| | | Discuss the contribution of other researchers to improve reliability and validity. | Frequently Asked QuestionsWhat is reliability and validity in research. Reliability in research refers to the consistency and stability of measurements or findings. Validity relates to the accuracy and truthfulness of results, measuring what the study intends to. Both are crucial for trustworthy and credible research outcomes.  What is validity?Validity in research refers to the extent to which a study accurately measures what it intends to measure. It ensures that the results are truly representative of the phenomena under investigation. Without validity, research findings may be irrelevant, misleading, or incorrect, limiting their applicability and credibility. What is reliability?Reliability in research refers to the consistency and stability of measurements over time. If a study is reliable, repeating the experiment or test under the same conditions should produce similar results. Without reliability, findings become unpredictable and lack dependability, potentially undermining the study’s credibility and generalisability. What is reliability in psychology?In psychology, reliability refers to the consistency of a measurement tool or test. A reliable psychological assessment produces stable and consistent results across different times, situations, or raters. It ensures that an instrument’s scores are not due to random error, making the findings dependable and reproducible in similar conditions. What is test retest reliability?Test-retest reliability assesses the consistency of measurements taken by a test over time. It involves administering the same test to the same participants at two different points in time and comparing the results. A high correlation between the scores indicates that the test produces stable and consistent results over time. How to improve reliability of an experiment?- Standardise procedures and instructions.
- Use consistent and precise measurement tools.
- Train observers or raters to reduce subjective judgments.
- Increase sample size to reduce random errors.
- Conduct pilot studies to refine methods.
- Repeat measurements or use multiple methods.
- Address potential sources of variability.
What is the difference between reliability and validity?Reliability refers to the consistency and repeatability of measurements, ensuring results are stable over time. Validity indicates how well an instrument measures what it’s intended to measure, ensuring accuracy and relevance. While a test can be reliable without being valid, a valid test must inherently be reliable. Both are essential for credible research. Are interviews reliable and valid?Interviews can be both reliable and valid, but they are susceptible to biases. The reliability and validity depend on the design, structure, and execution of the interview. Structured interviews with standardised questions improve reliability. Validity is enhanced when questions accurately capture the intended construct and when interviewer biases are minimised. Are IQ tests valid and reliable?IQ tests are generally considered reliable, producing consistent scores over time. Their validity, however, is a subject of debate. While they effectively measure certain cognitive skills, whether they capture the entirety of “intelligence” or predict success in all life areas is contested. Cultural bias and over-reliance on tests are also concerns. Are questionnaires reliable and valid?Questionnaires can be both reliable and valid if well-designed. Reliability is achieved when they produce consistent results over time or across similar populations. Validity is ensured when questions accurately measure the intended construct. However, factors like poorly phrased questions, respondent bias, and lack of standardisation can compromise their reliability and validity. You May Also LikeAction research for my dissertation?, A brief overview of action research as a responsive, action-oriented, participative and reflective research technique. What are the different research strategies you can use in your dissertation? Here are some guidelines to help you choose a research strategy that would make your research more credible. Experimental research refers to the experiments conducted in the laboratory or under observation in controlled conditions. Here is all you need to know about experimental research. USEFUL LINKS LEARNING RESOURCES  COMPANY DETAILS  - First Online: 14 May 2021
Cite this chapter - Cecil R. Reynolds 4 ,
- Robert A. Altmann 5 &
- Daniel N. Allen 6
3306 Accesses 2 Citations Validity is a fundamental psychometric property of psychological tests. For any given test, the term validity refers to evidence that supports interpretation of test results as reflecting the psychological construct(s) the test was designed to measure. Validity is threatened when the test does not measure important aspects of the construct of interest, or when the test measures characteristics, content, or skills that are unrelated to the test construct. A test must produce reliable test scores to produce valid interpretations, but even highly reliable tests may produce invalid interpretations. This chapter considers these matters in depth, including various types of validity and validity evidence, sources of validity evidence, and integration of validity evidence across different sources to support a validity argument for the test. The chapter ends with a practical discussion of how validity evidence is reported in test manuals, using as an example the Reynolds Intellectual Assessment Scales, second edition. Validity refers to the degree to which evidence and theory support interpretations of test scores for the proposed uses of the test. Validity is, therefore, the most fundamental consideration in developing and evaluating tests. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Access this chapterSubscribe and save. - Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout Purchases are for personal use only Institutional subscriptions American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (2014). Standards for educational and psychological testing . Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association. Google Scholar American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (1999). Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association. American Psychological Association. (1954). Technical recommendations for psychological tests and diagnostic techniques. Psychological Bulletin, 51 (2 Pt. 2), 1–28. Article Google Scholar American Psychological Association. (1966). Standards for educational and psychological tests and manuals . Washington, DC: Author. American Psychological Association, American Educational Research Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (1974). Standards for educational and psychological testing . Washington, DC: Author. American Psychological Association, American Educational Research Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (1985). Standards for educational and psychological testing . Washington, DC: Author. Anastasi, A., & Urbina, S. (1997). Psychological testing (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Campbell, D. T., & Fiske, D. W. (1959). Convergent and discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod matrix. Psychological Bulletin, 56 (2), 546–553. Carroll, J. B. (1993). Human cognitive abilities: A survey of factor-analytic studies . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. Book Google Scholar Cattell, R. (1966). Handbook of multivariate experimental psychology . Chicago, IL: Rand McNally. Chan, D., Schmitt, N., DeShon, R. P., Clause, C. S., & Delbridge, K. (1997). Reaction to cognitive ability tests: The relationship between race, test performance, face validity, and test-taking motivation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 82 , 300–310. Cronbach, L. J. (1990). Essentials of psychological testing (5th ed.). New York, NY: HarperCollins. Cronbach, L. J., & Gleser, G. C. (1965). Psychological tests and personnel decisions (2nd ed.). Champaign, IL: University of Illinois Press. Hunter, J. E., Schmidt, F. L., & Rauschenberger, L. (1984). Methodological, statistical, and ethical issues in the study of bias in psychological tests. In C. R. Reynolds & R. T. Brown (Eds.), Perspectives on bias in mental testing (pp. 41–100). New York, NY: Plenum Press. Chapter Google Scholar Lawshe, C. H. (1975). A quantitative approach to content validity. Personnel Psychology, 28 , 563–575. Lee, D., Reynolds, C., & Willson, V. (2003). Standardized test administration: Why bother? Journal of Forensic Neuropsychology, 3 (3), 55–81. Linn, R. L., & Gronlund, N. E. (2000). Measurement and assessment in teaching (8th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. McFall, R. M., & Treat, T. T. (1999). Quantifying the information value of clinical assessment with signal detection theory. Annual Review of Psychology, 50 , 215–241. Messick, S. (1989). Validity. In R. L. Linn (Ed.), Educational measurement (3rd ed., pp. 13–103). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill Prentice Hall. Messick, S. (1994). The interplay of evidence and consequences in the validation of performance assessments. Educational Researcher, 23 , 13–23. Meyer, G. J., Finn, S. E., Eyde, L. D., Kay, G. G., Moreland, K. L., Dies, R. R., … Reed, G. M. (2001). Psychological testing and psychological assessment: A review of evidence and issues. American Psychologist, 56 , 128–165. Pearson. (2009). WIAT-III: Examiners manual . San Antonio, TX: Author. Popham, W. J. (2000). Modern educational measurement: Practical guidelines for educational leaders . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon. Reynolds, C. R. (1998). Fundamentals of measurement and assessment in psychology. In A. Bellack & M. Hersen (Eds.), Comprehensive clinical psychology (pp. 33–55). New York, NY: Elsevier. Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2003). Reynolds Intellectual Assessment Scales . Lutz, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources. Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2015). Reynolds Intellectual Assessment Scales (2nd ed.). Lutz, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources. Schmidt, F. L., & Hunter, J. (1998). The validity and utility of selection methods in personnel psychology: Practical and theoretical implications of 85 years of research findings. Psychological Bulletin, 124 (2), 262–274. Sireci, S. G. (1998). Gathering and analyzing content validity data. Educational Assessment, 5 , 299–321. Wechsler, D. (2014). Wechsler intelligence scale for children (5th ed.). Bloomington, MN: NCS Pearson. Recommended ReadingAmerican Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, & National Council on Measurement in Education. (1999). Standards for educational and psychological testing . Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association. Chapter 1 is a must read for those wanting to gain a thorough understanding of validity. Cronbach, L. J., & Gleser, G. C. (1965). Psychological tests and personnel decisions (2nd ed.). Champaign, IL: University of Illinois Press. A classic, particularly with regard to validity evidence based on relations to external variables! Gorsuch, R. L. (1983). Factor analysis (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. A classic for those really interested in understanding factor analysis. Hunter, J. E., Schmidt, F. L., & Rauschenberger, J. (1984). Methodological, statistical, and ethical issues in the study of bias in psychological tests. In C. R. Reynolds & R. T. Brown (Eds.), Perspectives on bias in mental testing (pp. 41–100). New York, NY: Plenum. Lee, D., Reynolds, C. R., & Willson, V. L. (2003). Standardized test administration: Why bother? Journal of Forensic Neuropsychology, 3 , 55–81. McFall, R. M., & Treat, T. T. (1999). Quantifying the information value of clinical assessments with signal detection theory. Annual Review of Psychology, 50 , 215–241. Messick, S. (1989). Validity. In R. L. Linn (Ed.), Educational measurement (3rd ed., pp. 13–103). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill/Prentice Hall. A little technical at times, but very influential. Schmidt, F. L., & Hunter, J. E. (1998). The validity and utility of selection methods in personnel psychology: Practical and theoretical implications of 85 years of research findings. Psychological Bulletin, 124 , 262–274. A must read on personnel selection! Sireci, S. G. (1998). Gathering and analyzing content validity data. Educational Assessment, 5 , 299–321. This article provides a good review of approaches to collecting validity evidence based on test content, including some of the newer quantitative approaches. Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidel, L. S. (1996). Using multivariate statistics (3rd ed.). New York, NY: HarperCollins. A great chapter on factor analysis that is less technical than Gorsuch (1993). Download references Author informationAuthors and affiliations. Austin, TX, USA Cecil R. Reynolds Minneapolis, MN, USA Robert A. Altmann Department of Psychology, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV, USA Daniel N. Allen You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar 5.1 Electronic Supplementary MaterialSupplementary file 5.1. (PPTX 258 kb) Rights and permissionsReprints and permissions Copyright information© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG About this chapterReynolds, C.R., Altmann, R.A., Allen, D.N. (2021). Validity. In: Mastering Modern Psychological Testing. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59455-8_5 Download citationDOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59455-8_5 Published : 14 May 2021 Publisher Name : Springer, Cham Print ISBN : 978-3-030-59454-1 Online ISBN : 978-3-030-59455-8 eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0) Share this chapterAnyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative Policies and ethics - Find a journal
- Track your research
Content Validity in Research: Definition & ExamplesCharlotte Nickerson Research Assistant at Harvard University Undergraduate at Harvard University Charlotte Nickerson is a student at Harvard University obsessed with the intersection of mental health, productivity, and design. Learn about our Editorial Process Saul McLeod, PhD Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology. Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc Associate Editor for Simply Psychology BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors. - Content validity is a type of criterion validity that demonstrates how well a measure covers the construct it is meant to represent.
- It is important for researchers to establish content validity in order to ensure that their study is measuring what it intends to measure.
- There are several ways to establish content validity, including expert opinion, focus groups , and surveys.
 What Is Content Validity?Content Validity is the degree to which elements of an assessment instrument are relevant to a representative of the targeted construct for a particular assessment purpose. This encompasses aspects such as the appropriateness of the items, tasks, or questions to the specific domain being measured and whether the assessment instrument covers a broad enough range of content to enable conclusions to be drawn about the targeted construct (Rossiter, 2008). One example of an assessment with high content validity is the Iowa Test of Basic Skills (ITBS). The ITBS is a standardized test that has been used since 1935 to assess the academic achievement of students in grades 3-8. The test covers a wide range of academic skills, including reading, math, language arts, and social studies. The items on the test are carefully developed and reviewed by a panel of experts to ensure that they are fair and representative of the skills being tested. As a result, the ITBS has high content validity and is widely used by schools and districts to measure student achievement. Meanwhile, most driving tests have low content validity. The questions on the test are often not representative of the skills needed to drive safely. For example, many driving permit tests do not include questions about how to parallel park or how to change lanes. Meanwhile, driving license tests often do not test drivers in non-ideal conditions, such as rain or snow. As a result, these tests do not provide an accurate measure of a person’s ability to drive safely. The higher the content validity of an assessment, the more accurately it can measure what it is intended to measure — the target construct (Rossiter, 2008). Why is content validity important in research?Content validity is important in research as it provides confidence that an instrument is measuring what it is supposed to be measuring. This is particularly relevant when developing new measures or adapting existing ones for use with different populations. It also has implications for the interpretation of results, as findings can only be accurately applied to groups for which the content validity of the measure has been established. Step-by-step guide: How to measure content validity?Haynes et al. (1995) emphasized the importance of content validity and gave an overview of ways to assess it. One of the first ways of measuring content validity was the Delphi method, which was invented by NASA in 1940 as a way of systematically creating technical predictions. The method involves a group of experts who make predictions about the future and then reach a consensus about those predictions. Today, the Delphi method is most commonly used in medicine. In a content validity study using the Delphi method, a panel of experts is asked to rate the items on an assessment instrument on a scale. The expert panel also has the opportunity to add comments about the items. After all ratings have been collected, the average item rating is calculated. In the second round, the experts receive summarized results of the first round and are able to make further comments and revise their first-round answers. This back-and-forth continues until some homogeneity criterion — similarity between the results of researchers — is achieved (Koller et al., 2017). Lawshie (1975) and Lynn (1986) created numerical methods to assess content validity. Both of these methods require the development of a content validity index (CVI). A content validity index is a statistical measure of the degree to which an assessment instrument covers the content domain of interest. There are two steps in calculating a content validity index: - Determining the number of items that should be included in the assessment instrument;
- Determining the percentage of items that actually are included in the assessment instrument.
The first step, determining the number of items that should be included in an assessment instrument, can be done using one of two approaches: item sampling or expert consensus. Item sampling involves selecting a sample of items from a larger set of items that cover the content domain. The number of items in the sample is then used to estimate the total number of items needed to cover the content domain. This approach has the advantage of being quick and easy, but it can be biased if the sample of items is not representative of the larger set (Koller et al., 2017). The second approach, expert consensus, involves asking a group of experts how many items should be included in an assessment instrument to adequately cover the content domain. This approach has the advantage of being more objective, but it can be time-consuming and expensive. Experts are able to assign these items to dimensions of the construct that they intend to measure and assign relevance values to decide whether an item is a strong measure of the construct. Although various attempts to numerize the process of measuring content validity exist, there is no systematic procedure that could be used as a general guideline for the evaluation of content validity (Newman et al., 2013). When is content validity used?Education assessment. In the context of educational assessment, validity is the extent to which an assessment instrument accurately measures what it is intended to measure. Validity concerns anyone who is making inferences and decisions about a learner based on data. This can have deep implications for students’ education and future. For instance, a test that poorly measures students’ abilities can lead to placement in a future course that is unsuitable for the student and, ultimately, to the student’s failure (Obilor, 2022). There are a number of factors that specifically affect the validity of assessments given to students, such as (Obilor, 2018): - Unclear Direction: If directions do not clearly indicate to the respondent how to respond to the tool’s items, the validity of the tool is reduced.
- Vocabulary: If the vocabulary of the respondent is poor, and he does not understand the items, the validity of the instrument is affected.
- Poorly Constructed Test Items: If items are constructed in such a way that they have different meanings for different respondents, validity is affected.
- Difficulty Level of Items: In an achievement test, too easy or too difficult test items would not discriminate among students, thereby lowering the validity of the test.
- Influence of Extraneous Factors: Extraneous factors like the style of expression, legibility, mechanics of grammar (spelling, punctuation), handwriting, and length of the tool, amongst others, influence the validity of a tool.
- Inappropriate Time Limit: In a speed test, if enough time limit is given, the result will be invalidated as a measure of speed. In a power test, an inappropriate time limit will lower the validity of the test.
