- Speech Crafting →

Examples of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Persuasive Speeches

Ever fumbled for words while convincing someone to sign up for your club or buy something you're promoting on stage?
It happens. For this reason, Aristotle came up with three essential tools you can use in your everyday speech to persuade people for almost anything: ethos, pathos, and logos.
Here are some vivid examples of ethos, pathos, and logos to help you understand what they are and how to use them in your arguments.
The Three Tools That Guide Your Speech
Ethos, pathos, and logos are Greek words that make up the rhetorical triangle. Aristotle was the first to come up with them and wrote these concepts in his book, Rhetoric .
You can use them in any argument if you want to drive your point across or sell something: an idea, a product, or a brand.
Whether it is a sales pitch, a compelling argument, or a speech, these three modes of persuasion can sway your audience's perspective. Their presence since ancient times depicts their strength and significance.
Ethos is Greek for “character,” "credibility," or "authority." It refers to a person's character when they are presenting an argument.
The stronger the character or, the more influential the speaker is, the more they can change someone’s point of view regarding a particular subject.
You wouldn’t be enraptured, hanging on to her every word when J.K Rowling was giving a TED talk if she wasn’t a famous author, right?
Therefore, many brands and companies try to get celebrities to advertise for them. When people become fans, they religiously love what the celebrity loves and hates what the celebrity doesn't like.
This is the power of ethos. Here is how to establish ethos in a speech .

There are tons of examples of ethos in advertisements, movies, speeches, and daily life. Highlighted below are some of them.
Albus Dumbledor used ethos in the movie The Goblet of Fire when he went against the Ministry of Magic to tell his students how Cedric Diggory died. He knew they would believe him because he was Headmaster. He said:
"I think, therefore, you have the right to know exactly how he died. You see, Cedric Diggory was murdered by Lord Voldemort. The Ministry of Magic does not wish me to tell you this. But I think to do so would be an insult to his memory."
In a commercial, you’d see 4 out of 5 dentists recommending a particular toothpaste. That's how brands convince viewers to buy their products by backing them up with credible people.
As a physics student, you tune in to a TED talk by Brian Greene and believe everything he says because he’s a theoretical physicist and a string theorist.
Pathos is Greek for “emotion,” “suffering,” or “experience.” This rhetorical strategy appeals to people's feelings when used in an argument.
It invokes people’s senses, nostalgia, memory, and experiences. It is used in ads and videos to persuade people to follow a call to action.
When pathos is embedded in a message, it moves people, driving them to take action. Pathos can trigger any intended emotion in people, such as sympathy, pity, and empathy.
Why do you think romance sells so much, be it novels, movies, or stories? It pulls at the reader’s heartstrings, connects them to the characters, and makes them want something similar.
Below are some examples of pathos in everyday life, movies, and ads.
An excellent way to convince people to donate to a puppy shelter is to show them how brutally they'll die if they don't donate.
The Evian commercial in which adults look like toddlers when they look at their reflections depicts the "bandwagon effect." Light-heartedly, it uses feel-good emotion to convince people to buy their water.
In their ad, IKEA convinces people to opt for home delivery for £3.95 by showing a person stuck in traffic after buying from the brand. This appeals to people because we like comfort, right?
Unlike ethos and pathos, logos rely on logic. It is a Greek word that means “logic” or “reason.” It uses logical reasons to convince people about something.
When you use logos in your everyday speech or arguments, you try to mention facts or data to support your idea.

While ethos uses the speaker's credibility to persuade people about something, pathos uses emotion to trigger people. Logos simply relies on logic and cuts to the chase.
You can easily persuade an audience using reason and logic in your argument; however, emotions do get the best of us as humans. For this reason, there are three modes of persuasion.
The following are a few examples of Logos.
Al Gore, a renowned environmentalist, used logos in his speech “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” in 2019. He tells people what exactly is happening that is causing climate change and cites scientific research and experts in his speech as well:
"I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face."
In the Versatile Stain Remover ad by OxiClean, you see Billy Mays use the stain remover to clean different products to showcase the product's ability as a stain remover.
An iPhone commercial shows the smartphone's different features that make it stand out from the rest.
Some More Examples of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
Almost everyone uses these three modes of persuasion in one form or the other in their arguments. Let’s see how famous people have used them through time.
"During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife.
Pixar went on to create the world's first computer-animated feature film, Toy Story and is now the most successful animation studio in the world.
In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple's current renaissance."
—Steve Jobs, 2005
Steve Jobs, the co-founder of Apple, relies heavily on ethos here. He uses his authority as a founder of successful tech companies to show people why they should listen to him.
"I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations.
Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality."
—Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
Martin Luther King Jr. was famous for fighting for civil rights. In the above excerpt from his speech “I Have a Dream,” he uses pathos to empathize with his audience.
He informs them that he understands they have suffered a lot and have come out of a painful time. This evokes emotion in the audience, and they can connect with King easily.
"Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be.
But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better-adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature that would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders.
In such a case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favored the individuals of any of the species by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement."
—Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species, 1859
Charles Darwin appeals to logic or logos in his book Origin of the Species by talking about the rationale of natural selection.
He talks about how species have evolved with time to better adapt to their environment, a.k.a survival of the fittest. You can see how he uses a logical argument to talk about natural selection.
Conclusion: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Ethos, pathos, and logos have survived the test of time and are used almost everywhere today. You can find them embedded in commercials, movies, speeches, TED talks, and day-to-day arguments.
These three tools of persuasion appeal to different aspects of humanity: authority, emotion, and logic. When used together, they form a solid argument that can convince anyone of its gist.
Ethos uses the speaker’s authority or credibility to persuade the audience. Pathos uses emotion to trigger people to take action. On the other hand, logos rely on facts and logic to drive a point across.
All three are very important to use in any argument.


Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
April 11, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
Persuasive speaking is a skill that you can apply regularly throughout your life, whether you are selling a product or being interviewed. 2,300 years ago, Aristotle determined the components needed for persuasive speaking. They are referred to as the three pillars of persuasion – ethos, pathos and logos. In this article, we discuss how to use the three pillars for public speaking.
What are ethos, pathos and logos?
Ethos, pathos and logos are modes of persuasion used to convince and appeal to an audience. You need these qualities for your audience to accept your messages.
- Ethos : your credibility and character
- Pathos : emotional bond with your listeners
- Logos : logical and rational argument
Ethos – The Ethical Appeal
Ethos is Greek for “character” and “ethic” is derived from ethos.
Ethos consists of convincing your audience that you have good character and you are credible therefore your words can be trusted. Ethos must be established from the start of your talk or the audience will not accept what you say.
In fact, ethos is often established before your presentation, for example, you may be the CEO of the company you’re presenting to so you’re already perceived as a specialist.
Why is ethos important?
| High Ethos | Low Ethos |
|---|---|
| Audience will concentrate and listen | Audience will not concentrate or listen |
| Audience assumes you will share something useful and they respect you | Low expectations and if you start poorly the audience will not listen |
| Audience are more likely to be persuaded | Audience are less likely to be persuaded |
| You can give a bad speech but you are still able to persuade the audience | Your speech needs to be very good to persuade the audience |
Characteristics of ethos
There are four main characteristics of ethos:
- Trustworthiness and respect
- Similarity to the audience
- Expertise and reputation/history
1. Trustworthiness and respect
The audience are more likely to be respect you and think that what you’re saying is true if they perceive you as trustworthy . This judgement is formed using factors such as:
- Ethics and values
- Generosity and sharing
- If you’re part of a group that stands for the above values, such as an NSPCC worker
2. Similarity to the audience
Listeners are more likely to be convinced by someone they can relate to. For example, you may share:
- Age and gender
- Race and culture
- Personality etc
If you do not share traits with your audience you can choose to adjust your:
- Mannerisms and gestures
- Visual aids
But don’t do too much as your listeners will seen you as not being genuine.

Tony Robbins, a well known authority in the life coaching space, giving a TED Talk on ‘Why we do what we do’.
3. Authority
If the audience perceive that you are an expert they are more likely to be persuaded by what you say. Remember that every presenter has authority because they are the speaker.
For example:
- Political authority e.g. a prime minister
- Educational authority e.g. teacher
4. Expertise and reputation
Expertise is your knowledge of the subject.
Reputation is what your audience knows about your knowledge of the subject.
Reputation depends on:
- Achievements or acknowledgments from others in the area, such as, awards and testimonials.
- Your experience and the amount of years you have worked in this area.
- How involved you were with this topic – are you a key character?
- Your expertise should be verified, for example, you may be talking about different therapy treatments and your expertise is shown by you being a successful Clinical Psychologist.
- Your contribution to the area , perhaps through blogs, books, papers and products.
- Your authority
Merging the four characteristics of ethos
Not all of characteristics have to be present to develop high ethos, for example, a university lecturer speaking to her students is most likely perceived as trustworthy as the lecturer is known to provide correct information, she has authority over the 18-21 year olds due to her job title and her age.
But she’s not similar to her students because of this. She has been working in this area for 30 years and at the university for 5 years (expertise) and has contributed largely to the area through a number of studies and subsequent papers (reputation). This is enough ethos for the audience to be persuaded by what she says.
Another person, such as a manager addressing her employees may have a different combination of these traits but still have enough ethos. It’s hard to achieve complete ethos, especially considering that having authority often reduces similarity.
Improve ethos
Authority and reputation are usually predetermined before your presentation so it’s difficult to change the audience’s mind about this. But it’s easier to change people’s perception about how trustworthy and how alike you are during the presentation.
Improve ethos day to day:
- Become an expert in the topics you present on because people are more likely to want to listen to someone who has researched a topic for 10 years rather than 2 years.
- Ensure that people know about your expertise by promoting yourself, for example, ensure that people can easily access testimonials, reviews, papers etc.
- Treat the trustworthy characteristics as your values, so practice being honest, ethical, compassionate etc.
Improve ethos before a speech:
- Research your audience , especially concentrating on the traits you share, so you know how to appeal to them.
- Show up early to the presentation venue to show the audience that you want to be there.
- If, for example, you are speaking at a wider event, such as a conference, try to attend as much of it as possible. This means that you and the audience are sharing an experience so they are more likely to perceive you as similar to them.
- If the venue requires information to advertise your presentation, emphasise your ethos in this material so people will know why they should come and see your talk.

Telling personal stories during a presentation is a great way to increase ethos.
Increase ethos during a speech:
- In your introduction draw attention to your ethos because this is the best way to demonstrate your credentials to that particular audience on that particular day. Highlight vital facts that demonstrate the main four traits of ethos but which are relevant to the topic and the audience. Don’t make the introduction long and irrelevant.
- Tell personal stories that show the audience that you follow your own recommendations because they are more likely to believe you on other points that cannot easily be confirmed.
- Facts, stats and quotes should be up-to-date and from reputable sources, for example, between choosing from social media or Mind’s website to quote a statistic about anxiety, you would choose Mind’s website as this has high ethos which in turn increases your ethos.
- Reference people in the audience or previous speakers or events earlier that day. This forms connections with the audience.
- Be unbiased by admitting that you and your opposition’s side agree on at least one matter. This highlights that you are credible because you are treating the topic with consideration and fairness.
Improve ethos after the presentation
- Always stay for as long as you can after your speech in case audience members want to speak with you. This will also help with future presentations as it’s likely that this will become part of your reputation.
- Stick to your promises, for example, during the questions and answers session you may have agreed to find out an answer to a question and tell everyone – ensure that you do this to be seen as honest.
Pathos – The Emotional Appeal
Pathos is Greek for suffering and experience. Empathy, sympathy and pathetic are derived from pathos.
Pathos is to persuade by appealing to the audience’s emotions. As the speaker, you want the audience to feel the same emotions you feel about something, you want to emotionally connect with them and influence them. If you have low pathos the audience is likely to try to find flaws in your arguments.
Why is pathos important?
Emotions are motivators so the audience is more likely to be persuaded and act on your requests by using pathos. Pathos is more likely to increase the chances of your audience:
- Understanding your point of view.
- Accepting your arguments.
- Acting on your requests.
Example of pathos during a speech
Girls Who Code Founder Reshma Saujani explains how one of her students created an algorithm to detect false positives in breast cancer testing after her dad was diagnosed with cancer.
Watch the full video here: Why We Need Women in Tech
Improving pathos
- Choose emotional points and topics , for example “Beat your social anxiety” would trigger more powerful emotions than “Learn how to speak in a group.”
- Use analogies and metaphors – linking your ideas with something your listeners already know about and feel strongly about can trigger emotional responses. For example, “They are awful” compared to “They are poisonous.” This will use the audience’s knowledge that poison is bad and therefore this issue needs to be dealt with.
- Use emotionally charged words , for example, say “This kitchen roll is a life-saver” rather than “This kitchen roll is great”. Another way to make a statement more emotional is to use vivid and sensory words which allow the audience to experience the emotion. For instance, “The smell of your grandparents’ house” will increase the recollection of hopefully warm memories, and therefore will trigger certain emotions.
- Positive emotions, such as joy, should be linked with your claims.
- Negative emotions, such as anger, should be linked to your rival’s claims.
- Using humour increases the likelihood that the audience are enjoying themselves and so they are more likely to like you and listen to you.
- Visual aids can sometimes be more powerful than words, for example, showing an image of a scared small child will have more impact than saying that children are often victims of domestic violence.
- Research your audience and find out what their shared values are. Target these values and beliefs because they are strongly associated to emotions.
- Storytelling is a quick way to form an emotional connection. It’s often used to link a part of a key message with an emotional response – you’ll be familiar with seeing this in adverts asking for charity donations.
- Match what you’re saying with your body language , face and eyes. People often mirror emotions so by matching your body language with your words you increase the chances of triggering the desired emotions.
- Also match your voice to your words , for example, if you want to show sadness speak in a soft voice , if you want to show excitement then increase your pace etc.
- Stand as close as you can to the audience so the speech feels more personal – don’t hide behind the computer screen.
- Use words that carry suitable connotations , for example, if you asked a group of men whether they would like to be called “tall”, “lanky” or “big”. Even though the words have essentially the same meaning, the men are more likely to choose the word that has the most positive connotation, in this case the word “tall”.
- If you have accidentally caused a negative emotion find out why and apologise . For example, perhaps there have been severe interpersonal conflicts that you were unaware of and a joke you made upset audience members.
Logos – The Logical Appeal
The word “logic” is derived from logos.
Logos is to appeal to logic by relying on the audience’s intelligence and offering evidence in support of your argument. Logos also develops ethos because the information makes you look knowledgeable. Ask the following questions to decide if you have achieved logos:
- Are my messages coherent?
- Does the evidence support my claims?
- Will the audience’s actions lead to my desired outcome?
Why is logos important?
Essentially, logical arguments that make sense are not easily dismissed.
Improving logos
- Be comprehensive : Make sure your points and arguments can be understood
- Be logical : Ensure that your arguments make sense and that your claims and evidence are not implausible. Have a plan for dealing with opposing viewpoints that your listeners may already believe.
- Be specific : Base your claims on facts and examples as your arguments will be accepted quicker than something nonspecific and non-concrete. The more easily the evidence is accepted, the more easily the conclusions will be accepted.
Be comprehensive
- Use language that your audience will understand. Avoid jargon and technical terminology.
- Use simple figures and charts to make the presentations more understandable.
- Make the relationship between your evidence and conclusions clear.
- Analogies and metaphors are helpful especially when explaining new ideas and theories.

Engage the audience by asking them questions during your speech to increase logos.
- Ensure that the audience is involved by asking them engaging questions. This will make them active listeners so they may even come to your conclusion themselves.
- Talk about opposing views as this allows you to explain why your logical arguments are more reasonable.
- Deductive reasoning is looking at the evidence and coming to a conclusion . For example. “I don’t like loud places. That restaurant is really loud. So I won’t like that restaurant.”
- Inductive reasoning is when you add rational pieces, perhaps beliefs, to the evidence and come to a conclusion. The evidence is used to infer a conclusion but the conclusion is not guaranteed. For example: “All the vegan restaurants I have eaten in have been good. This is a vegan restaurant. So it must be good.”
The audience are using both types of reasoning as you speak, so their beliefs may interfere with them accepting your conclusions. Overcome these by building your argument on the audience’s widely held beliefs – commonplaces. For example, a company’s main value and therefore commonplace may be “Compassion makes us the best company”.
Use the audience’s commonplace like a fact and apply it to a new situation. So if you want to encourage your staff to join a committee, use their commonplace, for example, rather than your belief say: “This committee needs considerate and kind-hearted people.”
Be specific
- Facts and stats cannot be debated and they signify the truth.
- Visual evidence, such as, objects and videos are hard to challenge.
- Citing specialists and authorities on a topic increases the quality of your evidence and therefore your claims.
- Tell stories, such as, case studies or personal experiences. The audience would like to hear your own stories if you’re a specialist, for example, “When I was excavating in Nottingham…”
There is uncertainty over which pillar is the most important – Aristotle thought that logos was vital but when used by itself it lacks impact. So ensure that you treat all three pillars with equal importance to succeed in persuading your audience.

