Business Dissertation Topics
2020 was a year of drastic change, with many businesses shut down by the pandemic. However 2021-22 onwards promises rapid economic growth, as business activity sharply expands. So, to help you out we’ve provided a selection of free and original business dissertation topics, suitable for both Master’s and Bachelor’s degree dissertations. These topics cover a large range of subjects within the business discipline, so you are sure to find one suited to your own interests. Each of these topics will allow you to produce an original and ambitious dissertation that will contribute to the existing knowledge of your subject area. So, if you’ve been searching far and wide for a great business dissertation topic, look no further!

Global Politics and Global Business Dissertation Topics
Global strategy for business dissertation topics, technology and innovation management business dissertation topics, corporate social responsibility business dissertation topics, international human resource management dissertation topics, management of international change dissertation topics, leadership and innovation business dissertation topics, globalisation and strategy business dissertation topics.
This is one of the most important aspects of international business as it examines the connection between global politics and global business. It looks at some of the most important factors, institutions, and processes that affect international business and studies the political environment of business, which has been particularly volatile over the last five years.
- Evaluating the performance of global business teams within multinational corporations: the test of an intervening process model.
- How does Corporate Governance affect internationalisation, globalisation and the performance of firms?
- What sorts of themes and images might create trans-cultural resonance and dissonance within an international classroom comprised of diverse nationalities and cultural backgrounds?
- Can production for global markets help business groups to mobilise collectively? Under what conditions does globalisation enable the private sector to develop independent organisational bases and create effective relationships with the state?
- How different patterns of business-government relations affect processes of industrial upgrading: A case study of emerging economies.
- How do multinational organisations tackle the growing complexity of managing themselves in light of the rise to significant power of non-governmental organisations?
- A look at the effect that Brexit is likely to have on British businesses, especially the average small and medium enterprise (SME).
- How will Brexit impact on the regulatory burden of large business and corporations in the United Kingdom and Europe?
- Business-Government relations within a contingency theory framework: strategy, structure, fit, and performance.
- What is the meaning and process of globalisation and how does it impact the way in which business teams work together?
- In the aftermath of the Covid-19 crisis, is globalisation still going to be a key market driver?
- Global strategy and local implementation: Examining how multinational corporations apply Corporate Governance in China.
- How will firms investing in China manage the political undercurrents, as talk increases of a new Cold War between the West and China?
- What factors affect multinational corporations’ choice of corporate political strategy? Examining the influence of perceived regulatory pressure on company’s political strategies.
- Using a legitimacy perspective to examine how firms entering the Chinese market manage political risk.
- A critical examination of the potential implications of Brexit for UK firms’ EU-based supply chain.
- Brexit and foreign direct investment into the UK: An examination of the potential impact on new venture start-ups in the UK.
Global business strategy focuses on understanding the main strategic issues that organisations face when they operate as a global business. Specifically, the issues relate to three areas: understanding global strategic analysis, formulating a global strategy, and developing sources of competitive advantage in a given company.
- What are the risks and benefits of an International Joint Venture?
- How should a business strategy be developed to expand a business in an international market?
- A comparative study of Mergers and Acquisitions within the Aviation sector: Case study of Qatar Airways’ joint venture with the International Airlines Group.
- A research on the exit strategy of foreign venture capital investment in international private business sector.
- What are the business strategies and key success factors of Financial Holding Companies in the international environment?
- How does an organisation benefit from an effective vendor management strategy?
- Why are some vendor relationships more successful than others?
- Developing an effective framework for knowledge sharing and utilisation in global project teams.
- Can entrepreneurship be utilised as an effective management strategy within a business unit?
- What effects will the consumers’ increasing use of the online channel to fashion shopping have on the strategies used by UK clothing retailers?
- An assessment of sustainable competitive advantage within the UK DIY multiple market sector.
- Develop your own definition of logistics, that you think reflects how logistics is evolving and explain why you think it is appropriate for today and the next decade.
- A study of the problems of managing international collaboration in the military aero-engine business.
- New possibilities in logistics and supply chain management provided by Big Data: examining the birth and growth of supply chain analytics.
- Designing a closed-loop supply chain for improving sustainability of global business practices.
- Developing a strategy for winning in the Indian market: A case study of Suzuki Motor Corporation.
These topics consider the ways in which business firms develop and implement technology as a strategy and integrate technological and innovative capabilities in support of their business operations. These topics mainly investigate how technology has revolutionised the business environment causing disruption, new opportunities and challenges for firms to deal with.
- A study of how business operations have improved as a result of innovation: Are they converging towards one universal approach?
- What are the market challenges experienced by new UK mobile telecommunication companies?
- How will 5G technology impact on the growth of digital consumer markets in the UK?
- How does online branding provide competitive advantage in the digital era: a study of the consumer electronics industry?
- A study into how ICT integration has transformed procurement of goods and services.
- Building virtual dominions – A comparative study of mergers, acquisitions and strategic alliances in e-commerce: case studies of Amazon.com and eBay.
- What are the technological factors surrounding the relationship between organisational growth and performance?
- A study into the role of online marketing in creating global supply chain networks.
- A study into how organisations suffer the negative effects of modern day technology.
- What are the main factors impacting on the success of online branding for corporations?
- Assessing the role of social media in global branding: cases of Facebook, Instagram and Twitter.
- Exploring the impact of technology on CRM operations within call centres in the UK and analyse the factors that affect the well-being of the employee?
- A study into the opportunities of implementing an e-HR system: Case of British Energy.
- A study into how companies influence technology and innovation within suppliers: Case of Apple.
- Assessing technology diffusion models among online shoppers in the UK.
- Business process reengineering and the challenges facing airlines, a critical study of the factors influencing Saudi Airlines’ BPR initiatives.
- What are the barriers to successful/profitable e-commerce deployment in government organisations?
- Comparing and contrasting government e-commerce portals with private ones such as eBay and Amazon: which offers the better user experience and business outcomes?
- How has integration of technology into HR improved organisational efficiency?
- What is the impact of technology on FMCG industry towards meeting consumer demands in the UK market?
- Assessing the role of innovation towards creation of new opportunities for SMEs in the UK.
- What determinant factors influence integration of technology in the Supply Chain Management (SCM) sector.
Governments, activists and the media have become adept at holding companies to account for the social consequences of their actions. In response, corporate social responsibility has emerged as an inescapable priority for business leaders in every country. The fact is many prevailing approaches to CSR are quite disconnected from strategy. Business should treat CSR as something central to their strategy and hence contribute as a core competence for many organisations. These topics evaluate how business can utilise CSR practices to enhance opportunities for organisational success.
- How does Corporate Social Responsibility impact on customer loyalty?
- What is the role of staff training in developing and executing CSR skills?
- What are the key strategic decisions facing companies in order to improve their performance in Corporate Social Responsibility?
- Does Corporate Social Responsibility enhance corporate reputation? A case study of Tesco.
- What are the challenges facing ethical businesses in the UK for moving to the mainstream?
- How can businesses gain advantage from adopting CSR practices with respect to climate change?
- A study into the impact of green and lean practices on organisational performance.
- How have environmental policies transformed CSR practices within organisations: Case of BAT.
- What are the effects of CSR on sustainability: Case of Coca Cola.
- How will multinational organisations deal with the growing emphasis on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in large markets like Germany and India?
- To what extent will CSR be sacrificed for greater economic growth in the aftermath of the Coronavirus pandemic?
- How can firms successfully make Corporate Social Responsibility operable in the modern corporate environment?
- Is there a relationship between diversity and Corporate Social Responsibility, what is its contribution to organisational performance?
- What is the impact of CSR on brand equity: Case study of Toyota UK?
- How does CSR impact on organisational performance?
- CSR and societal expectations: A case study of Unilever.
International Human Resource Management refers to activities that are designed to support organisations in managing human resources at an international level so that competitive advantage can be maintained at both the national and international level. The subject area includes understanding of culture factors, both in terms of beliefs and attitudes of international employees and in relation to international employment legislation. Studying the area provides insights into the way that corporate HR functions can contribute to international business strategy and build functional knowledge of the main developments in the management of expatriates and other forms of international management. Changing perspectives are crucial as more and more organisations operate on a global basis and have head offices in a home country and operational sites in host nations. Functionally this can involve expatriates but increasingly includes high usage of virtual technology to create links between home and host country operational sites. The following topics are an indication of key areas of current interest in the field.
- What are the benefits and challenges of inter-cultural team working in virtual environments and how these teams influence competitive advantage.
- Virtual working environments became something of a norm during the pandemic. Will this apply to home countries of international corporations as well?
- What are the bases of employee commitment in terms of affective, normative and calculative commitment in a global multi-national?
- What are the effects of organisational transition on employee commitment in large multinational companies?
- How do mergers impact on employee motivation and commitment, and how can any fallout be managed?
- How can cultural differences in international collaborative projects be managed?
- Can job-swaps between international workers improve inter-cultural working in multi-national organisations?
- What is the relationship between the three components of commitment to organisational change and the perceived success of an organisational change?
- What effect will the UK’s decision to leave the EU have on economic migrants, and how can this be managed by IHRM practices and polices?
- How will Brexit impact on British workers in the EU, and to what extent can this be managed by IHRM practices and policies?
- How does one manage employee commitment in the not-for-profit sector across different national cultures?
- Using models of Strategic Human Resource Management assess and appraise how BAE Systems is achieving strategy through effective people management practices.
- What are the main factors that affect employee retention at international call centres?
- What are the most effective practices for working a unique Human Resource policy across multiple divisions of large diversified companies?
- A study of the constantly changing global business environment and how effective human resource planning enables organisations to achieve their strategic objectives.
- What effect does the Brexit decision and subsequent negotiations have on the management of EU operational sites by UK based companies?
- What is the role and value of effective IHRM strategic thinking to effective negotiation of joint ventures between the UK and BRIC countries?
- Can IHRM be effective in delivering culturally appropriate work-life balance and flexible working patterns for multi-national firms?
Change, at the organisational level is vital for continued innovation and retention of competitive advantage. Therefore, understanding the different aspects of this topic is vital in creating awareness of existing views and practices for implementing and managing successful change, particularly at the international level. This topic area is therefore focused on the what, why and how involving managing change in contemporary organisations and social systems in general, and how they may impact on the effectiveness of change. In particular, it examines the issues and dilemmas facing those managing change, as well as the skills required for successful adaptation and evolution, especially in an international context.
- What internal and external factors have the greatest impact on employees in cross-national mergers and acquisitions?
- Managing change across multi-cultural teams through technology and virtual project management: The impact of social understanding and use of digital media.
- What are the biggest changes in home working practises going to be following Coronavirus, and what impact will they have on employee retention?
- Managing change: Developing a framework that links intended strategies and unanticipated outcomes.
- Employee adjustment during organisational change: The role of organisational level and occupation.
- How can employee motivation levels be sustained during organizational restructuring?
- Success of a Product Lifecycle Management Implementation – an investigation into the electronics manufacturing industry.
- How power works through managing emotion in organisational change: emotion management as power.
- How can the measurement of levels of work stress in individuals employed in an organisation undergoing change benefit it?
- Encouraging gender equality across international firms – what role can change management approaches take in supporting increased female representation in traditionally masculine firms?
- Managing change in Asian business – A comparison between Chinese-educated and English-educated Chinese entrepreneurs in Singapore.
- What is the impact of feedback during organisational culture change: a case study of a financial firm?
- Stakeholder Communication and Transformational Change: A case study in the use of a proprietary change management system.
- What effect is there on levels of resistance and conflict when organisational change is lead by a servant or spiritual leader?
- How social media can facilitate acceptance of change in international organisations.
- Soft skills are not enough: Why change management approaches also need strong project management planning to be successful.
- What are the key project management skills needed to execute a major change in the working culture of an organization?
Innovation has become a primary force driving the growth, performance, and valuation of companies. However, sometimes there is a wide gap between the aspirations of executives to innovate and their ability to execute. Many companies make the mistake of trying to spur innovation by turning to unreliable best practices, and to organisational structures and processes. Moreover, executives who focus on stimulating and supporting innovation by their employees can promote and sustain it with the current talent and resources more effectively than they could by using other incentives. This area focuses on innovation at the individual level and at the group level within organisations.
- What are the effects of team innovation and leadership clarity in organisations? A health care case study.
- Does socio-cultural context moderate the relationship of leadership with top-management influence on innovation?
- What are the effects of leadership style and team process on performance and innovation in functionally heterogeneous teams?
- An exploratory study of leadership, organisational culture and organisational innovativeness in a sample of non-profit organisations.
- Is there a difference in leadership style between profit and non-organisations, and what are the reasons for this?
- How do business leaders see their role in enabling innovation in large organisations?
- Transformation or transactional? The role of leadership in supporting individual-level creativity within organisations.
- How exactly do we put leadership and innovation together? How does a company lead in a way that generates innovation?
- What are the key factors required for a creative organisation? How are barriers to implementing these factors overcome?
- Organising for team creativity: Creating an organisational system for harvesting ideas for leadership and innovation.
- What is the nature and role of leadership in three ideal types of public management innovation: politically-led, organisational turnarounds and bottom-up innovations?
- How is leadership different in the engineering function? An assessment of Airbus UK?
- What are the behavioural and personality correlations of transactional and transformational leadership?
- What is the relationship between leadership style and creativity? Systematically reviewing the literature.
- From managing to enabling innovation: Leaders’ facilitating innovation through cultural change.
- The role of leaders in balancing creativity and standardisation in the firm.
Globalisation is a complex trend, encompassing many forces and many effects. Globalisation has revolutionised the global market as Multinational Enterprises renew their strategies to attain competitive edge. These topics evaluate different strategies adopted by business firms to uniquely position themselves in the global market.
- The analysis of suitability and applicability of Porter’s Generic Strategies in the light of emerging business trends and an unpredictable operating environment post-pandemic.
- Does globalisation have a future in the aftermath of the Coronavirus pandemic?
- What is the significance of ICT integration as a business strategy?
- How globalisation has broken trade barriers and its impact on trade tariffs: the case of BRIC countries.
- What current strategies are in place for businesses to meet dynamic consumer demands?
- To what extent is consumer demand shaped by corporate innovation? A comparative study of Apple and Samsung.
- Assessing the impact of globalisation on UK businesses operating on both international and local levels.
- Does Brexit signal a rollback in globalisation in the UK and Europe?
- An examination of empowerment, conflict and corporate vision as factors in developing global business strategies for multinational firms.
- What are the transformational strategies adopted by companies in the globalisation era?
- How have countries changed their trade policies in the face of new global market challenges?
- A study into the FDI strategies used by UK multinational companies: case study of Vodafone.
- Investigating the role of strategic alliances in creating global supply chain networks.
- Assessing the impact of internationalisation strategies on multinational corporations: case study Tullow Oil.
Copyright © Ivory Research Co Ltd. All rights reserved. All forms of copying, distribution or reproduction are strictly prohibited and will be prosecuted to the full extent of the law.

