and beyond.
Homework encouraged students to become proactive in their educational journey. It taught them the importance of accountability and the satisfaction of completing tasks on their own. These life skills would prove invaluable in their future endeavors, both academically and in the broader context of their lives.
When Was Homework Invented?
The roots of homework stretch deep into the annals of history, tracing its origins to ancient civilizations and early educational practices. While it has undergone significant evolution over the centuries, the concept of extending learning beyond the classroom has always been an integral part of education.
Earliest Origins of Homework and Early Educational Practices
The idea of homework, in its most rudimentary form, can be traced back to the earliest human civilizations. In ancient Egypt , for instance, students were tasked with hieroglyphic writing exercises. These exercises served as a precursor to modern homework, as they required students to practice and reinforce their understanding of written language—an essential skill for communication and record-keeping in that era.
In ancient Greece , luminaries like Plato and Aristotle advocated for the use of written exercises as a tool for intellectual development. They recognized the value of practice in enhancing one’s knowledge and skills, laying the foundation for a more systematic approach to homework.
The ancient Romans also played a pivotal role in the early development of homework. Young Roman students were expected to complete assignments at home, with a particular focus on subjects like mathematics and literature. These assignments were designed to consolidate their classroom learning, emphasizing the importance of practice in mastering various disciplines.
READ MORE: Who Invented Math? The History of Mathematics
The practice of assigning work to be done outside of regular school hours continued to evolve through various historical periods. As societies advanced, so did the complexity and diversity of homework tasks, reflecting the changing needs and priorities of education.
The Influence of Educational Philosophers
While the roots of homework extend to ancient times, the ideas of renowned educational philosophers in later centuries further contributed to its development. John Locke, an influential thinker of the Enlightenment era, believed in a gradual and cumulative approach to learning. He emphasized the importance of students revisiting topics through repetition and practice, a concept that aligns with the principles of homework.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau, another prominent philosopher, stressed the significance of self-directed learning. Rousseau’s ideas encouraged the development of independent study habits and a personalized approach to education—a philosophy that resonates with modern concepts of homework.
Homework in the American Public School System
The American public school system has played a pivotal role in the widespread adoption and popularization of homework. To understand the significance of homework in modern education, it’s essential to delve into its history and evolution within the United States.
History and Evolution of Homework in the United States
The late 19th century marked a significant turning point for homework in the United States. During this period, influenced by educational reforms and the growing need for standardized curricula, homework assignments began to gain prominence in American schools.
Educational reformers and policymakers recognized the value of homework as a tool for reinforcing classroom learning. They believed that assigning tasks for students to complete outside of regular school hours would help ensure that knowledge was retained and skills were honed. This approach aligned with the broader trends in education at the time, which aimed to provide a more structured and systematic approach to learning.
As the American public school system continued to evolve, homework assignments became a common practice in classrooms across the nation. The standardization of curricula and the formalization of education contributed to the integration of homework into the learning process. This marked a significant departure from earlier educational practices, reflecting a shift toward more structured and comprehensive learning experiences.
The incorporation of homework into the American education system not only reinforced classroom learning but also fostered self-discipline and responsibility among students. It encouraged them to take ownership of their educational journey and develop valuable study habits and time management skills—a legacy that continues to influence modern pedagogy.
Controversies Around Homework
Despite its longstanding presence in education, homework has not been immune to controversy and debate. While many view it as a valuable educational tool, others question its effectiveness and impact on students’ well-being.
The Homework Debate
One of the central controversies revolves around the amount of homework assigned to students. Critics argue that excessive homework loads can lead to stress, sleep deprivation, and a lack of free time for students. The debate often centers on striking the right balance between homework and other aspects of a student’s life, including extracurricular activities, family time, and rest.
Homework’s Efficacy
Another contentious issue pertains to the efficacy of homework in enhancing learning outcomes. Some studies suggest that moderate amounts of homework can reinforce classroom learning and improve academic performance. However, others question whether all homework assignments contribute equally to learning or whether some may be more beneficial than others. The effectiveness of homework can vary depending on factors such as the student’s grade level, the subject matter, and the quality of the assignment.
Equity and Accessibility
Homework can also raise concerns related to equity and accessibility. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds may have limited access to resources and support at home, potentially putting them at a disadvantage when it comes to completing homework assignments. This disparity has prompted discussions about the role of homework in perpetuating educational inequalities and how schools can address these disparities.
Alternative Approaches to Learning
In response to the controversies surrounding homework, educators and researchers have explored alternative approaches to learning. These approaches aim to strike a balance between reinforcing classroom learning and promoting holistic student well-being. Some alternatives include:
Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning emphasizes hands-on, collaborative projects that allow students to apply their knowledge to real-world problems. This approach shifts the focus from traditional homework assignments to engaging, practical learning experiences.
Flipped Classrooms
Flipped classrooms reverse the traditional teaching model. Students learn new material at home through video lectures or readings and then use class time for interactive discussions and activities. This approach reduces the need for traditional homework while promoting active learning.
Personalized Learning
Personalized learning tailors instruction to individual students’ needs, allowing them to progress at their own pace. This approach minimizes the need for one-size-fits-all homework assignments and instead focuses on targeted learning experiences.
The Ongoing Conversation
The controversies surrounding homework highlight the need for an ongoing conversation about its role in education. Striking the right balance between reinforcing learning and addressing students’ well-being remains a complex challenge. As educators, parents, and researchers continue to explore innovative approaches to learning, the role of homework in the modern educational landscape continues to evolve. Ultimately, the goal is to provide students with the most effective and equitable learning experiences possible.
Unpacking the Homework Enigma
Homework, without a single inventor, has evolved through educators, philosophers, and students. It reinforces learning, fosters discipline and prepares students. From ancient times to modern education, it upholds timeless values. Yet, controversies arise—debates on balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility persist. Innovative alternatives like project-based and personalized learning emerge. Homework’s role evolves with education.
How to Cite this Article
There are three different ways you can cite this article.
1. To cite this article in an academic-style article or paper , use:
<a href=" https://historycooperative.org/who-invented-homework/ ">The Homework Dilemma: Who Invented Homework?</a>
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Who Invented Homework? A Big Question Answered with Facts

Crystal Bourque

Delving into the intriguing history of education, one of the most pondered questions arises: Who invented homework?
Love it or hate it, homework is part of student life.
But what’s the purpose of completing these tasks and assignments? And who would create an education system that makes students complete work outside the classroom?
This post contains everything you’ve ever wanted to know about homework. So keep reading! You’ll discover the answer to the big question: who invented homework?
Who Invented Homework?
The myth of roberto nevilis: who is he, the origins of homework, a history of homework in the united states, 5 facts about homework, types of homework.
- What’s the Purpose of Homework?
- Homework Pros
- Homework Cons
When, How, and Why was Homework Invented?

Daniel Jedzura/Shutterstock.com
To ensure we cover the basics (and more), let’s explore when, how, and why was homework invented.
As a bonus, we’ll also cover who invented homework. So get ready because the answer might surprise you!
It’s challenging to pinpoint the exact person responsible for the invention of homework.
For example, Medieval Monks would work on memorization and practice singing. Ancient philosophers would read and develop their teachings outside the classroom. While this might not sound like homework in the traditional form we know today, one could argue that these methods helped to form the basic structure and format.
So let’s turn to recorded history to try and identify who invented homework and when homework was invented.
Pliny the Younger
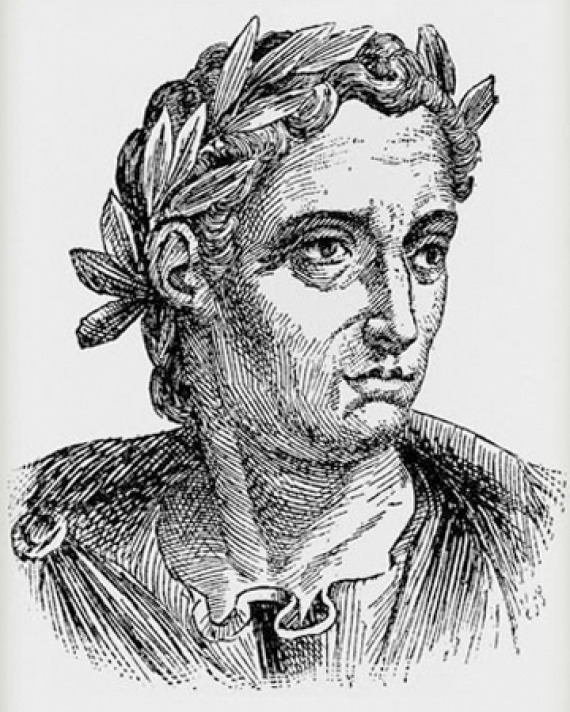

Credit: laphamsquarterly.org
Mention of homework appears in the writings of Pliny the Younger, meaning we can trace the term ‘homework’ back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger (61—112 CE) was an oratory teacher, and often told his students to practice their public speaking outside class.
Pliny believed that the repetition and practice of speech would help students gain confidence in their speaking abilities.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte

Credit: inlibris.com
Before the idea of homework came to the United States, Germany’s newly formed nation-state had been giving students homework for years.
The roots of homework extend to ancient times, but it wasn’t until German Philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762—1814) helped to develop the Volksschulen (People’s Schools) that homework became mandatory.
Fichte believed that the state needed to hold power over individuals to create a unified Germany. A way to assert control over people meant that students attending the Volksshulen were required to complete assignments at home on their own time.
As a result, some people credit Fichte for being the inventor of homework.
Horace Mann
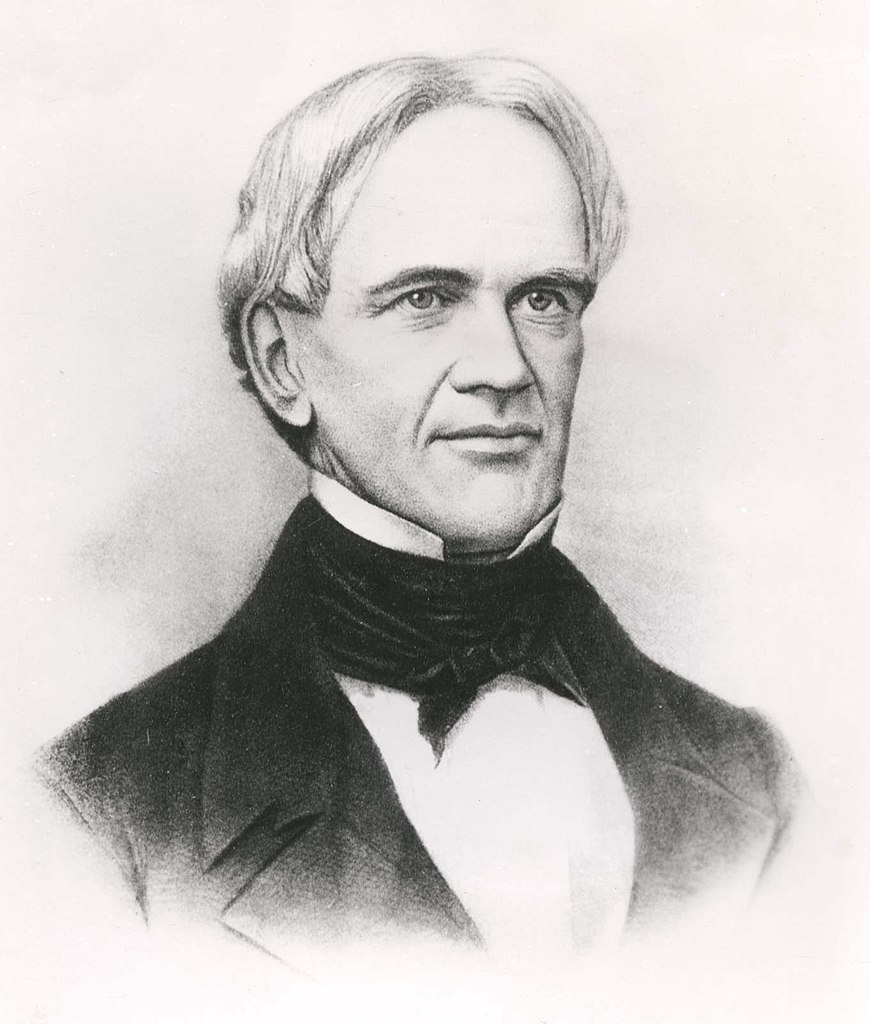

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
The idea of homework spread across Europe throughout the 19th century.
So who created homework in the United States?
The history of education and homework now moves to Horace Mann (1796—1859), an American educational reformer, spent some time in Prussia. There, he learned more about Germany’s Volksshulen, forms of education , and homework practices.
Mann liked what he saw and brought this system back to America. As a result, homework rapidly became a common factor in students’ lives across the country.
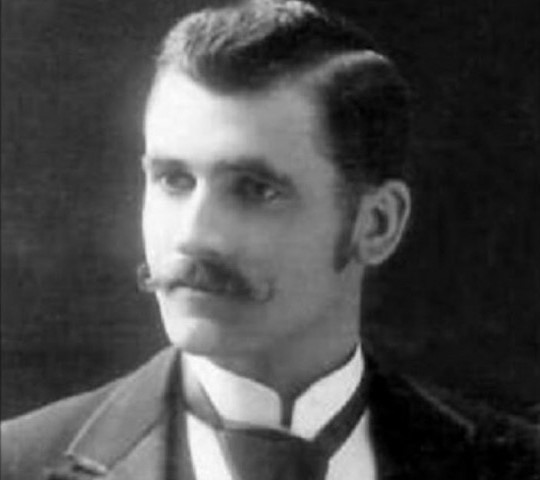

Credit: medium.com
If you’ve ever felt curious about who invented homework, a quick online search might direct you to a man named Roberto Nevilis, a teacher in Venice, Italy.
As the story goes, Nevilis invented homework in 1905 (or 1095) to punish students who didn’t demonstrate a good understanding of the lessons taught during class.
This teaching technique supposedly spread to the rest of Europe before reaching North America.
Unfortunately, there’s little truth to this story. If you dig a little deeper, you’ll find that these online sources lack credible sources to back up this myth as fact.
In 1905, the Roman Empire turned its attention to the First Crusade. No one had time to spare on formalizing education, and classrooms didn’t even exist. So how could Nevilis spread the idea of homework when education remained so informal?
And when you jump to 1901, you’ll discover that the government of California passed a law banning homework for children under fifteen. Nevilis couldn’t have invented homework in 1905 if this law had already reached the United States in 1901.

