Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning


To Improve Critical Thinking, Don’t Fall into the Urgency Trap

Too often at work, people rely on expertise and past experiences to jump to a conclusion. Yet research consistently shows that when we rush decisions, we often regret them—even if they end up being correct. [i]
Why we hasten decision making is quite clear. We’re inundated with incessant distractions that compete for our attention, and, at the same time, we’re facing profound pressure to go faster and drive our businesses forward, even when the path ahead is unclear.
In the aftermath of information overwhelm, evolving technology, and rapidly changing business environments, people often unconsciously fall into a pernicious paradox called the “urgency trap.”
The Urgency Trap
The urgency trap, which can be defined as the habitual, unbridled, and counterproductive tendencies to rush through decision making when under the pressure of too many demands, is a paradox because it limits the very thing that could help us be more innovative, efficient, and effective: Our critical thinking.
The ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue to make a decision or solve a problem in novel ways is sorely lacking in today’s workforce, with most employers reporting that their employees’ critical thinking skills are average at best. [ii]
The good news? Critical thinking is a teachable skill, and one that any person can learn to make time for when making decisions. To improve and devote time for critical thinking at work, consider the following best practices.
1. Question assumptions and biases
Consider this common scenario: A team is discussing a decision that they must make quickly. The team’s options—and the arguments for and against them—have been assembled, but no clear evidence supports a particular course of action. Under pressure to move fast, the team relies on their expertise and past experiences to rapidly provide a solution. Yet, in the months following their decision, the issues that prompted the original discussion persist, and the team wonders why.
The issue here may be that the team failed to question their own assumptions and biases. Indeed, when we view situations solely based on our own personal experiences and beliefs, we limit our options and provide solutions that are often short-sighted or superficial. [iii] To improve critical thinking skills, we must step back and ask ourselves,
- “Am I seeking out information that confirms my pre-conceived idea?”
- “Am I perceiving a past experience as more predictable than it actually was?”
- “Am I overemphasizing information that comes to mind quickly, instead of calculating other probabilities?”
2. Reason through logic
When presented with an argument, it is important to analyze it logically in order to determine whether or not it is valid. This means looking at the evidence that is being used to support the argument and determining whether or not it actually does support the conclusion that is being drawn.
Additionally, consider the source of the information. Is it credible? Trustworthy? Finally, be aware of common logical fallacies people tend to use when trying to speed up decision making, such as false dilemma (erroneously limiting available options) and hasty generalizations (making a claim based on a few examples rather than substantial proof).
3. Listen actively and openly
When we’re in a rush to make a decision, we often focus more on how we want to respond rather than what the speaker is saying. Active listening, on the other hand, is a critical thinking skill that involves paying close attention to what someone else is saying with the intent to learn, and then asking questions to clarify and deepen understanding.
When engaging in active listening, it’s important to avoid interrupting and instead allow the other person to fully express their thoughts. Additionally, resist the urge to judge or criticize what the other person is saying. Rather, focus on truly understanding their perspective. This may mean practicing open-mindedness by considering new ideas, even if they challenge existing beliefs. By keeping an open mind, this ensures that all sides of an issue are considered before coming to a conclusion.
4. Ask better questions
In an article for Harvard Business Review, John Coleman, author of the HBR Guide to Crafting Your Purpose , writes, “At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions.” [iv]
To ask better questions, first consider the audience for the question (who is hearing the question and who might respond?) and the purpose (what is the goal of asking this question?). Then, approach queries with rigor and curiosity by asking questions that:
- Are open-ended yet short and direct (e.g., “How might you help me think about this differently?”)
- Challenge a group’s conventional thinking (e.g., “What if we tried a new approach?”)
- Help others reconsider their first principles or hypotheses (e.g., “As we look at the data, how might we reconsider our initial proposed solution?”)
- Encourage further discussion and analysis (e.g., “How can we deepen our understanding of this issue?”)
- Thoughtfully follow up on the solution (e.g., “How do we feel about the progress so far?”)
5. Create space for deliberation
The recommendations outlined thus far are behaviors and capabilities people can use in the moment, but sometimes, the best solutions are formulated after consideration. In fact, research shows that a deliberate process often leads to better conclusions. [v] And sleep has even been proven to help the brain assimilate a problem and see it more clearly. [vi]
When issues are complex, it’s important to find ways to resist unnecessary urgency. Start by mapping out a process that allows several days or longer to sit with a problem. Then, create space in the day to formulate in quiet reflection, whether that’s replacing your first thirty minutes in the morning with thinking instead of checking email, or going on a walk midday, or simply journaling for a few moments before bed.
Critical Thinking Cannot Be Overlooked
In the face of rapidly-evolving business environments, the ability to make smart decisions quickly is one of a company’s greatest assets—but to move fast, people must first slow down to reason through pressing issues, ask thoughtful questions, and evaluate a topic from multiple angles.
To learn more about how organizations can enhance their critical thinking and decision-making skills, download the full paper: Who Is Really Making the Decisions in Your Organization — and How?
[i] Grant Halvorson, Heidi, “Quick Decisions Create Regret, Even When They Are Good Decisions,” Fast Company. https://www.fastcompany.com/1758386/quick-decisions-create-regret-even-when-they-are-good-decisions .
[ii] Plummer, Matt, “A Short Guide to Building Your Team’s Critical Thinking Skills,” Harvard Business Review, October 2019. https://hbr.org/2019/10/a-short-guide-to-building-your-teams-critical-thinking-skills .
[iii] Benjamin Enke, Uri Gneezy, Brian Hall, David Martin, Vadim Nelidov, Theo Offerman, and Jeroen van de Ve, “Cognitive Biases: Mistakes or Missing Stakes?” Harvard Business School, 2021. https://www.hbs.edu/ris/Publication%20Files/21-102_1ed838f2-8ef3-4eec-b543-d00eb1efbe10.pdf
[iv] Coleman, John, “Critical Thinking Is About Asking Better Questions,” Harvard Business Review, April 2022. https://hbr.org/2022/04/critical-thinking-is-about-asking-better-questions .
[v] Markovitz, Daniel, “How to Avoid Rushing to Solutions When Problem-Solving,” Harvard Business Review, November 2020. https://hbr.org/2020/11/how-to-avoid-rushing-to-solutions-when-problem-solving .
[vi] Miller, Jared, “Does ‘Sleeping On It’ Really Work?” WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders/features/does-sleeping-on-it-really-work .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
- Open training
- Team training
What is Critical Thinking and Why is it Valuable in the Workplace?
- Articles and Resources
- > Personal Effectiveness and Preparing for Change
- > What is Critical Thinking and Why is it Valuable in the Workplace?
There are times at work when you simply have to “do.” A tight deadline, a demanding project outline, or a highly particular superior might mean that it makes sense to complete a task without too much mental tinkering. But work like this can be unsustainable and worse — it won’t leverage your ability to think critically.
There is value in thinking critically in every aspect of your life. From making decisions in your personal life, to interrogating the media you consume, to assessing your work with a critical eye, applying critical thinking is an essential skill everyone should be trying to hone.
At your workplace, critical thinking can distinguish you as a leader, and a valuable mind to bounce ideas off. It can help improve the quality of your work, and the perception those higher up the chain have of you.
Here’s what you need to know about critical thinking in the workplace:
What Exactly is “Critical Thinking”?
In a nutshell, critical thinking is the ability to think reasonably, detaching yourself from personal bias, emotional responses, and subjective opinions. It involves using the data at hand to make a reasoned choice without falling prey to the temptations of doing things simply because they’ve always been done a certain way.
Critical thinking takes time. It might be quicker simply to take instruction at face value, or rely on the traditions of your team. But without analyzing the reasons behind decisions and tasks, it becomes extremely easy to adopt bad habits. This might be time-wasting meetings, inefficient uses of effort, or poor interactions with team members. Taking the time to ask “why” you’re doing something is the first step to thinking critically.
Sometimes, data is available which allows you to make reasoned decisions based on absolute facts. If you can show that a new best practice can objectively improve current processes with hard data, you’ve used the very basics of critical thinking. That said, actual numbers aren’t always available when making a decision. Real critical thinking involves taking a careful look at situations and making a decision based on what is known, not what is felt.
Why Is Critical Thinking Important in the Workplace?
The short answer to the above question is this: critical thinkers make the best decisions, most often. And in the workplace, where choices about how to complete tasks, communicate information, relate with coworkers, and develop strategy are so common, critical thinkers are extremely valuable.
A savvy hiring manager will make this part of the recruitment process. It’s pretty easy to gauge how someone is inclined to solve a problem — ask them how they would deal with a specific situation, and give them the opportunity to use their critical thinking skills, versus deferring to an emotional, or prescribed reaction. Employing people who can think and act reasonably will pay enormous dividends down the road.
Using your critical thinking skills in the workplace will define you as a problem solver. This is not only useful career-wise (although having upper-level people at your company think highly of you is undoubtedly a benefit) it also establishes you as a leader among your fellow team members. Demonstrating your ability to solve problems and accomplish goals effectively will help instill confidence in you with all your coworkers.
How to Use Critical Thinking in the Workplace
The first step to actually using critical thinking is approaching every situation with an open mind. You need to be receptive to all information available, not just the kind that satisfies your preconceived notions or personal biases. This can be easier said than done, of course — lessons learned and beliefs held are often done so with a reason. But when it comes to critical thinking, it’s important to analyze each situation independently.
Once you’ve analyzed a situation with an open mind, you need to consider how to communicate it properly. It’s all very well and good to approach situations with objective logic, but it doesn’t do you any favours to sound like Mr. Spock when you’re conveying your conclusions. Be tactful, patient and humble when you are explaining how and why you’ve come to decisions. Use data if available to support your findings, but understand that not everyone is able to remove emotion from situations.
The final, and perhaps least obvious, application with critical thinking is creativity. Often, getting creative means pushing boundaries and reshaping convention. This means taking a risk — one that can often be worth the reward. Using a critical thinking approach when getting creative can help you mitigate the risk, and better determine what value your creativity can bring. It will help you and your team try new things and reinvent current processes while hopefully not rocking the boat too much.
Learn More About Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a valuable skill for all aspects of your life. It benefits problem solving, creativity, and teamwork. And it translates particularly well to the workplace, where it can distinguish you as a valuable employee and leader.
Taking the extra time to examine things objectively, make decisions based on logic, and communicate it tactfully will help you, those you work with, and your work goals prosper. To learn more about how to do that, have a look at our Critical Thinking and Problem Solving for Effective Decision-Making workshop and register today!
Let us help you create your training solution
Hello we'd love to hear from you.
Complete the form below or reach us at: [email protected] , or 613-234-2020
Contact details
To help you.
- I wish to subscribe to PMC Training content.
Welcome to our new website!
We appreciate your patience as we add the finishing touches. In the meantime, go and explore!
Cookie Usage Disclaimer: This website uses cookies to enhance your browsing experience. By continuing to use this site, you consent to our use of cookies. For more information, please review our Privacy Policy .

Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer
Work Life is now on YouTube! Watch our new short documentary series here .

How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making
It’s simple in theory, but tougher in practice – here are five tips to get you started.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Have you heard the riddle about two coins that equal thirty cents, but one of them is not a nickel? What about the one where a surgeon says they can’t operate on their own son?
Those brain teasers tap into your critical thinking skills. But your ability to think critically isn’t just helpful for solving those random puzzles – it plays a big role in your career.
An impressive 81% of employers say critical thinking carries a lot of weight when they’re evaluating job candidates. It ranks as the top competency companies consider when hiring recent graduates (even ahead of communication ). Plus, once you’re hired, several studies show that critical thinking skills are highly correlated with better job performance.
So what exactly are critical thinking skills? And even more importantly, how do you build and improve them?
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to evaluate facts and information, remain objective, and make a sound decision about how to move forward.
Does that sound like how you approach every decision or problem? Not so fast. Critical thinking seems simple in theory but is much tougher in practice, which helps explain why 65% of employers say their organization has a need for more critical thinking.
In reality, critical thinking doesn’t come naturally to a lot of us. In order to do it well, you need to:
- Remain open-minded and inquisitive, rather than relying on assumptions or jumping to conclusions
- Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value
- Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible
- Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation
So, critical thinking isn’t just being intelligent or analytical. In many ways, it requires you to step outside of yourself, let go of your own preconceived notions, and approach a problem or situation with curiosity and fairness.
It’s a challenge, but it’s well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems.
7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper
Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you’ll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it’s better to think of critical thinking less as a distinct skill and more as a collection or category of skills.
To think critically, you’ll need to tap into a bunch of your other soft skills. Here are seven of the most important.
Open-mindedness
It’s important to kick off the critical thinking process with the idea that anything is possible. The more you’re able to set aside your own suspicions, beliefs, and agenda, the better prepared you are to approach the situation with the level of inquisitiveness you need.
That means not closing yourself off to any possibilities and allowing yourself the space to pull on every thread – yes, even the ones that seem totally implausible.
As Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D. writes in a piece for Psychology Today , “Even if an idea appears foolish, sometimes its consideration can lead to an intelligent, critically considered conclusion.” He goes on to compare the critical thinking process to brainstorming . Sometimes the “bad” ideas are what lay the foundation for the good ones.
Open-mindedness is challenging because it requires more effort and mental bandwidth than sticking with your own perceptions. Approaching problems or situations with true impartiality often means:
- Practicing self-regulation : Giving yourself a pause between when you feel something and when you actually react or take action.
- Challenging your own biases: Acknowledging your biases and seeking feedback are two powerful ways to get a broader understanding.
Critical thinking example
In a team meeting, your boss mentioned that your company newsletter signups have been decreasing and she wants to figure out why.
At first, you feel offended and defensive – it feels like she’s blaming you for the dip in subscribers. You recognize and rationalize that emotion before thinking about potential causes. You have a hunch about what’s happening, but you will explore all possibilities and contributions from your team members.
Observation
Observation is, of course, your ability to notice and process the details all around you (even the subtle or seemingly inconsequential ones). Critical thinking demands that you’re flexible and willing to go beyond surface-level information, and solid observation skills help you do that.
Your observations help you pick up on clues from a variety of sources and experiences, all of which help you draw a final conclusion. After all, sometimes it’s the most minuscule realization that leads you to the strongest conclusion.
Over the next week or so, you keep a close eye on your company’s website and newsletter analytics to see if numbers are in fact declining or if your boss’s concerns were just a fluke.
Critical thinking hinges on objectivity. And, to be objective, you need to base your judgments on the facts – which you collect through research. You’ll lean on your research skills to gather as much information as possible that’s relevant to your problem or situation.
Keep in mind that this isn’t just about the quantity of information – quality matters too. You want to find data and details from a variety of trusted sources to drill past the surface and build a deeper understanding of what’s happening.
You dig into your email and website analytics to identify trends in bounce rates, time on page, conversions, and more. You also review recent newsletters and email promotions to understand what customers have received, look through current customer feedback, and connect with your customer support team to learn what they’re hearing in their conversations with customers.
The critical thinking process is sort of like a treasure hunt – you’ll find some nuggets that are fundamental for your final conclusion and some that might be interesting but aren’t pertinent to the problem at hand.
That’s why you need analytical skills. They’re what help you separate the wheat from the chaff, prioritize information, identify trends or themes, and draw conclusions based on the most relevant and influential facts.
It’s easy to confuse analytical thinking with critical thinking itself, and it’s true there is a lot of overlap between the two. But analytical thinking is just a piece of critical thinking. It focuses strictly on the facts and data, while critical thinking incorporates other factors like emotions, opinions, and experiences.
As you analyze your research, you notice that one specific webpage has contributed to a significant decline in newsletter signups. While all of the other sources have stayed fairly steady with regard to conversions, that one has sharply decreased.
You decide to move on from your other hypotheses about newsletter quality and dig deeper into the analytics.
One of the traps of critical thinking is that it’s easy to feel like you’re never done. There’s always more information you could collect and more rabbit holes you could fall down.
But at some point, you need to accept that you’ve done your due diligence and make a decision about how to move forward. That’s where inference comes in. It’s your ability to look at the evidence and facts available to you and draw an informed conclusion based on those.
When you’re so focused on staying objective and pursuing all possibilities, inference can feel like the antithesis of critical thinking. But ultimately, it’s your inference skills that allow you to move out of the thinking process and onto the action steps.
You dig deeper into the analytics for the page that hasn’t been converting and notice that the sharp drop-off happened around the same time you switched email providers.
After looking more into the backend, you realize that the signup form on that page isn’t correctly connected to your newsletter platform. It seems like anybody who has signed up on that page hasn’t been fed to your email list.
Communication

