- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide

Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Research Problem
Definition:
Research problem is a specific and well-defined issue or question that a researcher seeks to investigate through research. It is the starting point of any research project, as it sets the direction, scope, and purpose of the study.
Types of Research Problems
Types of Research Problems are as follows:
Descriptive problems
These problems involve describing or documenting a particular phenomenon, event, or situation. For example, a researcher might investigate the demographics of a particular population, such as their age, gender, income, and education.
Exploratory problems
These problems are designed to explore a particular topic or issue in depth, often with the goal of generating new ideas or hypotheses. For example, a researcher might explore the factors that contribute to job satisfaction among employees in a particular industry.
Explanatory Problems
These problems seek to explain why a particular phenomenon or event occurs, and they typically involve testing hypotheses or theories. For example, a researcher might investigate the relationship between exercise and mental health, with the goal of determining whether exercise has a causal effect on mental health.
Predictive Problems
These problems involve making predictions or forecasts about future events or trends. For example, a researcher might investigate the factors that predict future success in a particular field or industry.
Evaluative Problems
These problems involve assessing the effectiveness of a particular intervention, program, or policy. For example, a researcher might evaluate the impact of a new teaching method on student learning outcomes.
How to Define a Research Problem
Defining a research problem involves identifying a specific question or issue that a researcher seeks to address through a research study. Here are the steps to follow when defining a research problem:
- Identify a broad research topic : Start by identifying a broad topic that you are interested in researching. This could be based on your personal interests, observations, or gaps in the existing literature.
- Conduct a literature review : Once you have identified a broad topic, conduct a thorough literature review to identify the current state of knowledge in the field. This will help you identify gaps or inconsistencies in the existing research that can be addressed through your study.
- Refine the research question: Based on the gaps or inconsistencies identified in the literature review, refine your research question to a specific, clear, and well-defined problem statement. Your research question should be feasible, relevant, and important to the field of study.
- Develop a hypothesis: Based on the research question, develop a hypothesis that states the expected relationship between variables.
- Define the scope and limitations: Clearly define the scope and limitations of your research problem. This will help you focus your study and ensure that your research objectives are achievable.
- Get feedback: Get feedback from your advisor or colleagues to ensure that your research problem is clear, feasible, and relevant to the field of study.
Components of a Research Problem
The components of a research problem typically include the following:
- Topic : The general subject or area of interest that the research will explore.
- Research Question : A clear and specific question that the research seeks to answer or investigate.
- Objective : A statement that describes the purpose of the research, what it aims to achieve, and the expected outcomes.
- Hypothesis : An educated guess or prediction about the relationship between variables, which is tested during the research.
- Variables : The factors or elements that are being studied, measured, or manipulated in the research.
- Methodology : The overall approach and methods that will be used to conduct the research.
- Scope and Limitations : A description of the boundaries and parameters of the research, including what will be included and excluded, and any potential constraints or limitations.
- Significance: A statement that explains the potential value or impact of the research, its contribution to the field of study, and how it will add to the existing knowledge.
Research Problem Examples
Following are some Research Problem Examples:
Research Problem Examples in Psychology are as follows:
- Exploring the impact of social media on adolescent mental health.
- Investigating the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy for treating anxiety disorders.
- Studying the impact of prenatal stress on child development outcomes.
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to addiction and relapse in substance abuse treatment.
- Examining the impact of personality traits on romantic relationships.
Research Problem Examples in Sociology are as follows:
- Investigating the relationship between social support and mental health outcomes in marginalized communities.
- Studying the impact of globalization on labor markets and employment opportunities.
- Analyzing the causes and consequences of gentrification in urban neighborhoods.
- Investigating the impact of family structure on social mobility and economic outcomes.
- Examining the effects of social capital on community development and resilience.
Research Problem Examples in Economics are as follows:
- Studying the effects of trade policies on economic growth and development.
- Analyzing the impact of automation and artificial intelligence on labor markets and employment opportunities.
- Investigating the factors that contribute to economic inequality and poverty.
- Examining the impact of fiscal and monetary policies on inflation and economic stability.
- Studying the relationship between education and economic outcomes, such as income and employment.
Political Science
Research Problem Examples in Political Science are as follows:
- Analyzing the causes and consequences of political polarization and partisan behavior.
- Investigating the impact of social movements on political change and policymaking.
- Studying the role of media and communication in shaping public opinion and political discourse.
- Examining the effectiveness of electoral systems in promoting democratic governance and representation.
- Investigating the impact of international organizations and agreements on global governance and security.
Environmental Science
Research Problem Examples in Environmental Science are as follows:
- Studying the impact of air pollution on human health and well-being.
- Investigating the effects of deforestation on climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Analyzing the impact of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems and food webs.
- Studying the relationship between urban development and ecological resilience.
- Examining the effectiveness of environmental policies and regulations in promoting sustainability and conservation.
Research Problem Examples in Education are as follows:
- Investigating the impact of teacher training and professional development on student learning outcomes.
- Studying the effectiveness of technology-enhanced learning in promoting student engagement and achievement.
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to achievement gaps and educational inequality.
- Examining the impact of parental involvement on student motivation and achievement.
- Studying the effectiveness of alternative educational models, such as homeschooling and online learning.
Research Problem Examples in History are as follows:
- Analyzing the social and economic factors that contributed to the rise and fall of ancient civilizations.
- Investigating the impact of colonialism on indigenous societies and cultures.
- Studying the role of religion in shaping political and social movements throughout history.
- Analyzing the impact of the Industrial Revolution on economic and social structures.
- Examining the causes and consequences of global conflicts, such as World War I and II.
Research Problem Examples in Business are as follows:
- Studying the impact of corporate social responsibility on brand reputation and consumer behavior.
- Investigating the effectiveness of leadership development programs in improving organizational performance and employee satisfaction.
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful entrepreneurship and small business development.
- Examining the impact of mergers and acquisitions on market competition and consumer welfare.
- Studying the effectiveness of marketing strategies and advertising campaigns in promoting brand awareness and sales.
Research Problem Example for Students
An Example of a Research Problem for Students could be:
“How does social media usage affect the academic performance of high school students?”
