4.2 Marketing Research: an aid to decision making
Learning objectives.
The objectives of this section is to help students …
- Understanding the role of marketing research
- Understanding the marketing research process and the techniques employed
Discovering why they chew
Juicy Fruit Gum, the oldest brand of the Wm. Wrigley Jr. Company, was not chewing up the teen market, gum’s top demographic. In 1997, the company found itself under pressure from competitors. Sales and market share were down. How could Wrigley make more kids chomp on Juicy Fruit?
What qualities about Juicy Fruit might appeal to teens? Wrigley went to the source to find out. It found kids who chew five sticks or more of Juicy Fruit each week and promptly gave them a homework assignment. Find pictures that remind them of the gum and write a short story about it. From the focus group, Wrigley learned that teens chew Juicy Fruit because it is sweet. It refreshes and energizes them.
Their ad agency, BBDO, confirmed what the teens were saying. BBDO asked more than 400 heavy gum chewers to rate various brands by attributes that best represented them. For Juicy Fruit, respondents picked phrases such as “has the right amount of sweetness” and “is made with natural sweetness”.
Another study by BBDO looked into why teens chew gum. Was it because they are stressed out—or because they forgot to brush their teeth before going to school? Nearly three out of four kids said they stick a wad into their mouth when they crave something sweet. And Juicy Fruit was the top brand they chose to fulfill that need (Big Red was a distant second). (10)

Introduction
Although the marketing research conducted by the Wrigley Co. was fairly simple, it provided a new direction for their marketing strategy. BBDO developed four TV commercials with the “Gotta Have Sweet” theme. Roughly 70 per cent of respondents voluntarily recalled the Juicy Fruit name after watching the commercial (the average recall for a brand of sugar gum is 57 per cent). Sales of 100-stick boxes of Juicy Fruit rose 5 per cent after the start of the ad campaign, reversing a 2 per cent decline prior to it. Juicy Fruit’s market share also increased from 4.9 per cent to 5.3 per cent, the biggest gain of any established chewing gum brand during the year following the campaign.
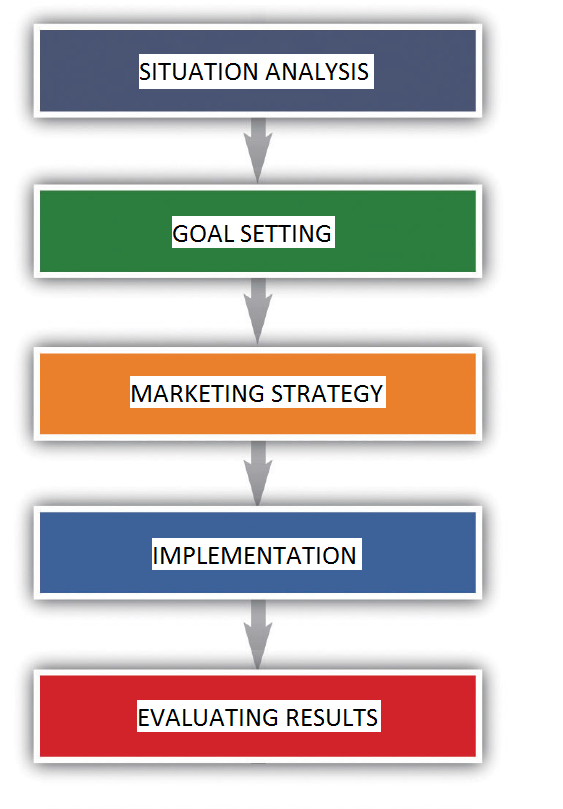
Figure 4.5: The marketing planning process
Marketing research addresses the need for quicker, yet more accurate, decision making by the marketer. The impetus for this situation is the complex relationship between the business firm and the ever-changing external environment. In particular, most marketers are far removed from their customers; yet most know who their customers are, what they want, and what competitors are doing. Often the marketer relies on salespeople and dealers for information, but more and more the best source of information is marketing research.
It should be noted that most marketing decisions are still made without the use of formal marketing research. In many cases, the time required to do marketing research is not available. In other cases, the cost of obtaining the data is prohibitive or the desired data cannot be obtained in reliable form. Ultimately, successful marketing executives make decisions on the basis of a blend of facts and intuition.
The nature and importance of marketing research
Informal and, by today’s standards, crude attempts to analyze the market date back to the earliest days of the marketing revolution. Only in recent years, however, has the role of research as it relates to management been clearly recognized.
Reflecting this change in orientation, the following definition of marketing research is offered: marketing research is the scientific and controlled gathering of non-routine marketing information undertaken to help management solve marketing problems. There is often hearty disagreement over the answer to the question of whether marketing research is a science. One’s answer depends on the employed definition of “science”. To be specific, a research activity should use the scientific method. In this method, hypotheses (tentative statements of relationships or of solutions to problems) are drawn from informal observations. These hypotheses are then tested. Ultimately, the hypothesis is accepted, rejected, or modified according to the results of the test. In a true science, verified hypotheses are turned into “laws”. In marketing research, verified hypotheses become the generalizations upon which management develops its marketing programs. (To simplify our discussion, we will use “questions” as a synonym of “hypothesis”.)
The mechanics of marketing research must be controlled so that the right facts are obtained in the answer to the correct problem. The control of fact-finding is the responsibility of the research director, who must correctly design the research and carefully supervise its execution to ensure that it goes according to plan. Maintaining control in marketing research is often difficult because of the distance that separates the researcher and the market and because the services of outsiders are often required to complete a research project. (1)
Student Example
Apple creating and updating their products consistently always leads to consumers waiting to see what else could possibly be done to help improve their products. This is where marketing research can ve utilized and can really help the company to advance in their sales.
Tarrah Clark
Class of 2020
What needs researching in marketing?
An easy, and truthful, answer to this question is “everything”. There is no aspect of marketing to which research cannot be applied. Every concept presented in this marketing text and every element involved in the marketing management process can be subjected to a great deal of careful marketing research. One convenient way to focus attention on those matters that especially need researching is to consider the elements involved in marketing management. Many important questions relating to the consumer can be raised. Some are:
• Who is/are the customer(s)?
• What does he/she desire in the way of satisfaction?
• Where does he/she choose to purchase?
• Why does he/she buy, or not buy?
• When does he/she purchase?
• How does he/she go about seeking satisfaction in the market?
Another area where research is critical is profits. Two elements are involved. First, there is the need to forecast sales and related costs—resulting in profits. Second, there is the necessity to plan a competitive marketing program that will produce the desired level of sales at an appropriate cost. Sales forecasting is the principal tool used in implementing the profit-direction element in the marketing management concept. Of course, the analysis of past sales and interpretation of cost information are important in evaluation of performance and provide useful facts for future planning.
A great deal of marketing research is directed toward rather specialized areas of management. These activities are broken down into five major areas of marketing research. Briefly, these activities are:
• research on markets —market trends, market share, market potentials, market characteristics, completion, and other market intelligence
As a business development intern, I work a lot with the marketing team in helping them get the time-consuming, yet necessary research on either specific markets we are entering or potential new clients. For example, I conducted research on the retail market in the Philippines. When I do this kind of research, I look at the market trends, forecasts, and things like the relationship between brick-and-mortar stores vs. online shopping in this case.
Cassidy Lane
• research on sales —sales analysis, sales forecasting, quota-setting, sales territory design, sales performance measurement, trade channels, distribution costs, and inventories • research on products—new product research, product features, brand image, concept tests, product tests, and market tests
When I worked at a retail store, we would forecast our sales for the day based on how much was sold on that day last year and then set our individual quotas based on that information. We would also analyze at the end of the day why we either met or missed our goals. For example, if the weather was bad, that could affect our sales for the day regardless of whether it was a big day the year before. We did a lot of product research, especially on new products, because it made our customers’ experience better if we were able to tell them about why the products were of better quality than others.
• research on advertising and promotion —promotion concepts, copy research, media research, merchandising, packaging, advertising effectiveness measurement
• research on corporate growth and development —economic and technological forecasting, corporate planning inputs, corporate image, profitability measurement, merger and acquisition, and facilities location.
| Sales forecast Cost forecast Product testing Consumer needs Consumer attitudes Consumer product usage Market size/trends Product replacement | Demographic trends Legislative impact Price testing Marketing communication testing Channel locations Competition Psychographic trends Environmental trends |
Table 4.1: Areas of research application.
Newsline: How execs use research
Creating and introducing new products is the most important research priority among marketing executives. The Marketing Science Institute of Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, surveyed 160 executives from its sponsoring organizations. The executives, representing 60 major consumer and industrial goods and services corporations, were asked to divide 100 points among several research areas.
After successful new product introductions, the executives said that market orientation and customer relationships are the next most important areas. Those issues displaced improving the use of marketing information and measuring brand equity as the second- and third-highest concerns, respectively, in the previous survey.
“The new research priorities indicate that a shift is taking place in marketing practice”, notes Donald Lehmann, executive director of the institute. “Market orientation has taken hold and the increasing power of the consumer is apparent in the movement away from product-driven strategies. Marketers also realize that they need to make choices about who their customers should be and whose needs they are best equipped to meet … and most significantly, they are looking for better ways to anticipate adoption and diffusion of really new products.” said Marni Clippenger, communications director at MSI, “Companies seem to be shifting away from using the brand to really figuring out what customers want.” (11)
1. Marketing research is the scientific and controlled gathering of nonroutine marketing information undertaken to help management solve marketing problems.
2. Any business that is consumer-oriented will benefit from marketing research.
3. Research can be applied to every facet of marketing.
(10): “How Sweet It Is,” American Demographics, March 2000, p, S 18; “Flavor du Jour,” American Demographics, March 2000, p, SI0; Erika Rasmusson, “Cool for Sale,” Sales & Marketing Management, March 1998, pp. 20-22,+
(11): Rachel Rosenthal. “New Products Reign as Research Priority,” Advertising Age, August 8, 1994, p. 26; Robert McMath, “To Test or Not To Test,” American Demographics, June 1998, p. 64; John McManus, “Mission Invisible,” American Demographics, March 1999, p. 6.
(1) Ralph H. Sprague, Jr. and Hugh J. Watson, Decision Support Systems:Putting Theory Into Practice, Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall,1986, p. 1
(2) Claire Selitz, Lawrence S. Wrightsman, and Stuart W. Cook, Research Methods in Social Relations, New York: Holt, Reinhart and Winston, 1976, pp. 11 4-115.
(3) Ian P. Murphy, “Research with Bottom Line in Mind Only,” Marketing News, March 3, 1997, p. 10.
(4) Pamela L. Alreck and Robert D. Settle, The Survey Research Hand book, Richard D. Irwin, Inc., 1995.
(5) Seymour Sudman, Applied Sampling, New York: Academic Press, 1976
Share This Book
- Increase Font Size
- Media Center
- E-Books & White Papers
- Knowledge Center
Why Market Research Is Important for Strategic Decision Making
by Sarah Schmidt , on May 29, 2018

Consider the following scenarios:
- A CEO who is thinking about making a large acquisition to enter a new market
- A product developer working to stay ahead of shifting trends
- A management consultant advising a client on how to reboot their business
- A brand manager creating buyer personas to shape marketing efforts
- An entrepreneur building a pitch to secure funding from venture capitalists
Each of these individuals may have previous experiences and gut instincts that inform their thinking and planning, but they must also incorporate high-quality data and analysis into their decision-making process in order to understand the bigger picture, persuade key stakeholders, and back up their conclusions.
Risk is inherent in each of these situations, and a fumble at the wrong moment can lead to serious consequences for an individual’s career success and a company’s longevity. When the competition is fierce and the margin of error is thin, relying on faulty assumptions can be fatal.
As we explore in the white paper The Importance of Market Research for Validation and Decision Making , high-quality industry research can mitigate these risks by helping to test your hypotheses, validate your insights, and build your sense of confidence.
Why You Need an Outside Point of View
Since 2000, more than half of the companies in the Fortune 500 have merged, gone bankrupt, or been acquired, according to Forbes . A new generation of innovative companies has sprung up, creating unique business paradigms for the organizations of tomorrow.
In this volatile environment, it’s not enough to just predict or forecast within the existing scope of business (though you should). To avoid getting “Ubered” like the cab industry, companies must leverage accurate data and qualitative assessments about the industry direction and identify gaping holes in customer satisfaction that outsiders may prey on. Rigorous analysis should be used to drive decision making and adapt in a timely manner, and in this regard, third-party market research can protect you in more ways than one.
Market research can open your eyes to products and trends beyond your own company and help you become more aware of influential variables such as:
- New technology
- Rising competitors
- Shifting consumer preferences
- Socio-economic changes
- New regulations
- Growing and shrinking markets
- Potential new partners and suppliers
With adequate research, you can seize valuable opportunities for product development and new market entry. You can also make more prudent investments — increasing spending on markets that still have room for growth and re-evaluating investments in markets with lower demand.
Market research can also give you the foundation you need to make other pivotal shifts in your business. For example, you may find that you need to build new external partnerships to quickly adapt to technological changes (such as cloud computing, virtual reality, or automation), or it may be in the best interest of your company to acquire a start-up to maintain a foothold in an evolving industry (such as Walmart acquiring Jet.com to boost its e-commerce side of the business).
Making smart business decisions — and gaining buy-in from stakeholders along the way — is much easier when you have credible evidence to back up your strategies.
Interested to learn more? Download MarketResearch.com's free white paper for more practical insights and recommendations.

