Username or email *
Password *
Forgotten password?
[email protected]
+44 (0)20 8834 4579

How to Write a First-Class Law Essay
Studying law at university entails lots of essay writing. This article takes you through the key steps to writing a top law essay.
Writing a law essay can be a challenging task. As a law student, you’ll be expected to analyse complex legal issues and apply legal principles to real-world scenarios. At the same time, you’ll need to be able to communicate your ideas clearly and persuasively. In this article, we’ll cover some top tips to guide you through the process of planning, researching, structuring and writing a first-class law essay with confidence.
1. Start In Advance
Give yourself plenty of time to plan, research and write your law essay. Always aim to start your law essay as soon as you have the question. Leaving it until the last minute does not only create unnecessary stress, but it also leaves you insufficient time to write, reference and perfect your work.
2. Understand The Question
Do not begin until you fully comprehend the question. Take the time to read the question carefully and make sure that you understand what it’s asking you to do. Highlight key terms and annotate the question with definitions of key concepts and any questions that you have have. Think about how the question links back to what you’ve learned during your lectures or through your readings.
3. Conduct Thorough Research
Conducting thorough research around your topic is one of the most fundamental parts of the essay writing process. You should aim to use a range of relevant sources, such as cases, academic articles, books and any other legal materials. Ensure that the information you collect is taken from relevant, reliable and up to date sources. Use primary over secondary material as much as possible.
Avoid using outdated laws and obscure blog posts as sources of information. Always aim to choose authoritative sources from experts within the field, such as academics, politicians, lawyers and judges. Using high-quality and authoritative sources and demonstrating profound and critical insight into your topic are what will earn you top marks.
4. Write A Detailed Plan
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to plan your essay. When writing your plan, you’ll need to create an outline that clearly identifies the main points that you wish to make throughout your article. Try to write down what you wish to achieve in each paragraph, what concepts you want to discuss and arguments you want to make.
Your outline should be organised in a clear, coherent and logical manner to ensure that the person grading your essay can follow your line of thought and arguments easily. You may also wish to include headings and subheadings to structure your essay effectively This makes it easier when it comes to writing the essay as starting without a plan can get messy. The essay must answer the question and nothing but the question so ensure all of your points relate to it.
Start Writing Like A Lawyer
Read our legal writing tips now
5. Write A Compelling Introduction
A great introduction should, firstly, outline the research topic. The introduction is one of the most crucial parts of the law essay as it sets the tone for the rest of the paper. It should capture the readers attention and provide the background context on the topic. Most importantly, it should state the thesis of your essay.
When writing your introduction, avoid simply repeating the given question. Secondly, create a road map for the reader, letting them know how the essay will approach the question. Your introduction must be concise. The main body of the essay is where you will go into detail.
6. Include A Strong Thesis Statement
Your thesis should clearly set out the argument you are going to be making throughout your essay and should normally go in the introduction. Your thesis should adopt a clear stance rather than being overly general or wishy-washy. To obtain the best grades, you’ll need to show a unique perspective based upon a critical analysis of the topic rather than adopting the most obvious point of view.
Once you’ve conducted your research and had a chance to reflect on your topic, ask yourself whether you can prove your argument within the given word count or whether you would need to adopt a more modest position for your paper. Always have a clear idea of what your thesis statement is before you begin writing the content of your essay.
7. Present the Counter-argument
To demonstrate your deeper understanding of the topic, it’s important to show your ability to consider the counter-arguments and address them in a careful and reasoned manner. When presenting your counterarguments, aim to depict them in the best possible light, aiming to be fair and reasonable before moving on to your rebuttal. To ensure that your essay is convincing, you will need to have a strong rebuttal that explains why your argument is stronger and more persuasive. This will demonstrate your capacity for critical analysis, showing the reader that you have carefully considered differing perspectives before coming to a well-supported conclusion.
8. End With A Strong Conclusion
Your conclusion is your opportunity to summarise the key points made throughout your essay and to restate the thesis statement in a clear and concise manner. Avoid simply repeating what has already been mentioned in the body of the essay. For top grades, you should use the conclusion as an opportunity to provide critical reflection and analysis on the topic. You may also wish to share any further insights or recommendations into alternative avenues to consider or implications for further research that could add value to the topic.
9. Review The Content Of Your Essay
Make sure you factor in time to edit the content of your essay. Once you’ve finished your first draft, come back to it the next day. Re-read your essay with a critical perspective. Do your arguments make sense? Do your paragraphs flow in a logical manner? You may also consider asking someone to read your paper and give you critical feedback. They may be able to add another perspective you haven’t considered or suggest another research paper that could add value to your essay.
10. Proofread For Grammatical Mistakes
Once you’re happy with the content of your essay, the last step is to thoroughly proofread your essay for any grammatical errors. Ensure that you take time to ensure that there are no grammar, spelling or punctuation errors as these can be one of the easiest ways to lose marks. You can ask anyone to proofread your paper, as they would not necessarily need to have a legal background – just strong grammar and spelling skills!
11. Check Submission Guidelines
Before submitting, ensure that your paper conforms with the style, referencing and presentation guidelines set out by your university. This includes the correct font, font size and line spacing as well as elements such as page numbers, table of content etc. Referencing is also incredibly important as you’ll need to make sure that you are following the correct referencing system chosen by your university. Check your university’s guidelines about what the word count is and whether you need to include your student identification number in your essay as well. Be thorough and don’t lose marks for minor reasons!
12. Use Legal Terms Accurately
Always make sure that you are using legal terms accurately throughout your essay. Check an authoritative resource if you are unsure of any definitions. While being sophisticated is great, legal jargon if not used correctly or appropriately can weaken your essay. Aim to be concise and to stick to the point. Don’t use ten words when only two will do.
12. Create a Vocabulary Bank
One recurring piece of advice from seasoned law students is to take note of phrases from books and articles, key definitions or concepts and even quotes from your professors. When it comes to writing your law essay, you will have a whole range of ideas and vocabulary that will help you to develop your understanding and thoughts on a given topic. This will make writing your law essay even easier!
13. Finally, Take Care of Yourself
Last but certainly not least, looking after your health can improve your attitude towards writing your law essay your coursework in general. Sleep, eat, drink and exercise appropriately. Take regular breaks and try not to stress. Do not forget to enjoy writing the essay!
Words by Karen Fulton
Free Guides
Our free guides cover everything from deciding on law to studying and practising law abroad. Search through our vast directory.
Upcoming Events
Explore our events for aspiring lawyers. Sponsored by top institutions, they offer fantastic insights into the legal profession.
Join Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list for weekly updates and advice on how to get into law.
Law Quizzes
Try our selection of quizzes for aspiring lawyers for a fun way to gain insight into the legal profession!
PREVIOUS ARTICLE
Legal Writing: Start Writing Like a Lawyer!
NEXT ARTICLE
LLM Jobs for Graduates
Loading More Content
How to Write a First-Class Law Essay: Mastering the FIRAC Model
Law essays can be challenging, but they contribute significantly to the mastery of legal principles and enhancing a student’s legal research skills. A first-class law essay does not only demonstrate a thorough understanding of legal principles, but is also clearly structured and incredibly well-written. In this article, we will guide you on how to write a first-class law essay, delve into the FIRAC model of legal writing, and address frequently asked questions on law essay writing.
Below is an outline of the points that will be discussed in detail throughout the article:
Understanding the Essay Question and Planning
Comprehensive legal research, writing techniques for a first-class law essay, common faqs on law essay writing.
Table of Contents
The first step in writing a top-notch law essay is to understand the essay question and planning your response. You should take care to read and analyze the question provided, identifying the main issues, required legal areas, and the keywords that will guide your research. Create a rough essay plan, outlining the main arguments and research resources necessary to address the topic.
Thorough researched is necessary in order to write a first-class law essay.This involves examining relevant cases, statutes, academic articles, and other authoritative sources. It is crucial to:
- Build a strong foundation of understanding for the specific legal topics involved
- Identify any contrary viewpoints and conflicting interpretations of the law
- Familiarize yourself with critical legal developments that may affect your essay’s arguments
It is essential to keep track of your sources and their essential details, as you will need to reference them accurately in your essay.
Structuring a Law Essay: The FIRAC Model
The FIRAC model is a universally recognized method of organizing and presenting legal arguments in writing. It consists of:
Start by providing a concise and relevant summary of the facts and background of the issue beingaddressed. Be objective and neutral in your presentation, ensuring that your readers have a clear understanding of the context.