This research problem is specific, measurable, and relevant. It is specific because it focuses on a particular area of interest, which is the impact of social media on academic performance. It is measurable because the researcher can collect data on social media usage and academic performance to evaluate the relationship between the two variables. It is relevant because it addresses a current and important issue that affects high school students.
To conduct research on this problem, the researcher could use various methods, such as surveys, interviews, and statistical analysis of academic records. The results of the study could provide insights into the relationship between social media usage and academic performance, which could help educators and parents develop effective strategies for managing social media use among students.
Another example of a research problem for students:
“Does participation in extracurricular activities impact the academic performance of middle school students?”
This research problem is also specific, measurable, and relevant. It is specific because it focuses on a particular type of activity, extracurricular activities, and its impact on academic performance. It is measurable because the researcher can collect data on students’ participation in extracurricular activities and their academic performance to evaluate the relationship between the two variables. It is relevant because extracurricular activities are an essential part of the middle school experience, and their impact on academic performance is a topic of interest to educators and parents.
To conduct research on this problem, the researcher could use surveys, interviews, and academic records analysis. The results of the study could provide insights into the relationship between extracurricular activities and academic performance, which could help educators and parents make informed decisions about the types of activities that are most beneficial for middle school students.
Applications of Research Problem
Applications of Research Problem are as follows:
- Academic research: Research problems are used to guide academic research in various fields, including social sciences, natural sciences, humanities, and engineering. Researchers use research problems to identify gaps in knowledge, address theoretical or practical problems, and explore new areas of study.
- Business research : Research problems are used to guide business research, including market research, consumer behavior research, and organizational research. Researchers use research problems to identify business challenges, explore opportunities, and develop strategies for business growth and success.
- Healthcare research : Research problems are used to guide healthcare research, including medical research, clinical research, and health services research. Researchers use research problems to identify healthcare challenges, develop new treatments and interventions, and improve healthcare delivery and outcomes.
- Public policy research : Research problems are used to guide public policy research, including policy analysis, program evaluation, and policy development. Researchers use research problems to identify social issues, assess the effectiveness of existing policies and programs, and develop new policies and programs to address societal challenges.
- Environmental research : Research problems are used to guide environmental research, including environmental science, ecology, and environmental management. Researchers use research problems to identify environmental challenges, assess the impact of human activities on the environment, and develop sustainable solutions to protect the environment.
Purpose of Research Problems
The purpose of research problems is to identify an area of study that requires further investigation and to formulate a clear, concise and specific research question. A research problem defines the specific issue or problem that needs to be addressed and serves as the foundation for the research project.
Identifying a research problem is important because it helps to establish the direction of the research and sets the stage for the research design, methods, and analysis. It also ensures that the research is relevant and contributes to the existing body of knowledge in the field.
A well-formulated research problem should:
- Clearly define the specific issue or problem that needs to be investigated
- Be specific and narrow enough to be manageable in terms of time, resources, and scope
- Be relevant to the field of study and contribute to the existing body of knowledge
- Be feasible and realistic in terms of available data, resources, and research methods
- Be interesting and intellectually stimulating for the researcher and potential readers or audiences.
Characteristics of Research Problem
The characteristics of a research problem refer to the specific features that a problem must possess to qualify as a suitable research topic. Some of the key characteristics of a research problem are:
- Clarity : A research problem should be clearly defined and stated in a way that it is easily understood by the researcher and other readers. The problem should be specific, unambiguous, and easy to comprehend.
- Relevance : A research problem should be relevant to the field of study, and it should contribute to the existing body of knowledge. The problem should address a gap in knowledge, a theoretical or practical problem, or a real-world issue that requires further investigation.
- Feasibility : A research problem should be feasible in terms of the availability of data, resources, and research methods. It should be realistic and practical to conduct the study within the available time, budget, and resources.
- Novelty : A research problem should be novel or original in some way. It should represent a new or innovative perspective on an existing problem, or it should explore a new area of study or apply an existing theory to a new context.
- Importance : A research problem should be important or significant in terms of its potential impact on the field or society. It should have the potential to produce new knowledge, advance existing theories, or address a pressing societal issue.
- Manageability : A research problem should be manageable in terms of its scope and complexity. It should be specific enough to be investigated within the available time and resources, and it should be broad enough to provide meaningful results.
Advantages of Research Problem
The advantages of a well-defined research problem are as follows:
- Focus : A research problem provides a clear and focused direction for the research study. It ensures that the study stays on track and does not deviate from the research question.
- Clarity : A research problem provides clarity and specificity to the research question. It ensures that the research is not too broad or too narrow and that the research objectives are clearly defined.
- Relevance : A research problem ensures that the research study is relevant to the field of study and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. It addresses gaps in knowledge, theoretical or practical problems, or real-world issues that require further investigation.
- Feasibility : A research problem ensures that the research study is feasible in terms of the availability of data, resources, and research methods. It ensures that the research is realistic and practical to conduct within the available time, budget, and resources.
- Novelty : A research problem ensures that the research study is original and innovative. It represents a new or unique perspective on an existing problem, explores a new area of study, or applies an existing theory to a new context.
- Importance : A research problem ensures that the research study is important and significant in terms of its potential impact on the field or society. It has the potential to produce new knowledge, advance existing theories, or address a pressing societal issue.
- Rigor : A research problem ensures that the research study is rigorous and follows established research methods and practices. It ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic, objective, and unbiased manner.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
Published on November 2, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on May 31, 2023.
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in existing knowledge that you aim to address in your research. You may choose to look for practical problems aimed at contributing to change, or theoretical problems aimed at expanding knowledge.
Some research will do both of these things, but usually the research problem focuses on one or the other. The type of research problem you choose depends on your broad topic of interest and the type of research you think will fit best.
This article helps you identify and refine a research problem. When writing your research proposal or introduction , formulate it as a problem statement and/or research questions .
Table of contents
Why is the research problem important, step 1: identify a broad problem area, step 2: learn more about the problem, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research problems.
Having an interesting topic isn’t a strong enough basis for academic research. Without a well-defined research problem, you are likely to end up with an unfocused and unmanageable project.
You might end up repeating what other people have already said, trying to say too much, or doing research without a clear purpose and justification. You need a clear problem in order to do research that contributes new and relevant insights.