Home > Colleges and Schools > Business > Business Administration ETDs
Theses and Dissertations in Business Administration
Theses and dissertations published by graduate students in the Business Administration program, College of Business, Old Dominion University, since Fall 2016 are available in this collection. Backfiles of all dissertations (and some theses) have also been added.
In late Fall 2025, all theses will be digitized and available here. In the meantime, consult the Library Catalog to find older items in print.
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
Dissertation: Two Essays on Industry Tournament Incentives , Sarah Almisher
Dissertation: Two Essays on Investor Sentiment , Amin Amoulashkarian
Dissertation: Two Essays on Retail Trading , Qiqi Liang
Dissertation: Two Essays in Real Estate Dynamics , Navid Safari
Dissertation: Firm Capabilities, Great Power Competition, and the Structural Reshaping of Globalization , Samuel Wilson
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Dissertation: Three Essays on Stock Price Informativeness, Stock Price Momentum, and Firm Investment Efficiency , Chen Chen
Dissertation: Exploring Blockchain-Based Digital Transformation In Organizations , Weiru Chen
Dissertation: Two Essays on Antecedents and Effects of Award-Winning CEOS , Veronika Ciarleglio
Dissertation: Two’s a Crowd? Implications of Economic Geography for Corporate Governance , Matthew Farrell
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Effects of CEO Social Activism , Habib Islam
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Role of Empathy in Consumer Response to User-Generated Content , Mohammadali Koorank Beheshti
Dissertation: Three Essays on the Effects of Other Customer Brand Tie and Employee Behavior on Consumer Behavior , Saeed Zal
Dissertation: Three Essays on CEO Traits, Corporate Investment Decisions, and Firm Value , Rongyao Zhang
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
Dissertation: Two Essays on Antecedents and Effects of Board Female Representation Non-Conformity , Fatemeh Askarzadeh
Dissertation: Application of Optimization Techniques in Corporate Cash Management , Venkateswara Reddy Dondeti
Dissertation: Two Essays on Corruption, FDI, and Digitalization , Mahdi Forghani Bajestani
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Information Embedded in Flow of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) , Hamed Yousefi
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
Dissertation: The Influence of Mating Motives on Reliance on Form Versus Function in Product Choice , Seyed Hamid Abbassi Hosseini
Dissertation: Three Essays on CEO Characteristics and Corporate Bankruptcy , Rajib Chowdhury
Dissertation: The Effects of CEO Dismissal Risk and Skills on Risky Corporate Decisions and CEO Compensation , Son T. Dang
Dissertation: Essay 1: How We Feel: The Role of Macro-Economic Sentiment in Advertising Spending-Sales Relationship; Essay 2: It Was the Best of Times; It Was the Worst of Times: The Effect of Emotional Uncertainty and Arousal on Healthy Food Choices , Leila Khoshghadam
Dissertation: The Accumulation of IT Capability And Its Long-Term Effect on Financial Performance , Jin Ho Kim
Dissertation: Three Essays on the Roles of Review Valence and Conflict in Online Relationships , Ran Liu
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Microstructure of the Housing Market: Agents' Diffused Effort and Sellers' Behavior Bias , Zhaohui Li
Dissertation: Two Essays on CEO Overconfidence in Relation to Speed of Adjustment of Firm Financial Policy and CEO Inside Debt , Xiang Long
Dissertation: Pricing the Cloud: An Auction Approach , Yang Lu
Dissertation: Two Essays on Consumer Envy , Murong Miao
Dissertation: Two Essays on Negotiations Between Entrepreneurs and Angel Investors , Aydin Selim Oksoy
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Dissertation: Two Essays on Bitcoin Price and Volume , Mohammad Bayani Khaknejad
Dissertation: Two Essays on Investor Attention, Investor Sentiment, and Earnings Pricing , Qiuye Cai
Dissertation: Success Factors Impacting Artificial Intelligence Adoption --- Perspective From the Telecom Industry in China , Hong Chen
Dissertation: Early Information Access to Alleviate Emergency Department Congestion , Anjee Gorkhali
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Consumer Acculturation Process – A Need for and Development of a Consumer Acculturation Measure , Kristina Marie Harrison
Dissertation: Three Essays on CEO Characteristics and Corporate Decisions , Trung Nguyen
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Effects of Organization Capital on Firm Behavior , Andrew Root
Dissertation: Underlying Factors Behind Generation of Different Types of User-Generated Content - Impact of Individual and Brand/Product Level Factors in Generation of Brand-Oriented Content and Community-Oriented Content , Kemal Cem Soylemez
Dissertation: Customers’ Goal-Related Behavior in Loyalty Programs , Junzhou Zhang
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
Dissertation: Security Risk Tolerance in Mobile Payment: A Trade-off Framework , Yong Chen
Dissertation: Numerical Framing and Emotional Arousal as Moderators of Review Valence and Consumer Choices , Anh Dang
Dissertation: Three Essays on CEO Risk Preferences, and Ability, Corporate Hedging Decisions, and Investor Sentiment , Sonik Mandal
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Creation and Success of New Ventures , Amirmahmood Amini Sedeh
Dissertation: Effectiveness of Social Media Analytics on Detecting Service Quality Metrics in the U.S. Airline Industry , Xin Tian
Dissertation: Two Essays on Value Co-Creation , Hangjun Xu
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Dissertation: Two Essays on Forced CEO Turnover During Envy Merger Waves, and Dividends , Bader Almuhtadi
Dissertation: The Role of Consumer Ethnocentrism on the Effects of Domestic vs Foreign Product Failure on Post Consumption Emotions and Complaint Behaviors , Kittinand Bandhumasuta
Dissertation: The Impact of Help-Self and Help-Others Appeals Upon Participation in Clinical Research Trials , Susan Lewis Casey
Dissertation: Is Every Tweet Created Equal? A Framework to Identify Relevant Tweets for Business Research , Thad Chee
Dissertation: Three Essays on Mutual Funds, Fund Management Skills, and Investor Sentiment , Feng Dong
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Impact of Institutional Structures on Entrepreneurship: Country Level Analysis , Mehdi Sharifi Khobdeh
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Antecedents and Effects of Internationalizing Out of Emerging and Developed Economies , Mark Robert Mallon
Dissertation: From Placebo to Panacea: Exploring the Influence of Price, Suspicion, and Persuasion Knowledge on Consumers’ Perception of Quality , Vahid Rahmani
Dissertation: Essays on the El Niño Anomaly and Stock Return Predictability , Zhijun Yang
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
Dissertation: The Effect of XBRL and Social Media on Information Asymmetry: Evidence from Bank Loan Contracts , Dazhi Chong
Dissertation: Two Essays on CEO Inside Debt Holding in Relation to Firm Payout Policy and Financial Reporting , Asligul Erkan
Dissertation: Two Essays on The Internationalization Speed of New Ventures , Orhun Guldiken
Dissertation: Two Essays on Shareholder Base, Firm Behavior, and Firm Value , Yi Jian
Dissertation: Valence or Volume? Maximizing Online Review Influence Across Consumers, Products, and Marketing , Elika Kordrostami
Dissertation: Essays on the Equity Risk Premium , Mohamed Mehdi Rahoui
Dissertation: A Study of the Impact of Information Blackouts on the Bullwhip Effect of a Supply Chain Using Discrete-Event Simulations , Elizabeth Rasnick
Dissertation: Two Essays on Investor Emotions and Their Effects in Financial Markets , Jiancheng Shen
Dissertation: Two Studies on The Use of Information Technology in Collaborative Planning, Forecasting & Replenishment (CPFR) , David McCaw Simmonds
Dissertation: Founder CEOs and Initial Public Offerings: The Role of Narratives, Institutions and Cultural Context , Christina Helen Tupper
Dissertation: Ambidexterity: The Interplay of Supply Chain Management Competencies and Enterprise Resource Planning Systems on Organizational Performance , Serdar Turedi
Dissertation: Two Essays on Short Selling , Zhaobo Zhu
Dissertation: Buying Love Through Social Media: How Different Types Of Incentives Impact Consumers’ Online Sharing Behavior , Yueming Zou
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
Dissertation: Three Essays on Dividend Policy , Mehmet Deren Caliskan
Dissertation: "The Magic Formula: Scent and Brand"- The Influence of Olfactory Sensory Co-Branding on Consumer Evaluations and Experiences , Ceren Ekebas
Dissertation: The Value of Integrated Information Systems for U.S. General Hospitals , Liuliu Fu
Dissertation: Two Essays on Managerial Horizon, Cash Holdings and Earnings Management , Sanjib Guha
Dissertation: Three Essays on Opportunistic Claiming Behavior in a Services Setting: Customers and Front Line Employees Perspectives , Denis Khantimirov
Dissertation: Spillover Effects of Brand Alliance and Service Experience on Host Brands in Loyalty Program Partnerships , Gulfem Cigdem Kutlu
Dissertation: Measuring Consumer Expectations of Salesperson Unethicality: A Scale Development , Amiee Mellon
Dissertation: Essays on International Risk-Return Trade-Off Relations , Liang Meng
Dissertation: Two Essays on Investor Attention and Asset Pricing , Nadia Asmaa Nafar
Dissertation: International Venture Capital Firms Syndication and Performance: A Social Network Perspective , Amir Pezeshkan
Dissertation: Three Essays on Institutions, Entrepreneurship, and Development , Adam Smith
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
Dissertation: An Empirical Examination of the Antecedents and Consequences of Earnings Management in Emerging Markets , Shuji Rosey Bao
Dissertation: Dynamic Capabilities and Resilient Organizations Amid Environmental Jolts , Stav Fainshmidt
Dissertation: An Empirical Examination of the Moderators of Direct Versus Indirect Comparative Advertising , Chun-Kai Hsu
Dissertation: Two Essays on Attracting Foreign Direct Investment: From Both a National and Firm Level Perspective , Ryan Lawrence Mason
Dissertation: The Effect of Online Reviews on Attitude and Purchase Intention: How Consumers Respond to Mixed Reviews , Chatdanai Pongpatipat
Dissertation: Three Essays on the Enterprise Strategy for Multinational Firms , Veselina Plamenova Vracheva
Dissertation: The Antecedents and Effects of Strategic Caring: A Cross-National Empirical Study , Thomas Weber
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 2013
Dissertation: International Banking sector Linkages: Did the Global Financial Crisis Strengthen or Weaken the Linkages? , James Edward Benton
Dissertation: Three Essays on Corporate Liquidity, Financial Crisis, and Real Estate , Kimberly Fowler Luchtenberg
Dissertation: Three Essays on Immigrant Entrepreneurship , Kaveh Moghaddam
Dissertation: The Response of Commercial Banks to Credit Stimuli , Denise Williams Streeter
Theses/Dissertations from 2012 2012
Dissertation: An Examination of Middle Manager Innovation Behaviors and Institutional Factors Impact on Organizational Innovation in the USA and Mexico , J. Lee Brown III
Dissertation: Essays on Foreign Reverse Mergers and Bond ETF Mispricing , Charles William Duval
Dissertation: Three Essays on Strategic Risk Taking , Krista Burrill Lewellyn
Dissertation: Two Essays on Executive Pay and Firm Performance , Thuong Quang Nguyen
Dissertation: A Study of Risk-Taking Behavior in Investment Banking , Elzotbek Rustambekov
Dissertation: A Study of Failures in the US Banking Industry , Joseph Trendowski
Dissertation: Two Essays on Behavioral Finance , Quang Viet Vu
Theses/Dissertations from 2011 2011
Dissertation: Three Essays on Individual Currency Traders , Boris Sebastian Abbey
Dissertation: Cross-listing Premium or Market Timing , Moustafa M. Abu El Fadl
Dissertation: Warranty and Price as Quality Signals: The effect of Signal Consistency and Unexpectedness on Product Perception , Sultan Alaswad Alenazi
Dissertation: The Behavior and Choices of Serial Bidders in M&A Transactions: A Prospect Theory Approach , Ahmed Essam El-Din El-Bakry
Dissertation: Two Essays on the Effect of Macroeconomic News on the Stock Market , Ajay Kongera
Dissertation: Intercultural Accommodation of Ethnic Minority Consumers: An Empirical Examination of the Moderating Effects in Service Encounters , Sarah Mady
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
- Author Guidelines
- Strome College of Business
- Other Digital Collections
- ODU Libraries
- Old Dominion University
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Business Management Dissertation Topics
Published by Owen Ingram at January 4th, 2023 , Revised On July 18, 2024
A degree in business administration is intended for those wishing to start their own business or expand an existing one. When you choose business management as your field of study, you are not a typical student because you want to learn about all possible aspects of managing a business.
However, if you are struggling to develop a trending and meaningful business management dissertation topic and need a helping hand, there’s no need to worry! Our unique business management dissertation topic ideas have been developed specifically to ensure you have the best idea to investigate as part of your project.
You may want to read about our business writers to see how we can help ease your workload. Check our free example dissertations and free business and business management dissertation examples to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation.
- International Development Dissertation Topics
- Cooperate Governance Dissertation Topics
- Business Intelligence Dissertation Topics
- Business Information Technology Dissertation Topics
- International Business Dissertation Topics
- Business Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Business Law Dissertation Topics
- Project Management Dissertation Topics
- Business Dissertation Topics
- HRM Dissertation Topics
- Management Dissertation Topics
- Operations Management Dissertation Topics
Unique Business Management Dissertation Topics
- Coordinating communications and teamwork among remote workers
- How business attract their customers
- Artificial intelligence investment and its effect on customer satisfaction
- Impact of globalisation on corporate management
- Customer viewpoint on how they use their data when using mobile banking
- Investigating the procedure for business model innovation
- Evaluation of dynamic capability modelling
- An investigation of managerial strategies in the hospitality sector
- Important project management abilities required to implement a significant change in an organisation’s workplace culture
- Voice and silence’s effects on destructive leadership
- Influence of store atmosphere on customers’ spontaneous buying habits
- Evaluating the effect of forwarding integration on operational efficiency
- The contribution of employee training and development to surviving the economic crisis
- Comparative comparison of the biggest consumer trends in the United States and the United Kingdom in the automotive industry
- A case study demonstrating how cutting-edge businesses like Microsoft and Google acquire a competitive edge through efficient technology management in developing nations
- To demonstrate the necessity of economic and social variables for developing a viable chemical engineering industry in the UK.
- Assessing the full impact of technological advances on business management techniques in America.
- A case study showed how top companies such as Microsoft and Google gain a competitive advantage through effective technology management in developing countries.
- Illumination of the challenges facing American companies in terms of sustainability and ethical corporate governance
- Assessing the significance and value of eBay’s and Craigslist’s e-commerce industry assumptions, alliances and strategic partnership
- demonstrating the need for social and economic variables in the development of a viable chemical engineering industry in the UK.
- Study of SONY and Microsoft’s employee retention rates while contrasting their approaches to business management
- Psychosocial risks’ effects on workplace risk control
- Leadership’s function in a company’s transformative shift
- Individual performance factors in SMEs
- Business tactics to draw in foreign capital
- Enterprise social networking platforms’ effects on knowledge management and organisational learning
- How do internal marketing and employee empowerment affect organisational productivity?
- Improving the sustainability of American business operations worldwide by developing a closed supply chain.
- How do different approaches to leadership affect employee relations improvement and solving conflicts in the workplace?
- What strategies help entrepreneurs bounce back from failure effectively?
- How can technology help distant teams connect and work together more effectively?
- How does globalisation affect the practices and strategies of enterprise control?
- How does gender equality influence business management?
- What role does powerful communication play in accomplishing success in control practices?
- What is the impact of alternate control on the sustainability of corporations?
- What is the effect of change control on the sustainability of companies?
- What role does forensic accounting serve in law enforcement investigations?
- What impact do enterprise rankings have on worldwide change?
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service!
Choosing a business management dissertation topic can be extremely stressful for anyone. You can research your topics online and find topics on any subject, for example, nursing dissertation topics or even those related to business, such as marketing dissertation topics.
You must consider several factors when choosing your business management dissertation topics, such as your lecturers’ or supervisor’s specifications and guidelines. Those who break the rules will have their dissertations rejected, so it is important to follow them.
To ensure that your dissertation captures the reader’s attention, choose a dissertation topic that is currently popular. Once you have selected a topic, you can take help from proposal writing services before you start working on the actual thesis paper.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find business management dissertation topics.
To discover business management dissertation topics:
- Research recent industry challenges.
- Analyse emerging trends.
- Examine managerial theories.
- Consider global perspectives.
- Interview professionals.
- Select a topic aligning with your career aspirations.
You May Also Like
Go through some of the dissertation topics related to Forensic science given below, with their research aim, and get an idea to begin your dissertation.
Pick from our top 50 taxation dissertation topic ideas varying from laws in taxation to the effects of tax evasion to help you in your taxation dissertation
Urban geography is a growing field of study that provides learners with a comprehensive understanding of how cities, towns and other human settlements develop and change over time.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Webinars
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Entering Class Profile
- Education & CV
- GMAT & GRE
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Letters of Recommendation
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Fields of Study
- Student Life
The dissertation is the final requirement for the PhD degree.
The research required for the dissertation must be of publishable quality and a significant contribution in a scholarly field. The dissertation is evidence of the candidate’s proficiency and future potential in research.
Students work closely with faculty throughout the program, and especially in the final phase of dissertation research. These faculty members share with the student the exploration of the field, first as advisors and teachers, and later as colleagues joined to advance the science of management.
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Annual Alumni Dinner
- Class of 2024 Candidates
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Dean’s Remarks
- Keynote Address
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Marketing
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Get Involved
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- Career Change
- Career Advancement
- Career Support and Resources
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Subscribe to Corporate Governance Emails
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Reading Materials
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
- Founding Donors
- Program Contacts
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- RKMA Market Research Handbook Series
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships

- Doctor of Business Administration
- Dissertations
Doctor of Business Administration Dissertations

