- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Don't Miss the Grand Prize: A $2,500 Office Depot/OfficeMax Card!

57 Fun End-of-Year Activities and Assignments
Wrap up the year on a happy note.

As the school year draws to a close, it’s important to plan end-of-year activities that help bring closure to your time together with students. Talk with your students about what made this year special, recall the good memories, and reflect on all you’ve learned. After all, you’ve all put in a lot of work to get to this point. Have fun with these end-of-year activities and assignments, and let the countdown begin!
1. Hold a class family circle
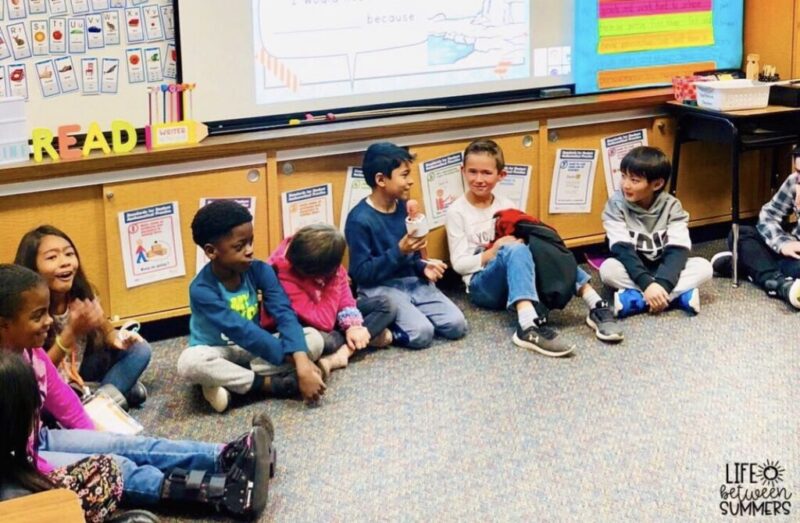

A family circle is a great way to wrap up a terrific year. Prepare a set of reflection questions, then allow students to take the mic and ask a friend one of the questions. Continue around the circle until every student has had a chance to answer.
Learn more: Class Family Circle
2. Solve a mystery together
Awesome for building reading comprehension skills, whodunits are also a hoot for students to solve! Students must read the clues and collaborate to solve the mystery. Try this one: Who Freed the Fish? And pretty soon your students will be tapping into their inner Sherlock.
Learn more: Class Mystery at Minds in Bloom
3. Create blackout poetry
It’s amazing what beautiful poetry can come from just about any piece of writing. All you need is a photocopied article, essay, or book excerpt and a Sharpie marker.
Learn more: Blackout Poetry at Just Add Students via YouTube
4. Let students teach
Have your students sign up to teach their classmates a 20- to 30-minute mini-lesson about something they’re passionate about. Some examples include leading the class in a game, song, or other group activity.
Learn more: Let Students Teach at Minds in Bloom
5. Hold a friendly competition

Kids love a little friendly competition, especially when it’s quick and easy. Sneak in rounds between activities and hold the finals on the last day of school.
Learn more: Rock, Paper, Scissors Bracket
6. Have a class “snowball fight”
Split your class into two teams facing each other. Have each student write three things about themselves and wad it into a snowball, then let the snowball fight commence! Set a time for a few minutes of “fight” time, then have students each grab a snowball and read the items listed, guessing whose paper it is.
Learn more: Snowball Fight at TeachStarter
7. Create memories that stick

Commemorate the memories that “stuck” with your students this year with this fun end-of-year activity.
Learn more: Cactus Memories
8. Serve up a scoop of memories

Here’s a sweet way to celebrate the end of the year! Make paper ice cream sundaes with a different memory on each scoop. You can have kids draw these themselves or buy a printable version at the link below.
Learn more: Ice Cream Scoop Memories
9. Post Flip farewell videos
Flip is one of our favorite classroom tools , especially when it comes to end-of-year activities. Post topics like “What did you learn this year?” or “Share your favorite memory from the past year.” Kids post their video responses and check out other students’ contributions too.
10. Create a collaborative puzzle

Give each student a piece of the puzzle and let them get creative! Suggest a theme such as best memory or most important thing I learned or I’ll never forget, etc. Students can write on their puzzle pieces. Once the puzzle is done, you can take a picture and make sure every student gets a copy.
Learn more: Collaborative Puzzle
11. Compile an end-of-year playlist
Songs are like smells—just hearing one can bring back all kinds of memories. Ask students (as a class or individually) to compile a list of songs that relate to the past school year and have them write about why each tune has a place on the list. Celebrate the last day of school by listening to songs from the playlist as you reflect on the year gone by. And while you’re at it, check out 85 Awesome Songs for Your End-of-the-Year Playlist .
Learn more: End of Year Playlist at Reading and Writing Haven
12. Fill up a memory bag
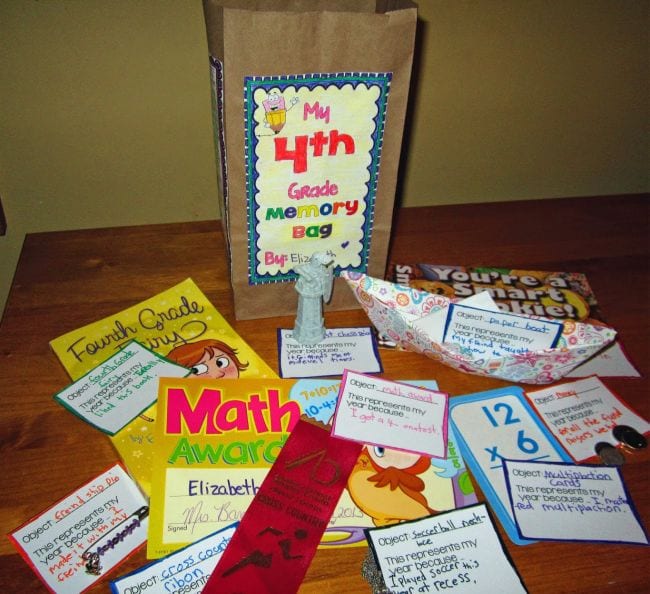

Give each student a brown paper bag, then ask them to decorate the front and add some reflections about the year on the other three panels. Then, each student adds 10 items from the year to their bag, with notes about why each is important. Finish up by having each kid lay out their items on their desk. Have a gallery walk around the room for everyone to see one another’s selections.
Learn more: Memory Bags
13. Write commencement speeches
Commencement speeches aren’t only for graduations! Finish out the year by reading or watching other great commencements speeches (the web is full of them). Then challenge students to write—and deliver, if you like—their own speeches for the year they’ve just finished.
Learn more: Commencement Speeches at 2 Peas and a Dog
14. List what they’ve learned from A to Z

What a great way to look back over what kids have learned! For each letter of the alphabet, have them write and illustrate something they learned or did throughout the year. Hit the link below to get a free printable template for this project. Learning virtually? Have students create a Google Slideshow instead.
Learn more: End of Year A to Z
15. Send thank-you notes
This is a skill every kid should learn: writing and sending thank-you notes. So why not incorporate it into your lineup of end-of-year activities? Have kids write a note to someone who made their school year special, then seal them in envelopes, address them, and deliver them by hand or mail. And while you’re at it, why not write a thank-you note to your own class ?
Learn more: Thank-You Notes at Cult of Pedagogy
16. Post best-of-the-year snapshots

Ask your students to sum up their favorite school-year memory (Science fair? Field day? Creative class presentations?) in one snapshot. Younger kids can draw pictures of the event, while older kids are likely to have a photo on their phone they’d be willing to share. Assemble them on a bulletin board—real-world or digital—with a few words from each student about what made that moment so special.
Learn more: Snapshots of Our Year
17. Count the days
Instead of counting down the days until the end, count up the days from the year behind you! Get students counting by having them use a calendar to figure out how many Mondays you’ve had this year, how many Fridays, how many P.E. days, and how many Jell-O-in-the-cafeteria days. Then work together to make a bar graph and hang it on the wall.
Learn more: End-of-Year Countdown at Teaching Made Practical
18. Let the students become the teachers
Take a break and let the students lead the class for a change. If you’re reviewing material for finals or another end-of-year test, have each student (or a group) lead the review session on a particular topic. You can also have your students create their own lesson on a topic they’re passionate about. Or have kids in one grade make and present lessons on what students in the grade below them can expect to learn the following year. There are a lot of options here, and all of them give you time to take a breather!
19. Talk behind each other’s backs (really!)
Have your students help tape a piece of lined paper to one another’s backs. Have each student get out a felt-tipped marker (not a Sharpie—it may bleed through). Set a timer and put on some favorite music. Let the students mix around the room and write a positive message on each student’s paper. For example, The best thing about you is …, What I appreciate most about you is …, I remember …, etc. After a set amount of time, have students stop, remove their papers from their backs, and enjoy reading the words of love from their classmates. (For a socially distanced spin, create a Google Slide or Padlet template for each student instead.)
20. Coast into summer
So fun! These DIY memory coasters are easy to make and give kids an end-of-year souvenir to take home. Get the free printable templates and complete instructions here.
21. Read end-of-year books
Little ones especially have a hard time with the end of a school year. Next year lots of things will be different, and that can be a sad and even scary thought for some. Read-alouds are simple but powerful end-of-year activities. Check out these 11 End-of-Year Books To Bring Your Class Closure , like The Egg by M.P. Robertson, to spark conversations about what kids have learned and what lies ahead.
22. Dream about the summer ahead
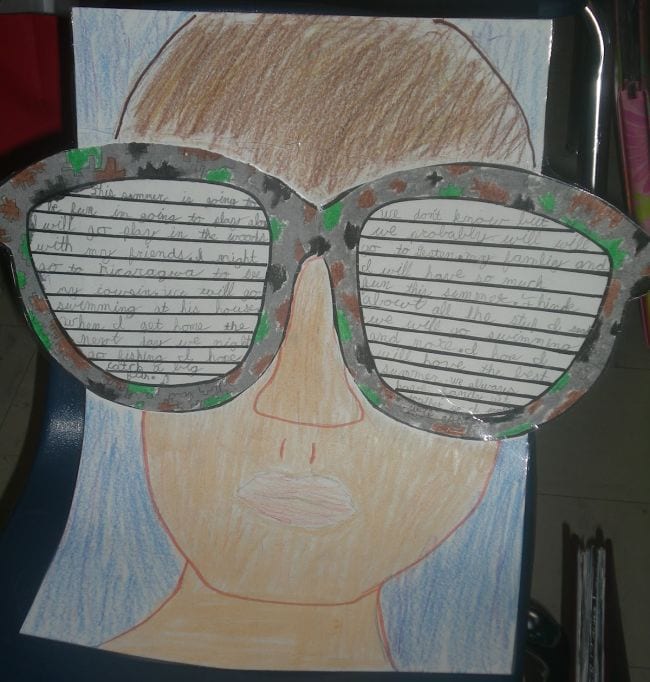

Here’s an end-of-year assignment that includes both art and writing. Have kids draw a portrait of themselves, then use the template at the link below to cut out and decorate an enormous pair of sunglasses. On the glasses, have them write about their summer plans (or the things they’d like to do).
Learn more: End-of-Year Writing
23. Raise a glass and toast your class
Students get a chance to practice public speaking in a very meaningful way with this end-of-year activity. Get a few liters of ginger ale and plastic champagne flutes from a party store, arrange your students in a circle, and have everyone say something—maybe a goal for the next school year, well-wishes for their peers, a favorite memory. After everyone has spoken, lift your glasses with a cheer and celebrate to end the school year.
24. Author a six-word memoir

This project has taken the world by storm. In six words, can you capture the essence of your school year? Kids can spend a little or a lot of time on this one, refining their words and even illustrating them. Collect them all into a slideshow (anonymous, if kids prefer) to share on the last day.
Learn more: Six-Word Memoirs
25. Take a field trip to the next grade
This is one of the most exciting end-of-year activities for students. Take them to visit the classrooms they’ll be in next year. Arrange to spend some time with the teachers, talk to the students, and hear more about what they’ll be learning. This is a good way to allay fears many kids have about moving on from a classroom where they’ve been comfortable. (You can do this as a Zoom tour and meet-and-greet too.)
Learn more: Next Year Classrooms Tour at Inspire Me ASAP!
26. Design a school seal
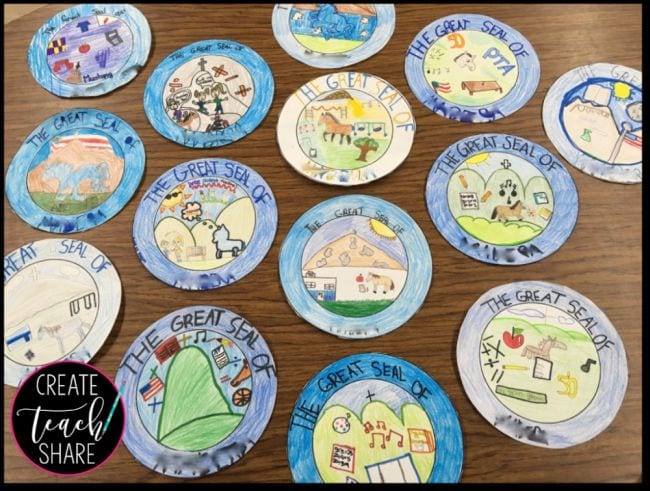

In this fun end-of-year activity that’s perfect for social studies, have your students design a “Great Seal” for their school. First, break them into groups to talk about what makes your school special and memorable for them. Then, have each kid (or group) create their own “seal” based on the ones used by states and cities. This project is especially meaningful for kids about to move on to another school like junior high.
Learn more: School Seals
27. Determine your “People of the Year”
Time magazine can’t have all the fun! Help your students compile a list of the “People of the Year” for your class. Include people important to your classroom (the custodian, the principal, everyone’s favorite “lunch lady”) along with classroom visitors and speakers from the year. Add in some people from current events and pop culture (the current president, a favorite musician) and even folks they studied throughout the year (Abraham Lincoln, Amelia Earhart). Try to take or draw portraits of each, and assign each student to write a brief bio of one of the people included.
28. Write letters or tips for next year’s class

Who better to advise next year’s class on what they’ll need to succeed than the kids who’ve just finished doing it? They can write letters on their own or work together to create a master list of what it takes to make it in the next grade.
Learn more: Survival Guide
29. Create science-inspired art
Ask your students to create a wall-worthy piece of art that reflects something they learned in science. Did you study plants? Maybe a watercolor of flowers. Or if you studied space, a cosmic-inspired number. Send their work home to help them remember, or collect them to create a bulletin board that will inspire next year’s class about what they’ll be learning.
30. Host an open-mic night
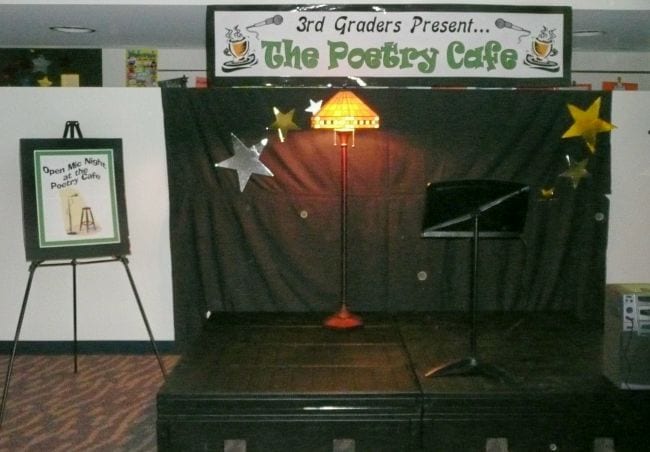

Encourage kids to share the writing they’ve done in (and out of) class with an open mic event. Set up a stage complete with microphone and stool—get great tips for this at the link below—then bring kids up to tell a story or recite a poem. Overcome stage fright with a cool casual vibe and plenty of snacks. Invite friends and family to attend or watch virtually via Zoom.
Learn more: Poetry Cafe
31. Compose an end-of-year continuing story
Write several story titles like “The Great Summer Adventure,” “How My Teacher Lost Her Mind,” or “My Teacher, My Hero” at the top of blank pages. Then, have each student start a story and, after five minutes, pass the story to a neighbor who will continue writing. (Do this digitally on Google Docs if you’re not able to share supplies from person to person.) Continue writing round-robin style until you have several stories to read aloud to the class.
32. Publish a year-end newspaper

You can do this one as a group or individually. Create a basic newspaper template and have the class fill in the front page news. Recap the year, offer advice, illustrate favorite memories, and more. Then, pass these on to the grade below to give them an idea of what lies ahead.
Learn more: Class Newspaper
33. Perform a high school (or middle or elementary school) musical number
Break your students into groups and have them create (and perform) musical numbers commemorating the year. They can write new words to existing tunes, choreograph a lip-synch performance to an inspiring or memorable song, or even come up with something entirely new. Invite parents or other classes to a final-day performance, in person or online.
34. Assemble a Book Hall of Fame
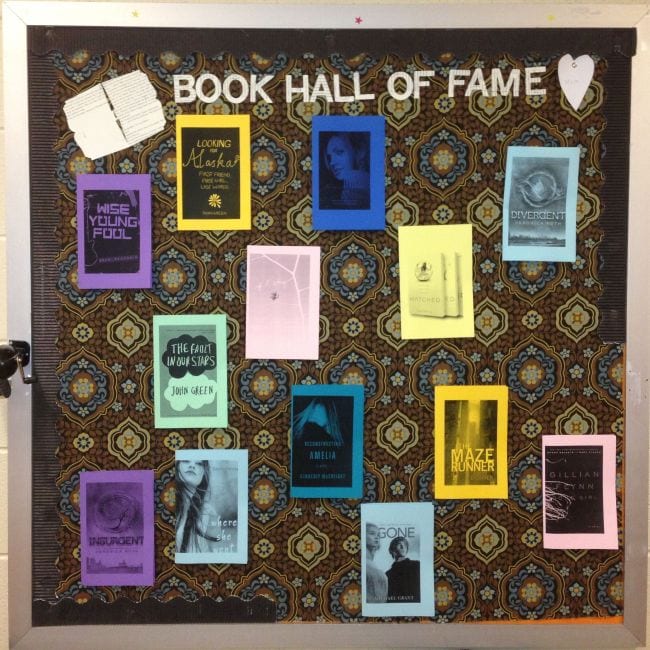

Have each student write (or draw) a reflection on the best book they read during the year. Then, save their reflections and post them on a bulletin board or Padlet so that next year’s students can glean reading ideas.
Source: Book Hall of Fame
35. Play end-of-year charades
Looking for game-based end-of-year activities? Play charades! Have each student write out one memorable moment from the school year on a slip of paper. Collect all the slips in a bag, hat, or the like. Divide kids into teams and have them come up one team at a time, choose a slip, and act out the memory for the group. No need to keep score—the goal is just to relive all the happy memories from the year.
36. Start a school graffiti wall

Choose a wall in your school or classroom and encourage kids to sign their names and date with a quote or other memory. Use permanent markers or small paintbrushes. Each year, photograph the wall and then paint over it to start anew. If you have enough space, these walls can last longer and only be painted over every so many years, creating much more enduring memories. No wall room? Try a bulletin board or large sheet of paper instead.
Learn more: Graffiti Wall
37. Hold a “Stuff You Should Know” event
Take a day or a week to pass on important things you want your kids to know as they move on in life without you. Share poems, songs, TED Talks, quotes, books, and tips that you think will help them along the way. Don’t forget to include simple life lessons (registering and preparing to vote, protecting yourself online, how to behave on an elevator) that school usually doesn’t teach you. Learn more about this end-of-year activity here.
38. Print up a growing tree

Capture each student’s fingerprint as a tree leaf. Label them with their names, then hang them in your room from year to year so kids can see who’s come before them.
Source: End-of-Year Fingerprint Tree
39. Build a portfolio showcase
Throughout the year, have students save their best work in a folder or box. At the end of the year, each student chooses their favorite items to display in a portfolio like a binder or display board. Invite parents and friends to come to view everyone’s achievements.
40. Put together time capsules

Time capsules are classic end-of-year activities. Students will have so much fun assembling time capsules to be opened someday in the future. These can be as simple as a plastic water bottle filled with written memories or a shoebox stuffed with items to represent what kids did and learned over the school year.
Learn more: Class Time Capsule
41. Draw a school-year timeline
Classroom walls can start to look empty at the end of the year as you take things down to prepare for summer. Temporarily fill in the space with a long strip of butcher paper, then have kids create a timeline of the year. Break it down by month, then ask kids what they remember. Prompt their memories by having them look over their work (what a fun way to review!), and don’t forget to include events, speakers, and holiday celebrations.
42. Fill out an end-of-year roundup

Sometimes you just need a quick activity that doesn’t take a lot of prep, and that’s where this free printable comes in. Personalize it by taking and printing a photo of each student, or have them draw their own portrait in the space provided.
Learn more: End-of-the-Year Roundup
43. Go outside!