Additional Articles
- What Is a Market Analysis?
- 5 Benefits of Market Research Reports
- The Power of Market Research: One MBA Student's Story

About This Blog
Our goal is to help you better understand your customer, market, and competition in order to help drive your business growth.
Popular Posts
- 5 Steps to Estimate Your Market Size
- 6 Booming Industries to Watch in 2018
- 5 Top Apparel Industry Trends
- The Beverage Industry: New Forecasts & Trends
- 12 Leading Companies in Clinical Laboratory Services
Recent Posts
Posts by topic.
- Industry Insights (831)
- Market Research Strategy (273)
- Food & Beverage (135)
- Healthcare (126)
- The Freedonia Group (121)
- How To's (109)
- Market Research Provider (95)
- Manufacturing & Construction (81)
- Pharmaceuticals (81)
- Packaged Facts (78)
- Telecommunications & Wireless (70)
- Heavy Industry (69)
- Marketing (58)
- Profound (57)
- Retail (56)
- Software & Enterprise Computing (56)
- Transportation & Shipping (54)
- House & Home (50)
- Materials & Chemicals (47)
- Medical Devices (46)
- Consumer Electronics (45)
- Energy & Resources (43)
- Public Sector (40)
- Biotechnology (37)
- Demographics (37)
- Business Services & Administration (36)
- Education (36)
- Custom Market Research (35)
- Diagnostics (34)
- Academic (33)
- Travel & Leisure (33)
- E-commerce & IT Outsourcing (32)
- Financial Services (29)
- Computer Hardware & Networking (26)
- Simba Information (24)
- Kalorama Information (21)
- Knowledge Centers (19)
- Apparel (18)
- Cosmetics & Personal Care (18)
- Market Research Subscription (16)
- Social Media (16)
- Advertising (14)
- Big Data (14)
- Holiday (11)
- Emerging Markets (8)
- Associations (1)
- Religion (1)
MarketResearch.com 6116 Executive Blvd Suite 550 Rockville, MD 20852 800.298.5699 (U.S.) +1.240.747.3093 (International) [email protected]
From Our Blog
Subscribe to blog, connect with us.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Decision-Driven Marketing
- Aditya Joshi
- Eduardo Giménez
Good decision processes break down silos and improve performance.
Reprint: R1407D
The gap between marketers’ aspirations and what their organizations can accomplish creates intense pressure to reshape how marketing is done. In recent years some leading companies have developed an innovative approach that focuses on the seams between marketing and the other functions it interacts with—the C-suite, IT, sales, finance, and so on. It is at these seams that communication most often breaks down and processes stall.
Typically, three categories of marketing-related decisions cross organizational seams: strategy and planning; execution; and operations and infrastructure. When marketing works closely with other units to execute key decisions, it can get things done far more quickly and effectively than in the past. But divergent assumptions or a lack of alignment and shared commitment between functions can get in the way. When the authors asked people in marketing and other relevant units what roles they played in a decision, the answers were all over the map. In a classic example, both marketers and product developers in one automaker’s European division believed that they had the final say on which features to include in a new model.
The authors provide a tool for revamping the decision process at the boundaries between functions and describe how Target, Nordstrom, and other large companies have identified important decisions at the seams and increased the impact of their marketing organizations.
Marketers have always had to build brands, create demand, promote sales, and help their companies earn customers’ loyalty. But today’s turbulent environment means they must play critical new roles: They must be strategists, allocating scarce resources to support company priorities and increasing return on investment. They must be technologists, tracking and capitalizing on the most useful of the sophisticated technologies that are flooding their field. And they must be scientists, because the future of their business may not look much like the past: Experiments that were once sideshows to preplanned campaigns are increasingly central to a marketer’s job.
Aditya Joshi is a partner at Bain & Company and head of the firm’s Marketing Excellence area. He is the co-author of “ Decision Driven Marketing ” in the July-August 2014 issue of Harvard Business Review.
- EG Eduardo Giménez is a partner at Bain and a member of the firm’s Consumer Goods practice in Europe, with a focus on marketing organizations.
Partner Center
What is Marketing Research? Examples and Best Practices
12 min read

Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which aids in identifying consumer demands, anticipating market trends, and staying ahead of the competition.
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. If you are seeking insight into how marketing research can influence the trajectory of your SaaS, then you have come to the right place!
- Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
- Primary market research gathers specific data directly from the target audience using tools like surveys and focus groups, while secondary market research utilizes existing data from various sources to provide broader market insights.
- Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Defining marketing research

Launching a product without knowing what your target audience wants is like walking in the dark. Market research lights the way, helping you collect, analyze, and understand information about your target market. This allows you to refine your business strategies and make decisions based on solid evidence.
Gone are the days when just intuition or subjective judgment was enough. Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product’s potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts.
Market research is a systematic approach that provides essential information, helping businesses navigate the complexities of the commercial world. Partnering with market research companies can offer additional benefits, leveraging their expertise in understanding market demands, trends, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing. Whether starting a new business, developing products, or updating marketing plans, understanding how to conduct effective market research is key to success.
To conduct market research effectively, businesses must determine study goals, identify target consumers, collect and analyze data, and use the findings to make informed decisions. This process is vital for evaluating past performance, measuring changes over time, and addressing specific business needs. It guides businesses in product development, marketing strategies, and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye-opening view of the market through various research methods, whether conducted in-house or outsourced.
The purpose of marketing research
Conducting marketing research is more than just gathering data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights to refine your business strategies. This process helps you understand what motivates your customers, enabling you to tailor your products and services to minimize risks from the start. Importantly, market research plays a pivotal role in measuring and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for understanding key demographics, improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention. Customer satisfaction is measured as a key outcome, directly linked to the success of marketing strategies and business activities.
For SaaS product managers, market research, including competitive analysis, is crucial. It evaluates past strategies and gauges the potential success of new offerings. This research provides essential insights into brand strength, consumer behavior, and market position, which are vital for teams focused on sales, marketing, and product development.
A key aspect of market research is analyzing customer attitudes and usage. This analysis offers detailed insights into what customers want, the choices they make, and the challenges they face. It helps identify opportunities in the market and aids in formulating effective strategies for market entry.
Overall, market research equips SaaS entrepreneurs with the knowledge to meet their target audience’s needs effectively, guiding product adjustments and innovations based on informed decisions.
Key components of market research
Conducting market research is analogous to preparing a cake, requiring precise ingredients in specific quantities to achieve the intended outcome. Within this realm, necessary components consist of primary and secondary data gathering, thorough analysis, and insightful interpretation.
Primary research techniques such as exploratory studies, product evolution inquiries, estimations of market dimensions and shares, and consumer behavior examinations play a crucial role in collecting targeted information that can be directly applied. These methods afford a deeper understanding of your target demographic, allowing for customized strategy development.
In contrast, secondary research enriches the specificity of primary findings by adding wider context. It taps into external resources encompassing works from other investigators, sector-specific reports, and demographics data, which provide an expansive yet less particularized landscape view of the marketplace.
The subsequent phase involves meticulous analysis of collated data offering unbiased perspectives critical for identifying deficiencies while recognizing emerging patterns. Technological progress now facilitates examination efforts on both structured and unstructured datasets effectively addressing large-scale analytical complexities.
Ultimately, it’s through expert-led interpretation that value transcends raw figures, yielding strategies grounded in deep comprehension. Akin to decoding recipes using selected ingredients—this interpretative step enables crafting optimal business maneuvers just as one would bake their ideal confectionery creation utilizing proper culinary guidance.
Types of market research: primary and secondary
Now that you know the importance of clear research objectives, let’s explore the different types of market research and the techniques available to achieve these goals. Market research methods can be divided into two main categories: primary research and secondary research . The choice between these depends on factors like your budget, time constraints, and whether you need exploratory data or definitive answers.
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from sources. This process is like mining for precious metals, as it requires using various methods to gather fresh insights.
- Surveys (here – in-app survey templates from Userpilot ).
- Interviews.
- Focus groups.
- Product trials.
This approach gives you first-hand insight into your target audience.
Conversely, secondary research uses already established datasets of primary data – which can add depth and reinforcement to your firsthand findings.
Conducting your own market research using primary research tools can be a cost-effective strategy, allowing businesses to gather valuable insights directly and tailor their research to specific needs.
Let’s look a bit deeper into them now.
What is primary market research?
Market research uses primary market research as an essential tool. This involves collecting new data directly from your target audience using various methods, such as surveys , focus groups, and interviews.
Each method has its benefits. For example, observational studies allow you to see how consumers interact with your product.
There are many ways to conduct primary research.
Focus Groups : Hold discussions with small groups of 5 to 10 people from your target audience. These discussions can provide valuable feedback on products, perceptions of your company’s brand name, or opinions on competitors. Additionally, these discussions can help understand the characteristics, challenges, and buying habits of target customers, optimizing brand strategy.
Interviews : Have one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information from individuals in your target audience.
Surveys : These are a common tool in primary market research and can be used instead of focus groups to understand consumer attitudes. Surveys use structured questions and can reach a broad audience efficiently.
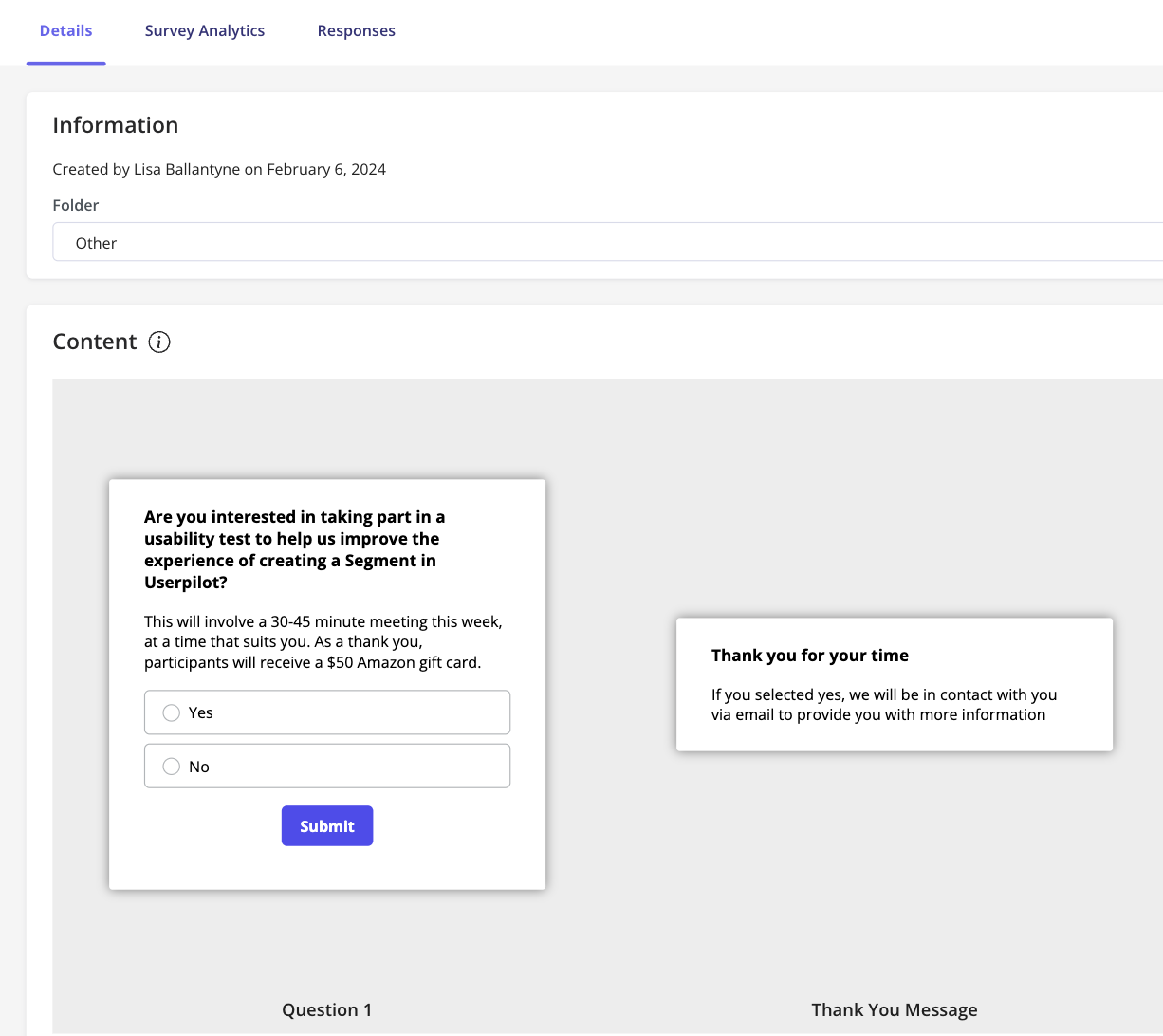
Navigating secondary market research
While marketing research using primary methods is like discovering precious metals, secondary market research technique is like using a treasure map. This approach uses data collected by others from various sources, providing a broad industry view. These sources include market analyses from agencies like Statista, historical data such as census records, and academic studies.
Secondary research provides the basic knowledge necessary for conducting primary market research goals but may lack detail on specific business questions and could also be accessible to competitors.
To make the most of secondary market research, it’s important to analyze summarized data to identify trends, rely on reputable sources for accurate data, and remain unbiased in data collection methods.
The effectiveness of secondary research depends significantly on how well the data is interpreted, ensuring that this information complements the insights from primary research.
Qualitative vs quantitative research
Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. Qualitative research aims to understand consumer behaviors and motivations through detailed analysis, while quantitative research collects measurable data for statistical analysis.
The selection of qualitative or quantitative methods should align with your research goals. If you need to uncover initial insights or explore deep consumer motivations, qualitative techniques like surveys or interviews are ideal.
On the other hand, if you need data that can be measured and analyzed for reliability, quantitative methods are more suitable.
However, these approaches don’t have to be used separately. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed-method studies allows you to capture both detailed exploratory responses and concrete numerical data. This integration offers a comprehensive view of the market, leveraging the strengths of both approaches to provide a fuller understanding of market conditions.
Implementing market research tools: Userpilot’s role
Similar to how a compass is essential for navigation at sea, businesses need appropriate instruments to carry out effective market research. Userpilot’s suite of product analytics and in-app engagement tools are critical components for this purpose.
Acting as a Buyer Persona Research instrument, Userpilot’s product analytics provide key quantitative research capabilities. This helps clearly define and comprehend the attributes and behaviors of potential customers, providing you with insights into your ICP (Ideal Customer Persona), user preferences, and product-market fit.
Beyond product analytics, Userpilot offers robust in-app engagement features such as modals and surveys that support real time collection of market research information. These interactive features work synergistically with the analytical tools to enable companies to gather detailed data and feedback crucial for informed business decision-making.
Marketing research process: Step-by-step guide
Marketing research conists of several critical stages:
- Defining precise goals.
- Delving into the knowledge of your target demographic.
- Collecting and scrutinizing data.
- Revealing insights that can be translated into tangible actions.
Following these steps allows you to gather critical information that guides business decisions.
An effective research strategy is crucial and involves:
- Properly allocating funds.
- Formulating testable hypotheses.
- Choosing appropriate methods for the study.
- Determining the number of study participants.
- Considering external variables.
A well-planned strategy ensures that your market research is focused, efficient, and produces useful outcomes.
After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves comparing the data to your initial questions to draw conclusions relevant to your business strategies.
Userpilot makes your data analysis easier by providing handy analytics dashboards for key user metrics such as activation, engagement, core feature adoption, and retention out of the box:
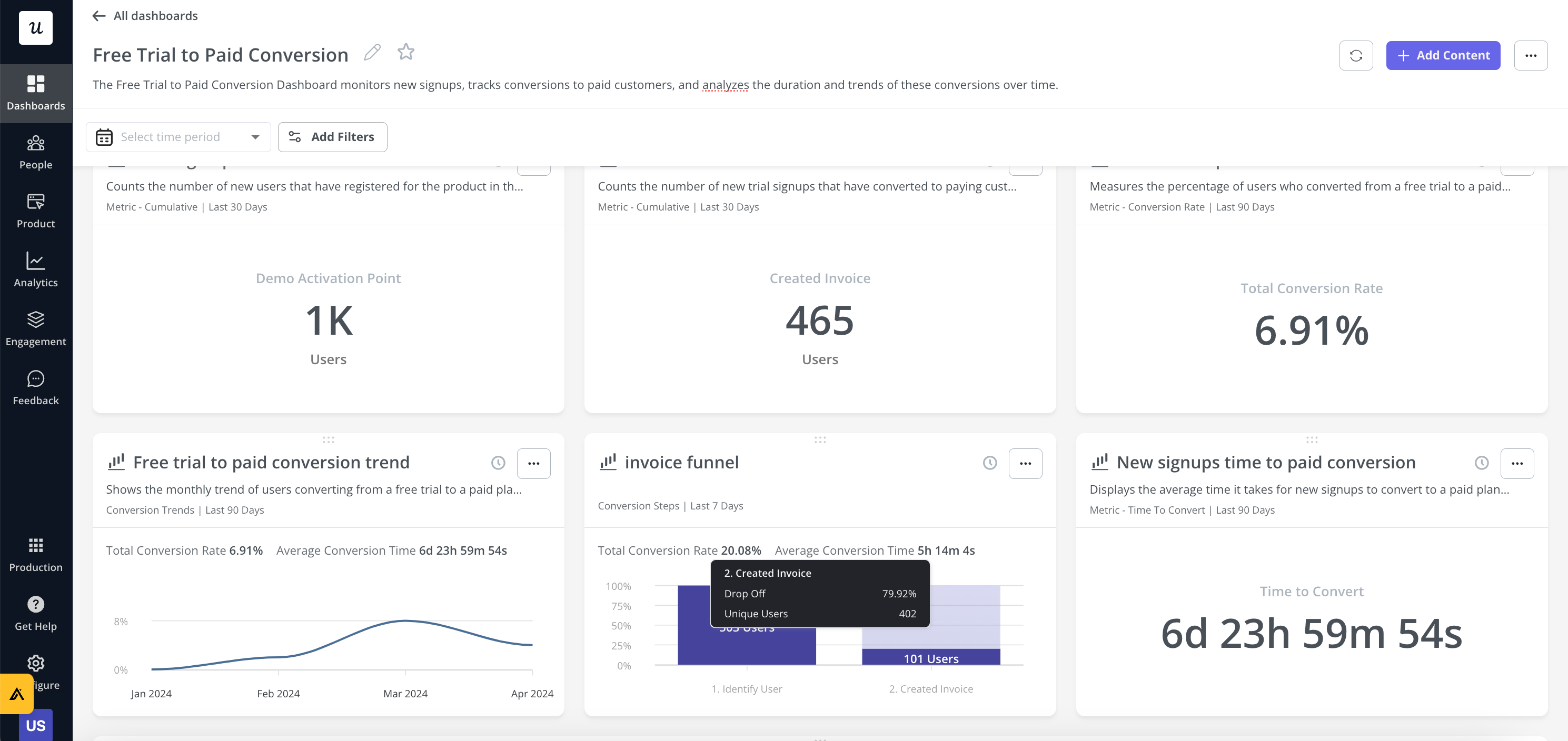
Finally, you report the findings and the process, providing recommendations based on the evidence. This is like solving a puzzle: each piece helps to complete the overall picture.
Challenges and best practices in market research
Delving into market research comes with its own set of hurdles. Those conducting the research must deliver more profound insights within increasingly shorter timespans, and they need to cultivate strategic, continuous research methods to stay abreast of an ever-changing business landscape.
Ensuring high-quality data can be demanding due to issues such as disjointed tools or insufficient analytical expertise. New solutions like Userpilot are surfacing that make these obstacles less daunting by offering accessible and user-friendly options. Maintaining clear lines of communication with your market research team is crucial for achieving both punctuality and quality in outcomes.
The advantages of engaging in marketing research cannot be overstated.
Real-life examples of successful market research
Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit.
For instance, Slack, the communication platform, utilized extensive market research to identify gaps in communication tools and understand the workflows of teams. This led to the development of features that seamlessly integrated with other tools and catered to the needs of various team sizes and structures.
Another example is HubSpot, which conducted market research to understand the pain points of small to medium-sized businesses in managing customer relationships. The insights gained helped shape their all-in-one inbound marketing, sales, and service platform, which has become integral to their users’ daily operations. These examples demonstrate how SaaS companies can employ market research to inform product development, improve user experience, and strategically position themselves in a competitive market.
Choosing the right market research tools
For B2B SaaS product managers aiming to do market research, having the right set of tools can make a significant difference. Here’s a list of valuable SaaS tools that can be leveraged for effective market research:
- Userpilot : A comprehensive Product Growth Platform offering in-depth product analytics, a code-free in-app experience builder, bespoke in-app survey capabilities, and robust integration options with platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot. This tool is particularly useful for understanding user behavior, enhancing user engagement, and gathering targeted feedback.
- Qualtrics : Known for its powerful survey tools, Qualtrics helps businesses gather and analyze customer feedback effectively. Its advanced analytics features are ideal for testing market hypotheses and understanding customer sentiments.
- SurveyMonkey : A versatile tool that enables product managers to create, send, and analyze surveys quickly and easily. SurveyMonkey is suitable for gauging customer satisfaction and collecting feedback on potential new features.
- Mixpanel : Specializes in user behavior analytics, offering detailed insights into how users interact with your product. This is essential for identifying patterns and optimizing product features.
- Hotjar : Combines analytics and feedback tools to give teams insights into user behavior and preferences. Hotjar’s heatmaps and session recordings are invaluable for understanding the user experience on a deeper level.
- Tableau : A leading platform for business intelligence and data visualization, Tableau allows product managers to create comprehensive visual reports that can inform strategic decisions based on user data analysis.
Each of these tools provides unique functionalities that can assist SaaS product managers in conducting thorough market research, thereby ensuring that their products are perfectly aligned with user needs and market demands.
Measuring the impact of market research
The pivotal challenge for market research lies in demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) and overall influence on corporate success sufficiently enough to justify regular financial commitment from company leaders. The worth attributed to a market research firm hinges not only on their ability to deliver relevant and high-caliber information, but also on their pricing structures and their contribution towards propelling organizational growth.
To gauge how effectively business choices made based on market research findings succeed, various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are utilized. These numerical tools act as navigational aids directing enterprises toward achieving objectives while simultaneously verifying that efforts invested in conducting market analysis are yielding fruitful guidance.
Throughout our look at market research, we’ve seen its importance and impact. Our discussion covered the basics of market research, its key components, and different types, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, and the role of Userpilot’s tools. We’ve examined the details of the market research process, tackled challenges, identified best practices, and shared success stories. We also provided advice on choosing the right market research partner and how to measure the effectiveness of your market research.
In today’s data-driven world, comprehensive market research is crucial for companies that want to succeed. It acts like a guide, helping businesses navigate the complex market landscape. Start your own detailed research today, supported by insightful analytics to help you succeed.
Frequently asked questions
What is market research and why is it important.
Understanding your target market, honing business strategies, and making informed decisions are all essential components that depend heavily on effective market research. It offers objective insights to help avoid expensive errors and foresees the needs of customers .
What is the difference between primary and secondary market research?
Primary market research is characterized by the direct gathering of data, in contrast to secondary market research which leverages existing information from alternative sources for addressing research inquiries.
Such a distinction can guide you in selecting an approach that aligns with your precise needs for conducting specific research.
What are some examples of successful market research?
Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such as Starbucks, Apple, and McDonald’s. They have harnessed this tool to fine-tune their business strategies and make decisions based on solid information.
By employing market research, these businesses have managed to gain insight into their customers’ desires and needs, which has contributed significantly to their success.
How can I choose the right market research partner?
Selecting an ideal market research ally involves identifying a firm that resonates with your project requirements, financial plan, and corporate goals while also verifying their track record of dependability and consistency via reviews from previous clients.
Best wishes on your endeavor!
How is the impact of market research measured?
The effectiveness of market research hinges on the precision, representativeness, and pertinence of its data, along with how successful business decisions are when they’re based on the findings from this research. These elements define the impact of the research conducted.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
11 product marketing metrics to track + benchmarks in 2024.
Aazar Ali Shad
Product-Led vs Sales-Led: What’s the Difference, and Which One Is Right for You?
Userpilot Content Team
What Are Marketing Funnels? A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Your User Journey