Clearly identify the specific legal issues that arise from the facts. This may involve direct questions or problems that need to be resolved by referring to legal authorities, such as legislation, case law, or academic commentary.
Set out the relevant legal rules, principles, and precedents that apply to the issues in question. Present a clear and comprehensive explanation of the legal authorities and how they apply to the facts.
d. Analysis:
In this section, critically analyze and weigh the various arguments and approaches concerning the legal issues at hand. Provide a detailed evaluation of the relevant legal authorities,discussing their strengths and weaknesses, and highlighting any ambiguities, disagreements, or gaps in the law that are relevant to the issues being addressed.
e. Conclusion:
Wrap up your essay by summarizing the main points, integrating your key findings and the implications of your analysis. Be sure to address the initial essay question and provide a clear answer or position based on your research and discussion. Finally, offer any recommendations or propose potential legal reforms if appropriate.
To ensure that your law essay stands out as first-class, it is essential to embrace effective writing techniques, such as:
- Clarity and precision: Use clear, concise language and avoid unnecessary jargon or verbosity. 2.Coherent organization: Organize your essay logically, ensuring that each section flows smoothly into the next.
- Strong argumentation: Build well-reasoned arguments supported by solid evidence, authoritative sources, and persuasive analysis.
- Critical thinking: Question assumptions, explore alternative viewpoints, and engage in thoughtful reflection and analysis.
- Proper citation and referencing: Adhere to a consistent citation style and accurately credit all sources used in your essay.
- Proofreading and editing: Always proofread and edit your essay meticulously, eliminating grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and awkward phrasing.
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about law essay writing:
How long should my law essay be?
The length of your law essay may vary, depending on the specific requirements and guidelines given by your instructor or institution. Typically, law essays range from 1,500 to 3,000 words, but it is crucial to adhere to the specified word count in your assignment.
How do I choose a citation style for my law essay?
Consult your assignment guidelines or ask your instructor for the preferred citation style used in legal writing at your institution, such as the Bluebook, Oxford Standard, or AGLC. Always use one citation style consistently throughout your essay.
Is it acceptable to use non-legal references in my essay?
While law essays primarily rely on legal authorities, it may be appropriate toinclude non-legal references, such as scholarly articles, reports, or empirical studies, to support your arguments or provide additional context. Always check with your instructor or assignment guidelines if you are unsure about using specific non-legal sources.
Can I use headings and subheadings in my law essay?
Headings and subheadings help organize your essay and guide your readers through your arguments. They are generally acceptable in law essays unless prohibited by your institution’s guidelines or your instructor’s preferences. Be sure to use a consistent formatting style for all headings and subheadings.
How can I avoid plagiarism in my law essay?
To avoid plagiarism, always accurately cite and reference any sources you use in your essay,whether they are direct quotes, paraphrased ideas, or summarized information. Also, ensure that your essay is primarily composed of your own original analysis and ideas, rather than relying too heavily on other sources. Make use of plagiarism-checking tools to identify potential areas of concern and correct them prior to submission.
By adhering to these guidelines and employing effective writing techniques, you can enhance the quality of your law essay and increase the likelihood of earning a first-class grade. Always remain diligent, focused, and committed to delivering thorough and engaging legal analysis throughout your academic writing endeavors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Law Essays
In addition to following the guidelines and writing techniques, it’s important to avoid common mistakes when writing your law essay:
- Irrelevant or excessive detail : Stay focused on the essay question and avoid providing unnecessary or excessive details that don’t contribute to your central argument.
- Lack of structure: Ensure that your essay is logically organized, with clearly defined sections and a coherent flow from one section to another.
- Misunderstanding the question: Read the essay prompt carefully, and make sure you clearly understand what is being asked before drafting your response. Seek clarification if needed.
- Unsupported claims or arguments: Back up your claims with solid evidence and credible sources. Avoid makingassertions without sufficient justification or analysis.
- Overly complex language or jargon: Write in a clear and concise manner, using language that is accessible to your readers. Be mindful of using overly technical terms or legal jargon without explanation.
- Plagiarism: Always provide proper citation and referencing for all sources used. Take the necessary steps to ensure your work is original and does not plagiarize from other sources.
- Inadequate proofreading: Thoroughly proofread and edit your essay to correct grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and clumsy phrasing. Additionally, make sure your citations and references are accurate and formatted correctly.
By avoiding these common mistakes and adhering to the aforementioned guidelines andwriting techniques, you will significantly improve the quality of your law essay and increase your chances of achieving a high grade. Remember that practice makes perfect, and continually refining your skills in legal writing and analysis will contribute to your overall success in your academic and professional pursuits. So, stay committed, diligent, and focused on producing well-reasoned and coherent essays that demonstrate your understanding and mastery of legal principles and concepts.
Happy writing!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Law Essay: 8 Steps
December 28, 2023
1. Choosing an Essay Topic
When it comes to writing a law essay, choosing an appropriate topic is crucial. A well-chosen topic will make your research and writing process smoother and more enjoyable, while a poorly chosen topic can lead to frustration and a lackluster essay.
Firstly, consider what has piqued your interest in your law studies so far. Perhaps there was a case or topic that you found particularly intriguing, or an aspect of law that you feel needs further exploration. Alternatively, you could focus on a current legal issue that you feel strongly about and want to delve deeper into.
It’s also important to make sure your topic isn’t too broad or too narrow. Too broad of a topic can result in a lack of focus, while a topic that is too narrow won’t give you enough research material to work with.
Ultimately, choosing a law essay topic is about finding a balance between your personal interests and the practical aspects of your assignment. Take the time to carefully consider your options, and don’t be afraid to ask for input or guidance from your professor or classmates.
Possible Law Essay Topics
- The impact of social media on defamation laws.
- Analyzing the constitutionality of mandatory minimum sentencing.
- The effectiveness of restorative justice in reducing recidivism rates.
- Legal implications of artificial intelligence in the workplace.
- Exploring the rights of privacy versus national security in the digital age.
- Examining the legal and ethical issues surrounding euthanasia.
- Assessing the role of international law in combating climate change.
- Analyzing the legal framework for cyberbullying and online harassment.
- The legalization and regulation of recreational marijuana: a critical analysis.
- Exploring the intersection of intellectual property rights and emerging technologies.
Remember to choose a topic that aligns with your interests and research availability, while ensuring that it is adequately focused for a detailed analysis within the scope of your essay.
2. Researching the Topic
Before diving into writing a law essay, it’s essential to conduct thorough research on the chosen topic. This step is critical to ensure that the essay is factually correct, well-supported, and logically structured. Here are some tips on how to research effectively for a law essay:
- Begin by gathering basic information. Use specialized textbooks, journals, and databases to gain a foundational understanding of the topic.
- Use secondary sources to gain a broader perspective on the topic. Utilize reputable news sources, government publications, and online legal databases to broaden your search.
- Access case law. To support your arguments, cite legal cases that illustrate your argument. Access online case law databases that have accessible search functions.
- Use primary sources. Primary sources include statutes, regulation, and the constitution. It’s important to have a good grasp of the primary sources since they are the basis of much of legal research.
- Take notes. Keep track of all relevant information, including sources and citations. Use an organized format that will make outlining and writing the essay a simpler process.
- Evaluate and analyze. Through the research process, it’s important to analyze the information found. Determine what is and is not relevant, and how it factors into your argument.
By conducting thorough research, you will be able to support your argument with a well-evidenced and structured essay. Remember to keep track of all sources and citations as they will be necessary in the writing process.
3. Developing Strong Thesis Statement
Developing a strong thesis statement is essential when writing a law essay. This powerful statement sets the tone for the entire article and guides the reader’s understanding of your argument. To create an effective thesis statement, you must first fully understand the topic and question at hand. Take your time to research and gather relevant information to support your viewpoint. As you delve deeper into the subject, analyze different perspectives and identify the key arguments surrounding the topic. Once you have a clear understanding of the various viewpoints, narrow down your focus and craft a concise and persuasive thesis statement that clearly states your position. Remember, a strong thesis statement should be debatable, specific, and assertive. Spend time honing your thesis to ensure it effectively conveys your argument and engages the reader’s interest.
Example thesis statement:
“The death penalty should be abolished in the United States because it violates the Eighth Amendment, fails to act as an effective deterrent, and disproportionately affects marginalized communities.”