Build in time to celebrate the end of the year with some fun outdoor activities. Rotate teams for each activity so your students get a chance to mingle with all of their classmates. Here are 25 Clever Outdoor Games to choose from.
44. Put on a show
This is a fun end-of-year activity that could be presented to parents, a younger class, your whole school, or just for your own class. Students can perform skits, dramatic readings, act out a story, showcase a talent, or read a favorite piece from a book they read.
45. Create an end-of-year ABC book

You use them for novel studies, so why not create an ABC book for highlights of the school year? For each letter, students come up with one memorable event or lesson, write a few sentences, and draw a picture. Think of it as a literacy lesson/memory book activity.
Learn more: ABC Booklet
46. Hold a book museum walk
One of our favorite end-of-year activities is a book museum walk. Students choose one of their favorite books and create a poster, diorama, trifold, or even dress up as a character. They can work on their projects at home or at school, and their project should provide a sneak peek or trailer of the book. When the students are ready to present, invite another class or grade level in to view the “museum.”
Learn more: Museum Walk With Favorite Books at Teaching With Jennifer Findley
47. Create your own iPads

End-of-year activities can help wrap up subject matters like geography. For this fun assignment, have your students research different symbols that represent something unique about your state. Each symbol they discover will become an app for their homemade iPad. Have them draw the symbols on the outside of each app, and then write a brief summary about the symbols on the inside.
Learn more: Geography iPad apps
48. Go on a virtual field trip
Traditionally, one of the classic school end-of-year activities was field trips. But sometimes budgets don’t cooperate, so why not take it virtual? They’re fun and easy, and no permission slips, chaperones, or packed lunches are needed! Check out our favorite Amazing Educational Virtual Field Trips .
49. Pump up the school spirit

From dress-up days and community-building activities to outreach and volunteer projects, Spirit Week activities are a great way to end the year on a high note. Check out our massive list of School Spirit Week Ideas .
50. Story writing
Have each student start a story and then leave it on their desk. At your signal, have students rotate to the next desk, and give them a minute to read the story there and then add to the story. Keep rotating, giving students the chance to add to as many stories as you have time for. Let students know when you’re on your last rotation so they can wrap the story up.
51. Make a wearable keepsake
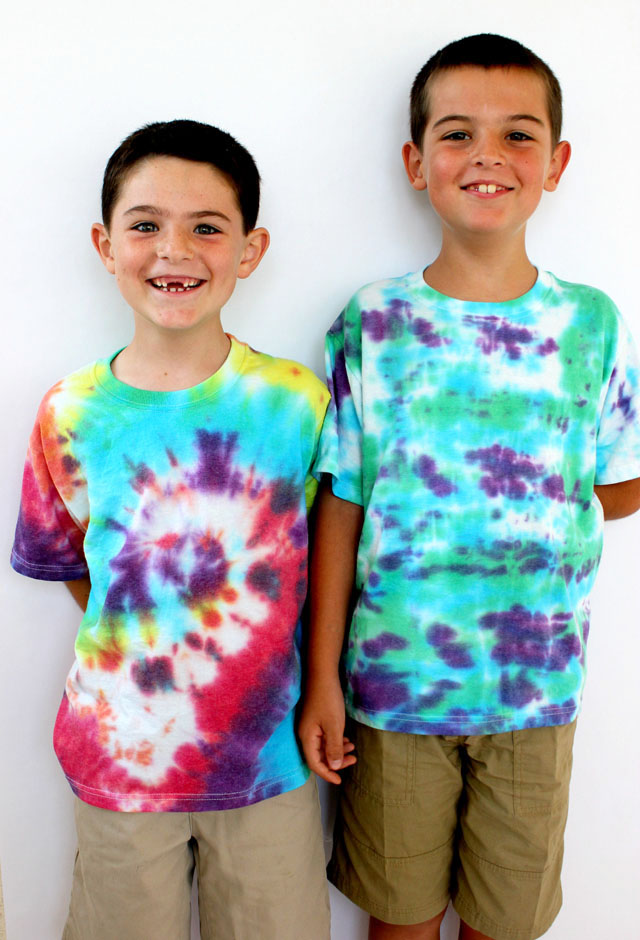

Mark your time together by making fun tie-dyed bandannas or decorating T-shirts with everyone’s signature or handprint. Or try making friendship bracelets or necklaces. Every time your students wear one of these items, they’ll fondly remember your year together.
Learn more: How To Tie-Dye Shirts With Kids
52. Set up a photo booth

Photo booths are a great way to start the school year, but they’re also terrific for the last days of the year. Help kids capture memories with their friends before they part for the summer.
Learn more: Photo Booth
53. Plan a dream vacation
Kids are already dreaming of how they’ll fill the summer hours, so this last-minute math activity will be pure fun! Give kids a budget (say, $2,500), then send them off to research whether their dream trip can be accomplished. Make sure they include airfare or gas money, lodgings, food, spending money, and all the incidentals that add up when you travel.
54. Host a book tasting

Expand your readers’ palates with a book tasting and set them up for summer reading. A book tasting gives students the opportunity to sample some juicy reads in a short period of time and come away with a wish list of titles.
Learn more: Book Tasting
55. Create a summer bucket list

Provide kids with lots of options, then have them compile their own bucket lists for the summer days ahead. In addition to fun items, encourage them to add ways to help others or learn something new too.
Learn more: Bucket List
56. Focus on kindness
Add a Random Acts of Kindness Challenge to your lineup of end-of-year activities and make it all the way to the finish line with good vibes. To get started, check out Random Acts of Kindness: 30 Activities for Elementary Students from American Montessori Society
57. See who knows you best

Challenge your kiddos to show who knows you best. Record your students’ answers on chart paper with markers or use Google Slides. It’s amazing how much kids pick up on our likes and dislikes!
Learn more: Who Knows Teacher Best
What are your favorite end-of-year activities? Come and share in our We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out end-of-year student gifts that won’t break the bank .

You Might Also Like

11 End-of-Year Books to Bring Your Class Closure
Say farewell to this year's students with the perfect read aloud. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Teaching, Learning, & Professional Development Center
- Teaching Resources
- TLPDC Teaching Resources
How Do I Create Meaningful and Effective Assignments?
Prepared by allison boye, ph.d. teaching, learning, and professional development center.
Assessment is a necessary part of the teaching and learning process, helping us measure whether our students have really learned what we want them to learn. While exams and quizzes are certainly favorite and useful methods of assessment, out of class assignments (written or otherwise) can offer similar insights into our students' learning. And just as creating a reliable test takes thoughtfulness and skill, so does creating meaningful and effective assignments. Undoubtedly, many instructors have been on the receiving end of disappointing student work, left wondering what went wrong… and often, those problems can be remedied in the future by some simple fine-tuning of the original assignment. This paper will take a look at some important elements to consider when developing assignments, and offer some easy approaches to creating a valuable assessment experience for all involved.
First Things First…
Before assigning any major tasks to students, it is imperative that you first define a few things for yourself as the instructor:
- Your goals for the assignment . Why are you assigning this project, and what do you hope your students will gain from completing it? What knowledge, skills, and abilities do you aim to measure with this assignment? Creating assignments is a major part of overall course design, and every project you assign should clearly align with your goals for the course in general. For instance, if you want your students to demonstrate critical thinking, perhaps asking them to simply summarize an article is not the best match for that goal; a more appropriate option might be to ask for an analysis of a controversial issue in the discipline. Ultimately, the connection between the assignment and its purpose should be clear to both you and your students to ensure that it is fulfilling the desired goals and doesn't seem like “busy work.” For some ideas about what kinds of assignments match certain learning goals, take a look at this page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons.
- Have they experienced “socialization” in the culture of your discipline (Flaxman, 2005)? Are they familiar with any conventions you might want them to know? In other words, do they know the “language” of your discipline, generally accepted style guidelines, or research protocols?
- Do they know how to conduct research? Do they know the proper style format, documentation style, acceptable resources, etc.? Do they know how to use the library (Fitzpatrick, 1989) or evaluate resources?
- What kinds of writing or work have they previously engaged in? For instance, have they completed long, formal writing assignments or research projects before? Have they ever engaged in analysis, reflection, or argumentation? Have they completed group assignments before? Do they know how to write a literature review or scientific report?
In his book Engaging Ideas (1996), John Bean provides a great list of questions to help instructors focus on their main teaching goals when creating an assignment (p.78):
1. What are the main units/modules in my course?
2. What are my main learning objectives for each module and for the course?
3. What thinking skills am I trying to develop within each unit and throughout the course?
4. What are the most difficult aspects of my course for students?
5. If I could change my students' study habits, what would I most like to change?
6. What difference do I want my course to make in my students' lives?
What your students need to know
Once you have determined your own goals for the assignment and the levels of your students, you can begin creating your assignment. However, when introducing your assignment to your students, there are several things you will need to clearly outline for them in order to ensure the most successful assignments possible.
- First, you will need to articulate the purpose of the assignment . Even though you know why the assignment is important and what it is meant to accomplish, you cannot assume that your students will intuit that purpose. Your students will appreciate an understanding of how the assignment fits into the larger goals of the course and what they will learn from the process (Hass & Osborn, 2007). Being transparent with your students and explaining why you are asking them to complete a given assignment can ultimately help motivate them to complete the assignment more thoughtfully.
- If you are asking your students to complete a writing assignment, you should define for them the “rhetorical or cognitive mode/s” you want them to employ in their writing (Flaxman, 2005). In other words, use precise verbs that communicate whether you are asking them to analyze, argue, describe, inform, etc. (Verbs like “explore” or “comment on” can be too vague and cause confusion.) Provide them with a specific task to complete, such as a problem to solve, a question to answer, or an argument to support. For those who want assignments to lead to top-down, thesis-driven writing, John Bean (1996) suggests presenting a proposition that students must defend or refute, or a problem that demands a thesis answer.
- It is also a good idea to define the audience you want your students to address with their assignment, if possible – especially with writing assignments. Otherwise, students will address only the instructor, often assuming little requires explanation or development (Hedengren, 2004; MIT, 1999). Further, asking students to address the instructor, who typically knows more about the topic than the student, places the student in an unnatural rhetorical position. Instead, you might consider asking your students to prepare their assignments for alternative audiences such as other students who missed last week's classes, a group that opposes their position, or people reading a popular magazine or newspaper. In fact, a study by Bean (1996) indicated the students often appreciate and enjoy assignments that vary elements such as audience or rhetorical context, so don't be afraid to get creative!
- Obviously, you will also need to articulate clearly the logistics or “business aspects” of the assignment . In other words, be explicit with your students about required elements such as the format, length, documentation style, writing style (formal or informal?), and deadlines. One caveat, however: do not allow the logistics of the paper take precedence over the content in your assignment description; if you spend all of your time describing these things, students might suspect that is all you care about in their execution of the assignment.
- Finally, you should clarify your evaluation criteria for the assignment. What elements of content are most important? Will you grade holistically or weight features separately? How much weight will be given to individual elements, etc? Another precaution to take when defining requirements for your students is to take care that your instructions and rubric also do not overshadow the content; prescribing too rigidly each element of an assignment can limit students' freedom to explore and discover. According to Beth Finch Hedengren, “A good assignment provides the purpose and guidelines… without dictating exactly what to say” (2004, p. 27). If you decide to utilize a grading rubric, be sure to provide that to the students along with the assignment description, prior to their completion of the assignment.
A great way to get students engaged with an assignment and build buy-in is to encourage their collaboration on its design and/or on the grading criteria (Hudd, 2003). In his article “Conducting Writing Assignments,” Richard Leahy (2002) offers a few ideas for building in said collaboration:
• Ask the students to develop the grading scale themselves from scratch, starting with choosing the categories.
• Set the grading categories yourself, but ask the students to help write the descriptions.
• Draft the complete grading scale yourself, then give it to your students for review and suggestions.
A Few Do's and Don'ts…
Determining your goals for the assignment and its essential logistics is a good start to creating an effective assignment. However, there are a few more simple factors to consider in your final design. First, here are a few things you should do :
- Do provide detail in your assignment description . Research has shown that students frequently prefer some guiding constraints when completing assignments (Bean, 1996), and that more detail (within reason) can lead to more successful student responses. One idea is to provide students with physical assignment handouts , in addition to or instead of a simple description in a syllabus. This can meet the needs of concrete learners and give them something tangible to refer to. Likewise, it is often beneficial to make explicit for students the process or steps necessary to complete an assignment, given that students – especially younger ones – might need guidance in planning and time management (MIT, 1999).
- Do use open-ended questions. The most effective and challenging assignments focus on questions that lead students to thinking and explaining, rather than simple yes or no answers, whether explicitly part of the assignment description or in the brainstorming heuristics (Gardner, 2005).
- Do direct students to appropriate available resources . Giving students pointers about other venues for assistance can help them get started on the right track independently. These kinds of suggestions might include information about campus resources such as the University Writing Center or discipline-specific librarians, suggesting specific journals or books, or even sections of their textbook, or providing them with lists of research ideas or links to acceptable websites.
- Do consider providing models – both successful and unsuccessful models (Miller, 2007). These models could be provided by past students, or models you have created yourself. You could even ask students to evaluate the models themselves using the determined evaluation criteria, helping them to visualize the final product, think critically about how to complete the assignment, and ideally, recognize success in their own work.
- Do consider including a way for students to make the assignment their own. In their study, Hass and Osborn (2007) confirmed the importance of personal engagement for students when completing an assignment. Indeed, students will be more engaged in an assignment if it is personally meaningful, practical, or purposeful beyond the classroom. You might think of ways to encourage students to tap into their own experiences or curiosities, to solve or explore a real problem, or connect to the larger community. Offering variety in assignment selection can also help students feel more individualized, creative, and in control.
- If your assignment is substantial or long, do consider sequencing it. Far too often, assignments are given as one-shot final products that receive grades at the end of the semester, eternally abandoned by the student. By sequencing a large assignment, or essentially breaking it down into a systematic approach consisting of interconnected smaller elements (such as a project proposal, an annotated bibliography, or a rough draft, or a series of mini-assignments related to the longer assignment), you can encourage thoughtfulness, complexity, and thoroughness in your students, as well as emphasize process over final product.
Next are a few elements to avoid in your assignments:
- Do not ask too many questions in your assignment. In an effort to challenge students, instructors often err in the other direction, asking more questions than students can reasonably address in a single assignment without losing focus. Offering an overly specific “checklist” prompt often leads to externally organized papers, in which inexperienced students “slavishly follow the checklist instead of integrating their ideas into more organically-discovered structure” (Flaxman, 2005).
- Do not expect or suggest that there is an “ideal” response to the assignment. A common error for instructors is to dictate content of an assignment too rigidly, or to imply that there is a single correct response or a specific conclusion to reach, either explicitly or implicitly (Flaxman, 2005). Undoubtedly, students do not appreciate feeling as if they must read an instructor's mind to complete an assignment successfully, or that their own ideas have nowhere to go, and can lose motivation as a result. Similarly, avoid assignments that simply ask for regurgitation (Miller, 2007). Again, the best assignments invite students to engage in critical thinking, not just reproduce lectures or readings.
- Do not provide vague or confusing commands . Do students know what you mean when they are asked to “examine” or “discuss” a topic? Return to what you determined about your students' experiences and levels to help you decide what directions will make the most sense to them and what will require more explanation or guidance, and avoid verbiage that might confound them.
- Do not impose impossible time restraints or require the use of insufficient resources for completion of the assignment. For instance, if you are asking all of your students to use the same resource, ensure that there are enough copies available for all students to access – or at least put one copy on reserve in the library. Likewise, make sure that you are providing your students with ample time to locate resources and effectively complete the assignment (Fitzpatrick, 1989).
The assignments we give to students don't simply have to be research papers or reports. There are many options for effective yet creative ways to assess your students' learning! Here are just a few:
Journals, Posters, Portfolios, Letters, Brochures, Management plans, Editorials, Instruction Manuals, Imitations of a text, Case studies, Debates, News release, Dialogues, Videos, Collages, Plays, Power Point presentations
Ultimately, the success of student responses to an assignment often rests on the instructor's deliberate design of the assignment. By being purposeful and thoughtful from the beginning, you can ensure that your assignments will not only serve as effective assessment methods, but also engage and delight your students. If you would like further help in constructing or revising an assignment, the Teaching, Learning, and Professional Development Center is glad to offer individual consultations. In addition, look into some of the resources provided below.
Online Resources
“Creating Effective Assignments” http://www.unh.edu/teaching-excellence/resources/Assignments.htm This site, from the University of New Hampshire's Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning, provides a brief overview of effective assignment design, with a focus on determining and communicating goals and expectations.
Gardner, T. (2005, June 12). Ten Tips for Designing Writing Assignments. Traci's Lists of Ten. http://www.tengrrl.com/tens/034.shtml This is a brief yet useful list of tips for assignment design, prepared by a writing teacher and curriculum developer for the National Council of Teachers of English . The website will also link you to several other lists of “ten tips” related to literacy pedagogy.
“How to Create Effective Assignments for College Students.” http:// tilt.colostate.edu/retreat/2011/zimmerman.pdf This PDF is a simplified bulleted list, prepared by Dr. Toni Zimmerman from Colorado State University, offering some helpful ideas for coming up with creative assignments.
“Learner-Centered Assessment” http://cte.uwaterloo.ca/teaching_resources/tips/learner_centered_assessment.html From the Centre for Teaching Excellence at the University of Waterloo, this is a short list of suggestions for the process of designing an assessment with your students' interests in mind. “Matching Learning Goals to Assignment Types.” http://teachingcommons.depaul.edu/How_to/design_assignments/assignments_learning_goals.html This is a great page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons, providing a chart that helps instructors match assignments with learning goals.
Additional References Bean, J.C. (1996). Engaging ideas: The professor's guide to integrating writing, critical thinking, and active learning in the classroom . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Fitzpatrick, R. (1989). Research and writing assignments that reduce fear lead to better papers and more confident students. Writing Across the Curriculum , 3.2, pp. 15 – 24.
Flaxman, R. (2005). Creating meaningful writing assignments. The Teaching Exchange . Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008 from http://www.brown.edu/Administration/Sheridan_Center/pubs/teachingExchange/jan2005/01_flaxman.pdf
Hass, M. & Osborn, J. (2007, August 13). An emic view of student writing and the writing process. Across the Disciplines, 4.
Hedengren, B.F. (2004). A TA's guide to teaching writing in all disciplines . Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's.
Hudd, S. S. (2003, April). Syllabus under construction: Involving students in the creation of class assignments. Teaching Sociology , 31, pp. 195 – 202.
Leahy, R. (2002). Conducting writing assignments. College Teaching , 50.2, pp. 50 – 54.
Miller, H. (2007). Designing effective writing assignments. Teaching with writing . University of Minnesota Center for Writing. Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008, from http://writing.umn.edu/tww/assignments/designing.html
MIT Online Writing and Communication Center (1999). Creating Writing Assignments. Retrieved January 9, 2008 from http://web.mit.edu/writing/Faculty/createeffective.html .
Contact TTU

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend
- Copyright 2007-2021 пїЅ
- Submit a worksheet
- Mobile version
Creative Ways to Design Assignments for Student Success
There are many creative ways in which teachers can design assignments to support student success. We can do this while simultaneously not getting bogged down with the various obstructions that keep students from both completing and learning from the assignments. For me, assignments fall into two categories: those that are graded automatically, such as SmartBook® readings and quizzes in Connect®; and those that I need to grade by hand, such as writing assignments.
For those of us teaching large, introductory classes, most of our assignments are graded automatically, which is great for our time management. But our students will ultimately deliver a plethora of colorful excuses as to why they were not completed and why extensions are warranted. How do we give them a little leeway to make the semester run more smoothly, so there are fewer worries about a reading that was missed or a quiz that went by too quickly? Here are a few tactics I use.
Automatically graded assignments:
Multiple assignment attempts
- This eases the mental pressure of a timed assignment and covers computer mishaps or human error on the first attempt.
- You can deduct points for every attempt taken if you are worried about students taking advantage.
Automatically dropped assignments
- Within a subset or set of assignments, automatically drop a few from grading. This can take care of all excuses for missing an assignment.
- Additionally, you can give a little grade boost to those who complete all their assignments (over a certain grade).
Due dates
- Consider staggering due dates during the week instead of making them all due on Sunday night.
- Set the due date for readings the night before you cover the material, so students are prepared.
Requirements
- If we want our students to read, then make a reading assignment a requirement of a quiz.
The tactics above might be applied to written assignments, too. An easy way to bolster a student’s interest and investment in these longer assignments is to give them a choice. This could be in the topic, location of study, or presentation style. For example, if you want them to analyze the susceptibility of a beach to hurricane threat, why not let them choose the location? In this way, you will also be gaining a lot of new information for your own use.
With a small amount of effort, we can design our classes, so students concentrate on learning the subject matter rather than the logistics of completing the assignments.
Attending a conference?
Checkout if mcgraw hill will be in attendance:.
- Our Mission
Differentiating by Offering Choices
Elementary students have a better chance of showing what they’ve learned when they have a choice about how to show it.

