Random Assignment in Psychology: Definition & Examples
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
In psychology, random assignment refers to the practice of allocating participants to different experimental groups in a study in a completely unbiased way, ensuring each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group.
In experimental research, random assignment, or random placement, organizes participants from your sample into different groups using randomization.
Random assignment uses chance procedures to ensure that each participant has an equal opportunity of being assigned to either a control or experimental group.
The control group does not receive the treatment in question, whereas the experimental group does receive the treatment.
When using random assignment, neither the researcher nor the participant can choose the group to which the participant is assigned. This ensures that any differences between and within the groups are not systematic at the onset of the study.
In a study to test the success of a weight-loss program, investigators randomly assigned a pool of participants to one of two groups.
Group A participants participated in the weight-loss program for 10 weeks and took a class where they learned about the benefits of healthy eating and exercise.
Group B participants read a 200-page book that explains the benefits of weight loss. The investigator randomly assigned participants to one of the two groups.
The researchers found that those who participated in the program and took the class were more likely to lose weight than those in the other group that received only the book.

Importance
Random assignment ensures that each group in the experiment is identical before applying the independent variable.
In experiments , researchers will manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables. Random assignment increases the likelihood that the treatment groups are the same at the onset of a study.
Thus, any changes that result from the independent variable can be assumed to be a result of the treatment of interest. This is particularly important for eliminating sources of bias and strengthening the internal validity of an experiment.
Random assignment is the best method for inferring a causal relationship between a treatment and an outcome.
Random Selection vs. Random Assignment
Random selection (also called probability sampling or random sampling) is a way of randomly selecting members of a population to be included in your study.
On the other hand, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and treatment groups.
Random selection ensures that everyone in the population has an equal chance of being selected for the study. Once the pool of participants has been chosen, experimenters use random assignment to assign participants into groups.
Random assignment is only used in between-subjects experimental designs, while random selection can be used in a variety of study designs.
Random Assignment vs Random Sampling
Random sampling refers to selecting participants from a population so that each individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This method enhances the representativeness of the sample.
Random assignment, on the other hand, is used in experimental designs once participants are selected. It involves allocating these participants to different experimental groups or conditions randomly.
This helps ensure that any differences in results across groups are due to manipulating the independent variable, not preexisting differences among participants.
When to Use Random Assignment
Random assignment is used in experiments with a between-groups or independent measures design.
In these research designs, researchers will manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables.
There is usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable at the onset of the study.
How to Use Random Assignment
There are a variety of ways to assign participants into study groups randomly. Here are a handful of popular methods:
- Random Number Generator : Give each member of the sample a unique number; use a computer program to randomly generate a number from the list for each group.
- Lottery : Give each member of the sample a unique number. Place all numbers in a hat or bucket and draw numbers at random for each group.
- Flipping a Coin : Flip a coin for each participant to decide if they will be in the control group or experimental group (this method can only be used when you have just two groups)
- Roll a Die : For each number on the list, roll a dice to decide which of the groups they will be in. For example, assume that rolling 1, 2, or 3 places them in a control group and rolling 3, 4, 5 lands them in an experimental group.
When is Random Assignment not used?
- When it is not ethically permissible: Randomization is only ethical if the researcher has no evidence that one treatment is superior to the other or that one treatment might have harmful side effects.
- When answering non-causal questions : If the researcher is just interested in predicting the probability of an event, the causal relationship between the variables is not important and observational designs would be more suitable than random assignment.
- When studying the effect of variables that cannot be manipulated: Some risk factors cannot be manipulated and so it would not make any sense to study them in a randomized trial. For example, we cannot randomly assign participants into categories based on age, gender, or genetic factors.
Drawbacks of Random Assignment
While randomization assures an unbiased assignment of participants to groups, it does not guarantee the equality of these groups. There could still be extraneous variables that differ between groups or group differences that arise from chance. Additionally, there is still an element of luck with random assignments.
Thus, researchers can not produce perfectly equal groups for each specific study. Differences between the treatment group and control group might still exist, and the results of a randomized trial may sometimes be wrong, but this is absolutely okay.
Scientific evidence is a long and continuous process, and the groups will tend to be equal in the long run when data is aggregated in a meta-analysis.
Additionally, external validity (i.e., the extent to which the researcher can use the results of the study to generalize to the larger population) is compromised with random assignment.
Random assignment is challenging to implement outside of controlled laboratory conditions and might not represent what would happen in the real world at the population level.
Random assignment can also be more costly than simple observational studies, where an investigator is just observing events without intervening with the population.
Randomization also can be time-consuming and challenging, especially when participants refuse to receive the assigned treatment or do not adhere to recommendations.
What is the difference between random sampling and random assignment?
Random sampling refers to randomly selecting a sample of participants from a population. Random assignment refers to randomly assigning participants to treatment groups from the selected sample.
Does random assignment increase internal validity?
Yes, random assignment ensures that there are no systematic differences between the participants in each group, enhancing the study’s internal validity .
Does random assignment reduce sampling error?
Yes, with random assignment, participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either a control group or an experimental group, resulting in a sample that is, in theory, representative of the population.
Random assignment does not completely eliminate sampling error because a sample only approximates the population from which it is drawn. However, random sampling is a way to minimize sampling errors.
When is random assignment not possible?
Random assignment is not possible when the experimenters cannot control the treatment or independent variable.
For example, if you want to compare how men and women perform on a test, you cannot randomly assign subjects to these groups.
Participants are not randomly assigned to different groups in this study, but instead assigned based on their characteristics.
Does random assignment eliminate confounding variables?
Yes, random assignment eliminates the influence of any confounding variables on the treatment because it distributes them at random among the study groups. Randomization invalidates any relationship between a confounding variable and the treatment.
Why is random assignment of participants to treatment conditions in an experiment used?
Random assignment is used to ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study. This allows researchers to conclude that the outcomes of the study can be attributed to the intervention at hand and to rule out alternative explanations for study results.