There are a few reasons why interviews may lack content validity . First, interviewers may ask different questions or place different emphases on certain topics across different candidates. This can make it difficult to compare candidates on a level playing field. Second, interviewers may have their own personal biases that come into play when making judgments about candidates. Finally, the interview format itself may be flawed. For example, many companies ask potential programmers to complete brain teasers — such as calculating the number of plumbers in Chicago or coding tasks that rely heavily on theoretical knowledge of data structures — even if this knowledge would be used rarely or never on the job. QuestionnairesQuestionnaires rely on the respondents’ ability to accurately recall information and report it honestly. Additionally, the way in which questions are worded can influence responses. To increase content validity when designing a questionnaire, careful consideration must be given to the types of questions that will be asked. Open-ended questions are typically less biased than closed-ended questions, but they can be more difficult to analyze. It is also important to avoid leading or loaded questions that might influence respondents’ answers in a particular direction. The wording of questions should be clear and concise to avoid confusion (Koller et al., 2017). Is content validity internal or external?Most experts agree that content validity is primarily an internal issue. This means that the concepts and items included in a test should be based on a thorough analysis of the specific content area being measured. The items should also be representative of the range of difficulty levels within that content area. External factors, such as the opinions of experts or the general public, can influence content validity, but they are not necessarily the primary determinant. In some cases, such as when developing a test for licensure or certification, external stakeholders may have a strong say in what is included in the test (Koller et al., 2017). How can content validity be improved?There are a few ways to increase content validity. One is to create items that are more representative of the targeted construct. Another is to increase the number of items on the assessment so that it covers a greater range of content. Finally, experts can review the items on the assessment to ensure that they are fair and representative of the skills being tested (Koller et al., 2017). How do you test the content validity of a questionnaire?There are a few ways to test the content validity of a questionnaire. One way is to ask experts in the field to review the questions and provide feedback on whether or not they believe the questions are relevant and cover all important topics. Another way is to administer the questionnaire to a small group of people and then analyze the results to see if there are any patterns or themes emerging from the responses. Finally, it is also possible to use statistical methods to test for content validity, although this approach is more complex and usually requires access to specialized software (Koller et al., 2017). How can you tell if an instrument is content-valid?There are a few ways to tell if an instrument is content-valid. The first of these involves looking at two subsets of content validity: face and construct validity. Face validity is a measure of whether or not the items on the test appear to measure what they claim to measure. This is highly subjective but convenient to assess. Another way is to look at the construct validity, which is whether or not the items on the test measure what they are supposed to measure. Finally, you can also look at the criterion-related validity, which is whether or not the items on the test predict future performance. What is the difference between content and criterion validity?Content validity is a measure of how well a test covers the content it is supposed to cover. Criterion validity, meanwhile, is an index of how well a test correlates with an established standard of comparison or a criterion. For example, if a measure of criminal behavior is criterion valid, then it should be possible to use it to predict whether an individual will be arrested in the future for a criminal violation, is currently breaking the law, and has a previous criminal record (American Psychological Association). Are content validity and construct validity the same?Content validity is not the same as construct validity. Content validity is a method of assessing the degree to which a measure covers the range of content that it purports to measure. In contrast, construct validity is a method of assessing the degree to which a measure reflects the underlying construct that it purports to measure. It is important to note that content validity and construct validity are not mutually exclusive; a measure can be both valid and invalid with respect to content and construct. However, content validity is a necessary but not sufficient condition for construct validity. That is, a measure cannot be construct valid if it does not first have content validity (Koller et al., 2017). For example, an academic achievement test in math may have content validity if it contains questions from all areas of math a student is expected to have learned before the test, but it may not have construct validity if it does not somehow relate to tests of similar and different constructs. How many experts are needed for content validity?There is no definitive answer to this question as it depends on a number of factors, including the nature of the instrument being validated and the purpose of the validation exercise. However, in general, a minimum of three experts should be used in order to ensure that the content validity of an instrument is adequately established (Koller et al., 2017). American Psychological Association. (n.D.). Content Validity. American Psychological Association Dictionary. Haynes, S. N., Richard, D., & Kubany, E. S. (1995). Content validity in psychological assessment: A functional approach to concepts and methods. Psychological assessment , 7 (3), 238. Koller, I., Levenson, M. R., & Glück, J. (2017). What do you think you are measuring? A mixed-methods procedure for assessing the content validity of test items and theory-based scaling. Frontiers in psychology , 8 , 126. Lawshe, C. H. (1975). A quantitative approach to content validity. Personnel psychology , 28 (4), 563-575. Lynn, M. R. (1986). Determination and quantification of content validity. Nursing research . Obilor, E. I. (2018). Fundamentals of research methods and Statistics in Education and Social Sciences. Port Harcourt: SABCOS Printers & Publishers. OBILOR, E. I. P., & MIWARI, G. U. P. (2022). Content Validity in Educational Assessment. Newman, Isadore, Janine Lim, and Fernanda Pineda. “Content validity using a mixed methods approach: Its application and development through the use of a table of specifications methodology.” Journal of Mixed Methods Research 7.3 (2013): 243-260. Rossiter, J. R. (2008). Content validity of measures of abstract constructs in management and organizational research. British Journal of Management , 19 (4), 380-388.  InformationInitiativesYou are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader. All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess . Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers. Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal. Original Submission Date Received: . - Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia
 Article Menu - Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website. Please let us know what you think of our products and services. Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI. JSmol ViewerImbalance between employees and the organisational context: a catalyst for workplace bullying behaviours in both targets and perpetrators.  1. Introduction1.1. theoretical approaches—the three-way model, 1.2. theoretical approaches—job demands and resources model, 1.3. theoretical approaches combined—the dimensions of imbalances created by organisations triggering wb, 1.3.1. organisational focus, 1.3.2. organisational atmosphere, 1.3.3. organisational hierarchy, 1.3.4. research hypotheses, 2.1. participants, 2.2. measures, 2.3. procedure, 2.4. data analysis, 3.1. descriptive statistics, 3.2. correspondence analysis on hypothesis, 3.3. correspondence analysis of wb experiences, 4. discussion, 4.1. limitations and future research, 4.2. theoretical and practical implications, 5. conclusions, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest. - Ashforth, B.E.; Gioia, D.A.; Robinson, S.L.; Treviño, L.K. Introduction to special topic forum: Reviewing organisational corruption. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2008 , 33 , 670–684. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kessler, S.R.; Spector, P.E.; Chang, C.-H.; Parr, A.D. Organisational violence and aggression: Development of the three-factor Violence Climate Survey. Work Stress 2008 , 22 , 108–124. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Skogstad, A.; Torsheim, T.; Einarsen, S.; Hauge, L.J. Testing the work environment hypothesis of bullying on a group level of analysis: Psychosocial factors as precursors of observed workplace bullying. Appl. Psychol. Int. Rev. 2011 , 60 , 475–495. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Einarsen, S.; Hoel, H.; Zapf, D.; Cooper, C.L. (Eds.) Workplace Bullying: Developments in Theory, Research and Practice ; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Salin, D. Organisational responses to workplace harassment. Pers. Rev. 2009 , 38 , 26–44. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Samnani, A.; Singh, P. 20 Years of workplace bullying research: A review of the antecedents and consequences of bullying in the workplace. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2012 , 17 , 581–589. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tuckey, M.; Dollard, M.; Hosking, P.; Winefield, A. Workplace bullying: The role of psychosocial work environment factors. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2009 , 16 , 215–232. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Demerouti, E.; Bakker, A.B.; Nachreiner, F.; Schaufeli, W.B. The job demands–resources model of burnout. J. Appl. Psychol. 2001 , 86 , 499–512. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Baillien, E.; Rodriguez-Muñoz, A.; Van den Broeck, A.; De Witte, H. Do demands and resources affect victim’s and perpetrators’ reports of workplace bullying? A two-wave cross-lagged study. Work Stress 2011 , 25 , 128–146. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Balducci, C.; Cecchin, M.; Fraccaroli, F. The impact of role stressors on workplace bullying in both victims and perpetrators, controlling for personal vulnerability factors: A longitudinal analysis. Work Stress 2012 , 26 , 195–212. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Özer, G.; Escartín, J. The making and breaking of workplace bullying perpetration: A systematic review on the antecedents, moderators, mediators, outcomes of perpetration and suggestions for organisations. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2023 , 69 , 101823. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bakker, A.B.; Demerouti, E. The Job Demands-Resources model: State of the art. J. Manag. Psychol. 2007 , 22 , 309–328. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart, P.M.; Cooper, C.L. Occupational stress: Toward a more integrated framework. In Handbook of Industrial, Work and Organizational Psychology ; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 93–114. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baillien, E.; Neyens, I.; De Witte, H.; De Cuyper, N. A qualitative study on the development of workplace bullying: Towards a three-way model. J. Community Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2009 , 19 , 1–16. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Berkowitz, L. The frustration-aggression hypothesis: An examination and reformulation. Psychol. Bull. 1989 , 106 , 59–73. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Felson, R.B.; Tedeschi, J.T. Aggression and Violence: Social Interactionists’ Perspectives ; American Psychological Association: Worcester, MA, USA, 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Salanova, M.; Agut, S.; Peiró, J.M. Linking organisational resources and work engagement to employee performance and customer loyalty: The mediating role of service climate. J. Appl. Psychol. 2005 , 90 , 1217–1227. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Demerouti, E.; Bakker, A.B. The Job Demands–Resources model: Challenges for future research. SA J. Ind. Psychol. 2011 , 37 , 974–983. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Bakker, A.B.; Van Rhenen, W. How changes in job demands and resources predict burnout, work engagement, and sickness absenteeism. J. Organ. Behav. 2009 , 30 , 893–917. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xanthopoulou, D.; Bakker, A.B.; Demerouti, E.; Schaufeli, W.B. The role of personal resources in the job demands-resources model. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2007 , 14 , 121–141. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behavior ; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bakker, A.B.; Van Veldhoven, M.J.P.M.; Xanthopoulou, D. Beyond the Demand-Control model: Thriving on high job demands and resources. J. Pers. Psychol. 2010 , 9 , 3–16. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bruursema, K.; Kessler, S.R.; Spector, P.E. Bored employees misbehaving: The relationship between boredom and counterproductive work behavior. Work Stress 2011 , 5 , 93–107. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Karasek, R.A. Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Adm. Sci. Q. 1979 , 24 , 285–308. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Meijman, T.F.; Mulder, G. Psychological aspects of workload. In Handbook of Work and Organisational Psychology , 2nd ed.; Drenth, P.J., Thierry, H., de Wolff, C.J., Eds.; Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 5–33. [ Google Scholar ]
- Van den Broeck, A.; Baillien, E.; De Witte, H. Workplace bullying: A perspective from the job demands-resources model. Scand. J. Ind. Psychol. 2011 , 37 , 1–12. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ceja, L.; Escartín, J.; Rodríguez-Carballeira, A. Organisational contexts that foster positive behaviour and well-being: A comparison between family-owned firms and non-family businesses. Rev. De Psicol. Soc. 2012 , 27 , 69–84. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Parzefall, M.R.; Salin, D. Perceptions of and reactions to workplace bullying: A social exchange perspective. Hum. Relat. 2010 , 63 , 761–780. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- VanOudenhoven, J.P. Do organisations reflect national cultures? A 10-nation study. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 2001 , 25 , 89–107. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gioia, D.A.; Schultz, M.; Corley, K.G. Organisational identity, image, and adaptative instability. Acad. Manag. J. 2000 , 25 , 63–81. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stiles, D.R. Pictorial representation. In Essential Guide to Qualitative Methods in Organizational Research ; Cassell, C., Symon, G., Eds.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 127–139. [ Google Scholar ]
- Escartín, J.; Sora, B.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, A.; Rodríguez-Carballeira, A. Adaptación y validación de la versión Española de la escala de conductas negativas en el trabajo realizadas por acosadores: NAQ-Perpetrators. Rev. Psicol. Trab. Organ. 2012 , 28 , 157–170. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Escartín, J.; Rodríguez-Carballeira, A.; Gómez-Benito, J.; Zapf, D. Development and validation of the workplace bullying scale “EAPA-T. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2010 , 10 , 519–539. [ Google Scholar ]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977 , 33 , 159–174. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Leymann, H. The content and development of mobbing at work. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 1996 , 5 , 165–184. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- van de Velden, M.; van den Heuvel, W.; Galy, H.; Groenen, P.J. Retrieving a contingency table from a correspondence analysis solution. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020 , 283 , 541–548. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fernández-del-Río, E.; Ramos-Villagrasa, P.J.; Escartín, J. The incremental effect of Dark personality over the Big Five in workplace bullying: Evidence from perpetrators and targets. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2021 , 168 , 110291. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- George, D.; Mallery, P. IBM SPSS Statistics 26 Step by Step. In Routledge eBooks ; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2019. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Rayner, C.; Cooper, C.L. The black hole in “bullying at work research”. Int. J. Manag. Decis. Mak. 2003 , 4 , 47–64. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bakker, A.B.; Demerouti, E.; Sanz-Vergel, A. Job Demands–Resources Theory: Ten years later. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 2023 , 10 , 25–53. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Özer, G.; Griep, Y.; Escartín, J. The relationship between organisational environment and perpetrators’ physical and psychological State: A three-wave of longitudinal study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022 , 19 , 3699. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jenkins, M.F.; Zapf, D.; Winefield, H.; Sarris, A. bullying allegations from the accused bully’s perspective. Br. J. Manag. 2011 , 23 , 489–501. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Vranjes, I.; Elst, T.V.; Griep, Y.; De Witte, H.; Baillien, E. What goes around comes around: How perpetrators of workplace bullying become targets themselves. Group Organ. Manag. 2022 , 48 , 1135–1172. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- O’Neill, R.E.; Vandenberghe, C.; Stroink, M.L. Implicit reciprocity norms between employees and their employers: A psychological contract perspective. J. Organ. Behav. 2009 , 30 , 203–221. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience ; Harper & Row: Manhattan, NY, USA, 1990. [ Google Scholar ]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. Finding Flow: The Psychology of Engagement with Everyday Life ; Basic Books; Hachette: London, UK, 1997. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glambek, M.; Skogstad, A.; Einarsen, S.V. Do the bullies survive? A five-year, three-wave prospective study of indicators of expulsion in working life among perpetrators of workplace bullying. Ind. Health 1997 , 54 , 68–73. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Özer, G.; Griep, Y.; Escartín, J. A matter of health? A 24-week daily and weekly diary study on workplace bullying perpetrators’ psychological and physical health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023 , 20 , 479. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Salin, D.; Hoel, H. Organisational causes of workplace bullying. In Workplace Bullying: Development in Theory, Research and Practice ; Einarsen, S., Hoel, H., Zapf, D., Cooper, C., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Salin, D. Ways of explaining workplace bullying: A review of enabling, motivating and precipitating structures and processes in the work environment. Hum. Relat. 2003 , 56 , 1213–1232. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Escartín, J.; Dollard, M.; Zapf, D.; Kozlowski, S. Multilevel emotional exhaustion: Psychosocial safety climate and workplace bullying as higher level contextual and individual explanatory factors. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 2021 , 30 , 742–752. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure | Baseline Characteristics | n | % | | n | % |
|---|
| Gender | | | Supervisor | | | | Males | 404 | 38.7 | Not a supervisor | 872 | 83.5 | | Females | 640 | 61.3 | Supervisor | 172 | 16.5 | | Sector | | | Civil Status | | | | Education | 257 | 24.6 | Single | 431 | 41.3 | | Industry | 96 | 9.2 | Married/Living together | 523 | 50.1 | | Trade | 151 | 14.5 | Separated/divorced | 80 | 7.7 | | Services | 540 | 51.7 | Widowed | 10 | 1.0 | | Education | | | Income | | | | No studies | 14 | 1.3 | Equal or less than €10k | 221 | 21.2 | | Basic | 123 | 11.8 | €10,001–€20,000 | 338 | 32.4 | | Secondary | 409 | 39.2 | €20,001–€30,000 | 303 | 29.0 | | Diploma | 211 | 20.2 | €30,001–€40,000 | 117 | 11.2 | | Undergraduate | 219 | 21.0 | €40,001–€50,000 | 32 | 3.1 | | Postgraduate | 68 | 6.5 | More than €50,000 | 33 | 3.2 | | Contract | | | | | | | No permanent contract | 304 | 29.1 | | | | | Permanent contract | 740 | 70.9 | | | | | Organisational Dimensions | Continuum | Example Adjectives |
|---|
| 1. Organisational Focus | Task-Focused | Exploitative, obsolete, statistical | | | Balanced Focus | Organised, participative, supportive | | | Employee-Focused | Unstructured, disorganised, chaotic | | 2. Organisational Atmosphere | Hostile or Negative | Controlling, manipulative, inhumane | | | Balanced or Positive | Amiable, respectful, empathetic | | | Too Informal | Overwhelmed, unmotivated, suffocating | | 3. Organisational Hierarchy | Too Much | Authoritarian, inefficient, dictatorial | | | Balanced Hierarchy | Hierarchical, cheerful, coherent | | | Too Little | Uncoordinated, little prepared, unclear | | Variables | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|
| 1 | Age | 35.43 | 10.91 | - | | | | | | 2 | Gender | 1.61 | 0.49 | 0.06 | - | | | | | 3 | Supervisor | 1.16 | 0.37 | 0.10 ** | −0.08 * | - | | | | 4 | WB Target Score | 0.24 | 0.41 | −0.07 * | −0.04 | 0.01 | - | | | 5 | WB Perpetration Score | 0.22 | 0.39 | −0.06 | −0.08 * | −0.00 | 0.52 ** | - | | | WB Perpetration Level | |
|---|
| WB Target Level | No WBP | Low WBP | Medium WBP | High WBP | Total | No WBP | Low WBP | Medium WBP | High WBP | Total |
|---|
| No WBT | 295 | 131 | 7 | 12 | 445 | 28.3% | 12.5% | 0.7% | 1.1% | 42.6% | | Low WBT | 173 | 228 | 19 | 15 | 435 | 16.6% | 21.8% | 1.8% | 1.4% | 41.7% | | Medium WBT | 12 | 43 | 17 | 4 | 76 | 1.1% | 4.1% | 1.6% | 0.4% | 7.3% | | High WBT | 26 | 28 | 21 | 13 | 88 | 2.5% | 2.7% | 2.0% | 1.2% | 8.4% | | Total | 506 | 430 | 64 | 44 | 1044 | 48.5% | 41.2% | 6.1% | 4.2% | 100.0% | | Categories | N | % |
|---|
| Target not a perpetrator | 211 | 20.2 | | Target perpetrator | 388 | 37.2 | | Perpetrator not a target | 150 | 14.4 | | Uninvolved | 295 | 28.3 | | Total | 1044 | 100.0 | | WB Categories | Task
Focus | Balanced
Focus | Employee
Focus | Total | Task
Focus | Balanced
Focus | Employee
Focus | Total |
|---|
| Target not a perpetrator | 55 | 66 | 29 | 150 | 7.3% | 8.8% | 3.9% | 20.0% | | Target perpetrator | 112 | 107 | 75 | 294 | 15.0% | 14.3% | 10.0% | 39.3% | | Perpetrator not a target | 30 | 54 | 17 | 101 | 4.0% | 7.2% | 2.3% | 13.5% | | Uninvolved | 52 | 125 | 27 | 204 | 6.9% | 16.7% | 3.6% | 27.2% | | Total | 249 | 352 | 148 | 749 | 33.2% | 47.0% | 19.8% | 100.0% | | WB Categories | Negative A | Balanced
A | Too Informal A | Total | Negative A | Balanced
A | Too Informal A | Total |
|---|
| Target not a perpetrator | 40 | 78 | 28 | 146 | 5.5% | 10.6% | 3.8% | 19.9% | | Target perpetrator | 98 | 132 | 60 | 290 | 13.4% | 18.0% | 8.2% | 39.6% | | Perpetrator not a target | 17 | 65 | 16 | 98 | 2.3% | 8.9% | 2.2% | 13.4% | | Uninvolved | 24 | 153 | 22 | 199 | 3.3% | 20.9% | 3.0% | 27.1% | | Total | 179 | 428 | 126 | 733 | 24.4% | 58.4% | 17.2% | 100.0% | | WB Categories | Too Little H | Balanced H | Too High H | Total | Too Little H | Balanced H | Too High H | Total |
|---|