Most classrooms are filled with students of varying academic abilities. Even within a gifted and talented classroom like mine, the ability levels can range drastically. As teachers strive to meet each student’s individual needs, differentiation is key because it’s about giving more opportunities for students to grow to their highest potential, and it is beneficial for all students .
In the digital era, we can provide all of our students with technological ways to enhance their learning, no matter their academic label. Every student is different and needs to be offered a variety of ways to show what they’ve learned in a way that reflects their individuality.
One way to differentiate within the curriculum is to provide students with choices for completing an assignment. Students learn in various ways, and we can let them show their learning in various ways. When I give my students a choice on how they’ll complete a project, they have to meet certain criteria, but I allow them to find an outlet they find most enjoyable, such as creating a Google Slides presentation, a trifold board, or a pamphlet. Giving students a choice allows them to take ownership of their learning as well as create a product that feels authentic to them. They work on something that they’re good at creating, or try something they want to get better at.
An excellent way to ensure differentiation is to have each student create an e-portfolio—a technology-based assessment tool that collects a student’s authentic work samples, providing a quick way for a teacher to assess growth and skills. In a sense, the e-portfolio is a window into a student’s learning, one that allows the student to choose what to include.
An e-portfolio can follow the student across grades, too. And once the time is spent creating one, the process of adding content becomes easier and quicker as the student adds to it in later grades. Since e-portfolios offer a way for students to show authentic learning , they allow students to exhibit their individual growth through their academic experiences.
Differentiating by Giving Choices
The best way to differentiate instruction is to give students a choice in how they show their learning. All students learn in their own way, and they need to be able to show their individual skills and interests. As long as they’re able to demonstrate a certain skill, assessment should be more about the process than the product.
Giving choices may seem like more work for the teacher, and it can be, but it’s also worthwhile because it encourages more students to take more ownership of their learning.
Adding a technology component to an assignment can drastically increase student engagement, especially if they haven’t been given such options in the past. Using a novel app, such as Flipgrid, adds an element of fun while also giving students practice with tech skills.
But technology is not the only way to provide choice—try using choice boards, which provide students with many options for presenting content. Students may present the water cycle stages in a song, for example, or create a comic that lays out those stages. Such choices can be fun for the students, and can show teachers hidden talents their students possess that they wouldn’t see otherwise.
Differentiating With Portfolios
Few applications offer the opportunity for students to reflect on their learning, but pushing students to do that is important in getting them to think about how they learn best and take an active role in their own learning. Quick assessment applications such as Flipgrid and Kahoot allow for student reflection, but the e-portfolio—which showcases an individual student’s personality—is even better.
With e-portfolios, students reflect on their learning while putting their own mark on their assignments. Students are able to showcase their learning and the process they used to create their final product while individualizing it with their likes and interests.
A teacher may require some items to be present—such as name, class section, pictures of hobbies, or content-related materials—but seeing the ways that students make the e-portfolio their own is what a teacher wants. The e-portfolio is a tool that students can use to express their thinking in a way that is unique to them.
Teachers can assess e-portfolios to measure growth and skills instead of just knowledge of course content. Students are able to take ownership of what they have learned , choose how they present the content, and take control of their learning.
Differentiating allows students to have their voice heard, which can lead them to become self-motivated learners. And that in turn can help increase both their learning growth and their self-awareness of that growth.
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Submit feedback
- Announcements
- Organize and communicate with your class
- Create assignments
Create an assignment
This article is for teachers.
When you create an assignment, you can post it immediately, save a draft, or schedule it to post at a later date. After students complete and turn in their work, you can grade and return it to the students.
Open all | Close all
Create & post assignments
When you create an assignment, you can:
- Select one or more classes
Select individual students
Add a grade category, add a grading period, change the point value, add a due date or time, add a topic, add attachments, add a rubric.
- Turn on originality reports
Go to classroom.google.com and click Sign In.
Sign in with your Google Account. For example, [email protected] or [email protected] . Learn more .
- Enter the title and any instructions.
You can continue to edit and customize your assignment. Otherwise, if you’re ready, see below to post, schedule, or save your assignment .
Select additional classes
Assignments to multiple classes go to all students in those classes.
- Create an assignment (details above).
Unless you’re selecting multiple classes, you can select individual students. You can’t select more than 100 students at a time.
- Click a student's name to select them.
Use grade categories to organize assignments. With grade categories, you and your students can see the category an assignment belongs to, such as Homework or Essays . Teachers also see the categories on the Grades page.
For more information on grade categories, go to Add a grade category to posts or Set up grading .
To organize assignments and grades into your school or district’s grading structure, create grading periods, such as quarters or semesters.
- From the menu, select a grading period.
Tip: Before adding a grading period to an assignment, create a grading period for the class first. Learn how to create or edit grading periods .
You can change the point value of an assignment or make the assignment ungraded. By default, assignments are set at 100 points.
- Under Points , click the value.
- Enter a new point value or select Ungraded .
By default, an assignment has no due date. To set a due date:
- Click a date on the calendar.
- To create a topic, click Create topic and enter a topic name.
- Click a topic in the list to select it.
Note : You can only add one topic to an assignment.
Learn more about how to add topics to the Classwork page .
- Create an assignment.
- Important: Google Drive files can be edited by co-teachers and are view-only to students. To change these share options, you can stop, limit, or change sharing .
- To add YouTube videos, an admin must turn on this option. Learn about access settings for your Google Workspace for Education account .
- You can add interactive questions to YouTube video attachments. Learn how to add interactive questions to YouTube video attachments .
- Tip: When you attach a practice set to an assignment, you can't edit it.
- If you see a message that you don’t have permission to attach a file, click Copy . Classroom makes a copy of the file to attach to the assignment and saves it to the class Drive folder.
- Students can view file —All students can read the file, but not edit it.
- Students can edit file —All students share the same file and can make changes to it.
Note : This option is only available before you post an assignment.
Use an add-on
For instructions, go to Use add-ons in Classroom
For instructions, go to Create or reuse a rubric for an assignment .
For instructions, go to Turn on originality reports .
You can post an assignment immediately, or schedule it to post later. If you don’t want to post it yet, you can save it as a draft. To see scheduled and drafted assignments, click Classwork .
Post an assignment
- Follow the steps above to create an assignment.
- Click Assign to immediately post the assignment.
Schedule the assignment to post later
Scheduled assignments might be delayed up to 5 minutes after the post time.
- To schedule the same assignment across multiple classes, make sure to select all classes you want to include.
- When you enter a time, Classroom defaults to PM unless you specify AM.
- (Optional) Select a due date and topic for each class.
- (Optional) To replicate your selected time and date for the first class into all subsequent classes, click Copy settings to all .
- Click Schedule . The assignment will automatically post at the scheduled date and time.
After scheduling multiple assignments at once, you can still edit assignments later by clicking into each class and changing them individually.
Save an assignment as a draft
- Follow the steps above to create an assignment
You can open and edit draft assignments on the Classwork page.
Manage assignments
Edits affect individual classes. For multi-class assignments, make edits in each class.
Note : If you change an assignment's name, the assignment's Drive folder name isn't updated. Go to Drive and rename the folder.
Edit a posted assignment
- Enter your changes and click Save .
Edit a scheduled assignment
- Enter your changes and click Schedule .
Edit a draft assignment
Changes are automatically saved.
- Assign it immediately (details above).
- Schedule it to post at a specific date and time (details above).
- Click a class.
You can only delete an assignment on the Classwork page.
If you delete an assignment, all grades and comments related to the assignment are deleted. However, any attachments or files created by you or the students are still available in Drive.
Related articles
- Create or reuse a rubric for an assignment
- Create a quiz assignment
- Create a question
- Use add-ons in Classroom
- Create, edit, delete, or share a practice set
- Learn about interactive questions for YouTube videos in Google Classroom
Was this helpful?
Need more help, try these next steps:.
for Education
- Google Classroom
- Google Workspace Admin
- Google Cloud
Easily distribute, analyze, and grade student work with Assignments for your LMS
Assignments is an application for your learning management system (LMS). It helps educators save time grading and guides students to turn in their best work with originality reports — all through the collaborative power of Google Workspace for Education.
- Get started
- Explore originality reports
Bring your favorite tools together within your LMS
Make Google Docs and Google Drive compatible with your LMS
Simplify assignment management with user-friendly Google Workspace productivity tools
Built with the latest Learning Tools Interoperability (LTI) standards for robust security and easy installation in your LMS
Save time distributing and grading classwork
Distribute personalized copies of Google Drive templates and worksheets to students
Grade consistently and transparently with rubrics integrated into student work
Add rich feedback faster using the customizable comment bank
Examine student work to ensure authenticity
Compare student work against hundreds of billions of web pages and over 40 million books with originality reports
Make student-to-student comparisons on your domain-owned repository of past submissions when you sign up for the Teaching and Learning Upgrade or Google Workspace for Education Plus
Allow students to scan their own work for recommended citations up to three times
Trust in high security standards
Protect student privacy — data is owned and managed solely by you and your students
Provide an ad-free experience for all your users
Compatible with LTI version 1.1 or higher and meets rigorous compliance standards
Product demos
Experience google workspace for education in action. explore premium features in detail via step-by-step demos to get a feel for how they work in the classroom..
“Assignments enable faculty to save time on the mundane parts of grading and...spend more time on providing more personalized and relevant feedback to students.” Benjamin Hommerding , Technology Innovationist, St. Norbert College
Classroom users get the best of Assignments built-in
Find all of the same features of Assignments in your existing Classroom environment
- Learn more about Classroom
Explore resources to get up and running
Discover helpful resources to get up to speed on using Assignments and find answers to commonly asked questions.
- Visit Help Center
Get a quick overview of Assignments to help Educators learn how they can use it in their classrooms.
- Download overview
Get started guide
Start using Assignments in your courses with this step-by-step guide for instructors.
- Download guide
Teacher Center Assignments resources
Find educator tools and resources to get started with Assignments.
- Visit Teacher Center
How to use Assignments within your LMS
Watch this brief video on how Educators can use Assignments.
- Watch video
Turn on Assignments in your LMS
Contact your institution’s administrator to turn on Assignments within your LMS.
- Admin setup
Explore a suite of tools for your classroom with Google Workspace for Education
You're now viewing content for a different region..
For content more relevant to your region, we suggest:
Sign up here for updates, insights, resources, and more.

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Google Classroom - Creating Assignments and Materials
Google classroom -, creating assignments and materials, google classroom creating assignments and materials.

Google Classroom: Creating Assignments and Materials
Lesson 2: creating assignments and materials.
/en/google-classroom/getting-started-with-google-classroom/content/
Creating assignments and materials
Google Classroom gives you the ability to create and assign work for your students, all without having to print anything. Questions , essays , worksheets , and readings can all be distributed online and made easily available to your class. If you haven't created a class already, check out our Getting Started with Google Classroom lesson.
Watch the video below to learn more about creating assignments and materials in Google Classroom.
Creating an assignment
Whenever you want to create new assignments, questions, or material, you'll need to navigate to the Classwork tab.

In this tab, you can create assignments and view all current and past assignments. To create an assignment, click the Create button, then select Assignment . You can also select Question if you'd like to pose a single question to your students, or Material if you simply want to post a reading, visual, or other supplementary material.
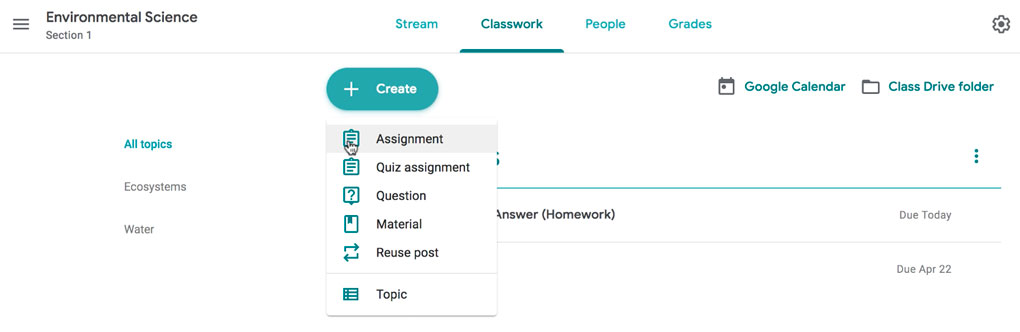
This will bring up the Assignment form. Google Classroom offers considerable flexibility and options when creating assignments.
Click the buttons in the interactive below to become familiar with the Assignment form.
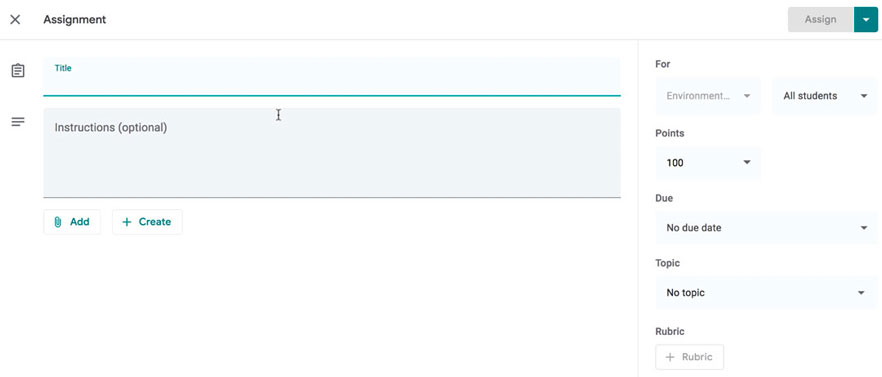
This is where you'll type the title of the assignment you're creating.
Instructions
If you'd like to include instructions with your assignment, you can type them here.
Here, you can decide how many points an assignment is worth by typing the number in the form. You can also click the drop-down arrow to select Ungraded if you don't want to grade an assignment.
You can select a due date for an assignment by clicking this arrow and selecting a date from the calendar that appears. Students will have until then to submit their work.
In Google Classroom, you can sort your assignments and materials into topics. This menu allows you to select an existing topic or create a new one to place an assignment under.
Attachments
You can attach files from your computer , files from Google Drive , URLs , and YouTube videos to your assignments.
Google Classroom gives you the option of sending assignments to all students or a select number .
Once you're happy with the assignment you've created, click Assign . The drop-down menu also gives you the option to Schedule an assignment if you'd like it to post it at a later date.
You can attach a rubric to help students know your expectations for the assignment and to give them feedback.
Once you've completed the form and clicked Assign , your students will receive an email notification letting them know about the assignment.
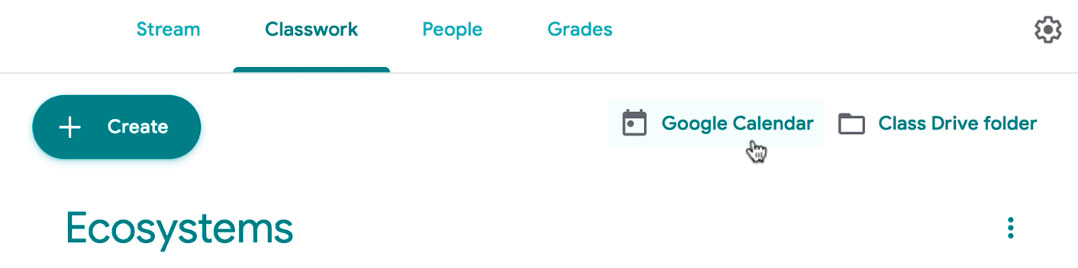
Google Classroom takes all of your assignments and automatically adds them to your Google Calendar. From the Classwork tab, you can click Google Calendar to pull this up and get a better overall view of the timeline for your assignments' due dates.
Using Google Docs with assignments
When creating an assignment, there may often be times when you want to attach a document from Google Docs. These can be helpful when providing lengthy instructions, study guides, and other material.
When attaching these types of files, you'll want to make sure to choose the correct setting for how your students can interact with it . After attaching one to an assignment, you'll find a drop-down menu with three options.
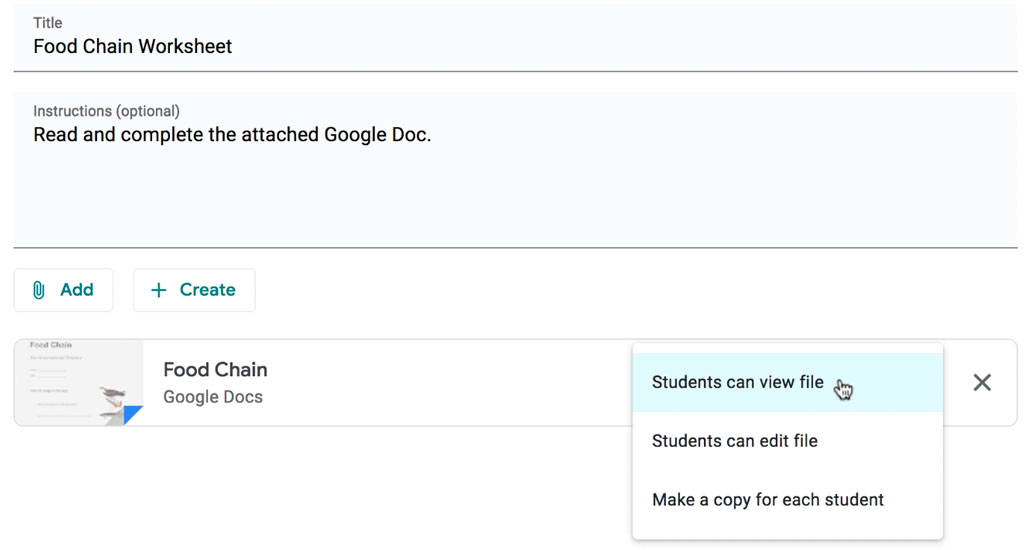
Let's take a look at when you might want to use each of these:
- Students can view file : Use this option if the file is simply something you want your students to view but not make any changes to.
- Students can edit file : This option can be helpful if you're providing a document you want your students to collaborate on or fill out collectively.
- Make a copy for each student : If you're creating a worksheet or document that you want each student to complete individually, this option will create a separate copy of the same document for every student.
Using topics
On the Classwork tab, you can use topics to sort and group your assignments and material. To create a topic, click the Create button, then select Topic .
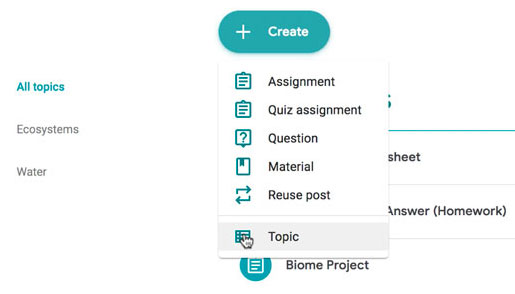
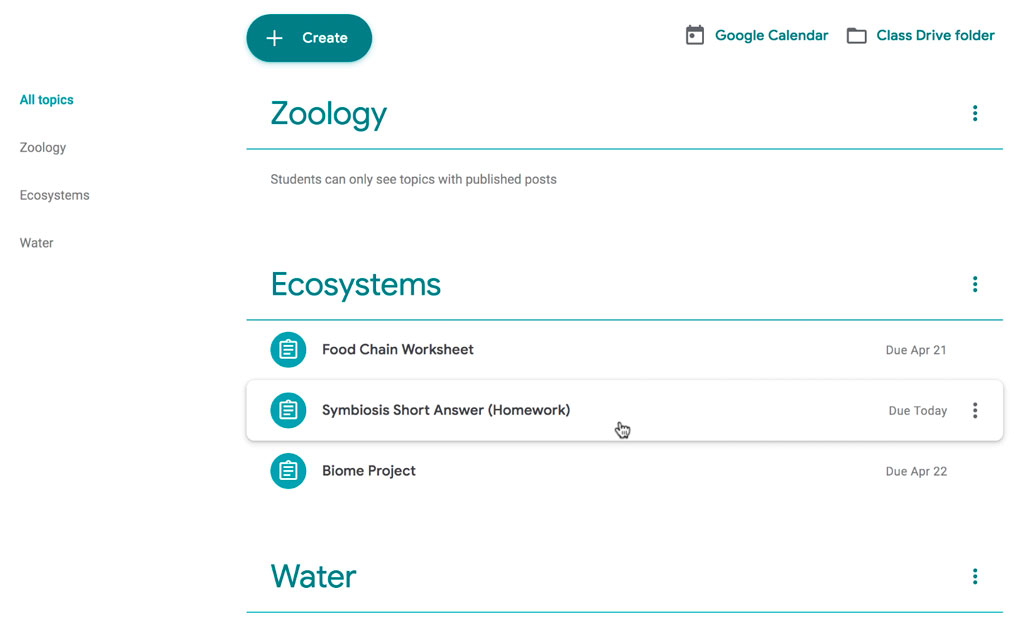
Topics can be helpful for organizing your content into the various units you teach throughout the year. You could also use it to separate your content by type , splitting it into homework, classwork, readings, and other topic areas.
In our next lesson , we'll explore how to create quizzes and worksheets with Google Forms, further expanding how you can use Google Classroom with your students.
/en/google-classroom/using-forms-with-google-classroom/content/
- Sign Up for Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me


Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.
Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.
- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Resources and Guides
Getting Started with Creative Assignments
Creative teaching and learning can be cultivated in any course context to increase student engagement and motivation, and promote thinking skills that are critical to problem-solving and innovation. This resource features examples of Columbia faculty who teach creatively and have reimagined their course assessments to allow students to demonstrate their learning in creative ways. Drawing on these examples, this resource provides suggestions for creating a classroom environment that supports student engagement in creative activities and assignments.
On this page:
- The What and Why of Creative Assignments
Examples of Creative Teaching and Learning at Columbia
- How To Get Started
Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2022). Getting Started with Creative Assignments. Columbia University. Retrieved [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/resources/creative-assignments/
The What and Why of Creative Assignments
Creative assignments encourage students to think in innovative ways as they demonstrate their learning. Thinking creatively involves combining or synthesizing information or course materials in new ways and is characterized by “a high degree of innovation, divergent thinking, and risk-taking” (AAC&U). It is associated with imagination and originality, and additional characteristics include: being open to new ideas and perspectives, believing alternatives exist, withholding judgment, generating multiple approaches to problems, and trying new ways to generate ideas (DiYanni, 2015: 41). Creative thinking is considered an important skill alongside critical thinking in tackling contemporary problems. Critical thinking allows students to evaluate the information presented to them while creative thinking is a process that allows students to generate new ideas and innovate.
Creative assignments can be integrated into any course regardless of discipline. Examples include the use of infographic assignments in Nursing (Chicca and Chunta, 2020) and Chemistry (Kothari, Castañeda, and McNeil, 2019); podcasting assignments in Social Work (Hitchcock, Sage & Sage, 2021); digital storytelling assignments in Psychology (Sheafer, 2017) and Sociology (Vaughn and Leon, 2021); and incorporating creative writing in the economics classroom (Davis, 2019) or reflective writing into Calculus assignment ( Gerstle, 2017) just to name a few. In a 2014 study, organic chemistry students who elected to begin their lab reports with a creative narrative were more excited to learn and earned better grades (Henry, Owens, and Tawney, 2015). In a public policy course, students who engaged in additional creative problem-solving exercises that included imaginative scenarios and alternative solution-finding showed greater interest in government reform and attentiveness to civic issues (Wukich and Siciliano, 2014).
The benefits of creative assignments include increased student engagement, motivation, and satisfaction (Snyder et al., 2013: 165); and furthered student learning of course content (Reynolds, Stevens, and West, 2013). These types of assignments promote innovation, academic integrity, student self-awareness/ metacognition (e.g., when students engage in reflection through journal assignments), and can be made authentic as students develop and apply skills to real-world situations.
When instructors give students open-ended assignments, they provide opportunities for students to think creatively as they work on a deliverable. They “unlock potential” (Ranjan & Gabora and Beghetto in Gregerson et al., 2013) for students to synthesize their knowledge and propose novel solutions. This promotes higher-level thinking as outlined in the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy’s “create” cognitive process category: “putting elements together to form a novel coherent whole or make an original product,” this involves generating ideas, planning, and producing something new.
The examples that follow highlight creative assignments in the Columbia University classroom. The featured Columbia faculty taught creatively – they tried new strategies, purposefully varied classroom activities and assessment modalities, and encouraged their students to take control of what and how they were learning (James & Brookfield, 2014: 66).

Dr. Cruz changed her course assessment by “moving away from high stakes assessments like a final paper or a final exam, to more open-ended and creative models of assessments.” Students were given the opportunity to synthesize their course learning, with options on topic and format of how to demonstrate their learning and to do so individually or in groups. They explored topics that were meaningful to them and related to the course material. Dr. Cruz noted that “This emphasis on playfulness and creativity led to fantastic final projects including a graphic novel interpretation, a video essay that applied critical theory to multiple texts, and an interactive virtual museum.” Students “took the opportunity to use their creative skills, or the skills they were interested in exploring because some of them had to develop new skills to produce these projects.” (Dr. Cruz; Dead Ideas in Teaching and Learning , Season 3, Episode 6). Along with their projects, students submitted an artist’s statement, where they had to explain and justify their choices.
Dr. Cruz noted that grading creative assignments require advanced planning. In her case, she worked closely with her TAs to develop a rubric that was shared with students in advance for full transparency and emphasized the importance of students connecting ideas to analytical arguments discussed in the class.
Watch Dr. Cruz’s 2021 Symposium presentation. Listen to Dr. Cruz talk about The Power of Blended Classrooms in Season 3, Episode 6 of the Dead Ideas in Teaching and Learning podcast. Get a glimpse into Dr. Cruz’s online classroom and her creative teaching and the design of learning experiences that enhanced critical thinking, creativity, curiosity, and community by viewing her Voices of Hybrid and Online Teaching and Learning submission.

As part of his standard practice, Dr. Yesilevskiy scaffolds assignments – from less complex to more complex – to ensure students integrate the concepts they learn in the class into their projects or new experiments. For example, in Laboratory 1, Dr. Yesilevskiy slowly increases the amount of independence in each experiment over the semester: students are given a full procedure in the first experiment and by course end, students are submitting new experiment proposals to Dr. Yesilevskiy for approval. This is creative thinking in action. Students not only learned how to “replicate existing experiments, but also to formulate and conduct new ones.”
Watch Dr. Yesilevskiy’s 2021 Symposium presentation.
How Do I Get Started?: Strategies to Support Creative Assignments
The previous section showcases examples of creative assignments in action at Columbia. To help you support such creative assignments in your classroom, this section details three strategies to support creative assignments and creative thinking. Firstly, re-consider the design of your assignments to optimize students’ creative output. Secondly, scaffold creative assignments using low-stakes classroom activities that build creative capacity. Finally, cultivate a classroom environment that supports creative thinking.
Design Considerations for Creative Assignments
Thoughtfully designed open-ended assignments and evaluation plans encourage students to demonstrate their learning in authentic ways. When designing creative assignments, consider the following suggestions for structuring and communicating to your students about the assignment.
Set clear expectations . Students may feel lost in the ambiguity and complexity of an open-ended assignment that requires them to create something new. Communicate the creative outcomes and learning objectives for the assignments (Ranjan & Gabora, 2013), and how students will be expected to draw on their learning in the course. Articulare how much flexibility and choice students have in determining what they work on and how they work on it. Share the criteria or a rubric that will be used to evaluate student deliverables. See the CTL’s resource Incorporating Rubrics Into Your Feedback and Grading Practices . If planning to evaluate creative thinking, consider adapting the American Association of Colleges and Universities’ creative thinking VALUE rubric .
Structure the project to sustain engagement and promote integrity. Consider how the project might be broken into smaller assignments that build upon each other and culminate in a synthesis project. The example presented above from Dr. Yesilevskiy’s teaching highlights how he scaffolded lab complexity, progressing from structured to student-driven. See the section below “Activities to Prepare Students for Creative Assignments” for sample activities to scaffold this work.
Create opportunities for ongoing feedback . Provide feedback at all phases of the assignment from idea inception through milestones to completion. Leverage office hours for individual or group conversations and feedback on project proposals, progress, and issues. See the CTL’s resource on Feedback for Learning . Consider creating opportunities for structured peer review for students to give each other feedback on their work. Students benefit from learning about their peers’ projects, and seeing different perspectives and approaches to accomplishing the open-ended assignment. See the CTL’s resource Peer Review: Intentional Design for Any Course Context .
Share resources to support students in their work. Ensure all students have access to the resources they will need to be successful on the assigned project. Connect students with campus resources that can help them accomplish the project’s objectives. For instance, if students are working on a research project – connect them to the Library instruction modules “ From Books to Bytes: Navigating the Research Ecosystem ,” encourage them to schedule a consultation with a specialist for research support through Columbia Libraries , or seek out writing support. If students will need equipment to complete their project, remind them of campus resources such as makerspaces (e.g., The Makerspace @ Columbia in Room 254 Engineering Terrace/Mudd; Design Center at Barnard College); borrowing equipment (e.g., Instructional Media and Technology Services (IMATS) at Barnard; Gabe M. Wiener Music & Arts Library ).
Ask students to submit a self-reflection with their project. Encourage students to reflect on their process and the decisions they made in order to complete the project. Provide guiding questions that have students reflect on their learning, make meaning, and engage their metacognitive thinking skills (see the CTL’s resource of Metacognition ). Students can be asked to apply the rubric to their work or to submit a creative statement along with their work that describes their intent and ownership of the project.
Collect feedback from students and iterate. Invite students to give feedback on the assigned creative project, as well as the classroom environment and creative activities used. Tell students how you will use their suggestions to make improvements to activities and assignments, and make adjustments to the classroom environment. See the CTL’s resource on Early and Mid-Semester Student Feedback .
Low-Stakes Activities to Prepare Students for Creative Assignments
The activities described below are meant to be scaffolded opportunities leading to a larger creative project. They are low-stakes, non-graded activities that make time in the classroom for students to think, brainstorm, and create (Desrochers and Zell, 2012) and prepare them to do the creative thinking needed to complete course assignments. The activities can be adapted for any course context, with or without the use of technology, and can be done individually or collaboratively (see the CTL’s resource on Collaborative Learning to explore digital tools that are available for group work).
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a process that students can engage in to generate as many ideas as possible related to a topic of study or an assignment topic (Sweet et al., 2013: 87). As they engage in this messy and jugement-free work, students explore a range of possibilities. Brainstorming reveals students’ prior knowledge (Ambrose et al., 2010: 29). Brainstorm activities are useful early on to help create a classroom culture rooted in creativity while also serving as a potential icebreaker activity that helps instructors learn more about what prior knowledge and experiences students are bringing to the course or unit of study. This activity can be done individually or in groups, and in class or asynchronously. Components may include:
- Prompt students to list off (individually or collaboratively) their ideas on a whiteboard, free write in a Google Doc or some other digital space.
- Provide formative feedback to assist students to further develop their ideas.
- Invite students to reflect on the brainstorm process, look over their ideas and determine which idea to explore further.
Mind mapping
A mind map, also known as a cognitive or concept map, allows students to visually display their thinking and knowledge organization, through lines connecting concepts, arrows showing relationships, and other visual cues (Sweet et al., 2013: 89; Ambrose et al. 2010: 63). This challenges students to synthesize and be creative as they display words, ideas, tasks or principles (Barkley, 2010: 219-225). A mind mapping activity can be done individually or in groups, and in class or asynchronously. This activity can be an extension of a brainstorming session, whereby students take an idea from their brainstormed list and further develop it.
Components of a mind mapping activity may include:
- Prompt students to create a map of their thinking on a topic, concept, or question. This can be done on paper, on a whiteboard, or with digital mind mapping or whiteboard tools such as Google Drawing.
- Provide formative feedback on the mind maps.
- Invite students to reflect on their mind map, and determine where to go next.
Digital storytelling
Digital storytelling involves integrating multimedia (images, text, video, audio, etc.) and narrative to produce immersive stories that connect with course content. Student-produced stories can promote engagement and learning in a way that is both personal and universal (McLellan, 2007). Digital storytelling contributes to learning through student voice and creativity in constructing meaning (Rossiter and Garcia, 2010).
Tools such as the CTL-developed Mediathread as well as EdDiscussion support collaborative annotation of media objects. These annotations can be used in writing and discussions, which can involve creating a story. For freeform formats, digital whiteboards allow students to drop in different text and media and make connections between these elements. Such storytelling can be done collaboratively or simply shared during class. Finally, EdBlogs can be used for a blog format, or Google Slides if a presentation format is better suited for the learning objective.
Asking questions to explore new possibilities
Tap into student imagination, stimulate curiosity, and create memorable learning experiences by asking students to pose “What if?” “why” and “how” questions – how might things be done differently; what will a situation look like if it is viewed from a new perspective?; or what could a new approach to solving a problem look like? (James & Brookfield, 2014: 163). Powerful questions are open-ended ones where the answer is not immediately apparent; such questions encourage students to think about a topic in new ways, and they promote learning as students work to answer them (James & Brookfield, 2014: 163). Setting aside time for students to ask lots of questions in the classroom and bringing in questions posed on CourseWorks Discussions or EdDiscussion sends the message to students that their questions matter and play a role in learning.
Cultivate Creative Thinking in the Classroom Environment
Create a classroom environment that encourages experimentation and thinking from new and diverse perspectives. This type of environment encourages students to share their ideas without inhibition and personalize the meaning-making process. “Creative environments facilitate intentional acts of divergent (idea generation, collaboration, and design thinking) and convergent (analysis of ideas, products, and content created) thinking processes.” (Sweet et al., 2013: 20)
Encourage risk-taking and learning from mistakes . Taking risks in the classroom can be anxiety inducing so students will benefit from reassurance that their creativity and all ideas are welcome. When students bring up unexpected ideas, rather than redirecting or dismissing, seize it as an opportunity for a conversation in which students can share, challenge, and affirm ideas (Beghetto, 2013). Let students know that they can make mistakes, “think outside of the box” without penalty (Desrochers and Zell, 2012), and embrace failure seeing it as a learning opportunity.
Model creative thinking . Model curiosity and how to ask powerful questions, and encourage students to be curious about everything (Synder et al., 2013, DiYanni, 2015). Give students a glimpse into your own creative thinking process – how you would approach an open-ended question, problem, or assignment? Turn your own mistakes into teachable moments. By modeling creative thinking, you are giving students permission to engage in this type of thinking.
Build a community that supports the creative classroom environment. Have students get to know and interact with each other so that they become comfortable asking questions and taking risks in front of and with their peers. See the CTL’s resource on Community Building in the Classroom . This is especially important if you are planning to have students collaborate on creative activities and assignments and/or engage in peer review of each other’s work.
Plan for play. Play is integral to learning (Cavanagh, 2021; Eyler, 2018; Tatter, 2019). Play cultivates a low stress, high trust, inclusive environment, as students build relationships with each. This allows students to feel more comfortable in the classroom and motivates them to tackle more difficult content (Forbes, 2021). Set aside time for play (Ranjan & Gabora, 2013; Sinfield, Burns, & Abegglen, 2018). Design for play with purpose grounded in learning goals. Create a structured play session during which students experiment with a new topic, idea, or tool and connect it to curricular content or their learning experience. Play can be facilitated through educational games such as puzzles, video games, trivia competitions, scavenger hunts or role-playing activities in which students actively apply knowledge and skills as they act out their role (Eyler, 2018; Barkley, 2010). For an example of role-playing games explore Reacting to the Past , an active learning pedagogy of role-playing games developed by Mark Carnes at Barnard College.
The CTL is here to help!
CTL consultants are happy to support instructors as they design activities and assignments that promote creative thinking. Email [email protected] to schedule a consultation.
Ambrose et al. (2010). How Learning Works: 7 Research-Based Principles for Smart Teaching. Jossey-Bass.
Barkley, E. F., Major, C. H., and Cross, K. P. (2014). Collaborative Learning Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty .
Barkley, E. F. (2010) Student Engagement Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty.
Beghetto, R. (2013). Expect the Unexpected: Teaching for Creativity in the Micromoments. In M.B. Gregerson, H.T. Snyder, and J.C. Kaufman (Eds.). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Cavanagh, S. R. (2021). How to Play in the College Classroom in a Pandemic, and Why You Should . The Chronicle of Higher Education. February 9, 2021.
Chicca, J. and Chunta, K, (2020). Engaging Students with Visual Stories: Using Infographics in Nursing Education . Teaching and Learning in Nursing. 15(1), 32-36.
Davis, M. E. (2019). Poetry and economics: Creativity, engagement and learning in the economics classroom. International Review of Economics Education. Volume 30.
Desrochers, C. G. and Zell, D. (2012). Gave projects, tests, or assignments that required original or creative thinking! POD-IDEA Center Notes on Instruction.
DiYanni, R. (2015). Critical and creative thinking : A brief guide for teachers . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Eyler, J. R. (2018). How Humans Learn. The Science and Stories Behind Effective College Teaching. West Virginia University Press.
Forbes, L. K. (2021). The Process of Play in Learning in Higher Education: A Phenomenological Study. Journal of Teaching and Learning. Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 57-73.
Gerstle, K. (2017). Incorporating Meaningful Reflection into Calculus Assignments. PRIMUS. Problems, Resources, and Issues in Mathematics Undergraduate Studies. 29(1), 71-81.
Gregerson, M. B., Snyder, H. T., and Kaufman, J. C. (2013). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Henry, M., Owens, E. A., and Tawney, J. G. (2015). Creative Report Writing in Undergraduate Organic Chemistry Laboratory Inspires Non Majors. Journal of Chemical Education , 92, 90-95.
Hitchcock, L. I., Sage, T., Lynch, M. and Sage, M. (2021). Podcasting as a Pedagogical Tool for Experiential Learning in Social Work Education. Journal of Teaching in Social Work . 41(2). 172-191.
James, A., & Brookfield, S. D. (2014). Engaging imagination : Helping students become creative and reflective thinkers . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Jackson, N. (2008). Tackling the Wicked Problem of Creativity in Higher Education.
Jackson, N. (2006). Creativity in higher education. SCEPTrE Scholarly Paper , 3 , 1-25.
Kleiman, P. (2008). Towards transformation: conceptions of creativity in higher education.
Kothari, D., Hall, A. O., Castañeda, C. A., and McNeil, A. J. (2019). Connecting Organic Chemistry Concepts with Real-World Context by Creating Infographics. Journal of Chemistry Education. 96(11), 2524-2527.
McLellan, H. (2007). Digital Storytelling in Higher Education. Journal of Computing in Higher Education. 19, 65-79.
Ranjan, A., & Gabora, L. (2013). Creative Ideas for Actualizing Student Potential. In M.B. Gregerson, H.T. Snyder, and J.C. Kaufman (Eds.). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Rossiter, M. and Garcia, P. A. (2010). Digital Storytelling: A New Player on the Narrative Field. New Directions for Adult and Continuing Education. No. 126, Summer 2010.
Sheafer, V. (2017). Using digital storytelling to teach psychology: A preliminary investigation. Psychology Learning & Teaching. 16(1), 133-143.
Sinfield, S., Burns, B., & Abegglen, S. (2018). Exploration: Becoming Playful – The Power of a Ludic Module. In A. James and C. Nerantzi (Eds.). The Power of Play in Higher Education . Palgrave Macmillan.
Reynolds, C., Stevens, D. D., and West, E. (2013). “I’m in a Professional School! Why Are You Making Me Do This?” A Cross-Disciplinary Study of the Use of Creative Classroom Projects on Student Learning. College Teaching. 61: 51-59.
Sweet, C., Carpenter, R., Blythe, H., and Apostel, S. (2013). Teaching Applied Creative Thinking: A New Pedagogy for the 21st Century. Stillwater, OK: New Forums Press Inc.
Tatter, G. (2019). Playing to Learn: How a pedagogy of play can enliven the classroom, for students of all ages . Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Vaughn, M. P. and Leon, D. (2021). The Personal Is Political Art: Using Digital Storytelling to Teaching Sociology of Sexualities. Teaching Sociology. 49(3), 245-255.
Wukich, C. and Siciliano, M. D. (2014). Problem Solving and Creativity in Public Policy Courses: Promoting Interest and Civic Engagement. Journal of Political Science Education . 10, 352-368.
CTL resources and technology for you.
- Overview of all CTL Resources and Technology
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .
10 Creative Ways to Better Engage Your Students
Explore more.
- Classroom Management
- Student Engagement
S tarting out as a young adjunct instructor, I can painfully recall reading my lesson notes from index cards as my students sat passively with blank stares. Fortunately that didn’t last long, thanks to a mentor observing my class. But I doubt my experience was much different from that of other emerging educators. After all, I had modeled these ineffective teaching practices after my own experiences as a university student.
Today, however, there has been a huge push in higher education to move beyond these passive methods of instruction that lead to less student engagement and low motivation. As Jennifer Stanchfield discovered , “More is learned through exploring and struggling than by being provided the answer.”
It’s harder than ever these days to keep our students’ attention. But I have improved my approach over the past 30 years based on the simple belief that telling is not teaching . Because of this, I am continually exploring interesting and creative ways to engage my students.
I have identified some outstanding techniques, which I will share here, that have helped to enhance my students’ engagement and motivation for learning. Many of these strategies have come from the book Total Participation Techniques: Making Every Student an Active Learner by Himmele and Himmele, which has truly transformed my teaching. So let’s get started on transforming yours.
10 Engagement Strategies to Energize and Motivate Your Students
Before we break down specific strategies you can use to enhance participation, it’s important to understand that there are five different types of engagement: social, behavioral, emotional, intellectual, and physical. As teachers, we may organically hit two or three of these engagement types, but some we are likely to miss, especially if we’re not aware of them. I’ve struggled with ideas for how to get my students physically engaged, for example.
Below, I’ve categorized my top engagement strategies by these types to help you address all five. They have been designed for use in university classes and can easily be adapted for any area of study.
WHAT WE’LL COVER: 10 CREATIVE ENGAGEMENT STRATEGIES
In this article, Pamela Kramer Ertel breaks down the following engagement strategies to improve student participation and enhance learning retention.
Getting to Know You
Find Someone Who…
Bounce Cards
The Lecture T-Chart
The Ripple Method
Drama, Please!
Whiteboard Splash and Gallery Walk
Inside-Outside Circles
Origami Review Game
Social Engagement: Creating Connections with Students Through Collaboration and Sharing
Social engagement involves social interactions. The key to having effective social engagement is to help students get to know and trust you and other students early in the semester. The following strategies are designed to allow students to make these important connections as they help build a collaborative learning environment of support and trust.
1. Getting to Know You
Prior to the start of a new semester, I email my students a survey to learn more about their interests and preferences. Here are the key questions I ask:
What are your career goals?
How do you learn best?
Share five facts about yourself that will help me get to know you and best meet your needs.
What are your three favorite songs or musicians?
Is there anything else you would like to share that will help me better support your learning?
I also prepare a PowerPoint presentation that I use to introduce myself on the first day of class. I share personal and professional stories and family photos with the hope that my students will feel more connected to me and thus more motivated to open up themselves. I also love sharing stories about my latest connections to the country music stars I meet in Nashville (like that time I got a huge hug from Chris Janson in church).
I then have my students create name tents: They display their names on large, folded index cards to quickly familiarize the class. I also have them use this card to draw or write brief ideas about their interests, which form the basis for how they introduce themselves to their peers.
2. Find Someone Who . . .
I plan first-day-of-class activities that give students simple opportunities to get to know one another in a light-hearted way. For one such activity, I create a template with a nine-space grid in which various criteria are listed. Students must find a different person in the class who meets the criteria listed in each grid space (see Figure 1). For example, “Find someone who is an early riser.”
As they circulate around the room, they must find someone for each grid space and fill in that person’s name. This activity serves as a great icebreaker and helps students learn each other’s names, which is important for helping them feel connected to their peers.
Pamela Kramer Ertel, Harvard Business Publishing Education, 2022.
Figure 1: Find Someone Who... is a great first-day-of-class game that gives students the opportunity to learn more about each other in a fun, light-hearted way.
Behavioral Engagement: Establishing Rules, Routines, and Roles
Behavioral engagement deals with routines and behaviors that help promote learning. It is important to teach the routines and behaviors that you want your students to use to improve the quality of peer discussions and the efficiency of class activities. These strategies also help to create a sense of security as students know what to expect from you.
For example, before my students can enter the classroom, I have them wait until I open the door, as I want to be sure I have the room prepared for the day’s activities. They also know that I will have a daily prompt posted for them to discuss with their peers as they arrive, which is designed to engage them in the lesson topic of the day.
Here are some other strategies for behavioral engagement.
3. Bounce Cards
With the “Bounce Card” strategy , I provide a card for each student that lists key questions or prompts I want them to discuss with a partner or small group. The questions can be generic so that the card can be used to discuss any topic. (For example, “Rephrase what your partner just said,” or, “That’s a great point because . . .”) The questions are designed to help students strengthen their listening skills and deepen their conversations. The prompts require students to extend, rephrase, and ask follow-up questions to their bounce partners, rather than just give a simple answer.
For example, if I ask students to discuss a video clip, they might just say whether they liked it. But using a Bounce Card forces them to dig deeper. You can adapt the questions on the card to suit your educational purposes, but for the students who struggle with conversational skills, this can be a great template for helping them develop more thoughtful responses.
4. The Lecture T-Chart
You may have noticed that sometimes as students take notes, they don’t seem to really be processing what they are learning. The “Lecture T-Chart” consists of a simple template where students record their notes on the left side of a page. Periodically throughout my lecture, I pause and have them use their own words to summarize the key ideas I’ve just presented, which they write on the right side of the template.
This pause-review-summarize process helps to strengthen comprehension and can be extended by having students share their summaries with others to further process the information through social engagement.
Emotional Engagement: Facilitating Joy, Connection, and Memories
Emotional engagement entails creating safe, positive learning experiences for everyone involved. Students will not be open to sharing their thoughts and responses in class if they feel they will be mocked or disrespected by their professor or peers.
One of the ways I create emotional connection is through music. I’ll start each class playing a different student’s favorite song or music video (based on what they told me in that initial survey). They love it and appreciate that I actually read their responses.
Here are some other strategies to emotionally engage your students.
5. The Ripple Method
Himmele and Himmele propose the use of the ripple method : Instead of just calling on students who raise their hand, you “ripple” your questions by first having each student respond individually to the prompt (either in their mind or in writing). They then share their responses with one to three peers before you open up the floor to volunteers willing to share with the whole class. This process ensures that every student has time to think of a response.
For example, I use the ripple method when I ask my students each week to share an “aha moment” from their clinical experiences. This relieves pressure for those students who are less motivated to engage in discussion. The students soon realize that their experiences are just as valid as everyone else’s and that we are all in this together. They also realize that some of their perceived failures in the field become some of their most precious learning experiences.
Intellectual Engagement: Promoting Choice, Challenge, and Curiosity
Intellectual engagement involves curiosity and meaningful explorations. Whenever possible, give students choices in terms of tasks, topics, and strategies for demonstrating their learning. The more relevant and authentic the task, the higher the level of engagement and motivation.
Here are some activities to spur curiosity and meaning.
6. Drama, Please!
Consider using problem solving, role playing, and acting as ways of demonstrating learning. You will need to be specific about your expectations, but the freedom to explore interests and determine a mode of presentation of ideas will be motivating for many students.
In my teacher education class, I have my students roleplay parent-teacher conferences. I preface this by showing a video clip from the sitcom Everybody Loves Raymond . While the clip is humorous, it helps the students recognize the vulnerability of parents (and teachers) in these situations, which is an essential understanding when conducting an effective parent-teacher conference.
7. IQ Cards
IQ cards provide an interesting and efficient way for students to share insights about what they have learned, as well as raise questions after a lecture or class activity. Students write an insight (representing the “I” in IQ) on one side of an index card. This insight can be related to something new they learned during that class, or it can be a “so what” statement, indicating how this information can be applied in professional or personal practice.
On the other side of the card, the students write a question (Q) that they have about the information. Typically, I like to have students share their cards with their peers in pairs and then I collect the cards to gather informal assessment data about student learning. This works as an excellent closure activity as it reviews key lesson content and helps me assess whether students are grasping the material.
Physical Engagement: Making Movement Meaningful
Physical engagement involves some type of movement and is an often-neglected engagement strategy in the higher ed classroom. John Ratey , author of Spark (Hatchett, 2008), states that “exercise is the single most powerful tool you have to optimize your brain function.” While time and space may be challenges to including physical movement in the classroom, small efforts to engage students physically help to keep them focused and may help change their brains by strengthening neuropathways leading to improved storage and retrieval of information.
While physical engagement can introduce novelty to your class, it’s important to think about the physical and mobile abilities of your students, and to provide accommodations and make room for modifications when necessary.
The following strategies help to engage students in movement connected with their learning.
8. Whiteboard Splash and Gallery Walk
Whiteboard Splash (sometimes known as “chalkboard splash” or “graffiti wall”) involves students responding to a prompt with words or pictures to explain an idea or concept by writing on the whiteboard (or large chart paper).
For example, I might ask my teacher education students, “What are the activities that should be included in the schedule for the first day of school for young children?” or “What are some strategies you can use to reflect on your teaching practice?” Students work individually or in small groups to illustrate their ideas. Then students circulate around the room for a “gallery walk” to view and discuss the displayed information.
To ensure that students don’t passively walk by the work, have them write down the ideas they found new, different, surprising, or worth remembering. Students can then share the results and address additional questions.
9. Inside-Outside Circles
This is one of my students’ favorite strategies for physical movement and social engagement. I have students create two concentric circles where each person is in front of or behind someone in the other circle. The inside circle group is then told to turn and face their outside circle group partner. I provide a prompt for the pairs to discuss (for example, “What are some reasons for student misbehavior?”) and set a time limit for each partner to share a brief response to the question.
Students then take turns listening to their partner’s response. Be sure to set a timer so students know when to end their conversations. Then I have the outside circle group move two places to the left so they are facing a different person. You can provide the same or a different prompt and the process repeats.
To hold students accountable, be sure to circulate and listen to the conversations so you get an idea of their level of understanding and interaction, which you can then use in conducting a closing discussion with the whole group. If space is an issue, consider using the hallway or go outdoors (weather permitting). If you have students with limited mobility, you can conduct this activity with chairs (and wheelchairs) and students can still have rich interactions. Be sure to position any students with mobility limitations in the inner circle so just the students in the outside circle have to move during the activity.
For online classes, assign pairs of students to breakout rooms and give them a short amount of time (one to two minutes) to share their ideas with their partners. Then you can randomly assign them a new partner using a new set of breakout rooms.
10. Origami Review Game
Depending on your age, you may recall playing a game with origami paper creations with questions and answers on them. Partners can take turns telling each other’s fortunes or quizzing each other. I use this often as a content review activity before exams. (You can find directions for the construction and implementation of this game here .)
Your role is to create eight close-ended questions that have simple (i.e., short) answers so they fit on the game board. (for example, “What type of engagement involves movement?” followed by the answer, “Physical engagement.”) Each pair of students receives an origami paper creation (see Figure 2), and they take turns asking each other questions from the game piece until all the questions have been covered.