3 ways to improve your communication skills at work
If and when you identify a solution or answer, you can’t keep it close to the vest. You’ll need to use your communication skills to share your findings with the relevant stakeholders – like your boss, team members, or anybody who needs to be involved in the next steps.
Your analysis skills will come in handy here too, as they’ll help you determine what information other people need to know so you can avoid bogging them down with unnecessary details.
In your next team meeting, you pull up the analytics and show your team the sharp drop-off as well as the missing connection between that page and your email platform. You ask the web team to reinstall and double-check that connection and you also ask a member of the marketing team to draft an apology email to the subscribers who were missed.
Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you’re often doing so with the objective of solving a problem.
The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow. You’re focused on finding a solution.
In contrast, you can use critical thinking for a variety of use cases beyond solving a problem – like answering questions or identifying opportunities for improvement. Even so, within the critical thinking process, you’ll flex your problem-solving skills when it comes time to take action.
Once the fix is implemented, you monitor the analytics to see if subscribers continue to increase. If not (or if they increase at a slower rate than you anticipated), you’ll roll out some other tests like changing the CTA language or the placement of the subscribe form on the page.
5 ways to improve your critical thinking skills

Beyond the buzzwords: Why interpersonal skills matter at work
Think critically about critical thinking and you’ll quickly realize that it’s not as instinctive as you’d like it to be. Fortunately, your critical thinking skills are learned competencies and not inherent gifts – and that means you can improve them. Here’s how:
- Practice active listening: Active listening helps you process and understand what other people share. That’s crucial as you aim to be open-minded and inquisitive.
- Ask open-ended questions: If your critical thinking process involves collecting feedback and opinions from others, ask open-ended questions (meaning, questions that can’t be answered with “yes” or “no”). Doing so will give you more valuable information and also prevent your own biases from influencing people’s input.
- Scrutinize your sources: Figuring out what to trust and prioritize is crucial for critical thinking. Boosting your media literacy and asking more questions will help you be more discerning about what to factor in. It’s hard to strike a balance between skepticism and open-mindedness, but approaching information with questions (rather than unquestioning trust) will help you draw better conclusions.
- Play a game: Remember those riddles we mentioned at the beginning? As trivial as they might seem, games and exercises like those can help you boost your critical thinking skills. There are plenty of critical thinking exercises you can do individually or as a team .
- Give yourself time: Research shows that rushed decisions are often regrettable ones. That’s likely because critical thinking takes time – you can’t do it under the wire. So, for big decisions or hairy problems, give yourself enough time and breathing room to work through the process. It’s hard enough to think critically without a countdown ticking in your brain.
Critical thinking really is critical
The ability to think critically is important, but it doesn’t come naturally to most of us. It’s just easier to stick with biases, assumptions, and surface-level information.
But that route often leads you to rash judgments, shaky conclusions, and disappointing decisions. So here’s a conclusion we can draw without any more noodling: Even if it is more demanding on your mental resources, critical thinking is well worth the effort.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
Business.com aims to help business owners make informed decisions to support and grow their companies. We research and recommend products and services suitable for various business types, investing thousands of hours each year in this process.
As a business, we need to generate revenue to sustain our content. We have financial relationships with some companies we cover, earning commissions when readers purchase from our partners or share information about their needs. These relationships do not dictate our advice and recommendations. Our editorial team independently evaluates and recommends products and services based on their research and expertise. Learn more about our process and partners here .
Building Critical Thinking Skills to Solve Problems at Work
Follow this six-step discussion process to foster critical thinking among your team.

Table of Contents
Critical thinking is a vital soft skill that uses one’s experiences and analytical skills to deduce information and make educated decisions. It’s an essential skill to have in the workplace, as the ability to use information from a broader and more impartial perspective allows your employees to make more informed decisions and see a comprehensive view of any situation.
The U.S. Department of Labor identified critical thinking as a key component for essential workplace skills, including problem-solving and decision-making. Here’s how to build – and implement – critical thinking skills in the workplace.
>> Learn more: 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
How to use critical thinking to problem-solve
Here is a six-step problem-solving process to try with your team to build and use this skill.
1. Name the situation.
When you name the situation, you present a single discussion point that everyone in the discussion can identify. This statement can be written on a whiteboard as a visual prompt so that the team can focus on the point and redirect the discussion when the topic shifts. Critical thinking involves keeping an open mind about situations. You help participants remember the goal of the group by naming the situation.
2. List all possible solutions.
Brainstorming takes place during this part of the process. There is nothing outside the realm of possibilities at this point in the discussion. When you open the conversation to unlimited options, you expand thinking beyond one person. The ability to expand your thinking offers the conversation many possible solutions that you may not have considered without the expression of thoughts and opinions. Make sure that all potential solutions discussed during this time stay on task for the situation that has been named in the first step. Critical thinking includes the ability to keep an open mind to other considerations and viewpoints without losing track of the end goal. You expand the discussion to see new options and stay on task by identifying multiple opportunities.
3. Narrow your solutions to three options.
Everyone on the team needs to agree with at least one of the three options. Individuals who can find a compromise and create solutions from many perspectives are better able to bring a team together. Write each solution at the top of a whiteboard and include below each one a list of its advantages and disadvantages. Critical-thinking skills offer the ability to look at situations rationally without judgments of good and bad or wrong and right. You can maintain a rational discussion when you bring consensus to a few intentionally chosen solutions.
4. Choose one option from the three choices.
Make a final choice that offers the best chance of success based on rational discussion about the situation. Review this choice in relation to how well it solves the designated problem. Critical thinking skills help individuals use a more systematic way to come to conclusions. This reduces the chance of making decisions based on incorrect inferences arising from emotional conclusions.
5. Put a plan in place to implement the chosen solution.
Your chosen solution should have timelines and a list that identifies which participants are responsible for what parts of the final plan. Critical-thinking skills include the ability to commit to the chosen solution. You increase attention to detail and interest from the participants in implementing the solution when they are an integral part of the process.
6. Complete the plan.
Some employees find this part of the process the most difficult. Think of the number of times a great plan floundered because there was no follow-up. Make sure each person from the team has a part to play in the process that emphasizes their areas of expertise and interest. Complete regular reviews of people and timelines for project management. Critical thinking involves the ability to see the value of the overall plan. At this point in the process, individuals should be able to see the value of the solution and have buy-in since they were part of the process.
This problem-solving process creates an environment where critical thinking becomes a working part of finding a solution. For individuals who struggle with this method, you may want to consider some training in critical thinking. Overall, though, this process promotes critical thinking in your employees. You can also integrate this activity for making plans and creating a mission. The value added to your organization includes improved engagement , insight and productivity from your team.
Why critical thinking is essential in the workplace
In recent decades, companies have recognized the need for integrating critical thinking into the workplace to help build the success of their organizations. Strong critical-thinking skills can greatly benefit everybody in the workplace. Not only does thinking more openly introduce ideas and solutions that widen the opportunities for success, but it also provides an increase in teamwork and productivity and a decrease in conflict . Here are some additional benefits of critical thinking in the workplace.
Required in certain professions
In many professions – particularly those based on research or that require deductive reasoning, such as finance, education, research and law – acquiring critical-thinking skills is necessary. With critical thinking, employees can solve problems objectively by considering varying perspectives and analyzing facts without bias, allowing for smart decision-making and problem-solving.
Improves decision-making
Those with critical-thinking skills mull over their decisions thoroughly by researching, looking at information objectively, asking questions, and weighing the pros and cons before acting. This skill can help businesses stay on track when making decisions by thoroughly reviewing the risk versus reward of each decision.
Boosts happiness
Critical thinking can boost happiness , as it is empowering to have the skills to make your own, well-informed decisions. Those who possess this skill are more in tune with their goals, needs and personal ethics, and they have a better understanding of what in their situation needs to change to make themselves happy or grow. [Read related article: How Hiring a Chief Happiness Officer Can Save Your Business ]
How to build critical-thinking skills
Here are a few ways you can polish your critical-thinking skills.
Practice active listening.
Practice actively listening by keeping an open mind and being attentive to those around you, from associates to executives. Listen to what others are saying to gain an understanding of each person’s individual perspective, needs and expectations, and show them empathy. This level of understanding will allow you to work together more effectively and make decisions that everyone is satisfied with.
Ask critical questions.
Instead of taking information at face value, be curious and ask questions to ensure you have everything you need to make a well-informed decision. Using open-ended questions offers an opportunity for further exploration, as they dive deeper and provide insightful details that can be helpful when making decisions.
Vet new information.
Don’t assume all new information you hear is true; instead, take time to thoroughly vet it by ensuring it’s up to date and it comes from a trustworthy source. Look at the existing evidence and the new facts being presented, then question thought processes and consider whose voice is missing.
Consider more than one perspective.
While you may feel that you have the “right” perspective, consider all points of view to fully understand others and their reasoning. This will help you improve your working relationships, better understand where your peers are coming from and tailor your communication to meet their needs.
Question your own biases.
Regardless of whether or not you try to avoid it in your decision-making process, everybody has their own biases, which are the foundation of their thinking. By uncovering your own biases and being actively aware of them, you can grow as a critical thinker and work to keep them separate from your decision-making process.
Conduct research.
If there are any unanswered questions or gaps in the information provided, conduct research to further your understanding and reach a decision. Consider a source’s intention when conducting research, avoiding any that are sales-based or contain ill will. Don’t use social media to obtain information; stick to reputable publications free of bias and cite their sources.
Form your own opinion.
Be an independent thinker and form your own opinions by considering the information presented to you, including facts and evidence. Listen to and consider the opinions of others, but use deductive reasoning to form your own opinion – and stay true to it.
Lynette Reed contributed to the writing and reporting in this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
- How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business
Small Business Resources
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions
Business News Daily provides resources, advice and product reviews to drive business growth. Our mission is to equip business owners with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions. As part of that, we recommend products and services for their success.
We collaborate with business-to-business vendors, connecting them with potential buyers. In some cases, we earn commissions when sales are made through our referrals. These financial relationships support our content but do not dictate our recommendations. Our editorial team independently evaluates products based on thousands of hours of research. We are committed to providing trustworthy advice for businesses. Learn more about our full process and see who our partners are here .
Why Critical Thinking Matters in Your Business
Critical thinking should become a second-nature skill for leaders and employees across your organization.

