Persuasive Essay Writing
Persuasive Essay About Covid 19


Top Examples of Persuasive Essay about Covid-19
Published on: Jan 10, 2023
Last updated on: Oct 25, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
Easy and Unique Persuasive Essay Topics with Tips
The Basics of Crafting an Outstanding Persuasive Essay Outline
Ace Your Next Essay With These Persuasive Essay Examples!
Persuasive Essay About Gun Control - Best Examples for Students
Learn How To Write An Impressive Persuasive Essay About Business
Learn How to Craft a Compelling Persuasive Essay About Abortion With Examples!
Make Your Point: Tips and Examples for Writing a Persuasive Essay About Online Education
Learn How To Craft a Powerful Persuasive Essay About Bullying
Craft an Engaging Persuasive Essay About Smoking: Examples & Tips
Learn How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Social Media With Examples
Craft an Effective Argument: Examples of Persuasive Essay About Death Penalty
Share this article
In these recent years, covid-19 has emerged as a major global challenge. It has caused immense global economic, social, and health problems.
Writing a persuasive essay on COVID-19 can be tricky with all the information and misinformation.
But don't worry! We have compiled a list of persuasive essay examples during this pandemic to help you get started.
Here are some examples and tips to help you create an effective persuasive essay about this pandemic.
On This Page On This Page -->
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
The coronavirus pandemic has everyone on edge. You can expect your teachers to give you an essay about covid-19. You might be overwhelmed about what to write in an essay.
Worry no more!
Here are a few examples to help get you started.
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Pandemic
Sample Of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 In The Philippines - Example
Check out some more persuasive essay examples to get more inspiration and guidance.
Examples of Persuasive Essay About the Covid-19 Vaccine
With so much uncertainty surrounding the Covid-19 vaccine, it can be challenging for students to write a persuasive essay about getting vaccinated.
Here are a few examples of persuasive essays about vaccination against covid-19.
Check these out to learn more.
Persuasive essay on the covid-19 vaccine
Tough Essay Due? Hire a Writer!

Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
Writing a persuasive essay on Covid-19 integration doesn't have to be stressful or overwhelming.
With the right approach and preparation, you can write an essay that will get them top marks!
Here are a few samples of compelling persuasive essays. Give them a look and get inspiration for your next essay.
Integration of Covid-19 Persuasive essay
Integration of Covid-19 Persuasive essay sample
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid-19
Writing an argumentative essay can be a daunting task, especially when the topic is as broad as the novel coronavirus pandemic.
Read the following examples of how to make a compelling argument on covid-19.
Argumentative essay on Covid-19
Argumentative Essay On Covid-19
Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
Writing a persuasive speech about anything can seem daunting. However, writing a persuasive speech about something as important as the Covid-19 pandemic doesn’t have to be difficult.
So let's explore some examples of perfectly written persuasive essays.
Persuasive Speech About Covid-19 Example
Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay
Here are seven tips that can help you create a strong argument on the topic of covid-19.
Check out this informative video to learn more about effective tips and tricks for writing persuasive essays.
1. Start with an attention-grabbing hook:
Use a quote, statistic, or interesting fact related to your argument at the beginning of your essay to draw the reader in.
2. Make sure you have a clear thesis statement:
A thesis statement is one sentence that expresses the main idea of your essay. It should clearly state your stance on the topic and provide a strong foundation for the rest of your content.
3. Support each point with evidence:
To make an effective argument, you must back up each point with credible evidence from reputable sources. This will help build credibility and validate your claims throughout your paper.
4. Use emotional language and tone:
Emotional appeals are powerful tools to help make your argument more convincing. Use appropriate language for the audience and evokes emotion to draw them in and get them on board with your claims.
5. Anticipate counterarguments:
Use proper counterarguments to effectively address all point of views.
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and address them directly by providing evidence or reasoning why they are wrong.
6. Stay focused:
Keep your main idea in mind throughout the essay, making sure all of your arguments support it. Don’t stray off-topic or introduce unnecessary information that will distract from the purpose of your paper.
7. Conclude strongly:
Make sure you end on a strong note. Reemphasize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and challenge the reader to respond or take action in some way. This will leave a lasting impression in their minds and make them more likely to agree with you.
Writing an effective persuasive essay is a piece of cake with our guide and examples. Check them out to learn more!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
We hope that you have found the inspiration to write your next persuasive essay about covid-19.
However, If you're overwhelmed by the task, don't worry - our professional essay writing service is here to help.
Our expert and experienced persuasive essay writers can help you write a persuasive essay on covid-19 that gets your readers' attention.
Besides, our professional essay writer can provide you with all the resources and support you need to craft a well-written, well-researched essay. Opt for our persuasive essay writing service today, offering top-notch quality and guaranteed results.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you begin a persuasive essay.
To begin a persuasive essay, you must choose a topic you feel strongly about and formulate an argument or position. Start by researching your topic thoroughly and then formulating your thesis statement.
What are good topics for persuasive essays?
Good topics for persuasive essays include healthcare reform, gender issues, racial inequalities, animal rights, environmental protection, and political change. Other popular topics are social media addiction, internet censorship, gun control legislation, and education reform.
What impact does COVID-19 have on society?
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a major impact on society worldwide. It has changed the way we interact with one another. The pandemic has also caused economic disruption, forcing many businesses to close or downsize their operations.
Cathy A. (Literature, Education)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Need Help With Your Essay?
Also get FREE title page, Turnitin report, unlimited revisions, and more!
Keep reading

OFF ON CUSTOM ESSAYS
Essay Services
- Argumentative Essay Service
- Descriptive Essay Service
- Persuasive Essay Service
- Narrative Essay Service
- Analytical Essay Service
- Expository Essay Service
- Comparison Essay Service
Writing Help
- Term Paper Writing Help
- Research Writing Help
- Thesis Help
- Dissertation Help
- Report Writing Help
- Speech Writing Help
- Assignment Help
Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.
Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2025 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
What to wear to a college interview.
LaMont Jones, Jr. Nov. 19, 2024

