Quantitative Research Methods: Meaning and Characteristics
What are quantitative research methods? What is its definition, when are these research methods used, and what are its characteristics?

Table of Contents
When to use quantitative or qualitative research.
The methods used by researchers may either be quantitative or qualitative . The decision to select the method largely depends on the researcher’s judgment and the nature of the research topic . Some research topics are better studied using quantitative methods, while others are more appropriately explored using qualitative methods.
J. Pizarro has already described qualitative research in this site, so this article focuses on quantitative methods, its meaning and characteristics.
What are quantitative research methods?
The numbers used in statistical analysis originate from objective scales of measurement of the units of analysis called variables . Four types of measurement scale exist namely nominal, ordinal, ratio, and interval (see 4 Statistical Scales of Measurement ).
The data that will serve as the basis for explaining a phenomenon, therefore, can be gathered through surveys . Such surveys use instruments that require numerical inputs or direct measurements of parameters that characterize the subject of investigation (e.g. pH, dissolved oxygen, salinity, turbidity, and conductivity to measure water quality).
7 Characteristics of Quantitative Research Methods
Seven characteristics discriminate qualitative methods of research from qualitative ones. I enumerate the characteristics of quantitative research methods in the following list.
1. Contain Measurable Variables
2. use standardized research instruments, 3. assume a normal population distribution.
For more reliable data analysis of quantitative data, a normal population distribution curve is preferred over a non-normal distribution. This requires a large population, the numbers of which depend on how the characteristics of the population vary. This requires adherence to the principle of random sampling to avoid researcher bias in interpreting the results that defeat the purpose of the research.
4. Present Data in Tables, Graphs, or Figures
5. use repeatable method.
Researchers can repeat the quantitative method to verify or confirm the findings in another setting. This reinforces the validity of groundbreaking discoveries or findings, thus eliminating the possibility of spurious or erroneous conclusions.
6. Can Predict Outcomes
Quantitative models or formula derived from data analysis can predict outcomes. If-then scenarios can be constructed using complex mathematical computations with the aid of digital computers or computer-controlled robots commonly referred to as artificial intelligence or AI.
7. Use Measuring Devices
The characteristics of quantitative research methods listed in this article make this research approach popular among researchers. Using qualitative research methods, however, is appropriate on issues or problems that need not require quantification or exploratory in nature .
University of Southern California (2015). Quantitative methods. Retrieved on 3 January, 2015 from http://goo.gl/GMiwt
© 2015 January 3 P. A. Regoniel updated : 2020 October 26
Related Posts
10 research paper presentation tips, statistical research questions: five examples for quantitative analysis, the importance of scoping in research, about the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a hobbyist writer, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
24 Comments
Simplyeducate.me privacy policy.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions . This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected. It often involves the use of surveys, experiments, or other structured data collection methods to gather quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Methods

Quantitative Research Methods are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used to describe the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. This research method is used to answer the questions of what, where, when, and how. Descriptive research designs use a variety of methods such as observation, case studies, and surveys to collect data. The data is then analyzed using statistical tools to identify patterns and relationships.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to investigate the relationship between two or more variables. Researchers use correlational research to determine whether a relationship exists between variables and to what extent they are related. This research method involves collecting data from a sample and analyzing it using statistical tools such as correlation coefficients.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks full control over the independent variable. Researchers use quasi-experimental research designs when it is not feasible or ethical to manipulate the independent variable.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method involves manipulating the independent variable and observing the effects on the dependent variable. Researchers use experimental research designs to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. This research method is used to gather information on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors of individuals. Researchers use survey research to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large sample size. Survey research can be conducted through various methods such as online, phone, mail, or in-person interviews.
Quantitative Research Analysis Methods
Here are some commonly used quantitative research analysis methods:
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis is the most common quantitative research analysis method. It involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Researchers use regression analysis to identify and quantify the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical technique used to identify underlying factors that explain the correlations among a set of variables. Researchers use factor analysis to reduce a large number of variables to a smaller set of factors that capture the most important information.
Structural Equation Modeling
Structural equation modeling is a statistical technique used to test complex relationships between variables. It involves specifying a model that includes both observed and unobserved variables, and then using statistical methods to test the fit of the model to the data.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is collected over time. It involves identifying patterns and trends in the data, as well as any seasonal or cyclical variations.
Multilevel Modeling
Multilevel modeling is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels. For example, researchers might use multilevel modeling to analyze data that is collected from individuals who are nested within groups, such as students nested within schools.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has many applications across a wide range of fields. Here are some common examples:
- Market Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions.
- Health Research: Quantitative research is used in health research to study the effectiveness of medical treatments, identify risk factors for diseases, and track health outcomes over time. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from clinical trials, surveys, and other sources to inform medical practice and policy.
- Social Science Research: Quantitative research is used in social science research to study human behavior, attitudes, and social structures. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform social policies, educational programs, and community interventions.
- Education Research: Quantitative research is used in education research to study the effectiveness of teaching methods, assess student learning outcomes, and identify factors that influence student success. Researchers use experimental and quasi-experimental designs, as well as surveys and other quantitative methods, to collect and analyze data.
- Environmental Research: Quantitative research is used in environmental research to study the impact of human activities on the environment, assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies, and identify ways to reduce environmental risks. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from field studies, experiments, and other sources.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research:
- Numerical data : Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
- Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves collecting data from a large sample of individuals or groups in order to increase the reliability and generalizability of the findings.
- Objective approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and impartial in its approach, focusing on the collection and analysis of data rather than personal beliefs, opinions, or experiences.
- Control over variables: Quantitative research often involves manipulating variables to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers aim to control for extraneous variables that may impact the results.
- Replicable : Quantitative research aims to be replicable, meaning that other researchers should be able to conduct similar studies and obtain similar results using the same methods.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to produce findings that can be generalized to larger populations beyond the specific sample studied. This is achieved through the use of random sampling methods and statistical inference.
Examples of Quantitative Research
Here are some examples of quantitative research in different fields:
- Market Research: A company conducts a survey of 1000 consumers to determine their brand awareness and preferences. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns that can inform marketing strategies.
- Health Research : A researcher conducts a randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of a new drug for treating a particular medical condition. The study involves collecting data from a large sample of patients and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Social Science Research : A sociologist conducts a survey of 500 people to study attitudes toward immigration in a particular country. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify factors that influence these attitudes.
- Education Research: A researcher conducts an experiment to compare the effectiveness of two different teaching methods for improving student learning outcomes. The study involves randomly assigning students to different groups and collecting data on their performance on standardized tests.
- Environmental Research : A team of researchers conduct a study to investigate the impact of climate change on the distribution and abundance of a particular species of plant or animal. The study involves collecting data on environmental factors and population sizes over time and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Psychology : A researcher conducts a survey of 500 college students to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify correlations and potential causal relationships.
- Political Science: A team of researchers conducts a study to investigate voter behavior during an election. They use survey methods to collect data on voting patterns, demographics, and political attitudes, and analyze the results using statistical methods.
How to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here is a general overview of how to conduct quantitative research:
- Develop a research question: The first step in conducting quantitative research is to develop a clear and specific research question. This question should be based on a gap in existing knowledge, and should be answerable using quantitative methods.
- Develop a research design: Once you have a research question, you will need to develop a research design. This involves deciding on the appropriate methods to collect data, such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies. You will also need to determine the appropriate sample size, data collection instruments, and data analysis techniques.
- Collect data: The next step is to collect data. This may involve administering surveys or questionnaires, conducting experiments, or gathering data from existing sources. It is important to use standardized methods to ensure that the data is reliable and valid.
- Analyze data : Once the data has been collected, it is time to analyze it. This involves using statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables. Common statistical techniques include correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
- Interpret results: After analyzing the data, you will need to interpret the results. This involves identifying the key findings, determining their significance, and drawing conclusions based on the data.
- Communicate findings: Finally, you will need to communicate your findings. This may involve writing a research report, presenting at a conference, or publishing in a peer-reviewed journal. It is important to clearly communicate the research question, methods, results, and conclusions to ensure that others can understand and replicate your research.
When to use Quantitative Research
Here are some situations when quantitative research can be appropriate:
- To test a hypothesis: Quantitative research is often used to test a hypothesis or a theory. It involves collecting numerical data and using statistical analysis to determine if the data supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- To generalize findings: If you want to generalize the findings of your study to a larger population, quantitative research can be useful. This is because it allows you to collect numerical data from a representative sample of the population and use statistical analysis to make inferences about the population as a whole.
- To measure relationships between variables: If you want to measure the relationship between two or more variables, such as the relationship between age and income, or between education level and job satisfaction, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data on both variables and use statistical analysis to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
- To identify patterns or trends: Quantitative research can be useful for identifying patterns or trends in data. For example, you can use quantitative research to identify trends in consumer behavior or to identify patterns in stock market data.
- To quantify attitudes or opinions : If you want to measure attitudes or opinions on a particular topic, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data using surveys or questionnaires and analyze the data using statistical methods to determine the prevalence of certain attitudes or opinions.
Purpose of Quantitative Research
The purpose of quantitative research is to systematically investigate and measure the relationships between variables or phenomena using numerical data and statistical analysis. The main objectives of quantitative research include:
- Description : To provide a detailed and accurate description of a particular phenomenon or population.
- Explanation : To explain the reasons for the occurrence of a particular phenomenon, such as identifying the factors that influence a behavior or attitude.
- Prediction : To predict future trends or behaviors based on past patterns and relationships between variables.
- Control : To identify the best strategies for controlling or influencing a particular outcome or behavior.
Quantitative research is used in many different fields, including social sciences, business, engineering, and health sciences. It can be used to investigate a wide range of phenomena, from human behavior and attitudes to physical and biological processes. The purpose of quantitative research is to provide reliable and valid data that can be used to inform decision-making and improve understanding of the world around us.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
There are several advantages of quantitative research, including:
- Objectivity : Quantitative research is based on objective data and statistical analysis, which reduces the potential for bias or subjectivity in the research process.
- Reproducibility : Because quantitative research involves standardized methods and measurements, it is more likely to be reproducible and reliable.
- Generalizability : Quantitative research allows for generalizations to be made about a population based on a representative sample, which can inform decision-making and policy development.
- Precision : Quantitative research allows for precise measurement and analysis of data, which can provide a more accurate understanding of phenomena and relationships between variables.
- Efficiency : Quantitative research can be conducted relatively quickly and efficiently, especially when compared to qualitative research, which may involve lengthy data collection and analysis.
- Large sample sizes : Quantitative research can accommodate large sample sizes, which can increase the representativeness and generalizability of the results.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
There are several limitations of quantitative research, including:
- Limited understanding of context: Quantitative research typically focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, which may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the context or underlying factors that influence a phenomenon.
- Simplification of complex phenomena: Quantitative research often involves simplifying complex phenomena into measurable variables, which may not capture the full complexity of the phenomenon being studied.
- Potential for researcher bias: Although quantitative research aims to be objective, there is still the potential for researcher bias in areas such as sampling, data collection, and data analysis.
- Limited ability to explore new ideas: Quantitative research is often based on pre-determined research questions and hypotheses, which may limit the ability to explore new ideas or unexpected findings.
- Limited ability to capture subjective experiences : Quantitative research is typically focused on objective data and may not capture the subjective experiences of individuals or groups being studied.
- Ethical concerns : Quantitative research may raise ethical concerns, such as invasion of privacy or the potential for harm to participants.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide

One-to-One Interview – Methods and Guide

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is Quantitative Research? Definition, Methods, Types, and Examples

If you’re wondering what is quantitative research and whether this methodology works for your research study, you’re not alone. If you want a simple quantitative research definition , then it’s enough to say that this is a method undertaken by researchers based on their study requirements. However, to select the most appropriate research for their study type, researchers should know all the methods available.
Selecting the right research method depends on a few important criteria, such as the research question, study type, time, costs, data availability, and availability of respondents. There are two main types of research methods— quantitative research and qualitative research. The purpose of quantitative research is to validate or test a theory or hypothesis and that of qualitative research is to understand a subject or event or identify reasons for observed patterns.
Quantitative research methods are used to observe events that affect a particular group of individuals, which is the sample population. In this type of research, diverse numerical data are collected through various methods and then statistically analyzed to aggregate the data, compare them, or show relationships among the data. Quantitative research methods broadly include questionnaires, structured observations, and experiments.
Here are two quantitative research examples:
- Satisfaction surveys sent out by a company regarding their revamped customer service initiatives. Customers are asked to rate their experience on a rating scale of 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent).
- A school has introduced a new after-school program for children, and a few months after commencement, the school sends out feedback questionnaires to the parents of the enrolled children. Such questionnaires usually include close-ended questions that require either definite answers or a Yes/No option. This helps in a quick, overall assessment of the program’s outreach and success.

Table of Contents
What is quantitative research ? 1,2
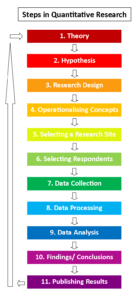
The steps shown in the figure can be grouped into the following broad steps:
- Theory : Define the problem area or area of interest and create a research question.
- Hypothesis : Develop a hypothesis based on the research question. This hypothesis will be tested in the remaining steps.
- Research design : In this step, the most appropriate quantitative research design will be selected, including deciding on the sample size, selecting respondents, identifying research sites, if any, etc.
- Data collection : This process could be extensive based on your research objective and sample size.
- Data analysis : Statistical analysis is used to analyze the data collected. The results from the analysis help in either supporting or rejecting your hypothesis.
- Present results : Based on the data analysis, conclusions are drawn, and results are presented as accurately as possible.
Quantitative research characteristics 4
- Large sample size : This ensures reliability because this sample represents the target population or market. Due to the large sample size, the outcomes can be generalized to the entire population as well, making this one of the important characteristics of quantitative research .
- Structured data and measurable variables: The data are numeric and can be analyzed easily. Quantitative research involves the use of measurable variables such as age, salary range, highest education, etc.
- Easy-to-use data collection methods : The methods include experiments, controlled observations, and questionnaires and surveys with a rating scale or close-ended questions, which require simple and to-the-point answers; are not bound by geographical regions; and are easy to administer.
- Data analysis : Structured and accurate statistical analysis methods using software applications such as Excel, SPSS, R. The analysis is fast, accurate, and less effort intensive.
- Reliable : The respondents answer close-ended questions, their responses are direct without ambiguity and yield numeric outcomes, which are therefore highly reliable.
- Reusable outcomes : This is one of the key characteristics – outcomes of one research can be used and replicated in other research as well and is not exclusive to only one study.
Quantitative research methods 5
Quantitative research methods are classified into two types—primary and secondary.
Primary quantitative research method:
In this type of quantitative research , data are directly collected by the researchers using the following methods.
– Survey research : Surveys are the easiest and most commonly used quantitative research method . They are of two types— cross-sectional and longitudinal.
->Cross-sectional surveys are specifically conducted on a target population for a specified period, that is, these surveys have a specific starting and ending time and researchers study the events during this period to arrive at conclusions. The main purpose of these surveys is to describe and assess the characteristics of a population. There is one independent variable in this study, which is a common factor applicable to all participants in the population, for example, living in a specific city, diagnosed with a specific disease, of a certain age group, etc. An example of a cross-sectional survey is a study to understand why individuals residing in houses built before 1979 in the US are more susceptible to lead contamination.
->Longitudinal surveys are conducted at different time durations. These surveys involve observing the interactions among different variables in the target population, exposing them to various causal factors, and understanding their effects across a longer period. These studies are helpful to analyze a problem in the long term. An example of a longitudinal study is the study of the relationship between smoking and lung cancer over a long period.
– Descriptive research : Explains the current status of an identified and measurable variable. Unlike other types of quantitative research , a hypothesis is not needed at the beginning of the study and can be developed even after data collection. This type of quantitative research describes the characteristics of a problem and answers the what, when, where of a problem. However, it doesn’t answer the why of the problem and doesn’t explore cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Data from this research could be used as preliminary data for another study. Example: A researcher undertakes a study to examine the growth strategy of a company. This sample data can be used by other companies to determine their own growth strategy.

– Correlational research : This quantitative research method is used to establish a relationship between two variables using statistical analysis and analyze how one affects the other. The research is non-experimental because the researcher doesn’t control or manipulate any of the variables. At least two separate sample groups are needed for this research. Example: Researchers studying a correlation between regular exercise and diabetes.
– Causal-comparative research : This type of quantitative research examines the cause-effect relationships in retrospect between a dependent and independent variable and determines the causes of the already existing differences between groups of people. This is not a true experiment because it doesn’t assign participants to groups randomly. Example: To study the wage differences between men and women in the same role. For this, already existing wage information is analyzed to understand the relationship.
– Experimental research : This quantitative research method uses true experiments or scientific methods for determining a cause-effect relation between variables. It involves testing a hypothesis through experiments, in which one or more independent variables are manipulated and then their effect on dependent variables are studied. Example: A researcher studies the importance of a drug in treating a disease by administering the drug in few patients and not administering in a few.
The following data collection methods are commonly used in primary quantitative research :
- Sampling : The most common type is probability sampling, in which a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are—simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling.
- Interviews : These are commonly telephonic or face-to-face.
- Observations : Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research . In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review : Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the quantitative research .
- Surveys and questionnaires : Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
The data collected can be analyzed in several ways in quantitative research , as listed below:
- Cross-tabulation —Uses a tabular format to draw inferences among collected data
- MaxDiff analysis —Gauges the preferences of the respondents
- TURF analysis —Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis; helps in determining the market strategy for a business
- Gap analysis —Identify gaps in attaining the desired results
- SWOT analysis —Helps identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a product, service, or organization
- Text analysis —Used for interpreting unstructured data
Secondary quantitative research methods :
This method involves conducting research using already existing or secondary data. This method is less effort intensive and requires lesser time. However, researchers should verify the authenticity and recency of the sources being used and ensure their accuracy.
The main sources of secondary data are:
- The Internet
- Government and non-government sources
- Public libraries
- Educational institutions
- Commercial information sources such as newspapers, journals, radio, TV