Understanding Ethos, Pathos, and Logos: The Foundations of Persuasive Speaking
- Carolyn Manion Kinnie
- January 30, 2024
Table of Contents
Here at The Speaker Lab, we talk a lot about how to launch a speaking business. Usually, we focus on the “business” part. Fundamentals like establishing your pipeline and setting your speaker fee are key to really succeeding as a speaker. But mastering the business side will only take you so far if your talk isn’t persuasive! How do you make sure your message sticks with your audience? That’s what we’re diving into today. Learning how to speak persuasively will help you deliver a compelling talk that listeners remember. And what do we find at the heart of persuasive speaking? Three age old terms coined by an ancient Greek: ethos, pathos, and logos.
Today we’re breaking down how ethos, pathos, and logos play a role in persuasive speaking in any field, on any topic. If you’re busy crafting your signature talk , it’s easy to get caught up in the weeds and forget to look at the big picture. That’s why we’re getting back to the basics–all the way back to the fourth century B.C.
Aristotle and Persuasive Rhetoric
Aristotle’s Rhetoric is one of the foundational philosophical works at the basis of what we consider persuasive speaking. In the Rhetoric, he explains that ethos, pathos, and logos are three ways that any speech–no matter what kind of speech–can have a persuasive effect. So what exactly do these words mean?
Ethos refers to the character of the speaker. Good, bad, old, young, famous, obscure…any attribute that belongs to the speaker as a person . Would you more willingly listen to someone whose character is honest and trustworthy or a well-known con man? The ancient Greeks felt the same way. Listeners are more likely to take advice from a speaker whose character they trust.
Keep in mind that character qualities in a speaker can be positive or negative depending on context. A speaker’s age on either end of the spectrum can give a negative impression of either inexperience or outdatedness. But youthfulness characterized by drive and ambition (or old age characterized by wisdom and self-reflection) comes across extremely favorably, especially to other young people!
If ethos centers on the speaker, pathos centers on the audience. A speaker leveraging e thos appeals to their own character, one using pathos appeals to emotion. To master pathos, you must influence your audience’s emotional state throughout your talk in a way that contributes to your message. While your credibility goes a long way toward winning their trust, if you fail to evoke the right emotions you will quickly lose their interest. You can be the most rational, data-driven speaker and ruin the impact of your talk by “giving someone the ick,” as the kids say these days! By using vivid words and dynamic nonverbal cues, you can profoundly impact your audience’s feelings as they listen to your talk.
Logos is where the rubber meets the road. This is your argument–how you prove your point with evidence and logic. No good speech can go without logos, though it can play a greater or lesser role depending on the context. Logos is especially important when the desired impact of your talk requires big changes from your audience in thought or action. Industries and events that rely heavily on research and data will also have high expectations for the logos in your talk.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Applying ethos, pathos, and logos to your own talk.
Now, we’ll go through a few practical applications of ethos, pathos, and logos to your professional speaking business. As you book speaking gigs, keep in mind how your marketing, content, and delivery can reflect these principles. We don’t intend to burden you with extra steps on the route to your next speaking gig. You don’t have to be a Greek philosopher to figure this out! Often, it just requires a little extra introspection as you compose and rehearse your talk.
Applying Ethos
Your ethos is the story your personal brand tells on and off the stage. Focus on establishing expertise, authority, and credibility before and during your talk. Your audience will find you more persuasive if they already trust you. That’s why it’s important to write your speaker bio effectively with references to your experience in the field.
Relating to your audience in your talk will also establish a powerful ethos. If they know that you are someone like them, they are more likely to agree with your argument. Tell stories that connect your experiences to those of your audience.
Citing data and known authorities also contributes to a positive ethos. Without realizing it, your audience will associate the authorities to whom you appeal with you. Appeal to inspiring figures and well-reputed sources already trusted by your audience–they will trust you. Appealing to a screenshot of a random tweet you found on the internet or treating unverified theories as facts will simply discredit you.
Offstage interactions play a huge role in ethos too. Try to take the time to chat with your audience after your talk, even if it’s just for a few minutes. Make friends with mission-driven speakers in your field who are easy to work with and genuinely care about their audience. Event planners and audience members alike will see you as someone accessible rather than aloof. As your reputation precedes you to each speaking engagement, back it up with the version of yourself who goes onstage.
Applying Pathos
Swaying your audience’s emotions can rarely carry your entire argument. But it can be a huge help. Feeling a variety of emotions will keep your listeners from getting bored and put them in the right headspace to receive the information you want to communicate.
Think of your talk as an emotional journey on which you embark with your audience. When you write your speech section by section, think about what you want the audience to be feeling at each point. Anticipation, as you introduce a meaningful story that leaves them breathless? Somber gravity, as you present facts and data about a troubling situation to which you present solutions? Enthusiasm, as you offer a transformative business solution that, while difficult, might get them out of a rut? Amusement, as you tell a funny joke to hook their attention?
You are their guide on this journey, so it’s up to you to tell them (without literally telling them) how to feel. Delivery and nonverbal communication are key here. Voice intonations, hand gestures , pauses, and facial expressions can add emotional weight to even the driest of phrases. Often, the best way to elicit a new emotion is to tell a story ! Stories can support your message, offer humorous diversion, or transition to a new topic…all while guiding emotions along the way.
Applying Logos
Neither ethos nor pathos directly concern the content of your talk, but logos does. Logos is the logical argument you make. You can ruin the effects of great pathos and ethos by failing to adequately support your argument. Sure, if your main purpose is to hype up your audience, you will likely rely more on pathos. But if you fail to connect everything you say to the point or (even worse) cite exaggerated facts or falsehoods, any listening ear will immediately discredit what you have to say. On the other hand, if you struggle to emotionally connect with your audience and have little experience in your field, great logos can still carry your point across and convince a skeptical audience.
Think of Logos as simply speaking the truth with clarity. Back up your claims and cite any important data or statistics. Use compelling examples from client results you were responsible for with or well-established research. Avoid fallacies and over-fluffy modes of speaking that might throw your audience off. Many speakers try to cover up weak links in their argument with jargon or convoluted palaver. Don’t do that! If the data doesn’t back up your argument, it’s time to reevaluate your argument.
Many speakers unintentionally obscure a good point by going off track. Your stories, jokes, and elaborations should all support one clear message. If you try to communicate too many messages at once, you’ll leave your audience adrift. Some tips? Replace long tangents with more relevant stories. For a talk on a broad topic, only delve into one or two examples in detail. If you’re speaking about something specific or granular, only give the most necessary background information.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Exemplary Persuasive Speeches
To wrap up, let’s look at some classic examples of how speakers use ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade their audiences.
Winston Churchill’s address to Congress in December 1941 utilizes ethos remarkably well to assure the assembly that he is speaking as a friend, not a foreigner. He reminds them that his own mother was American. He emphasizes his understanding of the American system of representation as a “child of the House of Commons.” Then, he further details that the King himself gave him permission to meet with the president! This way, he appeals to two very venerable heads of authority. As he moves on into a grim but stirring vision of the war, its past present and future, his credibility and trustworthiness are well-established.
Marc Antony’s speech from Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar is a timeless example of powerful pathos . He immediately plays into the emotions of his audience by reminding them that his purpose is not to deliver a panegyric, but to bury a friend. “When that the poor have cried, Caesar hath wept” he reminds the Romans, giving them cause for self-reflection upon whether their empathy matched Caesar’s. As if his appeal “You all did love him once” was not stirring enough? He finishes off “My heart is in the coffin there with Caesar, / And I must pause till it come back to me.” Absolutely gutting! (Incidentally, Marc Antony also leverages some reverse psychology ethos by referring to Caesar’s murderer Brutus as “an honourable man” throughout.)
Frederick Douglass ’ moving address “What to the Slave Is the Fourth of July?” is a long speech worth reading. Indeed, it could be used as an example for all three pillars of persuasion! He appeals especially to logos by examining the documents of the American Founding and pointing out the hypocrisy with which they have long been interpreted regarding slavery. Then he declares: “Take the constitution according to its plain reading, and I defy the presentation of a single proslavery clause in it. On the other hand it will be found to contain principles and purposes, entirely hostile to the existence of slavery.” He supports his point with facts (the text of the constitution was easy to fact-check) and clear, concise argumentation. The powerful impact of his words even today stands a testament to his mastery of rhetoric.
You should always use a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos to speak persuasively. Your niche will likely determine which you spend the most time emphasizing. For example, a motivational speaker in an intensely personal field like relationships, grief, or mental health will likely need to leverage a lot of pathos. A speaker who tries to convince professionals of any kind to make big changes will need a great deal of logos to show why their proposed solution is better than “what we’ve always done.” And any speaker in any field offering a potentially controversial solution will need to establish an ethos that is authoritative and trustworthy.
Ethos, pathos, and logos have played an integral role in the art of persuasive speaking for over 2000 years. Even the greatest speakers continue working on this skill well into their careers. While we are no longer Greek orators in marble amphitheaters, Aristotle’s principles can help you craft your speech and finesse your delivery for maximum impact.
- Last Updated: March 7, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos – A Simple Guide

4-minute read
- 12th April 2023
Ethos, logos, and pathos are three essential components of persuasive communication . They’ve been used for centuries by great communicators to influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. In this simple guide, we’ll take a closer look at these three components using examples from famous writing and speeches.
What Is Ethos?
Ethos is a persuasive appeal based on the credibility or character of the speaker or writer. It refers to the trustworthiness, expertise, or authority that they bring to the argument. It’s crucial in establishing the credibility of the speaker or writer and can be built in through a variety of means, such as reputation and sources, or language and tone.
How To Use Ethos
Ethos can be established through the speaker or writer’s reputation: if they are known for being knowledgeable, honest, and trustworthy, this can lend credibility to their argument. For example, in his famous “I Have a Dream” speech, Martin Luther King Jr. established his ethos by highlighting his role as a civil rights leader and his personal experience with racial injustice.
Another way you can achieve ethos in speech or writing is through the use of credible sources. For example, Rachel Carson established ethos in her book Silent Spring by providing extensive scientific evidence to support her argument that pesticides were harming the environment.
Finally, ethos can be accomplished through the use of language and tone . Using a professional and respectful tone can create the impression of credibility and authority. For instance, in his second inaugural address, President Abraham Lincoln employed ethos by using a solemn, reflective tone to convey the gravity of the situation.
What Is Logos?
Logos is a persuasive appeal based on logic and reasoning. It refers to the use of evidence and logical arguments to support the speaker or writer’s position.
How To Use Logos
One way you can implement logos in your speech or writing is through the use of statistics and data. When writing, or constructing a speech, try to incorporate reliable and credible stats or figures to strengthen your claims or argument and persuade your audience.
You can also employ examples and analogies to achieve logos. These can make your argument more accessible and understandable to a wider audience. For example, in his book The Tipping Point , Malcolm Gladwell uses the example of “the broken windows” theory to illustrate his argument that small changes can have a big impact on social behavior.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Finally, logos can be established through the use of logical arguments . To ensure you have a logical argument, you should have a clear statement with definitions, examples, and evidence to support it. For instance, in his essay “Civil Disobedience,” Henry David Thoreau made a logical argument that individuals have a moral obligation to resist unjust laws.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos is a persuasive appeal based on emotion. It refers to the use of language and imagery that elicits an emotional response. Pathos can be used to create a sense of urgency, inspire empathy, or evoke a particular mood.
How To Use Pathos
Vivid imagery is a great way in which a writer or speaker can implement pathos. Using descriptive language to paint a picture in your audience’s mind is a powerful and persuasive skill. For example, in his poem “Dulce et Decorum Est,” Wilfred Owen used vivid imagery to describe the horrors of war and elicit an emotional response in his readers.
Pathos can also be accomplished by using personal anecdotes. The power of storytelling is an invaluable skill for any writer or speaker because it creates rapport and an emotional connection with your audience. For example, in her TED talk “The Power of Vulnerability,” Brene Brown shares personal stories about her struggles with shame and vulnerability to inspire empathy and connection with her audience.
Finally, pathos can be established through the use of rhetorical questions and appeals to shared values. A good example can be heard in Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech. He poses his biggest question to his audience (and the world): “Now, what does all of this mean in this great period of history?” In response to this rhetorical question, he beautifully tries to persuade the audience to work together toward a common goal, stating, “It means that we’ve got to stay together. We’ve got to stay together and maintain unity.”
Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting change in the world.
Interested in learning how to elevate your writing with more literary devices? Check our other articles .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, ethos, pathos, logos, kairos: the modes of persuasion and how to use them.
General Education

Ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos all stem from rhetoric—that is, speaking and writing effectively. You might find the concepts in courses on rhetoric, psychology, English, or in just about any other field!
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising.
Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they’re used, and how to identify them!
What Are the Modes of Persuasion?
As you might have guessed from the sound of the words, ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos go all the way back to ancient Greece. The concepts were introduced in Aristotle’s Rhetoric , a treatise on persuasion that approached rhetoric as an art, in the fourth century BCE.
Rhetoric was primarily concerned with ethos, pathos, and logos, but kairos, or the idea of using your words at the right time, was also an important feature of Aristotle’s teachings.
However, kairos was particularly interesting to the Sophists, a group of intellectuals who made their living teaching a variety of subjects. The Sophists stressed the importance of structuring rhetoric around the ideal time and place.
Together, all four concepts have become the modes of persuasion, though we typically focus on ethos, pathos, and logos.

What Is Ethos?
Though you may not have heard the term before, ‘ethos’ is a common concept. You can think of it as an appeal to authority or character—persuasive techniques using ethos will attempt to persuade you based on the speaker’s social standing or knowledge. The word ethos even comes from the Greek word for character.
An ethos-based argument will include a statement that makes use of the speaker or writer’s position and knowledge. For example, hearing the phrase, “As a doctor, I believe,” before an argument about physical health is more likely to sway you than hearing, “As a second-grade teacher, I believe.”
Likewise, celebrity endorsements can be incredibly effective in persuading people to do things . Many viewers aspire to be like their favorite celebrities, so when they appear in advertisements, they're more likely to buy whatever they're selling to be more like them. The same is true of social media influencers, whose partnerships with brands can have huge financial benefits for marketers .
In addition to authority figures and celebrities, according to Aristotle, we’re more likely to trust people who we perceive as having good sense, good morals, and goodwill —in other words, we trust people who are rational, fair, and kind. You don’t have to be famous to use ethos effectively; you just need whoever you’re persuading to perceive you as rational, moral, and kind.

What Is Pathos?
Pathos, which comes from the Greek word for suffering or experience, is rhetoric that appeals to emotion. The emotion appealed to can be a positive or negative one, but whatever it is, it should make people feel strongly as a means of getting them to agree or disagree.
For example, imagine someone asks you to donate to a cause, such as saving rainforests. If they just ask you to donate, you may or may not want to, depending on your previous views. But if they take the time to tell you a story about how many animals go extinct because of deforestation, or even about how their fundraising efforts have improved conditions in the rainforests, you may be more likely to donate because you’re emotionally involved.
But pathos isn’t just about creating emotion; it can also be about counteracting it. For example, imagine a teacher speaking to a group of angry children. The children are annoyed that they have to do schoolwork when they’d rather be outside. The teacher could admonish them for misbehaving, or, with rhetoric, he could change their minds.
Suppose that, instead of punishing them, the teacher instead tries to inspire calmness in them by putting on some soothing music and speaking in a more hushed voice. He could also try reminding them that if they get to work, the time will pass quicker and they’ll be able to go outside to play.
Aristotle outlines emotional dichotomies in Rhetoric . If an audience is experiencing one emotion and it’s necessary to your argument that they feel another, you can counterbalance the unwanted emotion with the desired one . The dichotomies, expanded upon after Aristotle, are :
- Anger/Calmness
- Friendship/Enmity
- Fear/Confidence
- Shame/Shamelessness
- Kindness/Unkindness
- Pity/Indignation
- Envy/Emulation
Note that these can work in either direction; it’s not just about swaying an audience from a negative emotion to a positive one.
However, changing an audience's emotion based on false or misleading information is often seen as manipulation rather than persuasion. Getting into the hows and whys requires a dive into the ethics of rhetoric , but suffice to say that when you attempt to deceive an audience, that is manipulation.
If you really want to get an audience fired up about something, you can inspire righteous anger, which may or may not be manipulation. If somebody is offended that you’ve asked them for something, you can try making them feel sorry for you by turning indignation into pity— that’s manipulation.

What Is Logos?
Logos comes from a Greek word of multiple meanings, including “ground,” “speech,” and “reason.” In rhetoric, it specifically refers to having a sense of logic to your persuasion; logos-based rhetoric is founded in logic and reason rather than emotion, authority, or personality.
A logic-based argument appeals to a person’s sense of reason— good logos-based rhetoric will persuade people because the argument is well-reasoned and based in fact. There are two common approaches to logos: deductive and inductive arguments.
Deductive arguments build on statements to reach a conclusion —in effect, the conclusion is reached in reverse. A common method is to propose multiple true statements which are combined to reach a conclusion, such as the classic method of proving that Socrates is mortal.
All men are mortal, and Socrates is a man, therefore Socrates must be mortal.
That’s not really a case that needs to be argued, but we can apply the same framework to other arguments as well. For example, we need energy to live. Food gives the body energy. Therefore, we need food to live.
All of this is based on things we can prove, and results in a conclusion that is true , not just theorized. Deductive reasoning works on the assumption that A = B, B = C, so therefore A = C. But this also supposes that all the information is true, which is not always the case.
Sometimes the conclusions you reach with deductive reasoning can be valid, as in the reasoning makes sense, but the conclusion may not be necessarily true. If we return to the Socrates argument, we could propose that:
All men eat apples. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates must eat apples.
The problem is that we can’t prove that all men eat apples —some do, some don’t. Some might eat an apple once but never again. But based on our arguments, the conclusion that Socrates must eat apples is valid.
A strong deductive argument for logos-based reasoning will be composed of provable facts that can reach a provable conclusion. However, a valid but not entirely sound argument can also be effective—but be wary of shifting from persuasion to manipulation!
Another approach to logos-based rhetoric is inductive reasoning, which, unlike deductive reasoning, results in a probable argument rather than a definite one. That doesn’t mean that it is less effective—many scientific concepts we accept as truth are inductive theories simply because we cannot travel back in time and prove them— but rather that inductive reasoning is based on eliminating the impossible and ending in an argument that is based in sound logic and fact, but that may not necessarily be provable.
For example, all people with a cough have a cold. Kelly has a cough. Therefore, Kelly likely has a cold.
Our conclusion is likely , but not absolute. It’s possible that Kelly doesn’t have a cold—not because she doesn't have a cough, but because there are other possible causes, such as having allergies or having just breathed in some dust. The conclusion that she has a cold is likely based on data, but not absolute.
Another example would be that Kelly picks her nose. Kelly is a woman, therefore all women must pick their nose.
Inductive reasoning is based on generalizations. The first example, in which Kelly likely has a cold, makes sense because it’s based on something provable—that a sampling of people who have a cough have colds—and followed up with a likely conclusion. In the second example, this is a less sensible conclusion because it’s based on extrapolation from a single reference point.
If we reverse the claim and say that all women pick their noses, and Kelly is a woman, therefore Kelly must pick her nose, that would be more sound logic. Still not necessarily true—not all women pick their noses—but a more sound example of inductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning can still be incredibly effective in persuasion, provided that your information is well-reasoned. Inductive reasoning creates a hypothesis that can be tested; its conclusion is not necessarily true, but can be examined.
As always, be wary of venturing into manipulation, which is more likely to be based on erroneous or misleading facts.

What Is Kairos?
Kairos is the Greek word for the opportune moment, which is precisely what it means in rhetoric. According to this principle, the time in which an argument is deployed is as important as the argument itself. An argument at the wrong time or to the wrong audience will be wasted; to be effective, you must also consider when you are speaking and to whom.
In effect, kairos means choosing the correct rhetorical device to match the audience and space in which you’re attempting to persuade. If you wanted to persuade people to go vegetarian, the middle of a hot dog-eating contest is probably not the right time. Likewise, you’re probably not going to persuade a room of data-driven scientists of something by appealing to pathos or ethos; logos is probably your best bet.
In essence, kairos asks you to consider the context and atmosphere of the argument you’re making. How can you deploy your argument better considering time and space? Should you wait, or is time of the essence?
As Aristotle famously said, “Anybody can become angry—that is easy, but to be angry with the right person and to the right degree and at the right time and for the right purpose, and in the right way—that is not within everybody's power and is not easy.”
The goal of kairos is to achieve exactly that. Effective use of kairos strengthens your persuasion ability by considering how people are already feeling based on context. How can you influence or counteract that? Or maybe pathos isn’t the right approach—maybe cold hard facts, using logos, is more suited. Kairos works in conjunction with the other modes of persuasion to strengthen your argument, so as you’re putting a persuasive piece together, consider how and when it’ll be deployed!

How to Identify Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Understanding how the modes of persuasion work can make you better at identifying and picking them out. Not only is a better understanding of them useful for composing your own arguments, but it’s also beneficial when seeing other people’s arguments. When you understand how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos work, you’re less susceptible to them.
Advertising is one of the places we see the modes of persuasion most often. Looking at each of these advertisements, you can see how they use each mode of persuasion to convince audiences to convince an audience of something.
Using celebrities is a classic example of ethos, which uses authority or recognition to convince an audience of something. In this case, celebrities like Michelle Obama, Lin-Manuel Miranda, and Janelle Monáe discuss the importance of voting.
It doesn’t matter that they’re not politicians or political scientists; audiences find them appealing and genuine. When they speak of the importance of voting, audiences listen because they like what these figures have to say . If talented, famous people like this are taking the time to vote, it must be important!
Historians or those well-versed in politics might make different arguments about why audiences should vote, but in this case, the goal is to inspire people. When we see people we admire doing things, we want to do them too; hence the reason that ethos works so well.
ASPCA’s commercials are some of the most infamous examples of pathos in advertising. Sarah McLachlan’s “Angel” plays over footage of abused animals in shelters, encouraging viewers to donate money to support the organization.
It’s not hard to understand why it works; both the song and the imagery are heartbreaking! You can’t help but feel sad when you see it, and that sadness, when followed up by a prompt to donate, encourages you to take immediate action. And these ads are effective— the campaign raised millions of dollars for ASPCA .
By appealing to our emotions and making us feel sad, this advertisement encourages us to act. That’s a classic use of ethos—it influences our feelings through the one-two punch of sad music and imagery, encouraging us to perform the desired action.
In some cases, emotion and authority aren’t the right tactic. Logos often appears in tech advertisements, such as this one for the iPhone XS and XR.
Notice how the advertisement focuses on product shots and technological terms. Most audiences won’t know what an A12 bionic neural engine is, but it sounds impressive. Likewise, that “12 MPf/1.8 wide-angle lens, with larger, deeper 1.4 micron pixels” is pretty meaningless to most people, but the numbers suggest that this phone is something special because it uses scientific-sounding language.
It doesn’t matter whether audiences really understand what’s being said or not. What matters is that they feel confident that the ad is selling them something they need —in this case, impressive technological specifications that make this phone an improvement over others.
Kairos should ideally factor into all uses of the modes of persuasion, but timeliness can also be a big selling point. In this Christmas-themed M&Ms advertisement, the company uses timely humor to forge a connection between the holidays and M&Ms.
Because these commercials have been running for such a long time, there’s also a nostalgic attachment to them. Just as people look forward to new Budweiser advertisements during the Super Bowl, others look forward to seeing M&Ms or the Coca-Cola polar bear during the holidays.
Though this commercial doesn’t go out of its way to tell you the benefits of M&Ms, it does forge a connection between M&Ms and Christmas, encouraging people to purchase them around the holidays.

Examples of the Modes of Persuasion
Now that you’ve had some exposure to how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos function and what they can do, you can test your ability to recognize them using the images below!

There are a few things to notice about this image:
- The anonymous figure
- The language
- The use of a statistic
Can you figure out which mode of persuasion this represents?
The fact that the figure is anonymous tells us it’s probably not ethos. While we might be influenced by a person who’s in shape, there’s not really an appeal here based on the person—they’re just an image to support the ad.
“DOMINATE” is a pretty loaded word, suggesting that this may have elements of pathos.
However, take a look at that statistic. Whether it’s true or not, a hard statistic like that suggests that this ad is using logos to appeal to viewers. You can draw out an argument from there—75% of users lose weight within weeks. You’re a user. Therefore, you will likely lose weight within weeks.

What do you notice about this image?
- The way the text frames the woman’s body
- The name of the perfume
- The color choice
What mode of persuasion is this?
Again, we don’t know who the model is, and perfume isn’t going to make us look like her, so we can count ethos out.
The ad seems pretty intent on making us look at certain things—the woman’s lips and chest in particular. What is it trying to make us feel?
“FORBIDDEN FRUIT” has a connotation of sensuality.
Red is a color commonly associated with passion.
When you combine the photo, the framing, the perfume name, and the color, you get a strong sense of sex appeal from the advertisement. This makes it an example of pathos—the ad is trying to make us feel a certain way . If we buy this perfume, maybe we would feel attractive, too.