Make informed decisions with the marketing research process
Reading time: about 7 min
Who is your target consumer? What does their buying journey look like? How should you price your new product or service?
Today’s business markets are complex and rapidly evolving. So when answering questions like these, you can’t afford to guess. You need data.
That’s where the marketing research process comes in.
The marketing research process encompasses a number of activities focused on gathering product and consumer data to understand your target customers, validate new product ideas, iterate on existing products, and improve marketing and business decisions.
If you want to understand your customer and set your products and marketing strategies up for success, you need marketing research. But where should you begin? And how can you ensure your efforts lead to actionable insights?
Below we’ll walk you through the 5 main marketing research steps.
What is the marketing research process?
The marketing research process is a series of steps used to plan and conduct research on your target market. This process starts before the research ever begins, and it covers everything needed to make research effective, from planning to conducting to analyzing—all the way to finally presenting the results.
As much as we might want to believe our instincts are always right, that’s simply not the case. Research may back up your gut feeling, but it often reveals new, unexpected facts as well. The marketing research process helps you get all the information you need to make and justify a choice–and even gain a competitive edge.
Types of marketing research
There are multiple ways to conduct marketing research, depending on the question you’re trying to answer or the problem you’re trying to solve. Some marketing research process examples include:
- Customer interviews
- Focus groups
- Competitive analysis
- Surveys or questionnaires
- Observation
Which method you should choose will depend on your objectives.
Benefits of doing market research
In 2018, less than 40% of marketers used consumer research to drive decisions. By 2021, 60% of marketers said they use customer data the majority of the time when making decisions.
Why the jump? Marketers have realized the significant value of the marketing research process and are using it to improve their decision making across the business.
Market research is powerful because it can help solve real problems. The marketing research process helps leaders answer questions and gain insight into their business, such as:
- Why do customers buy certain products or behave a certain way
- What problems do customers have and what pain points the business can address
- What’s trending in the industry and what the competitive landscape looks like
- The level of demand for a type of product or service
- Customer perceptions or opinions on pricing
- Untapped opportunities for product development or marketing
Bottom line? The marketing research process helps your bottom line.
When you understand customer behavior and needs, the market landscape, and your own product performance, you can make better, strategic decisions that drive the business forward.
5 marketing research process steps
There are five basic steps to the marketing research process. The specific execution of these steps will vary based on your company’s specific needs and capabilities, but the outline below provides a good starting point.
1. Define the problem
In this initial step, determine why you need to conduct research in the first place. Once you’ve defined why you need research, decide what kind of information you need and how your team will use that information. This will make it easy to design an appropriate research plan in the next step.
For example, let’s say the business is seeing a drop in sales on one product. Your research question could be “Why are sales for product A dropping?” There could be a few reasons, such as loss of customer interest based on product performance or industry competition. Your marketing research can then be designed around investigating those possibilities.
Pro tip: Consult with decision-makers in your company. You’ll want to be sure that your marketing research adequately addresses their concerns and gives them the information they need to make a decision. Work with them to determine any specific metrics they’ll use to make their decision so you can tailor your research process to include their needs.
2. Develop a research plan
Next, begin outlining your research approach. Develop a hypothesis, and then determine how you will conduct research. There are many ways to gather data, including surveys and focus groups, so it’s important to choose a method that will give you the information you need from the people you care about.
- Your target audience
- The research tools you will use
- Who will be involved in the research process (e.g., customers, internal staff, or both?)
- How you will select research participants
- Your research timeline
- Project resources
If you’re conducting a survey, interviews, or focus group, consider how you will incentivize participants, what kinds of questions you will ask, and how to collect the responses.
3. Collect data
With a research plan in place, you can begin conducting your research. As you do so, ensure that everyone involved in collecting data has received training to do so effectively. You’ll want to supervise and evaluate their efforts throughout the research process to ensure you get quality data.
Make sure to collect and record data in a secure place, preferably using a standardized format, to ensure you have accurate, usable data.
4. Analyze data
As your research concludes, begin data analysis . This step includes editing, coding, or transcribing data as needed to make it readable and manipulatable. Data analysis can take many forms, but it often includes making graphs and tables to spot trends. Remember, your analysis should reveal whether your hypothesis established in step two was correct.
5. Prepare a report
The marketing research process concludes with a presentation of your research. Generally, this takes the form of a written report that includes the initial problem, an outline of the research, and recommendations for how to proceed. This step can also take the form of oral reports or presentations—anything that communicates your research clearly.

However you present this information, make your report clear and understandable for any individuals who weren’t directly involved in the research process. Give them all the information necessary for decision-making. At this point, your company can take action based on your findings, thus concluding the marketing research process.
Lucidchart and the marketing research process
One size does not fit all when it comes to the marketing research process. While the basic steps are applicable to most organizations, they will often be executed very differently. Your organization needs to personalize your process, and Lucidchart makes it easy to do so.
For example, the formality of the marketing research process varies from company to company. Smaller businesses might conduct casual research with a Google survey. A large company, however, might require carefully selected focus groups and formal questionnaires. With Lucidchart, you can customize your marketing research process to fit your organization’s needs.
Marketing research can play a key role in making the right decisions for your company. Developing your own marketing research process will help you achieve even better results from your data collection and analysis, in turn helping you make more informed choices.

