- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file

People also looked at
Original research article, spatial management to reduce entanglement risk to north atlantic right whales in fishing gear: a case study of u.s. northeast lobster fishery 2002–2009.

- 1 Northeast Fisheries Science Center, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA-Fisheries), Woods Hole, MA, United States
- 2 Economics, Statistics, and Data Governance, Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO), Ottawa, ON, Canada
Despite the use of gear requirements and access restrictions to manage lobster fishery interactions with north Atlantic right whales since 1997, the population is likely below 370 animals. The Dynamic Area Management (DAM) program (2002–2009) used “real-time” right whale sightings data to provide temporary protection using closures or whale-modified-gear to reduce entanglement. Our ex-post evaluation uses a flexible framework to identify strengths and weaknesses of the program. Biological and economic implications of the program are evaluated using a relative risk of entanglement index (RREI) calculated with spatially and temporally explicit data on density of right whales and fishing effort. An illustrative closure optimization model demonstrates the trade-offs between the non-monetary benefits of risk reduction and the opportunity cost of closures under alternative decision rules (benefit-ranking and cost-effectiveness). Annual aerial sampling to detect DAM areas was low (<3%), yet in some months’ the 17% of area covered by all northeast right whale management areas encompassed up to 70% of the region’s population. Despite their small spatial footprint, dynamic and static measures may have reduced total risk by 6.5% on average, and DAM zones may have created an indirect economic incentive for some fishers to adopt the whale-modified-gear. Similar RREI index values in some months with inverse levels of fishing effort and whale presence highlight the need to consider fishing and whales jointly to reduce risk. These temporal-spatial patterns are critical in policy instrument design. Further, optimization results illustrate how different decision rules can attain equivalent non-monetary benefits of risk reduction at different opportunity costs to industry; the implications of whale-modified-gear and compliance factors are explored. We recommend that DAMs be considered as part of a suite of policy instruments, and highlight how recent technological advances may support lower cost data collection and faster implementation given limited public sector budgets. This case study highlights the need for evaluation of past policy instruments with a lens beyond biological outcomes, and sets the stage for further empirical analysis to better understand harvester responses to management measures designed to protect right whales and the resulting private and public sector trade-offs.
Introduction
The complex interplay between commercial fisheries and marine protected species may require multiple policy instruments to support conservation, as in the case with the north Atlantic right whale ( Eubalena glacialis ; right whale) and the American lobster ( Homarus americanus ) fishery in the northeast United States (U.S.). Bycatch is the single greatest cause of cetacean mortality ( Read et al., 2006 ). Over the past 20 years a growing regime of policy instruments have been applied to the American lobster fishery to reduce the entanglement of right whales in fishing gear in order to allow the endangered population to recover; however, recovery has not occurred ( National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2017 ). While past regulatory measures have been assessed prior to implementation (ex-ante), there has been relatively few ex-post evaluations of the effectiveness or success of past measures for marine mammals and fishing interactions as there is rarely a control or counterfactual to determine what would have occurred in the absence of bycatch management ( Little et al., 2015 ). Such studies can provide insights and guidance in the modification of existing measures and development of new measures. We use a case study approach to develop a framework to jointly consider the conservation and economic considerations of management focused on risk reduction for a large migratory protected species. The case study evaluates the Dynamic Area Management (DAM) program for right whale protection between 2002 and 2009, adding to the literature on policy instruments used to protect marine protected species from interactions with commercial fishing activity (see Fonner et al., 2020 for a recent review).
The right whale population is endangered. The population was as high as 500 in 2010 but is declining ( Pace et al., 2017 ); the most recent abundance estimate is 428 animals ( National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2020 ), with the 2019 population likely less than 370 ( Pettis et al., 2020 ). The leading known causes of mortality for right whales are entanglement in fishing gear and vessel strikes ( National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2020 ). The distribution between the two causes of mortality is unknown, however, recent information indicates the vast majority of serious injuries are entanglement-related and this mortality is widely underestimated ( Pace et al., 2021 ). Further, based on the distribution of vertical lines by gear type, roughly 96% of the vertical lines in U.S. east coast waters were attached to lobster trap/pots for any month on average ( National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2014 : Exhibit 5–4), suggesting lobster gear likely poses the greatest probability of a whale entanglement. Implementation of measures to reduce the likelihood and severity of entanglements for right whales and other large whales began in 1997, with the first Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan (the Plan), while implementation of measures to reduce mortality from ship strikes began in 2008 (73 FR 60173, October 10, 2008). 1 Ex-post evaluations of the measures for vessel speed and traffic relocation, which are not part of the Plan, have considered biological outcomes ( Laist et al., 2014 ) and compliance ( Lagueux et al., 2011 ; Silber et al., 2014 ). Ex-post evaluation of the Plan’s success has focused on biological outcomes for the combined measures in the Plan ( Knowlton et al., 2012 ; Pace et al., 2014 ) and on the Take Reduction Team process ( Borggaard et al., 2017 ). However, the lack of data on entanglement or bycatch rates and the impacts of fishing practices, gear characteristics, area, and/or environmental factors on those rates ( Borggaard et al., 2017 ) make the ex-post evaluation of biological outcomes of a specific management measure, such as DAM, difficult. Evaluation of biological outcomes is further complicated by the progression and overlap of management measures over time. However, policy instruments may be designed to achieve multiple goals or objectives, and the use of other evaluation criteria including, among others, economic, social-normative and longevity ( Bisack and Magnusson, 2016 ) may be appropriate for evaluation of individual measures, such as the DAM program.
All the policy instruments in the Plan were based on a command-and-control, direct regulatory approach, such as input controls (time-area closures) to reduce fishing effort and technical standards (gear modifications) to reduce entanglement rates ( Squires and Garcia, 2014 ; Lent and Squires, 2017 ). The instruments within the Plan progressed from seasonal closures of critical habitat to static and dynamic gear-modification zones, then to broad-based mandatory gear modifications. This sequence follows the first two stages of the mitigation hierarchy ( Squires and Garcia, 2014 ; Milner-Gulland et al., 2018 ) of avoidance (closures) and minimization (gear modifications). 2 The mitigation hierarchy approach suggests a sequence of steps (avoid, minimize, restore, compensate) that minimizes ecological risk across all steps ( Squires and Garcia, 2014 ), which may be implemented simultaneously and will interact in the achievement of the biological goal or target ( Milner-Gulland et al., 2018 ). If each step in the hierarchy is implemented to the maximum extent practicable before moving to the next step, diminishing conservation returns per monetary unit spent can result with suboptimal conservation; this can be reduced using a least-cost approach within and between steps ( Squires and Garcia, 2018 ; Squires et al., 2018 ). Alternatively, incentive-based policy instruments that incorporate the social cost of entanglement in fishing may outperform other instruments and provide an alternative approach to command-and-control.
The team tasked with developing the Plan must deal with the complexity of designing policy instruments that implicitly minimize economic impacts to the target fishery (e.g., cost to lobster fishery) while explicitly minimizing the entanglement of non-target species (i.e., benefit to right whales). Cost-benefit analysis identifies options that maximize net benefits and yield an efficient solution; however, cost-benefit analysis requires monetization of benefits and costs which may not be possible. The formal joint consideration of both biological or non-monetary benefits and economic costs has grown in conservation planning ( Ando et al., 1998 ; Naidoo et al., 2006 ; Robin et al., 2006 ), including in the marine environment (e.g., Stewart and Possingham, 2005 ; Delavenne et al., 2012 ; Oinonen et al., 2016 ). For protected species, ex-ante regulatory economic analysis often takes the form of cost-effectiveness analysis, 3 with a comparison of non-monetary biological benefits (i.e., minimize risk of entanglement) with costs (i.e., profit reductions of the fishery) for a discrete number of alternatives. Joint consideration of costs and non-monetary benefits within a optimization framework can yield different outcomes (i.e., compared to when costs not considered) where the magnitude of the efficiency gains depends on the correlations between, and relative variabilities of, benefits and costs across investment or management measures ( Ferraro, 2003 ). One of the challenges of this type of analysis is a quantitative measure of non-monetized benefits of the policy instrument (i.e., management measures).
The focus of the Plan on measures to reduce the likelihood and severity of entanglement by large whales in commercial fixed-gear fisheries suggests it is appropriate to discuss benefits from the Plan in the context of “risk reduction.” The common concept of risk includes what can happen, the likelihood of that happening, and the consequence if it happens ( Kaplan and Garrick, 1981 ). Several measures of entanglement risk have focused on the likelihood aspect defined as a co-occurrence between the gear of concern and whales. Wiley et al. (2003) developed an index of Relative Interaction Potential between large whales and commercial fisheries gear in Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary, United States. To evaluate alternatives for the reopening of the winter black sea bass fishery in the southeastern United States, Farmer et al. (2016) developed Relative Risk Units which considered right whale survey encounters (a proxy for density) and fishing effort measured in soak time. Brilliant et al. (2017) used the probability of encounter of right whales for the Atlantic waters of Canada, which multiplied the annual probability of occurrence of a fishing set within a grid cell by the probability of a right whale within the cell. Vanderlaan et al. (2011) considered the third component of risk by including a measure of lethality to individual whales. Depth was used as an estimate of end-buoy line length, with an encounter based on the relative probability of whale presence and gear presence for the Fundy-Scotia area, Canada. 4
The DAM program was an innovative “real-time” instrument when introduced, an early example of dynamic ocean management which uses near real-time data to guide the spatial distribution of commercial activities ( Lewison et al., 2015 ). Actual examples of dynamic management remain relatively novel, despite analyses that suggest dynamic area management for fisheries (e.g., Hobday and Hartmann, 2006 ; Hobday et al., 2010 ; Needle and Catarino, 2011 ; Dunn et al., 2016 ) and marine protected species (e.g., Grantham et al., 2008 ; Hazen et al., 2018 ), and reduce bycatch and protected species interactions ( Lewison et al., 2015 ). Using an optimization approach to achieve defined reductions in bycatch, Grantham et al. (2008) found that bycatch reductions could be achieved with lower costs to fishers with spatially and temporally moveable (dynamic) closures as compared to static temporary or permanent closures. Based on 10 case studies of real-time spatial management approaches, Little et al. (2015) concluded that for dynamic management, greater monitoring and control of individual practices may be required to allow for better management and utilization of target and bycatch quota if individual incentives to avoid bycatch are weak. In a review of nine examples, Lewison et al. (2015) identify regulatory frameworks and incentive structures, stakeholder participation, and user aligned technological applications as key to successful implementation of dynamic ocean management. While Little et al. (2015) called for additional evaluation of dynamic management, they note that in many cases rigorous assessment of performance is made difficult by the lack of a control or counterfactual. Empirical evaluations using quasi-experimental data, such as difference-in-difference, require the identification of a counterfactual (e.g., Ardini and Lee, 2018 ).
We develop a flexible framework that considers biological and economic factors simultaneously that can be used to assess alternative policy instruments including closures and gear modifications, and use this framework for the evaluation of the DAM program. This is an initial step toward an analysis that can assess a broader range of policy instruments. To set the stage for an evaluation of the DAM program we provide background on the U.S. American lobster fishery and the DAM program as part of the Plan to reduce fishery interactions with right whales. Given the critical role of the NOAA-Fisheries aerial survey in the implementation of the DAM program, we review monthly flights. We then assess the biological and economic implications of the DAM program relative to other spatial measures, using spatially and temporally explicit data on whale and fishing effort density to develop a relative risk of entanglement index (RREI) for right whales. Using reductions in risk as the non-monetary benefit measure and fishing revenues as a proxy for opportunity costs, we develop an illustrative closure optimization model. We evaluate two management decision rules (benefits-ranking and cost-effectiveness) subject to the same risk reduction constraint, solving for the optimal number of closures (i.e., avoidance) under each decision rule. Then under the cost-effectiveness rule, we consider minimization measures (i.e., gear modifications) to reduce the risk of entanglement, and the implications of non-compliance with gear requirements. Taking into account data quality issues, we demonstrate the utility of our framework and present general results that highlight the tradeoffs between biological and economic objectives. Finally, we summarize our general observations on DAM for right whales, discuss the strengths and challenges of implementing dynamic management, and offer recommendations for future policy instrument design.
The U.S. American Lobster Fishery
The American lobster ( Homarus americanus ) has been one of the top three most valuable individual commercial species landed in the United States since 1997, accounting for an average of 9% of the national value of domestic landings. 5 The fishery occurs from Maine to Cape Hatteras, North Carolina although the vast majority of landings come from waters of Maine ( Figure 1 ). Maine’s dominance of the fishery has increased from 57% of all landings in 1997 rising to 82% in 2018. During the period 2002–2009, the United States landed an average of 39,856 metric tons of lobster with an average annual dockside-value of $393M (US$2012), with about 79% of landings and 75% of value from Maine.
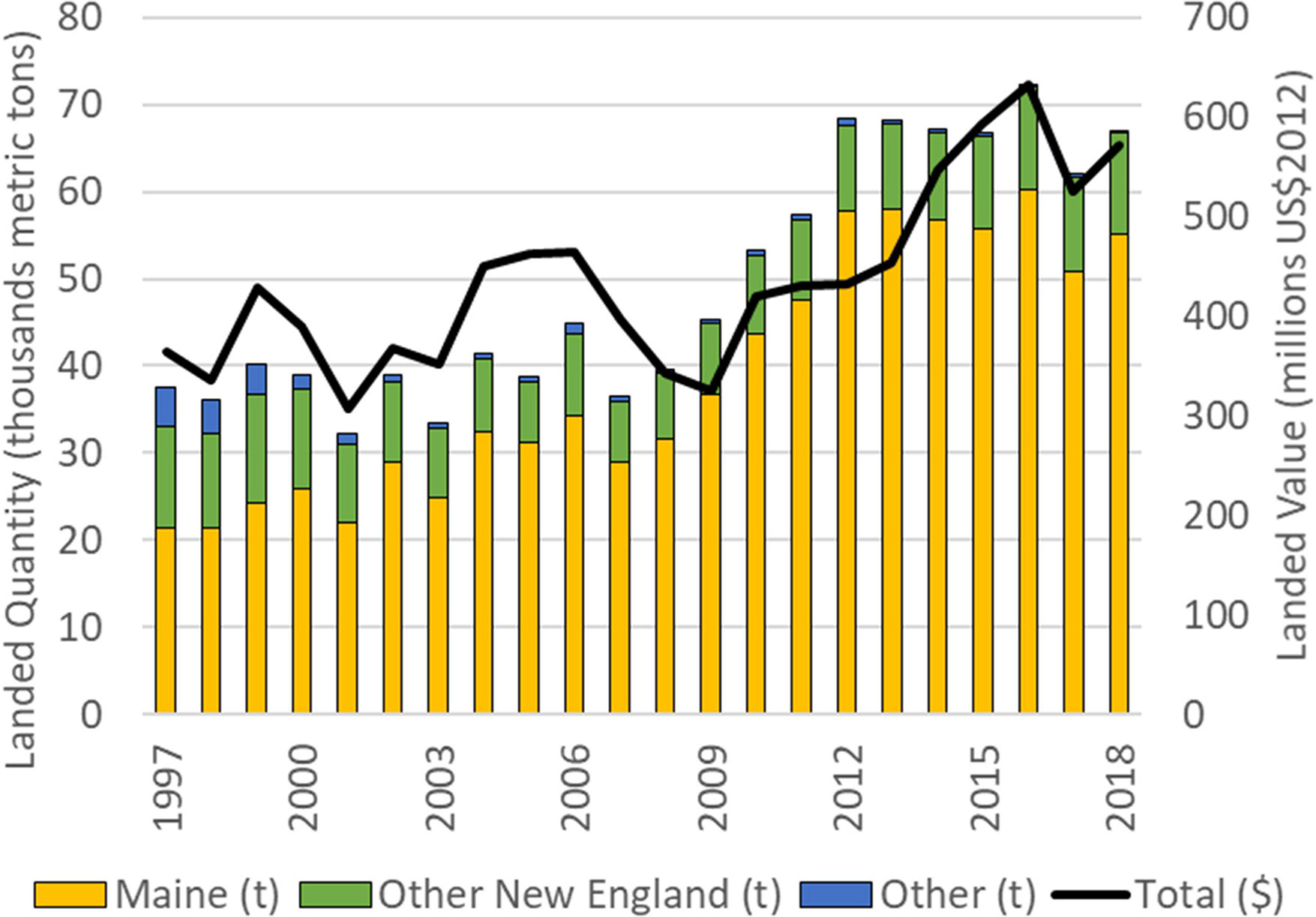
Figure 1. United States Lobster ( Homarus americanus ) landings for Maine (stacked yellow column), other New England states (stacked green column) and the rest of the United States (stacked blue bar) in thousands of metric tons and total landed value (solid line, right axis) in millions of United States dollars (US$2012), 1997–2018. New England coastal states include Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut. Source: NOAA Fisheries. Commercial Fisheries Statistics. https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/national/sustainable-fisheries/commercial-fisheries-landings .
The fishery is cooperatively managed by the states and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Fisheries (NOAA-Fisheries) under the framework of the Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission. States have jurisdiction for implementing measures in state waters within 3 nautical miles of shore, while NOAA-Fisheries implements complementary regulations in offshore federal waters 3–200 nautical miles from shore. The reporting requirements for vessels have changed over time and vary by the type of permit held. Vessels that hold a federal lobster permit as well as any other federal fishery permit must submit vessel trip reports (VTR), which include amongst other information, catch and an average fishing location for each trip. However, if the vessel only holds a federal permit for lobster, VTR are not required. State-level data collection exists, but varies by state and over time.
The lobster fishery predominantly uses pots and traps, with the term “lobster trap” broadly referring to any structure or device, other than a net, that is designed to be placed on the ocean bottom and is capable of catching lobsters. A number of traps may be linked together with “groundline” to create a “trawl,” the location of which is identified using one or more buoys attached to the trawl using a vertical line arrangement. Specific gear requirements vary by area, but include requirements for marking and deployment. Management measures include biological requirements (e.g., minimum and maximum size), as well as effort constraints including limited access and either individual trap allocations or caps on the number of traps per permit.
The market for lobster is for human consumption and it is sold live or it is processed and primarily sold frozen ( Pereira and Josupeit, 2017 ). There is a high degree of integration in the processing and trade of lobster between the United States and Canada, with each country being the largest trade partner for the other ( Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO), 2018 ). Parts of the Maine lobster fishery first received sustainability certification from the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) in 2013; however, the most recent certification was suspended in summer 2020 as a result of concerns regarding right whale entanglement. 6
Measures to Reduce Right Whale-Fisheries Interactions 7
The range of the north Atlantic right whale, which historically included much of the north Atlantic, is primarily in the northwest Atlantic from northern Florida, United States to Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada ( National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2020 ). The species is protected under the Endangered Species Act ( Endangered Species Act (ESA), 1973 ) and the ( Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA), 1972 ) of the United States and the Species at Risk Act ( Species at Risk Act, 2002 ) of Canada. This species has been extensively studied within the south and central part of this range in U.S. waters and the Scotian Shelf in Canada, and biologically important areas for calving, migrating, feeding and mating have been identified ( LaBrecque et al., 2015 ).
To protect these whales, in 1994 two areas of critical habitat as defined by the ESA were designated in the United States, the Great South Channel ( Figure 2 , solid gray area) and Cape Cod Bay ( Figure 3 , solid gray area) (59 Federal Register 28805, 3 June 1994). This was followed in 1997 by the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan (the Plan), which was developed under the authority of the MMPA to address incidental takes or bycatch of large whales, defined as non-intentional, accidental death or injury that occurs during an otherwise lawful activity, such as permitted fishing. While the Plan was developed to implement measures to reduce the likelihood and severity of entanglement in commercial fixed-gear fisheries, including lobster, for north Atlantic right whale, north Atlantic humpback whale ( Megaptera novaeangliae ) and fin whale ( Balaenoptera physalus ), and benefited minke whales ( Balaenoptera acutorostrata) , the spatial management rules in the Plan focused on the right whale.
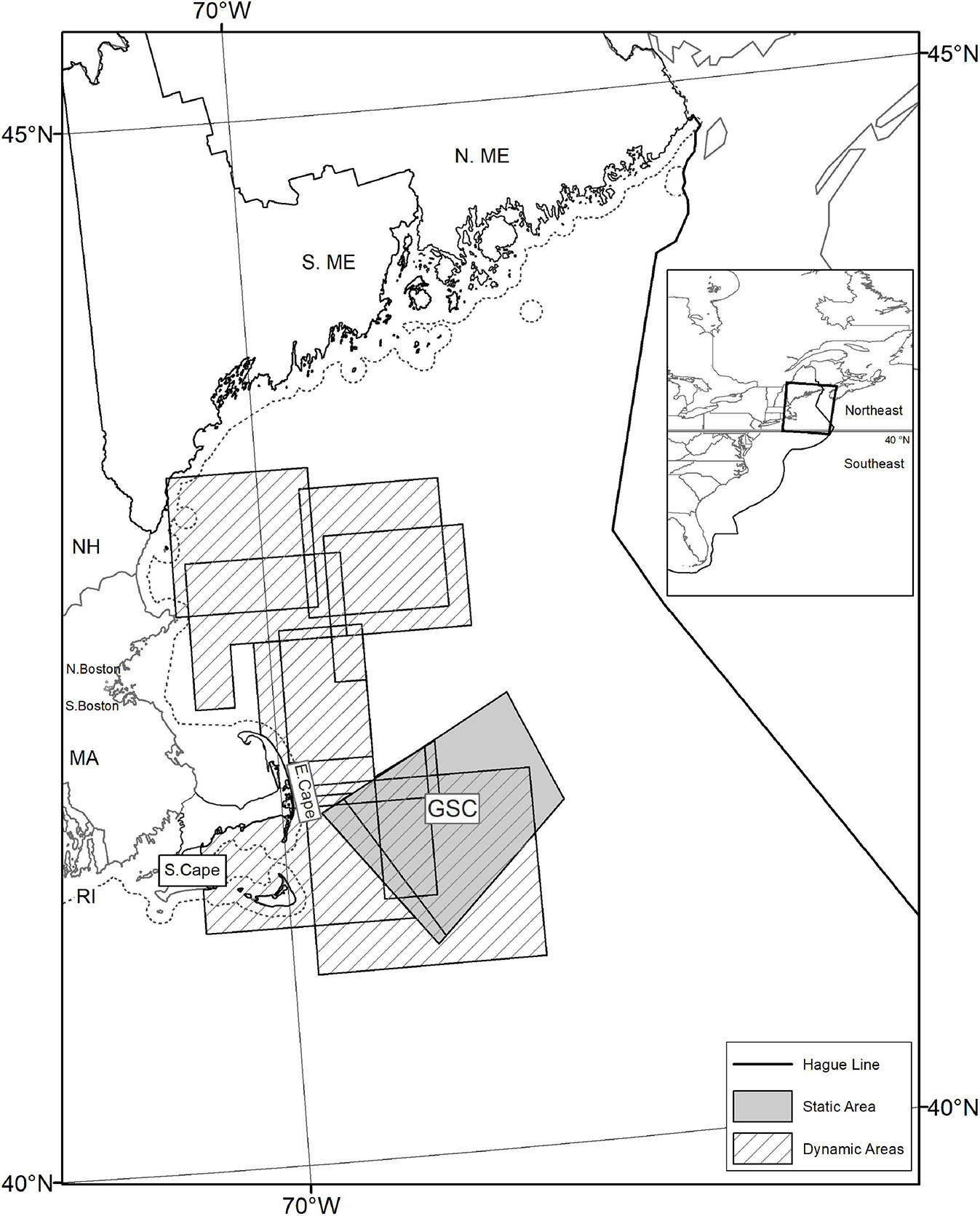
Figure 2. Right whale management areas in the northeast United States that required removal of lobster fishing gear during certain times of year (i.e., avoid risk), as identified in the Atlantic Large Whale Take Recovery Plan, 2002–2009, with port groups and state waters (dash line 3 nm from shore) identified. Great South Channel (GSC) critical habitat area (solid gray area), and Dynamic Area Management (DAM) zones (hatched area).
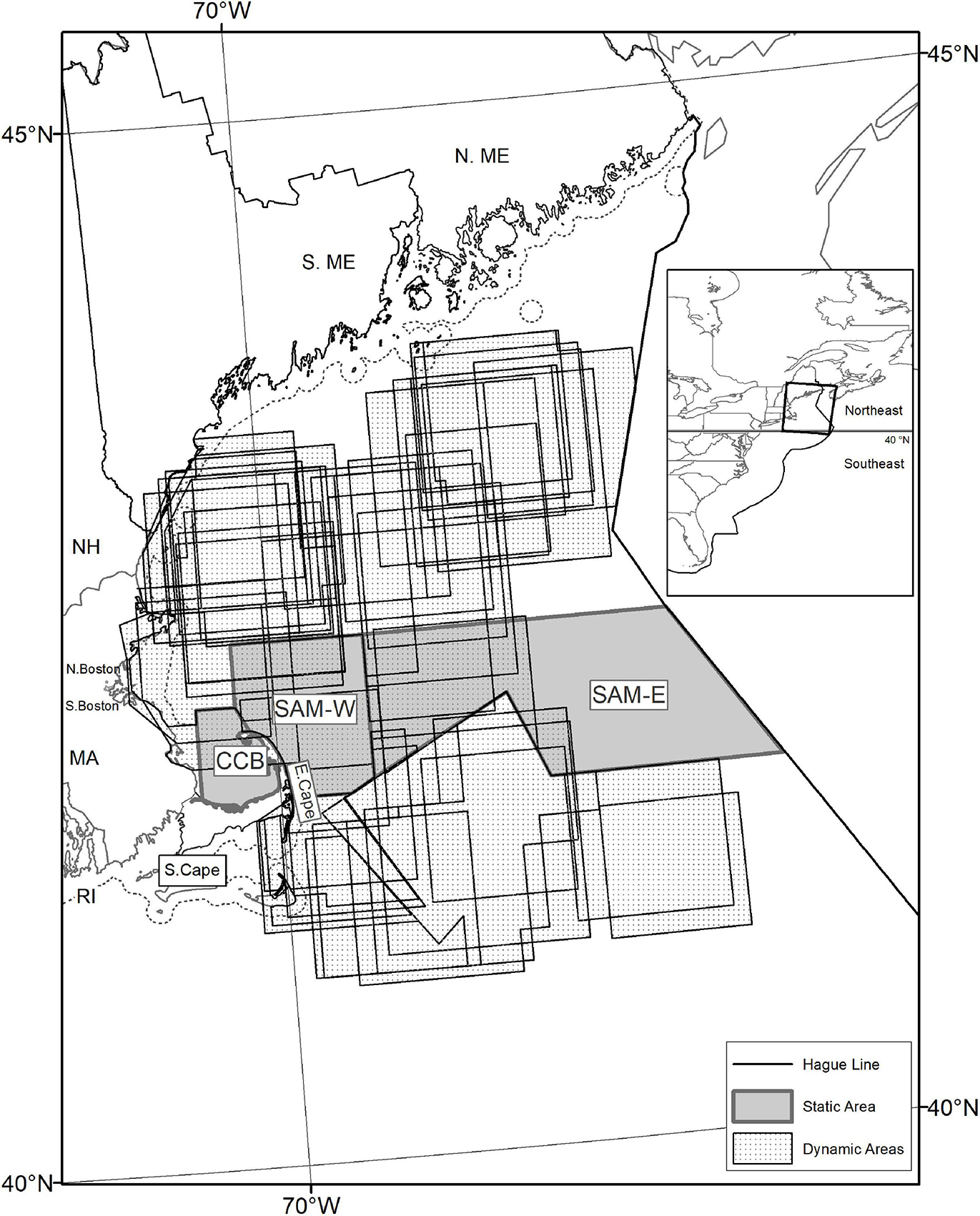
Figure 3. Right whale management areas that required the use of whale-modified-gear during certain times of year (i.e., minimize risk), as identified in the Atlantic Large Whale Take Recovery Plan, 2002–2009, with port groups and state waters (dash line 3 nm from shore) identified. Static areas included Cape Cod Bay (CCB) critical habitat area and Seasonal Area Management zones East (SAM-E) and West (SAM-W) (solid gray area). Dynamic areas include Dynamic Area Management (DAM) zones (hatched area).
Marine animals can become entangled in fishing gear, with impacts ranging from no permanent injury to immediate drowning. Large whales, such as right whales may not be in danger of immediate drowning as they can often pull all or parts of the gear off the ocean floor, and so the likelihood of observing an entanglement at the contact point is low. When these whales travel with gear they can suffer serious injury and potentially mortality, even if they eventually lose the gear. Most adult right whales have scarring evidence of multiple encounters with gear which can affect health, reproduction and survival ( Robbins et al., 2015 ; Knowlton et al., 2016 ).
The objectives of the Plan are determined by statutory benchmarks of the MMPA, which require reductions in levels of bycatch in relation to the Potential Biological Removal level ( Wade and Angliss, 1997 ) and timelines to achieve the reductions. Observed fishing mortality for right whale was, and continues to be, above the Potential Biological Removal level. 8 Borggaard et al. (2017) provides a timeline for the major rule making actions under the Plan between July 1997 and May 2015, as well as the process for the development of the rules; the Plan continues to be adapted based on need with the most recent proposed changes published December 31, 2020 (85 Federal Register 86878, December 31, 2020).
Assessing the biological effectiveness of the Plan in achieving a reduction in entanglements has been challenging ( Borggaard et al., 2017 ). This can be illustrated by data from 1990 to 2017, where of the total modeled right whale mortalities, on average only 36% of right whale carcasses were detected annually 9 and approximately half of the carcasses had sufficient information to determine the cause of death based on necropsies and other analyses ( Henry et al., 2019 ; Pace et al., 2021 ). Given right whales ability to carry gear for long distances, in instances where gear is recovered there is significant uncertainty in assigning the location, type and configuration of the gear involved in an entanglement, despite ongoing gear marking requirements starting with the first Plan (62 FR 39157, July 22, 1997). These technical difficulties, coupled with the statistical rarity of observing entanglements for large whales, makes it nearly impossible to assess the biological success of a particular policy instrument within the Plan.
The first Plan limited closures to critical habitat areas and gear modifications were identified as the preferred alternative to minimize economic impacts (62 FR 16519, April 7, 1997: 16531), despite the uncertainties regarding the effectiveness of these modifications. In response to high levels of serious injury and mortality, regulations were temporarily implemented in 1997 to seasonally manage lobster gear, and later made permanent. Lobster gear was prohibited in Great South Channel (April 1–June 30) while modified lobster gear could be used in Cape Cod Bay (January 1–May 15) (50 CFR 229.30). A limit on floating buoy lines and the need to select modifications from a list of options applied to almost the entire U.S. lobster fishery and changed over the years.
Both the Seasonal Area Management (SAM) and DAM programs were implemented in 2002 as part of the second amendments to the Plan. The SAM program (67 FR 1142, January 9, 2002) included additional gear restrictions for two temporally and spatially static areas ( Figure 3 , solid gray area) defined by historical north Atlantic right whale aggregations ( Merrick et al., 2001 ). SAM West (March 1–April 30) and SAM East (May 1–July 31) zones required sinking or neutrally buoyant groundline and a single buoy line per trawl in addition to the sinking or neutrally buoyant buoy line and weak links required more broadly. 10
The DAM program was a complement to the SAM program (67 FR 1133. January 2, 2002) ( Figures 2 , 3 , hatched area). The program operated year round in U.S. waters north of 40°N with restrictions for each individual zone to be in place for 2 weeks, unless extended or removed. The implementing regulations laid out criteria for when a DAM zone would be triggered, how the size of the zone would be determined and the process for notifying fishers of the DAM zone and requirements. The ex-ante regulatory analysis of mandatory gear removal in DAM zones estimated forgone lobster revenues of $3.2M (US$2000, or $4.1M US$2012) for the first year ( National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), 2001 ). Within the regulation, however, authority remained with the NOAA-Fisheries administrator to determine on a case-by-case basis if an area would be subject to a mandatory or voluntary closure. Of the seven DAM zones implemented between April 1, 2002 and September 25, 2003, only one mandated gear removal while the others were notices for voluntary removal of gear ( Figure 2 , hatched areas).
As an alternative to gear removal in the DAM zone, the NOAA-Fisheries administrator could determine if gear with specific modifications could be allowed to fish in the zone. In September 2003, a standardized list of acceptable gear requirements became available for use in DAM zones (68 FR 51195, August 26, 2003). Gear that did not meet the requirements was to be removed within two days of the publication in the Federal Register of a notice of a DAM zone. The gear specifications were required no matter where the DAM zone was identified unless more restrictive requirements were in place; for example, the Great South Channel critical habitat closure would prevail over DAM gear requirements. The gear specifications identified for use in DAM zones in 2003 followed those for SAM areas with the exception that an additional buoy line was allowed in the DAM zones, meaning SAM requirements were considered more restrictive. The ex-ante regulatory analysis to allow use of modified gear in DAM zones was estimated as $31,100–$93,700 (US$2002 or $38,400–$115,600 US$2012) for the fleet ( National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), 2003 ).
In April 2009, amendments to the Plan ended the SAM and DAM programs (73 FR 51228, September 2, 2008), and marked the next step in implementation of the management strategy identified in 2003. Broad-base gear modification requirements for the gillnet and trap/pot fisheries, over much of the United States Atlantic coast from Maine to Florida, became effective year-round in the northeast and seasonally in other areas ( Borggaard et al., 2017 ). Amendments in 2014 and 2015 focused on reducing risk from vertical line, as well as expanded gear marking requirements and time and area closures ( Borggaard et al., 2017 ).
Materials and Methods
Assessing the performance of policy instruments for right whale protection requires an understanding of the spatial-temporal density of the whales and fishing effort in the management areas to assess the risk of entanglement. We compare dynamic (i.e., DAM zones) and static (i.e., SAM zones and Cape Cod Bay critical habitat) and closed (Great South Channel critical habitat) right whale management areas, to the remaining “open” area, in U.S. waters north of 40 degrees N latitude to The Hague line with Canada, an area of approximately 176,400 km 2 .
In the “Data” section we present the data on the NOAA-Fisheries aerial surveys used to trigger the DAM zones, commercial lobster fishing data, and right whale data. The “Methods” section describes the methods used to calculate a RREI, and an illustrative optimization closure model under two management decision rules, a management objective based strictly on benefits (“benefit-ranking”) vs. an objective that simultaneously considers costs and non-monetized benefits (“cost-effectiveness”). Additional scenarios then consider implications of the use of whale-modified-gear and non-compliance.
The temporal scale for all data are at the month level for April 2002 to March 2009, the period in while the DAM program was active. ArcGIS software is used to establish a standardized coordinate system to produce an initial 20 km 2 vector grid of the data (see Supplementary Section 1 ).
Data for Detecting and Implementing a DAM
The North Atlantic Right Whale Sighting Survey, a NOAA-Fisheries aerial survey program, provided real-time data to NOAA-Fisheries managers to determine if and where to trigger a DAM. The Survey locates and records the seasonal distribution of right whales off the northeastern coast of the United States ( Khan et al., 2010 ). The goal of each flight is to identify locations of large aggregations of right whales. After each flight, the sightings data were used to determine whether the density of right whales was above the threshold to trigger a DAM (i.e., 0.04 right whales per nm 2 ). If the density threshold was reached, the survey team notified the Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office. The Regional Office was responsible for issuing a Federal Register notice to notify the public, the fishing industry in particular, that a DAM zone was to be implemented. The notification included whether the DAM was voluntary or mandatory, the location coordinates, any specific conditions (e.g., gear requirements), and the start and end date of the DAM zone requirements. The Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office provided the authors the notice details for each DAM zone, along with the GIS shape files for all right whale management areas, including critical habitat, SAM and DAM zones ( Figures 2 , 3 ). Roberts et al. (2016) incorporates these data from the North Atlantic Right Whale Sighting Survey in the density map estimates discussed below. The recorded NOAA aerial survey flight track line data were assigned to the 20 km 2 vector grid (see Supplementary Section 1 ).
The aerial survey data are the primary source for detecting potential DAMs and are considered an important element of the overall performance of the DAM program. We are interested in measuring the sampling coverage, the actual number of flight-days per year compared to the number of flights required to sample the Bay of Fundy/Gulf of Maine water body for each of 365 days of the year. A bare-bone survey without any fly-backs over areas (C. Khan, pers. comm., August 2020), would require 2,920 flight-days (=8 simultaneous flights per day for a one-day-snapshot × 365 days) to have 100% sampling coverage ( Palka, 2012 ). 11 The annual and temporal frequency distribution of flights can shed light on how well U.S. waters were sampled to detect DAMs and therefore provide additional right whale protection beyond the static right whale management areas.
Right Whale Data
For the United States Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico, Roberts et al. (2016) integrated 23 years of aerial and shipboard cetacean surveys, linked them to environmental covariates obtained from remote sensing and ocean models, and built habitat-based density models for 26 species and 3 multi-species guilds using distance sampling methodology. The density maps for these regions are the first to be published in the peer-reviewed literature. We use the monthly right whale density maps supplied by Roberts et al. (2016) to quantify the total right whale population within our spatial-temporal strata ( W ta for month t , area a ). The aggregate monthly data are static across years and are based on survey effort from 1998 to 2017, and therefore they do not represent the density of whales in a given area in a particular year ( Roberts et al., 2016 ; Center of Independent Experts, 2019 ). The right whale density map data was converted to the 20 km 2 vector grid, consistent with the aerial survey track lines.
Commercial Fishing Data
Data from several sources were used to provide an overall estimate of the spatial distribution of lobster fishing trips. In the northeast United States, NOAA-Fisheries collects VTR; these records identify northeast “lobster trap/pot” fishing trips. This is the only source for trip locations. For each trip (i.e., the “raw” data), a single location point is recorded to represent the place where the most hauls occurred for a trip. NOAA-Fisheries also collects first-point of sale data for federally managed fish from entities that buy fish directly from federally permitted fishing vessels; these data are referred as “dealer” data and include value and volume but do not include trip location. The Atlantic Coastal Cooperative Statistic Program collects “dealer” data for state permitted vessels and shares these data with NOAA-Fisheries. The NOAA-Fisheries “dealer” data used in this analysis includes both federal and state landings data. A common variable across all datasets is port of landing and weight of catch. The NOAA-Fisheries Greater Atlantic Regional Office’s vessel permit database identifies federally permitted vessels’ physical characteristics, such as horsepower, length and gross registered tons. We use the Atlantic Coastal Cooperative Statistic Program as an additional source of information to identify vessel characteristics for state permitted vessels.
We assume the NOAA-Fisheries dealer data are a census of lobster landings and VTR data are a subset of these data. The 2002–2009 NOAA-Fisheries dealer data contains roughly 94–100% of lobster landings as reported by the Atlantic State Marine Fisheries Commission (2018) . Trips recorded in the VTR are used to spatially allocate dealer landing not recorded in the VTR to six different port groups (see Figures 2 , 3 for location of port groups). This provides data to estimate the overall spatial and temporal distribution of trips for the American lobster fishery.
In 2002, the NOAA-Fisheries dealer data indicated that northern and southern Maine combined landed approximately 66% of the total lobster weight ( Table 1 ) while 34% was landed by the remaining southern port groups. The distribution was similar in 2009. The share of total lobster landings reported in the VTR ranged from high of 99–100% in New Hampshire to a low of 6–7% in northern Maine. Trips from northern Maine were largely allocated to the open area, as the majority of right whale management areas are adjacent to southern ports ( Figures 2 , 3 ). Since exclusion of northern Maine data would provide an incomplete picture of the scale and distribution of fishing trips within the lobster fishery, we include northern Maine dealer data despite the low VTR reporting rates.
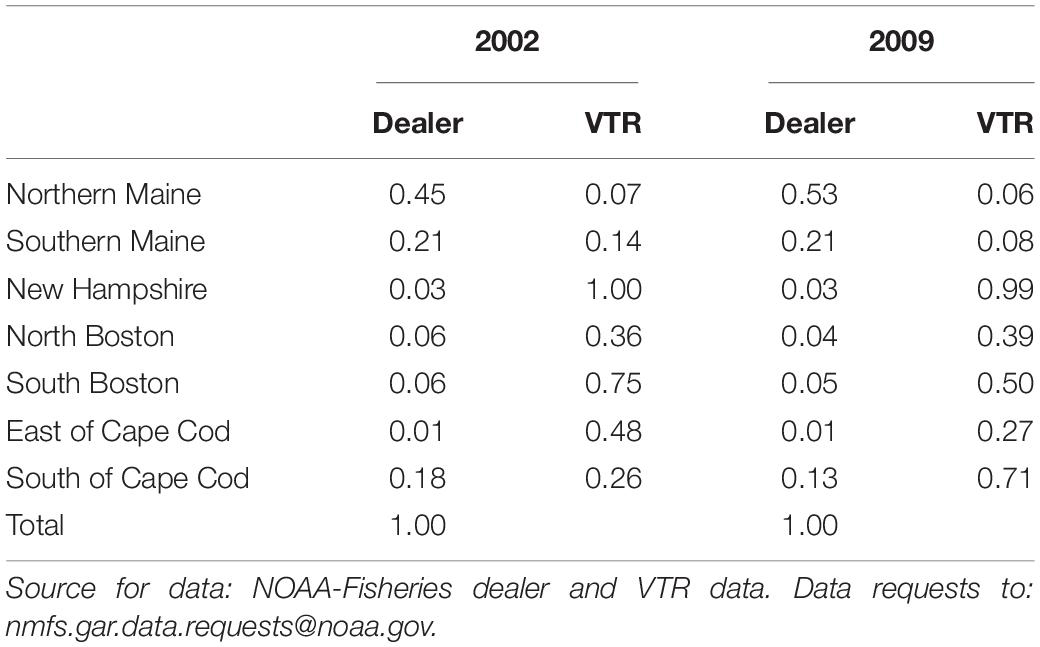
Table 1. The distribution by port group of total lobster landings (dealer), and the percent of landings for that port group in the Vessel Trip Report (VTR).
The large difference in VTR coverage by port groups would allow for finer spatial resolution for some (e.g., New Hampshire) port groups but not others (e.g., northern Maine). To accommodate this difference in data resolution, the spatial stratification chosen for fishing areas is at the level of right whale management area (i.e., dynamic, static, closed) and open (i.e., remaining area with general lobster gear requirements). Trip, the decision point for every harvester, is our unit of fishing effort for this analysis. We estimate trips by year y, month t , port group p , and fishing area a for each year; we then sum over port groups to estimate fishing effort, E y ta . Fishing area a is either a dynamic, static, closed or open management area. Details on E y ta calculations can be found in the Supplementary Section 2 . 12
In the northeast, the total number of lobster trap/pot fishing trips ranged between 210,320 and 284,951 between 2002 and 2009, using the combined VTR and Dealer data ( Table 2 ). Total landings range between 32,603 and 45,026 metric tons, while revenues range between $324.4M and $457.1M (US$2012). New Hampshire and north Boston port groups fished as much as 6.6 and 6.2% of their annual lobster trips in right whale management areas in later years, respectively. See Supplementary Table 2 for the total number of fishing trips by port group and the percent of trips in right whale management areas.