The 9 Black Fraternities and Sororities

Terrible Advice Given to Premed Students
Renee Marinelli, M.D. Nov. 19, 2024

Avoid Money Problems in Med School
Sammy Allen Nov. 15, 2024

Seek Mentors at U.S. Colleges
Anayat Durrani Nov. 13, 2024

10 HBCUs With Low Acceptance Rates
Cole Claybourn Nov. 13, 2024

Applying to College as Undecided Major
Anthony Todd Carlisle Nov. 11, 2024

How to Make a College List
Cole Claybourn Nov. 6, 2024

Weighing LSAT Test Prep Options
Gabriel Kuris Nov. 4, 2024

Data Privacy Tips for College Students
Cole Claybourn Nov. 4, 2024

An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Persuasive messaging to increase COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions
Erin k james, scott e bokemper, alan s gerber, saad b omer, gregory a huber.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Corresponding author at: Department of Political Science, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA
Received 2021 Mar 26; Revised 2021 Oct 12; Accepted 2021 Oct 18; Issue date 2021 Dec 3.
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre - including this research content - immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
Widespread vaccination remains the best option for controlling the spread of COVID-19 and ending the pandemic. Despite the considerable disruption the virus has caused to people’s lives, many people are still hesitant to receive a vaccine. Without high rates of uptake, however, the pandemic is likely to be prolonged. Here we use two survey experiments to study how persuasive messaging affects COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions. In the first experiment, we test a large number of treatment messages. One subgroup of messages draws on the idea that mass vaccination is a collective action problem and highlighting the prosocial benefit of vaccination or the reputational costs that one might incur if one chooses not to vaccinate. Another subgroup of messages built on contemporary concerns about the pandemic, like issues of restricting personal freedom or economic security. We find that persuasive messaging that invokes prosocial vaccination and social image concerns is effective at increasing intended uptake and also the willingness to persuade others and judgments of non-vaccinators. We replicate this result on a nationally representative sample of Americans and observe that prosocial messaging is robust across subgroups, including those who are most hesitant about vaccines generally. The experiments demonstrate how persuasive messaging can induce individuals to be more likely to vaccinate and also create spillover effects to persuade others to do so as well.
The first experiment in this study was registered at clinicaltrials.gov and can be found under the ID number NCT04460703 . This study was registered at Open Science Framework (OSF) at: https://osf.io/qu8nb/?view_only=82f06ecad77f4e54b02e8581a65047d7.
1. Introduction
The global spread of COVID-19 created an urgent need for safe and effective vaccines against the disease. However, even though several successful vaccines have become available, vaccine hesitancy in the general population has the potential to limit the efficacy of vaccines as a tool for ending the pandemic. For instance, in the United States, the public’s willingness to receive a vaccine has declined from 72 % saying they would be likely to get a COVID-19 vaccine in May 2020 to 60 % of people reporting that they would receive a vaccine as of November 2020 [ 1 ]. Given the considerable amount of skepticism about the safety and efficacy of a COVID-19 vaccine, it has become increasingly important to understand how public health communication can play a role in increasing COVID-19 vaccine uptake.
Vaccination is both a self-interested and a prosocial action [ [2] , [3] , [4] , [5] , [6] , [7] , [8] , [9] ]. By getting vaccinated, people protect themselves from a disease, but they also reduce the chance that they become a vector through which the disease spreads to others. If enough people receive a vaccine, the population gains protection through herd immunity, but this also creates an incentive for an individual to not get vaccinated because they can forgo vaccination and receive protection from others who do vaccinate. Recent research on vaccination in general has demonstrated that people view vaccination as a social contract and are less willing to cooperate with those who choose not to get inoculated [ 10 ]. This work also implies that highlighting the reputational costs of choosing not to vaccinate could be an effective strategy for increasing uptake. Further, appeals to herd immunity and the prosocial aspect of vaccination have been shown to increase uptake intentions [ [11] , [12] , [13] ], but emphasizing the possibility of free riding on other’s immunity reduces the willingness to get vaccinated [ 14 ].
Focusing specifically on vaccination against COVID-19, recent studies have found that messages that explain herd immunity increase willingness to receive a vaccine [ 15 ] and reduces the time that people would wait to get vaccinated when a vaccine becomes available to them [ 16 ]. However, other work has found that prosocial appeals did not increase average COVID-19 vaccination intentions [ 17 ] and the effect of prosocial concerns was present in sparsely populated places, but absent in more densely populated ones [ 18 ]. Given the current state of evidence, it is unclear whether appealing to getting a COVID-19 vaccine as a way to protect others will increase willingness to vaccinate.
Viewing vaccination through the lens of a collective action problem suggests that in addition to increasing individuals’ intentions to receive a vaccine, effective public health messages would also increase people’s willingness to encourage those close to them to vaccinate and to hold negative judgments of those who do not vaccinate. By encouraging those close to them to vaccinate, people are both promoting compliance with social norms and increasing their own level of protection against the disease. Also, by judging those who do not vaccinate more negatively, they apply social pressure to others to promote cooperative behavior. This would be consistent with theories of cooperation, like indirect reciprocity or partner choice, that rely on free riders being punished or ostracized for their past actions to encourage prosocial outcomes [ [19] , [20] , [21] , [22] , [23] ]. Thus, effective messaging could have outsized effects on promoting vaccination if it both causes people to vaccinate themselves and to encourage those around them to do so.
We conducted two pre-registered experiments to study how different persuasive messages affect intentions to receive a COVID-19 vaccine, willingness to persuade friends and relatives to receive one, and negative judgments of people who choose not to vaccinate. In the first experiment, we tested the efficacy of a large number of messages against an untreated control condition (see Table 1 for full text of messages). A subgroup of the messages in Experiment 1 drew on this collective action framework of vaccination and emphasized who benefits from vaccination or how choosing not to vaccinate hurts one’s social image. A second subgroup drew on contemporary arguments about restrictions on liberty and economic activity during the COVID-19 pandemic. In Experiment 2, we retested the most effective messages from Experiment 1 on a nationally representative sample of American adults. By utilizing this test and re-test design, we guard against false positive results that are observed by chance among the large number of messages tested in Experiment 1. In our analysis of both experiments, we examined whether specific messages were more effective among certain subgroups of the population.
Experimental treatment messages for Experiment 1 and Experiment 2. All messages add the prose in the table to the content of the Baseline informational control. All of the messages in the table were tested in Experiment 1. The messages that are bolded were retested in Experiment 2.
Experiment 1 was fielded in early July 2020. Participants were randomly assigned to either a placebo control condition in which they read a story about the effectiveness of bird feeders or one of eleven treatment messages. The first message is a Baseline informational control condition that describes how it is important to receive a vaccine to reduce your risk of contracting COVID-19 or spreading it to others. Informational messages have been shown to be effective at increasing COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions [ 24 ]. This message also emphasized that vaccines are safe and estimated to save millions of lives per year. The other messages add additional content to this baseline message.
The subgroup of messages that emphasized collective action varied who would benefit from vaccination or what other people might think of someone who chooses to be a free rider by not vaccinating. Focusing on who benefits from vaccination, the second message invoked Self Interest and reinforced the idea that vaccination is a self-protecting action (“Remember, getting vaccinated against COVID-19 is the single best way to protect yourself from getting sick.”). The third message, Community Interest, instead argued that vaccination is a cooperative action to protect other people (“Stopping COVID-19 is important because it reduces the risk that members of your family and community could get sick and die.”). This message also invoked reciprocity by emphasizing the importance of every-one working together to protect others.
The fourth, fifth, and sixth messages added an invocation of an emotion, Guilt, Embarrassment, or Anger, to the Community Interest message. These messages prompted people to think about how they would feel if they chose not to get vaccinated and spread COVID-19 to someone else in the future. Emotions are thought to play a role in cooperation, either by motivating an individual to take an action because of a feeling that they experience or restraining them from taking an action because of the emotional response it would provoke in others [ [25] , [26] , [27] ]. Further, anticipated emotional states have been shown to promote various health behaviors, like vaccination [ [28] , [29] ].
The seventh and eighth messages evoked concerns about one’s reputation and social image, which influences their attractiveness as a cooperative partner to others. The seventh, a Not Bravery message, reframed the idea that being unafraid of the virus is not a brave action, but instead selfish, and that the way to demonstrate bravery is by getting vaccinated because it shows strength and concern for others (“To show strength get the vaccine so you don’t get sick and take resources from other people who need them more”). The eighth message was a Trust in Science message that highlights that scientists believe a vaccine will be an effective way of limiting the spread of COVID-19. This message suggests that those who do not get vaccinated do not understand science and signal this ignorance to others (“Not getting vaccinated will show people that you are probably the sort of person who doesn’t understand how infection spreads and who ignores or are confused about science.”).
The final three messages drew on concerns about restrictions on freedom and economic activity that were widespread during the COVID-19 pandemic. A pair of messages focused on how vaccination would allow for a restoration of Personal Freedom (“Government policies to prevent the spread of COVID-19 limit our freedom of association and movement”) or Economic Freedom (“Government policies to prevent the spread of COVID-19 have stopped businesses from opening up”). These messages take a value that is commonly invoked in individuals’ decision to not vaccinate [ [30] , [31] ] and reframed vaccination as something that would actually restore freedoms that had been taken away. The final message, Community Economic Benefit, argues that a vaccine will help return people’s financial security and strengthen the economy This message is similar to the Community Interest messages that are described above, but instead focuses on cooperating to restore the economy (“We can all end this outbreak and strengthen the national economy by working together and getting vaccinated”).
2.1. Experiment 1 results
Panel A of Fig. 1 plots the effect of each vaccine message relative to the untreated control group on intention to vaccinate. The intention to vaccinate measure was formed by combining responses to a question about the likelihood of getting a COVID-19 vaccine within the first 3 months that one is available with a question about getting a vaccine within the first year that one is available. Specifically, for respondents who did not answer that they were very likely to vaccinate within the first three months that a vaccine is available to them, we asked how likely they would be to vaccinate within a year. This measure coded those who are very likely in the first three months at the highest value on the scale followed by very likely within a year descending down to very unlikely within the first year. Analyzing the vaccination item separately does not substantively change the results. All outcome variables were scored 0 to 1, with higher values indicating greater willingness to endorse the pro-vaccine action or belief (Underlying regressions appear in Table S1 and unless otherwise noted, all analyses were pre-registered).
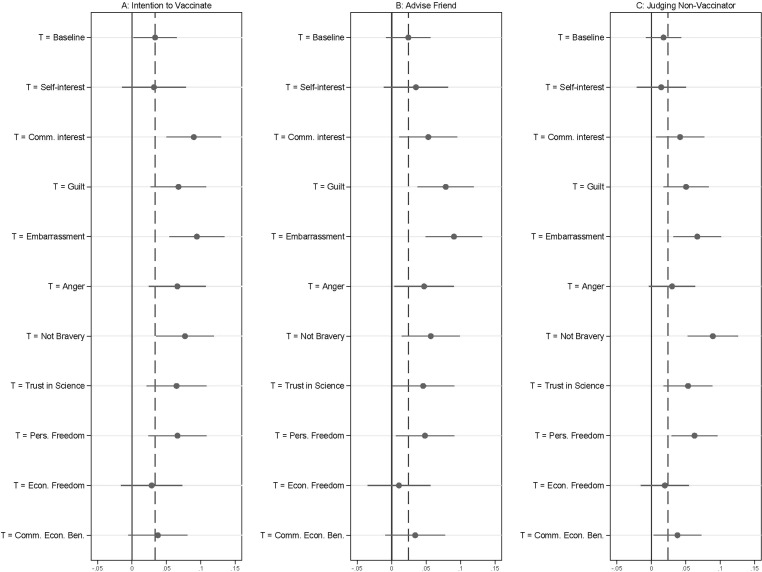
Experiment 1. Messages that frame vaccination as a cooperative action to protect others or emphasize how non-vaccination might negatively affect one’s social image increase reported willingness to advise a friend, and judgment of non-vaccinators. Panel A displays treatment effects for the combined measure of intention to vaccinate, Panel B displays the advise a friend outcome, and Panel C displays the judging a non-vaccinator outcome. Treatment effects for both panels were estimated using OLS regression that included covariates. The effects displayed are a comparison against the placebo control baseline and are presented with 95% confidence intervals. The dashed vertical line is the effect of the Baseline informational control for each outcome.
Compared to the untreated control, the Baseline informational message was associated with modest increases in intention to vaccinate by 0.034 units (95 % CI:0.002, 0.065; p < .05). This effect represents an increase of approximately 6 % in the scale score compared to the outcome in the control condition.
By comparison, the Community Interest, Community Interest + Guilt, Embarrassment, or Anger, Not Bravery, Trust in Science and Personal Freedom messages all produce larger effects, at least qualitatively, than the Baseline informational message on the intention to vaccinate outcome. Effects for the Self-Interest, Economic Freedom, and Community Economic benefit messages were not consistently distinguishable from the untreated control group outcomes, and their effects were indistinguishable from the effects of the Baseline informational message.
The most promising messages were the Not Bravery, Community Interest, and Community Interest + Embarrassment messages. These messages were associated with effects that were statistically distinguishable from the untreated control group (Not Bravery: 0.077 units, 95 % CI: 0.035, 0.119; p < .01, Community Interest: 0.090 units, 95 % CI: 0.050, 0.129; p < .01, Community Interest + Embarrassment: 0.094 units, 95 % CI: 0.054, 0.134; p < .01) at p < .01. Moreover, their effects were always more than twice as large as the Baseline informational treatment and these differences were significant at p < .05 (two-tailed tests). The effects of the Trust in Science message and the Personal Freedom message were not statistically significant when compared to the Baseline informational message.
To put the magnitudes of the effects into context, we re-estimated our analysis after dichotomizing the intended vaccine uptake measure such that those who report they were “somewhat” or “very” likely to get the vaccine, either with three months or a year, are coded as 1 and those who do not are coded 0 (this analysis was not pre-registered). This produced a predicted rate of intended vaccination in the control group of 58.2 %. Respondents who read the Baseline informational message were 7.4 percentage points (95 % CI: 2.9 pp, 12.0 pp; p < .01) more likely to receive a vaccine. Among those assigned to the Not Bravery or Community Interest messages it was predicted to increase by 10.4 percentage points and 12.7 percentage points (Not Bravery: 95 % CI: 4.3 pp, 16.4 pp; p < .01, Community Interest: 95 % CI: 6.7 pp, 18.7 pp; p < .01) respectively, while among those assigned to the Community Interest + Embarrassment message it was predicted to increases by 15.9 percentage points (95 % CI: 10.2 pp, 21.6 pp; p < .01). This last difference was substantively large, representing a proportional increase of 27 % (0.159/0.582) compared to the control condition and a 13 % increase compared to the Baseline informational condition (0.159-0.074)/(0.582 + 0.074).
Turning to the other regarding outcomes that focused on spurring action by others, Panel B plots the effects of each vaccine message relative to the untreated control for advising a friend to receive a vaccine and Panel C plots the effects for negatively judging someone who refuses to receive one. Here, the effect of the Baseline informational intervention was modest and statistically insignificant. However, the Not Bravery, Trust in Science, Personal Freedom, Community Interest, Community Interest + Guilt, and Community Interest + Embarrassment messages had larger effects on both outcomes that were statistically distinguishable from the control outcome.
The most promising message was the Community Interest + Embarrassment message for the advise a friend outcome, which was associated with a 0.09 unit increase in the scale outcome (95 % CI: 0.049, 0.132; p < .01 two-tailed test), an effect that represents an increase of 27 % compared to the mean scale score in the control group. The effect was 0.067 units compared to the Baseline informational message (95 % CI: 0.027, 0.105; p = .001, two-tailed test). We conducted a similar exercise to the one describe above to gauge the relative magnitude of these treatment effects. For the Community Interest + Embarrassment message we estimated a 15 percentage point increase (95 % CI: 0.088, 0.209; p < .01, two tailed test,) in a binary intention to advise others to vaccinate outcome, a proportional increase of 27 % compared to the control group baseline of 53 % (0.15/0.53). This effect was also 6 percentage points larger than the effect of the baseline message (95 % CI: 0.008, 0.121; p = .03, two-tailed test).
The most promising outcome for the negative judgment of non-vaccinators was the Not Bravery message, which had an effect of 0.09 scale points (95 % CI: 0.052, 0.126; p < .01, two-tailed test) compared to the untreated control and 0.072 scale points versus the Baseline information (95 % CI: 0.037, 0.106; p < .01 Baseline message, two-tailed tests). This corresponded to a 21 % increase compared to the scale outcome in the control group (0.09/0.43). These are both substantively and statistically meaningful effects. The Community Interest, Community Interest + Guilt, Community Interest + Embarrassment, Trust in Science, and Personal Freedom messages all produced effects that were statistically distinguishable from the control condition.
We also investigated the robustness of these findings to sample restrictions and whether certain subgroups were more responsive to specific treatment messages (reported in Figures S2-S12 ). Results were generally robust to restricting the sample to those who were over the 10th percentile and under the 90th percentile for completion time. For subgroup analyses, those scoring low in liberty endorsement appeared more responsive to the Baseline treatment and to the Not Bravery message than are those who scored high in liberty endorsement. Those who report being less likely to take risks appeared robustly more responsive to the Not Bravery message than those who were high in risk taking. Those who were high in risk taking appear more responsive to the Personal Freedom message with regard to their own behavioral intentions. Certain groups appeared generically easier to persuade (Democrats rather than Republicans, an important divide that has emerged during the pandemic [ 32 ], and Women rather than Men), but there were no clear differences in which treatments appeared most effective across these groups. We explored the robustness of these subgroup differences in Experiment 2.
Taken together, the most successful messages in Experiment 1 were those that were theoretically motivated by viewing vaccination as a collective action problem. Consistent with previous work that demonstrates that prosocial appeals are effective in promoting vaccination, the Community Interest message and Community Interest + Guilt, Embarrassment, or Anger messages increased COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions. Moving beyond who benefits from vaccination, the Not Bravery and Trust in Science messages that invoked concerns about one’s social image if they choose not to vaccinate also increased uptake intentions. All of the collective action oriented messages increased intentions to advise a friend to vaccinate and negative judgments of those who do not, potentially creating spillover effects that induce others to vaccinate. In addition to this subgroup of messages, we found that reframing vaccination as a way to restore freedom was also effective, though the other messages motivated by contemporary debates about the pandemic were generally no more effective than the Baseline condition.
2.2. Experiment 2 results
Experiment 2 tested the subset of the best performing messages from Experiment 1 on a nationally representative sample in September 2020. Notably, in the several month period between Experiment 1 and Experiment 2, the public had grown increasingly skeptical of a potential COVID-19 vaccine [ 1 ]. Panel A of Fig. 2 plots the effect of each vaccine message, relative to the untreated control group, on the same measure of intention to vaccinate used in Experiment 1. (The model specifications shown in the figure were from our pre-registered specifications, underlying regression appear in Table S2.). Given that we observed the messages from Experiment 1 were effective at increasing vaccine uptake, we pre-registered directional hypotheses for Experiment 2 that tested whether the effects could be replicated on a nationally representative sample. Accordingly, we report one-tailed hypothesis tests and 90 % confidence intervals in the results presented below. Results largely confirmed the patterns observed in Experiment 1.
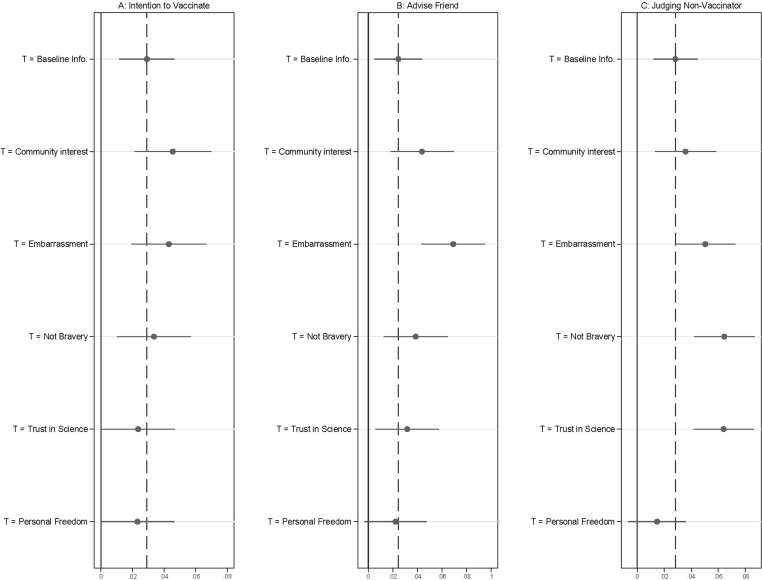
Experiment 2. The Not Bravery, Community Interest, and Community Interest + Embarrassment messages increase both intentions to vaccinate and other-regarding outcomes. Panel A displays treatment effects for intentions to vaccinate, Panel B displays the advise a friend, and Panel C displays the judging a non-vaccinator outcomes. Treatment effects for both panels were estimated using OLS regression that included covariates. The effects displayed are a comparison against the placebo control baseline and are presented with 90 % confidence intervals. The dashed vertical line is the effect of the Baseline informational control for each outcome.
The Baseline informational treatment was associated with a modest increase, 0.029 units, in intention to vaccinate (90 % CI: 0.011, 0.046; p < .01, one-tailed test). This effect was a 6 % increase of the observed scale outcome in the untreated control group.
The Community Interest and Community Interest + Embarrassment messages were associated with qualitatively larger effects on intended vaccine uptake. These messages were associated with increases of 0.045 units (90 % CI: 0.021, 0.070; p < .01, one-tailed test) and 0.043 units (90 % CI: 0.019, 0.067; p < .01, one-tailed test), respectively. As with Experiment 1, we recoded those who stated they were “somewhat” or “very” likely to receive the vaccine as 1 and those who did not report that they were likely to receive it as 0 (this analysis was not pre-registered: for consistency we report 90 % confidence intervals). This binary measure produced a predicted rate of intended vaccination in the control group of 51.4 %. Intended uptake was 3.3 percentage points higher in the Baseline information condition (90 % CI: 0.5 pp, 6.0 pp; p < .05, one-tailed test), 3.5 percentage points higher in the Community Interest + Embarrassment condition (90 % CI: −0.1 pp, 7.0 pp; p = .06, one-tailed test), and 5 percentage points higher in the Community Interest condition (90 % CI: 1.3 pp, 0.8.7 pp; p < .05, one-tailed test). The latter effect was proportionally large—10 % compared to the baseline predict rate in the control group (0.050/0.514).
On average, the Not Bravery, Trust in Science, and Personal Freedom messages were approximately as effective as the informational content to which they were added in increasing intention to vaccinate, which differs from Experiment 1 where they modestly outperformed the Baseline informational condition.
Turning to other regarding outcomes, Panel B of Fig. 2 plots effects for advice given to others and Panel C does so for negative judgments of non-vaccinators. The Baseline informational treatment was again associated with statistically significant increases in each outcome. For these outcomes, the Not Bravery, Trust in Science, and both Community Interest messages produced effects that were at least descriptively larger than the Baseline treatment. The effects for the Personal Freedom message were smaller than the Baseline informational treatment, a result that again diverged from Experiment 1.
In terms of advising others to vaccinate, the most effective message was the Community Interest + Embarrassment message, which was also the most effective message in Experiment 1. This effect was 0.07 scale points (90 % CI: 0.043, 0.095; p < .01, one-tailed test), an increase of 14 % compared to the control group average scale score of 0.51 (0.07/0.51). This effect was also statistically distinguishable from the effect of the Baseline informational treatment (difference = 0.045; 90 % CI: 0.020, 0.069; p < .01, one-tailed test). When dichotomizing the advise a friend outcome to better describe the magnitude of the effect, we estimated that the Community interest + Embarrassment message was associated with a 10 percentage point increase (90 % CI: 0.064, 0.140; p < .01, one-tailed test) in intention to advise others to vaccinate compared to the control group, a proportional increase of 27 % compared to the control group baseline of 38 % (0.10/0.38). This effect was approximately 6 points larger than the effect of the Baseline message (90 % CI: 0.026, 0.099; p < .01, one-tailed test).
In terms of judging non-vaccinators, the largest effects were for the Not Bravery and Trust in Science messages, with each effect also statistically distinguishable from the Baseline message. Notably, in this sample the Trust in Science message had large effects on beliefs and actions toward others but appeared ineffective in changing an individual’s own intended vaccination behavior. The Not Bravery message was also the most effective message in this regard in Experiment 1.
We examined three pre-registered differences in subgroup treatment effects to test the patterns observed in Experiment 1. First, confirming Experiment 1 we found that those who did not endorse liberty values were more responsive to the Not Bravery message (compared to the baseline message) than those who endorsed liberty values for the three outcome measures. Second, we did not confirm either preregistered prediction with regard to differences in treatment effects by risk taking that were observed in Experiment 1.
The remaining subgroup comparisons were not pre-registered. Beginning with gender, in comparison to the untreated control, women responded more to the Trust in Science and Community Interest + Embarrassment message than did men (all five outcomes), while men responded more to the Not Bravery and Community Interest (without embarrassment) messages. Democrats were more responsive than Republicans across the board to the different treatment messages, while Republicans appeared to react only to the Community Interest and Community Interest + Embarrassment messages (magnitudes similar to those of Democrats). We observed a similar pattern for differences by baseline vaccine confidence, measured pre-treatment with a multi-item battery of questions [ 33 ]. Those high in vaccine confidence responded to all messages, while those low in confidence responded reliably only to the Community Interest messages.
3. Discussion
Overall, the results point both to a set of effective messages and the potential efficacy of specific messages for some particular subgroups. On average, a simple informational intervention is effective, but it is even more effective to add language framing vaccine uptake as protecting others and as a cooperative action. Not only does emphasizing that vaccination is a prosocial action increase uptake, but it also increases people’s willingness to pressure others to do so, both by direct persuasion and negative judgment of non-vaccinators. The latter social pressure effects may be enhanced by highlighting how embarrassing it would be to infect someone else after failing to vaccinate. The Not Bravery and Trust in Science messages had substantial effects on other regarding outcomes and for some subgroups, but do not appear to be as effective as the Community Interest messages in promoting own vaccination behavior. Importantly, in distinct samples fielded several months apart, the Community Interest, Community Interest + Embarrassment, and the Not Bravery messages produced substantively meaningful increases for all outcomes measures relative to the untreated control, and in some instances did so in comparison to the Baseline information condition.
Our findings are consistent with the idea that vaccination is often treated as a social contract in which people are expected to vaccinate and those who do not are sanctioned [ 10 ]. In addition to messages emphasizing the prosocial element of vaccination, we observed that messages that invoked reputational concerns were successful at altering judgment of those who would free ride on the contributions of others. This work could also help explain why social norm effects appear to overwhelm the incentive to free ride when vaccination rates are higher [ [34] , [35] ]. That is, messages that increased intentions to vaccinate also increased the moralization of non-vaccinators suggesting that they are fundamentally linked to one another. These messages will need to be adapted in specific cultural contexts with relevant partners, such as community leaders.
The robust effect of the Community Interest message advances our current understanding of whether public health messaging that deploys prosocial concerns could be effective at increasing COVID-19 vaccine uptake. The results of both experiments presented here support prior work that demonstrated the effectiveness of communication that explains herd immunity on promoting vaccination [ [15] , [16] ]. It also suggests that a detailed explanation of herd immunity may not be necessary to induce prosocial behavior.
Beyond the theoretical contribution, the results have practical implications for vaccine communication strategies for increasing COVID-19 vaccine acceptance. We identified multiple effective messages that provide several evidence-based options to immunization programs as they develop their vaccine communication strategies. Importantly, the insights into differential effectiveness of various messages by subgroup (e.g. men vs women) could inform messaging targeted to specific groups. Understanding heterogeneous treatment effects and the mechanisms that cause differential responses to persuasive messaging strategies requires additional testing and theoretical development. We view this as a promising avenue for future work.
The experiments presented here are not without limitations. First, we measured intentions to vaccinate at a time when a vaccine was not currently available and the effectiveness and side effects of potential vaccines were not known. This also meant that we could not observe actual vaccination behavior, which is ultimately the outcome of interest. While intentions predict behavior in many contexts [ [36] , [37] ] including vaccination [ [38] , [39] , [40] ], past research examining the effect of behavioral nudges on COVID-19 vaccine uptake has produced divergent evidence when testing the effect of the same treatments in the field on behavior and in a survey experiment on a behavioral intention [ 41 ]. This observation highlights the need for field testing messages that have shown to be successful on increasing uptake intentions in survey experiments to ascertain whether they also increase vaccine uptake. It may be that field tests reveal certain messages are particularly less effective than in the survey context, or that messages are uniformly less effective. Second, given the rapidly evolving nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, attitudes about vaccines may have changed since the experiments were fielded which could also change the efficacy of the messages that we tested. Third, we cannot be sure whether, or how long, the effects we observe here persist. Finally, we only tested text-based messages, but public health messaging is delivered through many mediums, like public service announcements, videos, and images. Future work can adapt the successful messaging strategies found here and test their efficacy when delivered in alternative formats.
Efforts to vaccinate individuals against COVID-19 are currently underway in the United States and it remains important to convince the mass public of the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines to ensure that the threshold for herd immunity is reached. Our experiments provide robust evidence that appealing to protecting others has effects on intentions to get vaccinated and to apply social pressure to others to do so as well.
4. Materials and methods
4.1. ethics statement.
The experiments reported here were fielded under an exemption granted by the Yale University IRB. Informed consent was obtained from participants and they were informed that they could stop the study at any time. Data was collected anonymously and contained no personally identifiable information.
4.2. Experiment 1
Participants and Procedure. Participants were recruited by the vendor Luc.id to take a survey. Of those who were recruited, 4,361 participants completed the survey. An examination of attrition during the survey reveals that attrition was balanced across groups which minimizes concerns that the treatment effects estimated in the main manuscript are affected by attrition. The survey was programmed using the survey software Qualtrics. The survey was fielded between July 3, 2020 and July 8, 2020.
Experimental Design. Participants first completed basic demographic and pre-treatment attitudinal questions and were asked about their experience with COVID-19. After this, participants read a treatment message. They were required to spend at least 20 s on the survey page that contained the message to given them an adequate amount of time to read it. We allocated 2/15 of the sample to the untreated control condition and 1/5 of the sample to the Information baseline condition due to the number of comparisons that would utilize these conditions. Each of the remaining conditions received 1/15 of the sample. The design and analysis were pre-registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (protocol ID: 2000027983).
Outcome Measures. For COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions, participants were asked “How likely are you to get a COVID-19 vaccine within the first 3 months that it is available to you?” and “How likely are you to get a COVID-19 vaccine in the first year that it is available to you?” Respondents answered this question on a five-point scale with end points of “Extremely unlikely” and “Extremely likely.” The main text describes how these items were combined for analysis. Turning to the likelihood of advising someone to vaccinate, respondents were asked “How likely are you to advise a close friend or relative to get vaccinated against COVID-19 once a vaccine becomes available?” Respondents also answered this question on a five-point scale with end points of “Extremely unlikely” and “Extremely likely.” Finally, for judging someone who chooses not to vaccinate, respondents read “we would like you to think about a friend or relative who chose not to receive a COVID-19 vaccine when it is available. What would you think about this person? Are they…”. This prompt was followed by four traits: trustworthy, selfish, likeable, and competent. The response options were “not at all”, “slightly”, “somewhat”, “mostly”, and “very.”
Analysis. We used OLS regression with robust Huber-White standard errors and indicators for assigned treatment to estimate treatment effects. We use robust standard errors to address the heteroscedasticity observed when estimating our primary analysis models without them. We included covariates as described in the Supplementary Materials . Comparisons across treatments are from linear combination of coefficients tests. For the subgroup analyses, we restricted the sample to the stated criteria and estimate the model specified here on the subsample. For liberty endorsement and risk taking, we determined who was high and low by splitting the sample at the mean.
4.3. Experiment 2
Participants and Procedure. Participants ( n = 5,014) were recruited by the vendor YouGov/Polimetrix. YouGov provides subjects using a sampling procedure that is designed to match a number of Census demographics. To determine the sample size, we conducted a power analysis to detect effects that were 80 % as large as those observed in Experiment 1. The experiment was fielded between September 9, 2020 and September 22, 2020.
Experimental Design. Participants first completed basic demographic and pre-treatment attitudinal questions and were asked about their experience with COVID-19. Participants were randomly assigned to one of seven conditions: the untreated control, the Information baseline control, Community Interest, Community Interest + Anticipated Embarrassment, Not Bravery, Trust in Science, or Personal Freedom. As in Experiment 1, more participants were assigned to the untreated control condition and the Baseline information control condition, 1/5 and 3/10 of the sample respectively. The remaining five conditions each received 1/10 of the sample. Participants were required to spend at least 30 s on the survey page that had the treatment message. The design and analysis were pre-registered at Open Science Framework.
Outcome Measures. The outcome measurement was the same as described in Experiment 1 with the exception of intelligent being added to the judgment of a non-vaccinator scale.
Analysis. We used the same modeling approach described above to produce the results displayed in Fig. 2 . We included covariates as described in the Supplementary Materials . For subgroup analyses, we estimated OLS regression models with an indicator variable if a person was a member of a subgroup (e.g. high endorsement of liberty) and zero otherwise.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Erin K. James: Conceptualization, Writing- original draft, Writing- review and editing. Scott E. Bokemper: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analyses. Alan S. Gerber: Conceptualization, Writing- review and editing. Saad B. Omer: Conceptualization, Writing- review and editing. Gregory A. Huber: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analyses, Writing- original draft, Writing- review and editing.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge support for the Tobin Center for Economic Policy at Yale University. EKJ and SBO were supported by the Yale Institute for Global Health.
SEB, ASG, and GAH received support from the Institution for Social and Policy Studies and the Center for the Study of American Politics at Yale University.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.10.039 .
Appendix A. Supplementary material
The following are the Supplementary data to this article:
- 1. Funk C., Tyson A. (Pew Research Center Science & Society); 2020. Intent to get a COVID-19 vaccine rises to 60% as confidence in research and development process increases. [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Bauch C.T., Galvani A.P., Earn D.J.D. Group interest versus self-interest in smallpox vaccination. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2003;100(18):10564–10567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1731324100. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Bauch C.T., Earn D.J.D. Vaccination and the theory of games. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004;101(36):13391–13394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403823101. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Böhm R., Betsch C., Korn L. Self-rational non-vaccination: Experimental evidence from an interactive vaccination game. J Econ Behav Organ. 2016;131:183–195. [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Böhm R., Betsch C., Korn L., Holtmann C. Exploring and promoting prosocial vaccination: a cross-cultural experiment on vaccination of health care personnel. Biomed Res Int:6870984. 2016;2016:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2016/6870984. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Chapman G.B., et al. Using game theory to examine incentives in influenza vaccine behavior. Psychol Sci. 2012;23(9):1008–1015. doi: 10.1177/0956797612437606. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Galvani A.P., Reluga T.C., Chapman G.B. Long-standing influenza vaccination policy is in accord with individual self-interest but not with the utilitarian optimum. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104(13):5692–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606774104. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Wells C.R., Huppert A., Fitzpatrick M.C., Pandey A., Velan B., Singer B.H., et al. Prosocial polio vaccination in Israel. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2020;117(23):13138–13144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922746117. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Shim E., Chapman G.B., Townsend J.P., Galvani A.P. The influence of altruism on influenza vaccination decisions. J R Soc Interface. 2012;9(74):2234–2243. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0115. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Korn L., Böhm R., Meier N.W., Betsch C. Vaccination as a social contract. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2020;117(26):14890–14899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1919666117. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Betsch C., Böhm R., Korn L., Holtmann C. On the benefits of explaining herd immunity in vaccine advocacy. Nat Hum Behav. 2017;1(3):0056. [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Betsch C., Böhm R. Moral values do not affect prosocial vaccination. Nat Hum Behav. 2018;2(12):881–882. doi: 10.1038/s41562-018-0478-1. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Sprengholz P., Betsch C. Herd immunity communication counters detrimental effects of selective vaccination mandates: Experimental evidence. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;22:100352. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100352. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Betsch C., Böhm R., Korn L. Inviting free-riders or appealing to prosocial behavior? Game-theoretical reflections on communicating herd immunity in vaccine advocacy. Health Psychol. 2013;32(9):978–985. doi: 10.1037/a0031590. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Pfattheicher S, Petersen MB, & Böhm R. Information about herd immunity through vaccination and empathy promote COVID-19 vaccination intentions. PsyArXiv [preprint] . 2020. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ]
- 16. Trueblood JS, Sussman AB, O’Leary D. The role of risk preferences in responses to messaging about COVID-19 vaccine uptake. Social Psychology and Personality Science. 2021 doi: 10.1177/1948550621999622. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 17. Duquette N. Heard” immunity: Messages emphasizing the safety of others increase intended uptake of a COVID-19 vaccine in some groups. Covid Economics. 2020:39. [ Google Scholar ]
- 18. Jung H., Albarracin D. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118:e2007538118. 2020. Concerns for others increase the likelihood of vaccination against influenza and COVID-19 more in sparsely rather than densely populated areas. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 19. Delton A.W., Cosmides L., Guemo M., Roberston T.E., Tooby J. The psychosemantics of free riding: Dissecting the architceture of a moral concept. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2012;102(6):1252–1270. doi: 10.1037/a0027026. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 20. Nowak M.A., Sigmund K. Evolution of indirect reciprocity. Nature. 2005;437(7063):1291–1298. doi: 10.1038/nature04131. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 21. Boyd R., Richerson P.J. The evolution of reciprocity in sizable groups. J Theor Biol. 1988;132(3):337–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80219-4. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 22. Barclay P., Willer R. Partner choice creates competitive altruism in humans. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2007;274(1610):749–753. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.0209. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 23. Kiyonari T., Barclay P. Cooperation in social dilemmas: Free riding may be thwarted by second-order reward rather than by punishment. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2008;95(4):826–842. doi: 10.1037/a0011381. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 24. Davis C.J., Golding M., McKay R. Efficacy information influences intention to take COVID-19 vaccine. British Journal of Health Psychology. 2021 doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12546. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 25. Frank RH. Passions within reason: The strategic role of the emotions (W W Norton & Co, New York, NY, US) 1988; pp xiii, 304-xiii, 304.
- 26. Fessler D & Haley KJ. The strategy of affect: Emotions in human cooperation 12. The Genetic and Cultural Evolution of Cooperation, P. Hammerstein, ed : 2003; 7-36.
- 27. Sell A, Tooby J, & Cosmides L (2009) Formidability and the logic of human anger. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106(35):15073. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- 28. Chapman G.B., Coups E.J. Emotions and preventive health behavior: Worry, regret, and influenza vaccination. Health Psychol. 2006;25(1):82–90. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.25.1.82. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 29. Brewer N.T., DeFrank J.T., Gilkey M.B. Anticipated regret and health behavior: A meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2016;35(11):1264–1275. doi: 10.1037/hea0000294. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 30. Amin A.B., Bednarczyk R.A., Ray C.E., Melchiori K.J., Graham J., Huntsinger J.R., et al. Association of moral values with vaccine hesitancy. Nat Hum Behav. 2017;1(12):873–880. doi: 10.1038/s41562-017-0256-5. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 31. Kalimeri K , et al. Human values and attitudes towards vaccination in social media. in Companion Proceedings of The 2019 World Wide Web Conference (Association for Computing Machinery, San Francisco, USA), 2019. pp 248–254.
- 32. Bokemper S.E., Huber G.A., Gerber A.S., James E.K., Omer S.B. Timing of COVID-19 vaccine approval and endorsement by public figures. Vaccine. 2021;39(5):825–829. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.12.048. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 33. Larson HJ, Schulz WS, Tucker JD, & Smith DM. Measuring vaccine confidence: introducing a global vaccine confidence index. PLoS currents 2015; 7. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- 34. McKillop C.N., Leonard T., Pruitt S.L., Tiro J.A. Do traditional economic theories of free riding behavior explain spatial clustering of HPV vaccine uptake? SSM - Population Health. 2019;8:100421. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2019.100421. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 35. Verelst F, Kessels R, Willem L, & Beutels P. No such thing as a free-rider? Understanding multicountry drivers of childhood and adult vaccination. medRxiv :2020.2012.2007.20245118. 2020. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- 36. Chandon P., Morwitz V.G., Reinartz W.J. Do intentions really predict behavior? Self-generated validity effects in survey research. Journal of Marketing. 2005;69(2):1–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- 37. Eccles M.P., Hrisos S., Francis J., Kaner E.F., Dickinson H.O., Beyer F., et al. Do self-reported intentions predict clinicians' behaviour: a systematic review. Implementation Science. 2006;1(1) doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-28. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 38. daCosta DiBonaventura M., Chapman G.B. Moderators of the intention–behavior relationship in influenza vaccinations: Intention stability and unforeseen barriers. Psychology and Health. 2005;20(6):761–774. [ Google Scholar ]
- 39. Fall E., Izaute M., Chakroun-Baggioni N. How can the health belief model and self-determination theory predict both influenza vaccination and vaccination intention? A longitudinal study among university students. Psychology & health. 2018;33(6):746–764. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2017.1401623. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 40. Lehmann B.A., Ruiter R.A.C., Chapman G., Kok G. The intention to get vaccinated against influenza and actual vaccination uptake of Dutch healthcare personnel. Vaccine. 2014;32(51):6986–6991. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.10.034. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 41. Dai H., et al. Behavioral nudges increase COVID-19 vaccinations. Nature. 2021;597:404–409. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03843-2. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.