| Target not a perpetrator | 25 | 79 | 44 | 148 | 3.4% | 10.8% | 6.0% | 20.2% | | Target perpetrator | 68 | 124 | 96 | 288 | 9.3% | 16.9% | 13.1% | 39.3% | | Perpetrator not a target | 16 | 61 | 22 | 99 | 2.2% | 8.3% | 3.0% | 13.5% | | Uninvolved | 17 | 143 | 38 | 198 | 2.3% | 19.5% | 5.2% | 27.0% | | Total | 126 | 407 | 200 | 733 | 17.2% | 55.5% | 27% | 100.0% | | The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and CiteÖzer, G.; Escartín, J. Imbalance between Employees and the Organisational Context: A Catalyst for Workplace Bullying Behaviours in Both Targets and Perpetrators. Behav. Sci. 2024 , 14 , 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090751 Özer G, Escartín J. Imbalance between Employees and the Organisational Context: A Catalyst for Workplace Bullying Behaviours in Both Targets and Perpetrators. Behavioral Sciences . 2024; 14(9):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090751 Özer, Gülüm, and Jordi Escartín. 2024. "Imbalance between Employees and the Organisational Context: A Catalyst for Workplace Bullying Behaviours in Both Targets and Perpetrators" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 9: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090751 Article MetricsArticle access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.  Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals  An official website of the United States government The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site. The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely. - Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now . - Advanced Search
- Journal List
- CBE Life Sci Educ
- v.15(1); Spring 2016
Contemporary Test Validity in Theory and Practice: A Primer for Discipline-Based Education ResearchersTodd d. reeves. *Educational Technology, Research and Assessment, Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, IL 60115 Gili Marbach-Ad† College of Computer, Mathematical and Natural Sciences, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742 This essay offers a contemporary social science perspective on test validity and the validation process. The instructional piece explores the concepts of test validity, the validation process, validity evidence, and key threats to validity. The essay also includes an in-depth example of a validity argument and validation approach for a test of student argument analysis. In addition to discipline-based education researchers, this essay should benefit practitioners (e.g., lab directors, faculty members) in the development, evaluation, and/or selection of instruments for their work assessing students or evaluating pedagogical innovations. Most discipline-based education researchers (DBERs) were formally trained in the methods of scientific disciplines such as biology, chemistry, and physics, rather than social science disciplines such as psychology and education. As a result, DBERs may have never taken specific courses in the social science research methodology—either quantitative or qualitative—on which their scholarship often relies so heavily. One particular aspect of (quantitative) social science research that differs markedly from disciplines such as biology and chemistry is the instrumentation used to quantify phenomena. In response, this Research Methods essay offers a contemporary social science perspective on test validity and the validation process. The instructional piece explores the concepts of test validity, the validation process, validity evidence, and key threats to validity. The essay also includes an in-depth example of a validity argument and validation approach for a test of student argument analysis. In addition to DBERs, this essay should benefit practitioners (e.g., lab directors, faculty members) in the development, evaluation, and/or selection of instruments for their work assessing students or evaluating pedagogical innovations. INTRODUCTIONThe field of discipline-based education research ( Singer et al ., 2012 ) has emerged in response to long-standing calls to advance the status of U.S. science education at the postsecondary level (e.g., Boyer Commission on Educating Undergraduates in the Research University, 1998 ; National Research Council, 2003 ; American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2011 ). Discipline-based education research applies scientific principles to study postsecondary science education processes and outcomes systematically to improve the scientific enterprise. In particular, this field has made significant progress with respect to the study of 1) active-learning pedagogies (e.g., Freeman et al. , 2014 ); 2) interventions to support those pedagogies among both faculty (e.g., Brownell and Tanner, 2012 ) and graduate teaching assistants (e.g., Schussler et al. , 2015 ); and 3) undergraduate research experiences (e.g., Auchincloss et al. , 2014 ). Most discipline-based education researchers (DBERs) were formally trained in the methods of scientific disciplines such as biology, chemistry, and physics, rather than social science disciplines such as psychology and education. As a result, DBERs may have never taken specific courses in the social science research methodology—either quantitative or qualitative—on which their scholarship often relies so heavily ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). While the same principles of science ground all these fields, the specific methods used and some criteria for methodological and scientific rigor differ along disciplinary lines. One particular aspect of (quantitative) social science research that differs markedly from research in disciplines such as biology and chemistry is the instrumentation used to quantify phenomena. Instrumentation is a critical aspect of research methodology, because it provides the raw materials input to statistical analyses and thus serves as a basis for credible conclusions and research-based educational practice ( Opfer et al ., 2012 ; Campbell and Nehm, 2013 ). A notable feature of social science instrumentation is that it generally targets variables that are latent, that is, variables that are not directly observable but instead must be inferred through observable behavior ( Bollen, 2002 ). For example, to elicit evidence of cognitive beliefs, which are not observable directly, respondents are asked to report their level of agreement (e.g., “strongly disagree,” “disagree,” “agree,” “strongly agree”) with textually presented statements (e.g., “I like science,” “Science is fun,” and “I look forward to science class”). Even a multiple-choice final examination does not directly observe the phenomenon of interest (e.g., student knowledge). As such, compared with work in traditional scientific disciplines, in the social sciences, more of an inferential leap is often required between the derivation of a score and its intended interpretation ( Opfer et al ., 2012 ). Instruments designed to elicit evidence of variables of interest to DBERs have proliferated in recent years. Some well-known examples include the Experimental Design Ability Test (EDAT; Sirum and Humburg, 2011 ); the Genetics Concept Assessment ( Smith et al. , 2008 ); the Classroom Undergraduate Research Experience survey ( Denofrio et al. , 2007 ); and the Classroom Observation Protocol for Undergraduate STEM ( Smith et al. , 2013 ). However, available instruments vary widely in their quality and nuance ( Opfer et al. , 2012 ; Singer et al. , 2012 ; Campbell and Nehm, 2013 ), necessitating understanding on the part of DBERs of how to evaluate instruments for use in their research. Practitioners, too, should know how to evaluate and select high-quality instruments for program evaluation and/or assessment purposes. Where high-quality instruments do not already exist for use in one’s context, which is commonplace ( Opfer et al ., 2012 ), they need to be developed, and corresponding empirical validity evidence needs to be gathered in accord with contemporary standards. In response, this Research Methods essay offers a contemporary social science perspective on test validity and the validation process. It is intended to offer a primer for DBERs who may not have received formal training on the subject. Using examples from discipline-based education research, the instructional piece explores the concepts of test validity, the validation process, validity evidence, and key threats to validity. The essay also includes an in-depth example of a validity argument and validation approach for a test of student argument analysis. In addition to DBERs, this essay should benefit practitioners (e.g., lab directors, faculty members) in the development, evaluation, and/or selection of instruments for their work assessing students or evaluating pedagogical innovations. TEST VALIDITY AND THE TEST VALIDATION PROCESSA test is a sample of behavior gathered in order to draw an inference about some domain or construct within a particular population (American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, and National Council on Measurement in Education [ AERA, APA, and NCME], 2014 ). 1 In the social sciences, the domain about which an inference is desired is typically a latent (unobservable) variable. For example, the STEM GTA-Teaching Self-Efficacy Scale ( DeChenne et al. , 2012 ) was developed to support inferences about the degree to which a graduate teaching assistant believes he or she is capable of 1) cultivating an effective learning environment and 2) implementing particular instructional strategies. As another example, the inference drawn from an introductory biology final exam is typically about the degree to which a student understands content covered over some extensive unit of instruction. While beliefs or conceptual knowledge are not directly accessible, what can be observed is the sample of behavior the test elicits, such as test-taker responses to questions or responses to rating scales. Diverse forms of instrumentation are used in discipline-based education research ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). Notable subcategories of instruments include self-report (e.g., attitudinal and belief scales) and more objective measures (e.g., concept inventories, standardized observation protocols, and final exams). By the definition of “test” above, any of these instrument types can be conceived as tests—though the focus here is only on instruments that yield quantitative data, that is, scores. The paramount consideration in the evaluation of any test’s quality is validity: “the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores for proposed uses of tests” ( Angoff, 1988 ; AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 , p. 11). 2 , 3 In evaluating test validity, the focus is not on the test itself, but rather the proposed inference(s) drawn on the basis of the test’s score(s). Noteworthy in the validity definition above is that validity is a matter of degree (“the inferences supported by this test have a high or low degree of validity”), rather than a dichotomous character (e.g., “the inferences supported by this test are or are not valid”). Assessment validation is theorized as an iterative process in which the test developer constructs an evidence-based argument for the intended test-based score interpretations in a particular population ( Kane, 1992 ; Messick, 1995 ). An example validity argument claim is that the test’s content (e.g., questions, items) is representative of the domain targeted by the test (e.g., body of knowledge/skills). With this argument-based approach, claims within the validity argument are substantiated with various forms of relevant evidence. Altogether, the goal of test validation is to accumulate over time a comprehensive body of relevant evidence to support each intended score interpretation within a particular population (i.e., whether the scores should in fact be interpreted to mean what the developer intends them to mean). CATEGORIES OF TEST VALIDITY EVIDENCEHistorically, test validity theory in the social sciences recognized several categorically different “types” of validity (e.g., “content validity,” “criterion validity”). However, contemporary validity theory posits that test validity is a unitary (single) concept. Rather than providing evidence of each “type” of validity, the charge for test developers is to construct a cohesive argument for the validity of test score–based inferences that integrates different forms of validity evidence. The categories of validity evidence include evidence based on test content, evidence based on response processes, evidence based on internal structure, evidence based on relations with other variables, and evidence based on the consequences of testing ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 ). Figure 1 provides a graphical representation of the categories and subcategories of validity evidence.  Categories of evidence used to argue for the validity of test score interpretations and uses ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 ). Validity evidence based on test content concerns “the relationship between the content of a test and the construct it is intended to measure” ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 , p. 14). Such validity evidence concerns the match between the domain purportedly measured by (e.g., diagnostic microscopy skills) and the content of the test (e.g., the specific slides examined by the test taker). For example, if a test is intended to elicit evidence of students’ understanding of the key principles of evolution by means of natural selection (e.g., variation, heredity, differential fitness), the test should fully represent those principles in the sample of behavior it elicits. As a concrete example from the literature, in the development of the Host-Pathogen Interaction (HPI) concept inventory, Marbach-Ad et al. (2009) explicitly mapped each test item to one of 13 HPI concepts intended to be assessed by their instrument. Content validity evidence alone is insufficient for establishing a high degree of validity; it should be combined with other forms of evidence to yield a strong evidence-based validity argument marked by relevancy, accuracy, and sufficiency. In practice, providing validity evidence based on test content involves evaluating and documenting content representativeness. One standard approach to collecting evidence of content representativeness is to submit the test to external systematic review by subject matter–area experts (e.g., biology faculty) and to document such reviews (as well as revisions made on their basis). External reviews focus on the adequacy of the test’s overall elicited sample of behavior in representing the domain assessed and any corresponding subdomains, as well as the relevance or irrelevance of particular questions/items to the domain. We refer the reader to Webb (2006) for a comprehensive and sophisticated framework for evaluating different dimensions of domain–test content alignment. Another approach used to design a test, so as to support and document construct representativeness, is to employ a “table of specifications” (e.g., Fives and DiDonato-Barnes, 2013 ). A table of specifications (or test blueprint) is a tool for designing a test that classifies test content along two dimensions, a content dimension and a cognitive dimension. The content dimension pertains to the different aspects of the construct one intends to measure. In a classroom setting, aspects of the construct are typically defined by behavioral/instructional objectives (i.e., students will analyze phylogenetic trees). The cognitive dimension represents the level of cognitive processing or thinking called for by test components (e.g., knowledge, comprehension, analysis). Within a table of specifications, one indicates the number/percent of test questions or items for each aspect of the construct at each cognitive level. Often, one also provides a summary measure of the number of items pertaining to each content area (regardless of cognitive demand) and at each cognitive level (regardless of content). Instead of or in addition to the number of items, one can also indicate the number/percent of available points for each content area and cognitive level. Because a table of specifications indicates how test components represent the construct one intends to measure, it serves as one source of validity evidence based on test content. Table 1 presents an example table of specifications for a test concerning the principles of evolution by means of natural selection. Example table of specifications for evolution by means of natural selection test showing numbers of test items pertaining to each content area at each cognitive level and total number of items per content area and cognitive level | Cognitive process | |
|---|
| Content (behavioral objective) | Comprehension | Application | Analysis | Total |
|---|
| 1. Students will define evolution by means of natural selection. | 1 | | | 1 | | 2. Students will define key principles of evolution by means of natural selection (e.g., heredity, differential fitness). | 5 | | | 5 | | 3. Students will compute measures of absolute and relative fitness. | | 5 | | 5 | | 4. Students will compare evolution by means of natural selection with earlier evolution theories. | | | 3 | 3 | | 5. Student will analyze phylogenetic trees. | | | 4 | 4 | | Total | 6 | 5 | 7 | 18 |
Evidence of validity based on response processes concerns “the fit between the construct and the detailed nature of the performance or response actually engaged in by test takers” ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 , p. 15). For example, if a test purportedly elicits evidence of undergraduate students’ critical evaluative thinking concerning evidence-based scientific arguments, during the test the student should be engaged in the cognitive process of examining argument claims, evidence, and warrants, and the relevance, accuracy, and sufficiency of evidence. Most often one gathers such evidence through respondent think-aloud procedures. During think alouds, respondents verbally explain and rationalize their thought processes and responses concurrently during test completion. One particular method commonly used by professional test vendors to gather response process–based validity evidence is cognitive labs, which involve both concurrent and retrospective verbal reporting by respondents ( Willis, 1999 ; Zucker et al ., 2004 ). As an example from the literature, developers of the HPI concept inventory asked respondents to provide open-ended responses to ensure that their reasons for selecting a particular response option (e.g., “B”) were consistent with the developer’s intentions, that is, the student indeed held the particular alternative conception presented in response option B ( Marbach-Ad et al. , 2009 ). Think alouds are formalized via structured protocols, and the elicited think-aloud data are recorded, transcribed, analyzed, and interpreted to shed light on validity. Evidence based on internal structure concerns “the degree to which the relationships among test item and test components conform to the construct on which the proposed test score interpretations are based” ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 , p. 16). 4 For instance, suppose a professor plans to teach one topic (eukaryotes) using small-group active-learning instruction and another topic (prokaryotes) through lecture instruction; and he or she wants to make within-class comparisons of the effectiveness of these methods. As an outcome measure, a test may be designed to support inferences about the two specific aspects of biology content (e.g., characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells). Collection of evidence based on internal structure seeks to confirm empirically whether the scores reflect the (in this case two) distinct domains targeted by the test ( Messick, 1995 ). In practice, one can formally establish the fidelity of test scores to their theorized internal structure through methodological techniques such as factor analysis, item response theory, and Rasch modeling ( Harman, 1960 ; Rasch, 1960 ; Embretson and Reise, 2013 ). With factor analysis, for example, item intercorrelations are analyzed to determine whether particular item responses cluster together (i.e., whether scores from components of the test related to one aspect of the domain [e.g., questions about prokaryotes] are more interrelated with one another than they are with scores derived from other components of the test [e.g., questions about eukaryotes]). Item response theory and Rasch models hypothesize that the probability of a particular response to a test item is a function of the respondent’s ability (in terms of what is being measured) and characteristics of the item (e.g., difficulty, discrimination, pseudo-guessing). Examining test score internal structure with such models involves examining whether such model-based predictions bear out in the observed data. There are a variety of such models for use with test questions with different (or different combinations of) response formats such as the Rasch rating-scale model ( Andrich, 1978 ) and the Rasch partial-credit Rasch model ( Wright and Masters, 1982 ). Validity evidence based on relations with other variables concerns “the relationship of test scores to variables external to the test” ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 , p. 16). The collection of this form of validity evidence centers on examining how test scores are related to both measures of the same or similar constructs and measures of distinct and different constructs (i.e., respectively termed “convergent validity” and “discriminant validity” 5 evidence). In other words, such evidence pertains to how scores relate to other variables as would be theoretically expected. For example, if a new self-report instrument purports to measure experimental design skills, scores should correlate highly with an existing measure of experimental design ability such as the EDAT ( Sirum and Humburg, 2011 ). On the other hand, scores derived from this self-report instrument should be considerably less correlated or uncorrelated with scores from a personality measure such as the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory ( Greene, 2000 ). As another discipline-based education research example, Nehm and Schonfeld (2008) collected discriminant validity evidence by relating scores from both the Conceptual Inventory of Natural Section (CINS) and the Open Response Instrument (ORI), which both purport to assess understanding of and conceptions concerning natural selection, and a geology test of knowledge about rocks. A subcategory of evidence based on relations with other variables is evidence related to test-criterion relationships, which concerns how test scores are related to some other nontest indicator or outcome either at the same time (so-called concurrent validity evidence) or in the future (so-called predictive validity evidence). For instance, developers of a new biostatistics test might examine how scores from the test correlate as expected with professor ability judgments or mathematics course grade point average at the same point in time; alternatively, the developer might follow tested individuals over time to examine how scores relate to the probability of successfully completing biostatistics course work. As another example, given prior research on self-efficacy, scores from instruments that probe teaching self-efficacy should be related to respondents’ levels of teacher training and experience ( Prieto and Altmaier, 1994 ; Prieto and Meyers, 1999 ). Examination of how test scores are related or not to other variables as expected is often associational in nature (e.g., correlational analysis). There are also two other specific methods for eliciting such validity evidence. The first is to examine score differences between theoretically different groups (e.g., whether scientists’ and nonscientists’ scores from an experimental design test differ systematically on average)—the “known groups method.” The second is to examine whether scores increase or decrease as expected in response to an intervention ( Hattie and Cooksey, 1984 ; AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 ). For example, Marbach-Ad et al. (2009 , 2010 ) examined HPI concept inventory score differences between majors and nonmajors and students in introductory and upper-level courses. To inform the collection of validity evidence based on relations with other variables, individuals should consult the literature to formulate a theory around how good measures of the construct should relate to different variables. One should also note that the quality of such validity evidence hinges on the quality (e.g., validity) of measures of external variables. Finally, validity evidence based on the consequences of testing concerns the “soundness of proposed interpretations [of test scores] for their intended uses” ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 , p. 19) and the value implications and social consequences of testing ( Messick, 1994 , 1995 ). Such evidence pertains to both the intended and unintended effects of test score interpretation and use ( Linn, 1991 ; Messick, 1995 ). Example intended consequences of test use would include motivating students, better-targeted instruction, and populating a special program with only those students who are in need of the program (if those are the intended purposes of test use). An example of an unintended consequence of test use would be significant reduction in instructional time because of overly time-consuming test administration (assuming, of course, that this would not be a desired outcome) or drop out of particular student populations because of an excessively difficult test administered early in a course. In K–12 settings, a classic example of an unintended consequence of testing is the “narrowing of the curriculum” that occurred as a result of the No Child Left Behind Act testing regime; when faced with annual tests focused only on particular content areas (i.e., English/language arts and mathematics), schools and teachers focused more on tested content and less on nontested content such as science, social studies, art, and music (e.g., Berliner, 2011 ). Evidence based on the consequences of a test is often gathered via surveys, interviews, and focus groups administered with test users. TEST VALIDITY ARGUMENT EXAMPLEIn this section, we provide an example validity argument for a test designed to elicit evidence of students’ skills in analyzing the elements of evidence-based scientific arguments. This hypothetical test presents text-based arguments concerning scientific topics (e.g., global climate change, natural selection) to students, who then directly interact with the texts to identify their elements (i.e., claims, reasons, and warrants). The test is intended to support inferences about 1) students’ overall evidence-based science argument-element analysis skills; 2) students’ skills in identifying particular evidence-based science argument elements (e.g., claims); and 3) errors made when students identify particular argument elements (e.g., evidence). Additionally, the test is intended to 4) support instructional decision-making to improve science teaching and learning. The validity argument claims undergirding this example test’s score interpretations and uses (and the categories of validity evidence advanced to substantiate each) are shown in Table 2 . Example validity argument and validation approach for a test of students’ ability to analyze the elements of evidence-based scientific arguments showing argument claims and subclaims concerning the validity of the intended test score interpretations and uses and relevant validity evidence used to substantiate those claims | Validity argument claims and subclaims | Relevant validity evidence based on |