Inside Creative House/Shutterstock.com
When it comes to the origins of homework, looking at the past shows us that there isn’t one person who created homework. Instead, examining the facts shows us that several people helped to bring the idea of homework into Europe and then the United States.
In addition, the idea of homework extends beyond what historians have discovered. After all, the concept of learning the necessary skills human beings need to survive has existed since the dawn of man.
More than 100 years have come and gone since Horace Mann introduced homework to the school system in the United States.
Therefore, it’s not strange to think that the concept of homework has changed, along with our people and culture.
In short, homework hasn’t always been considered acceptable. Let’s dive into the history or background of homework to learn why.
Homework is Banned! (The 1900s)
Important publications of the time, including the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times, published articles on the negative impacts homework had on American children’s health and well-being.
As a result, California banned homework for children under fifteen in 1901. This law, however, changed again about a decade later (1917).
Children Needed at Home (The 1930s)
Formed in 1923, The American Child Health Association (ACHA) aimed to decrease the infant mortality rate and better support the health and development of the American child.
By the 1930s, ACHA deemed homework a form of child labor. Since the government recently passed laws against child labor , it became difficult to justify homework assignments. College students, however, could still receive homework tasks as part of their formal schooling.

Studio Romantic/Shutterstock.com
A Shift in Ideas (The 1940s—1950s)
During the early to mid-1900s, the United States entered the Progressive Era. As a result, the country reformed its public education system to help improve students’ learning.
Homework became a part of everyday life again. However, this time, the reformed curriculum required teachers to make the assignments more personal.
As a result, American students would write essays on summer vacations and winter breaks, participate in ‘show and tell,’ and more.
These types of assignments still exist today!
Homework Today (The 2000s)
The focus of American education shifted again when the US Department of Education was founded in 1979, aiming to uplevel education in the country by, among other things, prohibiting discrimination ensuring equal access, and highlighting important educational issues.
In 2022, the controversial nature of homework in public schools and formal education is once again a hot topic of discussion in many classrooms.
According to one study , more than 60% of college and high school students deal with mental health issues like depression and anxiety due to homework. In addition, the large number of assignments given to students takes away the time students spend on other interests and hobbies. Homework also negatively impacts sleep.
As a result, some schools have implemented a ban or limit on the amount of homework assigned to students.
Test your knowledge and check out these other facts about homework:
- Horace Mann is also known as the ‘father’ of the modern school system and the educational process that we know today (read more about Who Invented School ).
- With a bit of practice, homework can improve oratory and writing skills. Both are important in a student’s life at all stages.
- Homework can replace studying. Completing regular assignments reduces the time needed to prepare for tests.
- Homework is here to stay. It doesn’t look like teachers will stop assigning homework any time soon. However, the type and quantity of homework given seem to be shifting to accommodate the modern student’s needs.
- The optimal length of time students should spend on homework is one to two hours. Students who spent one to two hours on homework per day scored higher test results.
- So, while completing assignments outside of school hours may be beneficial, spending, for example, a day on homework is not ideal.
Explore how the Findmykids app can complement your child’s school routine. With features designed to ensure their safety and provide peace of mind, it’s a valuable tool for parents looking to stay connected with their children throughout the day. Download now and stay informed about your child’s whereabouts during their academic journey.

Ground Picture/Shutterstock.com
The U.S. Department of Education provides teachers with plenty of information and resources to help students with homework.
In general, teachers give students homework that requires them to employ four strategies. The four types of homework types include:
- Practice: To help students master a specific skill, teachers will assign homework that requires them to repeat the particular skill. For example, students must solve a series of math problems.
- Preparation: This type of homework introduces students to the material they will learn in the future. An example of preparatory homework is assigning students a chapter to read before discussing the contents in class the next day.
- Extension: When a teacher wants to get students to apply what they’ve learned but create a challenge, this type of homework is assigned. It helps to boost problem-solving skills. For example, using a textbook to find the answer to a question gets students to problem-solve differently.
- Integration: To solidify the student learning experience , teachers will create a task that requires the use of many different skills. An example of integration is a book report. Completing integration homework assignments helps students learn how to be organized, plan, strategize, and solve problems on their own. Encouraging effective study habits is a key idea behind homework, too.
Ultimately, the type of homework students receive should have a purpose, be focused and clear, and challenge students to problem solve while integrating lessons learned.
What’s the Purpose of Homework?

LightField Studios/Shutterstock.com
Homework aims to ensure individual students understand the information they learn in class. It also helps teachers to assess a student’s progress and identify strengths and weaknesses.
For example, school teachers use different types of homework like book reports, essays, math problems, and more to help students demonstrate their understanding of the lessons learned.
Does Homework Improve the Quality of Education?
Homework is a controversial topic today. Educators, parents, and even students often question whether homework is beneficial in improving the quality of education.
Let’s explore the pros and cons of homework to try and determine whether homework improves the quality of education in schools.
Homework Pros:
- Time Management Skills : Assigning homework with a due date helps students to develop a schedule to ensure they complete tasks on time. Personal responsibility amongst students is thereby promoted.
- More Time to Learn : Students encounter plenty of distractions at school. It’s also challenging for students to grasp the material in an hour or less. Assigning homework provides the student with the opportunity to understand the material.
- Improves Research Skills : Some homework assignments require students to seek out information. Through homework, students learn where to seek out good, reliable sources.
Homework Cons:
- Reduced Physical Activity : Homework requires students to sit at a desk for long periods. Lack of movement decreases the amount of physical activity, often because teachers assign students so much homework that they don’t have time for anything else. Time for students can get almost totally taken up with out-of-school assignments.
- Stuck on an Assignment: A student often gets stuck on an assignment. Whether they can’t find information or the correct solution, students often don’t have help from parents and require further support from a teacher. For underperforming students, especially, this can have a negative impact on their confidence and overall educational experience.
- Increases Stress : One of the results of getting stuck on an assignment is that it increases stress and anxiety. Too much homework hurts a child’s mental health, preventing them from learning and understanding the material.
Some research shows that homework doesn’t provide educational benefits or improve performance, and can lead to a decline in physical activities. These studies counter that the potential effectiveness of homework is undermined by its negative impact on students.
However, research also shows that homework benefits students—provided teachers don’t give them too much. Here’s a video from Duke Today that highlights a study on the very topic.
Homework Today
The question of “Who Invented Homework?” delves into the historical evolution of academic practices, shedding light on its significance in fostering responsibility among students and contributing to academic progress. While supported by education experts, homework’s role as a pivotal aspect of academic life remains a subject of debate, often criticized as a significant source of stress. Nonetheless, when balanced with extracurricular activities and integrated seamlessly into the learning process, homework continues to shape and refine students’ educational journeys.
Maybe one day, students won’t need to submit assignments or complete tasks at home. But until then, many students understand the benefits of completing homework as it helps them further their education and achieve future career goals.
Before you go, here’s one more question: how do you feel about homework? Do you think teachers assign too little or too much? Get involved and start a discussion in the comments!
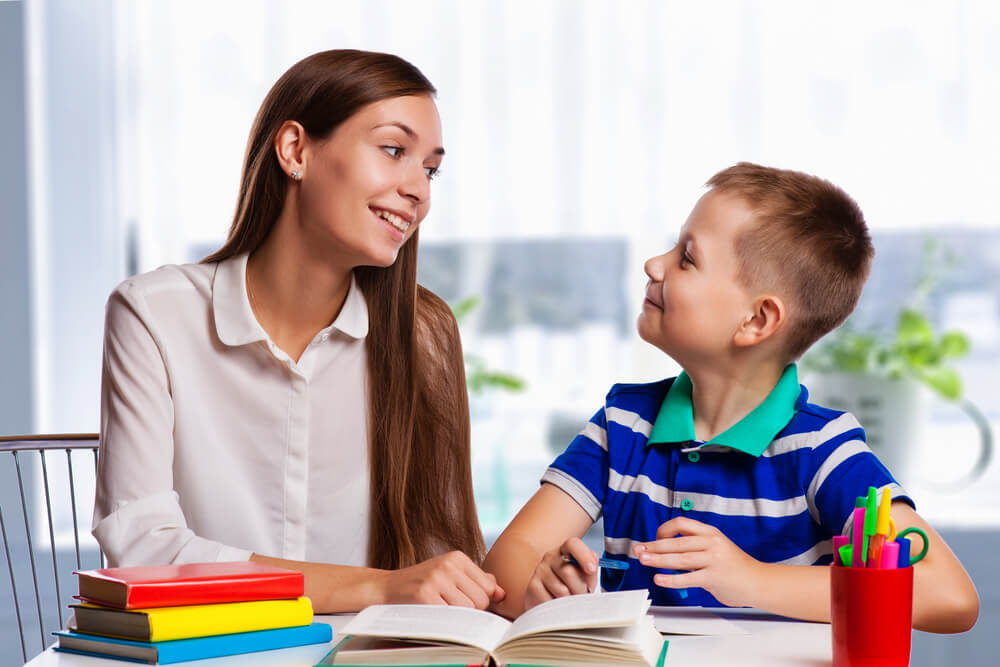

Elena Kharichkina/Shutterstock.com
Who invented homework and why?
The creation of homework can be traced back to the Ancient Roman Pliny the Younger, a teacher of oratory—he is generally credited as being the father of homework! Pliny the Younger asked his students to practice outside of class to help them build confidence in their speaking skills.
Who invented homework as a punishment?
There’s a myth that the Italian educator Roberto Nevilis first used homework as a means of punishing his students in the early 20th century—although this has now been widely discredited, and the story of the Italian teacher is regarded as a myth.
Why did homework stop being a punishment?
There are several reasons that homework ceased being a form of punishment. For example, the introduction of child labor laws in the early twentieth century meant that the California education department banned giving homework to children under the age of fifteen for a time. Further, throughout the 1940s and 1950s, there was a growing emphasis on enhancing students’ learning, making homework assignments more personal, and nurturing growth, rather than being used as a form of punishment.
The picture on the front page: Evgeny Atamanenko/Shutterstock.com

Even in today’s world, child trafficking is still a huge problem. Incidents of human trafficking…

When your child is entering third grade, it is better for them to know the…

An aggressive child is not uncommon in the modern world. Unfortunately, for many parents this…
Subscribe now!
Glad you've joined us🎉🎉.
20 Reasons Why Homework is Good: Unlocking the Benefits