Whether you’re planning your thesis , starting a research paper , or writing a research proposal , the research problem is the first step towards knowing exactly what you’ll do and why.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

As you read about your topic, look for under-explored aspects or areas of concern, conflict, or controversy. Your goal is to find a gap that your research project can fill.
Practical research problems
If you are doing practical research, you can identify a problem by reading reports, following up on previous research, or talking to people who work in the relevant field or organization. You might look for:
- Issues with performance or efficiency
- Processes that could be improved
- Areas of concern among practitioners
- Difficulties faced by specific groups of people
Examples of practical research problems
Voter turnout in New England has been decreasing, in contrast to the rest of the country.
The HR department of a local chain of restaurants has a high staff turnover rate.
A non-profit organization faces a funding gap that means some of its programs will have to be cut.
Theoretical research problems
If you are doing theoretical research, you can identify a research problem by reading existing research, theory, and debates on your topic to find a gap in what is currently known about it. You might look for:
- A phenomenon or context that has not been closely studied
- A contradiction between two or more perspectives
- A situation or relationship that is not well understood
- A troubling question that has yet to be resolved
Examples of theoretical research problems
The effects of long-term Vitamin D deficiency on cardiovascular health are not well understood.
The relationship between gender, race, and income inequality has yet to be closely studied in the context of the millennial gig economy.
Historians of Scottish nationalism disagree about the role of the British Empire in the development of Scotland’s national identity.
Next, you have to find out what is already known about the problem, and pinpoint the exact aspect that your research will address.
Context and background
- Who does the problem affect?
- Is it a newly-discovered problem, or a well-established one?
- What research has already been done?
- What, if any, solutions have been proposed?
- What are the current debates about the problem? What is missing from these debates?
Specificity and relevance
- What particular place, time, and/or group of people will you focus on?
- What aspects will you not be able to tackle?
- What will the consequences be if the problem is not resolved?
Example of a specific research problem
A local non-profit organization focused on alleviating food insecurity has always fundraised from its existing support base. It lacks understanding of how best to target potential new donors. To be able to continue its work, the organization requires research into more effective fundraising strategies.
Once you have narrowed down your research problem, the next step is to formulate a problem statement , as well as your research questions or hypotheses .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them.
In general, they should be:
- Focused and researchable
- Answerable using credible sources
- Complex and arguable
- Feasible and specific
- Relevant and original
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, May 31). How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved October 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-problem/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a strong hypothesis | steps & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Research Problem
Ai generator.

A research problem is a specific issue or gap in knowledge that a researcher aims to address through systematic investigation. It forms the foundation of a study, guiding the research question, research design , and potential outcomes. Identifying a clear research problem is crucial as it often emerges from existing literature, theoretical frameworks, and practical considerations. In a student case study , the research question and hypothesis stem from the identified research problem.
What is a Research Problem?
A research problem is a specific issue, difficulty, contradiction, or gap in knowledge that a researcher aims to address through systematic investigation. It forms the basis of a study, guiding the research question, research design, and the formulation of a hypothesis.
Examples of Research Problem
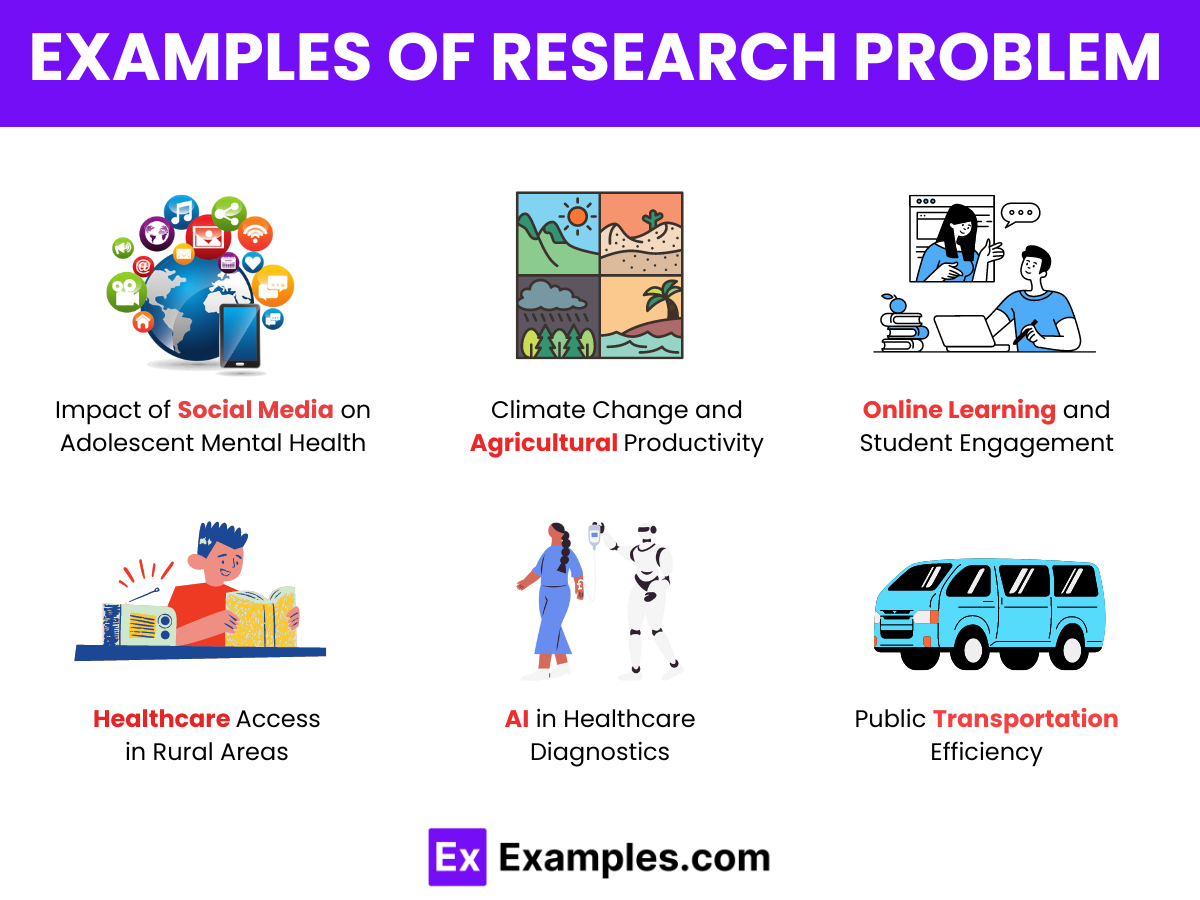
- Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health : Investigating how social media usage affects the mental health and well-being of teenagers.