Define your marketing research process today with Lucidchart.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
Master the 5-step email marketing funnel.
A well-thought-out email marketing funnel and campaign have the power to turn browsers into shoppers and one-time fans into lifelong brand ambassadors.
How to refine your marketing funnel and earn devoted customers
Marketing teams can use the marketing funnel to see how customers find their company and why they choose it. See how to make one in Lucidchart!
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
BUS203: Principles of Marketing
Marketing Research: An Aid to Decision Making
Read this chapter. The American Marketing Association defines marketing research this way: "Marketing research is the function that links the consumer, customer, and public to the marketer through information--information used to identify and define marketing opportunities and problems; generate, refine, and evaluate marketing actions; monitor marketing performance; and improve understanding of marketing as a process. Marketing research specifies the information required to address these issues, designs the methods for collecting information, manages and implements the data collection process, and analyzes and communicates the findings and their implications".
Introduction
Having completed this chapter, you should
- Understand the role of marketing research
- Understand the marketing research process and the techniques employed
DISCOVERING WHY THEY CHEW
Juicy Fruit Gum, the oldest brand of the Wm. Wrigley Jr. Company, wasn't chewing up the teen market, gum's top demographic. In 1997, the company found itself under pressure from competitors. Sales and market share were down. How could Wrigley make more kids chomp on Juicy Fruit?
What qualities about Juicy Fruit might appeal to teens? Wrigley went to the source to find out. It found kids who chew five sticks or more of Juicy Fruit each week and promptly gave them a homework assignment. Find pictures that remind them of the gum and write a short story about it. From the focus group, Wrigley learned that teens chew Juicy Fruit because it's sweet. It refreshes and energizes them.
Their ad agency, BBDO, confirmed what the teens were saying. BBDO asked more than 400 heavy gum chewers to rate various brands by attributes that best represented them. For Juicy Fruit, respondents picked phrases such as "has the right amount of sweetness" and "is made with natural sweetness".
Another study by BBDO looked into why teens chew gum. Was it because they 're stressed out-or because they forgot to brush their teeth before going to school? Nearly three out of four kids said they stick a wad into their mouth when they crave something sweet. And Juicy Fruit was the top brand they chose to fulfill that need (Big Red was a distant second).
Although the marketing research conducted by the Wrigley Co. was fairly simple, it provided a new direction for their marketing strategy. BBDO developed four TV commercials with the "Gatta Have Sweet" theme. Roughly 70 percent of respondents voluntarily recalled the Juicy Fruit name after watching the commercial (the average recall for a brand of sugar gum is 57 percent). Sales of 100-stick boxes of juicy Fruit rose 5 percent after the start of the ad campaign , reversing a 2 percent decline prior to it. Juicy Fruit's market share also increased from 4.9 percent to 5.3 percent, the biggest gain of any established chewing gum brand during the year following the campaign.
FIGURE 3.1 The marketing planning process

Marketing research addresses the need for quicker, yet more accurate, decision making by the marketer. The impetus for this situation is the complex relationship between the business firm and the ever-changing external environment. In particular, most marketers are far removed from their customers; yet must know who their customers are, what they want, and what competitors are doing. Often the marketer relies on salespeople and dealers for information, but more and more the best source of information is marketing research.
It should be noted that most marketing decisions are still made without the use of formal marketing research. In many cases, the time required to do marketing research is not available. In other case s, the cost of obtaining the data is prohibitive or the desired data cannot be obtained in reliable form. Ultimately, successful marketing executives make decisions on the basis of a blend of facts and intuition.
In this chapter, we provide an overview of the marketing research process. We start the discussion with a look at business information. As noted in Figure 3.1, marketing research is applicable throughout the marketing planning process.

Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
Market research definition
Market research – in-house or outsourced, market research in the age of data, when to use market research.
- Types of market research
Different types of primary research
How to do market research (primary data), how to do secondary market research, communicating your market research findings, choose the right platform for your market research, try qualtrics for free, the ultimate guide to market research: how to conduct it like a pro.
27 min read Wondering how to do market research? Or even where to start learning about it? Use our ultimate guide to understand the basics and discover how you can use market research to help your business.
Market research is the practice of gathering information about the needs and preferences of your target audience – potential consumers of your product.
When you understand how your target consumer feels and behaves, you can then take steps to meet their needs and mitigate the risk of an experience gap – where there is a shortfall between what a consumer expects you to deliver and what you actually deliver. Market research can also help you keep abreast of what your competitors are offering, which in turn will affect what your customers expect from you.
Market research connects with every aspect of a business – including brand , product , customer service , marketing and sales.
Market research generally focuses on understanding:
- The consumer (current customers, past customers, non-customers, influencers))
- The company (product or service design, promotion, pricing, placement, service, sales)
- The competitors (and how their market offerings interact in the market environment)
- The industry overall (whether it’s growing or moving in a certain direction)
Free eBook: 2024 market research trends report
Why is market research important?
A successful business relies on understanding what like, what they dislike, what they need and what messaging they will respond to. Businesses also need to understand their competition to identify opportunities to differentiate their products and services from other companies.
Today’s business leaders face an endless stream of decisions around target markets, pricing, promotion, distribution channels, and product features and benefits . They must account for all the factors involved, and there are market research studies and methodologies strategically designed to capture meaningful data to inform every choice. It can be a daunting task.
Market research allows companies to make data-driven decisions to drive growth and innovation.
What happens when you don’t do market research?
Without market research, business decisions are based at best on past consumer behavior, economic indicators, or at worst, on gut feel. Decisions are made in a bubble without thought to what the competition is doing. An important aim of market research is to remove subjective opinions when making business decisions. As a brand you are there to serve your customers, not personal preferences within the company. You are far more likely to be successful if you know the difference, and market research will help make sure your decisions are insight-driven.
Traditionally there have been specialist market researchers who are very good at what they do, and businesses have been reliant on their ability to do it. Market research specialists will always be an important part of the industry, as most brands are limited by their internal capacity, expertise and budgets and need to outsource at least some aspects of the work.
However, the market research external agency model has meant that brands struggled to keep up with the pace of change. Their customers would suffer because their needs were not being wholly met with point-in-time market research.
Businesses looking to conduct market research have to tackle many questions –
- Who are my consumers, and how should I segment and prioritize them?
- What are they looking for within my category?
- How much are they buying, and what are their purchase triggers, barriers, and buying habits?
- Will my marketing and communications efforts resonate?
- Is my brand healthy ?
- What product features matter most?
- Is my product or service ready for launch?
- Are my pricing and packaging plans optimized?
They all need to be answered, but many businesses have found the process of data collection daunting, time-consuming and expensive. The hardest battle is often knowing where to begin and short-term demands have often taken priority over longer-term projects that require patience to offer return on investment.
Today however, the industry is making huge strides, driven by quickening product cycles, tighter competition and business imperatives around more data-driven decision making. With the emergence of simple, easy to use tools , some degree of in-house market research is now seen as essential, with fewer excuses not to use data to inform your decisions. With greater accessibility to such software, everyone can be an expert regardless of level or experience.
How is this possible?
The art of research hasn’t gone away. It is still a complex job and the volume of data that needs to be analyzed is huge. However with the right tools and support, sophisticated research can look very simple – allowing you to focus on taking action on what matters.
If you’re not yet using technology to augment your in-house market research, now is the time to start.
The most successful brands rely on multiple sources of data to inform their strategy and decision making, from their marketing segmentation to the product features they develop to comments on social media. In fact, there’s tools out there that use machine learning and AI to automate the tracking of what’s people are saying about your brand across all sites.
The emergence of newer and more sophisticated tools and platforms gives brands access to more data sources than ever and how the data is analyzed and used to make decisions. This also increases the speed at which they operate, with minimal lead time allowing brands to be responsive to business conditions and take an agile approach to improvements and opportunities.
Expert partners have an important role in getting the best data, particularly giving access to additional market research know-how, helping you find respondents , fielding surveys and reporting on results.
How do you measure success?
Business activities are usually measured on how well they deliver return on investment (ROI). Since market research doesn’t generate any revenue directly, its success has to be measured by looking at the positive outcomes it drives – happier customers, a healthier brand, and so on.
When changes to your products or your marketing strategy are made as a result of your market research findings, you can compare on a before-and-after basis to see if the knowledge you acted on has delivered value.
Regardless of the function you work within, understanding the consumer is the goal of any market research. To do this, we have to understand what their needs are in order to effectively meet them. If we do that, we are more likely to drive customer satisfaction , and in turn, increase customer retention .
Several metrics and KPIs are used to gauge the success of decisions made from market research results, including
- Brand awareness within the target market
- Share of wallet
- CSAT (customer satisfaction)
- NPS (Net Promoter Score)
You can use market research for almost anything related to your current customers, potential customer base or target market. If you want to find something out from your target audience, it’s likely market research is the answer.
Here are a few of the most common uses:
Buyer segmentation and profiling
Segmentation is a popular technique that separates your target market according to key characteristics, such as behavior, demographic information and social attitudes. Segmentation allows you to create relevant content for your different segments, ideally helping you to better connect with all of them.
Buyer personas are profiles of fictional customers – with real attributes. Buyer personas help you develop products and communications that are right for your different audiences, and can also guide your decision-making process. Buyer personas capture the key characteristics of your customer segments, along with meaningful insights about what they want or need from you. They provide a powerful reminder of consumer attitudes when developing a product or service, a marketing campaign or a new brand direction.
By understanding your buyers and potential customers, including their motivations, needs, and pain points, you can optimize everything from your marketing communications to your products to make sure the right people get the relevant content, at the right time, and via the right channel .
Attitudes and Usage surveys
Attitude & Usage research helps you to grow your brand by providing a detailed understanding of consumers. It helps you understand how consumers use certain products and why, what their needs are, what their preferences are, and what their pain points are. It helps you to find gaps in the market, anticipate future category needs, identify barriers to entry and build accurate go-to-market strategies and business plans.
Marketing strategy
Effective market research is a crucial tool for developing an effective marketing strategy – a company’s plan for how they will promote their products.
It helps marketers look like rock stars by helping them understand the target market to avoid mistakes, stay on message, and predict customer needs . It’s marketing’s job to leverage relevant data to reach the best possible solution based on the research available. Then, they can implement the solution, modify the solution, and successfully deliver that solution to the market.
Product development
You can conduct market research into how a select group of consumers use and perceive your product – from how they use it through to what they like and dislike about it. Evaluating your strengths and weaknesses early on allows you to focus resources on ideas with the most potential and to gear your product or service design to a specific market.
Chobani’s yogurt pouches are a product optimized through great market research . Using product concept testing – a form of market research – Chobani identified that packaging could negatively impact consumer purchase decisions. The brand made a subtle change, ensuring the item satisfied the needs of consumers. This ability to constantly refine its products for customer needs and preferences has helped Chobani become Australia’s #1 yogurt brand and increase market share.
Pricing decisions
Market research provides businesses with insights to guide pricing decisions too. One of the most powerful tools available to market researchers is conjoint analysis, a form of market research study that uses choice modeling to help brands identify the perfect set of features and price for customers. Another useful tool is the Gabor-Granger method, which helps you identify the highest price consumers are willing to pay for a given product or service.
Brand tracking studies
A company’s brand is one of its most important assets. But unlike other metrics like product sales, it’s not a tangible measure you can simply pull from your system. Regular market research that tracks consumer perceptions of your brand allows you to monitor and optimize your brand strategy in real time, then respond to consumer feedback to help maintain or build your brand with your target customers.
Advertising and communications testing
Advertising campaigns can be expensive, and without pre-testing, they carry risk of falling flat with your target audience. By testing your campaigns, whether it’s the message or the creative, you can understand how consumers respond to your communications before you deploy them so you can make changes in response to consumer feedback before you go live.
Finder, which is one of the world’s fastest-growing online comparison websites, is an example of a brand using market research to inject some analytical rigor into the business. Fueled by great market research, the business lifted brand awareness by 23 percent, boosted NPS by 8 points, and scored record profits – all within 10 weeks.
Competitive analysis
Another key part of developing the right product and communications is understanding your main competitors and how consumers perceive them. You may have looked at their websites and tried out their product or service, but unless you know how consumers perceive them, you won’t have an accurate view of where you stack up in comparison. Understanding their position in the market allows you to identify the strengths you can exploit, as well as any weaknesses you can address to help you compete better.
Customer Story
See How Yamaha Does Product Research
Types of market research
Although there are many types market research, all methods can be sorted into one of two categories: primary and secondary.
Primary research
Primary research is market research data that you collect yourself. This is raw data collected through a range of different means – surveys , focus groups, , observation and interviews being among the most popular.
Primary information is fresh, unused data, giving you a perspective that is current or perhaps extra confidence when confirming hypotheses you already had. It can also be very targeted to your exact needs. Primary information can be extremely valuable. Tools for collecting primary information are increasingly sophisticated and the market is growing rapidly.
Historically, conducting market research in-house has been a daunting concept for brands because they don’t quite know where to begin, or how to handle vast volumes of data. Now, the emergence of technology has meant that brands have access to simple, easy to use tools to help with exactly that problem. As a result, brands are more confident about their own projects and data with the added benefit of seeing the insights emerge in real-time.
Secondary research
Secondary research is the use of data that has already been collected, analyzed and published – typically it’s data you don’t own and that hasn’t been conducted with your business specifically in mind, although there are forms of internal secondary data like old reports or figures from past financial years that come from within your business. Secondary research can be used to support the use of primary research.
Secondary research can be beneficial to small businesses because it is sometimes easier to obtain, often through research companies. Although the rise of primary research tools are challenging this trend by allowing businesses to conduct their own market research more cheaply, secondary research is often a cheaper alternative for businesses who need to spend money carefully. Some forms of secondary research have been described as ‘lean market research’ because they are fast and pragmatic, building on what’s already there.
Because it’s not specific to your business, secondary research may be less relevant, and you’ll need to be careful to make sure it applies to your exact research question. It may also not be owned, which means your competitors and other parties also have access to it.
Primary or secondary research – which to choose?
Both primary and secondary research have their advantages, but they are often best used when paired together, giving you the confidence to act knowing that the hypothesis you have is robust.
Secondary research is sometimes preferred because there is a misunderstanding of the feasibility of primary research. Thanks to advances in technology, brands have far greater accessibility to primary research, but this isn’t always known.
If you’ve decided to gather your own primary information, there are many different data collection methods that you may consider. For example:
- Customer surveys
- Focus groups
- Observation
Think carefully about what you’re trying to accomplish before picking the data collection method(s) you’re going to use. Each one has its pros and cons. Asking someone a simple, multiple-choice survey question will generate a different type of data than you might obtain with an in-depth interview. Determine if your primary research is exploratory or specific, and if you’ll need qualitative research, quantitative research, or both.
Qualitative vs quantitative
Another way of categorizing different types of market research is according to whether they are qualitative or quantitative.
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is the collection of data that is non-numerical in nature. It summarizes and infers, rather than pin-points an exact truth. It is exploratory and can lead to the generation of a hypothesis.
Market research techniques that would gather qualitative data include:
- Interviews (face to face / telephone)
- Open-ended survey questions
Researchers use these types of market research technique because they can add more depth to the data. So for example, in focus groups or interviews, rather than being limited to ‘yes’ or ‘no’ for a certain question, you can start to understand why someone might feel a certain way.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research is the collection of data that is numerical in nature. It is much more black and white in comparison to qualitative data, although you need to make sure there is a representative sample if you want the results to be reflective of reality.
Quantitative researchers often start with a hypothesis and then collect data which can be used to determine whether empirical evidence to support that hypothesis exists.
Quantitative research methods include:
- Questionnaires
- Review scores
Exploratory and specific research
Exploratory research is the approach to take if you don’t know what you don’t know. It can give you broad insights about your customers, product, brand, and market. If you want to answer a specific question, then you’ll be conducting specific research.
- Exploratory . This research is general and open-ended, and typically involves lengthy interviews with an individual or small focus group.
- Specific . This research is often used to solve a problem identified in exploratory research. It involves more structured, formal interviews.
Exploratory primary research is generally conducted by collecting qualitative data. Specific research usually finds its insights through quantitative data.
Primary research can be qualitative or quantitative, large-scale or focused and specific. You’ll carry it out using methods like surveys – which can be used for both qualitative and quantitative studies – focus groups, observation of consumer behavior, interviews, or online tools.
Step 1: Identify your research topic
Research topics could include:
- Product features
- Product or service launch
- Understanding a new target audience (or updating an existing audience)
- Brand identity
- Marketing campaign concepts
- Customer experience
Step 2: Draft a research hypothesis
A hypothesis is the assumption you’re starting out with. Since you can disprove a negative much more easily than prove a positive, a hypothesis is a negative statement such as ‘price has no effect on brand perception’.
Step 3: Determine which research methods are most effective
Your choice of methods depends on budget, time constraints, and the type of question you’re trying to answer. You could combine surveys, interviews and focus groups to get a mix of qualitative and quantitative data.
Step 4: Determine how you will collect and analyze your data.
Primary research can generate a huge amount of data, and when the goal is to uncover actionable insight, it can be difficult to know where to begin or what to pay attention to.
The rise in brands taking their market research and data analysis in-house has coincided with the rise of technology simplifying the process. These tools pull through large volumes of data and outline significant information that will help you make the most important decisions.
Step 5: Conduct your research!
This is how you can run your research using Qualtrics CoreXM
- Pre-launch – Here you want to ensure that the survey/ other research methods conform to the project specifications (what you want to achieve/research)
- Soft launch – Collect a small fraction of the total data before you fully launch. This means you can check that everything is working as it should and you can correct any data quality issues.
- Full launch – You’ve done the hard work to get to this point. If you’re using a tool, you can sit back and relax, or if you get curious you can check on the data in your account.
- Review – review your data for any issues or low-quality responses. You may need to remove this in order not to impact the analysis of the data.
A helping hand
If you are missing the skills, capacity or inclination to manage your research internally, Qualtrics Research Services can help. From design, to writing the survey based on your needs, to help with survey programming, to handling the reporting, Research Services acts as an extension of the team and can help wherever necessary.
Secondary market research can be taken from a variety of places. Some data is completely free to access – other information could end up costing hundreds of thousands of dollars. There are three broad categories of secondary research sources:
- Public sources – these sources are accessible to anyone who asks for them. They include census data, market statistics, library catalogs, university libraries and more. Other organizations may also put out free data from time to time with the goal of advancing a cause, or catching people’s attention.
- Internal sources – sometimes the most valuable sources of data already exist somewhere within your organization. Internal sources can be preferable for secondary research on account of their price (free) and unique findings. Since internal sources are not accessible by competitors, using them can provide a distinct competitive advantage.
- Commercial sources – if you have money for it, the easiest way to acquire secondary market research is to simply buy it from private companies. Many organizations exist for the sole purpose of doing market research and can provide reliable, in-depth, industry-specific reports.
No matter where your research is coming from, it is important to ensure that the source is reputable and reliable so you can be confident in the conclusions you draw from it.
How do you know if a source is reliable?
Use established and well-known research publishers, such as the XM Institute , Forrester and McKinsey . Government websites also publish research and this is free of charge. By taking the information directly from the source (rather than a third party) you are minimizing the risk of the data being misinterpreted and the message or insights being acted on out of context.
How to apply secondary research
The purpose and application of secondary research will vary depending on your circumstances. Often, secondary research is used to support primary research and therefore give you greater confidence in your conclusions. However, there may be circumstances that prevent this – such as the timeframe and budget of the project.
Keep an open mind when collecting all the relevant research so that there isn’t any collection bias. Then begin analyzing the conclusions formed to see if any trends start to appear. This will help you to draw a consensus from the secondary research overall.
Market research success is defined by the impact it has on your business’s success. Make sure it’s not discarded or ignored by communicating your findings effectively. Here are some tips on how to do it.
- Less is more – Preface your market research report with executive summaries that highlight your key discoveries and their implications
- Lead with the basic information – Share the top 4-5 recommendations in bullet-point form, rather than requiring your readers to go through pages of analysis and data
- Model the impact – Provide examples and model the impact of any changes you put in place based on your findings
- Show, don’t tell – Add illustrative examples that relate directly to the research findings and emphasize specific points
- Speed is of the essence – Make data available in real-time so it can be rapidly incorporated into strategies and acted upon to maximize value
- Work with experts – Make sure you’ve access to a dedicated team of experts ready to help you design and launch successful projects
Trusted by 8,500 brands for everything from product testing to competitor analysis, Our Strategic Research software is the world’s most powerful and flexible research platform . With over 100 question types and advanced logic, you can build out your surveys and see real-time data you can share across the organization. Plus, you’ll be able to turn data into insights with iQ, our predictive intelligence engine that runs complicated analysis at the click of a button.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

