You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

How to Write an Essay in French
Have something to say?
When it comes to expressing your thoughts in French , there’s nothing better than the essay.
It is, after all, the favorite form of such famed French thinkers as Montaigne, Chateaubriand, Houellebecq and Simone de Beauvoir.
In this post, I’ve outlined the four most common types of essays in French, ranked from easiest to most difficult, to help you get to know this concept better.
Why Are French Essays Different?
Must-have french phrases for writing essays, 4 types of french essays and how to write them, 1. text summary (synthèse de texte).
- 2. Text Commentary (Commentaire de texte)
3. Dialectic Dissertation (Thèse, Antithèse, Synthèse)
- 4. Progressive Dissertation (Plan progressif)
And one more thing...
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Writing an essay in French is not the same as those typical 5-paragraph essays you’ve probably written in English.
In fact, there’s a whole other logic that has to be used to ensure that your essay meets French format standards and structure. It’s not merely writing your ideas in another language .
And that’s because the French use Cartesian logic (also known as Cartesian doubt) , developed by René Descartes , which requires a writer to begin with what is known and then lead the reader through to the logical conclusion: a paragraph that contains the thesis. Through the essay, the writer will reject all that is not certain or all that is subjective in his or her quest to find the objective truth.
Sound intriguing? Read on for more!
Before we get to the four main types of essays, here are a few French phrases that will be especially helpful as you delve into essay-writing in French:
Introductory phrases , which help you present new ideas.
| firstly | |
| firstly |
Connecting phrases , which help you connect ideas and sections.
| and | |
| in addition | |
| also | |
| next | |
| secondly | |
| so | |
| as well as | |
| when, while |
Contrasting phrases , which help you juxtapose two ideas.
| on the other hand | |
| however | |
| meanwhile, however |
Concluding phrases , which help you to introduce your conclusion.
| finally | |
| finally | |
| to conclude | |
| in conclusion |
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
The text summary or synthèse de texte is one of the easiest French writing exercises to get a handle on. It essentially involves reading a text and then summarizing it in an established number of words, while repeating no phrases that are in the original text. No analysis is called for.
A synthèse de texte should follow the same format as the text that is being synthesized. The arguments should be presented in the same way, and no major element of the original text should be left out of the synthèse.
Here is an informative post about writing a synthèse de texte , written for French speakers.
The text summary is a great exercise for exploring the following French language elements:
- Synonyms , as you will need to find other words to describe what is said in the original text.
- Nominalization , which involves turning verbs into nouns and generally cuts down on word count.
- Vocabulary , as the knowledge of more exact terms will allow you to avoid periphrases and cut down on word count.
While beginners may wish to work with only one text, advanced learners can synthesize as many as three texts in one text summary.
Since a text summary is simple in its essence, it’s a great writing exercise that can accompany you through your entire learning process.
2. Text Commentary (Commentaire de texte)