Figure 2: An example of the Origami Review Game.
Keep It Fresh and Meaningful
Adding these simple but meaningful engagement strategies into my instructional practices has not only helped create a stimulating, joyful learning environment for my students, but it has also made me a more motivated teacher. I teach a three-hour class and the time now passes quickly for everyone.
Simply put: To keep our students motivated, we have to stay motivated. These strategies can help you avoid the rut of doing the same thing all the time. But keep in mind that even a clever idea can become stale if overused, so make sure to mix and match.
Just remember that novelty and fun are additional benefits of students’ cognitive engagement; they are not the main focus of our efforts. So use your class time wisely by choosing meaningful questions and engagement strategies that are related to your learning goals. If you do so, I think you’ll find that your students quickly get on board.

Pamela Kramer Ertel is an associate professor of education at Middle Tennessee State University in Murfreesboro, Tennessee. She is a former professor and Dean of the College of Education at East Stroudsburg University and a past president of Kappa Delta Pi, the International Honor Society in Education. Her research interests include teacher education, student engagement, trauma-informed schools, and adoption.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
13 ESL Homework Ideas
Homework may not be many students’ favorite thing, but research says it’s truly an effective learning tool that teachers should use .
The trick is assigning great homework.
To help you do this with ease, we’ve compiled an awesome list of 13 homework assignments that will have your ESL students begging for more.
1. Read a Short Story
2. share a passion, 3. start a chat group, 4. listen to a podcast, 5. write a letter, 6. write an amazon review, 7. do a wikipedia edit, 8. write a short story or poem, 9. share their culture, 10. catch a movie, 11. meet new people, 12. analyze a song, 13. go on a photo scavenger hunt, what makes homework effective.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Have students read a short story for homework and then ask them to tell the class about the story in the next session.
I would recommend giving students some suggestions on what short stories to read, depending on the level of your students.
Here are some suggestions of short story collections for each level of ESL learner:
- “The Very First Americans” by Cara Ashrose: This collection of short stories features Native American culture and history, written in simple language.
- “Oxford Bookworms Library: Starter Level” This series offers simplified versions of classic stories, such as fairy tales, adventure stories and more.
- “Classic Tales for ESL Students” by L.A. Hill: This collection of classic stories from literature is retold with easier vocabulary and sentence structure.
Intermediate
- Thousands of learner friendly videos (especially beginners)
- Handpicked, organized, and annotated by FluentU's experts
- Integrated into courses for beginners

- “The Best American Short Stories” This series features contemporary short stories from a wide range of American writers, so there’s something for everyone here.
- “Short Stories in English for Intermediate Learners” by Olly Richards: This collection of engaging stories is designed specifically for intermediate ESL students.
- “Roald Dahl: The Collected Short Stories” This delightful collection of quirky and imaginative tales has become a favorite of many of my students.
- “Interpreter of Maladies” by Jhumpa Lahiri: This Pulitzer Prize-winning collection of short stories explores the immigrant experience, something which many ESL students can relate to.
- “Dubliners” by James Joyce: This classic collection of interconnected stories captures the essence of Dublin in 1914. But it still feels modern to many students.
- “Nine Stories” by J.D. Salinger: This classic collection of short stories is a class favorite when I’ve used it.
What do your students really care about? Give them a chance to talk about it in front of the class.
Have each person choose something they’re passionate about, something they might consider themselves an expert on.
Challenge students to think of a creative way to present five must-know facts about that subject. They might make a movie, create a poster or brochure, write a song or even put on a skit.
Have each person present their creative project to the class, and then give the class five minutes to ask questions of the presenter.
Set certain parameters like students must speak in complete sentences or require that every student ask at least two questions at some point during the presentations.
- Interactive subtitles: click any word to see detailed examples and explanations
- Slow down or loop the tricky parts
- Show or hide subtitles
- Review words with our powerful learning engine
Students will love sharing about their passions, and they’ll get some great speaking, listening and discourse information in the process, as well as teach the rest of the class some interesting vocabulary.
Ask for class for a volunteer to start a class WhatsApp chat group. They can also decide to use another messaging app like Telegram, Viber, Voxer or any other app that has a group chat function.
Encourage them to send at least one message and to respond to a couple others for their homework.
This text group has the added advantage of students being able to make friends with one another, and a place to ask about missed homework assignments on days when they can’t make it to class.
Note that if a student doesn’t want to be included in the chat group, you should have a back up assignment prepared for them.
Listening is one of the ESL student’s most difficult skills to acquire, so listening to a short podcast episode is ideal homework.
You can ask students to write a little about the podcast to turn in to you, or you can ask them to briefly summarize what they heard for the class in the next session.
- Learn words in the context of sentences
- Swipe left or right to see more examples from other videos
- Go beyond just a superficial understanding

Here are some suggestions for well done podcasts:
The English We Speak : Produced by the BBC, this podcast focuses on teaching commonly used phrases and idioms in conversational English.
The Moth : A storytelling podcast where real people share their personal experiences and anecdotes in English.
Stuff You Should Know : Though not specifically designed for ESL students, this podcast covers a vast array of interesting topics, providing exposure to diverse vocabulary and subject matters.
Ask your students to write a letter . The letter can be written to a friend or family member (which they could then actually mail or email), or it could be a fan letter to a favorite musician or actor. They could even write a letter to Santa Claus or a historical figure.
For example, a student might choose to write a letter to Marie Antoinette, asking her what it was like to be the queen of France at such a young age.
You can also choose to have students write letters to one another. Then the next homework can be writing that letter writer back.
- FluentU builds you up, so you can build sentences on your own
- Start with multiple-choice questions and advance through sentence building to producing your own output
- Go from understanding to speaking in a natural progression.
Ask you students to review a product on Amazon (or any other shopping website that has reviews). Ask them to select a product they have really used, so they have a genuine opinion on the quality of the product and whether it lived up to their expectations.
Then, in the next session, show the reviews on the overhead projector to the class and ask a student to read the review.
You can then go over any errors in vocabulary, grammar or sentence structure and revise the review together as a class.
Since anyone can edit a Wikipedia article, it’s a great place for ESL students to hone their writing and editing skills, and they’ll have a built-in readership, too!
Ask students to select a person that they know a lot about—a well-known figure from history, pop culture, music or film would all work. Then ask them to read the Wikipedia entry to see if they can add anything else to the article.
Perhaps the article on Ryan Gosling is missing a key detail about his recent Ken performance. If so, the student will revise and edit the article. They should take notes on what they changed, so they can explain it to you or the class the next day.
- Images, examples, video examples, and tips
- Covering all the tricky edge cases, eg.: phrases, idioms, collocations, and separable verbs
- No reliance on volunteers or open source dictionaries
- 100,000+ hours spent by FluentU's team to create and maintain
Ask your students to get creative. Have them write a short story or a poem . This can get them to use descriptive language that they don’t always have a chance to use.
One good activity to do before you assign this homework is an adjective bubble chart. For this, you start with one adjective. For example, write “moist” on the board, circle it and then draw 4-5 lines coming off of the”moist” bubble.
Ask your students to come up with other adjectives that are related to “moist” and so on. They may come up with “wet,” “watery,” “soaked” or “damp.” Then draw lines from each of those. This can lead to words that you never expected to come up.
Have your students select 3-4 adjectives from this introduction activity that they’ll use in their story or poem.
Ask your students to prepare a short presentation on an aspect of their home culture to tell the class about in the next session.
For example, a student from China may explain the Lunar New Year, a student from Vietnam may explain Tet or a student from El Salvador may tell the class about their quinceañera .

They can use photos, art, a PowerPoint presentation or they can just explain in their own words.
Then open the class up for questions.
Can you legitimately send students to the movies for homework? You can when you’re teaching ESL.
Your students don’t have to commit to a full-length movie. Instead, you can use the videos on FluentU to screen mini-lessons using clips from TV shows and movies, movie trailers, news segments, vlogs or music videos.
Use these videos in the classroom or assign homework to watch a few and complete the subsequent quizzes. You can also ask students to complete flashcard quizzes based on vocabulary words you want them to pay special attention to. These quizzes are adaptable so every student will have a unique experience catered to his learning level.
There are plenty of ways to use a movie for language development. And whether students watch a new release or catch an old Elvis flick on TV, they can do any of the following activities as homework:
- Summarize the plot.
- Describe a main character.
- Note new or interesting vocabulary (particularly slang) they hear while watching.
- Write an interview with one of the characters in the movie.
I’m sure you also have your favorite movie-related language activities and many work as homework assignments. So get creative with how you have students share about what they watched.
For the most part, people are willing to help someone in need, and that is doubly true for someone who needs to complete an assignment for school.
That’s why sending students out to interview native speakers on campus is such a fun homework assignment.
Start by helping your students write a list of questions they’ll use for their interviews. Students can choose a topic or you can assign one, like leisure activities or celebrity news.
Tell students to list five to ten questions they might ask on that topic that will elicit specific answers.
As a class, discuss how students might introduce themselves to a potential interviewee.
Then send students out to their interviews after class. They can share the answers they got in the next session.
Music is great for English learners since it stresses many aspects of language that can otherwise be hard to isolate, like the emotion of language, intonation and stress.
Have students choose their favorite English language song to listen to for homework and then ask them to do the following:
- Practice the lyrics to learn intonation and rhythm.
- Note slang and cultural references in the songs.
- Summarize the theme of the song, or just what it’s about.
- Have students share their favorite lyrics and what a particular song means to them.
Give individual students or groups of up to three students a list of items to find on their homework scavenger hunt. But instead of being specific in your list (for example, including items such as cat), be descriptive in your list.
You might include items such as something frightening, something beautiful, something quiet, something cool.
Students find items they think fit the description. For example, someone who is claustrophobic might choose an elevator for something frightening. They then take a picture of it.
The next day, have each person get with a partner and show them the pictures they took for each item on the list.
If the connection is not obvious, students should ask their partner to explain why they chose a particular item, such as the elevator.
Assigning homework that works isn’t as hard as you might think, especially if you focus on the following points.
- Put your homework in writing. It can be tempting to just announce homework assignments to students at the end of class, but language learners benefit when you reinforce what you say with what they can see. So take a minute to write any homework assignment on the board so students can read it as well as listen to it.
- Let students know what goals you have for a particular assignment. Is it practicing a certain grammar point ? Improving their listening skills ? Pronunciation practice ? When students know why they’re doing something, they’ll be able to tell on their own when they’ve successfully completed their homework assignment.
- Keep your homework practical . Your students may not find themselves planning out a menu for Thanksgiving when they leave your ESL classroom, but odds are they’ll have to order food at a restaurant at some point. Think about realistic ways students will have to use English in the real world and try to make your homework practical.
- Let your students be creative . Give your students choices on how they express themselves or present information. It’s okay for students to make a home movie, put on a one-man play or paint a picture to present to the class. Just because you prefer a particular type of creative expression doesn’t mean your students do, so give them choices and let them express themselves.
- Make homework fun! Every class has its own personality, so what’s fun for one might not be fun for another. Tailor your assignments to the personality of your class. Think about what they would think is fun, and go with that.
No matter what you believed in your student days, homework doesn’t have to be boring. With a little creativity when assigning homework, you might find that the activities you assign for outside of class become the highlights of your students’ days.
Related posts:
Enter your e-mail address to get your free pdf.
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

- Utility Menu
GA4 tracking code
Giving feedback to your students.