The Importance of Marketing Research in Decision Making (And Next-Level Campaigns)
Why your next campaign needs marketing research. marketing research is your ticket to better campaign decisions..
Looking to get more out of your marketing spend? Are you struggling with the inspiration needed to produce that new, award-winning, paradigm-shifting viral campaign ? In both cases, I cannot overstate the importance of marketing research – and, sure, that sounds a tad biased coming from a market researcher 😉. There’s no need to take my word for it, though. These case studies speak for themselves.
What Is the Purpose of Marketing Research?
You might wonder why it is important to conduct market research in the first place – or whether it’s even necessary at all.
For a small business, hit-and-miss marketing is not only demotivating but also costly (and possibly quite damaging to your reputation). The solution to this is to switch to informed marketing.
Research provides intelligence to guide informed, enhanced decisions. Ultimately, helping you to:
- hit the bull’s eye with your target audience ,
- increase your campaign success,
- and make every penny spent yield greater returns.
Good data saves time, money—and gives you a competitive edge.
Why Market Research Works.
You can liken the importance of marketing research to military reconnaissance. Observing the landscape enables you to identify strategic features, locate your targets and formulate a winning battle plan.
David Ogilvy, arguably the most prolific publicist of our time, thought the same way. He said, “Advertisers who ignore research are as dangerous as generals who ignore the signs of the enemy.”
Ogilvy understood the business value of keeping your messaging on point.
“Write great headlines, and you’ll have successfully invested 80% of your money.”—David Ogilvy.
He advocated the importance of marketing research, knowing that accurate data is a sure-fire way to find those golden nuggets of inspiration.
Research uncovers your market’s thoughts, questions, propensity towards specific behaviour. It provides key insights needed to craft compelling headlines and content that converts
It works because you’re not creating content on a hunch and hoping it will resonate. You’re developing content, campaigns or products that speak to the consumer’s heart based on facts.
Learn from the Big Brands : 3 Case Studies that Illustrate the Impact of Marketing Research.
It makes sense then that international brands invest heavily in market research. Learning from a few case studies, see how multinationals relied on sound research to inform product decisions, to-market strategies, elevate business, and seriously level-up advertising.
First Direct Used Marketing Research to Regain Market Share
The problem:
First Direct (established in 1989 as a telephone bank) expanded into online banking as technology changed with the turn of the century. Despite evolving in line with market trends, the bank struggled to make ground against stronger market competition.
The research:
The market research consultancy used various methodologies similar to ours. These included case study personas <ink to https://sapioresearch.com/persona-research-for-marketing>, user profiles and quantitative research methods like collating stats to indicate customer brand perception. Qualitative research like focus groups and in-depth interviews revealed how customers felt about First Direct’s move to online banking.
The findings:
Customer brand perception research pinpointed weaknesses in customer service as the cause and identified which areas required focus. The research results enabled the bank to make changes that their customer base genuinely appreciated.
The results:
Nowadays, they consistently rank as a top customer service provider. In January of 2021, First Direct was named Britain’s best brand for customer service delivery in the latest Customer Satisfaction Index.
Lego’s Love of Research Lead the Brand to Parity
The problem:
Market research is frequently credited with LEGO’s continued success. Throughout the 20th century, the LEGO market lay firmly with young boys. Commissioned market research revealed that only 9% of their customer base comprised females.
The research:
LEGO made the high-profile decision to rely on qualitative and quantitative research. Lengthy focus groups, case studies and trials lasted over four years and involved research into the habits of 3,500 young girls and their mothers. Data analysis helped quantify consumer interest in female-orientated LEGO
The findings:
Further investigation was commissioned to guide decisions around product development that targeted young girls’ interests.
The results:
LEGO’s ‘Friends’ was launched in 2012. The company confirmed in a press conference that the share of girls among LEGO players had increased sharply since its release.
Mitsubishi Pajero’s Research Failure Folly
There are countless examples of brand wins underpinned by research, but what happens when a brand skips this step?
Mitsubishi found out the hard way, losing significant sales in Spanish-speaking regions. This happened when the Japanese car manufacturer launched the “Pajero”, unaware that this is a derogatory term in Spanish. Their failure to conduct international research before entering the market resulted in a highly costly exercise, ending with the model’s name eventually being changed to “Moderno” in Spain and other Spanish-speaking territories.
Key Take-Away: Research Is the Catalyst for Creativity
Research provides deep insights that encourage product innovations and compelling copy. Nothing quite inspires creativity like a juicy finding that the world needs to know. The right statistic can create an exciting headline that entices readers.
I’d argue that research is as vital for content creation as top-notch copywriters and designers are. But then, of course, I would. I’m a researcher! What do you say? Leave a comment.
Need help figuring out the research you need?
Get topical tips, insights and more delivered to your inbox.
Be the first to know about the latest international business sentiments, behaviours and plans to stay one step ahead of your competition.
How to Do Market Research: The Complete Guide
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.
Access best-in-class company data
Get trusted first-party funding data, revenue data and firmographics
What are your customers’ needs? How does your product compare to the competition? What are the emerging trends and opportunities in your industry? If these questions keep you up at night, it’s time to conduct market research.
Market research plays a pivotal role in your ability to stay competitive and relevant, helping you anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. It involves gathering these insights using a wide range of techniques, from surveys and interviews to data analysis and observational studies.
In this guide, we’ll explore why market research is crucial, the various types of market research, the methods used in data collection, and how to effectively conduct market research to drive informed decision-making and success.
What is market research?
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a specific market or industry. The purpose of market research is to offer valuable insight into the preferences and behaviors of your target audience, and anticipate shifts in market trends and the competitive landscape. This information helps you make data-driven decisions, develop effective strategies for your business, and maximize your chances of long-term growth.

Why is market research important?
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you’re asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include:
- Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you identify opportunities, assess risks and tailor your strategies to meet the demands of the market. Without market research, decisions are often based on assumptions or guesswork, leading to costly mistakes.
- Customer-centric approach: A cornerstone of market research involves developing a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. This gives you valuable insights into your target audience, helping you develop products, services and marketing campaigns that resonate with your customers.
- Competitive advantage: By conducting market research, you’ll gain a competitive edge. You’ll be able to identify gaps in the market, analyze competitor strengths and weaknesses, and position your business strategically. This enables you to create unique value propositions, differentiate yourself from competitors, and seize opportunities that others may overlook.
- Risk mitigation: Market research helps you anticipate market shifts and potential challenges. By identifying threats early, you can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively to changing circumstances. This proactive approach is particularly valuable in volatile industries.
- Resource optimization: Conducting market research allows organizations to allocate their time, money and resources more efficiently. It ensures that investments are made in areas with the highest potential return on investment, reducing wasted resources and improving overall business performance.
- Adaptation to market trends: Markets evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts and changing consumer attitudes. Market research ensures that you stay ahead of these trends and adapt your offerings accordingly so you can avoid becoming obsolete.
As you can see, market research empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, cater to customer needs, outperform competitors, mitigate risks, optimize resources and stay agile in a dynamic marketplace. These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026 . Now, let’s dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
Types of market research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
- Cross-sectional research
- Longitudinal research
Despite its advantages, 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy. Part of developing a strategy involves choosing the right type of market research for your business goals. The most commonly used approaches include:
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying motivations, attitudes and perceptions of individuals or groups. It is typically conducted through techniques like in-depth interviews, focus groups and content analysis — methods we’ll discuss further in the sections below. Qualitative research provides rich, nuanced insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies and brand positioning.
2. Quantitative research
Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. This approach allows for statistical analysis and the measurement of trends, making it suitable for large-scale market studies and hypothesis testing. While it’s worthwhile using a mix of qualitative and quantitative research, most businesses prioritize the latter because it is scientific, measurable and easily replicated across different experiments.
3. Exploratory research
Whether you’re conducting qualitative or quantitative research or a mix of both, exploratory research is often the first step. Its primary goal is to help you understand a market or problem so you can gain insights and identify potential issues or opportunities. This type of market research is less structured and is typically conducted through open-ended interviews, focus groups or secondary data analysis. Exploratory research is valuable when entering new markets or exploring new product ideas.
4. Descriptive research
As its name implies, descriptive research seeks to describe a market, population or phenomenon in detail. It involves collecting and summarizing data to answer questions about audience demographics and behaviors, market size, and current trends. Surveys, observational studies and content analysis are common methods used in descriptive research.
5. Causal research
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It investigates whether changes in one variable result in changes in another. Experimental designs, A/B testing and regression analysis are common causal research methods. This sheds light on how specific marketing strategies or product changes impact consumer behavior.
6. Cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional market research involves collecting data from a sample of the population at a single point in time. It is used to analyze differences, relationships or trends among various groups within a population. Cross-sectional studies are helpful for market segmentation, identifying target audiences and assessing market trends at a specific moment.
7. Longitudinal research
Longitudinal research, in contrast to cross-sectional research, collects data from the same subjects over an extended period. This allows for the analysis of trends, changes and developments over time. Longitudinal studies are useful for tracking long-term developments in consumer preferences, brand loyalty and market dynamics.
Each type of market research has its strengths and weaknesses, and the method you choose depends on your specific research goals and the depth of understanding you’re aiming to achieve. In the following sections, we’ll delve into primary and secondary research approaches and specific research methods.
Primary vs. secondary market research
Market research of all types can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: primary research and secondary research. By understanding the differences between these approaches, you can better determine the most appropriate research method for your specific goals.
Primary market research
Primary research involves the collection of original data straight from the source. Typically, this involves communicating directly with your target audience — through surveys, interviews, focus groups and more — to gather information. Here are some key attributes of primary market research:
- Customized data: Primary research provides data that is tailored to your research needs. You design a custom research study and gather information specific to your goals.
- Up-to-date insights: Because primary research involves communicating with customers, the data you collect reflects the most current market conditions and consumer behaviors.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Despite its advantages, primary research can be labor-intensive and costly, especially when dealing with large sample sizes or complex study designs. Whether you hire a market research consultant, agency or use an in-house team, primary research studies consume a large amount of resources and time.
Secondary market research
Secondary research, on the other hand, involves analyzing data that has already been compiled by third-party sources, such as online research tools, databases, news sites, industry reports and academic studies.