Explore past dissertations from members of the Doctor of Business Administration program at Weatherhead School of Management at Case Western Reserve University.
2024 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Implementing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Principles in Organizations: The Role of Leadership and Impacts on Corporate Financial Performance
- Dissertation: African Energy Crisis: Designing Sustainable Solutions
- Dissertation: Predictive Accuracy of Performance in Knowledge Work: Comparison of Human Judgment, Regression and Artificial Intelligence Models
- Dissertation: Individual-Level Factors Affecting the Success of New Product Development Teams
- Dissertation: Thriving Together: The Virtuous Cycle of Business for Good, Positive Leadership, and Employee Well-Being
- Dissertation: The Concept of Awe and Its Role in Idea Creation
- Dissertation: At the Boundary of Risk and Uncertainty: Behavioral Insights Into Enterprise Risk Management
- Dissertation: Telemedicine's Evolutionary Sociotechnical Fit
- Dissertation: What Are the Impacts of Leader Political Skill on Organizational Change?
2023 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Do Emergency Physicians Treat Patients with Opioid Use Disorder Differently? A Mixed-Methods Integrative Paper
- Dissertation: Reliability and Resilience at U.S. Hospitals During the Global COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mixed Methods Study on the Effect of Leader and Team Behavior on Crisis Response
- Dissertation: The Experience of American Frontline Health Care Workers with Electronic Medical Records Technology During the Time of COVID-19: A Phenomenological Inquiry Following the Systems Approach
- Dissertation: The Impact of Business Unit (BU)-Information Technology (IT)-Relationships on Business Transformations: A Mixed Methods Study
- Dissertation: Cognitive Load, EHR Use, and Psychological Stressors Influence on Decision-Making Performance Within Healthcare
- Dissertation: Are Food Banks Impacting Food Retail? Examining the Relationship Between Hunger Relief Distributions and Retail Transactions in a Local Food Environment
2022 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Factors Influencing the Advancement Of African American Women In Banking: “Yet None Have Advanced Into The C-Suite Of The Top Four U.S. Banks”
- Dissertation: Embodied Awareness, Embodied Practice: A Powerful Path to Practical Wisdom
- Dissertation: The Dynamics and Impacts of Conference Change in Intercollegiate Athletics: A Strategy Group and Institutional Analysis
- Dissertation: Heuristics and Bias in New Venture Valuations
- Dissertation: Mixed Methods Study Examining Organizational and Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Management of Pet Populations in Shelters
- Dissertation: Factors Influencing Academic Engagement: A Social Support Perspective
- Dissertation: Latino Entrepreneurship in the United States: A Fresh Perspective
- Dissertation: The Effect of Supply Chain Strategies on Direct-to-Consumer Industry Evolution: A Mixed-Methods Study
- Dissertation: Building Character and Leading Through The "Eyes of Others:" A Qualitative and Quantitative Study of Ethical Decision-Making
- Dissertation: Unveiling the Arab Mind: What are the Characteristics of Leaders Who Need to Capture Followers' Hearts and Minds?
2021 Dissertations
- Dissertation: System Influence Framework: IT Project Managers’ Influence to Form Critical Stakeholder Alignments and Promote Value Realization
- Dissertation: A Mixed-Method Study of Investigating the Effects of Organizational Preparedness of Supply Chain Management Performance in the Food and Manufacturing Industry
- Dissertation: Managing Successful Strategic Turnarounds: A Mixed Methods Study of Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities
- Dissertation: Price Wars and Managerial Sensemaking: A Mixed-Methods Study
- Dissertation: Integrative Ecosystem Management: Designing Cities and Co-creating the Flourishing Ecosystem
- Dissertation: Effectiveness of Nonprofits on Factors That Influence the Social Aspects of Well-Being in Food Deserts
- Dissertation: Managing Scholar/Practitioner Tensions in Professional Programs: A Study of Library and Information Science Faculty
- Dissertation: Three Studies of Unexpected Organizational Decisions: Some Commonalities in Decisions to Report Workplace Violence and Decisions of Scope in Audit Testing for Complex IT Environments
2020 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Operational Excellence and Organic Revenue Growth
- Dissertation: Breakthrough Teams & Innovation in Orbit: Entrepreneurial Group Initiatives in Established Organizations
- Dissertation: The Human Side of Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): An Exploratory Sequential Mixed Methods Inquiry Into the Factors Influencing M&A Outcomes
- Dissertation: Coaching and Development as Part of a Manager-Subordinate Relationship: A Mixed-Methods Study of Tools, Dynamics and Outcomes
- Dissertation: Role of a CEO in the Era of Technology Disruption: Influence on Timing of Adoption
- Dissertation: Why Do People Bribe and Is It Worth It? A Mixed Methods Study of Bribing Antecedents and Outcomes in Former Soviet Countries
- Dissertation: Cross-Functional Team Performance: Inquiry, Identity and Shared Reality
- Dissertation: Managing Rational Divergence: Testing the Effects of a Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Technique on Collaborative Versus Competitive Behaviors in a Game Theoretic Setting
- Dissertation: Equity and Justice For All: The Absence of Subjective Well-Being for the African American Male
- Dissertation: How Do Professionals Find Life Meaning?
- Dissertation: Do You Have the "S" Factor for Service Innovation? How Stewardship Contributes to Service Innovation Capabilities in Service-Dominant Logic
- Dissertation: Coaching Millennials
- Dissertation: Antecedents Of Radicality And Commercial Success Outcomes In SBIR Projects
- Dissertation: Omni-Brand: The Paradox of Global Acceptance and Local Authenticity
- Dissertation: What drives individual decision-making of Foreign Direct Investments (FDI) to Sub-Saharan Africa
2019 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Designing the Framework of Entrepreneurial Relationship Management (ERM) for Strategic Actions and Effective-Decision Making
- Dissertation: Building Big Data Analytics as a Strategic Capability in Industrial Firms: Firm Level Capabilities and Project Level Practices
- Dissertation: The Influence of Individual, Organizational and Contextual Factors on Saudi Women Career Commitment and Satisfaction in Nontraditional Occupations
- Dissertation: The Patient Perspective: Exploring the Influence of Social Interactions on Chronic Disease Outcomes
- Dissertation: Hyperconnectivity Giveth and Taketh Away: Reconciling Being an "Always-On" Empowered Consumer and Privacy in an Era of Pervasive Personal Data Exchanges
- Dissertation: Inspirational Professors, Their Emotional Intelligence and its role on Relational Climate
- Dissertation: Emergent Learning in Digital Product Teams
- Dissertation: Improving Job Satisfaction for Nurses in Acute Healthcare Facilities through Engagement and Teamwork
- Dissertation: Leadership and Practices for Strategic Adaptation in Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
- Dissertation: A Mixed Methods Study Exploring How IRS Special Agents Choose Cases for Investigation
2018 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Green Investment and Organizational Performance: Evidence from the Nigerian Pulp and Paper Industry
- Dissertation: Antecedents of Managerial Moral Stress: A Mixed Methods Study
- Dissertation: Purposing: How Purpose Develops Self-Organizing Capacities
- Dissertation: The Changing Landscape of Finance in Higher Education: Bridging the Gap Through Data Analytics
- Dissertation: Barriers and Facilitators of Growth in Black Entrepreneurial Ventures: Thinking Outside the Black Box
- Dissertation: Honorable Mavericks: A Mixed-Method Study of what Influences Subsidiary Managers Compliance with Headquarters Instructions
- Dissertation: Fifteen Minutes of Shame: A Multilevel Approach of the Antecedents and Effects of Corporate Accounting Scandals
- Dissertation: What Really Matters to NFL Fans: The Effects of Team Performance and Self-confidence on Fan Commitment and Purchase Intention
- Dissertation: Crossing the Quality Chasm: A Mixed Methods Study of Physician Decision-Making when Treating Chronic Disease
- Dissertation: The Power of Relationships: Navigating the Dance of Change through Executive Coaching
- Dissertation: Learning Within and During IT/IS Projects: Its Process, Antecedents, and Outcomes
- Dissertation: The Complexity of Change: The Middle Managers’ Emergent Contributions
- Dissertation: STEM Entrepreneurs: Educating Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Underrepresented Minorities (URM) and Non-Minorities for Job Satisfaction and Career Success
- Dissertation: Mixed Methods Study of Factors Influencing Business to Business (b2b) Sales Performance: The Role of Design Attitude
- Dissertation: Making Heads and Tails of Distributional Patterns in Private-Equity-Owned Companies: A Value-Creation-Type and Industry-Based Analysis
- Dissertation: The Professional Development Mindset
2017 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Legislators as Leaders: Investigating and Elucidating the Influence of Gender, Religious Beliefs, and Mindfulness on Legislative Decision Making
- Dissertation: Purpose Matters to Leaders at a Personal and Company Level
- Dissertation: Forecast Revision as an Antecedent to Strategic Change
- Dissertation: An Examination of Followers' Upward Influence
- Dissertation: Empowering the 99%...One ESOP at a Time! A Mixed Method Study of Employee Owned Company Acquisitions
- Dissertation: Factors Contributing to Sustainable Brand Growth
- Dissertation: Looking Beyond Culture: Determining Success Factors for Transnational Multiparty Collaboration
- Dissertation: Bringing Social Innovation to Scale: Leveraging Relational Capital and Risk-Taking Behaviors of Actors in Complex Ecosystems
- Dissertation: Positive Impact: Factors That Drive Businesses Toward Shared Prosperity, Environmental Regeneration and Human Wellbeing
- Dissertation: The Role of an Ethos of Sustainability: The Hidden Value of Intangible Resources
- Dissertation: What is Retirement in the 21st Century?
- Dissertation: The Potency of Informal Learning in Paid and Non-Paid Work: A Mixed Study
- Dissertation: Strategy as Configuration: Recursive Organization of Strategy Implementation Factors and Their Effect on Strategy Execution Effectiveness
- Dissertation: Are we Having Fun Yet?: What is the Relationship Between Mentoring, Fun at Work and Job Satisfaction?
- Dissertation: Senior Information Technology (IT) Leader Credibility: Knowledge Scale, Mediating Knowledge Mechanisms, and Effectiveness
2016 Dissertations
- Dissertation: The Intersection of Auditor Independence, Objectivity, and Integrity in High Risk Audit Conditions
- Dissertation: Characteristics of Effective Leadership of Community College Presidents - A Mixed Method Analysis
- Dissertation: Cultural Factors: Entrepreneurial Orientation or Not – Innovation Drivers in Small to Medium Sized Enterprises
- Dissertation: Igniting the Fire: The Impact of Anticipatory Entrepreneurial Passion on Effort and Affect in Nascent Entrepreneurs
- Dissertation: Frontline Employee Role Passion and the Impact on Service Encounters
- Dissertation: An Original Microgrid Business Model Determines Conditions for a New Asset Market
- Dissertation: Sustainable Value And Eco-Communal Management: Systemic Measures For The Outcome Of Renewable Energy Businesses In Developing, Emerging, And Developed Economies
- Dissertation: A Theory of Micro-Level Dynamic Capabilities: How Technology Leaders Innovate with Human Connection
- Dissertation: When is Earnings Guidance a Treacherous Servant?
- Dissertation: Routines of New Venture Conceptualization: Evidence and Extension of an Entrepreneurial Dynamic Capability
- Dissertation: Remote and Onsite Knowledge Worker Productivity and Engagement: A Comparative Study of the Effect of Virtual Intensity and Work Location Preference
- Dissertation: Who We Are Matters: The Identity of the Information Technology Organization and Outsourcing Success
- Dissertation: A Theory of Steering Committee Capabilities for Implementing Large Scale Enterprise-Wide Information Systems
- Dissertation: Financial Stress in an Adaptive System: From Empirical Validity to Theoretical Foundations
- Dissertation: Experiential Workplace Design in Knowledge Work Organizations: A Worker-Centered Approach
- Dissertation: Understanding the Journey of Inner-City Communities to a Sense of Community and Well-Being
- Dissertation: Deliberate Disruption: How Corporate Leaders' Break the Liability of Expertise
- Dissertation: The Role of Mentorship in Developing Leadership Ready Gen X and Gen Y Females
- Dissertation: Antecedents and Outcomes of Perceived Creepiness in Online Personalized Communications
- Dissertation: The Effects of Visual Analytic Strategies on Organizational Decision Making
2015 Dissertations
- Dissertation: What Influences the Economic Model In the Private and Public Sectors In the Two Emirates of Abu Dhabi and Dubai? A Comparative Study
- Dissertation: Design Attitude and Social Innovation: Empirical Studies of the Return on Design
- Dissertation: Attentional Change Decisions: Exploring the Role of Attention in Shaping Change Decisions: A Mixed Methods Approach
- Dissertation: Interprofessional Teams in Healthcare: A Mixed-Methods Study
- Dissertation: Helping Top Talent To Thrive: The Significance of Relational Capacity, Teamwork and Organizational Support
- Dissertation: Narrative Shock: Helping North Korean Defectors Narrate Their Lives Fully in South Korea
- Dissertation: Team Adaptation and Mindful Boundary Management: The Dynamics of Internal and External Balancing
- Dissertation: The Collaboration Blueprint: Designing and Building Effective Strategies for Innovation and Rejuvenative Collaboration
- Dissertation: Developing the Next-Generation Leadership Talent in Family Business: The Family Effect
- Dissertation: Creating Customer Love: How Organizations Can Engender Positive Affect in Online Product-Centered Communities
- Dissertation: Playing to Win: Dynamics of Teams That Innovate
- Dissertation: Organizational Commitment - A Requisite for Quality of Life in Assisted Living.
- Dissertation: Promethean Framework and Measurement Instrument: Career Development, Maintenance and Transitions in Convulsive Economic Cycles
- Dissertation: Cohesion, Flexibility, and the Mediating Effects of Shared Vision and Comparison on Engagement in Army Acquisition Teams
- Dissertation: Title How Hackers Think: A Mixed Method Study of Mental Models and Cognitive Patterns of High-Tech Wizards
- Dissertation: Procedural Rationality as a Means for Evidence-Based Management in Conflicted Decision-Making: A Mixed-Methods Study
- Dissertation: Disempowering the "Robin Hood" Fraudster: Empathetic Pathways Weaken Regulators and Enable Fraudulent Behavior – A Framework For Redesigining Controls
- Dissertation: Organizational Adoption of Social Media Technologies: A Mixed-Methods, Multi-Level Study of Effects on Productivity and Work-Home Life Balance
- Dissertation: Trust by Design: The Affective and Cognitive Antecedents Among African Americans, Building Long-Term Business Relationships
- Dissertation: Thriving in Transition: Cognitive, Social & Behavioral Resources For Times of Change
2014 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Towards Flourishing: How Sellers Can Forge Stronger B2B Relations and Increase Buyer Loyalty
- Dissertation: Improving the Capacity for Strategic Anticipation: How Upstream, Downstream and Lateral Immersion Contribute to the Capacity to Anticipate Strategic Moves
- Dissertation: Does Upper Echelons Team Dynamic Matter? The Criticality of Executive Team Behavior in Economic Value Creation
- Dissertation: Facilitating Radical Innovation in Consumer Electronics and Information Technology Industries
- Dissertation: Staying Alive: The Experience of In Extremis Leadership
- Dissertation: The Significance of Influence in Our Current Work Environment: Understanding and Exploring the Shift and Emergent Domains
- Dissertation: Understanding Managerial Influences: A Mixed Methods Study of employee engagement, well-being, and performance
- Dissertation: Factors That Influence Firms' Environmental Performance: An Examination of Large Companies
- Dissertation: Title A Theoretical, Empirical and Practical Approach to Academic Knowledge Production and Job Satisfaction: The Role of Academic Alignment
- Dissertation: Equine-Assisted Experiential Learning: Implications for Management Development and Education
- Dissertation: Bridging the Medical Knowledge and Practice Gap: Antecedents of Successful Scientist Physician Collaboration
- Dissertation: Supply Chain Management Performance: Factors Contributing to Successful Risk Mitigation & Resiliency
- Dissertation: A Theory of Overload and Equivocality Effects on Learning during Knowledge Transfer within Policy Making Dyads
2013 Dissertations
- Dissertation: A Theory of Viral Growth of Social Networking Sites
- Dissertation: Socio-Cognitive Foundations of Entrepreneurial Venturing
- Dissertation: The Belief System and Behavior of Financial Advisors After a Market Disruption
- Dissertation: Relationships Matter, Even for CPAs
- Dissertation: Designing Successful Social Ventures: Hands-On Feedback-Seeking Engagement with Stakeholders to Unravel What to Do Next
- Dissertation: Pricing Capabilities and Firm Performance: A Socio-Technical Framework for the Adoption of Pricing as a Transformational Innovation
- Dissertation: Coming Out and Being Out in the C-Suite: The Experiences of Openly Gay and Lesbian Executives
- Dissertation: The Impact of Social Competencies and Role Factors on the Relational Construction of Identity and Participation of Physician Leaders
- Dissertation: Credibility: A Foundation for All Leaders
- Dissertation: Why We Care: The Mediating Effect of Positive and Negative Emotional Attractors on Social Responsibility
- Dissertation: Systemic Corruption: A Multi-Theoretic, Multi-Level and Mixed Methods Analysis of the Interplay among Institutional Logics, Strategic Agency and Reward Expectancy
2012 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Tenure, Charisma and Conflict in Venture Backed Teams
- Dissertation: Decision Making in the Corporate Boardroom: Designing the Conditions for Effectiveness
- Dissertation: How and To What Extent Does Collaboration Affect Employee and Cross-Functional Team Performance?
- Dissertation: Women Persisting in the Engineering Profession: A Paradoxical Explanation Adapting Intentional Change Theory
- Dissertation: Organizational Agility and Complex Enterprise System Innovations: A Mixed Methods Study of the Effects of Enterprise Systems on Organizational Agility
- Dissertation: How a Learning Orientation, Modern Portfolio Theory and Absorptive Capacity Contribute to University Endowment Performance
- Dissertation: A Multi-Level Investigation into the Antecedents of Enterprise Architecture (EA) Assimilation in the U.S. Federal Government: A Longitudinal Mixed Methods Research Study
- Dissertation: The Impact IT Professionals Have On Performance: What Differentiates Superior from Average Performers and Understanding How to Keep Them Engaged
2011 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Pluralistic Diversity in Voluntary Associations on College Campuses: A Multi-Method study
- Dissertation: Managing the Unexpected: Detecting, Preventing and Mitigating Surprises in the Banking Industry
- Dissertation: The Strategic Decision-Making Process of the Board and Its Impact on Decision Outcomes
- Dissertation: Worlds Connected and Worlds Apart: Postures and Dependencies Influencing Government - Agency Relations
- Dissertation: A Multi-Method Exploration of the Role of Legitimacy in Cross-Sector Partnerships for the Natural Environment
- Dissertation: Knowledge Sharing in Bioscience Clusters: Nature, Utilization and Effects
- Dissertation: Impact of School Leadership on Academic Achievement in Kenyan Secondary Schools
- Dissertation: Non-Financial Perspectives on Family Firm Performance
- Dissertation: The Great Recession and Nonprofit Endurance: Framing the Mission-Defensive Paradox
- Dissertation: The Global Financial Crisis: Bankers Shaken, But Some Awaken
2010 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Causal Ambiguity and Its Impacts on Firm Performance
- Dissertation: Exploring Sustained Collaborations: Activities and Behaviors That Make a Difference
- Dissertation: Adoption of High Trust-High Risk Technologies: The Case of of Computer Assisted Surgery
- Dissertation: Bridging Structure-Agency Divide: A Structurational Approach to Institutional Adaptation and Innovation
- Dissertation: The Effect of Social Factors on Project Success Within Enterprise-Class System Development
- Dissertation: Nonprofit Leaders and Their Organizations: Routes to and Repertoires for Effectiveness
- Dissertation: Drivers of Employee Engagement and Teamwork Performance
- Dissertation: Payoffs of Championing "Tough Issues": Why Corporations Need to Nurture Quixotic Champions at the Board and Within Senior Management Teams
- Dissertation: Improving the Effectiveness of Microfinance in Reducing Household Poverty
- Dissertation: How Many Hands Does a Team Have? Developing Ambidextrous Teams in Academic Medical Centers
- Dissertation: The Delicate Balance of Organizational Leadership: Encouraging Learning and Driving Successful Innovation
- Dissertation: Dare to Restore Trust and Drive Loyalty in Distrust-Dominated Environments: A Stakeholder Perspective
- Dissertation: The Impact of Charisma on Employee Volunteer Programs
2009 Dissertations
- Dissertation: A Study of the Impact of Informational Complexity, Transparency and Stewardship on Decision Usefulness: The Users' Perspective
- Dissertation: Generative Characteristics as Antecedents to Engagement
- Dissertation: Managing Commitment as Antecedents to Engagement in Faith-based Organizations: Chinese Protestant Churches in the United States
- Dissertation: When Practice and Theory Conflict: Do Performance Incentives Drive Management Behaviors in Mergers and Acquisitions?
- Dissertation: Ethical Ideologies and Decision Making Among College Student Athletes
- Dissertation: The Role of Human Capital in Predicting Business Outcomes
- Dissertation: Inside the Outsourcing of Innovation
- Dissertation: The Role of Organizational Learning in Renewing Competitive Advantage
- Dissertation: The Private Sector and Anti-Terrorism Spending for Physical Security
- Dissertation: Unraveling Adaptive Selling: An Empirical Analysis of Underlying Relational Behavior
- Dissertation: Design and Discovery: The Structure and Function of a Research Network
- Dissertation: Into the Family and Business Nexus: Succession and Daughters in Family Owned Businesses
- Dissertation: Executive Leader Development: Mentoring in U.S. Government and Commercial Organizations
- Dissertation: An Examination of the Antecedents and Consequences of Accreditation in the Nonprofit Sector
- Dissertation: Beyond Financial Transparency and Institutional Structure: Emergent Forms of Accountability in the New Era of Responsibility
2008 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Developing a Regional High Tech Environment: What Factors Matter
- Dissertation: The Impact of the Internet on Airline Fares
- Dissertation: Managing Multiple and Interacting Congregations Within the Same Church: The Case of Chinese Protestant Immigrant Churches in North America
- Dissertation: Heaven, Hell and Everything In Between: How Do Authentic Leaders' Values Contribute to Organizations in Which Followers Flourish?
- Dissertation: They're Making All the Wrong Decisions: Managing Cognitive and Emotive Balance
- Dissertation: The Pathfinder Leader and Complex Decision Making: The Role in Collective Action Governance
- Dissertation: College Environments as Enablers and Barriers to Youth Entrepreneurship
- Dissertation: The Role of Learning and Care Giving Style in Practitioner-Patient Co-Production of Therapeutic Outcomes
- Dissertation: Effective Leadership of Financial Service Firms: A Study in Resonance and Emotional Intelligence
- Dissertation: Selling Money: Success Factors for Financial Advisors
- Dissertation: Role Engagement in Co-operative Organizations: A Relational Framework for Understanding Board Commitment
- Dissertation: Virtual Teams: Can They Be More Effective
- Dissertation: Commitment to Change as Dynamic Push-Pull Alignment of Messages
- Dissertation: The Impact of Organizational Destruction in Social Capital
- Dissertation: The Duplicity Effect: Professional Investment Decisions for Others Versus Self
- Dissertation: You Can Change Strategies in a Conversation: Decision Making in Innovation in the Durable Goods Industry
2007 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Disconnected: A Consumer Study of Mobile Telephone Technology Rejection in the United States
- Dissertation: The Social-Technical Project Manager Practices That Motivate Knowledge Sharing and Learning in Information Technology Project Team Environments
- Dissertation: Social Change – Making the Improbable Possible through Collaboration: A Series of Studies on NGO Collaboration in South Africa
- Dissertation: Employee Reactions to Mergers and Acquisitions - The ‘ME-I Syndrome’; Avoiding ‘Merger-Enabled-Individualism’
- Dissertation: Service Feature Considerations for Developing Consumer Satisfaction in Online Environments
- Dissertation: Studies in Workplace Behaviors and Organizations
- Dissertation: Transitioning from Staff Nurse to Nurse Manager-A Change in Identity
- Dissertation: Resilience in Action: Exploring Constructive Transitions Among Mid-Career Leaders
- Dissertation: Change Leader Retention and Career Development: The Role of Social Capital and Balancing Commitments
- Dissertation: Venture “TERROIR” Can We Define It ? VC Decision Processes for Investing in Genesis/ Pre-seed ICT Entrepreneurial Teams
- Dissertation: The Effects of Ownership, Control Rights and Experience on Joint Venture Success
- Dissertation: Social Entrepreneurship: Creating Impact in the Social Sector
- Dissertation: An Investigation of Electronic Medical Record Technology Adoption by Family Practice Physicians
2006 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Three Aspects of Social Change Management: Project Ownership, Ethical Project Transfer and Economic Correlate
- Dissertation: Corporate Governance in the Era of Sarbanes-Oxley
- Dissertation: The Practice of Medical Error Reporting
- Dissertation: The Social Construction of the Interactive Practices of Multicultural Professionals
- Dissertation: Practicing Pragmatic Collaboration: The Challenge of Recognizing and Managing Rational Divergence
- Dissertation: Focusing on the End User: Promoting the Successful Deployment of Workplace Programs and Initiatives
- Dissertation: Exploration of Social Capital in the Context of Elected Public School Officials
- Dissertation: A Journey with the End in Mind: An Examination of How Advance Planning May Influence End-of-Life Decisions
- Dissertation: Innovative or Expendable Human Capital: The Effect of Labor Market Choices, Career System Practices and Self-Directed Career Orientation on Organization Outcomes
- Dissertation: Immigrants Transnational Activities for Home Community Development: The Nigerian Immigrants in the United States
- Dissertation: Factors that Facilitate Entrepreneurship Among Students and Nascent Entrepreneurs
- Dissertation: An investigation of Customer Perceived Value, Exchange Partner Trustworthiness and Service Perceptions in e-Commerce
- Dissertation: Impact of Knowledge on Electricity Markets
2005 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Corporate Responses to Accounting Regulation
- Dissertation: Information Technology Adoption by Middle Managers: The Case of Trial Court Judges
- Dissertation: Strangers in the Commons: Understanding and Measuring Successful Aging for Low-Income Seniors in Affordable Housing
- Dissertation: Adolescent Leadership Development: The Role of Authoritative Parenting and the Mediating Effect of Psychological Autonomy and Mastery Orientation
- Dissertation: Trust, Education and Development in Jamaica, 1950-2000
- Dissertation: The Link Between Governance Responsibilities and Performance in Healthcare Organizations: A Trustees Perspective
- Dissertation: Nonprofit Intrapreneurship: How Nonprofit Managers Facilitate and Balance Entrepreneurial Activity
- Dissertation: All Cake and No Icing: An Exploration of Female Executive Leadership in the Nonprofit Sector
- Dissertation: A Framework for Maximizing Board Member Outcomes in Nonprofit Organizations
- Dissertation: The Impact of Electronic Medical Records on the Doctor-Patient Relationship in Hospitals in Japan, Korea and the United States: A Cross-Cultural Comparison
2004 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Sparks of Innovation: Observing the Elements that Lead to Creative and Innovative Success
- Dissertation: Pastoral Leadership and Parish Vibrancy
- Dissertation: A Tale of Two Colleges: The Fiscal Crisis of the 1990's Strategies for Managing in Uncertainty
- Dissertation: Converting Highly Legitimized Structural Barriers into Vehicles of Change: A Case for Transformational Leadership in Liberal Arts Colleges
- Dissertation: The Social Capital of Nonprofit Leaders
- Dissertation: Synthesizing Managerial Agency and Institutionalism in Manufacturing Facilities
- Dissertation: The Evolving Nonprofit Board: Relational Practices and Effective Governance
- Dissertation: Entrepreneurial Emergence: The Challenge of Growth in Urban Contexts
- Dissertation: Change On the Frontlines: A Perspective from the Trenches
- Dissertation: Perspectives on Life Insurance Selling, Retirement Savings among African Americans and Precautionary Saving of Blacks compared to Whites
- Dissertation: Managers, Micro-entrepreneurs and Performance Outcomes: Lessons from Two Worlds
- Dissertation: Trust in Project Management Relationships
- Dissertation: Free at Last? Culturally Rooted Differences in the Workplace Experience
- Dissertation: Organization and Empowerment: Policy, Practice and Outcome - The Study of Development Organizations in St. Lucia, West Indies
2003 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Individual Behavioral Competencies & Organizational Constraints: Some Insights From Health Care
- Dissertation: From Sitting on Top of the World to Crunched in the Back of the Bus: The Transformation of the U.S. Domestic Airline Industry From 2000 Through 2003
- Dissertation: Stakeholders and Organizations: A Three Part Approach to Better Understandings of Who and What Counts
- Dissertation: Research Reports: Strength of Strong Ties: Two Studies on EVA in Cyclic Markets
- Dissertation: Beyond the Requirements: Using Technology and Implementing Service Learning
- Dissertation: What Tangled Webs We Weave: A Comparative Study of Cooperation, Coping, and Networking Strategies of Women Professionals and Entrepreneurs
- Dissertation: Customer Service Satisfaction in Inter-Cultural Service Encounters
- Dissertation: Research Into the Effectiveness of an Alternatives to Violence Program in a Prison System
- Dissertation: A Qualitative Analysis of the Historical and Social Significance of the African American Male Oral Tradition: A Study in Linguistic Anthropology
- Dissertation: Leadership Pathways: How Leaders Communicate, Network, and Find Success in Diverse Environments
- Dissertation: Reciprocal Learning in Teams: Relational Practices for Securing the Best From Leadership Volunteers in Nonprofit Organizations
2002 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Workforce Development in a Small Manufacturing Organization
- Dissertation: Forces Shaping the Extent of Markets: An Exploration of Wholesale Distributors in Latin America
- Dissertation: The Meaning of Decision and Choice to a Leader in a Nonprofit Organization
- Dissertation: Another Thrice-Told Tale: Strategy Formation, Accountability, and Competent Governance in a Nonprofit Organization
- Dissertation: Study of Direct Internet Selling by Airlines in the U.S. Air Travel Distribution Industry
- Dissertation: The Impact of Emotional Intelligence on Work Team Cohesiveness and Performance
- Dissertation: Political Economy and Price Ratio Changes: Electric Industry Under Transition
- Dissertation: Understanding the Characteristics of an Effective Physician-Hospital Contractual Arrangement from a Dyadic Perspective
- Dissertation: The Connected Celebrity and Nonprofit Advertising
2001 Dissertations
- Dissertation: A Study of the Impact of Ohio’s Instructional Support Funding Process On Institutional Behavior At Two-Year Colleges
- Dissertation: The Contributions and Status of Women Inside Directors in Fortune 1000 Companies
- Dissertation: The Influence of Self-Development, Experimental Learning and Networking on the Career Satisfaction of EMBA Graduates
- Dissertation: Toward A Theory of Technical Change
- Dissertation: More Than Directing Money: Theories in Use for Helping Distressed Communities as Practiced by Independent Foundations
2000 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Money and Theology - It's Not an Oxymoron!!
- Dissertation: Parental Choice of Elementary Schools Within the Cleveland Catholic Diocese and Its Implications for the Financial Policies of Diocesan Schools
- Dissertation: Business Is War: An Investigation Into Metaphor Use in Internet and Non-Internet IPOs
- Dissertation: Theoretical Aspects of the Japanese Institutional Relations Model and Its Effectiveness for Corporate Governance in the Context of Globalization
- Dissertation: Sensemaking in a Hospital Strategic Planning Process
- Dissertation: Strategic Alliance Decisions: The Interpersonal Experience of Alliance Building
1999 Dissertations
- Dissertation: Environomics: Managing Environmental Change from Rio de Janiero to Buenos Aires (Via Berlin and Kyoto
- Dissertation: Habitus Wars and Field(s) of Dreams: Using Bourdieu to Reframe the Sense of a Crisis
- Dissertation: Managers in the Middle: A Study of Long Term Care Regional Managers Dealing With Organizational Stress
- Dissertation: The Relationship of Error-Based Experimental Learning to Organizational Change: How and Why What We Learn May or May Not Change How We Behave
- Dissertation: Back to the Future: A Search for Economic Progress or Roots? A Comparison of Experiences Between African American Entrepreneurs in the United States
- Dissertation: The Quest for Sustainable Leadership: The Importance of Connecting Leadership Principles to Concepts Of Organizational Sustainability
- Dissertation: Achieving Potential in Hospital Mergers
- Dissertation: Mill Creek: A Case Study Applying Actor Network and Transformational Leadership Theories to Urban Housing Development
1998 Dissertations
- Dissertation: America in the 21st Century: Finding Harmony Between Economic and Social Goals
- Dissertation: The Social Construction of Workforce Development Organizations in Singapore and Penang, Malaysia
- Dissertation: The Marketplace of Management Ideas
- Dissertation: The Changing Face Of Money: Will Electronic Money Be Adopted in the United States?
- Dissertation: Ordinary Canadians: Identity of Time and Place
- Dissertation: Straight to the Heart: Cleveland Leaders Shaping the Next Millennium
- Dissertation: Capacity Building: An Appreciative Approach
- Dissertation: The Structure of Management Practices and the Formation of Coping Habitus