- Post author By admin
- October 26, 2023
Explore the compelling 20 reasons why homework is good, fostering skills and knowledge that extend beyond the classroom
Ah, homework – a topic that has fueled countless debates in the world of education. Is it a valuable learning tool or a relentless academic burden?
In this article, we’re going to shift the spotlight onto the often-overlooked positive side of homework. We’ll unveil not one or two, but a whopping 20 compelling reasons why homework is genuinely good for students.
From solidifying classroom knowledge to honing critical thinking skills, homework is far more than just an academic chore. It’s an essential building block of learning.
So, whether you’ve questioned the purpose of homework or are simply curious about its merits, join us on this journey as we explore the myriad ways homework benefits students of all ages.
Get ready to discover why homework is a treasure trove of learning opportunities!
Table of Contents
20 Reasons Why Homework is Good
Check out 20 reasons why homework is good:-
1. Reinforcement of Classroom Learning
Homework isn’t just a mundane task; it’s your secret weapon for becoming a true subject matter aficionado. It’s the place where classroom theories transform into real-world skills.
Homework, in all its wisdom, lets you roll up your sleeves and practice what you’ve learned in class, turning those lightbulb moments into permanent knowledge fixtures.
Just like a musician perfecting a melody or an artist refining their masterpiece, homework is your training ground for excellence. So, embrace it, for every assignment is a stepping stone on your path to mastery.
2. Development of Responsibility
Homework isn’t just about books and assignments; it’s a grooming ground for something equally important – responsibility.
It’s like a trusty mentor, teaching students to take charge, manage their time, and complete tasks independently.
It’s that early taste of adulthood, where you learn that success often depends on your own commitment and effort.
So, think of homework as your guide on the journey to becoming a responsible, self-reliant individual, armed with skills that will serve you well in all walks of life.
3. Improved Time Management Skills
Homework is more than just assignments; it’s a boot camp for one of life’s essential skills – time management. Think of it as a mini dress rehearsal for adulthood.
Homework teaches students to allocate their time wisely, ensuring they meet deadlines and complete tasks efficiently. It’s like learning to juggle multiple balls, a skill that will serve them well in their adult lives. So, embrace homework as your friendly time-management coach, preparing you for the real world’s challenges.
4. Enhanced Critical Thinking
Homework is not just about finding answers; it’s your secret laboratory for unleashing the power of critical thinking.
It’s the arena where you get to be the detective, dissect problems, and engineer ingenious solutions. Think of it as mental gymnastics, where your cognitive muscles get a thorough workout.
The more you dive into those homework challenges, the sharper your critical thinking skills become. So, consider homework your daily brain boot camp, molding you into a savvy problem-solver with talents that extend way beyond the classroom.
5. Preparation for the Future
Homework isn’t just about cracking textbooks; it’s your sneak peek into the future. Think of it as your personal time machine, where you’re not just solving equations but honing skills that will propel you to success in higher education and the professional arena.
It’s like laying the stepping stones to your dream career. From mastering time management to sharpening critical thinking, homework is your trusted mentor, preparing you for the exciting journey ahead.
So, when you’re poring over those assignments, remember – you’re not just studying, you’re shaping a future filled with possibilities.
6. Encouragement of Self-Discipline
Homework isn’t just about filling out worksheets; it’s the canvas on which students paint their self-discipline and self-motivation masterpieces.
It’s like training for life’s grand adventure. With homework, you’re the captain, setting sail on a sea of assignments.
Completing homework isn’t merely about meeting deadlines; it’s about cultivating skills that become your secret weapons in the real world.
So, think of homework as your personal training ground for self-discipline, sculpting you into a resilient and motivated individual who’s ready to conquer life’s challenges.
7. Review of Material
Homework isn’t just an additional task; it’s your golden opportunity to revisit and cement what you’ve learned in class.
Think of it as your personal review session, where you go through the key points and solidify your understanding. Just as an artist refines their masterpiece or a musician practices their chords, homework is your tool for perfection.
The more you review and consolidate, the stronger your grasp on the subject matter becomes. So, embrace homework as your trusted ally in mastering the art of revision, making you a confident and knowledgeable learner.
8. Practice Makes Perfect
Homework isn’t a chore; it’s your backstage pass to perfection. It’s like the endless rehearsals of a musician or the tireless drills of an athlete.
Homework is your playground for practice, where you can fine-tune your skills, ensuring you become a true master in various subjects. Just as a chef perfects a recipe through repetition, your homework is the recipe for excellence.
So, when you’re diving into those assignments, think of them as your chance to practice, practice, and practice some more, turning you into a subject maestro.
9. Teacher-Student Interaction
Homework isn’t just about cracking the books; it’s your backstage pass to building strong connections with your teachers.
It’s like sending an open invitation to ask questions and seek guidance. Homework transforms the student-teacher relationship from a formal handshake into a hearty conversation.
When you embrace homework, you’re not just solving problems; you’re forging connections that can last a lifetime.
So, think of homework as your golden opportunity for dialogue, where you can foster positive relationships with your teachers and make your educational journey all the more engaging and rewarding.
10. Parental Involvement
Homework isn’t just a student’s duty; it’s a chance for families to bond over learning. It’s like the thread that weaves the classroom and home together, allowing parents to actively participate in their child’s education.
Homework transforms the learning experience into a shared adventure where everyone can join in the fun. When parents dive into homework with their kids, it’s not just about helping with math problems.
It’s about creating moments of connection, offering support, and sharing in the educational journey. So, think of homework as the gateway to family engagement in education, making learning a joyful family affair.
11. Real-Life Application
Homework isn’t just about hitting the books; it’s your backstage pass to making knowledge practical. It’s like a secret bridge that connects the world of theory with the realm of real-life application.
Homework transforms you from a passive learner into an active doer. It’s where you take those classroom ideas and put them into action, just like a scientist testing a hypothesis or an engineer building a bridge.
So, consider homework your personal laboratory for bringing theories to life, where you turn bookish knowledge into real-world magic, making your education a thrilling adventure.
12. Different Learning Styles
Homework isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal; it’s more like a treasure map that caters to diverse learning styles. Imagine it as a chameleon, changing its colors to suit both visual and kinesthetic learners.
Homework knows that we’re all unique, with our own special ways of learning. For those who thrive on visuals, it serves up graphs and illustrations, while the hands-on learners get to dive into practical tasks.
It’s a bit like having a tailor-made suit for education. So, consider homework your personal guide, offering a learning experience that’s as unique as you are, making education a captivating and natural journey.
13. Time for Creativity
Homework isn’t a creativity crusher; it’s your chance to let your imagination soar. Think of it as a blank canvas waiting for your ideas to paint it with vibrant colors.
Homework isn’t about rules and conformity; it’s about independent thinking and the freedom to express yourself. Whether you’re crafting an essay, brainstorming a unique solution, or designing a project, homework is your invitation to let your creativity shine.
So, consider homework your personal creative playground, where you can set your ideas free, turning learning into an exciting and imaginative adventure.
14. Enhancement of Research Skills
Homework isn’t just about checking off tasks; it’s your secret lair for honing research skills, those superpowers that will supercharge your success in both academics and the real world.
Think of it as your personal training ground where you become a detective of knowledge, learning to explore, dig deep, and unearth answers.
Whether you’re delving into the depths of the library, surfing the web, or conducting surveys, research-based homework transforms you into a skilled investigator.
So, consider homework your gateway to the world of research, where you unlock skills that will not only power your academic journey but also your lifelong adventures.
15. Test Preparation
Homework isn’t just a mundane task; it’s your secret weapon for conquering exams. Think of it as your personal exam prep coach, crafting a roadmap for success.
Homework lets you revisit, revise, and sharpen your skills, so when test day arrives, you’re ready to shine. It’s not just about finishing assignments; it’s about building your confidence for those crucial exams.
So, consider homework your trusty sidekick on the path to acing tests, making your educational journey an exciting adventure.
16. Increased Engagement
Homework isn’t a homework. It’s more like an after-class adventure that keeps the excitement of learning alive. Think of it as your personal quest, where you get to explore the subjects that genuinely pique your interest.
Homework isn’t about killing time; it’s your ticket to stay engaged with your learning journey, even when the school day ends.
So, when you’re tackling your assignments, remember you’re not just checking off tasks; you’re stoking the flames of curiosity, making education an exhilarating and never-ending journey.
17. Achievement of Learning Objectives
Homework isn’t just a jumble of tasks; it’s your trusted guide leading you to specific educational victories. Picture it as your personal GPS, keeping you on track to reach those learning milestones.
Homework is where you make the connections, reinforce classroom knowledge, and make your education rock-solid. It’s not just about answering questions; it’s about ensuring you hit those educational bullseyes.
So, when you’re diving into your assignments, remember you’re not just ticking off tasks; you’re on a journey to academic success, turning each homework into a stepping stone toward your goals.
18. Inclusivity
Homework isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal; it’s your versatile tool to celebrate the uniqueness of every student. Imagine it as a buffet, serving up options for both fast learners and those who want some extra practice.
Homework understands that every student is as unique as a fingerprint, each with their own pace and learning style.
For the quick learners, it offers challenges and exciting extensions, while those who prefer more practice can dive into additional exercises.
It’s like a school that dances to your rhythm, ensuring every student has a path to success. So, think of homework as your personal learning adventure, offering choices that fit your taste, making education an exciting and inclusive journey.
19. Fosters Independence
Homework isn’t about spoon-feeding answers; it’s your nurturing ground for independent thinking and decision-making.
Think of it as a playground where you get to flex your decision muscles and spread your intellectual wings. Homework is your training camp for self-reliance, where you take charge of your learning adventure.
20. Overall Academic Improvement
Homework isn’t just a stack of assignments; it’s the secret ingredient for overall academic improvement. Think of it as the magic wand that, when waved effectively, leads to better grades and educational triumphs.
Homework isn’t a mere task list; it’s your strategic ally in the journey of learning. When used wisely, it’s your key to success, a bridge to better understanding and superior educational outcomes.
So, when you’re tackling your homework, remember you’re not just ticking off tasks; you’re paving the way for academic excellence, turning each assignment into a step towards achieving your educational goals.
What are 5 benefits of homework?
Homework is more than just a list of tasks; it’s a powerhouse of benefits that can transform a student’s learning journey. Here are the top five advantages:
1. Supercharging Learning
Homework isn’t about mindless repetition; it’s your secret weapon to reinforce what you’ve learned in class. It’s like a memory boost that makes sure you remember the important stuff for the long haul.
2. Mastering Time and Study Skills
Homework teaches you real-world skills that go way beyond the textbook. It’s your personal coach for time management and setting priorities.
Plus, it’s your go-to guide for developing top-notch study habits like staying organized, taking killer notes, and acing those tests.
3. Fueling Grit and Responsibility
Homework is your training ground for building self-discipline and a sense of responsibility. It’s where you learn to motivate yourself and tackle challenges head-on, no matter how tough they seem.
4. Sparking Creativity and Critical Thinking
Homework isn’t a one-way street. It’s your canvas for thinking outside the box and analyzing what you’re learning from all angles. It’s your chance to bring your unique ideas to the table.
5. Strengthening Home-School Bonds
Homework isn’t just about you; it’s a connection point for your parents and teachers. It’s where they get a front-row seat to your education and can lend a hand when you need it.
But, remember, like any tool, homework works best when used wisely. Too much of a good thing can lead to stress, so strike that balance, and make homework your learning ally.
Who invented homework 😡?
The roots of homework can be traced back to a frustrated Italian educator, Roberto Nevilis, who lived in the 17th century.
He was perplexed by his students’ struggles to retain their classroom lessons, and so, he devised a novel solution – homework.
By assigning tasks that required students to practice and reinforce what they’d learned in class, Nevilis hoped to bridge the knowledge gap. His ingenious idea didn’t stop at the classroom door; it spread like wildfire, first across Europe and eventually finding its way to the United States.
While Nevilis is often credited with inventing homework, history leaves some room for debate. Some scholars argue that homework may have had earlier incarnations in ancient Greece and Rome, although concrete evidence is scarce.
What’s more likely is that Nevilis was among the first to formalize the concept of homework as we understand it today.
No matter its true origin, homework has become an integral part of education worldwide. It spans across the spectrum, from the youngest elementary students to those pursuing higher education.
The purpose of homework has also evolved over time. While Nevilis initially introduced homework to help students retain information, today, its role is multifaceted. It serves as a training ground for critical thinking, problem-solving, and nurturing creativity.
Whether you view homework as a boon or a bane, one thing is certain – it has a rich and varied history, and it’s likely to continue shaping the educational landscape for the foreseeable future.
Why is homework good for your brain?
Homework isn’t just about completing assignments; it’s a brain-boosting wizard. Let’s delve into the captivating reasons why homework is a mind-enhancing elixir:
Fortifying Neural Pathways
Imagine your brain as a labyrinth of pathways. When you learn something new, it’s like carving a fresh trail. Homework? It’s your trusty path-paver, helping you practice and reinforce what you’ve learned. This makes recalling information a breeze down the road.
Mastering Executive Function Skills
Executive function skills are like your brain’s personal assistants. They help you plan, organize, and manage your time effectively.
Homework transforms you into the CEO of your tasks, requiring you to set goals, juggle priorities, and work independently.
Cultivating Cognitive Flexibility
Ever wished you could tackle problems from various angles? That’s cognitive flexibility, a superpower for your brain. Homework serves as the playground where you can flex your mental muscles, applying your knowledge to novel challenges.
Boosting Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy is your belief in your own success. Homework is your arena for personal victories. Achieving your homework goals and witnessing your growth over time? That’s a confidence booster like no other.
Stress Alleviation
While homework might occasionally seem like a stress-inducing monster, it’s also your coach for the stress-relief Olympics. How?
It equips you with the skills to tackle challenges and manage your time wisely, ultimately reducing stress in the long run.
But, here’s the catch: balance is key. Too much homework can tip the scales. To maximize the magical benefits, you need to find harmony between homework and other essential activities like sleep, exercise, and hanging out with friends.
In a nutshell, homework isn’t just about completing assignments; it’s your secret weapon for unlocking your brain’s potential. It boosts learning and memory, nurtures executive function skills, hones cognitive flexibility, elevates self-efficacy, and even helps you conquer stress.
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of the twenty compelling reasons that make homework a valuable asset, it’s evident that homework is more than just a to-do list. It’s a treasure trove of advantages that students can unearth on their academic journey.
From fortifying those neural pathways to nurturing independence, and from honing research skills to prepping for the challenges that await in the future, homework is a versatile tool. It’s the canvas where creativity flourishes, bridging the gap between theory and practice, and inviting parents into their child’s scholastic odyssey.
Homework doesn’t just aid in academic mastery; it’s a comprehensive roadmap for personal growth and development. It nudges you towards self-discipline, sprinkles in a dash of responsibility, and offers a slice of the sweet taste of accomplishment.
However, as in any art, balance is key. The right amount of homework, harmonized with other life activities, is the secret recipe for success.
So, as you tackle your next homework assignment, remember this: you’re not just completing tasks; you’re shaping a brighter future, one thought at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is homework always beneficial for students.
Homework can be beneficial when thoughtfully assigned, but excessive or irrelevant homework may have negative effects.
How can parents support their child’s homework routine?
Parents can provide a quiet, organized workspace, offer assistance when needed, and encourage good study habits.
How much homework is too much?
The right amount of homework varies by grade level and individual needs. It should challenge without overwhelming students.
What can teachers do to make homework more effective?
Teachers should assign purposeful, relevant homework, provide clear instructions, and offer support when necessary.
How does homework help prepare students for the future?
Homework instills responsibility, time management, and critical thinking skills, all of which are valuable in higher education and the workforce.
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (284)
- General (77)
- How To (18)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts

The Edvocate
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- Write For Us
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Assistive Technology
- Best PreK-12 Schools in America
- Child Development
- Classroom Management
- Early Childhood
- EdTech & Innovation
- Education Leadership
- First Year Teachers
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
- Parental Involvement
- Policy & Reform
- Best Colleges and Universities
- Best College and University Programs
- HBCU’s
- Higher Education EdTech
- Higher Education
- International Education
- The Awards Process
- Finalists and Winners of The 2023 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Award Seals
- GPA Calculator for College
- GPA Calculator for High School
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Grade Calculator
- Weighted Grade Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
- The Tech Edvocate
- AI Powered Personal Tutor
Teaching Students About Animal Skeletons
Haworth & mien announce partnership, unlocking the secrets that protect mt. diablo’s student data, meet the new ministers of education, higher education, ohio state president speaks on the future of higher education at city club of cleveland, vanderbilt university gets approval for $520m florida graduate campus, a new boldyn networks for higher education study explores the need for college campus connectivity, georgian court university president joseph r. marbach, ph.d. to retire in summer 2025, intelligent.com ranks cmu programs among nation’s best, anthology’s blackboard ranked as a top learning management system by leading edtech analyst firm, who invented homework.