Here are the main characteristics of secondary market research:
- Cost-effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective than primary research since it doesn’t require building a research plan from scratch. You and your team can look at databases, websites and publications on an ongoing basis, without needing to design a custom experiment or hire a consultant.
- Leverages multiple sources: Data tools and software extract data from multiple places across the web, and then consolidate that information within a single platform. This means you’ll get a greater amount of data and a wider scope from secondary research.
- Quick to access: You can access a wide range of information rapidly — often in seconds — if you’re using online research tools and databases. Because of this, you can act on insights sooner, rather than taking the time to develop an experiment.
So, when should you use primary vs. secondary research? In practice, many market research projects incorporate both primary and secondary research to take advantage of the strengths of each approach.
One rule of thumb is to focus on secondary research to obtain background information, market trends or industry benchmarks. It is especially valuable for conducting preliminary research, competitor analysis, or when time and budget constraints are tight. Then, if you still have knowledge gaps or need to answer specific questions unique to your business model, use primary research to create a custom experiment.
Market research methods
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Online research tools
- Experiments
- Content analysis
- Ethnographic research
How do primary and secondary research approaches translate into specific research methods? Let’s take a look at the different ways you can gather data:
1. Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular methods for collecting structured data from a large number of respondents. They involve a set of predetermined questions that participants answer. Surveys can be conducted through various channels, including online tools, telephone interviews and in-person or online questionnaires. They are useful for gathering quantitative data and assessing customer demographics, opinions, preferences and needs. On average, customer surveys have a 33% response rate , so keep that in mind as you consider your sample size.
2. Interviews
Interviews are in-depth conversations with individuals or groups to gather qualitative insights. They can be structured (with predefined questions) or unstructured (with open-ended discussions). Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics, uncovering motivations and obtaining detailed feedback.
3. Focus groups
The most common primary research methods are in-depth webcam interviews and focus groups. Focus groups are a small gathering of participants who discuss a specific topic or product under the guidance of a moderator. These discussions are valuable for primary market research because they reveal insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions and emotions. Focus groups are especially useful for idea generation, concept testing and understanding group dynamics within your target audience.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves observing and recording participant behavior in a natural setting. This method is particularly valuable when studying consumer behavior in physical spaces, such as retail stores or public places. In some types of observational research, participants are aware you’re watching them; in other cases, you discreetly watch consumers without their knowledge, as they use your product. Either way, observational research provides firsthand insights into how people interact with products or environments.
5. Online research tools
You and your team can do your own secondary market research using online tools. These tools include data prospecting platforms and databases, as well as online surveys, social media listening, web analytics and sentiment analysis platforms. They help you gather data from online sources, monitor industry trends, track competitors, understand consumer preferences and keep tabs on online behavior. We’ll talk more about choosing the right market research tools in the sections that follow.
6. Experiments
Market research experiments are controlled tests of variables to determine causal relationships. While experiments are often associated with scientific research, they are also used in market research to assess the impact of specific marketing strategies, product features, or pricing and packaging changes.
7. Content analysis
Content analysis involves the systematic examination of textual, visual or audio content to identify patterns, themes and trends. It’s commonly applied to customer reviews, social media posts and other forms of online content to analyze consumer opinions and sentiments.
8. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research immerses researchers into the daily lives of consumers to understand their behavior and culture. This method is particularly valuable when studying niche markets or exploring the cultural context of consumer choices.

How to do market research
- Set clear objectives
- Identify your target audience
- Choose your research methods
- Use the right market research tools
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Interpret your findings
- Identify opportunities and challenges
- Make informed business decisions
- Monitor and adapt
Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let’s delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here’s a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts.
1. Set clear objectives
When you set clear and specific goals, you’re essentially creating a compass to guide your research questions and methodology. Start by precisely defining what you want to achieve. Are you launching a new product and want to understand its viability in the market? Are you evaluating customer satisfaction with a product redesign?
Start by creating SMART goals — objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Not only will this clarify your research focus from the outset, but it will also help you track progress and benchmark your success throughout the process.
You should also consult with key stakeholders and team members to ensure alignment on your research objectives before diving into data collecting. This will help you gain diverse perspectives and insights that will shape your research approach.
2. Identify your target audience
Next, you’ll need to pinpoint your target audience to determine who should be included in your research. Begin by creating detailed buyer personas or stakeholder profiles. Consider demographic factors like age, gender, income and location, but also delve into psychographics, such as interests, values and pain points.
The more specific your target audience, the more accurate and actionable your research will be. Additionally, segment your audience if your research objectives involve studying different groups, such as current customers and potential leads.
If you already have existing customers, you can also hold conversations with them to better understand your target market. From there, you can refine your buyer personas and tailor your research methods accordingly.
3. Choose your research methods
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for gathering high-quality data. Start by considering the nature of your research objectives. If you’re exploring consumer preferences, surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights. For in-depth understanding, focus groups or observational research might be suitable. Consider using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a well-rounded perspective.
You’ll also need to consider your budget. Think about what you can realistically achieve using the time and resources available to you. If you have a fairly generous budget, you may want to try a mix of primary and secondary research approaches. If you’re doing market research for a startup , on the other hand, chances are your budget is somewhat limited. If that’s the case, try addressing your goals with secondary research tools before investing time and effort in a primary research study.
4. Use the right market research tools
Whether you’re conducting primary or secondary research, you’ll need to choose the right tools. These can help you do anything from sending surveys to customers to monitoring trends and analyzing data. Here are some examples of popular market research tools:
- Market research software: Crunchbase is a platform that provides best-in-class company data, making it valuable for market research on growing companies and industries. You can use Crunchbase to access trusted, first-party funding data, revenue data, news and firmographics, enabling you to monitor industry trends and understand customer needs.
- Survey and questionnaire tools: SurveyMonkey is a widely used online survey platform that allows you to create, distribute and analyze surveys. Google Forms is a free tool that lets you create surveys and collect responses through Google Drive.
- Data analysis software: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are useful for conducting statistical analyses. SPSS is a powerful statistical analysis software used for data processing, analysis and reporting.
- Social listening tools: Brandwatch is a social listening and analytics platform that helps you monitor social media conversations, track sentiment and analyze trends. Mention is a media monitoring tool that allows you to track mentions of your brand, competitors and keywords across various online sources.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports. Power BI by Microsoft is a business analytics tool for creating interactive visualizations and reports.
5. Collect data
There’s an infinite amount of data you could be collecting using these tools, so you’ll need to be intentional about going after the data that aligns with your research goals. Implement your chosen research methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews or pulling from secondary research platforms. Pay close attention to data quality and accuracy, and stick to a standardized process to streamline data capture and reduce errors.
6. Analyze data
Once data is collected, you’ll need to analyze it systematically. Use statistical software or analysis tools to identify patterns, trends and correlations. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis to extract common themes and insights. Visualize your findings with charts, graphs and tables to make complex data more understandable.
If you’re not proficient in data analysis, consider outsourcing or collaborating with a data analyst who can assist in processing and interpreting your data accurately.

7. Interpret your findings
Interpreting your market research findings involves understanding what the data means in the context of your objectives. Are there significant trends that uncover the answers to your initial research questions? Consider the implications of your findings on your business strategy. It’s essential to move beyond raw data and extract actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Hold a cross-functional meeting or workshop with relevant team members to collectively interpret the findings. Different perspectives can lead to more comprehensive insights and innovative solutions.
8. Identify opportunities and challenges
Use your research findings to identify potential growth opportunities and challenges within your market. What segments of your audience are underserved or overlooked? Are there emerging trends you can capitalize on? Conversely, what obstacles or competitors could hinder your progress?
Lay out this information in a clear and organized way by conducting a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Jot down notes for each of these areas to provide a structured overview of gaps and hurdles in the market.
9. Make informed business decisions
Market research is only valuable if it leads to informed decisions for your company. Based on your insights, devise actionable strategies and initiatives that align with your research objectives. Whether it’s refining your product, targeting new customer segments or adjusting pricing, ensure your decisions are rooted in the data.
At this point, it’s also crucial to keep your team aligned and accountable. Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities and timelines for implementing the recommendations derived from your research.
10. Monitor and adapt
Market research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, customer behaviors and industry trends. Set up mechanisms to collect real-time data and feedback. As you gather new information, be prepared to adapt your strategies and tactics accordingly. Regularly revisiting your research ensures your business remains agile and reflects changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Online market research sources
As you go through the steps above, you’ll want to turn to trusted, reputable sources to gather your data. Here’s a list to get you started:
- Crunchbase: As mentioned above, Crunchbase is an online platform with an extensive dataset, allowing you to access in-depth insights on market trends, consumer behavior and competitive analysis. You can also customize your search options to tailor your research to specific industries, geographic regions or customer personas.
- Academic databases: Academic databases, such as ProQuest and JSTOR , are treasure troves of scholarly research papers, studies and academic journals. They offer in-depth analyses of various subjects, including market trends, consumer preferences and industry-specific insights. Researchers can access a wealth of peer-reviewed publications to gain a deeper understanding of their research topics.
- Government and NGO databases: Government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and other institutions frequently maintain databases containing valuable economic, demographic and industry-related data. These sources offer credible statistics and reports on a wide range of topics, making them essential for market researchers. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau , the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Pew Research Center .
- Industry reports: Industry reports and market studies are comprehensive documents prepared by research firms, industry associations and consulting companies. They provide in-depth insights into specific markets, including market size, trends, competitive analysis and consumer behavior. You can find this information by looking at relevant industry association databases; examples include the American Marketing Association and the National Retail Federation .
- Social media and online communities: Social media platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter (X) , forums such as Reddit and Quora , and review platforms such as G2 can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, opinions and trends.
Market research examples
At this point, you have market research tools and data sources — but how do you act on the data you gather? Let’s go over some real-world examples that illustrate the practical application of market research across various industries. These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions.
Example 1: Apple’s iPhone launch
Apple ’s iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone’s release, Apple conducted extensive market research to understand consumer preferences, pain points and unmet needs in the mobile phone industry. This research led to the development of a touchscreen smartphone with a user-friendly interface, addressing consumer demands for a more intuitive and versatile device. The result was a revolutionary product that disrupted the market and redefined the smartphone industry.
Example 2: McDonald’s global expansion
McDonald’s successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald’s conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances. This research informs menu customization, marketing strategies and store design. For instance, in India, McDonald’s offers a menu tailored to local preferences, including vegetarian options. This market-specific approach has enabled McDonald’s to adapt and thrive in diverse global markets.
Example 3: Organic and sustainable farming
The shift toward organic and sustainable farming practices in the food industry is driven by market research that indicates increased consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly food options. As a result, food producers and retailers invest in sustainable sourcing and organic product lines — such as with these sustainable seafood startups — to align with this shift in consumer values.
The bottom line? Market research has multiple use cases and is a critical practice for any industry. Whether it’s launching groundbreaking products, entering new markets or responding to changing consumer preferences, you can use market research to shape successful strategies and outcomes.
Market research templates
You finally have a strong understanding of how to do market research and apply it in the real world. Before we wrap up, here are some market research templates that you can use as a starting point for your projects:
- Smartsheet competitive analysis templates : These spreadsheets can serve as a framework for gathering information about the competitive landscape and obtaining valuable lessons to apply to your business strategy.
- SurveyMonkey product survey template : Customize the questions on this survey based on what you want to learn from your target customers.
- HubSpot templates : HubSpot offers a wide range of free templates you can use for market research, business planning and more.
- SCORE templates : SCORE is a nonprofit organization that provides templates for business plans, market analysis and financial projections.
- SBA.gov : The U.S. Small Business Administration offers templates for every aspect of your business, including market research, and is particularly valuable for new startups.
Strengthen your business with market research
When conducted effectively, market research is like a guiding star. Equipped with the right tools and techniques, you can uncover valuable insights, stay competitive, foster innovation and navigate the complexities of your industry.
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the definition of market research, different research methods, and how to conduct it effectively. We’ve also explored various types of market research and shared practical insights and templates for getting started.
Now, it’s time to start the research process. Trust in data, listen to the market and make informed decisions that guide your company toward lasting success.
Related Articles

- Entrepreneurs
- 15 min read
What Is Competitive Analysis and How to Do It Effectively
Rebecca Strehlow, Copywriter at Crunchbase
17 Best Sales Intelligence Tools for 2024

- Market research
- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with Crunchbase, the all-in-one prospecting solution. Start your free trial.
Quick links
- Case Studies
- White Papers
Send Inquiry
Market Research Role: Guide to Decision Making in Business

Published on Apr 11, 2023
With every passing year, businesses are witnessing a rapid shift in consumer behavior. This change in perspective can be based on several factors, such as the introduction of newer tech tools, refined user experience, or price fluctuation in the economy.
Marketers today are exploring innovative ideas to make their content and campaigns viral. However, this might not be the only effective way to make an impression on the audience, especially when it concerns the long-term perspective. To cater to these changing demands, businesses need to formulate a plan worthwhile for the marketing spend while driving decisions based on the current market scenario. For the ship to sail, businesses need to steer their efforts in the right direction. And this can be made possible when they have the right compass for accurate information.
And this change in dynamic has made market research a necessity for small businesses.
Market research forms the crux of averting all kinds of risks - from decision-making to planning and designing methods to market a product or service. It enables businesses to build efficiency for their brand's value by offering them a direct approach to developing a better presence across social platforms. By investing in market research, brands lower their chances of witnessing failures
What is Market Research?
Before understanding the significance of market research, it is important to know what it is. Market research is not just a specific method or activity; it is a driven approach that enables businesses to learn more about their target audience.
Read more: The Ultimate Guide: Tips to Choose a Top Marketing Analytics Company
Market research assists businesses in gathering relevant insights on the target market, along with buyer persona, competitor analysis, and economic market shifts. It guides them to create a blueprint that yields desirable results for their marketing team.
From marketing managers to researchers, everyone takes part in discovering relevant information that could eventually benefit the business. These insights can then be used to design unique advertisements, to achieve the goal of gasping for customers' attention.
A business can choose different means to conduct research and gather relevant information to design a unique marketing strategy and launch it. While primary data accumulation may seem reliable for their existing customers, for a brand to grow, it is important to tap into new audiences. And for that, understanding the customers' thoughts is vital. The ultimate idea is to create a standard decision-making process that is bulletproof and goal-oriented.
While tasks, including surveys and focus groups, can help businesses, they do not always provide the necessary information. Some of the tasks that businesses can undertake as a part of their market research include:
Engaging in short conversations with the consumers who are part of the target market. This will help businesses understand the consumer's perspective and their requirements.
Search relevant social media groups within the target market. This will provide businesses with a free, low-effort way to connect with their target customers online. This will eventually help in promoting the business in the groups.
Integrating survey forms on the website. If you have a website for your small business, it will enable you to offer your potential customers discounts in exchange for filling in a survey.