How about this advertisement?
- A serious-looking photo
- Text promising “no more back pain”
- “Doctor recommended.”
Seeing a doctor might make you tempted to think the answer is logos, but there’s no appeal to logic here.
“No more back pain,” is a nice promise, but there’s no attempt to appeal to emotions, so it can’t be pathos.
What’s important in this image is the combination of the doctor in the image and the line “doctor recommended.” This doctor might not be famous, but he does have authority, making this an example of ethos.
Our confidence in this treatment grows because we trust that a doctor understands how to address back pain.

What mode of persuasion is this? Think about:
- The framing
She does look fashionable and the ad mentions stylists, so it’s possible that this is ethos.
There are no statistics or arguments being made, so the answer probably isn’t logos.
Pathos is possible, but despite having a heavily made-up model, this ad is far less about sex appeal than the previous one.
But the text mentions a specific holiday—New Year’s—suggesting that this is kairos. Kairos can, and often should, be combined with all the modes of persuasion to be even more effective. In this case, the model’s appearance could suggest either ethos or pathos in addition to kairos. The message here is that you should act now, at the beginning of the year, to take advantage of the deal and to start the year off with a new style, much like the one the model is sporting.

Key Tips for Identifying Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Now that you know the difference between all the modes of persuasion, you’ll have a much easier time identifying them. If you run into trouble, you can always ask questions about what you’re seeing, hearing, or reading to understand what mode of persuasion it’s using.
#1: Is It Related to a Specific Time?
If the argument is based on a specific day or context, such as Valentine’s Day or appealing only to a select group of people, such as people with dogs, it’s more likely to be kairos.
#2: Does It Involve a Celebrity or Authority Figure?
Celebrities are often a dead giveaway that an argument is using ethos. But authority figures, such as doctors, dentists, or politicians, can also be used to appeal to ethos. Even regular, everyday people can work, particularly when combined with pathos, to appeal to you based on a mutual connection you have.
#3: Does It Involve Statistics?
Statistics are a huge clue that an argument is using logos. But logos can also just be a logical argument, such as that if plants need water, and it’s hard to remember to water them, you should buy an automatic plant waterer. It makes perfect sense, making you more likely to buy it, rather than changing your habits to remember to water your plants more frequently.
#4: Does It Influence Your Emotions?
If an argument tries to change your emotions, whether by making you sad, happy, angry, or something else entirely, it’s a good indicator that it’s using pathos. Sex appeal is one of the biggest examples of pathos in advertising, appearing everywhere from makeup ads to car commercials to hamburger advertisements.
What’s Next?
Need help understanding the historical context for The Great Gatsby to perfect your kairos-based argument?
You can always combine the modes of persuasion with literary devices to make your arguments even stronger!
Learn how to say "good morning" in Japanese ! Even if it's not a mode of persuasion, it's just good manners.

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Ethos, Logos, & Pathos: The Three Parts of a Persuasive Presentation
Every persuasive speech you’ve heard in your life—a marketing spiel, a political campaign speech, a call to action—is governed by the same three pillars of speech. These pillars have already been laid out more than 2,000 years ago, but they remain as relevant to the persuasive speeches you endeavor today.
In his work, On Rhetoric , the great philosopher Aristotle spelled out the three elements of appeal that work together to make a speech persuasive: ethos, logos, and pathos. If you want to make your public speaking more compelling, looking into these three pillars is valuable in convincing your audience to hear your message.
Find your bootcamp match
In this article, we’ll go into detail about what these three pillars mean, and actionable points of how to maximize them on your next presentation.
What Are Ethos, Logos, and Pathos?
To successfully give a persuasive presentation, you must look to master these three pillars of persuasive speech:
- Ethos : the ethical appeal; your authority, credibility, and character
- Logos : the logical appeal; your arguments’ strength, soundness, and coherence
- Pathos : the emotional appeal; your arguments’ emotional bond and impact on your listeners
Let’s put these elements into context and see how they work. Let’s say you are a salesperson trying to sell your company’s newest car to a customer. If you are going for strong Ethos, you can say, “As someone who has worked with cars for 15 years, I can guarantee that this model is the most economical one.”
If you want to attack with Logos, you can load up on the car’s newest features and go, “This car is designed with a new camera system, smart suspension, a multizone climate system, and more latest features to make your drive 200% better than other models.”
And if you’re going for Pathos, you can say, “Your kids will just love this new car, and it’s perfect in bringing your whole family on a road trip to the beach.”
Do you see how these pillars each persuade the customer in a different way? All persuasive speakers use a combination of Ethos, Logos, and Pathos to drive the message home and win over their listeners. Understanding the rhetorical triangle and its components is one of the first steps toward improving your presentation skills.
Now let’s go a little deeper to see how you can employ these three pillars to deliver a strong, persuasive presentation yourself.
But First, Invention
Before you can decide how you’re going to appeal to your audience, you must first gather the necessary information that will guide you on your feat. As the famous Roman orator Cicero explained, this step is called Invention , the discovery and development of the arguments that govern your message.
You must do ample research and information gathering, not only about your topic but also about your audience. You must understand your listeners, their interests, inclinations, biases, and expectations. Without this grounding, you’re setting yourself up to blindly create strategies that are not targeted to your listeners.
Using this research, you can now decide on how you’re going to entice your audience by leveraging the three pillars of persuasion.
Ethos: The Ethical Appeal
Ethos is all about character. It defines how credible, trustworthy, and relatable you are as a speaker. Before your audience listens to what you have to say, they first examine you to see if you have locus standi , or the right to be heard.
It’s not enough that you have the credentials or the expertise to talk about the subject, but you need to translate this by building trust and rapport with your audience. You can exude more Ethos if you are confident when you’re presenting, shown in your voice, gait, mannerisms, and even attire.
Another thing that increases Ethos is similarity and relatability. When presenting, you can use a shibboleth —a specialized term used by a specific group of people—to show that you are in the know. Make the effort to show that you are part of the group and that your message heeds listening to.
Logos: The Logical Appeal
Logos is all about your arguments. Does your message make sense? Is it supported by facts and evidence? Can it counter any opposing opinion?
Logos appeals to your audience’s reason and intelligence, and what your listeners are looking for is to find the truth through the facts of the argument. This not only entails traditional facts like statistical data and figures but relevant stories as well. Depending on the context, you can include personal experience and case studies to further amplify the Logos of your speech.
Your arguments must also be comprehensive and easy to understand. If the context allows, effective visual aids are powerful in making sure your audience grasps the message. To make your slides more appealing and reach your audience, you can design a killer presentation by using free & good backgrounds for presentations .
Pathos: The Emotional Appeal
Pathos is all about emotional impact. The most memorable and persuasive speeches all had high Pathos, those that stirred strong emotions within us and compelled us to understand and follow the speaker’s point of view.
Source: free Ethos Pathos Logos PowerPoint template
Choose which emotion you want to evoke in your audience that will amplify your message. If you’re trying to sell a product, induce joy and desire. If you’re asking for donations for a sick patient, induce pity and hope. And don’t forget the power of humor in engaging your audience and increasing your likeability.
One of the most effective strategies to increase Pathos is to tell a story. Paint a picture, and link an emotional response to the most important parts of your message to make them memorable.
Understanding Ethos, Pathos, and Logos and how they work is the first step in improving your public speaking and presentation skills . The next step would be to put them into practice. Using some of the actionable points we have shared, plan out how you’re going to best appeal to your audience. Once you’ve mastered the three pillars, your speech is guaranteed to drive its message home.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos are valuable benchmarks that you can follow to make sure your presentation is compelling and impactful to your listeners. While some may argue that one pillar is more important than the others, a persuasive speech with a balanced combination of all three pillars of a rhetorical triangle will always be more successful than a speech only focusing on one.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Skip to main content
- Skip to header right navigation
- Skip to site footer

Farnam Street
Mastering the best of what other people have already figured out
Ethos, Logos and Pathos: The Structure of a Great Speech
“A speech is like a love affair. Any fool can start it, but to end it requires considerable skill.” — Lord Mancroft
The structure of a great oral argument has been passed down through the ages, starting with Aristotle. Not only is it an incredibly valuable skill to have, it’s important to know how you’re being persuaded when you’re a part of the audience. So using Sam Leith’s Words Like Loaded Pistols as our guide, let’s discuss Aristotle’s three modes of persuasion: Ethos, Logos, and Pathos.
But before we get into the specifics of the three modes, we need to decide on the structure of our argument itself. How? By doing the work required to have an opinion .
This phase is referred to as invention , but it’s not about making something up, it’s more about the information gathering or research phase of your work.
Invention is doing your homework: thinking up in advance exactly what arguments can be made both for and against a given proposition, selecting the best on your own side, and finding counterarguments to those on the other.
This research phase should not be limited to the subject matter, it should also include your audience. If there is one theme that resonates throughout Leith’s book, it’s that you must know your audience; their interests, prejudices and expectations. Without that grounding, you’re already setting yourself up for failure. (In other words, your moving speech on why we all need to take a social media holiday may not resonate at the Twitter shareholder meeting.)
Ethos is about establishing your authority to speak on the subject, logos is your logical argument for your point and pathos is your attempt to sway an audience emotionally. Leith has a great example for summarizing what the three look like.
Ethos: ‘Buy my old car because I’m Tom Magliozzi.’ Logos: ‘Buy my old car because yours is broken and mine is the only one on sale.’ Pathos: ‘Buy my old car or this cute little kitten, afflicted with a rare degenerative disease, will expire in agony, for my car is the last asset I have in the world, and I am selling it to pay for kitty’s medical treatment.’
The first part of ethos is establishing your credentials to be speaking to the audience on the specific subject matter. It’s the verbal equivalent of all those degrees hanging up in your doctor’s office. And once you’ve established why you are an authority on the subject, you need to build rapport. Ethos, when everything is stripped away, is about trust.
Your audience needs to know (or to believe, which in rhetoric adds up to the same thing) that you are trustworthy, that you have a locus standi to talk on the subject, and that you speak in good faith. You need your audience to believe that you are, in the well-known words, ‘A pretty straight kind of guy.’
So if you’re a politician and you’re speaking about reforming the legal system, it’s great to be a lawyer or a judge, but it’s even better to be a lawyer or a judge who comes from the same community as your audience. Between two speakers with identical credentials, the more closely relatable one will win the audience.
You’ll even see a reverse ethos appeal at times, an attack on an opponent which questions their credentials and trustworthiness and serves to alienate them from the audience. To head that off, it’s best to establish your ethos early on, both to give your attackers more of a challenge and to create a hook for your logos to hang on.
Here’s how Leith describes logos , the next link in the chain:
If ethos is the ground on which your argument stands, logos is what drives it forward: it is the stuff of your arguments, the way one point proceeds to another, as if to show that the conclusion to which you are aiming is not only the right one, but so necessary and reasonable as to be more or less the only one.
Think of this as the logic behind your argument. You want your points to seem so straightforward and commanding that your audience can’t conceive of an alternative.
Aristotle had a tip here: He found that the most effective use of logos is to encourage your audience to reach the conclusion to your argument on their own, just moments before your big reveal. They will relish in the fact that they were clever enough to figure it out, and the reveal will be that much more satisfying.
Another logos trick used often is the much abused syllogism.
The syllogism is a way of combining two premises and drawing a fresh conclusion that follows logically from them. The classic instance you always hear quoted is the following: All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.
While you need to take care with the syllogisms you use — false syllogisms can lead to obvious logical fallacies — they can be a powerful tool for helping your audience draw certain conclusions.
Aristotle also advocated the use ‘commonplaces’, or accepted premises shared with the audience. The best arguments are soaked in them.
Associated with these general topics are ‘commonplaces’ (topos is Greek for a ‘place’). Any form of reasoning has to start from a set of premises, and in rhetoric those premises are very often commonplaces. A commonplace is a piece of shared wisdom: a tribal assumption. In the use of commonplaces, you can see where logos and ethos intersect. Commonplaces are culturally specific, but they will tend to be so deep-rooted in their appeal that they pass for universal truths. They are, in digested form, the appeal to ‘common sense.’ You get nowhere appealing to commonplaces alien to your audience. The wise persuader starts from one or two commonplaces he knows he has in common with his audience – and, where possible, arrives at one too.
Your use of commonplaces is also a good point to interject pathos , as many of these common beliefs can illicit an emotional response. Let’s dig into pathos .
Your logical argument will be that much more persuasive if it’s wrapped up with a good dose of emotion. Because of the way we use the word pathos in the modern world, you may be thinking of something dramatic and sad. But pathos is more nuanced than that; it can be humor, love, patriotism, or any emotional response.
The key here once again is to know your audience . If you are trying to evoke a sense of anger or sadness regarding mankind’s role in the decline of the honeybee, you might not get the response you want from the bee allergy support group.
You can even invoke pathos by admitting a wrong. ( We all make mistakes …) This can be a clever way to put your opponent off balance.
This is the figure, called paromologia in the Greek, where you concede, or appear to concede, part of your opponent’s point. It turns what is often necessity to advantage, because it makes you look honest and scrupulous, takes the wind out of your opponent’s sails, and allows you to shift the emphasis of the argument in a way finally favorable to you. It’s the equivalent of a tactical retreat, or of the judo fighter using an opponent’s momentum against him.
Another tool you can use with pathos is something the ancients called aposiopesis.
Aposiopesis – a sudden breaking off as if at a loss for words – can be intended to stir pathos. And even where something appears merely decorative – a run of alliteration or a mellifluously turned sentence – it serves to commend the speech more easily to memory, and to give pleasure to the audience. Delight is an end, as well as a means.
And we can’t forget joy and laughter. A well received joke can help you both connect with the audience (ethos) and bring home the pathos appeal.
… the joke can do more than just perk up a drowsing audience. It can be a powerful rhetorical tool. It participates in the pathos appeal inasmuch as it stirs an audience’s emotions to laughter – but more importantly, it participates in the ethos appeal, inasmuch as laughter is based on a set of common assumptions. As Edwin Rabbie argues in ‘Wit and Humour in Roman Rhetoric,’ ‘Jokes usually presuppose (even rest on) a significant amount of shared knowledge.
Ultimately, the three modes of persuasion are interconnected. It’s helpful not to think of them in a linear way but more like three overlapping circles. If you can create something with ethos, logos, and pathos peppered throughout, and tie it all into your audience’s belief system, you will have a very strong argument.
While Aristotle’s three persuasive appeals make appearances throughout the book, there is so much more to Words Like Loaded Pistols . Leith goes into depth regarding the five parts of rhetoric and the three branches of oratory. He also spend considerable time explaining the different figures, also known as the ‘flowers of rhetoric, which can be thought of as the literary weapons you can use in your war of words. If you have an interest in making your own presentations or speeches better, or in understanding the techniques a speaker is using when you are in the audience then this book is definitely worth the read. In the meantime check out our post on Wartime Rhetoric for some inspiration.

Ethos, Pathos, Logos For Trust, Sympathy, And Reason
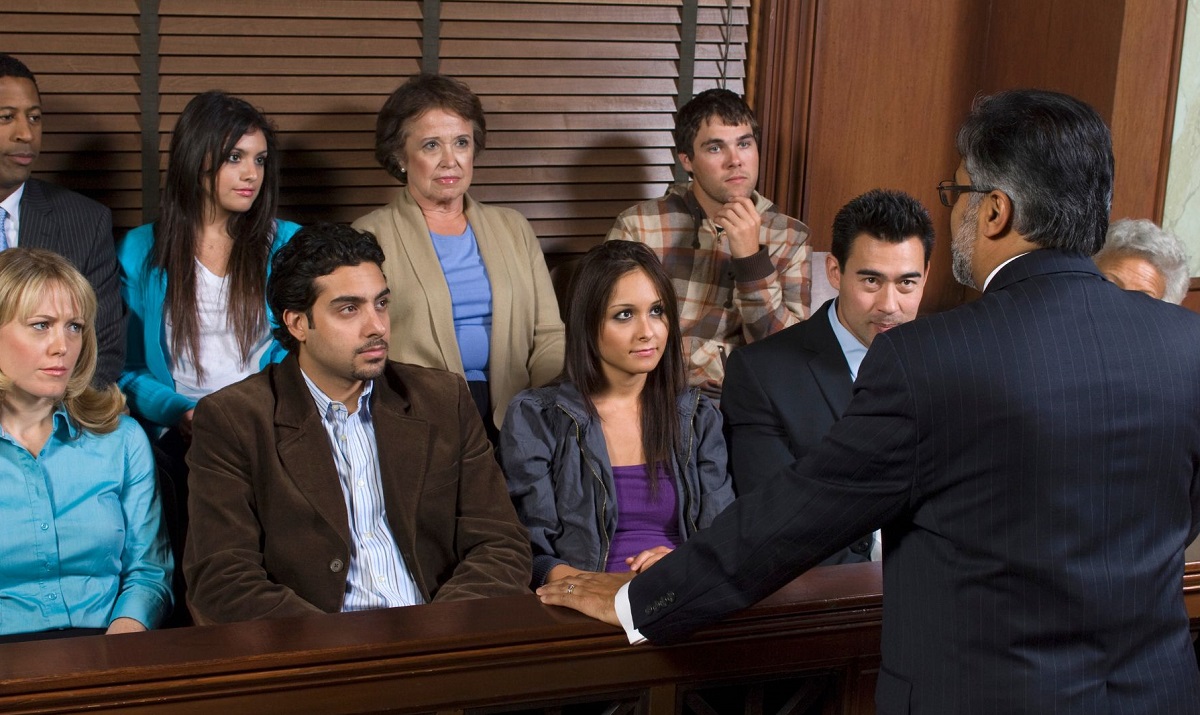

Ethos, pathos, and logos are three modes of persuasion in public speaking. The concepts are based on Aristotle’s three artistic proofs. They refer to how speakers use credibility, emotion, and reason to elicit trust, sympathy, and reason.
Based on the Greek philosopher Aristotle’s groundbreaking treatise on rhetoric, ethos, pathos, and logos have remained at the core of effective communication. Ethos appeals to the credibility and authority of the speaker, pathos stirs emotions, and logos employs logical reasoning and evidence.
These three modes of persuasion have proven to be potent tools in crafting compelling arguments, mobilizing movements, and captivating audiences . They are at the core of modern-day debates and political speeches.
This article will unravel the intricacies of ethos, pathos, and logos, uncovering their individual strengths and discovering how they work harmoniously to create a persuasive impact.
Table of Contents
What Are The Three Types Of Appeals?
Here are the definitions of the three types of appeals:
Ethos bases its fundamentals on the credibility, expertise, and moral character of the speaker or source. It establishes credibility and trust with the audience by showcasing the speaker’s authority, knowledge, and integrity on a particular subject.
Ethos relies on the audience’s perception of the speaker as someone trustworthy, reliable, and knowledgeable. This gains the audience’s confidence and willingness to listen. By employing ethos, speakers aim to demonstrate their expertise and ethical standing, ensuring that their arguments are perceived as valid and trustworthy.

What Is An Example Of Ethos?
An example of ethos can be seen in a renowned surgeon giving a presentation on the benefits of a specific medical procedure. They begin by sharing their extensive experience and expertise in the field, highlighting their successful track record and years of practice.
They also mention their affiliation with prestigious medical institutions and research publications. By establishing their credibility and expertise, the surgeon appeals to ethos, instilling confidence in the audience and lending credibility to their persuasive argument.
Pathos targets the emotions, values, and beliefs of the audience. It seeks to elicit an emotional response, such as empathy, compassion, anger, or joy, to influence the audience’s decision-making process.
Speakers create a connection and a sense of shared experience by tapping into the audience’s emotions. Pathos is often used to evoke empathy for a cause, stir enthusiasm for a product, or generate a sense of urgency and motivation. It relies on storytelling, vivid language, imagery, and personal anecdotes to engage the audience’s emotions and foster a persuasive impact.
What Is An Example Of Pathos?
When pathos is used in a speech, the examples often show worst-case and best-case scenarios to manipulate the audience’s emotions so that they take action or pull out their credit cards. Risks and benefits may be real, but appeal to pathos exaggerates them.

Advocates of climate change note that the temperature of the earth is rising as a result of global warming, and, as a result, temperatures and weather patterns are shifting. A speech relying on pathos might quote statistics and give examples that appeal to emotions by discussing severe weather patterns, more wildfires, rising energy costs, and even growth spurts among pests such as mosquitoes and ticks.
Animal rights activists pull the heartstrings with stories of abandoned pets and overcrowded animal shelters. Representatives of charity organizations that fight hunger and homelessness raise visions of starving children and desperate homeless people.
Speeches directed at teens talk about the risk of taking drugs and stress how not watching you drink at a party could result in somebody drugging you.
L ogos is based on logic, reason, and rationality and presents a well-structured and reasoned argument supported by evidence, facts, and logical reasoning. It aims to persuade the audience by appealing to their intellect and sense of logic.
Logos often involves using statistics, data, expert opinions, analogies, and logical frameworks to support the speaker’s claims and convince the audience of the validity of their argument. Logos aims to provide a logical sequence of thoughts, highlighting cause-and-effect relationships and constructing a coherent and compelling case.

