

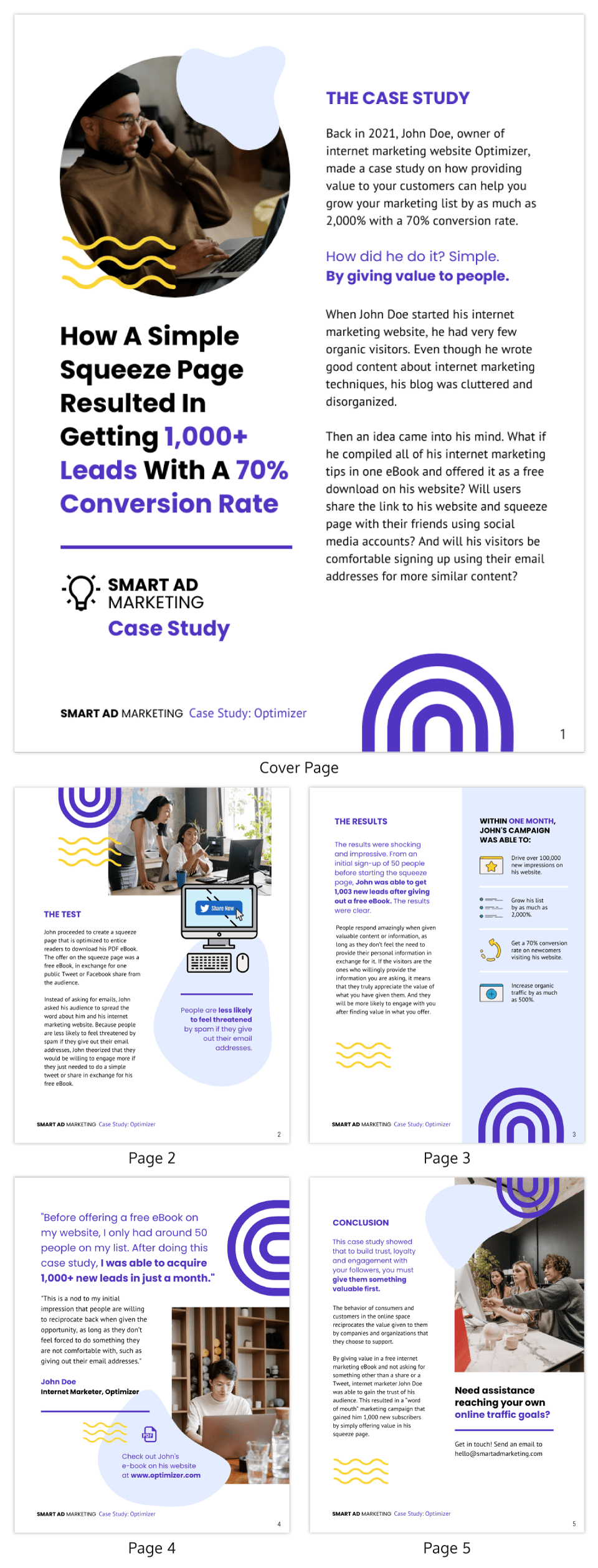
How to Write a Case Study: A Complete Guide with Templates

Writing compelling and insightful case studies is a marketer’s biggest job, yet most get frustrated with this content. The challenge? Figuring out how to write a case study that not only highlights the company’s strongest suit but engages new clients with strategic information. If you often struggle with making case studies as more than just dry facts and figures, you’re leading your efforts to missed opportunities.
How to Write a Case Study Step-by-Step
- Craft a Compelling Headline: Highlight the main success with a clear, direct title.
- Start with a Strong Introduction: Provide a broad overview and hook the reader.
- Discuss Unique Client Challenges: Highlight specific industry-related challenges.
- Highlight the Solution: Showcase your strategies and key results.
- Present Quantifiable Results: Use data and visuals to demonstrate impact.
- Be Clear and Concise: Stick to the point and support claims with data.
- Treat Your Case Study Like a Story: Focus on the customer’s journey and success.
- Use Direct Quotes from the Client: Add authenticity with client testimonials.
- Make the Key Takeaway Clear: Reinforce your expertise and the solution’s value.
- Include a Call to Action (CTA): Guide the reader on what to do next.
- Make It Readable: Use simple language, short paragraphs, and bullet points.
- Finalize and Proofread: Review for errors and ensure a smooth flow.
In this blog, you’ll discover a step-by-step guide that simplifies the process, making it easier to create interesting case studies. From planning to writing, I’ve got you covered. So, let’s start with some basics.
Table of Contents
What is the format of a case study.
- How to Plan a Case Study
How to Write a Case Study
How to summarize a case study, how to cite a case study.
A well-structured case study isn’t just a collection of facts—it’s a powerful marketing tool that tells a compelling story. Using the right format for a case study ensures that your message is clear, engaging, and impactful.
The proper format guides readers through the narrative with hierarchy and scannability, helping them connect with your brand on a deeper level. Most importantly, it empowers you as a marketer to set clear goals for presenting your case studies and ensures you deliver the correct information effectively!

Case studies format helps you to plan and write the case study for your clients. With this outline in mind, you can create steps to complete the process of writing and publishing your case study research. There are eight components of a case study that are essential for building a layout of information in the correct order that makes sense to the viewers.
Start with a catchy “Title” that grabs attention and an “Overview” that sets the stage. Clearly define the “Problem” your client faced, and then showcase your “Solution” in detail. Highlight the success with “Results” that are measurable and impactful. Add authenticity with “Testimonials and Quotes” from satisfied clients. Wrap it up with a firm “Conclusion” and a compelling “Call to Action” in the “About Us” section that guides the reader on what to do next.
By following this format, you create a case study design that resonates with your audience and effectively showcases your brand’s value.
Check out the marketing case study template I’ve included below—it has a clear outline that makes it easy to see how sticking to a format can help you plan and write the entire thing.

How to Plan a Case Study
Now comes the big part! Understanding what to include in a case study outline is just the starting point for beginners. The real challenge lies in creating a step-by-step plan to craft that outline and filling it in with the right information!

1. Set Clear Goals for Your Case Study
Before diving into how to write a case study, defining your ultimate objective is essential. Think about it—what do you want your audience to take away from this case study? For example, your goal is to showcase how your SEO strategies boosted a client’s organic traffic by 150% in just six months. This clear goal will shape your entire narrative and ensure that your case study is laser-focused on demonstrating your expertise and the value you bring.
2. Select a Client that Highlights Your Strongest Suit
Choosing the right client or subject is vital while creating case studies. Imagine you’ve worked with a small e-commerce brand struggling to rank for competitive keywords. Your strategies helped them rank on the first page and increase conversions. This is the perfect client for your case study because their success story directly showcases your SEO prowess.
By picking a client whose experience aligns with your goals, you’ll create a case study that resonates with your target audience.
3. Reach Out to Your Client for Collaboration
Now that you’ve identified the ideal client, it’s time to reach out. Let’s say you contact your client and explain how a case study can highlight their remarkable success story. It’s a great way to spotlight a mutual collaboration based on credibility. Their buy-in is crucial; their insights and data will authenticate your case study.
4. Gather Comprehensive Data and Insights
Data is the lifeblood of any compelling case study. For instance, in your SEO case study, you’ll need to gather data on key metrics like keyword rankings, organic traffic, and conversion rates before and after implementing your strategies. Let’s say your client saw a 50% increase in organic traffic within three months of optimizing their website. Collecting this data will help you build a robust, evidence-based narrative highlighting your impact.
It’s essential to monitor the before-and-after data to track the effectiveness of implementing your strategies.
5. Prepare Insightful Questions and Conduct Interviews
It would be best to ask the right questions to get the most out of your client interviews. Imagine asking your client, “What specific challenges were you facing with your organic search rankings before we started working together?” or “How did our SEO strategies help you achieve your business goals?” These questions will lead to detailed responses that add depth to your case study, making it more than just numbers on a page.
Always ask questions that uncover the key challenges your clients face. This way, your prospects will know when to turn to you to navigate or overcome similar obstacles in their business.
Since I’m giving an example of an SEO case study in marketing, you can try these questions to interview your existing client. Obviously, you can modify the sentences according to your industry basics, but these types of questions are fundamental for collecting structured data from your clients.
- What were your business’s main SEO challenges before we started working together?
- Can you describe your initial expectations for implementing our SEO strategies?
- What specific SEO tactics did we implement that you found most effective?
- How did you monitor and measure the impact of these strategies on your organic traffic?
- What were the key metrics or results that stood out to you after the first three months?
6. Ask Questions That Drive the Story Forward
Impactful questions are the backbone of a strong case study. They allow you to highlight the unique value you delivered to your clients. You can effortlessly showcase your USPs within the case study by asking the right questions.
Focus on inquiring about the effectiveness of your services and strategies, their impact, and which aspects of the solution were most beneficial. This insight will be your key to demonstrating the tangible benefits you offer your clients.
Consider asking questions like:
- Can you share a moment when you first noticed a significant improvement in your website’s organic traffic?
- How did the increase in organic traffic impact other business areas, such as lead generation or sales?
- What feedback did your team or customers receive regarding the changes in your site’s performance?
- Looking back, what do you believe was the most critical factor in achieving these results?
- How has this success with SEO influenced your overall marketing strategy moving forward?
These types of questions encourage clients to share their experiences in a way that paints a vivid picture for your readers, making the case study more relatable and engaging.
7. Draft a Clear and Organized Outline
With all the data and insights gathered, it’s time to create a well-structured case study outline. Let’s say you start with a brief overview of your client’s business and its challenges, followed by a detailed account of the SEO strategies you implemented. Then, you showcase the results with hard data and close with client testimonials and a solid call to action.
As mentioned above, organizing your content in a logical, easy-to-follow format will help you write a case study that not only informs but also captivates your audience.
These steps are the cornerstones of designing a case study. Once you complete this checklist, you can proceed to the next step, which is writing a case study. Since I discussed planning an SEO case study extensively, here is a case study template that perfectly illustrates the process.

You want to create an informative case study for your prospects. But how do you make sure it’s done right? Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write a case study that drives results.
1. Craft a Compelling Headline
Your headline is the first thing readers see, so make it count! It should grab attention and hint at the success story you’re about to share.
How to Write a Case Study Title:
1. Highlight the Result: Showcase the critical success, like “Increased Sales by 200%.”
2. Be Clear and Direct: Make sure the headline is straightforward to grasp.
3. Use Action Words: Start with strong verbs like “How We” or “Achieved.”
4. Mention Client or Industry: Include relevant details for specificity.
5. Keep It Short: Make it concise and attention-grabbing.
2. Start with a Strong Introduction
Kick off your case study with a broad overview that sets the stage. Provide the big picture and construct a clear narrative that draws readers in, making them eager to learn more about how you solved a significant challenge.
Look at the consulting case study template , which includes a stunning overview description and precise instructions for writing a short and compelling introduction. You can add every little detail to hook the reader.

Get This Template and More
3. Discuss Specific Challenges of Your Client
This is where your prospect can truly connect. By highlighting unique yet specific challenges to their industry, you give them insight into issues they might not have encountered yet—or ones they’ve already faced. This way, they’ll know exactly who to turn to when similar challenges arise.
The following financial case study template provides a brief flow of the company’s common challenges in the financial analysis process. The template is almost ready to use with this domain-specific content, requiring minimal adjustments to design your case study.

4. Highlight the Solution
Now, dive into the heart of the story. Highlight the solution you provided, and make sure to include a notable achievement or key result. This is your chance to shine!
Check out the format for presenting the implications of your service on your client’s business. The benefits should be well-written and data-driven to convince your upcoming clients. This graphic design case study format helps you understand the specific impacts a company seeks from a reputable graphic design firm.

5. Present Quantifiable Results
When sharing the outcome, numbers speak louder than words. Present quantifiable results that clearly demonstrate the impact of your solution. Use graphs or charts to make the data easy to digest and visually appealing.
6. Be Clear and Concise
Less is more. Stick to the point and offer just the right amount of detail to keep your readers engaged. Include data that supports your claims, but avoid overwhelming them with too much information.
Here’s a stunning sales consulting case study that uses a simple case study layout and details written in readable, plain language to gauge more utility.

7. Treat Your Case Study Like a Story
Focus on your customer’s journey. Think of your case study as a story in which your client is the hero, and your solution is the tool that helped them succeed. This approach will make your case study relatable and compelling.
8. Be as Specific as Possible
Don’t be vague—details matter. Mention the specific company and its industry to let your audience know that the challenge and solution are relevant to them. The more precise you are, the more credible and trustworthy your case study will be.
Check out the sample case study below for payroll accounting. The details are clearly organized and grouped to emphasize the type of case study.

Also, the next case study template displays very specific problems that a company faces when it lacks digital marketing expertise.

These templates make it a breeze to craft a case study that’s perfect for your niche.
9. Use Direct Quotes from the Client
Quotes from your client add authenticity and credibility. They give readers insight into the client’s perspective and make your case study more relatable. Plus, a glowing testimonial is always a nice touch!
The following inbound marketing case study has a prominent client testimonial. With the brief instructions on this template, it’s easier for you to understand how to capture the golden words of your client and use them as a word-of-mouth strategy within the case study.

10. Pick an Interesting Angle
Find a unique angle that makes your case study stand out. Maybe it’s an unexpected challenge you overcame, or perhaps it’s a particularly innovative solution. Whatever it is, make it intriguing.
11. Make the Key Takeaway Crystal Clear
Your readers should walk away with a clear understanding of the main point of your case study. This takeaway should reinforce your expertise and the value of your solution.
12. Include a Call to Action (CTA)
Don’t leave your readers hanging—tell them what to do next! Include a compelling summary about your company, showcase your happy client base, and conclude the journey with a strong CTA, whether to contact you for a consultation, download a related resource, or learn more about your services on social media, like the following case study template design.

12. Format Professionally
The design of the case study is just as important as the content. A well-formatted, visually appealing document makes a great impression and enhances readability. With ready-to-use niche-oriented templates, you can easily create a professional-looking case study that impresses and converts. Here is an eye-catching template for an AI assistant software case study that displays a sleek and well-navigated format.

13. Make It Readable
Easy readability is key. Use simple language, short paragraphs, and bullet points where appropriate. Your case study should be easy to scan and digest. Follow the thirteen design principles to create a standout piece that enhances your marketing efforts.
To understand this, take a look at the following consulting case study template.

14. Finalize and Proofread Your Case Study
In order to excel in how to write case studies, give your case study a final review before you hit publish. Proofread carefully to catch any typos or errors, and make sure everything flows smoothly. A polished case study reflects your attention to detail and professionalism.
To effectively summarize a case study, start by completing all sections, including the introduction, challenges, solutions, and results. This approach helps marketers identify key points to highlight, making it easier to craft a succinct and engaging summary.
One tricky thing is the length of the case study summary. So, how long should a case study summary be?
The length of a case study summary can vary depending on the details you’re covering. Generally, it should be kept concise, usually spanning a couple of lines or up to a single page with several paragraphs. If you’re crafting a customer case study and want to flex your storytelling muscles, it’s perfectly fine for the summary to stretch to a full page.
If summarizing a case study seems daunting, try DocHipo’s advanced AI Writer tool, which effortlessly creates a crisp and concise summary.
Watch this short video to use it.
This is the last step in writing a case study analysis. Citation in a case study is the practice of giving proper credit to the sources you reference or use in your research. It helps validate your work, shows the depth of your research, and avoids plagiarism. Follow the below steps to cite a case study:
- Identify the Source: Gather details like the author, title, publication year, and where the case study was published.
- Choose a Citation Style: Follow the specific formatting style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) required for your work.
- Format the Citation: Arrange the details according to the chosen citation style.
- Include In-Text Citations: Place citations within the text or paragraphs for the case study.
- Create a References List: At the end of your case study, compile all your sources in a bibliography or reference list.
For case studies, citations in APA and MLA styles are very common. If you are just beginning, then you might be confused about these case study citation formats.
Hence, take a look at the picture below, which easily comprehends the APA vs MLA citation features.
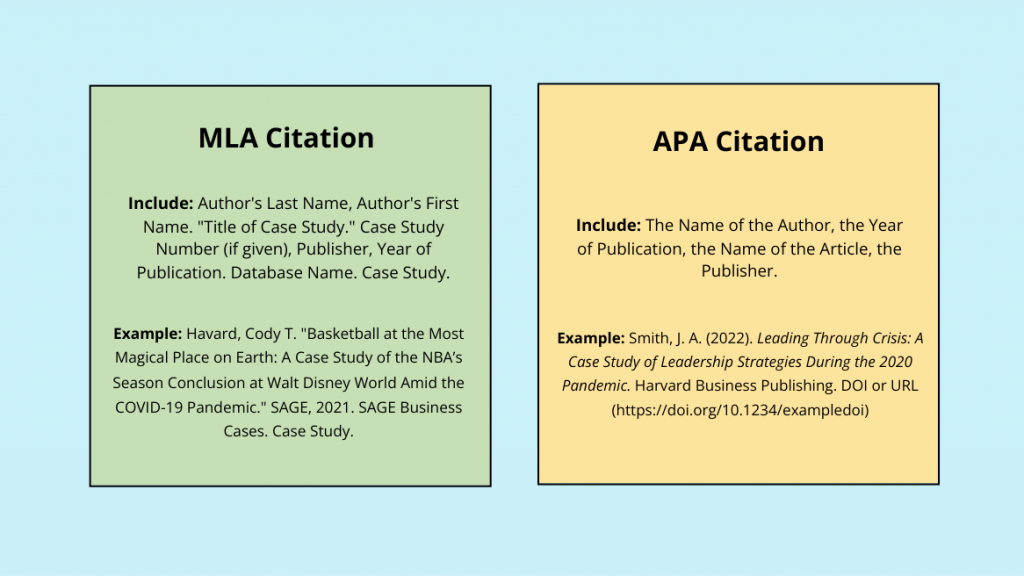
Still feeling overwhelmed about case studies? Be stress-free with the most convenient case study maker, which saves time and allows you to present data in the most attention-grabbing way.
Watch the video to create case studies in minutes with DocHipo’s case study maker.
Conclusion
To summarize, if you want to write a case study, start with a proper case study format, plan the case study, and finally write it with all the information in hand. Then, write a summary to provide an overview of your case study, and finally, add citations for reference.
Meanwhile, if you want to design a case study, Try DocHipo templates. Sign up to explore all the case study templates.
What is the structure of a case study?
A case study typically includes the following sections: Title, Introduction, Background, Problem Statement, Solutions, Results, and Conclusion. Each section serves to tell a comprehensive story of the business, from the issue at hand to the resolution and outcomes.
What are the 5 essential elements of a great case study?
The 5 essential elements are: 1) Clear Objective, 2) Detailed Background, 3) Specific Challenges, 4) Effective Solutions, and 5) Measurable Results. These components provide a compelling narrative that highlights the value delivered.
How to begin a case study?
Start a case study by defining the purpose and scope of the study. Introduce the subject, outline the problem, and provide background information to give readers context. This sets the stage for the detailed analysis that follows.
How to make an introduction in case study?
To craft a compelling introduction, briefly describe the subject, outline the problem they faced, and explain why the study is relevant. This section should grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in the rest of the study.
How to make a business case study?
A business case study should begin with a clear objective and background information. Identify the problem, explain the solutions implemented, and conclude with the results achieved. Use real data and quotes from stakeholders to enhance credibility.
How to write a case study step by step?
To write a case study step by step, start by identifying the case you want to explore and gathering relevant data on the subject. Outline the structure of your case study, then craft an engaging Introduction to set the context. Next, detail the Background and Challenges faced, followed by the Solutions applied. Share the Results and Conclusion to highlight the impact. Finally, edit and proofread your case study to ensure clarity and accuracy.

Turn your ideas into beautiful design
No prior design skill required

Talk to Sales
Wherever you are on your Dochipo journey, you can always get in touch.

Talk to Support
How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: July 18, 2024
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a major challenge. Before you can expect to earn their business, you’ll need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on the promises of your product or service. The best way to win new business is with cold, hard proof.

A great way to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. HubSpot’s 2024 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so captivating that they were the fifth most commonly used type of content that marketers relied on.
That statistic still holds true in Forbes Advisor’s 2024 study, which adds that 78% of B2B businesses report using case studies and customer stories because they are “ crucial for demonstrating real-world value. ”
Having written these ever more frequently over the past ten years, I hope to serve as your guide through a process that can feel daunting, but I promise is worth the effort. Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic.
Table of Contents
Case Study Definition
- Why Write a Case Study?
- How Long Should a Case Study Be?
Case Study Templates
How to write a case study, case study format, business case study examples.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A case study is coverage of a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it‘s common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client.
Perhaps the success you’re highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers, helping you attract new clients.
Why write a case study?
I know, it sounds like a huge endeavor — is it really worth it?
The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples.
Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain complex topics or concepts.
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies, showing how they can be applied in a practical way.
You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that demonstrates how your product solved their issue. Most importantly, it explains how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar, successful results.
2. Show expertise.
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build trust and credibility.
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework.
A robust case study instills confidence in the solutions you present because the reader has now vicariously experienced the problem — and they followed, step-by-step, what it took to solve it. These elements work together, enabling you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create social proof.
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof .
People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — put your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes play together like an orchestra to help you gain more clients. Afterward, the case study acts as a reference. You can pull quotes from customers that were featured in these studies to repurpose them in other marketing content.
How long should a case study be?
Now that you’re more acquainted with the benefits of producing a case study, let’s explore how long these documents should be.
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved.
This may be easier said than done, but it‘s important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader’s interest.
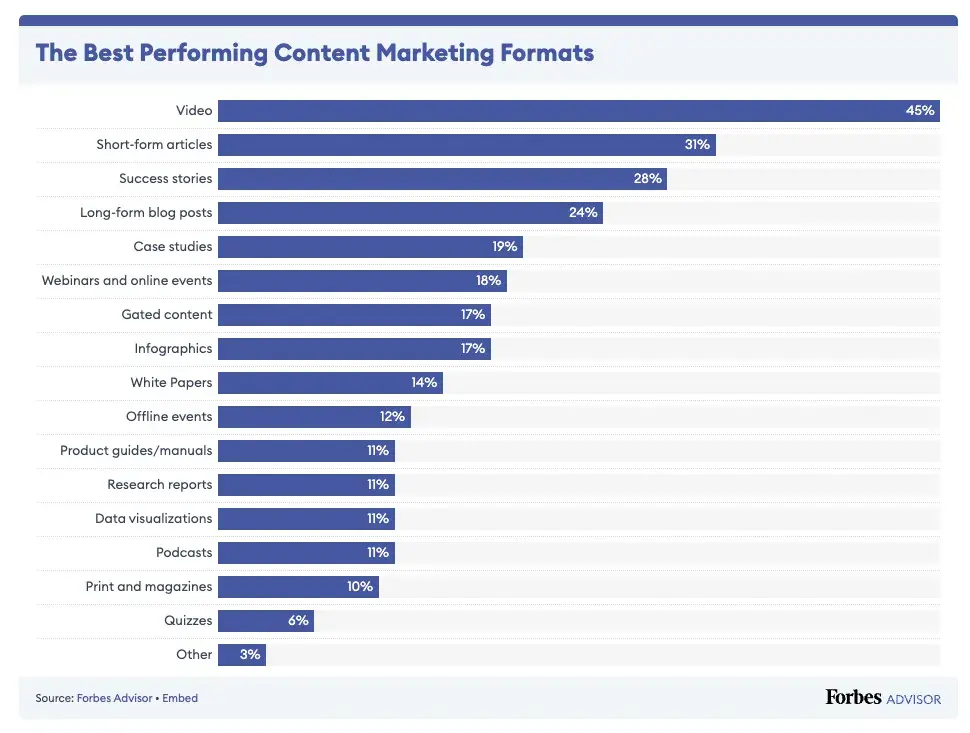
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Make it attractive to dive into by using headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers.
I’ve also seen more and more brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience, which is highly recommended given that video is currently the best performing marketing content format.
In terms of the interview structure, I recommend categorizing the questions in a way that the answers flow into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, plus how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context that helps match the customer's needs with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes.
Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
It’s a smart idea to send a copy of your interview questions to your subject ahead of time so they can prepare strong answers and collect the numerical data you need from them.
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you‘ve collected and actually turn it into something useful, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. I always do, but I also know that it works out in the end, so I just jump on in and work it through.
So where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
It‘s important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study.
They can be very visual, which you’ll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated through video or photos with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections I’d suggest, and I'll cover these in more detail after #11 below:
- Title. Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle. Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary . A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject. An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives. A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped. A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results. A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes. Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans. Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call-to-Action (CTA). Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible.
Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you‘ve completed your case study, it’s time to publish and promote it.
Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas.
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF.
To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client‘s success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they’d like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people to it from your homepage with a “Case Studies” or “Testimonials” button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

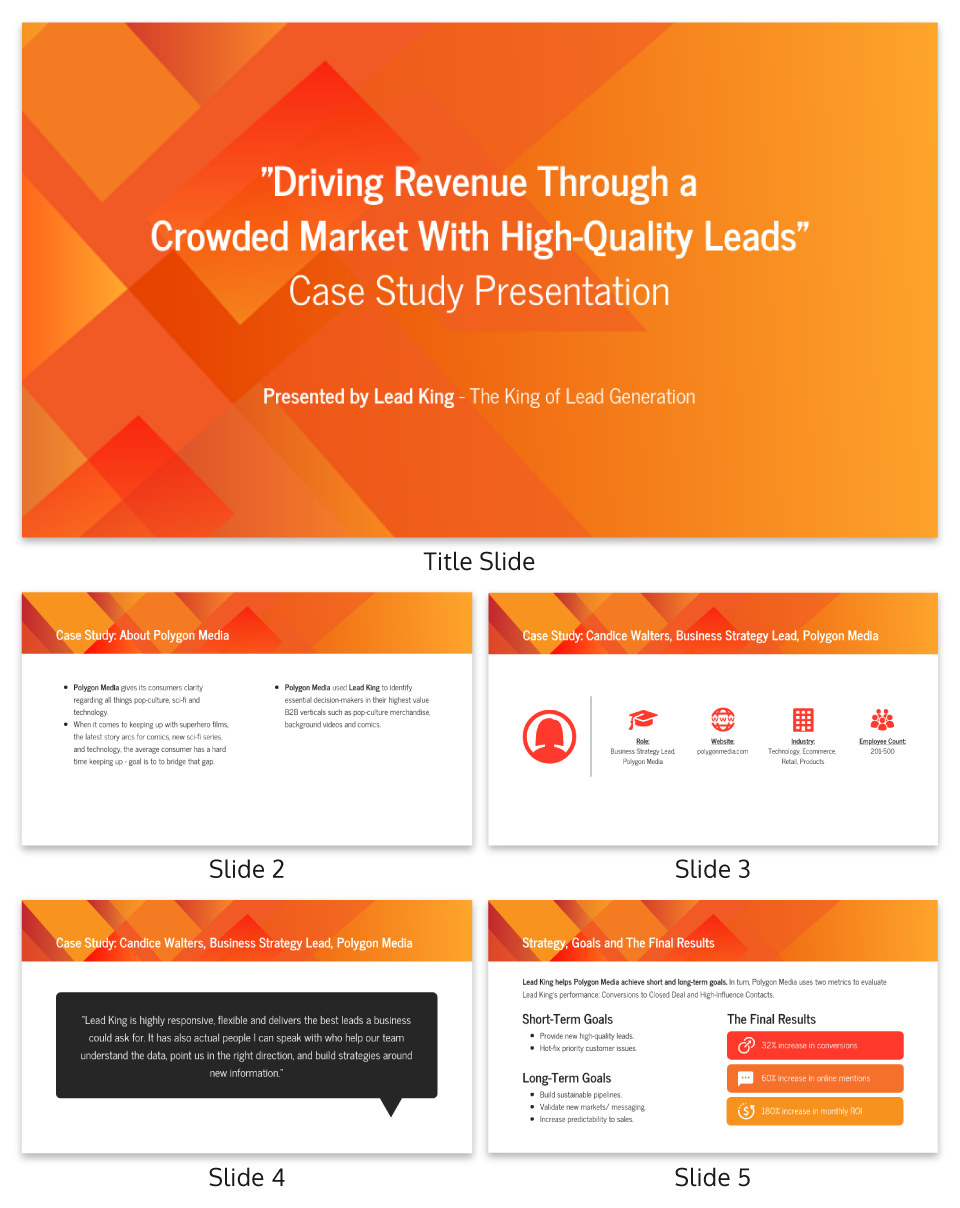
27 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![case study how to prepare 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/contenttypes.webp)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![case study how to prepare How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]
![case study how to prepare What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://53.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/53/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
How to Write a Case Study: A Step-by-Step Guide (+ Examples)
by Todd Brehe
on Jan 3, 2024

If you want to learn how to write a case study that engages prospective clients, demonstrates that you can solve real business problems, and showcases the results you deliver, this guide will help.
We’ll give you a proven template to follow, show you how to conduct an engaging interview, and give you several examples and tips for best practices.
Let’s start with the basics.

What is a Case Study?
A business case study is simply a story about how you successfully delivered a solution to your client.
Case studies start with background information about the customer, describe problems they were facing, present the solutions you developed, and explain how those solutions positively impacted the customer’s business.
Do Marketing Case Studies Really Work?
Absolutely. A well-written case study puts prospective clients into the shoes of your paying clients, encouraging them to engage with you. Plus, they:
- Get shared “behind the lines” with decision makers you may not know;
- Leverage the power of “social proof” to encourage a prospective client to take a chance with your company;
- Build trust and foster likeability;
- Lessen the perceived risk of doing business with you and offer proof that your business can deliver results;
- Help prospects become aware of unrecognized problems;
- Show prospects experiencing similar problems that possible solutions are available (and you can provide said solutions);
- Make it easier for your target audience to find you when using Google and other search engines.
Case studies serve your clients too. For example, they can generate positive publicity and highlight the accomplishments of line staff to the management team. Your company might even throw in a new product/service discount, or a gift as an added bonus.
But don’t just take my word for it. Let’s look at a few statistics and success stories:
5 Winning Case Study Examples to Model
Before we get into the nuts and bolts of how to write a case study, let’s go over a few examples of what an excellent one looks like.
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure.
1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory

This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable.
2. WalkMe Mobile and Hulyo
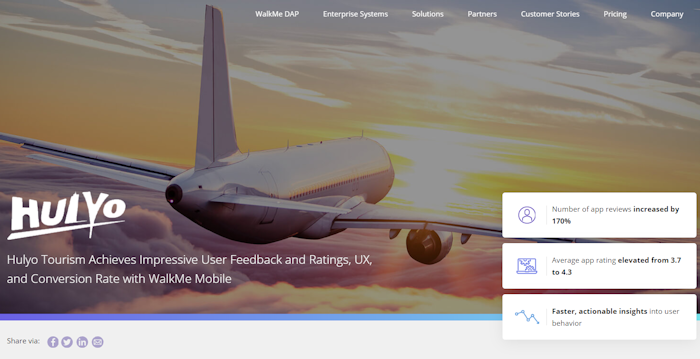
This case study from WalkMe Mobile leads with an engaging headline and the three most important results the client was able to generate.
In the first paragraph, the writer expands the list of accomplishments encouraging readers to learn more.
3. CurationSuite Listening Engine

This is an example of a well-designed printable case study . The client, specific problem, and solution are called out in the left column and summarized succinctly.
4. Brain Traffic and ASAE

This long format case study (6 pages) from Brain Traffic summarizes the challenges, solutions, and results prominently in the left column. It uses testimonials and headshots of the case study participants very effectively.
5. Adobe and Home Depot

This case study from Adobe and Home Depot is a great example of combining video, attention-getting graphics, and long form writing. It also uses testimonials and headshots well.
Now that we’ve gone over the basics and showed a few great case study examples you can use as inspiration, let’s roll up our sleeves and get to work.
A Case Study Structure That Pros Use
Let’s break down the structure of a compelling case study:
Choose Your Case Study Format
In this guide, we focus on written case studies. They’re affordable to create, and they have a proven track record. However, written case studies are just one of four case study formats to consider:
- Infographic
If you have the resources, video (like the Adobe and Home Depot example above) and podcast case studies can be very compelling. Hearing a client discuss in his or her own words how your company helped is an effective content marketing strategy
Infographic case studies are usually one-page images that summarize the challenge, proposed solution, and results. They tend to work well on social media.
Follow a Tried-and-True Case Study Template
The success story structure we’re using incorporates a “narrative” or “story arc” designed to suck readers in and captivate their interest.
Note: I recommend creating a blog post or landing page on your website that includes the text from your case study, along with a downloadable PDF. Doing so helps people find your content when they perform Google and other web searches.
There are a few simple SEO strategies that you can apply to your blog post that will optimize your chances of being found. I’ll include those tips below.
Craft a Compelling Headline
The headline should capture your audience’s attention quickly. Include the most important result you achieved, the client’s name, and your company’s name. Create several examples, mull them over a bit, then pick the best one. And, yes, this means writing the headline is done at the very end.
SEO Tip: Let’s say your firm provided “video editing services” and you want to target this primary keyword. Include it, your company name, and your client’s name in the case study title.
Write the Executive Summary
This is a mini-narrative using an abbreviated version of the Challenge + Solution + Results model (3-4 short paragraphs). Write this after you complete the case study.
SEO Tip: Include your primary keyword in the first paragraph of the Executive Summary.
Provide the Client’s Background
Introduce your client to the reader and create context for the story.
List the Customer’s Challenges and Problems
Vividly describe the situation and problems the customer was dealing with, before working with you.
SEO Tip: To rank on page one of Google for our target keyword, review the questions listed in the “People also ask” section at the top of Google’s search results. If you can include some of these questions and their answers into your case study, do so. Just make sure they fit with the flow of your narrative.
Detail Your Solutions
Explain the product or service your company provided, and spell out how it alleviated the client’s problems. Recap how the solution was delivered and implemented. Describe any training needed and the customer’s work effort.
Show Your Results
Detail what you accomplished for the customer and the impact your product/service made. Objective, measurable results that resonate with your target audience are best.
List Future Plans
Share how your client might work with your company in the future.
Give a Call-to-Action
Clearly detail what you want the reader to do at the end of your case study.
Talk About You
Include a “press release-like” description of your client’s organization, with a link to their website. For your printable document, add an “About” section with your contact information.
And that’s it. That’s the basic structure of any good case study.
Now, let’s go over how to get the information you’ll use in your case study.
How to Conduct an Engaging Case Study Interview
One of the best parts of creating a case study is talking with your client about the experience. This is a fun and productive way to learn what your company did well, and what it can improve on, directly from your customer’s perspective.
Here are some suggestions for conducting great case study interviews:
When Choosing a Case Study Subject, Pick a Raving Fan
Your sales and marketing team should know which clients are vocal advocates willing to talk about their experiences. Your customer service and technical support teams should be able to contribute suggestions.
Clients who are experts with your product/service make solid case study candidates. If you sponsor an online community, look for product champions who post consistently and help others.
When selecting a candidate, think about customer stories that would appeal to your target audience. For example, let’s say your sales team is consistently bumping into prospects who are excited about your solution, but are slow to pull the trigger and do business with you.
In this instance, finding a client who felt the same way, but overcame their reluctance and contracted with you anyway, would be a compelling story to capture and share.
Prepping for the Interview
If you’ve ever seen an Oprah interview, you’ve seen a master who can get almost anyone to open up and talk. Part of the reason is that she and her team are disciplined about planning.
Before conducting a case study interview, talk to your own team about the following:
- What’s unique about the client (location, size, industry, etc.) that will resonate with our prospects?
- Why did the customer select us?
- How did we help the client?
- What’s unique about this customer’s experience?
- What problems did we solve?
- Were any measurable, objective results generated?
- What do we want readers to do after reading this case study analysis?
Pro Tip: Tee up your client. Send them the questions in advance.
Providing questions to clients before the interview helps them prepare, gather input from other colleagues if needed, and feel more comfortable because they know what to expect.
In a moment, I’ll give you an exhaustive list of interview questions. But don’t send them all. Instead, pare the list down to one or two questions in each section and personalize them for your customer.
Nailing the Client Interview
Decide how you’ll conduct the interview. Will you call the client, use Skype or Facetime, or meet in person? Whatever mode you choose, plan the process in advance.
Make sure you record the conversation. It’s tough to lead an interview, listen to your contact’s responses, keep the conversation flowing, write notes, and capture all that the person is saying.
A recording will make it easier to write the client’s story later. It’s also useful for other departments in your company (management, sales, development, etc.) to hear real customer feedback.
Use open-ended questions that spur your contact to talk and share. Here are some real-life examples:
Introduction
- Recap the purpose of the call. Confirm how much time your contact has to talk (30-45 minutes is preferable).
- Confirm the company’s location, number of employees, years in business, industry, etc.
- What’s the contact’s background, title, time with the company, primary responsibilities, and so on?
Initial Challenges
- Describe the situation at your company before engaging with us?
- What were the initial problems you wanted to solve?
- What was the impact of those problems?
- When did you realize you had to take some action?
- What solutions did you try?
- What solutions did you implement?
- What process did you go through to make a purchase?
- How did the implementation go?
- How would you describe the work effort required of your team?
- If training was involved, how did that go?
Results, Improvements, Progress
- When did you start seeing improvements?
- What were the most valuable results?
- What did your team like best about working with us?
- Would you recommend our solution/company? Why?
Future Plans
- How do you see our companies working together in the future?
Honest Feedback
- Our company is very focused on continual improvement. What could we have done differently to make this an even better experience?
- What would you like us to add or change in our product/service?
During the interview, use your contact’s responses to guide the conversation.
Once the interview is complete, it’s time to write your case study.
How to Write a Case Study… Effortlessly
Case study writing is not nearly as difficult as many people make it out to be. And you don’t have to be Stephen King to do professional work. Here are a few tips:
- Use the case study structure that we outlined earlier, but write these sections first: company background, challenges, solutions, and results.
- Write the headline, executive summary, future plans, and call-to-action (CTA) last.
- In each section, include as much content from your interview as you can. Don’t worry about editing at this point
- Tell the story by discussing their trials and tribulations.
- Stay focused on the client and the results they achieved.
- Make their organization and employees shine.
- When including information about your company, frame your efforts in a supporting role.
Also, make sure to do the following:
Add Testimonials, Quotes, and Visuals
The more you can use your contact’s words to describe the engagement, the better. Weave direct quotes throughout your narrative.
Strive to be conversational when you’re writing case studies, as if you’re talking to a peer.
Include images in your case study that visually represent the content and break up the text. Photos of the company, your contact, and other employees are ideal.
If you need to incorporate stock photos, here are three resources:
- Deposit p hotos
And if you need more, check out Smart Blogger’s excellent resource: 17 Sites with High-Quality, Royalty-Free Stock Photos .
Proofread and Tighten Your Writing
Make sure there are no grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors. If you need help, consider using a grammar checker tool like Grammarly .
My high school English teacher’s mantra was “tighten your writing.” She taught that impactful writing is concise and free of weak, unnecessary words . This takes effort and discipline, but will make your writing stronger.
Also, keep in mind that we live in an attention-diverted society. Before your audience will dive in and read each paragraph, they’ll first scan your work. Use subheadings to summarize information, convey meaning quickly, and pull the reader in.
Be Sure to Use Best Practices
Consider applying the following best practices to your case study:
- Stay laser-focused on your client and the results they were able to achieve.
- Even if your audience is technical, minimize the use of industry jargon . If you use acronyms, explain them.
- Leave out the selling and advertising.
- Don’t write like a Shakespearean wannabe. Write how people speak. Write to be understood.
- Clear and concise writing is not only more understandable, it inspires trust. Don’t ramble.
- Weave your paragraphs together so that each sentence is dependent on the one before and after it.
- Include a specific case study call-to-action (CTA).
- A recommended case study length is 2-4 pages.
- Commit to building a library of case studies.
Get Client Approval
After you have a final draft, send it to the client for review and approval. Incorporate any edits they suggest.
Use or modify the following “Consent to Publish” form to get the client’s written sign-off:
Consent to Publish
Case Study Title:
I hereby confirm that I have reviewed the case study listed above and on behalf of the [Company Name], I provide full permission for the work to be published, in whole or in part, for the life of the work, in all languages and all formats by [Company publishing the case study].
By signing this form, I affirm that I am authorized to grant full permission.
Company Name:
E-mail Address:
Common Case Study Questions (& Answers)
We’ll wrap things up with a quick Q&A. If you have a question I didn’t answer, be sure to leave it in a blog comment below.
Should I worry about print versions of my case studies?
Absolutely.
As we saw in the CurationSuite and Brain Traffic examples earlier, case studies get downloaded, printed, and shared. Prospects can and will judge your book by its cover.
So, make sure your printed case study is eye-catching and professionally designed. Hire a designer if necessary.
Why are good case studies so effective?
Case studies work because people trust them.
They’re not ads, they’re not press releases, and they’re not about how stellar your company is.
Plus, everyone likes spellbinding stories with a hero [your client], a conflict [challenges], and a riveting resolution [best solution and results].
How do I promote my case study?
After you’ve written your case study and received the client’s approval to use it, you’ll want to get it in front of as many eyes as possible.
Try the following:
- Make sure your case studies can be easily found on your company’s homepage.
- Tweet and share the case study on your various social media accounts.
- Have your sales team use the case study as a reason to call on potential customers. For example: “Hi [prospect], we just published a case study on Company A. They were facing some of the same challenges I believe your firm is dealing with. I’m going to e-mail you a copy. Let me know what you think.”
- Distribute printed copies at trade shows, seminars, or during sales presentations.
- If you’re bidding on a job and have to submit a quote or a Request for Proposal (RFP), include relevant case studies as supporting documents.
Ready to Write a Case Study That Converts?
If you want to stand out and you want to win business, case studies should be an integral part of your sales and marketing efforts.
Hopefully, this guide answered some of your questions and laid out a path that will make it faster and easier for your team to create professional, sales-generating content.
Now it’s time to take action and get started. Gather your staff, select a client, and ask a contact to participate. Plan your interview and lead an engaging conversation. Write up your client’s story, make them shine, and then share it.
Get better at the case study process by doing it more frequently. Challenge yourself to write at least one case study every two months.
As you do, you’ll be building a valuable repository of meaningful, powerful content. These success stories will serve your business in countless ways, and for years to come.
Content Marketing
The ultimate toolkit for becoming one of the highest-paid writers online. Premium training. Yours for free.
Written by Todd Brehe
Latest from the blog.
9+ X/Twitter Username Ideas to Craft the Perfect Handle