Table of Contents
Many professionals hope to pursue careers they’re passionate about so they can find joy and meaning in their work. Caring deeply about your work is vital for engagement and productivity, but balancing emotions with critical thinking is essential in the workplace.
When employees engage in critical thinking, they use an independent, reflective thought process to evaluate issues and solve problems based on knowledge and objective evidence.
Critical thinking skills can guide your organization toward success, but to truly maximize the problem-solving benefits of critical thinking, it’s crucial to teach this skill to your entire team. We’ll explore critical thinking skills and how to teach them in the workplace to help your business improve its decision-making and problem-solving.
What is critical thinking?
Jen Lawrence, co-author of Engage the Fox: A Business Fable About Thinking Critically and Motivating Your Team , defines critical thinking as “the ability to solve problems effectively by systematically gathering information about an issue, generating further ideas involving a variety of perspectives, evaluating the information using logic, and making sure everyone involved is on board.”
This is a complex definition for a challenging concept. Though critical thinking might seem as straightforward as stepping back and using a formal thinking process instead of reacting instinctively to conflicts or problems, it is actually a much more challenging task.
Critical thinking’s ultimate goal is ensuring you have the best answer to a problem with maximum buy-in from all parties involved – an outcome that will ultimately save your business time, money and stress.
Why is critical thinking essential in the workplace?
A World Economic Forum report revealed that critical thinking is one of the most in-demand career skills employers seek when trying to attract and retain the best employees – and employers believe critical thinking skills will become even more necessary in the coming years.
Critical thinking in the workplace guarantees objective and efficient problem-solving, ultimately reducing costly errors and ensuring that your organization’s resources are used wisely. Team members employing critical thinking can connect ideas, spot errors and inconsistencies, and make the best decisions most often.
Employees with critical thinking are also more likely to accomplish the following:
- Analyzing information
- Thinking outside the box
- Coming up with creative solutions to sudden problems
- Devising thought-through, systematic plans
- Requiring less supervision
What are critical thinking skills?
Critical thinking is a soft skill that comprises multiple interpersonal and analytical abilities and attributes. Here are some essential critical thinking skills that can support workforce success.
- Observation: Employees with critical thinking can easily sense and identify an existing problem – and even predict potential issues – based on their experience and sharp perception. They’re willing to embrace multiple points of view and look at the big picture.
- Analytical thinking: Analytical thinkers collect data from multiple sources, reject bias, and ask thoughtful questions. When approaching a problem, they gather and double-check facts, assess independent research, and sift through information to determine what’s accurate and what can help resolve the problem.
- Open-mindedness: Employees who demonstrate critical thinking are open-minded – not afraid to consider opinions and information that differ from their beliefs and assumptions. They listen to colleagues; they can let go of personal biases and recognize that a problem’s solution can come from unexpected sources.
- Problem-solving attitude: Critical thinkers possess a positive attitude toward problem-solving and look for optimal solutions to issues they’ve identified and analyzed. They are usually proactive and willing to offer suggestions based on all the information they receive. [Related article: How to Develop a Positive Attitude in the Workplace ]
- Communication: When managers make a decision, they must share it with the rest of the team and other stakeholders. Critical thinkers demonstrate excellent communication skills and can provide supporting arguments and evidence that substantiate the decision to ensure the entire team is on the same page.
What are the benefits of critical thinking in the workplace?
Many workplaces operate at a frantic tempo that reinforces hasty thinking and rushed business decisions, resulting in costly mistakes and blunders. When employees are trained in critical thinking, they learn to slow the pace and gather crucial information before making decisions.
Along with reducing costly errors, critical thinking in the workplace brings the following benefits:
- Critical thinking improves communication. When employees think more clearly and aren’t swayed by emotion, they communicate better. “If you can think more clearly and better articulate your positions, you can better engage in discussions and make a much more meaningful contribution in your job,” said David Welton, managing partner at Grove Critical Thinking.
- Critical thinking boosts emotional intelligence. It might seem counterintuitive to associate analytical rationality with emotional intelligence . However, team members who possess critical thinking skills are less prone to rash, emotion-driven decisions. Instead, they take time to analyze the situation and make the most informed decision while being mindful and respectful of the emotional and ethical implications.
- Critical thinking encourages creativity. Critical thinkers are open to new ideas and perspectives and accumulate a significant amount of information when facing decisions. Because of this, they’re more likely to come up with creative solutions . They are also curious and don’t shy away from asking open-ended questions.
- Critical thinking saves time and money. By encouraging critical thinking in the workplace, you minimize the need for supervision, catch potential problems early, promote independence and initiative, and free managers to focus on other duties. All this helps your company save valuable time and resources.
How do you teach critical thinking in the workplace?
Experts agree that critical thinking is a teachable skill. Both Lawrence and Welton recommend exploring critical thinking training programs and methods to improve your workplace’s critical thinking proficiency. Here’s a breakdown of how to teach critical thinking in the workplace:
- Identify problem areas. Executives and managers should assess workplace areas most lacking in critical thinking. If mistakes are consistently made, determine whether the issue is a lack of critical thinking or an inherent issue with a team or process. After identifying areas that lack critical thinking, research the type of training best suited to your organization.
- Start small. Employees newly embracing critical thinking might have trouble tackling large issues immediately. Instead, present them with smaller challenges. “Start practicing critical thinking as a skill with smaller problems as examples, and then work your way up to larger problems,” Lawrence said.
- Act preemptively. Teaching and implementing critical thinking training and methodology takes time and patience. Lawrence emphasized that critical thinking skills are best acquired during a time of calm. It might feel urgent to seek critical thinking during a crisis, but critical thinking is a challenging skill to learn amid panic and stress. Critical thinking training is best done preemptively so that when a crisis hits, employees will be prepared and critical thinking will come naturally.
- Allow sufficient time. From a managerial perspective, giving employees extra time on projects or problems might feel stressful in the middle of deadlines and executive pressures. But if you want those working for you to engage in critical thinking processes, it’s imperative to give them ample time. Allowing employees sufficient time to work through their critical thinking process can save the company time and money in the long run.
How do you identify successful critical thinking?
Successful critical thinking happens during a crisis, not after.
Lawrence provided an example involving restaurants and waitstaff: If a customer has a bad experience at a restaurant, a server using critical thinking skills will be more likely to figure out a solution to save the interaction, such as offering a free appetizer or discount. “This can save the hard-earned customer relationship you spent a lot of marketing dollars to create,” Lawrence said. This concept is applicable across many business and organizational structures.
You should also be aware of signs of a lack of critical thinking. Lawrence pointed out that companies that change strategy rapidly, moving from one thing to the next, are likely not engaging in critical thinking. This is also the case at companies that seem to have good ideas but have trouble executing them.
As with many issues in business, company leadership determines how the rest of the organization acts. If leaders have excellent ideas but don’t follow critical thinking processes, their team will not buy into those ideas, and the company will suffer. This is why critical thinking skills often accompany positive communication skills.
“Critical thinking doesn’t just help you arrive at the best answer, but at a solution most people embrace,” Lawrence said. Modeling critical thinking at the top will help the skill trickle down to the rest of the organization, no matter your company’s type or size.
Critical thinking is the key to your business success
When critical thinking is actively implemented in an organization, mistakes are minimized, and operations run more seamlessly.
With training, time and patience, critical thinking can become a second-nature skill for employees at all levels of experience and seniority. The money, time and conflict you’ll save in the long run are worth the extra effort of implementing critical thinking in your workplace.
Rebecka Green contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
Critical Thinking: Creating Job-Proof Skills for the Future of Work
Daniela dumitru.
1 Teacher Training Department, Bucharest University of Economic Studies, 010374 Bucharest, Romania
2 Doctoral School of Psychology and Educational Sciences, University of Bucharest, 050663 Bucharest, Romania
Diane F. Halpern
3 Department of Psychology, Claremont McKenna College, Claremont, CA 91711, USA; moc.liamg@nreplahfenaid
In this study, we explore the transformative impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on the job market and argue for the growing importance of critical thinking skills in the face of job automation and changing work dynamics. Advancements in AI have the potential to disrupt various professions, including, for example, programming, legal work, and radiology. However, solely relying on AI systems can lead to errors and misjudgments, emphasizing the need for human oversight. The concept of “job-proof skills” is introduced, highlighting the importance of critical thinking, problem-solving, empathy, ethics, and other human attributes that machines cannot replicate with the same standards and agility. We maintain that critical thinking can be taught and learned through appropriate classroom instruction and transfer-focused approaches. The need for critical thinking skills is further reinforced by the influx of information and the spread of misinformation in the age of social media. Moreover, employers increasingly value critical thinking skills in their workforce, yet there exists a gap between the demand for these skills and the preparedness of college graduates. Critical thinking is not only essential for the future of work, but also for informed citizenship in an increasingly complex world. The potential impact of AI on job disruption, wages, and employment polarization is discussed, highlighting the correlation between jobs requiring critical thinking skills and their resistance to automation. We conclude by discussing collaborative efforts between universities and labor market organizations to adapt curricula and promote the development of critical thinking skills, drawing on examples from European initiatives. The need to prioritize critical thinking skills in education and address the evolving demands of the labor market is emphasized as a crucial step for navigating the future of work and opportunities for workers.
1. Introduction: Critical Thinking: Creating Job-Proof Skills for the Future of Work
The rapid evolution of online technologies has ushered in a paradigm shift in employment, redefining the nature of work and the skills required to succeed in the digital age. This transformative landscape, characterized by the ubiquitous presence of the Internet, social media platforms, and advanced artificial intelligence systems, has created a plethora of new opportunities and challenges in the labor market. As we navigate this digital frontier, it is becoming increasingly clear that traditional employment paradigms are undergoing a profound transformation. The convergence of online technologies with the demands of a networked world has not only created new job opportunities, but it has also disrupted established industries, rendering some job roles obsolete while creating demand for previously unforeseen skills. In this era of unprecedented connectivity and innovation, examining the intricate interplay between online technologies and jobs is paramount as it holds the key to understanding the dynamics of our rapidly evolving workforce.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is disrupting many jobs and promises “to change the way the world works” ( adminGPT 2023, para. 13 ). The number and range of AI programs are increasing at a rapid pace, and they are likely to continually improve to meet user demands. Consider, for example, ChatGPT, which can respond to questions and requests in a way that seems to come from a human rather than a computer program. GPT stands for “generative pretrained transformer”. It is generative in that it can provide responses that it never “learned”; it is pretrained with a large language model ( Bushwick et al. 2023 ). Newer versions can describe visual images, although thus far, they cannot create visual images. Its uses are seemingly endless. It is easy to imagine how such programs can change the lives of blind individuals. In fact, it can and will change the lives of all of us.
In this paper, we argue that these advances in online technologies will make critical thinking (CT) more important than ever before. Many who are preparing to enter the job market, and many who are already employed, will need to adapt to new forms of job automation and different ways of working.
Consider, for example, that an early achievement of ChatGPT was its generation of Python code (a computer language) to compute various tasks, such as data analysis. Apparently, getting ChatGPT to generate code is so easy that several YouTube videos have popped up claiming that they can teach novice users to use ChatGPT to generate code in 90 s. ( Data Professor 2023 ). The benefits are obvious, but so are the potential job losses for people who work in Python. Python coders will need to upgrade their skills, perhaps first becoming experts in the use of ChatGPT and similar programs, but this also has a positive side--they can spend more time working on larger questions such as which analyses are needed, and, of course, carefully reviewing the work produced by AI to ensure that it is accurate and understandable. Early versions of ChatGPT responses often contained errors. A New York lawyer learned the hard way: Steven A. Schwartz, a lawyer for 30 years, used ChatGPT to create a legal document ( Weiser and Schweber 2023 ). It was filled with fake citations and bogus judicial opinions. Sadly, Mr. Schwartz never checked the accuracy of the document he filed in court. The judge was not amused. This highly public and embarrassing event should be a lesson for all of us. Current AI programs cannot be trusted to take over our work, though they may be able to aid or supplement it. However, other AI programs can “read” radiographs more accurately than human radiologists, which provides a benefit to both radiologists and patients. There is an immediate positive effect for this advancement: Radiologists will have more time to directly work with patients, and yes, they must also check the accuracy of the outputs from their programs when presenting diagnoses.
For the rest of us, whether we are students or early or late in our careers, we need to focus on the development of “job-proof skills” in the face of AI advances. A report from the United Nations defines job-proof skills as “conceptual and strategic thinking, problem-solving, empathy, optimism, ethics, emotional intelligence, and judgments are the future-proof skills and attributes that machines will not be able to replicate with the same standards and agility as qualified human beings” ( Elkeiy 2022, para. 5 ). In other words, critical thinking skills will always be needed.
2. What Is Critical Thinking?
Although some scholars in the field of critical thinking have emphasized differences among various definitions, we believe that the commonalities are evident (c.f., Dwyer 2017 ; Nisbett 2015 ; Lipman 1991 ; Fisher 2001 ). There are some differences in the use of terms and several skills might be more important, but all of the definitions (more or less) conform to our preferred definition: “Critical thinking is the use of those cognitive skills and abilities that increase the probability of a desirable outcome. It is purposeful, reasoned, and goal directed. It is the kind of thinking involved in solving problems, formulating inferences, calculating likelihoods, and making decisions. Critical thinkers use these skills appropriately, without prompting, and usually with conscious intent, in a variety of settings. That is, they are predisposed to think critically. When we think critically, we are evaluating the outcomes of our thought processes--how good a decision is or how well a problem is solved. Critical thinking also involves evaluating the thinking process--the reasoning that went into the conclusion we’ve arrived at, or the kinds of factors considered in making a decision” ( Halpern and Dunn 2023, pp. 6–7 ). The reason we need a common definition of critical thinking is that, without it, instructors can and have passed almost anything off as instruction in critical thinking. However, common ground is to be found concerning CT definitions. In a European project, which we shall refer to in Section 4.3 , the critical thinking definition is based on the works of Halpern and Dunn ( 2023 ), Facione ( 1990 ), Paul and Elder ( 2008 ), and Kuhn ( 1999 ). During two debate sessions, 33 international participants from higher education and the labor market defined critical thinking as a deliberate cognitive process guided by conscious, dynamic, self-directed, self-monitored, and self-correcting thought ( Rebelo et al. 2023 ). It relies on both disciplinary and procedural knowledge, along with metacognitive aspects (including metacognitive, meta-strategic, and epistemological dimensions). Critical thinking can be cultivated and enhanced through the development of competencies, and it is facilitated by various attitudes, such as systematic thinking, open-mindedness, empathy, flexibility, and cognitive maturity. Additionally, it encompasses intellectual skills such as reflection, self-regulation, analysis, inference, explanation, synthesis, and systematic thought. Critical thinking not only stimulates problem-solving capabilities but also facilitates effective communication, fosters independent and holistic thinking, and bolsters decision-making and active citizenship ( Pnevmatikos et al. 2021 ).