Supplementary Materials
- View on publisher site
- PDF (615.7 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 01 February 2022
Persuasive narrative during the COVID-19 pandemic: Norwegian Prime Minister Erna Solberg’s posts on Facebook
- Sanjana Arora ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0107-7061 1 ,
- Jonas Debesay 2 &
- Hande Eslen-Ziya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7113-6771 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 9 , Article number: 35 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
7739 Accesses
6 Citations
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Cultural and media studies
- Politics and international relations
This article explores the Facebook posts of Norway’s Prime Minister Erna Solberg to highlight the key features of her crisis communication during the COVID-19 pandemic. It draws on data from Solberg’s Facebook posts from February 27, 2020 to February 9, 2021 (i.e., starting from the day when the first case of COVID-19 was recorded in Norway until the time of data collection for this study). Out of her 271 posts, 157 of them were about COVID-19 and were chosen for analysis. The analyses identified five major themes: (1) Promoting responsibility and togetherness (2) Coping (3) Being in control amidst uncertainty (4) Fostering hope and (5) Relating with the followers. Drawing inspiration from Boin, Stern and Sundelius’, work on persuasive narratives, this study shows the ways that Solberg’s posts about COVID-19 exhibit all five identified frame functions. In addition, the findings add contextual nuances to the frame functions through the theme of ‘Responsibilization and togetherness’, which are reflected through references to Norwegianness and the cultural concept and practice of dugnad . This study adds to our knowledge about how persuasive narratives are incorporated into the social media communication strategies of leaders and highlights the usefulness of this framework for studying ongoing and future crises.
Similar content being viewed by others