Further Reading
- Bogomolnaia, A., & Moulin, H. (2001). A new solution to the random assignment problem . Journal of Economic theory , 100 (2), 295-328.
- Krause, M. S., & Howard, K. I. (2003). What random assignment does and does not do . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 59 (7), 751-766.
Random Assignment in Psychology (Definition + 40 Examples)

Have you ever wondered how researchers discover new ways to help people learn, make decisions, or overcome challenges? A hidden hero in this adventure of discovery is a method called random assignment, a cornerstone in psychological research that helps scientists uncover the truths about the human mind and behavior.
Random Assignment is a process used in research where each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group within the study. This technique is essential in experiments as it helps to eliminate biases, ensuring that the different groups being compared are similar in all important aspects.
By doing so, researchers can be confident that any differences observed are likely due to the variable being tested, rather than other factors.
In this article, we’ll explore the intriguing world of random assignment, diving into its history, principles, real-world examples, and the impact it has had on the field of psychology.
History of Random Assignment
Stepping back in time, we delve into the origins of random assignment, which finds its roots in the early 20th century.
The pioneering mind behind this innovative technique was Sir Ronald A. Fisher , a British statistician and biologist. Fisher introduced the concept of random assignment in the 1920s, aiming to improve the quality and reliability of experimental research .
His contributions laid the groundwork for the method's evolution and its widespread adoption in various fields, particularly in psychology.
Fisher’s groundbreaking work on random assignment was motivated by his desire to control for confounding variables – those pesky factors that could muddy the waters of research findings.
By assigning participants to different groups purely by chance, he realized that the influence of these confounding variables could be minimized, paving the way for more accurate and trustworthy results.
Early Studies Utilizing Random Assignment
Following Fisher's initial development, random assignment started to gain traction in the research community. Early studies adopting this methodology focused on a variety of topics, from agriculture (which was Fisher’s primary field of interest) to medicine and psychology.
The approach allowed researchers to draw stronger conclusions from their experiments, bolstering the development of new theories and practices.
One notable early study utilizing random assignment was conducted in the field of educational psychology. Researchers were keen to understand the impact of different teaching methods on student outcomes.
By randomly assigning students to various instructional approaches, they were able to isolate the effects of the teaching methods, leading to valuable insights and recommendations for educators.
Evolution of the Methodology
As the decades rolled on, random assignment continued to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of research.
Advances in technology introduced new tools and techniques for implementing randomization, such as computerized random number generators, which offered greater precision and ease of use.
The application of random assignment expanded beyond the confines of the laboratory, finding its way into field studies and large-scale surveys.
Researchers across diverse disciplines embraced the methodology, recognizing its potential to enhance the validity of their findings and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
From its humble beginnings in the early 20th century to its widespread use today, random assignment has proven to be a cornerstone of scientific inquiry.
Its development and evolution have played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of psychological research, driving discoveries that have improved lives and deepened our understanding of the human experience.
Principles of Random Assignment
Delving into the heart of random assignment, we uncover the theories and principles that form its foundation.
The method is steeped in the basics of probability theory and statistical inference, ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group, thus fostering fair and unbiased results.
Basic Principles of Random Assignment
Understanding the core principles of random assignment is key to grasping its significance in research. There are three principles: equal probability of selection, reduction of bias, and ensuring representativeness.
The first principle, equal probability of selection , ensures that every participant has an identical chance of being assigned to any group in the study. This randomness is crucial as it mitigates the risk of bias and establishes a level playing field.
The second principle focuses on the reduction of bias . Random assignment acts as a safeguard, ensuring that the groups being compared are alike in all essential aspects before the experiment begins.
This similarity between groups allows researchers to attribute any differences observed in the outcomes directly to the independent variable being studied.
Lastly, ensuring representativeness is a vital principle. When participants are assigned randomly, the resulting groups are more likely to be representative of the larger population.
This characteristic is crucial for the generalizability of the study’s findings, allowing researchers to apply their insights broadly.
Theoretical Foundation
The theoretical foundation of random assignment lies in probability theory and statistical inference .
Probability theory deals with the likelihood of different outcomes, providing a mathematical framework for analyzing random phenomena. In the context of random assignment, it helps in ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group.
Statistical inference, on the other hand, allows researchers to draw conclusions about a population based on a sample of data drawn from that population. It is the mechanism through which the results of a study can be generalized to a broader context.
Random assignment enhances the reliability of statistical inferences by reducing biases and ensuring that the sample is representative.
Differentiating Random Assignment from Random Selection
It’s essential to distinguish between random assignment and random selection, as the two terms, while related, have distinct meanings in the realm of research.
Random assignment refers to how participants are placed into different groups in an experiment, aiming to control for confounding variables and help determine causes.
In contrast, random selection pertains to how individuals are chosen to participate in a study. This method is used to ensure that the sample of participants is representative of the larger population, which is vital for the external validity of the research.
While both methods are rooted in randomness and probability, they serve different purposes in the research process.
Understanding the theories, principles, and distinctions of random assignment illuminates its pivotal role in psychological research.
This method, anchored in probability theory and statistical inference, serves as a beacon of reliability, guiding researchers in their quest for knowledge and ensuring that their findings stand the test of validity and applicability.
Methodology of Random Assignment
Implementing random assignment in a study is a meticulous process that involves several crucial steps.
The initial step is participant selection, where individuals are chosen to partake in the study. This stage is critical to ensure that the pool of participants is diverse and representative of the population the study aims to generalize to.
Once the pool of participants has been established, the actual assignment process begins. In this step, each participant is allocated randomly to one of the groups in the study.
Researchers use various tools, such as random number generators or computerized methods, to ensure that this assignment is genuinely random and free from biases.
Monitoring and adjusting form the final step in the implementation of random assignment. Researchers need to continuously observe the groups to ensure that they remain comparable in all essential aspects throughout the study.
If any significant discrepancies arise, adjustments might be necessary to maintain the study’s integrity and validity.