2.1. Can Critical Thinking Be Learned?
We teach writing, oral communication, and mathematics with the (often implicit) belief that these skills will be learned and transferred to multiple settings both inside and outside of the classroom. There is a large and growing research literature showing that, with appropriate classroom instruction in critical thinking, including specific instruction designed for transfer, the skills will spontaneously transfer and in uncued (i.e., there are no reminders to use the critical thinking skill that was learned in class) situations ( Dumitru 2012 ; Heijltjes et al. 2014 ; Tiruneh 2019 ). Several such studies were presented by Dwyer ( 2017 ) and Halpern and Dunn ( 2023 ). For the sake of brevity, we review just one recent study. The study was designed to counteract the effects of conspiracy theories. When people believe conspiracy theories, they often act in harmful ways–such as refusing to get the COVID-19 vaccine, which resulted in the death of large numbers of people around the world, or attacking the United State Capitol Building on 6 January 2021 in the belief that there was a conspiracy afoot designed to steal the United States 2020 presidential election from Donald Trump. In a review of the research literature on the efficacy of interventions, the researchers found “there was one intervention which was characteristically different to the rest” ( O’Mahony et al. 2023, para. 23 ). It was a semester-long university course in critical thinking that was designed to teach students the difference between good scientific practices and pseudoscience. These courses require effort and commitment, but they are effective. The same conclusion applies to all interventions designed to enhance critical thinking. There are no fast and easy “once and done” strategies that work. This is why we recommend continuous and pervasive coursework to make sure that the learning of CT skills “sticks.”
2.2. The Need for Critical Thinking Skills
Online technologies-related (including AI) job loss and redesign are not the only reasons why we need to concentrate on teaching and learning the skills of critical thinking. COVID-19 left 140 million people out of work, and many of their jobs will never return ( Roslansky 2021 ). We are drowning in a tsunami of information, confronted with advertisements online, in news reports, social media, podcasts, and more. The need to be able to distinguish good information from bad is critical. In addition, employers want to hire people with critical thinking skills. In a recent report by Hart Research Associated ( 2018 ), they found that in an employer survey of 501 business executives, 78% said that critical thinking/analytic reasoning is the most important skill they want in their employees, but they also added that only 34% of college graduates arrive well prepared in critical thinking. This gap between what employers want and their perception of the preparedness of the workforce was larger for critical thinking than for any other area. In fact, every report on the future of work made this same point. Consider this quote from The World Economic Forum ( 2020 ) on the future of jobs: “Skills gaps continue to be high as in-demand skills across jobs change in the next five years. The top skills and skill groups which employers see as rising in prominence in the lead up to 2025 include groups such as critical thinking and analysis as well as problem-solving.” (p. 5). In a report from the Office of the European Union: Key Competences for Lifelong Learning, the commissioner wrote “Critical thinking, media literacy, and communication skills are some of the requirements to navigate our increasingly complex world” ( Navracsics 2019, p. 3 ). Of course, critical thinking is not just needed in the world of work. A true democracy requires an educated citizenry with citizens who can think critically about world social issues, such as the use/threat of AI, war, poverty, climate change, and so much more. Irrational voters are a threat to all of us—and to themselves.
The need to think critically is not new, but it has taken on a new urgency as social media and other forms of communication have made the deliberate spread of misinformation move at the speed of light. There is nothing new about the use of lies, half-truths, and innuendos to get people to believe something that is not true. Anyone can post anything on popular media sites, and this “fake news” is often copied and shared thousands of times. Sometimes the information is spread with a deliberate attempt to mislead; other times, it is copied and spread by people who believe it is true. These messages are often used to discredit political adversaries, create social unrest, and incite fear. It can be a difficult task to determine what to believe and what to discard. Vosoughi et al. ( 2018 ) analyzed data from 126,000 tweets that were spread by approximately 3 million people. How did the researchers discriminate true data from false data? The same way we all should. They used several different fact-checking sites and found 95% to 98% agreement regarding the truth or falsehood of information. They found that false data spread more quickly and more widely than true data because the false data tended to be novel and sensational, rendering it salient and seductive.
In today’s landscape, the imperative to foster critical thinking skills is becoming increasingly apparent as we grapple with the rapid rise of social media and artificial intelligence technologies and their profound impact on the future of work. The confluence of these transformative forces has ushered in a new era characterized by the potential for significant job disruption. As online technologies advance and automation becomes more widespread, certain traditional job roles may become obsolete, requiring the development of innovative skills and adaptability in the workforce. In this context, critical thinking emerges as a central element in preparing individuals to navigate the evolving job market. It equips individuals with the ability to analyze complex information, discern credible sources from the proliferation of social media information, and make informed decisions in an era of blurring boundaries between human and machine contributions to the workforce. Cultivating critical thinking skills will be essential to ensuring that individuals can take advantage of the opportunities presented by new technologies while mitigating the challenges of job disruption in this AI-driven future.
3. Critical Thinking Skills and Job Disruption and Replacement
Eloundou et al. in 2023 estimated that about 15% of all U.S. workers’ jobs could be accomplished much faster and at the same level of quality with currently available AI. There are large differences in the extent to which various occupations and industries will be affected by advancements in AI. For example, tasks that require a high degree of human interaction, highly specialized domain knowledge, or creating innovative technologies will be minimally affected; whereas, other occupations such as providing captions for images or answering questions about a text or document are more likely to be affected. Routine-based jobs in general are more likely to be dislodged by advanced technologies ( Acemoglu 2002 ). Using the basic definitions of skills that are standard in O*Net, Eloundou et al. ( 2023 ) found a clear negative correlation between jobs requiring knowledge of science and critical thinking skills and the likelihood that AI will “take over” the job. These findings reinforce our main point—the best way to gain job-proof skills is with critical thinking.
The effect of online technologies on wages is complicated because of the large number of factors that come together to determine earnings. Acemoglu and Autor ( 2011 ) advocated for a model that simultaneously considers the level of the tasks required for any job (low, medium, and high), where a high level of skill is defined as one that allows employees to perform a variety of tasks, the demand for the tasks, and technological changes that can complement a task or replace it. They assert that employment has become increasingly polarized with the growth in both high education, high wage occupations and low education, and low wage occupations in the United States and the European Union. To understand and predict which occupations will be most disrupted by AI (and other developing technologies), an investigator will need to simultaneously consider all of these variables. Technological advancements can generate shifts in demand, favoring either high- or low-skilled workers. According to Acemoglu and Autor ( 2011 ), we can expect some of the largest disruptive effects at the middle level of skills, where some of the tasks performed at this level can be more easily replaced by new technologies, with widespread employment growth in high- and low-skilled occupations.
4. Business-University Collaborations
The pursuit of promoting high standards of critical thinking in university students across various academic disciplines is a challenging endeavor that should be leveraged through collaboration with stakeholders. In such collaborations, stakeholders can contribute to refining the skills required by learners and bring their own perspectives to academic instruction. This close partnership between universities and stakeholders helps minimize gaps and mismatches in the transition to the labor market, facilitates research collaboration, and increases student motivation.
Collaborations between businesses and universities have gained increasing importance in today’s rapidly evolving educational and economic landscape. These partnerships are instrumental in bridging the gap between academic learning and the real-world skills demanded by the job market. One key aspect of business-university collaboration (BUC) is the alignment of curricula with the dynamic needs of industries. This entails the joint effort of higher education institutions (HEIs) and industry experts to design, develop, and deliver educational programs that equip students with practical, job-ready skills. The curriculum design phase involves tailoring study programs, courses, and modules to address skills gaps and align with the specific requirements of employers.
Moreover, BUC extends beyond the classroom. Collaborations often involve business engagement in educational activities, including guest lectures, internships, co-op programs, and research projects. These interactions provide students with invaluable exposure to real-world scenarios, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings.
In essence, BUC is a multifaceted partnership that benefits both students and businesses. It ensures that educational programs remain relevant, fostering a seamless transition from academia to the workforce. This collaborative approach not only enhances students’ employability but also contributes to the overall growth and innovation of industries.
Operationalizing the collaboration implicates a particular focus on curriculum design, development, and delivery. These involve the collaboration between higher education institutions and labor market partners to create or enhance undergraduate or postgraduate study programs, courses, or modules. This collaborative effort aims to address skills gaps, align curricula with employers’ needs, integrate training initiatives, and improve graduates’ employability. Additionally, curriculum delivery includes various forms of business involvement, such as guest lectures, placements, supervision, mentoring, and work-based learning activities.
While the existing literature often discusses the barriers and motivations for university-business collaboration ( Healy et al. 2014 ; Orazbayeva et al. 2020 ), there is a need for more empirical insights into the roles and responsibilities of each party engaged in joint curriculum design, development, and delivery, as well as lessons learned from these collaborations ( Rebelo et al. 2023 ).
4.1. Why Do We Need Higher Education’s Help?
In the preceding sections of this paper, we delved into the disruptive forces of artificial intelligence (AI) on the job market and the critical need for individuals to adapt to these changes by developing “job-proof skills”. The rise of online technologies such as ChatGPT presents both opportunities and challenges, particularly in fields where middle-level skills are required. To effectively tackle these challenges, we must turn our attention to the pivotal role of education and the cultivation of essential skills such as critical thinking.
We highlighted how AI is rapidly transforming various industries and the need for individuals to adapt to these changes. Moreover, we explored the question of whether critical thinking can be learned, showcasing research evidence that supports the teachability of this skill. Now, we shall explore practical strategies for fostering critical thinking skills through collaborations between universities and businesses. The idea here is to create an educational framework that equips students with the capabilities needed to thrive in the evolving workforce.
Building upon the success of two European projects, “Critical thinking across higher education curricula—CRITHINKEDU” and “Critical thinking for successful jobs—THINK4JOBS”, we argue that incorporating practical experience and CT development through apprenticeships is a possible action for better higher education classes. This collaborative approach between HEI and LMO designed to address the differing perspectives and terminologies used by these two entities regarding critical thinking could be an important curriculum design for the better adaptation of job market technology disruptions.
Research conducted by Eloundou et al. ( 2023 ), which shows that critical thinking skills and science skills are less likely to be taken by AI, compels us to sustain the THINK4JOBS apprenticeship curricula as a possible teaching protocol for critical thinking enhancement to face challenges posed by AI at work.
The results from these projects demonstrate significant progress in students’ critical thinking skills and dispositions. These improvements, as highlighted below in Section 4.3 , underscore the effectiveness of embedding critical thinking in the curriculum. The guidelines formulated for implementing Critical Thinking Blended Apprenticeship Curricula provide a roadmap for educators to follow when effectively integrating critical thinking into their courses.
As we ponder the possibility of a world where critical thinking is widespread, we can envision a future where individuals are equipped to confront the ideological fanaticism that threatens global stability. Critical thinking, as both a cognitive skill and a disposition, has the potential to shape a workforce capable of adapting to the ever-changing landscape of work, making informed decisions, and contributing to a more rational and democratic world. The THINK4JOBS project emphasizes the practical steps taken to prepare students for the future job market and sets the stage for further exploration of the role of critical thinking in addressing global challenges, including AI presence in the job market.
4.2. CRITHINKEDU Proctocol for Critical Thinking Education across Curricula
Given that the best education for the future of work is the acquisition of critical thinking skills, how can we facilitate this sort of education? One way to obtain a job-proof education is to create classes with the help of labor market organizations. Two projects funded by the European Union were designed to bring to life the idea that better communication and collaboration between universities and employers result in a better adaptation of the curriculum, especially a curriculum involving critical thinking skill development.
Between 2016 and 2019, the project “Critical thinking across the European higher education curriculum—CRITHINKEDU” focused on how CT is taught in various academic domains. The CRITHINKEDU project, involving universities across Europe, exemplifies how academia and industry can join forces to bridge the gap between classroom learning and real-world job demands. This initiative aimed to enhance the curriculum by explicitly emphasizing critical thinking skill development. It revealed that employers across various fields value critical thinking, and they perceive it as essential for recent graduates entering the workforce.
The participants were eleven universities from nine European countries (Belgium, Czech Republic, Greece, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Romania, Lithuania, and Ireland; Dominguez 2018). Qualitative research was conducted with 32 focus groups comprised of professionals from various European countries and fields. The findings align with previous studies: “CT is a set of interconnected skills (interpretation, inference, analysis, explanation, evaluation, self-regulation”, see Payan-Carreira et al. ( 2023, p. 16 ), and dispositions (open-mindedness, refection, attentiveness, organization, perseverance, intrinsic goal motivation ( Payan-Carreira et al. 2023 ), essential for recent graduates in response to labor market demands. However, an important consideration is that the practical application of CT varies across professional fields. The participants in this study defined the ideal critical thinker as someone with a cultivated mindset, motivated to learn and improve, and equipped with cognitive and behavioral tools to anticipate, regulate, and monitor their thinking. CT is associated with problem-solving and decision-making and is intertwined with other skills such as proactivity, adaptability, creativity, emotional intelligence, communication, and teamwork. The report from this project also introduced “a European collection of the Critical Thinking skills and dispositions needed in different professional fields for the 21st century” ( Dominguez 2018 ), which categorizes CT skills and dispositions based on professional fields and offers a basis for defining learning objectives and adapting university curricula. This study provides valuable insights from 189 European employers into CT needs in the labor market for new graduates. The interviewed professionals had an obvious preference for CT skills in STEM fields and an obvious preference for dispositions in the Humanities. Social Sciences and bio-medical sciences professionals were equally interested in CT skills and dispositions, with a slight preference for dispositions ( Dominguez 2018, p. 28 ).