|---|
| 1. The overall score represents a student’s current level of argument-element analysis skills, because: | – | | a single higher-order construct (i.e., argument-element analysis skill) underlies all item responses. | Internal structure | | the overall score is distinct from content knowledge and thinking dispositions. | Relations with other variables | | the items represent a variety of arguments and argument elements. | Test content | | items engage respondents in the cognitive process of argument-element analysis. | Response processes | | the overall score is highly related to other argument analysis measures and less related to content knowledge and thinking disposition measures. | Relations with other variables | | 2. A subscore (e.g., claim identification) represents a student’s current level of argument-element identification skill, because: | – | | each subscore is distinct from other subscores and the total score (the internal structure is multidimensional and hierarchical). | Internal structure | | the items represent a variety of arguments and particular argument elements (e.g., claims). | Test content | | the subscore is distinct from content knowledge and thinking dispositions. | Relations with other variables | | items engage respondents in the cognitive process of identifying a particular element argument (e.g., claims). | Response processes | | subscores are highly related to other argument analysis measures and less related to content knowledge and thinking disposition measures. | Relations with other variables | | 3. Error indicators can be interpreted to represent students’ current errors made in identifying particular argument elements, because when students misclassify an element in the task, they are making cognitive errors. | Response processes | | 4. Use of the test will facilitate improved argument instruction and student learning, because: | – | | teachers report that the test is useful and easy to use and have positive attitudes toward it. | Consequences of testing | | teachers report using the test to improve argument instruction. | Consequences of testing | | teachers report that the provided information is timely. | Consequences of testing | | teachers learn about argumentation with test use. | Consequences of testing | | students learn about argumentation with test use | Consequences of testing | | any unintended consequences of test use do not outweigh intended consequences. | Consequences of testing |
ANALYSIS OF CINS VALIDITY EVIDENCEThe example validity argument provided in the preceding section was intended to model the validity argument formulation process for readers who intend to develop an instrument. However, in many cases, an existing instrument (or one of several existing instruments) needs to be selected for use in one’s context. The use of an existing instrument for research or practice requires thoughtful analysis of extant validity evidence available for an instrument’s score interpretations and uses. Therefore, in this section, we use validity theory as outlined in the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing to analyze the validity evidence for a particular instrument, the CINS. As reported in Anderson et al . (2002) , the CINS is purported to measure “conceptual understanding of natural selection” (as well as alternative conceptions of particular relevant ideas diagnostically) in undergraduate non–biology majors before instruction (p. 953). In their initial publication of the instrument, the authors supplied several forms of validity evidence for the intended score interpretations and uses. In terms of validity evidence related to test content, the authors argued that test content was aligned with Mayr’s (1982) five facts and three inferences about evolution by means of natural selection, and two other key concepts, the origin of variation and the origin of species. Two test items were mapped to each of these 10 concepts. Similarly, distractor (incorrect) multiple-choice responses were based on theory and research about students’ nonscientific, or alternative, conceptions of these ideas. Content-related validity evidence was also provided through reviews of test items by biology professors. Evidence based on test-taker response processes was elicited through cognitive interviews (think alouds) conducted with a small sample of students ( Anderson et al. , 2002 ). The authors provided validity evidence based on internal structure using principal components analysis, which is similar to factor analysis. In terms of validity evidence based on test-score relations with other variables, the authors examined correlations between CINS scores and scores derived from interviews. While Anderson and colleagues did note that a paper and pencil–based test would be more logistically feasible than interview-based assessment methods, validity evidence based on the consequences of testing was not formally provided. Anderson et al. ’s (2002) paper did present a variety of forms of validity evidence concerning the CINS instrument. However, and underscoring the continuous nature of test validation, subsequent work has built upon their work and provided additional evidence. For example, in light of concerns that the primary earlier source of validity evidence was correlations between CINS scores and scores based on oral interviews in a very small sample, Nehm and Schonfeld (2008) provided additional validity evidence based on relations with other variables. For example, Nehm and Schonfeld (2008) examined CINS score relations with two other instruments purported to assess the same construct (convergent validity evidence) and with a measure of an unrelated construct (discriminant validity evidence). Nehm and Schonfeld also expanded the body of CINS validity evidence based on internal structure by analyzing data using the Rasch model. The authors’ reporting of CINS administration times similarly shed light on possible consequences of testing. The evolution of validity evidence for the CINS noted here certainly speaks to the iterative and ongoing nature of instrument validation processes. With this in mind, future work might examine CINS scores’ internal structure vis-à-vis diagnostic classification models (see Rupp and Templin, 2008 ), since CINS is purportedly a diagnostic test. TEST VALIDITY THREATSThe two primary threats to test score validity are construct underrepresentation and construct-irrelevant variance. Construct underrepresentation is “the degree to which a test fails to capture important aspects of the construct” ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 ; p. 12). In other words, construct underrepresentation involves failing to elicit a representative sample of behavior from test takers (e.g., responses to multiple-choice questions) relative to the universe of possible relevant behaviors that might be observed. While it is neither necessary nor feasible to ask respondents to engage in every single possible relevant behavior, it is crucial that the behavior sampled by the test is sufficiently representative of the construct at large. If a test does not fully and adequately sample behavior related to the targeted domain, the test score’s meaning in actuality would be narrower than is intended. Content underrepresentation can be mitigated by initiating test design with a thorough analysis and conception of the domain targeted by the test ( Mislevy et al. , 2003 ; Opfer et al. , 2012 ). Knowledge of the construct, and variables that are related or not related to the construct, can also inform the validation process ( Mislevy et al. , 2003 ). Beginning test design with a thorough conception of the construct one intends to measure is analogous to the course design approach known as “backward design”; with backward design one first identifies what one wants students to know/be able to do after instruction (learning outcomes) and then designs a course to get students there ( Wiggins and McTighe, 2005 ). Other strategies to promote construct representation include building a test based on a table of specifications; submitting a text to external expert content review (as both noted above); and employing a sufficient number of test items to ensure good representation of domain content. Besides construct representation, the other primary threat to test score validity is construct-irrelevant variance—“the degree to which test scores are affected by processes that are extraneous to the test’s intended purpose” ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 , p. 12). Construct-irrelevant variance is test score variation caused systematically by factors other than (or in addition to) those intended; in other words, some part of the reason why one received a “high” or “low” score is due to irrelevant reasons. Two common examples of this are: English skills affecting test scores for non–native English speakers on tests written in English; and computer skills affecting test scores for tests administered via computer. Another example would be if items on a science teaching self-efficacy self-report instrument are written so generally that the scores represent not science teaching–specific self-efficacy but self-efficacy in general. It is critical to mitigate such threats through test design processes (e.g., minimizing test linguistic load). One can often identify potential threats in the course of a thorough analysis of the construct/domain done at early design stages. During test validation one should also disconfirm such threats wherein scores are driven by irrelevant factors; practitioners often conduct factor, correlational, and differential item functioning analyses toward this end. Systematic research on postsecondary science teaching and learning and evaluation of local innovations by practitioners hinges on the availability and use of sound instrumentation. Unfortunately, the field of discipline-based education research lacks sufficient existing and high-quality instruments for use in all of these efforts ( Opfer et al. , 2012 ; Singer et al. , 2012 ; Campbell and Nehm, 2013 ). DBERs and practitioners furthermore do not typically have formal training that equips them to evaluate and select existing instruments or develop and validate their own instruments for needed purposes. This essay reviewed contemporary test validity and validation theory for DBERs and practitioners in hopes of equipping them with such knowledge. 6 This essay was chiefly intended for two audiences: 1) those who will develop new instruments; and 2) those who will evaluate and select from among existing instruments. Here, we summarily denote the implications of this essay for members of these two populations. First, it behooves those developing and publishing their own instruments to explicitly frame, construct, and report an evidence-based validity argument for their proposed instruments’ intended score interpretations and uses. This argument should rely on multiple forms of validity evidence and specify the test-taker and user populations for which that argument pertains. If faced with space constraints in journal articles, test manuals or technical reports can be written to detail such validity evidence and made available to the scholarly community. Like any argument, an evidence-based argument formulated during test validation should be characterized by relevancy, accuracy, and sufficiency. As such, validity arguments should be held up to scientific scrutiny before a test’s operational use. The quality of a validity argument hinges on a number of factors discussed in this essay. Examples include the alignment of the validity argument claims with intended test score interpretations and uses; the representativeness of the samples from which validity evidence is gathered to the intended test-taker population; the relevance of the expertise held by content reviewers; and the technical quality of external measures. A final point to emphasize is that validation is an ongoing process; additional validity evidence may need to be gathered as theory concerning a construct evolves or as the community seeks to use an instrument with new populations. Second, potential test users should be critical in their evaluation of existing instruments, and should not merely assume a strong validity argument exists for an instrument’s score interpretations and uses with a particular population. Potential users should look to the instrumentation (or methods) sections of published articles for key information, such as whether the test was developed based on a sound theoretical conception of construct, whether the test underwent external content review, and whether scores correlate with other measures as they theoretically should, among other things. One may have to contact an author for such information. Altogether, such practices should advance the quality of measurement within the realm of discipline-based education research. AcknowledgmentsThe authors thank Drs. Beth Schussler and Ross Nehm and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive feedback on an earlier version of this article. 1 A test cannot be “stamped” valid for all purposes and test-taker populations; validity evidence needs to be gathered with respect to all intended instrument uses. 2 While other key dimensions for evaluating an instrument’s quality include reliability (i.e., test score consistency) and utility (i.e., feasibility; AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 ), the focus here is on validity only. 3 While this essay allies with test validity theory as codified in the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing ( AERA, APA, and NCME, 2014 ), the reader will note that there are alternative conceptions of validity as well ( Lissitz and Samuelsen, 2007 ). 4 This source of evidence has been termed “substantive validity” ( Messick, 1995 ). 5 This is not to be confused with item discrimination, a test item property pertaining to how an item’s scores relate to overall test performance. 6 While our focus is on instruments comprising sets of questions or items intended to elicit evidence of a particular construct or constructs, many of the ideas here apply also to questionnaire (survey) validation. For example, the developer of a questionnaire may interrogate how respondents interpret and formulate a response to a particular question as validity evidence based on response processes. - American Association for the Advancement of Science. Vision and Change in Undergraduate Biology Education: A Call to Action. Washington, DC: 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, and National Council on Measurement in Education. Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing. Washington, DC: 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson DL, Fisher KM, Norman GJ. Development and evaluation of the conceptual inventory of natural science. J Res Sci Teach. 2002; 39 :952–978. [ Google Scholar ]
- Andrich DA. A rating formulation for ordered response categories. Psychometrika. 1978; 43 :561–573. [ Google Scholar ]
- Angoff WH. Validity: an evolving concept. In: Wainer H, Braun H, editors. Test Validity. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1988. pp. 19–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Auchincloss LC, Laursen SL, Branchaw JL, Eagan K, Graham M, Hanauer DI, Lawrie G, McLinn CM, Palaez N, Rowland S, et al. Assessment of course-based undergraduate research experiences: a meeting report. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2014; 13 :29–40. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berliner D. Rational responses to high stakes testing: the case of curriculum narrowing and the harm that follows. Cambridge J Educ. 2011; 41 :287–302. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bollen KA. Latent variables in psychology and the social sciences. Annu Rev Psychol. 2002; 53 :605–634. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boyer Commission on Educating Undergraduates in the Research University. Reinventing Undergraduate Education: A Blueprint for America’s Research Universities. Stony Brook: State University of New York; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brownell SE, Tanner KD. Barriers to faculty pedagogical change: lack of training, time, incentives, and … tensions with professional identity. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2012; 11 :339–346. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Campbell CE, Nehm RH. A critical analysis of assessment quality in genomics and bioinformatics education research. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2013; 12 :530–541. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DeChenne SE, Enochs LG, Needham M. Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics graduate teaching assistants teaching self-efficacy. J Scholarship Teach Learn. 2012; 12 :102–123. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Denofrio LA, Russell B, Lopatto D, Lu Y. Linking student interests to science curricula. Science. 2007; 318 :1872–1873. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Embretson SE, Reise SP. Item Response Theory. Mahwah, NJ: 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fives H, DiDonato-Barnes N. Classroom test construction: the power of a table of specifications. Pract Assess Res Eval. 2013; 18 :2–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman S, Eddy SL, McDonough M, Smith MK, Wenderoth MP, Okoroafor N, Jordt H. Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014; 111 :8410–8415. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greene RL. The MMPI-2: An Interpretive Manual. Boston, MA: 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Harman HH. Modern Factor Analysis. Oxford, UK: 1960. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hattie J, Cooksey RW. Procedures for assessing the validities of tests using the “known-groups” method. Appl Psychol Meas. 1984; 8 :295–305. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kane MT. An argument-based approach to validity. Psychol Bull. 1992; 112 :527–535. [ Google Scholar ]
- Linn RL. Complex, performance-based assessment: expectations and validation criteria. Educ Researcher. 1991; 20 :15–21. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lissitz RW, Samuelsen K. A suggested change in terminology and emphasis regarding validity and education. Educ Researcher. 2007; 36 :437–448. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marbach-Ad G, Briken V, El-Sayed NM, Frauwirth K, Fredericksen B, Hutcheson S, Gao LY, Joseph S, Lee VT, McIver KS, et al. Assessing student understanding of host pathogen interactions using a concept inventory. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2009; 10 :43–50. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marbach-Ad G, McAdams K, Benson S, Briken V, Cathcart L, Chase M, El-Sayed N, Frauwirth K, Fredericksen B, Joseph S, et al. A model for using a concept inventory as a tool for students’ assessment and faculty professional development. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2010; 9 :408–436. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayr E. The Growth of Biological Thought: Diversity, Evolution and Inheritance. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1982. [ Google Scholar ]
- Messick S. The interplay of evidence and consequences in the validation of performance assessments. Educ Researcher. 1994; 23 :13–23. [ Google Scholar ]
- Messick S. Standards of validity and the validity of standards in performance assessment. Educ Meas. 1995; 14 :5–8. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mislevy RJ, Steinberg LS, Almond RG. On the structure of educational assessments. Measurement. 2003; 1 :3–62. [ Google Scholar ]
- National Research Council. BIO2010: Transforming Undergraduate Education for Future Research Biologists. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2003. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nehm RH, Schonfeld IS. Measuring knowledge of natural selection: a comparison of the CINS, an open-response instrument, and an oral interview. J Res Sci Teach. 2008; 45 :1131–1160. [ Google Scholar ]
- Opfer JE, Nehm RH, Ha M. Cognitive foundations for science assessment design: knowing what students know about evolution. J Res Sci Teach. 2012; 49 :744–777. [ Google Scholar ]
- Prieto LR, Altmaier EM. The relationship of prior training and previous teaching experience to self-efficacy among graduate teaching assistants. Res High Educ. 1994; 35 :481–497. [ Google Scholar ]