100+ Epic Short Story Ideas to Inspire Your Own in 2024

10+ Essential X/Twitter Tools to Amplify Your X/Twitter Marketing

With over 300k subscribers and 4 million readers, Smart Blogger is one of the world's largest websites dedicated to writing and blogging.
Best of the Blog
© 2012-2024 Smart Blogger — Boost Blog Traffic, Inc.
Terms | Privacy Policy | Refund Policy | Affiliate Disclosure
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
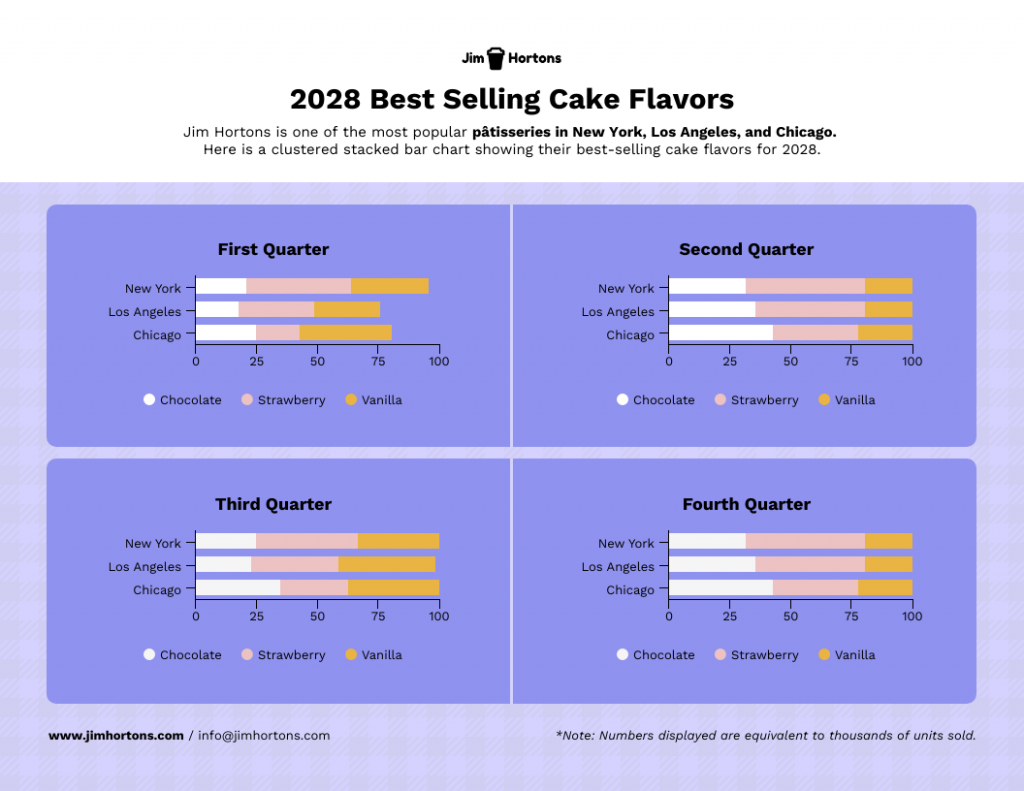
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
5 Steps for Writing a Case Study for Business (+Templates)
Get professional tips for writing a case study that drives business impact. Learn the best format and research method to use alongside examples & templates.
7 minute read

helped business professionals at:

SHORT ANSWER
What is a case study.
- Open with an introductory overview
- Explain the problem in question
- Detail the solutions that solved the problem
- Refer to key results
- Finish with recommendations and next steps
Why you need a case study
“I climbed Mount Everest and I did it all by myself.” “Yeah mate, pics or it didn’t happen.” The same logic applies to case studies. In business, it’s “case studies or it didn’t happen.” A well-written case study legitimizes your product or services. It proves the impact your actions have on the bottom line and is the single most important element of building trust amongst prospective clients. But… How do you write a *perfect* case study? One that engages readers and makes them care about your offering and excited to work with you?

In business, a case study , or customer success story, is a marketing tool that showcases how your product or service helped clients overcome business challenges. It uses statistics, quotes, and specific examples to convincingly highlight your ability to produce results.
What is the purpose of a case study?
The purpose of a case study, usually, is to provide your prospective clients with specific examples of how your products or services can help solve business problems they might be facing.
Case studies legitimize your business activities allowing you to go beyond explaining what you do and focus on how well you do it. (And, in case you were wondering just HOW important case studies are, here’s an item of data to ponder: according to a DemandGen report , 78% of B2B buyers want to review case studies before making a purchase decision. Another study by Uplift found that at the end of 2023, f or the third year in a row, marketers ranked case studies the #1 most effective marketing tactic to increase sales—ahead of general website content, SEO, blog posts, social media, paid ads and other tactics. )
There’s no magic behind it. Just a proven, simple formula I’m about to share with you. Spend the next 7 minutes reading this guide and you’ll learn how to write case studies better than any case study you’ve created in the past. Important caveat: this article explains how to write a case study for business purposes. If you’re interested in writing research case studies for academia, refer to this excellent guide by University of Southern California. If, in turn, you’re struggling with putting together a medical case study, here’s a fantastic 101 by the BMJ . I’m not going to pretend I know better than these guys do.
For your reference, here’s an example of our very own case study, showing how, at Storydoc, we helped the Spot company boost some of their key metrics: Learn How Spot by NetApp boosted their conversion rates 2x.
Spot's team used this deck to boost their conversion 2x
By drawing the bigger picture even deep-tech software products can be easily explained.

Browse interactive case study templates
No matter how great the contents of your case study might be, if you fail to present it in an eye-pleasing way, most likely, no one will really read it. The good news? I’ve put together a gallery of the most professional, attention-grabbing case study templates available online. You can find it here: Case Study Templates & Design Tips Or, take a shortcut to great case study design and use our presentation maker . Have a look below to see what your case study might look like.

And now, let’s get to the case study 101. (If you’re only interested in a specific section of a case study, simply click on a jump-to link in the table of contents below.
Here's how to write a case study:

1. Open with an introductory overview
The last thing you want is for someone to open your case study, give it a quick glance, and decide to skip. See— People don’t usually read case studies. At least not immediately. First, they skim the contents to see if the subject is relevant enough. How to make sure your case study sticks? At the beginning, place an introductory overview (also called an “executive summary”). Provide an overview of the whole case. It’s not supposed to be a catchy intro but a full synopsis, detailing the problem at hand, your assumptions, the solutions implemented, and the results achieved.
How to write a case study introduction?
Introduce the purpose of the case study—specify exactly what you were aiming to achieve.
Define the problem or the most significant challenge. For instance, low conversion rates, a technological issue or high costs. (It could also be a combination of such factors!)
Explain briefly what the solution to the problem was.
Share the most important results your actions produced. Don’t go into too much detail, a few key points will do. It’s best if you can quantify the results: numbers pop!
Keep it short. Usually, 2–4 paragraphs + a few bullet points with key results will do.
While, as its name implies, this section comes at the beginning of your case study, write it last. First, craft the rest of your document, then pick the most important bits and compile them into the introductory overview.
2. Explain the problem in question
“Adam caught a flat tire. In the middle of the desert. He had no spare, no signal, no food, and only enough water to keep him alive for 48 hours.” Oh dear, poor Adam! What could possibly be done to help him?! See, in your case study, make the client seem like Adam so that, later on, you can paint your company like the miraculous savior. Of course, I’m exaggerating, but only so much. The purpose of the “problem” section in a case study is to arouse emotions from the readers. Ideally, in such a way that they can picture themselves as Adam. Highlight a problem your product or services solve and present an example of when that problem was troubling a client really badly.
How to write a “problem” section in a case study?
In a single sentence, describe your customer’s business challenges and objectives.
Explain the problem your customer faced that prevented them from achieving those objectives prior to working with you.
If that was the case, mention other solutions your client experimented with that didn’t work out and explain why.
Make it clear how the issue or problem impacted the client’s business results so that it’s easy to understand why a solution was badly needed.
3. Detail the solutions implemented to solve the problem
Here comes the moment to toot your own horn a bit (and also that moment when you can get slightly technical). Present your solutions in reference to the issue your client was dealing with and make it obvious that those are easily replicable for all future cases. Of course, the exact formula for this section will depend on your industry and mode of operation. Sometimes a 2–3 paragraph summary will be enough, in other cases, you’ll need to include more detailed technical specs regarding the solution you implemented.
How to write a solutions section in a case study?
Focus on your customer’s experience in using your product or services.
Explain the process: say how long it took to get the solution up and running and what teams on your customer’s end were involved.
Highlight the features of your product or service that turned out to be the most beneficial to your customer.
If possible, attach or link to relevant assets that will work as real-life examples of your solution (unless, of course, the information is highly sensitive).
Always run your case study by your client’s marketing team before you go live. Even if you’re using direct quotes or verifiable results, it’s ultimately their decision whether or not to make certain information freely available.
4. Refer to key results
In business, nothing speaks louder than ROI and you know it. Prospective customers reading your case study won’t be bothered to take notice of your state-of-the-art technology or innovative approach. Neither will they care about your past customers’ happiness. What they want to know is this: Will that help me save or make money? When writing a case study, your job is to present results in a way that answers the above question with a resounding YES. You need to make it blatantly obvious that your solutions heavily impact the bottom line of the client in question and that such results are easily replicable.
Here’s how to write about results:
In a few bullet points, list numerical results your solution delivered to the client.
Ideally, you’ll want to include revenue-related data: increase in clients’ base, more demos booked, higher conversion rates, or optimized pricing.
If you can’t (or aren’t allowed to) share hard sales numbers, refer to softer KPIs: time saved, customer happiness scores, expanding the community, or enhancing brand visibility.
If possible, by all means include quotes from your client. Results should speak for themselves, obviously, but showing the real human whose problems you solved makes for a much more powerful narrative. Plus, it further adds credibility to the case study. Start by preparing a list of powerful case study questions to guide your client interviews.8
5. Finish with recommendations and next steps
Everyone enjoys a solid epilogue. To end on a high note, include a list of key findings from your case study. Even if a given reader won’t decide to get in touch with you, at least you’ll provide them with a valuable source of knowledge—sometimes that’s enough to keep your company top of mind in the future. Plus, if you’re planning to continue working with the subject of your case study, definitely mention that! It shows that your support is valuable enough to warrant long-term collaboration, not just a one-off endeavor. Now, not every case study requires a call to action (especially if your main purpose is to inform and educate rather than convert, which is okay, too), but for those more commercially-oriented ones, do add it. Make your CTA singular and clear —if the most desired action is to reach out to you, leave your contact details, if you’d rather direct prospects to a landing page or a welcome screen, add a button.
And that’s a wrap!
Here are the key points to keep in mind when writing a case study:
Put an introductory overview at the beginning.
Present the problem you were solving and your exact solutions to that problem.
Include numerical, verifiable results your product or services delivered for the client.
Explain what the next steps are, especially if you plan to continue working with the client.
Finish with a strong, clear CTA, making it easy for prospects to reach out to you.
Thanks for reading the guide. Keeping my fingers crossed for your case study and wishing many successful cases so that you’ll always have something to write about.

Hi, I'm John, Editor-in-chief at Storydoc. As a content marketer and digital writer specializing in B2B SaaS, my main goal is to provide you with up-to-date tips for effective business storytelling and equip you with all the right tools to enable your sales efforts.
Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.

Make your best case study to date
Try Storydoc for free for 14 days (keep anything you make for ever!)
How to Write a Case Study - All You Wanted to Know

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

| 📝 Step | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Draft Structure | 🖋️ Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references. |
| 2. Introduction | 📚 In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research. |
| 3. Research Process | 🔍 Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world. |
| 4. Quotes and Data | 💬 Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case. |
| 5. Offer Solutions | 💡 At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself. |
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
%20(1).webp)

Your competitors are optimizing their content. Are you?
✅ Analyze competitor strategies ✅ Plan a path to topical authority ✅ Find profitable keywords ✅ Create winning content ✅ Scale content strategy with AI ✅ Keep old content ranking ✅ Get more organic traffic
Don’t miss out. Join 150k+ Agencies, Marketers, and SEOs.
How To Write A Case Study [Template plus 20+ Examples]

In an era where every niche seems completely saturated, learning how to write a case study is one of the most important time investments you can make in your business.
That’s because case studies help you present a compelling story of success to bottom-of–funnel decision makers. Do it right, and a solid case study can greatly increase your chances of closing new deals.
A 2023 study from the Content Marketing Institute found that 36% of B2B marketers consider case studies to be effective tools for converting prospects into customers.
In this article, I’ll show you step-by-step exactly how to write a case study that makes an impact. Along the way, I’ll highlight several stellar case studies that illustrate how to do it right.
What you will learn
- What a case study is and what it's not.
- How an effective case study can help establish you as an expert and land more clients.
- How to choose the right topic for your case study, taking into account client successes and broad appeal in your customer's industry.
- The essential parts of a good case study and how to write each one.
- Style and formatting points that will make your case study stand out for readers to understand.
- 4 tips for conducting an effective client interview.
- 6 real-life case studies that you can use as examples for creating your own customer stories.
What is a case study?
A case study is a detailed story about how your products or services helped a client overcome a challenge or meet a goal. Its main purpose is to prove to potential customers that you understand their problems and have the experience and expertise to help solve them.
But, even though a case study can help you attract and win customers, it's not just an advertisement for your offerings.
In truth, your company shouldn’t even be the main focus of a good case study.
Instead, a winning case study follows a successful business transformation from beginning to end and shows how you made it all possible for your client.
An example of a case study that conveys a strong customer story is the deep dive we did into how ClickUp used SurferSEO to boost their blog traffic by 85% in a year.
Why you should write a case study
The most obvious reason why you should write a case study is that it's a great way to show potential customers how others in their position have benefited from your product or service.
Here are a few of the key benefits of writing a case study, all of which can help you turn readers into customers.
Demonstrates expertise
A well-written case study shows clearly how your company solved a complex problem or helped a particular customer make improvements using your solution.
This is the sort of expertise other potential clients will look for when they run into the same sort of issues.
For instance, one of CrowdStrike's case studies shows how they helped Vijilan scale its logging capacity so they could stop turning away business.

This positions CrowdStrike as experts in helping deal with log management issues.
Other companies dealing with their own logging problems will definitely find this to be a compelling story. And you can bet CrowdStrike will be on their short list of potential solution providers after reading this case study.
Educates potential customers
You might have the best product on the market, but it won't do you any good if potential clients don't understand how it might help them.
A case study breaks down those barriers by showing real-life examples of your product in action, helping other customers solve their problems.
A good example is the Trello case study library .
Each story gives detailed examples showing how the customer uses Trello and includes actual screenshots from their workflows.
Here is an interesting snapshot from the BurgerFi example.

Here, you get a glimpse of a live Trello board that BurgerFi uses to manage their marketing assets.
By showing how existing clients use your product, you make it a lot easier for future customers to imagine how it might work for their needs, too.
Generates leads
A strong case study is a valuable piece of content that provides insights and can help companies make decisions.
Many of them would be happy to give you their contact information in exchange for the chance to read about potential solutions to their problems.
That combination of valuable content and a hungry market makes case studies great tools for lead generation.
You can either gate part of your case study and leave the rest of it public, or require an email address and other contact information in order to download the full study.
That's the approach Pulsara took in detailing how their telehealth communication platform helped EvergreenHealth improve efficiency:

The names and addresses you collect with this approach will be about as warm as you could ever hope for since they probably have the same sort of problems you solved in your case study.
Along the same lines, case studies can be extremely effective in upselling or cross-selling other products to the decision-makers who read them.
And they are great tools for persuading a client to make a purchase with you.
Indeed, a great case study can often be the "final straw" that lands you a client considering your services.
A 2023 survey by Uplift Content , for example, found that 39% of SaaS marketers ranked case studies as being very effective for increasing sales.
That made it their #1 tactic for the second year in a row.
Builds trust
Potential clients want to know that they can trust you to handle their business with care and to deliver on your promises.
A case study is the perfect vehicle to show that you can do just that.
Take advantage of that opportunity to present statistics, client testimonials, graphics, and any other proof that you can get results.
For example, in their case study about helping a law firm uncover critical data for a tricky case, Kroll shows us just how much they were able to cut through the noise:

Any law firm staring at its own pile of documents to search through would love to have that haystack reduced by a factor of 32.5x, too.
And Sodexo makes good use of customer testimonials in their case studies, like this quote from the procurement lead for a Montana mining company.

Having existing customers tell the world that they count on you is powerful free advertising and builds trust with your readers. That can help transform them into customers down the road.
Provides social proof
You can also use your case study to show that your product or service works in a specific industry.
Real-world examples of customer success stories position you as someone their peers and competitors can turn to, too.
For instance, Stericycle details how they helped seven children's hospitals get a handle on their "sharps" management:

They also include glowing quotes from hospital leaders in the same study.
Other hospitals looking for help in disposing of their hazardous waste will know right away after reading this study that Stericycle understands their needs.
This is the type of social proof that can really help establish you as a go-to solution for the industries you serve.
How to choose a subject for your case study
In order to get the most bang for your buck from your case study, you need to make sure you pick a topic that resonates with your target audience. And one that can make your solution look its best.
Below are 4 ways to select the best subject for your case study.
1. Choose a popular topic
Make sure the topic you tackle in your case study is one that most of your potential clients are searching for.
You may be tempted to highlight an unusual project that you find especially interesting. But that usually won't have the same sort of selling power as a topic with more broad appeal.
For instance, Aruba Networks has helped colleges and universities with all sorts of networking projects. Some of those involve really fascinating edge cases like research labs, esports arenas, and other innovative solutions.
But what most schools are looking for in a network upgrade is improving connectivity across campus while enhancing security and saving money.
Those are exactly the outcomes Aruba focuses on in its Doane University case study .
Remember that your case study is likely to be read by decision-makers at the bottom of the sales funnel who are ready to buy.
Your content needs to resonate with them and address the questions they want answered in order to make their decision.
Aruba tackles their customers' concerns head-on throughout the Doane study, as you can see from their section headings:
- "Realizing a hyper-connected vision"
- "10X throughput eliminates academic barriers"
- "More secure with less effort"
- "Greener and more resilient at better insurance rates"
College administrators can see at a glance that Aruba understands their needs and has helped other institutions with similar problems.
2. Consider relevance and attractiveness
Although you want to choose a popular subject for your case study (as discussed above), it's also important to make sure it's relevant to your target audience.
For instance, if you provide design services, a one-off project you did to help a local company set up its website might have taught you a lot. But most of your potential readers will be much more interested in reading about how your designs helped that client improve brand perception.
It’s also best to choose a situation where your product or service is used in a way that you expect most potential users to adopt.
For example, Allegion's Mount Holyoke case study (PDF) details how one campus used their products to move to contactless and mobile entry systems.
Students today demand more control over their physical security than ever before. And the administrative overhead of managing thousands of doors and physical keys on a college campus is enormous.
As a result, most schools are interested in using technology to enable their students and reduce staffing costs.
Allegion hits those points dead-on with this case study.
An added benefit of choosing a topic with broad appeal among your target client base is that you can use the content in your normal distribution channels.
For example, you can publish all or part of it as a blog post, include it in your newsletter, or use it as the basis for a YouTube video. Wherever your audience is, that's probably a good place to promote your case study.
3. Identify a 5 star use case
A case study is like a sales executive for your company.
It needs to show your product or service in the best possible light and highlight its features and benefits while distinguishing it from other products.
Choose a client example that really makes your solution look like a superstar and showcases its most outstanding attributes.
You should also avoid showing your product or service being used in a novel or completely innovative way. While that can provide some solid insight, you risk alienating your typical client who needs to know that you can solve their specific problem.
Instead, your case study should demonstrate how your solution took on a common industry problem and delivered stellar results.
A great example is Beckman Coulter's case study that details their work with Alverno Labs.
The objective was to reduce the time it took Alverno to deliver lab test results while reducing operating costs, which are common goals for many testing labs.
The case study presents a detailed description of how Beckman Coulter implemented a continuous improvement process for Alverno. They enhance the discussion with several meaty visuals like this project roadmap:

They also include plenty of tangible data to prove their success.

And of course, include direct client testimonials:

From top to bottom, this case study proves that Beckman Coulter understands their customers business needs and can offer top-notch solutions.
4. Find a satisfied customer
You're going to need input from your client in order to build the most complete and accurate case study that you can.
So when you're trying to choose a customer story to use, look for a client who is happy to share their positive experience working with you.
Try to find one who seems genuinely eager to talk so that they will be timely with their responses to your questions.
If you have a customer who is willing to sit down for an actual interview with you, they're a great candidate. You'll get answers quickly, and the client is obviously comfortable enough with your relationship to talk with you directly.
A good example that focuses on a satisfied client comes from Aerofloat, an Australian wastewater treatment company.
In their Norco Food Case Study , Aerofloat reports that Norco hired them for additional projects as a result of their successful prior engagement:
It's always good to show prospective clients that your existing customers stick with you.
So try to pick a case study done in collaboration with a current client, not one from the past.
Aerofloat also highlights their ongoing relationship with Norco by also including them in the customer list on their About page:

How to write a case study
Now that we’ve covered the benefits of writing a case study and figured out how to pick the best topic for your situation, it’s time to get down to the business of writing.
Below is a rundown of the sections that make up the structure of a typical case study. For each piece, I’ll show you what types of content you should include and give you an example of a study that does it right.
Here are 8 tips to writing a case study.
1. Attention grabbing title
The title of your case study needs to grab potential readers attention and convince them that this is a valuable piece of content.
Make your title catchy, concise, and descriptive, just like you would for a good blog post. But you also need to make sure you give your readers a clear idea of what the case study is about.
Offer them at least a hint of the type of results you were able to deliver, too.
It’s a good idea to use numbers here – the higher, the better. It's especially effective if you can show how quickly you got results and how much money your client saved or made as a result of working with you.
Our ClickUp case study that I mentioned earlier is a good example. The full title is
SurferSEO Helps ClickUp Publish 150+ Articles And Achieve Blog Traffic Growth of 85% in 12 Months.
Here are some other case studies that make effective use of numbers in their titles:
- Healthcare Administrative Partners Increases Online Patient Payments by 20% in Two Months
- Case Study: Taylor Kotwa, Sprinter, Increases FTP 7% in 4 months
- Case Study: Lakeview Farms Reduced Downtime by 36% in 6 Months
- CASELY case study: Improved first response time by 10x while experiencing 16,954% growth
This type of headline gives potential clients a sense that you will work with urgency to improve their bottom-line results.
2. Hook readers in your introduction
The introduction of your case study should set the stage for the comprehensive narrative that follows.
Give a brief description of the problem for context and quickly introduce the customer's story. Touch on the results you helped them achieve, but don't go overboard on details.
Overall, the introduction should give your reader just enough information to keep them engaged and ready to move into the heart of the case study.
It should also establish that they're in the right place and that you are the right person to be telling this story.
This case study about the cybersecurity program at Investors Bank includes a solid example of an effective introduction:
3. Highlight the challenge
This section should clearly outline the problem or challenge that your customer is facing.
Help your readers understand why a solution was necessary, and why that specific pain point was bothering the client.
And, since this is the entire motivation for the project in the first place, don't skimp on details.
For instance, one of Verkada's case studies explains why maintaining security cameras is a huge challenge for Crystal Mountain Resort in Washington state. They start off with a direct quote from the resort's IT director:
The elevation tops out at a little over 7,000 feet, so the weather conditions can get extreme. We needed durable cameras capable of handling everything from snowstorms to 100 MPH winds.
That makes it crystal clear what sort of problem Crystal Mountain was facing.
The case study then adds more detail with separate subsections about hardware durability, image quality, and cumbersome footage retrieval.
By the time they finish reading this section, your readers should have no doubt about what the problem is and why a solution is needed.
4. Solve their problem
The solution section is one of the most important parts of a case study.
This is your chance to describe how your product or service provided a solution to the problem or challenge your client was having.
It's where you can really start to make a connection with potential new clients by showing them that you understand the issue at hand.
First, provide some details about how you analyzed the situation. The Kroll case study on handling critical legal data mentioned earlier does a great job of this with bullet points describing their research process.

This type of analysis helps build confidence that you take a thorough approach to your engagements and are looking out for your clients best interests.
Now you can move on to describe the solution you and your client chose based on your investigation.
In their legal case study, Kroll determined that the best solution involved digitizing thousands of paper documents and using AI to analyze more than a million documents.
Kroll describes in detail how they used their RelativityOne system to achieve those goals:

This level of detail helps prospective customers better understand the root cause of their problems and positions you as the right company to solve them.
5. Showcase your results
The results section is all about proving that you can actually deliver on the promise of your proposed solution. Go heavy on the details here, too, and make sure your readers understand the results you achieved.
Wherever possible, use specific numbers and data points to show exactly how effective your solution was for your client.
A good example is this BetterBricks case study showing how they helped an aerospace company slash energy costs.
They distilled their bottom line results into a simple table:

The text of the study then goes into more detail about what these numbers mean, but this quick graphic lets readers know right away the scope of the results achieved.
Here is a sampling of BetterBrick’s more detailed explanation of their results in this case:

This is your place to really crow about the success you achieved with your client, so make it as obvious as possible just how impactful you were.
6. Use multimedia well
One way to make a lasting impression on potential clients is to include relevant visuals throughout your case study.
Graphs, screenshots, and product photos help break up the text and make your study more engaging overall.
But they can also add details to your story and make a memorable visual impact beyond what mere words can accomplish.
We got a taste of that with the table of results in the BetterBricks example above, but that's just the start.
Inrix is a good example of a company that loads up its case studies with insightful and engaging media to tell a better story.
For instance, in their breakdown of a collaboration with the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (DOT), Inrix uses charts, tables, and graphs throughout.
One innovative example is this diagram about crash distances:

This really brings the idea to life in a way that words alone can't, and it's likely to stick with readers long after they've clicked off the case study.
Other types of media that companies use to good effect in their case studies include pictures of key client stakeholders, interactive charts, tables, and simple graphs.
You can see in this high-level overview that Inrix includes most of these in their Pennsylvania DOT case study:

You can even use video to demonstrate your solution or to share a client testimonial.
If possible, include direct quotes from your client to add authenticity to the case study.
This will show potential customers that you and your existing client have a good relationship and that they value your work.
It’s pretty compelling stuff to have a ringing endorsement like this one from an EnergyCAP case study , to show your readers:

You can place customer quotes throughout the case study to highlight important points, and you should definitely try to include at least one that shows overall customer satisfaction.
Chances are you have some of these quotes already in the form of testimonials or as part of the customer interview you conducted in preparing for your case study (more on that later).
You can use those quotes here if they fit the context of your case study.
That will save time and red tape for both you and your client since they'll be reviewing your final case study before it goes live anyway.
8. Conclusion
The conclusion should summarize the key points of the case study and reinforce the success of the solution. It could also include a call to action, encouraging readers to try your product or service or to get in touch for more information.
You might also include information about future plans with the client to reinforce the idea that your relationship is strong and ongoing.
That's the approach that Gravitate Design used in their case study about helping GoBeyond with their bounce rates and time on page:

Like the introduction, the conclusion section of a case study should be short and sweet, giving just enough detail to make the reader want to hear more from you.
Checklist for case studies
Beyond the story that you want to tell in your case study, you also need to pay attention to several other factors. Indeed, the layout and format of your study can have a big impact on how effective it is at keeping your readers engaged and delivering your message.
Here is a quick checklist for creating case studies.
Break up the text with headings and subheadings
Big blocks of text can be intimidating and make it tough for your audience to stay on track.
In contrast, a case study with clear headings and subheadings throughout breaks up the story and gives readers visual clues about what's coming.
This also makes the case study easier for readers to scan and helps you keep each section focused on a single idea.
Use bullet points for lists or key points
Along the same lines, bullet points let you present important information in small bits that are easy for readers to digest.
Some of the best uses of bullet points include:
- A series of facts or tips
- A list of product features or benefits
- A quick summary of results
- Steps in a how-to procedure
- A rundown of multiple statistics
For these bite-sized hunks of detail, bullets often make for a much cleaner and readable list than jamming all the information into a single paragraph.
Bullet point lists also make great quick references for readers to come back to later.
Highlight key points with bold or italic text
Bold and italic text draws the reader’s eyes to the words you highlight, which lets you really drive home key ideas in your case study.
You can use this technique to introduce new terms, place emphasis on a sentence, and showcase important parts of your approach or results.
Like bullet points, bold and italic text also give readers a visual anchor for reference as they’re working through your document.
Make paragraphs short and to-the-point
Aim for 3-4 sentences per paragraph to keep the text readable and engaging. Each paragraph should focus on one main idea to support the subject of the section it’s in.
Using short paragraphs tells readers at a glance that there are break points throughout your case study and helps keep them engaged.
Keep consistent length across the case study
Throughout all parts of your case study, try to cover your main points in detail without overwhelming the reader.
Your potential clients are there to find a possible solution to their problems, not to read a novel.
Give them an inviting document structure and then lead them through each section with clear explanations and no fluff.
Adjust the length based on the complexity of the subject
The flip side of the tip above about keeping your case study tight and focused is that you need to make sure you cover your topic in detail.
Very complex topics will require more explanation and longer overall case studies than simpler subjects.
For example, a case study about paving a church parking lot might be pretty short.
But a story about implementing a comprehensive information security program for a state government will likely be much longer and more detailed.
Include a summary with some takeaways
At the end of your case study, summarize the key takeaways and results to reinforce the message you’re trying to get across.
Briefly recap the problem your client was facing, the solution you came up with, and the results you achieved. Think of this as an executive summary that gives business leaders the TL;DR version of your customer’s success story.
Content Snare includes an eye-catching summary in the case study detailing their efforts to grow their email list:

The overall goal is to leave potential clients with a good last impression and invite them to contact you with questions.
Use visuals to break up text and illustrate points
As we saw in the "How to write a case study" section above, graphs, charts, or images can make your case study more engaging and help illustrate key ideas or results. They also add visual variety and help break up the monotony of text-heavy studies.
Use these types of visuals to help keep your readers interested and make your story more complete.
Below is a high-level view of a portion of Advanced HPC’s Philips case study , which does a great job of incorporating the points in this section. It pulls together all the visual elements to create a very appealing reader experience.

4 tips to create an effective case study
You’re going to need your customer’s input in order to craft the most effective case study possible. It’s their story, after all, and they’re the ones who know what it was like to work with you throughout the process.
They also hold key details that you probably don’t know.
So, once you have their permission to write about the project, you’ll need to talk to them about the specifics. But you also want to respect their time.
Here are 4 tips on how to conduct an interview for your case study.
Prepare questions in advance
Know what information you need and prepare questions to pull that information from your client.
Doing this in advance will help you formulate the questions and sequence them properly to avoid bias and wasting time.
Have a few follow-up or emergency questions ready, too, in case you run into a dead end.
Record the interview
With your client’s permission, record the interview to ensure accuracy and so you can come back to listen to important points again.
This helps you avoid bothering your clients with follow-up questions and also gives you more freedom to let the interview evolve in a natural conversational manner.
Make the interviewee comfortable
Explain the interview process to your client, why you're asking them to talk, and how the information will be used. Remember that you are the one who “needs” the case study, not them.
So you go the extra mile to ensure that your guest is as comfortable as possible.
That also means being flexible with the format of your interview.
If your client doesn’t have time for calls, offer to trade voice notes. Or give them a shared Google document for trading questions and answers.
And if you do end up conducting a live interview, agree to meet at a time that’s best for them.
No matter how you end up conducting your interview, make it clear that your client will be able to review the final version before you make it live.
Give them veto power over any of the information you put together.
Ask open-ended questions
Even though you’ll start out with a series of questions you need answered, don’t limit yourself to those. Instead, encourage your interviewee to share their story in their own words.
Leave some room to ask open-ended questions and let the conversation evolve naturally.
Here are a few examples of the types of questions for discussion:
- What would you do differently if you were starting this project again?
- What do you think about XYZ emerging technology in relation to your industry's challenges?
- What sorts of other projects do you think Acme's solution might help with?
- How do your company's day-to-day operations and needs from how the relevant theories describe the industry?
Especially if you’re recording the interview, as suggested above, you can go back later and put things in a logical order.
Once you have all of the raw material, then you can curate the information and edit it to come up with your final product.
6 case study examples to follow
Now that you know what makes a great case study and how to write one, let's finish up with a few more top-notch business case study examples.
Each of the case studies below hits many of the points in this article, but they all take a different approach. Use them for inspiration or when you need a little refresher on how to write a case study.
This case study provides a detailed account of how Monograph, a B2B SaaS company, improved its marketing projects and reporting using Databox.
It's a pretty straightforward example of the best practices we've discussed in this article, with an introduction followed by background information on the company (Monograph) and the challenges they faced with manual tracking of each data point.
It describes the solution that Databox helped put in place and then shows clear evidence of the results their customer achieved:

Case studies don't come much more textbook than this one, which makes it a great example to follow.
Growth Design on Airbnb
Growth Design takes a totally unique approach to case studies, each one is an online comic book!
Read through their case study about Airbnb , though, and you'll see that it meets all the criteria for a complete case study even if the setup is a little different than most.
Here is a look at the landing page for this beauty of a study.