4. Structuring the Law Essay
Structuring your law essay is crucial to ensure clarity, coherence, and a logical flow of ideas. Here’s a breakdown of how to structure your law essay:
Introduction:
- Provide a brief overview of the topic and its significance.
- Present the thesis statement, clearly stating your argument.
Background and Context:
- Provide necessary background information to help the reader understand the topic.
- Explain relevant legal concepts, principles, or statutes related to your argument.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Present your arguments and support them with evidence, case law, or legal authorities.
- Use clear and concise language to explain your points and provide analysis.
Counter-Argument:
- Acknowledge and present the counter-argument(s) objectively and logically.
- Refute the counter-argument(s) with reasoned explanations and supportive evidence.
Conclusion:
- Summarize your main arguments and their supporting evidence.
- Restate your thesis statement and highlight its significance.
- Offer some final thoughts or suggestions for further research or action.
Remember to use appropriate headings and subheadings to structure your essay effectively. Use transition words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs. Additionally, ensure proper citations and referencing throughout the essay to maintain academic integrity.
5. Writing the Introduction
Writing the introduction is your opportunity to grab the reader’s attention and set the tone for your entire law essay. Here’s how you can effectively structure your introduction:
Start with a hook:
- Use a compelling statement, anecdote, or a relevant quote to engage the reader and create interest in your topic.
Provide background information:
- Give a brief overview of the legal issue or topic you will be discussing.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the topic to the field of law or society at large.
State the purpose and scope of your essay:
- Clearly state your thesis statement, which should encapsulate your main argument.
- Mention the key points you will address and the legal principles, cases, or statutes you will analyze.
Outline the essay structure:
- Provide a brief outline of how your essay will be structured.
- Mention the main sections or arguments you will present.
Establish the context:
- Explain any necessary legal concepts, terms, or background information that the reader needs to understand.
Remember to keep your introduction concise and focused. It should provide enough information to orient the reader and generate interest in your essay. However, save the detailed arguments and evidence for the main body of your essay. Aim to make your introduction clear, engaging, and persuasive, setting the stage for the rest of your law essay.
6. Developing the Body Paragraphs
Developing the body paragraphs is the core of your law essay, where you present and support your arguments with evidence and analysis. Here’s how to effectively structure and develop your body paragraphs:
Start with a topic sentence:
- Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- The topic sentence sets the tone and direction for the paragraph.
Present your argument:
- Clearly state your argument or point of view in the opening sentences of each paragraph.
- Provide supporting evidence, such as case law, statutory provisions, or legal principles, to back up your argument.
Analyze and interpret the evidence:
- Explain the significance of the evidence in relation to your argument.
- Analyze how the evidence supports and strengthens your position.
Use legal authorities and sources:
- Cite relevant cases, statutes, or legal commentary to support your arguments.
- Refer to authoritative legal sources, such as court decisions or academic articles, to provide credibility.
Use clear and concise language:
- Clearly articulate your ideas using logical transitions and precise language.
- Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex language that may confuse the reader.
Remember to properly structure your paragraphs, provide sufficient evidence and analysis, and link your arguments back to your main thesis statement. Each paragraph should contribute to the overall coherence and flow of your essay, ensuring a convincing and well-supported argument.
7. Present the Counter-argument
Presenting the counter-argument is an essential component of writing a persuasive law essay. Failing to acknowledge opposing viewpoints weakens your argument and makes it appear biased. Therefore, it is crucial to identify different perspectives surrounding the topic and analyze these perspectives objectively. Once you have identified the counter-argument, you can present it in your essay, offering evidence and explanations to support it. Addressing counter-arguments in your essay strengthens your credibility as a writer and demonstrates your ability to look at a topic from multiple perspectives. Additionally, this approach makes your essay more convincing by acknowledging and addressing potential criticism of your argument. Keep in mind that effectively presenting the counter-argument requires thorough research, logical reasoning, and evidence-based arguments. Therefore, take your time to critically analyze opposing views to ensure your argument is backed up by relevant and reliable supporting evidence. By doing so, you can construct a well-reasoned and thoughtful essay that can withstand any counter-argument.
8. Crafting the Conclusion
Crafting a strong conclusion is essential to leave a lasting impression on the reader and effectively summarize your arguments in a law essay. Here are some key steps to consider when writing your conclusion:
Summarize your main points:
- Recapitulate the main arguments you presented in the body paragraphs.
- Provide a brief overview of the evidence you presented to support each argument.
Reinforce your thesis statement:
- Restate your thesis statement in a concise manner to remind the reader of your main argument.
- Emphasize the significance and relevance of your thesis in the context of the larger legal issue.
Offer a broader perspective:
- Connect your arguments to the wider legal or societal implications of the topic.
- Discuss the potential consequences or impact of your findings on the field of law or legal practice.
Suggest areas for further research:
- Highlight any unanswered questions or areas of debate that may require future exploration.
- Propose avenues for future research or policy development related to your topic.
Conclude with a compelling closing statement:
- Leave the reader with a thought-provoking final remark that leaves a lasting impression.
- Use a concise and powerful statement to tie together your essay and reinforce your main message.
Ensure that your conclusion is concise, focused, and aligned with your overall argument. It should serve as a strong ending to your law essay, leaving the reader with a clear understanding of your position and the importance of the topic discussed.
Use Legal Terms Accurately
In the realm of writing law essays, the accurate and precise use of legal terms is paramount. This subheading focuses on the importance of correctly employing legal terminology in order to craft an exceptional law essay.
Mastering legal terminology is essential for two reasons. Firstly, it demonstrates an understanding and grasp of the subject matter, showcasing your expertise to both professors and potential employers. Secondly, using legal terms accurately enhances the clarity and coherence of your arguments, making your essay more persuasive and compelling. However, it is crucial to strike a balance – overusing legal jargon may alienate readers who are not well-versed in the law.
To ensure accuracy, it is imperative to consult reliable legal sources such as authoritative textbooks, journals, or statutes. Moreover, reading and analyzing sample essays or exemplary legal writing can provide guidance on how to effectively incorporate legal terms into your own work. By diligently honing your legal language skills, you will significantly elevate the quality and impact of your law essays.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
In today’s digital era, the fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) with academic writing has revolutionized how students approach essay composition....
Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in education is changing how things are taught and learned in standard ways. With its ability...
The advancement of artificial intelligence has made it increasingly common for essays and articles to be written by AI. But...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
- Brightlink Blog
- Personal Development
- Professional Development

CRITICAL ANALYSIS IN LAW ESSAYS

By Lorna Baldry
Critical analysis is a skill that many learners tell us they find problematic. They can’t always grasp what it means, sometimes they think it means much more than it actually does and of course there is no substitute for knowing the law and the commentary on the law. That’s one of the things that will help all to become clear.
Chartered Institute of Legal Executives (CILEx) Chief Examiners identify in their reports that many candidates choose to stay away from essay questions which involve critical analysis. Instead preferring to respond to problem questions. For some learners this is because they have not had experience of further and higher education where they may have gained gradually increasing study skills, including analysis and critical interpretation. Graduate learners will have received guidance on writing legal essays, but practice is sometimes new and something they’re aspiring to be a part of or progress with.
Those without the background of formal study skills guidance tend to be drawn to problem questions where they can apply the law and advise fictional clients in a notional scenario. This is what they do in work, they feel really comfortable with it. Graduates on the other hand will often tend to stay away from and feel more unsure of advising clients. They prefer a more formal, academic style essay question. Sometimes this is one of the reasons that law graduates do not always pass their CILEx exams first time. It’s one of their moments of realisation that the CILEx exams are much more difficult and quite different to the ones they sat during their degree.
Guiding our learners in the skill
Our CILEx learners make a big jump from level 3 to level 6 and need to know the difference between short answer questions and essay questions and the difference between essay questions and problem essay questions.
We give everyone a 6 month access to a course full of tips, guidance and resources for revision and exam preparation. We run lots of workshops on study skills and transition between study levels as well as revision and exam preparation. Our tutors are always looking out for the individual needs of our learners to develop new and extended skills.
Learners making the transition between levels need to be mindful of the change in the marks available for their responses and what that means for how much they need to write and how sophisticated their writing needs to be. They need to become familiar with key words in a question and the responses those words are trying to elicit.