What Is An Example Of Logos?
Examples of logos might be present in a scientific research paper presenting evidence-based findings on climate change.
The paper carefully lays out the data collected from various sources, analyzes the trends, and presents logical arguments based on cause-and-effect relationships. It includes statistical analyses, charts, and references to peer-reviewed studies to support its claims.
By relying on factual information, logical reasoning, and scientific evidence, the paper appeals to logos, aiming to persuade readers through a rational and evidence-based approach.
How Does Logos Differ From Ethos?
Logos differs from ethos in its focus and persuasive strategy. While ethos relies on the credibility and character of the speaker or source, logos appeals to the audience’s sense of reason and logic.
Ethos seeks to establish trust and credibility by showcasing the speaker’s authority and expertise. On the other hand, logos rely on presenting a well-structured and reasoned argument supported by evidence, facts, and logical reasoning.
It emphasizes logical coherence, empirical evidence, and rational argumentation to convince the audience of the validity and soundness of the argument. Ethos appeals to the speaker’s character, while logos appeals to the intellect and logical thinking of the audience.
Maintaining The Integrity Of The Message
It is crucial to avoid logical fallacies and overly literal analogies to maintain the integrity of the message. With the advent of social media, the use of ethos, pathos, and logos has become even more influential in engaging subscribers and shaping public opinion.
By harnessing these rhetorical strategies effectively, communicators craft powerful messages that resonate and inspire change from their intended point of view.
How Are Ethos, Pathos, Logos Related To Aristotle?
The three appeals, ethos, pathos, and logos , are closely associated with Aristotle, a renowned Greek philosopher and rhetorician who extensively studied and wrote about the art of persuasion in his work, “Rhetoric.” Aristotle considered rhetoric the art of discovering all available means of persuasion and recognized the significance of these three appeals in effective communication.
Aristotle emphasized the importance of ethos, which he referred to as the speaker’s or writer’s character and credibility. According to Aristotle, a speaker’s ethos plays a vital role in persuading an audience.
Ethos, derived from the Greek word for character, leverages the credibility of a spokesperson or a credible source to establish trust and authority. People are more likely to be convinced by someone they perceive as trustworthy, knowledgeable, and possessing good moral character.
Aristotle believed establishing a strong ethos involved demonstrating expertise, displaying fairness and goodwill, and maintaining personal integrity. Ethos serves as a foundation for building trust and establishing the speaker’s authority, increasing the audience’s receptiveness to the message.
Aristotle recognized the persuasive power of emotions and their role in influencing human behavior. Pathos, for Aristotle, referred to the appeal to the audience’s emotions. He understood that making the audience feel connected could evoke sympathy, empathy, anger, or other strong feelings, enabling the speaker to forge a deeper connection and resonance with the audience.
Aristotle emphasized the importance of understanding the audience’s emotional state and utilizing rhetorical devices such as storytelling, vivid language, and metaphors to evoke specific emotions. By employing pathos effectively, speakers could elicit an emotional response that could motivate the audience to adopt their viewpoint or take the desired action.
Aristotle considered logos as the appeal to reason and logical argumentation. Logos presents a well-structured and reasoned argument supported by evidence, facts, and logical reasoning. Known as the logical appeal, it relies on evidence and rational arguments to construct a strong case.
Aristotle emphasized the need for speakers to provide a coherent and logical progression of thoughts, using examples, analogies, and syllogisms to support their claims. He believed effective persuasion required a careful balance of logical reasoning and supporting evidence.
By employing logos, speakers could appeal to the audience’s intellect and logic, presenting a rational case that could convince the audience of the validity of their argument.
Aristotle’s recognition and exploration of ethos, pathos, and logos laid the groundwork for understanding the power of persuasion and the role these appeals play in effective communication. His work continues to be influential in the fields of rhetoric, communication, and persuasive speaking, serving as a cornerstone for studying and mastering the art of persuasion.

Why Is Each Type Of Persuasion Useful In A Speech?
Each type of persuasion, ethos, pathos, and logos, serves a specific purpose and contributes to the effectiveness of a speech.
- Ethos is useful in a speech because it establishes the speaker’s credibility and trustworthiness. By showcasing expertise, experience, and integrity, the speaker gains the audience’s confidence and enhances their receptiveness to the message.
- Pathos is useful in a speech because it taps into the audience’s emotions, creating a connection and resonance. By evoking empathy, compassion, or other strong feelings, the speaker engages the audience on a deeper level, making the message more memorable and compelling.
- Logos is useful in a speech because it provides a logical and reasoned argument. The speaker appeals to the audience’s intellect and rationality by presenting facts, evidence, and logical reasoning. This helps to build a logical case, persuade through logical coherence, and convince the audience of the message’s validity.
Does The Audience Influence Which Type Of Persuasion To Use?
The audience plays a crucial role in determining which type of persuasion to employ in a speech. Different audiences have varying preferences, beliefs, values, and emotional triggers, and understanding these factors is essential for tailoring the persuasive strategy effectively.
Here’s how the audience influences the choice of persuasion:
The audience’s perception of credibility and authority depends on their background and prior knowledge. If the audience consists of experts or individuals who highly value expertise, emphasizing ethos by showcasing the speaker’s credentials, experience, and expertise will be particularly influential.
However, in certain situations where the audience is skeptical or holds different views, the focus on ethos may need to be adapted or supplemented with other appeals.
The emotional makeup and interests of the audience significantly impact the use of pathos. Some audiences may respond well to emotionally charged stories, personal anecdotes, or passionate appeals that resonate with their values and experiences.
It’s also crucial to consider cultural sensitivities and potential emotional triggers to ensure the emotional appeal resonates positively with the audience without alienating or offending them.
The level of analytical thinking and reliance on logical reasoning within the audience should guide the use of logos. Audiences valuing evidence-based arguments, logical coherence, and rational frameworks will be more receptive to a presentation heavily relying on logos.
Providing solid evidence and logical explanations and appealing to rational thinking helps win over audiences by prioritizing logical analysis and reasoning.
How Are These Concepts Used In Advertising?
In advertising , these three modes of persuasion are used strategically to capture attention, create an emotional connection, and persuade consumers to take action.
- Ethos is employed in advertising by featuring trustworthy spokespersons, experts, or celebrities who endorse a product or service. Their credibility and authority lend credibility to the advertised claims and influence consumer perceptions and purchasing decisions.
- Pathos is utilized in advertising to evoke emotions that resonate with the target audience. Advertisements often tap into feelings of joy, happiness, desire, or even fear to create an emotional response that captures attention and establishes a connection with consumers.
- Logos is present in advertising through logical reasoning and evidence to support claims. Advertisements may highlight product features, comparisons, statistics, or scientific research to persuade consumers based on logical analysis and rational decision-making.

What Is Kairos?
Understanding the rhetorical triangle and employing rhetorical strategies allows speakers to tailor their messages to specific audiences and contexts, such as high school students or activists inspired by Martin Luther King Jr.’s “ I Have a Dream ” speech. Additionally, recognizing the relevance of kairos, the opportune moment, ensures that persuasive appeals are timely and impactful.
Adam Howarth
Adam covers the topic of Public Speaking for Digital Authority. From his first experience of oratory with his school debating society to his more recent experiences of promoting the local business scene in Wrexham, Wales, he has always been involved in public speaking.
Recent Posts
Active Listening Absorbs The Whole Message, Not Just The Words
Active listening goes beyond hearing the words someone is saying to you and understanding the message they are conveying. Many only hear a small percentage of what is being said as they are...
Counteracting Fear Of Public Speaking With Coaching And Therapy
Nearly 75% of people experience the social phobia of fear of public speaking. The result may be nervousness before speaking or a full-blown panic attack. Practicing public speaking may lessen the...
- Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition and Examples
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are modes of persuasion used to convince audiences. They are also referred to as the three artistic proofs (Aristotle coined the terms), and are all represented by Greek words.
An author would use ethos to show to his audience that he is a credible source and is worth listening to. Ethos is the Greek word for “character.” The word “ethic” is derived from ethos.
Ethos can be developed by choosing language that is appropriate for the audience and topic (this also means choosing the proper level of vocabulary), making yourself sound fair or unbiased, introducing your expertise, accomplishments or pedigree, and by using correct grammar and syntax.
During public speaking events, typically a speaker will have at least some of his pedigree and accomplishments listed upon introduction by a master of ceremony.
Pathos or the emotional appeal, means to persuade an audience by appealing to their emotions.
Authors use pathos to invoke sympathy from an audience; to make the audience feel what what the author wants them to feel. A common use of pathos would be to draw pity from an audience. Another use of pathos would be to inspire anger from an audience, perhaps in order to prompt action. Pathos is the Greek word for both “suffering” and “experience.” The words empathy and pathetic are derived from pathos.
Pathos can be developed by using meaningful language, emotional tone, emotion evoking examples, stories of emotional events, and implied meanings.
Logos or the appeal to logic, means to convince an audience by use of logic or reason.
To use logos would be to cite facts and statistics, historical and literal analogies, and citing certain authorities on a subject. Logos is the Greek word for “word,” however the true definition goes beyond that, and can be most closely described as “the word or that by which the inward thought is expressed" and, "the inward thought itself" ( 1 ). The word “logic” is derived from logos.
Logos can be developed by using advanced, theoretical or abstract language, citing facts (very important), using historical and literal analogies, and by constructing logical arguments.
In order to persuade your audience, proper use of Ethos, Pathos, and Logos is necessary.
Examples of Ethos, Logos and Pathos:
Example of Ethos:
“Woz and I started Apple in my parents garage when I was 20. We worked hard, and in 10 years Apple had grown from just the two of us in a garage into a $2 billion company with over 4000 employees. We had just released our finest creation — the Macintosh — a year earlier, and I had just turned 30...
During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife. Pixar went on to create the worlds first computer animated feature film, Toy Story, and is now the most successful animation studio in the world. In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple's current renaissance. And Laurene and I have a wonderful family together.”
Stanford Commencement Speech by Steve Jobs. June 12, 2005.
Example of Pathos:
"I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. And some of you have come from areas where your quest -- quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality. You have been the veterans of creative suffering. Continue to work with the faith that unearned suffering is redemptive. Go back to Mississippi, go back to Alabama, go back to South Carolina, go back to Georgia, go back to Louisiana, go back to the slums and ghettos of our northern cities, knowing that somehow this situation can and will be changed."
I Have a Dream by Martin Luther King Jr. August 28th, 1963.
Example of Logos:
"However, although private final demand, output, and employment have indeed been growing for more than a year, the pace of that growth recently appears somewhat less vigorous than we expected. Notably, since stabilizing in mid-2009, real household spending in the United States has grown in the range of 1 to 2 percent at annual rates, a relatively modest pace. Households' caution is understandable. Importantly, the painfully slow recovery in the labor market has restrained growth in labor income, raised uncertainty about job security and prospects, and damped confidence. Also, although consumer credit shows some signs of thawing, responses to our Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey on Bank Lending Practices suggest that lending standards to households generally remain tight."
The Economic Outlook and Monetary Policy by Ben Bernanke. August 27th, 2010.
Popular Articles
- Modes of Persuasion: Ethos
- Ethos, Pathos, and Logos ‒ Examples
- Modes of Persuasion: Pathos
- Persuasive Writing
Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
You may be surprised to learn that much of your life consists of constructing arguments. If you ever plead a case to your parents—in order to extend your curfew or to get a new gadget, for example—you are using persuasive strategies. When you discuss music with friends and agree or disagree with them about the merits of one singer compared to another, you are also using strategies for persuasion.
Indeed, when you engage in these "arguments" with your parents and friends, you are instinctively using ancient strategies for persuasion that were identified by the Greek philosopher Aristotle a few thousand years ago. Aristotle called his ingredients for persuasion pathos , logos , and ethos .
Persuasion Tactics and Homework
When you write a research paper , write a speech , or participate in a debate , you also use the persuasion strategies mentioned above. You come up with an idea (a thesis) and then construct an argument to convince readers that your idea is sound.
You should become familiar with pathos, logos, and ethos for two reasons: First, you need to develop your own skills at crafting a good argument so that others will take you seriously. Second, you must develop the ability to identify a really weak argument, stance, claim, or position when you see or hear it.
Logos Defined
Logos refers to an appeal to reason based on logic. Logical conclusions come from assumptions and decisions derived from weighing a collection of solid facts and statistics . Academic arguments (research papers) rely on logos.
An example of an argument that relies on logos is the argument that smoking is harmful based on the evidence that, "When burned, cigarettes create more than 7,000 chemicals. At least 69 of these chemicals are known to cause cancer, and many are toxic," according to the American Lung Association. Notice that the statement above uses specific numbers. Numbers are sound and logical.
An everyday example of an appeal to logos is the argument that Lady Gaga is more popular than Justin Bieber because Gaga's fan pages collected 10 million more Facebook fans than Bieber's. As a researcher, your job is to find statistics and other facts to back up your claims. When you do this, you are appealing to your audience with logic or logos.
Ethos Defined
Trustworthiness is important in research. You must trust your sources, and your readers must trust you. The example above concerning logos contained two examples that were based on hard facts (numbers). However, one example comes from the American Lung Association. The other comes from Facebook fan pages. You should ask yourself: Which of these sources do you suppose is more credible?
Anyone can start a Facebook page. Lady Gaga may have 50 different fan pages, and each page may contain duplicate "fans." The fan page argument is probably not very sound (even though it seems logical). Ethos refers to the credibility of the person posing the argument or stating the facts.
The facts provided by the American Lung Association are probably more persuasive than those provided by fan pages since the American Lung Association has been around for more than 100 years. At first glance, you might think that your own credibility is out of your control when it comes to posing academic arguments, but that is incorrect.
Even if you write an academic paper on a topic that is outside your area of expertise, you can improve your credibility—using ethos to persuade—by coming across as a professional by citing credible sources and making your writing error-free and concise.
Pathos Defined
Pathos refers to appealing to a person by influencing his emotions. Pathos is involved in the strategy of convincing the audience by invoking feelings through their own imaginations. You appeal through pathos when you try to convince your parents of something. Consider this statement:
"Mom, there is clear evidence that cellphones save lives in emergency situations."
While that statement is true, the real power lies in the emotions that you will likely invoke in your parents. What mother wouldn't envision a broken-down automobile perched by the side of a busy highway upon hearing that statement?
Emotional appeals are extremely effective, but they can be tricky. There may or may not be a place for pathos in your research paper . For example, you may be writing an argumentative essay about the death penalty.
Ideally, your paper should contain a logical argument. You should appeal to logos by including statics to support your view such as data that suggests that the death penalty does/does not cut down on crime (there's plenty of research both ways).
Use Appeals to Emotion Sparingly
You may also use pathos by interviewing someone who witnessed an execution (on the anti-death penalty side) or someone who found closure when a criminal was executed (on the pro-death penalty side). Generally, however, academic papers should employ appeals to emotions sparingly. A long paper that is purely based on emotions is not considered very professional.
Even when you are writing about an emotionally charged, controversial issue like the death penalty, you can't write a paper that is all emotion and opinion. The teacher, in that circumstance, will likely assign a failing grade because you haven't provided a sound (logical) argument.
- “ What's In a Cigarette? ” American Lung Association,
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- Use Social Media to Teach Ethos, Pathos and Logos
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- Logos (Rhetoric)
- Words, Phrases, and Arguments to Use in Persuasive Writing
- Pathos in Rhetoric
- Artistic Proofs: Definitions and Examples
- Definition and Examples of Ethos in Classical Rhetoric
- What Is a Rhetorical Device? Definition, List, Examples
- Persuasion and Rhetorical Definition
- What is an Appeal in Rhetoric?
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- AP English Exam: 101 Key Terms
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- Proof in Rhetoric
What Are Logos, Pathos & Ethos?
A straight-forward explainer (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
If you spend any amount of time exploring the wonderful world of philosophy, you’re bound to run into the dynamic trio of rhetorical appeals: logos , ethos and pathos . But, what exactly do they mean and how can you use them in your writing or speaking? In this post, we’ll unpack the rhetorical love triangle in simple terms, using loads of practical examples along the way.
Overview: The Rhetorical Triangle
- What are logos , pathos and ethos ?
- Logos unpacked (+ examples)
- Pathos unpacked (+ examples)
- Ethos unpacked (+ examples)
- The rhetorical triangle
What are logos, ethos and pathos?
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument . At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority.
Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but it’s important to consider a few different factors to determine the best mix for any given context. Let’s look at each rhetorical appeal in a little more detail to understand how best to use them to your advantage.

Logos appeals to the logical, reason-driven side of our minds. Using logos in an argument typically means presenting a strong body of evidence and facts to support your position. This evidence should then be accompanied by sound logic and well-articulated reasoning .
Let’s look at some examples of logos in action:
- A friend trying to persuade you to eat healthier might present scientific studies that show the benefits of a balanced diet and explain how certain nutrients contribute to overall health and longevity.
- A scientist giving a presentation on climate change might use data from reputable studies, along with well-presented graphs and statistical analyses to demonstrate the rising global temperatures and their impact on the environment.
- An advertisement for a new smartphone might highlight its technological features, such as a faster processor, longer battery life, and a high-resolution camera. This could also be accompanied by technical specifications and comparisons with competitors’ models.
In short, logos is all about using evidence , logic and reason to build a strong argument that will win over an audience on the basis of its objective merit . This contrasts quite sharply against pathos, which we’ll look at next.

Contrasted to logos, pathos appeals to the softer side of us mushy humans. Specifically, it focuses on evoking feelings and emotions in the audience. When utilising pathos in an argument, the aim is to cultivate some feeling of connection in the audience toward either yourself or the point that you’re trying to make.
In practical terms, pathos often uses storytelling , vivid language and personal anecdotes to tap into the audience’s emotions. Unlike logos, the focus here is not on facts and figures, but rather on psychological affect . Simply put, pathos utilises our shared humanness to foster agreement.
Let’s look at some examples of pathos in action:
- An advertisement for a charity might incorporate images of starving children and highlight their desperate living conditions to evoke sympathy, compassion and, ultimately, donations.
- A politician on the campaign trail might appeal to feelings of hope, unity, and patriotism to rally supporters and motivate them to vote for his or her party.
- A fundraising event may include a heartfelt personal story shared by a cancer survivor, with the aim of evoking empathy and encouraging donations to support cancer research.
As you can see, pathos is all about appealing to the human side of us – playing on our emotions to create buy-in and agreement.

Last but not least, we’ve got ethos. Ethos is all about emphasising the credibility and authority of the person making the argument, or leveraging off of someone else’s credibility to support your own argument.
The ethos card can be played by highlighting expertise, achievements, qualifications and accreditations , or even personal and professional associations and connections. Ultimately, the aim here is to foster some level of trust within the audience by demonstrating your competence, as this will make them more likely to take your word as fact.
Let’s look at some examples of ethos in action:
- A fitness equipment brand might hire a well-known athlete to endorse their product.
- A toothpaste brand might make claims highlighting that a large percentage of dentists recommend their product.
- A financial advisor might present their qualifications, certifications and professional memberships when meeting with a prospective client.
As you can see, using ethos in an argument is largely about emphasising the credibility of the person rather than the logical soundness of the argument itself (which would reflect a logos-based approach). This is particularly helpful when there isn’t a large body of evidence to support the argument.
Ethos can also overlap somewhat with pathos in that positive emotions and feelings toward a specific person can oftentimes be extended to someone else’s argument. For example, a brand that has nothing to do with sports could still benefit from the endorsement of a well-loved athlete, just because people feel positive feelings about the athlete – not because of that athlete’s expertise in the product they’re endorsing.

How to use logos, pathos and ethos
Logos, pathos and ethos combine to form the rhetorical triangle , also known as the Aristotelian triangle. As you’d expect, the three sides (or corners) of the triangle reflect the three appeals, but there’s also another layer of meaning. Specifically, the three sides symbolise the relationship between the speaker , the audience and the message .
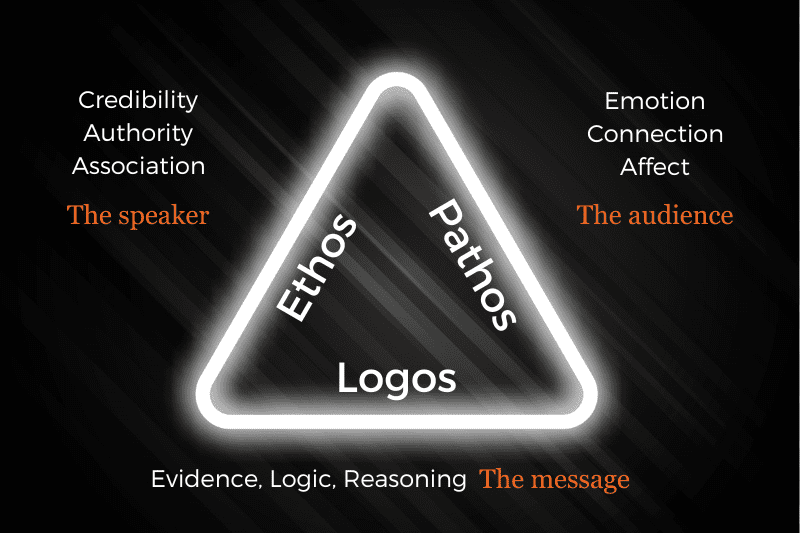
Without getting too philosophical, the key takeaway here is that logos, pathos and ethos are all tools that you can use to present a persuasive argument . However, how much you use each tool needs to be informed by careful consideration of who your audience is and what message you’re trying to convey to them.
For example, if you’re writing a research paper for a largely scientific audience, you’ll likely lean more heavily on the logos . Conversely, if you’re presenting a speech in which you argue for greater social justice, you may lean more heavily on the pathos to win over the hearts and minds of your audience.
Simply put, by understanding the relationship between yourself (as the person making the argument), your audience , and your message , you can strategically employ the three rhetorical appeals to persuade, engage, and connect with your audience more effectively in any context. Use these tools wisely and you’ll quickly notice what a difference they can make to your ability to communicate and more importantly, to persuade .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Instantly enhance your writing in real-time while you type. With LanguageTool
Get started for free
What Are Ethos, Logos, and Pathos?
Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of persuasion. We’ll be covering what they mean and how to include them in your writing.