Slovak MPs’ response to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine in light of conspiracy theories and the polarization of political discourse
Disinformation on the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine War: Two sides of the same coin?
The gendered dimensions of the anti-mask and anti-lockdown movement on social media
Introduction.
The economic and social disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic is having major impacts on people’s livelihoods and their health. As of 18 April 2021, there have been 140,322,903 confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 infections and 3,003,794 deaths (WHO, 2021 ), making the COVID-19 pandemic an unprecedented global health crisis of the century. As countries across the world grapple with mitigating the risks associated with the pandemic, communication—an essential component of planning, response, and recovery during crisis (Houston et al., 2014 )—has been one of the integral parts of the crisis management (Reddy and Gupta, 2020 ). Crisis communication highlights legitimation strategies, but also indicates how government institutions themselves make sense of crises (Brandt and Wörlein, 2020 ). Moreover, crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic can disrupt the socio-political order of societies, leaving a cognitive void in the minds of the public that can be filled with fear and uncertainty (Boin et al., 2016 ). In Norway, COVID-19 has been called a fear-driven pandemic that is based on alarming information of long-term illness and disability that is out of politicians control (Vogt and Pahle, 2020 ). Having control over the dramaturgy of political communication is thus central to effective leadership and crisis management (Boin et al., 2016 ). Effective communication can help societies handle uncertainty and promote adherence to behaviour change while fostering hope among the citizens (Finset et al., 2020 ).
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to rapidly evolve, and social media plays a pivotal role in meeting the communication needs of the public during such crisis (Van Dijck, 2013 ). As social media use increases during crises, leaders and public officials may utilise this platform to communicate, which in return helps reduce public panic and builds trust (Kavanaugh et al., 2012 ). As a result of the cultural and symbolic value of social media in contemporary times (Jenzen et al., 2021 ), the communication of public leaders in the midst of uncertainty and fear facilitates interpersonal and group interaction. Research has shown that, when compared to the traditional media platforms, social media platforms are used by leaders and elected officials to communicate, inform, and engage with their citizens (Golbeck et al., 2010 ). They use social media to spread messages farther and faster than it would be possible with traditional media (Sutton et al., 2013 ). What leaders post on social media can give insights into their communication and leadership strategies during crises. Understanding how leaders communicate with the public during crises will not only provide us with the knowledge about their governance styles but will also guide us to their meaning-making in times of uncertainty. Based on this assumption we will be studying the Facebook posts of Norwegian Prime Minister Erna Solberg, with the aim to highlight the key features of her communication. In doing so, we will take an exploratory rather than confirmatory perspective (Boudreau et al., 2001 ).
Solberg, member of the Conservative Party and in power since 2013, was defeated by the centre-left as this paper was being revised. Solberg has had a long career in politics, becoming a deputy representative to the Bergen City Council in 1979 when she was 18 years old. She was elected to the Parliament in 1989 where she was the youngest member of her party group (Notaker and Tvedt, 2021 ). Solberg’s tough stance on issues such as immigration earned her the nickname of ‘Jern-Erna’ [Iron Erna] (Reuters, 2013 ). However, upon her appointment as Prime Minister, Solberg displayed a ‘softer side’ by caring about voters’ jobs, health, and schools (Notaker and Tvedt, 2021 ).
The first Norwegian COVID-19 patient was diagnosed on February 26, 2020. While the initial spread of infection was relatively slow, cases increased quickly by March 12 th , after winter break for schools ended and many Norwegians returned from skiing holidays in Northern Italy (Dagsavisen, 2020 ). On March 12, the Norwegian Directorate of Health (NDH) adopted comprehensive measures to prevent the spread, which included closing day care centres, schools, and educational institutions. The measures also included a ban on cultural events, closed swimming gyms and pools, a halt to all service provisions that involved being less than one meter away from another person, and prohibiting visits to recreational cabins Footnote 1 , among others. Behavioural measures such as recommendations to keep physical distance, encourage handwashing, quarantine, stay home when ill, work from home, and avoid public transportation were also included. Following the lockdown, Norway became the first European country to announce that the situation was under control due to low levels of hospitalizations and mortalities (Christensen and Lægreid, 2020 ). In Norway, as of March 22, 2021, there have been over eighty thousand confirmed cases of coronavirus infection and more than six hundred deaths due to COVID-19. Norway has had far fewer COVID-19 cases, deaths, and hospitalizations per capita than most other countries in Western Europe or the United States (Christensen and Lægreid, 2020 ). Compared to its Scandinavian neighbours Denmark and Sweden, the proportion of cases of infections and deaths have been much lower (WHO, 2021 ), despite the three countries sharing similar social welfare and healthcare systems. Recently, a report submitted by the Corona Committee in Norway also concluded that the overall handling of the crisis by the government has been good. Not only has the number of infections and deaths in Norway been much lower than most countries in Europe, but the healthcare services have also remained stable, and society has remained relatively open (Lund, 2021 ). It is probable that good governance and responsible leadership demonstrated by the Norwegian cabinet and Prime Minister Erna Solberg contributed to this success.
In Norway, there is considerably less focus on individualization of candidates in political parties as compared to for instance the US, since the electoral system in Norway is based on proportional representation (Karlsen and Enjolras, 2016 ). Despite this, with the presence of digital and social media, there has been increasing focus on the individual candidates, leading to ‘decentralising personalisation’ (Karlsen and Enjolras, 2016 ; Balmas et al., 2014 ). Given this context, Erna Solberg’s Facebook account during the COVID-19 pandemic serves as an intermediary platform between the government’s role and her own personal profile as the Prime Minister who has been handling the COVID-19 crisis. Solberg has used Facebook more actively than other outlets like Twitter and has more followers on Facebook than any other platform. The proportion of Facebook users in Norway vis-a-vis other social media platform is also the highest (for example, 84% of people use Facebook compared to 22% who use Twitter who use Twitter) (Werliin and Kokholm, 2016 ). Facebook thus serves as an important platform for public leaders in Norway during crises, and therefore, by analysing Solberg’s Facebook posts, we aim to demonstrate the key features of her communication strategy during the COVID-19 crisis.
Background on crisis and crisis communication
Crisis is defined as a rare, and significant public situation creating undesirable consequences (Coombs, 2015 ; Gruber et al., 2015 ). In most cases it is ‘an unpredictable event that threatens important expectancies of stakeholders and can seriously impact an organization’s performance and generate negative outcomes’ (Coombs, 2015 : p. 3). Crisis communication on the other hand is referred as the strategies used to lessen the uncertainties during crisis via the dissemination and exchange of information (Collins et al., 2016 ). Effective crisis communication establishes reliability and maintains public trust. It should be frequent, consistent and involve compassionate messages conveyed in an inspired and transformational communication style. It is essential that public officials and leaders when communicating crisis relevant information be efficient and informative. Past research has shown the importance of repetition of the consistent interaction to help the message reach the recipients clearly and increase compliance behaviour in cases of crisis (Stephens et al., 2013 ). Inconsistent messages on the other hand were found to cause misperception and confusion, leading to a non-compliant behaviour by the recipients. The content of the message as well as its tone is also an important indicator of whether the recipients will comply or not (Sutton et al., 2013 ). Sources of crisis communication, such as leaders and public health officials, are perceived to be reliable and trustworthy when they exhibit concern and care (Heath and O’ Hair, 2010 ). In addition, they can be more effective in building relationship with the public, if they consider the cultural factors that play a role in their communicating about risks (Aldoory, 2010 ).
Boin et al. ( 2016 ) argue that crisis communication is one of the key challenges, which leaders face during a crisis situation. During crisis communication, leaders are required to frame ‘meaning’ of the crisis in order to shape how public perceives the risks, consequences and how they respond to the measures being taken. Developing a persuasive narrative in communication is thus integral to succesful framing of the crisis and for a strategic leadership. The construction of a successful persuasive narrative requires five frame functions: namely that the narrative will offer a credible explanation of what happened, it will provide guidance, instil hope, show empathy, and suggest that leaders are in control (Boin et al., 2016 ). In doing so, leaders aid the public’s understanding of the facts associated with crisis while sumltaneously acknolwedging and appealing to collective emotions. In incorporating these frame functions, leaders are posed with various choices and decision-making such as how they choose to or not choose to dramatise the situation, the language that they use and how they appeal to the colleactive emotions and stress.
As digital media technologies became popular resources for getting and spreading information, public officials and leaders also increasingly started using them as domains during the crises. In fact, for some scholars the use of social media while enabling mutual interaction between the leaders and recipients has altered the field of crisis communication altogether. For instance, it was found that as social media enables constant and effective communication, it was used more regularly than traditional media outlets during crisis (Kim and Liu, 2012 ). Similarly, Utz et al. ( 2013 ) discussed how for effective crisis communication strategy, the use of media channels, social media—Twitter, and Facebook—versus traditional— newspapers—was more critical than the type of the crisis. Moreover, Schultz et al. ( 2011 ) concluded that when compared to traditional media networks, crisis communication received less negative response when social media was used. Hence, it is not to our surprise that public officials nowadays are turning to social media platforms for communicating with the masses during crisis. They not only use these tools to communicate about crisis but also request information from the public. This was the case during the COVID-19 pandemic crisis where social media was employed by political leaders across the globe to mediate the communication of information about the pandemic as well as for reaching out to their citizens. This paper by focusing on the Norwegian case and more specifically on the Norwegian Prime Minister’s Facebook use during the time of COVID-19 pandemic aims to explore the use of social media platforms by political leaders during crisis. Our goal is to better understand how political leaders adapt social media technologies in their communication strategies during crises.
Our data that covers Erna Solberg’s Facebook posts between February 27, 2020, and February 10, 2021 (a total of 271 posts) were extracted from Footnote 2 into an Excel sheet. A total of 114 posts were removed as they were not related to COVID-19 leaving us 157 posts for further analysis. To aid the coding process, we noted the variables presented in Table 1 . These are: date, number of interactions, number, and type of reactions (e.g., angry, sad, like, etc.), URLs of links shared, and a description of the content of the posts that was later used in the qualitative analysis. We also noted if the posts were made during any particularly critical period (e.g., before, during or after new restrictive measures were introduced). The content of the posts and the number of likes and other reactions derived from this data should be considered a ‘snapshot’ of Solberg’s posts as they appeared at the time of data collection (Brügger, 2013 ), as it is possible that some posts have been subsequently removed, or that the numbers and types of reactions to the posts have changed by the publication date
The data was analysed through thematic analysis (Braun and Clarke, 2006 ): in the first step, we read all posts and generated the first set of codes. Next, we combined all the similar codes while labelling them in clusters and organised them into analytical themes/categories (see Fig. 1 ). The authors then discussed and reviewed these analytical themes and merged them into aggregate/conceptual themes. Lastly, we reviewed the aggregate themes through the lens of the five frame functions of persuasive narrative and identified commonalities and differences. We have included some posts under each theme to illustrate our analytical process and illuminate the themes (Sandelowski, 1994 ). All posts presented here were translated from Norwegian to English by the authors.