- Prieto LR, Meyers SA. Effects of training and supervision on the self-efficacy of psychology graduate teaching assistants. Teach Psychol. 1999; 26 :264–266. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rasch G. Probabalistic Models for Some Intelligence and Achievement Tests. Copenhagen: Danish Institute for Educational Research; 1960. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rupp AA, Templin JL. Unique characteristics of diagnostic classification models: a comprehensive review of the current state-of-the-art. Measurement. 2008; 6 :219–262. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schussler EE, Reed Q, Marbach-Ad G, Miller K, Ferzli M. Preparing biology graduate teaching assistants for their roles as instructors: an assessment of institutional approaches. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2015; 14 :ar31. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Singer SR, Nielsen NR, Schweingruber HA. Discipline-based Education Research: Understanding and Improving Learning in Undergraduate Science and Engineering. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirum K, Humburg J. The Experimental Design Ability Test (EDAT) Bioscene. 2011; 37 :8–16. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith MK, Jones FHM, Gilbert SL, Wieman CE. The Classroom Observation Protocol for Undergraduate STEM (COPUS): A new instrument to characterize university STEM classroom practices. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2013; 12 :618–627. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith MK, Wood WB, Knight JK. The Genetics Concept Assessment: a new concept inventory for gauging student understanding of genetics. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2008; 7 :422–430. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Webb N. Identifying content for student achievement tests. In: Downing SM, Haladyna TM, editors. Handbook of Test Development. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum; 2006. pp. 155–180. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiggins GP, McTighe J. Understanding by Design. Alexandria, VA: 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Willis GB. Cognitive Interviewing: A “How To” Guide. Research Triangle Park, NC: 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wright BD, Masters GN. Rating Scale Analysis. Chicago, IL: MESA; 1982. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zucker S, Sassman S, Case BJ. Cognitive Labs. 2004. http://images.pearsonassessments.com/images/tmrs/tmrs_rg/CognitiveLabs.pdf (accessed 29 August 2015)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. - View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 24 August 2024
Development and implementation of digital pedagogical support systems in the context of educational equity- Shuo-fang Liu 1 ,
- Juan Li 1 , 2 ,
- Hang-qin Zhang 3 ,
- Zhe Li ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6244-9167 4 &
- Meng Cheng ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9208-3584 5
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 1084 ( 2024 ) Cite this article 187 Accesses Metrics details - Science, technology and society
In response to the covid -19 pandemic, the digital strategy of education has become a key pedagogical approach for higher engineering disciplines. In this complex environment, the outcome-oriented higher engineering discipline faces the challenge of educational equity in terms of curriculum design and learning outcome assessment for its online engineering practical courses. In order to solve this problem, this study develops a digital teaching assistant system to facilitate the reform of educational equity in higher engineering disciplines. The teaching and learning functions of the system aim to support the interaction between teachers and students in the teaching process and the visual display of learning outcomes, and its intelligent evaluation and analysis function is based on the multi-criterion group decision-making model of Quality Function Deployment (QFD) combined with t-test to realize the evaluation of course learning outcomes. The results show that the academic performance of this system is significantly better than that of other similar systems. The statistical results of the teacher-student satisfaction survey of the two systems show that the teacher-student interaction and multi-dimensional learning evaluation analysis report function provided by the system are the most highly recognized, and the system also has better educational equity in resource recommendation, interaction and collaboration, learning achievement display and learning achievement evaluation, etc. In addition, the system is more in line with the teaching characteristics of higher engineering disciplines, which can provide effective assistance for teachers of higher engineering disciplines to improve teaching plan and cultivate students’ disciplinary practicality, consequently creating favorable conditions for the establishment of teaching equity. Similar content being viewed by others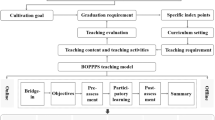 Developing a BOPPPS (Bridge-in, Objectives, Pre-assessment, Participatory Learning, Post-assessment and Summary) model combined with the OBE (Outcome Based Education) concept to improve the teaching outcomes of higher education Organization and planning of university faculty training in virtual classrooms for the inclusion of people with disabilities Quo vadis higher education? Post-pandemic success digital competencies of the higher educators – a Hungarian university case and actionsIntroduction. According to UN’s latest Policy Brief: Education during COVID-19 and beyond , the covid -19 epidemic has caused the most serious damage to the education system in history, affecting nearly 1.6 billion students in more than 190 countries on all continents. 94% of students all over the world have been affected by the suspension of schools and other learning places, and 99% of those in low-income and low-middle-income countries. This crisis has stimulates innovation of education sectors with digitized education emerging as a critical breakthrough in educational development. Governments and other stakeholders around the world, including the Global Education Alliance initiated by UNESCO, have swiftly responded by developing new modes of teaching and learning in a digital context. These digitized education solutions have successfully addressed the challenges posed by the suspension of schooling, teaching, and classes due to the pandemic, propelling global education swiftly towards digitization and informatization. Although digital technologies offer numerous advantages such as easier access to teaching data, diverse types, deeper processing, and timelier application, effectively transforming learning, meeting individual needs, and reducing educational inequities. However, the hasty implementation of digitized education without in-depth investigation or careful consideration can exacerbate digital inequities, thereby perpetuate educational disparities. This presents an excellent opportunity to re-examine the critical issue of digital inequities (Miller and Liu, 2023 ). According to a survey conducted by Times Higher Education , higher engineering education is increasingly adopting an Outcome-Based Education (OBE) approach. The OBE emphasizes a teaching design of taking students’ learning outcomes after education as the teaching goal, and a teaching evaluation design of considering both students’ cultivating core abilities and curriculum learning results, hereby to ensure better teaching results (Bhat et al., 2020 ). In the whole teaching process, teaching effect analysis is also mainly conducted around the evaluation of teachers, students, learning process and learning results. However, in the digitized education of higher engineering education, due to the existence of multiple factors such as differences in digital facilities and equipment or technologies, regional differences in the level of digital technology utilization, the complexity of the communication and interaction process between teachers and students, and differences in students’ learning acceptance of digital education, etc (Hebebci et al., 2020 ).The existence of multiple factors will greatly aggravate the occurrence of educational inequity. This not only seriously affects the quality of students’ teaching results, but also tests teachers’ digital teaching technology and management capabilities (Albrahim, 2020 ). Therefore, when it comes to the digital transformations of higher engineering education, how to make digital teaching course planning and student learning outcome assessment more equitable has become a key issue that urgently needs to be solved (Rajab et al., 2020 ). Digital teaching course planningDigital teaching refers to the teaching activities of teachers and students in a digital environment, following modern educational theories, using digital resources, and promoting knowledge acquisition through digital teaching mode. Curriculum planning for digital teaching requires teachers to systematically analyze and plan from multiple dimensions such as teaching materials, teaching time, as well as various digital resources and technologies. In the advanced engineering disciplines, whether it is design disciplines (such as environmental art design, urban planning and design), Mechanical engineering and automation disciplines (such as mechanical engineering, industrial design, intelligent manufacturing engineering), computer science and technology engineering disciplines (such as software engineering, information security, artificial intelligence), medical engineering disciplines (such as biology and medicine, pharmacy), It is also the discipline of information science and engineering (such as communication engineering, integrated circuit and system design, electronic information engineering), electrical engineering discipline (such as electrical equipment, power system), civil engineering discipline (such as civil engineering, water supply and drainage science and engineering), chemical engineering discipline (such as biotechnology, chemical engineering and technology) etc. The undergraduate education in the above disciplines has the highest commonality, which is to cultivate students’ professional abilities as the core, and is result-oriented, emphasizing the importance of students’ practical engineering skills, focusing on professional and soft skills, as well as team communication, creativity, leadership, and respect for others or partners, are essential for all the students of advanced engineering disciplines (Lantada, 2020 ). Therefore, the engineering practice courses offered by various disciplines play a leading role in the engineering education system, and such courses emphasize the learning by doing to guide students to independently construct cognitive frameworks, integrate knowledge, shape mindset, stimulate creativity, and ultimately achieve the purpose of strengthening students’ practical ability. When implementing their online courses, teachers usually employ the mixed mode of combining theoretical teaching with practical guidance, and take project or product design and development as the medium, and need to create a real learning environment and platform construction for engineering practice in the professional context in the digital teaching system, so as to realize the collaborative integration of educational elements. This not only requires teachers to pay attention to students’ classroom behavior in real time, but also emphasizes the characteristics of assisted teaching based on digital resources. Therefore, to promote the digital teaching of higher engineering disciplines, it is necessary to continuously enrich the digital teaching scenarios around the syllabus, integrate digital technology with traditional education, and innovate educational concepts, methods and forms. This initiative aims to empower education with digital resources and technology, create a more equal educational environment, and better serve the essence of education. According to the education industry standard JY/T 0644-2022 issued by the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China in November 2022, the types of interaction of digitized educational resources include presentation, conversational, interoperable, and blended. The types of resources are more abundant, including learning websites, online courses, educational tools and software, virtual simulation systems, exercises, assessment systems, online assignments or tests, digital library resources, etc. In addition, the course requires good online communication between teachers and students at all times to ensure that students receive guidance from teachers as much as possible. It also requires excellent continuous communication, discussion and collaboration among students, which not only promote effective communication and collaboration, but also enrich the cognitive process by eliciting emotional resonance among students, and ultimately realize the design and development of a project or product. In the whole process of course communication, the design and design results of the students’ practice process should be presented based on the teaching system. This requires a clear, concise, and convenient visual system interface and a variety of interactive forms (Rajab et al., 2020 ). Despite the fact that many digital assistance systems developed by businesses and research institutes have successfully supported online teaching in various subjects, it is precisely because of these particularities that they are not suitable for this type of course. This is confirmed in a study of 76 randomly selected digital teaching courses, which shows that most digital courses have high-quality teaching materials and presentations, but run short of the quality of lesson planning and undermine student learning outcomes (Margaryan et al., 2015 ). Another study also notes that lower student completion and engagement rates with digital courses are strongly correlated with poor quality curriculum planning. For example, there is a lack of problem-centered solving practices, peer coordination and collaboration for knowledge co-building, and the support students need (Shukor and Abdullah, 2019 ). Student engagement is directly related to the effectiveness of learning outcomes, and the biggest challenge in digital teaching of these subjects is to facilitate teacher-student communication in the learning process. Some teachers try to use multiple assistance systems to establish effective communication and facilitate student teamwork, but this approach often requires teachers and students to learn a wider range of digital technologies, which greatly increases the learning burden of teachers and students, resulting in a less-than-ideal user experience (Angelova, 2020 ). Compared to traditional teaching, the complexity of digital teaching is self-evident. Teachers need to design a feasible teaching method that stimulates student engagement based on the curriculum content, considers the diversity of students’ available devices, and chooses user-friendly digital tools to minimize the impact on student learning outcomes (Cullen et al., 2013 ). Therefore, to maintain educational equity and teaching quality in digital education impose a greater workload and difficulty on curriculum planning. Assessment of student learning outcomes in digitized educationAssessment of learning outcomes in teaching is a common practice in quality assurance in international higher education. Results-oriented, student-centered, and continuous improvement are the basic philosophies in higher engineering education. This is also an advanced mainstream concept advocated by developed countries and international organizations. It is very important to establish a scientific education evaluation orientation at the national level to ensure and improve the talent training quality of engineering education students. Compared with the courses with standard answers, the assessment of higher engineering disciplines practice courses is mostly presented in the form of design products. It is difficult to evaluate scores by judging between true and false. Teaching evaluation is a highly subjective cognitive activity, which is multidimensional, non-quantitative, and ambiguous (Li et al., 2020 ). This is mainly reflected in the diverse and vague assessment criteria of this type of design course. Traditionally, teachers have balanced their subjective judgment by understanding students’ design process in a live classroom environment. However, in digital teaching, it is difficult to obtain these insights in a timely manner, which poses a challenge to accurately define the scoring boundaries and the equity of the assessment results. Alternatively, when multiple teachers evaluate students’ performance in related courses, group decision-making involving multiple clear course evaluation criteria can help teachers objectively evaluate students’ online learning processes and outcomes. This includes aspects such as effective information organization, design language, and practical design solutions during the course learning process (Lin et al., 2021 ). The essence of this process is that one or more evaluators (teachers) evaluate the objectives (course evaluation criteria, student achievement) to determine the optimal or acceptable objectives. The uncertainty and subjectivity of the evaluator’s assessment target information under certain standards will aggravate the inequity of the assessment results. In addition, the process of assessing learning outcomes in digital courses faces problems such as computational complexity and unreasonable weighting (Chiao et al., 2018 ), and data mining and learning analytics techniques are needed to predict student performance (Namoun and Alshanqiti, 2021 ). It can be seen that in the digital teaching of higher engineering disciplines, how to objectively and fairly evaluate the course grading criteria and student learning outcomes is the biggest difficulty. In a nutshell, the digita teaching assistant system does not focus on educational equity, and the digital technology developed fails to fully consider the teaching characteristics of higher engineering disciplines courses, and its poor performance in technical support teaching plans, course interactions, teaching resource connections, and course achievement evaluation often makes the acceptance of teachers and students low, affects the course teaching effect of teachers, and leads to poor teaching quality of higher engineering disciplines. This is the biggest threat to the future of the development of online higher engineering disciplines education. At the same time, the lack of a good teaching system will seriously affect students’ enthusiasm for learning, resulting in poor academic performance and further lack of confidence in their professional abilities. An increasing number of students lack enthusiasm for their majors, and the phenomenon of graduates turning to non-advanced engineering and technical positions will become more and more frequent, and in the long run, the loss of a large number of engineering talents will also seriously affect the sustainable development of higher engineering industries and hinder the development of human civilization. In order to deeply analyze the adaptation of the current digital teaching assistant system and the teaching of higher engineering education disciplines based on educational equity, we conduct a survey on the digital teaching assistant system being used by many higher engineering schools. Scalability and many other advantages have become the inevitable embodiment of the development of colleges and universities. Many institutions of higher learning have tailored digitalteaching assistant systems to their specific needs to support their teaching and learning equity, and have set up a special department responsible for the development, operation, control, and guidance of teachers and students in the use of digital teaching assistant systems. For example, EDX, co-founded by Harvard University and MIT, was the first to offer Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) and their ancillary services for higher education in different disciplines (Aithal and Aithal, 2016 ). In September 2015, Malaysian universities also launched a large-scale online course (MOOCs) platform (Azizi, 2017 ) to support students to access more learning resources. The Universitas Pendidikan Ganesha in Indonesia provides a learning management system with multi-dimensional learning resources and interactive learning functions to improve inequities in learning resources in higher education (Dewanti et al., 2022 ). Taiwan Cheng Kung University’s digital learning platform provides features such as Webex video synchronous teaching, Moodle course teaching, and the integration of performance assessments to assist teaching. A review of the data from 69 highly relevant research articles in the past five years shows that the impact of digital teaching technology on students’ academic achievement is most prominent (Matthew et al., 2021 ), and therefore, the research and application of seeking relevant technological breakthroughs in the two dimensions of digital technology and educational equity account for the largest proportion, making digital teaching an important part of global higher education today. For example, Li and García-Díaz ( 2022 ) developed an intelligent education online assistance system that enables.The advantage is that the collaborative filtering algorithm can recommend corresponding teaching resources according to students’ interests, help students to expand their knowledge, fix the discontinuity of teachers’ guidance to students, and improve the effect and satisfaction of online education. Luo ( 2019 ), based on SPOC, is a teaching platform of the School of Public Curriculum Information, which uses a three-layer B/S architecture model to run advanced applications, and links with the database to develop a curriculum information module, a textbook module, a teaching activity module, an assessment module, and a statistical module, on which the platform can be operated and taught to achieve educational equity. However, due to the large amount of data that needs to be processed, the working speed of the system needs to be improved. Yang and Lin ( 2022 ) developed an intelligent education support system based on WEB using B/S structure mode, among which the biggest innovation is to propose a Bayesian-based digital cloud computing integration model for educational resources to effectively classify and optimize the allocation of educational resources. Villegas-Ch et al. ( 2020 ) combined technologies such as artificial intelligence and data analytics with learning management systems to improve learning, its artificial neural network can analyze input and output data through research, learn the underlying patterns between output and input, evaluate and measure new data, and estimate the desired output. Sun et al. ( 2021 ) developed a deep learning-assisted online intelligent teaching system based on artificial intelligence modules combined with knowledge recommendation, and used decision tree algorithms and neural networks to generate a teaching evaluation implementation model based on decision tree technology, provide valuable data from massive information, summarize rules and data, and help teachers improve teaching and student performance. Elmasry and Ibrahim ( 2021 ) adopted hybrid cloud typologies through cloud-hosted learning management systems as a solution for achieving educational equity among higher education institutions in technologically disadvantaged developingcountries. Other researchers have used educational function models, focus groups, and e-learning tool assessment scales to design online course assessment models to understand teacher and student satisfaction (Ibrahim et al., 2021 ). In addition, a number of studies hold that it is important to explore the problems of online teaching interaction process from the perspective of users (both teachers and students), so that the relevant research focusing on the two dimensions of user communication and educational equity to seek better forms of interaction is also relatively large. For example, Danjou ( 2020 ) proposed a method combining synchronous and asynchronous teaching to achieve educational equity. The asynchronous part of the asynchronous part is that students can learn at their own pace by watching the teacher play instructional videos on the social platform of Facebook, and the synchronous part of teaching is to keep the communication between teachers and students and the social connection between students smooth through the Discord platform. Mahmood et al. ( 2021 ) created an Interprofessional Simulation Education (IPSE) module and best practice simulations based on the TeamSTEPPS® framework to improve the effectiveness of undergraduate medical and nursing students in teamwork and communication skills. Sajja