The above tasks can be included as a vital part of a market research strategy, enabling businesses to know the requirements of their target markets as well as their behaviors and preferences.
Read more: Debt Ceiling Standoff - Will the World’s Renowned Economic Safe Haven go into Default?
Role of Market Research
Market research offers a systematic and objective approach to analyzing relevant information. This implies that businesses create a detailed and carefully designed research plan in which every stage of the research is specified. The research plan helps specify
the research problem in concise terms,
the data required to address the problem,
the approaches to be employed to gather the information
the analytical techniques to be used
Market research (MR) facilitates organizations with relevant, accurate, reliable, and current information. Market research also enables the marketing manager to link the marketing variables with the existing environment and consumers. It helps in removing some of the uncertainties by providing relevant data. Owing to the competitive marketing environment and the ever-increasing costs, businesses are transitioning to market research to accumulate sound information.

Importance of Market Research
Let us explore the significant reasons why market research is important for smaller businesses :
Spot Potential Business Opportunities
A thorough market research presents a clear understanding of whom to reach out to in the targeted customer base, which marketing channels to use to reach them, and their interests. Once these parameters are defined, marketing managers will be able to spot business opportunities like-
Forming partnerships with other businesses. By learning about the customers and their demographics, businesses can identify other small businesses that serve them. They can also approach other businesses for joint promotions to gain mutual benefits.
Create profitable upgrades. Understanding other products and services that customers tend to buy can help in adding or creating new product bundles or upselling to increase the average value.
Identifying new locations to sell to. Knowing the geographical areas of the target customers will help in creating compelling, targeted campaigns.
Read more: US Job Growth Report: Why is the Market Slowing Down?
Lower Risks
Around half of the businesses with employees are not able to survive past the fifth year, as per the data issued by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. To ensure that the business survives for longer, it is important to gain a steady stream of sales and customers. And to do that, market research is vital. Regular market research offers a way to check in with existing and potential customers. Here's how a business can apply this:
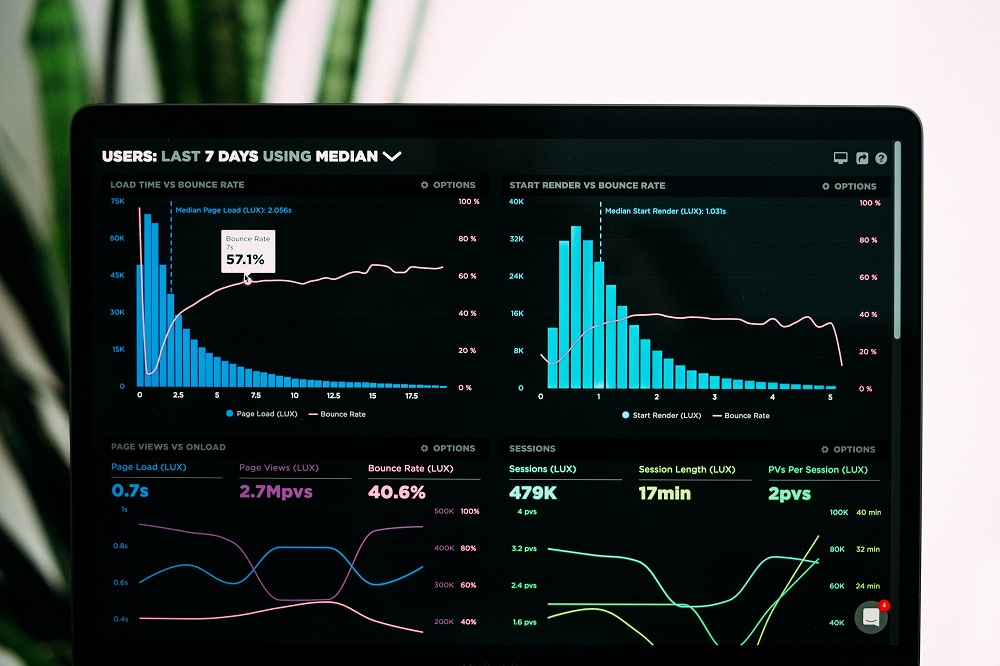
Testing modern designs and products before launching them in the market. Businesses can test new launches on a smaller subset of their audience to see if the change would be welcome.
Find out why customers discontinue any product. Ideally, small businesses have recurring customers. But if the customer is not returning, they can conduct a survey to focus on a specific group and identify why they are not making any repeat sales.
Get insights on different problem areas . If the hot-selling product experiences a drop in sales, businesses can conduct research to explore ways of fixing the crisis before it ruins the profits.
Create Relevant Materials for Promotions
It is important to plan the text or images that are put on fliers, websites, or social media accounts with thorough market research. As target customers have already expressed all their needs and frustrations, as a business, you will be in a better position to address the concerns and present new ways to create marketing materials.
Knowing what the customers see in the products and services - if it is a necessity or a luxury - will help in designing product labels, brochures, and websites that fit their perception.
Identifying the age range of customers to understand the type of language to be used in promotional materials.

Simplify Decision-Making
The need for market research arises when making tough business decisions. Instead of relying on arbitrary criteria for the decisions, businesses can undertake market research to discover relevant insights. While not all decisions can be based on market research, many of them can include the following:
where to spend the advertising budget?
identifying the demand for a new product
which products should be discontinued, and which ones can be improved
how to price offers for specific products
Businesses need market research as it offers them solid facts. Through market research, they can make more informed decisions rather than basing their decisions on intuition or guesswork.
Read more: National Cybersecurity Strategy: Net Positive for the Cyber and Cloud Security Sector
Conclusion: The Significance of Market Research
Customers today live in an era where Search Engine has answers to the silliest of questions one can imagine. They hold the power to buy products/services that aren't based on guesses but on thorough research and review. Similarly, for brands to make an impact on their target market, they need to integrate an effective decision-making process. It also depends on how well the marketing managers explore the market trends along with practices and technological shifts while doing market research. However, after gaining a deep understanding of the need for market research, it is important for businesses to commit a dedicated budget to focus on extensive surveys for market research.
New businesses today are exploring ways to boost their sales and customers as soon as possible. And market research can ensure that the incoming traffic of sales and customers doesn't stop coming. By creating elaborate plans to identify the factors that would drive the efficacy of a marketing campaign, marketing managers can include different marketing variables in the brand's strategy.
With a presence in New York, San Francisco, Austin, Seattle, Toronto, London, Zurich, Pune, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics, a pioneer in Research and Analytics, offers tailor-made services to enterprises worldwide.
A leader in Market intelligence consulting , SG Analytics enables organizations to achieve actionable insights into products, technology, customers, competition, and the marketplace to make insight-driven decisions. Contact us today if you are an enterprise looking to make critical data-driven decisions to prompt accelerated growth and breakthrough performance.
Our Services
Investment Insights
Market Research
Data Analytics
ESG Services
Data Solutions
ESG Data Services
Technology Services
Investment Banking
Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private Equity/VC
ESG Data and Research
Marketing Analytics
Advanced Analytics
Customer Analytics
Hedge Fund Services
Market Intelligence
Equity Research
Recent Blogs

10 Most Expensive Cities in the US & World in 2024

Data Monetization: Turning Data Streams into Gold with Analytics

Celebrating Pride Month: Genuine Pride or Corporate Rainbow-Washing

10 B2B Market Research Companies in the US

Measuring the ROI of Sustainability to Drive Profitability and Purpose

ATxSG Broadcast Asia 2024: Key Trends

Investment Insights: Healthcare Industry Report

NAB 2024 Key Trends

A Shift toward Sustainable Media Consumption Imminent

SGA Knowledge Team
We are a dynamic team of subject matter experts who create informative, relevant and...
Module 6: Marketing Information and Research
The marketing research process, learning objectives.
- Identify the steps of conducting a marketing research project
A Standard Approach to Research Inquiries
Marketing research is a useful and necessary tool for helping marketers and an organization’s executive leadership make wise decisions. Carrying out marketing research can involve highly specialized skills that go deeper than the information outlined in this module. However, it is important for any marketer to be familiar with the basic procedures and techniques of marketing research.
It is very likely that at some point a marketing professional will need to supervise an internal marketing research activity or to work with an outside marketing research firm to conduct a research project. Managers who understand the research function can do a better job of framing the problem and critically appraising the proposals made by research specialists. They are also in a better position to evaluate their findings and recommendations.
Periodically marketers themselves need to find solutions to marketing problems without the assistance of marketing research specialists inside or outside the company. If you are familiar with the basic procedures of marketing research, you can supervise and even conduct a reasonably satisfactory search for the information needed.

Step 1: Identify the Problem
The first step for any marketing research activity is to clearly identify and define the problem you are trying to solve. You start by stating the marketing or business problem you need to address and for which you need additional information to figure out a solution. Next, articulate the objectives for the research: What do you want to understand by the time the research project is completed? What specific information, guidance, or recommendations need to come out of the research in order to make it a worthwhile investment of the organization’s time and money?
It’s important to share the problem definition and research objectives with other team members to get their input and further refine your understanding of the problem and what is needed to solve it. At times, the problem you really need to solve is not the same problem that appears on the surface. Collaborating with other stakeholders helps refine your understanding of the problem, focus your thinking, and prioritize what you hope to learn from the research. Prioritizing your objectives is particularly helpful if you don’t have the time or resources to investigate everything you want.
To flesh out your understanding of the problem, it’s useful to begin brainstorming actual research questions you want to explore. What are the questions you need to answer in order to get to the research outcomes? What is the missing information that marketing research will help you find? The goal at this stage is to generate a set of preliminary, big-picture questions that will frame your research inquiry. You will revisit these research questions later in the process, but when you’re getting started, this exercise helps clarify the scope of the project, whom you need to talk to, what information may already be available, and where to look for the information you don’t yet have.
Applied Example: Marketing Research for Bookends
To illustrate the marketing research process, let’s return to Uncle Dan and his ailing bookstore, Bookends. You need a lot of information if you’re going to help Dan turn things around, so marketing research is a good idea. You begin by identifying the problem and then work to set down your research objectives and initial research questions:
| Identifying Problems, Objectives, and Questions | |
|---|---|
| Core business problem Dan needs to solve | How to get more people to spend more money at Bookends |
| Research objectives | 1) Identify promising target audiences for Bookends; 2) Identify strategies for rapidly increasing revenue from these target audiences |
| Initial research questions | Who are Bookends’ current customers? How much do they spend? Why do they come to Bookends? What do they wish Bookends offered? Who isn’t coming to Bookends, and why? |
Step 2: Develop a Research Plan
Once you have a problem definition, research objectives, and a preliminary set of research questions, the next step is to develop a research plan. Essential to this plan is identifying precisely what information you need to answer your questions and achieve your objectives. Do you need to understand customer opinions about something? Are you looking for a clearer picture of customer needs and related behaviors? Do you need sales, spending, or revenue data? Do you need information about competitors’ products, or insight about what will make prospective customers notice you? When do need the information, and what’s the time frame for getting it? What budget and resources are available?
Once you have clarified what kind of information you need and the timing and budget for your project, you can develop the research design. This details how you plan to collect and analyze the information you’re after. Some types of information are readily available through secondary research and secondary data sources. Secondary research analyzes information that has already been collected for another purpose by a third party, such as a government agency, an industry association, or another company. Other types of information need to from talking directly to customers about your research questions. This is known as primary research , which collects primary data captured expressly for your research inquiry. Marketing research projects may include secondary research, primary research, or both.
Depending on your objectives and budget, sometimes a small-scale project will be enough to get the insight and direction you need. At other times, in order to reach the level of certainty or detail required, you may need larger-scale research involving participation from hundreds or even thousands of individual consumers. The research plan lays out the information your project will capture—both primary and secondary data—and describes what you will do with it to get the answers you need. (Note: You’ll learn more about data collection methods and when to use them later in this module.)
Your data collection plan goes hand in hand with your analysis plan. Different types of analysis yield different types of results. The analysis plan should match the type of data you are collecting, as well as the outcomes your project is seeking and the resources at your disposal. Simpler research designs tend to require simpler analysis techniques. More complex research designs can yield powerful results, such as understanding causality and trade-offs in customer perceptions. However, these more sophisticated designs can require more time and money to execute effectively, both in terms of data collection and analytical expertise.
The research plan also specifies who will conduct the research activities, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and reporting on results. At times a singlehanded marketing manager or research specialist runs the entire research project. At other times, a company may contract with a marketing research analyst or consulting firm to conduct the research. In this situation, the marketing manager provides supervisory oversight to ensure the research delivers on expectations.
Finally, the research plan indicates who will interpret the research findings and how the findings will be reported. This part of the research plan should consider the internal audience(s) for the research and what reporting format will be most helpful. Often, senior executives are primary stakeholders, and they’re anxious for marketing research to inform and validate their choices. When this is the case, getting their buy-in on the research plan is recommended to make sure that they are comfortable with the approach and receptive to the potential findings.
Applied Example: A Bookends Research Plan
You talk over the results of your problem identification work with Dan. He thinks you’re on the right track and wants to know what’s next. You explain that the next step is to put together a detailed plan for getting answers to the research questions.
Dan is enthusiastic, but he’s also short on money. You realize that such a financial constraint will limit what’s possible, but with Dan’s help you can do something worthwhile. Below is the research plan you sketch out:
| Identifying Data Types, Timing and Budget, Data Collection Methods, Analysis, and Interpretation | |
|---|---|
| Types of data needed | 1) Demographics and attitudes of current Bookends customers; 2) current customers’ spending patterns; 3) metro area demographics (to determine types of people who aren’t coming to the store) |
| Timing & budget | Complete project within 1 month; no out-of-pocket spending |
| Data collection methods | 1) Current customer survey using free online survey tool, 2) store sales data mapped to customer survey results, 3) free U.S. census data on metro-area demographics, 4) 8–10 intercept (“man on the street”) interviews with non-customers |
| Analysis plan | Use Excel or Google Sheets to tabulate data; Marina (statistician cousin) to assist in identifying data patterns that could become market segments |
| Interpretation and reporting | You and Dan will work together to comb through the data and see what insights it produces. You’ll use PowerPoint to create a report that lays out significant results, key findings, and recommendations. |
Step 3: Conduct the Research
Conducting research can be a fun and exciting part of the marketing research process. After struggling with the gaps in your knowledge of market dynamics—which led you to embark on a marketing research project in the first place—now things are about to change. Conducting research begins to generate information that helps answer your urgent marketing questions.
Typically data collection begins by reviewing any existing research and data that provide some information or insight about the problem. As a rule, this is secondary research. Prior research projects, internal data analyses, industry reports, customer-satisfaction survey results, and other information sources may be worthwhile to review. Even though these resources may not answer your research questions fully, they may further illuminate the problem you are trying to solve. Secondary research and data sources are nearly always cheaper than capturing new information on your own. Your marketing research project should benefit from prior work wherever possible.
After getting everything you can from secondary research, it’s time to shift attention to primary research, if this is part of your research plan. Primary research involves asking questions and then listening to and/or observing the behavior of the target audience you are studying. In order to generate reliable, accurate results, it is important to use proper scientific methods for primary research data collection and analysis. This includes identifying the right individuals and number of people to talk to, using carefully worded surveys or interview scripts, and capturing data accurately.
Without proper techniques, you may inadvertently get bad data or discover bias in the responses that distorts the results and points you in the wrong direction. The module on Marketing Research Techniques discusses these issues in further detail, since the procedures for getting reliable data vary by research method.
Applied Example: Getting the Data on Bookends
Dan is on board with the research plan, and he’s excited to dig into the project. You start with secondary data, getting a dump of Dan’s sales data from the past two years, along with related information: customer name, zip code, frequency of purchase, gender, date of purchase, and discounts/promotions (if any).
You visit the U.S. Census Bureau Web site to download demographic data about your metro area. The data show all zip codes in the area, along with population size, gender breakdown, age ranges, income, and education levels.
The next part of the project is customer-survey data. You work with Dan to put together a short survey about customer attitudes toward Bookends, how often and why they come, where else they spend money on books and entertainment, and why they go other places besides Bookends. Dan comes up with the great idea of offering a 5 percent discount coupon to anyone who completes the survey. Although it eats into his profits, this scheme gets more people to complete the survey and buy books, so it’s worth it.