- Climate Change and Agricultural Productivity : Examining the effects of climate change on crop yields and farming practices.
- Online Learning and Student Engagement : Assessing the effectiveness of online learning platforms in maintaining student engagement and academic performance.
- Healthcare Access in Rural Areas : Exploring the barriers to healthcare access in rural communities and potential solutions.
- Workplace Diversity and Employee Performance : Analyzing how workplace diversity influences team dynamics and employee productivity.
- Renewable Energy Adoption : Studying the factors that influence the adoption of renewable energy sources in urban versus rural areas.
- AI in Healthcare Diagnostics : Evaluating the accuracy and reliability of artificial intelligence in medical diagnostics.
- Gender Disparities in STEM Education : Investigating the causes and consequences of gender disparities in STEM education and careers.
- Urbanization and Housing Affordability : Exploring the impact of rapid urbanization on housing affordability and availability in major cities.
- Public Transportation Efficiency : Assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of public transportation systems in reducing urban traffic congestion.
Research Problem Examples for Students
- The Impact of Homework on Academic Achievement in High School Students
- The Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and Academic Performance in College Students
- The Effects of Extracurricular Activities on Social Skills Development
- Influence of Parental Involvement on Students’ Attitudes Toward Learning
- The Role of Technology in Enhancing Classroom Learning
- Factors Contributing to Student Anxiety During Exams
- The Effectiveness of Peer Tutoring in Improving Reading Skills
- Challenges Faced by International Students in Adapting to New Educational Systems
- Impact of Nutrition on Concentration and Academic Performance
- The Role of Socioeconomic Status in Access to Higher Education Opportunities
Research Problems Examples in Education
- Effect of Class Size on Student Learning Outcomes
- Impact of Technology Integration in Classroom Instruction
- Influence of Teacher Professional Development on Student Achievement
- Challenges in Implementing Inclusive Education for Students with Disabilities
- Effectiveness of Bilingual Education Programs on Language Proficiency
- Role of Parental Involvement in Enhancing Academic Performance
- Impact of School Leadership on Teacher Retention and Job Satisfaction
- Assessment of Remote Learning Efficacy During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Barriers to STEM Education Participation Among Female Students
- Effect of Socioeconomic Status on Access to Quality Education
Research Problems Examples in Business
- Impact of Employee Engagement on Productivity and Retention
- Effectiveness of Social Media Marketing Strategies on Consumer Behavior
- Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Business Practices
- Influence of Leadership Styles on Organizational Performance
- Role of Corporate Culture in Driving Innovation
- Impact of Remote Work on Team Collaboration and Communication
- Strategies for Managing Supply Chain Disruptions
- Effect of Customer Feedback on Product Development
- Challenges in Expanding into International Markets
- Influence of Brand Loyalty on Customer Retention
Basic Research Problem Examples
- Effect of Sleep on Cognitive Function
- Impact of Exercise on Mental Health
- Influence of Diet on Academic Performance
- Role of Social Support in Stress Management
- Impact of Screen Time on Children’s Behavior
- Effects of Pollution on Public Health
- Influence of Music on Mood and Productivity
- Role of Genetics in Disease Susceptibility
- Impact of Advertising on Consumer Choices
- Effects of Climate Change on Local Wildlife
Research Problem in Research Methodology
A research problem in research methodology refers to an issue or gap in the process of conducting research that requires a solution. Examples include:
- Validity and Reliability of Measurement Tools : Ensuring that instruments used for data collection consistently produce accurate results.
- Selection of Appropriate Sampling Techniques : Determining the best sampling method to ensure the sample represents the population accurately.
- Bias in Data Collection and Analysis : Identifying and minimizing biases that can affect the validity of research findings.
- Ethical Considerations in Research : Addressing ethical issues related to participant consent, confidentiality, and data protection.
- Generalizability of Research Findings : Ensuring that research results are applicable to broader populations beyond the study sample.
- Mixed Methods Research Design : Effectively integrating qualitative and quantitative approaches in a single study.
- Data Interpretation and Reporting : Developing accurate and unbiased interpretations and reports of research findings.
- Longitudinal Study Challenges : Managing the complexities of conducting studies over extended periods.
- Control of Extraneous Variables : Identifying and controlling variables that can affect the dependent variable outside the study’s primary focus.
- Developing Theoretical Frameworks : Constructing robust frameworks that guide the research process and support hypothesis development.
Characteristics of a Research Problem
- Clarity : The research problem should be clearly defined, unambiguous, and understandable to all stakeholders.
- Specificity : It should be specific and narrow enough to be addressed comprehensively within the scope of the research.
- Relevance : The problem should be significant and relevant to the field of study, contributing to the advancement of knowledge or practice.
- Feasibility : It should be practical and manageable, considering the resources, time, and capabilities available to the researcher.
- Novelty : The research problem should address an original question or gap in the existing literature, providing new insights or perspectives.
- Researchability : The problem should be researchable using scientific methods, including data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Ethical Considerations : The research problem should be ethically sound, ensuring no harm to participants or the environment.
- Alignment with Objectives : The problem should align with the research objectives and goals, guiding the direction and purpose of the study.
- Measurability : It should be possible to measure and evaluate the outcomes related to the problem using appropriate metrics and methodologies.
- Contextualization : The problem should be placed within a broader context, considering theoretical frameworks, existing literature, and practical applications.
Types of Research Problems
- Aim: To describe the characteristics of a specific phenomenon or population.
- Example: “What are the key features of successful online education programs?”
- Aim: To compare two or more groups, variables, or phenomena.
- Example: “How does employee satisfaction differ between remote and on-site workers?”
- Aim: To determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
- Example: “What is the impact of leadership style on employee productivity?”
- Aim: To examine the relationship between two or more variables.
- Example: “What is the relationship between social media usage and self-esteem among teenagers?”
- Aim: To explore a new or under-researched area where little information is available.