When to use quantitative research 6
Here are some simple ways to decide when to use quantitative research . Use quantitative research to:
- recommend a final course of action
- find whether a consensus exists regarding a particular subject
- generalize results to a larger population
- determine a cause-and-effect relationship between variables
- describe characteristics of specific groups of people
- test hypotheses and examine specific relationships
- identify and establish size of market segments
A research case study to understand when to use quantitative research 7
Context: A study was undertaken to evaluate a major innovation in a hospital’s design, in terms of workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single-room hospital accommodations. The researchers undertook a mixed methods approach to answer their research questions. Here, we focus on the quantitative research aspect.
Research questions : What are the advantages and disadvantages for the staff as a result of the hospital’s move to the new design with all single-room accommodations? Did the move affect staff experience and well-being and improve their ability to deliver high-quality care?
Method: The researchers obtained quantitative data from three sources:
- Staff activity (task time distribution): Each staff member was shadowed by a researcher who observed each task undertaken by the staff, and logged the time spent on each activity.
- Staff travel distances : The staff were requested to wear pedometers, which recorded the distances covered.
- Staff experience surveys : Staff were surveyed before and after the move to the new hospital design.
Results of quantitative research : The following observations were made based on quantitative data analysis:
- The move to the new design did not result in a significant change in the proportion of time spent on different activities.
- Staff activity events observed per session were higher after the move, and direct care and professional communication events per hour decreased significantly, suggesting fewer interruptions and less fragmented care.
- A significant increase in medication tasks among the recorded events suggests that medication administration was integrated into patient care activities.
- Travel distances increased for all staff, with highest increases for staff in the older people’s ward and surgical wards.
- Ratings for staff toilet facilities, locker facilities, and space at staff bases were higher but those for social interaction and natural light were lower.
Advantages of quantitative research 1,2
When choosing the right research methodology, also consider the advantages of quantitative research and how it can impact your study.
- Quantitative research methods are more scientific and rational. They use quantifiable data leading to objectivity in the results and avoid any chances of ambiguity.
- This type of research uses numeric data so analysis is relatively easier .
- In most cases, a hypothesis is already developed and quantitative research helps in testing and validatin g these constructed theories based on which researchers can make an informed decision about accepting or rejecting their theory.
- The use of statistical analysis software ensures quick analysis of large volumes of data and is less effort intensive.
- Higher levels of control can be applied to the research so the chances of bias can be reduced.
- Quantitative research is based on measured value s, facts, and verifiable information so it can be easily checked or replicated by other researchers leading to continuity in scientific research.
Disadvantages of quantitative research 1,2
Quantitative research may also be limiting; take a look at the disadvantages of quantitative research.
- Experiments are conducted in controlled settings instead of natural settings and it is possible for researchers to either intentionally or unintentionally manipulate the experiment settings to suit the results they desire.
- Participants must necessarily give objective answers (either one- or two-word, or yes or no answers) and the reasons for their selection or the context are not considered.
- Inadequate knowledge of statistical analysis methods may affect the results and their interpretation.
- Although statistical analysis indicates the trends or patterns among variables, the reasons for these observed patterns cannot be interpreted and the research may not give a complete picture.
- Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate and generalizable analysis .
- Quantitative research cannot be used to address complex issues.

Frequently asked questions on quantitative research
Q: What is the difference between quantitative research and qualitative research? 1
A: The following table lists the key differences between quantitative research and qualitative research, some of which may have been mentioned earlier in the article.
| Purpose and design | ||
| Research question | ||
| Sample size | Large | Small |
| Data | ||
| Data collection method | Experiments, controlled observations, questionnaires and surveys with a rating scale or close-ended questions. The methods can be experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive, or correlational. | Semi-structured interviews/surveys with open-ended questions, document study/literature reviews, focus groups, case study research, ethnography |
| Data analysis |
Q: What is the difference between reliability and validity? 8,9
A: The term reliability refers to the consistency of a research study. For instance, if a food-measuring weighing scale gives different readings every time the same quantity of food is measured then that weighing scale is not reliable. If the findings in a research study are consistent every time a measurement is made, then the study is considered reliable. However, it is usually unlikely to obtain the exact same results every time because some contributing variables may change. In such cases, a correlation coefficient is used to assess the degree of reliability. A strong positive correlation between the results indicates reliability.
Validity can be defined as the degree to which a tool actually measures what it claims to measure. It helps confirm the credibility of your research and suggests that the results may be generalizable. In other words, it measures the accuracy of the research.
The following table gives the key differences between reliability and validity.
| Importance | Refers to the consistency of a measure | Refers to the accuracy of a measure |
| Ease of achieving | Easier, yields results faster | Involves more analysis, more difficult to achieve |
| Assessment method | By examining the consistency of outcomes over time, between various observers, and within the test | By comparing the accuracy of the results with accepted theories and other measurements of the same idea |
| Relationship | Unreliable measurements typically cannot be valid | Valid measurements are also reliable |
| Types | Test-retest reliability, internal consistency, inter-rater reliability | Content validity, criterion validity, face validity, construct validity |
Q: What is mixed methods research? 10
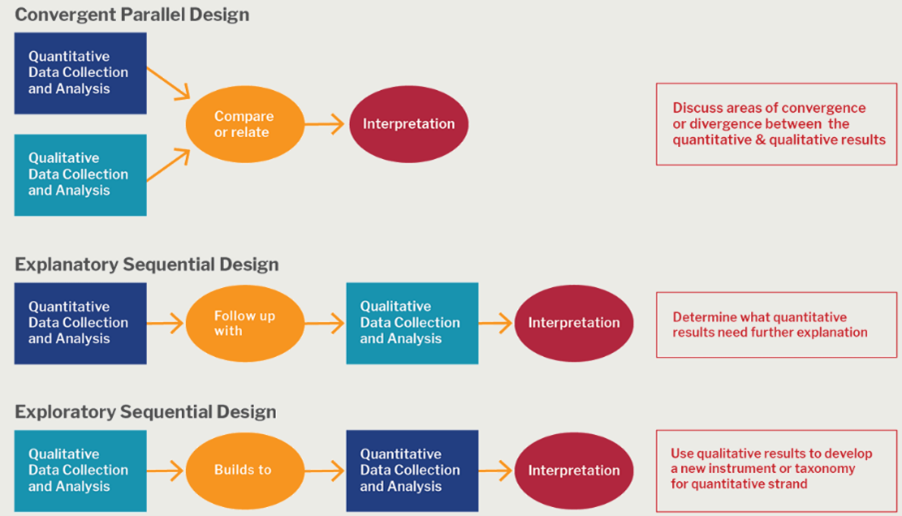
A: A mixed methods approach combines the characteristics of both quantitative research and qualitative research in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method. A mixed methods research design is useful in case of research questions that cannot be answered by either quantitative research or qualitative research alone. However, this method could be more effort- and cost-intensive because of the requirement of more resources. The figure 3 shows some basic mixed methods research designs that could be used.
Thus, quantitative research is the appropriate method for testing your hypotheses and can be used either alone or in combination with qualitative research per your study requirements. We hope this article has provided an insight into the various facets of quantitative research , including its different characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, and a few tips to quickly understand when to use this research method.
References
- Qualitative vs quantitative research: Differences, examples, & methods. Simply Psychology. Accessed Feb 28, 2023. https://simplypsychology.org/qualitative-quantitative.html#Quantitative-Research
- Your ultimate guide to quantitative research. Qualtrics. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.qualtrics.com/uk/experience-management/research/quantitative-research/
- The steps of quantitative research. Revise Sociology. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://revisesociology.com/2017/11/26/the-steps-of-quantitative-research/
- What are the characteristics of quantitative research? Marketing91. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://www.marketing91.com/characteristics-of-quantitative-research/
- Quantitative research: Types, characteristics, methods, & examples. ProProfs Survey Maker. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.proprofssurvey.com/blog/quantitative-research/#Characteristics_of_Quantitative_Research
- Qualitative research isn’t as scientific as quantitative methods. Kmusial blog. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://kmusial.wordpress.com/2011/11/25/qualitative-research-isnt-as-scientific-as-quantitative-methods/
- Maben J, Griffiths P, Penfold C, et al. Evaluating a major innovation in hospital design: workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single room hospital accommodation. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Feb. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 3.3.) Chapter 5, Case study quantitative data findings. Accessed March 6, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK274429/
- McLeod, S. A. (2007). What is reliability? Simply Psychology. www.simplypsychology.org/reliability.html
- Reliability vs validity: Differences & examples. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://statisticsbyjim.com/basics/reliability-vs-validity/
- Mixed methods research. Community Engagement Program. Harvard Catalyst. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://catalyst.harvard.edu/community-engagement/mmr
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What are the Best Research Funding Sources