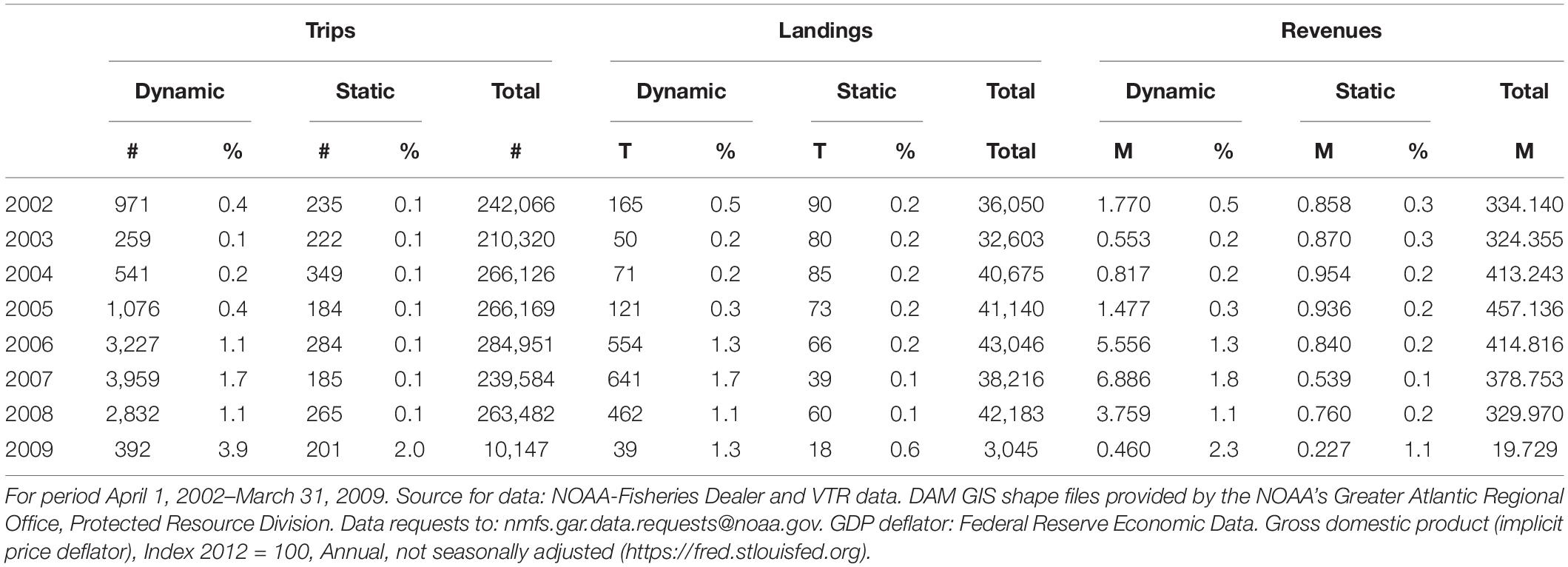
Table 2. Total trips, landings (metric tons) and landed value (revenues in millions of US$2012) and percent of total for the Dynamic Area Management (DAM) zones, the static whale-modified-gear areas and for entire area north of 40-degree north latitude from shore east to the Exclusive Economic Zone.
A relative risk of entanglement index (RREI) is calculated to allow spatial-temporal comparisons of potential non-monetary benefits of right whale management areas between 2002 and 2009. We develop an optimization model using closures to compare the cost frontier for alternative management decision rules (benefit-ranking vs. cost-effectiveness) to reduce the risk of entanglement.
Estimating Risk of Entanglement
Entanglement risk is jointly determined by the co-occurrence of gear and whales in the water in time and space, and the potential impact of the gear on whales. Following from others ( Wiley et al., 2003 ; Vanderlaan et al., 2011 ; Farmer et al., 2016 ; Brilliant et al., 2017 ), we use fishing effort and whale presence within an area to develop a risk of entanglement. We measure whale presence in terms of number of whales per grid cell (20 km 2 ) based on Roberts et al. (2016) . Comparisons are made between right whale management areas (static and dynamic) and the open area. 13
The risk of entanglement (RE) is the product of the number of whales and the density of trips. We use trips as a first proxy for vertical lines in the water. 14 An important risk factor is gear lethality ( Vanderlaan et al., 2011 ), although there is no scientific data to support parameter estimates of the impact on whales of alternative gear designs. Thus, for this first estimate of risk, we assume a homogenous gear configuration within a given time and area, such that the relationship between trips and lines is exact. The density of fishing trips is used as a proxy for the likelihood of a whale interaction with gear, where density is the number of trips divided by the total km 2 for the relevant area ( E y t a K m y t a 2 ), y is year, t is month, and a is area. We assume “a single line” in the water in different times and areas presents the same level of risk to whales. 15 In Roberts et al. (2016) monthly whale numbers, W_t are constant, however, the spatial temporal placement of DAM zones varies over the years resulting in a change in the number of whales ( W yta ) within a zone, as well as fishing effort ( E y t a ). The distribution of trips and whales is assumed uniformly distributed within a stratum. Here we estimate a risk of entanglement (RE y t a ) for any time-area, by assuming it is proportional to the product of the number of whales at risk ( W yta ) and the likelihood of a whale interaction ( E y t a K m y t a 2 ).
To make comparisons between management areas which differ in size, a RREI is calculated. The RREI is normalized 0–1, to the maximum RE yta , the open area in July 2006 (i.e., RREI y t a = RE y t a /RE 2006, 07 , open ). This provides a relative measure between months and areas against this base. Changes in the RREI provide a consistent proxy for the potential non-monetary benefits of risk reduction of alternative right whale management measures.
Reducing Risk Under an Optimization Framework
The optimization closure model minimizes a management objective, subject to a set of constraints, and is solved using the R package “lpSolve” version 5.6.15 ( Berkelaar, 2020 ). Two management decision rules are considered, one based strictly on non-monetized benefits (“benefit-ranking”) and the other which considers costs and non-monetized benefits simultaneously (“cost-effectiveness”). For this illustrative model, a representative year was generated by averaging monthly data across years for number of whales ( W t a )and trip density ( E t a K m t a 2 ) for the risk calculation, creating an average risk profile for each month and management area type, which is assumed exogenous. While the size of fishing areas vary, size is implicitly imbedded in the calculation of cost and risk. 16
The expected non-monetary benefit of a closure is a reduction in entanglement risk (RE ta ), which is a function of density of fishing trips and whale numbers. The required level of overall risk reduction ( R ¯ ) is exogenously determined based on legal mandates (e.g., MMPA and ESA). Risk is reduced along a continuum between no expected change (i.e., Status Quo: R ¯ = 0 % ) to a complete reduction in risk (e.g., complete closure: R ¯ = 100 % ). This allows us to trace out a cost frontier. More formally, let x ta be the control variable. A complete closure ( x ta = 1) or partial closure (0 ≤ x t a < 1) directly reduces fishing effort with an opportunity cost ( c ta ) to fishery participants. 17 We assume fishing effort does not shift to other times or areas. 18 Mathematically our model is:
where 0 % ≤ R ¯ ≤ 100 % ; 0 ≤ x t a ≤ 1 (0 is open and 1 is fully closed); 0 ≤ α a ≤ 1; 0 ≤ β a ≤ 1.
We include a measure of the efficacy of whale-modified-gear (α a ) in reducing the risk to right whales where 1.0 indicates the whale-modified-gear is 100% effective at reducing the impact on the whale (e.g., rope-less gear) and 0.0 indicates that there is no change in the impact on the whale and thus risk is not reduced (i.e., no whale-modified-gear). 19 The rate of non-compliance (β a ) can also impact the efficacy of the whale-modified-gear. The net entanglement risk for a given time and area is ( RE ta )( α a )(1 – β a ).
In scenario 1 (“benefit-ranking”), a decision to close a fishing area is based exclusively on the non-monetary benefits of a reduction in entanglement risk. The objective is to minimize the number of closures ( c t a = 1) while simultaneously meeting the risk constraint ( R ¯ ). Under scenario 2 (“cost-effectiveness”), a decision maker is interested in minimizing the opportunity costs to the fishing industry ( c at ) while also meeting the risk constraint ( R ¯ ). For these two scenarios we assume closing an area eliminates risk of a gear-whale-encounter ( α a = 1) and there is zero non-compliance (β a = 0, i.e., full compliance). We then investigate in Scenario 3 the impacts of closures when gear-modifications (α) are already in place and non-compliance (β) is zero ( Table 3 ). In the absence of data on the efficacy of whale-modified-gear, we assume the required gear modifications in dynamic and static areas are more effective (i.e., assume α dynamic and α static both equal 0.9) compared to the general gear requirements in the “open” area as described in the “Measures to Reduce Right Whale-Fisheries Interactions” section (i.e., assume α open = 0.45). 20 Scenario 4 then considers non-compliance with whale-modified-gear requirements that is greater than zero (β = 0.6). In scenarios 3 and 4, the gear efficacy and non-compliance assumptions result in risk reductions occurring prior to running the optimization closure model. The cost frontier illustrates the total cost to industry compared to the total non-monetary benefits of a reduction in risk along the continuum between no expected change to a complete reduction in risk, for each of the four scenarios.
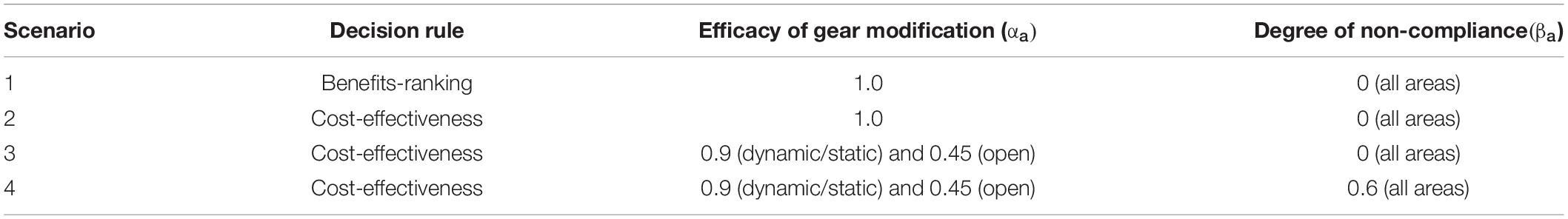
Table 3. Criteria for management decision rules in optimization framework, by scenario (Eqs. 1 and 2).
Public Sector: Detecting and Implementing DAMs
The degree to which DAMs could provide a reduction in risk to right whales was dependent on public investment in detection and the regulatory requirements for implementation. Of the 589 flight-days between April 2002 and March 2009, the NOAA North Atlantic Right Whale Sighting Survey detected right whale aggregations that triggered 66 DAMs with an average annual detection rate of 11% (=66/589) ( Table 4 ). Between 2002 and 2007, the annual DAM detection rate increased from 4 to 25%. 21 From a seasonal perspective, flights in November to March had the highest DAM detection rates; yet the frequency of flights was greatest from April to June.
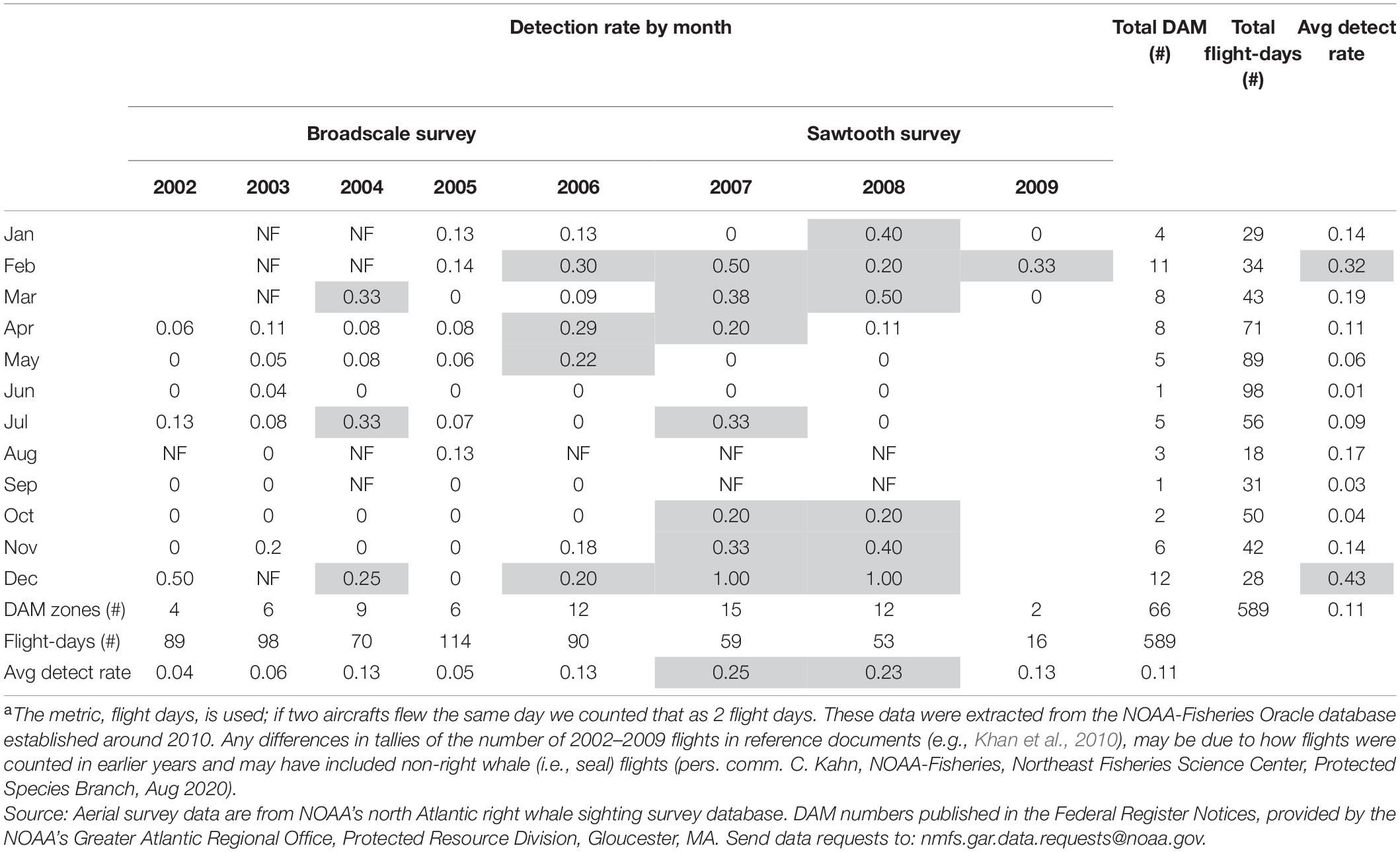
Table 4. The Dynamic Area Management (DAM) detection rate (=No. DAMs/No. flight-days) for broadscale and sawtooth survey methods by year and month. The total number of DAM zones triggered, North Atlantic Right Whale Sighting Survey flight days a and average detection rate (avg detect rate) across years and months. Shaded areas show detection rates of 20% or greater and NF = no flights.
The detection of DAM zones, designed to provide protection for large aggregations of right whales, was influenced by the sampling frequency. The aerial survey team flew 84 flight-days a year on average between 2002 and 2009 ( Table 4 ). Approximately 2.9% of the water was sampled on average in a year, based on the ratio of actual flight-days to number of flights required for 100% sampling (=84/2,920 flights). 22 Sampling varied by month. In May, the month with the largest percent of the population present in northeast U.S. waters ( Roberts et al., 2016 ), on average they sampled roughly 5.1% [=89 flights/7 years)/(8 flights/day × 31 days)] of the grid.
The speed at which a DAM can be implemented impacts its effectiveness in delivering right whale protection. The number of days it took to implement the DAM (12.8 days, CV = 0.21) was only slightly less than the number of days the DAM was in effect (14.9 days, CV = 0.25). Over the history of the DAM program, it took an average of 7.7 days ( CV = 0.36) from the day the DAM was triggered based on the date of the aerial survey, to the publication of the federal register notice. It took an additional 5.2 days ( CV = 0.38) on average, between the published Federal Register notice and the first day the DAM measures were implemented, as described in the notice. The data were insufficient to determine whether whales were still present during the implementation period (i.e., 12.8 days after trigger); flights over DAM zones after implementation were too limited to calculate any statistics.
Right Whale Management Areas and Distribution
The right whale density maps ( Roberts et al., 2016 ) indicate that more than 50% of the right whale population was in U.S. waters between November and June ( Figure 4 , stacked columns). The largest share of the total population is in the southeast United States during fall-winter (November to February), in the northeast United States in the spring (March to June) and outside U.S. waters in summer-fall (July to October).
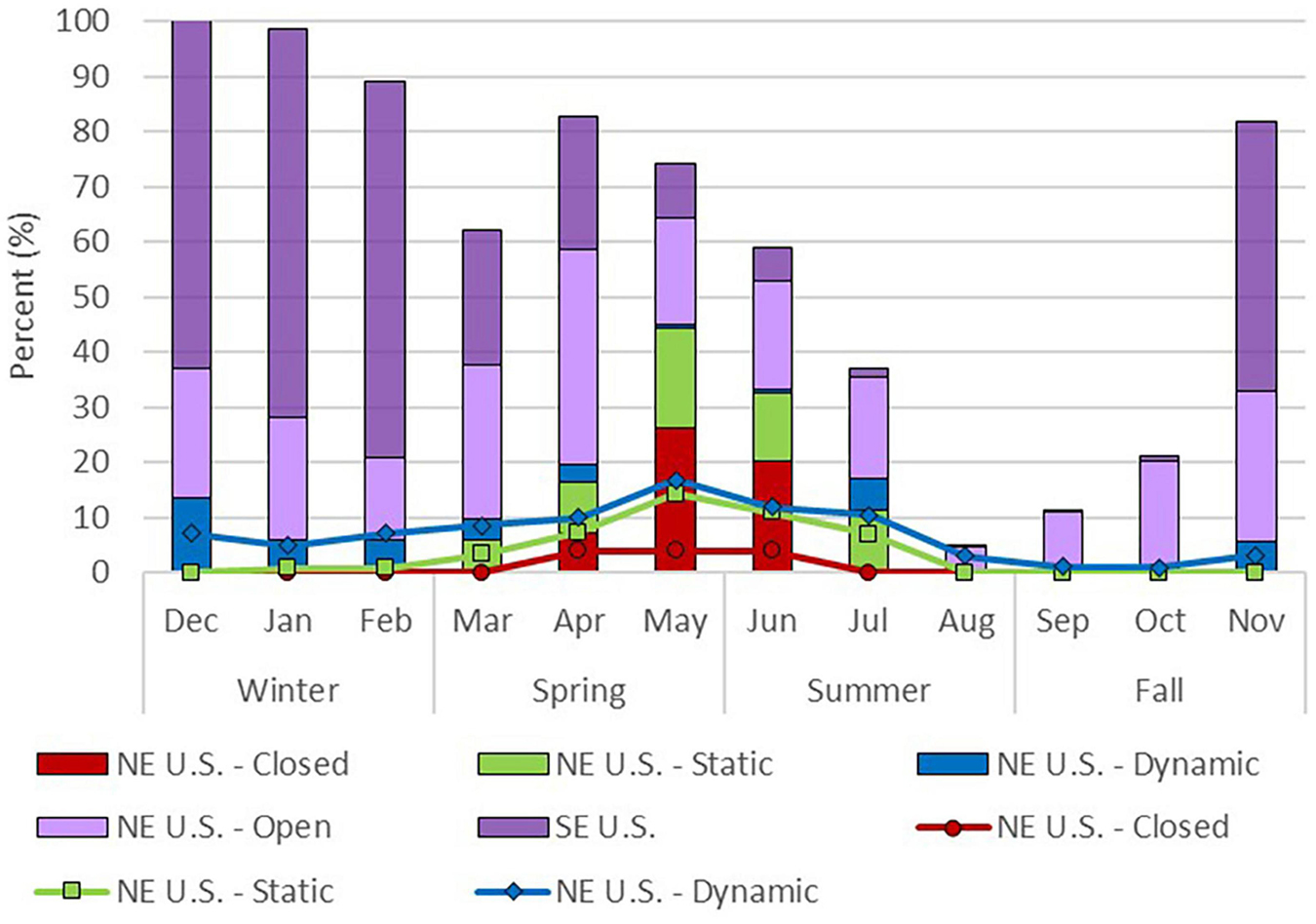
Figure 4. The spatial temporal distribution of right whale population estimates (stacked bars) are compared to the share of northeast (NE) waters (stacked lines) dedicated to right whale management areas (April 2002–March 2009). Distribution of the right whale population in U.S. waters by month (stacked columns) and northeast right whale management areas including dynamic (blue), static (green), closed (red), and outside northeast management areas (i.e., open, light purple), as well as southeast (SE) waters below 40 degrees N latitude (dark purple). As much as 95% of the population estimates (August) based on Roberts et al. (2016) are not in U.S. waters; these shares unaccounted for may be in Canadian waters. In addition, the share of northeast ocean waters north of 40 degrees N latitude (stacked lines), monthly average, shows shares by right whale management area including dynamic (blue), static (green) and closed (red); remaining northeast waters are classified as “open.” At the maximum, 17% of northeast waters are dedicated to right whale management in May on average.
Right whale management areas were spatially a small share of U.S. waters north of 40°N ( Figure 4 , stacked lines), yet a significant share of the right whale population was present in the management areas ( Figure 4 , stacked column). In May for example, on average 17% of the northeast area waters was dedicated to right whale management areas: 4% was closed to lobster fishing (i.e., Great South Channel), 10% was in static areas, and 3% in dynamic areas ( Figure 4 , stacked lines). During the same month, of the total right whale population, 26% was in the closed area (Great South Channel critical habitat), 18% in the static areas, 1% in dynamic areas, 19% in open northeast waters and 10% in the southeast waters ( Figure 4 , stacked columns). May is an example month where both avoidance and minimization strategies complement each other, and may have provided protection to 45% of the total population or 70% of the population in U.S. waters north of 40°N. 23
Fishing Effort and RREI
The DAM program may have created an economic incentive to whale-modified-gear to continue fishing in a DAM zone after it was triggered; this inference is based on increased fishing effort in DAMs, frequency of DAMs, and spatial overlap of zones. Between 2003 and 2008, years with complete data, the number of DAM zones varied from 6 to 15 with the maximum in 2007 ( Table 4 ), and exhibited a high degree of spatial overlap ( Figure 3 , hatched areas). During this period, the share of total trips in DAMs increased from 0.1% to as high 1.7% in 2007 ( Table 2 ). 24 The commercial fishing data show an increase in trips, landings and revenues within dynamic areas over time in both absolute value and share of total. Compared to dynamic areas, activity in static areas was lower, despite their larger spatial extent, and effort was more consistent. Much of the area within the static areas (e.g., Figure 3 , SAM East) is farther offshore in federal waters compared to the location of dynamic areas, so fewer vessels would be able to access these fishing areas.
The potential for dynamic areas to mitigate risk was highest in November to February ( Table 5 ). Risk in dynamic areas accounted for 27% of the average risk for December, which may have been mitigated with whale-modified-gear, a minimization strategy in the mitigation hierarchy. The total average monthly RREI was highest in the fall (Sept-Nov) followed by the summer (Jun-Jul) ( Table 5 and Figure 5 dashed line). Yet the percent of the right whale population present in the northeast is highest in the spring, from March to July ( Figure 5 solid line), signaling the influence of fishing effort in risk ( Figure 5 stacked bars). In some months, such as May and August the RREI value is equivalent, while the number of lobster trips ( Figure 5 stacked columns) and the percent of right whale population present ( Figure 5 solid line) have an inverse relationship.
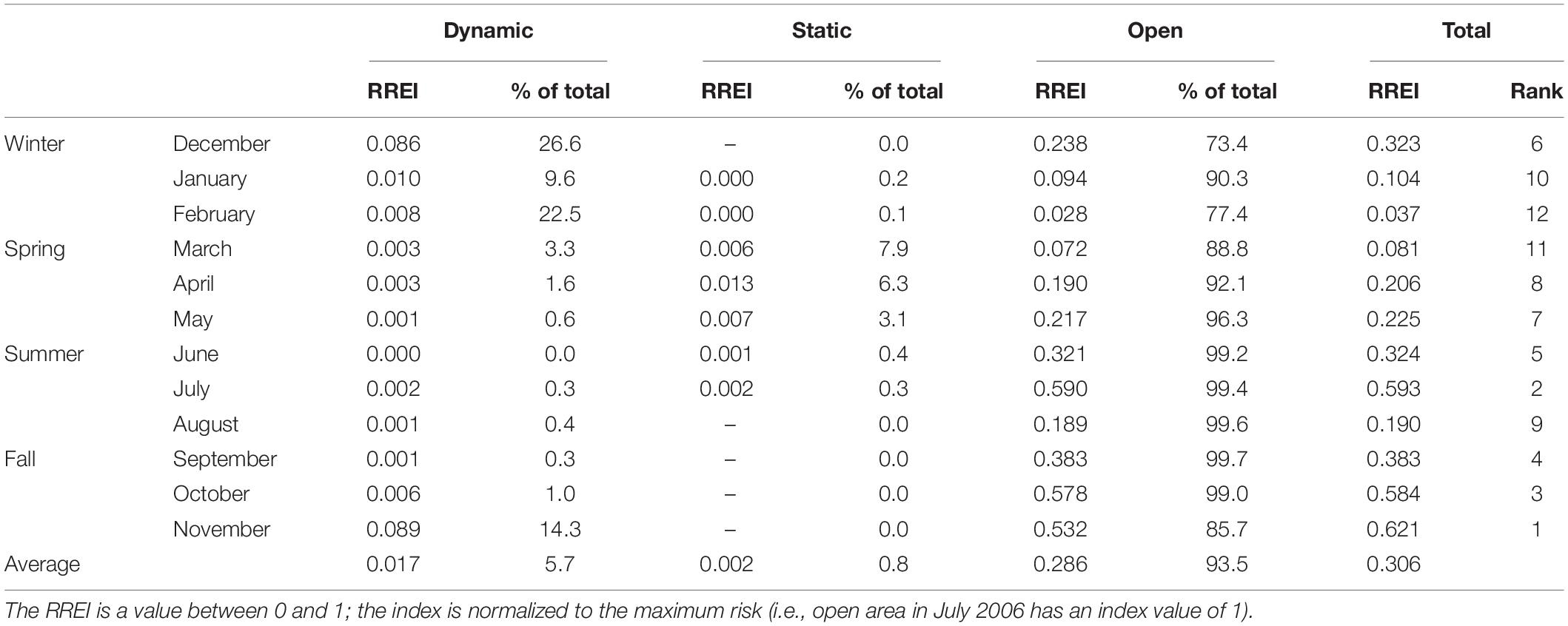
Table 5. Average monthly Relative Risk of Entanglement Index (RREI) for dynamic and static whale-modified-gear management areas, open areas, and total for the area north of 40-degree north latitude from shore east to the Exclusive Economic Zone, for April 2002 to March 2009.
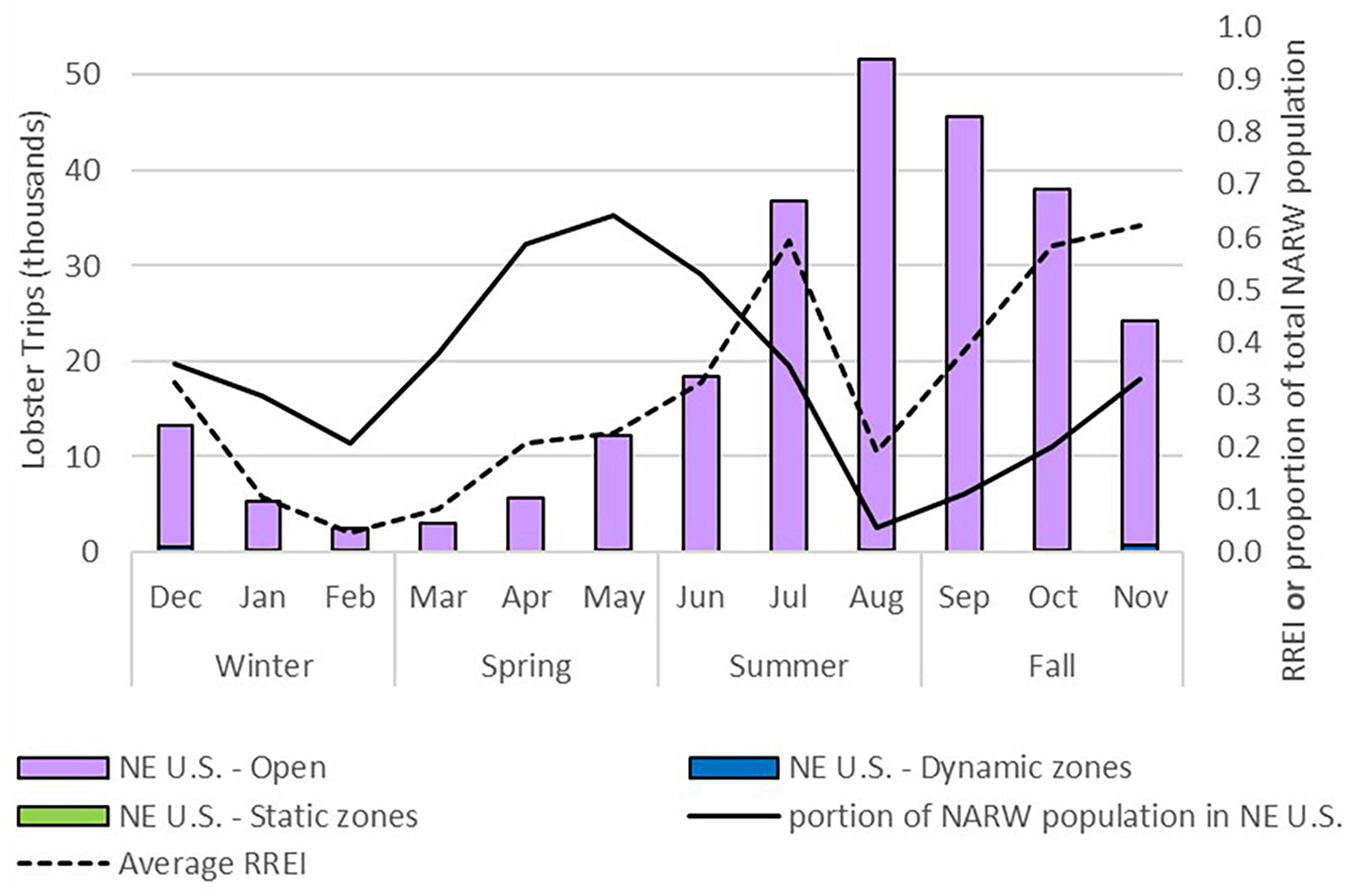
Figure 5. Spatial temporal distribution in the northeast U.S. waters of the percent of the north Atlantic right whale population present (solid line, right axis) ( Roberts et al., 2016 ), lobster fishing effort (trips, stacked columns, left axis) and the average relative risk of entanglement index (RREI, dashed line, right axis) by month (April 2002–March 2009). The average number of trips are by right whale management areas. The RREI is a consistent, relative measure of risk between areas and months with a value between 0 and 1; the base is the “open area” in July 2006 which has an index value of 1.
Optimization: Reducing Risk at Lower Cost
The optimization results illustrate how different decision rules can attain equivalent non-monetary benefits of risk reduction with different opportunity costs to industry. 25 Costs are consistently lower under the “cost-effectiveness” decision rule (scenario 2) as compared to the “benefit-ranking” decision rule (scenario 1) except for the two extreme endpoints ( Figure 6 solid lines). For example, under the “benefit-ranking” decision rule a 60% reduction in risk results in a cost of roughly 60% of average revenues vs. 40% of revenues for an equivalent reduction in risk under the “cost-effectiveness” rule. The solution paths also differ ( Table 6 ) in how the 60% risk reduction is achieved. For example, under the “benefit-ranking” rule four to five big open areas with high risk are the first to close. In contrast, under the “cost-effectiveness” rule, 20 smaller static and dynamic areas are closed, as these areas have a lower ratio of cost to non-monetary benefits ( Table 6 ). Each unit of risk reduced was achieved at a lower cost under the “cost-effectiveness” rule ( Figure 6 ). Consider May and August where total risk is somewhat equivalent ( Figure 5 and Table 5 ). Clearly the cost to reduce a unit of risk is much higher in August (low whales and high fishing effort) compared to May (high whales and low fishing effort). This leads to May being closed before August in all scenarios.
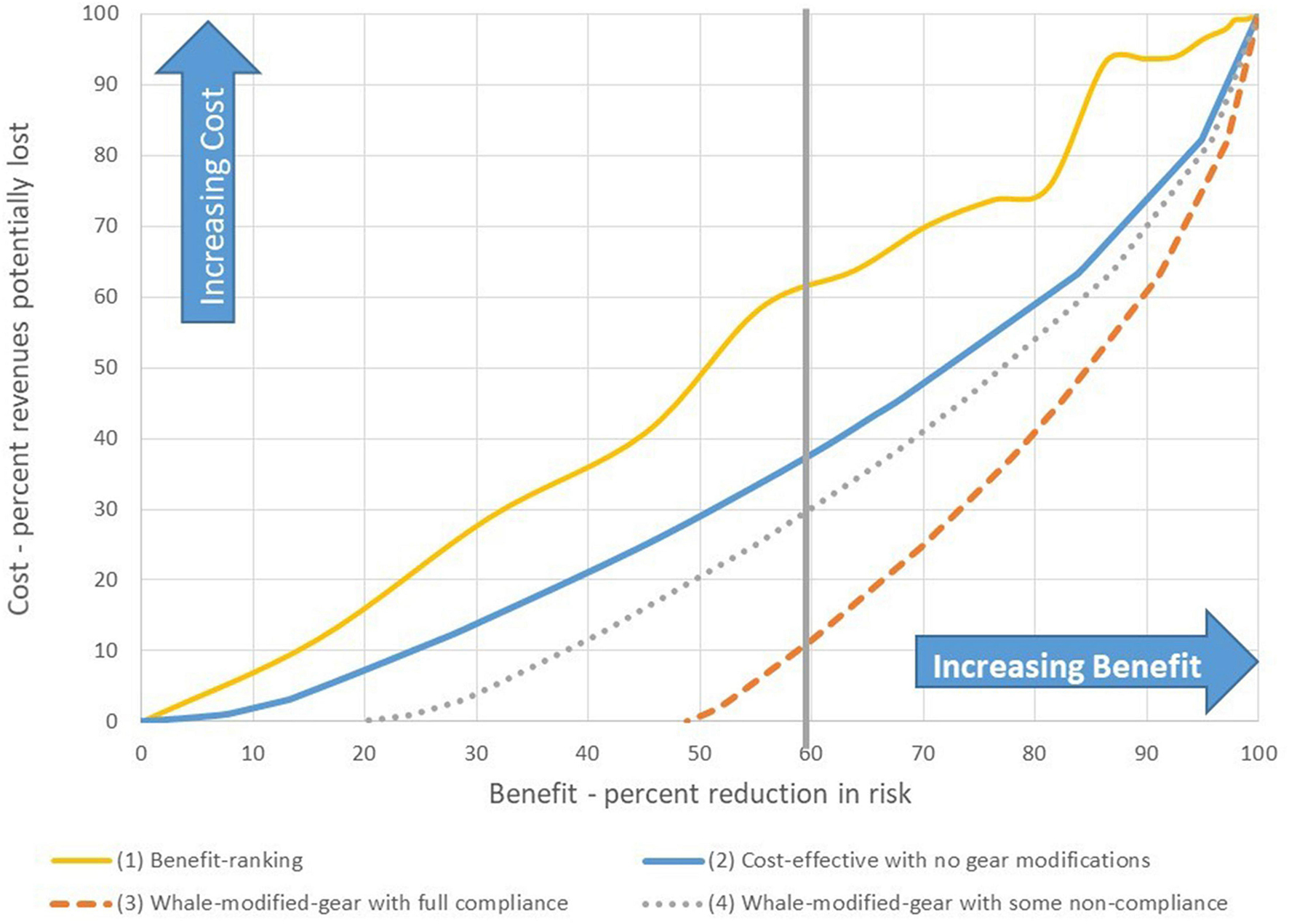
Figure 6. Optimization results of trade-off between the non-monetary benefit of risk reduction and potential cost of closing months and areas (i.e., avoidance) along a continuum of no change (i.e., status quo, R ¯ = 0 % ) to a complete reduction in risk (i.e., complete closure, R ¯ = 100 % ). Scenarios ( Table 3 ) include: (1) benefit-ranking with no gear modifications, (2) cost-effectiveness with no gear modifications, (3) cost-effectiveness with whale-modified-gear requirements and full compliance, and, (4) cost-effectiveness with whale-modified-gear requirements and some non-compliance.
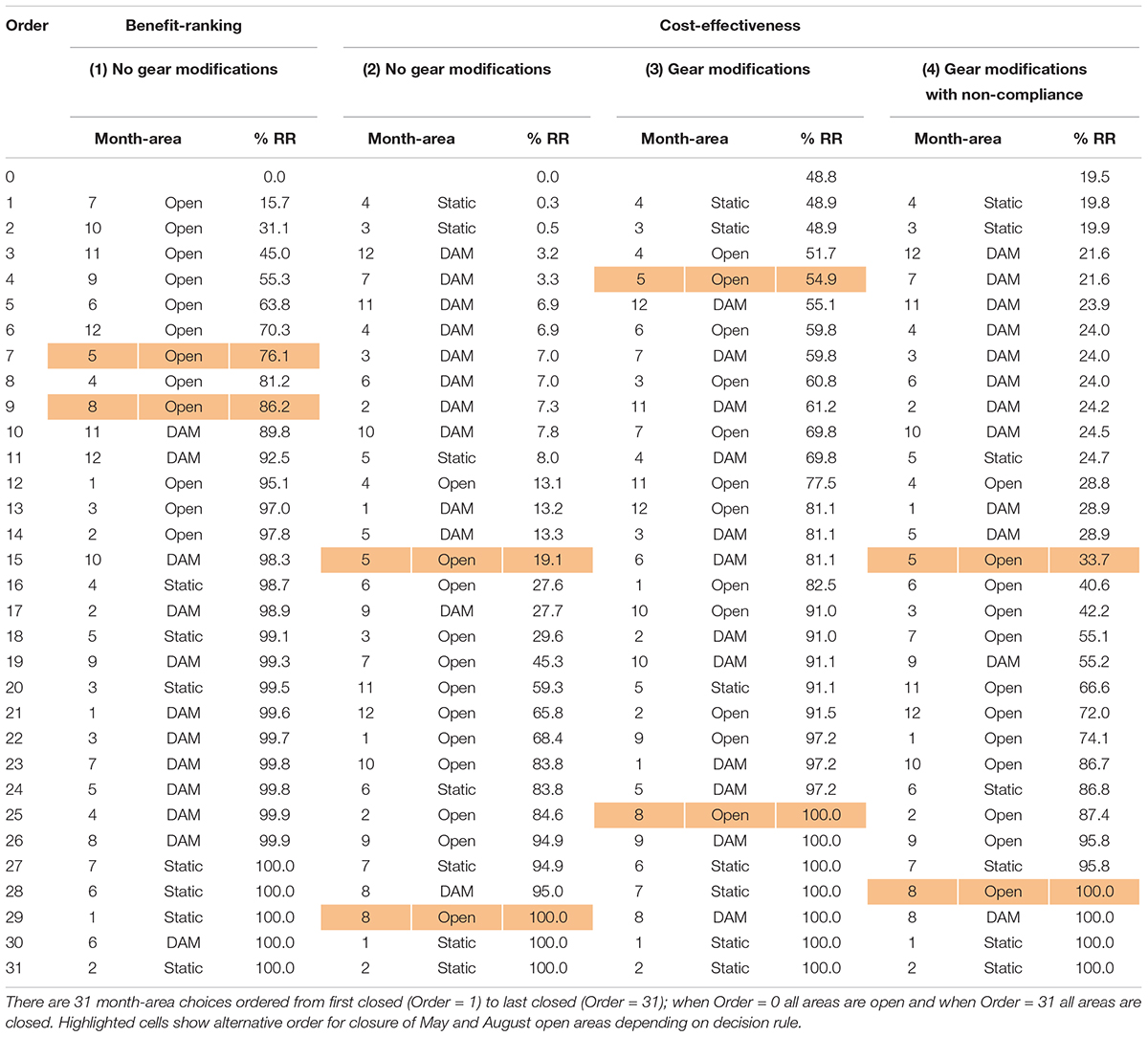
Table 6. Optimization results showing the solution paths with the cumulative percent reduction in risk (% RR) moving from no change (i.e., status quo, R ¯ = 0 % ) to a complete reduction in risk (i.e., complete closure, R ¯ = 100 % ) for scenarios 1–4.
Continuing with the “cost-effectiveness” decision rule, we introduce whale-modified-gear (scenario 3), a minimization step in the mitigation hierarchy. By requiring fishermen to use whale-modified-gear and given our gear efficacy assumptions ( Table 3 ), the risk of entanglement is immediately reduced by 50%, prior to any closures and assuming full compliance (scenario 3), but by only 20% in the case of non-compliance (scenario 4) ( Figure 6 dotted lines). Under these scenarios, to then reach a total reduction in risk of 60%, requires closure costs equivalent to about 10 and 30% of industry revenues, under compliance and non-compliance, respectively. Our example illustrates that when there is non-compliance there may be an economic incentive to first address the compliance issues with the existing gear requirements, rather than implementing additional measures, such as new whale-modified-gear requirements or closures to achieve the desired risk reduction. 26
When developing a list of management alternatives, the U.S. marine mammal Take Reduction Team process relies on stakeholder consensus to balance the need to reduce marine mammal takes and implicitly minimize economic impacts on fishermen ( Young, 2001 ). However, the assessment of costs, though informally addressed by stakeholders during the process (M. Asaro, pers. comm. October 9, 2020), are not formally considered until a small set of alternatives is identified and then ex-ante cost-effectiveness or cost-benefit analyses are conducted for regulatory purposes. As the optimization model illustrates, and economic theory predicts, a cost-effective solution can yield a given level of risk reduction for a lower cost than a decision based only on risk reduction. For a 60% reduction in risk from the status quo ( Figure 6 ), the potential costs to reduce risk were as much as 20% lower under a decision rule that considered fishing industry opportunity costs and non-monetary benefits simultaneously (i.e., cost-effectiveness, scenario 2), as compared to a decision rule based only on the benefits of risk reduction (i.e., benefit-ranking, scenario 1). This empirical example highlights the need to integrate economic considerations throughout the management process.
A least-cost implementation approach of the bycatch mitigation hierarchy ( Squires and Garcia, 2018 ; Squires et al., 2018 ) suggests that combining mitigation steps, such as was done in the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan with avoidance and minimization measures, could further reduce economic waste and support optimal conservation when both costs and benefits are considered. Theoretically, it is possible to solve for an optimal mix of policy instruments (avoidance and minimization) which is when the marginal cost between and within mitigation hierarchy steps equates, yielding a least-cost solution for a desired risk reduction. While briefly explored in the optimization (scenario 3), the lack of information on the effectiveness of minimization policy instruments limits the conclusions that could be made. Additionally, we suggest the uncertainty associated with effectiveness of alternative management measures be included formally in the decision framework. We discuss this in more detail in our fifth recommendation.
The DAM program with whale-modified-gear, a minimization measure, was anticipated to be a lower cost alternative than the closure of the DAM zones, an avoidance measure ( National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), 2003 ). This could not be evaluated due to voluntary nature of most closures and the short timeframe for the closure-based version of the program. However, the case study did identify a number of strengths of the dynamic program which can assist in the design of future mitigation measures. A major strength was the program’s ability to be a flexible instrument that provided protection in response to inter-annual variability in whale density, as demonstrated by the distribution and frequency of the DAM zones. The dynamic measures may have provided incremental protection during the “shoulder” months (i.e., November to February) prior to the protection provided by static management areas in the spring. The dynamic and static measures combined may have reduced the total risk by 6.5% on average ( Table 5 ), even with their small spatial footprint ( Figure 4 stacked lines). There was substantial spatial overlap of DAM zones over the years ( Figures 2 , 3 ) and the share of total fishing effort within these zones increased over time ( Table 2 ), suggesting the DAM program did not reduce fishing opportunities. Ongoing aerial surveys were required to ensure that aggregations of whales were detected and protected outside SAM and critical habitat areas. Those surveys are useful for analysis of habitat use, provide important sighting information to the Catalog and Sightings Database, and give valuable support to the disentanglement program ( Reeves et al., 2007 ). The DAM program also proved flexible in responding to a potential safety problem for fishermen, who could be required to remove large quantities of fixed gear on short notice in poor weather ( Reeves et al., 2007 ). By allowing whale-modified-gear and shifting to a minimization measures in 2003 the safety concern was eliminated. And while the DAM program was intended to be a temporary measure while broader gear requirements were designed and implemented ( Borggaard et al., 2017 ), it may have provided an economic incentive for some fishers to convert to whale-modified-gear as the frequency and spatial overlap of DAM zones grew. This in turn would have reduced the cost to implement the broad-based measures in 2009.
Our study highlights some of the challenges and tradeoffs associated with the critical and increased responsibilities of the public sector to implement a dynamic management program ( Grantham et al., 2008 ). While monitoring is required to support dynamic protection measures, such as the DAM program, it is also required for stock assessments, and to assess compliance with, and efficacy of the management measure—all public sector responsibilities. The protection delivered by DAM zones hinged on the United States government budget allocated to the NOAA-Fisheries aerial survey team for right whale detection flights. About 3% of the spatial-temporal Bay of Fundy/Gulf of Maine grid was sampled annually on average, although flights were not consistent spatially or temporally ( Table 3 ). Additionally, return flights (i.e., fly backs) to designated DAM zones were sparse and did not allow an analysis to determine if the whales were still present in DAMs despite the delay in implementation. Further, data to estimate compliance was not available. For other species, such a harbor porpoise, the observer logs provide information to estimate gear efficacy; however, this was not the case for right whales. The Northeast Fisheries Observer Program logs for gillnet and trap/pot fisheries were not modified until 2007 to capture the information required to calculate compliance rates by area for different gear modifications (e.g., weak links) and low observer coverage lead to low sample sizes ( National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2012 ).
To manage the risk, it is critical to recognize the RREI was similar in some months when there were inverse levels of fishing effort and whale presence. While in some months as much as 70% of the population in the northeast may have been protected by the combined right whale management areas ( Figure 4 ), the majority of the risk remained outside these areas and times. Fishing effort and whale distribution need to be considered jointly to reduce risk, the data on both were, and continues to be, a barrier to analysis. For our study, data related issues do limit our ability to evaluate with precision and accuracy the performance of the DAM program and other right whale management areas. However, the results of the optimization model and some general results are invariant of the data issues; this includes conclusions regarding aerial surveys, time to implement the DAMs, temporal distribution of landings and fishing effort, the reduced cost of implementing risk reduction measures to the fishing industry under a cost-effectiveness vs. a benefit ranking decision rule and that most importantly, most of the risk was outside right whale management areas for the study time period. The data related issues we encountered continue to exist (i.e., sparse spatial data for northern Maine and the constant monthly right whale density estimates). Still the lack of data (and ensuing uncertainty) does not take away from the utility of doing this modeling as long as the inherent biases and impacts on results are taken into account. Conservation decisions need to be made now, vs. waiting for new or perfect data. Although, characterizing parameter, process and/or model structural uncertainty could improve information for management decisions ( Geary et al., 2020 ).
A critical input parameter to our relative risk index is fishing trip density. The lowest coverage of VTR trips is for the northern Maine port group, which accounts for almost 50% of landings; this could bias our estimates of risk. To address this issue we chose a larger spatial stratification scale (i.e., right whale management area) to avoid overstating the results or giving the end-user an excessive sense of precision or accuracy. Consequently, most of the trips for northern Maine were allocated to the open areas ( Supplementary Table 2 ). To investigate how these data could bias our observations about the performance of right whale management areas, we tested excluding northern Maine fishing effort. 27 The test result suggested right whale management areas would have a greater impact on reducing risk (i.e., 12.6% annual reduction vs. 6.5% with northern Maine). However, including the data for northern Maine allows for a more complete estimate of risk and captures the seasonality relationship between whales and lobster fishing effort.
The main focus of our work is to examine fishing effort controls that were in place through 2009 with whale density treated as exogenous. Since the density maps are based on survey effort from 1998 to 2017, they do not reflect risk for any one-time period and we include this critical input parameter as a point estimate. We recognize the empirical estimates of the relative risk index would differ by including the variance of density of whales (and fishing effort). However, this exploratory study was not intended to provide tactical management advice, and in recognition of limited resources and simplicity, we did not incorporate this uncertainty. We expect general observations will not change with this decision, for example, the seasonal distribution of whales (and fishing) given the short period of our analysis, 2002–2009, are unlikely to change. 28 Appreciating the fact that uncertainty in whale density estimates is critical for tactical management decisions, further implementation of this model would need to take this into consideration. For instance, in recent years, there appear to be fairly large shifts in the distribution of whales; developers of the maps plan to create two density maps for separate time periods ( Center of Independent Experts, 2019 ). At this point in time we do not have annual density maps which would reveal inter-annual variability in monthly density estimates, although the variance reported in the current density maps does reflect this to some degree.
In terms of our optimization model structure, the use of large spatial strata allows us to make the assumption that fishing effort disappears when an area is closed. When large fishing areas are closed (i.e., open ocean) this effectively eliminates fishing opportunities for that month as alternative spatial fishing opportunities are limited. Whereas, when smaller dynamic and static areas are closed ( Table 2 ), the effect of this shift in fishing effort to the large open area has negligible impacts on relative risk index values. Recognizing that a harvester behavior model is critical for management decisions, a fuller implementation of the framework would require a finer spatial scale and allow uncertainty to be introduced. With a finer spatial scale, revenue differences between the two decision rules may decrease, however, it would remain an empirical question. Input parameter estimates of gear efficacy and compliance in our model were provided to demonstrate how they can impact risk reduction targets if not considered. While data can be collected for compliance, methods, such as expert elicitation may be necessary to estimate gear efficacy parameters since data do not currently exist.
Going forward, first, we recommend DAM programs be included for consideration in the suite of policy instruments for protection of large marine mammals, such as right whales. The U.S. DAM program provided a greater level of risk reduction than static management areas despite the small spatial and temporal extent of the zones. However, for dynamic management to be effective, measures must be able to be implemented quickly, responding to real-time information ( Hobday and Hartmann, 2006 ). Lengthy delays between sightings and implementation of United States DAM zones likely reduced protection provided to whales. Yet, mandatory changes can be implemented quickly in some regulatory systems. In Canada for example, within the “dynamic zone” in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, an area is closed on the day a whale is detected and notice through the Fisheries Notice system can require gear removal within 48 h. 29 Alternatively, voluntary dynamic measures may provide protection faster than mandatory measures. Under the voluntary speed reduction zones used to reduce the risk of ship strike mortality in the United States Dynamic Management Areas, a message is immediately sent to an industry contact email list once boundaries have been identified. The United States Coast Guard broadcasts the coordinates to mariners on the NOAA weather radio, and the media is contacted (73 FR 60173, October 10, 2008); this communication speed increases the degree of potential risk reduction from the action. While participation in voluntary measures can be limited (e.g., Silber et al., 2012 ), high participation has been demonstrated for a noise reduction strategy in Vancouver, Canada ( Fraser River Port Authority, 2019 ) where a reduction in port fees incentivized participation. 30 A growing literature on voluntary approaches is helping to identify the conditions to influence success ( Segerson, 2010 ), and positive incentives or the threat of regulatory measures can influence participation ( Bisack and Clay, 2020 , 2021 ). Understanding the conditions necessary for high participation should assist in determining whether incentives should be positive or negative.
Second, we recommend additional targeted research on the economics and norms (i.e., social, cultural, and legitimacy) of key fisheries, both in the United States and Canada, in addition to the ongoing biological research on the species. The issue of right whale entanglement is transboundary and extends along much of the Atlantic coast of both countries and overlaps with numerous fisheries, governance structures, and cultures. A single policy instrument (e.g., modified gear) is unlikely to fully address the issue. Understanding how harvesters’ respond to different instruments, such as closures (e.g., Smith and Wilen, 2003 ; Powers and Abeare, 2009 ), and the impact of the governance structure on the daily choices of fishermen, will assist in the design of policies that consider the associated incentives and disincentives ( Squires and Garcia, 2014 ). Additional solution pathways may also emerge by simultaneously modeling the economic benefits that can be attained by the lobster fishery under different lobster regulations. This will require an understanding of the yield of the resource stock, costs of harvesting the resource, and market demand models ( Richardson and Gates, 1986 ; Ardini and Lee, 2018 ), along with the implications of climate change and geographic shifts in lobster stocks ( Goode et al., 2019 ). From a management policy perspective, it is important to understand these relationships to steer clear of implementing measures that could unknowingly shift fishing effort into time-areas with a high density of right whales.
Third, we recommend that the collection of compliance data be included in the design and monitoring requirements for all regulations, even temporary regulations, such as the DAM program. While the Plan included enforcement to deter non-compliance along with outreach and education for compliance promotion ( National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2012 ), data that could be used to estimate compliance were not collected until the program was in its fifth year. Failure of current policy instruments to meet marine mammal management outcome goals cannot always be fixed with new instruments, and it is critical to understand if the goals of a policy instrument are being impeded by non-compliance. When assuming full compliance, the reduction in risk can be overestimated (i.e., scenario 3 vs. scenario 4). Compliance can be improved through enforcement with associated public sector costs, but alternative mechanisms exist. For example, cost-effective management may leave more revenues in the lobster fishery compared to benefit-ranking, which takes the economic needs of the entire lobster industry into account and may increase compliance. As well, incentives can influence choices people make on a daily basis, acting as what behavioral economics calls a “nudge” ( Thaler and Sunstein, 2010 ; Mackay et al., 2018 ). There is some evidence that compliance increases with at-sea observers, which in the United States do not perform any enforcement function but may provide such a “nudge” to increase compliance ( Bisack and Das, 2015 ; Bisack and Clay, 2020 , 2021 ), although with an increase in public sector costs. However, other tools, such as taxes and subsidies ( Squires and Garcia, 2014 ) and normative factors, such as social influences within a community ( Mackay et al., 2018 ) may also influence compliance choices, suggesting areas for further research.
Fourth, we recommended right whale detection sampling regimes be evaluated for the trade-offs between public and private sector benefits, costs and outcomes. Monitoring of both the species and harvesters is critical to evaluation of success or shortcomings of management measures. Identifying cost-effective resource allocations for right whale detection for management (e.g., flights for protection and/or stock assessments) could improve the performance of right whale protection measures given limited public sector funding envelopes. The outstanding question is, what is the optimal investment in right whale scientific data collection to support recovery? A simulation-based analysis that incorporates uncertainty and a cost-benefit framework of public and private sector trade-offs for right whale protection would allow for an evaluation of the economic value of scientific information for right whale protection. These types of analyses may identify incentives for the private sector to financially support some of scientific data collection costs currently carried by the public sector ( Bisack and Magnusson, 2014 ).
Finally, we recommend that the uncertainty associated with effectiveness of alternative management measures be considered when identifying an optimal mixed of policy instruments within the least-cost mitigation hierarchy framework. This is particularly relevant when there are very different levels of uncertainty associated with the different policy instruments. For example, the effectiveness of reducing risk with avoidance measures is known; if fishing effort is removed completely from an area, the entanglement risk for that area goes to zero (point estimate) with zero uncertainty (variance). However, for minimization measures, such as whale-modified-gear, where information on risk reduction is not available, there is no measure of uncertainty (i.e., variance). Uncertainty around risk can be decomposed into uncertainty around the presence of the species of concern (i.e., right whales), the threat (i.e., different gear configurations), and the mitigation methods (i.e., effectiveness of different policy instrument choices). The precautionary approach advocates a conservative management decision with priority to the resource when there is uncertainty ( FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization), 1996 ; Hildreth et al., 2004 ). In evaluating the mix of instruments, a benchmark for an acceptable level of uncertainty (variance) around total risk could be established, with the benchmark lowered for endangered species, such as right whales. A lower variance benchmark around risk reductions may result in more avoidance policy instruments rather than minimization policy instruments within the least-cost framework than would be the case otherwise.