Homework is a part of life for children, parents, and educators. But who came up with the concept of homework? What happened to make it a standard in education? Here’s a quick rundown of homework’s history in the United States .
Homework’s Origins: Myth vs. History
Who was the first person to invent homework? We may never know for sure. Its history has been shaped by a variety of persons and events. Let’s start with two of its key influencers.
The Dubious Roberto Nevelis of Venice
Homework is typically credited to Roberto Nevelis of Venice, Italy, who invented it in 1095—or 1905, depending on your sources. However, upon closer examination, he appears to be more of an internet legend than a genuine figure.
Horace Mann
Horace Mann, a 19th-century politician and educational reformer, was a pivotal figure in the development of homework. Mann, like his contemporaries Henry Barnard and Calvin Ellis Stowe, was passionate about the newly unified nation-state of Germany’s obligatory public education system.
Mandatory tasks were assigned to Volksschulen (“People’s Schools”) students to complete at home on their own time. When liberals like Johann Gottlieb Fichte were striving to organize support for a unified German state, this demand highlighted the state’s authority over the individual. While homework had been established before Fichte’s participation with the Volksschulen, his political goals can be considered a catalyst for its adoption as an educational requirement.
Horace Mann was a driving force behind creating government-run, tax-funded public education in America. During a journey to Germany in 1843, he witnessed the Volkschule system at work and brought back several of its ideals, including homework.
The American Public School System’s Homework
Homework has not always been generally embraced, despite being a near-universal element of the American educational experience. Parents and educators continue to dispute its benefits and drawbacks, as they have for more than a century.
The 1900s: Anti-homework sentiment and homework bans
A homework prohibition was enacted in the Pacific state of California in 1901, barely a few decades after the idea of homework crossed the Atlantic. The restriction, which applied to all students under the age of 15, lasted until 1917.
Around the same period, renowned magazines such as the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times published remarks from parents and medical professionals portraying homework as harmful to children’s health.1930: Homework as Child Labor
A group called the American Child Health Association deemed homework a form of child labor in 1930. This statement represented a less-than-favorable view of homework as an appropriate educational method, given that laws barring child labor had recently been implemented.
Early-to-Mid 20th Century: Homework and the Progressive Era
Teachers began looking for ways to make homework more personal and meaningful to individual students throughout the second half of the 19th and 20th-century modern educational changes. Could this be the origin of the enduring essay topic, “What I Did on My Summer Vacation?”
The Cold War: Homework Heats Up
Following WWII, the Cold War heightened tensions between the United States and Russia in the 1950s. The flight of Sputnik 1 in 1957 increased Russian-American enmity, particularly among their youngsters.
The best way to ensure that American students did not fall behind their Russian counterparts, especially in the extremely competitive fields of science and mathematics, was for education officials in the United States to assign demanding homework.
The 1980s: A Nation at Risk’s Homework
What Works, a 1986 publication from the US Department of Education, listed homework as one of the most effective instructional tactics. This followed three years after the groundbreaking study
Early 21st Century: Homework Bans Return
Many educators and other concerned individuals are questioning the value of homework once again. On the subject, several publications have been published.
These include:
- The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It by Sarah Bennett and Nancy Kalish (2006)
- The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents (Third Edition) by Duke University psychologist Dr. Harris Cooper (2007)
- The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning by education professor Dr. Etta Kralovec and journalist John Buell (2000)
Homework is still a contentious topic nowadays. Some schools are enacting homework bans similar to those enacted at the start of the century. Teachers have varying opinions on the bans, while parents attempt to cope with the disruption to their daily routine that such bans cause.

Flipped Classroom: Everything You Need to Know
25 black history month activities.
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

The Edvocate’s Guide to Weighted Grades

3 Apps to Empower College Students’ Study Skills

What Does a Future Ready Education Leader Look Like?

Managing Behavior In Classrooms: An Age-Old Challenge

How is Technology Revolutionizing Campus Libraries?

Pass or Fail: Social Promotion and Retention’s Effect on Families & Communities
- situs togel online
- situs toto 4d
- situs toto slot
The Surprising History of Homework Reform
Really, kids, there was a time when lots of grownups thought homework was bad for you.

Homework causes a lot of fights. Between parents and kids, sure. But also, as education scholar Brian Gill and historian Steven Schlossman write, among U.S. educators. For more than a century, they’ve been debating how, and whether, kids should do schoolwork at home .

At the dawn of the twentieth century, homework meant memorizing lists of facts which could then be recited to the teacher the next day. The rising progressive education movement despised that approach. These educators advocated classrooms free from recitation. Instead, they wanted students to learn by doing. To most, homework had no place in this sort of system.
Through the middle of the century, Gill and Schlossman write, this seemed like common sense to most progressives. And they got their way in many schools—at least at the elementary level. Many districts abolished homework for K–6 classes, and almost all of them eliminated it for students below fourth grade.
By the 1950s, many educators roundly condemned drills, like practicing spelling words and arithmetic problems. In 1963, Helen Heffernan, chief of California’s Bureau of Elementary Education, definitively stated that “No teacher aware of recent theories could advocate such meaningless homework assignments as pages of repetitive computation in arithmetic. Such an assignment not only kills time but kills the child’s creative urge to intellectual activity.”
But, the authors note, not all reformers wanted to eliminate homework entirely. Some educators reconfigured the concept, suggesting supplemental reading or having students do projects based in their own interests. One teacher proposed “homework” consisting of after-school “field trips to the woods, factories, museums, libraries, art galleries.” In 1937, Carleton Washburne, an influential educator who was the superintendent of the Winnetka, Illinois, schools, proposed a homework regimen of “cooking and sewing…meal planning…budgeting, home repairs, interior decorating, and family relationships.”
Another reformer explained that “at first homework had as its purpose one thing—to prepare the next day’s lessons. Its purpose now is to prepare the children for fuller living through a new type of creative and recreational homework.”
That idea didn’t necessarily appeal to all educators. But moderation in the use of traditional homework became the norm.
Weekly Newsletter
Get your fix of JSTOR Daily’s best stories in your inbox each Thursday.
Privacy Policy Contact Us You may unsubscribe at any time by clicking on the provided link on any marketing message.
“Virtually all commentators on homework in the postwar years would have agreed with the sentiment expressed in the NEA Journal in 1952 that ‘it would be absurd to demand homework in the first grade or to denounce it as useless in the eighth grade and in high school,’” Gill and Schlossman write.
That remained more or less true until 1983, when publication of the landmark government report A Nation at Risk helped jump-start a conservative “back to basics” agenda, including an emphasis on drill-style homework. In the decades since, continuing “reforms” like high-stakes testing, the No Child Left Behind Act, and the Common Core standards have kept pressure on schools. Which is why twenty-first-century first graders get spelling words and pages of arithmetic.
Support JSTOR Daily! Join our new membership program on Patreon today.

JSTOR is a digital library for scholars, researchers, and students. JSTOR Daily readers can access the original research behind our articles for free on JSTOR.
Get Our Newsletter
More stories.

All Travelers are Infiltrators: An Introduction to the Study of Travel Writing

Teaching Peace Between the Wars

Verbatim: Fredric Jameson

When “Traditional” Religion Shakes Up Gender Roles
Recent posts.
- Inventing Silk Roads
- Judy-Lynn del Rey
- Ghosts in the Machine
- How to Be a British Villain
- The Mayaguez Incident: The Last Chapter of the Vietnam War
Support JSTOR Daily
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, the homework debate: how homework benefits students.

This post has been updated as of December 2017.
In another of our blog posts, The Case Against Homework , we articulated several points of view against homework as standard practice for teachers. However, a variety of lessons, content-related and beyond, can be taught or reinforced through homework and are worth exploring. Read on!
Four ways homework aids students’ academic achievement
Homework provides an opportunity for parents to interact with and understand the content their students are learning so they can provide another means of academic support for students. Memphis Parent writer Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson says that, “When your child does homework, you do homework,” and notes that this is an opportunity for parents to model good behavior for their children.
Pryor-Johnson also identifies four qualities children develop when they complete homework that can help them become high-achieving students:
- Responsibility
- Time management
- Perseverance
- Self-esteem
While these cannot be measured on standardized tests, perseverance has garnered a lot of attention as an essential skill for successful students. Regular accomplishments like finishing homework build self-esteem, which aids students’ mental and physical health. Responsibility and time management are highly desirable qualities that benefit students long after they graduate.
NYU and Duke professors refute the idea that homework is unrelated to student success
In response to the National School Board Association’s Center for Public Education’s findings that homework was not conclusively related to student success, historian and NYU professor Diane Ravitch contends that the study’s true discovery was that students who did not complete homework or who lacked the resources to do so suffered poor outcomes.
Ravitch believes the study’s data only supports the idea that those who complete homework benefit from homework. She also cites additional benefits of homework: when else would students be allowed to engage thoughtfully with a text or write a complete essay? Constraints on class time require that such activities are given as outside assignments.
5 studies support a significant relationship between homework completion and academic success
Duke University professor Harris Cooper supports Ravitch’s assessment, saying that, “Across five studies, the average student who did homework had a higher unit test score than the students not doing homework.” Dr. Cooper and his colleagues analyzed dozens of studies on whether homework is beneficial in a 2006 publication, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003. ”
This analysis found 12 less-authoritative studies that link achievement to time spent on homework, but control for many other factors that could influence the outcome. Finally, the research team identified 35 studies that found a positive correlation between homework and achievement, but only after elementary school. Dr. Cooper concluded that younger students might be less capable of benefiting from homework due to undeveloped study habits or other factors.
Recommended amount of homework varies by grade level
“Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement?” also identifies the amount homework that serves as a learning tool for students. While practice improves test scores at all grade levels, “Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night. For high school students, the positive line continues to climb until between 90 minutes and 2.5 hours of homework a night, after which returns diminish.”
Dr. Cooper’s conclusion—homework is important, but discretion can and should be used when assigning it—addresses the valid concerns of homework critics. While the act of completing homework has benefits in terms of developing good habits in students, homework must prove useful for students so that they buy in to the process and complete their assignments. If students (or their parents) feel homework is a useless component of their learning, they will skip it—and miss out on the major benefits, content and otherwise, that homework has to offer.
Continue reading : Ending the Homework Debate: Expert Advice on What Works
Monica Fuglei is a graduate of the University of Nebraska in Omaha and a current adjunct faculty member of Arapahoe Community College in Colorado, where she teaches composition and creative writing.
You may also like to read
- The Homework Debate: The Case Against Homework
- Ending the Homework Debate: Expert Advice on What Works
- Elementary Students and Homework: How Much Is Too Much?
- Advice on Creating Homework Policies
- How Teachers Can Impart the Benefits of Students Working in Groups
- Homework Helps High School Students Most — But it Must Be Purposeful
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Leadership and Administration , Pros and Cons , Teacher-Parent Relationships
- Master's in Math and Science Education
- Online & Campus Bachelor's in Secondary Educa...
- Master's in PE, Sports & Athletics Administra...
The School House
Talking research, issues and ideas for teachers, students and learning
Homework – what’s the point of it?
Senior Lecturer in Language, Literacy and TESL, University of Canberra
University of Canberra provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
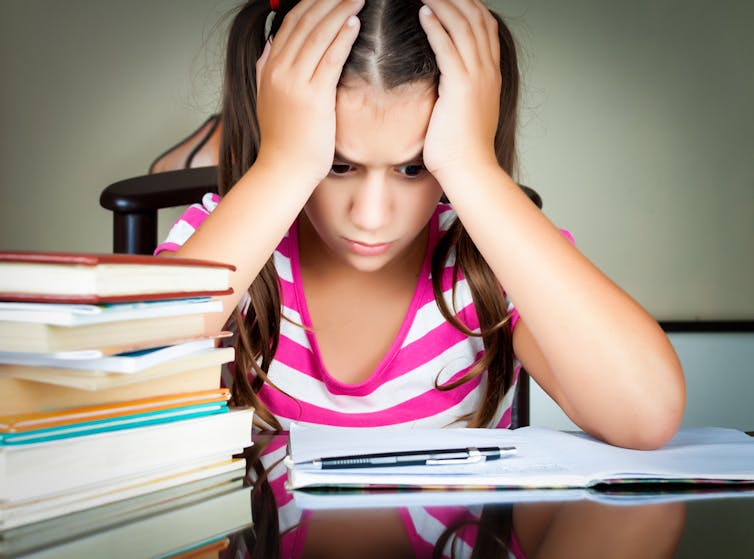