Tools and Techniques Used
The evolution of technology has introduced a variety of tools and techniques to facilitate random assignment.
Random number generators, both manual and computerized, are commonly used to assign participants to different groups. These generators ensure that each individual has an equal chance of being placed in any group, upholding the principle of equal probability of selection.
In addition to random number generators, researchers often use specialized computer software designed for statistical analysis and experimental design.
These software programs offer advanced features that allow for precise and efficient random assignment, minimizing the risk of human error and enhancing the study’s reliability.
Ethical Considerations
The implementation of random assignment is not devoid of ethical considerations. Informed consent is a fundamental ethical principle that researchers must uphold.
Informed consent means that every participant should be fully informed about the nature of the study, the procedures involved, and any potential risks or benefits, ensuring that they voluntarily agree to participate.
Beyond informed consent, researchers must conduct a thorough risk and benefit analysis. The potential benefits of the study should outweigh any risks or harms to the participants.
Safeguarding the well-being of participants is paramount, and any study employing random assignment must adhere to established ethical guidelines and standards.
Conclusion of Methodology
The methodology of random assignment, while seemingly straightforward, is a multifaceted process that demands precision, fairness, and ethical integrity. From participant selection to assignment and monitoring, each step is crucial to ensure the validity of the study’s findings.
The tools and techniques employed, coupled with a steadfast commitment to ethical principles, underscore the significance of random assignment as a cornerstone of robust psychological research.
Benefits of Random Assignment in Psychological Research
The impact and importance of random assignment in psychological research cannot be overstated. It is fundamental for ensuring the study is accurate, allowing the researchers to determine if their study actually caused the results they saw, and making sure the findings can be applied to the real world.
Facilitating Causal Inferences
When participants are randomly assigned to different groups, researchers can be more confident that the observed effects are due to the independent variable being changed, and not other factors.
This ability to determine the cause is called causal inference .
This confidence allows for the drawing of causal relationships, which are foundational for theory development and application in psychology.
Ensuring Internal Validity
One of the foremost impacts of random assignment is its ability to enhance the internal validity of an experiment.
Internal validity refers to the extent to which a researcher can assert that changes in the dependent variable are solely due to manipulations of the independent variable , and not due to confounding variables.
By ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being in any condition of the experiment, random assignment helps control for participant characteristics that could otherwise complicate the results.
Enhancing Generalizability
Beyond internal validity, random assignment also plays a crucial role in enhancing the generalizability of research findings.
When done correctly, it ensures that the sample groups are representative of the larger population, so can allow researchers to apply their findings more broadly.
This representative nature is essential for the practical application of research, impacting policy, interventions, and psychological therapies.
Limitations of Random Assignment
Potential for implementation issues.
While the principles of random assignment are robust, the method can face implementation issues.
One of the most common problems is logistical constraints. Some studies, due to their nature or the specific population being studied, find it challenging to implement random assignment effectively.
For instance, in educational settings, logistical issues such as class schedules and school policies might stop the random allocation of students to different teaching methods .
Ethical Dilemmas
Random assignment, while methodologically sound, can also present ethical dilemmas.
In some cases, withholding a potentially beneficial treatment from one of the groups of participants can raise serious ethical questions, especially in medical or clinical research where participants' well-being might be directly affected.
Researchers must navigate these ethical waters carefully, balancing the pursuit of knowledge with the well-being of participants.
Generalizability Concerns
Even when implemented correctly, random assignment does not always guarantee generalizable results.
The types of people in the participant pool, the specific context of the study, and the nature of the variables being studied can all influence the extent to which the findings can be applied to the broader population.
Researchers must be cautious in making broad generalizations from studies, even those employing strict random assignment.
Practical and Real-World Limitations
In the real world, many variables cannot be manipulated for ethical or practical reasons, limiting the applicability of random assignment.
For instance, researchers cannot randomly assign individuals to different levels of intelligence, socioeconomic status, or cultural backgrounds.
This limitation necessitates the use of other research designs, such as correlational or observational studies , when exploring relationships involving such variables.
Response to Critiques
In response to these critiques, people in favor of random assignment argue that the method, despite its limitations, remains one of the most reliable ways to establish cause and effect in experimental research.
They acknowledge the challenges and ethical considerations but emphasize the rigorous frameworks in place to address them.
The ongoing discussion around the limitations and critiques of random assignment contributes to the evolution of the method, making sure it is continuously relevant and applicable in psychological research.
While random assignment is a powerful tool in experimental research, it is not without its critiques and limitations. Implementation issues, ethical dilemmas, generalizability concerns, and real-world limitations can pose significant challenges.
However, the continued discourse and refinement around these issues underline the method's enduring significance in the pursuit of knowledge in psychology.
By being careful with how we do things and doing what's right, random assignment stays a really important part of studying how people act and think.
Real-World Applications and Examples

Random assignment has been employed in many studies across various fields of psychology, leading to significant discoveries and advancements.
Here are some real-world applications and examples illustrating the diversity and impact of this method:
- Medicine and Health Psychology: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) are the gold standard in medical research. In these studies, participants are randomly assigned to either the treatment or control group to test the efficacy of new medications or interventions.
- Educational Psychology: Studies in this field have used random assignment to explore the effects of different teaching methods, classroom environments, and educational technologies on student learning and outcomes.
- Cognitive Psychology: Researchers have employed random assignment to investigate various aspects of human cognition, including memory, attention, and problem-solving, leading to a deeper understanding of how the mind works.
- Social Psychology: Random assignment has been instrumental in studying social phenomena, such as conformity, aggression, and prosocial behavior, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of human interaction.
Let's get into some specific examples. You'll need to know one term though, and that is "control group." A control group is a set of participants in a study who do not receive the treatment or intervention being tested , serving as a baseline to compare with the group that does, in order to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Smoking Cessation Study: Researchers used random assignment to put participants into two groups. One group received a new anti-smoking program, while the other did not. This helped determine if the program was effective in helping people quit smoking.