Quick Summary on Using Ethos, Logos, and Pathos in Your Writing
- Ethos , logos , and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer’s credibility, logos appeals to the audience’s reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions.
- These three concepts, also known as the rhetorical triangle , three rhetorical appeals , or three modes of persuasion , were coined by Aristotle in his explanation of what makes rhetoric effective.

Ethos vs. Logos vs. Pathos
To understand what ethos, logos, and pathos are, you must first know what rhetoric is.
Rhetoric is defined by the Oxford Dictionary as “the art of effective or persuasive speaking or writing.” Aristotle defined rhetoric as “the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion.” In simpler terms, rhetoric is the effectiveness of the words (spoken or written) you choose to convey a message or change your audience’s perspective.
According to Aristotle, there are three means by which your rhetoric can be more powerful and that’s through the use of ethos, logos, and pathos. Knowing how to apply these three elements of persuasion can make your writing more compelling, so we’re going to teach you exactly what they mean and how to use them.
What Is Ethos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
Ethos establishes the writer’s credibility or authority. Imagine you’re at a climate change conference to learn how you can help planet Earth. Whose speech would you find more trustworthy—that of a CEO of a gas company that has profited millions of dollars by drilling for oil, or a speech by the CEO of a non-profit that helps clean oceans?
Ethos “appeals to the writer’s credibility, authority, or character” to get the audience to trust them.
My non-profit organization started with just one volunteer—me. I’d walk up and down the beaches collecting trash. Then, a friend joined me. The following week, that friend brought a friend. And then another. Until it grew to what it is today—an organization with more than 300 volunteers who have helped remove more than 15,000 pounds (6.8 tons) of trash from the beaches and the oceans. So, I know quite a bit on getting people together for a good cause.
Consider word choice, spelling, and grammar when incorporating ethos to your writing. It’s hard to trust a writer when their text is riddled with errors. Depending on what you’re writing, it may be a good idea to explicitly explain why you’re trustworthy and your expertise in the area you’re writing about.
To ensure your writing is error-free, try using LanguageTool as your writing assistant. This multilingual spelling and grammar checker can detect various types of mistakes in your writing and suggest stylistic improvements.
What Is Logos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
The word logic is derived from the word logos. As you might have imagined, logos is the “appeal to the reader’s logic.” This means that you use facts, data, and statistics to support your reasoning.
Using logos in your writing is effective because it provides evidence that makes it difficult for your audience to disagree with you. Proper use of logos in your writing requires thorough research. The following example includes logos:
According to NASA and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), “the influence of human activity on the warming of the planet has evolved from theory to established fact.” This can be proven through data collected from ice cores, rocks, and tree rings as well as modern equipment, like satellites.
What Is Pathos, and How Do You Include It in Your Writing?
The last of the three elements of persuasion we’ll be discussing is pathos, which appeals to the audience’s emotions. In other words, writers try to persuade their audience by having them feel a certain way. Consider the following example:
Climate change is already happening all around us. But let’s pretend that we’re at the liberty of not having to worry about it because its effects won’t be evident in our lifetimes. What about your children? Or your children’s children? Imagine the life they will live as they have to endure extreme heat, catastrophic hurricanes, unprecedented rainfalls, and more. Climate change may not affect you personally, but it will affect those you love.
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Makes For Effective Writing
Depending on what you’re writing and how you’re writing it, you may find yourself using more of either ethos, logos, or pathos. Truly effective writing finds a way to incorporate all three, even if one or two are used just a bit. As you read, try to recognize ethos, logos, and pathos. This will help you better incorporate it into your writing.

Unleash the Professional Writer in You With LanguageTool
Go well beyond grammar and spell checking. Impress with clear, precise, and stylistically flawless writing instead.
Works on All Your Favorite Services
- Thunderbird
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Word
- Open Office
- Libre Office
We Value Your Feedback
We’ve made a mistake, forgotten about an important detail, or haven’t managed to get the point across? Let’s help each other to perfect our writing.
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
3 Modes of Persuasion — Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
July 19, 2023
When structuring an argument, whether verbally or in written form, it is important to consider not only the ideas but the ways in which they might be persuasive. This article will explore the three primary modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and demonstrate the various ways you might use them to your advantage. They fall under the heading of rhetoric, which the Oxford English Dictionary defines as “the art of using language effectively so as to persuade or influence others.” These three modes of persuasion were first detailed in Aristotle’s Rhetoric . We’ll begin with the question, what is ethos in persuasion? Then we’ll discuss the pathos persuasive technique and, finally, logos in persuasion.
What Is Ethos in Persuasion?
While the term “ethos” may be unfamiliar you have certainly encountered its use in your day-to-day life. Of the three modes of persuasion, ethos is one that appeals to the speaker’s character or expertise. (The word itself has roots in the Latin and Greek words for “character.”) In this sense the use of ethos is contextual. It relies on some degree of shared knowledge between speaker and listener.
Here are two examples of ethos in practice:
- “As a licensed nutritionist, I strongly recommend you eliminate dairy from your diet.”
- “As a scholar of baroque architecture, I can assure you this local church is nothing out of the ordinary.”
What Is Ethos in Persuasion? (Continued)
Both of these examples use a common construction (“As a…”) in order to establish authority. This construction foregrounds the use of ethos and, as you might notice in the second example, can create a somewhat condescending tone. When we’re looking for it, this particular use of ethos is quite obvious. In everyday usage, however, we often find subtle ways of establishing authority. This might mean citing names or ideas or using a particular linguistic register. Ethos is working on a subtle level far more often than we realize. So, it’s important to keep asking ourselves, what is ethos in persuasion? Whether or not we recognize it for what it is, the persuasive effect is undeniable.
What Is Ethos in Persuasion? — Endorsements
Endorsements—by celebrities, authorities, or other trusted figures—are another example of ethos functioning as one of the modes of persuasion. Do political endorsements ever affect your choice of which candidate to support? How about a blurb on the back cover of a book? If a writer you admire—or a Nobel Prize winner or a former heavyweight champion of the world—describes the book as “life-changing” or a “must-read” or “absolutely spellbinding from start to finish” does it make you want to check out the book for yourself?
Pathos Persuasive Technique
Pathos, the second of the three modes of persuasion, involves an appeal to emotion. This is different from the speaker establishing their own authority. With the pathos persuasive technique, a speaker attempts to stir up emotion in their listener. This is in an effort to bring them to a desired conclusion. There is a wide range of emotions that one might appeal to when using pathos as mode of persuasion. In Rhetoric , Aristotle identified seven emotional dichotomies. These are:
- Anger/Calmness
- Friendship/Enmity
- Fear/Confidence
- Shame/Shamelessness
- Kindness/Unkindness
- Pity/Indignation
- Envy/Emulation
The pathos persuasive technique might involve creating one of these emotions. Thereby the listener might become more receptive to a desired conclusion. On the other hand, the pathos persuasive technique could involve counteracting one of these emotions in the direction of its opposite. It is often effective to move across these dichotomies, activating a nuanced spectrum of emotion in the listener.
For example, if a speaker is attempting to build political support it could be useful to drum up anger towards their opposition. At the same, however, too much reliance on anger will eventually become apparent to an audience. To this end, the speaker will want to fold in moments of calm reflection and create empathy toward the people they are promising to help. This technique would engage with a number of the dichotomies listed above, perhaps most clearly Anger/Calmness and Friendship/Enmity.
Pathos Persuasive Technique — Literary Devices
Literary devices are excellent tools for incorporating the pathos persuasive technique into your writing and speech. Literary devices can create rhythms and emphasize sonic or structural qualities that are particularly compelling. These effects will likely be familiar to you from English classrooms. A rhyme scheme or a metrical pattern, for example, can make a conclusion feel inevitable. Consider for instance the final stanza of John Keats’ “Ode on a Grecian Urn.” (In this context, “thou” refers to the urn.) Keats writes,
O Attic shape! Fair attitude! with brede Of marble men and maidens overwrought, With forest branches and the trodden weed; Thou, silent form, dost tease us out of thought As doth eternity: Cold Pastoral! When old age shall this generation waste, Thou shalt remain, in midst of other woe Than ours, a friend to man, to whom thou say’st, “Beauty is truth, truth beauty,—that is all Ye know on earth, and all ye need to know.
Isn’t there a sense that this is the only way the poem could’ve ended? That this is the only adequate conclusion? This early 19th-century literary example is clearly quite different from how you will be using the pathos persuasive technique. It does demonstrate, however, how pathos can operate through the use of literary devices. How language itself (rather than what’s being said) can be inherently persuasive. To this end, there is a wide range of literary devices that it will be helpful to familiarize yourself with.
Logos in Persuasion
Logos in persuasion refers to a mode of persuasion that relies on logic-based reason. This means structuring an argument in terms of premises (which are similar to hypotheses), supporting evidence, and conclusions. Deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning are two types of logic that it will be helpful to understand.
Logos in Persuasion — Deductive Reasoning
Deductive reasoning involves proving that a conclusion is incontrovertibly true. This is based on the truth of its premises and the ways in which they lead to a conclusion. Here is an example.
- Premise 1: Napoleon was human.
- Premise 2: All humans have mothers.
- Conclusion: Napoleon had a mother.
This example is based on the logical rule that if A=B and B=C then A=C. This rule, however, doesn’t imply that the premises are true (i.e. that A=B and B=C). The conclusion can only be proven to be true if the premises are taken to be true as well. In this example, there isn’t much to argue with, but the logical structure also has the potential to give a false impression of validity.
Logos in Persuasion — Inductive Reasoning
The above example of deductive reasoning proves (or at least claims to prove) the truth of a specific statement. Inductive reasoning, on the other hand, often brings us to more general conclusions. Instead of resulting in a definite, provable conclusion, inductive reasoning results in a probable one. This is the form of reasoning that we use most commonly in our day to day lives. While not definitive, inductive reasoning leads to valid conclusions that are often more compelling than those arrived at through deductive reasoning. As mentioned already, deductive reasoning can at times feel manipulative and overly formal.
Logos in Persuasion — Inductive Reasoning (Inference)
Inference is one of the most common forms of inductive reasoning. An inference is defined most simply as “an idea or conclusion that’s drawn from evidence and meaning.” This could mean recognizing a pattern and reaching a conclusion based on that. For example, based on the fact that the sun has risen each morning for as long as I can remember, I can infer that the sun will rise again tomorrow morning. The conclusion here is that the sun will rise tomorrow morning. The logic doesn’t prove this conclusion—the earth could stop rotating or the sun could suddenly extinguish—but, as you can tell, it’s still quite persuasive.
3 Modes of Persuasion — Practical Applications
Having a clear sense of these three modes of persuasion will be helpful when it comes to constructing an argument in a wide variety of contexts. These are good to keep in mind in the context of a job interview or when writing a statement of purpose for graduate school or even when you’re struggling to convey an idea to a friend.
Thinking in terms of ethos, pathos and logos is an especially good way to improve your public speaking skills . A dynamic speech will generally incorporate each of these modes of persuasion. So, if it feels like something might be missing, or if the tone of your speech seems to slacken, one recourse is to identify the modes of persuasion you are using and to find ways of incorporating others.
A speech that relies entirely on the pathos persuasive technique, for example, could start to feel somewhat redundant. If it goes on for too long it could appear to lack a logical argument or sense of authority. Switching to logos in persuasion or asking yourself, what is ethos in persuasion?, are good ways to keep the listener on their toes. When the listener gets the sense that they know exactly what will come next they often tune out. Even a powerful, and morally justified, appeal to anger will begin to seem rote after some time. Just as an excessive reliance on one’s character or authority (ethos) could have the listener rolling their eyes.
3 Modes of Persuasion — Final Thoughts
As a way to remember the three modes of persuasion, it will be helpful to associate one word with each of them. For ethos, think character. For pathos, think emotion. With logos, just change the last two letters and you have “logic.”
For further practice, try going through a piece of persuasive writing and sorting the paper into the modes of persuasion it is employing. You can use a different colored highlighter for each mode. Likewise, this can also be a good way to edit your own writing. Organizing arguments according to the mode they are employing will give you a sense of the piece’s balance. This can offer insight into how you might revise. It’s important to consider the audience and how the piece will likely be received. Depending on context, different balances of ethos, pathos, and logos will be desired. A political speech, for instance, might rely on pathos while an academic paper should be more heavily skewed towards logos.
In addition to ethos, pathos, and logos—which we can think of as rhetorical modes—there are a number of rhetorical devices that it would be a good idea to familiarize yourself with. These devices will offer a plethora of ways to deploy your understanding of the three modes of persuasion, providing a template for how you might keep a reader or listener engaged.
- College Success
- High School Success
Emmett Lewis
Emmett holds a BA in Philosophy from Vassar College and is currently completing an MFA in Writing at Columbia University. Previously, he served as a writing instructor within the Columbia Artists/Teachers community as well as a Creative Writing Teaching Fellow at Columbia, where he taught poetry workshops. In addition, Emmett is a member of the Poetry Board at the Columbia Journal , and his work has been published in HAD , Otoliths , and Some Kind of Opening , among others.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Marquette University Law School Faculty Blog