4.3. Next Steps: THINK4JOBS Blended Appreticeship Curricula
After the termination of the CRITHINKEDU project, partners from Romania, Greece, Lithuania, and Portugal, with the addition of a new partner from Germany, proposed a new research application: “Critical Thinking for Successful Jobs—THINK4JOBS” ( www.think4jobs.uowm.gr ). The idea was to utilize the results from the previous project and, together with labor market organizations, create new courses that are more adapted to the reality of the future of work. The core element of the classes was explicit teaching of critical thinking, using real-life cases and methods. In an apprenticeship model, critical thinking skills are embedded in a relevant context. The value of realistic contexts is that students can see the need for the skills being taught in a workplace scenario. Relevant contexts enhance student engagement and motivation to learn. Dumitru et al. ( 2021 ) focused on improving students’ critical thinking skills and dispositions through collaboration between Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) and Labor Market Organizations (LMOs). The aim was to bridge the gap between HEI curricula and the expectations of the labor market by incorporating apprenticeships that provide practical experience and CT development.
The process of mapping responses from those in the labor market organizations onto college curricula involved the use of research methods such as observation, focus groups, and documentary analysis, with stakeholders from HEIs and LMOs participating. The findings indicated that while there were no definitive “gaps” between HEIs and LMOs, there were contextual differences in the approach to CT. HEIs focus on long-term career preparation, while LMOs emphasize short-term learning strategies. The terminology and expression of CT also differed between the two contexts. Based on the findings, ten work-based scenarios were created, with one from each discipline involved in the project. Overall, the report ( Dumitru et al. 2021 ) highlighted the different goals and perspectives of HEIs and LMOs regarding CT, emphasizing the need for collaboration and a common understanding of which skills should be included in the college curriculum.
There is a different context in the approach to CT, since HEIs usually use different learning activities, focusing more on career preparation with long-term goals, while LMOs follow compact and short-term learning and teaching strategies. Furthermore, the findings suggest that CT is a new workplace requirement and that HEIs and LMOs do not choose the same terminology when referring to the concept, with HEIs usually choosing scientific terms. Another element that emerged is that CT is generally expressed in a declarative way in higher education institutions, while in LMOs the application to specific cases follows a more procedural approach. Put another way, LMOs are focused on making a profit, while HEI is focused on being socially responsible.
In the second phase of the project, partners ( Pnevmatikos et al. 2021 ) focused on the development of a collaborative training curriculum for Higher Education Instructors and LMO tutors. The purpose of the training was to enhance comprehension and knowledge of critical thinking for both sides of this collaboration, since previous research indicated a potential lack of conceptual and procedural understanding between these two entities. Additionally, the training aimed to facilitate the promotion, support, and evaluation of students’ CT skills within apprenticeship curricula, as well as the creation of blended curricula utilizing an open-source learning platform. The training course encompassed workshops that delved into various aspects of CT, including analyzing and reassembling ideas about CT, formulating a working definition of CT, instructional methodologies, blended learning techniques, usage of a learning platform, CT assessment, and the development of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between higher education institutions and LMOs. The participants’ knowledge about these topics was assessed through pre- and post-training online questionnaires. Although data analysis showed various predicted trends, only perceived self-confidence in the topics covered during the training obtained statistical significance ( Pnevmatikos et al. 2021 ).
In the final report from this project, Payan-Carreira et al. ( 2023 ) presented the results of the implementation of the critical thinking Blended Apprenticeships Curricula (CTBAC) and discussed the improvements in critical thinking skills and dispositions observed in students. The study involved cross-disciplinary analysis and assessed changes before and after the piloting activities. A total of 609 students participated, and their critical thinking skills and dispositions were evaluated.
The consortium chose the Critical Thinking Self-Assessment Scale (CTSAS) developed by Nair ( 2011 ) as an instrument to assess CT skills based on an earlier conceptualization ( Facione 1990 ). The questionnaire has been tested in various geographic and cultural contexts, demonstrating good reliability, internal consistency, and confirmatory factor analysis results. However, the original CTSAS was considered too long to complete, consisting of 115 items, so a shorter version was specifically developed for this project. The short form of the questionnaire (CTSAS-SF) was created through a two-step process. Items with loading weights below .500 were eliminated, resulting in 84 remaining items. Redundant and non-cognitive-focused items were marked for elimination, leaving 60 items. The short form maintained the original scale’s framework and utilized a seven-point Likert scale ranging from 0 (Never) to 6 (Always) for students to respond to items assessing various dimensions and subdimensions of CT skills.
The CTSAS-SF validation process, with confirmatory factor analysis, resulted in two models with equivalent satisfactory goodness-of-fit indices. Model 4, the second-order factor model (RMSEA = .051; TLI = .924; CFI = .927), had a chi-square/df ratio of 2.33. The Cronbach alpha of the overall instrument was excellent (α = .969). Sample items are shown in Table 1 .
Sample items forming Critical Thinking Self-Assessment Scale (CTSAS), Nair ( 2011 ).
| NO. of Item | Item | Skill |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Interpretation | |
| 10 | Analysis | |
| 22 | Evaluation | |
| 31 | Inference |
Compared to instruments for assessing CT skills, the availability of instruments for measuring critical thinking (CT) dispositions is limited. However, one of the instruments adopted by the consortium to assess CT dispositions is the Student-Educator Negotiated Critical Thinking Dispositions Scale (SENCTDS), which was developed by Quinn et al. ( 2020 ). The scale was validated with a mixed population of Irish and American undergraduate students. The scale considers a variety of CT dispositions that the authors consider important for the labor market and real-world decision-making. Some of the items in the scale combine Facione ’s ( 1990 ) original CT dispositions into new dimensions that are relevant to academic and labor market success, such as organization, perseverance, and intrinsic goal motivation. The scale consists of six dimensions (Reflection, Attentiveness, Open-mindedness, Organization, Perseverance, and Intrinsic Goal Motivation) and presents statements for students to respond to using a 7-point Likert scale. The Likert scale ranges from 1 (strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly agree). The original version of the SENCTDS contains 21 items. The validation process, with confirmatory factor analysis, identified only one model presenting a satisfactory goodness-of-fit index—model 3, comprised of six correlated factors (RMSEA = .054; TLI = .974; CFI = .969) with a chi-square/df ratio of 2.57. The instrument presented a high Cronbach alpha (α = .842), suggesting a strong internal consistency of the instrument. Sample items are presented in Table 2 .
Sample items from Student-Educator Negotiated Critical Thinking Dispositions Scale (SENCTDS), developed by Quinn et al. ( 2020 ).
| No. of Item | Item | Disposition |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Reflection | |
| 6 | Attentiveness | |
| 11 | Open-mindedness | |
| 13 | Organization | |
| 21 | Intrinsic goal motivation |
The analysis showed gains in critical thinking skills and indicated that changes were more prominent in skills than dispositions. All skills (interpretation, analysis, inference, explanation, self-regulation, and evaluation) obtained significant differences between the pretest and posttest, with p ≤ .0001 to all skills, plus the integrated critical thinking skills score was t = 9.705 and p ≤ .0001, which demonstrates strong significant difference between pre- and the posttest. Dispositions displayed no significant differences regarding the integrated score, but showed significant differences in reflection (t = 1.766, p = .079), open-mindedness (t = 2.636, p = .009), organization (t = 2.568, p = .011), and intrinsic goal motivation (t = 1.712, p = .088).
Based on the findings from the implementation of the blended apprenticeship curricula, the following guidelines were formulated for implementing Critical Thinking Blended Apprenticeship Curricula ( Payan-Carreira et al. 2023 ):
- Provide an explanation of the importance of critical thinking—Clearly communicate to students why critical thinking is a vital skill in today’s workforce and how it is valued in specific professions. Explicitly incorporate the development of critical thinking as an outcome of the course.
- Emphasize continuous and pervasive CT training—To achieve success, there should be a concerted effort across disciplinary curricula to foster students’ critical thinking skills and dispositions. Skills require training, and dispositions necessitate the internalization of desired attitudes. Therefore, sufficient time and a collaborative approach at the disciplinary level are necessary for consistent and significant progress.
- Allocate dedicated time—Building on the previous point, it is essential to allocate specific time within the course to work on the proposed critical thinking goals. Students and educators need to schedule activities and create opportunities for preparation, development, and feedback exchange. This ensures that the intervention leads to meaningful, lasting learning.
- Establish connections with real-world scenarios—Foster student engagement and improve their perception of learning experiences by incorporating case studies that reflect situations professionals encounter in their daily work. By grounding the learning content in reality, students are more likely to be motivated and actively participate in the educational process.
Foster reflection on CT skills and dispositions—Offer students the chance to reflect on their reasoning processes and the attitudes they have developed throughout their learning experiences. Encouraging reflective thinking enhances the effectiveness of learning interventions and helps cultivate a deeper understanding of one’s experiences.
These steps aim to guide educators in effectively implementing the critical thinking blended apprenticeship curricula while also maximizing the impact of critical thinking development in students.
The two European projects made a great start in integrating the skills that employers want employees to learn from university curricula, but the results are nonetheless provisional. There is not a clear agreement among participating universities regarding how best to teach critical thinking, nor any regarding its importance for future jobs. We urge that more work should be done to nurture critical thinking within university curricula in order to provide our current students—who represent the future of the workforce—the much-wanted job-proof skills they need.
5. European Recommendations and Good Practices
Critical thinking stands as a pivotal goal for European Higher Education Institutions. To facilitate the attainment of this objective, we present an educational protocol that draws from comprehensive research and practical experiences, including insights from the CRITHINKEDU project. This protocol amalgamates insights from both theoretical and empirical studies on critical thinking with practical strategies for its cultivation.
Recommendations go toward signing memorandums of understanding between universities and labor market organizations to cultivate strong partnerships ( Rebelo et al. 2023 ). Effective collaboration between universities and businesses is crucial in fostering critical thinking. This partnership thrives on the synergy that results when academic institutions and businesses combine their expertise, resources, and perspectives. Strategies such as aligning goals, fostering long-term commitment, and promoting a culture of collaboration can strengthen these partnerships and ensure that academic research is harmoniously aligned with real-world needs.
Another recommendation relates to the formulation of compelling goals . Accurate and transparent goals are fundamental to the successful implementation of university-industry collaborations to promote critical thinking. These goals must be clearly defined and easily understood at multiple levels, from the institutional to the program and course levels. Recognition of critical thinking as an overarching goal implies its integration into assessment and evaluation processes.
Another recommendation is to develop flexible curricula . To effectively foster critical thinking, curricula must demonstrate adaptability and responsiveness to emerging trends and market demands. The use of agile curriculum design methodologies and the involvement of business partners in curriculum development is of great value. Approaches such as problem-based and case-based learning facilitate rapid adaptation to evolving market needs, such as the use of AI-powered software to solve work tasks better and faster. Regular feedback mechanisms and ongoing collaboration with business partners ensure that curricula remain relevant and flexible.
Incorporating real-world challenges and case studies into curricula bridges the gap between academia and the business world, creating an environment that encourages experiential learning. The active involvement of business stakeholders in providing relevant challenges plays a key role. Students’ problem-solving skills are enhanced by shifting from traditional teaching methods to project-based, problem-based, or case-based learning. Engaging students through apprenticeships, internships, guest lectures, and seminars immerses them in authentic work environments and fosters their professional development.
Ongoing, multi-faceted evaluation is a cornerstone of the collaboration between higher education and the business community to cultivate critical thinking. Assessment includes measuring learners’ progress in critical thinking, the effectiveness of curricula, and the impact of partnerships through the use of key performance indicators.
Regarding how to implement a critical thinking curriculum, pedagogical research ( Elen et al. 2019 ) suggests that in the development of critical thinking, whether it is regarded as a skill, disposition, or a combination of both, three categories of supportive measures can be identified: modeling, induction, and declaration.
Modeling: Support the development of critical thinking skills by demonstrating what it means to think critically at the institutional, programmatic, and course levels, considering multiple perspectives and alternative viewpoints.
Induction: Support critical thinking development by provoking critical thinking through the presentation of open-ended questions, unstructured tasks, complex problems, and real-world issues. The exact nature of “induction” and how it is implemented may vary across fields and disciplines. Induction can be carried out in a variety of ways; for example, presenting unstructured problems, providing authentic tasks, encouraging constructive controversy, asking “why” questions, or encouraging student autonomy.
Explanation: Promote the development of critical thinking by articulating or explicitly stating what is at stake, what strategies can be used, and what criteria must be met. This explanation can take the form of oral or written communication and should always be explicit and specific. Declaring and making things explicit can be accomplished in a variety of ways, including using critical thinking rubrics, developing elaborate concept maps, providing feedback on critical thinking, and engaging in discussion and reflection on critical issues.
This integrated approach, encompassing university-business collaboration and an educational protocol, underscores the significance of critical thinking in higher education. It provides a structured framework for nurturing this essential skill by aligning objectives, fostering partnerships, adapting curricula, and implementing ongoing evaluation practices. In doing so, educational institutions are better poised to equip students with the critical thinking skills needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving world.
6. Concluding Remarks or Can Critical THINKING Save the World?
In summary, the dynamic interaction between universities, businesses, and the evolving technology landscape, including the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and online technologies, underscore the critical need to nurture and develop students’ critical thinking skills. As we navigate the challenges posed by AI and the ever-expanding digital realm, collaborative efforts between academia and industry have proven to be instrumental in preparing students for the future job market.
Incorporating real-world experiences, such as apprenticeships, into the curriculum is an important step toward improving students’ critical thinking skills in real-world contexts. Projects such as “Critical thinking across higher education curricula—CRITHINKEDU” and “Critical thinking for successful jobs—THINK4JOBS” have demonstrated the potential of these collaborations to bridge the gap between classroom learning and industry needs. In addition, the development of flexible curricula that can adapt to the evolving needs of the job market, especially considering online technologies, is essential. By integrating real-world challenges and case studies into the curriculum, students gain valuable problem-solving skills and are better prepared to navigate the complexities of the digital age.
Ongoing assessment and evaluation are critical components of this collaborative effort, ensuring that critical thinking remains a central focus and that students are making meaningful progress in acquiring this essential skill.
With the disruption of AI and the ubiquity of online technologies, the integration of critical thinking into higher education curricula is more important than ever. It enables students not only to thrive in a technology-driven world, but also to contribute to a rational, democratic, and globally interconnected society. The partnerships forged between universities and businesses, along with a well-defined educational protocol, provide a roadmap for cultivating these essential skills and preparing students for the challenges and opportunities of the future job market. The imperative to foster critical thinking in university curricula remains a fundamental step in equipping tomorrow’s workforce to navigate the complexities of an AI-influenced job market and a rapidly changing world.
Lilienfeld ( 2007, para. 3 ) said it well: “The greatest threat to the world is ideological fanaticism, by ideological fanaticism I mean the unshakeable conviction that one’s belief system and that of other in-group members is always right and righteous and that others’ belief systems are always wrong and wrong-headed”. Imagine a world where (most or even many) people use the skills of critical thinking. Just maybe, CT could save the world.
The job market will require a psychologically adaptable toolkit, and we propose that critical thinking is an essential component therein. The disruptions imposed by new technological advances such as AI will require students to learn new employable skills because we will need not just an engineer, but a critical thinking engineer; not just a programmer, but a critical thinking programmer; and not just a journalist, but a critical thinking journalist. The dignity of workers—their humanity and our collective survival—may well depend on CT, a very human creation.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Dana Dunn, Moravian University, for comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Funding Statement
Daniela Dumitru received funding from European Commission/EACEA, through the ERASMUS+ Programme, “Critical Thinking for Successful Jobs—Think4Jobs” Project, with the reference number 2020-1-EL01-KA203-078797.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.F.H. and D.D.; investigation, D.F.H. and D.D.; resources, D.F.H. and D.D.; writing—original draft preparation, D.F.H. and D.D.; writing—review and editing, D.F.H. and D.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
- Acemoglu Daron. Technical Change, Inequality, and the Labor Market. [(accessed on 15 May 2023)]; Journal of Economic Literature. 2002 40 :7–72. doi: 10.1257/jel.40.1.7. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2698593 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Acemoglu Daron, Autor David. Skills, Tasks and Technologies: Implications for Employment and Earnings. In: Ashenfelter Orley, Card David., editors. Handbook of Labor Economics. 1st ed. North Holland-Elsevier; San Diego: 2011. pp. 1043–71. [ Google Scholar ]
- adminGPT The Future Is Here: Analytics and Artificial Intelligence in Every Industry. May 22, 2023. [(accessed on 2 June 2023)]. @utopost. Available online: https://chatgpt.com/27739697/the-future-is-here-analytics-and-artificial-intelligence-in-every-industry#/
- Bushwick Sophie, Harper Kelso, Bose Tulika. What You Need to Know about GPT-4. Scientific American Podcasts. 2023. [(accessed on 31 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.scientificamerican.com/podcast/episode/what-you-need-to-know-about-gpt-4/
- Data Professor How to Use ChatGPT to Generate Code in 90 Seconds. 2023. [(accessed on 31 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ELJzUcYrAIQ
- Dominguez Caroline. (coord.) A European Collection of the Critical Thinking SKILLS and Dispositions Needed in Different Professional Fields for the 21st Century. UTAD; Vila Real: 2018. [(accessed on 2 June 2023)]. Available online: https://crithinkedu.utad.pt/en/intellectual-outputs/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Dumitru Daniela. Critical Thinking and Integrated Programs. [(accessed on 15 May 2023)]; The Problem of Transferability. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2012 33 :143–7. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.01.100. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877042812001085 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dumitru Daniela, Christodoulou Panagiota, Lithoxoidou Angeliki, Georgiadou Triantafyllia, Pnevmatikos Dimtrios, MarinDrămnescu Aurel, Enachescu Vladimir, Stăiculescu Camelia, Lăcătuş Maria Liana, Paduraru Monica Elisabeta, et al. Think4Jobs Toolkit: Ten Work-Based Learning Scenarios. University of Western Macedonia; Greece: 2021. [(accessed on 22 May 2023)]. Available online: https://think4jobs.uowm.gr/results/intellectualoutput1 [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwyer Cristopher P. Critical Thinking: Conceptual Perspectives and Practical Guidelines. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Elen Jan, Jiang Lai, Huyghe Steven, Evers Marleen, Verburgh Ann, Dumitru Daniela, Palaigeorgiou George. In: Promoting Critical Thinking in European Higher Education Institutions: Towards an Educational Protocol. Dominguez C., Payan-Carreira R., editors. UTAD; Vila Real: 2019. [(accessed on 30 August 2023)]. Available online: https://repositorio.utad.pt/bitstream/10348/9227/1/CRITHINKEDU%20O4%20%28ebook%29_FINAL.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Elkeiy Gabriel. Future-Proof Skills can Help Balance Individual and Societal Progress. United Nations, UN Chronicle. Aug 5, 2022. [(accessed on 25 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/un-chronicle/future-proof-skills-can-help-balance-individual-and-societal-progress#:~:text=Conceptual%20and%20strategic%20thinking%2C%20creativity,agility%20as%20qualified%20human%20beings
- Eloundou Tyna, Manning Sam, Mishkin Pamela, Rock Daniel. GPTs are GPTs: An Early Look at the Labor Market Impact Potential of Large Language Models. 2023. [(accessed on 1 June 2023)]. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.10130.pdf
- Facione Peter A. Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction. Research Findings and Recommendations. [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]; 1990 Available online: http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED315423.pdf
- Fisher Alec. Critical Thinking: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Halpern Diane F., Dunn Dana S. Thought and Knowledge: An Introduction to Critical Thinking. 6th ed. Routledge Taylor & Francis; New York: 2023. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hart Research Associated Fulfilling the America Dream: Liberal Education and the Future of Work. 2018. [(accessed on 20 June 2023)]. Conducted on Behalf of Association of American Colleges and Universities. Available online: https://dgmg81phhvh63.cloudfront.net/content/user-photos/Research/PDFs/2018EmployerResearchReport.pdf
- Healy Adrian, Perkmann Markus, Goddard John, Kempton Louise. Directorate General for Education and Culture, European Commission. European Union; Brussels: 2014. Measuring the Impact of University Business Cooperation. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heijltjes Anita, Gog Tamara, Paas Fred. Improving Students’ Critical Thinking: Empirical Support for Explicit Instructions Combined with Practice. Applied Cognitive Psychology. 2014; 28 :518–30. doi: 10.1002/acp.3025. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhn Deanna. A Developmental Model of Critical Thinking. Educational Researcher. 1999; 28 :16–46. doi: 10.3102/0013189X028002016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lilienfeld Scott. Can Psychology Change the World? The British Psychological Society, Research Digest. 2007. [(accessed on 31 May 2023)]. Available online: http://bps-research-digest.blogspot.com/2007/09/can-psychology-save-world.html
- Lipman Matthew. Thinking in Education. Cambridge University Press; New York: 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nair Girija. Preliminary Psychometric Characteristics of the Critical Thinking Self-Assessment Scale. University of Saskatchewan; Saskatoon: 2011. [(accessed on 18 May 2023)]. Available online: https://harvest.usask.ca/bitstream/handle/10388/ETD-2011-09-103/girija.nair.phd.thesis.pdf;jsessionid=F19CA2ACBE3978E8DF9E19C77CB3198E?sequence=3 [ Google Scholar ]
- Navracsics Tibor. Key Competences for Lifelong Learning. 2019. [(accessed on 22 May 2023)]. Foreword. European Commission, Directorate-General for Education, Youth, Sport and Culture. Publications Office. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2766/569540 [ Google Scholar ]
- Nisbett Richard. Mindware Tools for Smart Thinking. Doubleday Canada; Toronto: 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- O’Mahony Cian, Brassil Maryanne, Murphy Gillian, Linehan Conor. The efficacy of interventions in reducing belief in conspiracy theories: A systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2023; 18 :e0280902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280902. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Orazbayeva Balzhan, Daveyb Todd, Plewa Carolin, Galán-Muros Victoria. Engagement of academics in education-driven university-business cooperation: A motivation-based perspective. Studies in Higher Education. 2020; 45 :1723–36. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2019.1582013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul Richard, Elder Linda. The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools. Foundation for Critical Thinking Press; Santa Barbara: 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Payan-Carreira Rita, Rebelo Hugo, Sebastião Luis, Sacau Ana, Ferreira David, Simões Margarida, Pnevmatikos Dimitrios, Christodoulou Panagiota, Lithoxoidou Angeliki, Georgiadou Triantafyllia, et al. THINK4JOBS Guidelines: A Protocol for Critical Thinking Transfer from Curricula to Labour Market. University of Western Macedonia; Greece: 2023. [(accessed on 2 June 2023)]. Available online: https://think4jobs.uowm.gr/results/intellectualoutput4 [ Google Scholar ]
- Pnevmatikos Dimitios, Christodoulou Panagiota, Georgiadou Triantafyllia, Lithoxoidou Angeliki, Dimitriadou Catherine, Carreira Rita Payan, Simões Margarida, Ferreira David, Rebelo Hugo, Sebastião Luis. THINK4JOBS TRAINING: Critical Thinking Training Packages for Higher Education Instructors and Labour Market Tutors. University of Western Macedonia; Greece: 2021. [(accessed on 10 June 2023)]. Available online: https://think4jobs.uowm.gr/results/intellectualoutput2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Quinn Sarah, Hogan Michael, Dwyer Cristopher, Finn Patrick, Fogarty Emer. Development and Validation of the Student-Educator Negotiated Critical Thinking Dispositions Scale (SENCTDS) Thinking Skills and Creativity. 2020; 38 :100710. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100710. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rebelo Hugo, Christodoulou Panagiota, Payan-Carreira Rita, Dumitru Daniela, Mäkiö Elena, Mäkiö Juho, Pnevmatikos Dimitrios. University-Business Collaboration for the Design, Development and Delivery of Critical Thinking Blended Apprenticeships Curricula: Lessons Learned from a Three-Year Project. Education Sciences. 2023; 2023 :2023081992. doi: 10.20944/preprints202308.1992.v1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roslansky Ryan. You Need a Skills-Based Approach to Hiring and Developing Talent. Harvard Business Review. 2021. [(accessed on 1 June 2023)]. Available online: https://hbr.org/2021/06/you-need-a-skills-based-approach-to-hiring-and-developing-talent
- Tiruneh Dawit. Transfer of Critical Thinking Skills Across Domains: Implicit or Explicit Instructional Approaches?; Paper presented at 2019 AERA Annual Meeting; Toronto, ON, Canada. June 4; 2019. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vosoughi Soroush, Roy Deb, Aral Sinan. The spread of true and false news online. Science. 2018; 359 :1146–51. doi: 10.1126/science.aap9559. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weiser Benjamin, Schweber Nate. The ChatGPT Lawyer Explains Himself. The New York Times. 2023. [(accessed on 11 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/06/08/nyregion/lawyer-chatgpt-sanctions.html
- World Economic Forum The Future of Jobs Report 2020. 2020. [(accessed on 31 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2020.pdf