- Math Tutoring Program: A study on students used random assignment to place them into two groups. One group received additional math tutoring, while the other continued with regular classes, to see if the extra help improved their grades.
- Exercise and Mental Health: Adults were randomly assigned to either an exercise group or a control group to study the impact of physical activity on mental health and mood.
- Diet and Weight Loss: A study randomly assigned participants to different diet plans to compare their effectiveness in promoting weight loss and improving health markers.
- Sleep and Learning: Researchers randomly assigned students to either a sleep extension group or a regular sleep group to study the impact of sleep on learning and memory.
- Classroom Seating Arrangement: Teachers used random assignment to place students in different seating arrangements to examine the effect on focus and academic performance.
- Music and Productivity: Employees were randomly assigned to listen to music or work in silence to investigate the effect of music on workplace productivity.
- Medication for ADHD: Children with ADHD were randomly assigned to receive either medication, behavioral therapy, or a placebo to compare treatment effectiveness.
- Mindfulness Meditation for Stress: Adults were randomly assigned to a mindfulness meditation group or a waitlist control group to study the impact on stress levels.
- Video Games and Aggression: A study randomly assigned participants to play either violent or non-violent video games and then measured their aggression levels.
- Online Learning Platforms: Students were randomly assigned to use different online learning platforms to evaluate their effectiveness in enhancing learning outcomes.
- Hand Sanitizers in Schools: Schools were randomly assigned to use hand sanitizers or not to study the impact on student illness and absenteeism.
- Caffeine and Alertness: Participants were randomly assigned to consume caffeinated or decaffeinated beverages to measure the effects on alertness and cognitive performance.
- Green Spaces and Well-being: Neighborhoods were randomly assigned to receive green space interventions to study the impact on residents’ well-being and community connections.
- Pet Therapy for Hospital Patients: Patients were randomly assigned to receive pet therapy or standard care to assess the impact on recovery and mood.
- Yoga for Chronic Pain: Individuals with chronic pain were randomly assigned to a yoga intervention group or a control group to study the effect on pain levels and quality of life.
- Flu Vaccines Effectiveness: Different groups of people were randomly assigned to receive either the flu vaccine or a placebo to determine the vaccine’s effectiveness.
- Reading Strategies for Dyslexia: Children with dyslexia were randomly assigned to different reading intervention strategies to compare their effectiveness.
- Physical Environment and Creativity: Participants were randomly assigned to different room setups to study the impact of physical environment on creative thinking.
- Laughter Therapy for Depression: Individuals with depression were randomly assigned to laughter therapy sessions or control groups to assess the impact on mood.
- Financial Incentives for Exercise: Participants were randomly assigned to receive financial incentives for exercising to study the impact on physical activity levels.
- Art Therapy for Anxiety: Individuals with anxiety were randomly assigned to art therapy sessions or a waitlist control group to measure the effect on anxiety levels.
- Natural Light in Offices: Employees were randomly assigned to workspaces with natural or artificial light to study the impact on productivity and job satisfaction.
- School Start Times and Academic Performance: Schools were randomly assigned different start times to study the effect on student academic performance and well-being.
- Horticulture Therapy for Seniors: Older adults were randomly assigned to participate in horticulture therapy or traditional activities to study the impact on cognitive function and life satisfaction.
- Hydration and Cognitive Function: Participants were randomly assigned to different hydration levels to measure the impact on cognitive function and alertness.
- Intergenerational Programs: Seniors and young people were randomly assigned to intergenerational programs to study the effects on well-being and cross-generational understanding.
- Therapeutic Horseback Riding for Autism: Children with autism were randomly assigned to therapeutic horseback riding or traditional therapy to study the impact on social communication skills.
- Active Commuting and Health: Employees were randomly assigned to active commuting (cycling, walking) or passive commuting to study the effect on physical health.
- Mindful Eating for Weight Management: Individuals were randomly assigned to mindful eating workshops or control groups to study the impact on weight management and eating habits.
- Noise Levels and Learning: Students were randomly assigned to classrooms with different noise levels to study the effect on learning and concentration.
- Bilingual Education Methods: Schools were randomly assigned different bilingual education methods to compare their effectiveness in language acquisition.
- Outdoor Play and Child Development: Children were randomly assigned to different amounts of outdoor playtime to study the impact on physical and cognitive development.
- Social Media Detox: Participants were randomly assigned to a social media detox or regular usage to study the impact on mental health and well-being.
- Therapeutic Writing for Trauma Survivors: Individuals who experienced trauma were randomly assigned to therapeutic writing sessions or control groups to study the impact on psychological well-being.
- Mentoring Programs for At-risk Youth: At-risk youth were randomly assigned to mentoring programs or control groups to assess the impact on academic achievement and behavior.
- Dance Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: Individuals with Parkinson’s disease were randomly assigned to dance therapy or traditional exercise to study the effect on motor function and quality of life.
- Aquaponics in Schools: Schools were randomly assigned to implement aquaponics programs to study the impact on student engagement and environmental awareness.
- Virtual Reality for Phobia Treatment: Individuals with phobias were randomly assigned to virtual reality exposure therapy or traditional therapy to compare effectiveness.
- Gardening and Mental Health: Participants were randomly assigned to engage in gardening or other leisure activities to study the impact on mental health and stress reduction.
Each of these studies exemplifies how random assignment is utilized in various fields and settings, shedding light on the multitude of ways it can be applied to glean valuable insights and knowledge.
Real-world Impact of Random Assignment

Random assignment is like a key tool in the world of learning about people's minds and behaviors. It’s super important and helps in many different areas of our everyday lives. It helps make better rules, creates new ways to help people, and is used in lots of different fields.
Health and Medicine
In health and medicine, random assignment has helped doctors and scientists make lots of discoveries. It’s a big part of tests that help create new medicines and treatments.
By putting people into different groups by chance, scientists can really see if a medicine works.
This has led to new ways to help people with all sorts of health problems, like diabetes, heart disease, and mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
Schools and education have also learned a lot from random assignment. Researchers have used it to look at different ways of teaching, what kind of classrooms are best, and how technology can help learning.