This case study evaluated the reduction in risk provided by dynamic and static right whale management areas. Strengths identified included the year round operation of the DAM program and its flexibility to provide additional protection to occasional aggregations of right whales beyond the static areas, where they aggregate year after year. The extensive spatial distribution and repeated overlap of the DAM zones may have incentivized adoption of the whale-modified-gear. To improve the future performance of dynamic measures, we recommend the consideration of voluntary measures, additional social science research of relevant fisheries, the collection of compliance data, evaluation of detection sampling regimes, and consideration of the uncertainty within a least-cost mitigation hierarchy framework.
Despite the potential benefit of the DAM program for right whales, it is not possible to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the program due to a lack of linkage to goals and the absence of key information. The goals of the DAM program were wrapped into the larger goals of the Plan and were defined in terms of outcomes for right whales, with the link to the managed entity (i.e., fishers), not clear. The presence of marine mammal and fishing activity need to be jointly identified to manage reductions in entanglement risk and move toward more cost-effective management options. For a full evaluation, public sector cost must also be considered. The implementation of the DAM program required a high degree of sustained effort by the public sector that likely could not have been sustained indefinitely. However, there may have been additional benefits of the program and the circumstances may have changed. The DAM program reduced economic impacts on private sector harvesters in comparison to extensive closures and potentially provided supplemental protection to right whales. The high public cost of the DAM program may have been, in part, due to the era in which it was implemented. Costs today could be lower. Technological advances have yielded additional detection methods (e.g., passive and glider-based acoustics, etc., see Goulette et al., 2021 ) and strengthened computational methods (e.g., methods to integrate and assimilate data from the multiple detection methods), which can support improved dynamic decision support tools (e.g., Lewison et al., 2015 ; Welch et al., 2019 ).
This research provides important insights into the potential for dynamic management to support far-ranging marine protected species, such as right whales and other large cetaceans, while also raising the need for a larger research agenda to consider tradeoffs between the public and private sectors ( Lewison et al., 2015 ). Protection and recovery of transboundary right whales requires a multi-disciplinary and comprehensive consideration of multiple policy instruments, multiple fisheries, multiple detection methods, economic tradeoff considerations, and multiple governance structures ( Kitts et al., 2021 ). Biological, economic or social research in isolation is bound to miss key considerations, and potentially lead away from, rather than toward, second-best policy options. Bringing these components together within predictive, dynamic models of behavior of the harvesters, whales and lobsters could help steer the discussions and provide a solution path that is critical to the protection and recovery of right whales. In closing, conservation requires science-based decisions ( Carter et al., 2021 ), and the simultaneous inclusion of socio-economic objectives in decision-science models, such as the framework presented, will yield cost-effective solutions.
Data Availability Statement
For NOAA-Fisheries data requests, please contact [email protected] and for state data please contact the Atlantic Coastal Cooperative Statistics Program ( www.accsp.org ). Data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript will be made available by the authors, upon request.
Author Contributions
KB and GM contributed equally to the analysis and the writing of the manuscript. KB organized the database and performed the analysis. Both authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was funded by the Social Science Branch, Northeast Fisheries Science Center and Protected Resources Division, Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office, through the support of two research assistants. Support for KB by NOAA-Fisheries and for GM by DFO made this collaboration possible.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
This article is based on the case study presented at the 2017 Incentive-Based Bycatch Workshop at Institute de Recherche’ pour le Development in Sete, France 19–22 September 2017. Chao Zou prepared the datasets used to estimate fishing effort and Dennis Corvi created the standardized GIS coordinate system for the fishing effort and right whale density which allowed us to estimate the RREI. We thank Michael Asaro for providing information and financial support for Dennis Corvi, and Christin Khan and Allison Henry for their assistance with the NOAA-Fisheries aerial survey data and database. It is through peer review that manuscripts improve and we thank Barb Best, Eric Thunberg, Mike Simpkins, along with several anonymous reviewers.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2021.540966/full#supplementary-material
- ^ The Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan was first published in 1997 with amendments to the rule in 2000, 2002, 2007, 2014, and 2015. See: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/new-england-mid-atlantic/marine-mammal-protection/atlantic-large-whale-take-reduction-plan .
- ^ The development of “dis-entanglement teams” under the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan would be part of the third stage of the hierarchy (remediation), while offsetting seems difficult to imagine for large whales, such as the right whale.
- ^ Cost-effectiveness analysis compares mutually exclusive alternatives in terms of the ratio of costs to a single quantifiable, but not monetized, effectiveness measure ( Boardman et al., 2011 ).
- ^ Risk reduction was also used to evaluate alternatives measures to reduce ship strikes, not part of the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan. Examples of risk calculations included the co-occurrence (in time and space) of whales and vessels ( Fonnesbeck et al., 2008 ), the multiplication of predicted whale density by a measure of shipping intensity ( Williams and O’Hara, 2010 ), and the relative probability that a vessel will encounter a whale (in time and space) multiplied by the probability of lethality resulting from an encounter ( Vanderlaan et al., 2008 ; Wiley et al., 2011 ; Conn and Silber, 2013 ).
- ^ Calculated based on data from NOAA commercial landings, available here: https://foss.nmfs.noaa.gov .
- ^ Marine Stewardship Council. See documents associated with the Gulf of Maine Lobster fishery at: https://fisheries.msc.org/en/fisheries/@@search .
- ^ All Federal Register (FR) notices are available at https://www.federalregister.gov/ while links to final Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan regulatory documents (last accessed January 6, 2020) are here: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/action/atlantic-large-whale-take-reduction-plan-regulations-1997-2015 .
- ^ Stock assessment reports which include information on mortality and the Potential Biological Removal level can be found here: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/national/marine-mammal-protection/marine-mammal-stock-assessment-reports-species-stock (accessed August 13, 2020).
- ^ Pace et al. (2021) used an abundance estimation model to derive estimates of cryptic mortality for North Atlantic right whales and found that observed carcasses accounted for only 36% of all estimated deaths from 1990 to 2017.
- ^ Weak links are rope attachments that are manufactured to break at a strength lower than that of the rope used, or otherwise reducing the breaking strength of lines used in fishing.
- ^ The 2011 NOAA-Fisheries Northeast Fisheries Science Center aerial abundance line transect survey covered the Gulf of Maine/Bay of Fundy stratum ranging from New York, United States to St. John, New Brunswick, Canada (about 40°N–45°N latitude) and from the shore to about the 100 m depth contour, using a NOAA Twin Otter airplane during 4–26 Aug 2011 ( Palka, 2012 , see Figure 3 ). On-effort surveying occurred during 8 good weather flight days for a total of 34.5 h for a total of 5,313.2 km 2 track line. We assume flight-days is equivalent to number of individual flights.
- ^ VTR data records the configuration of fishing gear (i.e., number of hauls, traps-per-haul, soak time, and catch, etc.) for individual trips; however, the data for fixed gear (i.e., sink gillnet, lobster traps, etc.) was not recorded consistently by harvesters making it problematic for analysis. While the NOAA-Fisheries Northeast Fisheries Observer Program, which collects data for a sample of trips, records information at the haul level and provided details on fishing effort (e.g., number hauls, number of traps, soak time, catch, etc.), the data for 2002–2009 are too sparse to be used for spatially explicit estimates of the number of hauls per trip. This framework would have benefited from census level reporting of VTR records along with vertical line location and configurations, as would other management objectives.
- ^ Since the closed area (i.e., GSC) has no fishing effort, the risk of entanglement is zero.
- ^ This proxy can be modified by weighting the trips in different times or areas to reflect the average alternative gear configuration in terms of number of lines, should a complete set of data become available.
- ^ Individual trips could be weighted to account for lethality differences associated with different methods of deployment (i.e., number of traps in a trawl, depth) and characteristics (e.g., breaking strength of line), should that data become available.
- ^ Within a cost-effectiveness analysis the issue of scale can be a concern; however, the risk constraint within the optimization eliminates this issue.
- ^ For this illustration, the revenues potentially lost due to a closure are used as a proxy for opportunity costs.
- ^ If instead effort is displaced this would result in an overestimation of reductions in revenues and risk to whales. For use in a management setting we would incorporate a harvester behavioral model to reflect shifts in fishing effort in response to closures (e.g., Holland and Sutinen, 2000 ; NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), 2009 ; Dépalle et al., 2020 ).
- ^ Lethality of entanglement could be, but currently is not, incorporated in the model. As Vanderlaan et al. (2011) states, it is not possible to estimate in a robust manner the lethality of an entanglement among gear types. Additional information would be needed on the mechanics of a fishing-gear entanglement, the likelihood of each gear type entangling a whale, the likelihood of self-disentanglement by gear type, and the standardization of entanglement rates by fishing effort.
- ^ The assumed values for α, are for illustration only, as there is no empirical evidence available. Research on efficacy of gear modifications for other marine mammals, such as pingers for harbor porpoise, has been assessed using NOAA’s Northeast Fisheries Observer Program data ( Palka et al., 2008 ). However, as discussed in the “Background” and “Data and Methods” sections observer data are not available for assessing efficacy of whale-modified-gear for right whales.
- ^ Broadscale surveys were the primary survey type from 2002 to the spring of 2007 ( Khan et al., 2018 ). The survey covers all federal waters from New York to Maine. Survey lines were flown year round whenever good weather occurred, unless there was a pressing management issue. Starting in the summer of 2007 sawtooth surveys were implemented as part of the mark-recapture effort for stock assessments. Blocks were made around areas with high numbers of right whale sightings. Sawtooth surveys also supported other management area needs, such as DAM detection.
- ^ As an alternative to proportional sampling, a stratified random sampling approach ( Cochran, 1977 ) could be implemented to evaluate sampling tradeoffs. For example, increasing sampling in areas where the variance is higher, and vice versa, may reduce the total variance for improved precision around the statistic of choice (e.g., whale sightings per unit effort).
- ^ Calculated as 45% in management areas/64% of right whales in northeast waters.
- ^ While data on 3 months of the 2009 year were included in the analysis, they are not considered representative.
- ^ It is not possible to provide management level recommendations from the optimization results due to data limitations and the focus on pre-2010 fishing effort. For this analysis, we extrapolate the number of trips from the Dealer data not recorded in the VTR ( Table 1 ), using the VTR data, as the first step. Going forward, with additional at-sea observer data and more consistent VTR data, we should be able to construct a regression model to estimate vertical lines as a function of trip attributes.
- ^ The cost of gear modifications to the fishing industry are not captured within this optimization model. This could be the case where it was (almost) costless for industry to implement a gear modification (e.g., a change in deployment that does not add cost) or whale-modified-gear is gifted/subsidized for the private sector. This may be the case as the ex-ante cost estimates for the implementation of the gear modifications for the DAM program were negligible ( National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), 2003 ).
- ^ We would like to thank an reviewer for making this suggestion.
- ^ The empirical estimates of RREI would differ, if for example, both the number of whales and fishing effort were under-estimated (or over-estimated) in the right whale management areas, then the RREI in those areas would be under-estimated (over-estimated) and the RREI outside would be over-estimated (under-estimated). In the case where fishing effort and number of whales are in the opposite direction with magnitudes unknown, an empirical analysis would be required to address this question.
- ^ As described here: https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/fisheries-peches/commercial-commerciale/atl-arc/narw-bnan/index-eng.html .
- ^ See: https://www.portvancouver.com/news-and-media/news/vancouver-fraser-port-authority-expands-noise-reduction-criteria-to-encourage-quieter-waters-for-endangered-whales/ .
Ando, A., Camm, J., Polasky, S., and Solow, A. (1998). Species distribution, land values, and efficient conservation. Science 279, 2126–2128. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5359.2126
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ardini, G., and Lee, M. (2018). Do IFQs in the US Atlantic Sea Scallop fishery impact price and size. Mar. Res. Econ. 33, 263–288. doi: 10.1086/698199
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Atlantic State Marine Fisheries Commission (2018). 2018 Review of The Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission Fishery Management Plan For American Lobster (Homarus Americanus) 2017 Fishing Year. Arlington, VA: Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission (ASMFC).
Google Scholar
Berkelaar, M. (2020). lpSolve: Interface to ‘Lp_solve’ v. 5.5 to Solve Linear/Integer Programs. R package version 5.6.15.
Bisack, K., and Clay, P. M. (2020). Compliance with marine mammal protection: focus groups reveal factors in commercial fishermen’s decisions. Mar. Policy 15:103789. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2019.103789
Bisack, K., and Clay, P. M. (2021). Behavioral responses to competing incentives and disincentives: compliance with marine mammal protection. Mar. Policy 132:104674. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104674
Bisack, K., and Das, C. (2015). Understanding non-compliance with protected species regulations in the northeast USA gillnet fishery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2:91. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2015.00091
Bisack, K., and Magnusson, G. M. (2014). Measuring the economic value of increased precision in scientific estimates of marine mammal abundance and bycatch: harbor porpoise Phocoena phocoena in the Northeast U.S. Gill-Net Fishery. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 34, 311–321. doi: 10.1080/02755947.2013.869281
Bisack, K., and Magnusson, G. M. (2016). Measuring management success for protected species: looking beyond biological outcomes. Front. Mar. Sci. 3:61. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2016.00061
Boardman, A. E., Greenberg, D. H., Vining, A. R., and Weimer, D. L. (2011). Cost-Benefit Analysis Concepts and Practice , 4th Edn. Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc., 539.
Borggaard, D. L., Gouveia, D. M., Colligan, M. A., Merrick, R., Swails, K. S., Asaro, M. J., et al. (2017). Managing U.S. Atlantic large whale entanglements: four guiding principles. Mar. Policy 84, 202–212. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2017.06.027
Brilliant, S. W., Wimmer, T., Rangeley, R. W., and Taggart, C. T. (2017). A timely opportunity to protect North Atlantic right whales in Canada. Mar. Policy 81, 160–166. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2017.03.030
Carter, J., Goldman, G., Rosenberg, A., Reed, G., Desikan, A., and MacKinney, T. (2021). Strengthen scientific integrity under the Biden administration. Science 371, 668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.abg0533
Center of Independent Experts (2019). Peer Review Summary Report: Review of the North Atlantic Right Whale Decision Support Tool. Panel: Dvan der Hoop, How and Bowen. November 2019. Woods Hole, MA 02543. 27. Available online at: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/feature-story/decision-support-tool-helpful-those-finding-ways-reduce-whale-entanglement-fishing (accessed August 6, 2020)
Cochran, W. G. (1977). Sampling Techniques , 3rd Edn. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons.
Conn, P. B., and Silber, G. K. (2013). Vessel speed restrictions reduce risk of collision-related mortality for North Atlantic right whales. Ecosphere 4:43. doi: 10.1890/ES13-00004.1
Delavenne, J., Metcalfe, K., Smith, R. J., Vaz, S., Martin, C. S., Dupuis, L., et al. (2012). Systematic conservation planning in the eastern English Channel: comparing the Marxan and Zonation decision-support tools. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 69, 75–83. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsr180
Dépalle, M., Thébaud, O., and Sanchirico, J. (2020). Accounting for fleet heterogeneity in estimating the impacts of large-scale fishery closures. Mar. Resour. Econ. 35, 361–378. doi: 10.1086/710514
Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) (2018). Outlook to 2027 for Canadian Fish and Seafood. Ottawa, ON: Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO), 39.
Dunn, D. C., Maxwell, S. M., Boustany, A. M., and Halpin, P. N. (2016). Dynamic ocean management increase the efficiency and efficacy of fisheries management. PNAS 113, 668–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1513626113
Endangered Species Act (ESA) (1973). 16 U.S.C . ch. 35 §1531 et seq. (Washington, DC: United States Congress).
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) (1996). Precautionary Approach to Capture Fisheries and Species Introductions . FAO, Technical Guidelines for Responsible Fisheries 2. Rome: FAO.
Farmer, N. A., Gowan, T. A., Powell, J. R., and Zoodsma, B. J. (2016). Evaluation of alternatives to winter closure of black sea bass pot gear: projected impacts on catch and risk entanglement with north atlantic right whales Eubalaena glacialis . Mar. Coast. Fish. 8, 202–221. doi: 10.1080/19425120.2016.1146181
Ferraro, P. J. (2003). Assigning priority to environmental policy interventions in a heterogeneous world. J. Policy Anal. Manag. 22, 27–43. doi: 10.1002/pam.10094
Fonner, R., Bellanger, M., and Warlick, A. (2020). Economic analysis for marine protected resource management: challenges, tools and opportunities. Ocean Coast. Manage. 194:105222. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2020.105222
Fonnesbeck, C. J., Garrison, L. P., Ward-Geiger, L. I., and Baumstark, R. D. (2008). Bayesian hierarchical model for evaluating the risk of vessel strikes on North Atlantic right whales in the SE United States. Endanger. Species Res. 6, 87–94. doi: 10.3354/esr00134
Fraser River Port Authority (2019). ECHO Program 2018 Voluntary Vessel Slowdown in Haro Strait: Summary findings. 260. Available online at: https://www.portvancouver.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/ECHO-Program-2019-voluntary-vessel-slowdown-in-Haro-Strait-and-Boundary-Pass-final-report.pdf (accessed August 10, 2021).
Geary, W. L., Bode, M., Doherty, T. S., Fulton, E. A., Nimmo, D. G., Tulloch, A. I. T., et al. (2020). A guide to ecosystem models and their environmental applications. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 4, 1459–1471.
Goode, A. G., Brady, D. C., Steneck, R. S., and Wahle, R. A. (2019). The brighter side of climate change: how local oceanography amplified a lobster boom in the Gulf of Maine. Glob. Chang. Biol. 25, 3906–3917. doi: 10.1111/gcb.14778
Goulette, G., Hawkes, J., Kocik, J., Manning, J., Matzen, E., Van Parijs, S., et al. (2021). Opportunistic Acoustic Telemetry Platforms: An Update on the Northeast Fisheries Science Center’s Collaborative Monitoring Program in the Gulf of Maine, 2005-2018 . NOAA Tech. Mem. NMFS-NE-265. Washington, DC: NOAA, 28.
Grantham, H. S., Petersen, S. L., and Possingham, H. P. (2008). Reducing bycatch in the South African pelagic longline fishery: the utility of different approaches to fisheries closures. Endanger. Species Res. 5, 291–299. doi: 10.3354/esr00159
Hazen, E., Scales, K., Maxwell, S., Briscoe, D., Welch, H., Bograd, S., et al. (2018). A dynamic ocean management tool to reduce bycatch and support sustainable fisheries. Sci. Adv. 4:5. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar3001
Henry, A., Garron, M., Reid, A., Morin, D., Ledwell, W., and Cole, T. (2019). Serious Injury and Mortality Determinations for Baleen Whale Stocks Along the Gulf of Mexico, United States East Coast, and Atlantic Canadian Provinces, 2012-2016. US Dept Commer, Northeast Fish Sci Cent Ref Doc. 19-13. Washington, DC: NOAA, 54.
Hildreth, R. G., Jarman, M. C., and Langlas, M. (2004). Roles for a precautionary approach in U.S. marine resources management. Nat. Res. Environ. 19, 64–67.
Hobday, A., and Hartmann, K. (2006). Near real-time spatial management based on habitat predictions for a longline bycatch species. Fish. Manag.Ecol. 13, 365–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2400.2006.00515.x
Hobday, A., Hartog, J., Timmiss, T., and Fielding, J. (2010). Dynamic spatial zoning to manage southern bluefin tuna ( Thunnus maccoyii ) cap-ture in a multi-species longline fishery. Fish. Oceanogr. 19, 243–253.
Holland, D., and Sutinen, J. (2000). Location choice in New England trawl fisheries: old habits die hard. Land Econ. 76, 133–149. doi: 10.2307/3147262
Kaplan, S., and Garrick, B. (1981). On the quantitative definition of risk. Risk Anal. 1, 11–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.1981.tb01350.x
Khan, C., Cole, T., Duley, P., Glass, A., and Gatzke, J. (2010). North Atlantic Right Whale SightingSurvey (NARWSS) and Right Whale Sighting Advisory System (RWSAS). NortheastFish Sci. Cent. Ref. Doc. 10-07 . 7. Available online at: http://www.nefsc.noaa.gov/nefsc/publications/
Khan, C., Henry, A., Duley, P., Gatzke, J., Crowe, L., and Cole, T. (2018). North Atlantic Right Whale Sighting Survey (NARWSS) and Right Whale Sighting Advisory System (RWSAS) 2016 Results Summary . US Dept Commer, Northeast Fish Sci Cent Ref Doc. 18-01. Washington, DC: NOAA, 13.
Kitts, A., Benaka, L., Heinemann, D., Lovell, S., Olsen, N., and Squires, D. (2021). Workshop Report: Economic Aspects of Bycatch Reduction . NOAA Tech. Memo. NMFSF/SPO-214. Washington, DC: NOAA, 46.
Knowlton, A., Hamilton, P., Marx, M. K., Pettis, H. M., and Kraus, S. D. (2012). Monitoring North Atlantic right whale Eubalaena glacialis entanglement rates: a 30 yr retrospective. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 466, 293–302. doi: 10.3354/meps09923
Knowlton, A. R., Robbins, J., Landry, S., McKenna, H. A., Kraus, S. D., and Werner, T. (2016). Effects of fishing rope strength on the severity of large whale entanglements. Conserv. Biol. 30, 318–328. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12590
LaBrecque, E., Curtice, C., Harrison, J., Van Parijs, S. M., and Halpin, P. N. (2015). 2. Biologically important areas for cetaceans within U.S. waters–east coast region. Aquat. Mamm. 41, 17–29. doi: 10.1578/AM.41.1.2015.17
Lagueux, K. M., Zani, M. A., Knowlton, A. R., and Kraus, S. D. (2011). Response by vessel operators to protection measures for right whales Eubalaena glacialis in the southeast US calving ground. Endanger. Species Res. 14, 69–77. doi: 10.3354/esr00335
Laist, D. W., Knowlton, A. R., and Pendleton, D. (2014). Effectiveness of mandatory vessel speed limits for protecting North Atlantic right whales. Endanger. Species Res. 23, 133–147. doi: 10.3354/esr00586
Lent, R., and Squires, D. (2017). Reducing marine mammal bycatch in global fisheries: An economics approach. Deep Sea Res. 2 Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 40, 268–277. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.03.005
Lewison, R., Hobday, A., Maxwell, S., Hazen, E., Hartog, J., Dunn, D., et al. (2015). Dynamic ocean management: identifying the critical ingredients of dynamic approaches to ocean resource management. Bioscience 65, 486–498. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biv018
Little, A. S., Needle, C. L., Hilborn, R., Holland, D. S., and Marshall, T. (2015). Real-time spatial management approaches to reduce bycatch and discards: experiences from Europe and the United States. Fish Fish. 16, 576–602. doi: 10.1111/faf.12080
Mackay, M., Jennings, S., van Putten, E. I., Sibly, H., and Yamazaki, S. (2018). When push comes to shove in recreational fishing compliance, think ‘nudge’. Mar. Policy 95, 256–266. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2018.05.026
Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA) (1972). Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972, as Amended. U.S. Code, volume 31, Sections 1371–1423 .
Merrick, R. L., Clapham, P. J., Cole, T., Gerrior, P., and Pace, R. M. III (2001). Identification of Seasonal Area Management Zones for North Atlantic Right Whale Conservation . Northeast Fish. Sci. Cent. Ref. Doc. 01-14. Woods Hole, MA: National Marine Fisheries Service, 18.
Milner-Gulland, E. J., Garcia, S., Arlidge, W., Bull, J., Charles, A., Dagorn, L., et al. (2018). Translating the terrestrial mitigation hierarchy to marine megafauna by-catch. Fish Fish. 19, 547–561. doi: 10.1111/faf.12273
Naidoo, R., Balmford, A., Ferraro, P. J., Polasky, S., Ricketts, T. H., and Rouget, M. (2006). Integrating economic costs into conservation planning. Trends Ecol. Evol . 21, 681–687. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2006.10.003
National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) (2001). Environmental Assessment of the Final Rule amending the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan Dynamic Area Management. Gloucester MA: Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office, 41.
National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) (2003). Final Environmental Assessment of the Final Rule amending the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan Dynamic Area Management Gear Modifications. Gloucester MA: Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office, 108.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (2012). Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan (ALWTRP) Monitoring Strategy; Monitoring Effectiveness of and Regulatory Compliance with the ALWTRP , Vol. 2. Gloucester, MA: Grater Atlantic Region Fisheries Office, 22.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (2014). Final Environmental Impact Statement for Amending the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan: Vertical Line Rule Volume I OF II. 773. Available online at: https://cdxnodengn.epa.gov/cdx-enepa-II/public/action/eis/details?eisId=88316 (accessed 12 July 2021).
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (2017). North Atlantic Right Whale (Eubalaena glacialis) 5-Year Review: Summary and Evaluation , Vol. 34. Washington, DC: NOAA.
Needle, C. L., and Catarino, R. (2011). Evaluating the effect of real-time closures on cod targeting. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 68, 1647–1655. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsr092
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) (2009). Modifications to the Harbor Porpoise Take Reduction Plan. Final environmental assessment (includes regulatory review and final regulatory flexibility analysis) . National Marine Fisheries Service, Northeast Region [now Greater Atlantic Region]. (See closed area model 4.2.1.3). Washington, DC: NOAA.
Oinonen, S., Hyytiäinen, K., Ahlvik, L., Laamanen, M., Lehtoranta, V., Salojärvi, J., et al. (2016). Cost-effective marine protection – a pragmatic approach. PLoS ONE 11:e0147085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147085
Pace, R., Williams, R., Kraus, S., Knowlton, A., and Pettis, H. (2021). Cryptic mortality of North Atlantic right whales. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 3:e346.
Pace, R. M. III, Cole, T., and Henry, A. G. (2014). Incremental fishing gear modifications fail to significantly reduce large whale serious injury rates. Endanger. Species Res. 26, 115–126. doi: 10.3354/esr00635
Pace, R. M. III, Corkeron, P. J., and Kraus, S. D. (2017). State–space mark–recapture estimates reveal a recent decline in abundance of North Atlantic right whales. Ecol. Evol. 7, 8730–8741. doi: 10.1002/ece3.3406
Palka, D. (2012). Cetacean Abundance Estimates in US Northwestern Atlantic Ocean Waters from Summer 2011 Line Transect Survey . US Dept Commer, Northeast Fish Sci Cent Ref Doc. 12-29. Woods Hole, MA: National Marine Fisheries Service, 37.
Palka, D., Rossman, M., Vanatten, A., and Orphanides, C. (2008). Effect of pingers on harbor porpoise ( Phocoena phocoena ) bycatch in the US Northeast gillnet fishery. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 10, 217–226.
Pereira, G., and Josupeit, H. (2017). The World Lobster Market . FAO Globefish Research Programme. Volume 123. FAO: Rome.
Pettis, H. M., Pace, R. M. III, and Hamilton, P. K. (2020). North Atlantic Right Whale Consortium 2020 Annual Report Card . Report to the North Atlantic Right Whale Consortium. 22. Available online at: www.narwc.org (accessed August 10, 2021).
Powers, J. E., and Abeare, S. M. (2009). Fishing effort redistribution in response to area closures. Fish. Res. 99, 216–225. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2009.06.011
Read, A. J., Drinker, P., and Northridge, S. (2006). Bycatch of marine mammals in U.S. and global fisheries: bycatch of marine mammals. Conserv. Biol. 20, 163–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2006.00338.x
Reeves, R. A., Read, J., Lowry, L., Katona, S. K., and Boness, D. J. (2007). Report of the North Atlantic Right Whale Program Review. Woods Hole, MA: Marine Mammal Commission, 69.
Richardson, E. J., and Gates, J. M. (1986). Economic benefits of American lobster fishery management regulations. Mar. Res. Econ. 2, 353–382. doi: 10.1086/mre.2.4.42628910
Robbins, J., Knowlton, A. K., and Landry, S. (2015). Apparent survival of North Atlantic right whales after entanglement in fishing gear. Bio Conserv. 191, 421–427. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2015.07.023
Roberts, J. J., Best, B. D., Mannocci, L., Fujioka, E., Halpin, P. N., Palka, D. L., et al. (2016). Habitat-based cetacean density models for the U.S. Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico. Sci. Rep. 6:22615.
Robin, N., Balmford, A., Ferraro, P. J., Polasky, S., Ricketts, T. H., and Rouget, M. (2006). Integrating economic costs into conservation planning. Trends Ecol. Evol. 21, 681–687. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2006.10.003
Segerson, K. (2010). “Can Voluntary Programs Reduce Sea Turtle Bycatch? Insights from the Literature in Environmental Economics,” in Handbook of Marine Fisheries Conservation and Management , eds R. Q. Grafton, R. Hilborn, D. Squires, M. Tait, and M. Williams (New York, NY: Oxford University Press), 618–629.
Silber, G. K., Adams, J. D., and Bettridge, S. (2012). Vessel operator response to a voluntary measure for reducing collisions with whales. Endanger. Species Res. 17, 245–254. doi: 10.3354/esr00434
Silber, G. K., Adams, J. D., and Fonnesbeck, C. J. (2014). Compliance with vessel speed restrictions to protect North Atlantic right whales. PeerJ 2:e399. doi: 10.7717/peerj.399
Smith, M., and Wilen, J. (2003). Economic impacts of marine reserves: the importance of spatial behavior. JEEM 46, 183–206. doi: 10.1016/S0095-0696(03)00024-X
Species at Risk Act (2002). Available online at: https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/S-15.3/ . doi: 10.1016/s0095-0696(03)00024-x (accessed August 10, 2021).
Squires, D., and Garcia, S. M. (2014). Ecosystem-Level Impacts of Fisheries Bycatch on Marine Megafauna: Biodiversity Conservation Through Mitigation, Policy, Economic Instruments, and Technical Change . Report of an IUCN-CEM-FEG Scientific Workshop October 2013. Gland: International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Squires, D., and Garcia, S. M. (2018). The least-coast biodiversity impact mitigation hierarchy with a focus on marine fisheries and bycatch issues. Conserv. Biol. 32, 989–997. doi: 10.1111/cobi.13155
Squires, D., Restrepo, V., Garcia, S., and Dutton, P. (2018). Fisheries bycatch reduction within the least-cost biodiversity mitigation hierarchy: conservatory offsets with an application to sea turtles. Mar. Policy 93, 55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2018.03.018
Stewart, R. R., and Possingham, H. P. (2005). Efficiency, costs and trade-offs in marine reserve system design. Environ. Model. Assess. 10, 203–213. doi: 10.1007/s10666-005-9001-y
Thaler, R. H., and Sunstein, C. R. (2010). Nudge: improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness. Econ. Philos. 26, 369–376.
Vanderlaan, A. S., Smedbol, R. K., and Taggart, C. T. (2011). Fishing-gear threat to right whales ( Eubalaena glacialis ) in Canadian waters and the risk of lethal entanglement. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 68, 2174–2193. doi: 10.1139/F2011-124
Vanderlaan, A. S., Taggart, C. T., Serdynska, A. R., Kenney, R. D., and Brown, M. W. (2008). Reducing the risk of lethal encounters: vessels and right whales in the Bay of Fundy and on the Scotian Shelf. Endanger. Species Res. 4, 283–297. doi: 10.3354/esr00083
Wade, P. R., and Angliss, R. P. (1997). Guidelines for Assessing Marine Mammal Stocks: Report of the GAMMS Workshop. April 3-5. Seattle, WA . NOAA Tech Memo NMFS-OPR-12. Washington, DC: NOAA.
Welch, H., Brodie, S., Jacox, M. G., Bograd, S. J., and Hazen, E. L. (2019). Decision-support tools for dynamic management. Conserv. Biol. 34, 589–599. doi: 10.1111/cobi.13417
Wiley, D. N., Moller, J. C., and Zillnskas, K. A. (2003). The distribution and density of commercial fisheries and baleen whales within the Stellwagen Bank national marine sanctuary: July 2001–June 2002. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 37, 35–53. doi: 10.4031/002533203787537384
Wiley, D. N., Thompson, M., Pace, R. M. III, and Levenson, J. (2011). Modeling speed restrictions tomitigate lethal collisions between ships and whalesin the Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary, USA. Biol. Conserv. 144, 2377–2381. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2011.05.007
Williams, R., and O’Hara, P. (2010). Modelling ship strike risk to fin, humpback and killer whales in British Columbia, Canada. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 11, 1–8.
Young, N. M. (2001). The conservation of marine mammals using a multi-party approach: an evaluation of the take reduction team process. Ocean Coast. Law J. 6, 293–346.
Keywords : mitigation, Dynamic Area Management, bio-eoconomic tradeoffs, policy instruments, bycatch, marine mammal, cost-effectiveness (economics), compliance
Citation: Bisack KD and Magnusson GM (2021) Spatial Management to Reduce Entanglement Risk to North Atlantic Right Whales in Fishing Gear: A Case Study of U.S. Northeast Lobster Fishery 2002–2009. Front. Mar. Sci. 8:540966. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.540966
Received: 06 March 2020; Accepted: 28 July 2021; Published: 10 September 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Bisack and Magnusson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kathryn D. Bisack, [email protected]
† These authors share first authorship
This article is part of the Research Topic
Multidisciplinary Approaches to Mitigating Fisheries Bycatch
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Jennifer Brownell, Vivek Kandasamy, Peter Lam, Julia Naras, and Olivia Petropulos