Inductive vs. Deductive Research Approach

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

What Are The Characteristics Of Quantitative Research? Characteristics Of Quantitative Research In A Nutshell
The characteristics of quantitative research contribute to methods that use statistics as the basis for making generalizations about something. These generalizations are constructed from data that is used to find patterns and averages and test causal relationships.
To assist in this process, key quantitative research characteristics include:
- The use of measurable variables.
- Standardized research instruments.
- Random sampling of participants.
- Data presentation in tables, graphs, or figures.
- The use of a repeatable method.
- The ability to predict outcomes and causal relationships.
- Close-ended questioning.
Each characteristic also discriminates quantitative research from qualitative research, which involves the collecting and analyzing of non-numerical data such as text, video, or audio.
With that said, let’s now take a look at each of the characteristics in more detail.
But let’s first look at the importance of quantitative research and when it does matter!
| is a systematic and approach to gathering and analyzing to answer research questions or test hypotheses. It is often used in and studies. | |
| : Quantitative researchers often use with to collect data from a of participants. and are common tools. | |
| : In experimental research, researchers manipulate variables to study cause-and-effect relationships. Data is collected through measurements and observations. | |
| : Researchers may use to gather data on behaviors or events, often using checklists or coding schemes. | |
| , such as , , and . This data can be analyzed statistically to identify patterns, relationships, and trends. | |
| Quantitative studies typically involve to ensure that findings are statistically significant and can be generalized to a larger population. Samples are often selected through random or systematic methods. | |
| is a key characteristic of quantitative research. Researchers use and to analyze data and draw conclusions. Common statistical techniques include and . | |
| Quantitative research aims for and . The data collection process is often to minimize bias, and results should be replicable by other researchers. | |
| One of the primary goals of quantitative research is to make from the sample to a larger population. Statistical techniques allow researchers to estimate population parameters based on sample data. | |
| Quantitative researchers often formulate and use statistical tests to . The results help determine whether the data supports or rejects the proposed hypotheses. | |
| Quantitative research offers and over variables. Researchers can carefully design studies to control for confounding variables and isolate the impact of specific factors. | |
| Quantitative research generates , such as , , , and . These results provide clear and measurable insights into the research questions. | |
| Quantitative research is a valuable method for , , and making . It is widely used in various fields, including psychology, sociology, economics, and the natural sciences. |
Table of Contents
Importance of quantitative research
In the context of a business that wants to learn more about its market, customers, or competitors, quantitative research is a powerful tool that provides objective, data-based insights, trends, predictions, and patterns.
To clarify the importance of quantitative research as a method, we’ll discuss some of its key benefits to businesses below.
Before a company can develop a marketing strategy or even a single campaign, it must perform research to either confirm or deny a hypothesis it has around an ideal buyer or the target audience.
Before the proliferation of the internet, quantitative data collection was more cumbersome, less exhaustive, and normally occurred face to face.
Today, the ease with which companies can perform quantitative research is impressive – so much so that some would hesitate to even call it research.
Many businesses conduct questionnaires and surveys to have more control over how they test hypotheses, but any business with a Google Analytics account can passively collect data on key metrics such as bounce rate, discovery keywords, and value per visit.
The key thing to remember here is that there is little scope for uncertainty among the research data. Questionnaires ask closed-ended questions with no room for ambiguity and the validity of bounce rate data will never be up for debate.
Objective representation
Fundamentally speaking, quantitative research endeavors to establish the strength or significance of causal relationships.
There is an emphasis on objective measurement based on numerical, statistical, and mathematical data analysis or manipulation.
Quantitative research is also used to produce unbiased, logical, and statistical results that are representative of the population from which the sample is drawn.
In a marketer’s case, the population is usually the target audience of a product or service.
But in any case, organizations are dependent on quantitative data as it provides detailed, accurate, and relevant information on the problem at hand.
When it comes time to either prove or disprove the hypothesis, companies can either move forward with robust data or drop their current line of research and start afresh.
Versatility of quantitative statistical analysis
On the subject of proving a hypothesis are the statistical analyses a business must perform to arrive at the answer.
Fortunately, there are numerous techniques a company can employ depending on the context and the goals of the research.
These include:

Conjoint analysis

Used to identify the value of attributes that influence purchase decisions, such as cost, benefits, or features.
Unsurprisingly, this analysis is used in product pricing, product launch, and market placement initiatives.
GAP analysis

An analysis that determines the discrepancy that exists between the actual and desired performance of a product or service.
MaxDiff analysis
A simpler version of the conjoint analysis that marketers use to analyze customer preferences related to brand image, preferences, activities, and also product features.
This is also known as “best-worst” scaling.
TURF analysis
TURF, which stands for total unduplicated reach and frequency, is used to ascertain the particular combination of products and services that will yield the highest number of sales.
The use of measurable variables
During quantitative research, data gathering instruments measure various characteristics of a population.
These characteristics, which are called measurables in a study, may include age, economic status, or the number of dependents.
Standardized research instruments
Standardized and pre-tested data collection instruments include questionnaires, surveys, and polls. Alternatively, existing statistical data may be manipulated using computational techniques to yield new insights.
Standardization of research instruments ensures the data is accurate, valid, and reliable. Instruments should also be tested first to determine if study participant responses satisfy the intent of the research or its objectives.
Random sampling of participants
Quantitative data analysis assumes a normal distribution curve from a large population.
Random sampling should be used to gather data, a technique in which each sample has an equal probability of being chosen. Randomly chosen samples are unbiased and are important in making statistical inferences and conclusions.
Here are a few random sampling techniques.
True random sampling
Some consider true random sampling to be the gold standard when it comes to probabilistic studies. While it may not be useful in every situation or context, it is one of the most useful for enormous databases.
The method involves assigning numbers to a population of available study participants and then having a random number generator select them. This ensures that each individual in a study pool has an equal chance of being solicited for feedback.
Systematic sampling
Systematic sampling is similar to true random sampling but is more suited to smaller populations. In this technique, the sample is selected by randomly choosing a starting point in the population and then selecting every n th individual after that.
For example, if a researcher wanted to sample every twentieth person from a list of customers, they would randomly select one customer as the starting point and then sample every twentieth customer thereafter.
Cluster sampling
In cluster sampling, the population is divided into clusters or groups and a random sample of clusters is selected. After which, all members of the selected clusters are included in the sample.
If a HR team wanted to survey employees of a large organization, they might randomly select several departments as clusters, and then survey all the employees within those departments.
Cluster sampling can also be useful for businesses that have customers or products distributed over wide geographic areas.
To that end, cluster sampling is often used when the population is too large or too dispersed to sample individually. While it may be more efficient to sample clusters, the approach may be less precise if there is variability between them.
Data presentation in tables, graphs, and figures
The results of quantitative research can sometimes be difficult to decipher, particularly for those not involved in the research process.
Tables, graphs, and figures help synthesize the data in a way that is understandable for key stakeholders. They should demonstrate or define relationships, trends, or differences in the data presented.
Take McKinsey Global Institute (MGI), for example, the business and research arm of McKinsey & Company.
Established in 1990, MGI combines the disciplines of economics and management to examine the macroeconomic forces that influence business strategy and public policy.
Based on this analysis , MGI periodically releases reports covering more than 20 countries and 30 industries around six key themes: natural resources, labor markets, productivity and growth , the evolution of global financial markets, the economic impact of technology and innovation , and urbanization.
MGI’s mission is to “ provide leaders in the commercial, public, and social sectors with the facts and insights on which to base management and policy decisions .” To carry out this mission , McKinsey’s data presentation is key.
In one article that argued against the deglobalization trend , McKinsey skilfully used graphs and bar charts to synthesize quantitative data related to the global flow of intangibles, services, and students.
The company also used an 80-cell matrix and color-coded scale to show the share of domestic consumption met by inflows for various geographic regions.
The use of a repeatable method
Quantitative research methods should be repeatable.
This means the method can be applied by other researchers in a different context to verify or confirm a particular outcome.
Replicable research outcomes afford researchers greater confidence in the results. Replicability also reduces the chances that the research will be influenced by selection biases and confounding variables.
The ability to predict outcomes and causal relationships
Data analysis can be used to create formulas that predict outcomes and investigate causal relationships.
As hinted at earlier, data are also used to make broad or general inferences about a large population.
Causal relationships, in particular, can be described by so-called “if-then” scenarios, which can be modeled using complex, computer-driven mathematical functions.
Close-ended questioning
Lastly, quantitative research requires that the individuals running the study choose their questions wisely.
Since the study is based on quantitative data, it is imperative close-ended questions are asked.
These are questions that can only be answered by selecting from a limited number of options.
Questions may be dichotomous, with a simple “yes” or “no” or “true” or “false” answer.
However, many studies also incorporate multiple-choice questions based on a rating scale, Likert scale, checklist, or order ranking system.
Sample size
Sample size is a critical consideration in quantitative research as it impacts the reliability of the results.
In business quantitative research, sample size refers to the number of participants or data points included in a study, and it is vital that the sample size is appropriate for the research questions being addressed.
A sample size that is too small can lead to unreliable conclusions since it will not accurately represent the study population.
Conversely, a sample size that is too large can lead to unnecessary expenses and time constraints.
In general, however, larger sample sizes tend to increase the precision and reliability of study conclusions.
This is because they reduce the impact of random variation and increase the power to detect statistically significant differences or relationships. However, larger sample sizes also require more resources and time to collect and analyze data.
As a consequence, it is important for businesses to select a sample size that balances factors such as the research question, population size, variability of the data, and statistical power.
Four real-world examples of quantitative research
Now that we’ve described some key quantitative research examples, let’s go ahead and look at some real-world examples.
1 – A Quantitative Study of the Impact of Social Media Reviews on Brand Perception
In 2015, Neha Joshi undertook quantitative research as part of her thesis at The City University of New York.
The thesis aimed to determine the impact of social media reviews on brand perception with a particular focus on YouTube and Yelp.
Joshi analyzed the impact of 942 separate YouTube smartphone reviews to develop a statistical model to predict audience response and engagement on any given video.
The wider implications of the study involved using customer reviews as a feedback mechanism to improve brand perception.
2 – A Quantitative Study of Teacher Perceptions of Professional Learning Communities’ Context, Process, and Content
Daniel R. Johnson from Seton Hall University in New Jersey, USA, analyzed the effectiveness of the teacher training model known as Professional Learning Communities (PLC).
Specifically, Johnson wanted to research the impact of the model as perceived by certified educators across three specific areas: content, process, and context.
There was a dire need for this research since there was little quantitative data on an approach that was becoming increasingly popular at the government, state, and district levels.
Data were collected using Standard Inventory Assessment (SAI) surveys which were online, anonymous, and incorporated a Likert scale response system.
3 – A Quantitative Study of Course Grades and Retention Comparing Online and Face-to-Face Classes
This research was performed by Vickie A. Kelly as part of her Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership at Baker University in Kansas, USA.
Kelly wanted to know whether distance education and Internet-driven instruction were as effective a learning tool when compared to traditional face-to-face instruction.
A total of 885 students were selected for the research sample to answer the following two questions:
- Is there a statistically significant difference between the grades of face-to-face students and the grades of online students?
- Is there a statistically significant difference between course content retention in face-to-face students and online students?
In both cases, there was no significant difference, which suggested that distance education as a learning tool was as effective as face-to-face education.
4 – A quantitative research of consumer’s attitude towards food products advertising
At the University of Bucharest, Romania, Mirela-Cristina Voicu wanted to research consumer attitudes toward traditional forms of advertising such as television, radio, and print.
She reasoned that consumer attitudes toward advertising impacted attitudes toward the product or brand itself, with a positive attitude potentially driving purchase intent.
To determine whether there was a link between these factors, 385 consumers in the Bucharest area were interviewed and asked to fill out a questionnaire.
Voicu ensured the sample was representative of the broader population in terms of two variables: age and gender.
The quantitative study results found that 70% of participants considered traditional forms of advertising to be saturated.
In other words, they did not have a positive attitude toward the advertised brand or product.
However, consumer attitudes toward food advertising were much more positive, with 61% of participants categorizing their attitudes as either favorable or very favorable in the questionnaire.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
As the story goes, “data is the new oil,” yes, but what data?
Indeed, while quantitative research can be extremely powerful, it must be balanced with qualitative research .