Receiving feedback is an essential part of student learning and improvement. There are many approaches to how you give feedback to your students in your course, and the approach you choose should be an approach that suits your teaching style and the needs of your students.
Types of Feedback
The two predominant types of feedback are formative and summative. Formative can be viewed as feedback meant for revising, such as feedback on a draft or a low-stakes assignment. Think of it as the rest stop in a journey. Summative feedback is typically feedback on an assignment or project designed as a way for students to show their mastery. A typical example of a summative assessment is a final exam or project. You can read more about the different types of feedback here . Together, formative and summative feedback will help your students build on their work and understand how their work connects with the larger picture of the class.
Feedback can come in many different forms. The types of feeddback you give in your course will vary depending on your students needs, the assignment type, and your style:
- Personalized Feedback
- Automated Feedback
- Collective Feedback
- Peer Review
Check out our Real Time Connections Online: Feedback page to learn more about each type of feedback and how to make it happen in Canvas.
What will be different: the way your class community is built
- Feedback should center around what the student can do next. For formative feedback, this could be actionable steps for their next assignment. For summative feedback, it can be framed more broadly for future endeavors the student may take on.
- Feedback doesn’t equate to criticism. When discussing any weaknesses in student work, it is best to explore it through questions and how the weakness can be improved. If you find that written feedback doesn’t fully encapsulate the right tone, consider scheduling one-to-one meetings with students or recording audio or video feedback.
- Find balance. Give feedback when it matters. It’s not necessary to give in-depth feedback for everything -- it will burn your students out and it will certainly burn you out as well! Think about the assignments in your course where in-depth feedback could really impact your students’ future work.
Tools for Feedback
- Use Canvas. Canvas offers tools to help you give just-in-time feedback within small assignments. You can set feedback, based on student responses, to automatically appear after a student finishes a quiz. Providing feedback is also easy through Canvas’ Speedgrader tool. Check out our Instructional Technology Group’s guides or schedule an appointment with them here .
- Communicate expectations using rubrics. Rubrics are a good way to indicate to your students what’s important in your assignment. It’s also a way to maintain consistency when multiple members of the teaching staff are grading the same assignment. Here are some tips for creating and using rubrics in your class .
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, creating assignments.
Here are some general suggestions and questions to consider when creating assignments. There are also many other resources in print and on the web that provide examples of interesting, discipline-specific assignment ideas.
Consider your learning objectives.
What do you want students to learn in your course? What could they do that would show you that they have learned it? To determine assignments that truly serve your course objectives, it is useful to write out your objectives in this form: I want my students to be able to ____. Use active, measurable verbs as you complete that sentence (e.g., compare theories, discuss ramifications, recommend strategies), and your learning objectives will point you towards suitable assignments.
Design assignments that are interesting and challenging.
This is the fun side of assignment design. Consider how to focus students’ thinking in ways that are creative, challenging, and motivating. Think beyond the conventional assignment type! For example, one American historian requires students to write diary entries for a hypothetical Nebraska farmwoman in the 1890s. By specifying that students’ diary entries must demonstrate the breadth of their historical knowledge (e.g., gender, economics, technology, diet, family structure), the instructor gets students to exercise their imaginations while also accomplishing the learning objectives of the course (Walvoord & Anderson, 1989, p. 25).
Double-check alignment.
After creating your assignments, go back to your learning objectives and make sure there is still a good match between what you want students to learn and what you are asking them to do. If you find a mismatch, you will need to adjust either the assignments or the learning objectives. For instance, if your goal is for students to be able to analyze and evaluate texts, but your assignments only ask them to summarize texts, you would need to add an analytical and evaluative dimension to some assignments or rethink your learning objectives.
Name assignments accurately.
Students can be misled by assignments that are named inappropriately. For example, if you want students to analyze a product’s strengths and weaknesses but you call the assignment a “product description,” students may focus all their energies on the descriptive, not the critical, elements of the task. Thus, it is important to ensure that the titles of your assignments communicate their intention accurately to students.
Consider sequencing.
Think about how to order your assignments so that they build skills in a logical sequence. Ideally, assignments that require the most synthesis of skills and knowledge should come later in the semester, preceded by smaller assignments that build these skills incrementally. For example, if an instructor’s final assignment is a research project that requires students to evaluate a technological solution to an environmental problem, earlier assignments should reinforce component skills, including the ability to identify and discuss key environmental issues, apply evaluative criteria, and find appropriate research sources.
Think about scheduling.
Consider your intended assignments in relation to the academic calendar and decide how they can be reasonably spaced throughout the semester, taking into account holidays and key campus events. Consider how long it will take students to complete all parts of the assignment (e.g., planning, library research, reading, coordinating groups, writing, integrating the contributions of team members, developing a presentation), and be sure to allow sufficient time between assignments.
Check feasibility.
Is the workload you have in mind reasonable for your students? Is the grading burden manageable for you? Sometimes there are ways to reduce workload (whether for you or for students) without compromising learning objectives. For example, if a primary objective in assigning a project is for students to identify an interesting engineering problem and do some preliminary research on it, it might be reasonable to require students to submit a project proposal and annotated bibliography rather than a fully developed report. If your learning objectives are clear, you will see where corners can be cut without sacrificing educational quality.
Articulate the task description clearly.
If an assignment is vague, students may interpret it any number of ways – and not necessarily how you intended. Thus, it is critical to clearly and unambiguously identify the task students are to do (e.g., design a website to help high school students locate environmental resources, create an annotated bibliography of readings on apartheid). It can be helpful to differentiate the central task (what students are supposed to produce) from other advice and information you provide in your assignment description.
Establish clear performance criteria.
Different instructors apply different criteria when grading student work, so it’s important that you clearly articulate to students what your criteria are. To do so, think about the best student work you have seen on similar tasks and try to identify the specific characteristics that made it excellent, such as clarity of thought, originality, logical organization, or use of a wide range of sources. Then identify the characteristics of the worst student work you have seen, such as shaky evidence, weak organizational structure, or lack of focus. Identifying these characteristics can help you consciously articulate the criteria you already apply. It is important to communicate these criteria to students, whether in your assignment description or as a separate rubric or scoring guide . Clearly articulated performance criteria can prevent unnecessary confusion about your expectations while also setting a high standard for students to meet.
Specify the intended audience.
Students make assumptions about the audience they are addressing in papers and presentations, which influences how they pitch their message. For example, students may assume that, since the instructor is their primary audience, they do not need to define discipline-specific terms or concepts. These assumptions may not match the instructor’s expectations. Thus, it is important on assignments to specify the intended audience http://wac.colostate.edu/intro/pop10e.cfm (e.g., undergraduates with no biology background, a potential funder who does not know engineering).
Specify the purpose of the assignment.
If students are unclear about the goals or purpose of the assignment, they may make unnecessary mistakes. For example, if students believe an assignment is focused on summarizing research as opposed to evaluating it, they may seriously miscalculate the task and put their energies in the wrong place. The same is true they think the goal of an economics problem set is to find the correct answer, rather than demonstrate a clear chain of economic reasoning. Consequently, it is important to make your objectives for the assignment clear to students.
Specify the parameters.
If you have specific parameters in mind for the assignment (e.g., length, size, formatting, citation conventions) you should be sure to specify them in your assignment description. Otherwise, students may misapply conventions and formats they learned in other courses that are not appropriate for yours.
A Checklist for Designing Assignments
Here is a set of questions you can ask yourself when creating an assignment.
- Provided a written description of the assignment (in the syllabus or in a separate document)?
- Specified the purpose of the assignment?
- Indicated the intended audience?
- Articulated the instructions in precise and unambiguous language?
- Provided information about the appropriate format and presentation (e.g., page length, typed, cover sheet, bibliography)?
- Indicated special instructions, such as a particular citation style or headings?
- Specified the due date and the consequences for missing it?
- Articulated performance criteria clearly?
- Indicated the assignment’s point value or percentage of the course grade?
- Provided students (where appropriate) with models or samples?
Adapted from the WAC Clearinghouse at http://wac.colostate.edu/intro/pop10e.cfm .
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links

Before you go, check this out!
There are plenty of other articles to develop your skills and showing you how to make money teaching online!
27 Interactive Assignment Ideas For Online Students
When you are teaching students online it can sometimes be difficult to find engaging assignments for Students. This article will look at some ways you can make your assignments more interactive and engaging to provide better quality training.
Here are 27 Interactive Assignments you can use to engage students online:
Group Audio Chat
Interview a professional, participate in forum discussions, attend online industry seminars, online whiteboard brainstorming, group concept mapping, live group google docs, sourceforge or github, creating a podcast, starting a youtube channel, use quora or reddit, create a linkedin profile, build a website, use simulation software, research companies in industry, research latest technology, participate in social media, explore mobile apps, vendor certification, create training videos, local work experience, do a job on a freelancing website, compete in an online competition, contact an industry professional.
- Attend a Conference
Record Real World Event
Record completing task.
There are some great ideas to spice up your online training as individuals or groups but now let’s dig in deeper and review how these can be assignments for online students.
Having Students meet in an Audio only or Audio and Video chat that they record as team meetings, or mock-up business meetings, or act out scenarios is a great assignment method. It shows to the teacher the engagement of each student and what they have learned.
There are a lot of software solutions you can use to host a free video conference. The most noteworthy apps commonly used are
- GoToMeeting
- FreeConference
- GoToMeeting Free
- FreeConferenceCall
Each option has its advantages and disadvantages. Make sure you choose one that fits your requirements. Before making a decision try the demo version of each software to give you a better understanding of whether it meets your needs. Zoom allows for 40 mins meetings for free which is all students would need to record their session in most cases.
Who can tell you more about a job than an expert? An interview that the student records with their phone is a great assignment for them not only to meet real professionals but also to learn more about the job they are training for. Students can start the assignment by locating a professional on LinkedIn and politely asking for an interview for their studies. They can then submit as part 2 of the assignment their question list. And finally the recorded interview.
Here is an article with a list of questions students could potentially ask their industry professional:
ARTICLE: 47 Questions to Ask Network Peers About Their Job
Forum discussions are a great way of sharing ideas and increasing student engagement. You can mark students on their involvement in your forums or industry forums. There are various methods to increase students’ participation in online discussions . This type of activity gives students the opportunity to discuss their ideas with other students or industry professionals.
During forum discussions, students get to create and enhance their social relationships with other students. This decreases the feeling of isolation when they have friends in the class they can ask questions of for social learning.
Businesses of all types are putting on marketing and technical webinars of every subject you can think of. You can not visit a website these days without someone offering one to you. These are great places for students to get exposure to the real industry and interact with potential future industry peers.
They can chat with other participants and ask questions of the industry experts in each area. For their assignment, you can get them to write a report or record the session using screencasting software showing their engagement. These are a great learning tool for students to gain exposure to their future industry.
With so many online whiteboard tools available why not have an assignment for your students to work in teams on a shared whiteboard and brainstorm their group assignments. This always makes for a good part 1 of the assignment to show group engagement. They can submit the resulting image to you. You can also use an online whiteboard during online courses. If you do not know what whiteboard to use for your online course you should take a look at the 7 best online whiteboards .
A whiteboard brainstorming session is a great opportunity for your students. It gives them the chance to combine their ideas and be more creative.
As well as online whiteboards there are also online software tools specifically for brainstorming like StormBoard which can be found on their website .
Nothing helps students understand a topic more than trying to map out the key concepts. Whether you get them to do this on their own to show individual understanding or in groups to allow them to socially learn from each other, it is a great idea.
There is a great online tool students can use for free and save their work online for 6 months with MudMap .
For some other great tools they can use check out this article:
ARTICLE: Concept Mapping Tools
While most people probably already know this one it is still worth mentioning. The ability of a group of students to edit the same document at the same time and talk with others on group audio chat or text chat is extremely engaging. If you have not tried this yet get someone to do it with you by downloading Google Docs or using it in a web browser from your https://drive.google.com account.
If you are running IT training courses the ability for your students to create a code, document, or file repository that does versioning is a useful industry skill. Not only can the students create their own repository they could also join another open-source team to help them with their documentation, planning, or coding. This is not only something they can not only show proof of as an assignment but something they can put on their resume.
Sourceforge and Github are two of the most commonly used online hosting solutions when it comes to storing project files and source code for distributed projects. Either is fine for your online class but try both and see which one you think your students would prefer.
Sourceforge is the best option if you want to develop an open-source project that involves an application targeting the end-user. On the other hand, you should use GitHub if you are planning on creating a project that comprises a collection of packages.
To learn more about the different aspects of the two source code hosting solutions click here .
We often think of using Podcasts for disseminating information to large groups of people in an audio format. Have you ever thought of using it as a student assignment? Why not have the student start a podcast where they show what they have learned at each stage of the training?
They can record a quick session on their phone or and they can show their creativity by editing the audio if they want or getting in guest speakers or even just discussing it with another student from the class. This is a great way for students to show competence especially for those with poor written skills.
While Google is currently the number one search tool on the internet the next generation is using YouTube as their first search tool. So if this is the case why not give them an assignment that is creating a Youtube channel and uploading some content. Whether they do this in groups or alone they will learn many skills along the way that they will probably use in their working career.
This is a great way for them to start feeling comfortable on camera in certain industries or for creating screencasts of them using their computers for any task. Maybe showing you how to use a piece of software. Maybe the channel hosts all of their assignment submissions for the whole subject?
Quora and Reddit are two of the most commonly used forums worldwide. You can find a lot of interesting content by searching for a certain subject.
The fact that these platforms contain tons of professionals with various areas of expertise opens up new ideas your students can research for assignments. I know the information on there is neither quantitative or qualitative but it is great for expanding what students think on a topic.
Your students will benefit from different approaches to concepts. They can read multiple points of view. This way, they will get a better understanding of the subject.
LinkedIn is the working professional social media with their resumes linked to their accounts. Setting assignments to create a profile, or if they have a profile to connect to industry professionals, join industry groups, or even join company groups is a great opportunity for them.
This allows them to start their own networks and engage in the industries they will be part of. It is also a great way to find a Mentor to guide them through their career. Obviously you have to be careful depending on the age of your students and do this only with students old enough and with their parents’ permission if required.
There are various benefits of a LinkedIn profile for a student. If you want to learn more or inform your students about why they should open up a LinkedIn account go to LinkedIn for Students .
More and more websites appear online every day. You can ask your students to create a website that explains the concepts you are teaching them. Say you are teaching physics. Your students can create a free website that shows how physics is related to everyday life.
Another great example of using a website during your online course is to ask your students to create an online portfolio. This works well for all students but even more so for students that need a portfolio of work like those in photography, videography, or creative writing.
This is not difficult for them to do with a free WordPress website they can literally have up in minutes.
To recreate a real situation you can make use of simulation software. There are various domains that can benefit from simulation software solutions. This type of assignment allows students to test out their hypotheses in a semi real-world scenario.
This type of application is commonly used in:
- Mathematics
MatLab – Mathematics
For example, to recreate possible situations in terms of statistics, you can ask your students to use MatLab .
MatLab integrates visualization, computation, and programming of mathematical notation into a high-performance simulation tool. This would not be used for early math but for Years 10 and up you could definitely look at using this or for including into adult learning classes.
SimScale – Physics
If you are planning on simulating fluid dynamics, you should use SimScale in the Cloud. In the Cloud just means it is hosted for your online.
It can conduct graphical and numerical simulations of fluid dynamics. It is generally used for quick optimization of different systems, as well as overall improvements.
Your students can create different situations that involve fluids. They will understand how physics affects fluid dynamics. Moreover, they will be able to see in-depth stats of various liquids getting in contact with other materials.
Comsol Multiphysics – Chemistry and Physics
This software solution is definitely one of the best in terms of simulation apps. It offers finite element analysis as well as a multiphysics feature. It allows its users to simulate physic-based events. Additionally, it can provide effective simulations of chemical applications.
Among the most noteworthy multiphysics components that Comsol can handle are
This software is easy to integrate into your students’ assignments. It will help them to understand different components of physics. For example, they will be able to learn about movement and kinetic energy using graphic simulations.
I have personally interviewed students in Mock Interview sessions and hired many people over the years and one of the biggest issues they have is not knowing the industry they are part of or the company they are applying to.
To help online students understand the industry they are part of you can get them to research online the top 10 companies in their industry. If they are in an Arts related field may be the Top 10 Museums or if they are in Finance may be the Top 100 shares in the market.
They can look at the current news and events related to that company and who it is run by as well as the products and services they might offer or the artwork they have.
As well as knowing their industry, knowing the current and future technology gets them ready for their first job and shows them the gaps in their knowledge. If you combine this with the previous assignment type as Part 2 then they would already know the companies to research their latest products and services.
Looking at the latest industry trends which most people call Mega Trends if they are international in nature will add the scope to their research. Technology is a huge part of most industries these days and whether it is a new type of paint or a new type of building material every industry has them. These technologies are not just related to the Information Technology sectors.
For students this type of assignment is a research online one or if you want to make it more engaging see if they can contact someone from the business or organization that will do an online interview with them discussing this topic.
Social media is a part of our everyday life so we should integrate it into the online learning process. You can use social media platforms in various ways to create interactive assignments for your online classes.
Engaging in Social Media for students can::
- Introduce them to Market Influencers
- Introduce them to Current Trends
- Allow them to engage in Relevant Discussions
- Keep up with Current Industry News
- Understand the role of Social Media in Business
- Inspire them with new topics
These types of assignments will encourage them to engage with their industry peers and learn from them. Whether it is on LinkedIn, Quora, Instagram, Pinterest, Twitter, or Facebook they will have a community of people to bounce ideas off. They can then print to PDF the resultant conversations to use in their assignments.
Social media is a great way of developing communication skills. Using social platforms, your students can observe patterns that appear and understand what is trending. For instance, they can predict future trends by taking a closer look at the articles posted on social media. The trends depend on a lot of factors such as people’s interest, overall feedback on a certain subject, and the number of posts on a topic.
Mobile apps are a great idea when it comes to online teaching. Mobile devices have become an effective learning tool with extended uses in both online courses and real-world learning. You can use the applications as part of your delivery content, to do assignments in or for students to research the tools related to the course you are teaching.
For example, if you are teaching physical fitness online then you can use a mobile app that tracks your students’ workout habits. These types of apps also let you analyze the results.
Tasks that can be assigned to your students can integrate mobile apps very well. For example, if you are running an online course about photo edit, you can ask your students to find out what the best mobile photo editing app is.
And finally, if you are running a course about computer programming you can get them to code and test their code in the many apps that allow for this. The resulting code could then be submitted to your Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Obtaining a vendor certification is a tricky yet useful activity for any student in lots of different areas like IT, Project Management, Industrial Automation, Continuous Improvement, Reporting, and many other fields.
The course material can align with the Vendor Certification and can either have assignments based on that material with exams to suit. Alternately you can have them passing their Vendor Certification as the pass for the subject. There are heaps of universities that already do this method.
The easiest way to see most of these certifications is to look at the testing centers:
Pearson Vue List of Exams on Pearcon Vue
Prometric List of Exams on Prometric
There are heaps of other vendor certification for pretty much every form of software on computers so just check the vendor website.
To prove they know a subject they can always take a video on their phone to explain how to do the task in the real world. There are heaps of stands for your mobile phones from ones for the bench to ones on stands. You could also use a GoPro or equivalent.
As part 1 to the assignment, they can submit their topic and list of instructions, and Part 2 of the assignment could be the actual training video. Whether you get them to do post-production on the video is completely up to you. That basically just means use Windows Maker or a program like that to edit the video after recording.
If they are going to record what they are doing on their computer screen then check out this article:
ARTICLE: Spice Up Your eLearning With A Screencast
Even though Vocational Training has been doing this for years you could always organize with a local professional some work experience. During that work experience, they could submit their own assignment like baking a complex cake or welding something or even making a small software application.
If you are doing this in conjunction with a small business it could solve a problem that small business or non-profit has and they provide feedback on the result as well as you marking it.
There are various freelancing websites worldwide and your students can try to develop their skills by doing a job on one of them.
The most commonly used freelancing websites are:
- Freelancers.com
Ask your students to create an account on any of these websites and do a job to improve their skills. Apart from using the skills you have taught them they will also make some pocket money. This activity might open up new career paths for them or at least expose them to how the contracting industry works.
Whether the job they get paid to do succeeds or fails they will get invaluable knowledge on how to deal with customers. How to perform that particular task and also what the quality and expectations are for work in that industry.
Competitions are always interesting regardless of your students’ age. They will definitely be interested in participating in online contests. If you are trying to get a bit of competition going there is nothing like industry professionals judging student competitions. If you can’t find one online how about making one?
Examples of competition areas:
- Photo editing
- Video editing
There are a lot of different online competitions available in different areas. It is a great idea to find one contest that is suitable for the subject you are teaching and ask your students to join. They will work hard, being motivated by either the awards or the competitive spirit.
There are heaps of student competition websites and here are a couple: https://studentcompetitions.com/competitions https://www.weareteachers.com/student-contests-competitions/
NOTE: Make sure your students are eligible to enter
It used to be very hard to contact industry professionals and it used to take a phone book and heaps of phone calls. Now with LinkedIn, you can give the students a script to follow and they can contact heaps of Industry Professionals either locally or Internationally in any company.
Obviously, if your students are under the legal age you would work with a parent or with yourself to contact the industry professional. But it is never too early to start creating an industry network of people you can have as mentors or to ask for advice or to help you with a project.
Due to this being so simple now you really have no excuse to not include it in every course your teach.
Attend A Conference
Submitting a review or article on even recording an industry event in their field of study is great for students to expose themselves to the breadth of the industry. Whether they go with their parents or if old enough on their own. Looking at events that are on at your local convention center or with your local industry groups and introducing themselves get them to engage on a whole new level.
It starts to teach them real-world skills that are taught by professionals in their industry and keep up to date with what is happening in their local area and country. Seeing all the vendors during breaks and visiting their stands opens up whole new worlds for them.
There are conferences on everything from sewing to samurai swords and you just need to look at which ones suit your audience. With Covid-19 most of them have gone online as well. So since now, they have proven to themselves how to do this there will likely be way more done this way.
Here is an article on some creative conferences you could have students visit:
ARTICLE: Creative Conferences
Every day in every town in the world you there are things happening from space launches to recording a local chef cooking a meal. With a video camera in every pocket, the student can get into the world local to them and record something actually happening.
Whether they write a report on it or a detailed set of instructions to go with the video or narrate it like a sports commentator. There are heaps of creative and engaging ways to get students to learn in this way. They can also play around the video after it has been created to make it more professional or fun.
Recording themselves while completing certain tasks you have assigned is a great idea for your students. A video recording can be rewind back and forth as many times as you need. Whether you are a student or a teacher it is a great idea to have video proof of your task completion.
This works well for every type of class and thinking of how you can add more video recording to your classes will only make it more engaging for students.
I am a Technical Trainer and Manager with over 20 years experience in IT, Education and Business. I have multiple qualifications on each topic including post graduate qualifications. I have a passion for sharing knowledge and using technology to do this. If you would like to know more about me please see the about page of the website.
Recent Posts
How Do I Create An Online Training Or Teaching Website? Expert Secrets
Have you tried to setup or want to setup an online training or teaching website? Well then look no further as I will tell you exactly how in the simplest way possible. With over 20 years experience,...
What Are The Real Time Online Learning Pros And Cons
Having taught online for many years I wanted to give you some insights on what to expect. Here is my list of Pros and Cons. I have also suggest solutions for each of the Cons to save you time and...