With learners who are new to level 6 or new to level 6 with Brightlink, who do not have a law degree, we need to start right from the beginning on style.
Critical analysis is subjective writing expressing opinion and evaluation. It includes breaking down and studying the parts of an assertion or situation.
Critical analysis should include the learners evidenced opinion, matters of law and the commentary of knowledgeable and recognised third parties. Depending on the question that could be judiciary through obiter and ratio or in some responses it may be academics.
We direct learners to the suggested answers for past papers, which is what they are trying to emulate. We have our own style guides and tips and techniques to support our learners with this and other study skills. From August 2020 all Brightlink learners can learn much more about critical analysis as part of their study throughout levels 3 and 6.
Get in touch to ask about help and support available for your legal studies and how you can add critical analysis to your skill set.
Privacy Overview
- Directories
Writing in Law
Like writing in other disciplines, all academic writing in Law courses should be clearly structured, persuasive, and take a position. Despite these similarities, legal writing emphasises accessibility and precision when communicating ideas and interpretation of a case or topic. This is largely due to its practical application in the legal profession.
Being able to write persuasively and concisely are fundamental skills required of legal practitioners, so developing these communication skills at an early stage is crucial. Even if you do not go into a legal career, these written skills will be useful in other professional areas of employment, such as the public service.
Legal academic writing has its own conventions and standards that will be explored in the following topics. You will find useful strategies you can use to help refine, structure and present your position in some of the most common forms of law assessment
Using HIRAC
Most legal reasoning follows a particular convention: HIRAC. HIRAC provides a statement of the issue or concern (Issue); an explanation of the legal rules that are applicable to the issue (Rule); an application of the rule to a client's facts (Application); and a conclusion that summarises the explanation and application provided (Conclusion). HIRAC is useful as a way of organising and structuring a response to a problem question.
Typically, HIRAC is used to test your ability to analyse facts in a legal case and to apply the law to the facts to see what the possible outcome might be. They also test your ability to identify relevant legal issue(s) and to evaluate competing legal precedents. Whatever the legal problem is, a clear argument or position is required to be taken. This argument should use primary sources (legislation and cases) to persuade its audience and successfully address counterarguments relevant to each legal issue.
How to structure a HIRAC response?
What follows is a general guide for using HIRAC. HIRAC is generally understood to be a flexible framework which can be used in multiple contexts. As you practice using HIRAC during your degree, it is important to develop a fluid framework that suits you.
It should be noted that HIRAC should not be used too rigidly, but it does provide a useful way to structure a response to a legal question. When you write an assessment using HIRAC, remember that some lecturers will prefer you to follow the method carefully while others won't be as rigid. You will need to clarify your expectations with them.
Identify the legal issue and summarise it in your heading. This is usually phrased as a short question that encompasses the legal issue.
Identify the issues that are central to the case. This can be done briefly. Ask yourself what legal question(s) the facts raise. When writing down the issue(s) you should think about questions a judge might be asked to answer. Be aware there might several issues raised. If more than one issue needs to be analysed, the following sections might need to be repeated several times. For example, HIRAC 1, HIRAC 2, HIRAC3, etc, then an overall conclusion.
Identify the law or legal principle relevant to the issue. This should consist of a brief statement of the legal principles to be applied as a way of signposting your analysis in the next section. A citation for each rule should be included. This is done by referring to a primary source of law (legislation or a case). The rule will generally need to be broken down into its component parts and stated accurately to avoid misinterpretation.
Application
Apply the law to the facts. This is the main part of your answer. This is where you match each element of the legal rule(s) you have identified in the previous section with fact. You need to consider arguments on both sides. Are the facts of your case similar to a previous case or can they be distinguished? You need to make an argument here and support that argument by reference to the law. If the law is unclear on a particular set of facts, you are expected to engage in a detailed hypothetical discussion about how the courts are likely to respond to this ambiguous area of the law. Unlike a traditional essay, your main points or conclusions should be stated at the end of each paragraph of your application.
Based on your analysis in the previous section, state a conclusion as to the most likely outcome. This is where you summarise the points of your argument and suggest an answer to the question presented as the heading. You should make a clear statement about what you think is the strongest outcome is likely to be.
Sample HIRACs
Here is a sample of a HIRAC response, focusing on one issue. Note how it addresses the issue concisely. It provides the relevant rule, with references, and applies that rule to the scenario in question. The conclusion is a concise final sentence.
Mitomi v Trinity Beach Life-Saving Club Inc.
Duty of care.
Mitomi must establish the Club's personal liability by proving that it owed a duty of care. The defendant will owe a duty when their actions or omissions lead to a reasonably foreseeable risk of inury to a foreseeable plaintiff or class of plaintiffs. [1] Reasonable foreseeability is that which is 'not far-fetched or fanciful'. [2] The vulnerability [3] and special characteristics of the plaintiff [4] are also relevant to duty.
In taking responsibility for the safety of the beach it is reasonably foreseeable that the Club's omission to provide a universally recognisable warning sign led to a risk of injury to a class of plaintiffs of which Mitomi is one. It is foreseeable that a tourist not understanding the sign would swim in the enclosure. Mitomi is a foreseeable plaintiff as tourists frequently visit the area. Mitomi's vulnerability is increased because she cannot read English, the club owes a duty to all foreseeable plaintiffs not just English speaking plaintiffs. Therefore, a duty of care is likely to be found.
[1] Donoghue v Stevenson [1932] AC 562.
[2] Wyong Shire Council v Shirt (1980) 146 CLR 40 at 47 per Mason J.
[3] Sullivan v Moody; Thompson v Connon [2001] HCA 59.
[4] Haley v London Electricity Board [1965] AC 778.
Here is another sample HIRAC addressing the same scenario. Again, note how it concisely and clearly analyses one issue, follows the steps of heading, rule, issue, application and conclusion.
Mitomi v Trinity Beach Life-Saving Club Inc. ("the Club")
[1] [1932] AC 562 at 580.
[2] (1993) 177 CLR 423.
[3] Nos CA 40737/93 and CL 1275/91.

Essay writing in Law
The purpose of a legal essay is to advance or persuade your reader of a particular understanding, interpretation, or application of law. In order to do this, legal essay writing needs to be simple, compelling, and well-constructed. Unlike a paper that utilises HIRAC, a law essay involves detailed analysis and discussion of the law in a more abstract setting. When writing a legal essay, you are required to take up a position in response to a question. But how is this different from essays you write in other disciplines? The following information provides some suggestions about the specifics of writing a legal essay.
What distinguishes a law essay from an essay written in another discipline?
Like essays written in other disciplines, legal essays require a central argument, based on logical reasoning and critical analysis of evidence. They should have a clear structure with a strong introduction and conclusion. As Baron and Corbin (2016, p. 26) note, even though legal writing is perceived to be portrayed as logical, highly structured and formal, composition of law essays is much as the same as any other essay writing.
"The manipulation and use of language are at the heart of the common law legal tradition" (Webley 2013, p. ix).
There several features that, in one way or another, distinguish legal essays from essays written in other disciplines. Probably the most crucial difference is the use and control of language. Law essays should be written clearly, concisely and with precision. For example, a lot of emphasis is placed on the use of simple English. This is because much of the subject matter is complex and needs to be communicated clearly to a specific audience. Words should be chosen carefully and the use of clichés should be avoided. The following table summarises some of the other similarities and differences:
The best way to become familiar with the expectations of a good legal research essay is to read some articles in legal journals, taking note of style, tone and citation.
Is your essay writing clear and concise?
Clarity has been described as the most basic and paramount goal of legal writing (Baron & Corbin 2016, p. 70). Not only must your reader be able to understand the contents of your essay, they must be able to easily identify your position and follow your logic. In other words, you need to ensure that your writing makes its point efficiently and with an appropriate level of detail so as not to waste the time of your reader.
When it comes to the editing stage of your writing process, you should ask yourself the following questions:
- What information does the reader need?
- Is the work organised clearly so that the reader can find the information they need easily, and understand the points made?
- Is the language used clear and appropriate for the audience?
Like an essay written in the humanities or social sciences, it's important to make sure you take a clear position and have a clear thesis statement and signposting in the introduction (macro level). It is also important to make sure that your headings and topic sentences accurately reflects the sequence of the ideas presented in your signposting (micro level). Have you used clear and descriptive headings and subheadings? Are paragraphs and sentences connected smoothly? Do paragraphs build on each other or introduce new topics? Do your topic and concluding sentences reflect such transition?