Several qualitative methods might help enrich the quantitative data.

It’s critical to understand that quantitative data might be very effective in the short term.
Yet, it might not tell us anything in the long term.
For that, we need to use human judgment, intuition, and understanding of context.
In what we can label as second-order thinking .

Only by building qualitative understanding within quantitative methods combined with second-order effect thinking; can you leverage the best of the two worlds!
For instance, take the interesting case of how Amazon has integrated both quantitative and qualitative data into its business strategy .
This is part of Jeff Bezos’ “Day One” Mindset .

That enabled Amazon to understand when it makes sense to leverage quantitative vs. qualitative data .
As Jeff Bezos explained in 2006:
“ Many of the important decisions we make at Amazon.com can be made with data. There is a right answer or a wrong answer, a better answer or a worse answer, and math tells us which is which. These are our favorite kinds of decisions.”
As our shareholders know, we have made a decision to continuously and significantly lower prices for customers year after year as our efficiency and scale make it possible.
Indeed, this was the core tenet of Amazon’s flywheel .
And Jeff Bezos also explained:
This is an example of a very important decision that cannot be made in a math-based way. In fact, when we lower prices, we go against the math that we can do, which always says that the smart move is to raise prices.
Indeed, as Jeff Bezos further explained:
We have significant data related to price elasticity. With fair accuracy, we can predict that a price reduction of a certain percentage will result in an increase in units sold of a certain percentage. With rare exceptions, the volume increase in the short term is never enough to pay for the price decrease.
In short, optimization tools leveraging quantitative analysis are quire effective in the short-term and relation to first-order effects activities.
However, in many cases, that doesn’t tell you anything when it comes to its second-order long-term consequences!
Jeff Bezos explained that extremely well:
However, our quantitative understanding of elasticity is short-term. We can estimate what a price reduction will do this week and this quarter. But we cannot numerically estimate the effect that consistently lowering prices will have on our business over five years or ten years or more.
And he introduced the difference between quantitative data vs. human judgment, which is a qualitative measure!
Our judgment is that relentlessly returning efficiency improvements and scale economies to customers in the form of lower prices creates a virtuous cycle that leads over the long term to a much larger dollar amount of free cash flow, and thereby to a much more valuable Amazon.com.
He highlighted how long-term, unpredictable and counterintuitive bets were the result of human judgement:
We’ve made similar judgments around Free Super Saver Shipping and Amazon Prime, both of which are expensive in the short term and—we believe—important and valuable in the long term.
Quantitative research examples
There is a lot of discussion around the ideal length of social media posts online, and much of it is anecdotal or pure conjecture at best.
To cut through the noise and arrive at data-driven conclusions, brand building platform Buffer teamed up with analytics software company SumAll.
In this example, the research involved tabulating and quantifying social media engagement as a factor of post length.
Posts encompassed a variety of social media updates, such as tweets, blog posts, Facebook posts, and headlines. The study determined:
- The optimal width of a paragraph (140 characters).
- The optimal length of a domain name (8 characters).
- The optimal length of a hashtag (6 characters).
- The optimal length of an email subject (28 to 39 characters), and
- The optimal duration of a podcast (22 minutes) and YouTube video (3 minutes).
Where SumAll sourced its quantitative data varied according to the type of social media post.
To determine the optimal width of a paragraph, the company referenced social media guru Derek Halpern who himself analyzed data from two separate academic studies.
To determine the optimal length of an email subject line, SumAll referenced a 2012 study by Mailer Mailer that analyzed 1.2 billion email messages to identify trends.
Tallwave is a customer experience design company that performs quantitative research for clients and identifies potential trends.
In the wake of COVID-19, the company wanted to know whether consumer trends the pandemic spurred would continue after restrictions were lifted.
These trends included buy online, pick-up in-store (BOPIS), and blended, cook-at-home restaurant meals.
Tallwave also wanted to learn more about consumer expectations around branded communication.
In a post-pandemic world, were health and safety precautions more important than the inconvenience they caused?
Would customers abandon digital experiences and flock back to brick-and-mortar stores? Indeed, was it wise to continue to invest in infrastructure the customer didn’t want?
To collect quantitative data, Tallwave surveyed 1,010 individuals across the United States aged 24 and over in April 2021.
Consumers were asked various questions on their behaviors, perceptions, and needs pre and post-pandemic.
The company found that while customer behavior did change as a result of COVID-19, it had not changed to the extent predicted. Some of the key findings include:
- Convenience trumps all – while many brands continued to focus on health and safety, customers still value convenience above all else. Safety-related needs were the next most important for all age brackets (except Gen Z).
- The role of digital experiences – most survey participants who used a company’s digital experience viewed that company more favorably. This proved that in a post-COVID world, the flexibility for consumers to choose their own “adventure” is paramount.
- The accessibility of digital experiences – the survey data also showed that interest in digital experiences declined with age starting with the 45-54 year bracket. Since 66% of those aged 55 and older reported no desire to continue with online experiences after COVID-19, Tallwave argued that increasing digital literacy would drive greater adoption and engagement over the long term.
Additional Case Studies
Examples of Business Scenarios Using Quantitative Research :
- A company launching a new product conducts surveys to identify which age group is most interested in their product.
- A retail store uses conjoint analysis to determine the optimal price point for a new item.
- A beverage company tests various flavors and uses rating scales to determine which new flavor to launch.
- An e-commerce site analyzes click-through rates to optimize the layout of their product pages.
- A startup uses surveys to measure how many consumers are aware of their brand after a marketing campaign.
- A company conducts an online poll to gauge the effectiveness of their recent TV commercial.
- A tech firm analyzes past sales data to predict the number of units they will sell in the next quarter.
- A corporation uses standardized questionnaires to gauge employee satisfaction and identify areas of improvement.
- A manufacturing company analyzes lead times and delivery speeds to optimize their supply chain processes.
- A retail chain reviews sales data to determine the optimal shelf placement for products to maximize sales.
- An airline analyzes frequent flyer data to understand patterns and introduce loyalty rewards.
- A financial institution uses quantitative analysis to predict stock market trends.
- A supermarket uses sales data to understand which products sell best during promotional events.
- A restaurant reviews time-tracking data to optimize shift schedules during peak hours.
- A software company uses surveys to gather feedback on a new feature they’ve introduced.
- Businesses analyze macroeconomic indicators to forecast market conditions.
- Retailers review sales and inventory data to predict restocking needs.
- A hotel chain uses quantitative research to determine the best locations for new hotels based on travel and occupancy data.
- A company reviews market share data to understand their position relative to competitors.
- A service-based company analyzes call center data to reduce wait times and improve customer service.
Key takeaways
- The characteristics of quantitative research contribute to methods that use statistics as the basis for making generalizations about something.
- In a quantitative study, measurable variables are analyzed using standardized research instruments. Importantly, data must be sampled randomly from a large, representative population to avoid biases.
- Quantitative research data should also be presented in tables and graphs to make key findings more digestible for non-technical stakeholders. Methods must also be repeatable in different contexts to ensure greater outcome confidence and validity.
Key Highlights of Quantitative Research Characteristics:
- Quantitative research uses statistics to make generalizations based on measurable variables.
- Standardized research instruments like questionnaires and surveys are used for data collection.
- Random sampling of participants ensures unbiased results from a larger population.
- Data is presented in tables, graphs, or figures for better understanding.
- The research method is repeatable for verification and validity.
- It allows for predicting outcomes and causal relationships.
- Close-ended questioning is used to gather specific and structured responses.
Importance of Quantitative Research:
- Provides objective, data-based insights, trends, predictions, and patterns for businesses.
- Helps in developing marketing strategies and understanding the target audience.
- Focuses on objective measurement and producing unbiased results.
- Offers versatility in statistical analysis techniques for various research goals.
Real-world Examples of Quantitative Research:
- Impact of Social Media Reviews on Brand Perception.
- Teacher Perceptions of Professional Learning Communities.
- Comparison of Course Grades and Retention in Online vs. Face-to-Face Classes.
- Consumer Attitudes Towards Food Product Advertising.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research:
- Qualitative research involves non-numerical data and focuses on understanding human behavior and attitudes.
- Quantitative research relies on measurable variables and statistics to make broad inferences.
- The combination of both methods allows for a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena.
Sample Size Considerations:
- The sample size is critical in quantitative research to ensure reliable results.
- Larger sample sizes increase precision and reduce the impact of random variation.
- Properly balanced sample sizes are essential for valid and statistically significant conclusions.
Main Points
- Involves statistical analysis for making generalizations based on measurable variables.
- Uses standardized research instruments like surveys and questionnaires.
- Requires random sampling for unbiased representation from a larger population.
- Presents data through tables, graphs, or figures for visualization.
- Should follow a repeatable method for validation and reliability.
- Enables prediction of outcomes and identification of causal relationships.
- Utilizes close-ended questions to gather specific responses.
- Offers data-driven insights, patterns, trends, and predictions.
- Informs business strategies, marketing decisions, and audience understanding.
- Provides objective measurement and representation of trends.
- Enables informed decision-making through statistical analysis .
- Examines social media impact on brand perception.
- Investigates teacher perceptions of professional learning communities.
- Compares online and face-to-face class effectiveness.
- Studies consumer attitudes towards food product advertising.
- Qualitative research focuses on understanding human behavior through non-numerical data.
- Quantitative research emphasizes measurable variables and statistical analysis .
- Combining both methods offers a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena.
- Sample size is crucial for reliable and accurate results.
- Larger samples enhance precision and reduce random variation impact.
- Balanced sample sizes ensure valid and statistically significant findings.
Read Also: Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research .
Connected Analysis Frameworks
Cynefin Framework