This knowledge has helped make better school rules, develop what we learn in school, and find the best ways to teach students of all ages and backgrounds.

Workplace and Organizational Behavior
Random assignment helps us understand how people act at work and what makes a workplace good or bad.
Studies have looked at different kinds of workplaces, how bosses should act, and how teams should be put together. This has helped companies make better rules and create places to work that are helpful and make people happy.
Environmental and Social Changes
Random assignment is also used to see how changes in the community and environment affect people. Studies have looked at community projects, changes to the environment, and social programs to see how they help or hurt people’s well-being.
This has led to better community projects, efforts to protect the environment, and programs to help people in society.
Technology and Human Interaction
In our world where technology is always changing, studies with random assignment help us see how tech like social media, virtual reality, and online stuff affect how we act and feel.
This has helped make better and safer technology and rules about using it so that everyone can benefit.
The effects of random assignment go far and wide, way beyond just a science lab. It helps us understand lots of different things, leads to new and improved ways to do things, and really makes a difference in the world around us.
From making healthcare and schools better to creating positive changes in communities and the environment, the real-world impact of random assignment shows just how important it is in helping us learn and make the world a better place.
So, what have we learned? Random assignment is like a super tool in learning about how people think and act. It's like a detective helping us find clues and solve mysteries in many parts of our lives.
From creating new medicines to helping kids learn better in school, and from making workplaces happier to protecting the environment, it’s got a big job!
This method isn’t just something scientists use in labs; it reaches out and touches our everyday lives. It helps make positive changes and teaches us valuable lessons.
Whether we are talking about technology, health, education, or the environment, random assignment is there, working behind the scenes, making things better and safer for all of us.
In the end, the simple act of putting people into groups by chance helps us make big discoveries and improvements. It’s like throwing a small stone into a pond and watching the ripples spread out far and wide.
Thanks to random assignment, we are always learning, growing, and finding new ways to make our world a happier and healthier place for everyone!
Related posts:
- 19+ Experimental Design Examples (Methods + Types)
- Cluster Sampling vs Stratified Sampling
- 41+ White Collar Job Examples (Salary + Path)
- 47+ Blue Collar Job Examples (Salary + Path)
- McDonaldization of Society (Definition + Examples)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Definition of Random Assignment According to Psychology
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Materio / Getty Images
Random assignment refers to the use of chance procedures in psychology experiments to ensure that each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to any given group in a study to eliminate any potential bias in the experiment at the outset. Participants are randomly assigned to different groups, such as the treatment group versus the control group. In clinical research, randomized clinical trials are known as the gold standard for meaningful results.
Simple random assignment techniques might involve tactics such as flipping a coin, drawing names out of a hat, rolling dice, or assigning random numbers to a list of participants. It is important to note that random assignment differs from random selection .
While random selection refers to how participants are randomly chosen from a target population as representatives of that population, random assignment refers to how those chosen participants are then assigned to experimental groups.
Random Assignment In Research
To determine if changes in one variable will cause changes in another variable, psychologists must perform an experiment. Random assignment is a critical part of the experimental design that helps ensure the reliability of the study outcomes.
Researchers often begin by forming a testable hypothesis predicting that one variable of interest will have some predictable impact on another variable.
The variable that the experimenters will manipulate in the experiment is known as the independent variable , while the variable that they will then measure for different outcomes is known as the dependent variable. While there are different ways to look at relationships between variables, an experiment is the best way to get a clear idea if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables.
Once researchers have formulated a hypothesis, conducted background research, and chosen an experimental design, it is time to find participants for their experiment. How exactly do researchers decide who will be part of an experiment? As mentioned previously, this is often accomplished through something known as random selection.
Random Selection
In order to generalize the results of an experiment to a larger group, it is important to choose a sample that is representative of the qualities found in that population. For example, if the total population is 60% female and 40% male, then the sample should reflect those same percentages.
Choosing a representative sample is often accomplished by randomly picking people from the population to be participants in a study. Random selection means that everyone in the group stands an equal chance of being chosen to minimize any bias. Once a pool of participants has been selected, it is time to assign them to groups.
By randomly assigning the participants into groups, the experimenters can be fairly sure that each group will have the same characteristics before the independent variable is applied.
Participants might be randomly assigned to the control group , which does not receive the treatment in question. The control group may receive a placebo or receive the standard treatment. Participants may also be randomly assigned to the experimental group , which receives the treatment of interest. In larger studies, there can be multiple treatment groups for comparison.
There are simple methods of random assignment, like rolling the die. However, there are more complex techniques that involve random number generators to remove any human error.
There can also be random assignment to groups with pre-established rules or parameters. For example, if you want to have an equal number of men and women in each of your study groups, you might separate your sample into two groups (by sex) before randomly assigning each of those groups into the treatment group and control group.
Random assignment is essential because it increases the likelihood that the groups are the same at the outset. With all characteristics being equal between groups, other than the application of the independent variable, any differences found between group outcomes can be more confidently attributed to the effect of the intervention.
Example of Random Assignment
Imagine that a researcher is interested in learning whether or not drinking caffeinated beverages prior to an exam will improve test performance. After randomly selecting a pool of participants, each person is randomly assigned to either the control group or the experimental group.
The participants in the control group consume a placebo drink prior to the exam that does not contain any caffeine. Those in the experimental group, on the other hand, consume a caffeinated beverage before taking the test.
Participants in both groups then take the test, and the researcher compares the results to determine if the caffeinated beverage had any impact on test performance.
A Word From Verywell
Random assignment plays an important role in the psychology research process. Not only does this process help eliminate possible sources of bias, but it also makes it easier to generalize the results of a tested sample of participants to a larger population.