51 Constructive Feedback Examples for Students
Constructive feedback is feedback that helps students learn and grow.
Even though it highlights students’ weaknesses, it is not negative feedback because it has a purpose. It is designed to help them identify areas for improvement.
It serves both as an example of positive reinforcement and a reminder that there is always room for further improvement. Studies show that students generally like feedback that points them in the right direction and helps them to improve. It can also increase motivation for students.
Why Give Constructive Feedback?
Constructive feedback is given to help students improve. It can help people develop a growth mindset by helping them understand what they need to do to improve.
It can also help people to see that their efforts are paying off and that they can continue to grow and improve with continued effort.
Additionally, constructive feedback helps people to feel supported and motivated to keep working hard. It shows that we believe in their ability to grow and succeed and that we are willing to help them along the way.
How to Give Constructive Feedback
Generally, when giving feedback, it’s best to:
- Make your feedback specific to the student’s work
- Point out areas where the student showed effort and where they did well
- Offer clear examples of how to improve
- Be positive about the student’s prospects if they put in the hard work to improve
- Encourage the student to ask questions if they don’t understand your feedback
Furthermore, it is best to follow up with students to see if they have managed to implement the feedback provided.
General Constructive Feedback Examples for Students
The below examples are general templates that need to be edited so they are specific to the student’s work.
1. You are on the right track. By starting to study for the exam earlier, you may be able to retain more knowledge on exam day.
2. I have seen your improvement over time. As a next step, it is a good idea to…
3. You have improved a lot and should start to look towards taking on harder tasks for the future to achieve more self-development.
4. You have potential and should work on your weaknesses to achieve better outcomes. One area for improvement is…
5. Keep up the good work! You will see better results in the future if you make the effort to attend our study groups more regularly.
6. You are doing well, but there is always room for improvement. Try these tips to get better results: …
7. You have made some good progress, but it would be good to see you focusing harder on the assignment question so you don’t misinterpret it next time.
8. Your efforts are commendable, but you could still do better if you provide more specific examples in your explanations.
9. You have done well so far, but don’t become complacent – there is always room for improvement! I have noticed several errors in your notes, including…
10. It is great that you are trying your best, but don’t stop here – keep pushing yourself to get even better results. It would be good to see you editing your work to remove the small errors creeping into your work…
11. You have put in a lot of hard work, and it is starting to show. One area for improvement is your tone of voice, which sometimes comes across too soft. Don’t be afraid to project your voice next time.
12. You are making good progress, but don’t forget to focus on your weaknesses too. One weakness to focus on is…
13. Your efforts are commendable, but it would have been good to have seen you focus throughout as your performance waned towards the end of the session.
15. While your work is good, I feel you are becoming complacent – keep looking for ways to improve. For example, it would be good to see you concentrating harder on providing critique of the ideas explored in the class.
16. It is great that you are trying your best, but don’t stop here – keep pushing yourself to get even better results! Try to improve your handwriting by slowing down and focusing on every single letter.
17. You have put in a lot of hard work, and it is starting to show. Keep up the good work and you will see your grades slowly grow more and more. I’d like to see you improving your vocabulary for future pieces.
18. You are making good progress, but don’t forget to focus on your weaknesses too. One weakness to focus on is…
19. You have potential and should work on your using more appropriate sources to achieve better outcomes. As a next step, it is a good idea to…
Constructive Feedback for an Essay
1. Your writing style is good but you need to use more academic references in your paragraphs.
2. While you have reached the required word count, it would be good to focus on making sure every paragraph addresses the essay question.
3. You have a good structure for your essay, but you could improve your grammar and spelling.
4. You have made some good points, but you could develop them further by using more examples.
5. Your essay is well-written, but it would be helpful to provide more analysis of the topic.
6. You have answered the question well, but you could improve your writing style by being more concise.
7. Excellent job! You have covered all the key points and your writing is clear and concise.
8. There are a few errors in your essay, but overall it is well-written and easy to understand.
9. There are some mistakes in terms of grammar and spelling, but you have some good ideas worth expanding on.
10. Your essay is well-written, but it needs more development in terms of academic research and evidence.
11. You have done a great job with what you wrote, but you missed a key part of the essay question.
12. The examples you used were interesting, but you could have elaborated more on their relevance to the essay.
13. There are a few errors in terms of grammar and spelling, but your essay is overall well-constructed.
14. Your essay is easy to understand and covers all the key points, but you could use more evaluative language to strengthen your argument.
15. You have provided a good thesis statement , but the examples seem overly theoretical. Are there some practical examples that you could provide?
Constructive Feedback for Student Reports
1. You have worked very hard this semester. Next semester, work on being more consistent with your homework.
2. You have improved a lot this semester, but you need to focus on not procrastinating.
3. You are doing well in most subjects, but you could improve your grades by paying more attention in class and completing all your homework.
4. You are doing well in most subjects, but you could still improve your grades by studying more and asking for help when you don’t understand something.
5. You have shown great improvement this semester, keep up the good work! However, you might want to focus on improving your test scores by practicing more.
6. You have made some good progress this semester, but you need to continue working hard if you want to get good grades next year when the standards will rise again.
7. Next semester, focus on completing all your homework on time and paying more attention in class.
8. You have worked hard this semester, but you could still improve your grades by taking your time rather than racing through the work.
9. Next semester, focus on completing all your homework in advance so you have time to check it over before submission.
10. While you usually understand the instructions, don’t forget to ask for help when you don’t understand something rather than guessing.
11. You have shown great improvement this semester, but you need to focus some more on being self-motivated rather than relying on me to keep you on task.
Constructive feedback on Homework
1. While most of your homework is great, you missed a few points in your rush to complete it. Next time, slow down and make sure your work is thorough.
2. You put a lot of effort into your homework, and it shows. However, make sure to proofread your work for grammar and spelling mistakes.
3. You did a great job on this assignment, but try to be more concise in your writing for future assignments.
4. This homework is well-done, but you could have benefited from more time spent on research.
5. You have a good understanding of the material, but try to use more examples in your future assignments.
6. You completed the assignment on time and with great accuracy. I noticed you didn’t do the extension tasks. I’d like to see you challenging yourself in the future.
Related Articles
- Examples of Feedback for Teachers
- 75 Formative Assessment Examples
Giving and receiving feedback is an important part of any learning process. All feedback needs to not only grade work, but give advice on next steps so students can learn to be lifelong learners. By providing constructive feedback, we can help our students to iteratively improve over time. It can be challenging to provide useful feedback, but by following the simple guidelines and examples outlined in this article, I hope you can provide comments that are helpful and meaningful.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 7 Key Features of 21st Century Learning
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Sociocultural Theory of Learning in the Classroom
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ The 4 Principles of Pragmatism in Education
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 17 Deep Processing Examples
2 thoughts on “51 Constructive Feedback Examples for Students”
Very helpful to see so much great developmental feedback with so many different examples.
Great examples of constructive feedback, also has reinforced on the current approach i take.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Teach Online
6 Interesting Assignments to Engage Online Students
- February 28, 2021
- No Comments
OUR TOP PARTNER COURSES
120hr + Full Tutor Support
10% off with ESL102021

120hr Online TEFL Course
Best Online Option!

120hr Digital TEFL Course
15% Discount!

120hr Online TEFL Class
Most Reputable!
This post may contain affiliate links (at no extra cost to you). Please read our disclosure for more information.
For students, nothing is more boring than mundane assignments. They are a real motivation killer as well as a mood killer. You were a student once, too, so you’ll agree that education should be exciting and inspiring.
Online educators face increasing difficulties with keeping their students motivated and engaged because they do not meet in person. They cannot identify whether someone starts to lose motivation and try to help.
To help you avoid that in the first place, we have collected a number of fascinating online assignments that can really help engagement and motivation to learn.
A Meeting with a Prominent Individual
This one is designed to increase motivation by using creative skills of the students. The main idea of this assignment is simple: find a person, interview them, discuss certain topics discussed in the class, and enjoy the experience. Although any person can be selected for an interview, it could be even better if that person was a politician, a philosopher, an author, an athlete, or somehow prominent individual.

This assignment works great in increasing engagement, especially if you give the students all freedom in selecting the person for the interview. Also, it would be fascinating for you to read all those interviews as well! So, assign a deadline and make sure they focus on discussing class topics!
Here are some helpful resources for your students to prepare for this assignment.
- 25 Questions To Ask People To Draw Them Out
- 50 Brilliant, Original Questions to ask an Author
- Commentary: Interviewing athletes is easy, just follow these instructions
Group Discussion
The fact that you’re a teaching an online class should not stop you from nurturing the sense of community. Of course, your students may not know each other and they will probably never meet in life but group activities foster collaboration skills.

If your online learning environment has a discussion forum, let’s begin to take real advantage of it. Create a threat with a controversial topic and ask your students to discuss it and take specific stands. For example, if you’re teaching an astronomy class, you could ask whether humanity should colonize the planet next to ours, Mars.
Some of your students will support the idea of colonization arguing that it’s too dangerous to leave all life on one planet. On the other hand, others will take an opposing position, suggesting that we should fix our planet first and don’t contaminate other worlds. Just imagine how fascinating a discussion like this could be!
Here are more discussion topics for your class:
- Do celebrities earn too much money?
- Do curfews keep teens out of trouble?
- Is human activity a substantial cause of global climate change?
See How It’s Done
A direct observation of working process and practice are critical elements of effective education. In addition to a great opportunity to learn outside an online learning environment, the students can actually see how the knowledge is applied in real-life settings. This assignment works well for most professions.
For example, if you are teaching the history of English language , arrange a visit to a prominent history site and give the students the opportunity to speak with real scientists who make discoveries. As the result, they will get some valuable advice as well as great experience.
Ask your students to prepare a report and reflect on the visit.
A Random Photo Creative Assignment
You don’t have to be a photography teacher to use this incredible assignment. You know what they say: a picture is worth a thousand words. Use the power of a photo to convey some concepts and ideas from your subject.

It can be done in two ways: taking a random photo (works best for philosophy classes) or a photo of a specific object or a person (works well for sociology and history). Ask to characterize the photo using models, theories, or knowledge learned in the class.
As the result, your students have an opportunity to practice their creative skills as well as critical thinking skills. Check out these resources your students could use for this assignment
- How to Convey Meaning in Your Photos
- How to Take Good Pictures With Your Phone (for those who will use phones)
An Urgent Paper
This assignment is perfect for evaluating the knowledge retention of your students. The idea is to write a paper that summarizes the learning session in only one minute without preparation. It can be really challenging to beat the clock and complete a good paper, so your students will be tested for a real knowledge.

This one-minute paper can be assigned right after the end of a learning session or anytime you want. Just make sure that the amount of information is reasonable for this time limit. If you feel like you should provide more time for completion, feel free to expend the time to five and even ten minutes.
A Teacher for a Lesson
The last item on our list is another simple but powerful assignment. Here, you should ask your students to perform your duties for a little bit by grading the works of each other. For example, have them write an essay and send ungraded papers back to the class. Each student will read and grade the work of another learner.
As the result, the students become teachers for this lesson. Their feedback will demonstrate the effectiveness of their critical thinking skills and could be really helpful for others to identify some mistakes and shortcomings in their work.
The following resources will help your students to improve their feedback skills:
- Using Peer Review to Help Students Improve Their Writing
- How to Write Helpful Peer Review Comments
- Steps to Make Essay Writing Easy for Students
Final Thoughts
There are many fascinating assignments for online students that can help increase their motivation and engagement. Feel free to give a shot to the ones described in this article because online classes should not be boring but fascinating and exciting! Let these tips be helpful to you to keep your students engaged and thanks for reading!
Thanks to Diana for this post – Diana is an ESL Teacher with 5 years of successful work experience in teaching English as a second language, interactive teaching, and initiating supportive online lessons for ESL students. Feel free to follow Diana on Twitter
Guest Author
We* made a tefl.
*Made with love by the same people who run ESL Authority!

- 120hr Online Course with 11 Modules & 85 Lessons
- Full Tutor Support - All Questions Answered in 48hrs
- Fully Accredited and Valid Anywhere
- Perfect for online and classroom teachers
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
THE ONLY TEFL YOU NEED
- 120hr with 11 Modules & 85 Lessons
- Full Tutor Support
- Immediate Digital Certification

FOR TEACHERS
- HIRING GUIDES
- TEFL COURSES
FOR COMPANIES
- SUBMIT A COURSE
- GET IN TOUCH
- PRIVACY POLICY

You're signed out
Sign in to ask questions, follow content, and engage with the Community
- Canvas Instructor
- Instructor Guide
- How do I assign an assignment to an individual stu...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
How do I assign an assignment to an individual student?
in Instructor Guide
Note: You can only embed guides in Canvas courses. Embedding on other sites is not supported.
Community Help
View our top guides and resources:.
To participate in the Instructurer Community, you need to sign up or log in:
Subject Explorer
School Subjects
Math & Science
Business & Technology
Electives & Health
Board & Administration
Teaching & Learning
Audio/Video Lectures
Books & Documents
Classifieds
Jobs & Resources
Discussions
Language & Literature
Practice Projects for Excel