The author starts out with a problem: the need to book a place to stay in a foreign country in a hurry. So he heads to Airbnb but ends up overwhelmed by choices and bounces to Google Maps to make his reservation.
He concludes that Airbnb was not the full solution for him in this case and suggests several places they could make improvements.
It's a pretty neat dive into a well-known user experience, and it's also a great lesson in how to use visuals to keep your readers engaged in your case study.
This case study about how Grubhub used Webflow to build a viral marketing campaign hits you with stunning results right off the bat.

From there, the study tells the full story of how they achieved these results. Even though the author doesn't explicitly break out the problem, solution, and results sections, she still takes the reader through that journey.
It's a concise but complete story broken up by a few choice graphics.
This case study dives into how Employment Hero uses Slack to keep their remote employees engaged and productive as the company grows.
It details how Employee Hero continuously reevaluates its app usage to identify possible solutions to issues that arise and how Slack consistently helps meet the challenges.

This case study is a great example of picking a use case that is relevant to most of Slack's user base -- improving communication and productivity among remote employees.
Slack also makes effective use of quotes from the decision makers at Employment Hero.
We already talked about our ClickUp case study a little earlier in this article, but it's worth a deeper look as an example to help guide your writing.
As you would expect, this case study hits main points we've covered here: problem statement, solution, and results.
But there are a couple of "extras" that make this one stand out.
For starters, it doesn't just present a single solution. It presents three , each one addressing a different aspect of ClickUp's objectives and each one showcasing a different Surfer feature set.
For example, solution #1 describes how ClickUp improved their on-page SEO with the help of Surfer’s Content Editor .
This case study also provides a high-level view of ClickUp’s project management processes and describes how they incorporated Surfer into their content workflows.
It’s a really instructive example of how you can use a case study to help prospective clients envision how your product might fit their situation.
Zoom’s library
This one isn't a single case study at all but a library full of case studies designed to help potential clients understand how Zoom can benefit them.

Here you'll find stories about how very recognizable organizations like Capital One, Vox Media, and the University of Miami are using Zoom to boost connectivity and productivity among remote workers.
There are plenty of good examples here that you can consult when you get stuck writing your own case study.
And the entire library is a great example of using case studies to demonstrate expertise with the help of social proof:
The Zoom case study library also makes liberal use of video, which might give you some good ideas about how you can, too.
Key takeaways
- Case studies are one of the best ways to generate leads and convert readers into customers.
- By showcasing the success you've had helping previous customers, case studies position you as an expert in your field.
- Good case studies can be the final push businesses need in their decision making process to buy your products or services.
- Pick a use case for your study that has broad appeal in your industry and that showcases your products and services in the best light possible.
- Effective case studies follow a predictable format: introduction, problem statement, solution, results, and conclusion.
- Make your case studies as readable as possible by including visual elements like graphs and images, and by breaking up the text into smaller sections, subsections, and concise paragraphs.
- Be as thorough and accurate as possible by conducting client interviews to gather background information for your case studies.
- Follow top-notch case studies for inspiration and ideas about how to make your own case studies as good as possible.
A well-written case study shines a light on your products and services like nothing else and helps position you as an expert in your field.
By showing that you understand their problems and have helped others overcome similar issues, you can prove to prospective clients that you are well-suited to help them, too.
Use the step-by-step instructions in this article to craft a case study that helps you and your company stand out from the competition.
https://surferseo.com/blog/write-case-study/
7-day Money-Back Guarantee
Choose a plan that fits your needs and try Surfer out for yourself. If you won’t be satisfied, we’ll give you a refund (yes, that’s how sure we are you’ll love it)!

More From Forbes
Creating an effective case study: 12 important tips to remember.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
The practical application of a theory or idea is the most effective way of demonstrating its usefulness. Case studies allow for the dissection of practical applications to uncover the thinking that led to them.
The best thing about case studies is that they can be used as a learning tool for both successful concepts as well as failed ones, while also serving as a valuable business card when approaching new customers. Developing a case study, however, requires delving into the background of a project and uncovering what made it good or bad. In addition, the information has to be packed in such a way to emphasize your skills and creativity without being overly promotional.
To help, 12 members of Forbes Agency Council examine the key elements to keep in mind when creating an effective case study.
Members explain how to create an effective and powerful case study for your business.
1. Don't Make It About Yourself
The wrong way to approach a case study is to make it about you and your process. The reader cares less about your motivation and more about the results your efforts created. Start off by describing the results that you created and then go into the general detail of your strategic and tactical approach to delivering those results. - John Gumas , Gumas Advertising
2. Tell A Story
The best case studies tell a story, rather than recite a chronology of facts or data points. To create a story arc, start with a few sentences describing the situation, followed by a few sentences highlighting the "dramatic tension" (e.g. X almost happened, Y threatened to derail the effort), and conclude with a few sentences tying the resolution to the value or point of the product or service. - Beth Noymer Levine , SmartMouth Communications
3. Lead With A Solution
Case studies are, by their very nature, boring. It is important to break past that by creating case studies that strike at the very problem a lead needs help with. Leading with a problem and demonstrating how you fixed it is the best way to get attention -- especially if it can be produced in an engaging way, such as through video or audio media. - Stefan Pollack , The Pollack PR Marketing Group
4. Include Relevant Data
It's great that you worked with a certain company, but what did you really do for them? That should be defined in the case study. If you can't define it in numbers and results, then think about using the brand in a testimonial instead. A case study is just that -- a study of what happened in a particular case. Make sure you tell the whole story. - Christine Wetzler , Pietryla PR
5. Always Use Specific Numbers
If you're going to show an increase in a certain metric, use the actual number. When you say something like "we increased conversions by 500%," it sets off a red flag for people. They'll think you just made it up. But if you show real numbers and even have the screenshots to back it up, it'll become more relevant and believable. - Greg Trimble , Lemonade Stand
6. Keep It Succinct And Pass On The Fluff
The vast majority of people skim content, including case studies. You have to put yourself in your prospect's shoes and understand what they want. They're primarily looking for the success you've provided the client. So focus on that and skip on any fluff content that doesn't align around that. - Nishank Khanna , Demand Roll
7. Tailor Them To Your Audience
Sure, you're going to have generic case studies, but when seeing a client, ensure that you really understand the problem the client faces. Then make your case show how you've solved the problem before. You can highlight different capabilities based on different needs of the client. - Emilie Tabor , IMA - Influencer Marketing Agency
8. Make It Multi-Format
If you can get case studies, quotes and testimonials, always include hard data and tie it to revenue or cost stories. Beyond this, make it multi-format by leveraging graphics, video and text so that it can be consumed and promoted on various platforms. This will maximize the exposure and utility for your successful client case studies. - Zamir Javer , Jumpfactor
9. Let The Images Do The Work
Aside from ensuring a case study is focused on the problem your brand has solved for a customer, nothing brings it to life more than imagery. In lieu of a long-form case study, consider a photo essay with solid captions narrating the case study as a better option for illustrating the value of your product or service and keeping audiences truly engaged. - Emily Porter , Havas Formula
10. Paint A Picture For Your Prospect
Highlighting your wins is great, but remember that a case study should showcase how you solved a client's most pressing problem so that a new prospect can see how you got from point A to Z. This is how we like to tell our clients' success stories: client profile, the challenge, results, strategy and looking toward the future. Remember, the results are just one piece of the puzzle. - Bernard May , National Positions
11. Abstract It First
We think if we write it, someone will accept it. If you remove the outlet from the process, more often, you'll need to rewrite it. Develop the abstract or a couple of abstracts with four elements: company's expertise and solution; customer's industry and challenges; what solution you delivered; why that solution is so innovative. Offer the outlet a chance to contribute, then write with insight. - Dean Trevelino , Trevelino/Keller
12. Know When To Insert Them Into The Campaign
We've analyzed user footprint data on the inbound journey and see a clear trend. Most people are only interested in case studies once they are convinced that a service provider could be a good fit for them. Case studies usually come after reviewing staff profiles and thought leadership content. Insert them too soon and they lose their value in the sales campaign. - Randy Shattuck , The Shattuck Group
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

How to Write a Case Study: Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- October 7, 2022

Content Manager at SocialBee
Why is learning how to write a case study so important?
Well, because it provides your customers with social proof and supporting evidence of how effective your products and services are. Moreover, it eliminates the doubt that usually makes clients give up on their next purchase.
That is why today we are going to talk about the step-by-step process of writing a case study . We prepared five business case study examples guaranteed to inspire you throughout the process.
Let’s get started!
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a piece of content that focuses on a case from your business history. It describes the problems your client faced and the solutions you used to help them succeed.
The goal of a writing case study is to promote your business , so your aim should be to put together a compelling story with evidence that backs up all your claims.
Case studies use real-life examples to show your clients the quality and effectiveness of your products and services. It’s a marketing tool that provides credibility and it helps your potential clients gain confidence in your brand.
Case studies can be structured in different formats:
- A written document
- An infographic
- A blog post
- A landing page
Case Study Benefits
A great case study makes your potential customers want to benefit from the products and services that helped your client overcome their challenges.
Here are the benefits of writing a case study:
- It is an affordable marketing practice
- It decreases the perceived risk of your potential clients
- It provides transparency
- It builds trust and credibility among prospective customers
- It makes your potential clients relate to the problem
- It provides your potential clients with a solution for their problems
How to Write a Case Study
Now that you know what a case study is, let’s get into the real reason why you are here — learning how to write an in-depth study.
Here is the step-by-step process of writing a case study:
- Identify the topic of your case study
- Start collaborating with a client
- Prepare questions for the interview
- Conduct the case study interview
- Structure your case study
- Make it visual
Step 1: Identify the Topic of Your Case Study
A case study starts with a strategy. Choosing what you want to write about should be closely related to your business needs. More specifically, what service or product do you want to promote through your case study?
Because case studies focus on client challenges, business solutions, and results, you have to carefully pick the case that your potential clients will relate to the most.
To communicate the benefits of your business, you should focus on a customer story that appeals to a specific segment of your audience . Consequently, you will target clients that relate to your customer example while providing a solution for their needs and pain points — your products and services.
Start by focusing all your research methods on identifying your customers’ main pain points. Then find examples of how your products or services have helped them overcome their challenges and achieve their goals .
Furthermore, to make sure you choose the best case study topic for your buyer persona , you should have a meeting with your sales/customer service team. Because they are in close contact with your customers, they will be able to tell you:
- The main challenges your clients face
- The services/products that bring them the best results
These are the main two pieces of information you want your case study to focus on.
Step 2: Start Collaborating with a Client
With a clear topic in mind, you have to find the best fit for your case study.
However, that is not all. First, you must obtain the client’s permission. After all, your business story is theirs too.
So, craft an email to provide your client with an overview of the case study. This will help them make a decision.
Your message should include:
- The case study format (video, written, etc.) and where it will be published (blog, landing page , etc.)
- The topic of the document
- The timeline of the process
- The information that will be included
- The benefits they get as a result of this collaboration (brand exposure, backlinks)
Additionally, you can offer to schedule a call or a meeting to answer all their questions and curiosities and provide a means for clear and open communication.
Once you receive a positive response from your client, you can continue with the next step of the process: the actual interview.
PRO TIP: A great way to ensure a smooth and safe collaboration between you and your client is to sign a legal release form before writing the case study. This will allow you to use their information and protect you from issues that may occur in the future. Moreover, if the client is not comfortable with revealing their identity, you can always offer them anonymity.
Step 3: Prepare Questions for the Interview
Now that you have the subject for your case study, it’s time to write and organize your interview in several sets of questions.
Don’t forget that the whole structure of your case study is based on the information you get from your customer interview.
So pay attention to the way you phrase the questions. After all, your goal is to gather all the data you need to avoid creating a back-and-forth process that will consume your client’s time and energy.
To help you create the best questionnaire, we created a set of case study questions and organized them into different categories.
Here are the five main sections your case study interview should contain:
- The client’s background information
- The problem
- The start of the collaboration
- The solution
- The results
A. The Client’s Background Information
This part of the case study interview must give a comprehensive look into your customer’s business and allow your readers to get to know them better.
Here are some question ideas:
B. The Problem
Now it’s time to get into the reason your client came to you for assistance, the initial challenge that triggered your collaboration.
In this part of the interview process, you want to find out what made them ask for help and what was their situation before working with you.
You can ask your client the following case study questions:
C. The Start of the Collaboration
This part of the case study interview will focus on the process that made your collaboration possible. More specifically, how did your client research possible collaboration opportunities, and why they chose your business?
This information will not only be informative for your future customers but will also give you a behind-the-scenes look into their decision-making process.
D. The Solution
It’s time to get into one of the most significant parts of the case study interview — the solution. Here you should discuss how your services have helped their business recover from the problems mentioned before.
Make sure you ask the right questions so you can really paint the picture of a satisfied customer.
Have a look at these question examples:
E. The Results
The best proof you can give to your customers is through your results. And this is the perfect opportunity to let your actions speak for themselves.
Unlike the other marketing strategies you use to promote your business, the content is provided by your customer, not by your team. As a result, you end up with a project that is on another level of reliability.
Here is how you can ask your client about their results:
Step 4: Conduct the Case Study Interview
Now that you have a great set of case study questions, it’s time to put them to good use.
Decide on the type of interview you want to conduct: face-to-face, video call , or phone call. Then, consult with your client and set up a date and a time when you are both available.
It should be noted that during the interview it’s best to use a recording device for accuracy. Maybe you don’t have time to write down all the information, and you forget important details. Or maybe you want to be focused more on the conversational aspect of the interview, and you don’t want to write anything down while it’s happening.
Step 5: Structure Your Case Study
The hard part is over. Now it’s time to organize all the information you gathered in an appealing format. Let’s have a look at what your case study should contain.
Here are the components of a case study:
- Engaging title
- Executive summary
- Client description
- Introduction to the problem
- The problem-solving process
- Progress and results
A. Engaging Title
Putting that much work into a project, it would be a shame not to do your best to attract more readers. So, take into consideration that you only have a few seconds to catch your audience’s attention.
You can also use a headline analyzer to evaluate the performance of your title.
The best case study titles contain:
- Relevant keywords
- Customer pain points
- Clear result
Case study example :

B. Executive Summary
Your executive summary should include a thesis statement that sums up the main points of your case study. Therefore, it must be clear and concise. Moreover, to make your audience curious, you can add a statistic or a relevant piece of data that they might be interested in.
Here is what you should include in your executive summary:
- The business you are writing about (only if the clients wants to make themselves known)
- Relevant statistics

C. Client Description
Here is where you start to include the information you gained from your interview. Provide your readers with a clear picture of your client and create a context for your case study.
Take your client’s answers from the “Client Background” section of the interview and present them in a more appealing format.

D. Introduction to the Problem
In this section, use your client’s interview answers to write about the problem they were experiencing before working with you.
Remember to be specific because you want your audience to fully understand the situation and relate to it. At the end of the day, the goal of the case study is to show your potential customers why they should buy your services/products.

E. The Problem-Solving Process
Next, explain how your service/product helped your client overcome their problems. Moreover, let your readers know how and why your service/product worked in their case.
In this part of the case study, you should summarize:
- The strategy used to solve the problem of your customer
- The process of implementing the solution

F. Progress and Results
Tell your readers about what you and your client have achieved during your collaboration. Here you can include:
- Graphics about your progress
- Business objectives they have achieved
- Relevant metrics

Step 6: Make It Visual
To elevate the information you have written for your audience, you must make sure it’s appealing and easy to read. And a great way to achieve that is to use visuals that add value to your case study.
Here are some design elements that will make emphasize your text:
- Graphic symbols that guide the eye (arrows, bullet points, checkmarks, etc.)
- Charts, graphics, tables
- Relevant screenshots from business reports
- The colors and fonts of your brand
- Your client’s logo
Platforms like Canva can really come in handy while designing your case study. It’s easy to use and it has multiple free slide templates and graphics that save you time and money.
PRO TIP: Share Your Case Study Across All Marketing Channels
A case study is a perfect example of evergreen content that can be reshared endlessly on your social media channels .
Aside from helping you maintain a consistent posting schedule with ease, case study-related posts will increase your credibility and push leads toward the bottom of your marketing funnel . Other examples of social proof evergreen content are reviews, testimonials, and positive social media mentions.
To keep track of all your evergreen posts and have them scheduled on a continuous loop, use a social media tool like SocialBee.
Create evergreen content categories where all your posts get reposted regularly on your social media channels.
Start your 14-day trial today and start using SocialBee for free!
Aside from promoting your case study on social media, you can also feature it in your newsletter that you can create using email newsletter software , include it as a pop-up on your website, and even create a separate landing page dedicated to your customer study.
Share Your Case Study on Social Media with SocialBee!
Get to writing your own case study.
What do you think? Is writing a case study easier than you thought? We sure hope so.
Learning how to write a case study is a simple process once you understand the logical steps that go into it. So make sure you go over the guide a couple of times before you start documenting your customer success stories.
And remember that the goal of your case study is to attract more leads . Therefore you need to include tangible results and valuable details that will compel your audience to invest in your products and services.

Article written by

Content writer at SocialBee
Related articles

Understanding How the X (Twitter) Algorithm Works in 2024
Have you noticed that some tweets always seem to appear at the top of your feed while others get buried?

How to Use LinkedIn Hashtags to Grow Your Follower Base
#SocialMedia is all about #Networking, with a pinch of #Innovation in a world ruled by #DigitalMarketing. You probably recognized the
Level up your social media game with exclusive resources delivered straight to your inbox
Proudly supporting
Exciting news!
WebPros acquires SocialBee
Use SocialBee’s Free AI Post Generator to create content for your social media profiles.
- Customizable tone of voice
- Several content variations to choose from
- 1000+ pre-made AI prompts
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
Your Step-By-Step Guide To Writing a Case Study

Creating a case study is both an art and a science. It requires making an in-depth exploration of your chosen subject in order to extract meaningful insights and understand the dynamics that more general surveys or statistical research might not uncover. At the same time, your case study also needs to be a compelling read to ensure those insights get attention from other people!
Unsurprisingly, the prospect of crafting an effective case study can be daunting. It calls for strategic planning, careful organization, and clear communication, all of which can be challenging even for experienced researchers. That's why we've created this step-by-step guide, which breaks the process down into manageable steps, demystifying the journey from defining your research question to sharing your findings. Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a first-timer, this guide aims to equip you with the necessary tools and tips to create a case study that's not just informative, but also engaging and impactful.
Are you ready to unlock the potential of case studies? Let's dive in!

What is a case study?

First, it's important to understand what a case study is – and what it isn't.
A case study is a thorough exploration of a specific subject or event over a certain time frame. Case studies are utilized in numerous fields, including sociology, psychology, education, anthropology, business, and the health sciences, and employ various research techniques to shed light on complex issues.
A case study does not provide absolute proof or conclusions that can be universally applied. Because it concentrates on one particular case or just a few cases, the findings might not apply to different contexts or subjects. Case studies also aren't ideal for determining cause-and-effect relationships as they do not use controlled conditions to separate and measure the impacts of different factors. Lastly, it must be said that a case study isn't just a random assortment of facts or observations; it necessitates a clear research question, a methodical approach to data collection and analysis, and a thoughtful interpretation of the results.
Getting started

Now that we've established the definition and purpose of a case study, let's explore the process by which one is created. You can produce a case study by following these nine steps:
1. Define the purpose of your case study
Before you start writing a case study, you need to define its purpose clearly. Ask yourself: What is the research question or problem you aim to solve? What insights are you looking to uncover? Your goals will guide your research design and influence your choice of case. This initial stage of introspection and clarification is crucial as it acts as a roadmap for your study.
2. Select the case to study
Once you've defined your research objective, the next step is to choose a suitable case that can help answer your research question. This might be a unique, critical, or representative instance. Unique cases offer the opportunity to observe and analyze a situation that is unusual or not well-understood. In contrast, a representative or typical case is often chosen because it represents other cases or a broader phenomenon.
In any case, be sure to justify your choice. Explain why the case is of interest and how it can contribute to the knowledge or understanding of the issue at hand. For instance, if you're studying the effects of corporate restructuring on employee morale, you might choose to focus on a company that recently underwent a significant restructure.
3. Conduct a thorough literature review
Performing a literature review involves a careful examination of relevant scholarly articles, books, and other sources related to your research question or problem. In the process, you identify gaps in the current knowledge and determine how your case study can address them. By critically examining existing research, you will not only gain a comprehensive understanding of your chosen topic but also be able to refine your research question or hypothesis, if necessary.
4. Choose a methodological approach
The methodological approach used in your case study will depend on your research objectives and the nature of the case. Methodologies that can be employed in case studies include qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods .
Qualitative methods are often used when the goal is to explore, understand, or interpret certain phenomena. These involve approaches like interviews, focus groups, or ethnography. Quantitative methods, on the other hand, are used when the goal is to test hypotheses or examine relationships between variables. Quantitative approaches often include experiments. Also, surveys may be either qualitative or quantitative depending on the question design.
You may choose to use a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods (mixed methods) if it suits your research objectives.
5. Collect and organize your data
Data collection should be systematic and organized to maintain the integrity and reliability of your research. You need to plan how you will record and store your data to ensure that it's accessible and usable.
If you're conducting interviews or observations, consider using recording devices (with participant consent) to capture the data accurately. In addition, you may want to transcribe the recorded material for easier analysis. If you're using documents or archival records, develop a system for coding and categorizing the data.
6. Analyze the data
Analysis involves interpreting your data to draw out meaningful insights; it is in this stage that your findings start to take shape. Depending on the nature of your data and your research question, you might use any of a variety of analysis methods. For qualitative data, you might employ thematic analysis to identify key themes or grounded theory to generate a new theoretical framework. For quantitative data, you might use statistical analysis to identify patterns or correlations.
Always be open to unexpected findings. Your initial hypotheses might not be supported, or you might uncover new insights that you hadn't initially considered. Remember that all data, whether they fit neatly into your analysis or not, provide valuable insights and contribute to the holistic understanding of your case.
7. Write the case study report
After analyzing the data, it's finally time to compose your case study. In terms of structure, a typical case study might consist of an introduction, background information, the collected data (results), analysis of that data, and the conclusion. Here's a brief breakdown of each section:
- Introduction: The introduction should be brief but engaging, providing a clear statement of the research question or problem, explaining why the case was chosen, and outlining what the case study will cover.
- Background: The background provides the context for your case. Describe the case, its history, and any relevant information that will help readers understand the situation.
- Results: This section should provide a comprehensive account of what you found, without interpretation or opinion. Present your findings in a clear, organized manner. Use visuals such as charts or graphs if they aid comprehension.
- Analysis: This section should provide your interpretations and arguments. Discuss the patterns, themes, or relationships you've identified in your data. Explain what these findings mean in relation to your research question.
- Conclusion: Finally, summarize the key insights from your case study along with their implications. Discuss the limitations of your study and propose avenues for future research.
8. Review and revise
The process of writing a case study doesn't actually end when the report is written; you also need to review your writing for coherence, clarity, and correctness. Don't underestimate the importance of this step! Make sure the information flows logically and that your arguments are well-supported. Check for any grammar or spelling errors. Having a peer or mentor review your work can be incredibly helpful as they provide a fresh perspective and can catch mistakes you might have missed.
9. Get approval if required
If your case study involves human subjects, you may need to obtain approval from an ethical review board. You'll also need to obtain informed consent from your subjects and ensure you respect their privacy and confidentiality throughout the research process. Always follow your institution's ethical guidelines and any other relevant legislation .
Practical tips for writing a compelling case study

Getting through all those steps can feel like a formidable challenge, but here are some practical tips to make the process more manageable:
Be systematic and organized
Given the importance of detail in case studies, it's vital to be systematic and organized from the get-go. This means keeping meticulous records of your data, your sources, and any changes to your research design. A good practice is to maintain a research journal or log where you can record your process, thoughts, and reflections.
In addition, use technology to your advantage. Digital tools like citation managers can help you keep track of your sources and make formatting references a breeze, while spreadsheet or database software can assist in managing and organizing your data. Developing a consistent system for labeling and storing information at the outset will save you time and effort later when you need to retrieve data for analysis.
Stay focused
One common pitfall in research and writing is loss of focus: getting sidetracked by interesting but ultimately irrelevant digressions, which can be very easy, especially when you're dealing with a rich and complex case. Always remember your research question and objectives, and let these guide your study at every step. It's perfectly acceptable – and in fact advisable – to delineate what your study will not cover. Setting clear boundaries can help you stay focused and manage the scope of your study effectively.
Use visual aids
Visual aids such as charts, diagrams, or photographs can greatly enhance your case study. They provide readers with a break from the monotony of text and can communicate complex data or relationships more easily. For instance, if you're presenting a lot of numerical data, consider using a chart or graph. If you're describing a process or sequence of events, portraying it in a flowchart or timeline might be useful. Remember, the goal is to aid comprehension, so make sure your visual aids are clear, well-labeled, and integrated into the text.
Include direct quotes
If your case study involves interviews, including direct quotes can add depth and a sense of the personal to your findings. They provide readers with a firsthand perspective and make your case study more engaging.
When using quotes, be sure to integrate them smoothly into your text. Provide enough context so readers understand the quote's relevance. Also, remember to adhere to ethical guidelines– always respect confidentiality and anonymity agreements.
Maintain ethical standards
Ethics is a fundamental consideration in all research, including case studies. Ensure you have proper consent from participants, respect their privacy, and accurately present your findings without manipulation.
Misrepresenting data or failing to respect participants' rights can lead to serious ethical violations. Always follow your institution's ethical guidelines and any other relevant legislation. If in doubt, seek advice from a supervisor or your institution's ethics committee.
Acknowledge limitations
Every research study has limitations, which could relate to the research design, data collection methods, or other aspects of the study. Being transparent about the limitations of your study can enhance its credibility; moreover, not only does identifying limitations demonstrate your critical thinking and honesty, but it also helps readers accurately interpret your findings.
Finally, acknowledging the limitations of your work helps to set the stage for further research. By identifying aspects that your study couldn't address, you provide other researchers with avenues for building on your findings.
Learn from examples
Before you start writing your case study, it can be helpful to review some published case studies in your field. Different fields may have different conventions, and familiarizing yourself with case studies in your own field can help guide your writing. Look at the structure, tone, and style. Pay attention to how the authors present and analyze data, and how they link their findings back to the research question. You can also learn a lot from the strengths and weaknesses of previously published works. However, remember to develop your own unique voice and perspective – don't just mimic what others have done.
Design for triangulation
Triangulation involves using multiple data sources or methods to gain a more comprehensive and balanced understanding of your research topic. By coming at your research question from multiple directions, such as by examining different datasets or using different methods, you can increase the validity of your results and gain more nuanced insights.
For example, if you're studying the impact of a new teaching method in a school, you might observe classes, interview teachers, and also survey students. Each method will provide a slightly different perspective, and together, they allow you to develop a more complete picture of the teaching method's impact.
Practice reflexivity
Reflexivity involves reflecting on how your assumptions, values, or experiences might influence your research process and interpretations. As a researcher, it's essential to be aware of your potential biases and how they might shape your study.
Consider keeping a reflexivity journal where you can note your thoughts, feelings, and reflections throughout the research process. This practice can help you stay aware of your biases and ensure your research is as objective and balanced as possible.
Write for your audience
Always make sure that your writing is on target for your intended audience. If you're writing for an academic audience, for example, you'll likely use a more formal tone and include more detailed methodological information. If you're writing for practitioners or a general audience, you might use a more accessible language and focus more on practical implications.
Remember to define any technical terms or jargon, and provide sufficient context so your readers can understand your research. The goal is to communicate your findings effectively, regardless of who your readers are.
Seek feedback
Feedback is valuable for improving your case study. Consider sharing drafts with your peers, mentors, or supervisors and asking for their input. Fresh eyes can provide different perspectives, catch errors, or suggest ways to strengthen your arguments.
Remember, feedback is not personal; it's about improving your work. Be open to critique and willing to revise your work based on the feedback you receive.
Writing a case study is a meticulous process that requires clear purpose, careful planning, systematic data collection, and thoughtful analysis. Although it can be time-consuming, the rich, detailed insights a well-executed case study can provide make this study design an invaluable tool in research.
By following this guide and adopting its practical tips, you will be well on your way to crafting a compelling case study that contributes meaningful insights to your chosen field. Good luck with your research journey!
Header image by Kateryna Hliznitsova .
Plans and Pricing
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Business leadership
Communication & collaboration
CX / Customer experience
EX / Employee experience
Hybrid work
Productivity
Small business
Virtual events
UCaaS Roundup
Business Communications Roundup
Business Software Roundup
Life @ RingCentral
RingCentral newsdesk
RingCentral products
Customer stories
Industry insights
Reports & research
Strategic partnerships
Working at RC Bulgaria
Already a partner?
Interested in partnering with us? Tell us a little about your business here .
Sales: (877) 768-4369
How to write a case study: The ultimate guide + examples and templates

It would be great if we could wave a magic wand to convince prospects to buy your product or service… But we can’t. So, a case study is your next best option.
They’re a powerful sales and marketing tool for those prospects that are sitting on the fence. The problem is, they’re often dry, bland, and anything but magical. Never fear, though, as we’ve done some in-depth case study analysis.
We’re here to show you how to write a case study that will convince customers to choose you over your competitors. To create something so compelling they’ll have no doubt about your ability to deliver results.
Whether this is your first or 100th stab at it, we’ve got you covered with tips and best practices, real-world examples, and ideas for how to format a case study.
In this post, we’ll look at:
- What a case study is and why you need one
- What makes a good case study
What should a case study include?
Essential prep for creating a case study.
- How to write a good case study in 5 steps
- 8 further case study best practices
- 7 real-life case study examples
- 8 case study templates to get you started
🔍 Are you looking for some case study examples? This compilation of case study data and leadership input from just a few RingCentral SMB customers will show you exactly how they have modernized their business communication processes.
What is a case study and why should you create one?
A case study is basically a document— or it can be a video—that outlines how a customer used your product to overcome a problem. It’s real-world proof that your product works and gets results.
If your product or service has helped customers get great results, a case study will help you showcase those results to your future customers. They’re an excellent way to attract more business, and can mean the difference between a lost opportunity and a really good end-of-quarter.
Why are case studies important?
Case studies present a living, breathing witness to how effective your product or service is. In other words, they represent the ultimate in social proof. While customer reviews can also be valuable in influencing a potential client’s decision to buy from your company, they don’t pack the punch that case studies do.
That’s because with case studies, you can curate a story that highlights how well your product or service solved a real-life problem, and back it up with solid data. It demonstrates the value of your offering, while showing off your hard work in achieving success for a customer.
Case studies are relatable
Because you’re using real-world examples, rather than abstract concepts of what your product or service represents, case studies are fully relatable to potential new customers.
They can put themselves in the shoes of the subject and empathize with their pain points—and realize that there’s a way to get similar results for themselves.
They’re unbiased
Whereas a landing page or product page can be purely self-promotional, a case study comes across as more authentic and unbiased. Instead of you saying how awesome your product is, the subject is saying it, and that counts for a lot.
If they’ve switched to you from a competitor, that’s even better as it positions your product as superior without you having to spell it out.
They increase your authority
Case studies also demonstrate your ability to solve problems for your customers, positioning you as experts in your industry and building trust. The more case studies you have, the more established you’ll look. As in: “Wow, they have so many happy clients—they must be doing something right!”
They inspire readers
A narrative that’s engaging to read will get people interested in your company and inspire them to take a look around your website. And case studies give readers variety alongside other content formats such as product pages and blogs. They’re also an extra opportunity to add a CTA and nudge readers toward taking an action.
They have many uses
Case studies are versatile. You can publish and promote them in various places alongside your website—give a taster in social media posts with a link to the full article, add the video to your YouTube channel, share the stories in sales presentations. You can also extract elements like quotes from featured customers and repurpose them in other content, such as infographics.
In most cases it’s best to have case studies easily available on your website, not as downloadable gated content, but you do have this option for lead generation. You could write a blog post with a short version of the story, and offer the full version to readers in return for giving you their contact details.
They encourage loyalty
When you ask an existing customer to be the subject of a case study, it not only makes them feel special but it also reminds them of the benefits of your solution—which helps to reaffirm their loyalty. Plus, they’re getting extra brand exposure and a backlink to their own website, which boosts both their traffic and their authority online.
In fact, there’s nothing to stop you reaching out to former customers who achieved good results with you before moving on (it happens). You never know, a reminder of you might even bring them back!
What makes a good case study?
First, it’s helpful to highlight what makes a lot of case studies bad: most are painfully boring. What they have is research and detail, but what they lack is a cohesive, consumable story.
They list numbers and contain data, but the reader isn’t sure what it all means or why it’s relevant to their problem. They end up existing as technical documents that do little to persuade or excite anyone. That’s unfortunate because they have the potential to be a powerful sales tool that can help you close big deals in the decision-making phase.
So how do you write a case study that’s actually effective, then? Here are three characteristics every good case study should have:
It’s digestible
There’s no hard and fast rule on how long a case study should be. But it’s always a good idea to ask “how short can we make it?”
A good case study avoids the unnecessary minutiae, knows what it’s trying to say, and communicates it quickly and without ambiguity. With a few exceptions, effective case studies are concise and clear.
It’s thorough
On the other side of the length equation, being thorough is also important. Case study writing is all about making impressive claims about how a product helped someone achieve a certain result. However, it also needs to explain how it happened.
Good case studies include key details that show how the customer got from A to B using the product—something you don’t get with customer reviews . Don’t make your reader work too hard to visualize the story. If you can use images and videos, use them.
It’s a story
Yes, case studies are sales tools. But the ones really worth reading tell a compelling story with a beginning, middle, and end. They beg to be read all the way through. Often, they present a problem that creates tension and demands a solution. And remember, in this story, the customer is the hero—not you.
Caveat: There is no one-size-fits-all approach for what to include in a case study. But, in general, there is a recognized case study format with certain sections you should feature to make it clearer and more impactful. This format typically includes:
- Title: This should be concise and engaging. Naming your document “A Case Study of RingCentral” sounds dry. A headline like “Navigating Communications in a Remote World: A RingCentral Case Study” has more impact and explains what theme you’re exploring.
- Executive summary: Consider this like an abstract. Provide a brief overview of the case study, including the key purpose, approaches, findings, and solutions, without giving too much away.
- Introduction: Provide essential details about the customer in context.
- Challenges: Here’s where you highlight where your customer was before using your product or service and where they wanted to be. Present raw data where applicable and discuss any other background information that shows their struggles.
- Solution: Here’s where you get to show off. Explain how and why the customer chose your company, and how a specific product or service helped them achieve their objectives.
- Results: Time to get tangible. Dive into how the customer used your product, the results they saw, and long-lasting benefits. Incorporate any testimonials and statistics that showcase these results.
- Conclusion: Case studies are just as much about the future as the present. Use this closing section to highlight where your case study customer is going next thanks to your solution. Consider including a call-to-action here to encourage your prospect to take the next step.
How long should a case study be?
There isn’t a definitive answer to this question, as the length of a case study can vary depending on factors such as the size of the project you’re talking about. It also depends on the type of case study—for example, if it’s in the form of a video then a couple of minutes is enough. (We’ll explore the different types a little later on in this post.)
Balance is the key here. You’ll need to to include enough information to convey the story properly and hook the reader in, but not so much that they get overwhelmed or the message of the story gets lost amid the detail. The last thing you want them to think is “TL;DR”.
It’s about being concise, and not allowing yourself to get carried away with the story. Only include what needs to be included, so that readers can clearly understand the subject’s pain point, the reason your solution was a good fit, and the success it achieved.
Remember that not every part of the case study has to be in narrative form. You can pull out stats and display them as graphics, highlight direct quotes or other key information, or add a photo of the subject. If your case study is on the longer side, break up the text with subheadings, bullet points, and white space.
Before you start actually writing, there’s a bit of prep work you’ll need to do to make sure your case study is amazing.
1. Choose your customer
You may have many customers who’ve seen great results using your product (let’s hope!). But you can’t just pick a name out of a hat and showcase their results. So, what’s the best way of selecting a client for a case study?
Steer clear of customers who may not be the right fit for your audience or whose results may not be typical.
For example, don’t feature an enterprise company when most of your customers are small businesses. Or a business achieving a 90% customer retention rate when most of them see 70% on average (still impressive, though).
When considering which customer to use, start by creating a list of customers that meet these criteria:
They’ve seen good results with your product or service
The numbers are what really matter. So choose customers that have seen strong results using your product (like Conair did with RingCentral). But be careful about showcasing exceptionally good results if they’re not likely to be repeated by most.
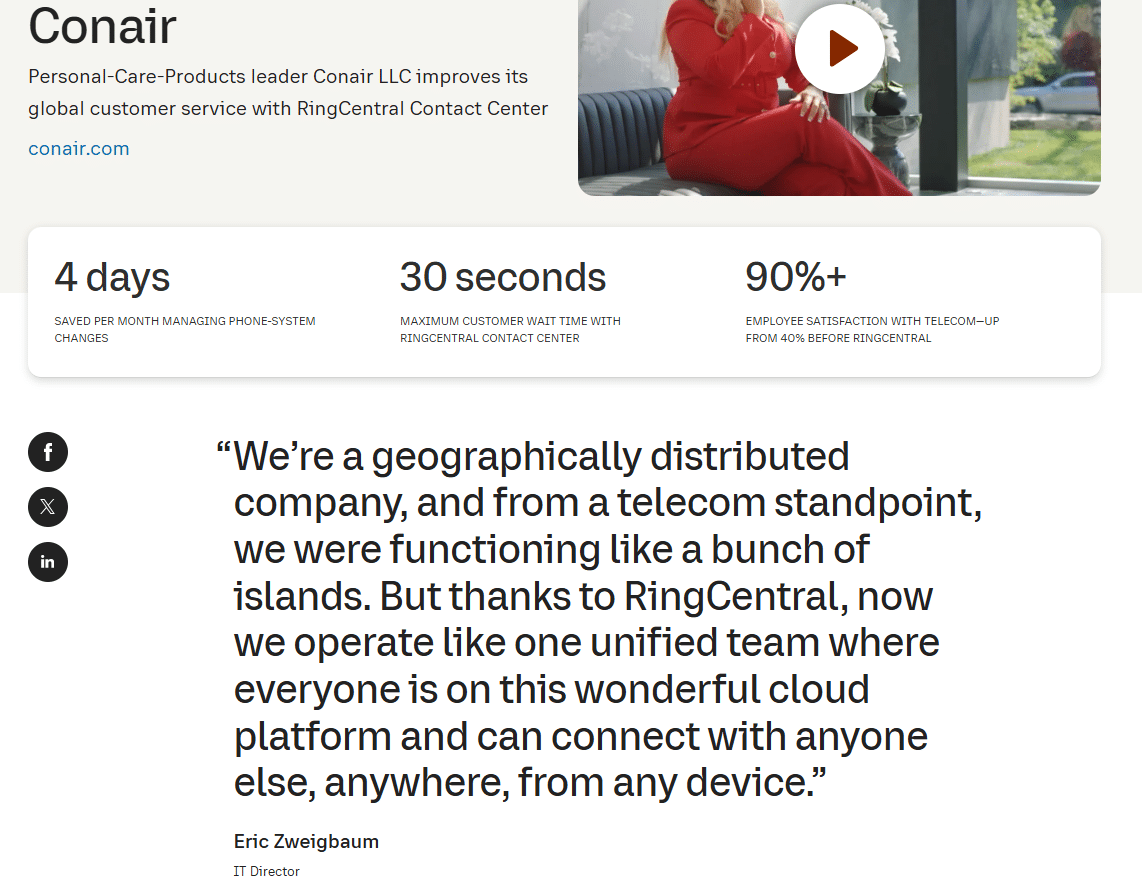
They have a respected and recognizable brand
Strong brands give your product instant social proof. They prove that you’re established and trustworthy. That alone can make you a front-runner in the decision-making process. After all, if Big Brand X trusts you, so can a prospect.
They’re a typical customer
Good results don’t carry as much weight when they’re achieved by companies in other industries or verticals. Identify current customers that are similar to your target audience. A client who has faced similar challenges and pain points will evoke empathy and stir up interest in the mind of your prospective clients.
So, if you sell enterprise software, choose enterprise customers. If you’re a consultant in the healthcare industry, choose a customer that works in healthcare.
With your list in hand, you can start reaching out. Picking up the phone can be a lot more effective than sending an email. It’s more personal, lets you build rapport, and is harder to ignore.
Try to get in touch with customers who use or are very familiar with your product or service—someone who can speak to results. Tell them you’re interested in writing a case study and you’d love to hear more about the results they’ve achieved. Be clear about what the process involves on their part—whether it’s a list of questions in an email, a phone call, or if it involves a camera and crew.
If you’ve provided value, your customer is more likely to see you as a partner rather than a vendor and, hopefully, will be happy to participate. Remember, you’re also shining a spotlight on their own success. So it’s a win-win.
That said, you may hear “no” a few times, too. Don’t get discouraged. Some customers will decline for different reasons, regardless of the results they’ve achieved with your product.