A text commentary or commentaire de texte is the first writing exercise where the student is asked to present an analysis of the materials at hand, not just a summary.
That said, a commentaire de texte is not a reaction piece. It involves a very delicate balance of summary and opinion, the latter of which must be presented as impersonally as possible. This can be done either by using the third person (on) or the general first person plural (nous) . The singular first person (je) should never be used in a commentaire de texte.
A commentaire de texte should be written in three parts:
- An introduction , where the text is presented.
- An argument , where the text is analyzed.
- A conclusion , where the analysis is summarized and elevated.
Here is a handy in-depth guide to writing a successful commentaire de texte, written for French speakers.
Unlike with the synthesis, you will not be able to address all elements of a text in a commentary. You should not summarize the text in a commentary, at least not for the sake of summarizing. Every element of the text that you speak about in your commentary must be analyzed.
To successfully analyze a text, you will need to brush up on your figurative language. Here are some great resources to get you started:
- Here’s an introduction to figurative language in French.
- This guide to figurative language presents the different elements in useful categories.
- This guide , intended for high school students preparing for the BAC—the exam all French high school students take, which they’re required to pass to go to university—is great for seeing examples of how to integrate figurative language into your commentaries.
- Speaking of which, here’s an example of a corrected commentary from the BAC, which will help you not only include figurative language but get a head start on writing your own commentaries.
The French answer to the 5-paragraph essay is known as the dissertation . Like the American 5-paragraph essay, it has an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion. The stream of logic, however, is distinct.
There are actually two kinds of dissertation, each of which has its own rules.
The first form of dissertation is the dialectic dissertation , better known as thèse, antithèse, synthèse . In this form, there are actually only two body paragraphs. After the introduction, a thesis is posited. Following the thesis, its opposite, the antithesis, is explored (and hopefully, debunked). The final paragraph, what we know as the conclusion, is the synthesis , which addresses the strengths of the thesis, the strengths and weaknesses of the antithesis, and concludes with the reasons why the original thesis is correct.
For example, imagine that the question was, “Are computers useful to the development of the human brain?” You could begin with a section showing the ways in which computers are useful for the progression of our common intelligence—doing long calculations, creating in-depth models, etc.
Then you would delve into the problems that computers pose to human intelligence, citing examples of the ways in which spelling proficiency has decreased since the invention of spell check, for example. Finally, you would synthesize this information and conclude that the “pro” outweighs the “con.”
The key to success with this format is developing an outline before writing. The thesis must be established, with examples, and the antithesis must be supported as well. When all of the information has been organized in the outline, the writing can begin, supported by the tools you have learned from your mastery of the synthesis and commentary.
Here are a few tools to help you get writing:
- Here’s a great guide to writing a dialectic dissertation .
- Here’s an example of a plan for a dialectic dissertation , showing you the three parts of the essay as well as things to consider when writing a dialectic dissertation.
4. Progressive Dissertation ( Plan progressif)
The progressive dissertation is slightly less common, but no less useful, than the first form.
The progressive form basically consists of examining an idea via multiple points of view—a sort of deepening of the understanding of the notion, starting with a superficial perspective and ending with a deep and profound analysis.
If the dialectic dissertation is like a scale, weighing pros and cons of an idea, the progressive dissertation is like peeling an onion, uncovering more and more layers as you get to the deeper crux of the idea.
Concretely, this means that you will generally follow this layout:
- A first, elementary exploration of the idea.
- A second, more philosophical exploration of the idea.
- A third, more transcendent exploration of the idea.
This format for the dissertation is more commonly used for essays that are written in response to a philosophical question, for example, “What is a person?” or “What is justice?”
Let’s say the question was, “What is war?” In the first part, you would explore dictionary definitions—a basic idea of war, i.e. an armed conflict between two parties, usually nations. You could give examples that back up this definition, and you could narrow down the definition of the subject as much as needed. For example, you might want to make mention that not all conflicts are wars, or you might want to explore whether the “War on Terror” is a war.
In the second part, you would explore a more philosophical look at the topic, using a definition that you provide. You first explain how you plan to analyze the subject, and then you do so. In French, this is known as poser une problématique (establishing a thesis question), and it usually is done by first writing out a question and then exploring it using examples: “Is war a reflection of the base predilection of humans for violence?”
In the third part, you will take a step back and explore this question from a distance, taking the time to construct a natural conclusion and answer for the question.
This form may not be as useful in as many cases as the first type of essay, but it’s a good form to learn, particularly for those interested in philosophy. Here’s an in-depth guide to writing a progressive dissertation.
As you progress in French and become more and more comfortable with writing, try your hand at each of these types of writing exercises, and even with other forms of the dissertation . You’ll soon be a pro at everything from a synthèse de texte to a dissertation!
FluentU has a wide variety of great content, like interviews, documentary excerpts and web series, as you can see here:
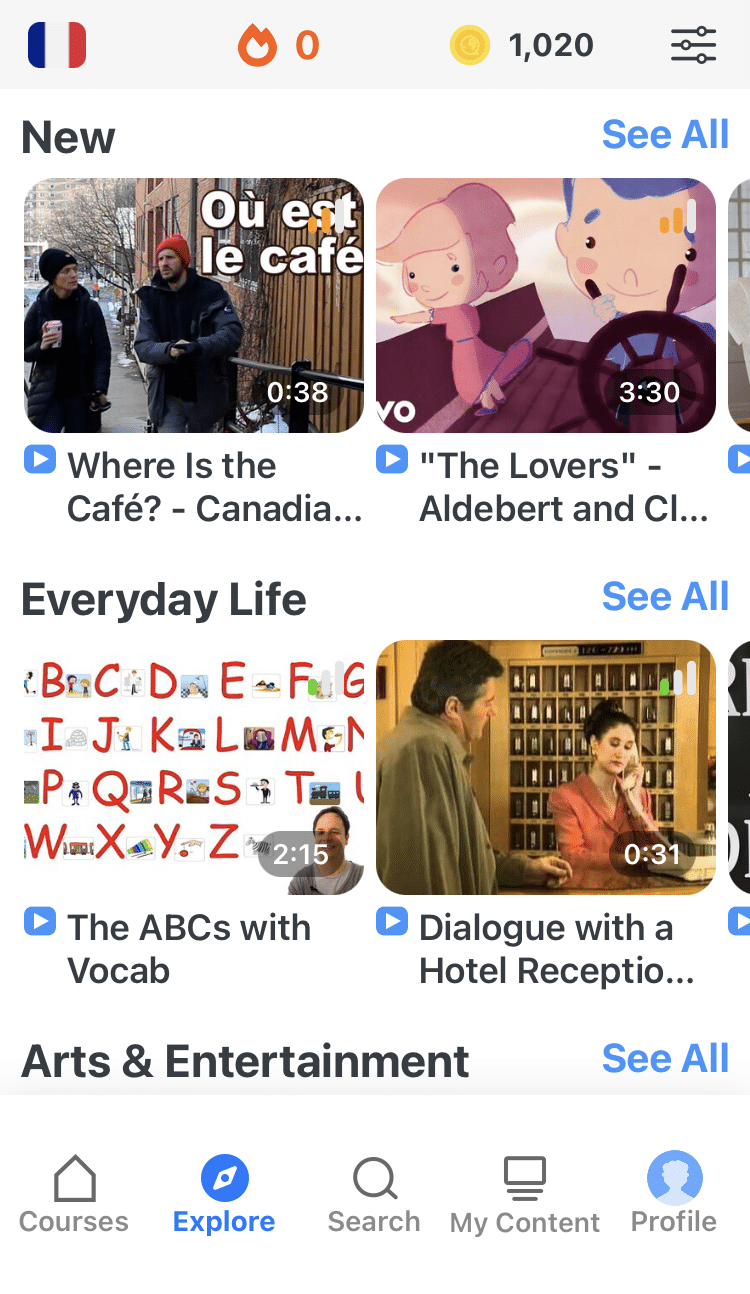
FluentU brings native French videos with reach. With interactive captions, you can tap on any word to see an image, definition and useful examples.
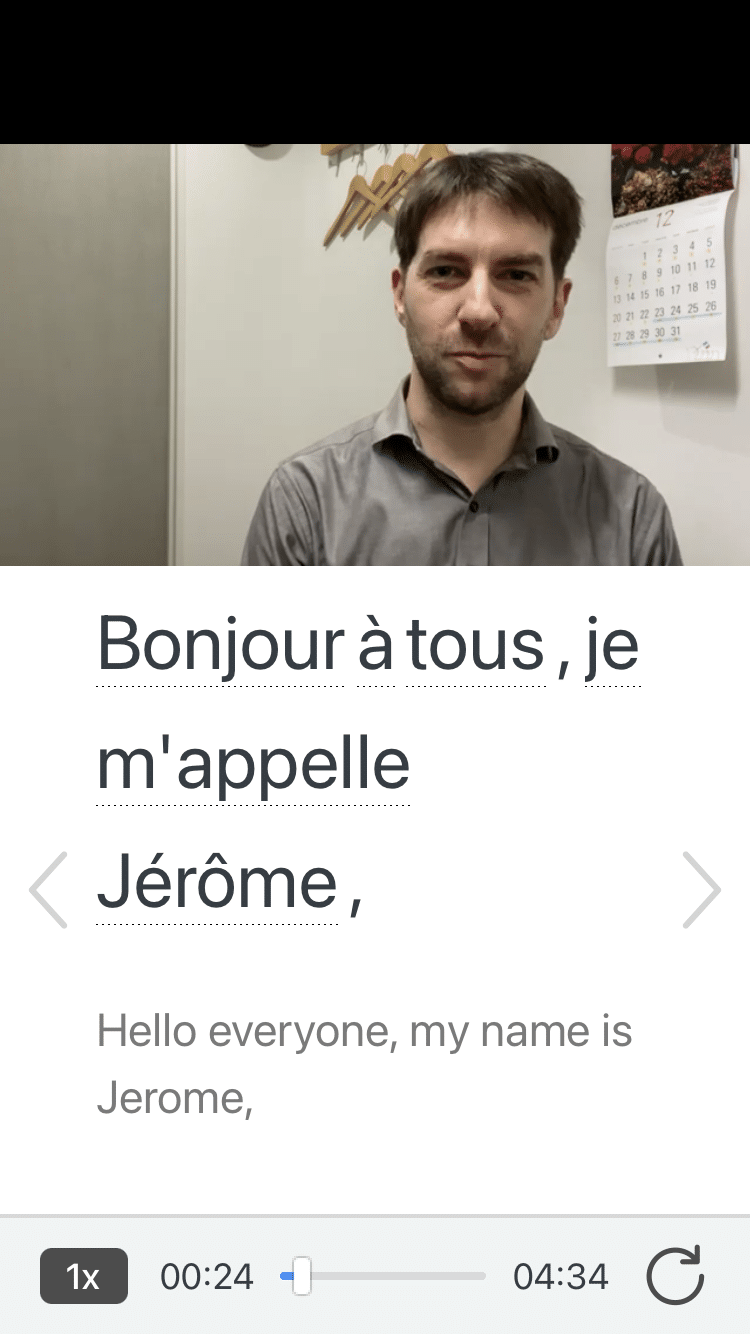
For example, if you tap on the word "crois," you'll see this:
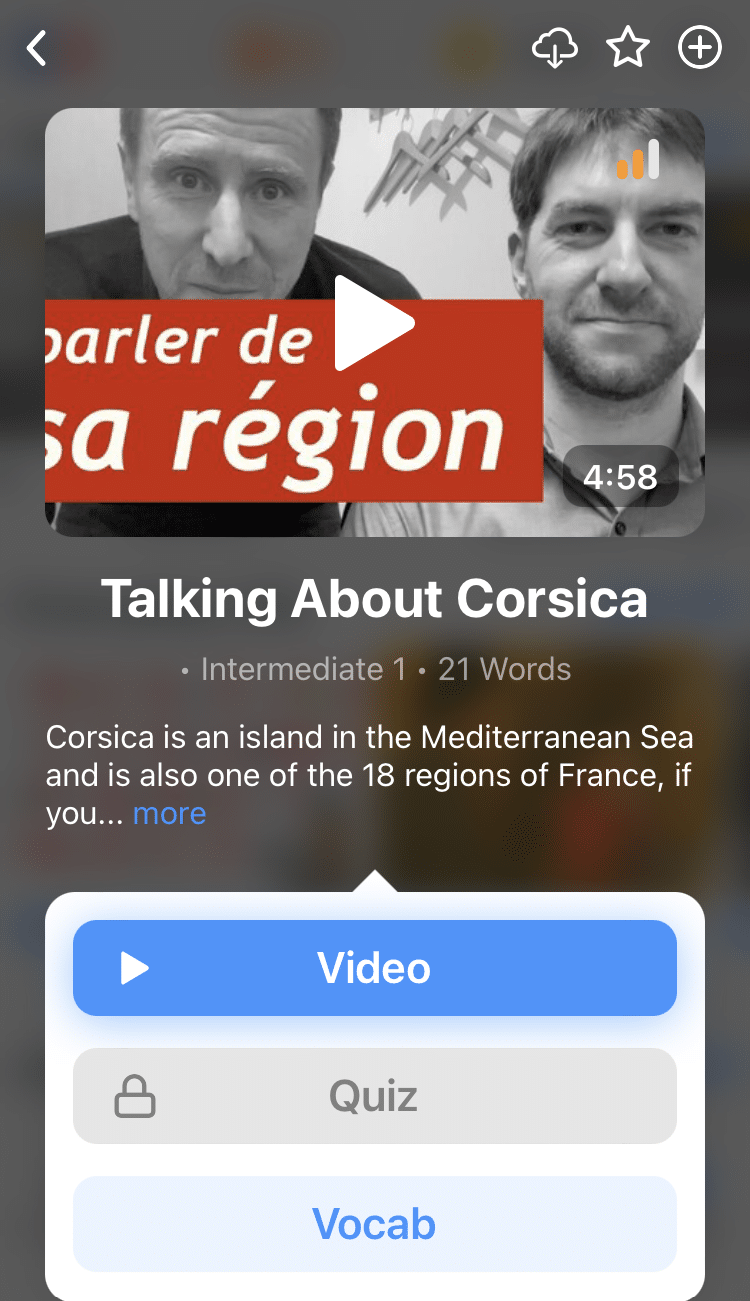
Practice and reinforce all the vocabulary you've learned in a given video with learn mode. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning, and play the mini-games found in our dynamic flashcards, like "fill in the blank."
All throughout, FluentU tracks the vocabulary that you’re learning and uses this information to give you a totally personalized experience. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