- Example: “What are the emerging trends in consumer behavior post-pandemic?”
- Aim: To solve a specific, practical problem faced by an organization or society.
- Example: “How can small businesses improve their cybersecurity measures?”
- Aim: To expand existing theories or develop new theoretical frameworks.
- Example: “How can existing theories of motivation be integrated to better understand employee behavior?”
- Aim: To evaluate the effects of policies or suggest improvements.
- Example: “What are the effects of the new minimum wage laws on small businesses?”
- Aim: To investigate ethical issues within a field or practice.
- Example: “What are the ethical implications of AI in decision-making processes?”
- Aim: To address issues that span multiple disciplines or fields of study.
- Example: “How can principles of environmental science and economics be combined to develop sustainable business practices?”
How to Define a Research Problem
Defining a research problem involves several key steps that help in identifying and articulating a specific issue that needs investigation. Here’s a structured approach:
- Choose a general area of interest or field relevant to your expertise or curiosity. This can be broad initially and will be narrowed down through the next steps.
- Review existing research to understand what has already been studied. This helps in identifying gaps, inconsistencies, or areas that need further exploration.
- Based on your literature review, refine your broad topic to a more specific issue or aspect that has not been adequately addressed.
- Ensure the problem is significant and relevant to the field. It should address a real-world issue or theoretical gap that contributes to advancing knowledge or solving practical problems.
- Clearly articulate the problem in a concise and precise manner. This statement should explain what the problem is, why it is important, and how it impacts the field.
- Develop specific research questions that your study will answer. These questions should be directly related to your problem statement and guide the direction of your research.
- Establish clear research objectives that outline what you aim to achieve. Formulate hypotheses if applicable, which are testable predictions related to your research questions.
- Consider the resources, time, and scope of your study. Ensure that the research problem you have defined is feasible to investigate within the constraints you have.
- Discuss your defined research problem with peers, mentors, or experts in the field. Feedback can help refine and improve your problem statement.
Importance of Research Problem
The research problem is crucial as it forms the foundation of any research study, guiding the direction and focus of the investigation. It helps in:
- Defining Objectives : Clarifies the purpose and objectives of the research, ensuring the study remains focused and relevant.
- Guiding Research Design : Determines the methodology and approach, including data collection and analysis techniques.
- Identifying Significance : Highlights the importance and relevance of the study, demonstrating its potential impact on the field.
- Focusing Efforts : Helps researchers concentrate their efforts on addressing specific issues, leading to more precise and meaningful results.
- Resource Allocation : Assists in the efficient allocation of resources, including time, funding, and manpower, by prioritizing critical aspects of the research.
FAQ’s
Why is defining a research problem important.
Defining a research problem is crucial because it guides the research process, helps focus on specific objectives, and determines the direction of the study.
How do you identify a research problem?
Identify a research problem by reviewing existing literature, considering real-world issues, discussing with experts, and reflecting on personal experiences and observations.
What is the difference between a research problem and a research question?
A research problem identifies the issue to be addressed, while a research question is a specific query the research aims to answer.

Can a research problem change during the study?
Yes, a research problem can evolve as new data and insights emerge, requiring refinement or redefinition to better align with findings.
How do you formulate a research problem?
Formulate a research problem by clearly stating the issue, outlining its significance, and specifying the context and scope of the problem.
What is the role of literature review in identifying a research problem?
A literature review helps identify gaps, inconsistencies, and unresolved issues in existing research, which can guide the formulation of a research problem.
How does a research problem impact the research design?
The research problem shapes the research design by determining the methodology, data collection techniques, and analysis strategies needed to address the issue.
What are common sources of research problems?
Common sources include academic literature, practical experiences, societal issues, technological advancements, and gaps identified in previous research.
How specific should a research problem be?
A research problem should be specific enough to guide focused research but broad enough to allow comprehensive investigation and meaningful results.
How do research objectives relate to the research problem?
Research objectives are specific goals derived from the research problem, detailing what the study aims to achieve and how it plans to address the problem.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Research Problem? Characteristics, Types, and Examples

A research problem is a gap in existing knowledge, a contradiction in an established theory, or a real-world challenge that a researcher aims to address in their research. It is at the heart of any scientific inquiry, directing the trajectory of an investigation. The statement of a problem orients the reader to the importance of the topic, sets the problem into a particular context, and defines the relevant parameters, providing the framework for reporting the findings. Therein lies the importance of research problem s.
The formulation of well-defined research questions is central to addressing a research problem . A research question is a statement made in a question form to provide focus, clarity, and structure to the research endeavor. This helps the researcher design methodologies, collect data, and analyze results in a systematic and coherent manner. A study may have one or more research questions depending on the nature of the study.

Identifying and addressing a research problem is very important. By starting with a pertinent problem , a scholar can contribute to the accumulation of evidence-based insights, solutions, and scientific progress, thereby advancing the frontier of research. Moreover, the process of formulating research problems and posing pertinent research questions cultivates critical thinking and hones problem-solving skills.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Problem ?
Before you conceive of your project, you need to ask yourself “ What is a research problem ?” A research problem definition can be broadly put forward as the primary statement of a knowledge gap or a fundamental challenge in a field, which forms the foundation for research. Conversely, the findings from a research investigation provide solutions to the problem .
A research problem guides the selection of approaches and methodologies, data collection, and interpretation of results to find answers or solutions. A well-defined problem determines the generation of valuable insights and contributions to the broader intellectual discourse.
Characteristics of a Research Problem
Knowing the characteristics of a research problem is instrumental in formulating a research inquiry; take a look at the five key characteristics below:
Novel : An ideal research problem introduces a fresh perspective, offering something new to the existing body of knowledge. It should contribute original insights and address unresolved matters or essential knowledge.
Significant : A problem should hold significance in terms of its potential impact on theory, practice, policy, or the understanding of a particular phenomenon. It should be relevant to the field of study, addressing a gap in knowledge, a practical concern, or a theoretical dilemma that holds significance.
Feasible: A practical research problem allows for the formulation of hypotheses and the design of research methodologies. A feasible research problem is one that can realistically be investigated given the available resources, time, and expertise. It should not be too broad or too narrow to explore effectively, and should be measurable in terms of its variables and outcomes. It should be amenable to investigation through empirical research methods, such as data collection and analysis, to arrive at meaningful conclusions A practical research problem considers budgetary and time constraints, as well as limitations of the problem . These limitations may arise due to constraints in methodology, resources, or the complexity of the problem.