- Appointments

- Resume Reviews

- Undergraduates
- PhDs & Postdocs
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- Online Students
- Career Champions
- I’m Exploring
- Architecture & Design
- Education & Academia
- Engineering
- Fashion, Retail & Consumer Products
- Fellowships & Gap Year
- Fine Arts, Performing Arts, & Music
- Government, Law & Public Policy
- Healthcare & Public Health
- International Relations & NGOs
- Life & Physical Sciences
- Marketing, Advertising & Public Relations
- Media, Journalism & Entertainment
- Non-Profits
- Pre-Health, Pre-Law and Pre-Grad
- Real Estate, Accounting, & Insurance
- Social Work & Human Services
- Sports & Hospitality
- Startups, Entrepreneurship & Freelancing
- Sustainability, Energy & Conservation
- Technology, Data & Analytics
- DACA and Undocumented Students
- First Generation and Low Income Students
- International Students
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Transfer Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Explore Careers & Industries
- Make Connections & Network
- Search for a Job or Internship
- Write a Resume/CV
- Write a Cover Letter
- Engage with Employers
- Research Salaries & Negotiate Offers
- Find Funding
- Develop Professional and Leadership Skills
- Apply to Graduate School
- Apply to Health Professions School
- Apply to Law School
- Self-Assessment
- Experiences
- Post-Graduate
- Jobs & Internships
- Career Fairs
- For Employers
- Meet the Team
- Peer Career Advisors
- Career Services Policies
- Walk-Ins & Pop-Ins
- Strategic Plan 2022-2025
Critical Thinking: A Simple Guide and Why It’s Important
- Share This: Share Critical Thinking: A Simple Guide and Why It’s Important on Facebook Share Critical Thinking: A Simple Guide and Why It’s Important on LinkedIn Share Critical Thinking: A Simple Guide and Why It’s Important on X
Critical Thinking: A Simple Guide and Why It’s Important was originally published on Ivy Exec .
Strong critical thinking skills are crucial for career success, regardless of educational background. It embodies the ability to engage in astute and effective decision-making, lending invaluable dimensions to professional growth.
At its essence, critical thinking is the ability to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information in a logical and reasoned manner. It’s not merely about accumulating knowledge but harnessing it effectively to make informed decisions and solve complex problems. In the dynamic landscape of modern careers, honing this skill is paramount.
The Impact of Critical Thinking on Your Career
☑ problem-solving mastery.
Visualize critical thinking as the Sherlock Holmes of your career journey. It facilitates swift problem resolution akin to a detective unraveling a mystery. By methodically analyzing situations and deconstructing complexities, critical thinkers emerge as adept problem solvers, rendering them invaluable assets in the workplace.
☑ Refined Decision-Making
Navigating dilemmas in your career path resembles traversing uncertain terrain. Critical thinking acts as a dependable GPS, steering you toward informed decisions. It involves weighing options, evaluating potential outcomes, and confidently choosing the most favorable path forward.
☑ Enhanced Teamwork Dynamics
Within collaborative settings, critical thinkers stand out as proactive contributors. They engage in scrutinizing ideas, proposing enhancements, and fostering meaningful contributions. Consequently, the team evolves into a dynamic hub of ideas, with the critical thinker recognized as the architect behind its success.
☑ Communication Prowess
Effective communication is the cornerstone of professional interactions. Critical thinking enriches communication skills, enabling the clear and logical articulation of ideas. Whether in emails, presentations, or casual conversations, individuals adept in critical thinking exude clarity, earning appreciation for their ability to convey thoughts seamlessly.
☑ Adaptability and Resilience
Perceptive individuals adept in critical thinking display resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges. Instead of succumbing to panic, they assess situations, recalibrate their approaches, and persist in moving forward despite adversity.
☑ Fostering Innovation
Innovation is the lifeblood of progressive organizations, and critical thinking serves as its catalyst. Proficient critical thinkers possess the ability to identify overlooked opportunities, propose inventive solutions, and streamline processes, thereby positioning their organizations at the forefront of innovation.
☑ Confidence Amplification
Critical thinkers exude confidence derived from honing their analytical skills. This self-assurance radiates during job interviews, presentations, and daily interactions, catching the attention of superiors and propelling career advancement.
So, how can one cultivate and harness this invaluable skill?
✅ developing curiosity and inquisitiveness:.
Embrace a curious mindset by questioning the status quo and exploring topics beyond your immediate scope. Cultivate an inquisitive approach to everyday situations. Encourage a habit of asking “why” and “how” to deepen understanding. Curiosity fuels the desire to seek information and alternative perspectives.
✅ Practice Reflection and Self-Awareness:
Engage in reflective thinking by assessing your thoughts, actions, and decisions. Regularly introspect to understand your biases, assumptions, and cognitive processes. Cultivate self-awareness to recognize personal prejudices or cognitive biases that might influence your thinking. This allows for a more objective analysis of situations.
✅ Strengthening Analytical Skills:
Practice breaking down complex problems into manageable components. Analyze each part systematically to understand the whole picture. Develop skills in data analysis, statistics, and logical reasoning. This includes understanding correlation versus causation, interpreting graphs, and evaluating statistical significance.
✅ Engaging in Active Listening and Observation:
Actively listen to diverse viewpoints without immediately forming judgments. Allow others to express their ideas fully before responding. Observe situations attentively, noticing details that others might overlook. This habit enhances your ability to analyze problems more comprehensively.
✅ Encouraging Intellectual Humility and Open-Mindedness:
Foster intellectual humility by acknowledging that you don’t know everything. Be open to learning from others, regardless of their position or expertise. Cultivate open-mindedness by actively seeking out perspectives different from your own. Engage in discussions with people holding diverse opinions to broaden your understanding.
✅ Practicing Problem-Solving and Decision-Making:
Engage in regular problem-solving exercises that challenge you to think creatively and analytically. This can include puzzles, riddles, or real-world scenarios. When making decisions, consciously evaluate available information, consider various alternatives, and anticipate potential outcomes before reaching a conclusion.
✅ Continuous Learning and Exposure to Varied Content:
Read extensively across diverse subjects and formats, exposing yourself to different viewpoints, cultures, and ways of thinking. Engage in courses, workshops, or seminars that stimulate critical thinking skills. Seek out opportunities for learning that challenge your existing beliefs.
✅ Engage in Constructive Disagreement and Debate:
Encourage healthy debates and discussions where differing opinions are respectfully debated.
This practice fosters the ability to defend your viewpoints logically while also being open to changing your perspective based on valid arguments. Embrace disagreement as an opportunity to learn rather than a conflict to win. Engaging in constructive debate sharpens your ability to evaluate and counter-arguments effectively.
✅ Utilize Problem-Based Learning and Real-World Applications:
Engage in problem-based learning activities that simulate real-world challenges. Work on projects or scenarios that require critical thinking skills to develop practical problem-solving approaches. Apply critical thinking in real-life situations whenever possible.
This could involve analyzing news articles, evaluating product reviews, or dissecting marketing strategies to understand their underlying rationale.
In conclusion, critical thinking is the linchpin of a successful career journey. It empowers individuals to navigate complexities, make informed decisions, and innovate in their respective domains. Embracing and honing this skill isn’t just an advantage; it’s a necessity in a world where adaptability and sound judgment reign supreme.
So, as you traverse your career path, remember that the ability to think critically is not just an asset but the differentiator that propels you toward excellence.
More From Forbes
The power of critical thinking: enhancing decision-making and problem-solving.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Dr. Ron Young, Founder and Board Chair of Trove, Inc . Ron specializes in psychological coaching & transition consulting.
Critical thinking is a fundamental cognitive process that enables individuals to objectively analyze, evaluate and interpret information to make informed decisions and solve complex problems. It involves employing reasoning and logic, questioning assumptions, recognizing biases and considering multiple perspectives. It requires self-monitored, self-directed, self-disciplined and self-corrective thinking. Critical thinking is essential in a world of information and diverse opinions. It helps us see things more clearly and avoid being misled or deceived.
Importance Of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is crucial in various aspects of life, including education, professional endeavors and personal decision-making. In academic settings, it allows students to comprehend and engage with complex subjects while discerning valid arguments from fallacious ones. In the workplace, critical thinking empowers individuals to analyze problems, devise creative solutions and make informed judgments. In everyday life, it helps individuals navigate an increasingly complex world by making sound choices and avoiding cognitive biases. It is our primary defense against misleading or "spun" information.
Benefits Of Critical Thinking
There are many benefits of critical thinking.
Enhanced Decision-Making
Critical thinking helps us trust our gut feelings and think independently. It enables individuals to make logical and well-reasoned decisions based on evidence and objective analysis. It encourages the consideration of all relevant factors and the evaluation of potential consequences, leading to more informed choices.
Effective Problem-Solving
Critical thinking facilitates the identification of underlying issues, the generation of innovative solutions and the evaluation of their viability. It encourages individuals to approach problems from different angles and consider various perspectives, increasing the likelihood of finding effective resolutions.
Reduction Of Cognitive Biases
Critical thinking supports self-reflection. It helps individuals recognize and challenge cognitive biases that hinder clear judgment. Individuals can better overcome confirmation bias, groupthink and the availability heuristic (judging the likelihood of an event based on recall of similar events) by understanding and questioning their assumptions and beliefs. It requires a commitment to overcoming the tendency to see the world from a narrow, self-centered perspective.
Enhanced Communication Skills
Practicing critical thinking fosters effective communication by enabling individuals to articulate and defend their ideas with logical reasoning and evidence. It encourages active listening, empathy and the ability to evaluate and respond to counterarguments, leading to more constructive and meaningful discussions.
More United Citizens
Using critical thinking enables citizens to see the whole picture by better protecting against biases and propaganda. It reduces partisanship and a “we/they” mentality.
Cultivating Critical Thinking
How can you cultivate critical thinking?
Be curious and inquisitive.
Foster a mindset of curiosity and an eagerness to explore and understand the world. Talk with people from different backgrounds, cultures, political affiliations or religions. Ask probing questions, seek new perspectives and engage in active learning. Learn from people who hold different viewpoints.
Develop analytical skills.
You can do this by learning to break down complex problems into manageable parts, recognize patterns and identify cause-and-effect relationships. Remember, not all opinions are equal, and some are flat-out wrong.
Evaluate information.
Develop skills to evaluate the credibility and reliability of information sources. Be aware of bias, assess evidence and differentiate between fact and opinion. Guard against "swallowing information whole" or believing that "If it's on the internet, it must be true."
Practice reflection.
Engage in reflective thinking by evaluating your thoughts, beliefs and assumptions. Consider alternative viewpoints, and be open to changing your perspective based on new information.
Embrace intellectual humility.
Be humble and aware that you could be wrong. Knowledge is an ongoing process; be open to admitting mistakes or gaps in understanding. Embrace a growth mindset that values continuous learning and improvement.
Develop your sense of belonging.
The third tier in Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a sense of belonging. One aspect of belonging is connection. All humans have this need. Without critical thinking, we are vulnerable to making our group's beliefs our own rather than evaluating which beliefs align with our values.
Align your view and your values.
Rather than defining yourself by a particular view, ask whether a different view aligns with your values. When we identify ourselves by the beliefs of our reference group (religious, political, etc.), we look for ways to justify our ideas. In doing so, we deny ourselves access to critical thinking.
Evidence Of Critical Thinking
When you practice critical thinking, it will be evident in several areas:
Evidence-Based Decision-Making
Rely on facts rather than emotions or personal biases. Follow five distinct steps, called the five A’s : ask, access, appraise, apply and audit. Gather relevant information, evaluate the evidence objectively and consider different perspectives before making decisions. Then reevaluate them as you learn new information.
Problem-Solving
Approach problems systematically by defining the issue, gathering relevant data, brainstorming potential solutions and evaluating feasibility. Engage in collaborative problem-solving to benefit from diverse perspectives. Open-mindedly consider alternative systems of thought. Recognize assumptions, implications and practical consequences, then adjust as needed.
Effective Communication
Solve complex problems by clearly and effectively communicating with others. Utilize critical thinking skills to articulate your thoughts clearly, listen actively and engage in respectful and constructive dialogue. Challenge ideas through logical arguments and evidence rather than resorting to personal attacks. Respecting people with different views does not mean you agree with their opinions. Evaluate, formulate and communicate questions with clarity and precision.
Continuous Learning
Apply critical thinking to ongoing personal and professional development. Seek opportunities for further education, engage in intellectual discourse and actively challenge your beliefs and assumptions.
Using Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a powerful cognitive tool that empowers individuals to navigate the complexities of the modern world. Critical thinking enhances decision-making, problem-solving and communication abilities by fostering logical reasoning, analytical skills and an open mindset. It enables individuals to overcome cognitive biases, evaluate information effectively and make informed choices. Cultivating and applying critical thinking skills benefits individuals and contributes to a more thoughtful and rational society. Embracing critical thinking is essential for fostering intellectual growth, facilitating progress and addressing the challenges of the 21st century.
Forbes Coaches Council is an invitation-only community for leading business and career coaches. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
mySmowltech

Critical thinking: definition and how to improve its skills

Recruitment
Discover our proctoring plans
Receive an ebook on proctoring solutions. SMOWL is the most complete and customizable proctoring software.
Recent posts

Training vs teaching: differences and similarities

HR technology trends: the future landscapes

Ghosting after interviews: tips and ideas to avoid it
Critical thinking is based on the observation and analysis of facts and evidences to return rational, skeptical and unbiased judgments.
This type of thinking involves a series of skills that can be created but also improved, as we will see throughout this article in which we will begin by defining the concept and end with tips to build and improve the skills related to critical thinking.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is a discipline based on the ability of people to observe, elucidate and analyze information, facts and evidences in order to judge or decide if it is right or wrong.
It goes beyond mere curiosity, simple knowledge or analysis of any kind of fact or information.
People who develop this type of outlook are able to logically connect ideas and defend them with weighty opinions that ultimately help them make better decisions.

How to build and improve critical thinking skills?
Building and improving critical thinking skills involves focusing on a number of abilities and capacities .
To begin the critical thinking process all ideas must be open and all options must be understood as much as possible.
Even the dumbest or craziest idea can end up being the gateway to the most intelligent and successful conclusion.
The problem with having an open mind is that it is the most difficult path and often involves a greater challenge and effort. It is well known that the easy thing to do is to go with the obvious and the commonly accepted but this has no place in critical thinking.
By contrast, it is helpful not to make hasty decisions and to weigh the problem in its entirety after a first moment of awareness.
Finally, practicing active listening will help you to receive feedback from others and to understand other points of view that may help you as a reference.
Impartiality
An important point in the critical thinking process is the development of the ability to identify biases and maintain an impartial view in evaluations.
To improve this aspect it is advisable to have tools to be able to identify and recognize the prejudices and biases you have and try to leave them completely aside when thinking about the solution.
Subscribe today to SMOWL’s weekly newsletter!
Discover the latest trends in eLearning, technology, and innovation, alongside experts in assessment and talent management. Stay informed about industry updates and get the information you need.
Simply fill out the form and stay up-to-date with everything relevant in our field.
Observation
Observation allows you to see each and every detail , no matter how small, subtle or inconsequential they may be or seem to be.
Behind the superficial information hides a universe of data, sources and experiences that help you make the best decision.
One of the pillars of critical thinking is objectivity. This forces you to base your value judgments on established facts that you will have gathered after a correct research process.
At this point in the process you should also be clear about the influencing factors to be taken into account and those that can be left out.
Remember that your research is not only about gathering a good amount of information that puts the maximum number of options, variables or situations on the table.
For the information to be of quality, it must be based on reliable and trustworthy sources.
If the information you have to collect is based on the comments and opinions of third parties, try to exercise quality control but without interference.
To do this, ask open-ended questions that bring all the nuances to the table and at the same time serve to sift out possible biases.

With the research process completed, it is time to analyze the sources and information gathered.
At this point, your analytical skills will help you to discard what does not conform to unconventional thinking, to prioritize among the information that is of value, to identify possible trends and to draw your own conclusions.
One of the skills that characterize a person with critical thinking is their ability to recognize patterns and connections between all the pieces of information they handle in their research.
This allows them to draw conclusions of great relevance on which to base their predictions with weighty foundations.
Analytical thinking is sometimes confused with critical thinking. The former only uses facts and data, while the latter incorporates other nuances such as emotions, experiences or opinions.
One of the problems with critical thinking is that it can be developed to infinity and beyond. You can always keep looking for new avenues of investigation and new lines of argument by stretching inference to limits that may not be necessary.
At this point it is important to clarify that inference is the process of drawing conclusions from initial premises or hypotheses.
Knowing when to stop the research and thinking process and move on to the next stage in which you put into practice the actions considered appropriate is necessary.
Communication
The information you collect in your research is not top secret material. On the contrary, your knowledge sharing with other people who are involved in the next steps of the process is so important.
Think that your analytical ability to extract the information and your conclusions can serve to guide others .