Write an essay in French
Beyond the fact that writing an essay in French can be a good practice to improve your writing, you may also be asked to write one during your schooling. So, it is important to study the topic of French essay writing and get some useful tips..
» Tips and tricks for your French essay » The structure of a French essay » Sample French Essay
Tips and tricks for your French essay
When writing a French essay for school, you should always use a structured approach and good French skills to present your arguments in a focused way. Beyond French skills, there are also important formal requirements for a successful French essay. We will come back to this in detail later. First, you will find some useful tips and tricks that will help you write more compelling and better French essays in the future.
- Have a clear thesis and structure
- Do sufficient research and use reliable sources
- Use examples and arguments to support your thesis
- Avoid plagiarism and cite correctly
- Always check structure, grammar and spelling
When you write your essay at school or university, you need to make sure that the general structure of your essay, the presentation of the arguments and, above all, your French language skills play a role in the mark you will get. This is why you should definitely take a closer look at the structure of an essay as well as the most important grammar rules and formulations for French essays.
The structure of a French essay
In an essay, you deal at length and in detail with a usually given topic. When you write an essay in French, you must follow a certain structure. Below we show you what this structure looks like and give you some tips for writing the most important parts of your essay.

The Introduction
The introduction prepares the main body of your essay. You think of a meaningful title for your essay, you describe your thesis or your question, you give general information on the subject and you prepare your argument by giving an overview of your most important arguments.
Below are examples and phrases that you can use to write the introduction to your essay in French.
The title should be meaningful, concise and reflect the content of the essay.
Introductory paragraph
The first paragraph of your French essay should briefly introduce the topic and engage the reader. Here are some examples to help you write your essay:
Proposal or question
The central proposition or question of your French essay should be a clear and concise definition of the purpose of the essay. Use these examples to get a clearer idea of how to write theses in French:
Overview of Arguments and Structure
At the end of your introduction, describe the structure of the main part of your essay (your outline) and outline your argument. Here are some French expressions that will certainly help you write your essay:
The body of your essay

The main part of your French essay deals with the given topic in detail. The subject is studied from all angles. The main body of your essay follows a thread of argument and discusses in detail the main arguments of your thesis previously made in the introduction.
In the body of the text, you should discuss the subject of your essay in clear and concise language. To achieve this, we give you some wording aids as well as vocabulary and phrases that you can use to write your essay in French.
Formulation tools:
French vocabulary for essays.
In the conclusion of your French essay, you address the thesis of your essay, summarize the main points of your discussion in the main body, and draw a conclusion. On the basis of the arguments and the resulting conclusions, you formulate in the conclusion of your dissertation final thoughts and suggestions for the future. It is important that you do not add new information or new arguments. This should only be done in the body of your text.
Here are some wording guides to help you write your essay in French:
Sample French Essay
Les avantages des voyages linguistiques
Malgré les difficultés potentielles, les voyages linguistiques offrent aux apprenants une occasion unique d'améliorer leurs compétences linguistiques et de découvrir de nouvelles cultures, ce qui en fait un investissement précieux pour leur développement personnel et académique.
Les séjours linguistiques sont des voyages organisés dans le but d'améliorer les compétences linguistiques des participants. Ces voyages peuvent se dérouler dans le pays ou à l'étranger et durer d'un week-end à plusieurs semaines. L'un des principaux avantages des séjours linguistiques est l'immersion. Entourés de locuteurs natifs, les apprenants sont contraints de pratiquer et d'améliorer leurs compétences linguistiques dans des situations réelles.Il s'agit d'une méthode d'apprentissage beaucoup plus efficace que le simple fait d'étudier une langue dans une salle de classe.
Un autre avantage des séjours linguistiques est l'expérience culturelle. Voyager dans un nouveau pays permet aux apprenants de découvrir de nouvelles coutumes, traditions et modes de vie, et de se familiariser avec l'histoire et la culture du pays. Cela enrichit non seulement l'expérience d'apprentissage de la langue, mais contribue également à élargir les horizons et à accroître la sensibilisation culturelle.
Cependant, les séjours linguistiques peuvent également présenter des inconvénients. Par exemple, le coût du voyage et de l'hébergement peut être élevé, en particulier pour les séjours de longue durée. En outre, les apprenants peuvent être confrontés à la barrière de la langue ou à un choc culturel, ce qui peut être difficile à surmonter. Le coût et les difficultés potentielles des séjours linguistiques peuvent sembler décourageants, mais ils offrent des avantages précieux en termes d'épanouissement personnel et scolaire.
Les compétences linguistiques et les connaissances culturelles acquises peuvent déboucher sur de nouvelles opportunités d'emploi et améliorer la communication dans un cadre professionnel. Les bourses et les aides financières rendent les séjours linguistiques plus accessibles. Le fait d'être confronté à une barrière linguistique ou à un choc culturel peut également être l'occasion d'un développement personnel. Ces avantages l'emportent largement sur les inconvénients et font des séjours linguistiques un investissement qui en vaut la peine.
En conclusion, malgré les difficultés potentielles, les séjours linguistiques offrent aux apprenants une occasion unique d'améliorer leurs compétences linguistiques et de découvrir de nouvelles cultures, ce qui en fait un investissement précieux pour le développement personnel et académique. Qu'il s'agisse d'un débutant ou d'un apprenant avancé, un voyage linguistique est une expérience à ne pas manquer.
Improve your writing style in French
Learn French with us. We will help you improve your writing skills.

Improve your French with Sprachcaffe

A Year abroad for high school students
Spend a unique school year abroad

Online French courses
Learn French from the comfort of your own home with an online course
Learn French on a language trip
Learn French in a French-speaking country
How to Write an Excellent French Essay (Resources Included)
Tips to write an excellent french essay.
Writing essays is challenging enough, but when you are asked to write a French essay, you are not only being asked to write in a foreign language, but to follow the conventions of another linguistic and literary tradition. Like essay-writing in any language, the essential part of writing a French essay is to convey your thoughts and observations on a certain topic in a clear and concise manner. French essays do come out of a certain tradition that is part of the training of all students who attend school in France – or at least secondary school – and when you are a French essay, it is important to be aware of this tradition.