For a couple of days, you and Dan take turns doing “man on the street” interviews (you interview the guy in the red hat, for instance). You find people who say they’ve never been to Bookends and ask them a few questions about why they haven’t visited the store, where else they buy books and other entertainment, and what might get them interested in visiting Bookends sometime. This is all a lot of work, but for a zero-budget project, it’s coming together pretty well.
Step 4: Analyze and Report Findings
Analyzing the data obtained in a market survey involves transforming the primary and/or secondary data into useful information and insights that answer the research questions. This information is condensed into a format to be used by managers—usually a presentation or detailed report.
Analysis starts with formatting, cleaning, and editing the data to make sure that it’s suitable for whatever analytical techniques are being used. Next, data are tabulated to show what’s happening: What do customers actually think? What’s happening with purchasing or other behaviors? How do revenue figures actually add up? Whatever the research questions, the analysis takes source data and applies analytical techniques to provide a clearer picture of what’s going on. This process may involve simple or sophisticated techniques, depending on the research outcomes required. Common analytical techniques include regression analysis to determine correlations between factors; conjoint analysis to determine trade-offs and priorities; predictive modeling to anticipate patterns and causality; and analysis of unstructured data such as Internet search terms or social media posts to provide context and meaning around what people say and do.
Good analysis is important because the interpretation of research data—the “so what?” factor—depends on it. The analysis combs through data to paint a picture of what’s going on. The interpretation goes further to explain what the research data mean and make recommendations about what managers need to know and do based on the research results. For example, what is the short list of key findings and takeaways that managers should remember from the research? What are the market segments you’ve identified, and which ones should you target? What are the primary reasons your customers choose your competitor’s product over yours, and what does this mean for future improvements to your product?
Individuals with a good working knowledge of the business should be involved in interpreting the data because they are in the best position to identify significant insights and make recommendations from the research findings. Marketing research reports incorporate both analysis and interpretation of data to address the project objectives.
The final report for a marketing research project may be in written form or slide-presentation format, depending on organizational culture and management preferences. Often a slide presentation is the preferred format for initially sharing research results with internal stakeholders. Particularly for large, complex projects, a written report may be a better format for discussing detailed findings and nuances in the data, which managers can study and reference in the future.
Applied Example: Analysis and Insights for Bookends
Getting the data was a bit of a hassle, but now you’ve got it, and you’re excited to see what it reveals. Your statistician cousin, Marina, turns out to be a whiz with both the sales data and the census data. She identified several demographic profiles in the metro area that looked a lot like lifestyle segments. Then she mapped Bookends’ sales data into those segments to show who is and isn’t visiting Bookends. After matching customer-survey data to the sales data, she broke down the segments further based on their spending levels and reasons they visit Bookends.
Gradually a clearer picture of Bookends’ customers is beginning to emerge: who they are, why they come, why they don’t come, and what role Bookends plays in their lives. Right away, a couple of higher-priority segments—based on their spending levels, proximity, and loyalty to Bookends—stand out. You and your uncle are definitely seeing some possibilities for making the bookstore a more prominent part of their lives. You capture these insights as “recommendations to be considered” while you evaluate the right marketing mix for each of the new segments you’d like to focus on.
Step 5: Take Action
Once the report is complete, the presentation is delivered, and the recommendations are made, the marketing research project is over, right? Wrong.
What comes next is arguably the most important step of all: taking action based on your research results.
If your project has done a good job interpreting the findings and translating them into recommendations for the marketing team and other areas of the business, this step may seem relatively straightforward. When the research results validate a path the organization is already on, the “take action” step can galvanize the team to move further and faster in that same direction.
Things are not so simple when the research results indicate a new direction or a significant shift is advisable. In these cases, it’s worthwhile to spend time helping managers understand the research, explain why it is wise to shift course, and explain how the business will benefit from the new path. As with any important business decision, managers must think deeply about the new approach and carefully map strategies, tactics, and available resources to plan effectively. By making the results available and accessible to managers and their execution teams, the marketing research project can serve as an ongoing guide and touchstone to help the organization plan, execute, and adjust course as it works toward desired goals and outcomes.
It is worth mentioning that many marketing research projects are never translated into management action. Sometimes this is because the report is too technical and difficult to understand. In other cases, the research conclusions fail to provide useful insights or solutions to the problem, or the report writer fails to offer specific suggestions for translating the research findings into management strategy. These pitfalls can be avoided by paying due attention to the research objectives throughout the project and allocating sufficient time and resources to do a good job interpreting research results for those who will need to act on them.
Applied Example: Bookends’ New Customer Campaign
Your research findings and recommendations identified three segments for Bookends to focus on. Based on the demographics, lifestyle, and spending patterns found during your marketing research, you’re able to name them: 1) Bored Empty-Nesters, 2) Busy Families, and 3) Hipster Wannabes. Dan has a decent-sized clientele across all three groups, and they are pretty good spenders when they come in. But until now he hasn’t done much to purposely attract any of them.
With newly identified segments in focus, you and Dan begin brainstorming about a marketing mix to target each group. What types of books and other products would appeal to each one? What activities or events would bring them into the store? Are there promotions or particular messages that would induce them to buy at Bookends instead of Amazon or another bookseller? How will Dan reach and communicate with each group? And what can you do to bring more new customers into the store within these target groups?
Even though Bookends is a real-life project with serious consequences for your uncle Dan, it’s also a fun laboratory where you can test out some of the principles you’re learning in your marketing class. You’re figuring out quickly what it’s like to be a marketer.
Well done, rookie!
Check Your Understanding
Answer the question(s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered in this outcome. This short quiz does not count toward your grade in the class, and you can retake it an unlimited number of times.
Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to (1) study the previous section further or (2) move on to the next section.
- Revision and Adaptation. Authored by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Chapter 3: Marketing Research: An Aid to Decision Making, from Introducing Marketing. Authored by : John Burnett. Provided by : Global Text. Located at : http://solr.bccampus.ca:8001/bcc/file/ddbe3343-9796-4801-a0cb-7af7b02e3191/1/Core%20Concepts%20of%20Marketing.pdf . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Urban life (Version 2.0). Authored by : Ian D. Keating. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/ian-arlett/19313315520/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
















COMMENTS
Marketing research is the scientific and controlled gathering of nonroutine marketing information undertaken to help management solve marketing problems. 2. Any business that is consumer-oriented will benefit from marketing research. 3.
This helps in directly linking the research findings to your marketing decisions. ... Use these learnings to refine your market research methods and decision-making processes for future projects. ...
Rigorous analysis should be used to drive decision making and adapt in a timely manner, and in this regard, third-party market research can protect you in more ways than one. Market research can open your eyes to products and trends beyond your own company and help you become more aware of influential variables such as: Disruption. New technology.
Decision-Driven Marketing. by. Aditya Joshi. and. Eduardo Giménez. From the Magazine (July-August 2014) Summary. The gap between marketers' aspirations and what their organizations can ...
decision making. Marketing research involves following a systematic sequence of steps that will produce reliable and valid data. Through analysis and interpretation the data are transformed into information suitable for decision-making purposes by managers. Typically, data alone are simply not usable.
Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product's potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts. ... and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye ...
Marketers have realized the significant value of the marketing research process and are using it to improve their decision making across the business. Market research is powerful because it can help solve real problems. The marketing research process helps leaders answer questions and gain insight into their business, ...
Provides empirical insights on managerial decision making in modern marketing. Uses a blend of situative and naturalistic perspectives as a theoretical lens. Adds a dynamic, interactive, and purposeful guise to extant decision-making models. Characterizes decision making behaviors as agile, inventive, and reflexive.
Marketing research is a scientific and controlled process, but ultimately, decisions are based on a blend of facts and intuition. Understanding marketing research allows managers to intelligently evaluate findings and recommendations. Determining the purpose and scope of the research is the first critical activity in any marketing research project.
FIGURE 3.1 The marketing planning process. Marketing research addresses the need for quicker, yet more accurate, decision making by the marketer. The impetus for this situation is the complex relationship between the business firm and the ever-changing external environment. In particular, most marketers are far removed from their customers; yet ...
Step 3: Determine which research methods are most effective. Your choice of methods depends on budget, time constraints, and the type of question you're trying to answer. You could combine surveys, interviews and focus groups to get a mix of qualitative and quantitative data.
Research provides intelligence to guide informed, enhanced decisions. Ultimately, helping you to: hit the bull's eye with your target audience, increase your campaign success, and make every penny spent yield greater returns. Good data saves time, money—and gives you a competitive edge.
5. Marketing research helps businesses make informed decisions. For decades, companies have made key business decisions based on gut feelings alone. But the new age of marketing revolves around data-driven decision-making: a process in which business decisions are informed by metrics and analytics.
Market research is defined as the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data about a specific market, industry, or consumer segment. ... By following these best practices, businesses can conduct effective market research that informs decision-making, helps identify growth opportunities, and supports the development of ...
21349. Having completed this chapter, you should: understand the role of marketing research. understand the marketing research process and the techniques employed.
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you're asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include: Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you ...
Marketing Research is the crux of eliminating all kinds of risks from your decision-making process and planning out the best methods to market your products. It helps build efficiency for your ...
The research plan helps specify. Market research (MR) facilitates organizations with relevant, accurate, reliable, and current information. Market research also enables the marketing manager to link the marketing variables with the existing environment and consumers. It helps in removing some of the uncertainties by providing relevant data.
Step 1: Identify the Problem. The first step for any marketing research activity is to clearly identify and define the problem you are trying to solve. You start by stating the marketing or business problem you need to address and for which you need additional information to figure out a solution.
It begins by discussing the marketing research process that is used to develop useful information for decision making. Then, marketing information systems are briefly discussed. The chapter is intended to provide a detailed introduction to many of the important topics in the area, but it does not provide a complete explanation of the plethora ...
Marketing research serves marketing management by providing information which is relevant to decision making. Marketing research does not itself make the decisions, nor does it guarantee success. Rather, marketing research helps to reduce the uncertainty surrounding the decisions to be made.
Improve your decision-making with decreased risks. Market research offers suggestions with concrete trend analysis and detailed facts. The quantitative and qualitative data helps you to evaluate ...
Data resulting from market research should drive strategic decision-making processes across the organization. By proactively performing market research on a routine basis, various teams and organizational leaders across departments will have access to data they can leverage when making a final decision. Imagine a CEO that is considering making ...
5. Marketing research helps businesses make informed decisions. For decades, companies have made key business decisions based on gut feelings alone. But the new age of marketing revolves around data-driven decision-making: a process in which business decisions are informed by metrics and analytics.
Interviewing is a key method for customer research due to the rich qualitative data it provides. This data can then be used to inform your design process to ensure that you're creating experiences that meet customers' goals. To make sure customer interviews are successful and produce data that drives decision-making, you need to have a research plan and clear objectives, but companies ...
In consumer decision-making, individuals often find themselves having to choose a brand from multiple alternatives (Joint evaluation) or when only one brand is available (Separate evaluation). ... We're here to help. Find guidance on Author Services. Home ... Benjamin Nobi d Marketing Research Analyst, eMoldino, Seoul, South Korea. Published ...
The intersection of AI and market research transforms vast volumes of qualitative, text-based data from a challenge to be managed into a valuable asset to be leveraged. ... This helps save time ...
VentureBeat | Transformative tech coverage that matters
The move towards Market-centric data layer represents a significant evolution in the way businesses manage and leverage data. This technology is set to become a fundamental element of business operations, driving innovation, enhancing decision-making accuracy, and ensuring operational agility in an increasingly data-driven world.
Speak to our team and see how Janes can help you The world's most complete foundational military data asset. 500,000+ analyst hours per year to keep data current.