For more information about essay argument and structure, see our page on essay writing .
Baron and Corbin (ref) recommend the following tips for achieving clarity:
- Use ordinary words and simple sentence structures. Avoid legalese (the use of Latin words; overcomplicated sentences; legal jargon) and keep sentences to no more than 22 words, although this should not be adhered to rigidly.
- Vary sentence structures, vocabulary and sentence length. This creates a more natural flow that helps maintain the reader's interest. Vary sentence length to create a rhythm and interest in your writing.
- Develop your own voice. The aim of good legal writing is to develop an authentic professional voice, one that has character and individuality. This is something that helps to engage the reader. Achieve this by using an active voice.
- Pay attention to tone. Tone, according to Baron and Corbin (p. 74), is the expression of the writer's attitude towards the subject, audience, and self. In legal writing, the tone should be clear, concise, confident and courteous. While legal writing must be sophisticated, it should not be pretentious, and while courteous, should not be overly familiar or informal.
- Presentation matters. Good presentation of your written work can make reading easier and more engaging for your reader. Things to consider include text alignment, use of headings, spacing, and fonts. Information regarding formatting can be found in the AGLC. Make sure you proof read your work, paying attention to matters of style, presentation, and citation.
Making summaries
Summaries are an important tool when studying law because they enable an efficient and effective way of preparing for assessment items and exams. They can be used to help you identify what you know and what you don't know. Creating clear and well-structured summaries saves time and helps you produce neat, tight arguments backed up by relevant cases in your answers. Your examiners will appreciate this.
It is essential for you to put in the effort to produce your own summaries. Don't rely on the summaries prepared by others. These summaries may be useful to you, but will normally only be a useful supplement to your own studies. You have to spend time reflecting and pulling apart what you have been taught and building it up into a framework that you can use to complete your assessments.
Different summaries will work for different people. Find what works best for you!
There is no one way to write a summary. When you are summarising, you are collating information from lecture notes, tutorial notes, cases you have read and the textbook reading you have done. In some courses, you will be provided with reading lists. You can use these lists as a way of organise or planning your summaries. Reading lists are typically based on topics you will cover in lectures and cases relevant to these topics.
You should aim to write you summary twice. The first summary should be like the rough draft of an essay. At this stage you are gathering ideas, listing key concepts and principles, using headings to structure your notes, and potentially useful flowcharts. You should aim to do this at least 6 weeks or so before the exam. This will ensure that you:
- Give yourself plenty of time to revise;
- Know that, if there is an emergency, you will have something prepared;
- Force yourself to consider ideas more than once and refine what you have;
- Begin working on the overall conceptual framework of the subject.
Make sure you practice using your summary before the exam. One of the other good ways of preparing for an exam is to do past exams. You don't need to wait until you have completely finished your summary before trying some practice questions. As you work through the exam questions you may be able to add to your summary.
For information about preparing for exams, see our page on exam preparation .
What makes a good summary?
- A good summary is typed and clearly formatted. Organisation is key. You need to be able to glance at each page in order to find what you are looking for. If each page is well set out you can read to the point instead of around it.
- They use bullet points and avoid using full sentences. This makes finding information in an exam easier. Write in a way that makes sense to you.
- They contain information to help you locate the original source. Provide full references, including case names and page numbers, where necessary. The additional effort required is well worthwhile since it can be used later.
- They make good use of the abbreviations and key phrases. Abbreviations are excellent shorthand because they save a great deal of time and writing space. Develop your own system and use them consistently when making notes.
- They use visual aids, colour, and highlighting effectively. Flow charts, diagrams and other visual aids, such as tables, can help you understand a concept or case. A summary which makes good use of colour is easier to read and use. Decide what is right for you and use it consistently.
Preparing case notes
A case note is similar to a summary in that both require you to summarise information that will be useful when it comes to completing an assessment or preparing for an exam. The differences between a case note and a summary is the breadth of subject matter covered and the fact that a case note requires taking a position and evaluating the value of a particular case. In terms of breadth, a case note should focus on a single case, while a summary address a wider area of the law, focusing on a collection of issues, cases, and legislation. A case note can be included as part of a summary.
Case notes are a common method of assessment in law subjects because they are typically short and useful when constructing legal arguments. The purpose of legal case notes is to summarise and synthesise "the pertinent parts" of a legal judgment, including the facts, issue(s), and reasoning that went into court's decision making process (Corbett-Jarvis & Grigg 2017, p. 148). What they require you to do is thoroughly familiarise yourself with a notable court decision or statute and its legal context. This generally means examining the relationship between the decision and the existing case and/or statutory law, discussing important issues, cases, and legislation within that area.
Case notes tend to focus on important changes or interpretations of the law in certain cases. This is what makes them notable in some sense. When writing a case note, you should ask yourself what makes this case significant in the context of your course:
- Does it represent a significant departure from precedent?
- Does it represent a significant area of concern?
- Does it represent a first of its kind?
- Does it represent an abandonment of logical reasoning?
- Does it represent a precedent with long lasting effects?
A case note requires you to take a position (make an argument) and critically analyse the significance of the case in question. As Baron and Corbin (2016, p. 91) write, "[b]y articulating and arranging the information contained in cases... the writer can influence or persuade others to think in a more detailed way about the legal reasoning process".
How can I structure my case notes?
When writing a case note, the emphasis should be on being as clear and concise as possible. There is no definitive structure for a case note, but the following provides a flexible guideline of the common features. As a general rule, HIRAC should be used to compile and organise case notes.
Introduction
You should begin by briefly introducing the area of law, the legal issue(s), and what was decided. Indicate your line of argument: was this a significant decision? Does the decision create legal precedent, or uphold legal precedent? Explain the significance of the case, which should also indicate the organisation (or signposting) of the case note.
Identify the important, relevant facts of the case and, if appropriate, its background. This section will generally be more descriptive rather than analytical since you are just identifying the parties to the case (e.g. buyer, seller, employer, employee), procedurally significant facts, and the arguments that were put forward on behalf of both parties. Significant conflicting evidence should also be briefly noted. Keep it as short as possible.
In this section, you should provide the reader with an outline of the court's holding (i.e. the court's decision) on each relevant issue, as well as the court's reasoning. What is the legal rule essential to the decision in this case? Were comments made by the judge that are not directly related to the decision in this case, but may be important to issues raised in other cases? Reasoning is the way in which the court applied the rules/legal principles to the particular facts in the case to reach its decision. Indicate whether there was dissenting judgement and what reasons were provided for dissent. In closing this section, relate the selected case to the prior law to illustrate how, if at all, the selected case affects prior law.
This is the most significant section of your case note: this is where you demonstrate your critical analysis and evaluation of the case in your own words. In other words, this is you provide your argument. Start by stating the existing and the major developments both supporting and opposing the decision of the court. Then critically analyse the court's reasoning and decision. The analysis should be presented logically and be signposted accordingly. If appropriate, attempt to predict the impact the case will have on future decisions. Address any ambiguous statements made by the court, and questions the court left unanswered. This section affords you the opportunity to demonstrate legal skill and prowess by dissecting the case and raising important issues involved.
These are useful questions to use when it comes to writing your analysis:
- Was the court's decision appropriate and persuasive? Was the court's decision influenced by policy issue or particular values?
- Does this decision change/conform with existing law? Was the reasoning consistent with previous reasoning in similar cases? Is it likely that the decision will significantly influence existing law?
- Did the court adequately justify its reasoning? Was its interpretation of the law appropriate? Was the reasoning logical/consistent? Did the court consider all/omit some issues and arguments? And, if there was omission, does this weaken the merit of the decision?
- What are the policy implications of the decision? Are there alternative approaches which could lead to more appropriate public policy in this area?
Your conclusion should summarise the main points of your analysis and reiterate the significance of the case. If your finding is that the decision creates legal precedent, or conversely, upholds legal precedent, what does that mean? What are the wider implications of this case? The length of the conclusion depends on the argument being made. If you reach the legal conclusion in a previous section, a brief summary is sufficient.
Reference List
Baron, Paula, and Lillian Corbin. Legal Writing: Academic and Professional Communication . South Melbourne, Vic: Oxford University Press, 2016.
Campbell, Enid, Richard Fox, Melissa de Zwart. Students' Guide to Legal Writing, Law Exams and Self Assessment , 3 rd Ed. Annandale, NSW: Federation Press, 2010.