Atlantic Cod ( Gadus morhua )
An introduction.
Cod has been integral to North American history and cultures since long before the arrival of European settlers. Indigenous Peoples of the East and West coasts have angled , jigged , spearfished, netted, and trapped the abundant fish for tens of thousands of years. The fish was nutritionally and culturally important in areas where the land could not support agriculture and is still recognized in Indigenous oral traditions as a fountainhead of life (Chaves 2014).

In New England, the commercial fishing of Atlantic cod became the first American industry and supported the growth of the Colonies (Chaves 2014). Fishing towns that still exist today—Provincetown, Gloucester, New Bedford, Nantucket, et cetera—thrived because of the healthy Atlantic cod fishery and guidance from Indigenous Peoples (Figure 2) (Dybas 2006). The fish was a symbol of New England’s economic prosperity and physically manifested in a five-foot-long Sacred Cod carved out of pine was hung in the Massachusetts State House. Three hundred and twenty years later, a replica still resides in the Massachusetts House of Representatives just west of Cape Cod Bay (Dietze 2017).
Now, however, this icon is fading away. As overexploited Atlantic cod stocks dwindle, New England fishing communities struggle with the loss of income (from commercial fishing and recreational guided fishing trips), food security, and regional culture. The ecosystems that once supported cod populations have changed irreversibly in their absence, and conservation efforts have had little to no success in recovering them.
Natural History and Significance