RingCentral: W2O
2. Begin your research
Start collecting information about your customer. This is easier if you work as a team. From sales to content marketing to customer service, everyone who’s been in touch with customers will have insight about their experience.
They can help you understand what your customers do and sell, and what challenges they’re facing. Identify the stakeholders you need to speak with—anyone in the company who uses your product—from the CEO to the marketing intern. Collect stats, even ones you don’t think are relevant—they may be later.
3. Ask the right questions
Smart questions get insightful answers. Here are some examples of great questions to start with:
- “What were some of the bigger challenges you faced before using our product?”
- “How does our product help you reach your individual goals?”
- “Which key metrics have improved most since using our product/service?”
- “Which parts of your business have been impacted most, and how?”
- “How long did it take to roll out our product?”
But don’t stop there. Use these questions to segue into deeper, more targeted questions that underscore the real-world benefits of your product. Let the conversation flow naturally—this is the magic of interviews. You can’t always plan for what interesting topics come up next.
4. Identify your target audience
Beyond your customer’s industry, consider who the target audience of the case study is. Who will see it? What group of people does it need to influence?
While it’s often high-level executives who make large purchase decisions, employees at all levels can act as a champion for your product or brand. Your case study may have to persuade an IT worker that your product or service is going to make their job easier. Meanwhile, it may also need to convince the CFO that they’ll see a real return on investment.
5. Identify the top three things you want to highlight
During the initial research phase, you’ve likely uncovered a lot of interesting information about your customer and their experiences with your product.
While it might be tempting to use it all, when you write a case study, you should quickly and clearly communicate the value of your product. Go through this information and identify the three most important business results you want to feature, like we did in the Barx Parx example shown below.
Stats and key performance indicators (KPIs) to consider using in your case study:
- Ramp up time : How long did it take to get started with your product? Did it improve any other facet of their workflow?
- Sales results : How did the product impact your customer’s bottom line?
- Total return on investment (ROI) : How long did it take to earn more than they spent on your product?
- Productivity increases : Which teams saw improvements in process and workflow? And by how much?
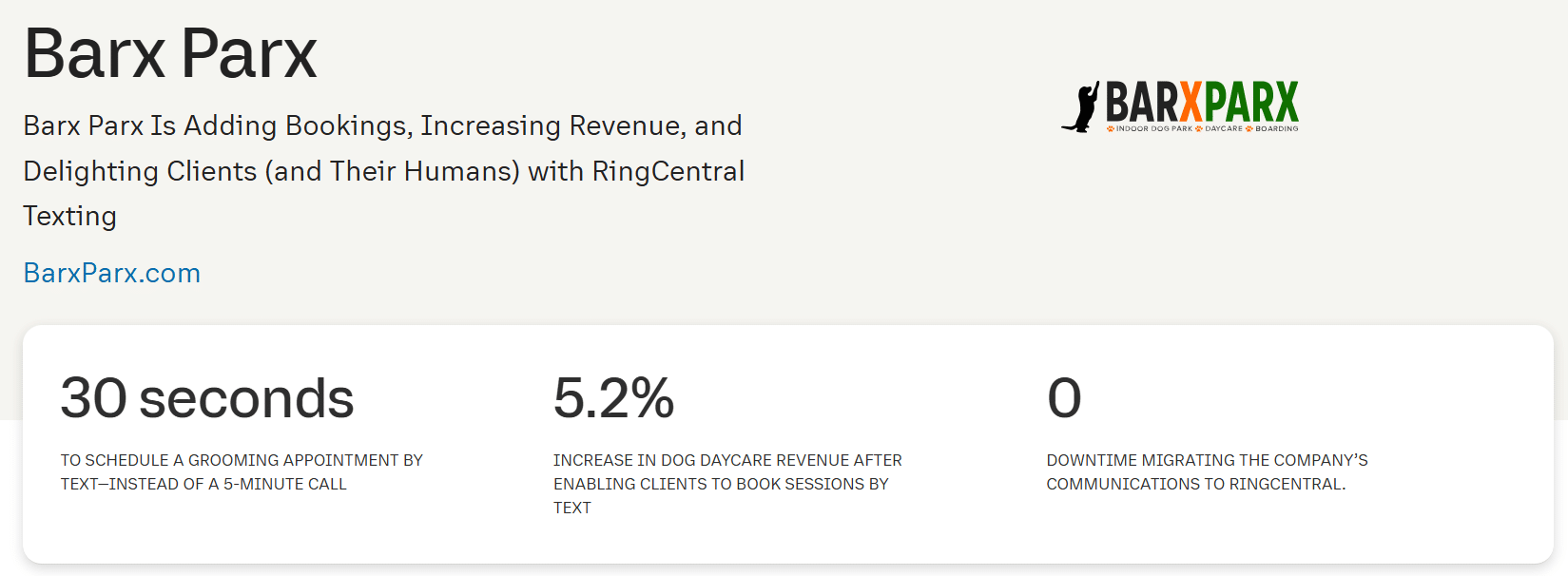
6. Choose your format
So, what does a case study look like visually? It doesn’t have to exist only as a PDF attachment in a late-stage deal email (although there’s nothing wrong with that). Consider the format. Think about who’s going to read it (or watch it).
Do you want to turn this into fancy interactive content? Does your prospect have the time and interest to dig into the details? Or do they just want the facts? Choose the format that you think best engages the audience that you’re selling to.
Here are some options:
Report format
This long-form document has been the gold standard for B2B case studies for many years. It’s effective when the subject matter is complex and demands detail.
Here’s how Zendesk presented their case study with IDC as a report .
Remember, a CTO who’s evaluating large-scale business communications platforms for a multi-year deal is going to want more information than a marketing manager who’s evaluating a new social media ad platform.
Keeping things short and sweet is often the best way to get your message heard. By focusing on the key points, you can highlight the biggest wins at just a glance.
Most report format case studies can be easily condensed into a one-page document. This is ideal for prospects (and salespeople) who are short on time and prefer something they can quickly scan.
Few things can tell a story the way that video can, and case studies are no exception. They give you an unmatched level of creative freedom and storytelling using music, lighting, pacing, and voice that can evoke emotions and persuade someone using more than just numbers and facts.
And at just a couple of minutes long, they can do a lot of heavy lifting in not a lot of time.

Dropbox: Expedia
Infographic
If you’re wondering how to make a case study more memorable, it’s worth noting that people love infographics. They’re an excellent way to convey important data in a simple, eye-pleasing way.
If your case study requires you to use a lot of data to prove a point—or if visualizing data can make the results more clear—building an infographic case study can be a great investment.

How to write a case study in 5 steps
Congrats. You’ve done the research. You’ve made the calls. You’ve pored over all the details. Now, all you have to do is write.
Here are five simple steps that’ll help you better understand how to create a case study that champions your customer and clearly showcases the real-world value of your products or services.
1. Introduce the customer
Set the stage for your case study with an introduction. Briefly explain who your customer is with a bit of background information that can include their industry, product, company size, and location.
You don’t have to dig into the nuts and bolts of their business, but you do want the reader to understand who they are and what they do. The more color you can provide here, the more impactful it’ll be when you show the awesome results this customer saw because they chose you.
2. State the problem
Every product or service is a possible solution to a problem. Explain the problem (or problems) that you helped your customer overcome. Describe the larger impact of the issue. Maybe it was customers leaving. Perhaps it was bad leads—or good leads that were never followed up on.
Use this as an opportunity to clearly show what was at stake, and make sure you leave the jargon out of it. Frame the problem in simple terms that any reader can understand.
3. Introduce your product
This is where you begin solving the problem. Briefly introduce your proposed solution and what it does.
Start on a general level, then apply it to the challenge the customer was experiencing. Talk about which teams or individuals used your product and how they used it. Be sure to make the connection between the customer’s problem and your solution crystal clear.
4. Show results
The big reveal. What kind of results was your customer able to achieve using your product or service? Speak to how they solved the problem descriptively, but also with cold, hard numbers.
Not everything can be measured in numbers (sometimes, peace of mind is a powerful benefit all on its own), but whenever you can, back up your story with the stats. At the very least, this will make it easy for a CFO—or a prospective customer who wants to buy—to justify buying your product.
For example:
The customer saw a 33% increase in web traffic, a large influx of social media activity, and a 10% boost in revenue over the duration of the campaign.
5. Prove it
Don’t forget to show your math. How you get the results is just as important as the results themselves. What specific steps were taken to get those results? Not only will this help validate your claims, it makes it easier to envision how the reader may be able to achieve them, too.
8 Further case study best practices
That’s how to write a case study in broad strokes, but you might be wondering how to write a business case study that stands out from the crowd? Here are some top tips:
1. Avoid jargon
As a subject matter expert in your line of work, it can be tempting to go into as much jargony detail as possible. This is normal as it’s often the language we use at work every day.
Remember, though, that your customer probably doesn’t speak that language. When in doubt, try to put yourself in the shoes of someone who doesn’t live and breathe your product or industry..
2. Spend time on your title
It’s tempting to use the case study’s most interesting or impressive KPI as your title. But that also gives away the ending before the story begins, and skips details that are important for context in the process. Try writing a title that piques interest without being a spoiler.
3. Edit. Then edit again.
Once you’ve got your first draft completed (and the jargon removed), edit the case study. When writing case studies, one proofread is never enough. A few best practices here:
- Look for and eliminate unnecessary adjectives—simple English is better.
- Speak in an active voice.
- Look for details that get in the way of the story.
And then do it all over again until you can’t edit it down anymore without losing the essence of the story.
4. Pay attention to the imagery
Well-designed charts, graphs, images, or infographics can do the heavy lifting of several pages of text in just seconds.
They can also help break up large pieces of text, making the case study easier to read—and nicer to look at. After all, the end goal is to have these read all the way through.
Here’s an example of a graphic from a longer CPA Canada infographic (that includes a short case study embedded inside it):
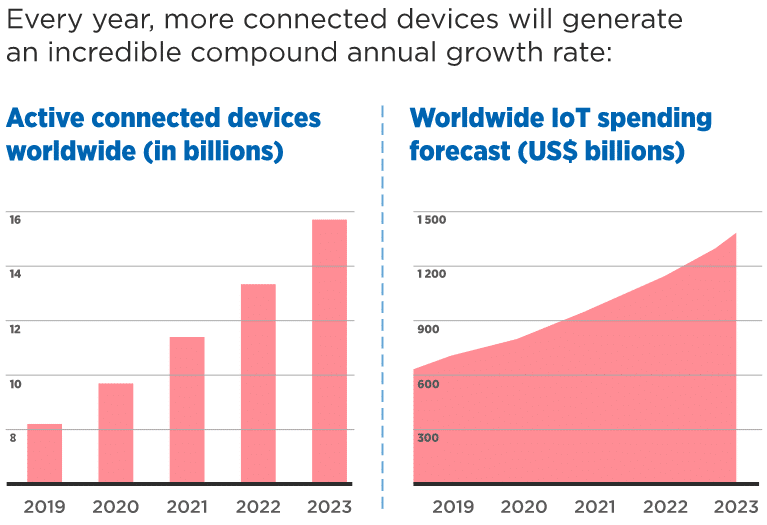
5. Pull quotes
Hard data and results are good. But a customer quote is a great piece of social proof and adds a human element to your case study. And that makes your results more believable.
Here’s an example of what that looks like, from a RingCentral case study :

6. Make it scannable
Some people will take the time to read your case study front to back and absorb every detail. Some won’t give it more than a single glance. And sometimes, that person is the decision-maker.
Make the most important results easy to spot, read, and retain at a glance. Write headings that are descriptive—if someone just scanned them, would they be able to get the gist of the story? Consider putting a summary at the very beginning of the study, or call out impressive results in a larger font size.
7. Record your interviews
Ditch the pen and paper. If you’re conducting one-on-one interviews over the phone, you can save yourself a lot of time and energy by recording the conversation (with your customer’s consent, of course).
There are tools that can make this easier too—you might find one or two in your marketing stack. For example, you could use RingSense AI for automatic note taking, summarizing, and transcribing.
8. Don’t forget the call to action (CTA)
Your prospect is excited because your case study has done an excellent job of showing how your product or service can help drive results for customers. Now, how do they get in touch with you to learn more?
Whether it’s a button that links to your website, an email address, or a phone number, make sure there’s an easy way of getting in touch with you in the case study.
7 Examples of great case studies from real-life companies
So, that’s the theory covered, but what do great case studies look like in practice? We’ve included a few elements from RingCentral customer stories as examples above, but let’s dig a little deeper into two more of our case studies:
RingCentral: How Ryder made significant savings with cloud communications
This case study is about Ryder Systems, a Fortune 500 transportation company who modernized their IT communications infrastructure with RingCentral.
We start off with a subheading that sums up the story, plus the key stats at a glance. There’s another stats panel farther down the page to help break up the wall of text. Pull quotes also achieve this, but that’s not the only reason why we like to use quotes.
When the quote comes directly from a senior manager at the company we’ve helped, they’re telling an important part of the story in their own words. In this case, there’s a reference to the amount of money Ryder has saved with RingCentral, and a mention of the platform’s all-in-one cloud capabilities.
The content introduces Ryder and makes it clear that they are a big name in transportation (the single largest truck supplier in the US) and a noteworthy firm in general, as evidenced by membership of the Fortune 500 and Forbes’ Most Admired Companies.
If a big player like this is happy to trust RingCentral with their business, that says a lot about our credentials too.
We mentioned earlier that customers are attracted to testimonials from companies similar to themselves. But RingCentral caters to businesses of all sizes—so if SMBs are reading this case study, we think they’ll see our association with a large company as “social proof” and a sign of our trustworthiness across the board.
The story goes on to explore Ryder’s pain points and how RingCentral solved them, inspiring other companies with similar problems to take action (i.e. to replace legacy systems that are slow and expensive). For further encouragement, it details how Ryder were so happy with the initial success that they also went on to implement RingCentral’s contact center solution.
RingCentral: Helping Dispute Nation to change lives
Just to illustrate our point about RingCentral serving all sizes of business, here’s a case study for a much smaller company—consumer advocacy organization Dispute Nation, which has 10 employees.
Again, the story begins with stats and a pull quote from a company representative. In keeping with Dispute Nation’s values, it focuses less on the financial savings or efficiency brought by RingCentral tools but on how our solution helps this company to help others.
Drawing empathy from other startups and fast-growing small businesses, we mention how demand for the company’s services grew very quickly. This makes it obvious why they needed a unified communications system to reach all their clients by phone, SMS, and fax.
The case study highlights how digital fax in particular helps Dispute Nation to get client cases resolved sooner. Another pull quote mentions some of the other benefits of RingCentral, like automation and integrations with other tools.
There are nods to mobility and flexibility, plus security and data privacy which will resonate with other highly-regulated industries.
The tale finishes strongly with the company founder’s assertion that “RingCentral is helping Dispute Nation improve more lives”. Readers who’ve been inspired to learn more can easily navigate from this page to explore products, resources, and get in touch.

RingCentral is far from the only company to have recognized the importance of this kind of content.
Here are some more real-life case studies from other businesses you might just recognize:
RingCentral iswe’re far from the only company to have recognized the importance of this kind of content.
Mailchimp: Make a connection in real life with postcards
What we like about it: The title doesn’t give everything away all at once, and the case study tells a story with a beginning, middle, and end. The sections are clearly titled and organized, and the results are easy to find. As a bonus: the video adds a believable human element.

LinkedIn: How Adobe achieves alignment and ABM success with LinkedIn
What we like about it: It’s detailed without being a novella. It understands and speaks to the enterprise customer. The key points are in bullet format and easy to read. The important wins are highlighted. And the video makes the content easy to engage with.

Hootsuite: How Meliá became one of the most influential hotel chains on social media
What we like about it: The title makes you want to read the whole customer story. They’ve embedded a well-produced video high on the page, so you can choose to watch it before you read on. The design and layout of the page makes the content and images easy to consume, and the results can’t be missed. Also, they weren’t shy about adding CTAs.
Slack: So yeah, we tried Slack
What we like about it: This case study follows the tried and true format of customer, problem, solution, and results. It uses humor and relatable characters throughout to support the story and keep your attention. And it’s only two minutes long so it gets the point across quickly.

Assetworks: South Carolina School Board Insurance Trust
What we like about it: This case study tackles the otherwise complex and technical topic, and simplifies it as an infographic using images to make the results clear. It’s concise and easy to follow because you can see the math without actually doing any math.
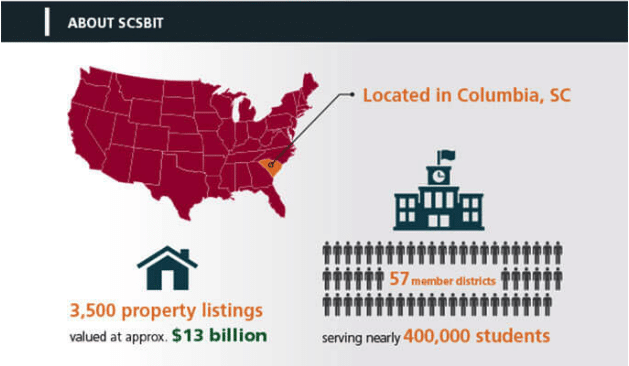
8 Case study templates to get you started
Starting from scratch can be time-consuming. To help you, we’ve drawn together a few templates:
The generic one
Generic doesn’t mean boring! Canva’s templates are great if you need something concise and simple that still looks professional . A free account will give you access to several well-designed templates, including this one :

The layout is provided for you, so it’s quick and easy to customize with your branding and content. Don’t be afraid to use this as a foundation, then add in visual elements like infographics and videos.
The data-driven one
If your key messages revolve around numbers, start with a template structure that lets you highlight these. HubSpot has a data-focused template where you can pack in graphs, charts, and other visuals to drive your message home:
The industry-specific one
Not every template suits every company. Visme offers different templates created for different industries, including real estate, financial services, and healthcare.

The problem-solution-impact one
This format takes a graphical rather than narrative approach, which helps readers to visualize the events and looks colorful and appealing on the page. The template is available as a free download from Smartsheet:
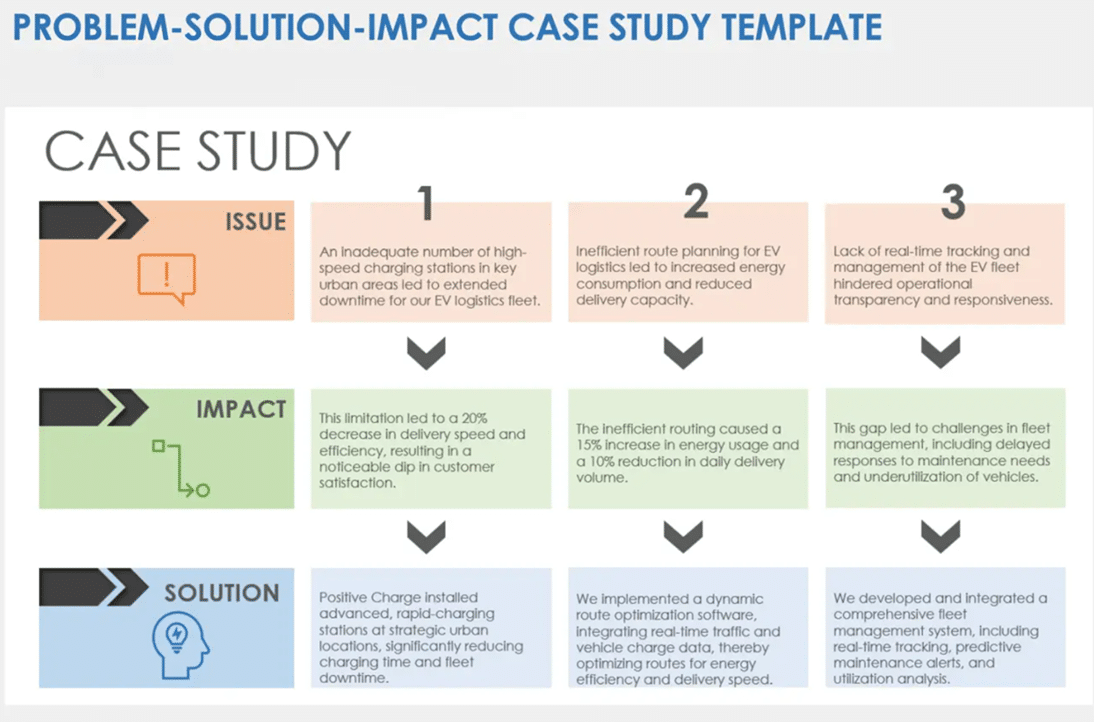
The idea of this is to present the story in a logical and sequential way. It starts with the challenge faced by the subject of the case study, looks at the solution your company provided, and shows what the outcome was.
Of course, you could choose to combine this with other elements like text content, stats, and quotes—making the “problem-solution-impact” graphic the main focus of the case study.
The product-specific one
You can choose to focus your case study on a particular product, highlighting key features and the practical applications in the real world.
It leans into the experience that the customer has had with the product—i.e., what it feels like to use it—and the specific benefits. This one is a good choice if the customer hasn’t been using the product for very long, and you haven’t yet gathered a lot of metrics.
HubSpot has a template for this purpose :

The in-depth report one
Using the style of an in-depth report can be useful when you’ve worked with the customer on a complex project and you need to include a lot of detail.
This template —another free one from Smartsheet—includes elements like decision criteria, data analysis, and the implementation plan:
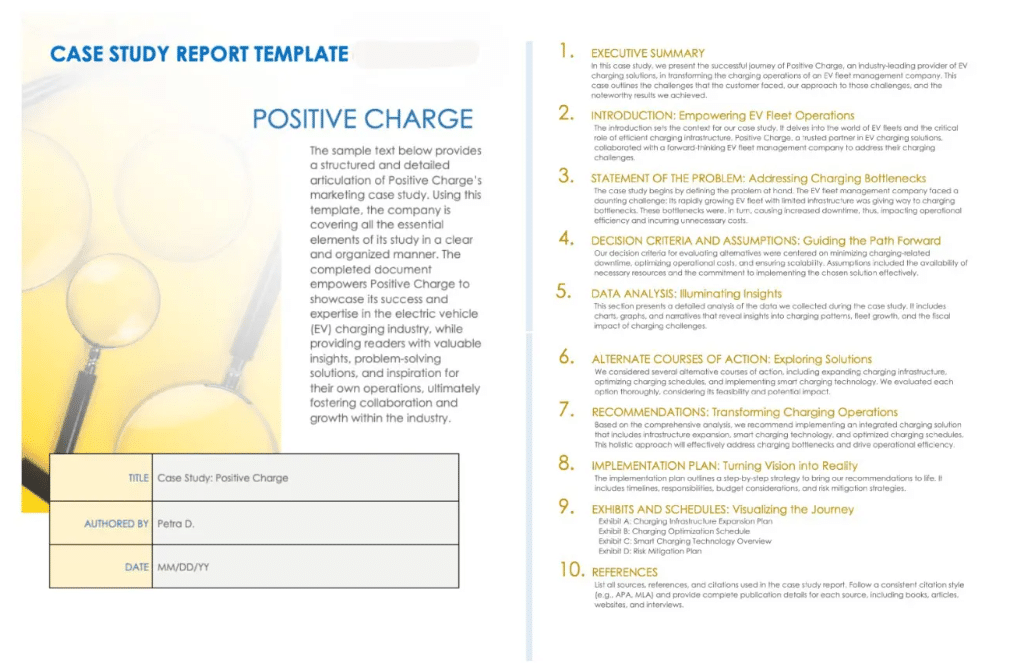
Just be careful with this one as you don’t want readers to be put off by a lot of text. Make sure the style is conversational and engaging, not dry and formal.
The employee story one
Okay, stick with us here—this one’s a little different. As well as asking customers to tell their stories, how about getting employees to share what it’s like to work for your company, or their experience of working on a particular project?
Employee stories or testimonials are often used for recruitment purposes, but they’re also a valuable form of marketing for potential customers. That’s because happy, engaged employees represent a company that cares about its people, which all helps you to build trust.
This example from Vanguard isn’t a template as such, but you can use it to inspire your own version. (It doesn’t have to be a video—you could still use a written narrative with direct quotes, photos, and stats on employee satisfaction.)
BONUS TEMPLATE: Form for customers participating in case studies
Earlier in this post, we briefly covered some of the questions you’ll need to ask your customers when putting together case studies. But it’s always helpful to have a visual guide, so we’re including this template from Vitally , which provides a framework for collaborating with customers and collecting the relevant data.
You can adapt this to your own needs by adding further questions.
The final word on how to write a case study…
Sure, an ad or boosted social media post can make someone aware of your brand or that your product exists, and a landing page can tell them how your product can solve their problem.
But there’s nothing quite as powerful as someone else singing your praises.
And that’s exactly what a case study does. Spend the time to do it right and it has the potential to deliver huge ROI no matter how big or small your company is. And not just once—but over and over again.
Originally published Jun 15, 2024, updated Aug 15, 2024

The 9 best free messaging apps for small businesses: The ultimate list for 2024
Updated June 2024 Even for small businesses, free messaging apps like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger can quickly become inadequate. Tasks and responsibilities can spiral out of control, security features can be lacking, and if you need to integrate it with your other business apps, good luck. Free consumer-facing apps aren’t designed for the level of ...
Thank you for your interest in RingCentral.
Related content