The French philosopher Michel de Montaigne is credited with popularizing the essay form as a literary genre. His work, Essais, first published in 1580, and undergoing several subsequent publications before his death in 1592, covers a wide breadth of topics, ranging from “amitié” to “philosopher c’est apprendre à mourir”, and includes many literary references, as well as personal anecdotes. The name for this genre, essai, is the nominal form of the verb essayer, “to attempt”. We have an archaic English verb essay, meaning the same thing. The limerick that includes the phrase, “... when she essayed to drink lemonade ...” indicates an attempt to drink a beverage and has nothing to do with writing about it. But the writing form does illustrate an attempt to describe a topic in depth with the purpose of developing new insights on a particular text or corpus.
French instructors are very specific about what they would like when they ask for an essay, meaning that they will probably specify whether they would like an explication de texte, commentaire composé, or dissertation. That last essay form should not be confused with the document completed for a doctorate in anglophone countries – this is called a thèse in French, by the way. There are different formats for each of these types of essay, and different objectives for each written form.
Types of Essay
1. l’explication de texte.
An explication de texte is a type of essay for which you complete a close reading. It is usually written about a poem or a short passage within a larger work. This close reading will elucidate different themes and stylistic devices within the text. When you are completing an explication de texte, make sure to follow the structure of the text as you complete a close examination of its form and content. The format for an explication de texte consists of:
i. An introduction, in which you situate the text within its genre and historical context. This is where you can point out to your readers the general themes of the text, its form, the trajectory of your reading, and your approach to the text.
ii. The body, in which you develop your ideas, following the structure of the text. Make sure you know all of the meanings of the words used, especially the key terms that point to the themes addressed by the author. It is a good idea to look words up in the dictionary to find out any second, third, and fourth meanings that could add to the themes and forms you describe. Like a student taking an oral examination based on this type of essay writing, you will be expected to have solid knowledge of the vocabulary and grammatical structures that appear in the text. Often the significance of the language used unfolds as you explain the different components of theme, style, and composition.
iii. A conclusion, in which you sum up the general meaning of the text and the significance of the figures and forms being used. You should also give the implications of what is being addressed, and the relevance of these within a larger literary, historical, or philosophical context.
NB: If you are writing about a poem, include observations on the verse, rhyme schemes, and meter. It is a good idea to refer to a reference work on versification. If you are writing about a philosophical work, be familiar with philosophical references and definitions of concepts.
Caveat: Refrain from paraphrasing. Instead show through careful analysis of theme, style, and composition the way in which the main ideas of the text are conveyed.
2. Le commentaire composé
A commentaire composé is a methodologically codified commentary that focuses on themes in a particular text. This type of essay develops different areas of reflection through analytical argument. Such argumentation should clarify the reading that you are approaching by presenting components of the text from different perspectives. In contrast to the explication de texte, it is organized thematically rather than following the structure of the text to which it refers. The format for a commentaire composé consists of:
i. An introduction, in which you present the question you have come up with, often in relation to a prompt commenting on a thematic or stylistic aspect of the text, such as “Montrez en quoi ce texte évoque l’amour courtois” or “Qu’apporte l’absence de la ponctuation dans ce texte ?” In this section, you will be expected to delineate your approach to the text and illustrate the trajectory of your ideas so that your readers will have a clear idea of the direction these ideas will take.
ii. A tripartite body, in which you explore the question you have come up with, citing specific examples in the text that are especially pertinent to the areas of reflection you wish to explore. These citations should be explained and connected to the broad themes of your commentary, all the while providing details that draw the readers’ attention to your areas of inquiry. These different areas of inquiry may initially seem disparate or even contradictory, but eventually come together to form a harmonious reading that addresses different aspects of the text. The more obvious characteristics of the text should illuminate its subtler aspects, which allows for acute insight into the question that you are in the process of exploring.
iii. A conclusion, in which you evaluate your reading and synthesize its different areas of inquiry. This is where you may include your own opinions, but make sure that the preceding sections of your commentaire remain analytical and supported by evidence that you find in the text.
NB: Looking at verb tenses, figures of speech, and other aspects that contribute to the form of the text will help situate your reader, as will commenting on the register of language, whether this language is ornate, plain, reflects a style soutenu, or less formal patterns of speech.
Caveat: Quotations do not replace observations or comments on the text. Explain your quotations and situate them well within your own text.
3. La dissertation
The dissertation is a personal, organized, and methodical reflection on a precise question that refers to a corpus of writing. Referring to this corpus, you may be asked questions along the lines of “Que pensez-vous de l’équivalence entre l’amour et la chanson exprimée dans ces textes ?” or “Est-ce que la sagesse et la folie ont les mêmes sources?” This type of essay allows for an exploration of a question through knowledge of a corpus as well as through an individual’s cultural knowledge. The format for a dissertation consists of:
i. An introduction, in which you present the topic addressed, the significance of your argument, and the trajectory of your ideas.
ii. The body which, like a commentaire composé, consists of a tripartite development of your argument. This can follow any one of the following structures: a dialectical schema, organized into thèse, antithèse, and synthèse – an argument, its counter-argument, and its rebuttal; an analytical schema, consisting of the description of a situation, an analysis of its causes, and commentary on its consequences; a thematic schema, which consists of a reflection on a topic which you proceed to examine from different angles in an orderly fashion.
iii. A conclusion, in which you address the different ways in which you have approached the question at hand and how this deepens your insights, while placing the question within a broader context that shows room for expansion. The conclusion can open up the topic addressed to show its placement within a literary movement, or in opposition to another literary movement that follows it, for example.
NB: Approach the question at hand with as few preconceptions as possible. If you are writing on a quotation, gather all of your knowledge about its author, the work in which it appears, and the body of literature with which it is associated.
Caveat: Even for a personal reflection, such as a dissertation, avoid using the first person pronoun je. Nous or on are preferable. It is advisable not to switch from one to the other, though.
For each of these essay forms, it is a good idea to make an outline to which you can refer as you write. As your writing progresses, things may shift a bit, but having a structure on which you can rely as you gather your various ideas and information into a coherent argument provides solid foundation for a clear and well-developed essay. This also facilitates smooth transitions from one section of your essay to the next.
During your reading, you may encounter a problem, a contradiction, or a surprising turn of phrase that is difficult to figure out. Such moments in a text give you the opportunity to delve into the unique characteristics of the text or corpus to which you are referring, to propose different solutions to the problems you encounter, and to describe their significance within a larger literary, philosophical, and historical context. Essay writing allows you to become more familiar with French works, with their cultural significance, and with the French language. You can refer to the following resources to guide you in this endeavor:
Auffret, Serge et Hélène. Le commentaire composé. Paris: Hachette, 1991. Dufau, Micheline et Ellen D'Alelio. Découverte du poème: Introduction à l'explication de textes. New York: Harcourt, Brace & World, 1967. Grammont, Maurice. Petit traité de versification française. Paris: A. Colin, 2015. Huisman, Denis et L. R. Plazolles. L’art de la dissertation littéraire : du baccalauréat au C.A.P.E.S. Paris : Société d’édition d’enseignement supérieur, 1965.
The French newspaper Le Monde also has good articles on these essay forms that prepare French students for the baccalauréat exam: CLICK HERE
This is also a website with thorough information on essay writing techniques that prepare students for the baccalauréat exam: CLICK HERE
In addition, the University of Adelaide has tips for general essay writing in French: CLICK HERE
🇫🇷 Looking for More French Resources?
Train with Glossika and get comfortable talking in French. The more you listen and speak, the better and more fluent you will be.
Glossika uses syntax to help you internalize grammatical structures and you can build up your French vocabulary along with way. You'll also learn to communicate in real-life situations, and achieve fluency by training your speaking and listening!
Sign up on Glossika and try Glossika for free:

You May Also Like:
- 10 Great Tips to Prepare to Study in France
- How to Maintain French and Continue Learning by Yourself
- Differences Between Spoken French and Written French
Subscribe to The Glossika Blog
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox

Stay up to date! Get all the latest & greatest posts delivered straight to your inbox
French Your Way
Learn French Online | Learn French Melbourne | French Voices Podcast
How to Write The Perfect French Essay For Your Exam
November 16, 2014 by Jessica 3 Comments
Here are tips to help you write a great French essay with exam requirements in mind. Once you’re done, I strongly suggest you proofread your text using my checklis t.
Note: if you’re preparing for the French VCE, there is an updated version of these exam tips in my guide “How to Prepare for the French VCE & Reach your Maximum Score” .
While supervising exams or tutoring for exam preparation, I’ve seen too many students writing straight away on their exam copies. Stop! Resist the urge to jump on your pen and take a step back to make sure that you will be addressing all the exam requirements or you may be shooting yourself in the foot and lose precious points.
I recommend that you train with exam sample questions so that you set up good working habits and respect the required length of the essay, as well as the timing (allow at least 10 minutes for proofreading).
Crafting your French Essay
1. identify the situation: preparation work.