Schematic formulation of a theme from the categories captured in posts.
Our analysis resulted in five themes: (1) Promoting responsibility and togetherness (2) Coping (3) Being in control amidst uncertainty (4) Fostering hope and (5) Relating with the followers. In reviewing our findings from the framework of Boin et al. ( 2016 ), we found that all five frame functions of persuasive narrative were embedded in Solberg’s posts and aligned with our themes. Below we discuss our themes with reference to frame functions of Boin et al. ( 2016 ) for a persuasive narrative and in doing so, add contextual nuances to each theme.
Promoting responsibility and togetherness: we are in this together
Analysis of Solberg’s posts revealed a strong message of responsibility and togetherness. In almost all shares, she not only emphasized solidarity but also called for courage and responsibility. This Facebook post, shared soon after comprehensive shut-down measures were introduced, shows how important, for Solberg, was Norwegian solidarity expressed as ‘we’ (March 12, 2020):
Dear everyone. In times of crisis, we understand how dependent we are on each other. What unites us is more important than what separates us. This is not the time for ‘I’. This is the time for ‘we’.
Lunn et al. ( 2020 ) note that citizens are isolated during government induced or self-imposed quarantines: appeals to collective action and a spirit of ‘we-are-in-it-together’ are important ways to ensure compliance with quarantine and hence curb the rate of infection. Leaders in countries such New Zealand, UK, Brazil have also been found to have used a similar narrative emphasizing patriotic duty, love of country, and coming together as one, to mobilise community action (Dada et al., 2021 ).
Her posts were also imbued with appreciation and expression of gratitude towards healthcare workers and those who follow rules. For example, after introduction of the ban to travel to cabins and after the government’s decision to extend regulations until after Easter, Solberg posted the following on April 4, 2020, receiving a high number of likes:
I feel proud when I see how we handle this together. Many thanks to everyone who follows the advice from the health authorities. Many thanks to everyone in the health service who works hard and perseveres. Many thanks to all Norwegians for the patience, love and solidarity we now show each other
The use of the word ‘I’ and how it was being used in reference to ‘feel[ing] proud’, we argue, highlights the ‘positioning of self’ by Solberg. Davies and Harré ( 1990 ) claim that development of the notion of ‘positioning’ is a contribution to the understanding of personhood, and how speakers choose to position their personal identity vis-a-vis their discontinuous personal diversity (such as being the Prime Minister, politician, Norwegian citizen, etc.). In such posts, whether intentionally or unintentionally, we also see the discursive practices through which Solberg allocates meaning to her position as a Prime Minister by emphasising that she feels proud upon seeing those who follow advice. At the same time, her emphasis on ‘we’, as in how ‘ we handle this together’, places her as a member of the Norwegian masses.
Moreover, such references to togetherness and solidarity also reflect attempts to utilise the existing nationalistic cultural repertoire of the Norwegian concept of dugnad . For example, on New Year’s Day following the Gjerdrum community disaster (a sudden and unexpected mudslide that destroyed several residential houses) and rise in the number of infections during the holiday period (2125 reported cases on December 29, 2020), Solberg posted the following post:
[…] During the year we have put behind us, Norway has lined up for the big dugnad . People have put their interests and dreams on hold to protect the elderly and the risk groups. It has saved lives. I am deeply grateful, proud and touched, for the way the Norwegian people have handled the biggest challenge for our society since World War II. We lined up for each other when it mattered most…
Dugnad in Norwegian is voluntary work that is performed as a collective effort (Moss and Sandbakken, 2021 ). Nilsen and Skarpenes ( 2020 ) discuss how the concept of dugnad is embedded in a moral repertoire of the socially responsible citizen that is indicative of a specifically Norwegian welfare mentality and conclude that dugnad is imperative for the sustainability and resilience of the Norwegian welfare model. Before the pandemic, Simon and Mobekk ( 2019 ) argued that the concept of dugnad is central to Norwegian culture, inculcating prosocial and cooperative behaviour, and thereby plays a role in Norway being one of the most egalitarian democracies and having high levels of equality and reciprocity. In the context of COVID-19, social anthropologist Thomas Hylland Eriksen ( 2020 ) pointed out that one reason for the success of the Norwegian approach was the mobilisation of broader society to fight COVID-19, driven by the notion of dugnad . Similarly, Moss and Sandbakken ( 2021 ) analysed data from press conferences and interviews with members of the public and found that many participants mentioned liking how the government talked of ‘a spirit of dugnad ’ ( dugnadsånd ), appealing to shared voluntary work rather than strict rules. The authors posit that in a pandemic it is crucial to create and use meta-narratives that are a good fit with the context in order to aid meaning-making and increase compliance. The use of dugnad as a cultural repertoire has, however, met with criticism from some scholars, who argue that ‘a word associated with solidarity, unity, and voluntary work obscures the forced nature of the measures’ (Tjora, 2020 ) and shifts the onus for finding solutions onto individual citizens or groups (Nilsen and Skarpenes, 2020 ; Hungnes, 2016 ).
Despite the criticism of imbibing such cultural repertoire, the alignment of the key values of Norwegian society with the core message of encouraging collective action is essential for a crisis narrative to be politically effective (Boin et al., 2016 ). Furthermore, the theme of ‘Promoting responsibility and togetherness’ shows the context specific nature of crisis communication narrative in the case of COVID-19 in Norway and therefore adds to the components for a persuasive narrative.
Coping: everything will be fine
Solberg’s Footnote 3 posts also carried messages that address the consequences of coping with COVID-19, namely self-isolation, and loneliness. For instance, her posts guided followers in dealing with loneliness and maintaining general physical and mental health. The Norwegian government, like that of many other countries, had introduced measures such as mandatory quarantine and social distancing rules to manage the spread of the virus. Studies have shown that home confinement during COVID-19 has negatively affected the emotional state of individuals due to depression and anxiety and has led to or increased a sedentary lifestyle (Sang et al., 2020 ). Thus, emphasis on the well-being of the population during COVID-19 is important for effective crisis management (WHO, 2020a ) because increased well-being would reinforce its coping abilities during illness and hardships. As these are not the direct effects of the COVID-19 infection, but a result of the contagion containment measures imposed on citizens by the government, we observe Solberg taking responsibility and providing solutions to help. In doing so, she appears sensitive and caring towards the public.
Christensen and Lægreid ( 2020 ) attribute the ‘high-performing’ handling of the pandemic in Norway to the initial focus on suppression, followed by a control strategy. The authors further examine the ideas that having successful communication with the public, a collaborative and pragmatic decision-making style, the country’s resourcefulness, and high trust of government all contributed to the relative success in Norway. Adopting the correct and effective strategy indeed heavily influences the outcomes of crises. However, to fill the ‘cognitive void’ that the public might be experiencing, leaders need to manage the meaning-making process and ensure legitimacy of their actions (Boin et al., 2016 ). Solberg and the other ministers played an important role in communicating with citizens and the media through daily media briefings together with the NDH (Norwegian Directorate of Health) and NIPH (Norwegian Institute of Public Health) (Christensen and Lægreid, 2020 )
Solberg emphasized the impact of loneliness, for example, during one of the first holiday periods during the pandemic when comprehensive shut-down measures were introduced, she wrote:
Many people may feel lonely during holidays such as Easter, and the corona crisis exacerbates this. Therefore, I would like to encourage everyone to call someone you know is alone at Easter. The little things can mean a lot. Happy Easter!
A study by Blix et al. ( 2021 ) on the topic of mental health in the Norwegian population during the COVID-19 pandemic found that a substantial proportion of the population experienced significant psychological distress in the early phases. More than one out of four reported ongoing psychological distress over the threshold for clinically significant symptoms. Two other categories of individuals (those recently exposed to violence and those with pre-existing mental health problems) were found to be at special risk but worrying about the consequences of the pandemic was also found to contribute negatively to mental health. In this regard, Shah et al. ( 2020 ) argued that several nations have failed to address the mental health aspect among the public, as far more effort is being focused on understanding the epidemiology, clinical features, transmission patterns, and management of COVID-19. Solberg’s open discussion about mental health during the pandemic implies a situation-specific and data-driven strategy of managing the less visible effects of the pandemic and show insight in anticipating future needs (Han et al., 2020 ).
Moreover, Solberg’s posts also subtly utilised the Norwegian concept of friluftsliv , which translates as ‘free air life,’ a philosophy of outdoor living and connection with nature (Henderson and Vikander 2007 ). Friluftsliv is associated with grand narratives of Norwegian national identity depicting outdoor adventures, foraging, and a deep connection to nature (Jørgensen-Vittersø, 2021 ). For example, with the re-opening of DNT [Den Norske Turistforening] cabins in mid-2020, Solberg in her post on June 11 emphasized the importance of being outdoors in fresh air:
We need to use our bodies and get out into the light and fresh air. It is important for both physical and mental health! I hope many have a good and active Norwegian holiday this year!
In these posts, Solberg also shared pictures of herself being outdoors. In such ways, Solberg appeared to be offering not only guidance for coping with the challenges and consequences of living during the pandemic, but also emphasizing one characteristic of the Norwegian culture, which they are proud of—spending time in nature. Be it advice to spend time in nature, or to keep social distance or self-isolation, we consider that Solberg’s approach to coping aligns with the frame function of ‘offering guidance’. During a crisis, leaders have a window of opportunity during which they can communicate a frame to not only make sense of the crisis but also to provide guidance and to portray themselves as attentive and concerned about the challenging circumstances faced by the public (Boin et al., 2016 ). By depicting herself as attuned to the emotions experienced by her followers during the pandemic and by utilising the moment to suggest ways of coping, Solberg’s communication encapsulates the frame function of offering guidance for a persuasive narrative.
Being in control amidst uncertainty
In her posts, Solberg presented a narrative of being in control amidst uncertainty, which aligns with two of the frame functions of Boin et al. ( 2016 ), namely offering a credible explanation and suggesting that leaders are in control. In times of a crisis, it is important that leaders do not downplay the gravity of the situation or claim unrealistically optimistic scenarios (Boin et al., 2016 ). We see that Solberg maintained a balance by providing a detailed explanation of her actions and the reasons behind the restrictive measures taken. At the same time, she acknowledged the uncertainty inherent in the ever-changing crisis and demonstrated her concern. According to Lunn et al. ( 2020 ), in situations characterised by uncertainty and fear, responsible leaders need to signal that they are in control of the situation, which can be demonstrated by making decisions with confidence and honesty. Moreover, it is also essential that leaders do not make promises that are impossible or unrealistic, because doing that can impede the persuasiveness of their narrative by affecting their credibility later (Boin et al., 2016 ). In Solberg’s posts, we see that she displays confidence but also the reality of uncertainty and concern, which is a sign of effective leadership and shows ‘bounded optimism’ (Brassey and Kruyt, 2020 ). The following post where she writes about her worries and concerns followed by advice is a good example of credibility and control:
I am worried. Right now, we have ongoing outbreaks in Bergen, Oslo, Trondheim and Hammerfest… We know that vigorous work is being done intensively in these municipalities with infection detection and other measures. Although Norway has relatively low infection rates, we also register here at home that the number of hospital admissions and the number of infected have increased recently. We now have the highest number of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 since May… We also see that the infection has begun to spread to older age groups. And there is a significant risk that the numbers will continue to rise as we see in Europe. That is why we have today announced new national austerity measures next week. We can still reverse the trend here at home…
A demonstration of concern from role models has been shown to have a role in persuading the public to adhere to recommendations (Simon and Mobekk, 2019 ). Tannenbaum et al. ( 2015 ) note that fear is easier to handle when it is acknowledged, which relates to the idea of ‘citizens being anxious enough to take the advice from the authorities to heart and optimistic enough as to feel that their actions make a difference’ (Petersen, 2020 ). Inculcating ‘optimistic anxiety’ (Tannenbaum et al., 2015 ) is therefore an important feature of crisis communication narratives.
Another important nuance that emerges from Solberg’s posts is her comparisons to other countries to draw attention to the seriousness of the situation. For example, on November 5, 2020, Solberg made the following post announcing new national measures, which received over 5000 likes:
My message to the Norwegian people is: Stay at home as much as possible. Have the least possible social contact with others. It is absolutely necessary to avoid a new shutdown. Norway is at the beginning of the second wave of infection… The virus is spreading rapidly and all counties now have outbreaks. The government is therefore introducing new national infection control measures… If the current rate of infection continues, the number of inpatients in intensive care units will increase sharply in the coming weeks. This will lead to less intensive capacity for other seriously ill people. We are now where the Netherlands was at the beginning of September. A very rapid increase in infection in the Netherlands quickly led to more patients in the intensive care unit… Other European countries have similar experiences. There is therefore a heavy seriousness about the situation. And we must take responsibility together
By giving detailed reasoning behind measures being taken amidst uncertainty, Solberg exhibits both confidence and honesty in her narratives (Lunn et al., 2020 ). Another key feature that emerges from the post above is the emphasis on the risks of an increase in infection, and the possibility of a new lockdown and overburdening of intensive care capacity, thereby reflecting a more strongly persuasive intent. Such emphasis on the risks is different from other posts where Solberg exhibits control and optimism much more strongly. This adaption from a communicative stance to a more persuasive one could result from not only the perceived severity of the situation, but also the perceived risks of pandemic fatigue. Pandemic fatigue has been defined by the WHO as a lack of motivation to adhere to recommended protective behaviours (WHO, 2020b ). According to surveys conducted in different countries, most people have been shown to possess adequate knowledge of COVID-19 and the precautions required to keep safe, yet factors like emotions and context have been found to have greater impact on behaviours than knowledge (Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, 2020 ). A study of different ways of communicating healthcare messages suggested that believability of the messages and the recipients’ reactions to them can be influenced by the persuasive intent (Wang and Shen, 2019 ). Koh et al. ( 2020 ) also discuss the importance of devising effective and successful communications for a sustained period without message fatigue setting in, which includes concern for the way the communication is framed. Overall, we see that Solberg’s posts provide a rationale with portrayal of the government being in control of managing the crisis.
Fostering hope and return to normalcy
Solberg’s posts also emphasized the hopeful aspects of the crisis by appealing to followers to look forward to a return to everyday life, and new educational and economic prospects, despite the difficult current circumstances. This theme aligns with the frame of ‘instilling hope’ as per frame functions for a persuasive narrative by Boin et al. ( 2016 ). During a crisis, more than ever, effective leaders embody the hopes and fears of the society under threat, and therefore they should strive to inculcate optimism of a better future (Boin et al., 2016 ). Previous research has documented that in times of turmoil, followers especially look up to leadership that serves as a beacon of hope for and faith in a positive future, more than they do in times of prosperity (Stam et al., 2018 ; Shamir et al., 1993 ). According to Boin et al., leadership during crisis always has a moral dimension. On January 10, 2021, by which time Norway had witnessed over 50000 cases of infection and over 400 deaths as well as the Gjerdrum disaster, Solberg made the following post:
Dear everyone. This year I hope we can take our dreams back. After a year of pandemic and fear. Then I look forward to seeing creativity unleashed…
Another post that emphasized the optimism for educational prospects was made on April 15, 2020, and drew over 5000 likes:
Today is the last deadline to apply to a vocational school, college or university. I understand that it can feel strange to apply for an education this autumn while the educational institutions keep their campuses closed. Maybe someone also thinks the idea of moving from home to a new city seems extra scary these days. To you I want to say that everyday life will return. Therefore, my appeal to you who want to study: do not put your life on hold, but apply for education this year!
Lessons from previous crises tell us that leaders need to pay attention to the fear of the ongoing threat, as well as sadness and grief, and to provide hope to mitigate social disruption (Maak et al., 2021 ). Here, we see that Solberg’s is attempting to convey hope while also acknowledging the challenges and impact of COVID-19. In doing so, the messages also emphasise self-efficacy and trust in the government. Hope and resilience are closely aligned constructs, as they both include a tendency towards maintaining an optimistic outlook in the face of adversity (Duggal et al., 2016 ). Thus, fostering hope during crisis can help the community cope with the consequences of the crisis. Moreover, by using emotional appeals, leaders can influence attitudes and behaviours as well as induce compassion (Ghio et al., 2020 ).
The theme of fostering hope in Solberg’s posts was found to be particularly emphasized during and before national holidays or important events. Her posts often utilised humour to foster positivity, particularly during critical periods such as during or after implementation of stricter COVID-19 measures. For example, a day after it was announced that infection-reduction measures would continue throughout Christmas, Solberg shared a snipped of her response to a question asked in a press conference and posted:
Can Santa actually come to visit this year?
Creating human moments and hope is a sign of compassionate leadership and helps to establish the relational foundation for widespread support for pandemic control measures (Maak et al., 2021 ). Also, by utilising humour, Solberg adapts the tone of her messages, a tactic that has been found to significantly affect audiences’ attitudes and behaviours, help people manage their emotions, and strengthen support for pandemic measures (Lee and Basnyat, 2013 )
Relating with followers
The last theme is about the posts in which Solberg relates to the public by providing personal information, acknowledging, and relating with the difficult circumstances, and using humour or a private tone in her posts. For example, the post below was made just before Easter and it received more than 13000 likes, making it to be the third-most liked post of Solberg related to COVID-19 during this period.
It will be a different Easter this year. Let’s make the best of it. We can play fun board games with our loved ones, read the book we never have time to read, listen to an audiobook or explore the local area. The last few weeks have been challenging for all of us, but we want to get through this… Sindre and I have recharged with board games and wish you all a very happy Easter!
Empathy is an important component of the persuasive narrative, especially during crises when the decisions made by authorities to mitigate, and control can also have consequences for people’s lives. For crisis communication to be effective, the information provided to the public should not be too factual or portray leaders as distant from the citizens (Shen, 2010 ; Lunn et al., 2020 ). By demonstrating concern and acknowledging the impact of crises, leaders can empathise with the public (Shen, 2010 ; Lunn et al., 2020 ). We see Solberg personifying the challenges of COVID-19 by referring to how the times have been challenging for ‘all of us’. According to Boin et al. ( 2016 ), a leader’s personification of suffering is instrumental in showing empathy because the public is then able to relate to them.
Further, previously in a study by Larsson ( 2015 ) about Norwegian party leaders on Facebook during the 2013 ‘short campaign’, it was found that personal content referencing private life is increasingly employed by Norwegian party leaders. Enli and Rosenberg ( 2018 ) investigated voters’ evaluations of politicians as authentic or ‘real,’ and Solberg was found to be one of the most perceived authentic politicians. Enli ( 2014 ) had earlier suggested that Erna Solberg’s public profile as predictable, anti-elitist and imperfect constructs her authenticity.
A similar example of relatability with followers during the pandemic was the instance when she forgot the rule of not shaking hands during public meetups and press conferences. After the event, she wrote:
It is important that we can have some humour in a difficult time Even a prime minister can forget, but now it is important that we all remember to follow the advice of the health authorities…
She also used an engaging communicative style when interacting with her followers:
Then the holiday is over… a different summer, a little cold, weekly meetings in the Government’s Corona Committee on video, beautiful nature experiences from Norway and a lot of rain. Let me share a wonderful little meeting with a lynx on the lawn on Varaldsøy… Have you had a nice summer?
Thus, Solberg embeds references to her private life, which also helps to personify the messages in her posts and thus relate with the public. In addition, by relating with the public on an everyday basis and through the acknowledgment of shared challenges during crisis, Solberg’s narrative also appears empathetic. Our theme of ‘Relating to the public’ thus encapsulates frame function of ‘showing empathy’ for developing a persuasive narrative, as per Boin et al. ( 2016 ).
Concluding remarks
This paper was an attempt to explore the Facebook posts of Norway’s Prime Minister Erna Solberg to highlight the key features of her crisis communication during the COVID-19 pandemic. By drawing on data from Solberg’s Facebook posts during the pandemic our analyses identified five major themes, (1) Promoting responsibility and togetherness (2) Coping (3) Being in control amidst uncertainty (4) Fostering hope and (5) Relating with the followers, where we went in detail explanation by using frame functions of a persuasive narrative by Boin et al. ( 2016 ). We furthermore discussed the specific Norwegian contextual nuances to the frame functions. These were the theme ‘Responsibilization and togetherness’, presented via the references to Norwegianness and the cultural concept and practice of dugnad . Hence, our paper showed how during crisis persuasive narratives are incorporated into the social media communication strategies of political leaders.
The paper also showed how persuasive narratives are delivered through praising the public’s efforts, promoting togetherness, caring about the public’s well-being, displaying optimism and confidence in the government’s measures. It elaborated on how crisis management on social media was done via the use of humour and personal information. Humour was used as a tool to engage with the public and help them relate and comply to the COVID-19 restrictions. Hence, Solberg used Facebook to capitalise on a wide-reaching social medium (Hallahan, 2010 ). While the communication of leaders during crises helps to fill the cognitive void, the use of social media helps build societal resilience by improving awareness and encouraging preparedness (Boin et al., 2016 )
Even so, the success of a persuasive narrative is to a great extent dependant on the credibility of its proponents (Boin et al., 2016 ). The reputation of the leader and the organisation that they represent plays a key role in framing a successful persuasive narrative. In general, Norwegians have more trust in each other and their institutions than most other countries (Skirbekk and Grimen, 2012 ). A survey conducted by the Norwegian Citizen’s Panel [Norsk Medborgerpanel] in March 2020 found that trust in government, in the health authorities, in parliament, and in national and local politicians had increased, as did trust in the Prime Minister during the pandemic (Dahl, 2020 ). Clearly, Solberg seems to have benefitted from the trust capital in Norwegian society with her Facebook communications during a crisis. More recently, Erna Solberg has received heavy criticism for breach of COVID-19 restrictions during a family trip to Geilo for her 60th birthday (The Guardian, 2021a ). Following which, Erna Solberg, has been investigated by police and fined (The Guardian, 2021b ). Thus, while her Facebook posts exhibiting components of a persuasive narrative received popularity, her actions have nevertheless been subjected to scrutiny and criticisms in mainstream media (Larsen, 2021 ). According to Boin et al. ( 2016 : p. 72), the retainment of confidence of the public is essential for the communication strategies to be effective. Therefore, such media criticism might undermine the credibility of Solberg and her cabinet, leading to less credible and politically ineffective narratives. On the other hand, past performances, and reputation also play an important role in increasing leaders’ personal credibility in the face of crisis (Boin et al., 2016 ). Consequently, Solberg’s long career in politics and her reputation of caring about the citizens as previously discussed, could buffer the recent impact on her credibility. Moreover, communication during and after a crisis affects long-term impressions (Coombs, 2007 ). With the personification of politics in Norway or ‘decentralising personalization’ (Balmas et al., 2014 ), the criticisms paved at Erna, however, reflect more of a personal crisis than a national crisis. And while we do not analyse Solberg’s posts beyond 9 th Feb. 2021 i.e., after Solberg spoke about the Geilo trip incident on her Facebook account, we see that she follows similar strategy in handling this personal crisis as the national crisis of COVID-19, through use of a persuasive narrative. Future studies can therefore focus on how Solberg and other political leaders utilise the strategy of persuasive narrative in management of personal crisis in nexus with national crisis such as that of COVID-19.
Further, we concur with Christensen and Lægreid ( 2020 ) who write that the ‘political leadership has succeeded well in connecting governance capacity and legitimacy using the argument that Norway had sufficient resources to deal with the crisis. While the health resource capacity and preparedness of Norway inarguably contributes to the outcomes of the crisis, communicating a successful persuasive narrative with credibility is integral to gaining legitimacy and filling the cognitive void (Boin et al., 2016 ). Erna Solberg’s use of persuasive narrative in Facebook posts, seems therefore to have been effective in the management of the COVID-19 pandemic, but her latest unfortunate incident goes to show how politicians’ management of crises is tenuous and highly dependent on public trust.
Our study adds to the significance and knowledge of how persuasive narratives are incorporated into the communication strategy of leaders on a social media platform and highlights the usefulness of this framework for studies about ongoing and future crises. By using data from social media, our findings also add to the understanding of the increased personification of politics and how leaders utilise this personification to communicate government measures and engage with the public during a crisis. Future research can further explore how public leaders and health authorities’ frame crises situations, actions, issues, and responsibility to dramatise and reinforce key ideas (Hallahan, 1999 ). Such insights can pave way for understanding public’s shaping of risk perceptions and compliance to behavioural measures during crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Data availability
The dataset analysed during the current study is available through the public profile of Erna Solberg on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ernasolberg/ . This dataset was derived from Crowd Tangle which can be accessed through request at https://www.crowdtangle.com/ .
Known as ‘hyttetur’, cabin trips are deeply rooted in Norwegian culture and way of life
Crowdtangle extracts both historical and current data of post contents and metadata such as the date the post was made, number of likes, other reactions and shares. Information about how to access raw material included in this study can be found in the data availability statement at the end of the article.
‘Everything will be fine’ [ Alt blir bra ] was one of the campaigns that spread because of the COVID-19 crisis in Norway depicting pictures of a rainbow.
Aldoory L (2010) The ecological perspective and other ways to (re)consider cultural factors in risk communication. In: Heath R, O’ Hair (eds) Handbook of risk and crisis communication. Routledge, New York, pp. 227–246
Google Scholar
Balmas M, Rahat G, Sheafer T, Shenhav SR (2014) Two routes to personalized politics: Centralized and decentralized personalization. Party Polit 20(1):37–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354068811436037
Article Google Scholar
Blix I, Birkeland MS, Thoresen S (2021) Worry and Mental Health in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Vulnerability Factors in the General Norwegian Population. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-192098/v1 . Accessed 10 Jun 2021
Boin A, Stern E, Sundelius B (2016) The politics of crisis management: Public leadership under pressure. Cambridge University Press
Boudreau MC, Gefen D, Straub DW (2001) Validation in information systems research: a state-of-the-art assessment. MIS Quart 25(1):1. https://doi.org/10.2307/3250956
Brandt P, Wörlein J (2020) Government crisis communication during the pandemic. https://www.sciencespo.fr/en/news/news/government-crisis-communications-during-the-pandemic/4862 . Accessed 20 May 2021
Braun V, Clarke V (2006) Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol 3(2):77–101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Brassey J, Kruyt M (2020) How to demonstrate calm and optimism in a crisis. McKinsey & Company, April. 2020. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/organization/our-insights/how-to-demonstrate-calm-and-optimism-in-a-crisis . Accessed 27 May 2021
Brügger N (2013) Historical network analysis of the web. Soc Sci Comput Review 31(3):306–21. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439312454267
Christensen T, Lægreid P (2020) Balancing governance capacity and legitimacy: how the Norwegian government handled the COVID‐19 crisis as a high performer. Public Admin Rev 80(5):774–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/puar.13241
Collins M, Neville K, Hynes W, Madden M (2016) Communication in a disaster-the development of a crisis communication tool within the S-HELP project. J Decis Syst 25(1):160–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2016.1187392
Coombs WT (2007) Protecting organization reputations during a crisis: the development and application of situational crisis communication theory. Corp Reput Rev 10(3):163–176. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.crr.1550049
Coombs WT (2015) Ongoing crisis communication: planning, managing and responding. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
CrowdTangle (2021) CrowdTangle Team. Facebook, Menlo Park, California, United States. List ID: 1504404 2021
Dada S, Ashworth HC, Bewa MJ, Dhatt R (2021) Words matter: political and gender analysis of speeches made by heads of government during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMJ Global Health 6(1):e003910. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.10.20187427
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dagsavisen (2020) FHI: Norge ble varslet om koronasmitte fra Østerrike allerede 4. mars 2020 (Norway was notified of corona infection from Austria as early as 4 March 2020). https://www.dagsavisen.no/nyheter/innenriks/2020/10/30/fhi-norge-ble-varslet-om-koronasmitte-fra-osterrike-allerede-4-mars/ . Accessed on 1 Apr 2021
Dahl T (2020) Stolar meir på Erna og mindre på naboen (Rely more on Erna and less on the neighbor). https://www.uib.no/aktuelt/135017/stolar-meir-p%C3%A5-erna-og-mindre-p%C3%A5-naboen . Accessed 3 Jul 2021
Davies B, Harré R (1990) Positioning: the discursive production of selves. J Theory Soc Behav 20(1):43–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-5914.1990.tb00174.x
Duggal D, Sacks-Zimmerman A, Liberta T (2016) The impact of hope and resilience on multiple factors in neurosurgical patients. Cureus 8(10). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.849
Enli G (2014) Mediated authenticity. Peter Lang Incorporated, New York
Enli G, Rosenberg LT (2018) Trust in the age of social media: Populist politicians seem more authentic. Soc Media Soc 4(1):2056305118764430. https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305118764430
Eriksen TH (2020) Norway’s response to Covid-19 and the Janus face of Nordic trust. https://www.coronatimes.net/norway-covid-19-nordic-trust/ . Accessed on 15 May 2021
Finset A, Bosworth H, Butow P, Gulbrandsen P, Hulsman RL, Pieterse AH et al. (2020) Effective health communication–a key factor in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. Patient Educ Couns 103(5):873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2020.03.027
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gavi the Vaccine Alliance (2020) 10 reasons why pandemic fatigue could threaten global health in 2021. https://www.gavi.org/vaccineswork/10-reasons-why-pandemic-fatigue-could-threaten-global-health-2021 . Accessed 15 Jun 2021
Ghio D, Lawes-Wickwar S, Tang M, Epton T, Howlett N, Jenkinson E (2020) What influences people’s responses to public health messages for managing risks and preventing infectious diseases? A rapid systematic review of the evidence and recommendations. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/nz7tr . Accessed 28 May 2021
Golbeck J, Grimes JM, Rogers A (2010) Twitter use by the US Congress. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 61(8):1612–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21344
Gruber DA, Smerek RE, Thomas-Hunt MC, James EH (2015) The real-time power of Twitter: Crisis management and leadership in an age of social media. Bus Horizon 58(2):163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.10.006
Hallahan K (1999) Seven models of framing: implications for public relations. J Public Relat Res 11(3):205–242. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532754xjprr1103_02
Hallahan K (2010) Crises and risk in cyberspace. In: Heath R, Hair O’ (ed) Handbook of risk and crisis communication. Routledge, New York, NY, pp. 412–445
Han RH, Schmidt MN, Waits WM, Bell AK, Miller TL (2020) Planning for mental health needs during COVID-19. Curr Psychiatry Rep 22(12):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-020-01189-6
Heath R, O’ Hair H (2010) The significance of crisis and risk communication. In: Heath R, Hair O’ (ed) Handbook of risk and crisis communication. Routledge, New York, pp. 5–30
Chapter Google Scholar
Henderson B, Vikander N (eds) (2007) Nature first: outdoor life the friluftsliv way. Dundurn
Houston JB et al. (2014) Social media and disasters: a functional framework for social media use in disaster planning, response, and research. Disasters 39(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/disa.12092
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hungnes S (2016) Den norske dugnadskulturen (The Norwegian voluntary culture. https://agendamagasin.no/kommentarer/den-norske-dugnadskulturen/ . Accessed 25 May 2021
Jenzen O, Erhart I, Eslen-Ziya H, Korkut U, McGarry A (2021) The symbol of social media in contemporary protest: Twitter and the Gezi Park movement. Convergence 27(2):414–37. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354856520933747
Jørgensen-Vittersø KA (2021) From fresh air and sunbathing to wildlife and snow caves: ‘Friluftsliv’in norwegian primary schools, 1939–1980. In: Roos M, Berge KL, Edgren H (eds) Exploring textbooks and cultural change in nordic education 1536–2020. Brill, pp 245–259
Karlsen R, Enjolras B (2016) Styles of social media campaigning and influence in a hybrid political communication system: linking candidate survey data with Twitter data. Inte J Press/Politics 21(3):338–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/1940161216645335
Kavanaugh AL, Fox EA, Sheetz SD, Yang S, Li LT, Shoemaker DJ et al. (2012) Social media use by government: from the routine to the critical. Gov Inform Q 29(4):480–91. https://doi.org/10.1145/2037556.2037574
Kim S, Liu BF (2012) Are all crises opportunities? A comparison of how corporate and government organizations responded to the 2009 flu pandemic. J Public Relat Res 24(1):69–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062726x.2012.626136
Koh PK-K, Chan LL, Tan E-K (2020) Messaging fatigue and desensitisation to information during pandemic. Arch Med Res 51(7):716–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.06.014
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Larsen K (2021) Erna Solbergs popularitet stuper (Erna Solberg’s popularity plummets). https://www.dagbladet.no/nyheter/erna-solbergs-popularitet-stuper/73597485 . Accessed 15th Apr
Larsson AO (2015) Pandering, protesting, engaging. Norwegian party leaders on Facebook during the 2013 ‘Short campaign’. Inform Commun Soc 18(4):459–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118x.2014.967269
Lee ST, Basnyat I (2013) From press release to news: mapping the framing of the 2009 H1N1 A influenza pandemic. Health Commun 28(2):119–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2012.658550
Lund J (2021) Somling, rot og ulovligheter (Procrastination, clutter and illegalities). https://www.aftenposten.no/meninger/kommentar/i/BlPRjw/somling-rot-og-ulovligheter . Accessed on 25 May 2021
Lunn P, Belton C, Lavin C, McGowan F, Timmons S, Robertson D (2020) Using behavioural science to help fight the coronavirus. J Behav Public Administration, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.30636/jbpa.31.147
Maak T, Pless NM, Wohlgezogen F (2021) The fault lines of leadership: Lessons from the global Covid-19 crisis. J Change Manag 21(1):66–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/14697017.2021.1861724
Moss SM, Sandbakken EM (2021) “Everybody needs to do their part, so we can get this under control.” reactions to the norwegian government meta‐narratives on COVID‐19 measures. Polit Psychol 42(5):881–898. https://doi.org/10.1111/pops.12727
Notaker H, Tvedt KA (2021) Stor Norske Leksikon: Erna Solberg ( https://snl.no/Erna_Solberg . Accessed on 20 Apr 2021
Nilsen ACE, Skarpenes O (2020) Coping with COVID-19. Dugnad: a case of the moral premise of the Norwegian welfare state. International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy. (ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/ijssp-07-2020-0263
Petersen MB (2020) The unpleasant truth is the best protection against coronavirus. Politiken. https://pure.au.dk/portal/files/181464339/The_unpleasant_truth_is_the_best_protection_against_coronavirus_Michael_Bang_Petersen.pdf . Accessed 11 Jun 2021
Reddy BV, Gupta A (2020) Importance of effective communication during COVID-19 infodemic. J Fam Med Prim Care 9(8):3793. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_719_20
Reuters (2013) Iron Erna’s softer side wins through in Norway election 2013. https://www.scmp.com/news/world/article/1307898/iron-ernas-softer-side-wins-through-norway-election . Accessed 27 Apr 2021
Sandelowski M (1994) Focus on qualitative methods. The use of quotes in qualitative research. Res Nurs Health 17(6):479–482. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.4770170611
Sang X, Menhas R, Saqib ZA, Mahmood S, Weng Y, Khurshid S, et al. (2020) The psychological impacts of CoViD-19 home confinement and physical activity: a structural equation model analysis. Front Psychol 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.614770
Schultz F, Utz S, Göritz A (2011) Is the medium the message? Perceptions of and reactions to crisis communication via twitter, blogs and traditional media. Public Relat Rev 37(1):20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2010.12.001
Shah K, Kamrai D, Mekala H, Mann B, Desai K, Patel RS (2020) Focus on mental health during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: applying learnings from the past outbreaks. Cureus 12(3). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7405
Shamir B, House RJ, Arthur MB (1993) The motivational effects of charismatic leadership: a self-concept based theory. Organ Sci 4(4):577–94. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.4.4.577
Shen L (2010) Mitigating psychological reactance: the role of message-induced empathy in persuasion. Hum Commun Res 36(3):397–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2958.2010.01381.x
Article ADS Google Scholar
Simon C, Mobekk H (2019) Dugnad: a fact and a narrative of Norwegian prosocial behavior. Perspect Behav Sci 42(4):815–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-019-00227-w
Skirbekk H, Grimen H (2012) Tillit i Norge (Trust in Norway). Res Publica, Oslo
Stam D, van Knippenberg D, Wisse B, Nederveen Pieterse A (2018) Motivation in words: promotion-and prevention-oriented leader communication in times of crisis. J Manag 44(7):2859–87. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206316654543
Stephens KK, Barrett AK, Mahometa MJ (2013) Organizational communication in emergencies: Using multiple channels and sources to combat noise and capture attention. Hum Commun Res 39(2):230–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/hcre.12002
Sutton J, Spiro E, Butts C, Fitzhugh S, Johnson B, Greczek M (2013) Tweeting the spill: Online informal communications, social networks, and conversational microstructures during the Deepwater Horizon oilspill. Int J Inform Syst Crisis Resp Manag 5(1):58–76. https://doi.org/10.4018/jiscrm.2013010104
Tannenbaum MB, Hepler J, Zimmerman RS, Saul L, Jacobs S, Wilson K et al. (2015) Appealing to fear: a meta-analysis of fear appeal effectiveness and theories. Psychol Bull 141(6):1178. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0039729
The Guardian (2021a) Norwegian PM Erna Solberg investigated for Covid rules breach. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/mar/19/norwegian-pm-erna-solberg-investigated-for-covid-rules-breach . Accessed 25th Mar 2021
The Guardian (2021b) Norwegian PM fined after breaking Covid rules with birthday party. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/apr/09/norway-prime-minister-erna-solberg-fined-breaking-covid-rules-birthday . Accessed 15th Mar 2021
Tjora A (2020) Tillitsfull dugnad eller instruert solidaritet (Trusting voluntary work or instructed solidarity) https://www.universitetsavisa.no/koronavirus-ytring/tillitsfull-dugnad-eller-instruert-solidaritet/111642 . Accessed on 21 May 2021
Utz S, Schultz F, Glocka S (2013) Crisis communication online: How medium, crisis type and emotions affected public reactions in the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. Public Relat Rev 39(1):40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2012.09.010
Van Dijck J (2013) Facebook and the engineering of connectivity: A multi-layered approach to social media platforms. Convergence 19(2):141–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354856512457548
Vogt H, Pahle A (2020) En fryktdrevet pandemi av varige helseproblemer (A fear-driven pandemic of lasting health problems) https://www.aftenposten.no/meninger/kronikk/i/opdB6a/en-fryktdrevet-pandemi-av-varige-helseproblemer . Accessed 20 May 2021
Wang W, Shen F (2019) The effects of health narratives: Examining the moderating role of persuasive intent. Health Market Q 36(2):120–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/07359683.2019.1575061
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Werliin R, Kokholm M (2016) Device study: Social media across the Nordics. https://www.audienceproject.com/wp-content/uploads/study_social_media_across_the_nordics.pdf . Accessed 18 Jun 2021
World Health Organization (2020a) Mental health and psychosocial considerations during the COVID-19 outbreak, 18 March 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/mental-health-considerations.pdf . Accessed 10 Jun 2021
World Health Organization (2020b) Pandemic fatigue: reinvigorating the public to prevent COVID-19: policy framework for supporting pandemic prevention and management: revised version November 2020. World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/337574 . Accessed 17 Jun 2021
World Health Organization (2021) WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard 2021 https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=Cj0KCQjw9_mDBhCGARIsAN3PaFNVuA3kABELXjY66cXUIVcTNNBkPrX57w1OtZL1GYBomSnvTRflQTcaAoxkEALw_wcB . Accessed 18 Apr 2021
Download references
Acknowledgements
This article is published as part of the research project ‘Fighting Pandemics with Enhanced Risk Communication: Messages, Compliance and Vulnerability During the COVID-19 Outbreak (PAN-FIGHT)’, which is financed by the Norwegian Research Council (Project number: 312767).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
Sanjana Arora & Hande Eslen-Ziya
Oslo Metropolitan University, Oslo, Norway
Jonas Debesay
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sanjana Arora .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Arora, S., Debesay, J. & Eslen-Ziya, H. Persuasive narrative during the COVID-19 pandemic: Norwegian Prime Minister Erna Solberg’s posts on Facebook. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9 , 35 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01051-5
Download citation
Received : 12 October 2021
Accepted : 17 January 2022
Published : 01 February 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01051-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Persuasive messaging to increase COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions
Affiliations.
- 1 Yale Institute for Global Health, New Haven, CT, USA; Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA.
- 2 Institution for Social and Policy Studies, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA; Center for the Study of American Politics, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA.
- 3 Institution for Social and Policy Studies, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA; Center for the Study of American Politics, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA; Department of Political Science, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA.
- 4 Yale Institute for Global Health, New Haven, CT, USA; Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA; Department of Epidemiology of Microbial Diseases, Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, CT, USA; Yale School of Nursing, West Haven, CT, USA.
- 5 Institution for Social and Policy Studies, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA; Center for the Study of American Politics, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA; Department of Political Science, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA. Electronic address: [email protected].
- PMID: 34774363
- PMCID: PMC8531257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.10.039
Widespread vaccination remains the best option for controlling the spread of COVID-19 and ending the pandemic. Despite the considerable disruption the virus has caused to people's lives, many people are still hesitant to receive a vaccine. Without high rates of uptake, however, the pandemic is likely to be prolonged. Here we use two survey experiments to study how persuasive messaging affects COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions. In the first experiment, we test a large number of treatment messages. One subgroup of messages draws on the idea that mass vaccination is a collective action problem and highlighting the prosocial benefit of vaccination or the reputational costs that one might incur if one chooses not to vaccinate. Another subgroup of messages built on contemporary concerns about the pandemic, like issues of restricting personal freedom or economic security. We find that persuasive messaging that invokes prosocial vaccination and social image concerns is effective at increasing intended uptake and also the willingness to persuade others and judgments of non-vaccinators. We replicate this result on a nationally representative sample of Americans and observe that prosocial messaging is robust across subgroups, including those who are most hesitant about vaccines generally. The experiments demonstrate how persuasive messaging can induce individuals to be more likely to vaccinate and also create spillover effects to persuade others to do so as well. The first experiment in this study was registered at clinicaltrials.gov and can be found under the ID number NCT04460703 . This study was registered at Open Science Framework (OSF) at: https://osf.io/qu8nb/?view_only=82f06ecad77f4e54b02e8581a65047d7.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Publication types
- Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
- COVID-19 Vaccines*
- United States
- Vaccination
- COVID-19 Vaccines
Associated data
- ClinicalTrials.gov/NCT04460703
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
current events
12 Ideas for Writing Through the Pandemic With The New York Times
A dozen writing projects — including journals, poems, comics and more — for students to try at home.