Random assignment helps ensure that members of each group in the experiment are the same, which means that the groups are also likely more representative of what is present in the larger population of interest. Through the use of this technique, psychology researchers are able to study complex phenomena and contribute to our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
Lin Y, Zhu M, Su Z. The pursuit of balance: An overview of covariate-adaptive randomization techniques in clinical trials . Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;45(Pt A):21-25. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2015.07.011
Sullivan L. Random assignment versus random selection . In: The SAGE Glossary of the Social and Behavioral Sciences. SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2009. doi:10.4135/9781412972024.n2108
Alferes VR. Methods of Randomization in Experimental Design . SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2012. doi:10.4135/9781452270012
Nestor PG, Schutt RK. Research Methods in Psychology: Investigating Human Behavior. (2nd Ed.). SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2015.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- NeuroLaunch
Random Assignment in Psychology: Essential Tool for Unbiased Research
- Psychometrics
- NeuroLaunch editorial team
- September 15, 2024
- Leave a Comment
Table of Contents
From the coin flip of chance to the pursuit of unbiased truth, random assignment has become an indispensable tool in the psychologist’s quest to untangle the complexities of human behavior. This seemingly simple concept has revolutionized the way researchers approach their studies, offering a powerful means to eliminate bias and draw meaningful conclusions from their experiments. But what exactly is random assignment, and why has it become such a cornerstone of psychological research?
Imagine, if you will, a world where every psychological study was tainted by the researcher’s preconceptions or the participants’ inherent characteristics. It’s a scary thought, isn’t it? That’s where random assignment swoops in like a superhero, cape fluttering in the wind of scientific progress. By ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any experimental condition, random assignment helps to level the playing field and gives us a clearer picture of the true effects of our manipulations.
The Birth of Random Assignment: A Brief History
The story of random assignment is like a coming-of-age tale for the field of psychology. Back in the day, researchers were often at the mercy of their own biases and the quirks of their participants. They’d scratch their heads, wondering why their results seemed so inconsistent or why their findings didn’t quite match up with reality.
Enter Sir Ronald Fisher, a British statistician and biologist who, in the 1920s, introduced the concept of randomization to experimental design. It was like he’d handed psychologists a pair of X-ray glasses, allowing them to see through the fog of confounding variables and into the heart of cause-and-effect relationships.
Fisher’s ideas didn’t catch on overnight, though. It took time for the psychological community to fully embrace random assignment. But as researchers began to see the power of this approach in action, it quickly became a gold standard in experimental design.
Random Assignment Psychology: Simple Definition and Concept
So, what exactly is random assignment in psychology? Well, it’s not rocket science, but it is pretty clever. At its core, random assignment is the process of allocating participants to different experimental conditions in a way that gives each person an equal chance of being placed in any group.
Think of it like a very scientific version of drawing names out of a hat. Except instead of picking teams for dodgeball, we’re assigning people to different experimental conditions. The key here is that the assignment is, well, random. No favoritism, no patterns, just pure, unadulterated chance.
But don’t confuse random assignment with its cousin, random sampling . While they might sound similar, they serve different purposes. Random sampling is all about how we select participants from a larger population, aiming to create a representative group. Random assignment, on the other hand, is about how we divvy up those participants once they’re in our study.
Let’s look at an example to make this clearer. Imagine we’re studying the effects of a new therapy for depression. We’ve got 100 participants, all diagnosed with depression. Using random assignment, we might use a computer program to randomly assign 50 participants to receive the new therapy and 50 to receive a standard treatment. This way, we can be reasonably confident that any differences we observe between the groups are due to the therapy itself, rather than other factors like age, gender, or severity of depression.
The Importance of Random Assignment in Psychological Research
Now, you might be wondering, “Why go to all this trouble? Can’t we just divide people up however we want?” Well, we could, but then we’d be opening a whole can of worms when it comes to interpreting our results.
Random assignment is like a secret weapon in the fight against bias and confounding variables. By distributing participants randomly, we’re spreading out all those pesky individual differences that could muddy our results. It’s like we’re creating a level playing field where the only real difference between our groups is the experimental manipulation we’re interested in.
This is crucial for enhancing the internal validity of our studies. Internal validity is all about being able to say with confidence that our independent variable (the thing we’re manipulating) is actually causing the changes we see in our dependent variable (the thing we’re measuring). Without random assignment, we’d always be left wondering whether our results were due to our manipulation or some other factor we hadn’t accounted for.
Random assignment also allows us to make causal inferences. In other words, it helps us move from saying “A and B are related” to “A causes B.” This is a big deal in psychology, where we’re often trying to understand the causes of behavior and mental processes.
Implementing Random Assignment in Psychological Experiments
So, how do we actually go about randomly assigning participants? Well, in the old days, it might have involved a lot of coin flipping or drawing names out of a hat. These days, we’ve got technology on our side.
Many researchers use specialized software or online tools to generate random assignments. These tools use complex algorithms to ensure true randomness, which is harder to achieve than you might think. After all, humans are notoriously bad at being random – we tend to see patterns even where none exist.
But implementing random assignment isn’t always a walk in the park. There can be challenges, especially in real-world settings. For example, in a study on a new educational intervention, it might not be feasible to randomly assign students to different classrooms. In cases like these, researchers might turn to quasi-experimental designs , which try to approximate the benefits of random assignment as closely as possible.
There are also ethical considerations to keep in mind. While random assignment is generally considered ethical in most psychological research, there can be exceptions. For instance, if we’re testing a potentially life-saving treatment, it might not be ethical to randomly assign some participants to a control group that doesn’t receive the treatment.
Random Assignment vs. Other Research Design Approaches
Random assignment isn’t the only game in town when it comes to research design. It’s important to understand how it stacks up against other approaches.
Compared to quasi-experimental designs, random assignment offers stronger internal validity. However, quasi-experimental designs can sometimes offer better external validity – that is, they might better reflect real-world conditions.
In longitudinal studies, where we follow participants over an extended period, random assignment can be particularly powerful. It allows us to track how our experimental manipulation affects participants over time, while still controlling for potential confounds.