- Read the topic carefully, slowly and at least twice to absorb every information/detail.
- Underline/highlight/jot down any piece of information that you are expected to reuse:
- What type of text do you need to write? (a journal entry? A formal letter? A speech? Etc). Note to VCE French exam students : refer to page 13 of the VCE French Study Design for more information about the different types of texts.
- Who are you in the situation? (yourself? A journalist? etc)
- Who are you addressing? (a friend? A large audience? Etc) à adjust the degree of formality to the situation (for example by using the “tu”/”vous” form, a casual or formal tone/register, etc)
- What are the characteristic features of the type of text you need to write? (eg a journal entry will have the date, a formal letter will start and end with a formal greeting, etc)
- What is your goal ? What are you expected to talk about / present / defend / convey?
- What are the length requirements for your French essay ? Respect the word count (there’s usually a 5% or so tolerance. Check the requirements specific to your exam)
Tip : when you practice at home, count how many words in average you fit on a line. This will give you a good indication of how many lines your text should be.
Ex: You write an average of 15 words per line. If you are required to write a 300-word French essay, you should aim for:
300 words / 15 words per line = 20 lines total.
2. Draft the outline of your essay
- An essay typically has an introduction, a body with 2 or 3 distinct parts and a conclusion . (See if that outline is relevant to the type of text you are expected to write and adjust accordingly.)
- Use bullet points to organize your ideas.
- Don’t remain too general. A good rule is to use one main idea for each part and to back it up/reinforce in/illustrate it with one concrete example (eg. data).
- Brainstorming about things to say will also help you use a wider range of vocabulary , which will get noticed by the examiner. Are there some interesting/specific words or expressions that you can think of using in your text (example: if you are writing about global warming, brainstorm the vocab related to this topic. Brainstorm expressions to convince or disagree with something, etc)?
- Make sure you have reused every point identified in part 1 .
3. Write your essay
- It’s better if you have time to write or at least draft a few sentences on your draft paper rather than writing directly because:
- You want to meet the word count requirements
- You don’t want multiple words to be barred cross crossed-out and your page looking messy and great anything but neat!
- you don’t want to have to rush so much that your handwriting is really unpleasant to read (or worse, impossible to read…)
- So… monitor your time carefully!
Structuring your text
- Visually, the eye should instantly be able to see the structure of your French essay: make paragraph and skip lines so that it doesn’t look like an unappealing large block of text.
- Use connectors/link words to structure your text and make good transitions.
4. Proofread, proofread, proofread!
- It’s important that you allow at least 10 minutes for proofreading because there most likely are a few mistakes that you can fix very easily. It would therefore be a shame not to give yourself your best chances of success! Check out my Proofreading Checklist.
Bonne chance!
If you need any help with your essay, you can submit it to me there.
- Articles & Tutorials
- French Voices Podcast
- French Your Way Podcast
- News & Updates
info (at) frenchyourway.com.au
PO Box 166, Balaclava, Vic 3183, Australia

Published on October 6th, 2023 | by Adrian Lomezzo
How to Write an Essay in French Without Giving Yourself Away as a Foreigner
Image source: https://www.pexels.com/photo/close-up-shot-of-a-quote-on-a-paper-5425603/
Bienvenue! Do you dream of unleashing your inner French literary genius, but worry that your writing might inadvertently reveal your foreign roots? Fret not, mes amis, as we have the ultimate guide to help you master the art of essay writing en Français!
Within these pages, we’ll navigate the intricate waters of linguistic nuances, cultural subtleties, and grammatical finesse, allowing you to exude the aura of a native French speaker effortlessly. Many students like you have embarked on this journey, seeking academic assistance from platforms like https://paperwritten.com/ to conquer their writing pursuits.
From crafting a compelling introduction to fashioning impeccable conclusions, we’ll unveil the secrets that will leave your professors applauding your newfound linguistic prowess. So, bid adieu to those awkward linguistic giveaways and embrace the sheer elegance of French expression – all while keeping your foreign identity beautifully concealed! Let’s embark on this adventure together and unlock the true essence of writing like a native French virtuoso.

1. Mastering French Grammar and Vocabulary: Building a Strong Foundation
To create a compelling French essay, it’s essential to lay a solid groundwork. Ensure that your French grammar is accurate and that you possess a rich vocabulary. Avoid relying on online translators, as they may yield awkward or incorrect sentences. Instead, embrace reputable dictionaries and language resources to enhance your language skills effectively.
2. Mimic Sentence Structures: The Art of Authentic Expression
To truly immerse yourself in the French language, observe and mimic the sentence structures used by native speakers. Analyzing essays written by experienced writers can prove invaluable in grasping the authentic style required to compose a captivating essay.
3. Use Transition Words: Crafting a Smooth Flow of Ideas
In French essays, the use of transition words and phrases plays a pivotal role in connecting ideas seamlessly. Incorporate expressions like “de plus,” “en outre,” “en conclusion,” “tout d’abord,” and “par conséquent” to add coherence and elegance to your writing.
4. Embrace French Idioms and Expressions: Unveiling Cultural Fluency
Demonstrate a deeper understanding of the French language and culture by incorporating idioms and expressions where appropriate. However, remember to use them sparingly to avoid overwhelming your essay.
5. Pay Attention to Formality: Striking the Right Tone
Tailor the formality of your writing to suit the context of your essay. Whether you are crafting an academic piece or a more personal creation, be mindful of your choice of vocabulary and sentence structures to match the required tone.
6. Research Cultural References: The Power of In-depth Knowledge
If your essay touches upon French culture, history, or literature, extensive research is key. Delve into your subjects to avoid mistakes and showcase your genuine interest in the matter at hand.
7. Avoid Direct Translations: Let French Be French
To avoid awkward phrasing, strive to think in French rather than translating directly from your native language. This will lead to a more natural and eloquent essay.
8. Practice Writing Regularly: The Path to Proficiency
Mastering the art of French writing requires regular practice. Embrace writing in French frequently to grow more comfortable with the language and refine your unique writing style.
9. Read French Literature: A Gateway to Inspiration
Explore the world of French literature to expose yourself to diverse writing styles. This practice will deepen your understanding of the language and immerse you further in French culture and history.
10. Connect with French Culture: Bridges of Cultural Resonance
Incorporate cultural references that resonate with French readers, such as art, cuisine, festivals, historical figures, or social customs. Authenticity is key, so avoid relying on stereotypes.