By Natalie Proulx
The coronavirus has transformed life as we know it. Schools are closed, we’re confined to our homes and the future feels very uncertain. Why write at a time like this?
For one, we are living through history. Future historians may look back on the journals, essays and art that ordinary people are creating now to tell the story of life during the coronavirus.
But writing can also be deeply therapeutic. It can be a way to express our fears, hopes and joys. It can help us make sense of the world and our place in it.
Plus, even though school buildings are shuttered, that doesn’t mean learning has stopped. Writing can help us reflect on what’s happening in our lives and form new ideas.
We want to help inspire your writing about the coronavirus while you learn from home. Below, we offer 12 projects for students, all based on pieces from The New York Times, including personal narrative essays, editorials, comic strips and podcasts. Each project features a Times text and prompts to inspire your writing, as well as related resources from The Learning Network to help you develop your craft. Some also offer opportunities to get your work published in The Times, on The Learning Network or elsewhere.
We know this list isn’t nearly complete. If you have ideas for other pandemic-related writing projects, please suggest them in the comments.
In the meantime, happy writing!
Journaling is well-known as a therapeutic practice , a tool for helping you organize your thoughts and vent your emotions, especially in anxiety-ridden times. But keeping a diary has an added benefit during a pandemic: It may help educate future generations.
In “ The Quarantine Diaries ,” Amelia Nierenberg spoke to Ady, an 8-year-old in the Bay Area who is keeping a diary. Ms. Nierenberg writes:
As the coronavirus continues to spread and confine people largely to their homes, many are filling pages with their experiences of living through a pandemic. Their diaries are told in words and pictures: pantry inventories, window views, questions about the future, concerns about the present. Taken together, the pages tell the story of an anxious, claustrophobic world on pause. “You can say anything you want, no matter what, and nobody can judge you,” Ady said in a phone interview earlier this month, speaking about her diary. “No one says, ‘scaredy-cat.’” When future historians look to write the story of life during coronavirus, these first-person accounts may prove useful. “Diaries and correspondences are a gold standard,” said Jane Kamensky, a professor of American History at Harvard University and the faculty director of the Schlesinger Library at the Radcliffe Institute. “They’re among the best evidence we have of people’s inner worlds.”
You can keep your own journal, recording your thoughts, questions, concerns and experiences of living through the coronavirus pandemic.
Not sure what to write about? Read the rest of Ms. Nierenberg’s article to find out what others around the world are recording. If you need more inspiration, here are a few writing prompts to get you started:
How has the virus disrupted your daily life? What are you missing? School, sports, competitions, extracurricular activities, social plans, vacations or anything else?
What effect has this crisis had on your own mental and emotional health?
What changes, big or small, are you noticing in the world around you?
For more ideas, see our writing prompts . We post a new one every school day, many of them now related to life during the coronavirus.
You can write in your journal every day or as often as you like. And if writing isn’t working for you right now, try a visual, audio or video diary instead.
2. Personal Narrative
As you write in your journal, you’ll probably find that your life during the pandemic is full of stories, whether serious or funny, angry or sad. If you’re so inspired, try writing about one of your experiences in a personal narrative essay.
Here’s how Mary Laura Philpott begins her essay, “ This Togetherness Is Temporary, ” about being quarantined with her teenage children:
Get this: A couple of months ago, I quit my job in order to be home more. Go ahead and laugh at the timing. I know. At the time, it was hitting me that my daughter starts high school in the fall, and my son will be a senior. Increasingly they were spending their time away from me at school, with friends, and in the many time-intensive activities that make up teenage lives. I could feel the clock ticking, and I wanted to spend the minutes I could — the minutes they were willing to give me, anyway — with them, instead of sitting in front of a computer at night and on weekends in order to juggle a job as a bookseller, a part-time gig as a television host, and a book deadline. I wanted more of them while they were still living in my house. Now here we are, all together, every day. You’re supposed to be careful what you wish for, but come on. None of us saw this coming.
Personal narratives are short, powerful stories about meaningful life experiences, big or small. Read the rest of Ms. Philpott’s essay to see how she balances telling the story of a specific moment in time and reflecting on what it all means in the larger context of her life.
To help you identify the moments that have been particularly meaningful, difficult, comical or strange during this pandemic, try responding to one of our writing prompts related to the coronavirus:
Holidays and Birthdays Are Moments to Come Together. How Are You Adapting During the Pandemic?
Has Your School Switched to Remote Learning? How Is It Going So Far?
Is the Coronavirus Pandemic Bringing Your Extended Family Closer Together?
How Is the Coronavirus Outbreak Affecting Your Life?
Another option? Use any of the images in our Picture Prompt series to inspire you to write about a memory from your life.
Related Resource: Writing Curriculum | Unit 1: Teach Narrative Writing With The New York Times