Atlantic cod is a species as unique physically as it is culturally. Both females and males have three spineless dorsal fins , two anal fins , and a single barbel on the chin. They can change color based on their depth in the water column, often appearing greyish-green or reddish-brown with a light belly. A pale lateral line runs from above each pectoral fin to the squared caudal fin (Figure 3) (NOAA 2020). Females grow slightly heavier and longer than males but otherwise, they are indistinguishable (Jakobsen et al 2016). According to current government sources, within their 20-year lifespan, they can reach up to 77 pounds and 51 inches long (NOAA 2020). However, 19th-century schooner records show that Atlantic cod once exceeded 210 pounds (Dybas 2006).
This species’ domain expands beyond New England’s watersheds but is limited to the Atlantic and the Arctic Oceans. To the west, they can be found from off the shores of Greenland, all the way to North Carolina. To the east, they can be found from the Arctic Ocean to the Bay of Biscay. This includes other bodies of water like the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, the Barents Sea, as well as a few more. They are found in Europe all the way east to Scandinavia because of their seasonal migrations (Figure 4) (Commonwealth of Massachusetts 2021).
A shoaling species, Atlantic cod finds itself in rocky habitats, as well as down in the ocean along the continental shelf. Cod tend to prefer colder temperatures and deep water during the day. On the other hand, they enjoy the warmer and shallower water at night (Neubauer et al. 2013). Factors such as temperature, depth, and salinity can affect “growth rate, age of maturity, migration patterns, and timing of spawning” (Brander 2018). They spawn near the ocean floor from winter to early spring, beginning at age 2 or 3. Females can lay anywhere from 3 million-9 million eggs. A study on commercial fishing of Atlantic cod found that “total egg abundance is significantly higher in years with more old and large individuals in the spawning stock” (Stige 2017). They reproduce through broadcast spawning: a type of sexual reproduction where females release eggs into the water column where they meet up with sperms. This helps protect the eggs from egg predators (Stige 2017).
Cod is a generalist species with an omnivorous and ontogenetic diet. As they develop from “codlings” to medium-sized cod, their diet shifts from pelagic invertebrates to benthic invertebrates, small fish, and crustaceans. In ecosystems where populations of large cod are stable, they are the dominant piscivore and consume more fish (including smaller cod and other gadoids), crustaceans, and mollusks as they grow. Cod are opportunistic hunters and prefer the most abundant prey (Link and Garrison 2002). As a result, the species plays multiple roles throughout the trophic levels.