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
35+ Business Dissertation Topics and Ideas to Get You Stared
by Antony W
June 27, 2024

With the world almost putting Covid-19 on its knees, economic growth will see an upward trend as it used to right before the global pandemic hit the human race hard. So far, statistics point to a potential growth that will see an expansion in business activities, making this an interesting area to study.
For business students taking their Master’s degree, the requirement to write a dissertation raises the need to select the best business dissertation topic for the assignment. To help you make the topic research process easier, we’ve put together a list of interesting topics for inspiration.
Keep in mind that business is a wide field, and therefore the topics provided in this guide cover various disciplines in the sector. As such, it should be easy for you to find a topic that’s not only interesting but also worth exploring.
Business Dissertation Topics: 25+ Examples for Inspiration
The following are examples of dissertation topics that you can improve and explore in your research assignment:
Dissertation Topics on Corporate Social Responsibility in Business
Corporate social responsibility is a serious issue in the business world, especially since activists and governments hold enterprise responsible for their actions. If anything, businesses have to take corporate social responsibility seriously because it’s part of what contributes to the competence of companies and organizations.
Some topics you can cover in this area include:
- What are the important strategic decisions that businesses must make in order to enhance their performance in terms of Corporate Social Responsibility?
- How can firms benefit from implementing CSR practices in relation to climate change?
- In the aftermath of the Coronavirus epidemic, how much CSR will be lost in order to achieve higher economic growth?
- Is there a link between diversity and corporate social responsibility, and what role does it play in organizational performance?
- What are the obstacles to the mainstreaming of ethical firms in the United Kingdom?
Free Features

Don’t wait for the last minute. Hire a writer today.
$4.99 Title page
$10.91 Formatting
$3.99 Outline
$21.99 Revisions
Get all these features for $65.77 FREE
Dissertation Topics on Global Strategy in Business
This area focuses on examining the key strategic issues that companies and organizations have to deal with when doing business in the global space. More often than not, researchers seek to understand strategic analysis, strategy formulation, and the way businesses identify sources of competitive advantages.
Here are some topic ideas that you may find interesting to cover in this area:
- How should a corporate plan for expanding into an international market be developed?
- An investigation on the exit strategy of foreign venture capital investment in the worldwide private sector.
- Is it possible to use entrepreneurship as a successful management technique inside a company unit?
- A study of the issues associated with managing international collaboration in the military aero-engine industry.
- Creating a closed-loop supply chain to improve global business practices’ sustainability.
- Creating an efficient structure for knowledge exchange and use in international project teams.
Global Business and Politics Dissertation Topics
The dissertation topic ideas in this category often examine the connection between global business and global politics. As an area that has been volatile for years, this sector evaluates institutions, processes and factors that influence businesses and politics.
Here are some topic ideas to consider:
- Evaluating the effectiveness of multinational businesses’ global business teams: a test of an intervening process model
- How diverse patterns of business-government ties influence industrial upgrading processes: A case study of developing economies
- Strategy, structure, fit, and performance in business-government relations within a contingency theory framework.
- Is globalization still going to be a significant market driver in the aftermath of the Covid-19 crisis?
- What impact does Corporate Governance have on internationalization, globalization, and company performance?
- Examining how enterprises entering the Chinese market manage political risk from a legitimacy standpoint.
Technology Business Topics for Dissertation
Your dissertation will focus on the strategies that businesses use to identify, develop, and implement technology to support their day-to-day operations. You may have to investigate the evolution of technology, new opportunities that technology presents, and the possible challenges that businesses have to deal with.
Some topics to consider in this area are as follows:
- How will 5G technology affect the expansion of digital consumer markets in the United Kingdom?
- How ICT integration has changed the way people buy products and services.
- An investigation on the influence of internet marketing in the development of global supply chain networks.
- Evaluating technology diffusion models among UK online customers.
- How has the incorporation of technology into human resources benefited organizational efficiency?
- Considering the role of innovation in the emergence of new prospects for SMEs in the United Kingdom.
- What are the primary variables influencing the effectiveness of corporate internet branding?
- An examination of how corporate operations have improved as a result of innovation: Are they convergent on a single universal approach?
International HR Management Dissertation Topics
The focus in this business segment is on how organizations handle human resources at an international level to maintain a competitive advantage. Notably, the area focuses on understanding culture factors that give insights on how human resource functions can contribute to building functional knowledge to national and international business.
Here are some dissertation topics that are likely to suit this area of business:
- What are the foundations of employee commitment in a global multi-national in terms of emotive, normative, and calculative commitment?
- How can cultural differences be managed in multinational collaborative projects?
- How do you manage employee commitment in the non-profit sector across national cultures?
- What are the most important elements influencing staff retention in international contact centers?
- Can IHRM offer culturally acceptable work-life balance and flexible working patterns for multinational corporations?
- What influence does organizational transformation have on employee engagement in major multinational corporations?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of intercultural teams operating in virtual settings, and how do these teams impact competitive advantage?
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Moscow Rules: A Quantitative Exposé
- Conference paper
- Open Access
- First Online: 09 June 2022
- Cite this conference paper
You have full access to this open access conference paper

- Eduardo Miranda ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8195-7506 10
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing ((LNBIP,volume 445))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Agile Software Development
8587 Accesses
1 Citations
This article analyzes the performance of the MoSCoW method to deliver all features in each of its categories: Must Have, Should Have and Could Have using Monte Carlo simulation. The analysis shows that under MoSCoW rules, a team ought to be able to deliver all Must Have features for underestimations of up to 100% with very high probability. The conclusions reached are important for developers as well as for project sponsors to know how much faith to put on any commitments made.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