Excel Project C9: Grades and Averages
Instructions for students to “create a spreadsheet that shows all of your classes and automatically averages all of your test grades for each subject and then shows an overall average of your test …
Excel Project C8: Attendance Record
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheets, students create a spreadsheet that automatically adds up all of the Sunday School classes each Sunday, gives an average attendance for …
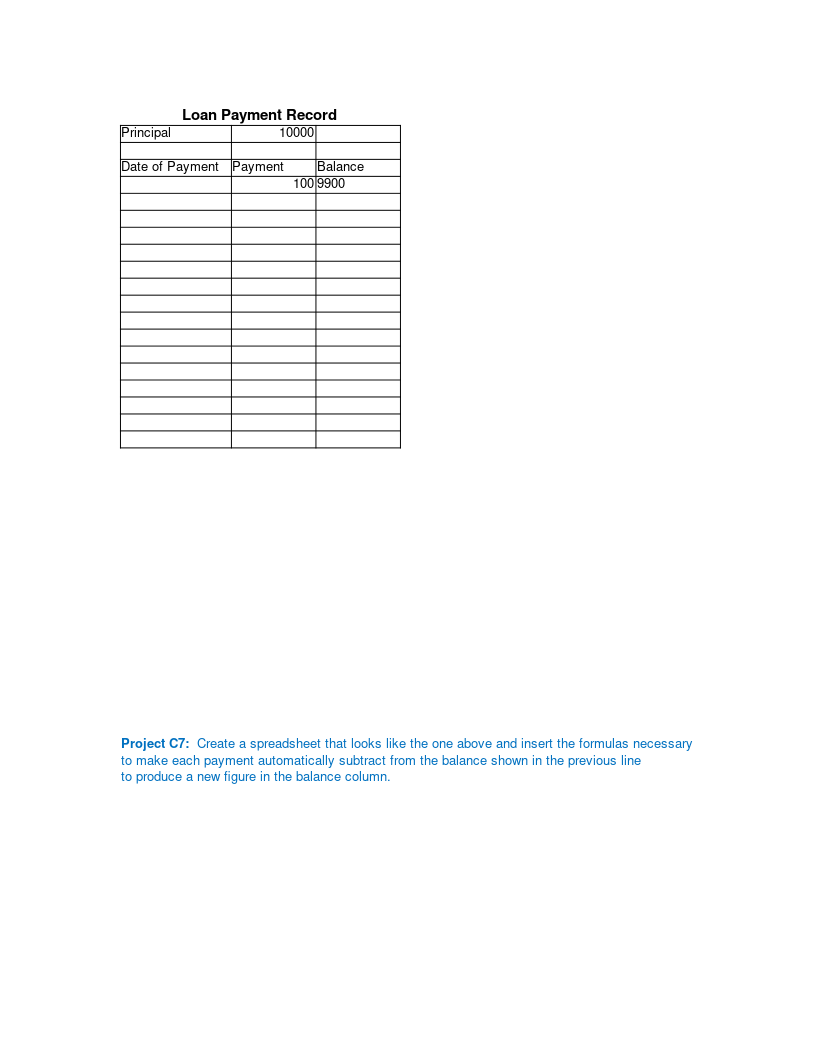
Excel Project C7: Loan Payment
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheet programs, students replicate a record of loan payments. They format columns to make each payment automatically subtract from the balance …
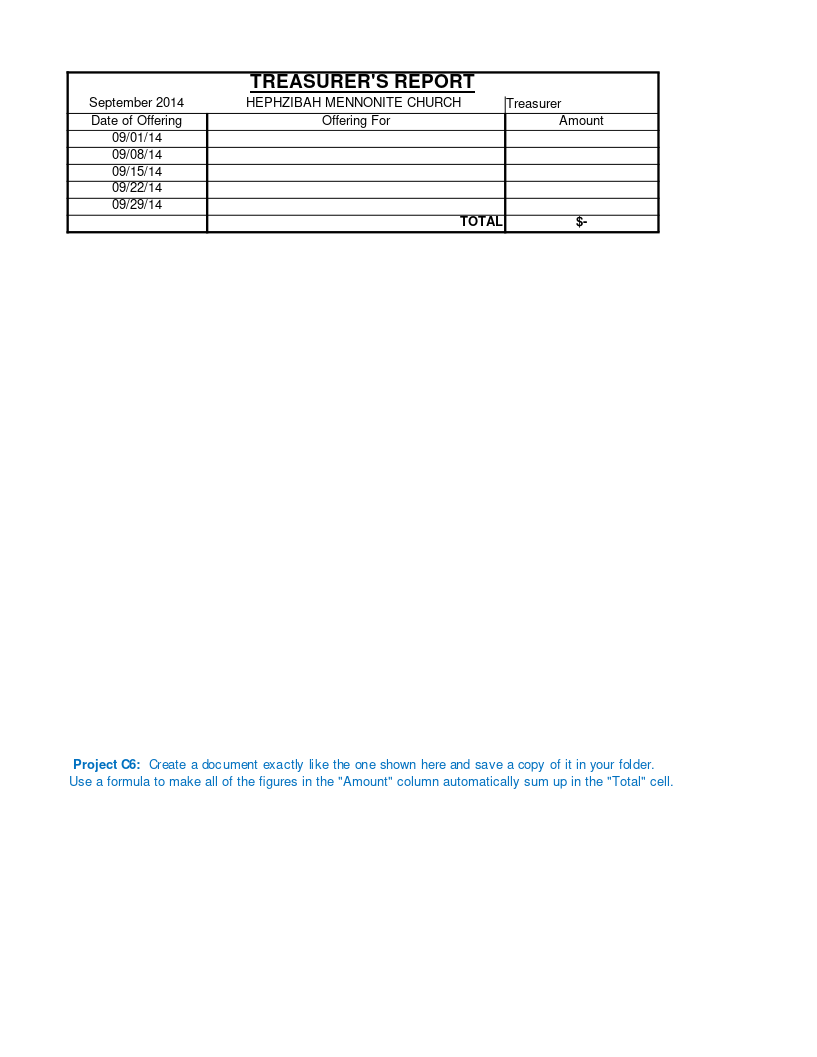
Excel Project C6: Treasurer’s Report
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheet programs, students replicate a treasurer’s report at an imaginary church. They also format a column to find the total at the bottom. …

Excel Project C5: Parent Directory
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheet programs, students replicate a parent directory with empty spaces for parent contact information. …
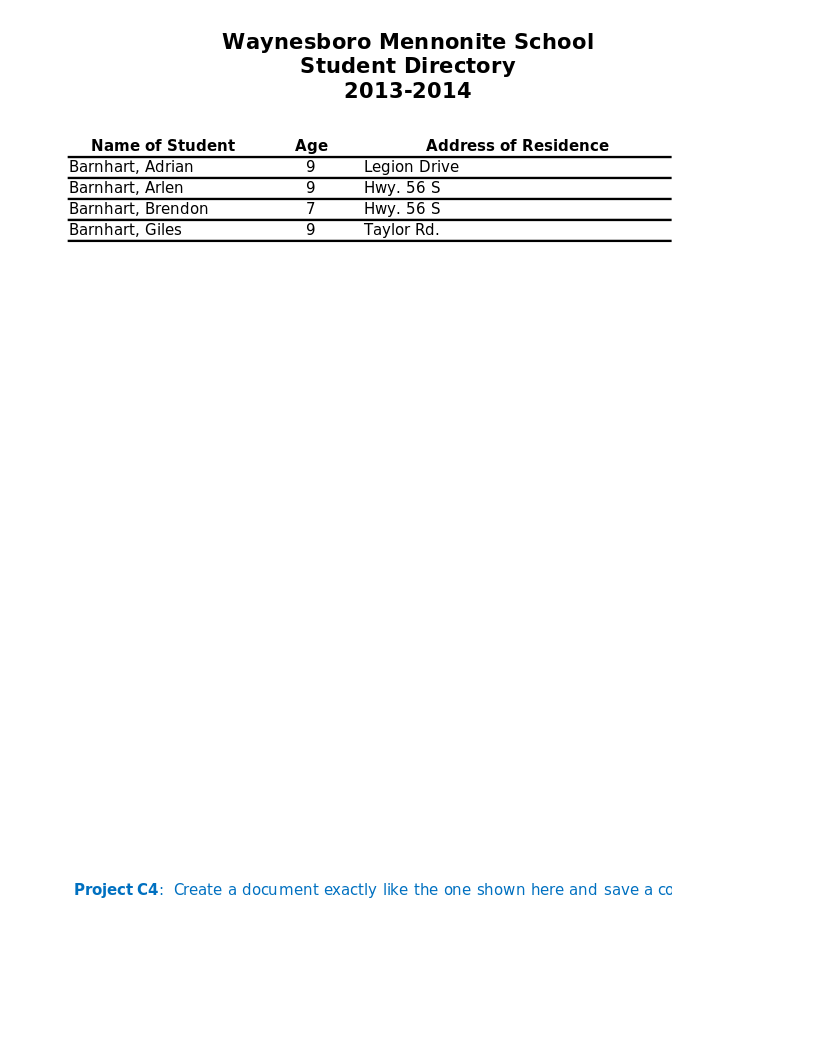
Excel Project C4: School Directory
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheet programs, students replicate a school directory with title and four columns of information. …
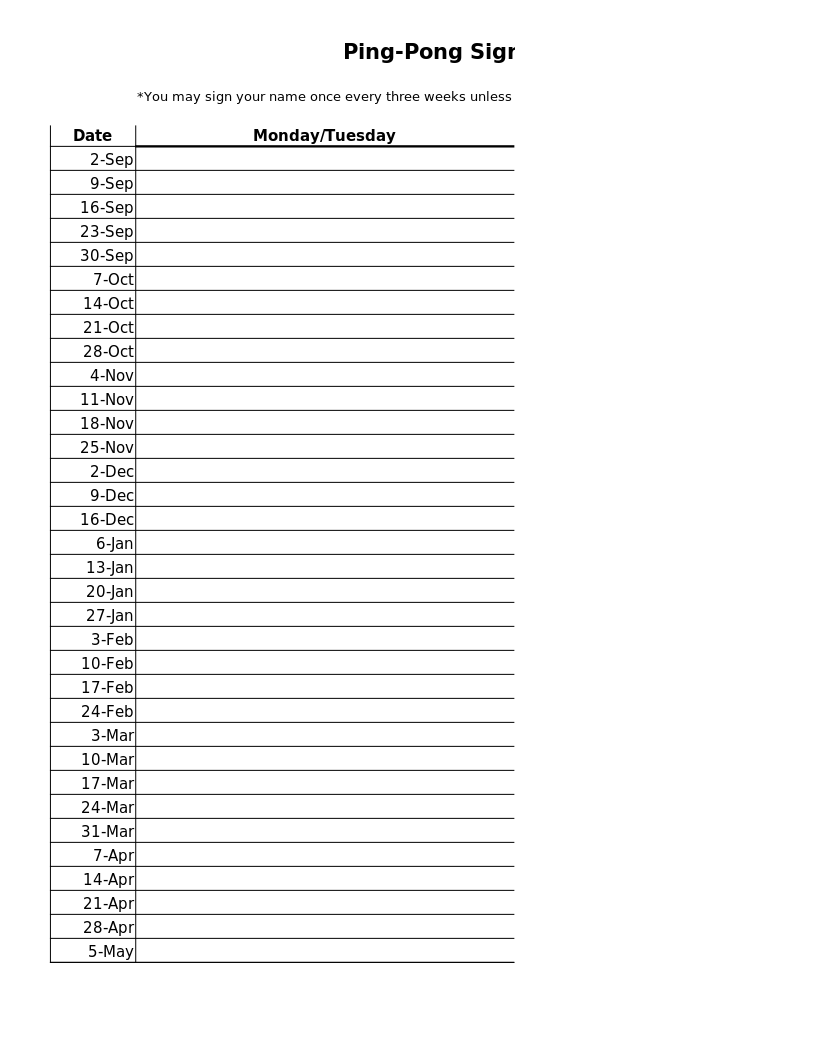
Excel Project C3: Sign Up Sheet
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheet programs, students replicate a weekly sign up sheet with a title and two columns. …
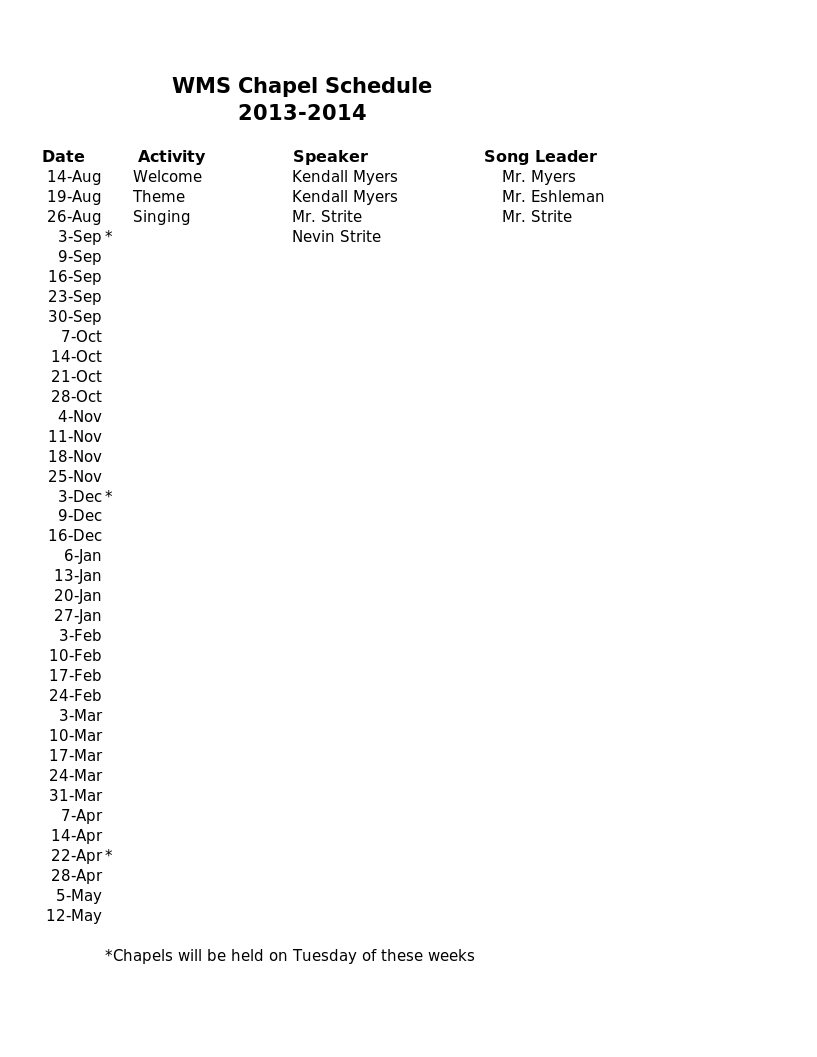
Excel Project C2: Chapel Schedule
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheet programs, students replicate a weekly chapel schedule including date, speaker, topic, and song leader. …
Excel Project C10: Invoice
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheets, students create an invoice template like the sample shown, entering the formulas for all of the cells so that the numbers total correctly …
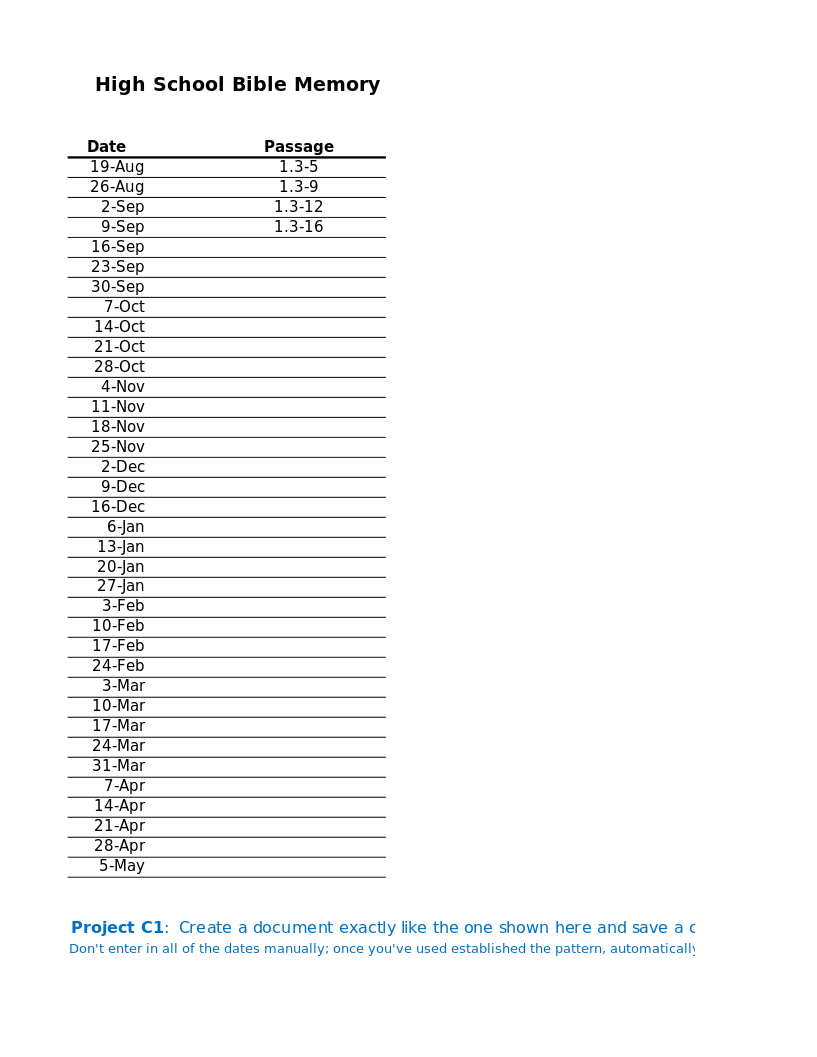
Excel Project C1: Bible Memory Chart
In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheet programs, students replicate a Bible memory chart. …
Categories:
Resource Type:
Pass it on:
Leave a Reply

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
8 fun assignments to give to your students. Photo credit: Paul Gilmore. 1. Take it outside. Moving any lesson or activity outside, particularly on a beautiful spring day, can be a fabulous way to brighten up everyone's spirits (yours included!). For starters, an abundant number of science lessons can take place outdoors — observing plants ...
Put on a show. This is a fun end-of-year activity that could be presented to parents, a younger class, your whole school, or just for your own class. Students can perform skits, dramatic readings, act out a story, showcase a talent, or read a favorite piece from a book they read. 45. Create an end-of-year ABC book.
The assignments we give to students don't simply have to be research papers or reports. There are many options for effective yet creative ways to assess your students' learning! Here are just a few: Journals, Posters, Portfolios, Letters, Brochures, Management plans, Editorials, Instruction Manuals, Imitations of a text, Case studies, Debates ...
2. RELEVANT WRITING. Picture this. Energetic lyrics fill the air as students listen, think critically, and analyze them. Or, students snap a photo of a page from an independent reading book, grinning as they annotate it with gifs, text, emojis, and more. Spotify and Snapchat are extremely popular apps for students.
5 Secrets Of Effective Homework Assignments. 1. Preparing for it. Homework should be a review or further practice of something learned in class so ensure that whatever homework you have assigned can be completed by students independently and with ease. To do this, conduct several comprehension tests and practice activities in class so that ...
If we want our students to read, then make a reading assignment a requirement of a quiz. The tactics above might be applied to written assignments, too. An easy way to bolster a student's interest and investment in these longer assignments is to give them a choice. This could be in the topic, location of study, or presentation style.
Differentiating by Giving Choices. The best way to differentiate instruction is to give students a choice in how they show their learning. All students learn in their own way, and they need to be able to show their individual skills and interests. As long as they're able to demonstrate a certain skill, assessment should be more about the ...
Create an assignment (details above). Under Due, click the Down arrow . Next to No due date, click the Down arrow . Click a date on the calendar. (Optional) To set a due time, click Time enter a time and specify AM or PM. Note: Work is marked Missing or Turned in late as soon as the due date and time arrive.
Easily distribute, analyze, and grade student work with Assignments for your LMS. Assignments is an application for your learning management system (LMS). It helps educators save time grading and guides students to turn in their best work with originality reports — all through the collaborative power of Google Workspace for Education. Get ...
In this tab, you can create assignments and view all current and past assignments. To create an assignment, click the Create button, then select Assignment.. You can also select Question if you'd like to pose a single question to your students, or Material if you simply want to post a reading, visual, or other supplementary material.
Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an "assignment sheet" tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment.
When instructors give students open-ended assignments, they provide opportunities for students to think creatively as they work on a deliverable. They "unlock potential" (Ranjan & Gabora and Beghetto in Gregerson et al., 2013) for students to synthesize their knowledge and propose novel solutions. This promotes higher-level thinking as ...
8. Whiteboard Splash and Gallery Walk. Whiteboard Splash (sometimes known as "chalkboard splash" or "graffiti wall") involves students responding to a prompt with words or pictures to explain an idea or concept by writing on the whiteboard (or large chart paper).
13 ESL Homework Ideas. Homework may not be many students' favorite thing, but research says it's truly an effective learning tool that teachers should use. The trick is assigning great homework. To help you do this with ease, we've compiled an awesome list of 13 homework assignments that will have your ESL students begging for more.
Think about the assignments in your course where in-depth feedback could really impact your students' future work. Tools for Feedback Use Canvas. Canvas offers tools to help you give just-in-time feedback within small assignments. You can set feedback, based on student responses, to automatically appear after a student finishes a quiz.
Name assignments accurately. Students can be misled by assignments that are named inappropriately. For example, if you want students to analyze a product's strengths and weaknesses but you call the assignment a "product description," students may focus all their energies on the descriptive, not the critical, elements of the task.
Compete in an Online Competition. Contact an Industry Professional. Attend a Conference. Record Real World Event. Record Completing Task. There are some great ideas to spice up your online training as individuals or groups but now let's dig in deeper and review how these can be assignments for online students.
24 other positive comments to give students. Here are 24 other positive and motivational comments you can give to your students or their parents to help encourage growth and continued excellence: This student is strong-willed. You have a positive attitude. Your love for learning is impressive.
Selecting a future start date will give your students the assignment on that date. Students will see the assignments listed in order by the due date, with assignments due soonest will show up at the top of their list. If you would like to sequence the assignments in a specific order, assign them with slightly different due dates. Creating ...
General Constructive Feedback Examples for Students. The below examples are general templates that need to be edited so they are specific to the student's work. 1. You are on the right track. By starting to study for the exam earlier, you may be able to retain more knowledge on exam day. 2.
This assignment works great in increasing engagement, especially if you give the students all freedom in selecting the person for the interview. Also, it would be fascinating for you to read all those interviews as well! So, assign a deadline and make sure they focus on discussing class topics!
Assign to Specific Student. To create an assignment that is assigned only to a specific student, click the Remove icon next to the Everyone label [1], then start to type the name of a student in the Assign to field [2]. Search fields are dynamic, and you can search for students by first or last name. When the full name appears, click the name.
Excel Project C8: Attendance Record. ★☆☆☆☆. Kendall Myers November 15, 2017. In this practice project for Excel and similar spreadsheets, students create a spreadsheet that automatically adds up all of the Sunday School classes each Sunday, gives an average attendance for ….
The positive feedback outweighs the negative feedback as well, so make it a common strategy to give positive feedback on students' papers. It is a tremendous opportunity for students to grow. 1. I never thought of it this way. Great job analyzing! 2. What an amazing sentence! 3. This is a wonderful thesis!