et al. ( 2023 ) developed an AI-enhanced intelligent teaching assistant systems based on powerful language models (i.e., GPT-3) provide students with access to a variety of curriculum-specific issues, from curriculum to logistics and curriculum policies, helping to increase student engagement and reduce learning barriers while also reducing teacher workload. In order to coordinate the various technological tools used by teachers and students for online teaching, the University of Urbino develops a digital system toolkit that includes the learning management system Moodle and the web conferencing tool Blackboard Collaborate, as well as the electronic proctoring tool Smowl for computer monitoring and the web conferencing tool Google Meet on students’ smartphones for environmental monitoring (Bernardo and Bontà, 2023 ). All of these studies show that teaching assistant systems built on digital information technology play a vital role in supporting the achievement of educational equity, contributing to better dissemination and understanding of knowledge, and making a significant contribution to the field of learning. However, the above studies only focus on solving the problem of educational equity between one or two dimensions, and it cannot be ignored that educational equity has diversified characteristics, and it also needs to be considered from more dimensions such as digital technology, user interaction, educational process, and environment (Marrinan et al., 2015 ). This view is also supported by the research results of Fadhil ( 2022 ), which holds that human factor is related to students’ attitudes and skills in the learning process, and although self-initiative, independence, and improving technical skills are positive user factors, lack of discipline, difficulty in understanding course topics, and lack of communication skills are the most common negative factors in digital teaching. Environmental factors determine students’ comfort and familiarity with learning using digital systems, and teachers’ use of systematic teaching to encourage students to learn at their own pace is seen as a positive online learning atmosphere experienced by students, but distraction, lack of face-to-face interaction, and self-learning leading to antisocial emotions are found to be negative environmental factors, It also confirms that the existing digital teaching system is insufficient for the interaction between teachers and teachers’ teaching planning and users. The technical element involves the stability of the system, and while the ability to access anytime and anywhere, the quick access or upload of various resources, access to a wider audience, and the ease of learning have been cited as the most frequently mentioned positives, while poor internet connection, technical issues, lack of a user-friendly website and interface, significant negative factors, such as lack of hardware, are the most prominent barriers to educational equity, and the problems that are prevalent in these digital teaching assistant systems have not been well addressed to this day (Sarker et al., 2019 ). However, so far, the specific research on the integration of multiple dimensions for educational equity to embed digital technology into teaching to enhance learning, teaching, assessment and curriculum skills is limited, and most of the word-based teaching assistant systems still have heterogeneous characteristics, the tight coupling between digital tools and between digital tools and subject courses is insufficient, a large number of educational resource systems cannot be interconnected, resource sharing and software reuse, and information resources a2re not updated in a timely mannerIt is difficult to fully ensure the orderly, intensive and optimized resource integration services, which ultimately makes it difficult for teachers to improve their teaching plans and assist in filtering educational resources through the system, making it more difficult for them to establish teaching practices under educational equity. On the part of students, it is also difficult for them to obtain personalized learning content and better collaborative communication methods through the system, which leads to their low motivation to learn and affects their academic performance (Garcia-Martinez and Hamou-Lhadj, 2013 ). In summary, in order to achieve equal and high-quality education, it is challenging to introduce the common goals, common values and sustainable development methods of higher engineering disciplines in order to achieve the rapid development of self-organizing digital teaching systems based on digital information technology, information and communication technology (ICT) and digital learning (Farias-Gaytan et al., 2023 ). The development of a multi-dimensional digital teaching system architecture is a potential research opportunity to effectively improve educational inequity in the teaching and learning process (Da Silva et al., 2023 ). It is also conducive to better realizing seamless communication, interaction, resource sharing and information processing between education authorities, teachers and students. There is an urgent need to create an intelligent online teaching assistant system that matches curriculum planning and teaching evaluation decisions to achieve more convenient teacher-student interaction and high-quality online education (Hodges et al., 2020 ). This requires not only untapping the relationship between online teaching courses, assessments, and participant interactions (Ní Shé et al., 2019 ), but also using digital technologies to collect and diversify learning outcomes in a timely manner. Carry out accompanying evaluation that is integrated into the whole process of teaching, provide clear and transparent evaluation criteria, and use a variety of evaluation methods such as regular performance observation, learning process analysis, and learning outcome analysis. This all-round, multi-layered approach aims to fully grasp students’ learning and help teachers realize the visualization and intelligence of teaching plans and assessments, thereby enhancing the data mining and analysis capabilities of education and promoting personalized teaching. In addition, it is also necessary to provide timely feedback on students’ learning outcome evaluation according to curriculum standards to help students understand their own learning status, and at the same time pay attention to students’ privacy, so as to avoid the physical and psychological burden caused by the unfair evaluation process, so as to protect students’ physical and mental health. Therefore, based on the multi-dimensional criteria of practical ability, this study is to find a fairer curriculum planning and student learning outcome evaluation method in the current digital teaching of higher engineering, so as to solve the problems of difficult interactive planning of teaching and learning in online courses of higher engineering disciplines, difficult teaching course arrangement, and lack of consistency in performance evaluation. Establishment of evaluation model and construction of intelligent teaching assistance systemTo better aid the realization of digitized education equity in higher engineering disciplines, this study proposes a mulch-criteria group decision-making (MCGDM) model that combines Quality Function Deployment (QFD) with the t-test method, based on literature exploration and analysis. An accompanying intelligent online teaching assistant system has been developed. This system utilizes digital technology to expand teaching time and space, provide learning resources and tools, enhance student experience and interaction, and support data collection and application. It assists in facilitating teacher-student interactions and collaborative team design processes, promoting deep student involvement in the teaching process, and helping teachers in digital teaching course planning, analysis of student learning processes, and evaluation of learning outcomes. Introduction of evaluation methodsAddressing the challenges of teaching evaluation in higher engineering online courses necessitates the introduction of suitable multi-criteria group decision-making methods. Based on the results of literature exploration, this study adopts the QFD and t-test methods for teacher evaluation of student learning outcomes, as detailed below: Quality Function Deployment (QFD)QFD is an effective modern quality control method, serving as a user-driven quality improvement tool that translates user needs into service design elements. It effectively aids quality management in enhancing user satisfaction and is highly esteemed in the field of intelligent products and services (Singh and Kumar, 2021 ). It is also believed to enhance the teaching quality in higher entrepreneurship education and improve the teaching quality of higher entrepreneurship education (Jiang and Cao, 2021 ). Research on the construction of curriculum systems in higher engineering disciplines reveals that the QFD correlation matrix demonstrates the relationship between the core competencies of the discipline and the construction of curriculum system modules, effectively transforming core competencies into improvement needs for curriculum modules. The QFD steps used in this study are as follows: First of all, a number of teachers evaluate the importance levels of the curriculum core training ability K i , which can be categorized into five levels, which are Level 1 (needs irrelevant to the realization of functions), Level 2 (needs not affecting the realization of main functions), Level 3 (needs of more importance), Level 4 (needs of importance) and Level 5 (needs of significant importance). Then, the weighted average method is used on the teachers’ evaluation results so that the importance of core training ability K i is obtained. Then, the teachers brainstorm to discuss the course grading standard items in correspondence to each core training ability, and then uses the three relation degrees 9 , 3 , and 1 to evaluate the correlation between the curricular core training ability items and the curricular grading standard items. The correlation level is represented by symbols, that is, ▲weak = 1; ○ medium = 3; ◎ strong = 9; blank = 0 (that is, no correlation), and the correlation between the two items is shown as Eq. ( 1 ): H j is the absolute weighted grade of the curricular grading standard item, j ( j = 1,2, …, n ); K i is the weighted degree of the curricular core training ability item, i ( i = 1,2, …, m ); R ij ( i = 1,2, …, m ; j = 1,2, …, n ) is the correlation level, which indicates the importance of correlation between the curricular core training ability item i and the curricular grading standard item j . If the j- th course grading standard item is closely associated to a number of curricular core training ability items, and the concerned curricular grading standard items are of greater importance ( K i is larger), then the value of H j is larger, that is, the course grading standard item is more important. The t-test statistical method is widely used in education research, and shows high reliability in the applications of intelligent teaching evaluation research (Hooshyar et al., 2016 ). In the research on solution-based intelligent teaching assistant system, Zhang and Jia ( 2017 ) developed the Lexue 100 Intelligent Teaching Assistant System . Higher engineering courses often take teamwork to accomplish the learning outcomes, and the number of groups normally does not exceed thirty, which fits the t-test for small sample size (for example, n < 30) and parameter inspect conditions of normal distribution with unknown population standard deviation σ. It uses the t-distribution theory to deduct the probability of difference, so as to determine whether the difference between two means is significant. The t-test includes independent-sample t-test, dependent-sample t-test, and single-sample t-test. The purpose of this teaching practice case is to understand whether there are differences between the two design methods in students’ learning, and the learning effectiveness of each group of students under different evaluation standards, so dependent sample t-test is the only appropriate method. Dependent sample t-test is mainly applicable for the same batch of participants before and after receiving two experimental observations involving repeated measurements. Each pairing group is composed of two people, and the features concerned are identical, which can be regarded as one participant undergoing two experiments (in pairing) and verifying the significance of difference between two averages. This method can be used only on the condition that normal distribution is hypothesized and the result shows that the samples come from a normal population. The calculation method of the dependent sample t-test is shown in Eq. ( 2 ). When the above formula is used, its degree of freedom df = N -1. In which, N refers to the number of samples (the number of paired groups), \(\bar{d}=\frac{\sum d}{N}{=\bar{x}}_{1}-{\bar{x}}_{2}\) is the sample means of the sum of the differences between the first and the second test, \({\bar{x}}_{1}\) , \({\bar{x}}_{2}\) the sample mean of the first and second test result respectively, and Sd the standard deviation of these differences, as shown in Eq. ( 3 ): \(S\bar{d}\) hypothesizes that after repeated extractions an infinite number of \({\rm{d}}=({x}_{1}-{x}_{2})\) is obtained, of which the standard deviation consists of the frequency distribution of d is shown in formula 4: Construction of evaluation modelTo address the challenges faced by teachers in course teaching planning, scientific evaluation of student learning outcomes, and difficulties in student evaluation of teaching, this study proposes a multi-criteria group decision-making model based on the QFD and T-test methods. The assessment process is divided into two stages. In the first stage, focusing on the teacher’s assessment of student learning performance, the teacher focus group first uses QFD to determine the optimal course evaluation standards. Then, the teachers assess the performance of student course outcomes according to these standards, followed by using the T-test to analyze the students’ performance under each grading criterion. The second stage involves obtaining the assessment results. Teachers gain a comprehensive understanding of students’ learning situations through the results of student performance assessments. Students, on the other hand, learn about the quality of their course learning and the differences compared to their classmates based on the assessment results provided by the teachers. The diagram of the evaluation model is shown in Fig. 1 . 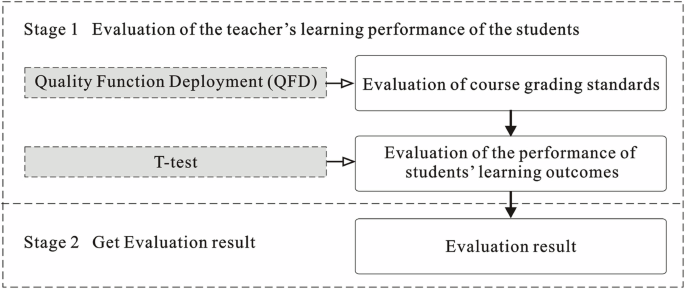 Evaluation model diagram. Construction of the intelligent teaching assistance systemBased on the aforementioned multi-criteria group decision-making model, this study has developed an intelligent online teaching assistance system (hereinafter referred to as the new system). The system offers both visualization display and intelligent assessment analysis functionalities. The former is realized through a system visualization interface that includes the presentation of student learning processes, outcomes, and teacher-student assessment analysis data. The latter is based on a backend programming system aligned with the assessment model, facilitating intelligent statistics and analysis of teacher-student assessment data. Teachers and students do not need to learn the calculation and analysis of the assessment methods; they simply need to fill out the assessment content according to the operational prompts provided by the new system’s interface. The results and analysis are then automatically calculated by the system’s backend and displayed on the interface. In developing this new system, we opted for a B/S structure (Browser/Web Server architecture) within an open-source framework comprising Apache (HTTP server), MySQL (relational database management system), and PHP (programming language), also known as the AMP stack, running on the Windows platform. This system is shared by teachers and students, allowing multiple users to perform online operations on the system interface simultaneously. The system settings for login and exit, account management, message feedback, and use of the help function are the same for both teachers and students.Based on the decision model and differing service requirements of teachers and students, the system has been designed and developed differently for each. Under the My Course submenu, the teacher interface is equipped with three interfaces for teaching material management, course grading standard assessment, and student evaluation results, while the student interface is set up for course material downloads and course grade queries. Under the Assignments Management submenu, the teacher interface has interfaces for learningprocess inspection and learning outcome evaluation, while the student interface only has interfaces for assignment modification and submission. The specific system processes for teachers and students are shown in Fig. 2 . Figures 3 and 4 respectively display the interfaces of the intelligent online teaching assistance system for the teacher and student interfaces (partial). 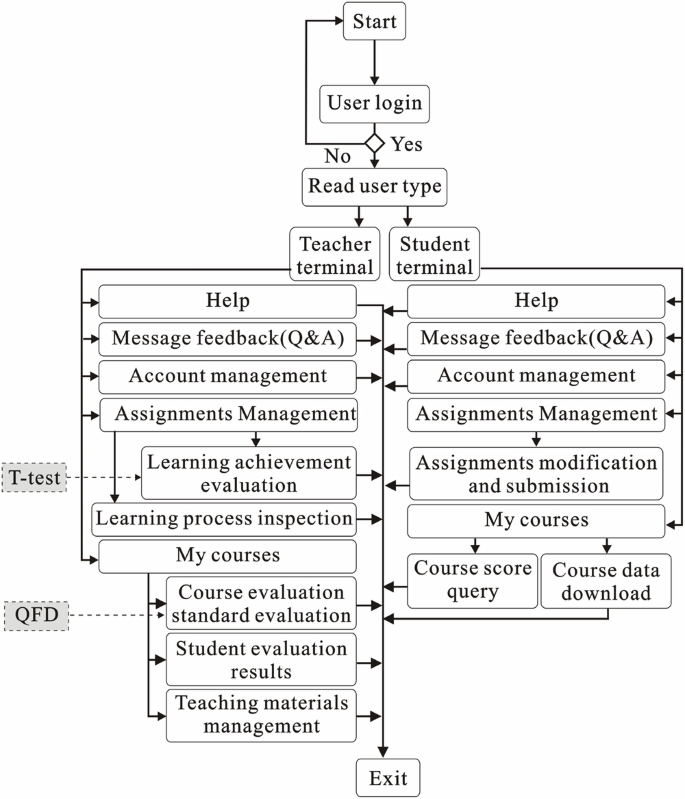 New system flow chart. 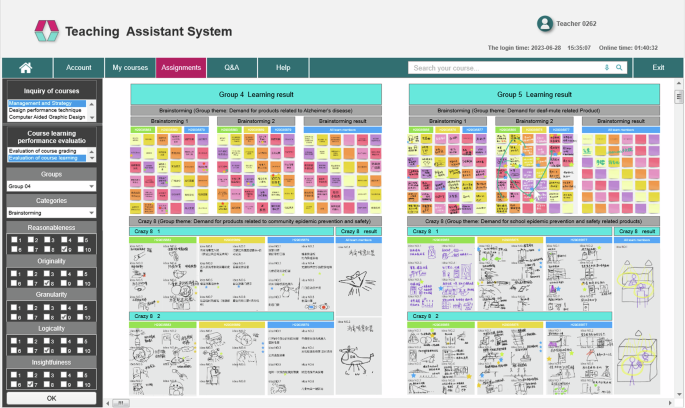 The teacher terminal interface display of the intelligent teaching assistant system (partial).  The student terminal interface display of the intelligent teaching assistant system (partial). Instructional practice and result analysisThis case study is based on an online course (Design Management and Strategy) offered at the College of Mechanical Engineering and Automation at a university in China. There were 48 participants, all senior students majoring in Industrial Design. The course required teamwork to complete learning outcomes, with students divided into 16 groups of three each. The entire course lasted for 7 weeks, totaling 21 class hours, with one session per week and each session lasting for 3 class hours, where each class hour was 50 min long. Among these, 9 class hours were dedicated to the course instructor introducing the teaching content and operational methods of the related online systems, while the remaining 12 class hours involved each group of students conducting online course training based on course topics designated by the teacher. The course utilized Tencent Meeting and the new system developed in this study for online teaching practice. Tencent Meeting was used for teaching course content, assigning tasks, and conducting voice communication with students, while the new system was used to display student learning performance results and teaching evaluation analysis outcomes. This case involves both teachers’ evaluation of program assessment criteria and evaluation of student learning outcomes. The following sections will discuss the acquisition, description, and intelligent computation analysis of the assessment data from both teachers and students based on the new system. Assessment of course grading standardsThe course is certified under the OBE concept in higher engineering education in a Chinese university. Majors seeking certification are required to define the grading standards of course learning outcomes based on core training abilities specified in the certification norms and evaluate the attainment of students’ learning outcomes according to these grading standards. This is also the key to achieving a more objective and fair assessment of students’ learning outcomes by teachers. Therefore, the three members of the course teaching focus group (one associate professor and two lecturers) used the four core training abilities specified for the course (expression, insight, analysis, and cooperation abilities) as preliminary guidelines. And through the QFD, it is translated into fourteen course grading criteria (see Table 1 for the relevant codes). Then, fill in all of them into the weight table set on the Course Grading Criteria Evaluation interface of the new system teacher, and the system will automatically generate the weight results of all grading criteria after obtaining the weight results of the importance of the core training ability items provided by the teacher and the importance of the relationship between the core training ability items and the course grading standard items (See Table 2 ). The results of Table 2 show that the highest weight value of core cultivation ability is Ability of Insights, followed by Ability of Expression, and the other two items are the lowest with the same weight. The relationship between the core training ability items and the course grading standard items and the weighted value of the importance of the ranking of the absolute advantages are Reasonable, Elaboration, Logicality, Insightful and Collaboration. Therefore, the course teaching team takes these five course grading criteria as the final evaluation criteria for the course and uses them to evaluate the student achievement performance in this case study. Finally, the results will be presented on the student side of the system, making evaluation criteria open and transparent, to guide students’ efforts in their course work. Teacher assessment of student learning performanceIn order to minimize the influence of external factors on learning practices, the research obtained the real performance of the students in the course in learning the Brainstorming and Crazy 8 methods. To minimize external influences on learning practice and to capture the true learning performance of students taught using the Brainstorming and Crazy 8 methods, standardized formats for these methods were designed by the course teacher and submitted to the teacher’s interface of the new system under teaching material management. Students can use them in the Assignment Management interface on the student side of the system to present the group’s learning process outcomes and final outcomes (see Fig. 3 ). Furthermore, the course implemented both methods by performing different tasks, with each method having the same execution process and duration (6 class hours for each method). The topic for the Brainstorming task was the development of product design requirements for users with disabilities, and for Crazy 8, it was the development of covid -19 epidemic prevention products. Both methods required each student group to conduct an ice-breaking survey task (2 class hours), then present results of two rounds of task ideation and convergence (1 class hour) on the student interface of the new system. This was followed by sharing and discussing with all course participants (1 class hour). Finally, group discussions determined the final user demand results and optimized and submitted the learning outcomes of the entire implementation process (2 class hours). The evaluation of learning outcomes will be carried out by a course focus group composed of three teachers with experience in teaching the course, which to obtain more objective and fair evaluation results. After students submitted their learning outcomes on the new system, the three teachers from the course focus group evaluated the learning outcomes of the 16 student groups based on the five course grading criteria using the homework management interface in the teacher’s side of the new system. The system then intelligently generated statistical results using weighted averages. The course teachers use the systematic Dependent Sample T-test to obtain statistical results of the learning performance of each group under five grading criteria of the two methods (see Tables 4 and 5 ). The data results in Table 3 show that among the 16 groups, the group with the highest academic score is Group 5, with a score of 90.85, and the grade is excellent. Group 6 is also excellent, with a score of 90.56; the group with the lowest score is Group 16, the failing score of 55.65 points. Judging from the overall results of various scoring standards, the learning performance of the whole class in Brainstorming is better than that of Crazy 8. However, among all the standards, the best performance of the class is Crazy 8’s standard Elaboration, while the worst performance is Crazy 8’s Logicality. In addition, the data in Table 3 also presents the evaluation results of each