Corbett-Jarvis, Nichola, and Brendan Grigg. Effective Legal Writing: A Practical Guide , 2 nd Ed. Chatswood, NSW: LexisNexis Butterworths, 2016.
Macken, Claire. Law student survival guide: 9 steps to law study success, 2 nd Ed. Rozelle, NSW: Thomson Reuters (Professional) Australia Limited, 2010.
Webley, Lisa. Legal Writing , 3 rd Ed. London; New York: Routledge, 2013.
Other assessments
Writing a creative piece
Writing a critical review
Writing a policy brief
Writing an abstract
Writing an annotated bibliography
Writing in Psychology
Related links
- ANU Law Student Society
- ANU Library Academic Skills
- +61 2 6125 2972
How to Write a Critical Essay
Hill Street Studios / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
Olivia Valdes was the Associate Editorial Director for ThoughtCo. She worked with Dotdash Meredith from 2017 to 2021.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Olivia-Valdes_WEB1-1e405fc799d9474e9212215c4f21b141.jpg)
- B.A., American Studies, Yale University
A critical essay is a form of academic writing that analyzes, interprets, and/or evaluates a text. In a critical essay, an author makes a claim about how particular ideas or themes are conveyed in a text, then supports that claim with evidence from primary and/or secondary sources.
In casual conversation, we often associate the word "critical" with a negative perspective. However, in the context of a critical essay, the word "critical" simply means discerning and analytical. Critical essays analyze and evaluate the meaning and significance of a text, rather than making a judgment about its content or quality.
What Makes an Essay "Critical"?
Imagine you've just watched the movie "Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory." If you were chatting with friends in the movie theater lobby, you might say something like, "Charlie was so lucky to find a Golden Ticket. That ticket changed his life." A friend might reply, "Yeah, but Willy Wonka shouldn't have let those raucous kids into his chocolate factory in the first place. They caused a big mess."
These comments make for an enjoyable conversation, but they do not belong in a critical essay. Why? Because they respond to (and pass judgment on) the raw content of the movie, rather than analyzing its themes or how the director conveyed those themes.
On the other hand, a critical essay about "Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory" might take the following topic as its thesis: "In 'Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory,' director Mel Stuart intertwines money and morality through his depiction of children: the angelic appearance of Charlie Bucket, a good-hearted boy of modest means, is sharply contrasted against the physically grotesque portrayal of the wealthy, and thus immoral, children."
This thesis includes a claim about the themes of the film, what the director seems to be saying about those themes, and what techniques the director employs in order to communicate his message. In addition, this thesis is both supportable and disputable using evidence from the film itself, which means it's a strong central argument for a critical essay .
Characteristics of a Critical Essay
Critical essays are written across many academic disciplines and can have wide-ranging textual subjects: films, novels, poetry, video games, visual art, and more. However, despite their diverse subject matter, all critical essays share the following characteristics.
- Central claim . All critical essays contain a central claim about the text. This argument is typically expressed at the beginning of the essay in a thesis statement , then supported with evidence in each body paragraph. Some critical essays bolster their argument even further by including potential counterarguments, then using evidence to dispute them.
- Evidence . The central claim of a critical essay must be supported by evidence. In many critical essays, most of the evidence comes in the form of textual support: particular details from the text (dialogue, descriptions, word choice, structure, imagery, et cetera) that bolster the argument. Critical essays may also include evidence from secondary sources, often scholarly works that support or strengthen the main argument.
- Conclusion . After making a claim and supporting it with evidence, critical essays offer a succinct conclusion. The conclusion summarizes the trajectory of the essay's argument and emphasizes the essays' most important insights.
Tips for Writing a Critical Essay
Writing a critical essay requires rigorous analysis and a meticulous argument-building process. If you're struggling with a critical essay assignment, these tips will help you get started.
- Practice active reading strategies . These strategies for staying focused and retaining information will help you identify specific details in the text that will serve as evidence for your main argument. Active reading is an essential skill, especially if you're writing a critical essay for a literature class.
- Read example essays . If you're unfamiliar with critical essays as a form, writing one is going to be extremely challenging. Before you dive into the writing process, read a variety of published critical essays, paying careful attention to their structure and writing style. (As always, remember that paraphrasing an author's ideas without proper attribution is a form of plagiarism .)
- Resist the urge to summarize . Critical essays should consist of your own analysis and interpretation of a text, not a summary of the text in general. If you find yourself writing lengthy plot or character descriptions, pause and consider whether these summaries are in the service of your main argument or whether they are simply taking up space.
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- Critical Analysis in Composition
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write and Format an MBA Essay
- Higher Level Thinking: Synthesis in Bloom's Taxonomy
- How To Write a Top-Scoring ACT Essay for the Enhanced Writing Test
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- How to Structure an Essay
- How to Write a Response Paper
- What Is a Critique in Composition?
How To Write a Good Law Essay?

An excellent law essay should demonstrate detailed arguments and legal analysis, with a thesis statement that sums the argument up succinctly and concisely in two or three sentences. The aim should be that you are able to prove your conclusions, and importantly demonstrate that you are able to disprove competing views (the counterarguments). In general, you should first understand that a law essay will normally be focused on resolving a legal controversy, rather than dealing with application of the law to facts or problem resolution. This can be challenging for many students but following some key steps and principles will ensure that you can deliver an essay that has the following elements.
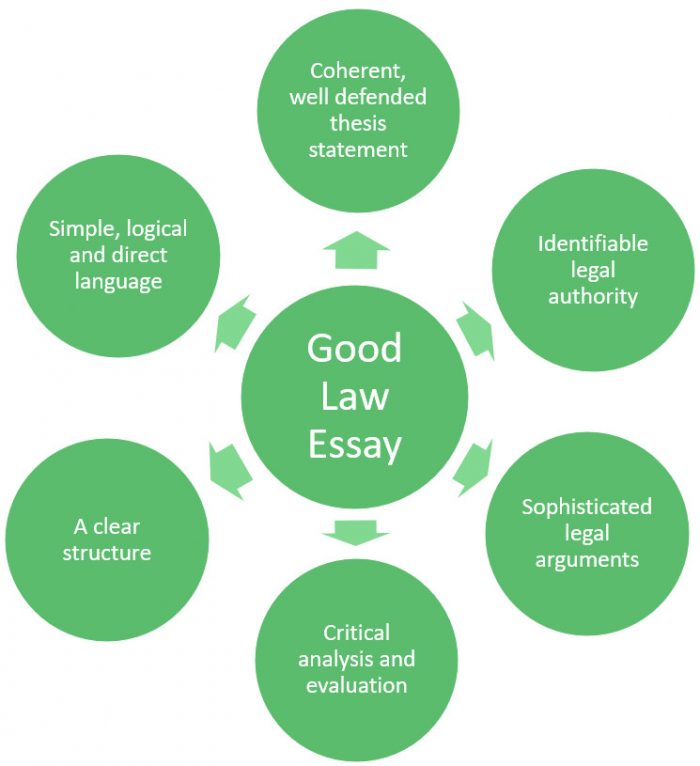
Plus, if you follow our tips and practical guidance you can be confident that your essay will deliver all of these pieces, in a way that ensures you demonstrate your ability to translate your knowledge of the law into a first-class assignment. The first thing to ensure is that you fully recognise the elements that all good essays share irrespective of the subject.
Key components of a good essay
Whatever your subject or discipline, but crucial in a law essay are the following elements for an outstanding essay:
- Attention to detail and a focus on the question posed.
- In-depth understanding of the right legal frameworks and laws clearly defined and described in simple language.
- Logical structure and flow
- Well-defended and clearly expressed thesis statement.
- Ability to demonstrate wider contextual issues, such as policy, history and clearly identifiable area of law.
- Critical application to answering the question.
- A level of creativity and original flair in the response, based on clear, well-researched legal arguments, including lateral thinking about less obvious points of law.
- Accurate referencing and use of any quotations or case law.
- Concise writing, and an effective style.
So, the list above shows what to incorporate into your essay but there are also some clear areas you should avoid.
What To Avoid In Your Law Essay
Do not use casual or informal language..
Keeping it simple does not mean informality; your style should remain academic and not include slang, abbreviations or colloquialisms, unless they are direct, properly referenced quotes.
Keep the overall look of the work balanced and always use full sentences.