SWOT Analysis

Personal SWOT Analysis

Pareto Analysis

Failure Mode And Effects Analysis

Blindspot Analysis

Comparable Company Analysis

Cost-Benefit Analysis

Agile Business Analysis

SOAR Analysis

STEEPLE Analysis

Pestel Analysis

DESTEP Analysis

Paired Comparison Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy , Marketing Strategy , Business Models , Tech Business Models , Jobs-To-Be Done , Design Thinking , Lean Startup Canvas , Value Chain , Value Proposition Canvas , Balanced Scorecard , Business Model Canvas , SWOT Analysis , Growth Hacking , Bundling , Unbundling , Bootstrapping , Venture Capital , Porter’s Five Forces , Porter’s Generic Strategies , Porter’s Five Forces , PESTEL Analysis , SWOT , Porter’s Diamond Model , Ansoff , Technology Adoption Curve , TOWS , SOAR , Balanced Scorecard , OKR , Agile Methodology , Value P
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Competition
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Marketing91
What are the Characteristics of Quantitative Research?
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
No matter whether you belong to a management field or science field, you must have come across quantitative research once in your life. People quite often come across one or two surveys or questionnaires. The purpose of conducting these surveys is to draw reliable analytical conclusions to understand a particular audience.
Quantitative research is a popular choice of research, especially in industries. As companies want to know about the demand for the product in the market and preference of customers before making huge investments. With the help of quantitative research, one can learn about the wishes and needs of target groups .
Quantitative research is used to get answers in numerical form. The output of quantitative research is usually in the form of graphs, statistical data, tables, and percentages, etc. The purpose of using quantitative research is to make the use of mathematical and statistical models to establish an understanding of the problem of research.
The outcome of quantitative research is analyzed with the help of statistics to get unbiased results. The results of quantitative research can be generalised because it is conducted on a large population size. Different types of quantitative research can be undertaken to obtain the results. Click Here To learn more about the different types of quantitative research.
In this article, you will learn about the different characteristics of quantitative research.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Quantitative Research

1. Large Sample Size
The first and foremost characteristic of quantitative research is the large sample size to conduct research. Quantitative research is done on a large number of audiences to ensure reliability. The sample size used in quantitative research represents the whole target market .
Because of this characteristic of quantitative research, most organizations prefer to invest in quantitative research rather than investing in qualitative research .
2. Structured Research Methods
Structural research methods like questionnaires, polls, and surveys are used to conduct quantitative research. In-depth information about the preferences of the audience can be drawn using these structured research methods.
Moreover, with the help of the Internet and social media, it is effortless to reach the vast population irrespective of geographical boundaries. You can pay to run your Survey ad on various social media platforms such as Facebook , YouTube , etc. and can collect the opinion of a large population.
In addition to this, these research methods are easy to conduct through offline means. Also, a participant is only required to fill out the questionnaire and is not required to be part of the research process for a long time.
3. Highly Reliable Outcome

The outcome of quantitative research methods is quite reliable, as participants of the research face close-ended questions. Therefore, there are fewer chances of getting vague information or wrong information from the participants.
Quantitative research methods are used for industrial research purposes because of its reliability. Moreover, the Outcome of quantitative research is easy to understand and explain.
The researchers present the outcome of the research to get the approval of the management, and management can understand this information quickly because it is represented in the form of tables and graphs.
4. Reusable Outcome
Another characteristic of quantitative research is that the outcome of quantitative research can be used multiple times. Data collected for one research purpose can be used for the prior study of another research problem.
Sometimes, researchers make the use of the outcome of research for similar research problems, which reduces the expense and time required for conducting research. For example, if you have researched how much money a man will be willing to pay to buy an electronic gadget.
You can use the output of the previous study to get a reliable answer to the research problem of how much a man will be willing to pay to buy an earphone. In this way, the outcome of the previous research problem is used to support the output of new but related research problems.
5. Close-ended questions

Another characteristic of quantitative research is close-ended questions. Close-ended question’s answers are more specific and right to the question than the open-ended questions. Responses to open-ended questions are more detailed and scattered, and it requires real skills to pick out the answers that you need.
Moreover, responses to Close-ended questions are more reliable than the answers to questions of open-ended questions. In addition to this, people also prefer to answer close-ended questions than open-ended questions for various reasons. The followings are a few examples of close-ended questions.
- How often do you shop online?
- How often do you pay for the subscription of a mobile app?
- How much are you ready to pay to buy a women’s health magazine?
The answer to the above questions would be in numerical form, which can be used to derive meaningful conclusions.
6. Numerical Outcome
The outcome of quantitative research is always in numerical form. For example, the result of research can be represented in percentage, range of numbers.
A numerical output is easy to read and understand, and it is easy to deduce a conclusion from the numerical outcome than a detailed result.
7. Generalization of Outcome