11 business email etiquette best practices | RingCentral

8 Top Zoom alternatives for 2024 and beyond

13 more effective alternatives to “just touching base” emails
- Case Interview: A comprehensive guide
- Pyramid Principle
- Hypothesis driven structure
- Fit Interview
- Consulting math
- The key to landing your consulting job
- What is a case interview?
- Types of case interview
- How to solve cases with the Problem-Driven Structure?
- What to remember in case interviews
- Case examples or building blocks?
- How do I prepare for case interviews
- Interview day tips
- How we can help
1. The key to landing your consulting job.
Case interviews - where you are asked to solve a business case study under scrutiny - are the core of the selection process right across McKinsey, Bain and BCG (the “MBB” firms). This interview format is also used pretty much universally across other high-end consultancies; including LEK, Kearney, Oliver Wyman and the consulting wings of the “Big Four”.
If you want to land a job at any of these firms, you will have to ace multiple case interviews.
It is increasingly likely that you will also have to solve online cases given by chatbots. You might need to pass these either before making it to interview or be asked to sit them alongside first round interviews.
Importantly, case studies aren’t something you can just wing . Firms explicitly expect you to have thoroughly prepared and many of your competitors on interview day will have been prepping for months.
Don’t worry though - MCC is here to help!
This article will take you through a full overview of everything you’ll need to know to do well, linking to more detailed articles and resources at each stage to let you really drill down into the details.
As well as traditional case interviews, we’ll also attend to the new formats in which cases are being delivered and otherwise make sure you’re up to speed with recent trends in this overall part of consulting recruitment.
Before we can figure out how to prepare for a case interview, though, we will first have to properly understand in detail what exactly you are up against. What format does a standard consulting case interview take? What is expected of you? How will you be assessed?
Let's dive right in and find out!
Professional help
Before going further, if this sounds like a lot to get your head around on your own, don't worry - help is available!
Our Case Academy course gives you everything you need to know to crack cases like a pro:
Case Academy Course
To put what you learn into practice (and secure some savings in the process) you can add mock interview coaching sessions with expereinced MBB consultants:
Coaching options
And, if you just want an experienced consultant to take charge of the whole selection process for you, you can check out our comprehensive mentoring programmes:
Explore mentoring
Now, back to the article!
2. What is a case interview?
Before we can hope to tackle a case interview, we have to understand what one is.
In short, a case interview simulates real consulting work by having you solve a business case study in conversation with your interviewer.
This case study will be a business problem where you have to advise a client - that is, an imaginary business or similar organisation in need of guidance.
You must help this client solve a problem and/or make a decision. This requires you to analyse the information you are given about that client organisation and figure out a final recommendation for what they should do next.
Business problems in general obviously vary in difficulty. Some are quite straightforward and can be addressed with fairly standard solutions. However, consulting firms exist precisely to solve the tough issues that businesses have failed to deal with internally - and so consultants will typically work on complex, idiosyncratic problems requiring novel solutions.
Some examples of case study questions might be:
- How much would you pay for a banking licence in Ghana?
- Estimate the potential value of the electric vehicle market in Germany
- How much gas storage capacity should a UK domestic energy supplier build?
Consulting firms need the brightest minds they can find to put to work on these important, difficult projects. You can expect the case studies you have to solve in interview, then, to echo the unique, complicated problems consultancies deal with every day. As we’ll explain here, this means that you need to be ready to think outside the box to figure out genuinely novel solutions.
2.1. Where are case interviews in the consulting selection process?
Not everyone who applies to a consulting firm will have a case interview - far from it!
In fact, case interviews are pretty expensive and inconvenient for firms to host, requiring them to take consultants off active projects and even fly them back to the office from location for in-person interviews (although this happens less frequently now). Ideally, firms want to cut costs and save time by narrowing down the candidate pool as much as possible before any live interviews.
As such, there are some hoops to jump through before you make it to interview rounds.
Firms will typically eliminate as much as 80% of the applicant pool before interviews start . For most firms, 50%+ of applicants might be cut based on resumes, before a similar cut is made on those remaining based on aptitude tests. McKinsey currently gives their Solve assessment to most applicants, but will use their resulting test scores alongside resumes to cut 70%+ of the candidate pool before interviews.
You'll need to be on top of your game to get as far as a case interview with a top firm. Getting through the resume screen and any aptitude tests is an achievement in itself! Also we need to note that the general timeline of an application can differ depending on a series of factors, including which position you apply, your background, and the office you are applying to. For example, an undergraduate applying for a Business Analyst position (the entry level job at McKinsey) will most likely be part of a recruitment cycle and as such have pretty fixed dates when they need to sit the pre-screening test, and have the first and second round interviews (see more on those below). Conversely, an experienced hire will most likely have a much greater choice of test and interview dates as well as more time at their disposal to prepare.
For readers not yet embroiled in the selection process themselves, let’s put case interviews in context and take a quick look at each stage in turn. Importantly, note that you might also be asked to solve case studies outside interviews as well…
2.1.1. Application screen
It’s sometimes easy to forget that such a large cut is made at the application stage. At larger firms, this will mean your resume and cover letter is looked at by some combination of AI tools, recruitment staff and junior consulting staff (often someone from your own university).
Only the best applications will be passed to later stages, so make sure to check out our free resume and cover letter guides, and potentially get help with editing , to give yourself the best chance possible.
2.1.2. Aptitude tests and online cases
This part of the selection process has been changing quickly in recent years and is increasingly beginning to blur into the traditionally separate case interview rounds.
In the past, GMAT or PST style tests were the norm. Firms then used increasingly sophisticated and often gamified aptitude tests, like the Pymetrics test currently used by several firms, including BCG and Bain, and the original version of McKinsey’s Solve assessment (then branded as the Problem Solving Game).
Now, though, there is a move towards delivering relatively sophisticated case studies online. For example, McKinsey has replaced half the old Solve assessment with an online case. BCG’s Casey chatbot case now directly replaces a live first round case interview, and in the new era of AI chatbots, we expect these online cases to quickly become more realistic and increasingly start to relieve firms of some of the costs of live case interviews.
Our consultants collectively reckon that, over time, 50% of case interviews are likely to be replaced with these kinds of cases . We give some specific advice for online cases in section six. However, the important thing to note is that these are still just simulations of traditional case interviews - you still need to learn how to solve cases in precisely the same way, and your prep will largely remain the same.
2.1.3. Rounds of Interviews
Now, let’s not go overboard with talk of AI. Even in the long term, the client facing nature of consulting means that firms will have live case interviews for as long as they are hiring anyone. And in the immediate term, case interviews are still absolutely the core of consulting selection.
Before landing an offer at McKinsey, Bain, BCG or any similar firm, you won’t just have one case interview, but will have to complete four to six case interviews, usually divided into two rounds, with each interview lasting approximately 50-60 minutes .
Being invited to first round usually means two or three case interviews. As noted above, you might also be asked to complete an online case or similar alongside your first round interviews.
If you ace first round, you will be invited to second round to face the same again, but more gruelling. Only then - after up to six case interviews in total, can you hope to receive an offer.
2.2. Differences between first and second round interviews
Despite case interviews in the first and second round following the same format, second/final round interviews will be significantly more intense . The seniority of the interviewer, time pressure (with up to three interviews back-to-back), and the sheer value of the job at stake will likely make a second round consulting case interview one of the most challenging moments of your professional life.
There are three key differences between the two rounds:
- Time Pressure : Final round case interviews test your ability to perform under pressure, with as many as three interviews in a row and often only very small breaks between them.
- Focus : Since second round interviewers tend to be more senior (usually partners with 12+ years experience) and will be more interested in your personality and ability to handle challenges independently. Some partners will drill down into your experiences and achievements to the extreme. They want to understand how you react to challenges and your ability to identify and learn from past mistakes.
- Psychological Pressure: While case interviews in the first round are usually more focused on you simply cracking the case, second round interviewers often employ a "bad cop" strategy to test the way you react to challenges and uncertainty.
2.3. What skills do case interviews assess?
Reliably impressing your interviewers means knowing what they are looking for. This means understanding the skills you are being assessed against in some detail.
Overall, it’s important always to remember that, with case studies, there are no strict right or wrong answers. What really matters is how you think problems through, how confident you are with your conclusions and how quick you are with the back of the envelope arithmetic.
The objective of this kind of interview isn’t to get to one particular solution, but to assess your skillset. This is even true of modern online cases, where sophisticated AI algorithms score how you work as well as the solutions you generate.
If you visit McKinsey , Bain and BCG web pages on case interviews, you will find that the three firms look for very similar traits, and the same will be true of other top consultancies.
Broadly speaking, your interviewer will be evaluating you across five key areas:
2.1.1.One: Probing mind
Showing intellectual curiosity by asking relevant and insightful questions that demonstrate critical thinking and a proactive nature. For instance, if we are told that revenues for a leading supermarket chain have been declining over the last ten years, a successful candidate would ask:
“ We know revenues have declined. This could be due to price or volume. Do we know how they changed over the same period? ”
This is as opposed to a laundry list of questions like:
- Did customers change their preferences?
- Which segment has shown the decline in volume?
- Is there a price war in the industry?
2.1.2. Structure
Structure in this context means structuring a problem. This, in turn, means creating a framework - that is, a series of clear, sequential steps in order to get to a solution.
As with the case interview in general, the focus with case study structures isn’t on reaching a solution, but on how you get there.
This is the trickiest part of the case interview and the single most common reason candidates fail.
We discuss how to properly structure a case in more detail in section three. In terms of what your interviewer is looking for at high level, though, key pieces of your structure should be:
- Proper understanding of the objective of the case - Ask yourself: "What is the single crucial piece of advice that the client absolutely needs?"
- Identification of the drivers - Ask yourself: "What are the key forces that play a role in defining the outcome?"
Our Problem Driven Structure method, discussed in section three, bakes this approach in at a fundamental level. This is as opposed to the framework-based approach you will find in older case-solving
Focus on going through memorised sequences of steps too-often means failing to develop a full understanding of the case and the real key drivers.
At this link, we run through a case to illustrate the difference between a standard framework-based approach and our Problem Driven Structure method.
2.1.3. Problem Solving
You’ll be tested on your ability to identify problems and drivers, isolate causes and effects, demonstrate creativity and prioritise issues. In particular, the interviewer will look for the following skills:
- Prioritisation - Can you distinguish relevant and irrelevant facts?
- Connecting the dots - Can you connect new facts and evidence to the big picture?
- Establishing conclusions - Can you establish correct conclusions without rushing to inferences not supported by evidence?
2.1.4. Numerical Agility
In case interviews, you are expected to be quick and confident with both precise and approximated numbers. This translates to:
- Performing simple calculations quickly - Essential to solve cases quickly and impress clients with quick estimates and preliminary conclusions.
- Analysing data - Extract data from graphs and charts, elaborate and draw insightful conclusions.
- Solving business problems - Translate a real world case to a mathematical problem and solve it.
Our article on consulting math is a great resource here, though the extensive math content in our MCC Academy is the best and most comprehensive material available.
2.1.5. Communication
Real consulting work isn’t just about the raw analysis to come up with a recommendation - this then needs to be sold to the client as the right course of action.
Similarly, in a case interview, you must be able to turn your answer into a compelling recommendation. This is just as essential to impressing your interviewer as your structure and analysis.
Consultants already comment on how difficult it is to find candidates with the right communication skills. Add to this the current direction of travel, where AI will be able to automate more and more of the routine analytic side of consulting, and communication becomes a bigger and bigger part of what consultants are being paid for.
So, how do you make sure that your recommendations are relevant, smart, and engaging? The answer is to master what is known as CEO-level communication .
This art of speaking like a CEO can be quite challenging, as it often involves presenting information in effectively the opposite way to how you might normally.
To get it right, there are three key areas to focus on in your communications:
- Top down : A CEO wants to hear the key message first. They will only ask for more details if they think that will actually be useful. Always consider what is absolutely critical for the CEO to know, and start with that. You can read more in our article on the Pyramid Principle .
- Concise : This is not the time for "boiling the ocean" or listing an endless number possible solutions. CEOs, and thus consultants, want a structured, quick and concise recommendation for their business problem, that they can implement immediately.
- Fact-based : Consultants share CEOs' hatred of opinions based on gut feel rather than facts. They want recommendations based on facts to make sure they are actually in control. Always go on to back up your conclusions with the relevant facts.
Being concise and to the point is key in many areas, networking being one for them. For more detail on all this, check out our full article on delivering recommendations .
Prep the right way
3. types of case interview.
While most case interviews share a similar structure, firms will have some differences in the particular ways they like to do things in terms of both the case study and the fit component.
As we’ll see, these differences aren’t hugely impactful in terms of how you prepare. That said, it's always good to know as much as possible about what you will be going up against.
3.1. Different case objectives
A guiding thread throughout this article and our approach in general will be to treat each case as a self-contained problem and not try to pigeonhole it into a certain category. Having said that, there are of course similarities between cases and we can identify certain parameters and objectives.
Broadly speaking, cases can be divided into issue-based cases and strategic decision cases. In the former you will be asked to solve a certain issue, such as declining profits, or low productivity whereas in the latter you will be ask whether your client should or should not do something, such as enter a specific market or acquire another company. The chart below is a good breakdown of these different objectives:
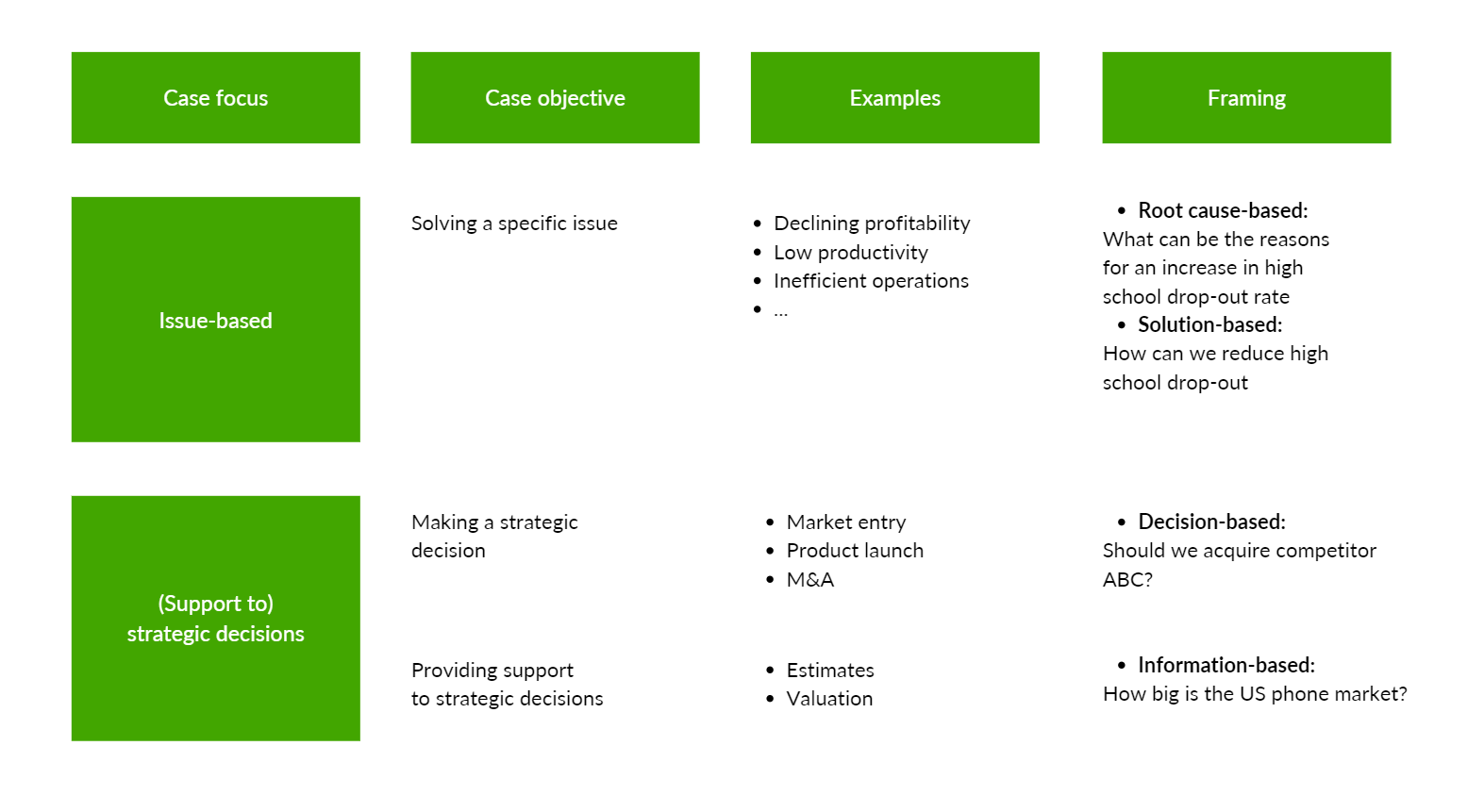
3.2. How do interviewers craft cases
While interviewers will very likely be given a case bank to choose from by their company, a good number of them will also choose to adapt the cases they would currently be working on to a case interview setting. The difference is that the latter cases will be harder to pigeonhole and apply standard frameworks to, so a tailored approach will be paramount.
If you’ve applied for a specific practice or type of consulting - such as operational consulting, for example - it’s very likely that you will receive a case geared towards that particular area alongside a ‘generalist’ consulting case (however, if that’s the case, you will generally be notified). The other main distinction when it comes to case interviews is between interviewer-led and candidate-led.
3.3. Candidate-led cases
Most consulting case interview questions test your ability to crack a broad problem, with a case prompt often going something like:
" How much would you pay to secure the rights to run a restaurant in the British Museum? "
You, as a candidate, are then expected to identify your path to solve the case (that is, provide a structure), leveraging your interviewer to collect the data and test your assumptions.
This is known as a “candidate-led” case interview and is used by Bain, BCG and other firms. From a structuring perspective, it’s easier to lose direction in a candidate-led case as there are no sign-posts along the way. As such, you need to come up with an approach that is both broad enough to cover all of the potential drivers in a case but also tailored enough to the problem you are asked to solve. It’s also up to you to figure out when you need to delve deeper into a certain branch of the case, brainstorm or ask for data. The following case from Bain is an excellent example on how to navigate a candidate-led case.
3.4. Interviewer-led cases
This type of case - employed most famously by McKinsey - is slightly different, with the interviewer controlling the pace and direction of the conversation much more than with other case interviews.
At McKinsey, your interviewer will ask you a set of pre-determined questions, regardless of your initial structure. For each question, you will have to understand the problem, come up with a mini structure, ask for additional data (if necessary) and come to the conclusion that answers the question. This more structured format of case also shows up in online cases by other firms - notably including BCG’s Casey chatbot (with the amusing result that practising McKinsey-style cases can be a great addition when prepping for BCG).
Essentially, these interviewer-led case studies are large cases made up of lots of mini-cases. You still use basically the same method as you would for standard (or candidate-led) cases - the main difference is simply that, instead of using that method to solve one big case, you are solving several mini-cases sequentially. These cases are easier to follow as the interviewer will guide you in the right direction. However, this doesn’t mean you should pay less attention to structure and deliver a generic framework! Also, usually (but not always!) the first question will ask you to map your approach and is the equivalent of the structuring question in candidate-led cases. Sometimes, if you’re missing key elements, the interviewer might prompt you in the right direction - so make sure to take those prompts seriously as they are there to help you get back on track (ask for 30 seconds to think on the prompt and structure your approach). Other times - and this is a less fortunate scenario - the interviewer might say nothing and simply move on to the next question. This is why you should put just as much thought (if not more) into the framework you build for interviewer-led cases , as you may be penalized if you produce something too generic or that doesn’t encompass all the issues of the case.
3.5. Case and fit
The standard case interview can be thought of as splitting into two standalone sub-interviews. Thus “case interviews” can be divided into the case study itself and a “fit interview” section, where culture fit questions are asked.
This can lead to a bit of confusion, as the actual case interview component might take up as little as half of your scheduled “case interview”. You need to make sure you are ready for both aspects.
To illustrate, here is the typical case interview timeline:

- First 15-30 minutes: Fit Interview - with questions assessing your motivation to be a consultant in that specific firm and your traits around leadership and teamwork. Learn more about the fit interview in our in-depth article here .
- Next 30-40 minutes: Case Interview - solving a case study
- Last 5 minutes: Fit Interview again - this time focussing on your questions for your interviewer.
Both the Case and Fit interviews play crucial roles in the finial hiring decision. There is no “average” taken between case and fit interviews: if your performance is not up to scratch in either of the two, you will not be able to move on to the next interview round or get an offer.
NB: No case without fit
Note that, even if you have only been told you are having a case interview or otherwise are just doing a case study, always be prepared to answer fit questions. At most firms, it is standard practice to include some fit questions in all case interviews, even if there are also separate explicit fit interviews, and interviewers will almost invariably include some of these questions around your case. This is perfectly natural - imagine how odd and artificial it would be to show up to an interview, simply do a case and leave again, without talking about anything else with the interviewer before or after.
3.5.1 Differences between firms
For the most part, a case interview is a case interview. However, firms will have some differences in the particular ways they like to do things in terms of both the case study and the fit component.
3.5.2. The McKinsey PEI
McKinsey brands its fit aspect of interviews as the Personal Experience Interview or PEI. Despite the different name, this is really much the same interview you will be going up against in Bain, BCG and any similar firms.
McKinsey does have a reputation for pushing candidates a little harder with fit or PEI questions , focusing on one story per interview and drilling down further into the specific details each time. We discuss this tendency more in our fit interview article . However, no top end firm is going to go easy on you and you should absolutely be ready for the same level of grilling at Bain, BCG and others. Thus any difference isn’t hugely salient in terms of prep.
3.6. What is different in 2023?
For the foreseeable future, you are going to have to go through multiple live case interviews to secure any decent consulting job. These might increasingly happen via Zoom rather than in person, but they should remain largely the same otherwise.
However, things are changing and the rise of AI in recent months seems pretty much guaranteed to accelerate existing trends.
Even before the explosive development of AI chatbots like ChatGPT we have seen in recent months, automation was already starting to change the recruitment process.
As we mentioned, case interviews are expensive and inconvenient for firms to run . Ideally, then, firms will try to reduce the number of interviews required for recruitment as far as possible. For many years, tests of various kinds served to cut down the applicant pool and thus the number of interviews. However, these tests had a limited capacity to assess candidates against the full consulting skillset in the way that case interviews do so well.
More recently, though, the development of online testing has allowed for more and more advanced assessments. Top consulting firms have been leveraging screening tests that better and better capture the same skillset as case interviews. Eventually this is converging on automated case studies. We see this very clearly with the addition of the Redrock case to McKinsey’s Solve assessment.
As these digital cases become closer to the real thing, the line between test and case interview blurs. Online cases don’t just reduce the number of candidates to case interview, but start directly replacing them.
Case in point here is BCG’s Casey chatbot . Previously, BCG had deployed less advanced online cases and similar tests to weed out some candidates before live case interviews began. Now, though, Casey actually replaces one first round case interview.
Casey, at time of writing, is still a relatively “basic” chatbot, basically running through a pre-set script. The Whatsapp-like interface does a lot of work to make it feel like one is chatting to a “real person” - the chatbot itself, though, cannot provide feedback or nudges to candidates as would a human interviewer.
We fully expect that, as soon as BCG and other firms can train a truer AI, these online cases will become more widespread and start replacing more live interviews.
We discuss the likely impacts of advanced AI on consulting recruitment and the industry more broadly in our blog.
Here, though, the real message is that you should expect to run into digital cases as well as traditional case interviews.
Luckily, despite any changes in specific case interview format, you will still need to master the same fundamental skills and prepare in much the same way.
We’ll cover a few ways to help prepare for chatbot cases in section four. Ultimately, though, firms are looking for the same problem solving ability and mindset as a real interviewer. Especially as chatbots get better at mimicking a real interviewer, candidates who are well prepared for case cracking in general should have no problem with AI administered cases.
3.6.1. Automated fit interviews
Analogous to online cases, in recent years there has been a trend towards automated, “one way” fit interviews, with these typically being administered for consultancies by specialist contractors like HireVue or SparkHire.
These are kind of like Zoom interviews, but if the interviewer didn’t show up. Instead you will be given fit questions to answer and must record your answer in your computer webcam. Your response will then go on to be assessed by an algorithm, scoring both what you say and how you say it.
Again, with advances in AI, it is easy to imagine these automated case interviews going from fully scripted interactions, where all candidates are asked the same list of questions, to a more interactive experience. Thus, we might soon arrive at a point where you are being grilled on the details of your stories - McKinsey PEI style - but by a bot rather than a human.
We include some tips on this kind of “one way” fit interview in section six here.
4. How to solve cases with the Problem-Driven Structure?
If you look around online for material on how to solve case studies, a lot of what you find will set out framework-based approaches. However, as we have mentioned, these frameworks tend to break down with more complex, unique cases - with these being exactly the kind of tough case studies you can expect to be given in your case interviews.
To address this problem, the MyConsultingCoach team has synthesized a new approach to case cracking that replicates how top management consultants approach actual engagements.
MyConsultingCoach’s Problem Driven Structure approach is a universal problem solving method that can be applied to any business problem , irrespective of its nature.
As opposed to just selecting a generic framework for each case interview, the Problem Driven Structure approach works by generating a bespoke structure for each individual question and is a simplified version of the roadmap McKinsey consultants use when working on engagements.
The canonical seven steps from McKinsey on real projects are simplified to four for case interview questions, as the analysis required for a six-month engagement is somewhat less than that needed for a 45-minute case study. However, the underlying flow is the same (see the method in action in the video below)
Let's zoom in to see how our method actually works in more detail:
4.1. Identify the problem
Identifying the problem means properly understanding the prompt/question you are given, so you get to the actual point of the case.
This might sound simple, but cases are often very tricky, and many candidates irretrievably mess things up within the first few minutes of starting. Often, they won’t notice this has happened until they are getting to the end of their analysis. Then, they suddenly realise that they have misunderstood the case prompt - and have effectively been answering the wrong question all along!
With no time to go back and start again, there is nothing to do. Even if there were time, making such a silly mistake early on will make a terrible impression on their interviewer, who might well have written them off already. The interview is scuppered and all the candidate’s preparation has been for nothing.
This error is so galling as it is so readily avoidable.
Our method prevents this problem by placing huge emphasis on a full understanding of the case prompt. This lays the foundations for success as, once we have identified the fundamental, underlying problem our client is facing, we focus our whole analysis around finding solutions to this specific issue.
Now, some case interview prompts are easy to digest. For example, “Our client, a supermarket, has seen a decline in profits. How can we bring them up?”. However, many of the prompts given in interviews for top firms are much more difficult and might refer to unfamiliar business areas or industries. For example, “How much would you pay for a banking license in Ghana?” or “What would be your key areas of concern be when setting up an NGO?”
Don’t worry if you have no idea how you might go about tackling some of these prompts!
In our article on identifying the problem and in our full lesson on the subject in our MCC Academy course, we teach a systematic, four step approach to identifying the problem , as well as running through common errors to ensure you start off on the right foot every time!
This is summarised here:

Following this method lets you excel where your competitors mess up and get off to a great start in impressing your interviewer!
4.2. Build your problem driven structure
After you have properly understood the problem, the next step is to successfully crack a case is to draw up a bespoke structure that captures all the unique features of the case.
This is what will guide your analysis through the rest of the case study and is precisely the same method used by real consultants working on real engagements.
Of course, it might be easier here to simply roll out one an old-fashioned framework, and a lot of candidates will do so. This is likely to be faster at this stage and requires a lot less thought than our problem-driven structure approach.
However, whilst our problem driven structure approach requires more work from you, our method has the advantage of actually working in the kind of complex case studies where generic frameworks fail - that is exactly the kind of cases you can expect at an MBB interview .
Since we effectively start from first principles every time, we can tackle any case with the same overarching method. Simple or complex, every case is the same to you and you don’t have to gamble a job on whether a framework will actually work
4.2.1 Issue trees
Issue trees break down the overall problem into a set of smaller problems that you can then solve individually. Representing this on a diagram also makes it easy for both you and your interviewer to keep track of your analysis.
To see how this is done, let’s look at the issue tree below breaking down the revenues of an airline:
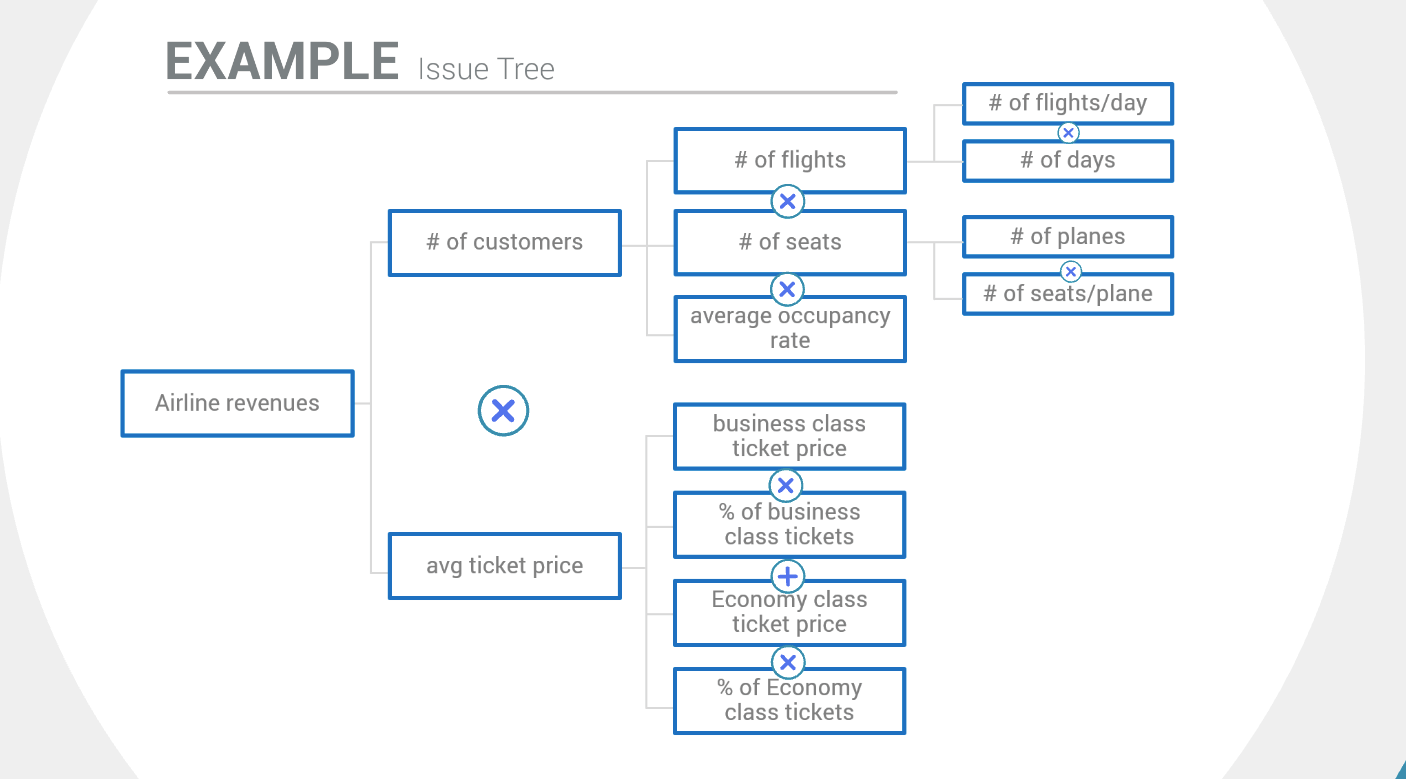
These revenues can be segmented as the number of customers multiplied by the average ticket price. The number of customers can be further broken down into a number of flights multiplied by the number of seats, times average occupancy rate. The node corresponding to the average ticket price can then be segmented further.
4.2.2 Hypothesis trees
Hypothesis trees are similar, the only difference being that rather than just trying to break up the issue into smaller issues you are assuming that the problem can be solved and you are formulating solutions.
In the example above, you would assume revenues can be increased by either increasing the average ticket price or the number of customers . You can then hypothesize that you can increase the average occupancy rate in three ways: align the schedule of short and long haul flights, run a promotion to boost occupancy in off-peak times, or offer early bird discounts.
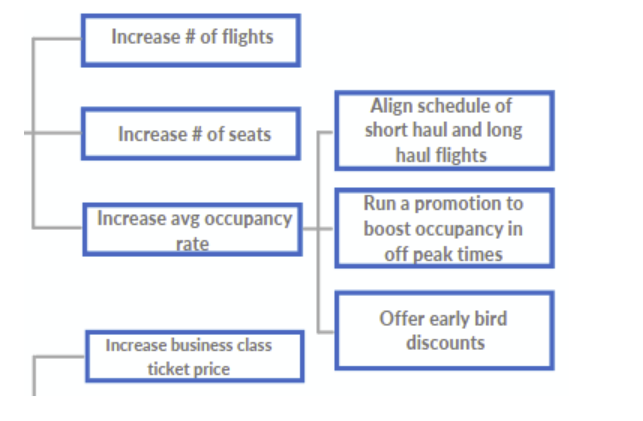
4.2.3 Other structures:structured lists
Structured lists are simply subcategories of a problem into which you can fit similar elements. This McKinsey case answer starts off by identifying several buckets such as retailer response, competitor response, current capabilities and brand image and then proceeds to consider what could fit into these categories.
Buckets can be a good way to start the structure of a complex case but when using them it can be very difficult to be MECE and consistent, so you should always aim to then re-organize them into either an issue or a hypothesis tree.
It is worth noting that the same problem can be structured in multiple valid ways by choosing different means to segment the key issues. Ultimately all these lists are methods to set out a logical hierachy among elements.
4.2.4 Structures in practice
That said, not all valid structures are equally useful in solving the underlying problem. A good structure fulfils several requirements - including MECE-ness , level consistency, materiality, simplicity, and actionability. It’s important to put in the time to master segmentation, so you can choose a scheme isn’t only valid, but actually useful in addressing the problem.
After taking the effort to identify the problem properly, an advantage of our method is that it will help ensure you stay focused on that same fundamental problem throughout. This might not sound like much, but many candidates end up getting lost in their own analysis, veering off on huge tangents and returning with an answer to a question they weren’t asked.
Another frequent issue - particularly with certain frameworks - is that candidates finish their analysis and, even if they have successfully stuck to the initial question, they have not actually reached a definite solution. Instead, they might simply have generated a laundry list of pros and cons, with no clear single recommendation for action.
Clients employ consultants for actionable answers, and this is what is expected in the case interview. The problem driven structure excels in ensuring that everything you do is clearly related back to the key question in a way that will generate a definitive answer. Thus, the problem driven structure builds in the hypothesis driven approach so characteristic of real consulting practice.
You can learn how to set out your own problem driven structures in our article here and in our full lesson in the MCC Academy course.
4.2. Lead the analysis
A problem driven structure might ensure we reach a proper solution eventually, but how do we actually get there?
We call this step " leading the analysis ", and it is the process whereby you systematically navigate through your structure, identifying the key factors driving the issue you are addressing.
Generally, this will mean continuing to grow your tree diagram, further segmenting what you identify as the most salient end nodes and thus drilling down into the most crucial factors causing the client’s central problem.
Once you have gotten right down into the detail of what is actually causing the company’s issues, solutions can then be generated quite straightforwardly.
To see this process in action, we can return to our airline revenue example:
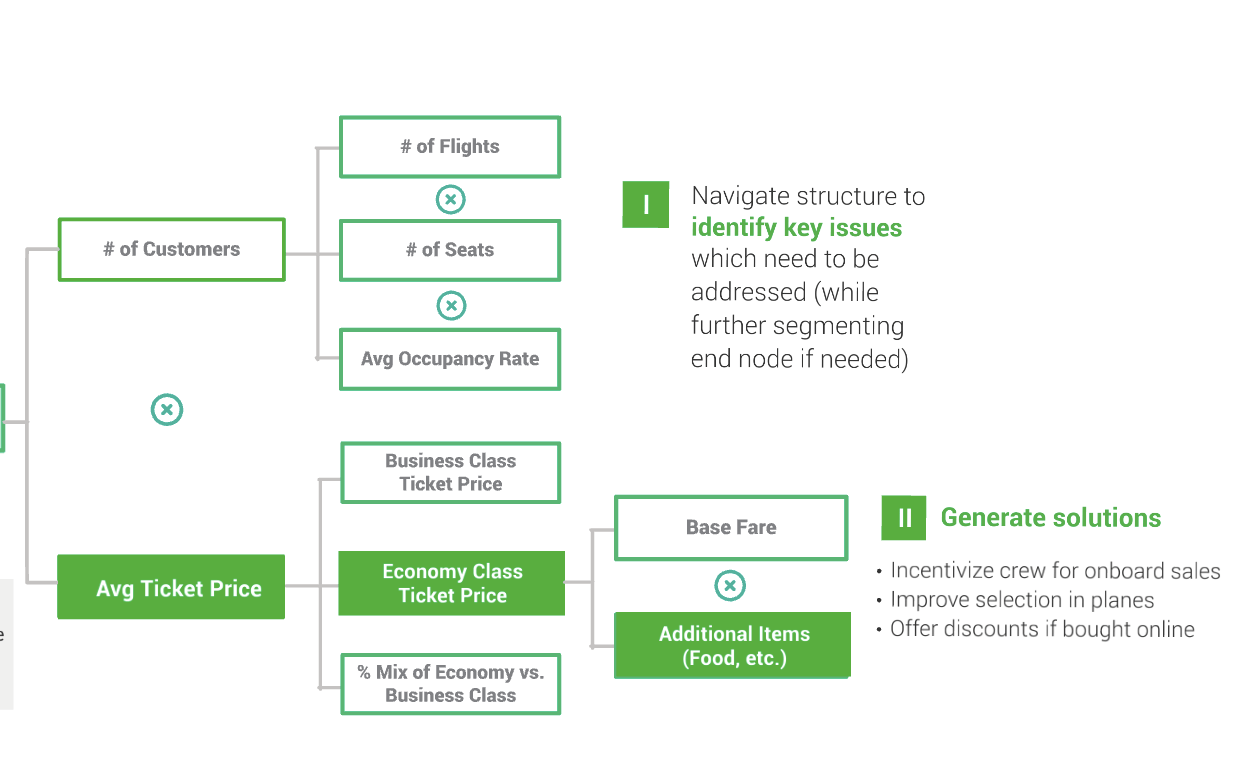
Let’s say we discover the average ticket price to be a key issue in the airline’s problems. Looking closer at the drivers of average ticket price, we find that the problem lies with economy class ticket prices. We can then further segment that price into the base fare and additional items such as food.
Having broken down the issue to such a fine-grained level and considering the 80/20 rule(see below), solutions occur quite naturally. In this case, we can suggest incentivising the crew to increase onboard sales, improving assortment in the plane, or offering discounts for online purchases.
Our article on leading the analysis is a great primer on the subject, with our video lesson in the MCC Academy providing the most comprehensive guide available.
4.4. Provide recommendations
So you have a solution - but you aren’t finished yet!
Now, you need to deliver your solution as a final recommendation.
This should be done as if you are briefing a busy CEO and thus should be a one minute, top-down, concise, structured, clear, and fact-based account of your findings.
The brevity of the final recommendation belies its importance. In real life consulting, the recommendation is what the client has potentially paid millions for - from their point of view, it is the only thing that matters.
In a case interview, your performance in this final summing up of your case is going to significantly colour your interviewer’s parting impression of you - and thus your chances of getting hired!
So, how do we do it right?
Barbara Minto's Pyramid Principle elegantly sums up almost everything required for a perfect recommendation. The answer comes first , as this is what is most important. This is then supported by a few key arguments , which are in turn buttressed by supporting facts .
Across the whole recommendation, the goal isn’t to just summarise what you have done. Instead, you are aiming to synthesize your findings to extract the key "so what?" insight that is useful to the client going forward.
All this might seem like common sense, but it is actually the opposite of how we relay results in academia and other fields. There, we typically move from data, through arguments and eventually to conclusions. As such, making good recommendations is a skill that takes practice to master.
We can see the Pyramid Principle illustrated in the diagram below:
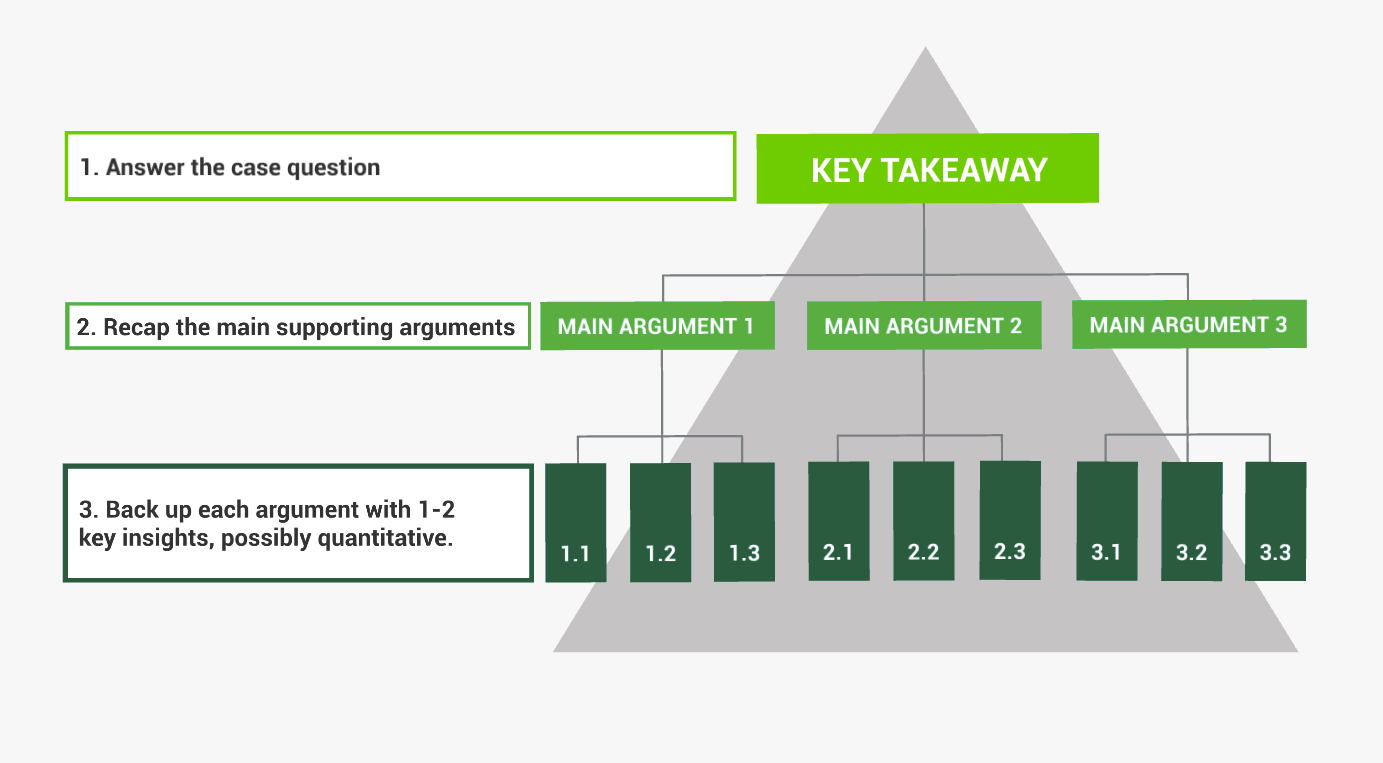
To supplement the basic Pyramid Principle scheme, we suggest candidates add a few brief remarks on potential risks and suggested next steps . This helps demonstrate the ability for critical self-reflection and lets your interviewer see you going the extra mile.
The combination of logical rigour and communication skills that is so definitive of consulting is particularly on display in the final recommendation.
Despite it only lasting 60 seconds, you will need to leverage a full set of key consulting skills to deliver a really excellent recommendation and leave your interviewer with a good final impression of your case solving abilities.
Our specific article on final recommendations and the specific video lesson on the same topic within our MCC Academy are great, comprehensive resources. Beyond those, our lesson on consulting thinking and our articles on MECE and the Pyramid Principle are also very useful.
4.5. What if I get stuck?
Naturally with case interviews being difficult problems there may be times where you’re unsure what to do or which direction to take. The most common scenario is that you will get stuck midway through the case and there are essentially two things that you should do:
- 1. Go back to your structure
- 2. Ask the interviewer for clarification
Your structure should always be your best friend - after all, this is why you put so much thought and effort into it: if it’s MECE it will point you in the right direction. This may seem abstract but let’s take the very simple example of a profitability case interview: if you’ve started your analysis by segmenting profit into revenue minus costs and you’ve seen that the cost side of the analysis is leading you nowhere, you can be certain that the declining profit is due to a decline in revenue.
Similarly, when you’re stuck on the quantitative section of the case interview, make sure that your framework for calculations is set up correctly (you can confirm this with the interviewer) and see what it is you’re trying to solve for: for example if you’re trying to find what price the client should sell their new t-shirt in order to break even on their investment, you should realize that what you’re trying to find is the break even point, so you can start by calculating either the costs or the revenues. You have all the data for the costs side and you know they’re trying to sell 10.000 pairs so you can simply set up the equation with x being the price.
As we’ve emphasised on several occasions, your case interview will be a dialogue. As such, if you don’t know what to do next or don’t understand something, make sure to ask the interviewer (and as a general rule always follow their prompts as they are trying to help, not trick you). This is especially true for the quantitative questions, where you should really understand what data you’re looking at before you jump into any calculations. Ideally you should ask your questions before you take time to formulate your approach but don’t be afraid to ask for further clarification if you really can’t make sense of what’s going on. It’s always good to walk your interviewer through your approach before you start doing the calculations and it’s no mistake to make sure that you both have the same understanding of the data. For example when confronted with the chart below, you might ask what GW (in this case gigawatt) means from the get-go and ask to confirm the different metrics (i.e. whether 1 GW = 1000 megawatts). You will never be penalised for asking a question like that.
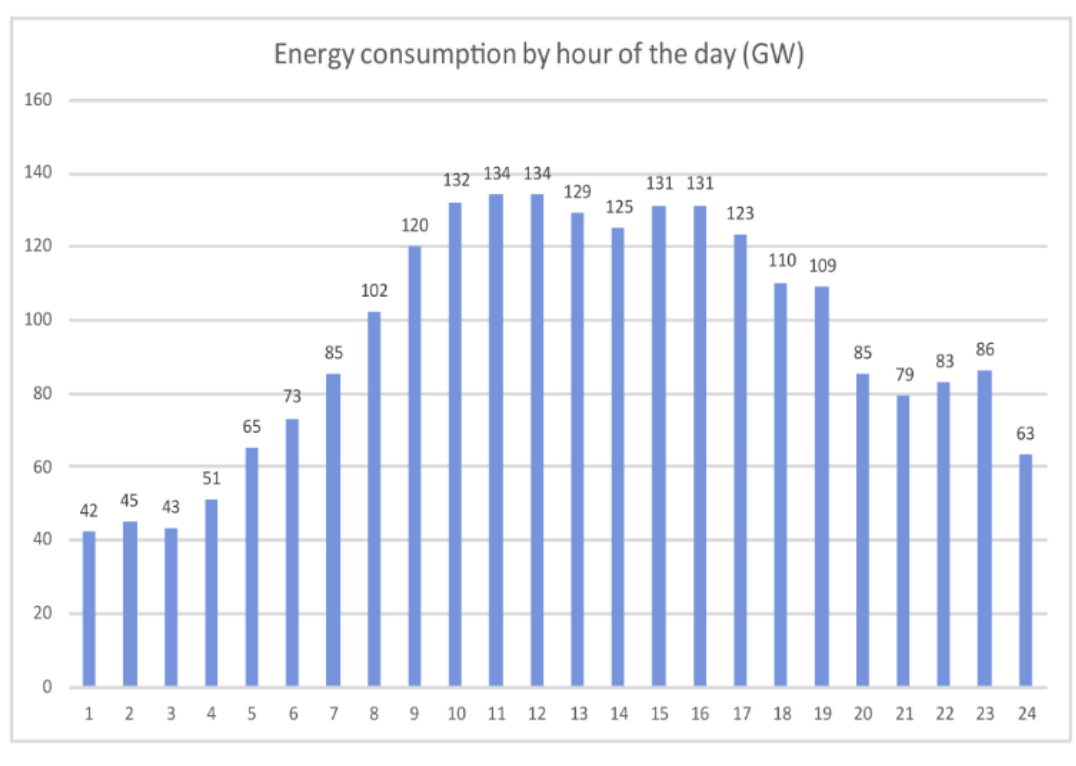
5. What to remember in case interviews
If you’re new to case cracking you might feel a bit hopeless when you see a difficult case question, not having any idea where to start.
In fact though, cracking case interviews is much like playing chess. The rules you need to know to get started are actually pretty simple. What will make you really proficient is time and practice.
In this section, we’ll run through a high level overview of everything you need to know, linking to more detailed resources at every step.
5.1. An overall clear structure
You will probably hear this more than you care for but it is the most important thing to keep in mind as you start solving cases, as not only it is a key evaluation criterion but the greatest tool you will have at your disposal. The ability to build a clear structure in all aspects of the case inteview will be the difference between breezing through a complicated case and struggling at its every step. Let’s look a bit closer at the key areas where you should be structured!
5.1.1 Structured notes
Every case interview starts with a prompt, usually verbal, and as such you will have to take some notes. And here is where your foray into structure begins, as the notes you take should be clear, concise and structured in a way that will allow you to repeat the case back to the interviewer without writing down any unnecessary information.
This may sound very basic but you should absolutely not be dismissive about it: taking clear and organized notes will allow what we found helps is to have separate sections for:
- The case brief
- Follow-up questions and answers
- Numerical data
- Case structure (the most crucial part when solving the case)
- Any scrap work during the case (usually calculations)
When solving the case - or, as we call it here, in the Lead the analysis step, it is highly recommended to keep on feeding and integrating your structure, so that you never get lost. Maintaining a clear high level view is one of the most critical aspects in case interviews as it is a key skill in consulting: by constantly keeping track of where you are following your structure, you’ll never lose your focus on the end goal.
In the case of an interviewer-led case, you can also have separate sheets for each question (e.g. Question 1. What factors can we look at that drive profitability?). If you develop a system like this you’ll know exactly where to look for each point of data rather than rummage around in untidy notes. There are a couple more sections that you may have, depending on preference - we’ll get to these in the next sections.
5.1.2 Structured communication
There will be three main types of communication in cases:
- 1. Asking and answering questions
- 2. Walking the interviewer through your structure (either the case or calculation framework - we’ll get to that in a bit!)
- 3. Delivering your recommendation
Asking and answering questions will be the most common of these and the key thing to do before you speak is ask for some time to collect your thoughts and get organised. What you want to avoid is a ‘laundry list’ of questions or anything that sounds too much like a stream of consciousness.
Different systems work for different candidates but a sure-fire way of being organised is numbering your questions and answers. So rather than saying something like ‘I would like to ask about the business model, operational capacity and customer personas’ it’s much better to break it down and say something along the lines of ‘I’ve got three key questions. Firstly I would like to inquire into the business model of our client. Secondly I would like to ask about their operational capacity. Thirdly I would like to know more about the different customer personas they are serving’.
A similar principle should be applied when walking the interviewer through your structure, and this is especially true of online case interviews (more and more frequent now) when the interviewer can’t see your notes. Even if you have your branches or buckets clearly defined, you should still use a numbering system to make it obvious to the interviewer. So, for example, when asked to identify whether a company should make an acquisition, you might say ‘I would like to examine the following key areas. Firstly the financial aspects of this issue, secondly the synergies and thirdly the client’s expertise’
The recommendation should be delivered top-down (see section 4.4 for specifics) and should employ the same numbering principle. To do so in a speedy manner, you should circle or mark the key facts that you encounter throughout the case so you can easily pull them out at the end.
5.1.3 Structured framework
It’s very important that you have a systematic approach - or framework - for every case. Let’s get one thing straight: there is a difference between having a problem-solving framework for your case and trying to force a case into a predetermined framework. Doing the former is an absolute must , whilst doing the latter will most likely have you unceremoniously dismissed.
We have seen there are several ways of building a framework, from identifying several categories of issues (or ‘buckets’) to building an issue or hypothesis tree (which is the most efficient type of framework). For the purpose of organization, we recommend having a separate sheet for the framework of the case, or, if it’s too much to manage, you can have it on the same sheet as the initial case prompt. That way you’ll have all the details as well as your proposed solution in one place.
5.1.4 Structured calculations
Whether it’s interviewer or candidate-led, at some point in the case you will get a bunch of numerical data and you will have to perform some calculations (for the specifics of the math you’ll need on consulting interviews, have a look at our Consulting Math Guide ). Here’s where we urge you to take your time and not dive straight into calculating! And here’s why: while your numerical agility is sure to impress interviewers, what they’re actually looking for is your logic and the calculations you need to perform in order to solve the problem . So it’s ok if you make a small mistake, as long as you’re solving for the right thing.
As such, make it easy for them - and yourself. Before you start, write down in steps the calculations you need to perform. Here’s an example: let’s say you need to find out by how much profits will change if variable costs are reduced by 10%. Your approach should look something like:
- 1. Calculate current profits: Profits = Revenues - (Variable costs + Fixed costs)
- 2. Calculate the reduction in variable costs: Variable costs x 0.9
- 3. Calculate new profits: New profits = Revenues - (New variable costs + Fixed costs)
Of course, there may be more efficient ways to do that calculation, but what’s important - much like in the framework section - is to show your interviewer that you have a plan, in the form of a structured approach. You can write your plan on the sheet containing the data, then perform the calculations on a scrap sheet and fill in the results afterward.
5.2. Common business knowledge and formulas
Although some consulting firms claim they don’t evaluate candidates based on their business knowledge, familiarity with basic business concepts and formulae is very useful in terms of understanding the case studies you are given in the first instance and drawing inspiration for structuring and brainstorming.
If you are coming from a business undergrad, an MBA or are an experienced hire, you might well have this covered already. For those coming from a different background, it may be useful to cover some.
Luckily, you don’t need a degree-level understanding of business to crack case interviews , and a lot of the information you will pick up by osmosis as you read through articles like this and go through cases.
However, some things you will just need to sit down and learn. We cover everything you need to know in some detail in our Case Academy Course course. However, some examples here of things you need to learn are:
- Basic accounting (particularly how to understand all the elements of a balance sheet)
- Basic economics
- Basic marketing
- Basic strategy
Below we include a few elementary concepts and formulae so you can hit the ground running in solving cases. We should note that you should not memorise these and indeed a good portion of them can be worked out logically, but you should have at least some idea of what to expect as this will make you faster and will free up much of your mental computing power. In what follows we’ll tackle concepts that you will encounter in the private business sector as well as some situations that come up in cases that feature clients from the NGO or governmental sector.
5.2.1 Business sector concepts
These concepts are the bread and butter of almost any business case so you need to make sure you have them down. Naturally, there will be specificities and differences between cases but for the most part here is a breakdown of each of them.
5.2.1.1. Revenue
The revenue is the money that the company brings in and is usually equal to the number of products they sell multiplied to the price per item and can be expressed with the following equation:
Revenue = Volume x Price
Companies may have various sources of revenue or indeed multiple types of products, all priced differently which is something you will need to account for in your case interview. Let’s consider some situations. A clothing company such as Nike will derive most of their revenue from the number of products they sell times the average price per item. Conversely, for a retail bank revenue is measured as the volume of loans multiplied by the interest rate at which the loans are given out. As we’ll see below, we might consider primary revenues and ancillary revenues: in the case of a football club, we might calculate primary revenues by multiplying the number of tickets sold by the average ticket price, and ancillary revenues those coming from sales of merchandise (similarly, let’s say average t-shirt price times the number of t-shirts sold), tv rights and sponsorships.
These are but a few examples and another reminder that you should always aim to ask questions and understand the precise revenue structure of the companies you encounter in cases.
5.2.1.2. Costs
The costs are the expenses that a company incurs during its operations. Generally, they can be broken down into fixed and variable costs :
Costs = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs
As their name implies, fixed costs do not change based on the number of units produced or sold. For example, if you produce shoes and are renting the space for your factory, you will have to pay the rent regardless of whether you produce one pair or 100. On the other hand, variable costs depend on the level of activity, so in our shoe factory example they would be equivalent to the materials used to produce each pair of shoes and would increase the more we produce.
These concepts are of course guidelines used in order to simplify the analysis in cases, and you should be aware that in reality often the situation can be more complicated. However, this should be enough for case interviews. Costs can also be quasi-fixed, in that they increase marginally with volume. Take the example of a restaurant which has a regular staff, incurring a fixed cost but during very busy hours or periods they also employ some part-time workers. This cost is not exactly variable (as it doesn’t increase with the quantity of food produced) but also not entirely fixed, as the number of extra hands will depend on how busy the restaurant is. Fixed costs can also be non-linear in nature. Let’s consider the rent in the same restaurant: we would normally pay a fixed amount every month, but if the restaurant becomes very popular we might need to rent out some extra space so the cost will increase. Again, this is not always relevant for case interviews.
5.2.1.3. Profit and profit margin
The profit is the amount of money a company is left with after it has paid all of its expenses and can be expressed as follows:
Profit = Revenue - Costs
It’s very likely that you will encounter a profitability issue in one of your case interviews, namely you will be asked to increase a company’s profit. There are two main ways of doing this: increasing revenues and reducing costs , so these will be the two main areas you will have to investigate. This may seem simple but what you will really need to understand in a case are the key drivers of a business (and this should be done through clarifying questions to the interviewer - just as a real consultant would question their client).
For example, if your client is an airline you can assume that the main source of revenue is sales of tickets, but you should inquire how many types of ticket the specific airline sells. You may naturally consider economy and business class tickets, but you may find out that there is a more premium option - such as first class - and several in-between options. Similarly to our football club example, there may be ancillary revenues from selling of food and beverage as well as advertising certain products or services on flights.
You may also come across the profit margin in case interviews. This is simply the percentage of profit compared to the revenue and can be expressed as follows:
Profit margin = Profit/Revenue x 100
5.2.1.4. Break-even point
An ancillary concept to profit, the break-even point is the moment where revenues equal costs making the profit zero and can be expressed as the following equation:
Revenues = Costs (Fixed costs + Variable costs)
This formula will be useful when you are asked questions such as ‘What is the minimum price I should sell product X?’ or ‘What quantity do I need to sell in order to recoup my investment?’. Let’s say in a case interview an owner of a sandwich store asks us to figure out how many salami and cheese salami sandwiches she needs to sell in order to break even. She’s spending $4 on salami and $2 for cheese and lettuce per sandwich, and believes she can sell the sandwiches at around $7. The cost of utilities and personnel is around $5000 per month. We could lay this all out in the break-even equation:
7 x Q ( quantity ) = (4+2) x Q + 5000 ( variable + fixed costs )
In a different scenario, we may be asked to calculate the break-even price . Let’s consider our sandwich example and say our owner knows she has enough ingredients for about 5000 sandwiches per month but is not sure how much to sell them for. In that case, if we know our break-even equation, we can simply make the following changes:
P ( price ) x 5000 = (4+2) x 5000 + 5000
By solving the equation we get to the price of $7 per sandwich.
5.2.1.5. Market share and market size
We can also consider the market closely with profit, as in fact the company’s performance in the market is what drives profits. The market size is the total number of potential customers for a certain business or product, whereas the market share is the percentage of that market that your business controls (or could control, depending on the case).
There is a good chance you will have to estimate the market size in one of your case interviews and we get into more details on how to do that below. You may be asked to estimate this in either number of potential customers or total value . The latter simply refers to the number of customers multiplied by the average value of the product or service.
To calculate the market share you will have to divide the company’s share by the total market size and multiply by 100:
Note, though, that learning the very basics of business is the beginning rather than the end of your journey. Once you are able to “speak business” at a rudimentary level, you should try to “become fluent” and immerse yourself in reading/viewing/listening to as wide a variety of business material as possible, getting a feel for all kinds of companies and industries - and especially the kinds of problems that can come up in each context and how they are solved. The material put out by the consulting firms themselves is a great place to start, but you should also follow the business news and find out about different companies and sectors as much as possible between now and interviews. Remember, if you’re going to be a consultant, this should be fun rather than a chore!
5.3 Public sector and NGO concepts
As we mentioned, there will be some cases (see section 6.6 for a more detailed example) where the key performance indicators (or KPIs in short) will not be connected to profit. The most common ones will involve the government of a country or an NGO, but they can be way more diverse and require more thought and application of first principles. We have laid out a couple of the key concepts or KPIs that come up below
5.3.1 Quantifiability
In many such scenarios you will be asked to make an important strategic decision of some kind or to optimise a process. Of course these are not restricted to non-private sector cases but this is where they really come into their own as there can be great variation in the type of decision and the types of field.
While there may be no familiar business concepts to anchor yourself onto, a concept that is essential is quantifiability . This means, however qualitative the decision might seem, consultants rely on data so you should always aim to have aspects of a decision that can be quantified, even if the data doesn’t present itself in a straightforward manner.
Let’s take a practical example. Your younger sibling asks you to help them decide which university they should choose if they want to study engineering. One way to structure your approach would be to segment the problem into factors affecting your sibling’s experience at university and experience post-university. Within the ‘at uni’ category you might think about the following:
- Financials : How much are tuition costs and accommodation costs?
- Quality of teaching and research : How are possible universities ranked in the QS guide based on teaching and research?
- Quality of resources : How well stocked is their library, are the labs well equipped etc.?
- Subject ranking : How is engineering at different unis ranked?
- Life on campus and the city : What are the living costs in the city where the university is based? What are the extracurricular opportunities and would your sibling like to live in that specific city based on them?
Within the ‘out of uni’ category you might think about:
- Exit options : What are the fields in which your sibling could be employed and how long does it take the average student of that university to find a job?
- Alumni network : What percentage of alumni are employed by major companies?
- Signal : What percentage of applicants from the university get an interview in major engineering companies and related technical fields?
You will perhaps notice that all the buckets discussed pose quantifiable questions meant to provide us with data necessary to make a decision. It’s no point to ask ‘Which university has the nicest teaching staff?’ as that can be a very subjective metric.
5.3.1 Impact
Another key concept to consider when dealing with sectors other than the private one is how impactful a decision or a line of inquiry is on the overarching issue , or whether all our branches in our issue tree have a similar impact. This can often come in the form of impact on lives, such as in McKinsey’s conservation case discussed below, namely how many species can we save with our choice of habitat.
5.4 Common consulting concepts
Consultants use basic business concepts on an every day basis, as they help them articulate their frameworks to problems. However, they also use some consulting specific tools to quality check their analysis and perform in the most efficient way possible. These principles can be applied to all aspects of a consultant’s work, but for brevity we can say they mostly impact a consultant’s systematic approach and communication - two very important things that are also tested in case interviews. Therefore, it’s imperative that you not only get to know them, but learn how and when to use them as they are at the very core of good casing. They are MECE-ness, the Pareto Principle and the Pyramid principle and are explained briefly below - you should, however, go on to study them in-depth in their respective articles.
Perhaps the central pillar of all consulting work and an invaluable tool to solve cases, MECE stands for Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive . It can refer to any and every aspect in a case but is most often used when talking about structure. We have a detailed article explaining the concept here , but the short version is that MECE-ness ensures that there is no overlap between elements of a structure (i.e. the Mutually Exclusive component) and that it covers all the drivers or areas of a problem (Collectively Exhaustive). It is a concept that can be applied to any segmentation when dividing a set into subsets that include it wholly but do not overlap.
Let’s take a simple example and then a case framework example. In simple terms, when we are asked to break down the set ‘cars’ into subsets, dividing cars into ‘red cars’ and ‘sports cars’ is neither mutually exclusive (as there are indeed red sports cars) nor exhaustive of the whole set (i.e. there are also yellow non-sports cars that are not covered by this segmentation). A MECE way to segment would be ‘cars produced before 2000’ and ‘cars produced after 2000’ as this segmentation allows for no overlap and covers all the cars in existence.
Dividing cars can be simple, but how can we ensure MECEness in a case-interview a.k.a. a business situation. While the same principles apply, a good tip to ensure that your structure is MECE is to think about all the stakeholders - i.e. those whom a specific venture involves.
Let’s consider that our client is a soda manufacturer who wants to move from a business-to-business strategy, i.e. selling to large chains of stores and supermarkets, to a business-to-consumer strategy where it sells directly to consumers. In doing so they would like to retrain part of their account managers as direct salespeople and need to know what factors to consider.
A stakeholder-driven approach would be to consider the workforce and customers and move further down the issue tree, thinking about individual issues that might affect them. In the case of the workforce, we might consider how the shift would affect their workload and whether it takes their skillset into account. As for the customers, we might wonder whether existing customers would be satisfied with this move: will the remaining B2B account managers be able to provide for the needs of all their clients and will the fact that the company is selling directly to consumers now not cannibalise their businesses? We see how by taking a stakeholder-centred approach we can ensure that every single perspective and potential issue arising from it is fully covered.
5.4.2 The Pareto Principle
Also known as the 80/20 rule, this principle is important when gauging the impact of a decision or a factor in your analysis. It simply states that in business (but not only) 80% of outcomes come from 20% of causes. What this means is you can make a few significant changes that will impact most of your business organisation, sales model, cost structure etc.
Let’s have a look at 3 quick examples to illustrate this:
- 80% of all accidents are caused by 20% of drivers
- 20% of a company’s products account for 80% of the sales
- 80% of all results in a company are driven by 20% of its employees
The 80/20 rule will be a very good guide line in real engagements as well as case interviews, as it will essentially point to the easiest and most straightforward way of doing things. Let’s say one of the questions in a case is asking you to come up with an approach to understand the appeal of a new beard trimmer. Obviously you can’t interview the whole male population so you might think about setting up a webpage and asking people to comment their thoughts. But what you would get would be a laundry list of difficult to sift through data.
Using an 80/20 approach you would segment the population based on critical factors (age groups, grooming habits etc.) and then approach a significant sample size of each (e.g. 20), analysing the data and reaching a conclusion.
5.4.3 The Pyramid Principle
This principle refers to organising your communication in a top-down , efficient manner. While this is generally applicable, the pyramid principle will most often be employed when delivering the final recommendation to your client. This means - as is implicit in the name - that you would organise your recommendation (and communication in general) as a pyramid, stating the conclusion or most important element at the top then go down the pyramid listing 3 supporting arguments and then further (ideally also 3) supporting arguments for those supporting arguments.
Let’s look at this in practice in a case interview context: your client is a German air-conditioning unit manufacturer who was looking to expand into the French market. However, after your analysis you’ve determined that the market share they were looking to capture would not be feasible. A final recommendation using the Pyramid Principle would sound something like this: ‘I recommend that we do not enter the German market for the following three reasons. Firstly, the market is too small for our ambitions of $50 million. Secondly the market is heavily concentrated, being controlled by three major players and our 5 year goal would amount to controlling 25% of the market, a share larger than that of any of the players. Thirdly, the alternative of going into the corporate market would not be feasible, as it has high barriers to entry.Then, if needed, we could delve deeper into each of our categories
6. Case examples or building blocks?
As we mentioned before, in your case interview preparation you will undoubtedly find preparation resources that claim that there are several standard types of cases and that there is a general framework that can be applied to each type of case. While there are indeed cases that are straightforward at least in appearance and seemingly invite the application of such frameworks, the reality is never that simple and cases often involve multiple or more complicated components that cannot be fitted into a simple framework.
At MCC we don’t want you to get into the habit of trying to identify which case type you’re dealing with and pull out a framework, but we do recognize that there are recurring elements in frameworks that are useful - such as the profitability of a venture (with its revenues and costs), the valuation of a business, estimating and segmenting a market and pricing a product.
We call these building blocks because they can be used to build case frameworks but are not a framework in and of themselves, and they can be shuffled around and rearranged in any way necessary to be tailored to our case. Hence, our approach is not to make you think in terms of case types but work from first principles and use these building blocks to build your own framework. Let’s take two case prompts to illustrate our point.
The first is from the Bain website, where the candidate is asked whether they think it’s a good idea for their friend to open a coffee shop in Cambridge UK (see the case here ). The answer framework provided here is a very straightforward profitability analysis framework, examining the potential revenues and potential costs of the venture:
While this is a good point to start for your case interview (especially taken together with the clarifying questions), we will notice that this approach will need more tailoring to the case - for example the quantity of coffee will be determined by the market for coffee drinkers in Cambridge, which we have to determine based on preference. We are in England so a lot of people will be drinking tea but we are in a university town so perhaps more people than average are drinking coffee as it provides a better boost when studying. All these are some much needed case-tailored hypotheses that we can make based on the initial approach.
Just by looking at this case we might be tempted to say that we can just take a profitability case and apply it without any issues. However, this generic framework is just a starting point and in reality we would need to tailor it much further in the way we had started to do in order to get to a satisfactory answer. For example, the framework for this specific case interview doesn’t cover aspects such as the customer’s expertise: does the friend have any knowledge of the coffee business, such as where to source coffee and how to prepare it? Also, we could argue there may be some legal factors to consider here, such as any approvals that they might need from the city council to run a coffee shop on site, or some specific trade licences that are not really covered in the basic profitability framework.
Let’s take a different case , however, from the McKinsey website. In this scenario, the candidate is being asked to identify some factors in order to choose where to focus the client’s conservation efforts. Immediately we can realise that this case doesn’t lend itself to any pre-packaged framework and we will need to come up with something from scratch - and take a look at McKinsey’s answer of the areas to focus on:

We notice immediately that this framework is 100% tailored to the case - of course there are elements which we encounter in other cases, such as costs and risks but again these are applied in an organic way. It’s pretty clear that while no standard framework would work in this case, the aforementioned concepts - costs and risks - and the way to approach them (a.k.a building blocks ) are fundamentally similar throughout cases (with the obvious specificities of each case).
In what follows, we’ll give a brief description of each building block starting from the Bain example discussed previously, in order to give you a general idea of what they are and their adaptability, but you should make sure to follow the link to the in-depth articles to learn all their ins and outs.
6.1 Estimates and segmentation
This building block will come into play mostly when you’re thinking about the market for a certain product (but make sure to read the full article for more details). Let’s take our Bain Cambridge coffee example. As we mentioned under the quantity bucket we need to understand what the market size for coffee in Cambridge would be - so we can make an estimation based on segmentation .
The key to a good estimation is the ability to logically break down the problem into more manageable pieces. This will generally mean segmenting a wider population to find a particular target group. We can start off with the population of Cambridge - which we estimate at 100.000. In reality the population is closer to 150.000 but that doesn’t matter - the estimation has to be reasonable and not accurate , so unless the interviewer gives you a reason to reconsider you can follow your instinct. We can divide that into people who do and don’t drink coffee. Given our arguments before, we can conclude that 80% of those, so 80.000 drink coffee. Then we can further segment into those who drink regularly - let’s say every day - and those who drink occasionally - let’s say once a week. Based on the assumptions before about the student population needing coffee to function, and with Cambridge having a high student population, we can assume that 80% of those drinking coffee are regular drinkers, so that would be 64.000 regular drinkers and 16.000 occasional drinkers. We can then decide whom we want to target what our strategy needs to be:
This type of estimation and segmentation can be applied to any case specifics - hence why it is a building block.
6.2 Profitability
We had several looks at this building block so far (see an in-depth look here ) as it will show up in most case interivew scenarios, since profit is a key element in any company’s strategy. As we have seen, the starting point to this analysis is to consider both the costs and revenues of a company, and try to determine whether revenues need to be improved or whether costs need to be lowered. In the coffee example, the revenues are dictated by the average price per coffe x the number of coffees sold , whereas costs can be split into fixed and variable .
Some examples of fixed costs would be the rent for the stores and the cost of the personnel and utilities, while the most obvious variable costs would be the coffee beans used and the takeaway containers (when needed). We may further split revenues in this case into Main revenues - i.e. the sales of coffee - and Ancillary revenues , which can be divided into Sales of food products (sales of pastries, sandwiches etc., each with the same price x quantity schema) and Revenues from events - i.e renting out the coffee shop to events and catering for the events themselves. Bear in mind that revenues will be heavily influenced by the penetration rate , i.e. the share of the market which we can capture.
6.3 Pricing
Helping a company determine how much they should charge for their goods or services is another theme that comes up frequently in cases. While it may seem less complicated than the other building blocks, we assure you it’s not - you will have to understand and consider several factors, such as the costs a company is incurring, their general strategic positioning, availability, market trends as well as the customers’ willingness to pay (or WTP in short) - so make sure to check out our in-depth guide here .
In our example, we may determine that the cost per cup (coffee beans, staff, rent) is £1. We want to be student friendly so we should consider how much students would want to pay for a coffee as well as how much are competitors are charging. Based on those factors, it would be reasonable to charge on average £2 per cup of coffee. It’s true that our competitors are charging £3 but they are targeting mostly the adult market, whose willingness to pay is higher, so their pricing model takes that into account as well as the lower volume of customers in that demographic.
6.4. Valuation
A variant of the pricing building block, a valuation problem generally asks the candidate to determine how much a client should pay for a specific company (the target of an acquisition) as well as what other factors to consider. The two most important factors (but not the only ones - for a comprehensive review see our Valuation article ) to consider are the net present value (in consulting interviews usually in perpetuity) and the synergies .
In short, the net present value of a company is how much profit it currently brings in, divided by how much that cash flow will depreciate in the future and can be represented with the equation below:
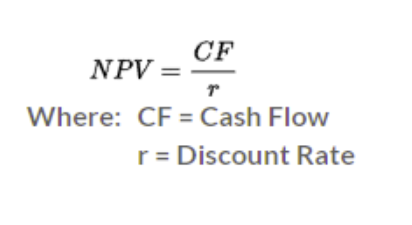
The synergies refer to what could be achieved should the companies operate as one, and can be divided into cost and revenue synergies .
Let’s expand our coffee example a bit to understand these. Imagine that our friend manages to open a chain of coffee shops in Cambridge and in the future considers acquiring a chain of take-out restaurants. The most straightforward example of revenue synergies would be cross-selling, in this case selling coffee in the restaurants as well as in the dedicated stores, and thus getting an immediate boost in market share by using the existing customers of the restaurant chain. A cost synergy would be merging the delivery services of the two businesses to deliver both food and coffee, thus avoiding redundancies and reducing costs associated with twice the number of drivers and vehicles.
6.5. Competitive interaction
This component of cases deals with situations where the market in which a company is operating changes and the company must decide what to do. These changes often have to do with a new player entering the market (again for more details make sure to dive into the Competitive Interaction article ).
Let’s assume that our Cambridge coffee shop has now become a chain and has flagged up to other competitors that Cambridge is a blooming market for coffee. As such, Starbucks has decided to open a few stores in Cambridge themselves, to test this market. The question which might be posed to a candidate is what should our coffee chain do. One way (and a MECE one) to approach the problem is to decide between doing something and doing nothing . We might consider merging with another coffee chain and pooling our resources or playing to our strengths and repositioning ourselves as ‘your student-friendly, shop around the corner’. Just as easily we may just wait the situation out and see whether indeed Starbucks is cutting into our market share - after all, the advantages of our product and services might speak for themselves and Starbucks might end up tanking. Both of these are viable options if argued right and depending on the further specifics of the case.
6.6. Special cases
Most cases deal with private sectors, where the overarching objective entails profit in some form. However, as hinted before, there are cases which deal with other sectors where there are other KPIs in place . The former will usually contain one or several of these building blocks whereas the latter will very likely have neither. This latter category is arguably the one that will stretch your analytical and organisational skills to the limit, since there will be very little familiarity that you can fall back on (McKinsey famously employs such cases in their interview process).
So how do we tackle the structure for such cases? The short answer would be starting from first principles and using the problem driven structure outlined above, but let’s look at a quick example in the form of a McKinsey case :
The first question addressed to the candidate is the following:

This is in fact asking us to build a structure for the case. So what should we have in mind here? Most importantly, we should start with a structure that is MECE and we should remember to do that by considering all the stakeholders . They are on the one hand the government and affiliated institutions and on the other the population. We might then consider which issues might arise for each shareholder and what the benefits for them would be, as well as the risks. This approach is illustrated in the answer McKinsey provides as well:
More than anything, this type of case shows us how important it is to practise and build different types of structures, and think about MECE ways of segmenting the problem.
7. How Do I prepare for case interviews
In consulting fashion, the overall preparation can be structured into theoretical preparation and practical preparation , with each category then being subdivided into individual prep and prep with a partner .
As a general rule, the level and intensity of the preparation will differ based on your background - naturally if you have a business background (and have been part of a consulting club or something similar) your preparation will be less intensive than if you’re starting from scratch. The way we suggest you go about it is to start with theoretical preparation , which means learning about case interviews, business and basic consulting concepts (you can do this using free resources - such as the ones we provide - or if you want a more through preparation you can consider joining our Case Academy as well).
You can then move on to the practical preparation which should start with doing solo cases and focusing on areas of improvement, and then move on to preparation with a partner , which should be another candidate or - ideally - an ex-consultant.
Let’s go into more details with respect to each type of preparation.
7.1. Solo practice
The two most important areas of focus in sole preparation are:
- Mental math
As we mentioned briefly, the best use of your time is to focus on solving cases. You can start with cases listed on MBB sites since they are clearly stated and have worked solutions as well (e.g. Bain is a good place to start) and then move to more complex cases (our Case Library also offers a range of cases of different complexities). To build your confidence, start out on easier case questions, work through with the solutions, and don't worry about time. As you get better, you can move on to more difficult cases and try to get through them more quickly. You should practice around eight case studies on your own to build your confidence.
Another important area of practice is your mental mathematics as this skill will considerably increase your confidence and is neglected by many applicants - much to their immediate regret in the case interview. Find our mental math tool here or in our course, and practice at least ten minutes per day, from day one until the day before the interview.
7.2. Preparation with a partner
There are aspects of a case interview - such as asking clarifying questions - which you cannot do alone and this is why, after you feel comfortable, you should move on to practice with another person. There are two options here:
- Practicing with a peer
- Practicing with an ex-consultant
In theory they can be complementary - especially if you’re peer is also preparing for consulting interviews - and each have advantages and disadvantages. A peer is likely to practice with you for free for longer, however you may end up reinforcing some bad habits or unable to get actionable feedback. A consultant will be able to provide you the latter but having their help for the same number of hours as a peer will come at a higher cost. Let’s look at each option in more detail.
7.2.1. Peer preparation
Once you have worked through eight cases solo, you should be ready to simulate the case interview more closely and start working with another person.
Here, many candidates turn to peer practice - that is, doing mock case interviews with friends, classmates or others also applying to consulting. If you’re in university, and especially in business school, there will very likely be a consulting club for you to join and do lots of case practice with. If you don’t have anyone to practice, though, or if you just want to get a bit more volume in with others, our free meeting board lets you find fellow applicants from around the world with whom to practice. We recommend practicing around 10 to 15 ‘live’ cases to really get to a point where you feel comfortable.
7.2.2. Preparation with a consultant
You can do a lot practising by yourself and with peers. However, nothing will bring up your skills so quickly and profoundly as working with a real consultant.
Perhaps think about it like boxing. You can practice drills and work on punch bags all you want, but at some point you need to get into the ring and do some actual sparring if you ever want to be ready to fight.
Practicing with an ex consultant is essentialy a simulation of a case interview. Of course, it isn’t possible to secure the time of experienced top-tier consultants for free. However, when considering whether you should invest to boost your chances of success, it is worth considering the difference in your salary over even just a few years between getting into a top-tier firm versus a second-tier one. In the light of thousands in increased annual earnings (easily accumulating into millions over multiple years), it becomes clear that getting expert interview help really is one of the best investments you can make in your own future.
Should you decide to make this step, MyConsultingCoach can help, offering bespoke mentoring programmes , where you are paired with a 5+ year experienced, ex-MBB mentor of your choosing, who will then oversee your whole case interview preparation from start to finish - giving you your best possible chance of landing a job!
7.3. Practice for online interviews
Standard preparation for interview case studies will carry directly over to online cases.
However, if you want to do some more specific prep, you can work through cases solo to a timer and using a calculator and/or Excel (online cases generally allow calculators and second computers to help you, whilst these are banned in live case interviews).
Older PST-style questions also make great prep, but a particularly good simulation is the self-assessment tests included in our Case Academy course . These multiple choice business questions conducted with a strict time limit are great preparation for the current crop of online cases.
7.4. Fit interviews
As we’ve noted, even something billed as a case interview is very likely to contain a fit interview as a subset.
We have an article on fit interviews and also include a full set of lessons on how to answer fit questions properly as a subset of our comprehensive Case Academy course .
Here though, the important thing to convey is that you take preparing for fit questions every bit as seriously as you do case prep.
Since they sound the same as you might encounter when interviewing for other industries, the temptation is to regard these as “just normal interview questions”.
However, consulting firms take your answers to these questions a good deal more seriously than elsewhere.
This isn’t just for fluffy “corporate culture” reasons. The long hours and close teamwork, as well as the client-facing nature of management consulting, mean that your personality and ability to get on with others is going to be a big part of making you a tolerable and effective co-worker.
If you know you’ll have to spend 14+ hour working days with someone you hire and that your annual bonus depends on them not alienating clients, you better believe you’ll pay attention to their character in interview.
There are also hard-nosed financial reasons for the likes of McKinsey, Bain and BCG to drill down so hard on your answers.
In particular, top consultancies have huge issues with staff retention. The average management consultant only stays with these firms for around two years before they have moved on to a new industry.
In some cases, consultants bail out because they can’t keep up with the arduous consulting lifestyle of long hours and endless travel. In many instances, though, departing consultants are lured away by exit opportunities - such as the well trodden paths towards internal strategy roles, private equity or becoming a start-up founder.
Indeed, many individuals will intentionally use a two year stint in consulting as something like an MBA they are getting paid for - giving them accelerated exposure to the business world and letting them pivot into something new.
Consulting firms want to get a decent return on investment for training new recruits. Thus, they want hires who not only intend to stick with consulting longer-term, but also have a temperament that makes this feasible and an overall career trajectory where it just makes sense for them to stay put.
This should hammer home the point that, if you want to get an offer, you need to be fully prepared to answer fit questions - and to do so excellently - any time you have a case interview.
8. Interview day - what to expect, with tips
Of course, all this theory is well and good, but a lot of readers might be concerned about what exactly to expect in real life . It’s perfectly reasonable to want to get as clear a picture as possible here - we all want to know what we are going up against when we face a new challenge!
Indeed, it is important to think about your interview in more holistic terms, rather than just focusing on small aspects of analysis. Getting everything exactly correct is less important than the overall approach you take to reasoning and how you communicate - and candidates often lose sight of this fact.
In this section, then, we’ll run through the case interview experience from start to finish, directing you to resources with more details where appropriate. As a supplement to this, the following video from Bain is excellent. It portrays an abridged version of a case interview, but is very useful as a guide to what to expect - not just from Bain, but from McKinsey, BCG and any other high-level consulting firm.
8.1. Getting started
Though you might be shown through to the office by a staff member, usually your interviewer will come and collect you from a waiting area. Either way, when you first encounter them, you should greet your interviewer with a warm smile and a handshake (unless they do not offer their hand). Be confident without verging into arrogance. You will be asked to take a seat in the interviewer’s office, where the case interview can then begin.
8.1.1. First impressions
In reality, your assessment begins before you even sit down at your interviewer’s desk. Whether at a conscious level or not, the impression you make within the first few seconds of meeting your interviewer is likely to significantly inform the final hiring decision (again, whether consciously or not).
Your presentation and how you hold yourself and behave are all important . If this seems strange, consider that, if hired, you will be personally responsible for many clients’ impressions of the firm. These things are part of the job! Much of material on the fit interview is useful here, whilst we also cover first impressions and presentation generally in our article on what to wear to interview .
As we have noted above, your interview might start with a fit segment - that is, with the interviewer asking questions about your experiences, your soft skills, and motivation to want to join consulting generally and that firm in particular. In short, the kinds of things a case study can’t tell them about you. We have a fit interview article and course to get you up to speed here.
8.1.2. Down to business
Following an initial conversation, your interviewer will introduce your case study , providing a prompt for the question you have to answer. You will have a pen and paper in front of you and should (neatly) note down the salient pieces of information (keep this up throughout the interview).
It is crucial here that you don’t delve into analysis or calculations straight away . Case prompts can be tricky and easy to misunderstand, especially when you are under pressure. Rather, ask any questions you need to fully understand the case question and then validate that understanding with the interviewer before you kick off any analysis. Better to eliminate mistakes now than experience that sinking feeling of realising you have gotten the whole thing wrong halfway through your case!
This process is covered in our article on identifying the problem and in greater detail in our Case Academy lesson on that subject.
8.1.3. Analysis
Once you understand the problem, you should take a few seconds to set your thoughts in order and draw up an initial structure for how you want to proceed. You might benefit from utilising one or more of our building blocks here to make a strong start. Present this to your interviewer and get their approval before you get into the nuts and bolts of analysis.
We cover the mechanics of how to structure your problem and lead the analysis in our articles here and here and more thoroughly in the MCC Case Academy . What it is important to convey here, though, is that your case interview is supposed to be a conversation rather than a written exam . Your interviewer takes a role closer to a co-worker than an invigilator and you should be conversing with them throughout.
Indeed, how you communicate with your interviewer and explain your rationale is a crucial element of how you will be assessed. Case questions in general, are not posed to see if you can produce the correct answer, but rather to see how you think . Your interviewer wants to see you approach the case in a structured, rational fashion. The only way they are going to know your thought processes, though, is if you tell them!
To demonstrate this point, here is another excellent video from Bain, where candidates are compared.
Note that multiple different answers to each question are considered acceptable and that Bain is primarily concerned with the thought processes of the candidate’s exhibit .
Another reason why communication is absolutely essential to case interview success is the simple reason that you will not have all the facts you need to complete your analysis at the outset. Rather, you will usually have to ask the interviewer for additional data throughout the case to allow you to proceed .
NB: Don't be let down by your math!
Your ability to quickly and accurately interpret these charts and other figures under pressure is one of the skills that is being assessed. You will also need to make any calculations with the same speed and accuracy (without a calculator!). As such, be sure that you are up to speed on your consulting math .
8.1.4. Recommendation
Finally, you will be asked to present a recommendation. This should be delivered in a brief, top-down "elevator pitch" format , as if you are speaking to a time-pressured CEO. Again here, how you communicate will be just as important as the details of what you say, and you should aim to speak clearly and with confidence.
For more detail on how to give the perfect recommendation, take a look at our articles on the Pyramid Principle and providing recommendations , as well the relevant lesson within MCC Academy .
8.1.5. Wrapping up
After your case is complete, there might be a few more fit questions - including a chance for you to ask some questions of the interviewer . This is your opportunity to make a good parting impression.
We deal with the details in our fit interview resources. However, it is always worth bearing in mind just how many candidates your interviewers are going to see giving similar answers to the same questions in the same office. A pretty obvious pre-requisite to being considered for a job is that your interviewer remembers you in the first place. Whilst you shouldn't do something stupid just to be noticed, asking interesting parting questions is a good way to be remembered.
Now, with the interview wrapped up, it’s time to shake hands, thank the interviewer for their time and leave the room .
You might have other case interviews or tests that day or you might be heading home. Either way, if know that you did all you could to prepare, you can leave content in the knowledge that you have the best possible chance of receiving an email with a job offer. This is our mission at MCC - to provide all the resources you need to realise your full potential and land your dream consulting job!
8.2. Remote and one-way interview tips
Zoom case interviews and “one-way” automated fit interviews are becoming more common as selection processes are increasingly remote, with these new formats being accompanied by their own unique challenges.
Obviously you won’t have to worry about lobbies and shaking hands for a video interview. However, a lot remains the same. You still need to do the same prep in terms of getting good at case cracking and expressing your fit answers. The specific considerations around remote case interviews are, in effect, around making sure you come across as effectively as you would in person.
8.2.1. Connection
It sounds trivial, but a successful video case interview of any kind presupposes a functioning computer with a stable and sufficient internet connection.
Absolutely don’t forget to have your laptop plugged in, as your battery will definitely let you down mid-interview. Similarly, make sure any housemates or family know not to use the microwave, vacuum cleaner or anything else that makes wifi cut out (or makes a lot of noise, obviously)
If you have to connect on a platform you don’t use much (for example, if it’s on Teams and you’re used to Zoom), make sure you have the up to date version of the app in advance, rather than having to wait for an obligatory download and end up late to join. Whilst you’re at it, make sure you’re familiar with the controls etc. At the risk of being made fun of, don’t be afraid to have a practice call with a friend.
8.2.2. Dress
You might get guidance on a slightly more relaxed dress code for a Zoom interview. However, if in doubt, dress as you would for the real thing (see our article here ).
Either way, always remember that presentation is part of what you are being assessed on - the firm needs to know you can be presentable for clients. Taking this stuff seriously also shows respect for your interviewer and their time in interviewing you.
8.2.3. Lighting
An aspect of presentation that you have to devote some thought to for a Zoom case interview is your lighting.
Hopefully, you long ago nailed a lighting set-up during the Covid lockdowns. However, make sure to check your lighting in advance with your webcam - bearing in mind what time if day your case interview actually is. If your case interview is late afternoon, don’t just check in the morning. Make sure you aren’t going to be blinded from light coming in a window behind your screen, or that you end up with the weird shadow stripes from blinds all over your face.
Natural light is always best, but if there won’t be much of that during your interview, you’ll likely want to experiment with moving some lamps around.
8.2.4. Clarity
The actual stories you tell in an automated “one-way” fit interview will be the same as for a live equivalent. If anything, things should be easier, as you can rattle off a practised monologue without an interviewer interrupting you to ask for clarifications.
You can probably also assume that the algorithm assessing your performance is sufficiently capable that it will be observing you at much the same level as a human interviewer. However, it is probably still worth speaking as clearly as possible with these kinds of interviews and paying extra attention to your lighting to ensure that your face is clearly visible.
No doubt the AIs scoring these interviews are improving all the time, but you still want to make their job as easy as possible. Just think about the same things as you would with a live Zoom case interview, but more so.
9. How we can help
There are lots of great free resources on this site to get you started with preparation, from all our articles on case solving and consulting skills to our free case library and peer practice meeting board .
To step your preparation up a notch, though, our Case Academy course will give you everything you need to know to solve the most complex of cases - whether those are in live case interviews, with chatbots, written tests or any other format.
Whatever kind of case you end up facing, nothing will bring up your skillset faster than the kind of acute, actionable feedback you can get from a mock case interview a real, MBB consultant. Whilst it's possible to get by without this kind of coaching, it does tend to be the biggest single difference maker for successful candidates.
You can find out more on our coaching page:
Explore Coaching
Of course, for those looking for a truly comprehensive programme, with a 5+ year experienced MBB consultant overseeing their entire prep personally, from networking and applications right through to your offer, we have our mentoring programmes.
You can read more here:
Comprehensive Mentoring
Account not confirmed
Access all the online resources you need for success in your case and fit interviews.
Build a successful application with our step-by-step resume advice videos, examples, and templates.
- Resources home
- Applications
- Interview tips
- Management consulting industry guide
- Top routes for joining McKinsey, BCG and Bain in 2023
- The top-10 management consulting firms
- How to practice case interviews alone
- Tips for last-minute case interview prep
Thank you for your review!
Free interview prep material in your inbox
WHAT'S INCLUDED?
You're subscribed!
What’s included?
28 emails packed with tips. 8 full cases with solutions (incl. FlashFash). Plus sample case and fit interview videos.
Case Interview: The Free Preparation Guide (2024)
The case interview is a challenging interview format that simulates the job of a management consultant , testing candidates across a wide range of problem-solving dimensions.
McKinsey, BCG and Bain – along with other top consulting firms – use the case interview because it’s a statistically proven predictor of how well a candidate will perform in the role. The format is not only used by management consulting firms. Other types of organizations – like tech companies, financial services institutions, and non-profits – often use case interviews to assess candidates who are interviewing for roles focused on shaping strategic initiatives.
If you’re preparing to face a case interview, you may be feeling a little apprehensive. The format is notoriously demanding and unlike any other type of recruitment assessment you may have experienced before. However, with the right preparation and investment of time and effort, it is possible to master.
In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about the case interview, outlining exactly what you need to do to prepare effectively and ace the case.
Key takeaways
- The classic case interview format follows the same steps that a management consultant would encounter on a client project. The interview is a little like a role-play where the interviewer plays the role of a client and the candidate plays the part of the consultant hired to solve the problem.
- Some firms occasionally deviate from the classic case interview format. Popular alternatives include written case studies – which require candidates to review paper documents and then prepare and deliver a presentation – and market sizing case interviews, which require candidates to estimate a number.
- Case interviews test candidates against a set of six problem-solving dimensions: structuring, math, judgment and insights, creativity, synthesis, and case leadership. The interviewer uses a scorecard to assess the candidate’s performance in each of these areas.
- Case interview questions can be about almost any type of challenge or opportunity. However, our research indicates that there are 10 types of questions that are asked most frequently at top consulting firms. These include questions on profit improvement, revenue growth, and market entry.
- To do well in a case interview, it’s vital to create custom interview structures that meet the conditions of the ‘AIM’ test. It helps to have a good working knowledge of key case interview frameworks, but this alone is not sufficient.
- A strong grasp of case math is also crucial when it comes to case interview performance. While only high-school level math skills are required, it’s an aspect of the case interview that many candidates find challenging.
- Successful candidates are able to summarize their findings effectively. They also demonstrate strong case leadership by progressing through the case proactively and remaining focused on its overarching objectives.
- To prepare for a case interview, it’s essential to learn every problem-solving skill that will be assessed. We teach all of these skills in our Interview Prep Course , which contains all the video lectures, sample interviews, case material, and practice tools you’ll need to ace any case interview.
- Most candidates who go on to receive an offer from a top consulting firm like McKinsey, BCG or Bain complete at least 25 live practice sessions with a partner before their interview. You’ll find over 100 high-quality cases in our Case Library and a diverse community of candidates available for practice in our Practice Room .
- Some candidates choose to supplement their preparation by working with a coach who has been an interviewer at a top consulting firm. Here at CaseCoach, our coaches have all been handpicked from the alumni of top firms such as McKinsey, BCG and Bain.
- Although the world’s top consulting firms all test candidates using similar methods, none of them approach the interview process in exactly the same way. If you’re preparing to interview at a top consulting firm, it’s important to do your research and find out what you can expect.
An introduction to the case interview
The case interview format, the classic case interview.
The vast majority of case interviews follow the same steps that management consultants encounter on real client projects.
- Brief: The interviewer gives the candidate a brief for the case. They explain the context in which the client is operating, and outline the challenge they’re facing.
- Clarification: The candidate then has the chance to ask clarifying questions. They might do this to ensure they’ve understood the context of the problem correctly or to confirm the client’s goals.
- Reflection: The candidate takes 60 to 90 seconds or so to reflect and lay out a structured approach to solving the case.
- Analysis: The candidate and interviewer then work through the case together, carrying out analyses and moving toward a recommendation. This is the part of the case where you’ll be handling numerical questions, reviewing exhibits, coming up with creative ideas, and so on. It comprises the vast majority of the time you’ll spend on the case.
- Synthesis: The case concludes with the candidate synthesizing their findings and making an overall recommendation to the client.
So what does this unique interview format look and feel like? In reality, a consulting case interview is a little like a role-play. The interviewer plays the role of a manager or client, and the candidate plays the part of the consultant hired to solve the problem. However, a case interview shouldn’t feel like a performance. The most successful candidates treat it as a natural conversation between two professional people.
In the video below you can see an example of exceptional case interview performance in action. The candidate and interviewer in the video are both former McKinsey interviewers.
Interviewer-led vs candidate-led cases
Although the classic case interview has an established format and assesses a specific set of skills, cases can be delivered in different ways. Some are more candidate-led, while others are more interviewer-led
In a candidate-led case, the candidate is in the driver’s seat and is free to explore different aspects of the problem. Interviewers don’t tell candidates what to focus on next. Instead, they provide additional information – like an exhibit or a new fact – when asked. The candidate then analyzes the information and suggests next steps to get to the answer.
In an interviewer-led case, the interviewer may interrupt the candidate and ask them to either perform a specific investigation or focus on a different aspect of the problem. This doesn’t mean the interview is going badly; the interviewer is simply following a script. As a result, in an interviewer-led case, candidates are less likely to take the wrong path.
It’s difficult to predict which style of case you’ll receive. Some firms are known for using one style of interview more frequently than another. However, in practice, most interviews fall somewhere between the two extremes, depending on the style of the interviewer and the case material they’re using. You should therefore always be ready to suggest next steps and have a view about how to get to the answer.
Other case interview formats
While the classic case interview is most common, there are a couple of other interview formats that top consulting firms use from time to time:
The written case study
Some management consulting firms use written case studies to simulate the experience of carrying out consulting work even more accurately than the classic, verbal case interview. In some locations, BCG and Bain have been known to adopt this approach for a small minority of candidates.
In written cases, candidates review a series of paper documents and then structure the problem, run some numbers, generate ideas and, finally, deliver a short presentation. You can learn more in our article on how to crack written case studies .
Market sizing case interviews
Management consulting firms and other employers sometimes use market sizing questions – also known as estimation questions – as a standalone interview format to assess candidates on a wide range of problem-solving dimensions.
In a market sizing interview, you’ll be asked to estimate a number. This might be something like the revenue of a sandwich store or how many ATMs there are in a certain city. The ability to size a market is also a skill required for solving many case interview questions. You can learn more in our article on how to nail market sizing case interviews .
Some key differences to expect
While case interviews are highly codified, it’s important to remember that every interview is unique.
In the final round of interviews, for example, cases may feel less scripted than they did in the first stage. Partners – who are part of the interviewing group in the final round – often use the same case for years at a time. This means they can deliver it without a script and, as a result, tend to give candidates more room to take the lead. You can learn more in our article on the differences between a first and final-round interview at McKinsey, BCG and Bain .
In addition, each firm or office might bring their own nuance or style to the classic case interview format. It’s important to do your research and find out what you can expect from the interview experience at your target firm or office. You can learn more in our article on how the interviews at McKinsey, BCG and Bain differ .
The skills assessed in case interviews
Case interviews are primarily about testing a set of problem-solving skills. The interviewer uses a scorecard to assess a candidate’s performance in the following dimensions:
- Structuring: This is the ability to break problems down into logical drivers. It’s most obviously required at the beginning of a case, where you can pause and take a moment to come up with an approach. But it’s also tested each time you have to consider a new aspect of the problem.
- Math: Most cases contain a quantitative component, such as estimation questions, break-even questions, or other calculations. To do well in this dimension, you need to lay out a clear and efficient approach, run calculations quickly and accurately, and then state their implications for the case.
- Judgment and insights: This dimension is about extracting insights from data, usually by interpreting information in a chart. Performing well in this area involves processing new information quickly, prioritizing what’s important, and connecting your findings to develop sound recommendations.
- Creativity: Cases often have a creative thinking component. Sharing numerous, varied and sound ideas – ideally in a structured way – can help you succeed here.
- Synthesis: This is all about wrapping up the case with a clear and practical recommendation, and delivering it convincingly.
- Case leadership: This dimension is about progressing through the case efficiently and staying focused on its objectives. Case leadership involves gathering facts effectively and building on new findings to develop a recommendation. It’s a particularly important dimension in candidate-led cases.
Questions to expect
If you’re preparing to interview at a top management consulting firm like McKinsey, BCG or Bain, you’re probably curious about the kind of case interview questions you can expect to receive.
To identify the most common case interview questions , we surveyed CaseCoach users who interviewed at either McKinsey, BCG or Bain for a generalist role in 2023. We found that of the 260+ case interviews reported by respondents:
- 20% focused on profit improvement
- 15% focused on revenue growth
- 12% focused on market entry
- 10% focused on cost cutting
- 9% focused on process optimization
These topics align with the typical challenges and opportunities faced by CEOs. Because the job of a management consultant is to help CEOs find solutions to these problems, it’s vital for candidates to demonstrate that they understand the issues behind these questions.
However, while there are some recurring topics, the context and nuances of each individual case mean that no two case questions are the same. Increasingly, firms are testing candidates on questions that fall outside of these recurring topics. One way they’re doing this is by focusing on non-traditional areas, like the public sector. If you’re interviewing for a generalist management consulting role, it’s therefore important to be ready for almost any type of case question.
If you’re interviewing for a role that’s focused on a specific industry or function, like financial services , you’ll likely be given a case focused on that particular area.
How to ace the case
Case interviews require you to think on your feet to solve a complex problem that you’ve never seen before, while being assessed against a number of problem-solving dimensions. Here’s what you need to do to rise to the challenge and ace the case:
1. Create case interview structures that meet the AIM test
Of all the case interview assessment dimensions, structuring is perhaps the most challenging, particularly for those who are just starting out. It requires candidates to propose a prioritized and insightful approach to the case that’s composed of a comprehensive set of independent drivers. Structuring plays a foundational role in the interview, setting the course for the entire conversation.
So, what does good case structuring look like? An effective structure should meet the conditions of the ‘AIM’ test. ‘AIM’ stands for:
- Answer-focused: The structure should identify the client’s goal and the question to solve. It should also provide an approach to answering that question.
- Insightful: The structure should be tailored to the specifics of the client or to the problem in question. You shouldn’t be able to apply it to another case of the same type.
- MECE: This is a well-known acronym among consultants. It stands for ‘mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive’. In plain English, if a structure is ‘MECE’ it has been broken down into an exhaustive set of independent drivers.
2. Know key case interview frameworks
In a case interview, you’ll be asked to structure a variety of problems. There are a number of frameworks that can help you do this, whether the problem you’re structuring corresponds to a common case question or a different topic entirely:
Business frameworks
You can use established business frameworks to craft custom structures for the most common types of case questions. These include frameworks for mastering profitability questions , answering revenue growth questions and nailing market sizing questions .
Academic frameworks
For unusual case questions that don’t relate to an obvious business framework, it can be helpful to draw on an academic framework like supply and demand, ‘the three Cs’, or Porter’s Five Forces. You can learn more about all of these in our ultimate guide to case interview frameworks . The article includes other business and academic frameworks that you can use to craft custom structures for case questions.
Logical frameworks
Finally, logical frameworks can help you look at the big picture in order to structure your approach. These options can be particularly useful when you’re faced with an unusual case question that doesn’t lend itself to a business or academic framework. Some examples of logical frameworks include:
- Structuring with equations: This approach is most helpful for quantitative case questions. Listen out for introductions that focus on a number. These cases can often be broken down into an equation and then structured along its variables.
- Structuring based on hypotheses: This approach is most helpful for structuring qualitative cases. It involves laying out what you most need to believe in order to validate a specific recommendation. These beliefs form your set of key hypotheses, which you then test as you progress through the case.
- Structuring with root causes: This approach works well for structuring cases that require identifying the reasons for a problem. It involves laying out its potential causes in a way that is mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive (i.e. MECE).
How to apply these frameworks
While business, academic, and logical frameworks can be helpful when it comes to structuring a problem, learning how to use them correctly is a skill in itself. Simply applying a framework to a case interview question in a ‘cookie-cutter’ fashion is not enough. To impress your interviewer and pass the AIM test, your structure will need to be heavily tailored to the situation at hand. In fact, many case questions can be best answered by combining different frameworks.
Ultimately, interviewers want to understand how your mind works and see you think on your feet. You’ll therefore need to demonstrate that you can propose a custom case interview structure to any question.
3. Be comfortable with simple math
Management consulting firms expect you to navigate mathematical problems confidently and reliably in case interviews. Regardless of your academic background or past experience, you’ll need to be able to set an approach to solve the problem, perform calculations quickly and accurately, and state the implications of your solution.
The good news is that you’ll only be required to demonstrate a high-school level of math skills in case interviews. However, with no calculators allowed and an interviewer looking over your shoulder, it’s natural to find this aspect of the experience a little intimidating.
So, what can you expect from case math? The problems you’ll be asked to solve may take the form of straight calculations, exhibits that require calculations, word problems, and estimation questions.
To do well in this part of the case interview, you’ll need to have a strong understanding of:
- The four operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
- Key math concepts such as fractions, percentages, and weighted averages
- Business math concepts such as income statements, investments, and valuations
To stand out to your interviewer, you’ll also need to work through math problems confidently and efficiently. Here are our top tips for doing this:
- Keep track of zeros: Case questions often involve large numbers, sometimes in the millions or even billions. Keeping close track of your zeros is therefore crucial. We recommend either counting the zeros in your calculation, using scientific notation, or assigning letter units to zeros.
- Simplify your calculations: This will help you work through problems quickly and efficiently while reducing the potential for mistakes. One way of simplifying calculations is by rounding numbers up or down to make them more ‘friendly’.
- Memorize frequently-used fractions: Some fraction values are used so frequently in case math that knowing them – along with their percentage value and decimal conversions – can save you significant time. We recommend memorizing the fraction and corresponding percentage and decimal values of 1/2, 1/3, all the way through to 1/10.
You can learn more in our guide to mastering case interview math .
4. Summarize your findings
Synthesis is a key skill assessed by interviewers, predominantly at the end of a case interview. You need to provide a clear and sound recommendation that answers the overall question convincingly. You must also describe the key supporting points that informed your recommendation and then outline any further steps you would advise the client to take.
When it comes to concluding cases effectively, this four-step framework can be extremely helpful:
- Quickly play the case question back to your interviewer.
- Answer the question directly and briefly by distilling your response into a single sentence, if possible.
- List the points that support your conclusion.
- Outline the next steps that you recommend to the client.
You can learn more in our article on how to conclude a case study interview .
5. Bring it all together with strong case leadership
Case leadership, more than any other dimension, will give your interviewer an indication of how independently you could handle your workstream as a consultant. It’s a particularly important skill in candidate-led cases, where you’ll set the course of the discussion without the interviewer steering you in a particular direction.
Demonstrating strong case leadership means progressing the case efficiently and staying focused on its overarching objectives. Using a ‘tracker page’ to capture your structure and organize your notes throughout the case will help you in this regard.
Another aspect of case leadership is gathering facts effectively. This includes making reasonable assumptions, requesting missing information, and asking probing questions.
Finally, you’ll be expected to build on new findings to develop your recommendation, adapt your approach, and suggest next steps.
Effective case leadership is all about showing your interviewer that you have a strong command of the problem-solving process. After investigating each key driver in your structure, you need to be able to articulate where you are in your overall approach to solving the problem, and what the next steps should be.
To do this, we recommend using a five-step process to handle every kind of analysis you conduct during the case, whether you’re responding to a numerical question, the data in an exhibit, or something else.
Here’s what that five-step process looks like:
- Set your approach. Define what you’re going to do upfront. It’s particularly important to be explicit here, especially if the analysis is in any way complex or ambiguous.
- Conduct your analysis. Your approach here will vary according to the kind of question you’re working through.
- State your findings. You may also want to make a note of your findings on your tracker page.
- State the implications of your findings. Explain how they impact both your answer to the question and the client’s broader goal.
- Suggest next steps. Your findings will sometimes change how you want to approach the rest of the case. This may mean altering your initial structure and editing it on your tracker page.
6. Be your best on the day
When the day of your interview comes around, you’ll want to be at your very best. But what exactly does this mean?
First, you should present yourself in a professional manner. It goes without saying that you should arrive on time but, ideally, you should plan to arrive early. You should also come equipped with the right material: a pen, squared A4 or letter-size paper pad, and copies of your resume. It’s also vital to dress appropriately for the occasion. Usually, this means wearing formal business dress, but this means different attires in different locations. We recommend doing some research to find out what consultants wear at your target firm and office.
To be at your best on the day of your interview, you must be well rested. Sadly, tiredness is one of the most common reasons for underperformance in consulting interviews. The day before is not the time to cram in further preparation. Instead, aim to have a quiet day and to get plenty of sleep at night.
Ultimately, consulting firms want to hire people who can represent the firm and interact with clients at every level, from the shop floor to the C-suite. Successful candidates treat the case interview as an opportunity to play the role of a management consultant advising a client (i.e. the interviewer). This means exhibiting a great deal of confidence and credibility, together with effective communication and an engaging attitude. It’s vital to stay focused on the overall problem and to drive the resolution of the case while being receptive to the interviewer’s input.
There are a lot of balls to juggle in a case interview, with the added pressure of a potentially life-changing outcome, but successful candidates don’t let their nerves get the better of them. We’ve provided some helpful hints and tips in our article on handling the stress of consulting interviews .
Being your best on the day of your interview requires extensive preparation. It means mastering each dimension of the case interview scorecard to the extent that the skills become second nature to you. It also means completing sufficient case practice to be able to focus on the big picture of the case you’re solving, rather than on simply demonstrating a set of skills.
How to prepare for case interview success
Delivering a standard of performance worthy of an offer from a top firm requires extensive case interview prep. In our experience, most successful candidates invest around 60 hours – or 10 hours each week over a six-week period – in their preparation. Failing to put this effort in is among the most common reasons why many candidates are unsuccessful.
Here’s what effective case interview preparation involves:
Learning the skills
In a case interview, your performance is assessed against a set of common problem-solving dimensions. To recap, these are structuring, math, judgment and insights, creativity, synthesis, and case leadership. It’s important to:
- gain a precise understanding of the expectations on each of these skills
- learn the techniques that will allow you to meet these expectations
- practice until your performance meets the required standard
We teach all these skills in our Interview Prep Course . In our bite-sized video lectures, we map out each of the key skills assessed in a case, and explain what you need to know to demonstrate each skill. We also share our tips on how to improve in each dimension, going above and beyond the advice we’ve included in this article.
In addition, our Interview Prep Course includes many more sample interviews that show real candidates – who went on to join top consulting firms – solving cases. Former consulting interviewers explain what the candidates did well on each dimension and where they could have improved.
Math is a critical prerequisite to handling cases and is something you should be comfortable with before you begin practicing. Our Case Math Course – provided as part of the Interview Prep Course – will help you brush up your skills. It contains 21 video lectures that cover everything you need to know, including the four operations, key math concepts, our pro tips, and business math.
After watching all our Interview Prep and Case Math video lectures, we recommend heading to the ‘Drills’ area of CaseCoach, where you can start practicing specific skills. Drills are interactive exercises that pose rapid-fire questions and provide instant feedback. They help you build your skills and confidence in specific case dimensions quickly, allowing you to make the most of your live case practice with partners. Our Interview Prep Course includes a comprehensive set of drills in four key areas: structuring, calculation, case math and chart interpretation.
When it comes to succeeding in a case interview, nothing beats live practice with a partner. Most candidates who go on to receive an offer from a top consulting firm like McKinsey, BCG or Bain complete at least 25 live practice sessions before their interview.
To practice live cases with a partner, you’ll need access to both case material and practice partners. In our Case Library , you’ll find over 100 cases – complete with solutions – developed by former management consultants. You can download eight of these cases right away by creating a free CaseCoach account. You’ll find a diverse community of fellow candidates who are all available for case interview practice in our Practice Room , where we facilitate over 3,000 practice sessions a week.
You can learn more in our article on how to practice case interviews .
Working with a coach
Some candidates choose to supplement their preparations by working with a consulting interview coach who has been an interviewer at a top firm.
These coaches have the skills and experience to gauge your level of performance and help you identify your areas of strength and weakness. They can also provide you with accurate and helpful feedback on your case-solving skills. This insight can help you accelerate your preparation and improve your performance. Getting used to interviewing with a professional should also help to reduce the stress of the consulting interview experience.
Here at CaseCoach, our coaches are all former consultants and interviewers who have been handpicked from the alumni of top firms such as McKinsey, BCG and Bain.
Do your research
Although employers who use case interviews all test candidates using similar methods, none of them approach the interview process in exactly the same way.
For instance, if you expect to interview with McKinsey, Bain or BCG, it’s helpful to know that these firms all give cases of similar complexity. However, there are some key differences. For example:
- Bain has been known to use estimation questions, such as market sizing, in interviews for its most junior (i.e. Associate Consultant level) roles.
- BCG and Bain occasionally use written cases.
- When it comes to the ‘fit’ interview, McKinsey uses its Personal Experience Interview format, while most Bain offices now use a ‘behavioral interview’ . Only BCG consistently uses the classic fit interview format .
Other differences include the number of rounds of interviews each firm conducts, and their preference for using interviewer-led or candidate-led cases. Wherever you interview, it’s vital to do your research and find out what you might be able to expect.
When it comes to getting ready for the case interview, knowing what you will be assessed on, learning how to succeed, and having access to the best practice resources can all go a long way. Now, you need to put in the hard work and prepare! Good luck.
Continue to learn

Explore other resources
Search resources, we value your privacy.
We are using cookies to give you the best experience on our website. By clicking "Accept all", you consent to our use of cookies. You can read our Privacy Information to learn more about how we use cookies.
- Harvard Business School →
Read posts from
- Author Alumni
- Author Career and Professional Development Staff
- Author HBS Community
- Author HBS Faculty
- Author MBA Admissions
- Author MBA Students
- 1st Year (RC)
- 2+2 Program
- 2nd Year (EC)
- Application Process
- Business & Environment
- Career Change
- Career and Professional Development
- Case Method
- Entrepreneurship
- Financial Aid
- Health Care
- Instagram Takeover
- Letters to Classmates
- MBA/MPP & MBA/MPA-ID
- MS/MBA Biotechnology: Life Sciences
- MS/MBA: Engineering Sciences
- Partners & Families
- Social Enterprise
- Student Life
- Student Loans
- Student Profile
- Sustainability
- Architecture
- Construction
- Consumer Packaged Goods
- Engineering
- Entertainment / Media
- Environment
- Family Business
- Health Care / BioTech
- Manufacturing
- Private Equity
- Real Estate
- Venture Capital
- Diverse Perspectives
- International
- Socioeconomic Inclusion
Geographies
- Middle East and North Africa
- South America
- United States

- 10 Jan 2018
8 Tips to Help You Prepare for the Case Method
Ninad Kulkarni just wrapped up the fall semester at HBS and wanted to share what he learned about the case method after his first few months in the classroom.
You Might Want to Read
- Insights From Harvard Business School’s Peek Program
- College Students, Take a Sneak Peek at the HBS MBA
- Getting a Peek Into the HBS Experience
Admissions Events
Check out our upcoming webinars, prospective student days, and information sessions on campus and around the world.
→ View Events
Recorded Virtual Events
Curious about HBS? We have prospective student virtual events, available by geography, industry and interest.
→ Recorded Virtual Events
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
How to Create a Case Study + 14 Case Study Templates

Written by: Brian Nuckols

When it comes to high impact marketing content, case studies are at the top of the list for helping show off your brand’s stuff.
In this post, I’ve put together a few high-level case study design tips as well as 14 professionally designed case study templates that you can use to start designing beautiful case studies today.
Let’s begin!
Here’s a short selection of 12 easy-to-edit case study templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

What is a Case Study?
A case study is a way for you to demonstrate the success you’ve already had with existing clients. When you create a case study, you explore how previous clients have used your product or service to reach their goals.
In particular, a case study highlights a specific challenge or goal one of your clients was struggling with before they discovered your product.
It then demonstrates how your work has assisted them on the journey towards overcoming the challenge or accomplishing the goal.
A case study’s outcome is typically to share the story of a company’s growth or highlight the increase of metrics the company tracks to understand success.
The case study includes an analysis of a campaign or project that goes through a few steps from identifying the problem to how you implemented the solution.
How to Write a Case Study
When it comes to adding irresistible design to your content from the start, using a helpful tool is a great start. Sign up for a free Visme account and start highlighting your own client success stories using one of our case study templates today.
Also, while you’re beginning to transition your case study workflow to include a professional design tool, it’s helpful to review some high level principles you can incorporate into your case study.
We’ll start by reviewing some of the critical style tips and structural elements to include in your case study before progressing to a more detailed design section.

Pinpoint Your Main Message
When designing an impactful case study, it’s essential to stay clear on the metrics that you’re highlighting. The process of overcoming business challenges is a dynamic process with many moving parts.
If you do not stay focused on what matters in your case study, you risk obscuring the big win your client experienced by using your product or service.
This is why you need to focus on a single message or metric. This is often called the north star metric .
The north star metric is the single most crucial rate, count or ratio that helped your client move closer towards their goals or overcame an obstacle.
While north star metrics are context dependent, a useful heuristic you can utilize is to figure out the most predictive metric of your client’s long term success.
In the template I’ll highlight below, cost per lead was the north star metric that The College for Adult Learning needed to optimize.
Build relationships with customers and drive sales growth
- Reach out to prospects with impressive pitch decks and proposals that convert
- Monitor clients' level of engagement to see what they are most interested in
- Build a winning sales playbook to maximize your sales team's efficiency
Sign up. It’s free.

Use Emotionally Rich Language
Recently researchers at Presado did an interesting study to understand the types of language that help readers take action. They broke the content included in marketing assets into several categories, including functional, emotional and descriptive.
In the most successful pieces of content, the researchers found that emotionally coded words were present in 61% of the content’s total volume.
This research shows the benefit of using emotionally engaging content in your case study. While it’s essential to focus on the concrete evidence of how you helped your client get from where they started to a successful outcome, do not forget to highlight the emotional journey.

Use Data For Concrete Evidence
Once you’ve decided on the north star metric to highlight and you choose the emotional response you want to reinforce in your case study, it’s important to use actual data from the project to share the concrete results your product helped to achieve.
To make sure your audience can follow your line of thinking, make sure the data in your case study is precise. If you track data across time, your readers must know whether you chose to track by month or years.
If there are any apparent trends, you can use color to highlight specific areas in a chart.
If you want to dig deeper into using data to tell compelling stories, check out our video data storytelling tips to improve your charts and graphs.

In the template below, The College for Adult Learning case study is an excellent example of how these elements can work together.
Cost per lead was a critical north star metric, so we chose to emphasize the increase in revenue and a decrease in cost per lead.
Additionally, the background section uses emotionally rich language by highlighting how the school helps students get ahead with their career goals. Also, the factual data is the centerpiece of this page in the case study.
If you’re ready to share how you impacted a client, use the College for Adult Learning case study template right now!

Include All Necessary Parts of a Case Study
After you’ve interviewed your client and you’re getting ready to start writing, it’s important to remember each piece you need to cover.
All good case studies consist of five parts: Introduction, Challenge, Solution, Benefit and Result.

While you don’t necessarily need to label each section like that, be sure that the flow makes sense and covers each section fully to give your audience the full scope of your case study.
RELATED: 15 Real-Life Case Study Examples & Best Practices
14 Case Study Templates
Now that we have explored some of the high level strategies you can use to create a business case study, we will transition to 14 case study design templates you can use with Visme.
1. Fuji Xerox Australia Case Study Template

Use the Fuji Xerox case study template to showcase the concrete results you achieved for your clients. It has sections where you can explain the goals you started with and the results you achieved.
2. College for Adult Learning Case Study Template

As we’ve explored already, the College for Adult Learning template has sections where you can embrace a data driven storytelling approach while also connecting with your audience using emotionally rich language.
Utilize the professionally designed business case study to connect with your audience.
3. Intel Case Study Template

The Intel case study has beautiful visual elements and gives you space to share the project’s context and the goals you set out to achieve. It also allows you to get concrete with the results you achieved.
You can always use the Visme Brand Kit to incorporate your unique brand colors into this stunning design.
4. Bit.ly Case Study Template

Bit.ly is a marketing product that helps brands track how they are doing with campaign results. The bit.ly business case study template showcases how they drove impressive results for an eCommerce business.
You can modify the professionally designed case study template to illustrate the key results you drive for your clients.
5. NVISIONCenters Case Study Template

The NVISIONCenters case study template is an excellent example of how powerful it is to pair beautiful designs with the results you generate for your clients. In this case study, we see how you can transform your past accomplishments into a powerful marketing asset.
6. Adobe Case Study Template

The Adobe case study is an exciting example of a business case study because it does a great job illustrating how you can use a specific result to create a powerful marketing asset.
Adobe had a particular goal of branding to position itself as a leader for the future of digital marketing. LinkedIn sponsored messages was an effective tactic to drive the outcome Adobe needed.
You can use the Adobe case study template to demonstrate the success of your most effective tactics.
7. Inkjet Wholesale Case Study Template

The Inkjet wholesale case study template is an excellent choice if you want to experiment with your case study’s visual element. The roadmap to objectives diagram is a powerful graphic that illustrates the journey of a successful campaign.
8. Neutrogena Case Study Template

If you have a strong visual brand to tell your case study’s story with visuals, the Neutrogena template is a great choice. It is already designed with plenty of space to highlight your visuals.
When it is all said and done, you have the results section to complete a successful client partnership story.
9. Weebly Case Study Template

The Weebly case study template is your choice if you want to add visual flair to your case study. The beautiful layout is a testament to the power of pairing minimal design with an exciting statistic.
10. Patagonia Case Study Template

The Patagonia case study is a perfect example of how crucial it is to make design choices based on your brand’s unique personality.
It is a fantastic choice if you have a project to showcase featuring a brand with a distinct brand aesthetic.
11. Think With Google Case Study Template

The Think With Google case study template tells the story of a mobile game that needed to create more engagement on their app.
It is a visually impactful case study design template that you can use to tell a compelling story about your results.
12. Kleenex Case Study Template

This case study template is the perfect way to show off search marketing results for a client or other highly specific KPIs that you managed to accomplish.
Insert the initial challenge followed by your company’s solution and adjust the included data visualization tools to showcase your specific results.
13. Customer Experience Presentation Case Study Template

The presentation case study template is an excellent choice for blending beautiful visual elements with the ability to give detailed information about the results you generated, as well as showcasing that data in a unique format.
If you are ready to show how the unique features of your product or service drove real world business results then it is a good choice for your case study.
14. Webinar Presentation Case Study Template

One small business saw incredible results when using Visme to optimize their webinar workflow. They saved 100 hours of their precious time by incorporating our collaborative design tools.
We designed the small business template using those results as an example. When you have an eye catching effect to showcase to your audience, you can use this template as a starting point.
Case Study Design Tips
Now that we’ve explored the 14 templates you can use with Visme to create your case study, let’s take a look at some practical design tips that will take your content to the next level.

Be Brief In Your Case Study
In discussions about writing with style, brevity is a common topic. However, it’s also an important design principle.
Brevity in design is when you find the best way to perform your intended objective in as few steps as possible.
When designing your case study, make sure you do not add extraneous visual elements where they are not needed. Instead, think of the effect you want to have on your reader and try to do it simply.
Describe Your Vision Clearly
Earlier in this article, I wrote about the north star metric, your case study’s emotional effect and using data to make the case study concrete. Your design choices should serve to reinforce these primary goals.
Clarity in design is when all of the visual elements add up to a whole.
A great example of this is in the small business case study template where the shapes, typography and color scheme all emphasize the main idea that Visme helps the reader save time.