11. Use a French Thesaurus: Expanding Your Linguistic Palette
Discovering new contextually appropriate words can elevate your writing. Embrace a French thesaurus to find synonyms that may not be apparent through direct translations.
12. Master French Punctuation: The Finishing Touch
Take care to use correct French punctuation marks, such as guillemets (« ») for quotes and proper accent marks. These subtle details add a professional touch to your essay.
13. Practice French Rhetorical Devices: Crafting Eloquent Prose
Experiment with rhetorical devices like parallelism, repetition, and antithesis to lend depth and sophistication to your writing.
14. Pay Attention to Word Order: Unlocking French Sentence Structure
French boasts a unique sentence structure distinct from English. Dive into the intricacies of subject-verb-object order and grasp the art of organizing sentences to sidestep common foreign mistakes. Embracing this essential aspect will elevate your writing to a truly native level.
15. Use French Idiomatic Expressions: Infuse Cultural Flair
Enrich your prose with the colorful tapestry of French idioms, reflecting the vibrant essence of the culture. Yet, a word of caution – wield them with finesse, for the strategic placement of an idiom can imbue your essay with unparalleled flair and authenticity.
16. Master Pronouns and Agreement: The Dance of Language
The dance of pronouns, nouns, and adjectives requires your keen attention. Like a skilled performer, ensure their seamless alignment to avoid inadvertently revealing your non-native status. Mastering this harmony is key to writing like a true Francophone.

17. Understand Subtle Connotations: Unveiling Linguistic Shades
Delve into the labyrinth of French words, where subtle connotations diverge from their English counterparts. Familiarize yourself with these delicate nuances, for it is in their mastery that your writing shall find refinement.
18. Study Formal and Informal Registers: Tailoring Language to Purpose
Akin to selecting the perfect outfit for each occasion, comprehend the art of using formal and informal language. Consider your essay’s purpose and audience, and with this knowledge, enhance your authenticity, seamlessly aligning with the appropriate linguistic register.
19. Practice Dialogue Writing: Conversing with Eloquence
Embark on the journey of dialogue writing to enrich your linguistic repertoire. As you hone your conversational skills, watch as authenticity gracefully weaves itself into your written work, enchanting readers with its charm.
20. Seek Feedback: A Second Set of Eyes
To refine your essay further, seek the guidance of a native French speaker or language tutor from the best cheap essay writing services . Their valuable feedback can uncover any language or cultural mistakes you may have made, allowing you to make necessary improvements.
Equip yourself with these priceless tips and set forth on your quest to master the art of French writing. Embrace the language’s allure, immerse in its rich culture, and watch your words flow with grace and poise. À la plume! Let the pen become your ally in crafting captivating prose that echoes with authenticity and charm.
Header Photo Credit by George Milton: https://www.pexels.com/photo/smiling-woman-in-eyeglasses-with-books-7034478/
About the Author
Adrian Lomezzo is a content writer and likes to write about technology and education. He understands the concern of parents due to the evolving technology and researches deeply in that area. When he is not researching, he buries himself in books along with his favorite cup of hot chocolate.
Related Posts

Veronique Gallo On Tour With Her Latest Show “Femme De Vie” In California →

Beyond Shakespeare: Expanding Horizons with London’s Diverse Theatre Scene →

Three French authors from San Diego present their new books →

Martine Couralet-Laing reveals behind the scenes of the city of angels in DreamLAnd →
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Welcome to French Quarter Magazine (FQM) – your passport to a journey through France, the United States and beyond!
French Quarter Magazine is a dynamic bilingual publication, based in Las Vegas, that celebrates the finest in art, culture, entertainment, lifestyle, fashion, food, travel, sports and history. Whether you're longing for a taste of Parisian elegance or the vibrancy of American culture, we've got you covered.
Our mission is to create a link and to bridge the gap between the United States and France by promoting exchanges and offering a unique reading experience through our bilingual publication. From the charming streets of Paris to the bustling avenues of New York City, our articles provide a captivating exploration of diverse cultural landscapes. Written by our dedicated team of contributors from around the world, they cover everything from the latest places to visit or stay, to new spectacles and exhibitions, to the opening of exciting restaurants or stores, fashion trends, and the nuanced history of French-American relations.
With a focus on women empowering women and excellence, we showcase individuals who make a positive impact in our communities. Through cultural events, conferences, and engaging content, we strive to enrich understanding of history, culture, and the arts, while preserving and transmitting valuable skills and knowledge.
At French Quarter Magazine, we cherish culture as a precious and diverse treasure that should be celebrated. That's why we provide a platform for individuals and businesses with interests in both countries to connect, network, and engage. Through our engaging content and cultural events, we strive to foster understanding and appreciation of the unique qualities of each culture, while also highlighting their shared values.
So why not join us on a journey of discovery? Whether you're seeking inspiration or information, French Quarter Magazine is the perfect publication for you.
Step into a world of lifestyle, entertainment, cultural exchanges with French Quarter Magazine! Subscribe today to receive our weekly newsletters and special offers, and step into a world of endless possibilities.

PROMOTE MY BUSINESS
Donate we need your help, become an ambassador, virtual and in-person events with fqm, your opinion matters , learning french, recent posts.

RECENT COMMENTS
Merci pour votre commentaire intéressant, Annick ! Désolée pour la réponse tardive. Nous avons dû restructurer notre équipe. Nous sommes…
Thank you for your continued support and for being a regular visitor to our website, Cameron! Sorry for the late…
Bonjour! Nous sommes ravis que vous ayez apprécié l'article ! Désolée pour la réponse très tardive. Nous avons dû restructurer…
Thank you for sharing that interesting piece of information, Mike! As for "Alors on Danse" by Stromae, while it didn't…
Thank you so much, Jaya! I'm delighted that you enjoyed the article and found it informative. Exploring the cultural differences…
©2023 French Quarter Magazine
- Sponsorships, Partnerships and Advertising
- Privacy Policies
Discover our new and improved website at www.frenchquartermagazine.com ! We look forward to welcoming you there !