Problem solving
It is important to note at this point that critical thinking can be aimed at solving a problem but can also be used to simply answer questions or even to identify areas for improvement in certain situations.
At Smowltech, our proctoring plans help with the creation of objective, respectful and innovative exchange and evaluation spaces.Request us a free demo in which we display all the remote supervision solutions we can offer you, as personalized and detailed reports on remote activities’ progress.
Download now!
8 interesting
about proctoring
Discover everything you need about online proctoring in this book to know how to choose the best software.
Fill out the form and download the guide now.
And subscribe to the weekly SMOWL newsletter to get exclusive offers and promotions .
You will discover all the trends in eLearning, technology, innovation, and proctoring at the hands of evaluation and talent management experts .
Discover how SMOWL works
- Register in mySmowltech indicating your LMS.
- Check your email and follow the steps to integrate the tool.
- Enjoy your free trial of 25 licenses.
Request a free demo with one of our experts
In addition to showing you how SMOWL works, we will guide and advise you at all times so that you can choose the plan that best suits your company or institution.
- Copyright © 2024 all rights reserved SMOWLTECH
Write below what you are looking for
Practicing Critical Thinking: Issues and Challenges
- First Online: 04 September 2024
Cite this chapter

- K. Venkat Reddy 3 &
- G. Suvarna Lakshmi 4
Despite acknowledging the importance of teaching or promoting critical thinking as part of education, practicing critical thinking in the real world and life has its own challenges to be resolved. Some of them are presented in the studies included in this chapter. The first article is on the gap between the perceptions on cognitive active learning of teachers and learners. The focus of the study is on exploring learners’ perceptions on deep learning particularly in Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). Instructors facing organizational difficulties, lack of experience in synchronous learning for the students, unable to have peer interaction while learning in VLE, inadequate training for the instructors and students to teach and learning virtually, students’ not experiencing the benefits of deep learning are among the major gaps or problems identified in this study. The second article is about techniques that enhance higher order thinking skills in EFL learners by using post-reading strategies resulting in better speech production and reasoning power. The output of the research states that concept mapping and argumentation enhance EFL learners’ reasoning power when private speech is used to understand the process of thinking. The third article in this chapter is on cross-cultural psychology where the cultural influence on making inferences and participating in debates by Asian students who are studying in western institutions. Though there are intercultural differences in the inferences made because of cultural backgrounds and first language variations, they are insignificant. Then the reasons for obvious differences could be learning environment, literacy and higher education. The statement that Asian students are unable to perform well in western logic might be true not because the Asian students are less capable of thinking critically but because they are not trained in or used to western logical problems. The last article of this chapter is on assessment of critical thinking in first year dental curriculum that establishes the importance of critical thinking in dental education. The assessment is on the importance of critical thinking and the need to change the curriculum incorporating critical thinking.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Smith, T. W., & Colby, S. A. (2007). Teaching for deep learning. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 80 (5), 205–210.
Article Google Scholar
Platow, M. J., Mavor, K. I., & Grace, D. M. (2013). On the role of discipline-related self-concept in deep and surface approaches to learning among university students. Instructional Science, 41 (2), 271–285.
Reinhardt, M. M. (2010). The use of deep learning strategies in online business courses to impact student retention. American Journal of Business Education, 3 (12), 49.
Google Scholar
Mimirinis, M., & Bhattacharya, M. (2007). Design of virtual learning environments for deep learning. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 18 (1), 55–64.
Smart, K., & Cappel, J. (2006). Students’ perceptions of online learning: A comparative study. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 5 (1), 201–219.
Jain, P. (2015). Virtual learning environment. International Journal in IT & Engineering, 3 (5), 75–84.
Molnár, G. (2013). Challenges and opportunities in virtual and electronic learning environments. In IEEE 11th international symposium on intelligent systems and informatics .
Riley, S. K. L. (2008). Teaching in virtual worlds: Opportunities and challenges. Setting Knowledge Free: The Journal of Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology, 5 (5), 127–135.
Warden, C. A., Stanworth, J. O., Ren, J. B., & Warden, A. R. (2013). Synchronous learning best practices: An action research study. Computers & Education, 63 , 197–207.
Yamagata-Lynch, L. C. (2014). Blending online asynchronous and synchronous learning. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 15 (2), 189–212.
Cole, M. (2009). Using wiki technology to support student engagement: Lessons from the trenches. Computers & Education, 52 (1), 141–146.
Tyler, J., & Zurick, A. (2014). Synchronous versus asynchronous learning-is there a measurable difference? In Proceedings of the 2014 Institute for Behavioral and Applied Management Conference, IBAM22 . October 9–11, 2014, 52.
Asikainen, H., & Gijbels, D. (2017). Do students develop towards more deep approaches to learning during studies? A systematic review on the development of students’ deep and surface approaches to learning in higher education. Educational Psychology Review, 29 (2), 205–234.
Biggs, J. B. (1993). From theory to practice: A cognitive systems approach. Higher Education Research and Development, 12 (1), 73–86.
Garrison, D. R., & Cleveland-Innes, M. (2005). Facilitating cognitive presence in online learning: Interaction is not enough. The American Journal of Distance Education, 19 (3), 133–148.
Van Raaij, E. M., & Schepers, J. J. (2008). The acceptance and use of a virtual learning environment in China. Computers & Education, 50 (3), 838–852.
Postareff, L., Parpala, A., & Lindblom-Ylänne, S. (2015). Factors contributing to changes in a deep approach to learning in different learning environments. Learning Environments Research, 18 , 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-015-9186-1
Dolmans, D., Loyens, S., Marcq, H., & Gijbels, D. (2016). Deep and surface learning in problem-based learning: A review of the literature. Advances in Health Science Education, 21 (5), 1087–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-015-9645-6
Wildemuth, B. M. (Ed.). (2016). Applications of social research methods to questions in information and library science . ABC-CLIO.
Silverman, D. (Ed.). (2016). Qualitative research . Sage.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: Classic definitions and new directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25 (1), 54–67.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1986). Thought and language . MIT Press.
McCafferty, S. G. (1994). The use of private speech by adult ESL learners at different levels of proficiency. In J. P. Lantolf & G. Appel (Eds.), Vygotskian approaches to second language research (pp. 135–156). Ablex.
Centeno-Cortes, B., & Jimenez Jimenez, A. F. (2004). Problem-solving tasks in a foreign language: The importance of the L1 in private verbal thinking. International Journal of Applied Linguistics, 14 (1), 7–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-4192.2004.00052.x
Ghanizadeh, A., & Mirzaee, S. (2012). Critical thinking: How to enhance it in language classes . Lambert Academic Publishing.
Choi, I., Nisbett, R., & Smith, E. E. (1997a). Culture, categorization and inductive reasoning. Cognition, 65 (1), 15–32.
Nisbett, R. E., Peng, K., Choi, I., & Norenzayan, A. (2001). Culture and systems of thought: Holistic versus analytic cognition. Psychological Review, 108 (2), 291–310.
Peng, K. (1997). Naive dialecticism and its effects on reasoning and judgement about contradiction . University of Michigan.
Peng, K., & Nisbett, R. (1996). Cross-cultural similarities and differences in the understanding of physical causality. In Paper presented at the science and culture: Proceedings of the seventh interdisciplinary conference on science and culture .
Cole, M. (1996). Cultural psychology: A once and future discipline . Belknap Press of Harvard University Press.
Nisbett, R. E. (2003). The geography of thought: How Asians and westerners think differently … and why . Free Press.
Ji, L.-J., Zhang, Z., & Nisbett, R. E. (2004). Is it culture or is it language? Examination of language effects in cross-cultural research on categorisation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87 (1), 57–65.
Norenzayan, A. (2001). Rule-based and experience-based thinking: The cognitive consequences of intellectual traditions. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences & Engineering, 62 (6-B), 2992.
Norenzayan, A., Smith, E. E., Kim, B. J., & Nisbett, R. E. (2002). Cultural preferences for formal versus intuitive reasoning. Cognitive Science, 26 (5), 653–684.
Peng, K., Ames, D. R., & Knowles, E. D. (2000). Culture and human inference: Perspectives from three traditions. In D. Matsumoto (Ed.), Handbook of cross-cultural psychology (pp. 1–2). Oxford University Press.
Whorf, B. L. (1962b). The relation of habitual thought to language, and an American Indian model of the universe from language. In J. B. Carroll (Ed.), Language, thought and reality: Selected writings of Benjamin . MIT Press.
Davidson, D. (1984). On the very idea of a conceptual scheme. In inquiries into truth and interpretation . Oxford University Press.
Devitt, M., & Sterelny, K. (1997). Language and reality . MIT Press.
Gellatly, A. (1995). Colourful whorfian ideas: Linguistic and cultural influences on the perception and cognition of colour and on the investigation of time. Mind and Language, 10 (3).
Pinker, S. (1994). The language instinct . Penguin Books.
Book Google Scholar
Davies, W. M. (2006b). Intensive teaching formats: A review. Issues in Educational Research, 16 (1), 1–20.
Felix, U., & Lawson, M. (1994). Evaluation of an integrated bridging program course on academic writing for overseas postgraduate students. Higher Education Research and Development, 13 (1), 59–70.
Felix, U., & Martin, C. (1991). A report on the program of instruction in essay writing techniques for overseas post-graduate students . School of Education, Flinders University.
Brand, D. (1987). The new whizz kids: Why Asian Americans are doing well and what it costs them. Time, August (42–50) .
Murphy, D. (1987). Offshore education: A Hong Kong perspective. Australian Universities Review, 30 (2), 43–44.
Wong, N.-Y. (2002). Conceptions of doing and learning mathematics among Chinese. Journal of Intercultural Studies, 23 (2), 211–229.
Accreditation standards for dental education programs. Commission on dental accreditation. Commission on dental Education 2019.
Elangovan, S., Venugopalan, S. R., Srinivasan, S., Karimbux, N. Y., Weistroffer, P., & Allareddy, V. (2016). Integration of basic-clinical sciences, PBL, CBL, and IPE in U.S. dental schools’ curricula and a proposed integrated curriculum model for the future. Journal of Dental Education, 80 , 281–290.
Duong, M. T., Cothron, A. E., Lawson, N. C., & Doherty, E. H. (2018). U.S. Dental schools’ preparation for the integrated national board dental examination. Journal of Dental Education, 82 , 252–259.
Annansingh, F. (2019). Mind the gap: Cognitive active learning in virtual learning environment perception of instructors and students. Education and Information Technologies . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09949-5
Mirzaee, S., & Maftoon, P. (2016). An examination of Vygotsky’s socio-cultural theory in second language acquisition: The role of higher order thinking enhancing techniques and the EFL learners’ use of private speech in the construction of reasoning. Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education . https://doi.org/10.1186/s40862-016-0022-7
Martin Davies, W. (2006). Cognitive contours: Recent work on cross-cultural psychology and its relevance for education. Studies in Philosophy and Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11217-006-9012-4
van der Hoeven, D., Truong, T. T. L. A., Holland, J. N., & Quock, R. L. (2020). Assessment of critical thinking in a first-year dental curriculum. Medical. Science Educator . https://doi.org/10.1007/s40670-020-00914-3
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Training and Development, The English and Foreign Languages University, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
K. Venkat Reddy
Department of English Language Teaching, The English and Foreign Languages University, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
G. Suvarna Lakshmi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of English Language Teaching, English and Foreign Languages University, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reddy, K.V., Lakshmi, G.S. (2024). Practicing Critical Thinking: Issues and Challenges. In: Reddy, K.V., Lakshmi, G.S. (eds) Critical Thinking for Professional and Language Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-37951-2_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-37951-2_5
Published : 04 September 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-37950-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-37951-2
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Critical Thinking Is About Asking Better Questions
- John Coleman

Six practices to sharpen your inquiry.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution. At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions. For effective questioning, start by holding your hypotheses loosely. Be willing to fundamentally reconsider your initial conclusions — and do so without defensiveness. Second, listen more than you talk through active listening. Third, leave your queries open-ended, and avoid yes-or-no questions. Fourth, consider the counterintuitive to avoid falling into groupthink. Fifth, take the time to stew in a problem, rather than making decisions unnecessarily quickly. Last, ask thoughtful, even difficult, follow-ups.
Are you tackling a new and difficult problem at work? Recently promoted and trying to both understand your new role and bring a fresh perspective? Or are you new to the workforce and seeking ways to meaningfully contribute alongside your more experienced colleagues? If so, critical thinking — the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution — will be core to your success. And at the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep, different, and effective questions.
- JC John Coleman is the author of the HBR Guide to Crafting Your Purpose . Subscribe to his free newsletter, On Purpose , or contact him at johnwilliamcoleman.com . johnwcoleman
Partner Center

Remembering Amy Rossiter: The Governing Effects of Self-Esteem Knowledge on Social Work Practice
- Heidi Zhang York University
Amy Rossiter has long called our attention to the governing effects of social work knowledge (i.e., how it directs both discursive thinking and the daily actions of people). For her, knowledge itself is neither neutral nor true but is produced and maintained by discourse that defines what is considered acceptable and true. The production of knowledge is a relation of power; therefore, social work knowledge itself should be a topic of scrutiny. Taking her argument to heart, we seek to show how the governing effects of knowledge discursively operates in a practice setting, using a pilot program training manual designed to help East Asian Canadian immigrants to build self-esteem as a case example. Instead of viewing the training manual as having discovered some truths regarding the nature of self-esteem, we take it as knowledge that reflects the dominant discourse of self-esteem that is constituted historically, materially, and discursively. In so doing, we attempt to show how the concept of self-esteem is produced and how it organizes and governs social work practice.
Copyright (c) 2024 Critical Social Work

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
- Israel at war
- Election 2024
- Antisemitism
- Republish our articles
- פֿאָרווערטס

In the courtyard where Hersh Goldberg-Polin danced on Oct. 6, grief and anger reign after his death
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Email
- Print Article
- Republish Article

Shira Ben-Sasson, a founder of the Hakhel synagogue in Jerusalem, lights a candle in memory of Hersh Goldberg-Polin, Sept. 1, 2024. (Deborah Danan)
By Deborah Danan September 1, 2024
( JTA ) — JERUSALEM — Three hundred and thirty-two days after Hersh Goldberg-Polin danced in the courtyard next to his Jerusalem synagogue on the holiday of Simchat Torah, more than a thousand people gathered there in grief and prayer to mourn his murder by Hamas terrorists in Gaza.
During the Sunday night vigil, the courtyard railings were lined with oversized yellow ribbons to symbolize advocacy for the hostages, Hapoel Jerusalem soccer flags — the 23-year-old’s favorite team — and posters that read, “We love you, stay strong, survive,” a mantra coined by his mother, Rachel Goldberg-Polin.
Just hours earlier, one of the posters had been hanging over the balcony of the home of Shira Ben-Sasson, a leader of Hakhel, the Goldberg-Polins’ egalitarian congregation in the Baka neighborhood of Jerusalem.