standard for each group. For example, the performance results of the two design methods of Group 5 with excellent results are excellent. Brainstorming has better learning results than Crazy 8, and the learning results of Logicality, the Brainstorming scoring standard, are the best.Taking Group 1 again for example, the learning effect of Brainstorming in this group is relatively better than that of Crazy 8, but among all performances, Crazy 8’s Elaboration has the highest performance, and the learning effect is the best among the five scoring criteria of Brainstorming. It is Reasonable, the Elaboration is relatively low, and the Insightful of Crazy 8 is also low. These can be used as learning goals for future efforts. The 16th group with the lowest ranking is not respectable in terms of expressiveness of both design methods, but the learning effect of Brainstorming is relatively better than Crazy 8. Among the five scoring criteria of Brainstorming, the best learning effect is Logicality. All standard projects except for these require intensive training in the future. The situation of other groups can be deduced similarly. Based on the results in Tables 4 and 5 , as indicated by the t-test critical value table prompted on the new system interface, it is known that \({{\rm{t}}}_{0.05\left(16-1\right)}=1.753\) ,16 groups using the Brainstorming and Crazy 8 methods is t = 2.491 > 1.753. This demonstrates that there is a significant difference in the learning outcomes between the Brainstorming method and the Crazy 8 method among the 16 groups, with Brainstorming showing a notably better learning effect than Crazy 8. Additionally, the t-values of the total scores in the five creativity performance indicators for both Brainstorming and Crazy 8 methods are greater than 1.753. This implies significant differences in the learning performance of Brainstorming over Crazy 8 in four of the grading standards, except for the grading standard Elaboration, where Crazy 8 outperformed Brainstorming. The biggest difference in learning outcomes between the two methods is in the grading standard Elaboration, indicating superior performance in Crazy 8’s Elaboration learning. The grading standard Collaboration also shows a significant difference, with Brainstorming performing much better than Crazy 8. The smallest difference between the two methods is in the grading standard Insightful, suggesting similar performance between the two learning methods. Teachers can use these results to gain a comprehensive understanding of student performance and tailor their teaching accordingly. Meanwhile, students can access these results through the new system’s course grade query function, understanding their group’s performance status among all groups, and focus on improving their weaker grading standards to enhance their academic performance. Results and discussionsThe main purpose of this section is to explore the impact of the new system on students’ academic performance, teacher and student experience attitudes and satisfaction compared with other currently used systems. The specific implementation is as follows. In order to further understand whether the new system can lead to better learning performance compared with other systems, this study is verified by the experiment group and the control group. The engineering practice course of this study is still design management and strategy, and since the course time is fixed in the first semester of each student’s senior year, this experimental test last for two years. The background conditions verified by this experiment are the same, the teacher is the same, and the teaching content, coursework content and teaching time arrangement are the same. The academic performance of the two groups of students before admission is basically similar. The most representative products are selected for the control group to make the verification results more comparative, so the teaching assistant system, which currently is the most frequently used in China’s higher engineering schools, is finally selected to provide the control group with the most frequent operation.Considering the protection of the rights and interests of the system, the name of the system is omitted here, and the name is referred to as System A. Although the system will be different from the new system developed in this study (referred to as System B) in terms of digital technology and interface, it also has the same teaching and learning-related functions for teachers and students, such as teaching management, classroom teaching, learning analysis and other functions on the teacher’s side, and course information resource download, learning results submission, grade viewing and other functions on the student side. However, it also needs to use the voice and video functions of other social platforms to assist teaching, and here it uses Tencent Meeting to assist teaching like the experiment group. The two groups of test subjects are the two consecutive classes of students from the same school and major, respectively. The experiment group (i.e., Class B) consists of 48 students who participate in the teaching practice of the new system, and their results are shown in Table 3 . Before the implementation of the course, the participants in the control group have not used System B, but were familiar with the operation of System A, so they do not need to be trained in system operation. The test subjects in the control group (i.e., Class A) were 54 students, and they are divided into eighteen groups to work in teams to complete the course learning tasks, including regular learning tasks (i.e., the process tasks of Brainstorming and Crazy 8) and assessment learning tasks (comprehensive learning tasks of Brainstorming and Crazy 8). After students complete the regular learning process results and assessment learning results submitted on the system, the teacher (one teacher) all the learning outcomes of each group on the teacher’s interface. The system adopts the traditional course assessment method, consisting of procedural outcome assessment results and exam outcome assessment results. The final score of the course is 100 points, of which the regular score accounts for 30% of the total score of the course, and the exam score accounts for 70% of the total score. Finally, the performance data obtained by each group of Class B are shown in Table 6 , in which the regular homework codes of Brainstorming are B-1 and B-2, the final exam homework codes are B-R, the regular homework codes of Crazy 8 are C-1, C-2, C-R, and the final exam homework code is C-R. The independent samples t-test is an analytical method to test the difference between the mean values of the two groups of cases, so the study is based on the actual course learning results of the students in the two classes under different systems, and the results obtained by the independent samples t-test are used to understand the overall learning effectiveness of the two classes, and the relevant data are shown in Table 7 , under the assumption of equal variance, F = 1.052, significance probability Sig. = 0.313 > 0.05, Indicates that the variance of learning outcomes between the two classes is equal. The two-tailed significance probability of the t-distribution Sig. = 0.048 < 0.05 indicates that there is a significant difference in learning effectiveness between the two groups. The average results of the two classes showed that Class B students had better learning outcomes than Class A, indicating that the new system was conducive to improving students’ learning outcomes. Then, the results of the questionnaire survey of digital teaching assistant system for teachers and students are used to obtain the experience attitude and satisfaction of teachers and students. Due to the different purposes of teachers and students using the system, the ways they consider the functions of the system are also different, so the survey uses the Likert five-point scale to design a questionnaire for teachers and students, in which 5-points indicate strongly agree , 4-points agree , and 3-points neutral , 2 points disagree and 1-point strongly disagree , and the participants are informed of the purpose of the study through online consent. A total of 33 questions are prepared for the students, including 5 questions on personal basic information, 20 questions on the satisfaction evaluation of system functions, and 8 questions on the experience of using the system. A total of 34 questions are prepared for teachers, including 5 questions on personal basic information, 19 questions on system function satisfaction evaluation, and 10 questions on system user experience. In the last two parts of the two questionnaires, each question is asked once for each system. The relevant codes are shown in Tables 8 and 9 . This questionnaire is collected from teachers and students who have used both systems. System A is the official teaching system of the school that has been used by both the teachers and students tested. At present, System B has been opened to the engineering disciplines of two universities, and the teachers of the engineering practice courses have applied the system to teach, and the students in the control group have used System B in other professional practice courses after the end of the course, so the questionnaire survey of the students is mainly collected from the two classes of students in this study case, and one abnormal questionnaire with no difference in the results of each option is eliminated, and a total of 101 valid questionnaires are collected. The questionnaire survey of teachers is mainly collected from teachers who have used two systems in two higher engineering disciplines, and a total of 57 valid questionnaires are collected after eliminating abnormal questionnaires. Since the questionnaire consists of two different types of questions, the attitude evaluation results of system functional satisfaction and user experience are statistically analyzed with SPSS 19, and the reliability and validity of the teacher-student questionnaire and related statistical results are shown in Table 10 . The results in Table 10 show that the reliability coefficient of the teacher-student questionnaire is greater than 0.9,indicating that the reliability is excellent and the questionnaire is internally consistent. The KMO of the student questionnaire was greater than 0.8, indicating that the validity of the questionnaire is suitable for principal component analysis of factor analysis, and the KMO of the teacher questionnaire is greater than 0.7, indicating that the validity of the questionnaire meets the requirements of principal component analysis of factor analysis, and the Sig of the teacher-student questionnaire is 0.000, and the Sig < 0.01 indicates that the questionnaire also has externalvalidity, indicating that there are significant differences between the two sets of questionnaires for teachers and students. The statistical results show that teachers and students are satisfied with the performance of most functions of System A, indicating that the system has met the basic functions required by teachers and students for online teaching courses, and shows excellent functional characteristics in terms of convenient operation, smooth operation, clear operation structure and navigation instructions, diversified resource types, and rapid access to the required resources. In addition, most of the students said that System A is also better than System B in terms of diversification of teaching forms, submitting students’ learning process results and assessment results, which can help them greatly improve their learning initiative, students’ creative ideas, and obtain more design solutions and enthusiasm for learning. The vast majority of engineering teachers and students who participate in this survey believe that the digital teaching assistant system of higher engineering disciplines has the functions of teaching and learning, which is in line with the characteristics of the curriculum of higher engineering disciplines, multi-dimensional learning evaluation analysis, reports, teacher-student interaction methods that are in line with the teaching characteristics of higher engineering disciplines, and has clear operating structures and navigation instructions, which are extremely important to help teachers and students establish a fair teaching environment. In addition, more than 40% of the teachers also show a high willingness to create a learning environment that supports the characteristics of the higher engineering curriculum, closely correlate the recommended resources with the curriculum content of the higher engineering discipline, and provide an interface for comprehensively observing the results of the students’ learning process and assessment. More than 40% of the students also emphasize that the systematic interface for the publication of course learning tasks and learning grading standards, the interface of the learning process and the evaluation record of the achievement evaluation is extremely important for the exchange of their learning information. In the face of the needs of teachers and students, the disadvantages of system A are also particularly obvious, and the vast majority of teachers clearly said that System A is very poor in creating a learning environment that supports the characteristics of higher engineering courses, the readability of logical connections between resources, and the multi-dimensional learning evaluation and analysis report, which leads to a poor overall user experience of the system, which will greatly affect their enthusiasm for teaching. The vast majority of students are mostly neutral in their satisfaction with the functions of System A, and relatively few are satisfied or very satisfied, indicating that the students’ experience of System A will not be too good, and there is still a lot of room for improvement in the system. We have found that teachers and students favor System B far more than System A, and there are 8 functions to achieve the satisfaction level of teachers and students, among which the functions that teachers and students are satisfied with are multi-dimensional learning evaluation analysis reports and teacher-student interaction methods that fits the teaching characteristics of higher engineering disciplines, and the satisfaction weights of these two items are far higher than those of System A. This shows that these two functions are the biggest advantages of System B. The teachers’ satisfaction with the functions of System B in providing an interface for comprehensive observation of students’ learning process results and assessment results. Student interaction and collaboration method that fits the characteristics of higher engineering disciplines teaching, and close relevance between recommended resources and content of advanced higher engineering disciplines are better than those of System A. In addition, the system provides a fair learning standard evaluation function, student learning process and achievement observation and evaluation record function is also outstanding, and the multi-dimensional learning evaluation analysis report function, improve the efficiency of teaching, and provide effective help for improving the teaching plan. The students believe that interface for publishing course learning tasks and learning grading standards, timely reminding of evaluation results of students’ learning process the performance of System B is much better than that of System A, which is not only more in line with the characteristics of their disciplines and majors, but also fully demonstrates the equity of education in terms of smooth learning communication, transparency of learning tasks and assessment standards, and multi-dimensional analysis of learning performance reports, and believes that System B can help improve their learning efficiency more than System A. The ability to independently construct the cognitive framework of professional courses and creative ideas to obtain more design solutions make them more enthusiastic about learning, and then their learning effectiveness is also greatly improved. The above student self-evaluation results were also confirmed in the results of the teacher questionnaire. In addition, the students said that there is not much difference between the two systems in terms of the interface and smooth operation of the evaluation records of the students’ learning process and the assessment results. However, this does not affect the students’ recognition of System B, which generally says that System B is better than System A in terms of improving learning efficiency and learning effectiveness. The analysis results show the successful development of a proposed digital teaching assistant system based on the multi-criterion group decision-making model, and the case study reflects the feasibility of the whole experiment. The advantage of the system lies in the fact that the teaching and learning functions developed are suitable for the teaching characteristics of higher engineering disciplines and create a fair educational environment. Compared with the existing teaching system, the system developed in this study is more effective in resource recommendation, teacher-student interaction, and student-student interaction and collaboration, which can provide a functional support more in line with the diversified needs of teachers in curriculum planning and students’ learning and collaboration. In addition, a better educational equity has been demonstrated in terms of the learning process and the assessment of learning outcomes. The system provides the publication of learning tasks and learning outcome grading standards, as well as the submission, observation, evaluation and feedback of learning processes and learning outcomes, in addition to the multi-dimensional learning evaluation analysis report obtained under the Coverage Criteria Group Decision Making (MCGDM) model based on QFD combined with t-test, which can help provide a fair learning environment and overcome the ambiguity of learning assessment in the design discipline. It is conducive to the transformation of evaluation from summative evaluation to formative evaluation and avoids unfair evaluation results. At the same time, it also allows teachers and students to better understand the overall learning situation of the course, provides all-round guidance for teachers to capture the characteristics and individual differences of student groups and improve teaching planning, and also provides students with targeted teaching content, diversified learning resources, differentiated learning paths, and personalized learning guidance. This is also the reason why the system’s teacher-student interaction and multi-dimensional learning evaluation analysis reports gain wide satisfaction among teachers and students. Therefore, we have reason to believe that the system has created good conditions for the establishment of teaching equity, and can effectively solve the problems in curriculum teaching planning, student learning performance evaluation, and teaching quality in higher engineering disciplines digitized education. This study also provides a new perspective on the teaching and evaluation of similar online courses, provides additional options for teachers of related disciplines to better reflect educational equity, develop core competencies, and deepen the learning experience, and also contributes to how higher engineering disciplines can understand and enhance digitized education learning at the university and national levels. In the future, it is necessary to carry out more run-in experiments with related disciplines to make the system function more suitable for the particularity of the course. By refining the specific implementation paths and strategies, carrying out point-to-point practice, and developing replicable and generalizable tools, we will promote the reform of curriculum teaching. In addition, the next plan is to improve the disadvantages of the new system identified in the user questionnaire to create a better user experience. Data availabilityThe data sets generated and/or analyzed during the present study include the personal information of the participants, so they are not in any repository, but an anonymized version is available to the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Aithal PS, Aithal S (2016) Impact of on-line education on higher education system. Int J Eng Res Mod Educ 1(1):225–235 Google Scholar Albrahim FA (2020) Online teaching skills and competencies. Turkish Online J Educ Technol 19(1):9–20 Angelova M (2020) Students’ attitudes to the online university course of management in the context of COVID-19. Int J Technol Educ Sci 4(4):283–292 Article Google Scholar Azizi NA (2017) Malaysia at the forefront of e-Learning. New Straits Times. Retrieved from https://www.nst.com.my/news/nation/2017/09/284259/malaysia-forefront-e-learning Bernardo M, Bontà E (2023) Teaching and learning centers and coordinated technologies for an effective transition at COVID-19 pandemic time to massive distance learning and online exams. J e-Learn Knowl Soc 19(2):22–29 Bhat S, D’Souza R, Bhat S, Raju R, Kumara BP (2020) Effective deployment of outcome based education: strategies based on motivational models. J Eng Educ Transform 33:164–169 Chiao HM, Chen YL, Huang WH (2018) Examining the usability of an online virtual tour-guiding platform for cultural tourism education. J Hospitality Leis Sport Tour Educ 23:29–38 Cullen R, Kullman J, Wild C (2013) Online collaborative learning on an ESL teacher education programme. ELT J 67(4):425–434 Da Silva FL, Slodkowski BK, da Silva KKA, Cazella SC (2023) A systematic literature review on educational recommender systems for teaching and learning: research trends, limitations and opportunities. Educ Inf Technol 28(3):3289–3328 Danjou PE (2020) Distance teaching of organic chemistry tutorials during the COVID-19 pandemic: focus on the use of videos and social media. J Chem Educ 97(9):3168–3171 Article CAS Google Scholar Dewanti P, Candiasa IM, Tegeh IM, Sudatha IGW (2022) The SMILE, A cyber pedagogy based learning management system models. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 13(4):142–153 Elmasry MA, Ibrahim MH (2021) Cloud computing for e-learning: a proposed model for higher education institutions in developing countries. Artic Int J Sci Technol Res 10(4):408–416 Fadhil NFM (2022) Using rich picture to understand the issues and challenges in e-learning environment: a case study of students in higher education institution. World J Engl Lang 12(2):189–189 Farias-Gaytan S, Aguaded I, Ramirez-Montoya MS (2023) Digital transformation and digital literacy in the context of complexity within higher education institutions: a systematic literature review. Humanit soc sci comm 10(1):1–11 Garcia-Martinez S, Hamou-Lhadj A (2013) Educational recommender systems: a pedagogical-focused perspective. Multimedia Serv Intell Environ Recommend Serv 113–124 Hebebci MT, Bertiz Y, Alan S (2020) Investigation of views of students and teachers on distance education practices during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. Int J Technol Educ Sci 4(4):267–282 Hodges CB, Moore S, Lockee BB, Trust T, Bond MA (2020) The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. https://er.educause.edu/articles/2020/3/the-difference-between-emergency-remote-teaching-and-online-learning Hooshyar D, Ahmad RB, Yousefi M, Fathi M, Horng SJ, Lim H (2016) Applying an online game-based formative assessment in a flowchart-based intelligent tutoring system for improving problem-solving skills. Comput Educ 94:18–36 Ibrahim AF, Attia AS, Asma’M B, Ali HH (2021) Evaluation of the online teaching of architectural design and basic design courses case study: college of architecture at JUST, Jordan. Ain Shams Eng J 12(2):2345–2353 Jiang H, Cao Y (2021) An empirical study of entrepreneurship education and teaching in Colleges and Universities under the concept of sustainable development. EDP Sciences 251:02084 Lantada AD (2020) Engineering education 5.0: Continuously evolving engineering education. Int J Eng Educ 36(6):1814–1832 Li J, Li Z, Liu SF, Cheng M (2020) Applying a fuzzy, multi-criteria decision-making method to the performance evaluation scores of industrial design courses. Interact Learn Environ 28(2):191–205 Li Y, García-Díaz V (2022) Design of distance assistance system for intelligent education based on WEB. Mob Netw Appl 27(6):2565–2574 Lin S, Dong Y, Lan X, Luyun Z (2021) Online Teaching and Reform of the “Intelligent Furniture Design” Course during the Covid-19 Epidemic. In 2021 2nd International Conference on Education, Knowledge and Information Management (ICEKIM) (pp. 150-153). IEEE Luo X (2019) Research on the construction and operation of information teaching platform of university public courses based on SPOC. Inf Sci 37(12):112–115 Margaryan A, Bianco M, Littlejohn A (2015) Instructional quality of massive open online courses (MOOCs). Comput Educ 80:77–83 Marrinan H, Firth S, Hipgrave D, Jimenez-Soto E (2015) Let’s take it to the clouds: the potential of educational innovations, including blended learning, for capacity building in developing countries. Int J Health Policy Manag 4(9):571 Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Matthew UO, Kazaure JS, Okafor NU (2021) Contemporary development in E-Learning education, cloud computing technology & internet of things. EAI Endorsed Trans Cloud Syst 7(20):e3–e3 Mahmood LS, Mohammed CA, Gilbert JH(2021) Interprofessional simulation education to enhance teamwork and communication skills among medical and nursing undergraduates using the TeamSTEPPS® framework. Med J Armed Forces India 77:S42–S48 Miller R, Liu K (2023) After the virus: disaster capitalism, digital inequity, and transformative education for the future of schooling. Educ Urban Soc 55(5):533–554 Namoun A, Alshanqiti A (2021) Predicting student performance using data mining and learning analytics techniques: a systematic literature review. Appl Sci 11(1):237 Ní Shé C, Farrell O, Brunton J, Costello E, Donlon E, Trevaskis S, Eccles S (2019) Teaching online is different: critical perspectives from the literature. https://doras.dcu.ie/23890/1/13758_Text_V3.pdf Rajab MH, Gazal AM, Alkattan K (2020) Challenges to online medical education during the COVID-19 pandemic. Cureus 12(7):e8966 PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Sajja R, Sermet Y, Cwiertny D, Demir I (2023) Platform-independent and curriculum-oriented intelligent assistant for higher education. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 20(1):42 Sarker FH, Mahmud R, Al, Islam MS, Islam K (2019) Use of e-learning at higher educational institutions in Bangladesh. Opportunities and challenges. J Appl Res High Educ 11(2):210–223 Shukor NA, Abdullah Z (2019) Using learning analytics to improve MOOC instructional design. Int J Emerg Technol Learn 14(24):6–17 Singh A, Kumar S (2021) Picture fuzzy set and quality function deployment approach based novel framework for multi-criteria group decision making method. Eng Appl Artif Intell 104:104395 Sun Z, Anbarasan M, Praveen Kumar DJCI (2021) Design of online intelligent English teaching platform based on artificial intelligence techniques. Comput Intell. 37(3):1166–1180 Article MathSciNet Google Scholar Villegas-Ch W, Román-Cañizares M, Palacios-Pacheco X (2020) Improvement of an online education model with the integration of machine learning and data analysis in an LMS. Appl Sci 10(15):5371 Yang C, Lin JCW (2022) Design of distance assistance system for intelligent education by web-based applications. Mob Netw Appl 27(3):1174–1185 Zhang B, Jia J (2017). Evaluating an intelligent tutoring system for personalized math teaching. In 2017 international symposium on educational technology (ISET) (pp. 126-130). IEEE Download references Author informationAuthors and affiliations. Department of Industrial Design, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan, ROC Shuo-fang Liu & Juan Li College of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Huaqiao University, Xiamen, China Fine Art and Design College, Quanzhou Normal University, Quanzhou, China Hang-qin Zhang Graduate School of Human Sciences, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan NingboTech University, Ningbo, China You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar ContributionsStudy conception and design: JL and SFL. Data collection: JL and HQZ. Analysis and interpretation of results: JL and ZL. Original draft preparation: JL and MC. Supervision: SFL. Revision: JL. All authors reviewed the results and accepted the published version of the manuscript. Corresponding authorCorrespondence to Juan Li . Ethics declarationsCompeting interests. The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approvalThis study examines the implementation of an online teaching assistant system designed to enhance teaching, assessment, and address educational inequity. Our institution deemed ethical approval unnecessary under the Declaration of Helsinki, as the study was not classified as medical research or human experimentation. Conducted in accordance with guidelines for research involving human participants, all participants were over 18 years old and provided informed consent. They were assured that their information would be kept confidential and anonymous, and used solely for educational research purposes. Informed consentParticipants were informed about the overall objectives and aim of the study, the validation procedures of the study requirements, confidentiality of information, voluntary participation, and ability to opt out of the study if needed. All experts gave their agreement to participate in the study and consented to processing of their data. Additional informationPublisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Supplementary informationSupplemental material 1, supplemental material 2, rights and permissions. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ . Reprints and permissions About this articleCite this article. Liu, Sf., Li, J., Zhang, Hq. et al. Development and implementation of digital pedagogical support systems in the context of educational equity. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 1084 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03616-y Download citation Received : 30 December 2023 Accepted : 19 August 2024 Published : 24 August 2024 DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03616-y Share this articleAnyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative Quick links- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
 Have a language expert improve your writingRun a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free. Methodology - External Validity | Definition, Types, Threats & Examples
External Validity | Definition, Types, Threats & ExamplesPublished on May 8, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on December 18, 2023. External validity is the extent to which you can generalize the findings of a study to other situations, people, settings, and measures. In other words, can you apply the findings of your study to a broader context? The aim of scientific research is to produce generalizable knowledge about the real world. Without high external validity, you cannot apply results from the laboratory to other people or the real world. These results will suffer from research biases like undercoverage bias . In qualitative studies , external validity is referred to as transferability. Table of contentsTypes of external validity, trade-off between external and internal validity, threats to external validity and how to counter them, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about external validity. There are two main types of external validity: population validity and ecological validity. 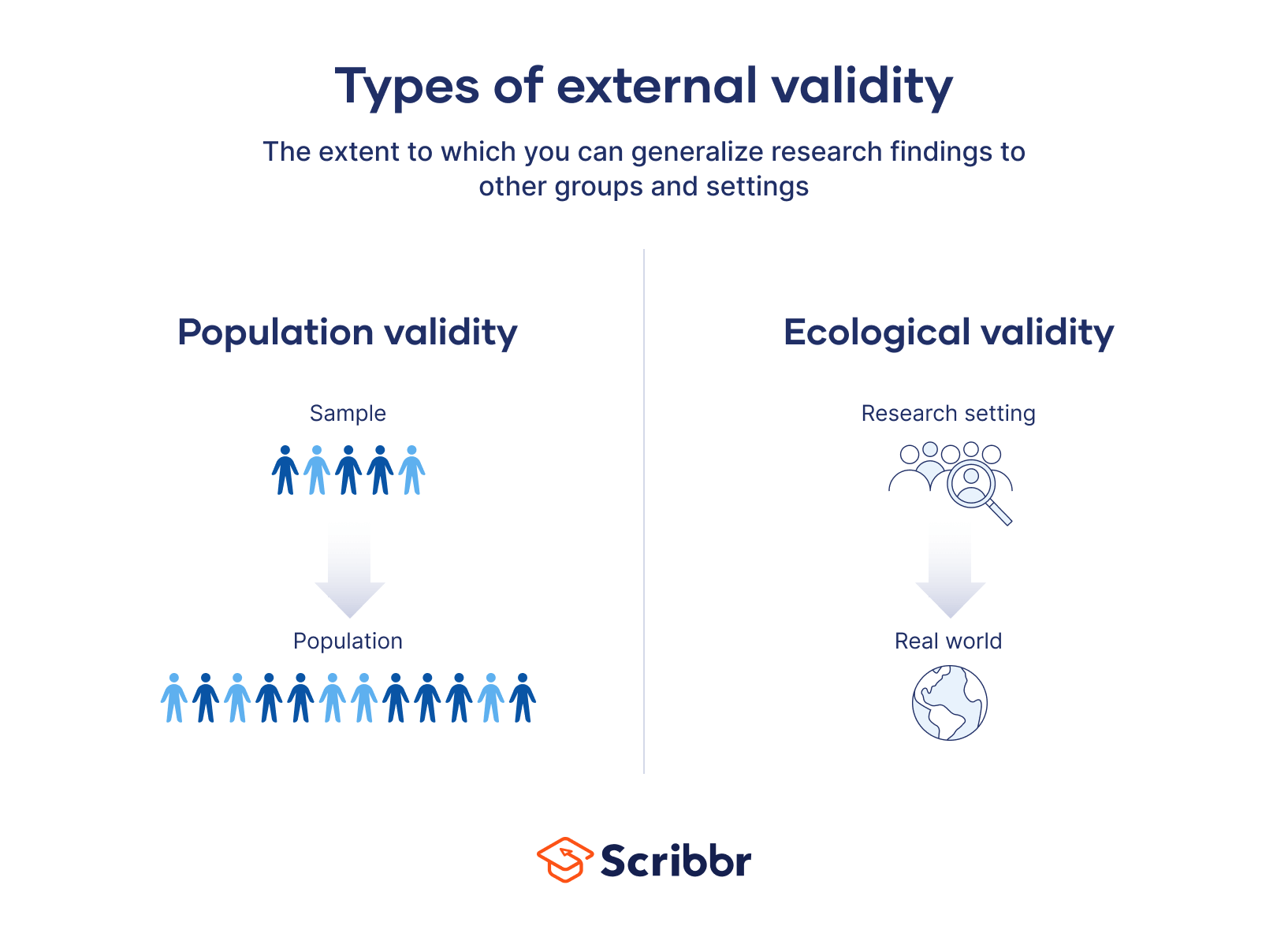 Population validityPopulation validity refers to whether you can reasonably generalize the findings from your sample to a larger group of people (the population). Population validity depends on the choice of population and on the extent to which the study sample mirrors that population. Non-probability sampling methods are often used for convenience. With this type of sampling, the generalizability of results is limited to populations that share similar characteristics with the sample. You recruit over 200 participants. They are science and engineering majors; most of them are American, male, 18–20 years old and from a high socioeconomic background. In a laboratory setting, you administer a mathematics and science test and then ask them to rate how well they think performed. You find that the average participant believes they are smarter than 66% of their peers. Here, your sample is not representative of the whole population of students at your university. The findings can only reasonably be generalized to populations that share characteristics with the participants, e.g. college-educated men and STEM majors. For higher population validity, your sample would need to include people with different characteristics (e.g., women, non-binary people, and students from different majors, countries, and socioeconomic backgrounds). Samples like this one, from Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich and Democratic (WEIRD) countries, are used in an estimated 96% of psychology studies , even though they represent only 12% of the world’s population. Since they are outliers in terms of visual perception, moral reasoning and categorization (among many other topics), WEIRD samples limit broad population validity in the social sciences. Ecological validity refers to whether you can reasonably generalize the findings of a study to other situations and settings in the ‘real world’. In a laboratory setting, you set up a simple computer-based task to measure reaction times. Participants are told to imagine themselves driving around the racetrack and double-click the mouse whenever they see an orange cat on the screen. For one round, participants listen to a podcast. In the other round, they do not need to listen to anything. After assessing the results, you find that reaction times are much slower when listening to the podcast. In the example above, it is difficult to generalize the findings to real-life driving conditions. A computer-based task using a mouse does not resemble real-life driving conditions with a steering wheel. Additionally, a static image of an orange cat may not represent common real-life hurdles when driving. To improve ecological validity in a lab setting, you could use an immersive driving simulator with a steering wheel and foot pedal instead of a computer and mouse. This increases psychological realism by more closely mirroring the experience of driving in the real world. Alternatively, for higher ecological validity, you could conduct the experiment using a real driving course. Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading servicesDiscover proofreading & editing Internal validity is the extent to which you can be confident that the causal relationship established in your experiment cannot be explained by other factors. There is an inherent trade-off between external and internal validity ; the more applicable you make your study to a broader context, the less you can control extraneous factors in your study. Threats to external validity are important to recognize and counter in a research design for a robust study. Participants are given a pretest and a post-test measuring how often they experienced anxiety in the past week. During the study, all participants are given an individual mindfulness training and asked to practice mindfulness daily for 15 minutes in the morning. Threats to external validity | Threat | Meaning | Example | | | The sample is not representative of the population. | The sample includes only people with depression. They have characteristics (e.g., negative thought patterns) that may make them very different from other clinical populations, like people with personality disorders or schizophrenia. | | History | An unrelated event influences the outcomes. | Right before the pre-test, a natural disaster takes place in a neighbouring state. As a result, pre-test anxiety scores are higher than they might be otherwise. | | | The characteristics or behaviors of the experimenter(s) unintentionally influence the outcomes, leading to bias and other . | The trainer of the mindfulness sessions unintentionally stressed the importance of this study for the research department’s funding. Participants work extra hard to reduce their anxiety levels during the study as a result. | | | The tendency for participants to change their behaviors simply because they know they are being studied. | The participants actively avoid anxiety-inducing situations for the period of the study because they are conscious of their participation in the research. | | Testing effect | The administration of a pre- or post-test affects the outcomes. | Because participants become familiar with the pre-test format and questions, they are less anxious during the post-test and remember less anxiety then, leading to . | | Aptitude-treatment | Interactions between characteristics of the group and individual variables together influence the dependent variable. | Interactions between certain characteristics of the participants with depression (e.g., negative thought patterns) and the mindfulness exercises (e.g., focus on the present) improve anxiety levels. The findings are not replicated with people with personality disorders or schizophrenia. | | Situation effect | Factors like the setting, time of day, location, researchers’ characteristics, etc. limit generalizability of the findings. | The study is repeated with one change; the participants practice mindfulness at night rather than in the morning. The outcomes do not show any improvement this time. | How to counter threats to external validityThere are several ways to counter threats to external validity: - Replications counter almost all threats by enhancing generalizability to other settings, populations and conditions.
- Field experiments counter testing and situation effects by using natural contexts.
- Probability sampling counters selection bias by making sure everyone in a population has an equal chance of being selected for a study sample.
- Recalibration or reprocessing also counters selection bias using algorithms to correct weighting of factors (e.g., age) within study samples.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. - Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
Research bias - Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formattingProfessional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on: - Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example  The external validity of a study is the extent to which you can generalize your findings to different groups of people, situations, and measures. I nternal validity is the degree of confidence that the causal relationship you are testing is not influenced by other factors or variables . External validity is the extent to which your results can be generalized to other contexts. The validity of your experiment depends on your experimental design . There are seven threats to external validity : selection bias , history, experimenter effect, Hawthorne effect , testing effect, aptitude-treatment and situation effect. The two types of external validity are population validity (whether you can generalize to other groups of people) and ecological validity (whether you can generalize to other situations and settings). Cite this Scribbr articleIf you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator. Bhandari, P. (2023, December 18). External Validity | Definition, Types, Threats & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/external-validity/ Is this article helpful? Pritha BhandariOther students also liked, internal vs. external validity | understanding differences & threats, internal validity in research | definition, threats, & examples, sampling bias and how to avoid it | types & examples, get unlimited documents corrected. ✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts  |











































IMAGES
COMMENTS
When a test has strong face validity, anyone would agree that the test's questions appear to measure what they are intended to measure. For example, looking at a 4th grade math test consisting of problems in which students have to add and multiply, most people would agree that it has strong face validity (i.e., it looks like a math test).
Research validity pertains to the accuracy and truthfulness of the research. It examines whether the research truly measures what it claims to measure. ... Context-Specific: Some validity types may not be universally applicable across all contexts. Subjectivity: Certain types of validity, like face validity, involve subjective judgments.
In psychology research, validity refers to the extent to which a test or measurement tool accurately measures what it's intended to measure. It ensures that the research findings are genuine and not due to extraneous factors. Validity can be categorized into different types, including construct validity (measuring the intended abstract trait), internal validity (ensuring causal conclusions ...
Reliability is about the consistency of a measure, and validity is about the accuracy of a measure.opt. It's important to consider reliability and validity when you are creating your research design, planning your methods, and writing up your results, especially in quantitative research. Failing to do so can lead to several types of research ...
Internal validity vs. external validity in research. While often terms associated more closely with quantitative research, internal and external validity can still be relevant concepts to understand within the context of qualitative inquiries. Grasping these notions can help qualitative researchers better navigate the challenges of ensuring ...
Whether the research question is valid for the desired outcome, the choice of methodology is appropriate for answering the research question, the design is valid for the methodology, the sampling and data analysis is appropriate, and finally the results and conclusions are valid for the sample and context. In assessing validity of qualitative ...
Learn about validity and reliability within the context of research methodology. Plain-language explainer video with loads of examples. ... In simple terms, validity (also called "construct validity") is all about whether a research instrument accurately measures what it's supposed to measure. For example, let's say you have a set of ...
OVERVIEW. In general terms, validity is "the quality of being true or correct", it refers to the strength of results and how accurately they reflect the real world. Thus 'validity' can have quite different meanings depending on the context! Reliability is distinct from validity, in that it refers to the consistency or repeatability of ...
Validity can be demonstrated by showing a clear relationship between the test and what it is meant to measure. This can be done by showing that a study has one (or more) of the four types of validity: content validity, criterion-related validity, construct validity, and/or face validity. Understanding Methods for Research in Psychology.
2. What is validity? 1. Validity in research refers to how accurately a study answers the study question or the strength of the study conclusions. For outcome measures such as surveys or tests, validity refers to the accuracy of measurement. Here validity refers to how well the assessment tool actually measures the underlying outcome of interest.
However, the question of validity can be asked in a meaningful way, if one interprets test results in the context of everyday language. We conclude that validity can be understood as the degree to which the variable measured by a test corresponds to concepts of everyday language.
Validity in research is the ability to conduct an accurate study with the right tools and conditions to yield acceptable and reliable data that can be reproduced. Researchers rely on carefully calibrated tools for precise measurements. However, collecting accurate information can be more of a challenge. Studies must be conducted in environments ...
Reliability refers to the consistency of the measurement. Reliability shows how trustworthy is the score of the test. If the collected data shows the same results after being tested using various methods and sample groups, the information is reliable. If your method has reliability, the results will be valid. Example: If you weigh yourself on a ...
The concept of validity is also applied to research studies and their findings. Internal validity examines whether the study design, conduct, and analysis answer the research questions without bias. External validity examines whether the study findings can be generalized to other contexts. Ecological validity examines, specifically, whether the ...
Internal validity makes the conclusions of a causal relationship credible and trustworthy. Without high internal validity, an experiment cannot demonstrate a causal link between two variables. Research example. You want to test the hypothesis that drinking a cup of coffee improves memory. You schedule an equal number of college-aged ...
Abstract. Validity is a fundamental psychometric property of psychological tests. For any given test, the term validity refers to evidence that supports interpretation of test results as reflecting the psychological construct (s) the test was designed to measure. Validity is threatened when the test does not measure important aspects of the ...
However, the increased importance given to qualitative information in the evidence-based paradigm in health care and social policy requires a more precise conceptualization of validity criteria that goes beyond just academic reflection. After all, one can argue that policy verdicts that are based on qualitative information must be legitimized by valid research, just as quantitative effect ...
In the context of educational assessment, validity is the extent to which an assessment instrument accurately measures what it is intended to measure. Validity concerns anyone who is making inferences and decisions about a learner based on data. This can have deep implications for students' education and future.
The validity of a research study includes two domains: internal and external validity. Internal validity is defined as the extent to which the observed results represent the truth in the population we are studying and, thus, are not due to methodological errors. In our example, if the authors can support that the study has internal validity ...
Find step-by-step Psychology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: In the research context, the term validity most commonly refers to _____.. ... When discussing research, the term validity describes how well a study responds to its research topic or the reliability of its findings. Validity describes the precision of ...
Content validity evaluates how well an instrument (like a test) covers all relevant parts of the construct it aims to measure. Here, a construct is a theoretical concept, theme, or idea: in particular, one that cannot usually be measured directly. Content validity is one of the four types of measurement validity. The other three are:
Research on workplace bullying from the perpetrators' perspective is limited, leading to few interventions tailored to them. This gap stems from insufficient understanding of how organisational conditions and individual dispositions trigger or amplify perpetrator behaviour. To develop effective interventions in preventing bullying, perceived organisational factors were examined. This study ...
In terms of validity evidence related to test content, the authors argued that test content was aligned with Mayr's (1982) five facts and three inferences about evolution by means of natural selection, and two other key concepts, the origin of variation and the origin of species. Two test items were mapped to each of these 10 concepts.
The t-test statistical method is widely used in education research, and shows high reliability in the applications of intelligent teaching evaluation research (Hooshyar et al., 2016).
External validity is the extent to which you can generalize the findings of a study to other situations, people, settings, and measures. In other words, can you apply the findings of your study to a broader context? The aim of scientific research is to produce generalizable knowledge about the real world.