Logos, Ethos, and Pathos in Persuasive Writing
- Post author: Lisa A. Mazzie
- Post published: January 27, 2014
- Post category: Legal Writing / Political Processes & Rhetoric / Public
- Post comments: 1 Comment
At their core, objective and persuasive legal writing share many of the same traits, such as maintaining the small scale organizational paradigm we refer to as CREAC (a/k/a IRAC). Because lawyers use that paradigm to advance their arguments, students need to master it, which makes the structure of the argument look similar to objective writing. But students need to make other, subtler changes in their writing (and thinking) to persuade effectively. It’s often challenging to succinctly explain these more subtle differences, but one easy way is to introduce the “why” behind the differences, which in turn helps explain those differences. Good persuasive writing argues a position by using a combination of three ancient rhetorical techniques: logos, ethos, and pathos.
The first technique is logos, which means logic. Persuasive writing that uses logos uses, where appropriate, literal or historical analogies as well as factual and historical data. Such writing contains citations to authorities or experts. As scholars Ruth Anne Robbins, Steve Johansen, and Ken Chestek say in their new book, Your Client’s Story: Persuasive Legal Writing 21 (2013), “Logos makes your audience think you are right.”
Logos is the easiest technique to understand when referring to legal writing. It makes sense that a persuasive legal document use logic to persuade readers, and logos is undoubtedly the starting point for a persuasive argument. But it’s just the start.
The second technique is ethos, which deals with the credibility of the writer. When we read something from someone we trust, we are more likely to believe what she is saying. As Professors Robbins, Johansen, and Chestek tell us, “[E]thos makes your audience trust you are right.” Id. Building ethos in legal writing means the writer must focus on providing substantively sound analyses and arguments, while appropriately acknowledging contrary law and counterarguments, but also focus on creating a professional and polished document that is error-free.
The final technique is pathos, which deals with emotions—specifically, with empathy. When a speaker or writer uses pathos, he is appealing to his audience’s sense of empathy for his position or his client. He may use vivid, concrete language and examples. He might use figurative language, such as alliteration, similes, or metaphors. “[P]athos makes your audience feel you are right.” Id.
There are two kinds of pathos: emotional substance and medium mood control. The speaker or writer uses emotional substance when she is trying to elicit an emotional response from her audience. One example that I use to illustrate this idea is the ten-second public service announcement popular in the late 1980s. The spot opens with butter sizzling in a hot pan. There’s an ominous bit of music and a serious voice tells you, “This is drugs.” We then see an egg cracked into the pan, which is so hot that the white of the egg cooks immediately. The voice returns. “This is your brain on drugs. [pause] Any questions?” Here, it seems clear that the viewer is to feel fear and to act on that fear: Look what happens to your brain when you use drugs! Don’t use drugs!
In legal writing, we use the emotional substance pathos when we attempt to create empathy for our client and when we appeal to grander themes of fairness or justice.
Another kind of pathos is medium mood control. “Medium” here applies to the mode of communication and how that mode of communication affects the audience’s mood. Humor is an often used technique. When the reader feels happy, he is more likely to be receptive to (and, thus, persuaded by) the reader’s message.
Humor is quite difficult to use in legal writing. Instead, a legal writer effectively uses medium mood control by using an appropriate tone, carefully choosing words, and avoiding techniques that might irritate a reader (like poor citation or sloppy organization, among others). Most of the things a writer does to build her ethos apply here as well: a well-crafted, accurate brief is a joy to read, which makes a reader happy to read it.
The trick with pathos is to use emotion appropriately. Heavy-handed pathos can make your reader feel manipulated, and no one likes to feel manipulated.
Using all three techniques in concert helps create a strong persuasive piece. The example I like to use is Martin Luther King, Jr.’s Letter from Birmingham Jail . In that piece, Dr. King so brilliantly uses all three rhetorical techniques to create a compelling and persuasive document that explains why white clergy’s call for gradualism in the early days of the civil rights movement was misguided. If you haven’t yet read the Letter, I encourage you to do so and to locate for yourself how and where Dr. King uses logos, ethos, and pathos.
How a reader responds to a writer’s persuasive techniques depends on two things: what the reader’s stock structures are and how the reader is being asked to respond.
First, when people are asked to confront new situations or new information, they rely on their stock structures to make sense of that situation or information. See Robbins et al., Your Client’s Story 29-36. Stock structures (which are known by different names in different fields) are our stereotyped models of experiences. Stock structures provide useful cognitive short cuts because we can quickly assess a new situation and know how we should respond based on our experiences with that situation. But—and it’s a very important “but”—while there may be some commonality between them, stock structures differ for different people because our experiences differ.
Second, readers can be asked to respond in one of three ways: response shaping, response reinforcing, and response changing. See id. Where a reader has little knowledge or experience and is being persuaded to adopt a new position, the writer has a chance to shape the reader’s response, to help build some stock structures, if you will. This situation does not occur frequently in law, mostly with issues of first impression. A reader who is being asked to simply reinforce what he already knows or has experienced may be easily persuaded. For example, when a trial judge is asked to simply apply precedent, she is being asked to simply reinforce what she knows she needs to do. More difficult is the reader who is being asked to respond by changing his existing beliefs in order to form new ones. Such a reader will need more persuasion.
As our students begin their foray into persuasive writing, share with them some of your favorite persuasive pieces (legal or otherwise).
You Might Also Like
Restorative justice skyping from milwaukee to austin, the link between the kennedy assassination and the onset of beatlemania, two flaws in the sopa, this post has one comment.
Great post.
I just came across a footnote in Law and Language: Effective Symbols of Community , by Harold Berman (edited by John Witte, Jr.), which explains the relationship between syllogistic logic and legal argument:
“‘However useful syllogistic logic may be in testing the validity of conclusions drawn from given premises, it is inadequate in practical science such as law, where the premises are not given but must be created. Legal rules, viewed as major premises, are always subject to qualification in light of the particular circumstances; it is a rule of English and American law, for example, that a person who intentionally strikes another is civilly liable for battery, but such a rule is subject, in legal practice to infinite modification in light of the possible defense (for example, self-defense, defense of property, parental privilege, immunity from suit, lack of jurisdiction, insufficiency of evidence, etc.). In addition, life continually presents new situations to which no existing rule is applicable; we simply do not know the legal limits of freedom of speech, for example, since the social context in which words are spoken is continually changing. Thus, legal rules are continually being made and remade.'”
73 n.23 (quoted in part, internal citations omitted). Syllogism is the starting point for discussing legal logic. I find it helpful to explain the structure of legal argument in the context of major premise/minor premise/conclusion. But Berman highlights the very point that allows two sides of an argument to be presented: that the major premises “are subject to qualification.” The same point could be made of the minor premises–the facts.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Understand The Difference Between Ethos, Pathos, And Logos To Make Your Point
- What Is Ethos?
- What Is Pathos?
- What Is Logos?
- Examples Of Each
- What Are Mythos And Kairos?
During an argument, people will often say whatever is necessary to win. If that is the case, they would certainly need to understand the three modes of persuasion, also commonly known as the three rhetorical appeals: ethos , pathos , and logos . In short, these three words refer to three main methods that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. As you’re about to find out, the modes of persuasion are important because a speaker who knows how to effectively use them will have a significant advantage over someone who doesn’t.
The terms ethos , pathos , and logos and the theory of their use can be traced back to ancient Greece to the philosophy of Aristotle . Aristotle used these three concepts in his explanations of rhetoric , or the art of influencing the thought and conduct of an audience. For Aristotle, the three modes of persuasion specifically referred to the three major parts of an argument: the speaker ( ethos ), the argument itself ( logos ), and the audience ( pathos ). In particular, Aristotle focused on the speaker’s character, the logic and reason presented by an argument, and the emotional impact the argument had on an audience.
While they have ancient roots, these modes of persuasion are alive and well today. Put simply, ethos refers to persuasion based on the credibility or authority of the speaker, pathos refers to persuasion based on emotion, and logos refers to persuasion based on logic or reason.
By effectively using the three modes of persuasion with a large supply of rhetorical devices, a speaker or writer can become a master of rhetoric and win nearly any argument or win over any audience. Before they can do that, though, they must know exactly what ethos , pathos , and logos mean. Fortunately, we are going to look closely at each of these three ideas and see if they are really as effective as they are said to be.
⚡️ Quick summary
Ethos , pathos , and logos are the three classical modes of persuasion that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. Specifically:
- ethos (character): known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” This is the method in which a person relies on their credibility or character when making an appeal or an argument.
- pathos (emotions): known as “the appeal to emotion.” Pathos refers to the method of trying to persuade an audience by eliciting some kind of emotional reaction.
- logos (logic): known as “the appeal to reason.” This method involves using facts and logical reasoning to support an argument and persuade an audience.
What is ethos ?
The word ethos comes straight from Greek. In Greek, ethos literally translates to “habit,” “custom,” or “character.” Ethos is related to the words ethic and ethical , which are typically used to refer to behavior that is or isn’t acceptable for a particular person.
In rhetoric, the word ethos is used to refer to the character or reputation of the speaker. As a rhetorical appeal, ethos is known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” When it comes to ethos , one important consideration is how the speaker carries themself and how they present themselves to the audience: Does it seem like they know what they are talking about? Do they even believe the words they are saying? Are they an expert? Do they have some experience or skills that tell us we should listen to them?
Ethos is important in rhetoric because it often influences the opinion or mood of the audience. If a speaker seems unenthusiastic, unprepared, or inexperienced, the audience is more likely to discount the speaker’s argument regardless of what it even is. On the other hand, a knowledgeable, authoritative, confident speaker is much more likely to win an audience over.
Ethos often depends on more than just the argument itself. For example, a speaker’s word choice, grammar, and diction also contribute to ethos ; an audience may react more favorably toward a professional speaker who has a good grasp of industry jargon and enunciates clearly versus a speaker who lacks the necessary vocabulary and fails to enunciate. Ethos can also be influenced by nonverbal factors as well, such as posture, body language, eye contact, and even the speaker’s choice of clothing. For example, a military officer proudly wearing their uniform bedecked with medals will go a long way to establishing ethos without them saying a single word.
Here as a simple example of ethos :
- “As a former mayor of this city, I believe we can solve this crisis if we band together.”
The speaker uses ethos by alerting the audience of their credentials and experience. By doing so, they rely on their reputation to be more persuasive. This “as a…” method of establishing ethos is common, and you have probably seen it used in many persuasive advertisements and speeches.
What are open-ended questions and how can you use them effectively? Find out here.
What is pathos ?
In Greek, pathos literally translates to “suffering, experience, or sensation.” The word pathos is related to the words pathetic , sympathy , and empathy , which all have to do with emotions or emotional connections. Aristotle used the word pathos to refer to the emotional impact that an argument had on an audience; this usage is still mainly how pathos is used in rhetoric today.
As a rhetorical appeal, pathos is referred to as “the appeal to emotion.” Generally speaking, an author or speaker is using pathos when they are trying to persuade an audience by causing some kind of emotional reaction. When it comes to pathos , any and all emotions are on the table: sadness, fear, hope, joy, anger, lust, pity, etc.
As you probably know from your own life, emotions are a powerful motivating factor. For this reason, relying on pathos is often a smart and effective strategy for persuading an audience. Both positive and negative emotions can heavily influence an audience: for example, an audience will want to support a speaker whose position will make them happy, a speaker who wants to end their sadness, or a speaker who is opposed to something that makes them angry.
Here is a simple example of pathos :
- “Every day, the rainforests shrink and innocent animals are killed. We must do something about this calamitous trend before the planet we call our home is damaged beyond repair.”
Here, the author is trying to win over an audience by making them feel sad, concerned, or afraid. The author’s choice of words like “innocent” and “calamitous” enforce the fact that they are trying to rely on pathos .
What is logos ?
In Greek, the word logos literally translates to “word, reason, or discourse.” The word logos is related to many different words that have to do with reason, discourse, or knowledge, such as logic , logical , and any words that end in the suffixes -logy or -logue .
As a mode of persuasion and rhetorical appeal, logos is often referred to as “the appeal to reason.” If a speaker or author is relying on logos , they are typically reciting facts or providing data and statistics that support their argument. In a manner of speaking, logos does away with all of the bells and whistles of ethos and pathos and cuts to the chase by trying to present a rational argument.
Logos can be effective in arguments because, in theory, it is impossible to argue against truth and facts. An audience is more likely to agree with a speaker who can provide strong, factual evidence that shows their position is correct. On the flip side, an audience is less likely to support an argument that is flawed or entirely wrong. Going further, a speaker that presents a lot of supporting evidence and data to the audience is likely to come across as knowledgeable and someone to be listened to, which earns bonus points in ethos as well.
While Aristotle clearly valued an argument based on reason very highly, we know that logos alone doesn’t always effectively persuade an audience. In your own life, you have likely seen a rational, correct speaker lose an argument to a charismatic, authoritative speaker who may not have the facts right.
Here is a simple example of logos :
- “According to market research, sales of computer chips have increased by 300% in the last five years. Analysis of the industry tells us that the market share of computer chips is dominated by Asian manufacturers. It is clear that the Asian technology sector will continue to experience rapid growth for the foreseeable future.”
In this paragraph, the author is using data, statistics, and logical reasoning to make their argument. They clearly hope to use logos to try to convince an audience to agree with them.
Do you need persuading to take this quiz on identifying ethos, pathos, and logos? We think you’ll be a champion at it.
Examples of ethos , pathos , and logos
Ethos , pathos , and logos can all be employed to deliver compelling and persuasive arguments or to win over an audience. Let’s look at a variety of examples to see how different speakers and authors have turned to these modes of persuasion over the years.
“Come I to speak in Caesar’s funeral. He was my friend, faithful and just to me […] You all did see that on the Lupercal I thrice presented him a kingly crown, Which he did thrice refuse: was this ambition?” —Marc Antony, Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
In this scene, Marc Antony is trying to win over the Roman people, so Shakespeare has Antony rely on ethos . Antony is establishing himself as both a person of authority in Rome (having the power to offer Caesar a crown) and an expert on Caesar’s true character (Antony was Caesar’s close friend and advisor).
“During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife. Pixar went on to create the world’s first computer animated feature film, Toy Story , and is now the most successful animation studio in the world. In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple’s current renaissance.” —Steve Jobs, 2005
Here, Steve Jobs is providing his background–via humblebrag – of being a major figure in several different highly successful tech companies. Jobs is using ethos to provide substance to his words and make it clear to the audience that he knows what he is talking about and they should listen to him.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
“Moreover, though you hate both him and his gifts with all your heart, yet pity the rest of the Achaeans who are being harassed in all their host; they will honour you as a god, and you will earn great glory at their hands. You might even kill Hector; he will come within your reach, for he is infatuated, and declares that not a Danaan whom the ships have brought can hold his own against him.” —Ulysses to Achilles, The Iliad by Homer
In this plea, Ulysses is doing his best to pile on the pathos . In one paragraph, Ulysses is attempting to appeal to several of Achilles’s emotions: his hatred of Hector, his infamous stubborn pride, his sympathy for civilians, and his desire for vengeance.
“I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest—quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality.” —Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
In this excerpt from his “I Have A Dream” speech, King is using pathos to accomplish two goals at once. First, he is connecting with his audience by making it clear is aware of their plight and suffering. Second, he is citing these examples to cause sadness or outrage in the audience. Both of these effects will make an audience interested in what he has to say and more likely to support his position.
Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech is recognizable and noteworthy for many reasons, including the rhetorical device he employs. Learn about it here.
“Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be. But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature which would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders. In such case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favoured the individuals of any of the species, by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement.” —Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species , 1859
In this passage, Darwin is using logos by presenting a rational argument in support of natural selection. Darwin connects natural selection to established scientific knowledge to argue that it makes logical sense that animals would adapt to better survive in their environment.
“I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face.” —Al Gore, “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” 2019
In this call to action, Al Gore uses logos to attempt to convince his audience of the significance of climate change. In order to do this, Gore both cites an expert in the field and provides a scientifically accurate simile to explain the scale of the effect that greenhouse gases have on Earth’s atmosphere.
What are mythos and kairos ?
Some modern scholars may also use terms mythos and kairos when discussing modes of persuasion or rhetoric in general.
Aristotle used the term mythos to refer to the plot or story structure of Greek tragedies, i.e., how a playwright ordered the events of the story to affect the audience. Today, mythos is most often discussed as a literary or poetic term rather than a rhetorical one. However, mythos may rarely be referred to as the “appeal to culture” or the “appeal to myth” if it is treated as an additional mode of persuasion. According to this viewpoint, a speaker/writer is using mythos if they try to persuade an audience using shared cultural customs or societal values.
A commonly cited example of mythos is King’s “I Have a Dream” speech quoted earlier. King says:
“When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men—yes, black men as well as white men—would be guaranteed the ‘unalienable rights’ of ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.’ ”
Throughout the speech, King repeatedly uses American symbols and American history ( mythos ) to argue that all Americans should be outraged that Black Americans have been denied freedom and civil rights.
Some modern scholars may also consider kairos as an additional mode of persuasion. Kairos is usually defined as referring to the specific time and place that a speaker chooses to deliver their speech. For written rhetoric, the “place” instead refers to the specific medium or publication in which a piece of writing appears.
Unlike the other modes of persuasion, kairos relates to the context of a speech and how the appropriateness (or not) of a setting affects how effective a speaker is. Once again, King’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a great example of the use of kairos . This speech was delivered at the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the 100th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation at the end of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Clearly, King intended to use kairos to enhance the importance and timeliness of this landmark speech.
Make your communication as smooth as can be by learning about filler words and when you should, and shouldn't, use them.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day

Ethos Pathos Logos: Persuasion Techniques To Appeal To Emotion
In the art of persuasion, mastering ethos, pathos, and logos is essential. These classical rhetorical strategies, introduced by Aristotle, help you appeal to your audience’s emotions, credibility, and logic.
Whether you’re crafting a speech, writing an article, or creating a marketing campaign, understanding how to effectively use ethos, pathos, and logos can significantly enhance your ability to influence and connect with your audience on a deeper level.
Let’s explore how these techniques can be your key to compelling persuasion.
| Ethos | Builds trust by showing credibility | Highlight your qualifications and use professional language |
| Pathos | Appeals to emotions | Use stories, vivid examples, and emotional language |
| Logos | Uses logic and facts to appeal | Present data, statistics, and logical arguments |
What Are Ethos, Pathos and Logos?
The easiest way to separate between the three is that Ethos, Pathos, and Logos focus on a particular side of a person. Combined, they form a strong force to persuade people.
Ethos is used when a person relies on their credibility or character when making an appeal or an argument.
Think about how Steve Jobs introduced himself at Stanford, detailing his journey with NeXT and Pixar. By highlighting his successful ventures, he used ethos to make the audience believe in his authority and expertise.
When an author uses ethos, they are leveraging their credentials to gain trust. This can be seen in political speeches, where leaders often cite their experiences to bolster their arguments.
Pathos is all about emotions. It’s the mode of persuasion that aims to make the audience feel, instead of thinking of something.
In Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech, he vividly describes the struggles and hopes of the people. His words evoke powerful emotions, from empathy to outrage.
Pathos can make the audience feel the urgency or importance of an issue, as seen in many charity appeals that use heart-wrenching images and stories to arouse compassion and spur action.
Logos is the appeal to logic and reason. It involves presenting a case and convince the audience by using:
- statistics, and
- rational arguments.
An example of this is Al Gore’s speeches on climate change, where he presents data and scientific evidence to support his claims.
By using logos, you provide a solid foundation for your argument, making it difficult for the audience to refute your points. The use of logical reasoning and factual evidence is crucial for establishing a strong argument.
Why Are Ethos, Pathos and Logos Effective?
Aristotle’s three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos are effective in persuading people, especially when combined. Here are a couple of ways they do this:
Ethos Builds Trust
Ethos builds trust. When you use ethos, you appeal to the audience’s perception of your character.

Think of Steve Jobs at Stanford, sharing his journey with NeXT and Pixar. He established his credibility by highlighting his success in creating the first computer animated feature film and the technology developed at NeXT, which is at the heart of Apple’s current renaissance.
This use of ethos makes the audience more likely to trust and believe in the speaker’s message.
Pathos Evokes Emotions
Pathos evokes emotions. Pathos, the appeal to emotion, taps into the audience’s feelings, making the message more relatable and impactful. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a prime example.
His words about freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality make the audience feel the urgency and importance of civil rights.
By using pathos, speakers can arouse both positive and negative emotions, driving their audience to action.
Logos Appeal To Logic & Reason
Logos provides logic and reason. Logos, the appeal to logic, involves presenting facts, statistics, and a logical argument.
Al Gore’s speeches on climate change effectively use logos by providing factual evidence and scientific data.
When an audience is presented with a strong logical argument, it becomes difficult to refute the speaker’s point. The use of logos creates a solid foundation for the argument, making it more persuasive.
Ethos Pathos & Logos Work Great Together
Ethos and pathos together create a compelling narrative. When combined, ethos and pathos can be particularly powerful.
Rhetorical appeals adapt to the audience. One of the strengths of using ethos, pathos, and logos is their flexibility. Depending on the audience and context, a speaker can adjust their use of these appeals to be more effective.

A presenter at a scientific conference might rely heavily on logos to appeal to the audience’s logical reasoning, while a political leader might use pathos to rally support during a campaign. This adaptability makes the three modes of persuasion essential tools for any communicator.
The effectiveness of ethos, pathos, and logos in persuasion lies in their ability to:
- build trust,
- evoke emotions,
- provide logical reasoning,
- create compelling narratives, and
- adapt to different audiences.
By mastering these rhetorical strategies, you can become a more persuasive and impactful communicator.
How To Recognise Ethos, Pathos and Logos in Content?
Recognising these rhetorical appeals in content involves looking for specific elements:
How To Recognise Ethos
Look for references to the speaker’s qualifications, experience, or character. When an author mentions their background or uses industry-specific jargon correctly, they are using ethos.
For example, a military officer in full uniform speaking about national security is leveraging their ethos.
In the video below, Admiral William McRaven’s worn his military uniform during his commencement speech to show his ethos, and be more persuasive to his audience – university graduates.
How To Recognise Pathos
Identify emotionally charged language or stories that aim to make the audience feel emotions – these can be positive, or negative emotions, depending on the intention of the presenter.
Descriptions of personal struggles, vivid imagery, or narratives that tap into universal human experiences are signs of pathos.
Advertisements often use this technique by showing happy families or sad animals to elicit emotional responses. One example is Nike:
How To Recognise Logos
Spot logical arguments supported by data, statistics, and factual evidence. When an author uses charts, graphs, or detailed analysis, they are relying on logos.
This mode of persuasion focuses on the logical structure of the argument and the credibility of the evidence. You are likely to see Logos in practice in university or corporate presentations, or videos as simple as ‘X reasons to Y’:
Understanding how to recognise ethos, pathos, and logos helps you critically evaluate content. It allows you to see beyond the surface and understand the underlying strategies used to persuade you.
When you encounter a persuasive piece, ask yourself these questions to dissect their work:
- How is the author using their character to build trust?
- What emotions are they trying to evoke?
- What logical evidence are they presenting?
How To Use Ethos, Pathos and Logos In Your Work?
Here’s how you can use ethos, pathos, and logos in your work.
Ethos: Establishing Credibility
Using ethos means leveraging your character and credentials to gain your audience’s trust. When you use ethos, you present yourself as an authority on the subject.

If you are giving a presentation on technology trends, mentioning your years of experience in the tech industry and any relevant projects you’ve worked on can establish your credibility.
Steve Jobs effectively used ethos in his Stanford commencement address by detailing his journey with Apple and Pixar.
His success stories, including how Pixar went on to create the first computer animated feature film, reinforced his authority and made his advice more impactful.
To use ethos in your work, always highlight your:
- qualifications,
- experience, and
- achievements.
Use correct grammar and syntax to present a polished, professional image. Your audience is more likely to believe and respect a well-spoken, knowledgeable communicator.
Pathos: Evoking Emotions
Pathos is about appealing to your audience’s emotions. This can make your message more relatable and memorable.
In advertising, pathos is often used to evoke emotions like happiness, fear, or sympathy. An ad campaign for a charity might show emotional images of people in need to arouse empathy and encourage donations.
Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a classic example of using pathos. He evoked strong emotions by describing the great trials and tribulations faced by African Americans, making his call for justice more compelling.
In your work, connect with your audience by sharing emotional things, using:
- vivid examples,
- stories, and
- meaningful language.
When you are writing a report, delivering a speech, or creating a marketing campaign, incorporating pathos can make your message resonate on a deeper level.
Be mindful of the emotions you want to evoke, and use language that will effectively arouse those feelings.
Logos: Using Logic and Reason
Logos relies on logic and reason to persuade your audience. This involves using facts, statistics, and logical arguments to support your message.
In a business proposal, you might present data and financial projections to show the potential success of a new project.
To use logos in your work, focus on:
- presenting clear, logical arguments supported by credible evidence.
- Use statistics that support your points, and
- make sure your reasoning is sound.
Avoid logical fallacies, as they can undermine your argument and make you appear untrustworthy.
Combining Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
The most persuasive pieces often combine ethos, pathos, and logos. For example, in Shakespeare’s “Julius Caesar,” Antony uses all three to persuade the crowd.
He establishes his ethos by reminding them of his close relationship with Caesar, evokes pathos by showing Caesar’s wounds and describing his virtues, and uses logos to argue against Brutus’s claims.
In your work, consider how you can blend these rhetorical appeals. For example, if you are presenting a new business strategy, you might:
- Use ethos by sharing your relevant experience and successes.
- Use pathos by telling a compelling story about how the strategy will positively impact employees and customers.
- Use logos by presenting data and logical arguments to demonstrate the strategy’s potential for success.
By effectively using ethos, pathos, and logos, you can create a well-rounded and persuasive argument.
Your audience will not only believe in your credibility but also feel emotionally connected to your message and be convinced by the logical reasoning behind it.
Whether you are writing, speaking, or presenting, mastering these rhetorical strategies will enhance your ability to persuade and engage your audience.
Are There Other Methods Than Ethos, Pathos and Logos?
Beyond ethos, pathos, and logos, there are other methods of persuasion that can be equally effective – Kairos, Telos, and Mythos.