Forwarding the News
Thoughtful, balanced reporting from the Forward and around the web, bringing you updated news and analysis of the crisis each day.
“We were sure we would take it down when he came home,” Ben Sasson said.
The community wanted to unite while respecting the Goldberg-Polins’ desire for privacy, she said, prompting them to organize the prayer gathering.
“But it’s like a Band-Aid or giving first aid, it’s what you do in an emergency. I don’t know how we go on after this,” she said.
She added that the community, which has a large contingent of English-speaking immigrants, was not prepared for the High Holidays, which begin in about a month. She said, “Seeing his empty seat is hard.”
For Ben-Sasson, who wore a T-shirt bearing the Talmudic dictum “There is no greater mitzvah than the redeeming of captives,” the tragedy is especially painful because, she said, it could have been avoided with a ceasefire agreement that freed hostages.
“Hersh was alive 48 hours ago. We think a deal could have saved him. There is no military solution to this,” she said.
That feeling of bereavement, often mixed with betrayal, pervaded gatherings across Israel on Sunday, as the country struggled with the news that six hostages who may have been freed in an agreement were now dead as negotiations continue to stall. Speakers at protests in Tel Aviv blamed Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, who himself apologized for not getting the hostages out alive but blamed Hamas for obstructing a deal. The country’s labor union, the Histadrut, has called a national strike on Monday to demand a deal.
Some at the Jerusalem gathering, including the relative of another former hostage, said Netanyahu had chosen defeating Hamas over freeing the captives.
Josef Avi Yair Engel, whose grandson Ofir was released from Hamas captivity in November during that month’s ceasefire deal, expressed shock over Hersh’s murder but said he was not surprised, given the wartime policies of Netanyahu’s government.
“We knew months ago this was going to happen. Bibi’s formula, to dismantle Hamas and return the hostages, wasn’t logical. It’s an either/or situation,” Engel said, referring to Netanyahu by his nickname. “He’s tearing the country apart. I’m afraid that in the coming months there won’t be a state at all.”
Engel said he felt a close bond with Hersh’s father Jon Polin, not only because of their joint activism in the hostage families’ tent outside the Prime Minister’s Residence, but also because of their shared identity as Jerusalemites.
“There aren’t many of us in the hostage circle,” he said. “We’re like family.”
Sarah Mann, who did not know the family personally, said the weekend’s tragedy reminded her of Oct. 7.
“This day has sparks of the seventh, which created numbness and an inability to talk. Just complete shock,” she said.
Part of the reason for that, Mann said, was Rachel, who she described as a “force of faith.” Goldberg-Polin’s mother emerged as the most prominent advocate for the hostages globally and became a symbol in her own right as she crisscrossed the world calling for her son’s freedom.
“Millions of people around the world held onto her. Once that was cut, people’s ability to hold onto faith was knocked out today. But even though this has shattered us, we need to keep holding onto God,” Mann said.
For Susi Döring Preston, the day called to mind was not Oct. 7 but Yom Kippur, and its communal solemnity.
She said she usually steers clear of similar war-related events because they are too overwhelming for her.
“Before I avoided stuff like this because I guess I still had hope. But now is the time to just give in to needing to be around people because you can’t hold your own self up any more,” she said, tears rolling down her face. “You need to feel the humanity and hang onto that.”
Like so many others, Döring Preston paid tribute to the Goldberg-Polins’ tireless activism. “They needed everyone else’s strength but we drew so much strength from them and their efforts, “she said. “You felt it could change the outcome. But war is more evil than good. I think that’s the crushing thing. You can do everything right, but the outcome is still devastating.”
Guy Gordon, a member of Hakhel who moved to Israel from Dublin, Ireland, in the mid-1990s, said the efforts towards ensuring Hersh’s safe return have been an anchor for the community during the war.
“It gave us something to hope for, and pray for and to demonstrate for,” he said. “We had no choice but to be unreasonably optimistic. Tragically it transpired that he survived until the very end.”
Gordon, like many others in the crowd, wore a piece of duct tape marked with the number of days since Oct. 7 — a gesture initiated by Goldberg-Polin’s mother. Unlike on previous days, though, his tape also featured a broken red heart beside the number.
Nadia Levene, a family friend, also reflected on the improbability of Hersh’s survival.
“He did exactly what his parents begged him to do. He was strong. He did survive. And look what happened,” Levene said.
She hailed Rachel Goldberg-Polin’s “unwavering strength and belief in God,” adding, “There were times I lost faith. I suppose I was angry with God. But she just kept inspiring us all to pray, pray, pray.”
Jerusalem resident Leah Silver rejected politicizing the hostages’ deaths.
“Everything turns political so quickly. I came here because I felt that before all the protests, we need to just mourn for a moment and to pray. And show respect for each other,” she said. “We’ve become confused about who the enemy is. It’s very sad.”
But not everyone at the gathering joined in to sing Israel’s national anthem at the closing of the prayer gathering.
“I’m sorry, I can’t sing ‘Hatikvah,’” Reza Green, a Baka resident who did not know the Goldberg-Polins personally, said. “I’m too angry. We shouldn’t be here.”
A message from our CEO & publisher Rachel Fishman Feddersen

I hope you appreciated this article. Before you go, I’d like to ask you to please support the Forward’s award-winning, nonprofit journalism during this critical time.
Now more than ever, American Jews need independent news they can trust, with reporting driven by truth, not ideology. We serve you, not any ideological agenda.
At a time when other newsrooms are closing or cutting back, the Forward has removed its paywall and invested additional resources to report on the ground from Israel and around the U.S. on the impact of the war, rising antisemitism and the protests on college campuses.
Readers like you make it all possible. Support our work by becoming a Forward Member and connect with our journalism and your community.
Make a gift of any size and become a Forward member today. You’ll support our mission to tell the American Jewish story fully and fairly.
— Rachel Fishman Feddersen, Publisher and CEO
Join our mission to tell the Jewish story fully and fairly.
- 2024 elections
- Chuck Schumer

Hapoel Jerusalem unveils new soccer jersey honoring the memory of Hersh Goldberg-Polin

Shabbos Kestenbaum, high-profile critic of campus antisemitism, says he’s broken with Democratic Party and will vote for Trump

An A-list Hollywood agent’s menacing pro-Israel message lands him in hot water

New archaeological research shows siege on Masada lasted just weeks, not years
Most popular.
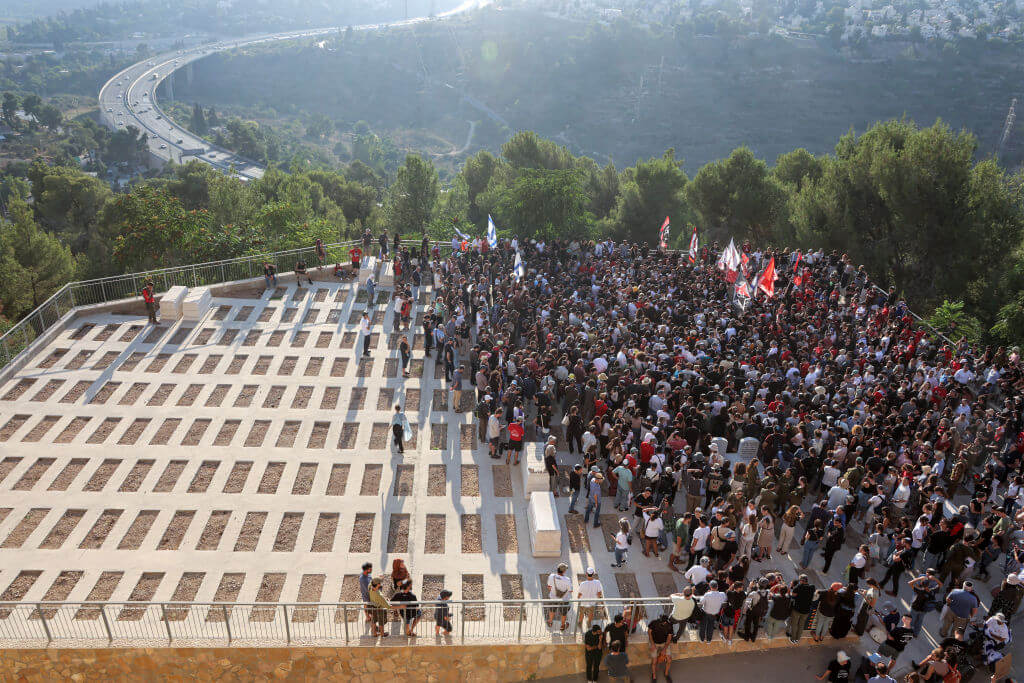

Watch: Tearful funeral of Hersh Goldberg-Polin, American-Israeli hostage killed by Hamas

Hersh Goldberg-Polin, 23, is one of 6 Israeli hostages killed by Hamas in Gaza, IDF reports
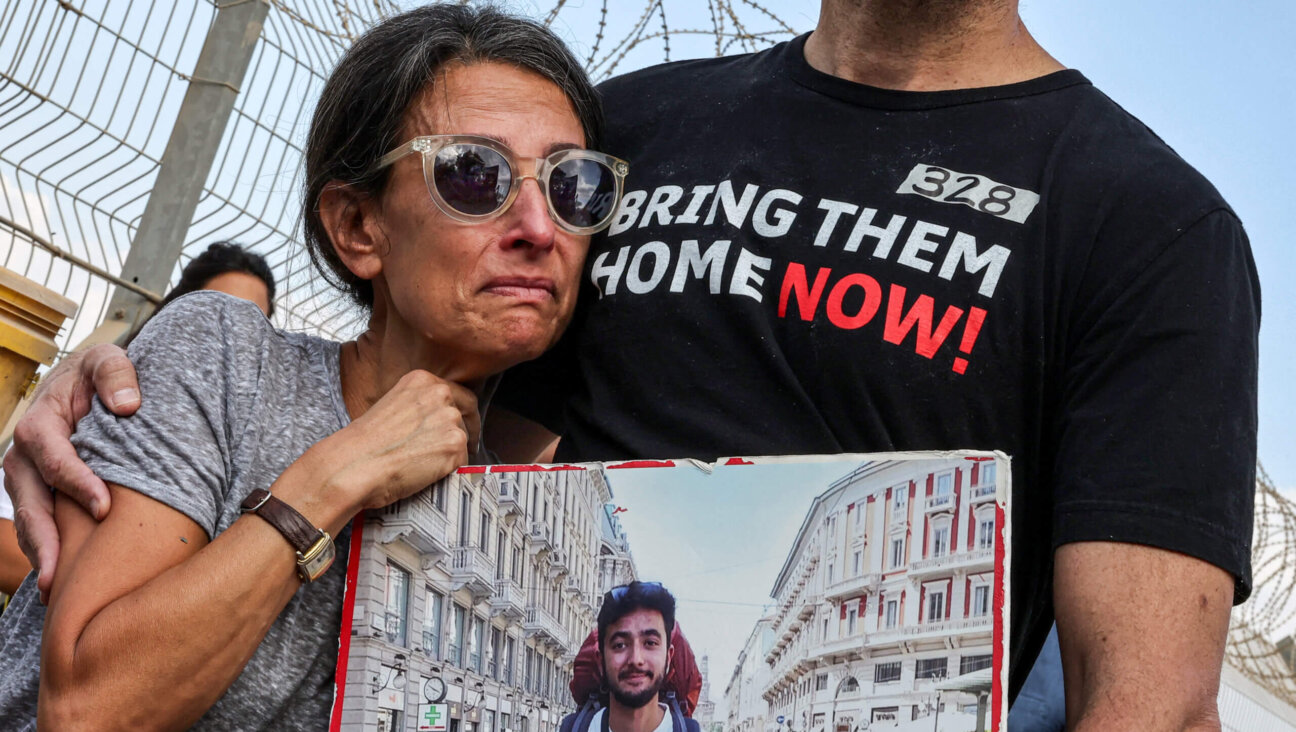

Thanks to his mother, we are all sitting shiva for Hersh Goldberg-Polin

Trump’s Israel adviser suggests diverting $1 billion from Palestinian aid to fund West Bank annexation
In case you missed it.
Hersh Goldberg-Polin’s last words are not just Hamas propaganda

Trump isn’t an antisemite — he just hates the Jews who won’t vote for him
Catch up on yiddish events.

Shop the Forward Store
100% of profits support our journalism

Our founder, Ab Cahan

1960s Yiddish hipi hoodie

It's spelled Khanike tee

The Forverts est. 1897 hoodie

Republish This Story
Please read before republishing
We’re happy to make this story available to republish for free, unless it originated with JTA, Haaretz or another publication (as indicated on the article) and as long as you follow our guidelines . You must credit the Forward, retain our pixel and preserve our canonical link in Google search. See our full guidelines for more information, and this guide for detail about canonical URLs.
To republish, copy the HTML by clicking on the yellow button to the right; it includes our tracking pixel, all paragraph styles and hyperlinks, the author byline and credit to the Forward. It does not include images; to avoid copyright violations, you must add them manually, following our guidelines . Please email us at [email protected] , subject line “republish,” with any questions or to let us know what stories you’re picking up.
We don't support Internet Explorer
Please use Chrome, Safari, Firefox, or Edge to view this site.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summary. Most employers lack an effective way to objectively assess critical thinking skills and most managers don't know how to provide specific instruction to team members in need of becoming ...
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [1]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
Instead, leaders should deliberately approach each problem and devote time thinking through possible solutions. The good news, she says, is that critical thinking skills can developed and ...
The good news? Critical thinking is a teachable skill, and one that any person can learn to make time for when making decisions. To improve and devote time for critical thinking at work, consider the following best practices. 1. Question assumptions and biases. Consider this common scenario: A team is discussing a decision that they must make ...
Critical thinking is considered a soft skill, which means it's a skill inherent in a person's personality. That said, it is possible to develop this skill. Related: 5 Examples of Critical Thinking Skills Critical thinking in the workplace Here are some of the ways critical thinking is important to the workplace: Some professions require it
In recent decades, approaches to critical thinking have generally taken a practical turn, pivoting away from more abstract accounts - such as emphasizing the logical relations that hold between statements (Ennis, 1964) - and moving toward an emphasis on belief and action.According to the definition that Robert Ennis (2018) has been advocating for the last few decades, critical thinking is ...
Using your critical thinking skills in the workplace will define you as a problem solver. This is not only useful career-wise (although having upper-level people at your company think highly of you is undoubtedly a benefit) it also establishes you as a leader among your fellow team members. Demonstrating your ability to solve problems and ...
Third, seek out fresh perspectives. It's tempting to rely on your inner circle to help you think through these questions, but that won't be productive if they all look and think like you. Get ...
Then we conducted employer interviews to learn about workplace critical thinking skills. Interviews provided insight about the importance of critical thinking, examples in the workplace, types of tools that employers use to evaluate critical thinking, insight about potential features of tasks, and flow of a critical thinking tool. 3.2. Participants
Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value. Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible. Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation. So, critical thinking isn't just being intelligent or analytical.
Critical-thinking skills include the ability to commit to the chosen solution. You increase attention to detail and interest from the participants in implementing the solution when they are an integral part of the process. 6. Complete the plan. Some employees find this part of the process the most difficult.
Here's a breakdown of how to teach critical thinking in the workplace: Identify problem areas. Executives and managers should assess workplace areas most lacking in critical thinking. If ...
This paper provides ways to foster better the workplace management and personal development especially for the employees at workplace through critical thinking. Discover the world's research 25 ...
Cultivating critical thinking skills will be essential to ensuring that individuals can take advantage of the opportunities presented by new technologies while mitigating the challenges of job disruption in this AI-driven future. Go to: 3. Critical Thinking Skills and Job Disruption and Replacement.
Critical thinking allows you to always soberly assess the situations taking place in your work, give an objective assessment, including your own actions and the actions of others, effectively ...
Work on projects or scenarios that require critical thinking skills to develop practical problem-solving approaches. Apply critical thinking in real-life situations whenever possible. This could involve analyzing news articles, evaluating product reviews, or dissecting marketing strategies to understand their underlying rationale.
2. Understand your mental process. Identify and evaluate how you receive and process information. Understanding how you listen, then interpret, and finally react to information is vital to becoming more mentally efficient in the workplace. Being a critical thinker means you recognize your prejudices and how they influence solutions and decisions.
The good news is that critical thinking is a learned behavior. There are three simple things you can do to train yourself to become a more effective critical thinker: question assumptions, reason ...
Critical thinking skills examples. There are six main skills you can develop to successfully analyze facts and situations and come up with logical conclusions: 1. Analytical thinking. Being able to properly analyze information is the most important aspect of critical thinking. This implies gathering information and interpreting it, but also ...
In today's fast-paced, complex, and dynamic work environment, critical thinking is more critical than ever before. It is crucial for organizations to prioritize critical thinking skills among ...
Critical thinkers aim to find the truth from the information they've collected. Employees with excellent critical thinking skills evaluate information by considering potential problems and solutions. 2. Assess the source of information. Critical thinkers always consider the source of their information.
In the workplace, critical thinking empowers individuals to analyze problems, devise creative solutions and make informed judgments. In everyday life, it helps individuals navigate an increasingly ...
Critical thinking is based on the observation and analysis of facts and evidences to return rational, skeptical and unbiased judgments. This type of thinking involves a series of skills that can be created but also improved, as we will see throughout this article in which we will begin by defining the concept and end with tips to build and improve the skills related to critical thinking.
The extensive research on teaching critical thinking at all levels in education and incorporating critical thinking in the curriculum of various courses help us conclude that most of the initial challenges and barriers to teach critical thinking are resolved now as various techniques to enhance critical thinking are proposed by researchers/studies.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and effectively break down an issue in order to make a decision or find a solution. At the heart of critical thinking is the ability to formulate deep ...
The modern construct of individual critical thinking originated in the work of John Dewey ... Of the 19 research articles, nine mentioned critical thinking just once or twice in the article (usually in a list of desirable pedagogical outcomes), leaving only 10 that deeply engaged with the construct. In other words, one in five AMLE articles ...
Rossiter, critical social work, knowledge, self-esteem, practice Abstract. Amy Rossiter has long called our attention to the governing effects of social work knowledge (i.e., how it directs both discursive thinking and the daily actions of people). For her, knowledge itself is neither neutral nor true but is produced and maintained by discourse ...
Print Article Republish Article Shira Ben-Sasson, a founder of the Hakhel synagogue in Jerusalem, lights a candle in memory of Hersh Goldberg-Polin, Sept. 1, 2024.