Effiziente rechnerunterstützte Entwicklung von Karosseriekonzepten

OpenTURNS: An Industrial Software for Uncertainty Quantification in Simulation
- Agile planning
- Release planning
- Requirements prioritization
- Feature buffers
- MosCoW method
1 Introduction
MoSCoW rules [ 1 ], also known as feature buffers [ 2 ], is a popular method to give predictability to projects with incremental deliveries. The method does this by establishing four categories of features: M ust Have, S hould Have, C ould Have and W on’t Have, from where the MoSCoW acronym is coined. Each of the first three categories is allocated a fraction of the development budget, typically 60, 20 and 20 percent, and features assigned to them according to the preferences Footnote 1 of the product owner until the allocated budgets are exhausted by subtracting from them, the development effort estimated for each feature assigned to the category. By not starting work in a lower preference category until all the work in the more preferred ones have been completed, the method effectively creates a buffer or management reserve of 40% for the Must Have features, and of 20% for those in the Should Have category. These buffers increase the confidence that all features in those categories will be delivered by the project completion date. As all the development budget is allocated by the method, there are no white spaces in the plan, which together with incentive contracts, makes the method palatable to sponsors and management.
Knowing how much confidence to place in the delivery of features in a given category is an important concern for developers and sponsors alike. For developers it helps in formulating plans consistent with the organization’s risk appetite, making promises they can keep, and in calculating the price of incentives in contracts as well as the risk of incurring penalties, should these exist. For sponsors, it informs them the likelihood the features promised will be delivered, so they, in turn, can make realistic plans based on it. To this purpose, the article will explore:
The probabilities of delivering all the features in each of the categories: Must Have, Should Have and Could Have, under varying levels of under and overestimation of the features’ development efforts
The impact of features’ sizes, dominance, number of features, and correlation between development efforts in said probabilities
The effect of budget allocations other than the customary 60/20/20 on them.
To calculate the probabilities of delivery (PoDs) we need to make suitable assumptions about the distribution of the efforts required to develop each feature since the single point estimate used in the MoSCoW method are insufficient to characterize them.
In this article, those assumptions are derived from two scenarios: a low confidence estimates scenario used to establish worst case Footnote 2 PoDs and a typical estimates scenario used to calculate less conservative PoDs.
The potential efforts required and the corresponding PoDs, are calculated using Monte Carlo simulations [ 3 , 4 ] to stochastically add the efforts consumed by each feature to be developed.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Sect. 2 provides an introduction to the MoSCoW method, Sect. 3 introduces the Monte Carlo simulation technique and describes the calculations used for the interested reader, Sect. 4 discusses the two scenarios used in the calculations, Sect. 5 analyzes the main factors affecting the method’s performance, Sect. 6 discuss the method’s effectiveness in each of the scenarios and Sect. 7 summarizes the results obtained.
2 The MoSCoW Method
The MoSCoW acronym was coined by D. Clegg and R. Baker [ 5 ], who in 1994 proposed the classification of requirements into Must Have, Should Have, Could Have and Won’t Have. The classification was made on the basis of the requirements’ own value and was unconstrained, i.e. all the requirements meeting the criteria for “Must Have” could be classified as such. In 2002, the SPID method [ 6 ] used a probabilistic backcasting approach to define the scope of three software increments roughly corresponding to the Must Have, Should Have and Could Have categories, but constraining the number of Must Have to those that could be completed within budget at a level of certainty chosen by the organization. In 2006, the DSDM Consortium, now the Agile Business Consortium, published the DSDM Public Version 4.2 [ 7 ] establishing the 60/20/20% recommendation although this, was probably used before by Consortium’s members on their own practices. The current formulation of the MoSCoW prioritization rules is documented in the DSDM Agile Project Framework [ 1 ].
During the project planning phase, see Fig. 1 .a, features are allocated to one of four sets: Must Have, Should Have, Could Have, and Won’t Have on the basis of customer preferences and dependencies until the respective budgets are exhausted.
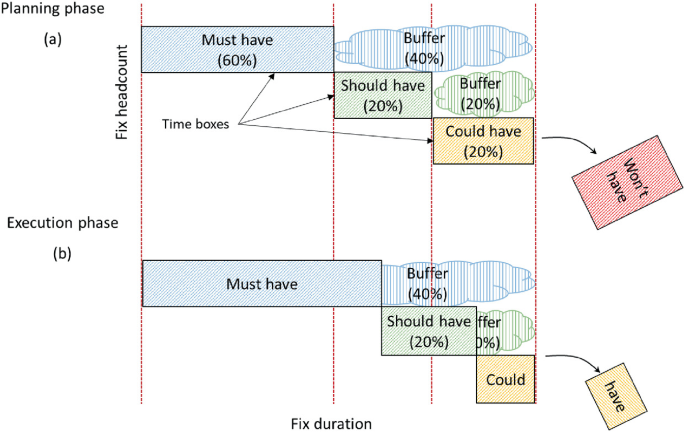
MoSCoW rules at play: a) During planning, b) in execution
During execution, Fig. 1 .b, features in the Must Have category are developed first, those in the Should Have second, and those in the Could Have, in third place. If at any time the work in any category requires more effort than planned, work on them will continue at the expense of those in the lower preference categories which will be pushed out of scope in the same amount as the extra effort required. The advantage for the project sponsor is that, whatever happens, he or she can rest assured of getting a working product with an agreed subset of the total functionality by the end of the project.
For the MoSCoW method to be accepted by the developer as well as by the sponsor of a project, the risk of partial deliveries must be shared between both of them through incentive contracts since approaches like firm fixed price or time and materials, that offloads most of the risk on only one of the parties could be either, prohibitive or unacceptable to the other. Contractually, the concept of agreed partial deliveries might adopt different forms. For example, the contract could establish a base price for the Must Have set, with increasingly higher bonuses or rewards for the Should Have and Could Have releases. Conversely the contract could propose a price for all deliverables and include penalties or discounts if the lower priority releases are not delivered. This way the incentives and disincentives will prevent the developer from charging a premium price to protect itself from not delivering all features while the sponsor, is assured the developer will do its best, in order to win the rewards.
3 The Monte Carlo Simulation
The Monte Carlo method is a random sampling technique used to calculate probability distributions for aggregated random variables from elementary distributions. The technique is best applied to problems not amenable to closed form solutions derived by algebraic methods.
The Monte Carlo method involves the generation of random samples from known or assumed elementary probability distributions, the aggregation or combination of the sample values according to the logic of the model been simulated and the recording of the calculated values for the purpose of conducting an ex-post statistical analysis.
The technique is widely used [ 3 , 4 ] in probabilistic cost, schedule and risk assessments and numerous tools Footnote 3 exist to support the computations needed.
The results presented in the paper were calculated using @Risk 7.5. As these are the product of simulation runs, they might slightly differ from one run to another, or when using a different number of iterations or platforms.
The rest of the section explains the model used to generate the cumulative probability curves and calculate the PoD for each MoSCoW category: Must Have (MH), Should Have (SH) and Could Have (CH), with the purpose of allowing interested readers replicate the studies or develop their own simulations. Those not so inclined might skip it, with little or no loss in understanding the paper. The name of the parameters should make them self-explanatory however, conceptual definitions about its meaning and usage will be provided throughout the paper.
The probability of completing all features in a given category in, or under, an \(x\) amount of effort is defined as:
The cumulative distribution functions: \(F_{MH} \left( x \right), \,F_{SH} \left( x \right)\, {\text{and}}\, F_{CH} \left( x \right)\) , are built by repeatedly sampling and aggregating the effort required by the features included in each category.
similarly, for features j and k, and:
subject to the maximum allocation of effort for each category:
The Probability of Delivery (PoD) of each category is defined as:
All quantities are normalized for presentation purposes by dividing them by the \(DevelopmentBudget\) .
4 Low and Typical Confidence Scenarios
Figure 2 contrasts the two scenarios mentioned in the introduction. The low confidence scenario is characterized by the uniform distribution of the potential efforts required to realize each feature, with the lower limit of each distribution corresponding to the team’s estimated effort for the feature and their upper to increments of 50, 100 and 200% above them, to express increasing levels of uncertainty. Since all values in the interval have equal probability, this scenario corresponds to a maximum uncertainty state [ 8 ]. This situation, however unrealistic it might seem, is useful to calculate a worst case for the PoD of each category. In the typical confidence scenario, the potential efforts are characterized by a right skewed triangular distributions, in which the team’s estimates correspond to the most likely value of the distribution, meaning the realization of many features will take about what was estimated, some will take some more and a few could take less.
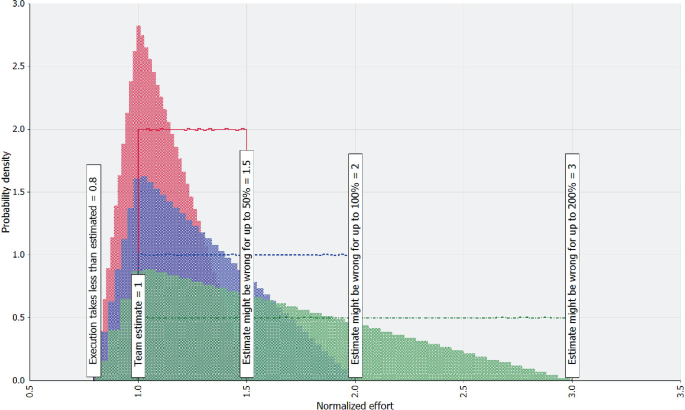
Probability distributions for the effort required by each feature in the low (uniform distributions) and typical (triangular distributions) confidence scenarios
The right skewness of the typical estimate distributions is predicated on our tendency to estimate based on imagining success [ 9 ], behaviors like Parkinson’s Law Footnote 4 and the Student Syndrome Footnote 5 , which limit the potential for completing development with less effort usage than estimated, and the fact that the number of things that can go wrong is practically unlimited [ 10 , 11 ]. Although many distributions fit this pattern, e.g. PERT, lognormal, etc., the triangular one was chosen for its simplicity and because its mass is not concentrated around the most likely point [ 12 ], thus yielding a more conservative estimate than the other distributions mentioned.
As before, the right extreme of the distribution takes values corresponding to 50, 100 and 200 percent underestimation levels. For the lower limit however, the 80 percent of the most likely value was chosen for the reasons explained above.
Considering this second scenario is important, because although having a worst case for the PoDs is valuable as they tell the lowest the probabilities could be, relying on them for decision making may lead to lost opportunities because of overcautious behaviors.
5 Level of Underestimation, Correlation, Number of Features in a Category, Feature Dominance and Non-traditional Budget Allocations
Before calculating the PoDs for each MoSCoW category under the two scenarios, the impact of different factors on the PoD is explored with the purpose of developing an appreciation for how they affect the results shown, i.e. what makes the PoDs go up or down. Understanding this is important for those wanting to translate the conclusions drawn here to other contexts.
Although the analysis will be conducted only for the low confidence estimates for reasons of space, the same conclusions applies to the typical estimates scenario, with the curves slightly shifted to the left.
Figure 3 shows the impact of underestimation levels of up to 50, 100 and 200% of the features’ individual estimates on the PoD of a Must Have category comprising 15 equal sized features, whose development efforts are independent from each other.
Independent, as used here, means the efforts required by any two features will not deviate from its estimates conjointly due to a common factor such as the maturity of the technology, the capability of the individual developing it or the consistent over optimism of an estimator. When this occurs, the efforts are correlated rather than independent. Having a common factor does not automatically mean the actual efforts are correlated. For example, a feature could take longer because it includes setting up a new technology, but once this is done, it doesn’t mean other features using the same technology would take longer since the it is already deployed. On the other hand, the use of an immature open source library could affect the testing and debugging of all the features in which it is included.
The higher the number of correlated features and the stronger the correlation between them, the more individual features’ efforts would tend to vary in the same direction, either requiring less or more of it, which would translate into higher variability at the total development effort level. This is shown by curves “r = 0.2”, “r = 0.6” and “r = 0.8” in Fig. 4 , becoming flatter as the correlation (r) increases.
Correlation brings good and bad news. If things go well, the good auspices will apply to many features, increasing the probability of completing all of them on budget. Conversely, if things do not go as well as envisioned, all affected features will require more effort, and the buffers would not provide enough slack to complete all of them.
Estimating the level of correlation between estimates is not an easy task, it requires assessing the influence one or more common factors could have on the items affected by them, a task harder than producing the effort estimates themselves. So while correlation cannot be ignored at risk of under or over estimating the safety provided by the method, the cost of estimating it, would be prohibitive for most projects. Based on simulation studies, Garvey et al. [ 13 ] recommend using a coefficient of correlation of 0.2 across all the estimated elements to solve the dilemma, while Kujawski et al. [ 14 ], propose to use a coefficient of 0.6 for elements belonging to the same subsystem, as these would tend to exhibit high commonality since in general, the technology used and the people building it would be the same, and 0.3 for elements on different subsystems, because of the lower commonality.
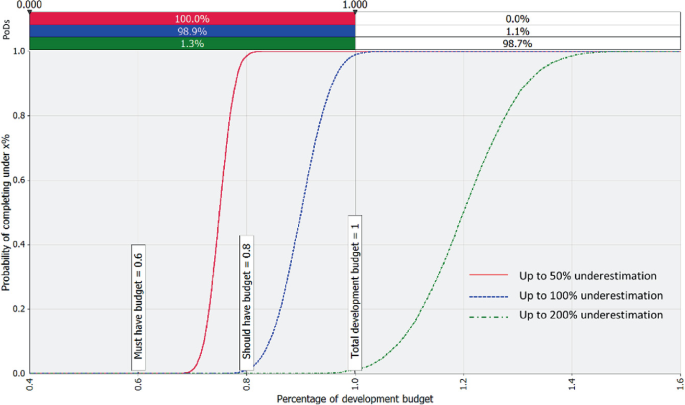
Cumulative completion probabilities under increasing levels of underestimation. The simulation shows a PoD for the Must Have features of 100% for an underestimation level of up to 50%, of 98.9% at up to 100%, and of 1.3% for an underestimation in which each feature can require up to 200% of the estimated budget.
The PoDs are also affected by the number of features in the category as well as by the existence of dominant features, which are features whose realization requires a significative part of the budget allocated to the category. See Figs. 5 and 6 .
As in the case of correlation, a small number of features and the presence of dominant features result in an increase in the variability of the estimates. Dominant features, contribute to this increase because it is very unlikely that deviations on their effort requirements could be counterbalanced by the independent deviations of the remaining features in the category. As for the increase of variability with a diminishing number of features, the reason is that with a fewer independent features, the probability of them going all in one direction, is higher than with many features.
The model in Fig. 7 challenges the premise of allocating 60% of the development budget to the Must Have category and explores alternative assignments of 50, 70 and 80% of the total budget. Reducing the budget allocation from 60 to 50% increases the protection the method affords at the expense of reducing the number of features a team can commit to. Increasing the budget allocation for the Must Have allows developers to promise more, but as will be shown, this is done at the expense of reducing the certainty of delivering it. For the 50% allocation level, there is a 100% chance of delivering the Must Have for underestimations of up to 100%, and of 68.2% for underestimations of up to 200%. At the 70% allocation level, the simulation shows that the PoD for the Must Have, when the possibility of underestimation is up to 50% still is 100%, but that it drops sharply to 34% when the underestimation level rises to up to 100%. For the 80% allocation level, the PoD for the Must Have falls to 49.7% for the up to 50% underestimation level and to 0 for the other two. The rest of the paper will then use the customary 60, 20 & 20% allocation scheme.
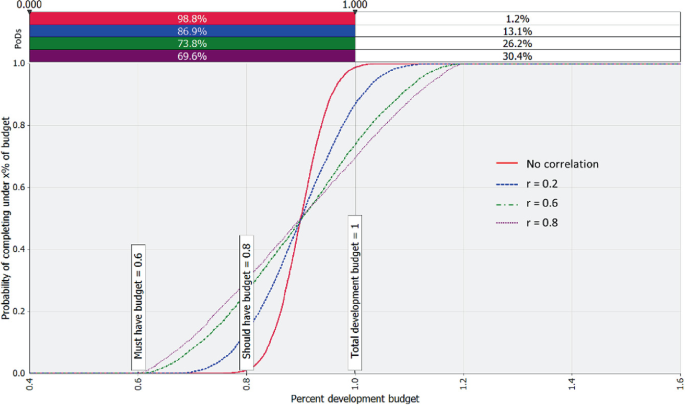
Probability of completing all features in the Must Have category under a given percent of the budget when the underestimation level is up to 100% and the efforts are correlated (r > 0)
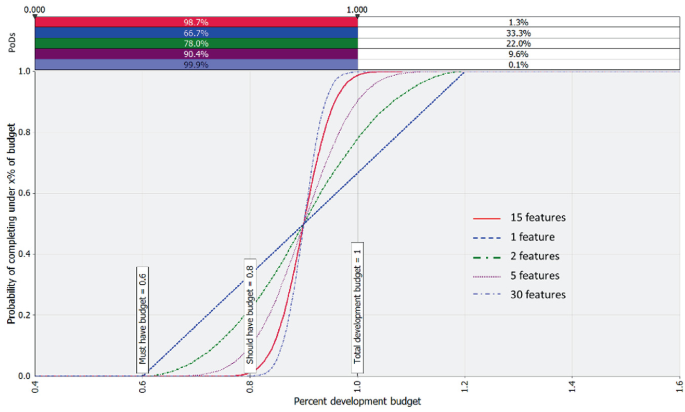
Influence of the number of features on the PoD for a Must Have set containing the number of equally sized independent features indicated by the legend on the chart, with an underestimation level of up to 100%. The PoD offered by the method drops sharply when the set contains less than 5 features
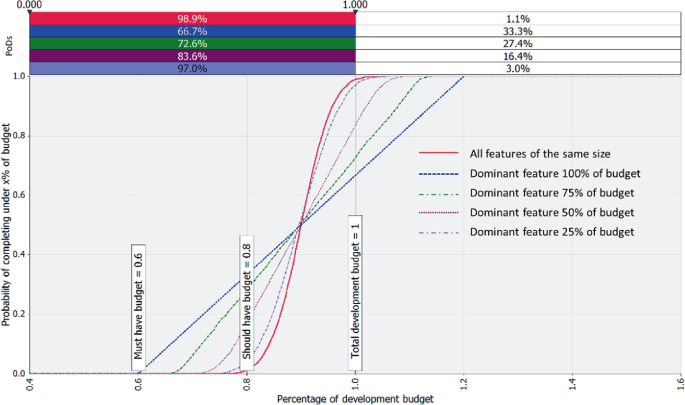
Influence of a dominant feature on the PoD. Each set, with the exception of the dominant at 100%, contained 15 features, with the dominant feature assigned the bulk of the effort as per the legend in the chart with the remaining budget equally distributed among the other 14 features. The safety offered by the method drops sharply when a feature takes more than 25% of the budgeted effort for the category. Underestimation of up to 100% and independent efforts
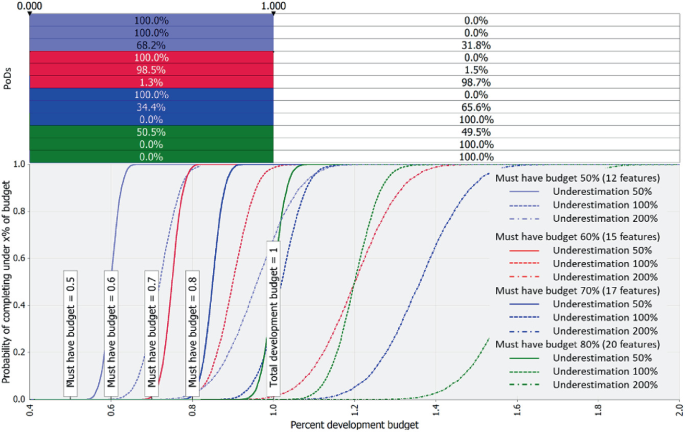
Probability of delivering all Must Have features for Must Have budget allocations of 50, 60, 70 and 80% under different underestimation conditions. The respective number of Must Have features for each budget allocation were 12, 15, 17, and 20.
6 Probabilities of Delivery for Each MoSCoW Category
This section discusses the PoDs for each MoSCoW category: Must Have, Should Have and Could Have under the following conditions:
Low confidence estimation, independent efforts
Low confidence estimation, correlated efforts
Typical estimation, independent efforts
Typical estimation, correlated efforts
In all cases, the underestimations considered are of up to 50, 100 and 200% of the estimated effort, a 60/20/20 effort allocation scheme and a Must Have category comprising 15 equal sized features with Should and Could Have categories comprising 5 equal sized features each. These assumptions are consistent with the precedent analysis and with the small criteria in the INVEST [ 15 ] list of desirable properties for user stories. For the correlated efforts cases, the article follows Kujaswki’s recommendation, of using an r = 0.6, as many of the attributes of an agile development project: dedicated small teams, exploratory work and refactoring, tend to affect all features equally.
6.1 Low Confidence, Independent Efforts
Figure 8 shows the PoDs for all MoSCoW categories for the low confidence, uncorrelated features, r = 0, model. At up to 50% underestimation, the probability of delivering all Must Have is 100%, as expected, and the probability of delivering all Should Have is 50.2%. At up to 100% underestimation, the probability of delivering all the Must Have still high, 98.9% but the probability of completing all the Should Have drops to 0. At up to 200% the probability of delivering all the Must Haves is pretty low, at 1.3%. In no case it was possible to complete the Could Have within budget.
6.2 Low Confidence, Correlated Efforts
As shown by Fig. 9 , in this case the variability of the aggregated efforts increases, with the outermost points of the distribution becoming more extreme as all the efforts tend to move in unison in one or another direction. Comparing the PoDs for this case with those of the previous one, it seems paradoxical, that while the PoD for the Must Have at 100% underestimation level goes down from 98.9 to 74.0, the PoD for the same category at 200% underestimation level goes up from 1.3 to 26.9%! This is what was meant when it was said that correlation brought good and bad news.
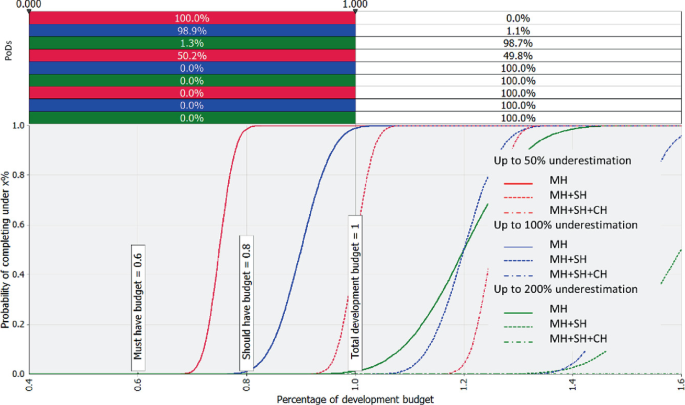
Probability of delivering all features in a category in the case of low confidence estimates under different levels of underestimation when the efforts required by each feature are independent (r = 0)
To understand what is happening, it suffices to look at Fig. 10 . Figure 10 .a shows histograms of the Must Have aggregated independent efforts for uncertainty levels of 50, 100 and 200%. Because of the relatively lower upper limit and the tightness of the distribution spread afforded by the sum of independent efforts, the 100% uncertainty distribution fits almost entirely to the left of the total budget, scoring this way a high PoD. A similar argument could be made for the 200% uncertainty level, except that this time, the distribution is almost entirely to the right of the total budget, thus yielding a very low PoD. As could be seen in Fig. 10 .b, when the efforts are correlated, the distributions spread more widely, making part of the 100% distribution fall to the right of the total budget line, reducing its PoD, and conversely, part of the 200% distribution might fall to the left of the line, thus increasing its PoD, which is what happened with this particular choice of parameter values.
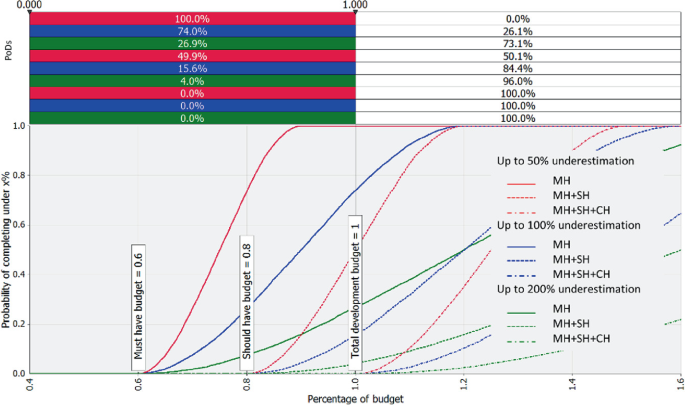
Probability of delivering all features in a category in the case of low confidence estimates under different levels of underestimation when the efforts required by each feature are highly correlated (r = 0.6)
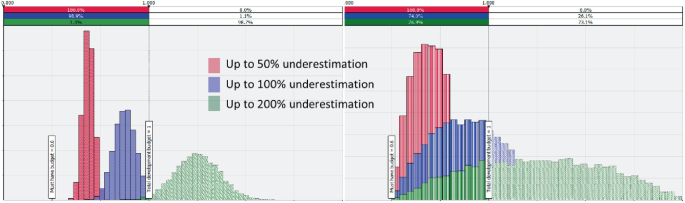
Histograms for Must Have features’ effort (a) left – independent efforts, (b) right – correlated efforts
6.3 Typical Estimates
Figures 11 and 12 show the typical estimates’ PoDs for uncorrelated and correlated efforts respectively. As expected, all the PoDs in this scenario are higher than in the case of the low confidence estimates. In the case of independent efforts, at up to 50% underestimation, the PoDs for the Must Have and the Should Have are 100%. At up to 100% underestimation, the PoD for the Must Have is 100% with the PoD for Should Have dropping to 39.7%. At up to 200% the probability of delivering all the Must Haves still high, at 70.5%, but there is no chance of delivering the Should Have. In no case, any Could Have were completed. For the correlated efforts case, the respective probabilities at 50% underestimation are: 100% for the Must Have, 88.7% for the Should Have and 20.6% for the Could Have. At 100% underestimation: 96.4, 50.3 and 8.6% respectively and at 200% underestimation: 59.8, 20.5 and 3%.
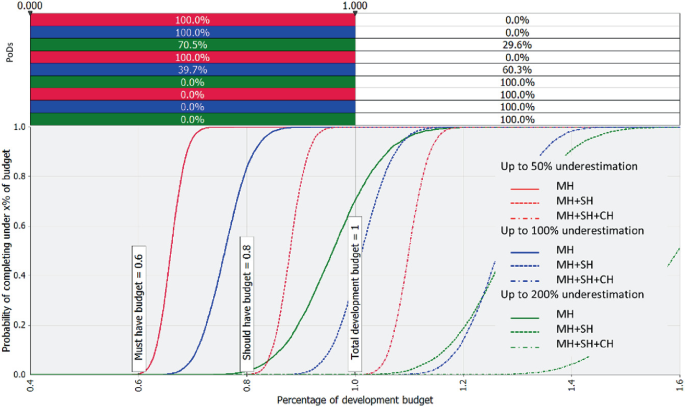
Probability of delivering all features in a category in the case of typical estimates under different levels of underestimation when the efforts required by each feature are independent (r = 0)
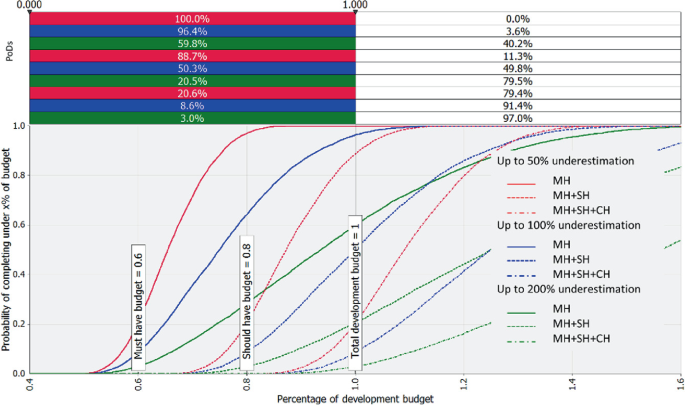
Probability of delivering all features in a category in the case of typical estimates under different levels of underestimation when the efforts required by each feature are highly correlated (r = 0.6).
This article sought to quantitatively answer the following questions:
What are the probabilities of delivering all the features in each of the categories: Must Have, Should Have and Could Have, under varying levels of under and overestimation of the features’ development efforts?
What is the influence of features’ sizes, feature dominance, number of features, and correlation between development efforts in said probabilities?
What is the effect of budget allocations other than the customary 60/20/20 on them?
To answer question 1, it is necessary to look at Table 1 which summarizes the results for the low confidence and typical estimates scenarios, for the three levels of underestimation studied: 50, 100 and 200%.
Not surprisingly, the results indicate that the method consistently yields a high PoD for the Must Have features. What is noteworthy, is its resilience in face of up to 100% underestimation of individual features in the category. For the Should Have, the results are robust for up to 50% of underestimation and with regards to the Could Have, they should only be expected if destiny is smiling upon the project.
Question 2 is important for practitioners preparing release plans. For the method to offer these levels of certainty, the number of features included in each category should be at least 5 with none of them requiring more than 25% of the effort allocated to the category. If these conditions are not met, the safety offered by the method drops sharply. Correlation, as mentioned before, is a mixed blessing. Depending on which direction things go, it can bring the only possibility of completing all the features in the project. Notice that in Table 1 , all the Could Have can only be completed when the efforts are highly correlated since all of them must be low. Under the independence assumption, when some could be low and others high, there is no chance of completing them on or under budget.
With regards to question 3, the 60, 20, 20% allocation seems to be the “Goldilocks” solution, balancing predictability with level of ambition. As shown by Fig. 7 , changing the allocation from 60 to 70%, has a dramatic impact on the safety margin which, at the up to 100% underestimation level, drops from 98.5 to 34%.
Finally, it is worth making clear, that the analysis refers to variations in execution times of planned work and not changes in project scope, which should be addressed differently.
The author gratefully acknowledges the helpful comments of Hakan Erdogmus. Diego Fontdevila and Alejandro Bianchi on earlier versions of this paper.
These preferences might induce dependencies that need to be addressed by the team, either by incorporating lower preference features in the higher categories or by doing additional work to mock the missing capabilities.
Worst case, means that if some of the assumptions associated with the scenario were to change, the probability of delivering within budget would increase.
@Risk by Palisade, Crystal Ball by Oracle, ModelRisk by Vose and Argo by Booz Allen among others.
Parkinson’s Law, the 1955 assertion by British economist Cyril Northcote Parkinson, that “Work expands so as to fill the time available for its completion”, regardless of what was strictly necessary.
Student Syndrome, a term introduced by Eliyahu M. Goldratt in his 1997 novel Critical Chain to describe the planned procrastination of tasks by analogy with a student leaving working in an assignment until the last day before its due date.
Agile Business Consortium: Chapter 10 MoSCoW Prioritization, January 2014. https://www.agilebusiness.org/page/ProjectFramework_10_MoSCoWPrioritisation . Accessed 10 Oct 2021
Cohn, M.: Agile Estimationg and Planning. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2006)
Google Scholar
Garvey, P.: Elements of Cost Risk Analysis. MITRE Corporation (2014)
Magennis, T.: Managing software development risk using modeling and Monte Carlo simulation. In: Lean Software and Systems Consortium Conference, Boston (2012)
Clegg, D., Baker, R.: CASE Method Fast-track: A RAD Approach. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1994)
Miranda, E.: Planning and Executing Time Bound Projects. IEEE Comput. (2002)
DSDM Consortium: Not longer accessible. http://www.dsdm.org/version4/2/public/default.asp
Shu-Cherng, F., Tsao, H.: Entropy optimization: shannon measure of entropy and its properties. In: Encyclopedia of Optimization, Springer, Boston (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-48332-7_119
Newby Clark, I., Buehler, R., Koehler, D., Griffin, D.: People focus on optimistic scenarios and disregard pessimistic scenarios while predicting task completion times. J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. (2000)
Halkjelsvik, T., Jørgensen, M.: Time Predictions: Understanding and Avoiding Unrealism in Project Planning and Everyday Life, Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74953-2
Kitchenham, B., Linkman, S.: Estimates, uncertainty and risk. IEEE Softw. (1997)
Hulett, D.: Practical Schedule Risk Analysis, Gower (2009)
Garvey, P., Book, S.C.R.: Probability Methods for Cost Uncertainty Analysis, 2nd. CRC Press (2016)
Kujawski, E., Edwards, W.R., Alvaro, M.L.: Incorporating psychological influences in probabilistic cost analysis. Syst. Eng. 7 (3) (2004)
Wake, B.: INVEST in Good Stories, and SMART Tasks. XP123, 17 8 (2003). https://xp123.com/articles/invest-in-good-stories-and-smart-tasks/ . Accessed 19 Nov 2021
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, 15213, USA
Eduardo Miranda
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Eduardo Miranda .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway
Viktoria Stray
University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
Klaas-Jan Stol
LUT University, Lahti, Finland
Maria Paasivaara
University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Philippe Kruchten
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s)
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Miranda, E. (2022). Moscow Rules: A Quantitative Exposé. In: Stray, V., Stol, KJ., Paasivaara, M., Kruchten, P. (eds) Agile Processes in Software Engineering and Extreme Programming. XP 2022. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 445. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08169-9_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08169-9_2
Published : 09 June 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-08168-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-08169-9
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Three Minute Thesis
The Three Minute Thesis (3MT®) competition challenges graduate students to present their thesis or dissertation topic in just three minutes + one slide.
An 80,000 word PhD thesis would take 9 hours to present. Their time limit... 3 minutes.
The Three Minute Thesis competition cultivates students’ academic, presentation and research communication skills, and celebrates exciting graduate research taking place at Boise State.
Winning participants earn the opportunity to move on to the statewide Three Minute Thesis competition, where they compete with graduate students from University of Idaho and Idaho State University.
About the 3MT
Learn more about the competition below!
Participant Information
Participants of the 3MT competition will be judged based on the following:
Communication Style: Was the thesis topic and its significance communicated in language appropriate to a non-specialist audience?
Comprehension: Did the presentation help the audience to understand the research?
Engagement: Did the oration make the audience want to know more?
Participants contend for first, second, and third place awards as determined by a panel of judges from the Boise community. Students are also eligible to win an audience choice award based on audience votes.
First Place: $750 Second Place: $500 Third Place: $250 Audience Choice: $250
3MT at Boise State
The Graduate College would like to congratulate the winners of Boise State’s 2024 3MT Finals and wish them luck at the 2024 Statewide 3MT competition.
- First Place : Haley Bridgewater – Biomolecular Sciences, Ph.D.
- Second Place : Jianna Gimenez – Master of Public Health
- Third Place : Matt Peck – Counselor Education and Supervision, Ph.D.
- Audience Choice : Caleb Merritt – Creative Writing, M.F.A.
The 2024 3MT Finals were held on January 24th, from 1:00 to 3:00 p.m., in the Simplot Ballroom in the SUB.
2024 Finals Competitors
2024 judging panel and criteria, evolution of the boise state 3mt, 2023 statewide three minute thesis.
On February 7, 2023, graduate students from Boise State, Idaho State, and University of Idaho competed in the Idaho Three Minute Thesis competition to each present their research in three minutes or less. Boise State competitors brought home first and second place!
First Place: Adrian Rodriguez — Master of Public Health
Second Place: Bridget Bittmann — Hydrologic Sciences, M.S.
Boise State Competitors
Statewide three minute thesis website, origin of the 3mt, 2023 wags annual conference.
Western Association of Graduate Schools (WAGS) Annual Conference 3MT Competition.