As a prey species, Atlantic cod links aquatic animals such as shrimp, crustaceans, and capelin, along with marine mammals such as harp seals and grey seals. Many types of fish prey on the Atlantic cod. Young and smaller cod are hunted by larger cod and pollock fish. Larger adults are hunted by sharks, spiny dogfish, and marine mammals (Link et al. 2009). Removal of cod will cause “an increase or decrease in abundance to every other species in the ecosystem in an alternating pattern” (Steele 2016) (Figure 5). As studied, a decline of the cod population has had an inverse effect for shrimp, crab, and foraging fish populations. However, this has led to large decreases in zooplankton which would be feasted on greatly from a now-unchecked predator (Bundy et al. 2009). While Atlantic cod plays a more predatory role in an ecosystem than prey, many species do still feed on cod “preying on the cod’s early life stages (eggs, larvae or early juveniles) or by competing with those early life stages for food” (Link et al. 2009). Cod plays a vital role in the economy, but more so in the ecosystems that they reside in.
Stock Collapse

Over the past 150 years, the population of Atlantic cod experienced significant changes. Through the 19th and early 20th centuries, Atlantic cod was a staple for the fisheries in the Northern Atlantic Ocean. However, starting in the late 1950s, offshore bottom trawlers began to fish in deeper parts of the stock (Walter et al. 2005). This led to a dramatic increase in the number of fish landings. Since there was a decrease in the number of fish, especially the most mature fish with the highest rates of reproduction, the population was unable to replenish the stock. The mass number of fish caught from the 1950s onwards led to a decline in the biomass of the Atlantic cod (Figure 6). While overfishing played a large role, it is not the only reason for the collapse of the Atlantic cod population (Walter et al. 2005). Other reasons for the decline include pollution, climate change, and human activity, which all led Atlantic cod to be declared a vulnerable species by 1996. Today, they remain vulnerable to extinction with some populations now being labeled as endangered (Ono et al. 2019).
Management Policies
In response to the cod stock depletion and its staggering effect on the fishing industry, Congress passed the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (MSFCMA) , the first and principal marine conservation law, in 1976. The legislation protected U.S. waters from foreign fishing vessels and established eight management councils, appointing them by region to the nation’s major marine fisheries (NOAA 2020). The New England Fishery Management Council accounts for both Atlantic cod stocks in U.S. waters: the Gulf of Maine and Georges Bank. All eight U.S. Regional Fishery Management Councils collaborate with scientists and workers in the fishing industry as well as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to regulate commercial and recreational fishing, protect habitats, and develop new strategies to restore overfished species (NOAA 2020).
Nevertheless, overfishing persisted and cod was listed as a vulnerable species in 1996 (Wilmot 2005). Many amendments have been made to the MSFCMA to address this, most notably the Sustainable Fisheries Act (1996) and the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Reauthorization Act (2006) , which further limited fishing access to vital habitats and enforced stricter catch limits (NOAA 2020). In 1986, the New England Fishery Management Council developed the Northeast Multispecies Fishery Management Plan to restore cod (and 12 other groundfish species) stocks (NEFMC 2021). Amendments and adjustments have also been made to the Northeast Multispecies FMP (and several are currently in progress); however, regulations have not reversed the decline of cod populations (Hayden et al. 2015; NEFMC 2021). New research analysis suggests that overharvested cod shoals group together, joining the once-fragmented populations. These metapopulations are easy targets for trawlers, making the fish vulnerable to overharvesting even when strict, traditional fishing regulations (e.g. landing limits) are in place (Hayden et al. 2015). This information is beneficial as organizations like the New England Fishery Management council work to develop new regulations to recover Atlantic cod.
With this new legislation, local fishermen had interesting opinions. At first, fishermen viewed the new restrictions as another barrier they must face. The restrictions also took away revenue. As time passed, the locals became better educated on the problems associated with the Atlantic cod collapse. Fishermen now recognize the importance of the government’s efforts to intervene in the collapse of an iconic and ecologically essential species. Locals adhere to the new restrictions and hope that this change in behavior can recover the species. This is a great example of how powerful education is. Not only do the people in power need to be educated to make a change, but the general public does as well. This issue highlights the fact that education brings about the knowledge to advocate for change (Oceana 2018).

Despite the action taken by Congress, there have been no substantial results to show that the Atlantic Cod population has recovered at all. These actions seem like they are making large strides, yet there is a lot more work to be done. Most importantly, there is no set recovery plan in place for this species. Even though this species started to collapse many years ago, a true plan has yet to be made. This is an alarming reality because as quickly as a population can disappear, restoring it is extremely challenging and time and resource-consuming. This means that there needs to be more actions taken and effort exerted by those who can bring change (Hutchings and Kuparinen 2020).
Firstly, there needs to be support from the community and local fishermen to have these changes make a difference. Some of these restrictions make it difficult for fishermen to keep the cod they catch, as there is a limit to what they can catch in a day. This results in a large amount of dead cod that has been caught and thrown overboard. In 2018, one study found that it was not uncommon for there to be over 3,000 pounds of cod throw out per trip. Without knowledge of the current population and management compliance, it is not possible to fully know how the population of cod is doing. This makes it nearly impossible for scientists and government officials to set forth rules and a specific course of action. To fix this issue, all groundfish trips in New England would need to be monitored. As of late, people are starting to recognize how important complete monitoring can be. In addition, locals must recognize how detrimental recreational fishing of Atlantic cod can be. Recreational fishing creates additional challenges in properly monitoring the species (Hutchings and Kuparinen 2020).
Secondly, refuges should be set up for the Atlantic cod to protect their important habitat. Protecting the fish’s habitat protects the fish. Actions like this would stop the fishing of cod in specific areas. One of the most important aspects of this effort is that it can protect young cod and highly productive females (Hutchings and Kuparinen 2020). This action poses a method to quickly increase populations in areas.
Another effort that could be made in the distant future is the creation of modified fishing gear to reduce the amount of cod caught by accident. It is very common for cod to be caught while other fish species are being targeted. The creation of new gear could minimize this issue. This would require help from scientists as well as major funding to make this gear commonplace (Hutchings and Kuparinen 2020).
Overall, we can see that Atlantic cod is a victim of human greed and lack of education. With the start of the Industrial Revolution came a wave of production, which also meant the consumption of resources faster than anyone could predict. Today, Atlantic cod habitat waters run 53 degrees Fahrenheit. As humans warm up the planet, so do the oceans. The Gulf of Maine “is one of the fastest-warming bodies of water on Earth” (Lawson 2019) and the Atlantic cod’s range grows smaller and smaller.
These warmer waters are a challenge and a result of negligent human behavior within the environment, which has stunted the growth of the Atlantic cod population along with many others like it. Acidity levels are rising along with the temperature. Studies have found “that increasing acidification makes cod embryos more sensitive to higher and lower temperatures, effectively narrowing the optimal temperature range for reproduction” (Berwyn 2018). Factors such as these limit cod spawning areas, inevitably slashing future cod populations and their re-build.
The current COVID-19 pandemic has only made it harder on the fishing industry and the groups associated with conservation efforts of the threatened fish species. Now more than ever, the fishing industry needs financial support from the government as well as support from the community. Something the community can do is continually advocate for advancing rebuilding plans, promote education to those around, and follow the rules already set in place to protect Atlantic cod.
Like all living entities, the Atlantic cod has a complex natural history. What’s remarkable about this fish, however, is how its natural history is interwoven with human history. For millennia, the species was so important to human survival that entire cultures and technologies were developed around it (Dexter and Speck 1948). Initially, cod was a nutritional staple to Indigenous Peoples in New England. Following European settlement, it then became valued for its economic significance within the Colonies. Now, cod is an internationally sought-after commodity, a direct result of commercial demand and the advancement of fishing technologies since the Industrial Revolution (Dybas 2006). Serial overharvesting, especially of large cod in indiscriminating trawls, inevitably led to the collapse of the fishery. Despite continued government intervention since the 1970s, cod stocks continue to fall, fishing towns continue to struggle, and the trophic levels that healthy cod populations once supported are damaged without them (Steele 2016). Conservation success stories for Atlantic cod are rare, and climate change is an added challenge to recovery efforts. Although minimal, the Gulf of Maine has seen improvement in the cod fishery, which is attributed to strict landing limits, but more importantly, to strict area limitations and habitat preservation (Alexander et al. 2009). If we protect the habitat, then we protect the Atlantic cod.

Alexander KE, Leavenworth WB, Cournanel J, Cooper AB, Claesson S, Brennan S, Smith G, Rains L, Magness K, Dunn R et al. 2009. Gulf of Maine cod in 1861: historical analysis of fisherylogbooks, with ecosystem implications. Fish and Fisheries 10(4): 428-449. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2979.2009.00334.x
Berwyn B. 2018 November 9. Warning for seafood lovers: Climate change crash these important fisheries. Inside Climate News. [Intenet] [cited 2021 March 8] Available from: https://insideclimatenews.org/news/29112018/atlantic-cod-climate-change-fish-population-crash-risk-arctic-food-web-impact-study/
Brander KM. 2018. Climate change not to blame for cod population decline. Nature Sustainability 1(6) : 262-264. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-018-0081-5
Brander KM. 2007. The role of growth changes in the decline and recovery of North Atlantic Cod stocks since 1970. ICES Journal of Marine Science 64(2): 211-217. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsl021
Comeau P. 1998. New endangered species plan unveiled. Canadian Geographic. [Internet] Available from: http://www.ucs.mun.ca/~kbell/cod/PRESS-sa_crspdnc/CG9807-28-30/CG9807p28-30.html
Dexter RW, Speck FG. 1948. Utilization of marine life by the Wampanoag Indians of Massachusetts. Journal of the Washington Academy of Science 38(8): 257-265. Available from: https://www.jstor.org/stable/24530881
Dietze MC. 2017. Case study: Natural resources. In: M Dietze, editor. Ecological Forecasting. Princeton (NJ): Princeton University Press. p. 131-137. https://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctvc7796h.14
Drinkwater KF. 2005. The response of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) to future climate change. ICES Journal of Marine Science 62(7): 1327-1337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icesjms.2005.05.015
Dybas CL. 2006. Ode to a codfish. Bioscience 56(3): 184-191. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2006)056[0184:OTAC]2.0.CO;2
Grafton RQ, Kompas T, Ha VP. 2009. Cod today and none tomorrow: the economic value of a marine reserve. Land Economics 85(3): 454-469. https://doi.org/10.3368/le.85.3.454
Hayden A, Acheson J, Kersula M, Wilson J. 2015. Spatial and temporal patterns in the cod fisheries of the North Atlantic. Conservation and Society 13(4): 414-425. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-4923.179878
Hutchings JA. 2005. Life history consequences of overexploitation to population recovery in Northwest Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62 (4): 824-832. https://doi.org/10.1139/f05-081
Hutchings JA, Kuparinen A. 2020. Implications of fisheries-induced evolution for population recovery: Refocusing the science and refining its communication. Fish and Fisheries 21(2): 453-464. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12424
Lawson G. 2019. Give Atlantic cod a break: The role of climate change. Conservation Law Foundation. Available from: https://www.clf.org/blog/give-atlantic-cod-a-break-climate-change/#:~:text=A%20warmer%20ocean%20also%20makes,and%20raise%20healthy%20young%20fish.&text=Scientists%20are%20working%20to%20understand,ocean%20is%20limiting%20population%20growth
Link JS, Bogstad B, Sparholt H, Lilly GR. 2009. Trophic role of Atlantic cod in the ecosystem. Fish and Fisheries 10(1): 58-87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2979.2008.00295.x
Link JS, Garrison LP. 2002. Trophic ecology of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua on the northeast US continental shelf. Marine Ecology Progress Series 227: 109-124. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps227109
Mason F. 2002. The Newfoundland cod stock collapse: a review and analysis of social factors. Electronic Green Journal 1(17). https://doi.org/10.5070/G311710480
Mirimin L, Desmet S, Romero DL, Fernandez SF, Miller DL, Mynott S, Brincau AG, Stefanni S, Berry A, Gaughan P, et al. 2021. Don’t catch me if you can – Using cabled observatories as multidisciplinary platforms for marine fish community monitoring: An in situ case study combining underwater video and environmental DNA data. The Science of the Total Environment 773: 145351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145351
Neubauer P, Jensen OP, Hutchings JA, Baum JK. 2013. Resilience and recovery of overexploited marine populations. Science 340(6130): 347-349. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1230441
Neuenfeldt S, Bartolino V, Orio A, Andersen KH, Andersen NG, Niiranen S, Bergström U, Ustups D, Kulatska N, Casini M. 2020. Feeding and growth of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) in the eastern Baltic Sea under environmental change. ICES Journal of Marine Science 77(2): 624–632. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsz224
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), USDOC. 2019. Atlantic cod overview. [Intenet] Available from: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/atlantic-cod#overview .
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), USDOC. 2020. Northeast multispecies (groundfish). [Internet] Available from: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/northeast-multispecies-groundfish#management .
Oceana. 2018. Fishermen explain: The Magnuson-Stevens Act (MSA) is vital. YouTube.com. [Internet] Available from: https://youtu.be/sfSnoxdFbOo .
Ono K, Knutsen H, Olsen EM, Ruus A, Hjermann DO, Stenseth, N. 2019. Possible adverse impact of contaminants on Atlantic cod population dynamics in coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Biological Sciences 286(1908). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2019.1167
Powles H, Bradford MJ, Bradford RG, Doubleday WG, Innes S, and Levings CD. 2000. Assessing and protecting endangered marine species. ICES Journal of Marine Science 57(3): 669-676. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.2000.0711
Rose GA. 2004. Reconciling overfishing and climate change with stock dynamics of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) over 500 years. Canadian Journal of Fisheries Aquatic Sciences 61(9): 1553-1557. https://doi.org/10.1139/f04-173
Rose GA, Rowe S. 2015. Northern cod comeback. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 72(12): 1789-1798. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-2015-0346
Schrank WE, Roy N. 2013. The Newfoundland fishery and economy twenty years after the northern cod moratorium. Marine Resource Economics 28(4): 397-413. https://doi.org/10.5950/0738-1360-28.4.397
Sellers AM. 2003. Environmental quality assessment of Georges Bank for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). [thesis] Worcester Polytechnic Institute. Available from: https://web.wpi.edu/Pubs/ETD/Available/etd-0428103-155152/unrestricted/sellers.pdf
Sguotti C, Otto SA, Frelat R, Langbehn TJ, Ryberg MP, Lindegren M, Durant JM, Chr Stenseth N, Möllmann C. 2019. Catastrophic dynamics limit Atlantic cod recovery. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Biological Sciences 286(1898): 20182877. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2018.2877
Trzcinski MK, Mohn R, Bowen WD. 2006. Continued decline of an Atlantic cod population: How important is gray seal predation? Ecological Applications 16(6): 2276–2292. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[2276:CDOAAC]2.0.CO;2
Angle is an archaic word for “hook”; angling is fishing with a rod, line, and hook
To fish with a rod, line, and a lure which is jerked through the water to attract fish
The fin located on the back of a fish
The fin located on the underside of a fish
A whisker-like organ used by bottom-feeding fish to search for food
The pair of fins on the left and right side of a fish behind the head
The tail fin of a fish
A ship with two or more masts
A group or school of fish
The reproductive process of most fish where eggs and sperm are released into the water
Consuming both plants and animals
Changing during an organism’s lifespan
An organism that consumes primarily fish
A fishing boat that carries a large net (a trawl)
The volume of organisms in an area
A listing of a species which is a higher species concern than "threatened" but not as serious as "endangered."
A large number of fish swimming together.
A collection of individual populations of the same species that interact with one another
A group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain
Extinction Stories Copyright © by Marja Bakermans and William San Martín is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Vertebrates
- Ichthyology
- Biological Science
Where are the North Atlantic fish going, and where should fishermen go?
- January 2021
- IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science 632(2):022028
- 632(2):022028
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.

- The University of Warwick
Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- And F Werner
- PROG OCEANOGR
- V M Trenkel

- CONT SHELF RES

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- Subscriber Services
- For Authors
- Publications
- Archaeology
- Art & Architecture
- Bilingual dictionaries
- Classical studies
- Encyclopedias
- English Dictionaries and Thesauri
- Language reference
- Linguistics
- Media studies
- Medicine and health
- Names studies
- Performing arts
- Science and technology
- Social sciences
- Society and culture
- Overview Pages
- Subject Reference
- English Dictionaries
- Bilingual Dictionaries
Recently viewed (0)
- Save Search


Edited by: John P. Grant and J. Craig Barker
- Find at OUP.com
- Google Preview
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
- View overview page for this topic
Related Content
In this work.
- Table of Abbreviations
Related Overviews
- Publishing Information
North Atlantic Fisheries Case
(1910) 11 R.I.A.A. 167 . In 1818, Great Britain and the United States concluded a treaty defining the rights ...
Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription.
Please subscribe or login to access full text content.
If you have purchased a print title that contains an access token, please see the token for information about how to register your code.
For questions on access or troubleshooting, please check our FAQs , and if you can''t find the answer there, please contact us .
- Oxford University Press
PRINTED FROM OXFORD REFERENCE (www.oxfordreference.com). (c) Copyright Oxford University Press, 2023. All Rights Reserved. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a PDF of a single entry from a reference work in OR for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice ).
date: 11 June 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [91.193.111.216]
- 91.193.111.216
Character limit 500 /500

Register/Add a study
Case Studies in North Atlantic Right Whale Fishing Gear Entanglements
Entanglement in commercial fishing ropes threatens the recovery of the North Atlantic right whale ( Eubalaena glacialis ), a species largely restricted to waters off of eastern North America. In recent years, serious entanglements have been increasing, and mortality from conflicts with fishing operations exceeds US legal mandates, with 83% of the population showing incidence of scarring as a consequence of these encounters.
What happens when whales encounter fishing gear is complex and poorly understood. The goal of creating the case studies associated with our publication (see: North Atlantic Right Whale Entanglement Case Studies on the Publications Page - scroll all the way down) was to combine what we know to date on the individual whales entangled, the configuration of ropes entangling them, the extent of their injuries, and what can be learned about the gear retrieved from them. There is much to learn about the nature of these conflicts, and increasing our understanding about these events can help point to some of the more promising ways to avoid them or reduce their severity.
The 30 whale entanglement publication case studies are a subset of total whale bycatch that has occurred off the eastern shores of the US and Canada, with a particular emphasis on the waters south and west of Nova Scotia. Featured here are cases involving the endangered North Atlantic right whales for which:
- Fishing gear was retrieved and warehoused by NOAA/NMFS;
- Gear archived prior to June 2010 was made available for analysis by an independent rope engineer reflecting 30 right whale events which occurred from 1994-2010;
- A disentanglement responder team or a necropsy team was able to document how ropes and other gear were attached to the animal; and
- A relatively good understanding exists of some or all the injuries produced by entangling ropes (from images, video or assessments made by disentanglers).
Each two-page case study integrates into five main categories a suite of information from a variety of different sources. Together they are intended to provide a comprehensive picture about the entangling gear and its impacts on individual animals. The information contains:
- Life history information of the individual whale including catalog number/name, gender, birth year if known, age/age class when first seen entangled, and reproductive status before and after entanglement (if known);
- Timing and duration of the entanglement, wounds acquired from entanglement, disentanglement efforts, the animal’s present status, and the number of prior entanglement events for the individual;
- A drawing of the gear configuration with explanatory text;
- Gear type and component if known, rope polymer, measurements of rope diameter, tested and new breaking strengths of ropes; and
- Photographs of entanglement configuration and injuries.
Appended to each two page case study, when available, are the findings of the gear analysis carried out during this study including images of the gear.
Documentation of each entanglement case originated with the efforts of the Atlantic Large Whale Disentanglement Network, a consortium of researchers, fishermen, government managers and other professional mariners, to provide safe and efficient responses to reports of entangled whales along the North American East Coast. Further assessment was done by the authors after reviewing all sightings data, response actions, photographs and videos of the animal over the duration of its entanglement or at a necropsy. The entanglement configuration diagrams were created by an entanglement case expert who was directly involved in many of the events (Scott Landry/Provincetown Center for Coastal Studies). The diagrams are intended to make as clear as possible the most plausible layout of gear on a whale’s body at the time of its first discovery, and not depict the details of the gear itself or the level of injury to whales.
Life history, sighting, and fate information for North Atlantic right whales was obtained by permission from the North Atlantic Right Whale Consortium Catalog (curated by the New England Aquarium [NEAq]).
Fishing ropes retrieved from the entanglements and warehoused by NMFS were examined by a rope engineer, Hank McKenna, to determine their polymer type, diameter, color, breaking strength, condition, and other properties of their construction. These data supplement reports already compiled by NMFS about these ropes.
Acknowledgments
These case studies resulted from the work of many individuals who have been involved in whale research, gear research, necropsies, and disentanglement interventions over several decades. The original 30 case studies were prepared by Amy Knowlton and Candace Borutskie of the New England Aquarium, and Scott Landry of the Provincetown Center for Coastal Studies. We would like to thank John Kenney from NMFS for access and assistance with retrieved gear, and Patrice McCarron and Heather Tetreault of Maine Lobstermen’s Association, Stormy Mayo and Brian Sharp of PCCS, and Michael Moore of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution for their guidance and input in developing the case studies.
This work would not have been possible without the efforts of the Atlantic Large Whale Disentanglement Network. Entanglement response activities were conducted under the authority of NMFS, the NOAA Marine Mammal Health and Stranding Response Program (Permits 932-1489 and 932-1905), DFO Canada and with major support from NMFS. Most right whale photos were obtained under a permit held by the contributing organization from NOAA or DFO Canada. Support for the Dynamics of Whale Entanglements Project is from the Consortium for Wildlife Bycatch Reduction at the New England Aquarium under US DOC-NOAA Grant # NA09NMF4520413. Additional support for development of the case studies or the information on which they were based was provided by NOAA grant NA09OAR4320129 through Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and private donors.
For more information, see also the Conservation Biology paper by Knowlton et al (2016) on the Publications Page, or on the Conservation Biology Website .
All right whale entanglement case studies
Updated July 2023
A full suite of case studies have been developed and can be found below. This includes all right whales observed with attached fishing gear (only a subset of cases had retrieved gear for our 2016 publication). For each case study, we review information found in NOAA Fisheries entanglement reports (see https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/new-england-mid-atlantic/marine-mammal-p… ) to assess whether gear type and country of origin have been determined and include this information. We also assess the timing of sightings pre and post entanglement and if we feel confident about country of origin based on that information, we will include this. If no country is noted under the gear type, it means this information is not available.
These case studies will be edited if additional information becomes available about the whale or the gear. New case studies will be added as they are created. These case studies are provided for information sharing only. Please contact Amy Knowlton with further questions about the case studies or use of the data therein.
It should be noted that right whales with attached gear represent just a subset of entanglements that right whales have experienced. Most entanglements leave scars only. For data assessed from 1980-2020, a total of 1748 entanglements have been documented and 139 of those cases (8%) had attached gear and are presented here.
Document Entanglement case studies - 1980-1989 - 7 cases.pdf
Document Entanglement case studies - 1990-1999 - 23 cases.pdf
Document Entanglement case studies - 2000-2004 - 24 cases.pdf
Document Entanglement case studies - 2005-2009 - 20 cases.pdf
Document Entanglement case studies - 2010-2014 - 31 cases.pdf
Document Entanglement case studies - 2015-2019 - 31 cases.pdf
Document Entanglement case studies - 2020 - 3 cases.pdf
Tweets by bycatchorg
More Fishing Gear Modifications Projects
- Cetacean Bycatch in Longlines
- Habitat Use by Loggerhead Sea Turtles
- International Marine Mammal - Gillnet Bycatch Mitigation Workshop
- International Marine Mammal - Longline Bycatch Mitigation Workshop
- International Marine Mammal Bycatch Assessment
- Species List
- Bycatch Reduction Techniques Fact Sheets
- Consortium Publications
- Funding Opportunities
- Join the Exchange