Avoid overly long or short paragraphs and resist the temptation to use bullet points in your law essay as this does not demonstrate clear analysis or evaluation.
Avoid Incorrect citations of legislation.
Each university has different rules regarding how these should be presented in your law essays, so ensure you know and understand your institution’s requirements.
Credit all sources.
If you do not have a source, any legal argument not only loses credibility but becomes meaningless. Of course, all sources should also be credible, relevant and checked. At the same time, do not pepper your essay with irrelevant sources, each case cited should be there for a valid reason, and clearly evaluated and analysed.
Steps for Creating the Perfect Law Essay
Deconstruct and understand the question.
This does not mean choosing a side in the presented controversy, the important factor in a good law essay is to ensure that you propose a thesis, discuss, and then prove this, with effective use of legal argument and legal precedent. Other arguments are therefore a key element of your answer, as you need to be able to prove your arguments. Therefore, breaking down the question to understand the controversy under discussion, and then developing a thesis around the controversy. The ability to deconstruct a question can be challenging being of the potential for subtle allusions and issues that make the core area to be analysed appear vague or out of reach. The answer is to identify what you are being asked to do and what level of legal analysis and insight is needed to achieve this.
For example, an essay title may be given as “The Data Protection Act 2018 is a curtailment of personal freedoms” (A Non). Discuss.
To effectively answer this question, you need to identify what you are being asked to do. To discuss the quotation, the first stage is to elicit the background to the (fictional) statement. So, in other words, the essay is not about the statement as such, but instead is about the question (or questions) it raises, from a legal standpoint to identify whether the quotation is legally accurate.
In order to do this, there is a need for you to consider any counterarguments to the declarative argument given in the quotation. Thus, in the example above, the broad controversy to be discussed in your essay is whether Data Protection Laws are an invasion of personal freedom, or whether they are there to protect individuals.
Having determined the actual question being asked, the next stage is to find the answer and present this as a thesis statement, fully supported and proved by convincing legal arguments and a strong and coherent essay structure.
IMPORTANT TIP: Do not simply agree or disagree with the statement given in the title, but present solid arguments and counterarguments to illustrate how you have arrived at your conclusion, backed by credible and legal evidence.
This approach does not matter whether you are asked to examine any number of law topics in your essay, and there are number of different types, including:
- Legal Theory essays focus on discussion of why the law evolves as it does, backed by evidence.
- Legal Reform essays based on the undertaking of a recent law reform and its effectiveness, or alternatively whether a particular area is in need of reform. In these essays, the focus is demonstrating familiarity with historical and current laws and proposals in law.
- Legal History essays are founded in giving you the opportunity to identify gradual changes in a legal area. Legal reform and theory have a role in this type of essay, but the discussion is grounded in historical changes. The challenge with this essay is not to be overly descriptive, but to show evaluation and critical analysis.
Whatever type of law essay you are dealing with, you should ensure you maintain the basic principles of effective essay writing we have already given you, even while you ensure the focus of your answer is in the right area of legal writing.
Identify the Sources for Your Legal Argument
When an essay question indicates “discuss”, this would suggest you need to give an opinion. However, the opinion you present in a law essay should be one that is backed up by clear analysis and evaluation of all the legal facets of the situation. In other words, analysis or legal argumentation needs to follow certain conventions.
Reading of real-life cases and academic articles in the area are a good basis for identifying sources. Legal analysis is reliant, far more than any other discipline or credible sources. The validity of an argument in law comes from the source and precedent, not opinion or logic/attractiveness. Source in law means not just what was said but crucially also refers to who made the statement or judgement or wrote the article. In law there are two main authorities – binding and unbinding authorities. The first emanates from case law or legislation, whilst the second comes from Public Policy, Legal commentary, Dissenting judgements, Reform Proposals, and International Law.
First-class law essays should contain a mix of both binding and non-binding (or persuasive authorities). Using only one type of source is insufficient to give a wide enough perspective and counter argument in a legal controversy.
IMPORTANT TIP: Do not use long quotes from statutes, paraphrase if necessary, to ensure your essay is concise and makes your points clearly and coherently. Also ensure your sources are relevant to the question, the aim is not to demonstrate your wide reading of the law overall, but to illustrate that you can make a pertinent, valid argument and counterargument with appropriate sources.
Structure Your Essay Correctly
Getting your structure right – a simple rule of thumb is “say what you are going to say, say it, then say that you’ve said it” translated as Introduction – body text – conclusion.
Introduction
Your introduction should clearly state the purpose of the essay, and importantly should include your thesis statement. In other words, tell your readers in a creative and engaging way what you will be discussing. Your essay needs to hook your reader into being interested in reading further.
Your body text should be separated into separate paragraphs, each dealing with a different point that you wish to make. You can either make a point for one side, then deliver the counterargument before drawing an initial conclusion. Or you can present all the points for one side before moving to the counterargument. The first option can deliver a more logical, focused essay but can lead to a lack of balance if one argument is given more emphasis than another.
Your conclusion should be a summary of everything you have already said, concisely written and drawing together all the evaluations and analysis undertaken, but crucially not introducing new information. The closing statement of your conclusion should refer back to your thesis statement and whether this has been proved or disproved.
IMPORTANT TIP: Focus on simple, but academically proficient language, and do not put too much of an emphasis on legal jargon in your essay. You are producing a law essay not a case file. In all cases, ensure any sources are correctly referenced according to the requirements of your institution.
Key Phrases and words for Law Essays
As a final tip, here are some key phrases that can help your law essay stand out from others.
- This question deals with …
- The principal issue raised by this question …
- The main issue is whether…
- The issues to be considered are …
- The problem also raises the issue of
- On the facts presented, it can be argued that …
- It would seem, (therefore), that …
- It is possible that …
- It could be argued that …
- It would appear that…
When summing up in your conclusion the following phrases can be useful:
- On balance, it seems that.
- It is therefore concluded that…
- It is submitted that …
- In conclusion, it can be stated that …
- In consideration of the facts presented, it fair to conclude that …
You may also like

What Is a Capstone Project vs. Thesis

As students near the end of their academic journey, they encounter a crucial project called the capstone – a culmination of all they've learned. But what exactly is a capstone project?
This article aims to demystify capstone projects, explaining what they are, why they matter, and what you can expect when you embark on this final academic endeavor.
Capstone Project Meaning
A capstone project is a comprehensive, culminating academic endeavor undertaken by students typically in their final year of study.
It synthesizes their learning experiences, requiring students to apply the knowledge, skills, and competencies gained throughout their academic journey. A capstone project aims to address a real-world problem or explore a topic of interest in depth.
As interdisciplinary papers, capstone projects encourage critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. They allow students to showcase their mastery of their field of study and demonstrate their readiness for future academic or professional pursuits.
Now that we’ve defined what is a capstone project, let’s discuss its importance in the academic landscape. In case you have short-form compositions to handle, simply say, ‘ do my essay for me ,’ and our writers will take care of your workload.
Why Is a Capstone Project Important
A capstone project is crucial because it allows students to combine everything they've learned in school and apply it to real-life situations or big problems.
It's like the ultimate test of what they know and can do. By working on these projects, students get hands-on experience, learn to think critically and figure out how to solve tough problems.
Plus, it's a chance to show off their skills and prove they're ready for whatever comes next, whether that's starting a career or going on to more schooling.
Never Written Capstones Before?
Professional writers across dozens of subjects can help you right now.
What Is the Purpose of a Capstone Project
Here are three key purposes of a capstone project:
%20(1).webp)
Integration of Knowledge and Skills
Capstones often require students to draw upon the knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout their academic program. The importance of capstone project lies in helping students synthesize what they have learned and apply it to a real-world problem or project.
This integration helps students demonstrate their proficiency and readiness for graduation or entry into their chosen profession.
Culmination of Learning
Capstone projects culminate a student's academic journey, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios.
tackling a significant project or problem, students demonstrate their understanding of concepts and their ability to translate them into practical solutions, reinforcing their learning journey.
Professional Development
Capstone projects allow students to develop skills relevant to their future careers. These projects can also be tangible examples of their capabilities to potential employers or graduate programs.
Whether it's conducting research, presenting findings, or collaborating with peers, students gain valuable experience that enhances their professional readiness.