The Three Minute Thesis Competition brings together some of the most significant research being conducted by graduate students today. Graduate students have three minutes and one slide to distill their thesis or dissertation into a compelling pitch for the audience. Boise State Graduate Student Adrian Rodriguez, a member of the Master of Public Health program, took home second place at the 2023 Western Association of Graduate Schools (WAGS).
Previous 3MT Competitions
History of the 3mt.
The Three Minute Thesis competition was developed by the University of Queensland and celebrates the exciting research conducted by graduate students. The first 3MT® competition was held in 2008, and now the competition is held in over 600 universities across more than 65 countries worldwide.
The competition cultivates student’s academic, presentation, and research communication skills, and helps graduate students to effectively explain their research in a language appropriate to a non-specialist audience.
In spring of 2016, the Graduate College hosted the first Boise State University Three Minute Thesis competition.
2024 Award Winners
2023 award winners.
- First Place: Adrian Rodriguez – Master of Public Health
- Second Place: Bridget Bittmann – Hydrologic Sciences, M.S.
- Third Place: Kym Couch – Public Policy and Administration, Ph.D.
- Audience Choice: Ashley Leavell – Biology, M.S.
2022 Award Winners
- First Place: Dalton Miller – Chemistry, M.S.
- Second Place: Jessica Bernardin – Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior, Ph.D.
- Third Place: Jacob Manzi – Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ph.D.
- Audience Choice: Rebecca Miller – Materials Science and Engineering, Ph.D.
2021 Award Winners
- First Place: Luke Tellers — Hydrologic Sciences, MS
- Second Place: Ember Sikorski — Materials Science and Engineering, PhD
- Third Place: Sam Haskell — Communication, MA
- Audience Choice: Bryan Rosenblatt — Geophysics, MS
2020 Award Winners
- First Place: Rachel Phinney – Health Promotion, MHS
- Second Place: Lisa Roggenbuck – Visual Arts, MFA
- Third Place: Allison Borzoni – English, Rhetoric and Composition, MA
- Third Place: Cristina Barber Alvarez-Buylla – Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior, PhD
- Audience Choice: Sherise Porchia – Counseling, MA
2019 Award Winners
- First Place: Alexander Regner – Materials Science and Engineering, MS
- Second Place: Roxanne Stone – Interdisciplinary Studies, MS
- Third Place: Nick Pollock – Geosciences, PhD
- Audience Choice: Vannessa Campfield – Chemistry, MS
- Audience Choice: Rezvan Joshaghani – Computer Science, MS
2018 Award Winners
- First Place: Sepideh Rastegar – Electrical and Computer Engineering, PhD
- Second Place: AuraLea Fain – Kinesiology, MS
- Audience Choice: Nikki Cannon – Communication, MA

Previous Competition Videos
View Past Boise State 3MTs
Graduate Student Success Center
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
The MoSCoW method for prioritization: A guide for agile teams

In the messy world of technology, there is an immeasurable demand for the resources from product and development teams. This is where prioritization comes into play.