The outcome of quantitative research can be generalised easily for the whole population. The reason behind this is that quantitative research is conducted on a large sample of the population.
A decision can be taken for the entire population based on the outcome of the sample population.
8. Prior study
The outcome of quantitative research can be used for a previous study of another research. Many scholars and researchers study and analyze the outcome of previous research to establish their research hypothesis or research problem.
The results of quantitative research are more reliable than qualitative research and can be used easily to deduce conclusions.
Here is a video by Marketing91 on Quantitative Research.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Market research
Related posts:
- Quantitative Market Research
- 11 Types Of Quantitative Research options that exist for Market Researchers
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research: What is the Difference?
- Importance of Quantitative Research
- What is Research Design? Type of Research Designs
- How to Write Research Proposal? Research Proposal Format
- 7 Key Differences between Research Method and Research Methodology
- Qualitative Research: Meaning, and Features of Qualitative Research
- Research Ethics – Importance and Principles of Ethics in Research
- 11 Characteristics of Qualitative Research
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Relate the characteristics of quantitative research to present time.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
Cross-Scale Quantitative and Qualitative Study of Grotto Sandstone Under Salt Weathering
- Original Paper
- Published: 25 August 2024
Cite this article

- Sicheng Lin 1 ,
- Luqi Wang 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 ,
- Wengang Zhang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6051-1388 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 ,
- Shuo Wang 1 ,
- Kaiqiang Zhang 1 ,
- Siwei Jiang 2 ,
- Huili Chen 2 ,
- Gang Zhao 2 &
- Xuemei Feng 2
Grottoes encounter significant challenges, such as weathering and water erosion, seriously threatening their preservation. Current laboratory research on grotto deterioration predominantly centers on characterizing the deterioration process, making it challenging to conduct cross-scale quantitative analysis of the intricate rock evolution process. This study examines sandstone from Baoding Mountain in Dazu and employs a cross-scale experimental approach to conduct dry–wet cycle tests on salt weathering. By integrating particle flow numerical simulation and inorganic salt deliquescence theory, the study elucidates the mechanism of aging degradation of sandstone caused by various salt solutions. The results indicate that the hierarchical order of the influence of salt solution types on rock degradation, ranked from highest to lowest, is as follows: sodium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, and sodium carbonate. The sandstone samples exhibited significant damage after 7 and 18 cycles of medium and high-concentration sodium sulfate solutions, respectively. In contrast, the strength of sandstone samples decreased by only 5.3% on average after 20 cycles of medium and low-concentration sodium carbonate solution. Subsequently, particle flow was analyzed numerically using the variable stiffness theory. The influence of salt solution on sandstone’s strength, deformation characteristics, internal pores, and fracture development can be quantitatively evaluated by examining five core mesoscopic parameters. Furthermore, the study highlights that the relative humidity required for the deliquescence of sodium sulfate and magnesium sulfate crystals exceeds 80%, making these crystals vulnerable to the repetitive dissolution–migration–precipitation processes in the climate conditions of Baoding Mountain, thereby accelerating the deterioration of rocks in the region.
A cross-scale quantitative and qualitative research method considering aging degradation.
A quantitative evaluation index system based on particle flow analysis is established.
Evaluated the dissolution-migration-precipitation process of inorganic salts in the grotto rock.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Data availability
The data supporting this study's findings are available upon reasonable request from the Corresponding author.
Abbreviations
The area of water sample collects
Axial force between balls
Tangential force between balls
Bending moment between balls
Geometric center of the ball
Geometric center between ball group
The gap between balls
Reference gap
Normal stiffness of the linear part
Shear stiffness of the linear part
Friction coefficient of the linear part
Normal stiffness of the parallel bond part
Shear stiffness of the parallel bond part
Tensile strength of the parallel bond part
Cohesion of the parallel bond part
Friction angle of the parallel bond part
Elastic modulus
Adjusted elastic modulus
A certain strain
Maximum strain of variable stiffness
Variable stiffness coefficient
Sample length
Sample width
Porosity of the ball
Particle friction angle of the ball
Particle density of the ball
Friction coefficient of the ball
Maximum particle size of the ball
Minimum particle size of the ball
Particle size ratio of the sample
Sample size ratio
The effective modulus of the linear part
The effective modulus of the bond part
The stiffness ratio of the linear part
The stiffness ratio of the bond part
Reference gap between balls
Tensile strength of the bonding material
Cohesion of the bonding material
The overall enthalpy change
The solubility of solutes in water
The enthalpy of dissolution
The heat of vaporization of water
An WB, Wang LG, Chen H (2020) Mechanical properties of weathered feldspar sandstone after experiencing dry-wet cycles. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2020:6268945. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6268945
Article Google Scholar
ASTM (2022) Standard test method for mineral characterization of equine surface materials by x-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. ASTM Int 15:07. https://doi.org/10.1520/F3419-22
Bai S, Li K, Li C et al (2024) Triaxial compression test of MICP sand column and simulation of failure process. Biogeotechnics 2024:10071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bgtech.2024.100071
Chen E, Zhang BJ, Zhao F (2020) Comprehensive analysis of polychrome grotto relics: a case study of the paint layers from Anyue, Sichuan. China Anal Lett 53(9):1455–1471. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2019.1709197
Article CAS Google Scholar
Hao BQ, Zhang CS, Wang CL et al (2022) Study on determination micro-parameters of rock PFC2D model. Coal Sci Techn 50(4):132–141. https://doi.org/10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2019-0906
Huang FM, Teng ZK, Guo ZZ et al (2023) Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction: Influences of different spatial resolutions, machine learning models and proportions of training and testing dataset. Rock Mech Bull 2(1):100028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rockmb.2023.100028
Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., 2019. PFC — Particle Flow Code, Ver.5.0 Minneapolis: Itasca.
Jia QQ, Chen WW, Tong YM et al (2022) Experimental study on capillary migration of water and salt in wall painting plaster—a case study at Mogao Grottoes. China Int J Archit Herit 16(5):705–716. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2020.1839598
Lan HX, Lu HT, Bao H et al (2023) Advances in degradation and instability mechanism of grotto temple rock mass. Earth Sci 48(4):1603–1633. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2022.307
Liu XR, Li DL, Zhang L et al (2016) Influence of wetting-drying cycles on mechanical properties and microstructure of shaly sandstone. Chin J Geotech Eng 38(7):1291–1300. https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201607017
Lu K, Li ZY, Niu R et al (2020) Using surface nuclear magnetic resonance and spontaneous potential to investigate the source of water seepage in the JinDeng Temple grottoes, China. J Cult Herit 45:142–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2020.05.006
Luo JZ, Cai YY, Yu J et al (2024) Development and applications of the quasi-dynamic triaxial apparatus for deep rocks. Deep Underground Sci Eng 3(1):70-90. https://doi.org/10.1002/dug2.12061
Ma J, Wu SC, Zhang XP et al (2020) Modeling acoustic emission in the Brazilian test using moment tensor inversion. Comput Geotech 123:103567 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103567
Peng C, Chen L, Tang MJ et al (2022) A database for deliquescence and efflorescence relative humidities of compounds with atmospheric relevance. Fundam Res 2(4):578–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fmre.2021.11.021
Pohl C (2017) Use of Ion Chromatography for Monitoring Ionic Contaminants in Water. Chemistry and Water. Elsevier, pp 353–391
Chapter Google Scholar
Potyondy DO, Cundall PA (2004) A bonded-particle model for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min 41(8):1329–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011
Qin Y, Wang YH, Li LL et al (2016) Experimental weathering of weak sandstone without direct water participation by using sandstone from the Yungang Grottoes in Datong. China Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(11):4473–4478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1003-3
Scrivano S, Gaggero L, Gisbert AJ (2018) Micro-porosity and minero-petrographic features influences on decay: experimental data from four dimension stones. Constr Build Mater 173:342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.041
Song C, Feng GR, Bai JW et al (2023) Progressive failure characteristics and water-induced deterioration mechanism of fissured sandstone under water–rock interaction. Theor Appl Fract Mec 128:104151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2023.104151
Steding S, Kempka T, Zirkler A et al (2021) Spatial and temporal evolution of leaching zones within potash seams reproduced by reactive transport simulations. Water 13(2):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13020168
Sun B, Ma FY, Zhang HY et al (2023) Carbon quantum dots as a tracer of water seepage sources and pathways in grottoes. Herit Sci 11(1):211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-023-01058-4
Tan QG, You LJ, Kang YL et al (2020) Changes in pore structures and porosity-permeability evolution of saline-lacustrine carbonate reservoir triggered by fresh water-rock reaction. J Hydrol 580:124375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124375
Wang JX (2023) Visualizing water seepage dynamics in grotto relics via atom-based representative model. Herit Sci 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-022-00832-0
Wang YX, Hua PD (1998) The environment, composition, and protection of Dazu rock inscriptions. Environ Geol 33(4):295–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050249
Wang FR, Jiao DD, Liu P et al (2020) Experimental study on the effect of sulfate on glutenite weathering in Maijishan grottoes. Rock Soil Mech 41(7):2199–2206. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2019.1508
Wang LQ, Yin YP, Zhou CY et al (2020b) Damage evolution of hydraulically coupled Jianchuandong dangerous rock mass. Landslides 17(5):1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01350-5