People have long turned to creative expression in times of crisis. During the coronavirus pandemic, artists are continuing to illustrate , play music , dance , perform — and write poetry .
That’s what Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell, an emergency room doctor in Boston, did after a long shift treating coronavirus patients. Called “ The Apocalypse ,” her poem begins like this:
This is the apocalypse A daffodil has poked its head up from the dirt and opened sunny arms to bluer skies yet I am filled with dark and anxious dread as theaters close as travel ends and grocery stores display their empty rows where toilet paper liquid bleach and bags of flour stood in upright ranks.
Read the rest of Dr. Mitchell’s poem and note the lines, images and metaphors that speak to you. Then, tap into your creative side by writing a poem inspired by your own experience of the pandemic.
Need inspiration? Try writing a poem in response to one of our Picture Prompts . Or, you can create a found poem using an article from The Times’s coronavirus outbreak coverage . If you have access to the print paper, try making a blackout poem instead.
Related Resources: 24 Ways to Teach and Learn About Poetry With The New York Times Reader Idea | How the Found Poem Can Inspire Teachers and Students Alike
4. Letter to the Editor
Have you been keeping up with the news about the coronavirus? What is your reaction to it?
Make your voice heard by writing a letter to the editor about a recent Times article, editorial, column or Opinion essay related to the pandemic. You can find articles in The Times’s free coronavirus coverage or The Learning Network’s coronavirus resources for students . And, if you’re a high school student, your school can get you free digital access to The New York Times from now until July 6.
To see examples, read the letters written by young people in response to recent headlines in “ How the Young Deal With the Coronavirus .” Here’s what Addie Muller from San Jose, Calif., had to say about the Opinion essay “ I’m 26. Coronavirus Sent Me to the Hospital ”:
As a high school student and a part of Generation Z, I’ve been less concerned about getting Covid-19 and more concerned about spreading it to more vulnerable populations. While I’ve been staying at home and sheltering in place (as was ordered for the state of California), many of my friends haven’t been doing the same. I know people who continue going to restaurants and have been treating the change in education as an extended spring break and excuse to spend more time with friends. I fear for my grandparents and parents, but this article showed me that we should also fear for ourselves. I appreciated seeing this article because many younger people seem to feel invincible. The fact that a healthy 26-year-old can be hospitalized means that we are all capable of getting the virus ourselves and spreading it to others. I hope that Ms. Lowenstein continues spreading her story and that she makes a full recovery soon.
As you read, note some of the defining features of a letter to the editor and what made these good enough to publish. For more advice, see these tips from Thomas Feyer, the letters editor at The Times, about how to write a compelling letter. They include:
Write briefly and to the point.
Be prepared to back up your facts with evidence.
Write about something off the beaten path.
Publishing Opportunity: When you’re ready, submit your letter to The New York Times.
5. Editorial
Maybe you have more to say than you can fit in a 150-word letter to the editor. If that’s the case, try writing an editorial about something you have a strong opinion about related to the coronavirus. What have you seen that has made you upset? Proud? Appreciative? Scared?
In “ Surviving Coronavirus as a Broke College Student ,” Sydney Goins, a senior English major at the University of Georgia, writes about the limited options for students whose colleges are now closed. Her essay begins:
College was supposed to be my ticket to financial security. My parents were the first ones to go to college in their family. My grandpa said to my mom, “You need to go to college, so you don’t have to depend on a man for money.” This same mentality was passed on to me as well. I had enough money to last until May— $1,625 to be exact — until the coronavirus ruined my finances. My mom works in human resources. My dad is a project manager for a mattress company. I worked part time at the university’s most popular dining hall and lived in a cramped house with three other students. I don’t have a car. I either walked or biked a mile to attend class. I have student debt and started paying the accrued interest last month. I was making it work until the coronavirus shut down my college town. At first, spring break was extended by two weeks with the assumption that campus would open again in late March, but a few hours after that email, all 26 colleges in the University System of Georgia canceled in-person classes and closed integral parts of campus.
Read the rest of Ms. Goins’s essay. What is her argument? How does she support it? How is it relevant to her life and the world?
Then, choose a topic related to the pandemic that you care about and write an editorial that asserts an opinion and backs it up with solid reasoning and evidence.
Not sure where to start? Try responding to some of our recent argumentative writing prompts and see what comes up for you. Here are a few we’ve asked students so far:
Should Schools Change How They Grade Students During the Pandemic?
What Role Should Celebrities Have During the Coronavirus Crisis?
Is It Immoral to Increase the Price of Goods During a Crisis?
Or, consider essential questions about the pandemic and what they tell us about our world today: What weaknesses is the coronavirus exposing in our society? How can we best help our communities right now? What lessons can we learn from this crisis? See more here.
As an alternative to a written essay, you might try creating a video Op-Ed instead, like Katherine Oung’s “ Coronavirus Racism Infected My High School. ”
Publishing Opportunity: Submit your final essay to our Student Editorial Contest , open to middle school and high school students ages 10-19, until April 21. Please be sure to read all the rules and guidelines before submitting.
Related Resource: An Argumentative-Writing Unit for Students Doing Remote Learning
Are games, television, music, books, art or movies providing you with a much-needed distraction during the pandemic? What has been working for you that you would recommend to others? Or, what would you caution others to stay away from right now?
Share your opinions by writing a review of a piece of art or culture for other teenagers who are stuck at home. You might suggest TV shows, novels, podcasts, video games, recipes or anything else. Or, try something made especially for the coronavirus era, like a virtual architecture tour , concert or safari .
As a mentor text, read Laura Cappelle’s review of French theater companies that have rushed to put content online during the coronavirus outbreak, noting how she tailors her commentary to our current reality:
The 17th-century philosopher Blaise Pascal once wrote: “The sole cause of people’s unhappiness is that they do not know how to stay quietly in their rooms.” Yet at a time when much of the world has been forced to hunker down, French theater-makers are fighting to fill the void by making noise online.
She continues:
Under the circumstances, it would be churlish to complain about artists’ desire to connect with audiences in some fashion. Theater, which depends on crowds gathering to watch performers at close quarters, is experiencing significant loss and upheaval, with many stagings either delayed indefinitely or canceled outright. But a sampling of stopgap offerings often left me underwhelmed.
To get inspired you might start by responding to our related Student Opinion prompt with your recommendations. Then turn one of them into a formal review.
Related Resource: Writing Curriculum | Unit 2: Analyzing Arts, Criticizing Culture: Writing Reviews With The New York Times
7. How-to Guide
Being stuck at home with nowhere to go is the perfect time to learn a new skill. What are you an expert at that you can you teach someone?
The Times has created several guides that walk readers through how to do something step-by-step, for example, this eight-step tutorial on how to make a face mask . Read through the guide, noting how the author breaks down each step into an easily digestible action, as well as how the illustrations support comprehension.
Then, create your own how-to guide for something you could teach someone to do during the pandemic. Maybe it’s a recipe you’ve perfected, a solo sport you’ve been practicing, or a FaceTime tutorial for someone who’s never video chatted before.
Whatever you choose, make sure to write clearly so anyone anywhere could try out this new skill. As an added challenge, include an illustration, photo, or audio or video clip with each step to support the reader’s understanding.
Related Resource: Writing Curriculum | Unit 4: Informational Writing
8. 36 Hours Column
For nearly two decades, The Times has published a weekly 36 Hours column , giving readers suggestions for how to spend a weekend in cities all over the globe.
While traveling for fun is not an option now, the Travel section decided to create a special reader-generated column of how to spend a weekend in the midst of a global pandemic. The result? “ 36 Hours in … Wherever You Are .” Here’s how readers suggest spending a Sunday morning:
8 a.m. Changing routines Make small discoveries. To stretch my legs during the lockdown, I’ve been walking around the block every day, and I’ve started to notice details that I’d never seen before. Like the fake, painted window on the building across the road, or the old candle holders that were once used as part of the street lighting. When the quarantine ends, I hope we don’t forget to appreciate what’s been on a doorstep all along. — Camilla Capasso, Modena, Italy 10:30 a.m. Use your hands Undertake the easiest and most fulfilling origami project of your life by folding 12 pieces of paper and building this lovely star . Modular origami has been my absolute favorite occupational therapy since I was a restless child: the process is enthralling and soothing. — Laila Dib, Berlin, Germany 12 p.m. Be isolated, together Check on neighbors on your block or floor with an email, text or phone call, or leave a card with your name and contact information. Are they OK? Do they need something from the store? Help with an errand? Food? Can you bring them a hot dish or home-baked bread? This simple act — done carefully and from a safe distance — palpably reduces our sense of fear and isolation. I’ve seen the faces of some neighbors for the first time. Now they wave. — Jim Carrier, Burlington, Vt.
Read the entire article. As you read, consider: How would this be different if it were written by teenagers for teenagers?
Then, create your own 36 Hours itinerary for teenagers stuck at home during the pandemic with ideas for how to spend the weekend wherever they are.
The 36 Hours editors suggest thinking “within the spirit of travel, even if many of us are housebound.” For example: an album or a song playlist; a book or movie that transports you; a particular recipe you love; or a clever way to virtually connect with family and friends. See more suggestions here .
Related Resources: Reader Idea | 36 Hours in Your Hometown 36 Hours in Learning: Creating Travel Itineraries Across the Curriculum
9. Photo Essay