Case Summary of Anglo Norwegian Fisheries Case | United Kingdom V Norway

Full Case Name – United Kingdom V Norway
Court Name – International Court of Justice
Citation – [1951] ICJ 3
Perhaps the most important function of international law is to determine which bits of Earth and sea belong to which countries. A nation is defined by the extent of its territory and over human history. Many wars have been fought over the specific location of borders. In this Anglo Norwegian Fisheries Case, there was a dispute between the United Kingdom and Norway about Norway’s maritime border in the North Sea.
The Anglo-Norwegian Fisheries Case, also known as the Fisheries Case is a landmark case in the history of international law and it deals with the issue of fishing rights in the North Sea. The case was brought before the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in 1951 by the United Kingdom, challenging Norway’s jurisdiction over fisheries in the area.
Facts of the Anglo Norwegian Fisheries Case
British fishing ships had been fishing in waters that Norway claimed as her own. Norway claimed all the waters within four nautical miles from its baseline. Britain agreed that this was appropriate. Normally the baseline is the low-watermark which is the shoreline at low tide. Norway, however, was a bit different just off the coast running up and down the coast where a series of hundreds of rocky outcrops like little islands in a geographic sense though these were really connected to the mainland. Norway for hundreds of years had counted these rocky outcrops as part of its mainland territory.

- What is Mens Rea and Actus Reus - February 13, 2024
- Case Summary of Anglo Norwegian Fisheries Case | United Kingdom V Norway - April 7, 2023
- What is a Solicitor? How to Become One - January 9, 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Search results
- Add to Alerts
- Save to folder
- Copy the reference
The North Atlantic Coast Fisheries Case
Documents of the case.
- Award - 7 Sept 1910
Grounds for the Dissent to the Award on Question V by Dr. Luis M. Drago
- Memorandum of 12 September 1906 - 12 Sept 1906
- Memorandum of 25 September 1906 - 25 Sept 1906
- Modus vivendi of 6 / 8 October 1906 - 6 Oct 1906
- Modus vivendi of 4 / 6 September 1907 - 4 Sept 1907
- Modus vivendi of 15 / 23 July 1908 - 15 July 1908
- Correspondence of 27 January - 4 March 1909 - 27 Jan 1909
- Resolution of 18 February 1909 - 18 Feb 1909
- Modus vivendi of 22 July - 8 September 1909 - 22 July 1909
- Agreement of 20 July 1912 - 20 July 1912
Lawyers, other representatives, expert(s), tribunal’s secretary
Article I begins with the statement that differences have arisen respecting the liberty claimed by the United States for the inhabitants thereof to take, dry and cure fish on " certain coasts, bays, harbours and creeks of His Britannic Majesty’s Dominions in America ", and then proceeds to locate the specific portions of the coast with its corresponding indentations, in which the liberty of taking, drying and curing fish should be exercised. The renunciatory clause, which the Tribunal is called upon to construe, runs thus: " And the United States hereby renounce, forever, any liberty heretofore enjoyed or claimed by the inhabitants thereof, to take, dry or cure fish on, or within three marine miles of any of the Coasts, Bays, Creeks or Harbours of His Britannic Majesty’s Dominions in America not included within the above mentioned limits. " This language does not lend itself to different constructions. If the bays in which the liberty has been renounced are those " of His Britannic Majesty’s Dominions in America ", they must necessarily be territorial bays, because in so far as they are not so considered they should belong to the high seas and consequently form no part of His Britannic Majesty’s Dominions, which, by definition, do not extend to the high seas. It cannot be said, as has been suggested, that the use of the word " dominions ", in the plural, implies a different meaning than would be conveyed by the same term as used in the singular, so that in the present case," the British dominions in America " ought to be considered as a mere geographical expression, without reference to any right of sovereignty or " dominion ". It seems to me, on the contrary, that " dominions ", or " possessions ", or " estates ", or such other equivalent terms, simply designate the places over which the " dominion " or property rights are exercised. Where there is no possibility of appropriation or dominion, as on the high seas, we cannot speak of dominions. The " dominions " extend exactly to the point which the " dominion " reaches; they are simply the actual or physical thing over which the abstract power or authority, the right, as given to the proprietor or the ruler, applies. The interpretation as to the territoriality of the bays as mentioned in the renunciatory clause of the treaty appears stronger when considering that the United States specifically renounced the " liberty ", not the " right " to fish or to cure and dry fish. " The United States renounce, forever, any liberty heretofore enjoyed or claimed, to take, cure or dry fish on, or within three marine miles of any of the coasts, bays, creeks or harbours of His Britannic Majesty’s Dominions in America ". It is well known that the negotiators of the Treaty of 1783 gave a very different meaning to the
incident, proceeds the British Case, is of importance, since it shows that the difference between the two phrases was intentional. " (British Counter Case, page 17). And the British Argument emphasizes again the difference. " More cogent still is the distinction between the words right and liberty. The word right is applied to the sea fisheries, and the word liberty to the shore fisheries. The history of the negotiations shows that this distinction was advisedly adopted. " If then a liberty is a grant and not the recognition of a right-, if, as the British Case, Counter Case and Argument recognize, the United States had the right to fish in the open sea in contradistinction with the liberty to fish near the shores or portions of the shores, and if what has been renounced in the words of the treaty is the " liberty " to fish on, or within three miles of the bays, creeks and harbours of His Britannic Majesty’s Dominions, it clearly follows that such liberty and the corresponding renunciation refers only to such portions of the bays which were under the sovereignty of Great Britain and not to such other portions, if any, as form part of the high seas.
And thus it appears that far from being immaterial the territoriality of bays is of the utmost importance. The treaty not containing any rule or indication upon the subject, the Tribunal cannot help a decision as to this point, which involves the second branch of the British contention that all so-called bays are not only geographical but wholly territorial as well, and subject to the jurisdiction of Great Britain. The situation was very accurately described on almost the same lines as above stated by the British Memorandum sent in 1870 by the Earl of Kimberley to Governor Sir John Young: " The right of Great Britain to exclude American fishermen from waters within three miles of the coasts is unambiguous, and, it is believed, uncontested. But there appears to be some doubt what are the waters described as within three miles of bays, creeks or harbors. When a bay is less than six miles broad its waters are within the three mile limit, and therefore clearly within the meaning of the treaty; but when it is more than that breadth, the question arises whether it is a bay of Her Britannic Majesty’s Dominions. This is a question which has to be considered in each particular case with regard to international law and usage. When such a bay is not a bay of Her Majesty’s dominions, the American fishermen shall be entitled to fish in it, except within three marine miles of the ‘ coast’; when it is a bay of Her Majesty’s dominions they will not be entitled to fish within three miles of it, that is to say (it is presumed) within three miles of a line drawn from headland to headland. " (American Case Appendix, page 629.)
Now, it must be stated in the first place that there does not seem to exist any general rule of international law which may be considered final, even in what
So it may be safely asserted that a certain class of bays, which might be properly called the historical bays such as Chesapeake Bay and Delaware Bay in North America and the great estuary of the River Plate in South America, form a class distinct and apart and undoubtedly belong to the littoral country, whatever be their depth of penetration and the width of their mouths, when such country has asserted its sovereignty over them, and particular circumstances such as geographical configuration, immemorial usage and above all, the requirements of self-defense, justify such a pretension. The right of Great Britain over the bays of Conception, Chaleur and Miramichi are of this description. In what refers to the other bays, as might be termed the common, ordinary bays, indenting the coasts, over which no special claim or assertion of sovereignty has been made, there does not seem to be any other general principle to be applied than the one resulting from the custom and usage of each individual nation as shown by their Treaties and their general and time honored practice.
The well known words of Bynkershoek might be very appropriately recalled in this connection when so many and divergent opinions and authorities have been recited: " The common law of nations, " he says, " can only be learnt from reason and custom. I do not deny that authority may add weight to reason, but I prefer to seek it in a constant custom of concluding treaties in one sense or another and in examples that have occurred in one country or another." (Questiones Jure Publici, Vol. 1, Cap. 3.)
It is to be borne in mind in this respect that the Tribunal has been called upon to decide as the subject matter of this controversy, the construction to be given to the fishery Treaty of 1818 between Great Britain and the United States. And so it is that from the usage and the practice of Great Britain in this and other like fisheries and from Treaties entered into by them with other nations as to fisheries, may be evolved the right interpretation to be given to the particular convention which has been submitted. In this connection the following Treaties may be recited:
Treaty between Great Britain and France. 2nd August, 1839. It reads as follows:
Article IX. The subjects of Her Britannic Majesty shall enjoy the exclusive right of fishery within the distance of 3 miles from low water mark along the whole extent of the coasts of the British Islands.
It is agreed that the distance of three miles fixed as the general limit for the exclusive right of fishery upon the coasts of the two countries, shall, with respect to bays, the mouths of which do not exceed ten miles in width, be measured from a straight line drawn from headland to headland.
Article X. It is agreed and understood, that the miles mentioned in the present Convention are geographical miles, whereof 60 make a degree of latitude.
(Hertslett’s Treaties and Conventions, Vol. V, p. 89.)
Art. II. The limits, within which the general right of fishery is exclusively reserved to the subjects of the two kingdoms respectively, are fixed with the exception of those in Granville Bay) at 3 miles distance from low water mark.
With respect to bays, the mouths of which do not exceed ten miles in width, the 3 mile distance is measured from a straight line drawn from headland to headland.
Art. III. The miles mentioned in the present regulations are geographical miles, of which 60 make a degree of latitude.
(Hertslett, Vol. VI, p. 416.)
Treaty between Great Britain and France. November 11, 1867.
Art. I. British fishermen shall enjoy the exclusive right of fishery within the distance of 3 miles from low water mark, along the whole extent of the coasts of the British Islands.
The distance of 3 miles fixed as the general limit for the exclusive right of fishery upon the coasts of the two countries shall, with respect to bays, the mouths of which do not exceed ten miles in width be measured from a straight line drawn from headland to headland.
The miles mentioned in the present convention are geographical miles whereof 60 make a degree of latitude.
(Hertslett’s Treaties, Vol. XII, p. 1126, British Case App., p. 38.)
Great Britain and North German Confederation. British notice to fishermen by the Board of Trade. Board of Trade, November 1868.
Her Majesty’s Government and the North German Confederation having come to an agreement respecting the regulations to be observed by British fishermen fishing off the coasts of the North German Confederation, the following notice is issued for the guidance and warning of British fishermen:
I. The exclusive fishery limits of the German Empire are designated by the Imperial Government as follows: that tract of the sea which extends to a distance of 3 sea miles from the extremest limits which the ebb leaves dry of the German North Sea Coast of the German Islands or flats lying before it, as well as those bays and incurvations of the coast which are ten sea miles or less in breadth reckoned from the extremest points of the land and the flats, must be considered as under the territorial sovereignty of North Germany.
(Hertslett’s Treaties, Vol. XIV, p. 1055.)
Great Britain and German Empire. British Board of Trade, December 1874.
(Same recital referring to an arrangement entered into between Her Britannic Majesty and the German Government.)
Then the same articles follow with the alteration of the words " German Empire " for " North Germany ".
(Hertslett’s, Vol. XIV, p. 1058.)
II. Les pécheurs nationaux jouiront du droit exclusif de peche dans le rayon de 3 milles, á partir de la laisse de basse mer, le long de toute l’étendue des cotes de leurs pays respectifs, ainsi que des iles et des bancs qui en dépendent.
Pour les baies le rayon de 3 milles sera mesuré á partir d’une ligne droite, tirée, en travers de la baie, dans la partie la plus rapprochée de l’entrée, au premier point ou l’ouverture n’excédera pas 10 milles.
(Hertslett, Vol. XV, p. 794.)
British Order in Council, October 23rd, 1877.
Prescribes the obligation of not concealing or effacing numbers or marks on boats, employed in fishing or dredging for purposes of sale on the coasts of England, Wales, Scotland and the Islands of Guernsey, Jersey, Alderney, Sark and Man, and not going outside;
(a) The distance of 3 miles from low water mark along the whole extent of the said coasts;
(b) In cases of bays less than 10 miles wide the line joining the headlands of said bays.
(Hertslett’s, Vol. XIV, p. 1032.)
To this list may be added the unratified Treaty of 1888 between Great Britain and the United States which is so familiar to the Tribunal. Such unratified Treaty contains an authoritative interpretation of the Convention of October 20th, 1818, sub-judice: " The three marine miles mentioned in Article I of the Convention of October 20th, 1818, shall be measured seaward from low-water mark; but at every bay, creek or harbor, not otherwise specifically provided for in this Treaty, such three marine miles shall be measured seaward from a straight line drawn across the bay, creek or harbor, in the part nearest the entrance at the first point where the width does not exceed ten marine miles ", which is recognizing the exceptional bays as aforesaid and laying the rule for the general and common bays.
It has been suggested that the Treaty of 1818 ought not to be studied as hereabove in the light of any Treaties of a later date, but rather be referred to such British international Conventions as preceded it and clearly illustrate, according to this view, what were, at the time, the principles maintained by Great Britain as to their sovereignty over the sea and over the coast and the adjacent territorial waters. In this connection the Treaties of 1686 and 1713 with France and of 1763 with France and Spain have been recited and offered as examples also of exclusion of nations by agreement from fishery rights on the high seas. I cannot partake of such a view. The treaties of 1686, 1713 and 1763 can hardly be understood with respect to this, otherwise than as examples of the wild, obsolete claims over the common ocean which all nations have of old abandoned with the progress of an enlightened civilization. And if certain nations accepted long ago to be excluded by convention from fishing on what is to-day considered a common sea, it is precisely because it was then understood that such tracts of water, now free and open to all, were the exclusive property of a particular power, who, being the owners, admitted or excluded others from their use. The Treaty of 1818 is in the meantime one of the few which mark an era in the diplomacy of the world. As a matter of fact it is the very much which commuted the rule of the cannon-shot into the three marine miles of coastal jurisdiction. And it really would appear unjustified to explain such historic document.
The Treaty of 1818 is not a separate fact unconnected with the later policy of Great Britain. Its negotiators were not parties to such international Convention and their powers disappeared as soon as they signed the document on behalf of their countries. The parties to the Treaty of 1818 were the United States and Great Britain, and what Great Britain meant in 1818 about bays and fisheries, when they for the first time fixed a marginal jurisdiction of three miles, can be very well explained by what Great Britain, the same permanent political entity, understood in 1839, 1843, 1867, 1874, 1878 and 1882, when fixing the very same zone of territorial waters. That a bay in Europe should be considered as different from a bay in America and subject to other principles of international law cannot be admitted in the face of it. What the practice of Great Britain has been outside the Treaties is very well known to the Tribunal, and the examples might be multiplied of the cases in which that nation has ordered its subordinates to apply to the bays on these fisheries the ten mile entrance rule or the six miles according to the occasion. It has been repeatedly said that such have been only relaxations of the strict right, assented to by Great Britain in order to avoid friction on certain special occasions. That may be. But it may also be asserted that such relaxations have been very many and that the constant, uniform, never contradicted practice of concluding fishery Treaties from 1839 down to the present day, in all of which the ten miles entrance bays are recognized, is the clear sign of a policy. This policy has but very lately found a most public, solemn and unequivocal expression. " On a question asked in Parliament on the 21st of February 1907, says Pitt Cobbett, a distinguished English writer, with respect to the Moray Firth Case, it was stated that, according to the view of the Foreign Office, the Admiralty, the Colonial Office, the Board of Trade and the Board of Agriculture and Fisheries, the term " territorial waters " was deemed to include waters extending from the coast line of any part of the territory of a State to three miles from the low-water mark of such coast line and the waters of all bays, the entrance to which is not more than six miles, and of which the entire land boundary
Is there a contradiction between these six miles and the ten miles of the treaties just referred to? Not at all. The six miles are the consequence of the three miles marginal belt of territorial waters in their coincidence from both sides at the inlets of the coast and the ten miles far from being an arbitrary measure are simply an extension, a margin given for convenience to the strict six miles with fishery purposes. Where the miles represent sixty to a degree in latitude the ten miles are besides the sixth part of the same degree. The American Government in reply to the observations made to Secretary Bayard’s Memorandum of 1888, said very precisely: "The width of ten miles was proposed not only because it had been followed in Conventions between many other powers, but also because it was deemed reasonable and just in the present case; this Government recognizing the fact that while it might have claimed a width of six miles as a basis of settlement, fishing within bays and harbors only slightly wider would be confined to areas so narrow as to render it practically valueless and almost necessarily expose the fishermen to constant danger of carrying their operations into forbidden waters. " (British Case Appendix, page 416.) And Professor John Basset Moore, a recognized authority on International law, in a communication addressed to the Institute of International law, said very forcibly: " Since you observe that there does not appear to be any convincing reason to prefer the ten mile line in such a case to that of double three miles, I may say that there have been supposed to exist reasons both of convenience and of safety. The ten mile line has been adopted in the cases referred to as a practical rule. The transgression of an encroachment upon territorial waters by fishing vessels is generally a grave offense, involving in many instances the forfeiture of the offending vessel, and it is obvious that the narrower the space in which it is permissible to fish the more likely the offense is to be committed. In order, therefore, that fishing may be practicable and safe and not constantly attended with the risk of violating territorial waters, it has been thought to be expedient not to allow it where the extent of free waters between the three miles drawn on each side of the bay is less than four miles. This is the reason of the ten mile line. Its intention is not to hamper or restrict the right to fish, but to render its exercise practicable and safe. When fishermen fall in with a shoal of fish, the impulse to follow it is so strong as to make the possibilities of transgression very serious within narrow limits of free waters. Hence it has been deemed wiser to exclude them from space less than four miles each way from the forbidden lines. In spaces less than this operations are not only hazardous, but so circumscribed as to render them of little practical value. " (Annuaire de l’Institut de Droit International, 1894, p. 146.)
So the use of the ten mile bays so constantly put into practice by Great Britain in its fishery Treaties has its root and connection with the marginal belt of three miles for the territorial waters. So much so that the Tribunal having decided not to adjudicate in this case the ten miles entrance to the bays of the treaty of 1818, this will be the only one exception in which the ten miles of the bays do not follow as a consequence the strip of three miles of territorial waters, the historical bays and estuaries always excepted.
And it is for that reason that an usage so firmly and for so long a time established ought, in my opinion, be applied to the construction of the Treaty under consideration, much more so, when custom, one of the recognized sources of law, international as well as municipal, is supported in this case by reason and by the acquiescence and the practice of many nations.
These are the reasons for my dissent, which I much regret, on Question Five.
Here are some suggestions to get you started
Access to the PDF of this document is reserved upon request to subscribers of Jus Mundi - Legal Practice offer. The HTML version of this document remains fully available on our website.
Request the PDF
This Wiki Note has not been submitted yet. We continuously identify new themes to add to the existing Wiki Notes as well as Contributors to author new Notes. Become a Contributor, submit your candidacy to author this Wiki Note.
Oops! You have reached the maximum limit for alerts (10 max. for arbitrators)
Delete an existing alert to create a new one
Oops! You have reached the maximum limit for alerts (10 max. for cases)
This feature requires a subscription.
Get access to the most extensive & reliable source of information in arbitration
Already registered ? Sign in
An error just occurred, please try again
You need Premium access to be able to use this feature.
Login to access this feature, jus ai acceleration program participants only.
Unlock access to Jus AI Assistant by joining the Jus AI Acceleration program
- Fisheries Disputes: The Real Potential for Arctic Conflict