Wang XD, Wang YW, Guo QL et al (2021) The history of rescuing reinforcement and the preliminary study of preventive protection system for the cliff of Mogao Grottoes in Dunhuang. China Herit Sci 9(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-021-00537-w
Wang YY, Ran LY, Ma LY et al (2023) Nanoscale chemomechanical variations of montmorillonite induced by the specificity of counterions—an in situ XRD and AFM study. Appl Clay Sci 232:106760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106760
Wang LQ, Wang L, Zhang WG et al (2024) Time series prediction of reservoir bank landslide failure probability considering the spatial variability of soil properties. J Rock Mech Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.11.040
Wu HR, Shi JQ, Xiao Y et al (2023) Microbial mineralization: a promising approach for stone cultural relics restoration. Biogeotechnics 1(4):100053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bgtech.2023.100053
Yan SJ, Xie N, Liu JH et al (2022) Salt weathering of sandstone under dehydration and moisture absorption cycles: An experimental study on the sandstone from Dazu rock carvings. Earth Surf Proc Land 47(4):977–993. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.5298
Yang XJ, Wang JM, Zhu C et al (2019) Effect of water on long-term strength of column rocks based on creep behavior in Yungang Grottoes. China Geotech Geol Eng 37(1):173–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0601-0
Yang HQ, Chen CW, Zhao G et al (2024) Electrical resistivity analysis for the internal capillary water migration mechanism of porous stone. Acta Geophys 72(1):213–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-023-01081-w
Yao SS, Yan ZF, Ma Q et al (2022) Analysis of the annual hygrothermal environment in the Maijishan Grottoes by field measurements and numerical simulations. Build Environ 221:109229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109229
Yin YP, Wang LQ, Zhang WG et al (2022) Research on the collapse process of a thick-layer dangerous rock on the reservoir bank. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81(3):109 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02618-x
Zhang HX, Lu KP, Zhang WZ et al (2022) Quantification and acoustic emission characteristics of sandstone damage evolution under dry–wet cycles. J Build Eng 48:103996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.103996
Zhang HH, Li T, Tang S et al (2023) The influence of environmental humidity change on the stability of rock caves in Longyou Grottoes. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 140:105291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2023.105291
Zhang Q, Zhang XP (2019) The crack nature analysis of primary and secondary cracks: A numerical study based on moment tensors. Eng Fract Mech 210:70-73 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.05.006
Zhang Q, Zhang XP, Yang SQ (2021) A numerical study of acoustic emission characteristics of sandstone specimen containing a hole-like flaw under uniaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 242:107430 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107430
Zhang WG, Lin SC, Wang LQ et al (2024a) A novel creep contact model for rock and its implement in discrete element simulation. Comput Geotech 167:106054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.106054
Zhang Y, Zheng Y, Huang JZ (2024) Determination of water vapor transmission properties of sandstones in the Yungang Grottoes. Int J Archit Herit 18(3):357–369. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2022.2147878
Zhao GY, Dai B, Ma C (2012) Study of effects of microparameters on macroproperties for parallel bonded model. Chinese J Rock Mech and Eng 31(7):1491–1498
Google Scholar
Zhou C, Hu YJ, Xiao T et al (2023) Analytical model for reinforcement effect and load transfer of pre-stressed anchor cable with bore deviation. Constr Build Mater 379:131219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131219
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52308340), Chongqing Natural Science Foundation Innovation and Development Joint Fund (CSTB2022NSCQ-LZX0001), the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection (SKLGP2024K021), and the Sichuan Transportation Science and Technology Project (2018-ZL-01).
Chongqing Natural Science Foundation Innovation and Development Joint Fund, CSTB2022NSCQ-LZX0001, Wengang Zhang,Sichuan Transportation Science and Technology Project, 2018-ZL-01, Wengang Zhang,National Natural Science Foundation of China, 52308340, Luqi Wang, the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection, SKLGP2024K021, Luqi Wang.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, People’s Republic of China
Sicheng Lin, Luqi Wang, Wengang Zhang, Shuo Wang & Kaiqiang Zhang
Academy of Dazu Rock Carvings, Chongqing, 402360, People’s Republic of China
Yu Lei, Siwei Jiang, Huili Chen, Gang Zhao & Xuemei Feng
Key Laboratory of New Technology for Construction of Cities in Mountain Area, Chongqing University, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China
Luqi Wang & Wengang Zhang
National Joint Engineering Research Center of Geohazards Prevention in the Reservoir Areas, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, People’s Republic of China
Chongqing Field Scientific Observation Station for Landslide Hazards in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, People’s Republic of China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wengang Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Lin, S., Wang, L., Zhang, W. et al. Cross-Scale Quantitative and Qualitative Study of Grotto Sandstone Under Salt Weathering. Rock Mech Rock Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-04130-y
Download citation
Received : 30 April 2024
Accepted : 09 August 2024
Published : 25 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-024-04130-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Salt weathering
- Cross-Scale analysis
- Aging deterioration
- Dazu rock carvings
- Particle flow code
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Quantitative research is a type of research that utilizes numerical data to analyze and interpret phenomena. Three characteristics of quantitative research are: Objective: Quantitative research is focused on facts and figures rather than personal opinions or experiences. It aims to obtain information that is unbiased and free from subjectivity.
Large Sample SizeThe first and foremost characteristic of quantitative research is the large sample size to conduct research. Quantitative research is done on a large number of audiences to ensure reliability. The sample size used in quantitative research represents the whole target market. 2.Structured Research Methods. 3.Highly Reliable Outcome.
Quantitative research in sociology is rooted in positivism and employs statistical methods to study behavior patterns. It relies on numerical data to form objective, generalizable conclusions, contrasting with subjective qualitative approaches. Explanation: Characteristics of Quantitative Research in Sociology
What are the characteristics of quantitative research methods? This article answers this question with a list of 7 characteristics.
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research: Numerical data: Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
Before adopting quantitative research for your study, you need to understand what is quantitative research. Read this article to learn the quantitative research definition, key characteristics, types of quantitative research, methods and examples, and pros and cons of quantitative research.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research. To assure reliability, quantitative research is conducted on a large number of people. In quantitative research, the sample size represents the entire target market. Quantitative research is conducted using structural research methodologies such as questionnaires, polls, and surveys.
Data are in the form of numbers and statistics, often arranged in tables, charts, figures, or other non-textual forms. 1. Identify the characteristics of quantitative research - 4696363
The characteristics of quantitative research contribute to methods that use statistics as the basis for making generalizations about something. These generalizations are constructed from data that is used to find patterns and averages and test causal relationships.
Quantitative--The results are based on larger sample sizes that are representative of the population. The research study can usually be replicated or repeated, given its high reliability. Qualitative--it contains 5 methods :-ethnography, narrative, phenomenological, grounded theory, and case study.
quantitative research:quantitative research is a type of research that relies on the methods of natural science, which produces numerical data and hard facts. its purpose is to establish cause-and-effect relationship between two variables using mathematical,computational and statistical methods.research is also known as empirical research because it can be measured accurately and accurately.
Write the characteristics of quantitative research the best describe the illustration. Answer: Its main characteristics are: The data is usually gathered using structured research instruments. The results are based on larger sample sizes that are representative of the population. The research study can usually be replicated or repeated, given ...
Characteristics of Quantitative Research. 1. Large Sample Size. The first and foremost characteristic of quantitative research is the large sample size to conduct research. Quantitative research is done on a large number of audiences to ensure reliability.
Quantitative research characteristics include the use of statistical analysis, reliance on quantitative data, and the aim to test hypotheses with quantifiable evidence, as opposed to exploring subjective experiences.
The main characteristics of quantitative research include its focus on objective measurement, the use of statistics for analysis, and the intention to establish patterns and generalize findings from a study population to a larger population.
Lesson 1 Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, And Kinds of Quanti - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
Major characteristic of quantitative research: - 26782014
characteristics on the other hand (i.e. independent). This study is based on data from a school personnel online survey that ran in Antwerp and Ghent, the two largest cities of Flanders (which is ...
Quantitative Research includes structured data collection methods, focusing on numerical data. It emphasizes objectivity, replicability, and the use of statistical techniques to analyze results.
Grottoes encounter significant challenges, such as weathering and water erosion, seriously threatening their preservation. Current laboratory research on grotto deterioration predominantly centers on characterizing the deterioration process, making it challenging to conduct cross-scale quantitative analysis of the intricate rock evolution process. This study examines sandstone from Baoding ...
Numerical data and close-ended responses are characteristics of quantitative research. Quantitative research involves collecting data that can be converted into numbers for analysis, such as through surveys with yes/no questions or Likert scales.