Types of Capstone Projects
Capstones vary widely depending on the academic discipline, institution, and specific program requirements. Here are some common types:
What Is the Difference Between a Thesis and a Capstone Project
Here's a breakdown of the key differences between a thesis and a capstone project:
How to Write a Capstone Project
Let's dive into the specifics with actionable and meaningful steps for writing a capstone project:
1. Select a Pertinent Topic
Identify a topic that aligns with your academic interests, program requirements, and real-world relevance. Consider issues or challenges within your field that merit further exploration or solution.
Conduct thorough research to ensure the topic is both feasible and significant. Here are some brilliant capstone ideas for your inspiration.
2. Define Clear Objectives
Clearly articulate the objectives of your capstone project. What specific outcomes do you aim to achieve?
Whether it's solving a problem, answering a research question, or developing a product, ensure your objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
3. Conduct Comprehensive Research
Dive deep into existing literature, theories, and empirical evidence related to your chosen topic. Identify gaps, controversies, or areas for further investigation.
Synthesize relevant findings and insights to inform the development of your project and provide a solid foundation for your analysis or implementation.
4. Develop a Structured Plan
What is a capstone project in college without a rigid structure? Outline a comprehensive plan for your capstone project, including key milestones, tasks, and deadlines.
Break down the project into manageable phases, such as literature review, data collection, analysis, and presentation. Establish clear criteria for success and regularly monitor progress to stay on track.
5. Implement Methodological Rigor
If your project involves research, ensure methodological rigor by selecting appropriate research methods, tools, and techniques.
Develop a detailed research design or project plan that addresses key methodological considerations, such as sampling, data collection, analysis, and validity. Adhere to ethical guidelines and best practices throughout the research process.
6. Analyze and Interpret Findings
Analyze your data or findings using appropriate analytical techniques and tools. Interpret the results in relation to your research questions or objectives, highlighting key patterns, trends, or insights.
Critically evaluate the significance and implications of your findings within the broader context of your field or industry.
7. Communicate Effectively
Present your capstone project clearly, concisely, and compellingly. Whether it's a written report, presentation, or multimedia deliverable, tailor your communication style to your target audience. Clearly articulate your research questions, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Use visuals, examples, and real-world applications to enhance understanding and engagement. Be prepared to defend your project and answer questions from peers, faculty, or stakeholders.
In wrapping up, what is a capstone project? It’s like the grand finale of your academic journey, where all the knowledge and skills you've acquired come together in one big project.
It's not just about passing a test or getting a grade – it's about proving you've got what it takes to make a real difference in the world. So, if you ever need capstone project help , our writers will gladly lend you a hand in no time.
Due Date Is Just Around the Corner?
Streamline the writing progress with our expert service!
What Is a Capstone Project in College?
How to do a capstone project, how long does a capstone project take to complete.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- T. (2023, June 16). What Is a Capstone Project? National University. https://www.nu.edu/blog/what-is-a-capstone-project/
- Lukins, S. (2024, May 12). What is a capstone project? And why is it important? Top Universities. https://www.topuniversities.com/student-info/careers-advice-articles/what-capstone-project-why-it-important
- Capstone Project vs. Thesis: What’s the Difference? (2021, December 9). UAGC. https://www.uagc.edu/blog/capstone-project-vs-thesis-whats-difference
Related Articles
.webp)
Pune Porsche crash: Essay contest held to protest juvenile’s initial bail order condition

Top Picks For You

Visual Stories


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In order to critically evaluate a law essay, you need to go beyond asking the basic questions. Just answering with the specific law on a certain issue isn't enough to make you a good lawyer. You need to build the ability to think for yourself and have an opinion on every case and statute, which you can defend with solid arguments.
At the same time, you'll need to be able to communicate your ideas clearly and persuasively. In this article, we'll cover some top tips to guide you through the process of planning, researching, structuring and writing a first-class law essay with confidence. 1. Start In Advance. Give yourself plenty of time to plan, research and write your ...
Critical Thinking. Critical thinking is the process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. In law many assignments will give you a quote from a ...
The first step in writing a top-notch law essay is to understand the essay question and planning your response. You should take care to read and analyze the question provided, identifying the main issues, required legal areas, and the keywords that will guide your research. Create a rough essay plan, outlining the main arguments and research ...
There are a number of strategies that may help you in starting, structuring and presenting a law essay. 1. Starting your answer. The first step to a successful law essay is understanding the question. One of the most effective ways of breaking down the question is to identify the direction, content, and scope or limiting words.
3. Clear, accurate writing. Good grammar, syntax, spelling and punctuation will be expected. Don't worry, the writing does not have to be flawless, but only a few mistakes will be tolerated. Eloquence, clarity and fluency of expression will always be appreciated and rewarded.
Let's say you are writing an EU law essay about how effective the preliminary reference procedure under Article 267 TFEU is. It might be tempting to look at that blank page and fill it with several hundred words about what the procedure is and how it works but that isn't the play here: it's not what the question is asking.
How to Write a Law Essay: 8 Steps. 1. Choosing an Essay Topic. When it comes to writing a law essay, choosing an appropriate topic is crucial. A well-chosen topic will make your research and writing process smoother and more enjoyable, while a poorly chosen topic can lead to frustration and a lackluster essay.
A good structure for a law report would be as follows: Title Page: showing the title of the report, the author, the person for whom the report is prepared, and the date of completion. Summary/Synopsis/Executive Summary: (approx 10% of word count) - this will identify: The purpose of the report, The scope of the report - issues covered/not ...
Critical thinking and analysis. 5. An organisation that is exact and clear. 6. The language that is simple, clear, and direct ... The writing of an essay on the law requires the same skills as the essay on problem-solving; these abilities are used and demonstrated in somewhat different ways. This guide will help you develop how use the skills ...
Hi guys, welcome back to my channel Don't forget to like and subscribe if you enjoyed the video & comment down below if there are any videos you would like ...
Critical analysis is subjective writing expressing opinion and evaluation. It includes breaking down and studying the parts of an assertion or situation. Critical analysis should include the learners evidenced opinion, matters of law and the commentary of knowledgeable and recognised third parties. Depending on the question that could be ...
Make a list of concerns that are generally addressed in regard to that area; Consult with a law tutor who can give you an up-to-date framework that can be used; and. Select a few topics (usually 3-5, depending on the word count) on which you will concentrate your efforts. #4 Research the area of law.
What distinguishes a law essay from an essay written in another discipline? Like essays written in other disciplines, legal essays require a central argument, based on logical reasoning and critical analysis of evidence. They should have a clear structure with a strong introduction and conclusion. As Baron and Corbin (2016, p. 26) note, even ...
1. Read Thoroughly and Carefully. You will need to accurately represent an author's point of view and techniques. Be sure you truly understand them before you begin the writing process. 2. Choose a Thesis Statement. Your thesis should make a claim about the author's point of view and writing style.
The law essay help guides below were written by our expert writers, as a learning aid to help you with your studies. If you are looking for help with your law essay help guide then we offer a comprehensive writing service provided by fully qualified academics in your field of study. Law Essay Writing Service.
A critical essay is a form of academic writing that analyzes, interprets, and/or evaluates a text. In a critical essay, an author makes a claim about how particular ideas or themes are conveyed in a text, then supports that claim with evidence from primary and/or secondary sources. In casual conversation, we often associate the word "critical ...
The challenge with this essay is not to be overly descriptive, but to show evaluation and critical analysis. Whatever type of law essay you are dealing with, you should ensure you maintain the basic principles of effective essay writing we have already given you, even while you ensure the focus of your answer is in the right area of legal writing.
The best way to do this is through using co-joining words such as 'in addition to,' 'moreover,' 'secondly', 'similarly', 'nevertheless.' etc. To show contrast, you could also use words such as, 'in contrast to, 'however, etc. This provides flow when a reader is going through the essay.
The example law essays below were written by students to help you with your own studies. If you are looking for help with your law essay then we offer a comprehensive writing service provided by fully qualified academics in your field of study. Law Essay Writing Service.
Law essay structure: 'Discuss': critique a specific topic, reaching a reasoned conclusion. Critically evaluate: subject the ideas contained within the essay title to careful assessment, paying attention to where the ideas have strengths or deficiencies and saying so. ... Writing problem answers. Have a good command of the relevant law ...
With a Master's degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she's a guest speaker at various business seminars.
An open essay-writing competition was organized in the city to protest the initial bail order given to a 17-year-old involved in a car crash. The competition aimed to highlight the injustice and ...