A U.S. Coast Guardsman with, embarked aboard the guided-missile destroyer USS Shoup (DDG 86), takes a photo of a fishing vessel in 2018. Photo: U.S. Pacific Fleet
Much recent discussion has focused on the contemporary militarization of Arctic and subarctic regions. Journalism and scholarship alike question if military conflict might occur, how peace can be maintained, and what war would look like in the Arctic. To provide insight on such queries, The Arctic Institute’s 2021 Conflict Series provides analysis on past Arctic militarization and military activities—seeking both historic context and lessons learned for modern Arctic politics.
The Arctic Institute Conflict Series 2021
- The History and Future of Arctic State Conflict: The Arctic Institute Conflict Series
- Environmental Détente: What can we learn from the Cold War to manage today’s Arctic Tensions and Climate Crisis?
- Knowledge is Power: Greenland, Great Powers, and Lessons from the Second World War
- The Impact of the Post-Arms Control Context and Great Power Competition in the Arctic
- The Arctic Institute Conflict Series: Conclusion
Conflict is a natural part of society. It describes a situation where two or more actors hold incompatible goals. Despite common usage, the term does not entail outright hostility or war. As described by the SAGE Handbook of Conflict Resolution : “conflict is normal, ubiquitous, and unavoidable.”
As sea ice diminishes in the Arctic, writings about conflict in the region have directed focus to accessing and potentially claiming undiscovered offshore oil and gas resources. However, oil and gas resources in the North have not yet generated conflict or aggression. Instead, small-scale disputes in the Arctic are being primarily driven by another ocean-based commodity: marine living resources.
In the Arctic, retreating sea ice and climate change are altering the distribution of marine living resources, while demand for these resources has risen. This, in turn, is challenging established management regimes for transboundary resources and calling for new forms of cooperation. Consequently, over the last decade several disputes have emerged over Arctic fisheries, at times even escalating into outright conflict.
This is not the same as claiming that outright hostilities amongst Arctic states are inevitable. Still, we should look at past and current examples of marine resource disputes, in order to say something about how the way forward might evolve.
Here we will examine three cases of conflict related to fisheries management impacted by global warming in the Bering Sea, Barents Sea, and the North Atlantic in an effort to tease out lessons, dynamics, and general relevance to the Arctic region. We start with the Bering Sea/Strait domain, before turning to some relevant examples in the North Atlantic. Thereafter, we assess what lessons these examples hold for future resource conflicts in the Arctic.
The Bering Sea / Strait
The Bering Sea and Bering Strait have long been an area of contention surrounding the harvesting and conservation of marine living resources. In 1887 and 1889, the U.S. – citing sustainability concerns – seized British-Canadian vessels harvesting seals in international waters of the Bering Sea. 1) Campbell C S (1963) The Bering Sea Settlements of 1892. Pacific Historical Review (32): 347-67. This dispute set the stage for larger discussions on sustainable harvesting in the region, ultimately leading to the North Pacific Sealing Convention of 1911 and setting the precedent for future agreements. 2) Bailey T A (1935) The North Pacific Sealing Convention of 1911. Pacific Historical Review 4: 1-14.
Today, the Bering Sea is home to one of the world’s largest fisheries 3) Blanchet M-A, Primicerio R, Frainer A, Kortsch A, Skern-Mauritzen M, Dolgov A V, Aschan M (2019) The role of marine mammals in the Barents Sea foodweb. ICES Journal of Marine Science (76): i37–i53. and its stocks are growing rapidly as fish migrate north due to rising ocean temperatures. 4) Stabeno P J, Thoman R L, and Wood K (2019) Recent Warming in the Bering Sea and Its Impact on the Ecosystem. NOAA Arctic Program , https://arctic.noaa.gov/report-card/report-card-2019/recent-warming-in-the-bering-sea-and-its-impact-on-the-ecosystem/ . The fishery has subsequently become a theatre of renewed U.S.-Russia competition: In 2020, fishing vessels were targeted by Russian military within the American exclusive economic zone (EEZ). Some 90 warships and military aircraft were part of the Russian effort to secure economic development in the North Pacific, a region that is becoming increasingly lucrative as melting sea ice makes way for resource extraction and trade routes. 5) Baker M (2020) ’Are We Getting Invaded?’: U.S. Boats Faced Russian Aggression Near Alaska. The New York Times , https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/12/us/russia-military-alaska-arctic-fishing.html .
Meanwhile, President Biden has signed executive orders regulating pollution associated with maritime vessels and restricting trawling practices across large portions of the Bering Sea, Bering Strait, and Chukchi Sea. The executive orders contrast with Russia’s moves towards economic development, suggesting renewed friction between economic priorities and environmental sustainability in the North Pacific.
The North Atlantic / Barents Sea
One particular issue in the North Atlantic has been the still unresolved division of mackerel quotas, as the stock has shifted its geographic positioning. On its own, mackerel constitutes one of the most profitable fish stocks in the North Atlantic. Since reaching an agreement on quotas in 1999, the Northeast Atlantic mackerel stock has predominantly been divided between the EU, Norway, and the Faroe Islands.
In 2006, the mackerel shifted northwards, in tandem with a rise in the sea temperature in the North Sea and North Atlantic. 6) Spijkers J and Boonstra W J (2017) Environmental Change and Social Conflict: The Northeast Atlantic Mackerel Dispute. Regional Environmental Change 17: 1835–51. From virtually no catches prior to the stock’s arrival in 2006, Icelandic fishermen caught more than 100,000 tonnes in 2008–2009, 7) ICES (2017) ICES Advice on Fishing Opportunities, Catch, and Effort -Northeast Atlantic. ICES, https://nasco.int/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/CNL_17_8_ACOM_Advice.pdf . constituting approximately 20–25 percent of the total catch of mackerel in the Northeast Atlantic. To date, however, Iceland remains outside of the total quota-setting scheme. Over time, the coastal states’ combined increase in fishing pressure resulted in ever-growing overfishing of the stock. By 2019 the fish stock had lost its “sustainable” certification through the Marine Stewardship Council. 8) MSC (2017) MSC Certificates Suspended for All North East Atlantic Mackerel Fisheries. MSC, https://www.msc.org/media-centre/press-releases/press-release/msc-certificates-suspended-for-all-north-east-atlantic-mackerel-fisheries . In late 2019, Icelandic officials stated they would not back down on the issue, while the remaining states criticized its unilateral quota setting for endangering the health of the fish stock. 9) Henley J (2019) Iceland Accused of Putting Mackerel Stocks at Risk by Increasing Its Catch. The Guardian , 21 November, https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2019/nov/21/iceland-accused-of-putting-mackerel-stocks-at-risk-by-increasing-its-catch .
Another relevant case just north of Iceland – in the Barents Sea – concerns snow crab and the Svalbard continental shelf. Snow crab was first recorded in the eastern Barents Sea in 1996. In Canada and the United States, snow crab ranks among the most valuable fisheries. Thus, expectations in Norway have been high concerning the economic potential of this new species, with some anticipating that it might even surpass cod, which is currently the most valuable fishery in the Norwegian EEZ. 10) Fiskeribladet (2014) Snøkrabbe: Fra Null Til Hundre Millioner i Fangstverdi. Fiskeribladet , 6 December.
Starting in 2015, however, Norway introduced a ban on the catching of snow crab on the Norwegian continental shelf, which includes the shelf around Svalbard. In practice, the Norwegian government permitted a limited number of licences to be issued to Norwegian fishermen exclusively, through special requests. 11) Østhagen A and Raspotnik A (2018) Crab! How a Dispute over Snow Crab Became a Diplomatic Headache between Norway and the EU. Marine Policy 98: 58–64.
Both the EU and Norway define the snow crab as belonging to the continental shelf regime. Therefore, the broader legal ramifications of this dispute go beyond the right to catch snow crab on the continental shelf around Svalbard, with potential applications to sedentary resources such as oil and gas and seabed minerals. Although there has thus far been no oil and gas drilling on the continental shelf around Svalbard, the outcome of the dispute over snow crab might set a precedent for future industrial activity. 12) Tiller R and Nyman E (2015) Having the Cake and Eating It Too: To Manage or Own the Svalbard Fisheries Protection Zone. Marine Policy 60: 141–48; Tiller R and Nyman E (2017) The Clear and Present Danger to the Norwegian Sovereignty of the Svalbard Fisheries Protection Zone: Enter the Snow Crab. Ocean and Coastal Management 137: 24–33.
Arctic (marine) Resource Conflicts
As shown in the cases here, although the potential for conflict over fisheries – access to or distribution of – is relatively high, states have generally preferred to keep these disputes and, at times, outright conflict separate from other issues. 13) Nyman E (2013) Oceans of Conflict: Determining Potential Areas of Maritime Disputes. SAIS Review of International Affairs 33 (2): 5–14; Nemeth S C et al. (2014) Ruling the Sea: Managing Maritime Conflicts through UNCLOS and Exclusive Economic Zones. International Interactions 40 (5): 711–36; Raspotnik A and Østhagen A (2020) How Much Is the Fish? When Foreign Policy Meets Fishing Interests in the EU’s Arctic Endeavour. International Relations 34 (3). The mackerel dispute has not hampered quota negotiations on other fish stocks amongst the Northeast Atlantic coastal states (although there have been issues concerning herring), nor has it affected their regional and bilateral foreign relations.
In the EU-Norway case, politicians and diplomats actively worked to keep the issue separate from larger Arctic governance questions, preferring to treat it as a fisheries concern rather than linking it to the EU’s continuous quest for a role in the Arctic. 14) Raspotnik A (2018) The European Union and the Geopolitics of the Arctic. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar; Raspotnik A and Østhagen A (2020) How Much Is the Fish? When Foreign Policy Meets Fishing Interests in the EU’s Arctic Endeavour. International Relations 34 (3). Similarly, the U.S. Coast Guard refrained from engaging Russian military in the Bering Sea – even as American fishing vessels were threatened – citing Russia’s right to conduct military operations in the EEZ. 15) Baker M (2020) ’Are We Getting Invaded?’: U.S. Boats Faced Russian Aggression Near Alaska. The New York Times , https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/12/us/russia-military-alaska-arctic-fishing.html .
Despite this relative compartmentalization, two trends suggest that relations and issues concerning fisheries are unlikely to become less sensitive in the near future. First, an increasing number of fisheries – American, Icelandic, Norwegian and Russian – are expected to venture further northwards in the Bering Sea, Bering Strait, and the Barents Sea. This development will prompt the coastal states to discuss changes to their management regimes and quota distribution. Second, the Barents Sea and Bering Sea are playing an increasing role in strategic posturing and military exercises, as NATO members and Russia showcase their Arctic capabilities and aim to secure rights to valuable trade routes.
Furthermore, although fisheries disputes are, to some extent, compartmentalized, they are also increasingly entangled in domestic politics. The interests that states hold in marine living resources—the Icelandic and Norwegian interests in mackerel fisheries, Russian fisheries interests in the waters around Svalbard, the interests of the EU and EU member states in snow crab fisheries, and conflicting economic and sustainability interests in the North Pacific—should not be underestimated. Although the monetary value of these fisheries might not dwarf that of other Arctic industrial or economic ventures, neither is it insignificant from a financial viewpoint.
Arctic states, driven by their fishers and fisheries, are not likely to forgo access to fish stocks or yield quotas simply because the fish stocks themselves have altered their distributional patterns. These dimensions could be evidenced here by European politicians’ statements over the snow crab dispute; by the U.S. Coast Guard’s lack of forewarning to fishing vessels of planned Russian military operations in U.S. waters; and by the arguments of Norwegian and Icelandic fisheries organisations when disagreeing on mackerel quotas.
Science to the Rescue?
The role of scientific advice in preventing future conflict stands out as a particularly useful dimension for further examination. The use of an assumedly neutral source of reliable information is crucial for trust in the relevant regime, especially when dealing with issues linked to climate change. 16) Sarewitz D (2004) How Science Makes Environmental Controversies Worse. Environmental Science and Policy 7 (5): 386. If, however, there is too much uncertainty surrounding reliable information, actors sometimes opt to ignore, be selective of, or even hide relevant information. 17) Polasky S et al. (2011) Decision-Making under Great Uncertainty: Environmental Management in an Era of Global Change. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 402.
One solution that states in the Arctic and beyond have used to alleviate such pressures is regional issue-specific multilateral cooperation. For example, the Barents Sea management regime – through the Joint Norwegian-Russian Fisheries Commission – has often been heralded as best practice with regards to marine resource co-management mechanisms. 18) Hønneland G (2014) Norway and Russia: Bargaining Precautionary Fisheries Management in the Barents Sea. Arctic Review on Law and Politics 5 (1): 75–99; Stokke O S (2000) Sub-Regional Cooperation and Protection of the Arctic Marine Environment: The Barents Sea in Protecting the Polar Marine Environment: Law and Policy for Pollution Prevention , ed. Davor Vidas. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Similarly, in the Bering Sea, as the pollock stock collapsed in the early 1990s after a decade of overfishing in the so-called “Donut Hole,” a regime came into existence to manage the stock. 19) Bailey K M (2011) An Empty Donut Hole: The Great Collapse of a North American Fishery. Ecology and Society 16 (2): 1–3. In 1994, an agreement on a temporary moratorium on pollock was reached by the various national stakeholders, including Japan, China, Poland, and South Korea, with stringent enforcement measures. 20) Dunlap W V (1994) A Pollock-Fishing Agreement for the Central Bering Sea. IBRU Boundary and Security Bulletin : 47.
More recently, in 2018, the five Arctic states with direct access to the Arctic Ocean – together with China, Japan, Iceland, South Korea and the EU – agreed to prevent unregulated commercial fishing in the high seas of the central Arctic Ocean. 21) Official Journal of the European Union (2019) Agreement to Prevent Unregulated High Seas Fisheries in the Central Arctic Ocean” https://publications.europa.eu/resource/cellar/f075cd03-46f3-11e9-a8ed-01aa75ed71a1.0006.03/DOC_1 . This was heralded as a “proactive rather than reactive approach, showcasing the Arctic states’ commitment in dealing with climate change”. 22) Sumaila U R (2015) Temporary Ban on Fishing Reflects How Fragile Arctic Ecosystem Is. The Conversation , 12 August, https://theconversation.com/temporary-ban-on-fishing-reflects-how-fragile-arctic-ecosystem-is-44954 . There are similar bans on commercial fishing within the EEZ in the Chukchi Sea (where the United States imposes the ban unilaterally) and the Beaufort Sea (with the United States and Canada imposing the ban bilaterally), which are in place pending further research on the potential fish stocks migrating to these areas.
In other words, although conflict potential exists concerning marine living resources in the Arctic, disputes over such issues are not destined to escalate and/or become protracted. However, taking proactive measures or diffusing an ongoing dispute requires both political engagement and concern over the long-term effects of a protracted dispute. Here, the mackerel dispute can serve as a staunch lesson, as the stock lost its rather valuable MSC-certification in 2019. 23) MSC (2017) MSC Certificates Suspended for All North East Atlantic Mackerel Fisheries. MSC, https://www.msc.org/media-centre/press-releases/press-release/msc-certificates-suspended-for-all-north-east-atlantic-mackerel-fisheries .
The future is blue
In the Arctic and beyond, we can observe rapid changes in the maritime domain over the last few decades. As these changes occur, attention is increasingly directed towards the question of “who has what rights” at sea. Some elements are central here: the state and use of scientific/external advice when agreeing on quotas for marine living resources; 24) Polacheck T (2012) Politics and Independent Scientific Advice in RFMO Processes: A Case Study of Crossing Boundaries. Marine Policy 36 (1): 132–41. the depth of institutionalisation between the states in question; 25) Young O R (1989) International Cooperation: Building Regimes for Natural Resources and the Environment. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. and the (un)willingness by states to forgo access to fisheries seen in conjunction with domestic interests and symbolism. 26) Vaquer i Fanés J (2003) The Domestic Dimension of EU External Policies: The Case of EU-Morocco 2000-01 Fisheries Negotiations. Mediterranean Politics 8 (1): 59–82; Ásgeirsdóttir Á (2008) Who Gets What? Domestic Influences on International Negotiations Allocating Shared Resources . Albany, NY: State University of New York Press.
It is no secret that humanity is experiencing a widespread reduction in the total biomass of marine resources, closely linked to human exploitative activities. 27) FAO (2018) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. https://www.fao.org/3/CA0190EN/ca0190en.pdf . At the same time, stocks are changing their migratory patterns because of changes in the geophysical marine environment. 28) Brander K (2010) Impacts of Climate Change on Fisheries. Journal of Marine Systems 79 (3–4): 389–402. It would be simple to conclude that the conflict potential between states over how best to manage marine living resources in the Arctic is likely to rise as a consequence of these factors. However, the Arctic states have a history of developing co-management mechanisms to solve problems with overfishing in northern waters.
International cooperative mechanisms have grown in all oceans bordering the Arctic, as well as in the Arctic basin itself. They have grown out of a realization that continued over-exploitation would lead to a lose-lose situation for all states concerned. As the Arctic is particularly prone to environmental changes, states will continue to navigate emerging issues with marine resource management and distribution. Fisheries is indeed where the real conflict potential in the Arctic lies, but that does not mean these conflicts cannot be managed, or even resolved.
References [ + ]
| 1 | Campbell C S (1963) The Bering Sea Settlements of 1892. (32): 347-67. |
|---|---|
| 2 | Bailey T A (1935) The North Pacific Sealing Convention of 1911. 4: 1-14. |
| 3 | Blanchet M-A, Primicerio R, Frainer A, Kortsch A, Skern-Mauritzen M, Dolgov A V, Aschan M (2019) The role of marine mammals in the Barents Sea foodweb. (76): i37–i53. |
| 4 | Stabeno P J, Thoman R L, and Wood K (2019) Recent Warming in the Bering Sea and Its Impact on the Ecosystem. , . |
| 5, 15 | Baker M (2020) ’Are We Getting Invaded?’: U.S. Boats Faced Russian Aggression Near Alaska. , . |
| 6 | Spijkers J and Boonstra W J (2017) Environmental Change and Social Conflict: The Northeast Atlantic Mackerel Dispute. 17: 1835–51. |
| 7 | ICES (2017) ICES Advice on Fishing Opportunities, Catch, and Effort -Northeast Atlantic. ICES, . |
| 8, 23 | MSC (2017) MSC Certificates Suspended for All North East Atlantic Mackerel Fisheries. MSC, . |
| 9 | Henley J (2019) Iceland Accused of Putting Mackerel Stocks at Risk by Increasing Its Catch. , 21 November, . |
| 10 | Fiskeribladet (2014) Snøkrabbe: Fra Null Til Hundre Millioner i Fangstverdi. , 6 December. |
| 11 | Østhagen A and Raspotnik A (2018) Crab! How a Dispute over Snow Crab Became a Diplomatic Headache between Norway and the EU. 98: 58–64. |
| 12 | Tiller R and Nyman E (2015) Having the Cake and Eating It Too: To Manage or Own the Svalbard Fisheries Protection Zone. 60: 141–48; Tiller R and Nyman E (2017) The Clear and Present Danger to the Norwegian Sovereignty of the Svalbard Fisheries Protection Zone: Enter the Snow Crab. 137: 24–33. |
| 13 | Nyman E (2013) Oceans of Conflict: Determining Potential Areas of Maritime Disputes. 33 (2): 5–14; Nemeth S C et al. (2014) Ruling the Sea: Managing Maritime Conflicts through UNCLOS and Exclusive Economic Zones. 40 (5): 711–36; Raspotnik A and Østhagen A (2020) How Much Is the Fish? When Foreign Policy Meets Fishing Interests in the EU’s Arctic Endeavour. 34 (3). |
| 14 | Raspotnik A (2018) Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar; Raspotnik A and Østhagen A (2020) How Much Is the Fish? When Foreign Policy Meets Fishing Interests in the EU’s Arctic Endeavour. 34 (3). |
| 16 | Sarewitz D (2004) How Science Makes Environmental Controversies Worse. 7 (5): 386. |
| 17 | Polasky S et al. (2011) Decision-Making under Great Uncertainty: Environmental Management in an Era of Global Change. 402. |
| 18 | Hønneland G (2014) Norway and Russia: Bargaining Precautionary Fisheries Management in the Barents Sea. 5 (1): 75–99; Stokke O S (2000) Sub-Regional Cooperation and Protection of the Arctic Marine Environment: The Barents Sea in , ed. Davor Vidas. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| 19 | Bailey K M (2011) An Empty Donut Hole: The Great Collapse of a North American Fishery. 16 (2): 1–3. |
| 20 | Dunlap W V (1994) A Pollock-Fishing Agreement for the Central Bering Sea. : 47. |
| 21 | Official Journal of the European Union (2019) Agreement to Prevent Unregulated High Seas Fisheries in the Central Arctic Ocean” . |
| 22 | Sumaila U R (2015) Temporary Ban on Fishing Reflects How Fragile Arctic Ecosystem Is. , 12 August, . |
| 24 | Polacheck T (2012) Politics and Independent Scientific Advice in RFMO Processes: A Case Study of Crossing Boundaries. 36 (1): 132–41. |
| 25 | Young O R (1989) Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. |
| 26 | Vaquer i Fanés J (2003) The Domestic Dimension of EU External Policies: The Case of EU-Morocco 2000-01 Fisheries Negotiations. 8 (1): 59–82; Ásgeirsdóttir Á (2008) . Albany, NY: State University of New York Press. |
| 27 | FAO (2018) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. . |
| 28 | Brander K (2010) Impacts of Climate Change on Fisheries. 79 (3–4): 389–402. |
Internet Explorer lacks support for the features of this website. For the best experience, please use a modern browser such as Chrome, Firefox, or Edge.

A Case Study in Connecting Fisheries Management Challenges With Models and Analysis to Support Ecosystem-Based Management in the California Current Ecosystem
June 30, 2021
We address the challenges of models and analyses for ecosystem-based fisheries management by presenting a case study of a process to identify management priorities and assess potential models and analyses that could help the identified policy concerns.
One of the significant challenges to using information and ideas generated through ecosystem models and analyses for ecosystem-based fisheries management is the disconnect between modeling and management needs. Here we present a case study from the U.S. West Coast, the stakeholder review of NOAA’s annual ecosystem status report for the California Current Ecosystem established by the Pacific Fisheries Management Council’s Fisheries Ecosystem Plan, showcasing a process to identify management priorities that require information from ecosystem models and analyses. We then assess potential ecosystem models and analyses that could help address the identified policy concerns. We screened stakeholder comments and found 17 comments highlighting the need for ecosystem-level synthesis. Policy needs for ecosystem science included: (1) assessment of how the environment affects productivity of target species to improve forecasts of biomass and reference points required for setting harvest limits, (2) assessment of shifts in the spatial distribution of target stocks and protected species to anticipate changes in availability and the potential for interactions between target and protected species, (3) identification of trophic interactions to better assess tradeoffs in the management of forage species between the diet needs of dependent predators, the resilience of fishing communities, and maintenance of the forage species themselves, and (4) synthesis of how the environment affects efficiency and profitability in fishing communities, either directly via extreme events (e.g., storms) or indirectly via climate-driven changes in target species availability. We conclude by exemplifying an existing management process established on the U.S. West Coast that could be used to enable the structured, iterative, and interactive communication between managers, stakeholders, and modelers that is key to refining existing ecosystem models and analyses for management use.
Tommasi D, deReynier YL, Townsend H, Harvey CJ, Satterthwaite W, Marshall KN, Kaplan IC, Brodie S, Field J, Hazen E, et al . 2021. A Case Study in Connecting Fisheries Management Challenges With Models and Analysis to Support Ecosystem-Based Management in the California Current Ecosystem. Frontiers in Marine Science. 8:776. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.624161.
Last updated by Pacific Islands Fisheries Science Center on 11/26/2021
Answer: Canada and the United States have similar political systems and cultures.
D. Canada and the United States have similar political systems and cultures.
- DalSpace Home
- Faculty of Science
- Marine Affairs Program
- Marine Affairs Program, Graduate Projects
How Decision-Making in Fisheries Management Contributes to Changes in the Fishery: A Case Study of North Atlantic Swordfish

Collections

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
U.S. National Marine Fisheries. *Guidelines gave rules about how many fish of a certain size could be caught in the waters of the United States. *Sustainable Fisheries Act of 1996- some areas were closed to fishing to allow the fish to recover and some other areas were closed to let the fish breed. *Aquaculture- process of farming fish ...
The Atlantic cod is a demersal ("bottom-dwelling") species that may attain lengths of up to 130 cm (51 inches) and weights of 25-35 kg (55-77 lbs). Maximum age is over 20 years but younger fish (2-5 years, weighing 5-10 lbs.) make up the majority of the catch. Sexual maturity is reached at 2-4 years.
XIII, 1911, p. 5. SYLLABUS'. The treaty of peace of 1783 between Great Britain and the United States stipulated that inhabitants of the United States should continue to exercise the privileges theretofore enjoyed in common with British subjects in the fisheries of Newfoundland, Labrador, and other parts of the North Atlantic Coast.
Introduction. The complex interplay between commercial fisheries and marine protected species may require multiple policy instruments to support conservation, as in the case with the north Atlantic right whale (Eubalena glacialis; right whale) and the American lobster (Homarus americanus) fishery in the northeast United States (U.S.).Bycatch is the single greatest cause of cetacean mortality ...
Through the 19th and early 20th centuries, Atlantic cod was a staple for the fisheries in the Northern Atlantic Ocean. However, starting in the late 1950s, offshore bottom trawlers began to fish in deeper parts of the stock (Walter et al. 2005). This led to a dramatic increase in the number of fish landings.
A recent study by Blackport, Fyfe, and Screen (Citation 2022) showe that CMIP6 models simulate a wide range of trends for sea-level pressure (SLP) and wind trends in the North Atlantic region. However, they generally strongly underestimate or even fail to simulate the observed increasing trend toward stronger zonal winds in the North Atlantic ...
This paper addresses these sensitivities, the reasons for non-reporting, and possible solutions, using bycatch of the critically endangered European sturgeon (Acipenser sturio L.) in the Northeast Atlantic fisheries as a case study. This study comprises 36 interviews with fishers, fisher representatives, environmental non-governmental ...
A. AMO-BP prediction model of future temperature change in the North Atlantic based on BP. neural network: (1) Data processing. In order to identify the most likely location of these two fish es ...
NATIONAL CENTER FOR CASE STUDY TEACHING IN SCIENCE ... North Atlantic. He described these shifts as being related to climate velocity, which is the rate and direction that temperature shifts across space. "We are seeing overall shifts in species at a rate of 0.24-0.70° latitude per decade, or ... Fisheries vessels during their spring fish ...
North Atlantic Fisheries Case. (1910) 11 R.I.A.A. 167. In 1818, Great Britain and the United States concluded a treaty defining the rights ... Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a ...
Case study #18 Mackerel in the north-east Atlantic #19 Flatfish in the North Sea ... Similar to all Northeast Atlantic fisheries, the mackerel fishery is sensitive to changes in fish price. In addition, pelagic ... Change in habitat suitability in the North Sea for Atlantic Mackerel by mid-century (2050) under RCP 4.5 (left) and
Entanglement in commercial fishing ropes threatens the recovery of the North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis), a species largely restricted to waters off of eastern North America. In recent years, serious entanglements have been increasing, and mortality from conflicts with fishing operations exceeds US legal mandates, with 83% of the population showing incidence of scarring as a ...
View full document. Case Study 2: North Atlantic Fisheries Commercial fish catches have declined in recent years. The cause is overfishing. Regulations closed some fishing grounds to allow fish stocks to replenish. In the mean time, aquaculture, or fish farming, also can provide food for people. Case Study 3: Climate Change Global warming, the ...
The Anglo-Norwegian Fisheries Case, also known as the Fisheries Case is a landmark case in the history of international law and it deals with the issue of fishing rights in the North Sea. The case was brought before the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in 1951 by the United Kingdom, challenging Norway's jurisdiction over fisheries in the ...
A Case Study Institute for Fisheries Management and Coastal Community Development Research Publication No. 48 Douglas C. Wilson Institute for Fisheries Management North Sea Center, Willemoesvej 2 P.O.Box 104, DK-9850 Hirtshals, Denmark phone : +45 98 94 28 55, fax : +45 98 94 42 68 e-mail : [email protected]
Treaty between Great Britain, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany and the Netherlands for regulating the police of the North Sea Fisheries, May 6, 1882. II. Les pécheurs nationaux jouiront du droit exclusif de peche dans le rayon de 3 milles, á partir de la laisse de basse mer, le long de toute l'étendue des cotes de leurs pays respectifs ...
The North Atlantic Swordfish Fishery is an interesting case study because of the migratory range of the target species, variability of the stock status, and the variety of management actions applied at national and international scales over the past six decades.
Another relevant case just north of Iceland - in the Barents Sea - concerns snow crab and the Svalbard continental shelf. ... (2017) MSC Certificates Suspended for All North East Atlantic Mackerel Fisheries. MSC, ... (2012) Politics and Independent Scientific Advice in RFMO Processes: A Case Study of Crossing Boundaries. Marine Policy 36 (1
Here we present a case study from the U.S. West Coast, the stakeholder review of NOAA's annual ecosystem status report for the California Current Ecosystem established by the Pacific Fisheries Management Council's Fisheries Ecosystem Plan, showcasing a process to identify management priorities that require information from ecosystem models ...
Case Study 2: North Atlantic Fisheries For Questions 8-10, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words. 8. Technologies that have led to large increases in the mass of ocean fish caught include large boats and high-tech_ equipment. 9. _caused the decline in fish catches since 1997. 10.
Case Study 2 North Atlantic Fisheries - We respect your right to privacy. That means you can choose to not allow some types of cookies. Click on the different types of cookies listed below to find out more about each one and to change our default settings for your browser.
Fisheries management must constantly adapt to changes in stock status, shifts in effort, and national and international policy. The North Atlantic Swordfish Fishery is an interesting case study because of the migratory range of the target species, variability of the stock status, and the variety of management actions applied at national and international scales over the past six decades.