One notable method is kairos, which involves the timing and appropriateness of an argument.
A well-timed message can have a greater impact, leveraging the current context or mood of the audience to enhance persuasiveness.
One good example is when you present a call for environmental action during a natural disaster – this will likely be more compelling.
Another method is telos, which refers to the purpose or goal of the communication. Understanding and clearly communicating the purpose can align the audience’s values and beliefs with the intended message, making it more persuasive.
A motivational speech aimed at students, rather than to retirees should focus on inspiring them towards their future goals.
Mythos, the appeal to cultural values and narratives, is also powerful. This method taps into shared stories, traditions, and beliefs, making the argument resonate on a cultural level.
Politicians often use mythos by referencing national history or cultural myths to unite and inspire people.
Ethos Pathos Logos – Three Modes Of Persuasion
Mastering ethos, pathos, and logos equips you with powerful tools to connect with and persuade your audience.
By appealing to their emotions, establishing your credibility, and presenting logical arguments, you can create compelling messages that resonate on multiple levels. Whether in speeches, writing, or marketing, these techniques help you influence and engage effectively.
Embrace these classical rhetorical strategies to enhance your communication and leave a lasting impact on your audience.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


- Scriptwriting
Ethos, Pathos & Logos — Definition and Examples of Persuasive Advertising Techniques
- What is Pathos
- What is Logos
- What is Telos
- What is Kairos
- What is Ethos
- Ethos, Pathos & Logos
- What is an EPK
- What is a Creative Director
- What is Branded Content
- What is a Creative Brief
- How to Pitch a TV Show Like a Pro
- How Does Rotten Tomatoes Work?
- How to Make a Movie Poster
- The Filmmaker’s Guide to The Clio Advertising Awards
- A Complete Guide To The Funniest Commercials
- How to Make a Commercial
- How to Develop Your Brand
- Complete Guide to Advertising on Instagram
- How Does Instagram Promotion Work and Is It Worth It?
- How Can You Kickstart Your Social Media Advertising?
- Small Business Advertising Ideas from LeBron James Commercials
- How To Create a Successful Branded Content Campaign
- How and Why To Make Facebook Video Ads That Work
- How to Make a Commercial People Will Actually Share
- Video Branding Strategies to Get More Followers Right Now
- Social Media and Digital Communications for Successful Short Films
- Digital Advertising Trends
- Most Inspiring Ads
- Best Movie Taglines
- Best Marketing and Advertising Campaigns
- Best Creative Brief Template
- Best Explainer Video Trends for Your Brand
E thos, pathos and logos are techniques of persuasion that form the rhetorical triangle. A compelling argument, sales pitch, speech, or commercial ideally uses elements of all three strategies. We’ll show you how to employ each of the techniques and present some awesome examples along the way.
VIDEO: Ethos, Pathos and Logos Explained
Ethos, Pathos, Logos, Definition
The rhetorical triangle.
Rhetoric is a type of communication a writer or speaker uses to persuade, inform or motivate. We can see rhetoric everywhere — politics, law, advertising, creative writing, and even our everyday conversations.
Rhetorical devices include irony , metaphor , hyperbole and many other techniques writers and speakers employ to great effect.
A subset of these devices are known as rhetorical appeals , often attributed to Aristotle, and include: ethos , pathos and logos .
This is also known as the Rhetorical Triangle and we still depend on it today.
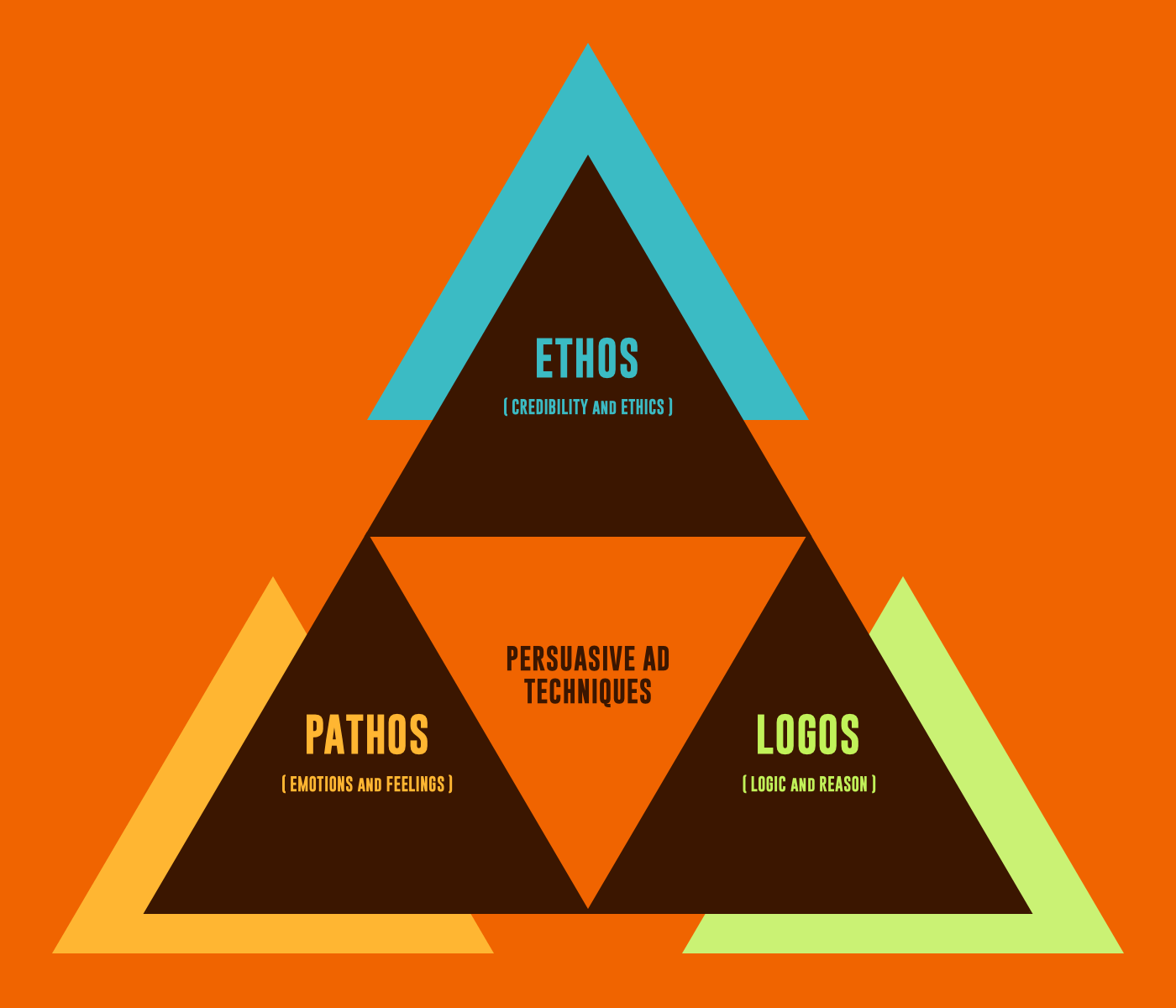
Ethos, pathos and logos are the three categories of persuasive advertising techniques
Each category invokes a different appeal between speaker and audience.
Ethos calls upon the ethics, or what we'd call the values, of the speaker. Pathos elicits emotions in the audience. Finally, logos puts logic into play by using evidence and facts.
Good persuasive advertising technique is when you balance all three.
But using ethos, pathos and logos in commercials sometimes means featuring one advertising technique prominently.
Learn More Logos Ethos and Pathos
Comparing other techniques.
There are many types of rhetorical strategies. To get a full picure on how they work together, or when to use which rhetorical strategies, explore the full guide below.
Everything About Rhetorical Appeals
Basics & terminology, appeal to credibility , appeal to emotion, appeal to logic, appeal to purpose, appeal to timeliness.
Each of these rhetorical strategies can be effective in its own way. When combined, their potential effects grow exponentially. To fully understand the power of persusaion, these are the tools you need.
ETHOS DEFINITION
What is ethos.
Ethos is the persuasive technique that appeals to an audience by highlighting credibility. Ethos advertisement techniques invoke the superior “character” of a speaker, presenter, writer, or brand.
Ethos examples aim to convince the audience that the advertiser is reliable and ethical. It’s easier to make a decision when someone you respect signs off on it, right? This is broadly the function of ethos in commercials.
When an esteemed public figure endorses a product, it validates it to the end consumer. An ethos advertisement plays off the consumer’s respect for a given spokesperson.
Through that respect, the spokesperson appears convincing, authoritative and trustworthy enough to listen to. Of the types of persuasive techniques in advertising, ethos is best used to unlock trust.
USE OF ETHOS IN ADVERTISING
How is ethos used in advertising.
So what does ethos mean?
It’s all about credibility. Famous people enjoy a high status in our society. So they’re the ones selling products to us — whether or not they have product-specific expertise.

Example of ethos in advertising: Jennifer Aniston in a campaign for Glaceau Smart Water
For example, an Infiniti commercial featured Steph Curry. Even though he’s not known for his taste in vehicles, his stature validates the product.
This is ethos in commercials at work.
Example of ethos in commercials: Steph Curry in a recent spot for Infiniti
Ethos rhetoric is also invoked to tie a brand to fundamental rights.
Brands build trust with their audience when they stand with an important cause. Anheuser-Busch illustrated this in their “Born the Hard Way” ad.
Ethos examples: This ethos advertisement by Anheuser-Busch underscores the value of multiculturalism
This spot focuses on the origin story of Anheuser-Busch’s founders.
It shows Busch’s turbulent immigration from Germany to St. Louis, and speaks to the importance of immigration and multiculturalism.
This is how ethos rhetoric is used in advertising.
Of the many types of persuasive advertising techniques in advertising, ethos is best for playing up the strength of a brand or spokesperson’s character.
ETHOS EXAMPLE IN COMMERCIALS
Ethos advert case study.
If you want a really strong example of ethos that also has a pretty funny meta quality to it, check out the shot list for this Heineken spot. See how many times they use foreground elements and OTS shots in this spot:
Ethos Examples • Shot Listed in StudioBinder
This Heineken commercial shows famous actor Benicio Del Toro at the bar enjoying a Heineken. Benicio chats about how both he, and Heineken, are world famous and instantly recognizable.
Then, a pair of goofy tourists spot him in the bar, and they call out for him to pose for a photo, but... they actually think he's Antonio Banderas.
Ethos Example in Heineken Commercial
This commercial not only uses ethos as a way to tie the celebrity of Benicio to the celebrity of Heineken, but it uses humor and the bold faced usage of ethos to make fun of the brand, people, and fame.
THE "PLAIN FOLKS" PERSUASIVE ADVERTISING TECHNIQUE
How is "plain folks" used in ads.
Ethos rhetoric often employs imagery of everyday, ordinary people.
Known as the Plain Folks persuasive advertising technique, in this approach a spokesperson or brand appears as an Average Joe to feel common and sensible. In doing so, they appear concerned and cut from the same cloth as you.
This approach is very common in political ads. Consider the “Family Strong” ad from Hillary Clinton’s 2016 presidential campaign.
Ethos Examples: Hillary Clinton underscores the “Plain Folks” definition in her campaign videos.
Despite her status and wealth, Clinton draws on imagery of her family and upbringing to make her feel more relatable. In this way, “Plain” folks is propaganda and also a logical fallacy.
But it’s also an effective and persuasive advertising technique.
Of the types of persuasive techniques in advertising, Plain Folks aligns your brand with the values of the everyday consumer.
Related Posts
- Creative Digital Advertising Trends →
- Steps to Make a Persuasive Commercial →
- Learn: How to Make a Storyboard in 9 Steps →
Pathos DEFINITION
What is pathos.
Pathos is persuasive technique that try to convince an audience through emotions. Pathos advertisement techniques appeal to the senses, memory, nostalgia, or shared experience. Pathos examples pull at the heartstrings and make the audience feel.
A quick way to appeal to a viewer’s emotions? A cute animal. A devastated family. A love story. Overcoming great odds. An inspirational song and imagery. A good zinger.
Emotions create responses and, in our increasingly consumer-driven culture, the response is to buy something. Pathos appeals to an audience’s basic emotions like joy, fear, and envy. All are easily triggered in many ways.
So what is pathos?
Well, it's a model enjoying a refreshing Coke. Or a frustrated infomercial character desperate for a better remedy. And "tired" of the "same old blah-blah-blah."
The many different pathos advertisement examples not only evoke your feelings but anticipate your responses too. If you want to explore pathos in advertising, language is the best place to start.
Because the words we hear and read trigger specific feelings. Positive words conjure feelings of love, excitement and wonder.

What is pathos? Cutting to the emotional core, really
Look at how General Mills and Cheerios achieved this in their “Good Goes Round” campaign.
Example of pathos: This Cheerios pathos advertisement injects good vibes with positive words
We see sunshine, smiles and bright colors while we hear the words “good goes around.” It invites positivity and encourages us to associate Cheerios accordingly.
On the other hand, pathos advertisements can also employ unpleasant emotions like fear and worry just as effectively.
Pathos examples: this somber pathos advertisement says don’t let heart disease happen to you
This ad by the British Heart Foundation underscores the dangers of heart disease. As the spot unfolds, you start to realize that the narrator suddenly died at her sister’s wedding.
Her tragic story encourages you to not let it happen to you.

Pathos examples: BMW warns against drinking and driving in this pathos advertisement example
Pathos example in commercials, pathos advert case study.
If you want a really strong example of pathos is an advertisement, check out this shot list from a particularly emotional Zillow spot. Notice how the shots on the son are often singles and medium close-ups :
Pathos Examples • Shot Listed in StudioBinder
This Zillow commercial shows a father and son who have just suffered the terrible loss of their wife/mother. The father tries to cheer his son up by finding a new home, one preferably near the boy's grandparents.
The son seems disinterested, but then the father finds his son and the family dog looking up at the stars, one of which is particularly bright. The son decides that the star is his mother, looking down on him.
That gives the father an idea:
Pathos example in Zillow Commercial
The father searches on Zillow, finds a home, and buys it. We then learn that the home is not only close to the grandparents, but it also has a skylight in the son's room, allowing him to see his Mother's star at night.
This commercial uses the emotions of the father, the son, the grandparents, and of course the viewer to suggest that Zillow is the type of website that can balm grief through its functionality.
USE OF PATHOS IN ADVERTISING
The appeal of pathos in advertising.
Sex appeal is of course also hugely successful among the pathos advertising techniques. Open any Cosmopolitan magazine and you’ll find scantily clad models, muscular men and sexual innuendo.
Although the common expression “sex sells” has been debated, sexually provocative ads do leave a lasting impression. Mr. Clean , for example, spiced up their eponymous mascot for comedic effect.
Pathos Examples: This Mr. Clean pathos advertisement gave their mascot a sexy upgrade
Their brawny Mr. Clean upgrade wears tight clothes and turns mopping the floor into something more... sensual?
Humor, patriotism and snob appeal are also all common in pathos advertisement examples. The pathos definition even extends to nostalgia and the strategic use of music in ads.
Pathos Examples: The pathos definition extends to evoking emotions with music ... even *NSYNC
The bandwagon advertising technique, what is the "bandwagon advertising".
“Bandwagon advertising” is commonly categorized under pathos advertisement examples. While it may sound unfamiliar, you're probably pretty familiar with it. It creates that impression that using certain product will put you on the “winning team.” It adheres to the pathos definition because it plays off your fear... of being left out.
Old Spice used this in their “The Man Your Man Could Smell Like” spot.
Bandwagon advertising: to be The Man Your Man Could Smell Like, you buy Old Spice
In its comical way, it puts pressure on men to smell as good as the Old Spice Guy. Like the “Plain Folks” technique, Bandwagon advertising is a very popular form of propaganda.
Of the persuasive advertising techniques, “Bandwagon” puts your brand on the right side of popular opinion. Remember the "Be like Mike" Ads?
Pathos example: Talk about putting the consumer on the "winning team"
- Learn from the Best Marketing and Ad Campaigns →
- Stock Video Sites That’ll Make Your Clients Happy →
- Storyboard your video with StudioBinder →
LOGOS DEFINITION
What is logos.
Logos is the persuasive technique that aims to convince an audience by using logic and reason. Also called “the logical appeal,” logos examples in advertisement include the citation of statistics, facts, charts, and graphs.

Logos Examples: This Samsung ad puts the Logos persuasive advertising technique to work
Ever told someone to “listen to reason” during an argument? This is what logos does. The best logos advertisement examples are when a speaker appeals to logic. Statistics, surveys, facts, and historical data can make a product seem like a more reasonable decision. Whether the data is sound or not is another story.
LOGOS EXAMPLE IN COMMERCIALS
Logos advert case study.
If you want a really strong example of logos is an advertisement, check out this shot list from a recent Nissan Commercial. You'll notice how the camera angles and shot size change when the "ProPilot" system clicks on:

Logos Advertisment Examples • Shot Listed in StudioBinder
This Nissan commercial shows a daughter and father driving on a highway. The daughter is about to drive past some scary construction, but then the father uses his sage like wisdom to instruct her to turn on the "ProPilot" system that Nissan now features in their cars.
Once the daughter does this, we see a Star Wars battle scene playing out in front of out eyes, and she becomes so distracted that she begin to veer off the road... but guess what? The "ProPilot" system saves her by auto-correcting the trajectory of the car based on the sensor system.
So how is this logos? Well, the commercial places the daughter in a relatively common situation and uses the machine logic behind having a guided system in the car to keep your distracted children safe.
Now... is it logical that this Star Wars homage suggests the daughter reach out to use the force by using a guided machine? Of course not! That's the opposite of what Luke does in the movie. Is it logical for your kid to be scared of driving past construction at 40mph? Of course not!
Is there anything in this spot that is logical? The basic fact that young drivers get distracted, and the Nissan "ProPilot" system might just save their lives one day, well that is how you use logic to sell cars.
- The Most Inspiring Ads That Every Agency Should See →
- Shot list your video with StudioBinder →
- Creative YouTube Video Ideas to Try on Your Channel →
LOGOS TECHNIQUES
How is logos being used in advertising.
Technology advertisements use logos because their goal is to showcase cool new features. Consider the example of logos in Apple’s ad for the iPhone:
A logos advertisement example: In Apple’s iPhone spot, the features pop out at you
In logos rhetoric, you have to the sell best reasons to buy your product..
How does Apple do that?
They have their new innovative features pop out at you. From durable glass to Face ID software. It effectively asks you why you would choose any phone but iPhone. Logos often use buzzwords to sell the product.
What's a great example of this?
Food companies capitalizing on the rising demand for healthy choices.
Logos Examples: I Can’t Believe It’s Not Butter underscore the health benefits
This I Can’t Believe It’s Not Butter ad hinges on the health benefits to prove their point. Of the types of persuasive techniques in advertising, logos will build your brand as the most logical, functional and helpful option.
Explore more rhetorical devices
Ethos , pathos , and logos are highly effective rhetorical appeals but there is much more to explore, including kairos and telos . Or dive into more rhetorical devices that help construct and support these appeals, including metaphor , hyperbole , and metonymy . When you've mastered these techniques, your ability to convince and persuade in your writing will be unmatched.
Up Next: Rhetorical Devices Index →
Showcase your vision with elegant shot lists and storyboards..
Create robust and customizable shot lists. Upload images to make storyboards and slideshows.
Learn More ➜
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- Ethos, Pathos & Logos — Definition and Examples of Persuasive Advertising Techniques
- Ultimate AV Script Template to Write Better Ads [FREE AV Script Template]
- What is Dramatic Irony? Definition and Examples
- What is Situational Irony? Definition and Examples
- How to Write a Buzzworthy Explainer Video Script [Free Template]
- 57.8K Facebook
- 240 Pinterest
- 7.2K LinkedIn
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
By melanie gagich and emilie zickel.
Rhetoric is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints or perhaps freedoms of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text .
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals, which are the three ways to classify authors’ intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to have the reaction that the author hopes for.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to craft their argument so that the outcome, audience agreement with the argument or point, is achieved. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective .
When an author relies on logos, it means that they are using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. An author can appeal to an audience’s intellect by using information that can be fact checked (using multiple sources ) and thorough explanations to support key points. Additionally, providing a solid and non-biased explanation of one’s argument is a great way for an author to invoke logos.
For example, if I were trying to convince my students to complete their homework, I might explain that I understand everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but the homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). I could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence).
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as
- Comparison – including a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic ) and another similar thing to help support your claim . It is important that the comparison is fair and valid–the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking – arguing that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim . Be careful with the latter–it can be difficult to predict that something will happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning – starting with a broad, general claim /example and using it to support a more specific point or claim
- Inductive reasoning – using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization
- Exemplification – using many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration – moving beyond just including a fact but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought – maintaining a well-organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that they are trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim . An author using pathetic appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies or sad-looking kittens and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic , the argument, or the author. Emotions can make us vulnerable, and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that their argument is a compelling one.
Pathetic appeals might include
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel like they are seeing those events
- Personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (What is the author trying to make the audience feel? And how are they doing that?)
- Information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience . This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text , try to locate when the author is trying to convince the reader using emotions because, if used to excess, pathetic appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. See the links below about fallacious pathos for more information.
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Ethical appeals have two facets: audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, they are attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds , for example, patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self-preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about to justify or support their argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., “My argument rests upon the values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument”). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos: the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and their character.
- Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by their knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school 30 years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics. To establish their credibility, an author may draw attention to who they are or what kinds of experience they have with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., “Because I have experience with this topic –and I know my stuff– you should trust what I am saying about this topic ”). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
- Character is another aspect of ethos. Character is different from credibility because it involves personal history and even personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates–those who might be the most credible candidates–fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that they have the type of character that the audience can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author gain the audience’s trust so that the audience will accept their argument? How can the author make him or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values? In building ethical appeals, we see authors referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker). Authors use language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker). Authors refer to their experience and/or authority with the topic as well (and therefore demonstrate their credibility).
When reading, you should think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as their character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first-person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
Rhetorical Appeals Misuse
When writers misuse logos, pathos, or ethos, arguments can be weakened. Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument. In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. And when that happens, arguments can be weakened.
To see what a misuse of logical appeals might consist of, see Logical Fallacies.
To see how authors can overuse emotional appeals and turn-off their target audience, visit the following link from WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Pathos .
To see how ethos can be misused or used in a manner that may be misleading, visit the following link to WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Ethos
Attributions
“Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined” by Melanie Gagich, Emilie Zickel is licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0
Writing Arguments in STEM Copyright © by Jason Peters; Jennifer Bates; Erin Martin-Elston; Sadie Johann; Rebekah Maples; Anne Regan; and Morgan White is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.
The New York Times
The learning network | skills practice | persuading an audience using logos, pathos and ethos.