Random assignment can be applied in various types of psychological research, from clinical trials testing new therapies to social psychology experiments examining group dynamics. However, it’s not always the best fit. In some cases, researchers might combine random assignment with other methodologies to get the best of both worlds.
Impact of Random Assignment on Psychology Research Outcomes
The proof, as they say, is in the pudding. So, what impact has random assignment had on psychological research outcomes?
Let’s look at a classic example: the Stanford Prison Experiment. While this study is now controversial for ethical reasons, it demonstrates the power of random assignment. By randomly assigning participants to be “guards” or “prisoners,” the researchers were able to show how situational factors can dramatically influence behavior, regardless of individual personalities.
Random assignment has also been crucial in clinical psychology research. For instance, studies comparing different types of psychotherapy often use random assignment to ensure that any differences in outcomes are due to the therapies themselves, rather than differences in the types of clients each therapy attracts.
In terms of statistical analysis, random assignment allows researchers to use powerful inferential statistics. These tools help us determine whether the differences we observe between groups are likely to be real effects or just due to chance.
Perhaps most importantly, random assignment has played a key role in the development of evidence-based practices in psychology. By allowing for more rigorous, controlled studies, it has helped psychologists identify which interventions and treatments are truly effective.
The Future of Random Assignment in Psychological Research
As we look to the future, random assignment is likely to remain a cornerstone of psychological research. However, new challenges and opportunities are emerging.
One exciting area is the integration of random assignment with big data approaches. As we collect more and more data on human behavior, random assignment can help us make sense of these vast datasets and draw meaningful conclusions.
There’s also growing interest in adaptive random assignment techniques. These approaches adjust the assignment probabilities based on incoming data, potentially allowing for more efficient and ethical studies.
Another frontier is the use of random assignment in online and mobile studies. As more research moves into digital spaces, new tools and techniques for implementing random assignment in these environments are being developed.
In conclusion, random assignment has come a long way since its introduction to psychological research. From a novel idea to a fundamental tool, it has shaped the way we understand human behavior and mental processes. As we continue to grapple with the complexities of the human mind, random assignment will undoubtedly remain an essential ally in our quest for knowledge.
But let’s not forget – while random assignment is a powerful tool, it’s not a magic wand. It’s one piece of the puzzle in conducting rigorous, meaningful psychological research. As with any scientific method, it must be used thoughtfully and in conjunction with other sound research practices.
So, the next time you read about a psychological study, spare a thought for random assignment. It might not be the most glamorous aspect of the research, but it’s working behind the scenes to ensure that what you’re reading is as close to the truth as we can get. And in the complex, often messy world of human behavior, that’s no small feat.
References:
1. Fisher, R. A. (1935). The Design of Experiments. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh.
2. Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Houghton Mifflin.
3. Schulz, K. F., & Grimes, D. A. (2002). Generation of allocation sequences in randomised trials: chance, not choice. The Lancet, 359(9305), 515-519.
4. Suresh, K. (2011). An overview of randomization techniques: An unbiased assessment of outcome in clinical research. Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences, 4(1), 8-11.
5. Haslam, S. A., & Reicher, S. D. (2012). Contesting the “nature” of conformity: What Milgram and Zimbardo’s studies really show. PLoS Biology, 10(11), e1001426.
6. Kendall, J. M. (2003). Designing a research project: randomised controlled trials and their principles. Emergency Medicine Journal, 20(2), 164-168.
7. Moher, D., Hopewell, S., Schulz, K. F., Montori, V., Gøtzsche, P. C., Devereaux, P. J., … & Altman, D. G. (2010). CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ, 340, c869.
8. Efron, B. (1971). Forcing a sequential experiment to be balanced. Biometrika, 58(3), 403-417.
9. Friedman, L. M., Furberg, C., DeMets, D. L., Reboussin, D. M., & Granger, C. B. (2015). Fundamentals of clinical trials (5th ed.). Springer.
10. Kazdin, A. E. (2016). Research design in clinical psychology (5th ed.). Pearson.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Cookie Policy
About NeuroLaunch
- Copyright Notice
- Accessibility Statement
- Advertise With Us
- Mental Health
Purpose and Limitations of Random Assignment
In an experimental study, random assignment is a process by which participants are assigned, with the same chance, to either a treatment or a control group. The goal is to assure an unbiased assignment of participants to treatment options.
Random assignment is considered the gold standard for achieving comparability across study groups, and therefore is the best method for inferring a causal relationship between a treatment (or intervention or risk factor) and an outcome.
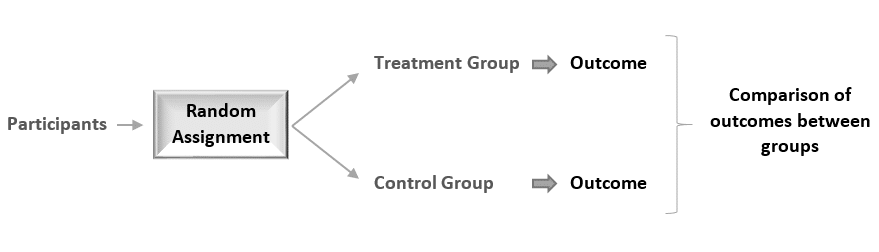
Random assignment of participants produces comparable groups regarding the participants’ initial characteristics, thereby any difference detected in the end between the treatment and the control group will be due to the effect of the treatment alone.
How does random assignment produce comparable groups?
1. random assignment prevents selection bias.
Randomization works by removing the researcher’s and the participant’s influence on the treatment allocation. So the allocation can no longer be biased since it is done at random, i.e. in a non-predictable way.
This is in contrast with the real world, where for example, the sickest people are more likely to receive the treatment.