A middle school student I know came home from school with the task to recreate a medieval fort out of cake. I expect the History teacher thought this was a creative and engaging activity. This particular student, from a refugee background living with his single uncle, first had to figure out how to make a cake and spend scarce money on cake tins and ingredients.
Even putting aside the cultural and economic challenges the task presented to this boy, what was the point of that homework?
What is the point of any homework?
Who likes homework?
It’s a question I pose my preservice teachers and the responses always fall into three categories, which I suspect are also reflective of the broader community.
There are the righteous supporters – they tend to be swats whose memories of gold stars give them warm feelings to this day. Who wouldn’t want to do homework, they wonder?
There are the vocal opponents – they tend to be parents who have wasted too many evenings trying to figure out how long division is taught these days, and too much money on sheets of coloured cardboard.
Then there’s the rest – they think you should do homework, because well, they had to do homework at school. They are the status quo majority. For some of them, the idea of setting and marking homework is inextricably tied up with the vision they have of themselves ‘doing’ teaching – but they’ve not really thought much about what homework achieves.
Does homework improve learning outcomes?
Research finds that homework doesn’t improve learning outcomes in primary school, and has a weak link to improved outcomes in junior high school. Those improvements are connected to parental involvement – but parents who are keen supporters of homework may be disappointed to hear that their positive contribution is largely just ensuring their children hand in their homework.
Parental involvement in the homework itself can actually reduce the child’s success at school . Parents rarely have the expertise to fill in gaps in their children’s understandings of concepts, and the predilection of some parents to take over the homework reduces the autonomy of the children, leaving them less able to work independently at school, and less confident of their own abilities.
There are many parents, dedicated and desperately interested in their children’s education, who cannot involve themselves in their children’s homework. They may not have had schooling opportunities themselves, they may speak English as an additional language, they may work long hours or shifts, or they may just be like most of us, and simply can’t remember what a quadratic equation is.
Those with spare cash buy the homework support, in the form of after hours tutoring. In high school, where homework tasks contribute substantially to the course grade, homework is the great unequaliser, contributing to the achievement gap.
Homework generally falls into two categories: practising or catching up on work done in the classroom, and creative extensions of work being done in the classroom. The latter – like making a fort out of cake – is really just busy work.
There are children who enjoy this busy out of school project work, but they don’t need a teacher to set a project for them. Kids find projects everywhere: they build the birdhouse they saw on the lifestyle channel, they create complicated archives for their card collections, they make shields out of paint can lids and they create secret languages for their secret clubs. Or they would, if they weren’t busy trying to make a fort out of cake.
Homework that involves practising or catching up on what was missed in class simply exacerbates the challenges those trailing students are already facing. If there is a child who is behind in classwork, an untrained parent is not going to achieve what a teacher is failing to. If success at school is dependent upon the work being sent home, then the work should be done at school.
There are enough hours in a school day to teach the curriculum. If a school thinks there aren’t, they should audit their use of the school day and teacher expertise. Colouring in, show and tell, roll call, whole school assemblies and assigning and marking homework during class are all examples of ineffective use of teachers’ skills and student learning time.
Homework does not enhance connections between home and the school
Perhaps the most beguiling of contemporary arguments for homework is that it provides the connection between home and school.
The raised voices and tears around the homework table suggest this particular home-school connection is rarely a productive one. Tired and emotional parents, feeling inadequate about their knowledge of improper fractions, helping tired and emotional children, feeling inadequate that they can’t understand what their parent is saying – and anyway it’s not what Ms J said in class today.
A recent photo story of a young child crying as she struggles with her homework makes a compelling case for how damaging homework can be for some.
Better connections between school and home are important, but homework seems more likely to kill the connection than build the connection.
So what should parents do?
Spend those precious after school hours talking to your children about anything and everything, reading to them and with them, loving them and being interested in them. It’s not work, but it is what home is for.
Postdoctoral Research Associate

Project Manager – Contraceptive Development

Editorial Internship

Integrated Management of Invasive Pampas Grass for Enhanced Land Rehabilitation

5 Ways to Make Homework More Meaningful
Use these insights from educators—and research—to create homework practices that work for everyone.
Your content has been saved!
Homework tends to be a polarizing topic. While many teachers advocate for its complete elimination, others argue that it provides students with the extra practice they need to solidify their learning and teach them work habits—like managing time and meeting deadlines—that have lifelong benefits.
We recently reached out to teachers in our audience to identify practices that can help educators plot a middle path.
On Facebook , elementary school teacher John Thomas responded that the best homework is often no-strings-attached encouragement to read or play academically adjacent games with family members. “I encourage reading every night,” Thomas said, but he doesn’t use logs or other means of getting students to track their completion. “Just encouragement and book bags with self selected books students take home for enjoyment.”
Thomas said he also suggests to parents and students that they can play around with “math and science tools” such as “calculators, tape measures, protractors, rulers, money, tangrams, and building blocks.” Math-based games like Yahtzee or dominoes can also serve as enriching—and fun—practice of skills they’re learning.
At the middle and high school level, homework generally increases, and that can be demotivating for teachers, who feel obliged to review or even grade halfhearted submissions. Student morale is at stake, too: “Most [students] don’t complete it anyway,” said high school teacher Krystn Stretzinger Charlie on Facebook . “It ends up hurting them more than it helps.”
So how do teachers decide when to—and when not to—assign homework, and how do they ensure that the homework they assign feels meaningful, productive, and even motivating to students?
1. Less is More
A 2017 study analyzed the homework assignments of more than 20,000 middle and high school students and found that teachers are often a bad judge of how long homework will take.
According to researchers, students spend as much as 85 minutes or as little as 30 minutes on homework that teachers imagined would take students one hour to complete. The researchers concluded that by assigning too much homework , teachers actually increased inequalities between students in exchange for “minimal gains in achievement.” Too much homework can overwhelm students who “have more gaps in their knowledge,” the researchers said, and creates situations where homework becomes so time-consuming and frustrating that it turns students off to classwork more broadly.
To counteract this, middle school math teacher Crystal Frommert said she focuses on quality over quantity. Frommert cited the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics , which recommends only assigning “what’s necessary to augment instruction” and adds that if teachers can “get sufficient information by assigning only five problems, then don’t assign fifty.”
Instead of sending students home with worksheets and long problem sets from textbooks that often repeat the same concepts, Frommert recommended assigning part of a page, or even a few specific problems—and explaining to students why these handpicked problems will be helpful practice. When students know there’s thought behind the problems they’re asked to solve at home, “they pay more attention to the condensed assignment because it was tailored for them,” Frommert said.
On Instagram , high school teacher Jacob Palmer said that every now and then he condenses homework down to just one problem that is particularly engaging and challenging: “The depth and exploration that can come from one single problem can be richer than 20 routine problems.”
2. Add Choice to the Equation
Former educator and coach Mike Anderson said teachers can differentiate homework assignments without placing unrealistic demands on their workload by offering students some discretion in the work they complete and explicitly teaching them “how to choose appropriately challenging work for themselves.”
Instead of assigning the same 20 problems or response questions on a given textbook page to all students, for example, Anderson suggested asking students to refer to the list of questions and choose and complete a designated number of them (three to five, for example) that give students “a little bit of a challenge but that [they] can still solve independently.”
To teach students how to choose well, Anderson has students practice choosing homework questions in class before the end of the day, brainstorming in groups and sharing their thoughts about what a good homework question should accomplish. The other part, of course, involves offering students good choices: “Make sure that options for homework focus on the skills being practiced and are open-ended enough for all students to be successful,” he said.
Once students have developed a better understanding of the purpose of challenging themselves to practice and grow as learners, Anderson also periodically asks them to come up with their own ideas for problems or other activities they can use to reinforce learning at home. A simple question, such as “What are some ideas for how you might practice this skill at home?” can be enough to get students sharing ideas, he said.
Jill Kibler, a former high school science teacher, told Edutopia on Facebook that she implemented homework choice in her classroom by allowing students to decide how much of the work they’ve recently turned in that they’d like to redo as homework: “Students had one grading cycle (about seven school days) to redo the work they wanted to improve,” she said.
3. Break the Mold
According to high school English teacher Kate Dusto, the work that students produce at home doesn’t have to come in the traditional formats of written responses to a problem. On Instagram , Dusto told Edutopia that homework can often be made more interesting—and engaging—by allowing students to show evidence of their learning in creative ways.
“Offer choices for how they show their learning,” Dusto said. “Record audio or video? Type or use speech to text? Draw or handwrite and then upload a picture?” The possibilities are endless.
Former educator and author Jay McTighe noted that visual representations such as graphic organizers and concept maps are particularly useful for students attempting to organize new information and solidify their understanding of abstract concepts. For example, students might be asked to “draw a visual web of factors affecting plant growth” in biology class or map out the plot, characters, themes, and settings of a novel or play they’re reading to visualize relationships between different elements of the story and deepen their comprehension of it.
Simple written responses to summarize new learning can also be made more interesting by varying the format, McTighe said. For example, ask students to compose a tweet in 280 characters or less to answer a question like “What is the big idea that you have learned about _____?” or even record a short audio podcast or video podcast explaining “key concepts from one or more lessons.”
4. Make Homework Voluntary
When elementary school teacher Jacqueline Worthley Fiorentino stopped assigning mandatory homework to her second-grade students and suggested voluntary activities instead, she found that something surprising happened: “They started doing more work at home.”
Some of the simple, voluntary activities she presented students with included encouraging at-home reading (without mandating how much time they should spend reading); sending home weekly spelling words and math facts that will be covered in class but that should also be mastered by the end of the week: “It will be up to each child to figure out the best way to learn to spell the words correctly or to master the math facts,” she said; and creating voluntary lesson extensions such as pointing students to outside resources—texts, videos or films, webpages, or even online or in-person exhibits—to “expand their knowledge on a topic covered in class.”
Anderson said that for older students, teachers can sometimes make whatever homework they assign a voluntary choice. “Do all students need to practice a skill? If not, you might keep homework invitational,” he said, adding that teachers can tell students, “If you think a little more practice tonight would help you solidify your learning, here are some examples you might try.”
On Facebook , Natisha Wilson, a K–12 gifted students coordinator for an Ohio school district, said that when students are working on a challenging question in class, she’ll give them the option to “take it home and figure it out” if they’re unable to complete it before the end of the period. Often students take her up on this, she said, because many of them “can’t stand not knowing the answer.”
5. Grade for Completion—or Don’t Grade at All
Former teacher Rick Wormeli argued that work on homework assignments isn’t “evidence of final level of proficiency”; rather, it’s practice that provides teachers with “feedback and informs where we go next in instruction.”
Grading homework for completion—or not grading at all, Wormeli said—can help students focus on the real task at hand of consolidating understanding and self-monitoring their learning. “When early attempts at mastery are not used against them, and accountability comes in the form of actually learning content, adolescents flourish.”
High school science teacher John Scali agreed , confirming that grading for “completion and timeliness” rather than for “correctness” makes students “more likely to do the work, especially if it ties directly into what we are doing in class the next day” without worrying about being “100% correct.” On Instagram , middle school math teacher Traci Hawks noted that any assignments that are completed and show work—even if the answer is wrong—gets a 100 from her.
But Frommert said that even grading for completion can be time-consuming for teachers and fraught for students if they don’t have home environments that are supportive of homework or if they have jobs or other after-school activities.
Instead of traditional grading, she suggested alternatives to holding students accountable for homework, such as student presentations or even group discussions and debates as a way to check for understanding. For example, students can debate which method is best to solve a problem or discuss their prospective solutions in small groups. “Communicating their mathematical thinking deepens their understanding,” Frommert said.
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce

Home » Tips for Teachers » 7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral part of learning is being reevaluated in light of new findings about its effectiveness and impact on students’ overall well-being.

The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:
- Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts →
- 7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework →
- Opposing Views on Homework Practices →
- Exploring Alternatives to Homework →
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
In the ongoing conversation about the role and impact of homework in education, the perspectives of those directly involved in the teaching process are invaluable. Teachers and education industry experts bring a wealth of experience and insights from the front lines of learning. Their viewpoints, shaped by years of interaction with students and a deep understanding of educational methodologies, offer a critical lens through which we can evaluate the effectiveness and necessity of homework in our current educational paradigm.
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences

The ongoing debate about homework often focuses on its educational value, but a vital aspect that cannot be overlooked is the significant stress and health consequences it brings to students. In the context of American life, where approximately 70% of people report moderate or extreme stress due to various factors like mass shootings, healthcare affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, presidential elections, and the need to stay informed, the additional burden of homework further exacerbates this stress, particularly among students.
Key findings and statistics reveal a worrying trend:
- Overwhelming Student Stress: A staggering 72% of students report being often or always stressed over schoolwork, with a concerning 82% experiencing physical symptoms due to this stress.
- Serious Health Issues: Symptoms linked to homework stress include sleep deprivation, headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems.
- Sleep Deprivation: Despite the National Sleep Foundation recommending 8.5 to 9.25 hours of sleep for healthy adolescent development, students average just 6.80 hours of sleep on school nights. About 68% of students stated that schoolwork often or always prevented them from getting enough sleep, which is critical for their physical and mental health.
- Turning to Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Alarmingly, the pressure from excessive homework has led some students to turn to alcohol and drugs as a way to cope with stress.
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
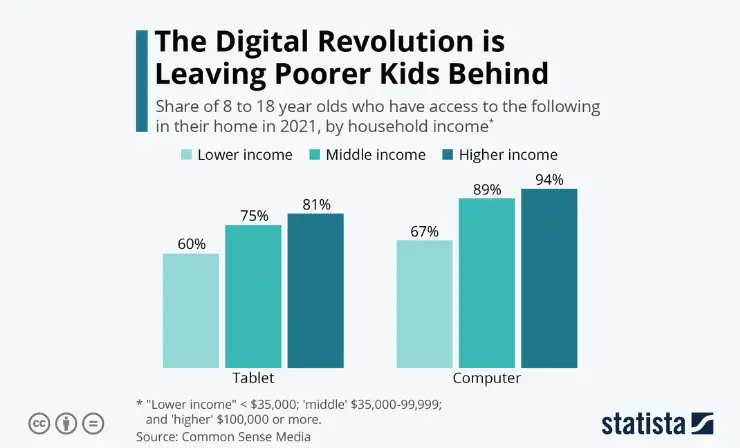
In the discourse surrounding educational equity, homework emerges as a factor exacerbating socioeconomic disparities, particularly affecting students from lower-income families and those with less supportive home environments. While homework is often justified as a means to raise academic standards and promote equity, its real-world impact tells a different story.
The inequitable burden of homework becomes starkly evident when considering the resources required to complete it, especially in the digital age. Homework today often necessitates a computer and internet access – resources not readily available to all students. This digital divide significantly disadvantages students from lower-income backgrounds, deepening the chasm between them and their more affluent peers.
Key points highlighting the disparities:
- Digital Inequity: Many students lack access to necessary technology for homework, with low-income families disproportionately affected.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic exacerbated these disparities as education shifted online, revealing the extent of the digital divide.
- Educational Outcomes Tied to Income: A critical indicator of college success is linked more to family income levels than to rigorous academic preparation. Research indicates that while 77% of students from high-income families graduate from highly competitive colleges, only 9% from low-income families achieve the same . This disparity suggests that the pressure of heavy homework loads, rather than leveling the playing field, may actually hinder the chances of success for less affluent students.
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
The issue of homework and its inequitable impact is not just an academic concern; it is a reflection of broader societal inequalities. By continuing practices that disproportionately burden students from less privileged backgrounds, the educational system inadvertently perpetuates the very disparities it seeks to overcome.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics

Homework, a staple of the educational system, is often perceived as a necessary tool for academic reinforcement. However, its impact extends beyond the realm of academics, significantly affecting family dynamics. The negative repercussions of homework on the home environment have become increasingly evident, revealing a troubling pattern that can lead to conflict, mental health issues, and domestic friction.
A study conducted in 2015 involving 1,100 parents sheds light on the strain homework places on family relationships. The findings are telling:
- Increased Likelihood of Conflicts: Families where parents did not have a college degree were 200% more likely to experience fights over homework.
- Misinterpretations and Misunderstandings: Parents often misinterpret their children’s difficulties with homework as a lack of attention in school, leading to feelings of frustration and mistrust on both sides.
- Discriminatory Impact: The research concluded that the current approach to homework disproportionately affects children whose parents have lower educational backgrounds, speak English as a second language, or belong to lower-income groups.
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
The need of the hour is to reassess the role and amount of homework assigned to students. It’s imperative to find a balance that facilitates learning and growth without compromising the well-being of the family unit. Such a reassessment would not only aid in reducing domestic conflicts but also contribute to a more supportive and nurturing environment for children’s overall development.
4. Consumption of Free Time

In recent years, a growing chorus of voices has raised concerns about the excessive burden of homework on students, emphasizing how it consumes their free time and impedes their overall well-being. The issue is not just the quantity of homework, but its encroachment on time that could be used for personal growth, relaxation, and family bonding.
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Key points of concern:
- Excessive Time Commitment: Students, on average, spend over 6 hours in school each day, and homework adds significantly to this time, leaving little room for other activities.
- Impact on Extracurricular Activities: Homework infringes upon time for sports, music, art, and other enriching experiences, which are as crucial as academic courses.
- Stifling Creativity and Self-Discovery: The constant pressure of homework limits opportunities for students to explore their interests and learn new skills independently.
The National Education Association (NEA) and the National PTA (NPTA) recommend a “10 minutes of homework per grade level” standard, suggesting a more balanced approach. However, the reality often far exceeds this guideline, particularly for older students. The impact of this overreach is profound, affecting not just academic performance but also students’ attitudes toward school, their self-confidence, social skills, and overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
- Homework as a Painful Endeavor: For students with learning disabilities, completing homework can be likened to “running with a sprained ankle.” It’s a task that, while doable, is fraught with difficulty and discomfort.
- Misconceptions about Laziness: Often, children who struggle with homework are perceived as lazy. However, Barish emphasizes that these students are more likely to be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious rather than unmotivated.
- Limited Improvement in School Performance: The battles over homework rarely translate into significant improvement in school for these children, challenging the conventional notion of homework as universally beneficial.
These points highlight the need for a tailored approach to homework for students with learning disabilities. It’s crucial to recognize that the traditional homework model may not be the most effective or appropriate method for facilitating their learning. Instead, alternative strategies that accommodate their unique needs and learning styles should be considered.
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
The longstanding belief in the educational sphere that more homework automatically translates to more learning is increasingly being challenged. Critics argue that this assumption is not only flawed but also unsupported by solid evidence, questioning the efficacy of homework as an effective learning tool.
Alfie Kohn , a prominent critic of homework, aptly compares students to vending machines in this context, suggesting that the expectation of inserting an assignment and automatically getting out of learning is misguided. Kohn goes further, labeling homework as the “greatest single extinguisher of children’s curiosity.” This critique highlights a fundamental issue: the potential of homework to stifle the natural inquisitiveness and love for learning in children.
The lack of concrete evidence supporting the effectiveness of homework is evident in various studies:
- Marginal Effectiveness of Homework: A study involving 28,051 high school seniors found that the effectiveness of homework was marginal, and in some cases, it was counterproductive, leading to more academic problems than solutions.
- No Correlation with Academic Achievement: Research in “ National Differences, Global Similarities ” showed no correlation between homework and academic achievement in elementary students, and any positive correlation in middle or high school diminished with increasing homework loads.
- Increased Academic Pressure: The Teachers College Record published findings that homework adds to academic pressure and societal stress, exacerbating performance gaps between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
These findings bring to light several critical points:
- Quality Over Quantity: According to a recent article in Monitor on Psychology , experts concur that the quality of homework assignments, along with the quality of instruction, student motivation, and inherent ability, is more crucial for academic success than the quantity of homework.
- Counterproductive Nature of Excessive Homework: Excessive homework can lead to more academic challenges, particularly for students already facing pressures from other aspects of their lives.
- Societal Stress and Performance Gaps: Homework can intensify societal stress and widen the academic performance divide.
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
Key points highlighting enforcement challenges:
- Difficulty in Enforcing Completion: Ensuring that students complete their homework can be a complex task, and not completing homework does not always correlate with poor grades.
- Reliability of Homework Practice: The reliability of homework as a practice tool is undermined when students, either out of desperation or lack of understanding, choose shortcuts over genuine learning. This approach can lead to the opposite of the intended effect, especially when assignments are not well-aligned with the students’ learning levels or interests.
- Temptation to Cheat: The issue of cheating is particularly troubling. According to a report by The Chronicle of Higher Education , under the pressure of at-home assignments, many students turn to copying others’ work, plagiarizing, or using creative technological “hacks.” This tendency not only questions the integrity of the learning process but also reflects the extreme stress that homework can induce.
- Parental Involvement in Completion: As noted in The American Journal of Family Therapy , this raises concerns about the authenticity of the work submitted. When parents complete assignments for their children, it not only deprives the students of the opportunity to learn but also distorts the purpose of homework as a learning aid.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance

Homework is commonly perceived as a means to enhance academic performance, with the belief that it directly contributes to better grades and test scores. This view posits that through homework, students reinforce what they learn in class, leading to improved understanding and retention, which ultimately translates into higher academic achievement.
However, the question of why students should not have homework becomes pertinent when considering the complex relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have indicated that excessive homework doesn’t necessarily equate to higher grades or test scores. Instead, too much homework can backfire, leading to stress and fatigue that adversely affect a student’s performance. Reuters highlights an intriguing correlation suggesting that physical activity may be more conducive to academic success than additional homework, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to education that prioritizes both physical and mental well-being for enhanced academic outcomes.
2. Reinforcement of Learning

Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
Furthermore, when homework surpasses a student’s capability, it may induce frustration and confusion rather than aid in learning. This challenges the notion that more homework invariably leads to better understanding and retention of educational content.
3. Development of Time Management Skills

Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges

Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
Contrarily, an excessive homework load, especially from a young age, can have the opposite effect . It can instill a negative attitude towards education, dampening students’ enthusiasm and willingness to embrace future academic challenges. Overburdening students with homework risks disengagement and loss of interest, thereby defeating the purpose of preparing them for future challenges. Striking a balance in the amount and complexity of homework is crucial to maintaining student engagement and fostering a positive attitude towards ongoing learning.
5. Parental Involvement in Education

Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
However, the line between involvement and over-involvement is thin. When parents excessively intervene by completing their child’s homework, it can have adverse effects . Such actions not only diminish the educational value of homework but also rob children of the opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and independence. This over-involvement, coupled with disparities in parental ability to assist due to variations in time, knowledge, or resources, may lead to unequal educational outcomes, underlining the importance of a balanced approach to parental participation in homework.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground

In the ongoing debate about the role of homework in education, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives and strategies to minimize its burden. While completely eliminating homework may not be feasible for all educators, there are several effective methods to reduce its impact and offer more engaging, student-friendly approaches to learning.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
- Project-Based Learning: This method focuses on hands-on, long-term projects where students explore real-world problems. It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and collaborative skills, offering a more engaging and practical learning experience than traditional homework. For creative ideas on school projects, especially related to the solar system, be sure to explore our dedicated article on solar system projects .
- Flipped Classrooms: Here, students are introduced to new content through videos or reading materials at home and then use class time for interactive activities. This approach allows for more personalized and active learning during school hours.
- Reading for Pleasure: Encouraging students to read books of their choice can foster a love for reading and improve literacy skills without the pressure of traditional homework assignments. This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida , where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes . Superintendent Heidi Maier’s decision was influenced by research showing that while homework offers minimal benefit to young students, regular reading significantly boosts their learning. For book recommendations tailored to middle school students, take a look at our specially curated article .
Ideas for Minimizing Homework
- Limiting Homework Quantity: Adhering to guidelines like the “ 10-minute rule ” (10 minutes of homework per grade level per night) can help ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on assigning meaningful homework that is directly relevant to what is being taught in class, ensuring it adds value to students’ learning.
- Homework Menus: Offering students a choice of assignments can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, making homework more engaging and personalized.
- Integrating Technology: Utilizing educational apps and online platforms can make homework more interactive and enjoyable, while also providing immediate feedback to students. To gain deeper insights into the role of technology in learning environments, explore our articles discussing the benefits of incorporating technology in classrooms and a comprehensive list of educational VR apps . These resources will provide you with valuable information on how technology can enhance the educational experience.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
- Is homework a good idea or not? by BBC
- The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype
- Alternative Homework Ideas
The evidence and arguments presented in the discussion of why students should not have homework call for a significant shift in homework practices. It’s time for educators and policymakers to rethink and reformulate homework strategies, focusing on enhancing the quality, relevance, and balance of assignments. By doing so, we can create a more equitable, effective, and student-friendly educational environment that fosters learning, well-being, and holistic development.
- “Here’s what an education expert says about that viral ‘no-homework’ policy”, Insider
- “John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”, Visible Learning
- HowtoLearn.com
- “Time Spent On Homework Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Stress in America”, American Psychological Association (APA)
- “Homework hurts high-achieving students, study says”, The Washington Post
- “National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report”, National Library of Medicine
- “A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools”, Frontiers
- “The Digital Revolution is Leaving Poorer Kids Behind”, Statista
- “The digital divide has left millions of school kids behind”, CNET
- “The Digital Divide: What It Is, and What’s Being Done to Close It”, Investopedia
- “COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it”, World Economic Forum
- “PBS NewsHour: Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income”, America’s Promise Alliance
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, Taylor & Francis Online
- “What Do You Mean My Kid Doesn’t Have Homework?”, EducationWeek
- “Excerpt From The Case Against Homework”, Penguin Random House Canada
- “How much homework is too much?”, neaToday
- “The Nation’s Report Card: A First Look: 2013 Mathematics and Reading”, National Center for Education Statistics
- “Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents”, Psychology Today
- “How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health”, The Lion’s Roar
- “ Breaking the Homework Habit”, Education World
- “Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement”, ScienceDirect
- “National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling”, Stanford University Press
- “When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework”, APA PsycNet
- “Is homework a necessary evil?”, APA PsycNet
- “Epidemic of copying homework catalyzed by technology”, Redwood Bark
- “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame”, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, ResearchGate
- “Kids who get moving may also get better grades”, Reuters
- “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003”, SageJournals
- “Is it time to get rid of homework?”, USAToday
- “Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework”, Stanford
- “Florida school district bans homework, replaces it with daily reading”, USAToday
- “Encouraging Students to Read: Tips for High School Teachers”, wgu.edu
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- 22 Essential Strategies to Check for Understanding: Enhancing Classroom Engagement and Learning - May 20, 2024
- 24 Innovative and Fun Periodic Table Project Ideas to Engage and Inspire Students in Chemistry Learning - May 9, 2024
- 28 Exciting Yarn Crafts for Preschool Kids: Igniting Creativity and Fine Motor Skills - April 29, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Inferences Worksheets
- Context Clues Worksheets
- Theme Worksheets
Main Idea Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Summary Worksheets
- Online Tests
- Figurative Language Worksheets
- Short Stories with Questions
- Nonfiction Passages
- Genre Worksheets
BECOME A MEMBER!
Are you looking for main idea worksheets and resources? This page features a collection of high-quality worksheets and a PowerPoint lesson! Many students have difficulties identifying main ideas in nonfiction texts. I hope that these resources will help.
Identifying main ideas may come simply and naturally to good readers. But it is actually a two or three step process . Struggling readers may trip up on any one of those steps. Here are some practice activities. Students can try to identify the main idea in a variety of texts with these main idea worksheets.

Main Idea Common Core State Standards
150 comments.
Congratulations on all the extraordinary, meaningful, helpful material you’ve created. Thanks to all your great ideas, which you have contributed since many years back, my students have been learning with such clear understanding and practice. Thanks, Thanks
These are wonderful resources. Bless you all!
Joy Perkins
As always – brilliant material
Margaret Chavis
Great for assessing and remediation
EMELIA C. PALURAY
I’m gratefully happy to use the worksheets from this website. thanks for the selfless effort you’ve impartially exerted. wonderful and amazing God bless everyone.
Valuable website for everyone
Thank you so much. This website has helped me understand lots of figurative language! Thank you again!!! Best wishes, Satnaam
very good website thanks for making!<3
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Author's Purpose Worksheets
- Characterization Worksheets
- Conflict Worksheets
- Fact and Opinion Worksheets
- Figurative Language Activities
- Figurative Language Poems with Questions
- Genre Activities
- Irony Worksheets
- Making Predictions
- Mood Worksheets
- Nonfiction Passages and Functional Texts
- Parts of Speech Worksheets
- Poetic Devices
- Point of View Worksheets
- School Project Ideas
- Setting Worksheets
- Simile and Metaphor Worksheets
- Story Structure Worksheets
- Text Structure Worksheets
- Tone Worksheets
- ALL PAGES AND WORKSHEETS
Why Dining Rooms Are Disappearing From American Homes
A once-ubiquitous feature of floor plans is becoming a rarity.

Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration.
The dining room is the closest thing the American home has to an appendix—a dispensable feature that served some more important function at an earlier stage of architectural evolution. Many of them sit gathering dust, patiently awaiting the next “dinner holiday” on Easter or Thanksgiving.
That’s why the classic, walled-off dining room is getting harder to find in new single-family houses. It won’t be missed by many. Americans now tend to eat in spaces that double as kitchens or living rooms—a small price to pay for making the most of their square footage.
But in many new apartments, even a space to put a table and chairs is absent. Eating is relegated to couches and bedrooms , and hosting a meal has become virtually impossible. This isn’t simply a response to consumer preferences. The housing crisis—and the arbitrary regulations that fuel it—is killing off places to eat whether we like it or not, designing loneliness into American floor plans. If dining space keeps dying, the U.S. might not have a chance to get it back.
The apex predator of the dining room is the “great room”—a combined living room and kitchen, bridged by an open dining space. “It’s not that Americans don’t want dining rooms. It’s that they want something else, and that takes up space,” explains Stephen Smith , the executive director of the Center for Building in North America , a nonprofit that advocates for building-code reform. “In a single-family home, that’s a great room. And so that’s what developers build.”
Read: The curse of an open floor plan
According to surveys in 2015 and 2016 by the National Association of Home Builders, 86 percent of households want a combined kitchen and dining room—a preference accommodated by only 75 percent of new homes. If anything, the classic dining room isn’t dying fast enough for most people’s taste.
The transition from the classic dining room to the great room mirrors the changes in gender norms and family formation that have occurred over the past 125 years. The dining room emerged in the early 20th century, when an ascendant upper middle class hired migrant laborers as servants. Many American homes from that era were designed around creating a separate sphere for “the help,” with sectioned-off kitchens, laundry rooms, and servants’ quarters. You can still find anachronistic allowances for servants’ quarters tucked away in zoning codes that otherwise ban secondary units.
In households where servants were unaffordable, domestic work fell to women. Separate dining rooms and kitchens thus reinforced the segregation of male and female spaces, while allowing generations of newly minted homeowners to ape the design norms of yesteryear’s elites. Women today still do most of the cooking and cleaning, but as dining rooms and kitchens fuse with living rooms, more members of the household spend time in all of those spaces—and even take on a little more of the labor .
If dining space is merging with other rooms in single-family homes, it’s vanishing altogether from newly constructed apartments. Americans might not mind what’s happening to their houses, but the evolution of apartments is a more complicated story.
“For the most part, apartments are built for Netflix and chill,” Bobby Fijan , a real-estate developer and floor-plan expert, told me. “The reason the dining room is disappearing is that we are allocating [our] limited space to bedrooms and walk-in closets.” Even though we’re dining at home more and more—going to restaurants peaked in 2000— many new apartments offer only a kitchen island as an obvious place to eat.
This is partly a response to shrinking household size. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the share of one-person households more than tripled from 1940 to 2020. A dedicated dining space might feel wasted on someone who lives alone. And for young, unmarried apartment dwellers with only a roommate or two, developers typically sacrifice a common dining space in order to maximize personal space.
As households and dining spaces have contracted, the number of people eating alone has grown. According to a 2015 report by the Food Marketing Institute, nearly half the time we spend eating is spent in isolation, a central factor in America’s loneliness epidemic and a correlate to a range of physical- and mental-health problems.
Do we want to live this way—or do we have to, thanks to America’s housing supply? “It’s a chicken-and-an-egg problem,” Fijan said. How many more dinners would be shared if we had the space to host guests?
Stephen Smith doesn’t buy that the death of dining space is purely a function of consumer preferences. In most U.S. cities, he told me, building codes mandate double-loaded corridors—or two rows of apartments along a hall—making larger units difficult to build. “When you can only build small apartments with one wall of windows, rooms will naturally disappear,” he said. “Nobody wants a dining room without a window.”
M. Nolan Gray: Cancel zoning
In cities across the country, apartments are shrinking , even as single-family homes continue to grow. The difference is that many of the former are subject to arbitrary zoning rules that limit the total amount of floor area that can be built—in places where apartments can be built at all. Combine an acute housing shortage with tight zoning rules (as in cities such as New York and Los Angeles ), and you end up with a lot of tiny apartments and few dining rooms.
In an age when Americans are spending less and less time with one another, a table and some chairs could be just what we need. For what it’s worth, scientists have begun to think that the appendix does have a use—as a reservoir for healthy gut bacteria. Dining rooms should be so lucky.
About the Author
More Stories
City Planning’s Greatest Innovation Makes a Comeback
The UCLA Students Who Live in Their Cars
Make your dream home a reality

Home Designing
- Inspiration
- Dream Home Kit
- AI Interior Design
- Living Room
- Dining Room
- Home Office
- House Tours
- Non-Residential
- Modern House Plans
- Accessories
- Designs by Style
- Future Buildings
- Technology At Home
How to Create a Cozy Reading Nook: 14 Best Ideas for Book Lovers -->

There’s something undeniably charming about curling up in a cozy corner with a good book. A reading nook provides that perfect sanctuary—a space to relax, escape, and immerse yourself in a great story. Whether working with a small space, a wide open room, or something in between, designing a cozy reading nook can transform any home corner into a personal haven.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about creating a reading nook that exudes warmth and invites you to unwind.
1. Choose the Right Spot

The first step in creating your ideal reading nook is selecting the perfect location. You don’t need a whole room; a couple of square feet can make your reading spot almost perfect for you.
Find a quiet area in your home where you can relax and read without any disturbances. A spot near the window gains natural light and enhances the cozy atmosphere of your nook. If you have limited space, an unused corner in a room might work. The aim is to carve out a grounded area that makes you feel relaxed.
Window seats are popular spots for reading nooks, offering natural light and a view. If your home has a bay window or big window ledge, that can be turned into a comfortable reading area. A corner in the living room or bedroom also works well.
2. Try a Hanging Chair

Comfortable seating is the center of any reading nook. Depending on the space you have to work with, you might choose several different seats. Adding a hanging chair to your reading nook is a fantastic way to create a cozy, whimsical retreat where you can escape with a book. Hanging chairs, with their gentle swaying motion and suspended design, provide both comfort and a sense of fun.
A big, soft armchair will give your nook a traditional echo, while a chaise lounge or daybed can produce an easygoing vibe. If the spot is near a window, an integrated bench with cushions can be elegant and space-saving.
Another choice is to have floor seating with a mix of a few plush cushions and a beanbag chair, which make for a more casual, laid-back feeling. No matter what you decide on, seating should invite long stretches of reading with its comfort.
3. Select Soft, Inviting Textiles

One of the simplest ways to depend on a cozy reading nook is with the aid of textiles. Soft textures play into the relaxed vibe, and the area feels warm and inviting. Begin with plush cushions and pillows — these are necessities when it comes to creating a more comfortable seating area in any home. Add a chunky knit throw, or even better, a faux fur blanket for that warm and textural feel.
Your selection of rug can function miracles too. A plush pile of rug underfoot gives a warm feeling and provides earthing to the space. Create a bohemian look in your reading nook by layering rugs for an exotic & casual feel. If your reading nook is part of a larger room (i.e. in the corner), introducing these textiles will single out the nook as an intimate escape.
4. Choose a Soothing Color Palette

The colors you use for your reading nook will greatly impact the mood. Soft, neutral tones such as cream, beige, or gray can create a tranquil environment. If you want a splash of color, go for pastel shades or subtle hints that won’t overpower the space.
It is a mild palette: blues, greens, or soft pinks can create a sanctuary to relax and read. If your nook is in a big room, color the same scheme for harmony with the rest of the space, but give that little zone its flair.
Darker moody tones such as navy and deep emerald can also be effective particularly when accompanied by rich textiles like velvet or wool. Those colors make the nook feel more intimate and cocoon-like
5. Set the Mood with Lighting

Good lighting is crucial for a reading nook, but it should also contribute to the cozy atmosphere. Natural light is perfect during daylight, so try to place your nook near a window .
For evening reading you will need warm ambient light that doesn’t strain your eyes A floor lamp with a dimmer switch or a subtly lit side table lamp can give just the right reading light effect and help to balance the excessive use of stark white in a room.
Others on the list include fairy lights and string lights; they help to conjure that ethereal, relaxing vibe in your nook. These lighting selections will set a calming atmosphere and give your nook a cozy feel around the clock.
6. Keep It Minimal but Comfortable

It is easy to succumb to the temptation of including all your favorites in your reading nook, but if you can keep that minimal then it will give a serene vibe. A cluttered space is uncomfortable and can hinder your work.
Try to figure out the proper degree of functionality that meets and complements a sense of comfort by putting in only those objects that are necessary for work or rest. Focus on incorporating key pieces like a comfy chair , soft lighting, and a few personal items.
Keep the space simple and uncluttered and you create an environment that feels open, breathable, and distraction-free. This kind of zen spot is perfect for diving into a good book.
7. Incorporate Functional Storage

To make it easy to reach for your favorite book whenever you want from a well-organized reading nook, the space should contain practical and stylish elements that serve just this purpose.
If you have the space, a small bookshelf or some built-in shelving can make a great addition to your nook. These shelves can hold everything from books to decorative items like plants or mementos from your travels abroad.
For those nooks that are smaller, a simple side table with storage underneath or a pile of books within arm’s reach can serve the purpose equally well.
You can also employ decorative baskets to keep books, blankets, and periodicals in order while you are not getting lost in a volume.
8. Create a Tent Space

One way to create a magical reading atmosphere is by designing a tented nook, with the bookshelf as an integral part of the setup. Imagine a cozy tented area, with fabric draped over a small seating arrangement, where the bookshelf forms one of the tent’s “walls.” This adds a whimsical, adventurous touch to the space, making you feel as though you’re reading in a hidden hideaway.
The bookshelf itself can be small and close to the floor, giving the feel of a secret reading fort. You can drape light, sheer fabric over the bookshelf, letting the books peek out through the soft folds. Add a few floor cushions or a low chair to complete the space, and the bookshelf becomes a part of the tent’s structure, blending storage with style.
9. Add Greenery and Plants

Bringing nature indoors is a wonderful way to make your bookshelf feel alive and vibrant. Adding plants around or on your bookshelf not only freshens the air but also creates a soothing environment.
If you have a larger nook with ample natural light, hanging plants or a plant stand next to the bookshelf can bring an additional layer of greenery to your cozy reading nook. The combination of books and plants makes the space feel organic and tranquil—perfect for getting lost in a good book.
10. Add Whimsical Details

Whimsical art and decor pieces are great ways to express your personality and set a lighthearted tone in your reading nook. You can hang artwork that features fantastical landscapes, animals in human clothes, or abstract designs to give your nook an otherworldly feel.
Few things are quite as magical as twinkling lights, and fairy lights are a whimsical addition to any reading nook. You can lay them around the bookcases, from the ceiling, or simply against your walls to create a gentle inviting glow that adds warmth and transforms your space into a lively retreat.
Look for old clocks, antique picture frames, or weathered trunks for storage or decor. A vintage armchair or an old rocking chair can also add to the whimsical feel of your reading nook.
11. Add Personal Touches

The beauty of a reading nook is how personal it can be. This is your key to relaxation and rejuvenation, so incorporating items that reflect your personality will make the space even more delightful. Start by incorporating items that bring you artwork, family photos, or a collection of favorite objects. These small details can give your nook character and help create a space that feels uniquely yours.
You can also experiment with wall art, like framed book quotes or serene nature scenes, that resonate with you. The key is to keep the decor simple and soothing, creating a space that inspires relaxation.
12. Use Vertical Spaces

When space is limited, vertical storage solutions can help you make the most of your nook without overcrowding the area. Tall bookshelves that stretch from floor to ceiling not only maximize storage but also create a dramatic visual effect. Using vertical space allows you to store more books while keeping the rest of the nook open and uncluttered.
Wall-mounted shelves are another great option for small spaces. They free up floor space and can be arranged in various configurations to fit the nook’s layout.
Floating shelves are perfect for displaying both books and decorative items, like framed quotes or small plants. With vertical shelving, you’ll have easy access to your entire collection, while the overall space remains airy and comfortable.
13. Layer Different Textures

One of the easiest ways to add warmth and comfort to your reading nook is by layering various textures. Start by selecting a soft rug or floor cushions to define the space and make it more comfortable to settle in. Then, drape a plush throw blanket over your chair or seating area. Add a few pillows in different fabrics—like velvet, wool, or faux fur—to bring a rich tactile experience to your nook.
These layered textures give the space a cozy, enveloping feel that encourages you to sink in and relax. You can also experiment with materials that contrast and complement each other, like pairing smooth cotton with chunky knit blankets. The interplay of textures adds visual interest and makes the nook feel like a sanctuary.
14. Create Mid-Century Modern Reading Nook

A mid-century modern reading nook blends sleek, functional design with comfort and style, creating a space that’s not only practical for reading but also aesthetically pleasing. This design style, characterized by clean lines, organic forms, and minimal ornamentation, focuses on simple elegance and functionality, making it a perfect fit for a reading nook where you want to feel both inspired and relaxed.
Start by selecting furniture that embodies mid-century modern characteristics. A sleek armchair with tapered wooden legs, smooth curves, and minimalist upholstery can serve as the focal point of your nook.
Lighting plays a key role in a mid-century modern reading nook. A floor lamp or table lamp with a sleek, sculptural design can not only provide the necessary illumination for reading but also serve as a striking design element. Decorative accents in a mid-century modern reading nook should be kept minimal yet thoughtful.
If you’re looking for more inspiration and expert advice on home decor, furniture, and interior design, be sure to visit Home Designing . With a wealth of resources, from creative design ideas to practical home styling tips, Home Designing is a go-to platform for anyone seeking to transform their living space into something unique and inviting. Explore their extensive collection of articles and discover how you can make your home, and your reading nook , a haven of comfort and style.
Like Architecture & Interior Design? Follow Us...
Just one more step. please click the confirmation link emailed to you..
Did you like this article?
Share it on any of the social media channels below to give us your vote.
Your feedback helps us improve.