Skills Practice | Persuading an Audience Using Logos, Pathos and Ethos

Academic Skills
Teaching Ideas Based on New York Times Content.
- See All in Academic Skills »
- See All Lesson Plans »
Update: Jan. 22, 2014
The Times is full of persuasive language every day. Editorials, Op-Eds, Room for Debate and even the Dining section use rhetoric, or persuasive language, to persuade readers to believe an idea or try something.
In this edition of Skills Practice, students explore how writers use the rhetorical devices of logos , ethos and pathos to appeal to an audience. They then try out their own use of rhetoric to make a persuasive argument.
1. Read the Opinion article “Rap Lyrics on Trial,” in which Erik Nielson and Charis E. Kubrin argue that lyrics are wrongly being used against amateur rappers in court.
2. As you read, highlight examples of logos , pathos and ethos used in the Op-Ed article. (See the definitions below if you are not familiar with these terms.) You might want to use a different color highlighter for each rhetorical appeal.
3. Write your own persuasive argument using rhetorical devices to convince an audience. Choose any topic that interests you, and write a speech or editorial that employs logos, pathos and ethos. You can use our archive of Student Opinion questions if you are having trouble finding a topic.
Before You Do This Task, You Might …
Become familiar with rhetorical devices.
There are three types of rhetorical strategies , as categorized by the famous Greek philosopher Aristotle. He believed that speakers needed to look at these three elements to compose a convincing argument.
- logos (rational appeal): Appeal to the audience’s logical reasoning ability. Examples of logos include facts, statistics and anecdotes.
- pathos (emotional appeal): Appeal to an audience’s heart and emotions. An author or speaker using pathos seeks to persuade someone emotionally using personal connections, stories or testimonials, and maybe spirituality. Pathos can aim to evoke hopes and fears and often employs figurative language.
- ethos (ethical appeal): Appeal to the credibility and authority of a speaker. Using ethos, a writer can convey trustworthiness through tone and style as well as by establishing her credentials in a field. An author’s reputation can also influence pathos.
Then think of something you tried to persuade a parent or friend to do. Maybe you wanted to borrow money or buy a new phone. What kinds of arguments did you use to try to persuade this person? Did you use statistics and logic? Did you try to present yourself as responsible? Did you attempt to make the person feel bad in order to persuade him or her? Which appeals worked best? Turn and talk to a partner about your experiences.

Going Further
1. Editorials: Read Times editorials that take a stand on a wide range of issues and practice looking for the use of the logos, pathos and ethos. Some editorials that might interest students include:
- “Scouting’s Incomplete Evolution”
- “Uncle Sam’s Sweatshops”
- “Missing From Science Class”
2. Speeches: Rhetorical devices are not just used in writing; they also play a large role in speaking. Read important speeches , political and otherwise, and practice identifying the speaker’s use of rhetorical devices.
Students can also analyze rhetorical devices used by politicians using social media.
Last year, Sarah Gross, Michelle Lampinen and Jonathan Olsen ran a Twitter chat during the presidential election. They wrote about their experience here . Using hashtags, they brought their students together to analyze rhetoric in the presidential debates alongside students in other states.
Students in grades 9-12 took a “crash course” in rhetoric thanks to Ms. Lampinen. Then they practiced recognizing rhetoric by looking for it in the newspaper before the debate. Finally, during the debate they participated on Twitter, blogs, Todaysmeet and a private Ning (wherever they felt most comfortable), discussing how the candidates used rhetoric to try to sway voters.
3. Advertisements: Recognizing rhetoric is an important skill for students who are surrounded by advertisements and media all day. They are inundated with information on a minute-by-minute basis, and understanding how the media is trying to persuade them is an important step in thinking critically about the world around them.
Students can use a critical eye to watch advertisements and examine how rhetoric is being employed to persuade the audience. One place to start is to analyze some of the commercials included in this NPR post on memorable political ads from 2013 .
4. More About Rhetoric: Draft is a Times series about the art and craft of writing, and this post, “Other Men’s Flowers,” is all about rhetoric and how it works. Here is a paragraph from the post:
It does help to keep in mind that, as Aristotle wrote, you have three forms of power over the reader: ethos , pathos and logos . That is, roughly: selling yourself, swaying the emotions and advancing your argument. Any sentence you write should be pulling one or more of those levers; the best will do all three. Even apparent decoration works to a purpose — if a phrase is beautiful, funny or memorable, it is doing work on its audience.
Read the whole post and apply some of the author’s observations and ideas to your own persuasive writing.
Update: A New Yorker article, “The Six Things That Make Stories Go Viral Will Amaze, and Maybe Infuriate, You,” identifies ethos, pathos and logos as elements:
In 350 B.C., Aristotle was already wondering what could make content—in his case, a speech—persuasive and memorable, so that its ideas would pass from person to person. The answer, he argued, was three principles: ethos, pathos, and logos. Content should have an ethical appeal, an emotional appeal, or a logical appeal. A rhetorician strong on all three was likely to leave behind a persuaded audience. Replace rhetorician with online content creator, and Aristotle’s insights seem entirely modern. Ethics, emotion, logic—it’s credible and worthy, it appeals to me, it makes sense. If you look at the last few links you shared on your Facebook page or Twitter stream, or the last article you e-mailed or recommended to a friend, chances are good that they’ll fit into those categories.
Invite students to find and analyze viral content from their social networks and analyze it to see which of these principles apply.
This resource may be used to address the academic standards listed below.
Common Core E.L.A. Anchor Standards
1 Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
4 Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone.
5 Analyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole.
6 Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a text.
8 Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, including the validity of the reasoning as well as the relevance and sufficiency of the evidence.
1 Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence.
3 Apply knowledge of language to understand how language functions in different contexts, to make effective choices for meaning or style, and to comprehend more fully when reading or listening.
Comments are no longer being accepted.
Thanks for this feature and especially for the links to editorials of interest to kids. It is perfect timing. My students logged on today to do the news quiz and were excited to see “ethos, logos and pathos” (terms they just learned this week) show up in the New York Times. This will definitely become part of my lesson plans for next week.
Hi Cathleen, and thanks for letting us know. We’d love to hear how it goes when you teach it next week. –Katherine (and I know I speak on behalf of Sarah and Michael, too.)
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I really like all of the points you made.
what i umderstand in this article ? you try to” pythos ”to your self by witch you have read and in real life .. LOGOS ..is one and only one thing (moral) to every one .. PATHOS is big sens moral too but with different way meaning Ethos is good to use for show your nationality (socila educated ) we have .. i think student’s in timing we live are very high educated with very low moral ..(general) i am not student this is not for me ..( i am sure) you there are confuse by who to talk or who to write ..so mistake’s are wellcome but not every time because after be come ‘banal”..you have timing to justice the life to one or three people (that is very low moral too ) ..but this doesnt give you right to make no one ..no one you understand ..fix life to otheres by your ruls.. so first of all is better to have time reading PLATON SOCRATE NOT WITH YOUR WAY BYT WITH WHAT EXACT THEY MEAN ..( TRY AGINE ) i have read many time and i continued for every not know very good to read . ” see my self after others ” if you like gossip if not JUST DO YOUR JOB WITH HIGH MORAL ..
Thanks a ton!! This article made my understanding easier
Hi! Here goes….
Now I know more about ethos,pathos,& logos,Thank You.
What's Next

Today's Hours
Political Rhetoric: Logos, ethos, pathos
- Logos, ethos, pathos
- Rhetorical devices
- Famous speeches and rhetorical strategies
- Sources of famous speeches
Basics of Rhetoric
Understanding rhetoric.
A speech is an address given to an audience for a variety of purposes. A speaker may aim to inspire or to motivate, to amuse, to inform or to persuade.
The focus of this guide will be persuasive speeches , those that are intended to sway the audience to agree with the speaker. We will examine the impact of rhetorical structure and devices.
A speech, no matter the subject, requires a speaker, an audience, and a purpose. You can think of a speech as a rhetorical triangle such as the one below.

To be persuasive, the speaker must take the audience into consideration and appeal to them in ways that will convince them. The Greek philosopher Aristotle (384 BC–322 BC) described three appeals that can be used to persuade an audience: ethos, pathos, and logos.
Logos: The speaker appeals to the audience’s sense of reason, using logic, facts, and statistics.
Ethos : The speaker tries to show the audience that he or she is reliable, credible, and trustworthy. The speaker also tries to build a bridge to the audience by using first-person plural pronouns (we, us).
Pathos : The speaker appeals to the audience’s emotions, using emotional language, sensory images, and anecdotes.
We can see an example of how these three types of appeal interact in a speech by former First Lady and Secretary of State Hillary Rodham Clinton to the fourth World Conference of the United Nations. Clinton speaks about the rights of women around the world. Look at these excerpts:

Source: https://www.texasgateway.org/resource/analyze-famous-speeches-rhetorical-structures-and-devices-english-i-reading

- Next: Rhetorical devices >>
- Last Updated: Feb 13, 2020 11:02 AM
- URL: https://library.centre.edu/POL120Fall2019
- DOI: 10.61194/ijjm.v5i2.1015
- Corpus ID: 270605270
Persuasive Through Ethos, Logos, and Pathos in BTS' Speech at The White House
- Renita Nabila Putri , Deddy Muharman , Fath Mashuri
- Published in Ilomata International Journal… 18 June 2024
- Sociology, Political Science
Related Papers
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
The Emotional: Pathos in English Literature and Musical Compositions
This essay is about the role of pathos in English literature and musical compositions, focusing on its ability to evoke emotional responses. Pathos, derived from the Greek word for suffering, is a rhetorical device that appeals to emotions such as pity, sorrow, and compassion. In literature, authors like Shakespeare and Dickens use pathos to create emotional connections with readers, enhancing the narrative’s impact. The essay also explores the parallels between pathos in literature and music, highlighting how composers like Beethoven and Tchaikovsky use similar techniques to elicit strong emotional reactions. Pathos, when used effectively, humanizes narratives and compositions, making them resonate deeply with audiences.
How it works
Pathos, derived from the Greek term for suffering or experience, is a powerful rhetorical device used to evoke emotional responses from an audience. This device, which appeals to the audience’s sense of pity, sorrow, or compassion, is not only pivotal in literature but also plays a significant role in musical compositions. By exploring the interplay of pathos in both literature and music, we can better understand its profound impact on human emotion and artistic expression.
In English literature, pathos is one of Aristotle’s three modes of persuasion, alongside ethos (ethical appeal) and logos (logical appeal).
While ethos establishes the credibility of the speaker and logos appeals to reason, pathos aims directly at the audience’s emotions. This emotional engagement can create a deep bond between the narrative and the reader, making the story more compelling and relatable.
Take, for instance, the tragic figure of Macbeth in William Shakespeare’s eponymous play. Shakespeare employs pathos to highlight Macbeth’s tragic downfall, evoking feelings of pity and fear in the audience. As Macbeth spirals into madness and guilt, the audience is drawn into his inner turmoil, reflecting on themes of ambition, power, and destiny. This emotional resonance is further amplified by the rhythmic and lyrical quality of Shakespeare’s language, akin to a musical composition that crescendos with the character’s despair.
Similarly, in Charles Dickens’ “A Tale of Two Cities,” pathos is used to underscore the suffering of individuals during the French Revolution. The poignant scenes of sacrifice and redemption stir the readers’ emotions, drawing them into the historical and personal struggles of the characters. Dickens’ use of pathos not only critiques social injustices but also advocates for empathy and compassion, much like a symphony that moves its audience through varying emotional landscapes.
Pathos also plays a crucial role in poetry, where it often serves to express the poet’s innermost feelings and to resonate with the reader on a personal level. John Keats’ “Ode to a Nightingale,” for example, is imbued with a deep sense of melancholy and longing. The poem’s rich imagery and lyrical beauty create an emotional tapestry that allows readers to share in Keats’ contemplation of mortality and desire for transcendence. The effect is similar to a melancholic musical piece that envelops the listener in its emotive power.
The connection between pathos in literature and music becomes even more evident when we consider how both art forms use rhythm, tone, and pacing to evoke emotions. Just as a novel or poem can build tension and release through its narrative structure, a musical composition can guide listeners through an emotional journey using crescendos, diminuendos, and key changes. This parallel highlights the universal language of emotion that both literature and music speak.
In musical compositions, pathos can be seen in the works of composers like Ludwig van Beethoven and Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky. Beethoven’s Symphony No. 9, particularly the “Ode to Joy” movement, is renowned for its emotional depth. The symphony transitions from somber and reflective passages to exuberant and triumphant crescendos, mirroring the emotional journey of the human experience. Tchaikovsky’s “Pathetique” Symphony similarly evokes a range of emotions, from the haunting melancholy of the first movement to the poignant beauty of the final adagio. These compositions, much like literary works, use pathos to connect with the audience on a visceral level.
The effectiveness of pathos in both literature and music lies in its ability to humanize the narrative, making abstract ideas and themes tangible through emotional experiences. When readers or listeners empathize with the characters’ or the music’s joys and sorrows, they become more invested in the story or composition. This emotional engagement can lead to a deeper understanding and appreciation of the work.
Moreover, pathos can serve as a catalyst for social and moral reflection. By presenting characters and situations that elicit strong emotional responses, authors and composers can prompt audiences to question their own values, beliefs, and actions. Harriet Beecher Stowe’s “Uncle Tom’s Cabin,” for example, uses pathos to expose the horrors of slavery, stirring the emotions of readers and playing a crucial role in the abolitionist movement. Similarly, Beethoven’s symphonies have been used to inspire hope and resilience in times of social and political upheaval.
While pathos is a powerful tool, it must be used judiciously to avoid manipulation or sentimentality. When overused or employed without sincerity, pathos can diminish the credibility of the narrative or composition and alienate the audience. Effective use of pathos requires a balance between emotional appeal and authenticity, ensuring that the emotions arise naturally from the characters, plot, or musical themes.
In conclusion, pathos is an essential component of both English literature and musical compositions, enriching narratives and melodies by appealing to the audience’s emotions. Through the strategic use of pathos, authors and composers can create memorable and impactful works that resonate with audiences on a profound level. By understanding and appreciating the role of pathos, we can gain deeper insights into the emotional and moral dimensions of artistic expression. Whether through the written word or the strains of a symphony, pathos has the power to connect us to the human experience in all its complexity and beauty.
Cite this page
The Emotional: Pathos in English Literature and Musical Compositions. (2024, Jun 28). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-emotional-pathos-in-english-literature-and-musical-compositions/
"The Emotional: Pathos in English Literature and Musical Compositions." PapersOwl.com , 28 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-emotional-pathos-in-english-literature-and-musical-compositions/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Emotional: Pathos in English Literature and Musical Compositions . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-emotional-pathos-in-english-literature-and-musical-compositions/ [Accessed: 29 Jun. 2024]
"The Emotional: Pathos in English Literature and Musical Compositions." PapersOwl.com, Jun 28, 2024. Accessed June 29, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-emotional-pathos-in-english-literature-and-musical-compositions/
"The Emotional: Pathos in English Literature and Musical Compositions," PapersOwl.com , 28-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-emotional-pathos-in-english-literature-and-musical-compositions/. [Accessed: 29-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Emotional: Pathos in English Literature and Musical Compositions . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-emotional-pathos-in-english-literature-and-musical-compositions/ [Accessed: 29-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It uses logical reasons to convince people about something. When you use logos in your everyday speech or arguments, you try to mention facts or data to support your idea. While ethos uses the speaker's credibility to persuade people about something, pathos uses emotion to trigger people. Logos simply relies on logic and cuts to the chase.
Persuasive speaking is a skill that you can apply regularly throughout your life, whether you are selling a product or being interviewed. 2,300 years ago, Aristotle determined the components needed for persuasive speaking. They are referred to as the three pillars of persuasion - ethos, pathos and logos.
Exemplary Persuasive Speeches. To wrap up, let's look at some classic examples of how speakers use ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade their audiences.. Ethos. Winston Churchill's address to Congress in December 1941 utilizes ethos remarkably well to assure the assembly that he is speaking as a friend, not a foreigner. He reminds them that his own mother was American.
Conclusion. Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting ...
Learn the definitions of ethos, logos, pathos, and kairos and check out examples of each. Call Direct: 1 (866) 811-5546 ... You can think of it as an appeal to authority or character—persuasive techniques using ethos will attempt to persuade you based on the speaker's social standing or knowledge. ... including "ground," "speech ...
To successfully give a persuasive presentation, you must look to master these three pillars of persuasive speech: Ethos: the ethical appeal; your authority, credibility, and character. Logos: the logical appeal; your arguments' strength, soundness, and coherence. Pathos: the emotional appeal; your arguments' emotional bond and impact on ...
Ethos is about establishing your authority to speak on the subject, logos is your logical argument for your point and pathos is your attempt to sway an audience emotionally. Leith has a great example for summarizing what the three look like. Ethos: 'Buy my old car because I'm Tom Magliozzi.'.
Unlock the secrets of persuasive speaking in this comprehensive guide to ethos, pathos, and logos. Join us as we delve into the ancient art of rhetoric, refi...
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three modes of persuasion in public speaking. The concepts are based on Aristotle's three artistic proofs. They refer to how speakers use credibility, emotion, and reason to elicit trust, sympathy, and reason. Based on the Greek philosopher Aristotle's groundbreaking treatise on rhetoric, ethos, pathos, and ...
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are modes of persuasion used to convince audiences. They are also referred to as the three artistic proofs (Aristotle coined the terms), and are all represented by Greek words. Ethos or the ethical appeal, means to convince an audience of the author's credibility or character. An author would use ethos to show to his ...
Pathos refers to appealing to a person by influencing his emotions. Pathos is involved in the strategy of convincing the audience by invoking feelings through their own imaginations. You appeal through pathos when you try to convince your parents of something. Consider this statement:
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument. At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority. Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but ...
Aristotle developed the concept of "ethos," "logos," and "pathos.". Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer's credibility, logos appeals to the audience's reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions. These three concepts, also known as the ...
A political speech, for instance, might rely on pathos while an academic paper should be more heavily skewed towards logos. In addition to ethos, pathos, and logos—which we can think of as rhetorical modes—there are a number of rhetorical devices that it would be a good idea to familiarize yourself with. These devices will offer a plethora ...
Good persuasive writing argues a position by using a combination of three ancient rhetorical techniques: logos, ethos, and pathos. The first technique is logos, which means logic. Persuasive writing that uses logos uses, where appropriate, literal or historical analogies as well as factual and historical data. Such writing contains citations to ...
Make sure your argument is persuasive by learning the three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and how to effectively use them in communication.
The use of logos creates a solid foundation for the argument, making it more persuasive. Ethos Pathos & Logos Work Great Together. ... Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech is a classic example of using pathos. He evoked strong emotions by describing the great trials and tribulations faced by African Americans, making his call ...
Ethos, Pathos & Logos — Definition and Examples of Persuasive Advertising Techniques. Ethos, pathos and logos are techniques of persuasion that form the rhetorical triangle. A compelling argument, sales pitch, speech, or commercial ideally uses elements of all three strategies. We'll show you how to employ each of the techniques and present ...
Pathos is a rhetorical appeal speakers use to connect with their audience and inspire change. President Lincoln's Gettysburg Address (1863) exemplifies the use of pathos (and ethos) while reflecting upon the significance of the American Civil War. In this speech, the war is presented in terms of the Founding Fathers' ideals ("a new nation ...
Rhetorical Appeals. Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to ...
Update: Jan. 22, 2014. The Times is full of persuasive language every day. Editorials, Op-Eds, Room for Debate and even the Dining section use rhetoric, or persuasive language, to persuade readers to believe an idea or try something.. In this edition of Skills Practice, students explore how writers use the rhetorical devices of logos, ethos and pathos to appeal to an audience.
The art of persuasion is as old as human kind. Dating back to the 4th century BC, Aristotle's Rhetoric influenced the development of rhetorical theory. The treatise was a collection of the students notes' and demonstrates the Greek philosopher and scientist's commitment to developing the art of "winning the soul through discourse" as a systematic, scientific study. He says: Rhetoric is the ...
You can think of a speech as a rhetorical triangle such as the one below. To be persuasive, the speaker must take the audience into consideration and appeal to them in ways that will convince them. The Greek philosopher Aristotle (384 BC-322 BC) described three appeals that can be used to persuade an audience: ethos, pathos, and logos.
Logos (plural: logoi) is logical appeal or the simulation of it,: 38 and the term logic is derived from it. It is normally used to describe facts and figures that support the speaker's claims or thesis. There are also more traditional forms of logical reasoning, such as syllogisms and enthymemes.: 38-39 Having a logos appeal also enhances ethos because information makes the speaker look ...
The purpose of this study is to analyze BTS' speech regarding racial issues towards Asians at The White House from the perspective of Rhetorical theory using the elements of ethos, logos, and pathos. The speech reflected the reality of racism towards Asian ethnic groups, as well as a solution to end this problem by fighting racism at all levels ...
By exploring the interplay of pathos in both literature and music, we can better understand its profound impact on human emotion and artistic expression. In English literature, pathos is one of Aristotle's three modes of persuasion, alongside ethos (ethical appeal) and logos (logical appeal).
appeals of logos, ethos, and pathos. These three form the so-called rhetorical triangle. Each of those appeals needs to be addressed to create a persuasive and appealing speech. Ethos refers to establishing the credibility and authority of the speaker to show the audience that he or she is trustworthy.