Prioritization is one of the core responsibilities of the product manager. With the proper prioritization framework and/or criteria, the product manager can save their team resources while moving closer to the business goals.
In this article, we will dive deep into one of the most widely used prioritization techniques, the MoSCoW method.
What is the MoSCoW method?
The MoSCoW method (also known as MoSCoW analysis) is one of many qualitative prioritization techniques used to prioritize features, user stories, and requirements.
The MoSCoW method groups the features into four groups:
- Should-have
- Could-have (or nice-to-have)
1. Must-have
Features or stories are critical for the product’s success. These features represent the non-negotiables which, if not implemented successfully, might put the product at risk of failing.
For example, let’s say you are the PM of a university’s e-learning system. A must-have feature might be the assignment submission feature because it serves a primary and essential need for both ideal customer profiles.
2. Should-have
This classification represents the features that are important, but not as crucial as the must-haves. These features, if not implemented, can cause a severe risk to the product’s success, but their risk is lower than the must-haves.
Typically, product teams use this classification for minor bug fixes and/or performance improvement initiatives.
Returning to our example, a should-have feature for our e-learning system might be an integrated plagiarism tool for teachers to use. This can be a should-have because it would not stop the teachers from doing their work, but not implementing it might lead them to churn and move to other platforms that save them time.
3. Could-have (or nice-to-have)
This classification represents desirable features that are not important to the core function of the product. Not implementing this feature will not cause any risk or failure.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Could-have features might help your product or do nothing at all. Features that are tagged with the could-have classification end up deprioritized and treated as a sprint filler.
For our e-learning, one feature could be the ability for the teachers to message other students through the platform. This is nice-to-have because this problem is typically dealt with through email and other platforms.
4. Won’t-have
This classification represents features that are not aligned with the vision and the strategy of the product. These are the features requested by other departments or stakeholders, but are entirely irrelevant.
If we were to reflect this in our e-learning example, this might be a feature that enables teachers to develop a curriculum collaboratively on the platform. This feature is a won’t-have because it doesn’t align with the vision of the product because the product is intended to mainly serve the students.
MoSCoW prioritization template
The MoSCoW prioritization method can be used to prioritize both the product backlog and the sprint backlog . This tells engineers what they need to deliver first and gives them an idea of what task could potentially spill over into the next sprint.
Below is a simple template that can get you up and running with the MoSCoW prioritization technique:
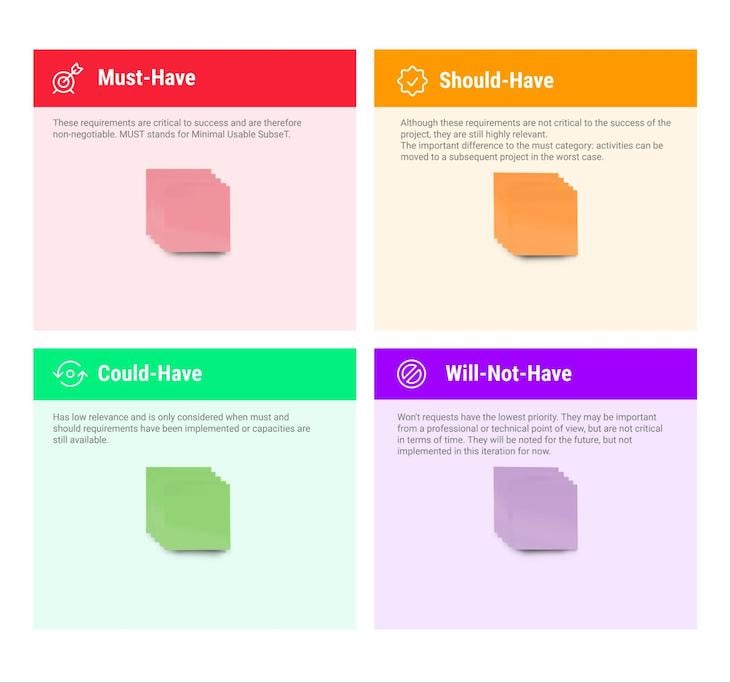
History of the MoSCoW method
The MoSCoW method was introduced first in 1994 by Dai Clegg , a British business consultant and software engineer.
Clegg was working on a software project with the British government and was looking for a method to prioritize the system requirements based on their urgency and criticality. He came up with the MoSCoW method to rank and prioritize the features and ensure the right investments were put into the top features.
How to use the MoSCoW prioritization method (5 steps)
Using the MoSCoW in the real world is more than tagging features with four different tags. It requires additional steps to ensure the proper prioritization is put into place and that features align with your stakeholders.
To apply the MoSCoW prioritization method in product management, take the following steps:
1. Groom your features
It is always a best practice to start by listing your features in your product backlog. Add some details to them like the basic idea of the feature, some simple user flows, and wireframes, and meet with your engineers/technical navigators, or system analysts to check on the technical feasibility and the edge cases.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
2. Prioritize initially
After you have all of your features groomed, start prioritizing them. Classify them into must-have, should-have, could-have, and won’t-have. Prioritize based on the available resources and insights gathered from any user research and product analytics.
3. Align with your stakeholders
Present your initial priority to your stakeholders. Gather their input and try to persuade them of your priority based on the insights and the data you have.
Don’t leave the meeting without alignment on the priority of each feature. The outcome of the meeting should be a prioritized list agreed on by each and every stakeholder.
4. Adjust your roadmap and announce
After finalizing the backlog, make sure to give it a final review and announce it publicly using your internal roadmap and any communication channel that includes all the stakeholders.
5. Communicate continuously
We are in the agile era . That means we should embrace change and understand that changes happen all the time.
A feature that is a could-have in this quarter might be a must-have in the next one. So make sure to communicate changes in the business and feature priorities continuously with your stakeholders.
Ensure all the related documents, like the roadmap and the backlog , are updated accordingly and on a timely basis to avoid any miscommunication and to make sure that everyone is aligned on the timeline and the priorities.
Final thoughts
The MoSCoW method is one of the most powerful and widely used prioritization techniques worldwide. It helps classify features and initiatives into four groups.
For the MoSCoW method to be applied effectively and deliver the intended value, it should include a lot of stakeholder alignment and involvement. The product manager should dedicate more time to the must-have features to come up with a killer solution that helps solve the major problem for the users.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #prioritization

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

A day in the life of a product manager with schedule
As a PM yourself, you know how difficult and multifaceted the role can be. You need to talk with customers and work on design simultaneously.

Understanding zero-to-one product development
Zero-to-one is all about creating something new. Move beyond iterations and build groundbreaking products that lead to entirely new markets.

Understanding subscriber acquisition cost
Subscriber acquisition cost (SAC) refers to the total expense incurred by the business to acquire a new customer or subscriber.

How simplifying our sales funnel led to a 30 percent lift in conversion to paid users
Although we did a good job moving people to the checkout page, we had problems converting checkout visitors to paying customers.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What is your plagiarism score?
Ten Scholars Recognized for the 16th Annual Student and Early Career Council Dissertation Research Funding Awards
SRCD congratulates the 2024 Student and Early Career Council Dissertation Funding Awardees.
Established in 2008 by the SRCD Student and Early Career Council (SECC) , the Dissertation Research Funding Awards (DFAs) are given to dissertation research proposals that are exceptionally noteworthy and display a strong potential to contribute to the field of child development. Each recipient is awarded $2,000 USD to use for research costs related to the proposed dissertation project.
SRCD is pleased to recognize the following ten scholars as the 2024 awardees: Samantha Basch , Inés Botto , Linyun Fu , Emma Hart , Yan Jiang , Virnaliz Jimenez , Taehee Kim , Elizabeth Perkovich , Sofia Sebben Colognese , Lucinda Sisk
Given the strength and quality of their applications, SRCD would also like to recognize the following five 2024 Honorable Mentions: Johana Bernard, Kaitlyn Pritzl, Gayane Baziyants, Minci Zhang, Qinyang Liu

Samantha Basch, University of California Santa Cruz
"Supporting Learning in the Second Year of life: Language, Culture, and Context"
Samantha Basch is a doctoral candidate in the Department of Psychology at the University of California, Santa Cruz, working under the mentorship of Dr. Su-hua Wang. Her research integrates cognitive and sociocultural frameworks to highlight the strengths young children and their families bring to learning. Specifically, she examines caregiver-child language in diverse contexts to understand how cultural practices foster cognitive development. Overall, her goal is to advance ecologically valid and culturally inclusive understandings of cognitive development in infancy and early childhood. Samantha’s dissertation investigates how mothers use different types of language to support learning in various home activities, focusing on how parental ethnotheories are expressed through language practices. This mixed-methods study involves naturalistic home observations of mothers with their 12- to 24-month-old infants collected as part of the PLAY project. Observations are followed by video-cued interviews, where participants watch and comment on videos of mother-child interactions to prompt reflections on cultural practices. The project aims to offer a nuanced view of how culture influences parenting, emphasizing the role of context and within-culture variation in approaches to early childhood learning.

Inés Botto, University of Wisconsin-Madison
“White Children’s Racial Learning in Contexts of Resistance: A Grounded Theory Study”
Inés Botto is a doctoral candidate in the Department of Human Development and Family Studies at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, under the mentorship of Dr. Margaret Kerr. Her research focuses on white children’s understanding of themselves as racialized actors, and their participation in their own racial socialization. Inés’ dissertation will explore young white children’s racial learning within white families who adopt intentional efforts to raise children committed to racial justice. Specifically, her study asks, 1) What understandings about race, personal racial identity, and racism do white children construct when raised in these contexts? 2) How are their understandings informed by the racial socialization practices enacted by their parents? and 3) How do these understandings reinforce or resist hegemonic narratives of race and whiteness? Inés hopes to use the findings that emerge from this study as a basis for future research exploring what moves white individuals from a state of ignorance or ambivalence about racial inequality, and towards a sense of responsibility for racial justice from the earliest stages of development.

Linyun Fu, University of Chicago
“Exploring the Dynamics of a Culturally Sensitive School-Based Social-Emotional Learning Program for Rural Chinese Children: Evaluating Effectiveness, Mediators, and Moderators”
Linyun Fu is a doctoral candidate in social work at the University of Chicago, where she is mentored by Dr. Curtis McMillen and works with Dr. Leyla Ismayilova. As a first-generation college student who grew up in a rural village in China, Linyun is passionate about developing and examining culturally sensitive prevention and intervention strategies for marginalized children in specific cultural contexts. She holds a particular interest in the impact of culturally grounded or adapted Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) programs for minoritized children. She has been a community-engaged researcher for over six years, working closely with the RICI Foundation, an NGO in China through supporting their SEL program development and program evaluation to promote rural children’s well-being. In partnership with the education bureau, her dissertation adopts a matched-pair, cluster-randomization design in a southwest county of China and seeks to: 1) assess the effectiveness of an 18-session culturally sensitive SEL program, co-developed with local experts, in enhancing rural children’s social-emotional competencies, reducing internalizing and externalizing behaviors, and improving educational outcomes; 2) investigate the mechanisms underlying the program's impact; and 3) identify subgroups of children who benefit most from the intervention. The findings from her dissertation have the potential to inform a large-scale initiative led by local governments to improve educational and emotional outcomes for marginalized children.

Emma Hart, Columbia University
“Understanding Child Skill Development by Examining Longitudinal Educational Intervention Impacts”
Emma Hart is a doctoral candidate in Developmental Psychology at Teachers College, Columbia University mentored by Drs. Tyler Watts and Kimberly Noble. Her research examines the role that early skills and contexts play in shaping later development. To this end, she studies the short-term and long-term effects of interventions that experimentally aim to modify these early influences. Her work has primarily focused on programs designed to support children experiencing poverty. Her dissertation investigates two unexpected patterns that have emerged from longitudinal intervention evaluations: 1) While interventions often improve child skills in the short term, these effects commonly fade over time, and 2) Despite this fadeout, some interventions have long-term effects on important adult outcomes. Using three unique datasets and meta-analytic methods, Emma’s dissertation seeks to identify the extent to which fadeout and emergence are broadly observed and whether we can forecast when programs are likely to have long-run effects. In doing so, she hopes to test the plausibility of skill-building processes that have been theorized to explain the fadeout-emergence paradox and child skill development more generally. The findings from her work have the potential to refine developmental theory and shape policymakers’ investments in programs most likely to benefit children and families.

Yan Jiang, University of California San Diego
“Reimagining Conceptions of Quality in Early Childhood Education and Care in Diverse Societies: A Comparative Analysis Leveraging Computational Methods Leveraging Computational Methods”
Yan Jiang is a doctoral candidate in Education Studies at the University of California, San Diego, under the mentorship of Dr. Alison Wishard Guerra and Dr. Amanda Datnow. Her research centers on promoting equitable access to high-quality early childhood education and redefining “high-quality” within a global context. As a methodology enthusiast, Yan applies computational social science techniques to social science research, devising innovative approaches to address pressing issues. Her dissertation, conducted in two phases, reimagines conceptions of quality in early childhood education and care (ECEC) across diverse societies. The first phase critically and computationally analyzes global ECEC quality research, identifying potential gaps where non-Western, non-middle-class perspectives may be marginalized. The second phase uses a comparative case study to explore educators’ perceptions of quality in preschools serving lower-income families in the U.S. and China, aiming to uncover how sociocultural contexts shape these perceptions. Yan’s findings will contribute to the theoretical, methodological, and practical dimensions of ECEC quality research, promoting a more equitable and inclusive understanding of ECEC quality and offering actionable insights for policymakers and educators.

Virnaliz Jimenez, University of Illinois Urbana Champaign
“Cultural Values and Parental Socialization of Coping in Latine Families: Implications for Adolescent Mental Health”
Virnaliz is a doctoral candidate in Human Development and Family Studies at the University of Illinois Urbana Champaign. She works with Dr. Kelly Tu in the Adolescent Development and Parenting during Transitions (ADAPT) lab. Virnaliz’s research focuses on how culture and parenting practices influence the ways that adolescents cope with stress. Her dissertation uses grounded theory methods to explain parent socialization of coping and youth coping processes among Latine families. She examines these processes within interpersonal and academic domains. Findings from her study will contribute to a better understanding of the cultural values that may influence parents’ socialization of coping and Latine youth coping with implications for their mental health. Moreover, knowledge gleaned can inform community interventions aimed at improving coping and mental health among Latine youth.
Virnaliz is also passionate about conducting community engaged research. She has partnered with a Latine parent organization in Illinois to disseminate findings to their network of parents. Her long-term career goal is to become a respected researcher focusing on promoting health equity and improving outcomes for underserved communities. She aims to contribute to evidence-based interventions and programs that support youth and families from diverse backgrounds.

Taehee Kim
“Role of School and Family Contexts in Shaping Parents’ and Teachers’ Perspectives on Social Skills”
Taehee Kim is a doctoral candidate in the Applied Cognition and Development program at the University of Georgia, under the mentorship of Dr. Kristen L. Bub. Her research centers on improving the measurement and development of social-emotional skills in middle childhood by examining the unique perspectives of parents and teachers. In her mixed-method dissertation, Taehee aims to (1) identify patterns of agreement and disagreement between parents and teachers regarding children’s social skills, (2) explore the contextual factors within families and schools that contribute to their differing views on children's social skills, and (3) delve into the experiences of parents and teachers when communicating their perspectives on social skills. Findings from her dissertation will help expand our understanding of the variations in parents' and teachers' views on social skills and the potential sources of these differing perspectives, thereby improving the quality of discussions about social skills and fostering school-family collaboration in social skill development. Ultimately, Taehee hopes to understand how cultural and linguistic backgrounds influence parent and teacher perspectives and communication about social skills, with the goal of promoting more equitable social-emotional development.

Elizabeth Perkovich, University of Houston, Texas
“How Parents Scaffold Joint Attention For Infants at High and Low Familial Likelihood for Autism”
Elizabeth Perkovich is a doctoral student in the Developmental, Cognitive, and Behavioral Neuroscience program at the University of Houston, Texas, under the mentorship of Dr. Hanako Yoshida in the Cognitive Development Lab. Broadly, her research uses head-mounted eye-tracking during parent-child social interaction to explore the influence of parental social scaffolding behaviors on children's dynamic visual experiences, particularly among families from diverse backgrounds. Her dissertation will use head-mounted eye-tracking among infants with and without a family history of autism to explore: (1) differences in joint attention, (2) differences in parental social scaffolding behaviors, and (3) how parental social scaffolding relates to joint attention as a function of infant familial group. The findings of this project will offer novel insights into the early perceptual and social environments that shape early joint attention behaviors. These insights will serve as a crucial foundation for designing evidence-based interventions tailored to increasing joint attention within play contexts. Furthermore, the results of this unique methodology can provide a new framework for how parents influence early social attention and enhance the ecological validity of using head-mounted eye-tracking among neurodivergent populations.