From HD & Partners
The Dream Home Kit
Design your dream home with this ultimate bundle from Home Designing

Other related interior design ideas you might like...

Comments? Let us know
What we are about.
Our mission is to help people visualize, create & maintain beautiful homes. We bring to you inspiring visuals of cool homes, specific spaces, architectural marvels and new design trends.
Follow us for a daily dose of outstanding homes, intelligent architecture & beautiful design.
- Cool Kitchen Gadgets
- Comfortable Reading Chairs
- Small 3 Bedroom House Plans
- Large Wall Clocks
- Unique Table Lamps
- Unique Wall Clocks
- Unique Ceiling Fans
- Unique Pots & Planters
- Unique Knives
- Best Housewarming Gifts
- Gifts For Architects
- Modern Classic Chairs
- 30 Cool & Unique Chess Sets
- Unique Coffee Mugs
SITES WE LOVE
- Shelterness
- Disclosure & Disclaimer
- Submit work
- Top Design Firms
- Give us a tip!
- Privacy Policy

Get the best in architecture and design
Delivered directly to your inbox. Free.
Loading…
Here is what you get free by subscribing:
- An ebook with 100+ images of some of the best work we have ever featured.
- A daily dose of outstanding design pictures and tips in your inbox.
- Inspiration from the best in the industry. Watch, adapt, adopt!
Advertisement
Supported by
Why the Kamala Harris of Four Years Ago Could Haunt Her in 2024
She ran to the left as progressive ideas dominated the last competitive Democratic primary. Now, in a tough general election, Republicans are digging up her old stances.
- Share full article

By Reid J. Epstein
Reporting from Washington
When she ran for president the first time, Kamala Harris darted to the left as she fought for attention from the Democratic Party’s liberal wing.
After she dropped out , social and racial justice protests swept across the country in the summer of 2020, and Ms. Harris joined other Democrats in supporting progressive ideas during what appeared to be a national realignment on criminal justice.
One presidential cycle later, with Vice President Harris less than a week into another race for the White House, video clips of her old statements and interviews are being weaponized as Republicans aim to define her as a left-wing radical who is out of step with swing voters.
Former President Donald J. Trump is calling out her past positions and statements at his rallies, and on Monday his campaign began reserving time for television advertisements that are likely to resurface videos of Ms. Harris.
“The archive is deep,” said Brad Todd, a Republican strategist and ad maker who is working with David McCormick, the G.O.P. Senate candidate in Pennsylvania, among other campaigns. “We will run out of time before we run out of video clips of Kamala Harris saying wacky California liberal things. I’m just not sure that the rest of this campaign includes much besides that.”
The first television ads to attack Ms. Harris for her past statements came not from Mr. Trump’s campaign but from Mr. McCormick, who is challenging Senator Bob Casey.
The 60-second ad , which Mr. McCormick’s campaign began airing Monday, resurfaces a laundry list of statements Ms. Harris made in 2019 and 2020.
She said then that she opposed fracking; would “think about” abolishing the Immigration and Customs Enforcement agency; called the idea of adding more police officers “wrongheaded thinking”; entertained the idea of allowing felons to vote; said she supported a “ mandatory buyback program” for some guns; and called for the elimination of private health insurance.
Fracking is a particularly tough issue for Ms. Harris. Banning it was a plank in her energy platform in the 2020 primary race. But fracking remains a key element of the economy in Pennsylvania, perhaps the most important battleground state this year.
“She pledged to ban fracking — no fracking, oh, that’s going to do well in Pennsylvania, isn’t it?” Mr. Trump said at a rally on Saturday in Minnesota . “Remember, Pennsylvania, I said it. She wants no fracking. She’s on tape. The beautiful thing about modern technology is when you say something, you’re screwed if it’s bad.”
The Harris campaign announced on Friday that the vice president no longer wanted to ban fracking, a significant shift from where she stood four years ago but one that is consistent with the policies of President Biden’s administration.
The Harris campaign will rebut most of Republicans’ attacks by arguing that they are exaggerating or lying about her record, said a campaign official briefed on the plans who was not authorized to discuss them publicly. Her campaign plans to lean into her record as a local prosecutor and state attorney general to burnish her image as a candidate with deep ties to law enforcement.
In addition to changing her position on fracking, campaign officials said she now backed the Biden administration’s budget requests for increased funding for border enforcement; no longer supported a single-payer health insurance program; and echoed Mr. Biden’s call for banning assault weapons but not a requirement to sell them to the federal government.
“Kamala Harris spent 20 years as a tough-as-nails prosecutor who sent violent criminals to prison,” said Brian Fallon, a Harris campaign spokesman. “Her years spent in law enforcement and her record in the Biden-Harris administration defy Trump’s attempts to define her through lies.”
On Monday, as Mr. Biden prepared a speech in Texas calling for term limits and ethics guidelines for Supreme Court justices , the Trump campaign resurfaced statements Ms. Harris made in 2019 saying she was “open to this conversation” about expanding the Supreme Court. Ms. Harris, in a statement released by her campaign, endorsed Mr. Biden’s proposal, which does not call for adding additional justices to the court.
Officials with Ms. Harris’s campaign also said they hoped to utilize the liberal cultural fervor around her candidacy to make the election a referendum on the future versus a past Democrats argue Mr. Trump represents.
Mr. Trump and his running mate, Senator JD Vance of Ohio, have themselves been on multiple sides of many issues, not least of which is Mr. Vance’s past stance as a prominent critic of Mr. Trump .
There is ample video of Mr. Trump making remarks unhelpful to his 2024 campaign. In 2016, he said women who sought abortions should face punishment , and as president he tried to bar immigrants from several predominantly Muslim countries and enacted a policy of separating immigrant children from their families at the southern border. He also was caught on tape bragging about groping women.
Matt Bennett, a co-founder of Third Way, a moderate Democratic think tank, said he was not worried that Ms. Harris had once espoused left-wing ideas. She has evolved, he said, into a Biden-style Democrat with more centrist views.
“There’s a tremendous difference in changing one’s policy ideas and changing one’s principles,” Mr. Bennett said. “She has not changed her principles. She still thinks climate change is an existential threat — she just doesn’t think the Green New Deal is the way to address it.”
Since she joined Mr. Biden’s ticket in 2020, Ms. Harris has seldom put forward policies that differ much from his. She is no longer pushing for a single-payer health care system, and on Friday her campaign said she would maintain Mr. Biden’s pledge not to raise income taxes on people making less than $400,000 per year.
But one issue on which Ms. Harris has already put some daylight between herself and Mr. Biden is abortion rights. Since the Supreme Court’s 2022 decision overturning Roe v. Wade, the president has said he would sign legislation restoring a federal right to abortion if such a bill came to his desk.
In her early speeches as a presidential candidate, Ms. Harris has offered to go a bit further.
“When Congress passes a law to restore reproductive freedoms, as president of the United States, I will sign it into law,” she told an audience in Wisconsin last week , using a broader term that suggested such legislation could extend beyond abortion rights to things like protecting in vitro fertilization or contraception.
During her 2020 presidential campaign, Ms. Harris had an even bolder plan on abortion rights. Her proposal would have required states and local jurisdictions that tried to restrict abortion rights to obtain federal approval before a new law could take effect — similar to the way that the Voting Rights Act of 1965 limited changes to voting laws in some states with a history of racial discrimination.
“On this issue, I’m kind of done,” she said of abortion rights during a 2019 interview on MSNBC . “When elected, I’m going to put in place and require that states that have a history of passing legislation that is designed to prevent or limit a woman’s access to reproductive health care, that those laws have to come before my Department of Justice for a review and approval. And until we determine that they are constitutional, they will not take effect.”
By 2023, Ms. Harris’s position on abortion rights had evolved to echoing Mr. Biden’s call to enact legislation codifying a federal right to abortion.
“We need to restore the protections of Roe v. Wade,” Ms. Harris said during a 2023 interview on CBS . “We’re not trying to do anything that did not exist before June of last year.”
That remains her position, said Lauren Hitt, a campaign spokeswoman.
Ms. Harris’s first presidential campaign was undone in part by staff turmoil that resulted in public finger-pointing and scathing resignation letters even before she dropped out of the race. Former aides interviewed for this article, who spoke on the condition of anonymity to protect their current employers, said Ms. Harris’s campaign had been undermined by a combination of unsteady leadership from its senior staff members and too much influence on the candidate from her family members.
But during that race, Ms. Harris also often appeared as if she were not sure what she believed. In a CNN town-hall event the day after what was widely viewed as a successful campaign rollout in Oakland, Calif., she appeared tentative while discussing health care policy, eventually saying she would eliminate private health insurance and institute a single-payer health care program.
She would go on to propose an array of policies popular with progressives. She sought to increase pay for public-school teachers by an average of $13,500 through a bump in the estate tax.
She also called for an assault weapons ban and said she would sign an executive order mandating background checks for customers of any dealer who sold more than five guns in a year. And she sought to close the gender pay gap by requiring large companies to certify that men and women were paid equally.
But for all her liberal policy proposals in the 2020 campaign, Ms. Harris was frequently viewed through her biography. She leaned into her record as a former prosecutor and California attorney general, but many voters were well aware of her status as a Black and South Asian woman who had marched with her immigrant mother in civil rights demonstrations in California.
“I don’t know that the policy stuff is what people were talking about — it was all biography,” said Sue Dvorsky, a former Iowa Democratic Party chairwoman who backed Ms. Harris in the 2020 campaign. “She’s always been complex policy-wise, but I think people look at her and expect a thing. She’s going to talk about law and order and being a prosecutor.”
Michael Gold contributed reporting from St. Cloud, Minn., and Shane Goldmacher from New York.
Reid J. Epstein covers campaigns and elections from Washington. Before joining The Times in 2019, he worked at The Wall Street Journal, Politico, Newsday and The Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. More about Reid J. Epstein

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mentions of the term "homework" date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger, an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches.
The idea of homework, in its most rudimentary form, can be traced back to the earliest human civilizations. In ancient Egypt, for instance, students were tasked with hieroglyphic writing exercises. These exercises served as a precursor to modern homework, as they required students to practice and reinforce their understanding of written ...
Before the idea of homework came to the United States, Germany's newly formed nation-state had been giving students homework for years. The roots of homework extend to ancient times, but it wasn't until German Philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762—1814) helped to develop the Volksschulen (People's Schools) that homework became mandatory.
A person doing geometry homework Children doing homework on the street, Tel Aviv, 1954. Homework is a set of tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed at home.Common homework assignments may include required reading, a writing or typing project, mathematical exercises to be completed, information to be reviewed before a test, or other skills to be practiced.
Check out 20 reasons why homework is good:-. 1. Reinforcement of Classroom Learning. Homework isn't just a mundane task; it's your secret weapon for becoming a true subject matter aficionado. It's the place where classroom theories transform into real-world skills.
The 1900s: Anti-homework sentiment and homework bans. A homework prohibition was enacted in the Pacific state of California in 1901, barely a few decades after the idea of homework crossed the Atlantic. The restriction, which applied to all students under the age of 15, lasted until 1917.
One teacher proposed "homework" consisting of after-school "field trips to the woods, factories, museums, libraries, art galleries.". In 1937, Carleton Washburne, an influential educator who was the superintendent of the Winnetka, Illinois, schools, proposed a homework regimen of "cooking and sewing…meal planning…budgeting, home ...
This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann, who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ] In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies' Home Journal , decried homework's negative impact on children's physical and mental health, leading ...
NYU and Duke professors refute the idea that homework is unrelated to student success. In response to the National School Board Association's Center for Public Education's findings that homework was not conclusively related to student success, historian and NYU professor Diane Ravitch contends that the study's true discovery was that ...
Jessica Meacham, a 17-year elementary school veteran who has taught every grade level between K-6, found a fun way to keep her students engaged at home—homework bags. "The homework bags are literacy and math-based," Meacham says. "Each bag contains all the necessary components to complete the activity. The bags typically take between 5 ...
This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann, who encountered the idea in Prussia. In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies' Home Journal, decried homework's negative impact on children's physical and mental health, leading ...
Busy work. Homework generally falls into two categories: practising or catching up on work done in the classroom, and creative extensions of work being done in the classroom. The latter - like ...
1. Less is More. A 2017 study analyzed the homework assignments of more than 20,000 middle and high school students and found that teachers are often a bad judge of how long homework will take. According to researchers, students spend as much as 85 minutes or as little as 30 minutes on homework that teachers imagined would take students one ...
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn. "Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of ...
"Teachers feel pressured to give homework because parents expect it to come home," says Galloway. "When it doesn't, there's this idea that the school might not be doing its job." Galloway argues teachers and school administrators need to set clear goals when it comes to homework — and parents and students should be in on the discussion, too.
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools—public and private, elementary and secondary. And it really doesn't make sense, in part because of what the research shows: • There is no evidence to demonstrate that homework benefits students below high school age.
Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the ...
Main Idea Worksheet 1. Here is a double-sided main idea worksheet. Students read seven original nonfiction passages and summarize the main idea of each passage. Also, students must think of a title for each passage that relates to the main idea of the text. Suggested reading level for this text: Grade 6-10.
One such myth, Lewis says, is the argument that homework is good at preparing pupils for secondary school. "It's a very weak argument. Even logically it makes no sense.". He dismisses the ...
The apex predator of the dining room is the "great room"—a combined living room and kitchen, bridged by an open dining space. "It's not that Americans don't want dining rooms.
A plush pile of rug underfoot gives a warm feeling and provides ...
Kamala Harris announcing her 2020 presidential campaign in Oakland, Calif., in January 2019. She often embraced liberal ideas during the Democratic primary race, but her candidacy failed to catch ...