Clear and specific : A well-defined research problem is clear and specific, leaving no room for ambiguity; it should be easily understandable and precisely articulated. Ensuring specificity in the problem ensures that it is focused, addresses a distinct aspect of the broader topic and is not vague.
Rooted in evidence: A good research problem leans on trustworthy evidence and data, while dismissing unverifiable information. It must also consider ethical guidelines, ensuring the well-being and rights of any individuals or groups involved in the study.

Types of Research Problems
Across fields and disciplines, there are different types of research problems . We can broadly categorize them into three types.
- Theoretical research problems
Theoretical research problems deal with conceptual and intellectual inquiries that may not involve empirical data collection but instead seek to advance our understanding of complex concepts, theories, and phenomena within their respective disciplines. For example, in the social sciences, research problem s may be casuist (relating to the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience), difference (comparing or contrasting two or more phenomena), descriptive (aims to describe a situation or state), or relational (investigating characteristics that are related in some way).
Here are some theoretical research problem examples :
- Ethical frameworks that can provide coherent justifications for artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, especially in contexts involving autonomous decision-making and moral agency.
- Determining how mathematical models can elucidate the gradual development of complex traits, such as intricate anatomical structures or elaborate behaviors, through successive generations.
- Applied research problems
Applied or practical research problems focus on addressing real-world challenges and generating practical solutions to improve various aspects of society, technology, health, and the environment.
Here are some applied research problem examples :
- Studying the use of precision agriculture techniques to optimize crop yield and minimize resource waste.
- Designing a more energy-efficient and sustainable transportation system for a city to reduce carbon emissions.
- Action research problems
Action research problems aim to create positive change within specific contexts by involving stakeholders, implementing interventions, and evaluating outcomes in a collaborative manner.
Here are some action research problem examples :
- Partnering with healthcare professionals to identify barriers to patient adherence to medication regimens and devising interventions to address them.
- Collaborating with a nonprofit organization to evaluate the effectiveness of their programs aimed at providing job training for underserved populations.
These different types of research problems may give you some ideas when you plan on developing your own.
How to Define a Research Problem
You might now ask “ How to define a research problem ?” These are the general steps to follow:
- Look for a broad problem area: Identify under-explored aspects or areas of concern, or a controversy in your topic of interest. Evaluate the significance of addressing the problem in terms of its potential contribution to the field, practical applications, or theoretical insights.
- Learn more about the problem: Read the literature, starting from historical aspects to the current status and latest updates. Rely on reputable evidence and data. Be sure to consult researchers who work in the relevant field, mentors, and peers. Do not ignore the gray literature on the subject.
- Identify the relevant variables and how they are related: Consider which variables are most important to the study and will help answer the research question. Once this is done, you will need to determine the relationships between these variables and how these relationships affect the research problem .
- Think of practical aspects : Deliberate on ways that your study can be practical and feasible in terms of time and resources. Discuss practical aspects with researchers in the field and be open to revising the problem based on feedback. Refine the scope of the research problem to make it manageable and specific; consider the resources available, time constraints, and feasibility.
- Formulate the problem statement: Craft a concise problem statement that outlines the specific issue, its relevance, and why it needs further investigation.
- Stick to plans, but be flexible: When defining the problem , plan ahead but adhere to your budget and timeline. At the same time, consider all possibilities and ensure that the problem and question can be modified if needed.

Key Takeaways
- A research problem concerns an area of interest, a situation necessitating improvement, an obstacle requiring eradication, or a challenge in theory or practical applications.
- The importance of research problem is that it guides the research and helps advance human understanding and the development of practical solutions.
- Research problem definition begins with identifying a broad problem area, followed by learning more about the problem, identifying the variables and how they are related, considering practical aspects, and finally developing the problem statement.
- Different types of research problems include theoretical, applied, and action research problems , and these depend on the discipline and nature of the study.
- An ideal problem is original, important, feasible, specific, and based on evidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to define a research problem?
Identifying potential issues and gaps as research problems is important for choosing a relevant topic and for determining a well-defined course of one’s research. Pinpointing a problem and formulating research questions can help researchers build their critical thinking, curiosity, and problem-solving abilities.
How do I identify a research problem?
Identifying a research problem involves recognizing gaps in existing knowledge, exploring areas of uncertainty, and assessing the significance of addressing these gaps within a specific field of study. This process often involves thorough literature review, discussions with experts, and considering practical implications.
Can a research problem change during the research process?
Yes, a research problem can change during the research process. During the course of an investigation a researcher might discover new perspectives, complexities, or insights that prompt a reevaluation of the initial problem. The scope of the problem, unforeseen or unexpected issues, or other limitations might prompt some tweaks. You should be able to adjust the problem to ensure that the study remains relevant and aligned with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
How does a research problem relate to research questions or hypotheses?
A research problem sets the stage for the study. Next, research questions refine the direction of investigation by breaking down the broader research problem into manageable components. Research questions are formulated based on the problem , guiding the investigation’s scope and objectives. The hypothesis provides a testable statement to validate or refute within the research process. All three elements are interconnected and work together to guide the research.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What Constitutes Good Research in Academia?

How to Structure a Dissertation?

Different types of research problems and their examples
The identification of the research problem is the first step in the research process. It is similar to the identification of the destination before a journey. It works as the foundation for the whole research process . In the field of social sciences, a research problem is presented in the form of a question. It helps in narrowing down the issue to something reasonable for conducting a study. Defining a research problem serves three main purposes (Pardede, 2018):
- It presents the importance of the research topic.
- It helps the researcher place the problem in a specific context to properly define the parameters of the investigation.
- It provides a framework that can help in presenting the results in the future.
In absolute terms, a research problem can be defined as a statement regarding the area of concern, a condition that needs to be improved, an unresolved question that exists in the literature, a difficulty that needs to be eliminated or any point that needs some meaningful investigation (Gallupe, 2007).
To ideally conclude the research, find logical answers to your research problems.