Create A Consistent Style
Visual consistency is a fundamental design principle that you can not afford to ignore in your case study. It will help you increase readability and make sure your audience does not get frustrated with jarring visual elements.
In short, a consistent style is when you use a uniform color scheme, typography and the same kinds of visual elements throughout the case study.
Use A Case Study Template For Readability
Readability is a crucial element of design, especially for case studies that are experienced on mobile devices. Contrast is an impactful readability principle.
Make sure any contrasting colors you chose are easy on the eye and your reader does not have to strain to read your case study.
Use Proper Alignment In Your Case Study
Alignment is one of the principles of design that sets professionally designed business case study templates apart. Great designers have an intuitive eye for the mathematically based ratios of proximity invisible in sound design and an eyesore in lousy design.
The good news is that you do not have to be a mathematician nor a professional designer to have a perfect alignment for your case study. Visme utilizes an easy to use drag and drop design tool that helps you achieve proper alignment in your case study.
Let Your Brand Personality Speak
When we make intentional design decisions, we want to create a positive emotional experience for our audience. One of the best ways to do that is to make decisions that showcase your brand’s unique personality .
Is the case study you are creating like a well dressed business person who is serious, trustworthy and capable of doing a great job? Is it more like an extravert at a party bouncing from person to person lighting up the room?
There is no right answer, but you need to infuse your viewpoint into the case study you create if you want to create a unique design.
Start Designing Your Case Study Today
A professionally designed case study template will help you create a stunning case study. While reviewing some high level design strategies is an important step, a tool like Visme will help you make a real impact on your audience.
If you’re ready to create your next case study, get started with Visme today .
Design beautiful visual content you can be proud of.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Brian Nuckols is a writer working in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He enjoys communicating visionary ideas in clear, action oriented language. When he’s not working on content for a transformative company you can find him analyzing dreams, creating music, and writing poetry.
Case Interview Math Guide: Everything You Need to Know
Master case interview math with our friendly guide! Learn essential tips, tricks, and strategies to ace every calculation and impress in your consulting interviews.
Posted August 20, 2024
Featuring Caitlin B.
How to prepare for MBB Internship Recruiting (first-year MBA students)
Starting sunday, august 25.
7:00 PM UTC · 60 minutes
Table of Contents
Are you ready to conquer case interview math? Whether you're aiming for a consulting career or preparing for a challenging case interview, mastering the art of case interview math is crucial to your success. This guide will enhance your ability to tackle complex math problems, crunch numbers efficiently, and impress your interviewers with your analytical skills. By refining these abilities, you'll be better prepared to meet the high standards of management consulting firms and stand out in the competitive interview process.
In this comprehensive case interview math guide , we'll explore the three main types of math problems you'll encounter, along with practical examples. You'll learn essential formulas to have at your fingertips and discover techniques to sharpen your consulting math skills. We'll also share tips to help you stand out, provide effective preparation strategies, and offer valuable practice drills and resources. By the end, you'll be well-equipped to handle any math challenge that comes your way in your case interviews.
3 Types of Math Problems with Examples
In case interviews , you'll encounter three main types of math problems: word problems, straight calculations, and estimation questions. Each type tests different aspects of your quantitative skills and problem-solving abilities.
Word Problems
Word problems in case interviews often require algebraic calculations. These questions are designed to assess your ability to translate real-world scenarios into mathematical equations. For example, you might need to calculate the breakeven point for a product launch or determine the impact of a cost-cutting initiative on a company's financials.
Word problems require you to analyze a business scenario and apply your case math skills to find a solution. For instance, you might be asked to determine the profitability of a new product line based on market math data like costs, revenues, and market share.
Key Strategy: Break down the problem into smaller steps. Start by identifying key variables (such as costs, revenues, or quantities), and then translate them into equations. Practice framing business scenarios into solvable math problems by focusing on what the interviewer is truly asking.
Tip: Stay organized by writing down your calculations step-by-step. This will allow you to clearly explain your thought process to the interviewer and minimize errors, while also demonstrating your structured thinking skills.
Straight Calculations
Straight calculations involve performing direct calculations, such as multiplying revenue figures or dividing costs by units produced. These problems assess your ability to quickly and accurately handle basic arithmetic operations, which are crucial in management consulting.
They are often presented as standalone questions or follow-up queries within a larger case study. These problems test your ability to perform quick mental math under pressure. For instance, you might need to divide 100,000 by 50 to determine employee productivity or calculate 13% of $160 million to find the cost of goods sold.
Key Strategy: Prioritize accuracy before speed. Focus on methodical, step-by-step calculations rather than rushing to an answer. If you're unsure about mental math, write out each step. It’s better to be slightly slower but accurate than to provide a wrong answer quickly.
Tip: Always verify your results by double-checking your work. While speed is important, accuracy is even more crucial. Mistakes in simple calculations can affect your overall analysis and the recommendation you give to the interviewer.
Estimation Questions
Also known as market sizing questions, estimation problems require you to arrive at a value with minimal initial data. These questions assess your structured problem-solving skills and business judgment. For example, you might need to estimate the number of pizzas sold in New York City annually or the market size for a new tech product.
Key Strategy: Focus on logical reasoning and simplification. Instead of breaking the problem into smaller pieces, start by setting up a logical framework. Use approximate numbers and relevant assumptions to guide your estimate, aiming for an answer that's reasonable within a broad range.
Tip: Use reasonable assumptions and round numbers to keep your calculations simple and easy to follow. Don’t hesitate to state your assumptions clearly to the interviewer; they care more about your approach and logic than the exact answer.
By mastering these types of math problems, you'll be better equipped to tackle the quantitative challenges that arise in case interviews for management consulting roles.
Essential Case Interview Math Formulas
While most case interviews only require basic algebra like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and fractions/percentages, it’s best to be prepared for the following math formulas just in case you have to use them in the case interview:
Revenue and Profit Margin Calculations
To excel in case interviews, you need to master key formulas.
Start with the basics : Revenue = Price x Volume. This formula helps you calculate a company's total sales.
Next, understand profit calculations. Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold, while Net Profit = Gross Profit - All other cost items.
These formulas are crucial for assessing a company's financial health.
Read : Unlocking Marginal Profit: A Step-by-Step Guide to Finding It
Market Sizing Equations
Market sizing is a common challenge in case interviews.
Use this formula : Market Size = # of Target Customers x Expected Annual Purchases. For market share, calculate: Market Share = Company Revenue / Total Market Revenue.
These equations help you estimate market potential and a company's position within it.
Break-Even Analysis
Break-even analysis is vital for assessing whether a company should put down an initial investment on a product or service.
The key formula is : Break-even Point = Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin.
Remember, contribution margin is (Price - Variable Cost) per unit. This analysis helps determine how many units a company needs to sell to cover its costs before generating profit.
Free trial!

From 133 top coaches
Access a library of videos, templates, and examples curated by Leland’s top coaches.
Example resumes.

Example Cases
Casing Drills
Mock Interviews

Master Mental Math Techniques
To excel in case interviews, you need to sharpen your mental calculations. These techniques will help you perform calculations quickly and accurately without a calculator, giving you an edge in tackling case interview math problems. By practicing these methods, you'll become more confident in solving consulting math problems, allowing you to approach each case interview with precision and ease.
Rounding and Estimation
Simplify large numbers by removing zeros and using labels (m, k, b). For example, 200 million becomes 200m. This method helps you manage zeros efficiently and makes calculations more manageable.
Percentage Calculations
For percentage growth, use the Rule of 72. Divide 72 by the growth rate to estimate doubling time. For instance, at 12% growth, a value doubles in approximately 6 years (72 ÷ 12 = 6).
Quick Multiplication and Division
Break down complex calculations into simpler steps. For 14 x 6, calculate (10 x 6) + (4 x 6) = 84. Use the Halve and Double Method for tricky multiplications. For 160 x 350, halve 160 and double 350, then multiply: 80 x 700 = 56,000.
How to Stand Out in Case Interview Math
To excel in case interview math, you need to demonstrate efficiency and confidence. Here are key strategies to help you stand out:
Simplify your calculations
If the question doesn’t demand a specific answer, round numbers to make them more manageable. For example, instead of calculating 29 x 4, round 29 to 30 and multiply by 4. This shows you're focused on solving math problems efficiently, rather than getting bogged down in trivial details.
Master the common fractions
Memorize common fractions, their percentage values, and decimal conversions from 1/2 to 1/10. This knowledge can save you significant time during calculations. For instance, knowing that 1/8 equals 0.125 can help you quickly arrive at an exact answer during case math exercises.
Do not miscount the zeros
When working with large numbers, keep close track of zeros to prevent errors. Instead of writing out long numbers, use scientific notation, like expressing 60,000,000 as 6 x 10^7. This simplifies consulting math calculations and reduces the risk of mistakes.
How to Prepare for Case Interview Math
Understand the theory.
To excel in case interview math, you need to master key formulas and concepts. Focus on revenue and profit calculations, market sizing equations , and break-even analysis. While in-depth understanding isn't required, having a rough idea of business terms and their formulas can be handy. Remember, calculators aren't allowed in case interviews, so practice mental math.
Put the Theory into Practice
Once you've grasped the theory, it's time to practice. Use calculation drills to sharpen your skills. Focus on simplifying calculations, factoring and expanding expressions, and dealing with growth rates efficiently. Memorize common statistics, like local population figures, to save time. Practice within full case contexts for the most realistic experience.
Practice Drills and Resources
Online math tools.
Strengthen your consulting math skills by using online tools designed specifically for case interview preparation. These resources offer a range of exercises to help you master essential consulting math formulas, such as percentages, ratios, and basic arithmetic, ensuring you can tackle quantitative problems with confidence during your interviews.
Sample Problems
Practice with real-world scenarios. For instance, try estimating the market demand for cell phones over 30 years or calculating the profit-maximizing layout for a convenience store. These problems mirror the types of questions you might encounter in actual case interviews.
Timed Exercises
Engage in timed math drills to improve your speed and accuracy. Aim to solve problems within 5-10 seconds, gradually increasing difficulty as you progress. Focus on areas where you struggle, and practice consistently to maintain your skills. Remember to verbalize your thought process while solving problems to simulate interview conditions.
Land Your Dream Consulting Job With the Help of an Expert
Trying to enter into the world of consulting is no small feat. That’s why at Leland, we have a broad network of world-class coaches who know what it takes to get into a consulting job and are ready to help review your resumes, conduct practice interviews, and give you refreshers on key skills needed to land the job. Browse our expert coaches here and find the highest-rated ones below.
Mastering case interview math is a game-changer for aspiring consultants. This comprehensive guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the types of math problems you'll face, essential formulas to memorize, and techniques to sharpen your mental math skills. By applying these strategies and consistently practicing, you'll be well-prepared to tackle any case interview math challenge that comes your way.
Remember, success in case interview math isn't just about crunching numbers quickly. It's also about demonstrating your structured thinking, problem-solving approach, and business acumen, all of which are crucial in management consulting. By honing these skills and staying calm under pressure, you'll be able to stand out and make a lasting impression on your interviewers. Keep practicing, stay confident, and you'll be well on your way to acing the math portion of your case interviews, especially when faced with market math scenarios.
What exactly is 'case math'?
- Case Interview Math involves analyzing data to form a well-informed recommendation to address a business issue. It assumes a basic understanding of operations like multiplication, addition, subtraction, division, and percentages. More importantly, it requires an understanding of how to interpret these mathematical results within the context of the case problem.
What mathematical abilities are essential for case interviews?
- In case interviews, the essential math skills include basic arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. You will also need to work with percentages, decimals, or fractions, and be able to calculate percentage values, which involves division.
How important is mental math in consulting interviews?
- Mental math is essential in consulting interviews as it allows you to perform quick calculations without relying on a calculator. This ability is particularly useful when you're under time constraints or need to make rapid decisions during the case interview process.
Is the math involved in case interviews difficult?
- The math typically encountered in case interviews is not particularly challenging. It involves basic algebra, including operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and working with fractions and percentages. Additionally, you may need to extract and interpret data from tables.
Why do consulting firms emphasize math skills in case interviews?
- Consulting firms prioritize math skills because consultants frequently need to analyze data, create models, and make recommendations based on numerical insights. Strong case math abilities allow you to approach problems methodically and deliver precise, actionable advice.
How can I enhance my mathematical skills for case interviews?
- Improving your math skills for case interviews primarily involves extensive practice. Engaging in numerous practice problems will help you become quicker, familiarize you with various problem types, and improve your ability to apply fundamental mathematical skills in different scenarios. Participating in mock case interviews is an effective way to practice.
How much time should I dedicate to practicing case interview math?
- Dedicating regular time to practice is crucial. Aim for at least 30 minutes a day of focused math drills. This consistency will help you build speed and confidence, especially in performing calculations under pressure during a consulting interview.
Read these next :
How to Excel in Mental Math Practice: A Comprehensive Guide
- A Guide to Mental Math for Your Private Equity Interview
- 50+ Case Interview Questions From Top Firms
- Big 4 Consulting Firms vs. MBB: What's the Difference
Browse hundreds of expert coaches
Leland coaches have helped thousands of people achieve their goals. A dedicated mentor can make all the difference.
Browse Related Articles

August 20, 2024
Boost your mental math skills with our comprehensive guide! Learn practical tips and techniques to excel in mental math and enhance your problem-solving abilities.

August 22, 2024
The 15 Most Common Consulting Interview Questions — With Answers
Discover the 15 most common consulting interview questions with sample answers. Prepare confidently with our friendly guide to acing your consulting interview.

Market Entry Framework: The Expert Guide
Unlock success in new markets with our expert guide! Learn the market entry framework step-by-step and discover strategies to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.

August 19, 2024
The Top 10 IT Consulting Firms (2024)
Explore the top 10 IT consulting firms of 2024. Discover industry leaders shaping the future of tech with innovative solutions and expertise.

How to Answer "Tell Me About Yourself" in Consulting Interviews
Learn how to craft a compelling answer to the 'Tell me about yourself' question in consulting interviews with tips, examples, and expert advice.

Top Pre-MBA Programs in Consulting
Discover the top pre-MBA programs for consulting. Learn how to boost your skills and gain a competitive edge before starting your MBA journey.

August 16, 2024
BCG Matrix: What to Know and How to Use It
Learn how to use the BCG Matrix for strategic planning. Explore key insights and tips to maximize growth and profitability in your business.

The McKinsey Sophomore Summer Business Analyst Program: What to Know
Learn what to expect from McKinsey's Sophomore Summer Business Analyst Program. Get insights, tips, and advice for a successful application.

The Expert Guide to Market Sizing Questions (With Examples)
Looking for an expert guide to market sizing questions? Learn how you can use the examples, key techniques, and frameworks to ace your consulting interviews by reading this article.
How to Answer the "Why Consulting" Interview Question
Discover top strategies for answering the "Why Consulting" interview question. Learn how to highlight your passion and fit for the consulting role.

The Ultimate 2024 Consulting Interview Prep Guide
Get ready for your consulting interview with our 2024 prep guide! Find expert tips, strategies, and resources to help you ace your interview.

What is Accenture?
Explore what Accenture is and what it does. Our comprehensive guide breaks down Accenture's services, expertise, and how it helps businesses thrive globally.
Patient underwent 1 surgery but was billed for 2. Even after being sued, she refused to pay
The patient underwent tubal ligation plus treatment of endometriosis.
This is a KFF Health News story .
Jamie Holmes says a surgery center tried to make her pay for two operations after she underwent only one. She refused to buckle, even after a collection agency sued her last winter.
Holmes, who lives in northwestern Washington state, had surgery in 2019 to have her fallopian tubes tied, a permanent birth-control procedure that her insurance company agreed ahead of time to cover.
During the operation, while Holmes was under anesthesia, the surgeon noticed early signs of endometriosis, a common condition in which fibrous scar tissue grows around the uterus, Holmes said. She said the surgeon later told her he spent about 15 minutes cauterizing the troublesome tissue as a precaution. She recalls him saying he finished the whole operation within the 60 minutes that had been allotted for the tubal ligation procedure alone.
MORE: Surprise medical bills are on the rise, study finds
She said the doctor assured her the extra treatment for endometriosis would cost her little, if anything.
Then the bill came.
The Patient: Jamie Holmes, 38, of Lynden, Washington, who was insured by Premera Blue Cross at the time.
Medical Services: A tubal ligation operation, plus treatment of endometriosis found during the surgery.
Service Provider: Pacific Rim Outpatient Surgery Center of Bellingham, Washington, which has since been purchased, closed and reopened under a new name.
Total Bill: $9,620. Insurance paid $1,262 to the in-network center. After adjusting for prices allowed under the insurer's contract, the center billed Holmes $2,605. A collection agency later acquired the debt and sued her for $3,792.19, including interest and fees.
What Gives: The surgery center, which provided the facility and support staff for her operation, sent a bill suggesting that Holmes underwent two separate operations, one to have her tubes tied and one to treat endometriosis. It charged $4,810 for each.

Holmes said there were no such problems with the separate bills from the surgeon and anesthesiologist, which the insurer paid.
Holmes figured someone in the center's billing department mistakenly thought she'd been on the operating table twice. She said she tried to explain it to the staff, to no avail.
She said it was as if she ordered a meal at a fast-food restaurant, was given extra fries, and then was charged for two whole meals. "I didn't get the extra burger and drink and a toy," she joked.
Her insurer, Premera Blue Cross, declined to pay for two operations, she said. The surgery center billed Holmes for much of the difference. She refused to pay.
Holmes said she understands the surgery center could have incurred additional costs for the approximately 15 minutes the surgeon spent cauterizing the spots of endometriosis. About $500 would have seemed like a fair charge to her. "I'm not opposed to paying for that," she said. "I am opposed to paying for a whole bunch of things I didn't receive."
The physician-owned surgery center was later purchased and closed by PeaceHealth, a regional health system. But the debt was turned over to a collection agency, SB & C, which filed suit against Holmes in December 2023, seeking $3,792.19, including interest and fees.
MORE: Biden administration moves forward on banning surprise medical bills
The collection agency asked a judge to grant summary judgment, which could have allowed the company to garnish wages from Holmes' job as a graphic artist and marketing specialist for real estate agents.
Holmes said she filed a written response, then showed up on Zoom and at the courthouse for two hearings, during which she explained her side, without bringing a lawyer. The judge ruled in February that the collection agency was not entitled to summary judgment, because the facts of the case were in dispute.
Representatives of the collection agency and the defunct surgery center declined to comment for this article.
Sabrina Corlette, co-director of Georgetown University's Center on Health Insurance Reforms, said it was absurd for the surgery center to bill for two operations and then refuse to back down when the situation was explained. "It's like a Kafka novel," she said.
Corlette said surgery center staffers should be accustomed to such scenarios. "It is quite common, I would think, for a surgeon to look inside somebody and say, 'Oh, there's this other thing going on. I'm going to deal with it while I've got the patient on the operating table.'"
It wouldn't have made medical or financial sense for the surgeon to make Holmes undergo a separate operation for the secondary issue, she said.
Corlette said that if the surgery center was still in business, she would advise the patient to file a complaint with state regulators.

The Resolution: So far, the collection agency has not pressed ahead with its lawsuit by seeking a trial after the judge's ruling. Holmes said that if the agency continues to sue her over the debt, she might hire a lawyer and sue them back, seeking damages and attorney fees.
She could have arranged to pay off the amount in installments. But she's standing on principle, she said.
"I just got stonewalled so badly. They treated me like an idiot," she said. "If they're going to be petty to me, I'm willing to be petty right back."
The Takeaway: Don't be afraid to fight a bogus medical bill, even if the dispute goes to court.
Debt collectors often seek summary judgment, which allows them to garnish wages or take other measures to seize money without going to the trouble of proving in a trial that they are entitled to payments. If the consumers being sued don't show up to tell their side in court hearings, judges often grant summary judgment to the debt collectors.
MORE: Surprise billing law pleases patients, frustrates doctors
However, if the facts of a case are in dispute -- for example, because the defendant shows up and argues she owes for just one surgery, not two -- the judge may deny summary judgment and send the case to trial. That forces the debt collector to choose: spend more time and money pursuing the debt or drop it.
"You know what? It pays to be stubborn in situations like this," said Berneta Haynes, a senior attorney for the National Consumer Law Center who reviewed Holmes' bill for KFF Health News.
Many people don't go to such hearings, sometimes because they didn't get enough notice, don't read English, or don't have time, she said.
"I think a lot of folks just cave" after they're sued, Haynes said.
Trending Reader Picks

Budget cuts and layoffs take hold in public health
- Aug 22, 5:05 AM

Woman charged for allegedly enticing tiger at zoo
- Aug 26, 2:14 PM

High school QB dies after suffering brain injury
- Aug 25, 8:08 PM

Danny Jansen to play for both teams in same game
- Aug 25, 12:35 PM

Massachusetts towns at high risk of mosquito virus
- Aug 25, 4:38 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.

User Research and the Paperwork Reduction Act
Highlighting case studies across the government.
In 2021, the Biden-Harris Administration issued an Executive Order to improve customer experience and make service delivery simple, seamless, and secure for Americans. Since then, government agencies have been hard at work making their services, tools, and content more effective in addressing the needs of the people they serve.
User research is at the heart of transforming customer experience. The best way to ensure services are effective, efficient, easy to use, fair, and safe is to include the people they are intended for when building it.
In this piece, we’ll demonstrate:
The importance of user research and how it helps mitigate risk in agency projects.
How and when to integrate user research into a project.
Examples of agencies successfully incorporating and conducting certain types of user research without needing Paperwork Reduction Act approval.
The basics of a customer-centered approach
Before we dive into the examples, let’s discuss the basics of a customer-centered approach, and why it’s important to ensure an agency is meeting the needs of the people using its products or services.
Creating a new digital tool or making changes to a website or service can affect the experience of millions. If working in isolation, agencies can miss important details that could slow down or prevent people from using your services.
The key to any successful project is to observe how real people interact with a government service or product . Failing to prioritize user research is risky and can lead to poorly designed products and services that are difficult to access.
Conducting user research by the rules
The Paperwork Reduction Act (PRA) ensures that the Federal Government collects information in a way that reduces unnecessary burden on the public. The PRA process generally involves notifying the public about each information collection and giving them a chance to provide feedback. It also includes review of a proposed information collection by the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs Management (OIRA) within the Office of Management and Budget. However, as discussed in regulation 5 CFR 1320.3(h) , information collection does not include items in categories that are common during user research. Agencies might not need PRA approval for most user research done on projects, depending on how the project is structured.
Specifically, there are activities common in user research that do not require PRA clearance because they do not qualify as an information collection under PRA regulations (5 C.F.R. § 1320.3). Those activities include:
Directly observing someone using a product (i.e., observing someone filling out a form or finding information on a website) or
Asking people non-standardized questions as part of a one-on-one research session (i.e., asking people questions orally, in an unstructured way, about navigating government benefits or signing up for an appointment). “Non-standardized,” in this context, means the questions asked vary from person to person, and are not drawn from a list of identical questions posed in every research session.
Unlike methods that constitute information collection and require PRA clearance (for example, surveys or large focus groups with a set of the same questions or tasks), these types of research conversations (direct observations or one-on-one sessions with non-standardized questions) do not require PRA approval, regardless of the number of users ultimately involved in the research.
Direct observations and one-on-one feedback sessions can be more valuable than focus groups or surveys , since they may provide a deeper understanding of people’s behavior rather than feelings and opinions and showcase what’s working well, what isn’t, and why. You can learn more about talking to people with tips from the Department of Homeland Security.
Incorporating user research into your project
Incorporating user research results in a better product and reduces risks. It helps address usability concerns, reduces the potential for major backlogs on call centers, increases customer satisfaction, and ensures agencies are prioritizing the right changes. Research is a continuous process, and certain project stages benefit from research, including:
Before a project
Look at comparable systems and services to learn lessons.
Gain a better understanding of the pain points people experience with this system or service.
Get to know stakeholders’ business needs or concerns, possibly using methods suggested by 18F, the digital services agency within the General Services Administration.
Do desk research, such as reading threads on social media websites and discussions on online forums. Find out where people are talking about the topic, go there, and read as much as you can.
Test high-level ideas or potential future solutions.
Start of a project
Observe people using the existing system or service.
Work with local groups, advocates, or nonprofits to identify people to talk to.
Review any comments or letters submitted by the public.
See what people who use the system or service are saying publicly online about their experience.
Read research conducted on this topic.
Middle of a project
Place the thing that your agency team is building in front of someone who will use it, and observe them using it.
- Create a few different product versions and solutions to each problem.
- Gather feedback on what people found easiest to use.
In operations
Conduct content testing to understand what people think the message means and make updates until it’s in plain language. (For example, the agency can write improvements to system messages and try to understand what people think the messages mean until the messages are plain, understandable, and straightforward. This approach could be used for emails, text messages, policy guidance, or webpage updates.)
Hold one-on-one listening sessions with people to learn about existing pain points and then prioritize new features based on feedback.
Now let’s take a look at seven government projects that have successfully incorporated user research and improved the customer experience without conducting an information collection requiring PRA clearance.
By exploring these projects, you can start thinking of ways to conduct more research or advocate for more research to enhance the customer experience. This list can generate new ideas and help you find ways to integrate user research more effectively.
Highlighting seven government projects
Case study 1: conducting user research for an informative website launch.
Reporting Unemployment Identity Theft, Department of Labor (DOL)- March 2021
In 2022, thousands of Americans received a fraudulent unemployment insurance tax form (government Form 1099-G) in the mail despite never applying for unemployment insurance (UI). These individuals were victims of unemployment identity theft, and fraudsters used their information to illegally receive unemployment benefits. For most victims, understanding what steps to take next was confusing.
The DOL met with victims of UI theft and developed a website to guide them through reporting the fraud. After the site went live, the DOL collaborated with other government agencies and organizations to incorporate the same tested language for reporting UI fraud on their sites. This created a consistent and reliable standard across all websites, fostering trustworthiness among victims.
User research
Ten unstructured, one-on-one user research sessions with victims helped the DOL learn more about the current process and what victims did when they received the fraudulent unemployment insurance form. Participants walked through their unique scenarios and researchers took detailed notes.
During the second round of research, the main focus was observing individuals as they navigated through the newly drafted website content. Participants were instructed to vocalize their thoughts as they started at the top of the page and explained what they saw. Any aspects of the website that people found confusing were revised and improved following the sessions.
Why did the PRA not cover this research?
In this project, the DOL directly observed the experiences of program applicants and participants and asked non-standardized questions on a particular process, theme, or issue without any specification of the information being sought. See 5 CFR 1320.3(h)(3).
Case study 2: Conducting user research for a new application launch
A New Digital Application for VA Health Care, Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) - July 2016
Many Veterans found the health care application process at the VA frustrating. Most weren’t able to open the fillable PDF online application because it required a certain software that wasn’t common in most browsers. As a result, over 70 percent of visitors had trouble accessing the health care application, according to USDS research.
The team developed a new, user-friendly online application that doesn’t require a certain software to use. For more details, check out the USDS blog post , “Introducing a new digital application for healthcare at VA.”
The team observed Veterans using the existing application to identify pain points and then worked on a new version. Then, they did user research sessions with the new form again to ensure it was easy and removed any previous pain points. Watch a real-life user research session, conducted by a VA employee with a Veteran at this video link .
In this project, the VA directly observed the experiences of program applicants and participants and engaged in unstructured one-on-one interactions. They asked non-standardized questions on a particular process, theme, or issue without any specification of the information being sought. See 5 CFR 1320.3(h)(3).
Case study 3: Conducting user research to inform policy and strategy
Welcome Corps, Department of State - February 2024
The Department of State launched a new program to allow Americans to sponsor refugees. The Welcome Corps program involves forming a sponsor group, completing pre-application steps, and then submitting an application. The process was burdensome to Americans seeking to sponsor a refugee, causing frustration and incomplete applications.
The team did user research to inform which steps in the process could be improved in order to reduce unnecessary burden on sponsors and increase successful application submissions. This research helped ensure any policy changes under consideration would actually support program goals. It also helped inform the agency’s roadmap.
The team met one-on-one with current sponsors to learn about their experience and met one-on-one with potential sponsors to understand what steps of the process were challenging. These research sessions used non-standardized questions. The research findings were presented to program leadership, and policy, tech, and operations teams to inform improvements to the application process.
Why the PRA did not cover this research?
In this project, the team observed the experiences of sponsors and potential sponsors and engaged in unstructured one-on-one interactions. They asked non-standardized questions on a particular process, theme, or issue without any specification of the information being sought. See 5 CFR 1320.3(h)(3).
Case study 4: Conducting user research to streamline digital experiences
My VA Dashboard for Veterans, Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) - November 2020
Many services are available to Veterans on the VA websites but it can be challenging to locate them and take action. Veterans asked for a centralized location that was relevant to their needs.
The team worked with a vendor to create My VA, a personalized dashboard for Veterans to access tools and information.
A vendor conducted user research to identify the information that Veterans expect to find in the My VA Dashboard tool and the best way to navigate it.
The contract required vendors to conduct user research to determine people’s goals, needs, and behaviors. The vendor conducted one-on-one, non-structured conversations with Veterans to inform how the agency should build the dashboard.
The contractor collected information and observed program applicants and participants by asking non-standardized questions on a particular process, theme, or issue without any specification of the information being sought. See 5 CFR 1320.3(h)(3), (h)(6).
Case study 5: Conducting user research to inform outreach strategies via text messages
Child Tax Credit Outreach, Department of Treasury and the White House - June 2021
When the American Rescue Plan Act became law in March 2021, millions of Americans were suddenly eligible for unprecedented tax relief by expanding both earned income and child tax credits. Americans who don’t make enough income to require a tax filing would benefit most from the expansion, but first, they needed to know about the credits and include them when they filed a tax return.
Outreach was key to reaching families in most need. The team learned throughout the year that:
Messages from official government entities work well, specifically, government benefits agencies.
Emails and text messages have worked when encouraging state and local governments to send messages directly to beneficiaries.
The team performed user research throughout the year by working with non-profits on the ground to identify research participants and understand what was working and not working. They partnered with Code for America to test several text messages to ensure clear language. They also joined research sessions to observe SNAP applicants engaging with a third-party app that helps them manage their SNAP benefits electronically.
In this project, the groups directly observed the experiences of program applicants and participants. They asked non-standardized questions on a particular process, theme, or issue without any specification of the information being sought. See 5 CFR 1320.3(h)(3).
Case study 6: Conducting user research with internal users of a system
Updates to the Unaccompanied Children Case Management System, Office of Refugee Resettlement (ORR), Administration for Children and Families, Department of Health and Human Services – August 2022
Case managers were updating both paper and digital forms when assessing a potential sponsor. Many duplications existed across the two forms, and filling out both caused inefficiencies.
The team changed the online form, eliminating the need for the paper form and transferred them to the digital experience, reducing burden for the sponsor and case manager. The updated digital form also included design improvements to enhance the flow of the questions.
ORR contacted case workers nationwide and observed them filling out both versions of the form to identify pain points. Another round of research was conducted later on, once they had an updated digital form. These were one-on-one conversations to confirm that the form was easy to use. Any areas where the case managers had questions or trouble were good indicators that the digital form needed tweaking. Finally, they arrived at a version that was easy to use and improved the previous safety and efficiency concerns.
In this project, the ORR directly observed case workers (not federal employees) using a form via one-on-one interviews to understand any usability concerns. They asked non-standardized questions on a particular process, theme, or issue without any specification of the information being sought. See 5 CFR 1320.3(h)(3).
Case study 7: Conducting user research with students and families
College Scorecard, Department of Education - August 2015
Deciding on a college can be an overwhelming task with limited access to reliable information on student outcomes like student earnings, graduates’ student debt, and borrowers’ repayment rates.
In September 2015, the Department of Education launched the College Scorecard, which made data transparent for the public about colleges by leveraging existing data on costs, graduation, etc. and providing new data points on earnings after attendance, student debt, and borrower repayment rates. As these data sets were published through an open application programming interface (API), researchers, policymakers, and the public could customize their analysis of college performance easily. For more information on this project, check out the Obama White House blog post , “Under the Hood: Building a College Scorecard with Students.”
The team conducted user research at every single step in the project. This user research involved one-on-one conversations with high school students in Washington, D.C.’s Anacostia neighborhood, guidance counselors, 4-H kids, parents, college advisors, and data journalists. They also conducted research and met one-on-one with a diverse set of stakeholders across the higher education community to learn about their concerns, ideas, and hopes for how they could help students and families make a more informed decision.
Based on this research, the team developed a College Scorecard prototype and then turned it into a website. The prototype was put in front of students during one-on-one sessions, to observe if the tool was easy to use. The research revealed that students were unlikely to use a mobile app and were hesitant to use government websites, so the team ensured other sites that were actually frequented by students had access to the same data.
Why did the PRA not cover this research ?
In this project, the Department of Education directly observed the program applicants and participants engaging with the College Scorecard. The Department of Education also asked non-standardized questions on a particular process, theme, or issue without any specification of the information being sought. See 5 CFR 1320.3(h)(3).
Ready to conduct user research?
Throughout this piece, we emphasized the significance of user research and described some ways to incorporate it into agency projects without conducting a PRA information collection. These examples showcase how an agency can successfully conduct user research to improve delivery of services.
Agencies should incorporate user research into their work to make well-informed decisions, minimize risk, and save time and money. These case studies are a reminder that by applying user research best practices, agencies can build trust in government and improve customer experience for all Americans.
If you’d like to work on projects like this, consider joining USDS! We’re hiring mission-driven engineers, product managers, designers, bureaucracy hackers, procurement specialists, and operations experts who want to make an impact on the lives of their fellow Americans.

Meeting veterans where they are with accessible mobile tech
This Veterans Day, we’re honoring our current and former service members by highlighting a collaboration between the Department of Veterans Affairs and the U.S. Digital Service.
Read full post

A quick guide to inclusive design
Designing for inclusion isn’t just about coding for accessibility or section 508 compliance, it’s about providing equitable and easy-to-use websites and services for diverse populations. Because good design is design that works for everyone.

Tackling the climate crisis with open source
Every one of us has the right to breathe clean air, drink clean water, eat safe, nourishing food, and live free from the threat of climate disasters wrecking our neighborhoods and livelihoods.
We need you.
Let’s help millions of people together.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
These templates make it a breeze to craft a case study that's perfect for your niche. 9. Use Direct Quotes from the Client Quotes from your client add authenticity and credibility. They give readers insight into the client's perspective and make your case study more relatable. Plus, a glowing testimonial is always a nice touch!
2. Determine the case study's objective. All business case studies are designed to demonstrate the value of your services, but they can focus on several different client objectives. Your first step when writing a case study is to determine the objective or goal of the subject you're featuring.
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences. Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly. 1. Lab report case study template.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Usually, 2-4 paragraphs + a few bullet points with key results will do. Pro Tip. While, as its name implies, this section comes at the beginning of your case study, write it last. First, craft the rest of your document, then pick the most important bits and compile them into the introductory overview. 2.
A case study is a document that focuses on a business problem and provides a clear solution. Marketers use case studies to tell a story about a customer's journey or how a product or service solves a specific issue. Case studies can be used in all levels of business and in many industries. A thorough case study often uses metrics, such as key ...
1. Make it as easy as possible for the client. Just like when asking for reviews, it's important to make the process as clear and easy as possible for the client. When you reach out, ask if you can use their story of achievement as a case study for your business. Make the details as clear as possible, including:
1. Draft Structure. 🖋️ Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references. 2. Introduction.
In this article, we explore the concept of a case study, including its writing process, benefits, various types, challenges, and more.. How to write a case study. Understanding how to write a case study is an invaluable skill. You'll need to embrace decision-making - from deciding which customers to feature to designing the best format to make them as engaging as possible.
1. Attention grabbing title. The title of your case study needs to grab potential readers attention and convince them that this is a valuable piece of content. Make your title catchy, concise, and descriptive, just like you would for a good blog post.
1. Don't Make It About Yourself. The wrong way to approach a case study is to make it about you and your process. The reader cares less about your motivation and more about the results your ...
Step 2: Start Collaborating with a Client. With a clear topic in mind, you have to find the best fit for your case study. However, that is not all. First, you must obtain the client's permission. After all, your business story is theirs too. So, craft an email to provide your client with an overview of the case study.
8. Review and revise. The process of writing a case study doesn't actually end when the report is written; you also need to review your writing for coherence, clarity, and correctness. Don't underestimate the importance of this step! Make sure the information flows logically and that your arguments are well-supported.
Case study writing is all about making impressive claims about how a product helped someone achieve a certain result. However, it also needs to explain how it happened. Good case studies include key details that show how the customer got from A to B using the product—something you don't get with customer reviews. Don't make your reader ...
1. The key to landing your consulting job. Case interviews - where you are asked to solve a business case study under scrutiny - are the core of the selection process right across McKinsey, Bain and BCG (the "MBB" firms). This interview format is also used pretty much universally across other high-end consultancies; including LEK, Kearney ...
By Enguerran Loos, Founder of CaseCoach. Updated on 20 February 2024. The case interview is a challenging interview format that simulates the job of a management consultant, testing candidates across a wide range of problem-solving dimensions. McKinsey, BCG and Bain - along with other top consulting firms - use the case interview because it ...
Here are eight tips that I hope will be as helpful to you as they have been to me. 1. Develop Your Viewpoint. Effective and efficient case prep is, at least for me, the most challenging part of the whole experience. You can easily spend 2-3 hours on a case if you focus on every detail and supplementary piece of reading.
14 Case Study Templates. Now that we have explored some of the high level strategies you can use to create a business case study, we will transition to 14 case study design templates you can use with Visme. 1. Fuji Xerox Australia Case Study Template. Customize this template and make it your own!
How to Prepare for Case Interview Math Understand the Theory. To excel in case interview math, you need to master key formulas and concepts. Focus on revenue and profit calculations, market sizing equations, and break-even analysis. While in-depth understanding isn't required, having a rough idea of business terms and their formulas can be handy.
Jamie Holmes says a surgery center tried to make her pay for two operations after she underwent only one. She refused to buckle, even after a collection agency sued her last winter.
Highlighting case studies across the government. In 2021, the Biden-Harris Administration issued an Executive Order to improve customer experience and make service delivery simple, seamless, and secure for Americans. Since then, government agencies have been hard at work making their services, tools, and content more effective in addressing the needs of the people they serve.