Daily life looks very different now. Unusual scenes are playing out in homes, parks, grocery stores and streets across the country.
In “ New York Was Not Designed for Emptiness ,” New York Times photographers document what life in New York City looks like amid the pandemic. It begins:
The lights are still on in Times Square. Billboards blink and storefronts shine in neon. If only there were an audience for this spectacle. But the thoroughfares have been abandoned. The energy that once crackled along the concrete has eased. The throngs of tourists, the briskly striding commuters, the honking drivers have mostly skittered away. In their place is a wistful awareness that plays across all five boroughs: Look how eerie our brilliant landscape has become. Look how it no longer bustles. This is not the New York City anyone signed up for.
Read the rest of the essay and view the photos. As you read, note the photos or lines in the text that grab your attention most. Why do they stand out to you?
What does the pandemic look like where you live? Create your own photo essay, accompanied by a written piece, that illustrates your life now. In your essay, consider how you can communicate a particular theme or message about life during the pandemic through both your photos and words, like in the article you read.
Publishing Opportunity: The International Center of Photography is collecting a virtual archive of images related to the coronavirus pandemic. Learn how to submit yours here.
10. Comic Strip
Sometimes, words alone just won’t do. Visual mediums, like comics, have the advantage of being able to express emotion, reveal inner monologues, and explain complex subjects in ways that words on their own seldom can.
If anything proves this point, it is the Opinion section’s ongoing visual diary, “ Art in Isolation .” Scroll through this collection to see clever and poignant illustrations about life in these uncertain times. Read the comic “ Finding Connection When Home Alone ” by Gracey Zhang from this collection. As you read, note what stands out to you about the writing and illustrations. What lessons could they have for your own piece?
Then, create your own comic strip, modeled after the one you read, that explores some aspect of life during the pandemic. You can sketch and color your comic with paper and pen, or use an online tool like MakeBeliefsComix.com .
Need inspiration? If you’re keeping a quarantine journal, as we suggested above, you might create a graphic story based on a week of your life, or just a small part of it — like the meals you ate, the video games you played, or the conversations you had with friends over text. For more ideas, check out our writing prompts related to the coronavirus.
Related Resource: From Superheroes to Syrian Refugees: Teaching Comics and Graphic Novels With Resources From The New York Times
11. Podcast
Modern love podcast: in the midst of the coronavirus pandemic, people share their love stories.
Are you listening to any podcasts to help you get through the pandemic? Are they keeping you up-to-date on the news? Offering advice? Or just helping you escape from it all?
Create your own five-minute podcast segment that responds to the coronavirus in some way.
To get an idea of the different genres and formats your podcast could take, listen to one or more of these five-minute clips from three New York Times podcast episodes related to the coronavirus:
“ The Daily | Voices of the Pandemic ” (1:15-6:50)
“ Still Processing | A Pod From Both Our Houses ” (0:00-4:50)
“ Modern Love | In the Midst of the Coronavirus Pandemic, People Share Their Love Stories ” (1:30-6:30)
Use these as models for your own podcast. Consider the different narrative techniques they use to relate an experience of the pandemic — interviews, nonfiction storytelling and conversation — as well as how they create an engaging listening experience.
Need ideas for what to talk about? You might try translating any of the writing projects above into podcast form. Or turn to our coronavirus-related writing prompts for inspiration.
Publishing Opportunity: Submit your finished five-minute podcast to our Student Podcast Contest , which is open through May 19. Please read all the rules and guidelines before submitting.
Related Resource: Project Audio: Teaching Students How to Produce Their Own Podcasts
12. Revise and Edit
“It doesn’t matter how good you think you are as a writer — the first words you put on the page are a first draft,” Harry Guinness writes in “ How to Edit Your Own Writing .”
Editing your work may seem like something you do quickly — checking for spelling mistakes just before you turn in your essay — but Mr. Guinness argues it’s a project in its own right:
The time you put into editing, reworking and refining turns your first draft into a second — and then into a third and, if you keep at it, eventually something great. The biggest mistake you can make as a writer is to assume that what you wrote the first time through was good enough.
Read the rest of the article for a step-by-step guide to editing your own work. Then, revise one of the pieces you have written, following Mr. Guinness’s advice.
Publishing Opportunity: When you feel like your piece is “something great,” consider submitting it to one of the publishing opportunities we’ve suggested above. Or, see our list of 70-plus places that publish teenage writing and art to find more.
Natalie Proulx joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2017 after working as an English language arts teacher and curriculum writer. More about Natalie Proulx

COMMENTS
Writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19 requires a thoughtful approach to present your arguments effectively. Here are some tips to help you craft a compelling persuasive essay on this topic: Choose a Specific Angle: Narrow your focus to a specific aspect of COVID-19, like vaccination or public health measures.
Check out this informative video to learn more about effective tips and tricks for writing persuasive essays. 1. Start with an attention-grabbing hook: Use a quote, statistic, or interesting fact related to your argument at the beginning of your essay to draw the reader in. 2.
DOI: 10.1001/JAMA.2020.7308. The author discusses the economic and healthcare crisis the COVID-19 pandemic created. The projections drawn in the paper predict a 10 to 25% contraction of the US economy in the second quarter. The writer asserts that the United States has entered a COVID-19 recession.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines have been instrumental in allowing the resumption of social and economic activities, highlighting their essential role in modern society. ... Why You Should Get Vaccinated Persuasive Essay. (2022, September 27). ... To Kill a Mockingbird Cyber Bullying Fahrenheit 451 Lord of The Flies Hamlet Domestic ...
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays. Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help ...
Home>Blog>Persuasive essay>Persuasive essay about COVID 19 Persuasive Speech About Covid 19 Example Good morning/afternoon. Today I'd like to talk about the very real and urgent threat posed by Covid-19. We have all been affected by this pandemic in some shape or form, and it's important for us to take action now before more people are put at risk.
The first message is a Baseline informational control condition that describes how it is important to receive a vaccine to reduce your risk of contracting COVID-19 or spreading it to others. Informational messages have been shown to be effective at increasing COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions [24].
Drawing inspiration from Boin, Stern and Sundelius', work on persuasive narratives, this study shows the ways that Solberg's posts about COVID-19 exhibit all five identified frame functions.
Without high rates of uptake, however, the pandemic is likely to be prolonged. Here we use two survey experiments to study how persuasive messaging affects COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions. In the first experiment, we test a large number of treatment messages. One subgroup of messages draws on the idea that mass vaccination is a collective ...
We want to help inspire your writing about the coronavirus while you learn from home. Below, we offer 12 projects for students, all based on pieces from The New York Times, including personal ...