Descriptive research problems
Descriptive research problems focus on questions like ‘what is ?’, with its main aim to describe the situation, state or the existence of certain specific phenomena. They seek to depict what already exists in a group or population. For such studies, surveys and opinion polls are best suitable because they require systematic observation of social issues.
What are the main factors affecting consumers’ purchase decisions?
These problems use two different ways to collect data- cross-sectional studies and longitudinal studies. Cross-sectional studies provide a snapshot of data at a certain moment in time. On the other hand, longitudinal studies involve a fixed and stable sample that is measured repeatedly over time. However, in both cases, methods that can be used to collect data include mail, online or offline surveys, and interviews. When a researcher is dealing with a descriptive research problem, there can be no manipulation in the variables and hypotheses as they are usually nondirectional (Hashimi, 2015).
Causal research problems
Causal research problems focus on identifying the extent and nature of cause-and-effect relationships. Such research problems help in assessing the impact of some changes on existing norms and processes. They thus identify patterns of relationships between different elements.
How does online education affect students’ learning abilities?
In such cases, experiments are the most popular way of collecting primary data. Here, the hypothesis is usually directional, i.e. explaining how one factor affects the behaviour of another one. Such studies give the researcher the freedom to manipulate the variables as desired. Data for causal research can be collected in two ways:
- laboratory experiments and,
- field experiments.
Laboratory experiments are generally conducted in an artificial environment which allows the researcher to carefully manipulate the variables. On the other hand, field experiments are much more realistic. It is sometimes not possible to control the variables. This makes it difficult for the researcher to predict with confidence what produced a given outcome (Muhammad and Kabir, 2018).
Relational research problem
This research problem states that some sort of relationship between two variables needs to be investigated. The aim is to investigate the qualities or characteristics that are connected in some way.
How is the teaching experience of a teacher with respect to their teaching style?
Thus, this sort of research problem requires more than one variable that describes the relationship between them (Hartanska, 2014).
Summarizing the differences
| Parameters | Descriptive research problem | Casual research problem | Relational research problem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aim/purpose | The aim is to depict what already exists in a group of the population. | To identify the extent and nature of cause and effect relationships. | The aim is to investigate the qualities or characteristics that are connected in some way or the other. |
| Directionality of hypothesis | Non-directional | Directional | Directional |
| Variable manipulation and control | No manipulations in terms of variables and hypotheses. | Can manipulate independent and dependent variables to find the effect. | No manipulation |
| Data collection method | Mail, online or offline surveys and interviews. | Field experiments, laboratory experiments. | Focus groups, surveys, case studies. |
| Research approach | Structured | Highly structured | Structured |
| Example | What are the views of primary teachers on how writing should be taught in a classroom? How do teachers teach writing in the classroom? Both these questions relate to the current state of affairs. To answer the first question there is a need to talk to teachers, ask their views and then describe their views. While in the second question there is a need to observe and then describe. Thus both are descriptive research problems. | What is the impact of advertising campaigns on the voting outcome? In this example, there is a need to test the effect of campaigns on the number of voters. | Do experienced teachers provide more help with corrections during writing than inexperienced teachers? In this example, there is a need to establish a relationship between teachers’ teaching experience and how much help they can provide with corrections while writing. |
How to choose the right research problem type?
While choosing the research problem type one must keep in mind the following points.
- The first step in direction of selecting the right problem type is to identify the concepts and terms that make up the topic. This involves identifying the variables of the study. For example, if there is only one variable then it is a descriptive research problem. If it contains two variables, then it is likely relational or causal research.
- The second step is to review the literature to refine the approach of examining the topic and finding the appropriate ways to analyze it. For example, how much research has already been conducted on this topic? What methods and data did the previous researchers use? What was lacking in their research? What variables were used by them? The answers to these questions will help in framing the best approach to your research.
- The third step is to look for sources that can help broaden, modify and strengthen your initial thoughts. A deeper look into the research will answer critical questions like, is a relational approach better than an investigative one? How will eliminating a few variables affect the outcome of the research?
- Gallupe, R. B. (2007) ‘Research contributions: The tyranny of methodologies in information systems research, ACM SIGMIS Database , 38(3), pp. 46–57.
- Hartanska, J. (2014) ‘THE RESEARCH PROBLEM’, pp. 1–48.
- Hashimi, H. (2015) ‘Types of research questions’, Nursing , 4(3), pp. 23–25.
- Muhammad, S. and Kabir, S. (2018) ‘Problem formulation and objective determination’, (June).
- Pardede, P. (2018) ‘Identifying and Formulating the Research Problem’, Research in ELT , 1(October), pp. 1–13.
- Priya Chetty
- Ashni walia
I am a management graduate with specialisation in Marketing and Finance. I have over 12 years' experience in research and analysis. This includes fundamental and applied research in the domains of management and social sciences. I am well versed with academic research principles. Over the years i have developed a mastery in different types of data analysis on different applications like SPSS, Amos, and NVIVO. My expertise lies in inferring the findings and creating actionable strategies based on them.
Over the past decade I have also built a profile as a researcher on Project Guru's Knowledge Tank division. I have penned over 200 articles that have earned me 400+ citations so far. My Google Scholar profile can be accessed here .
I now consult university faculty through Faculty Development Programs (FDPs) on the latest developments in the field of research. I also guide individual researchers on how they can commercialise their inventions or research findings. Other developments im actively involved in at Project Guru include strengthening the "Publish" division as a bridge between industry and academia by bringing together experienced research persons, learners, and practitioners to collaboratively work on a common goal.
I am a master's in Economics from Amity university. Besides my keen interest in Economics i have been an active member of the team Enactus. Apart from the academics i love reading fictions.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
proofreading

The Research Problem & Statement

I f you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Very interesting. Thank you. Please I need a PhD topic in climate change in relation to health.
Your posts have provided a clear, easy to understand, motivating literature, mainly when these topics tend to be considered “boring” in some careers.
Thank you, but i am requesting for a topic in records management
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- How it works

Research Problem – Definition, Steps & Tips
Published by Jamie Walker at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Once you have chosen a research topic, the next stage is to explain the research problem: the detailed issue, ambiguity of the research, gap analysis, or gaps in knowledge and findings that you will discuss.
Here, in this article, we explore a research problem in a dissertation or an essay with some research problem examples to help you better understand how and when you should write a research problem.