2. Random assignment prevents confounding
A confounding variable is one that is associated with both the intervention and the outcome, and thus can affect the outcome in 2 ways:
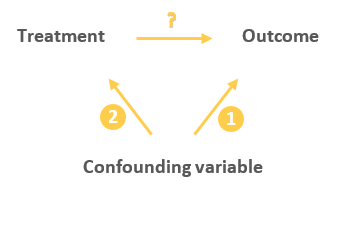
Either directly:

Or indirectly through the treatment:

This indirect relationship between the confounding variable and the outcome can cause the treatment to appear to have an influence on the outcome while in reality the treatment is just a mediator of that effect (as it happens to be on the causal pathway between the confounder and the outcome).
Random assignment eliminates the influence of the confounding variables on the treatment since it distributes them at random between the study groups, therefore, ruling out this alternative path or explanation of the outcome.
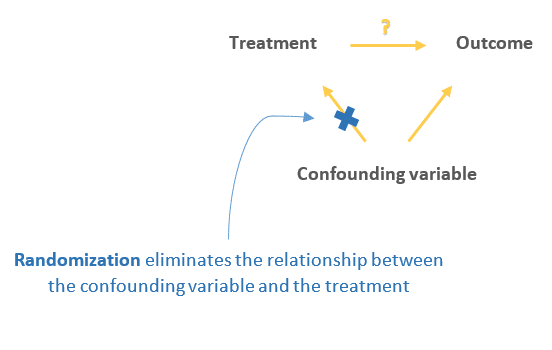
3. Random assignment also eliminates other threats to internal validity
By distributing all threats (known and unknown) at random between study groups, participants in both the treatment and the control group become equally subject to the effect of any threat to validity. Therefore, comparing the outcome between the 2 groups will bypass the effect of these threats and will only reflect the effect of the treatment on the outcome.
These threats include:
- History: This is any event that co-occurs with the treatment and can affect the outcome.
- Maturation: This is the effect of time on the study participants (e.g. participants becoming wiser, hungrier, or more stressed with time) which might influence the outcome.
- Regression to the mean: This happens when the participants’ outcome score is exceptionally good on a pre-treatment measurement, so the post-treatment measurement scores will naturally regress toward the mean — in simple terms, regression happens since an exceptional performance is hard to maintain. This effect can bias the study since it represents an alternative explanation of the outcome.
Note that randomization does not prevent these effects from happening, it just allows us to control them by reducing their risk of being associated with the treatment.
What if random assignment produced unequal groups?
Question: What should you do if after randomly assigning participants, it turned out that the 2 groups still differ in participants’ characteristics? More precisely, what if randomization accidentally did not balance risk factors that can be alternative explanations between the 2 groups? (For example, if one group includes more male participants, or sicker, or older people than the other group).
Short answer: This is perfectly normal, since randomization only assures an unbiased assignment of participants to groups, i.e. it produces comparable groups, but it does not guarantee the equality of these groups.
A more complete answer: Randomization will not and cannot create 2 equal groups regarding each and every characteristic. This is because when dealing with randomization there is still an element of luck. If you want 2 perfectly equal groups, you better match them manually as is done in a matched pairs design (for more information see my article on matched pairs design ).
This is similar to throwing a die: If you throw it 10 times, the chance of getting a specific outcome will not be 1/6. But it will approach 1/6 if you repeat the experiment a very large number of times and calculate the average number of times the specific outcome turned up.
So randomization will not produce perfectly equal groups for each specific study, especially if the study has a small sample size. But do not forget that scientific evidence is a long and continuous process, and the groups will tend to be equal in the long run when a meta-analysis aggregates the results of a large number of randomized studies.
So for each individual study, differences between the treatment and control group will exist and will influence the study results. This means that the results of a randomized trial will sometimes be wrong, and this is absolutely okay.
BOTTOM LINE:
Although the results of a particular randomized study are unbiased, they will still be affected by a sampling error due to chance. But the real benefit of random assignment will be when data is aggregated in a meta-analysis.
Limitations of random assignment
Randomized designs can suffer from:
1. Ethical issues:
Randomization is ethical only if the researcher has no evidence that one treatment is superior to the other.
Also, it would be unethical to randomly assign participants to harmful exposures such as smoking or dangerous chemicals.
2. Low external validity:
With random assignment, external validity (i.e. the generalizability of the study results) is compromised because the results of a study that uses random assignment represent what would happen under “ideal” experimental conditions, which is in general very different from what happens at the population level.
In the real world, people who take the treatment might be very different from those who don’t – so the assignment of participants is not a random event, but rather under the influence of all sort of external factors.
External validity can be also jeopardized in cases where not all participants are eligible or willing to accept the terms of the study.
3. Higher cost of implementation:
An experimental design with random assignment is typically more expensive than observational studies where the investigator’s role is just to observe events without intervening.
Experimental designs also typically take a lot of time to implement, and therefore are less practical when a quick answer is needed.
4. Impracticality when answering non-causal questions:
A randomized trial is our best bet when the question is to find the causal effect of a treatment or a risk factor.
Sometimes however, the researcher is just interested in predicting the probability of an event or a disease given some risk factors. In this case, the causal relationship between these variables is not important, making observational designs more suitable for such problems.
5. Impracticality when studying the effect of variables that cannot be manipulated:
The usual objective of studying the effects of risk factors is to propose recommendations that involve changing the level of exposure to these factors.
However, some risk factors cannot be manipulated, and so it does not make any sense to study them in a randomized trial. For example it would be impossible to randomly assign participants to age categories, gender, or genetic factors.
6. Difficulty to control participants:
These difficulties include:
- Participants refusing to receive the assigned treatment.
- Participants not adhering to recommendations.
- Differential loss to follow-up between those who receive the treatment and those who don’t.
All of these issues might occur in a randomized trial, but might not affect an observational study.
- Shadish WR, Cook TD, Campbell DT. Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs for Generalized Causal Inference . 2nd edition. Cengage Learning; 2001.
- Friedman LM, Furberg CD, DeMets DL, Reboussin DM, Granger CB. Fundamentals of Clinical Trials . 5th ed. 2015 edition. Springer; 2015.
Further reading
- Posttest-Only Control Group Design
- Pretest-Posttest Control Group Design
- Randomized Block Design

IMAGES
VIDEO