Sofia Sebben Colognese, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul
“Parental Reflective Functioning and Child Emotional Regulation in the Context of Screen Use in Childhood”
Sofia is a doctoral candidate in Psychology at the Psychology Graduate Program from Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul in southern Brazil. She works under the guidance of Dr. Giana Frizzo in Brazil with co-supervision from Dr. Caroline Fitzpatrick of the Université de Sherbrooke, Canada. Committed to the importance of fostering healthy and happy childhoods, Sofia is dedicated to exploring topics related to child development and family dynamics across various contexts. Her personal and academic experiences intersect with the rise of digital technology, leading her to investigate its implications for early childhood. Adopting an ecological approach to understand development, Sofia’s dissertation employs quantitative and qualitative methodologies to investigate young children's screen usage and its interaction with parental and child factors. Her aim is to leverage these findings to drive the development of evidence-based early childhood programs and policies that protect children's emotional well-being and assist parents in managing the complexities of parenting in the digital age. Sofia also intends to integrate academic insights into her future practice with children and families, thereby bridging research and practical applications to foster child development.

Lucinda Sisk, Yale University
“The Role of Adversity Exposure Timing in Shaping Youth Neurodevelopment and Mental Health”
Lucinda Sisk is a Ph.D. candidate in Neuroscience at Yale University, where she is mentored by Dr. Dylan Gee in the Clinical Affective Neuroscience and Development Lab. Lucinda’s program of research is centered on characterizing how the childhood environment, particularly adversity, influences neurodevelopment and risk for future psychopathology. While adversity can increase risk for psychopathology, there is tremendous heterogeneity in outcomes, potentially related to differential effects of adversity depending on the state of the developing brain. Lucinda’s dissertation research seeks to parse this heterogeneity by leveraging multivariate statistical approaches to examine how the timing of early life adversity exposure may inform individual variation in adversity-related changes in neurodevelopment and risk for, and resilience against, future psychopathology. Lucinda’s long-term aim is to enhance mechanistic understanding of individual variation in the effects of adversity on the developing brain, which may one day be applied to improve treatment and intervention options for youth exposed to adversity.
Honorable Mentions
Johanna Bernard, University of Pennsylvania “Understanding the Conditions and Contexts that Shape Skill Development in Childhood”
Kaitlyn Pritzl, University of Wisconsin - Madison “Parent-Child Contact During Parental Incarceration: Implications for Individual and Family Well-Being”
Gayane Baziyants, Duke University “The Impact of an Annual Unconditional Cash Transfer on Child Maltreatment Rates Among American Indian and Alaska Native Children”
Minci Zhang, University of Southern California “Peer Relationships Across Cultures”
Qingyang Liu, Syracuse University “Identifying heterogeneity in the Material Hardship Domains and Children’s Development of Behavioral Self-Regulation: A Multidimensional Person-Centered Approach”
- Integrations
- Learning Center
MoSCoW Prioritization
What is moscow prioritization.
MoSCoW prioritization, also known as the MoSCoW method or MoSCoW analysis, is a popular prioritization technique for managing requirements.
The acronym MoSCoW represents four categories of initiatives: must-have, should-have, could-have, and won’t-have, or will not have right now. Some companies also use the “W” in MoSCoW to mean “wish.”
What is the History of the MoSCoW Method?
Software development expert Dai Clegg created the MoSCoW method while working at Oracle. He designed the framework to help his team prioritize tasks during development work on product releases.
You can find a detailed account of using MoSCoW prioritization in the Dynamic System Development Method (DSDM) handbook . But because MoSCoW can prioritize tasks within any time-boxed project, teams have adapted the method for a broad range of uses.
How Does MoSCoW Prioritization Work?
Before running a MoSCoW analysis, a few things need to happen. First, key stakeholders and the product team need to get aligned on objectives and prioritization factors. Then, all participants must agree on which initiatives to prioritize.
At this point, your team should also discuss how they will settle any disagreements in prioritization. If you can establish how to resolve disputes before they come up, you can help prevent those disagreements from holding up progress.
Finally, you’ll also want to reach a consensus on what percentage of resources you’d like to allocate to each category.
With the groundwork complete, you may begin determining which category is most appropriate for each initiative. But, first, let’s further break down each category in the MoSCoW method.
Start prioritizing your roadmap
Moscow prioritization categories.

1. Must-have initiatives
As the name suggests, this category consists of initiatives that are “musts” for your team. They represent non-negotiable needs for the project, product, or release in question. For example, if you’re releasing a healthcare application, a must-have initiative may be security functionalities that help maintain compliance.
The “must-have” category requires the team to complete a mandatory task. If you’re unsure about whether something belongs in this category, ask yourself the following.

If the product won’t work without an initiative, or the release becomes useless without it, the initiative is most likely a “must-have.”
2. Should-have initiatives
Should-have initiatives are just a step below must-haves. They are essential to the product, project, or release, but they are not vital. If left out, the product or project still functions. However, the initiatives may add significant value.
“Should-have” initiatives are different from “must-have” initiatives in that they can get scheduled for a future release without impacting the current one. For example, performance improvements, minor bug fixes, or new functionality may be “should-have” initiatives. Without them, the product still works.
3. Could-have initiatives
Another way of describing “could-have” initiatives is nice-to-haves. “Could-have” initiatives are not necessary to the core function of the product. However, compared with “should-have” initiatives, they have a much smaller impact on the outcome if left out.
So, initiatives placed in the “could-have” category are often the first to be deprioritized if a project in the “should-have” or “must-have” category ends up larger than expected.
4. Will not have (this time)
One benefit of the MoSCoW method is that it places several initiatives in the “will-not-have” category. The category can manage expectations about what the team will not include in a specific release (or another timeframe you’re prioritizing).
Placing initiatives in the “will-not-have” category is one way to help prevent scope creep . If initiatives are in this category, the team knows they are not a priority for this specific time frame.
Some initiatives in the “will-not-have” group will be prioritized in the future, while others are not likely to happen. Some teams decide to differentiate between those by creating a subcategory within this group.
How Can Development Teams Use MoSCoW?
Although Dai Clegg developed the approach to help prioritize tasks around his team’s limited time, the MoSCoW method also works when a development team faces limitations other than time. For example:
Prioritize based on budgetary constraints.
What if a development team’s limiting factor is not a deadline but a tight budget imposed by the company? Working with the product managers, the team can use MoSCoW first to decide on the initiatives that represent must-haves and the should-haves. Then, using the development department’s budget as the guide, the team can figure out which items they can complete.
Prioritize based on the team’s skillsets.
A cross-functional product team might also find itself constrained by the experience and expertise of its developers. If the product roadmap calls for functionality the team does not have the skills to build, this limiting factor will play into scoring those items in their MoSCoW analysis.
Prioritize based on competing needs at the company.
Cross-functional teams can also find themselves constrained by other company priorities. The team wants to make progress on a new product release, but the executive staff has created tight deadlines for further releases in the same timeframe. In this case, the team can use MoSCoW to determine which aspects of their desired release represent must-haves and temporarily backlog everything else.
What Are the Drawbacks of MoSCoW Prioritization?
Although many product and development teams have prioritized MoSCoW, the approach has potential pitfalls. Here are a few examples.
1. An inconsistent scoring process can lead to tasks placed in the wrong categories.
One common criticism against MoSCoW is that it does not include an objective methodology for ranking initiatives against each other. Your team will need to bring this methodology to your analysis. The MoSCoW approach works only to ensure that your team applies a consistent scoring system for all initiatives.
Pro tip: One proven method is weighted scoring, where your team measures each initiative on your backlog against a standard set of cost and benefit criteria. You can use the weighted scoring approach in ProductPlan’s roadmap app .
2. Not including all relevant stakeholders can lead to items placed in the wrong categories.
To know which of your team’s initiatives represent must-haves for your product and which are merely should-haves, you will need as much context as possible.
For example, you might need someone from your sales team to let you know how important (or unimportant) prospective buyers view a proposed new feature.
One pitfall of the MoSCoW method is that you could make poor decisions about where to slot each initiative unless your team receives input from all relevant stakeholders.
3. Team bias for (or against) initiatives can undermine MoSCoW’s effectiveness.
Because MoSCoW does not include an objective scoring method, your team members can fall victim to their own opinions about certain initiatives.
One risk of using MoSCoW prioritization is that a team can mistakenly think MoSCoW itself represents an objective way of measuring the items on their list. They discuss an initiative, agree that it is a “should have,” and move on to the next.
But your team will also need an objective and consistent framework for ranking all initiatives. That is the only way to minimize your team’s biases in favor of items or against them.
When Do You Use the MoSCoW Method for Prioritization?
MoSCoW prioritization is effective for teams that want to include representatives from the whole organization in their process. You can capture a broader perspective by involving participants from various functional departments.
Another reason you may want to use MoSCoW prioritization is it allows your team to determine how much effort goes into each category. Therefore, you can ensure you’re delivering a good variety of initiatives in each release.
What Are Best Practices for Using MoSCoW Prioritization?
If you’re considering giving MoSCoW prioritization a try, here are a few steps to keep in mind. Incorporating these into your process will help your team gain more value from the MoSCoW method.
1. Choose an objective ranking or scoring system.
Remember, MoSCoW helps your team group items into the appropriate buckets—from must-have items down to your longer-term wish list. But MoSCoW itself doesn’t help you determine which item belongs in which category.
You will need a separate ranking methodology. You can choose from many, such as:
- Weighted scoring
- Value vs. complexity
- Buy-a-feature
- Opportunity scoring
For help finding the best scoring methodology for your team, check out ProductPlan’s article: 7 strategies to choose the best features for your product .
2. Seek input from all key stakeholders.
To make sure you’re placing each initiative into the right bucket—must-have, should-have, could-have, or won’t-have—your team needs context.
At the beginning of your MoSCoW method, your team should consider which stakeholders can provide valuable context and insights. Sales? Customer success? The executive staff? Product managers in another area of your business? Include them in your initiative scoring process if you think they can help you see opportunities or threats your team might miss.
3. Share your MoSCoW process across your organization.
MoSCoW gives your team a tangible way to show your organization prioritizing initiatives for your products or projects.
The method can help you build company-wide consensus for your work, or at least help you show stakeholders why you made the decisions you did.
Communicating your team’s prioritization strategy also helps you set expectations across the business. When they see your methodology for choosing one initiative over another, stakeholders in other departments will understand that your team has thought through and weighed all decisions you’ve made.
If any stakeholders have an issue with one of your decisions, they will understand that they can’t simply complain—they’ll need to present you with evidence to alter your course of action.
Related Terms
2×2 prioritization matrix / Eisenhower matrix / DACI decision-making framework / ICE scoring model / RICE scoring model
Prioritizing your roadmap using our guide
Talk to an expert.
Schedule a few minutes with us to share more about your product roadmapping goals and we'll tailor a demo to show you how easy it is to build strategic roadmaps, align behind customer needs, prioritize, and measure success.
Share on Mastodon
- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- Partner Content
- Web Stories
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
US Fed rate cut: How leading brokerages interpret the development
Us fed rate cut: policymakers, according to reports, expect the fed's benchmark to fall another half of a percentage point by 2024-end, and another one per cent in 2025.
)
Imaging: Ajay Mohanty
More From This Section
)
Market Highlights, Sept 19: Sensex, Nifty end at record closing high after US Fed announces rate cut
)
Nifty to gain upside momentum above 25,500; MphasiS, OFSS see short buildup
)
Dividend, Bonus, Split: RITES, NALCO, 121 others stocks go ex-date tomorrow
)
US Fed cuts 50 bps rate: Here're key takeaways from Jerome Powell statement
)
Asian stocks and dollar gain as Fed Reserve charts 'soft landing' path
Here's how leading brokerages have interpreted fed's move., rabobank international, nilesh shah, md, kotak mahindra amc, dhiraj relli, md & ceo at hdfc securities, geojit financial services, raghvendra nath, md, ladderup wealth management.
)
Gold, Equities, Oil, Bonds: What next for these assets after Fed rate cut?
)
Vodafone Idea shares tank 20%, Indus Towers 14% after SC rejects AGR plea
)
Tactically cautious on India, Fed rate cut quantum a surprise: Chris Wood
)
Mid, SmallCap indices bleed; US Fed's rate cut to blame? Analysts weigh
)
DCX Systems bags Rs 155-cr order from Israeli defence co; stock rises 5%
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: Sep 19 2024 | 9:45 AM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Reliance shares
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- ICC T20 World Cup 2024 Business Standard at 50 Paralympics 2024 Jammu Kashmir Elections 2024 Haryana Elections 2024 Happy Ganesh Chaturthi Wishes

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Latest Business Dissertation Topics. Topic 1: Impact of digital business on the economic growth of the country: A case study of XYZ country. Topic 2: Brand Marketing through social media. Topic 3: Impacts of social media on customer behaviour.
Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. If you've landed on this post, chances are you're looking for a business/management-related research topic, but aren't sure where to start.Here, we'll explore a variety of research ideas and topic thought-starters for management ...
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Leadership and Innovation Business Dissertation Topics. Innovation has become a primary force driving the growth, performance, and valuation of companies. However, sometimes there is a wide gap between the aspirations of executives to innovate and their ability to execute. Many companies make the mistake of trying to spur innovation by turning ...
Theses and dissertations published by graduate students in the Business Administration program, College of Business, Old Dominion University, since Fall 2016 are available in this collection. ... and Development, Adam Smith. Theses/Dissertations from 2014 Dissertation: An Empirical Examination of the Antecedents and Consequences of Earnings ...
Unique Business Management Dissertation Topics. Coordinating communications and teamwork among remote workers. How business attract their customers. Artificial intelligence investment and its effect on customer satisfaction. Impact of globalisation on corporate management. Customer viewpoint on how they use their data when using mobile banking.
This PhD thesis examines the dynamics of supply chain relationships across three levels: the interactions between firms and consumers, suppliers and buyers, and firms and governments. The research aims to provide insights into the complexities of supply chain dynamics and their implications for various stakeholders. Download Example.
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic. The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development ...
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
The diploma thesis deals with the company development through investments into new technologies of production facilities and business development. In the theoretical part the main concepts which form the structure of the business plan are defined. In the next section the actual situation of the company is analyzed.
The dissertation is the final requirement for the PhD degree. The research required for the dissertation must be of publishable quality and a significant contribution in a scholarly field. The dissertation is evidence of the candidate's proficiency and future potential in research. Students work closely with faculty throughout the program ...
Dissertation: Into the Family and Business Nexus: Succession and Daughters in Family Owned Businesses; Kevin Roots, DM Dissertation: Executive Leader Development: Mentoring in U.S. Government and Commercial Organizations; Lise Anne Slatten, DM Dissertation: An Examination of the Antecedents and Consequences of Accreditation in the Nonprofit Sector
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
Dongol Rina Neupane Basudha. ning: A Key to Successful EnterprisesYear 2014 Pages 38The main objective. of this thesis is to have knowledge of prope. business plan. Business plan is a backbone of any business. It is crucial to lay down the aims of the business plan; mission, goals, tasks an. action plan of the business plan clearly into the ...
The dissertation topic ideas in this category often examine the connection between global business and global politics. As an area that has been volatile for years, this sector evaluates institutions, processes and factors that influence businesses and politics. Here are some topic ideas to consider: Strategy, structure, fit, and performance in ...
Master thesis one year 15hp BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT IN A GROWTH PERSPECTIVE- BARRIERS TO GROWTH IN SMEs Authors: Fredrik Lemar & Najmoddin Nekzada Supervisor: Kiflemariam Hamde . Acknowledgements First of all we want to thank our supervisor Kiflemariam Hamde who in a professional way provided many useful insights to our thesis. ...
A Complete Dissertation The Big Picture OVERVIEW Following is a road map that briefly outlines the contents of an entire dissertation. This is a comprehensive overview, and as such is helpful in making sure that at a glance you understand up front the necessary elements that will constitute each section of your dissertation.
MoSCoW rules [], also known as feature buffers [], is a popular method to give predictability to projects with incremental deliveries.The method does this by establishing four categories of features: Must Have, Should Have, Could Have and Won't Have, from where the MoSCoW acronym is coined.Each of the first three categories is allocated a fraction of the development budget, typically 60, 20 ...
Abstract or executive summary. The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report - in other words, it should be able to ...
The Three Minute Thesis competition was developed by the University of Queensland and celebrates the exciting research conducted by graduate students. The first 3MT® competition was held in 2008, and now the competition is held in over 600 universities across more than 65 countries worldwide.
The MoSCoW method is one of the most powerful and widely used prioritization techniques worldwide. It helps classify features and initiatives into four groups. For the MoSCoW method to be applied effectively and deliver the intended value, it should include a lot of stakeholder alignment and involvement. The product manager should dedicate more ...
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
The MoSCoW method is a prioritization technique used in management, business analysis, project management, and software development to reach a common understanding with stakeholders on the importance they place on the delivery of each requirement; it is also known as MoSCoW prioritization or MoSCoW analysis.. The term MOSCOW itself is an acronym derived from the first letter of each of four ...
Established in 2008 by the SRCD Student and Early Career Council (SECC), the Dissertation Research Funding Awards (DFAs) are given to dissertation research proposals that are exceptionally noteworthy and display a strong potential to contribute to the field of child development. Each recipient is awarded $2,000 USD to use for research costs related to the proposed dissertation project.
MoSCoW prioritization, also known as the MoSCoW method or MoSCoW analysis, is a popular prioritization technique for managing requirements. The acronym MoSCoW represents four categories of initiatives: must-have, should-have, could-have, and won't-have, or will not have right now. Some companies also use the "W" in MoSCoW to mean "wish.".
Information about Ontario's economy and how to do business here. Includes economic development opportunities, research funding, tax credits for business and the Ontario Budget. Learn more. Education and Training. Learn about Ontario's early years, education and training systems. Includes information on child care, elementary schools ...
The great room in the model home at Falls Farm, a 30-acre development of custom-build houses on Georgetown Pike in Fairfax County, Va. (Benjamin C Tankersley/For The Washington Post) By Amy Worden ...
The US Federal Reserve (US Fed) has cut the target range for the federal funds rate by 50 basis points (bps), from 5.25 - 5.5 per cent earlier to 4.75 - 5.00 per cent on Wednesday, the first time since 2020. The cut comes amid concerns regarding the job market in the US, and ahead of the US presidential elections in November 2024.