“A research problem is a specific statement relating to an area of concern and is contingent on the type of research. Some research studies focus on theoretical and practical problems, while some focus on only one.”
The problem statement in the dissertation, essay, research paper, and other academic papers should be clearly stated and intended to expand information, knowledge, and contribution to change.
This article will assist in identifying and elaborating a research problem if you are unsure how to define your research problem. The most notable challenge in the research process is to formulate and identify a research problem. Formulating a problem statement and research questions while finalizing the research proposal or introduction for your dissertation or thesis is necessary.
Why is Research Problem Critical?
An interesting research topic is only the first step. The real challenge of the research process is to develop a well-rounded research problem.
A well-formulated research problem helps understand the research procedure; without it, your research will appear unforeseeable and awkward.
Research is a procedure based on a sequence and a research problem aids in following and completing the research in a sequence. Repetition of existing literature is something that should be avoided in research.
Therefore research problem in a dissertation or an essay needs to be well thought out and presented with a clear purpose. Hence, your research work contributes more value to existing knowledge. You need to be well aware of the problem so you can present logical solutions.
Formulating a research problem is the first step of conducting research, whether you are writing an essay, research paper, dissertation , or research proposal .
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step 1: Identifying Problem Area – What is Research Problem
The most significant step in any research is to look for unexplored areas, topics, and controversies . You aim to find gaps that your work will fill. Here are some research problem examples for you to better understand the concept.
Practical Research Problems
To conduct practical research, you will need practical research problems that are typically identified by analysing reports, previous research studies, and interactions with the experienced personals of pertinent disciplines. You might search for:
- Problems with performance or competence in an organization
- Institutional practices that could be enhanced
- Practitioners of relevant fields and their areas of concern
- Problems confronted by specific groups of people within your area of study
If your research work relates to an internship or a job, then it will be critical for you to identify a research problem that addresses certain issues faced by the firm the job or internship pertains to.
Examples of Practical Research Problems
Decreased voter participation in county A, as compared to the rest of the country.
The high employee turnover rate of department X of company Y influenced efficiency and team performance.
A charity institution, Y, suffers a lack of funding resulting in budget cuts for its programmes.
Theoretical Research Problems
Theoretical research relates to predicting, explaining, and understanding various phenomena. It also expands and challenges existing information and knowledge.
Identification of a research problem in theoretical research is achieved by analysing theories and fresh research literature relating to a broad area of research. This practice helps to find gaps in the research done by others and endorse the argument of your topic.
Here are some questions that you should bear in mind.
- A case or framework that has not been deeply analysed
- An ambiguity between more than one viewpoints
- An unstudied condition or relationships
- A problematic issue that needs to be addressed
Theoretical issues often contain practical implications, but immediate issues are often not resolved by these results. If that is the case, you might want to adopt a different research approach to achieve the desired outcomes.
Examples of Theoretical Research Problems
Long-term Vitamin D deficiency affects cardiac patients are not well researched.
The relationship between races, sex, and income imbalances needs to be studied with reference to the economy of a specific country or region.
The disagreement among historians of Scottish nationalism regarding the contributions of Imperial Britain in the creation of the national identity for Scotland.
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Step 2: Understanding the Research Problem
The researcher further investigates the selected area of research to find knowledge and information relating to the research problem to address the findings in the research.
Background and Rationale
- Population influenced by the problem?
- Is it a persistent problem, or is it recently revealed?
- Research that has already been conducted on this problem?
- Any proposed solution to the problem?
- Recent arguments concerning the problem, what are the gaps in the problem?
How to Write a First Class Dissertation Proposal or Research Proposal
Particularity and Suitability
- What specific place, time, and/or people will be focused on?
- Any aspects of research that you may not be able to deal with?
- What will be the concerns if the problem remains unresolved?
- What are the benefices of the problem resolution (e.g. future researcher or organisation’s management)?
Example of a Specific Research Problem
A non-profit institution X has been examined on their existing support base retention, but the existing research does not incorporate an understanding of how to effectively target new donors. To continue their work, the institution needs more research and find strategies for effective fundraising.
Once the problem is narrowed down, the next stage is to propose a problem statement and hypothesis or research questions.
If you are unsure about what a research problem is and how to define the research problem, then you might want to take advantage of our dissertation proposal writing service. You may also want to take a look at our essay writing service if you need help with identifying a research problem for your essay.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is research problem with example.
A research problem is a specific challenge that requires investigation. Example: “What is the impact of social media on mental health among adolescents?” This problem drives research to analyse the relationship between social media use and mental well-being in young people.
How many types of research problems do we have?
- Descriptive: Describing phenomena as they exist.
- Explanatory: Understanding causes and effects.
- Exploratory: Investigating little-understood phenomena.
- Predictive: Forecasting future outcomes.
- Prescriptive: Recommending actions.
- Normative: Describing what ought to be.
What are the principles of the research problem?
- Relevance: Addresses a significant issue.
- Re searchability: Amenable to empirical investigation.
- Clarity: Clearly defined without ambiguity.
- Specificity: Narrowly framed, avoiding vagueness.
- Feasibility: Realistic to conduct with available resources.
- Novelty: Offers new insights or challenges existing knowledge.
- Ethical considerations: Respect rights, dignity, and safety.
Why is research problem important?
A research problem is crucial because it identifies knowledge gaps, directs the inquiry’s focus, and forms the foundation for generating hypotheses or questions. It drives the methodology and determination of study relevance, ensuring that research contributes meaningfully to academic discourse and potentially addresses real-world challenges.
How do you write a research problem?
To write a research problem, identify a knowledge gap or an unresolved issue in your field. Start with a broad topic, then narrow it down. Clearly articulate the problem in a concise statement, ensuring it’s researchable, significant, and relevant. Ground it in the existing literature to highlight its importance and context.
How can we solve research problem?
To solve a research problem, start by conducting a thorough literature review. Formulate hypotheses or research questions. Choose an appropriate research methodology. Collect and analyse data systematically. Interpret findings in the context of existing knowledge. Ensure validity and reliability, and discuss implications, limitations, and potential future research directions.
You May Also Like
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
Find how to write research questions with the mentioned steps required for a perfect research question. Choose an interesting topic and begin your research.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

IMAGES
VIDEO