- Library Catalogue
Resources for academic writing in French
On this page, 1. purpose of this document, 2. orthographe et typographie, 3. grammaire, 4. structure de texte: vocabulaire, 5. comment construire une dissertation en français.
- 6. Outil utile : comment faire les caractères français sur n'importe quel clavier ?
- 7. Où trouver de l'aide en français ?
- 8. S'immerger d'avantage dans le français
This document offers resources to students writing in French at the undergraduate and postgraduate levels. It has been inspired by the recurring questions and issues encountered during consultations with students and it includes:
- Grammatical and vocabulary help
- Advice on dissertation structure and dissertation writing
- A useful tip on how to easily type special French characters on any keyboard
- Suggestions as to where students can find additional help
- Ideas on where to meet French speakers and how to get exposed to the language to improve fluency
Note: The information presented is valid as of December 2016. The rest of this information is written in French since it is intended for people with at least a basic understanding of the language.
This material is also available as a printable pdf and as a stand-alone website .
2.1.1 Majuscules
2.1.1.1 Noms et adjectifs de nationalité
En anglais, les noms et adjectifs se rapportant aux langues et aux pays prennent toujours des majuscules :
I am French I speak French The French are always on strike
Ce n'est pas le cas en français.
Les adjectifs ne prennent jamais de majuscule en français. Donc: adjectifs de nationalité ou se rapportant aux langues → pas de majuscule
Je suis française La langue française
Pour les noms, il ne faut pas de majuscule lorsque l'on parle des langues. Les langues → pas de majuscule
Je parle français Le français et l'anglais
Ceci dit, lorsque l'on parle de personnes, il faut la majuscule. Les habitants d'un pays → majuscule
Les Français sont tout le temps en grève
2.1.1.2 Jours de la semaine et mois
En anglais, les jours de la semaine et les mois prennent des majuscules. Mais pas en français :
Le lundi et le mardi Le jeudi 3 mars Tous les dimanches de novembre
2.1.2 Ponctuation
Contrairement à l'anglais, il faut un espace avant les deux points, le point d'interrogation et le point d'exclamation :
Tu viens ? Ah non !
Les guillemets sont différents et il faut un espace entre les guillemets et le texte :
Il lui dit : « d'accord »
Note : un éditeur de texte (par exemple MS Word ou OpenOffice Writer) corrigera tout cela automatiquement si vous le mettez en français.
2.1.3 « et » et la virgule
L'usage d'une virgule avec « et » est différent en français et en anglais :
En anglais, il faut une virgule avant « and » dans une énumération qui comprend plus de deux éléments : French, English, and Spanish
En français, il n'y a pas de virgule avant « et » : Le français, l'anglais et l'espagnol
Mettre un mot au féminin peut aider à trouver sa terminaison :
chat → chatte ouvert → ouverte remis → remise
3.1.1 Définition
Voix active : le sujet fait l'action
Voix passive : le sujet subit l'action et le complément d'agent (introduit par « par ») fait l'action
Le complément d'agent fait l'action (voix active) : Notre équipe a réalisé une étude
L'action est faite PAR le complément d'agent (voix passive) : Une étude a été réalisée PAR notre équipe
3.1.2 Formation
La voix passive se construit avec l'auxilaire être + le participe passé du verbe .
Attention donc à ne pas confondre un temps simple à la voix passive avec un temps composé.
Par exemple, il ne faut pas confondre un verbe au présent de la voix passive avec un passé composé :
Le lapin est mangé par le loup (Présent de la voix passive. Cela équivaut à : le loup mange le lapin - maintenant)
Le lapin a mangé la salade (Passé composé de la voix active. Le lapin a mangé la salade hier)
3.1.3 Écrivez à l'actif !
Pendant longtemps, il a été d'usage d'utiliser la voix passive dans les travaux académiques, probablement par modestie. Cette habitude est tombée en désuétude, mais malheureusement les étudiants continuent trop souvent à écrire au passif, rendant les textes tortueux et le style inutilement lourd. Je vous encourage vivement à utiliser la voix active :
- la construction est beaucoup plus directe
- il est maintenant d'usage d'annoncer clairement et sans détour que nous sommes l'auteur d'un travail
3.2.1 Les adjectifs
Les adjectifs s'accordent en genre et en nombre avec le nom auquel ils se rapportent
3.2.2 Les participes passés
- Avec l'auxiliaire être Les participes passés s'accordent en genre et en nombre avec le sujet
- Avec l'auxiliaire avoir Les participes passés s'accordent en genre et en nombre avec le complément d'objet direct, si celui-ci est placé avant le verbe
- Sinon, ils sont invariables En aucun cas, ils ne s'accordent avec le sujet
Pas de panique, c'est en fait simple :
Auxiliaire être
Il est tombé Ils sont tombés Elles sont tombées
Auxiliaire avoir - COD après le verbe
Il a pris un verre Il a pris une pomme Il a pris des pommes
Auxiliaire avoir - COD avant le verbe
Il l'a pris (=le verre) Il l'a prise (=la pomme) Il les a prises (=les pommes)
[[ collapse start " 3.3 « Nous » et « on » "]]
« On », techniquement, est un équivalent de l'anglais « it »
On dit souvent que...
Mais dans le langage courant, il est utilisé à la place de « nous »
On y va (=nous y allons) On arrive ! (=nous arrivons !)
Ceci est cependant à éviter à l'écrit, à moins que l'on veuille donner au texte une connotation familière.
3.4.1 Forme
3.4.1.1 Définis
| français : | le/la | les |
| anglais : | the | the |
le chat/les chats the cat/the cats
3.4.1.2 Indéfinis
| français : | un/une | des |
| anglais : | a | ∅ |
un chat/des chats a cat/cats
3.4.2 Usage
3.4.2.1 Définis
On sait exactement de quel individu/chose il s'agit. On pourrait le montrer du doigt. Le nom est défini
Le chat de mon voisin (Ceci suppose que mon voisin n'a qu'un chat et que, du coup, on sait exactement de quel chat il s'agit)
La Terre est ronde (Il n'y en a qu'une, donc on sait de laquelle il s'agit)
La lune (On suppose qu'il s'agit de notre lune, celle qui tourne autour de la terre, et que donc on sait de laquelle il s'agit)
3.4.2.2 Indéfinis
On ne sait pas de quel individu/chose il s'agit. Le nom est indéfini
J'ai vu un chat noir ce matin (On ne sait pas de quel chat noir il s'agit. L'information "noir" ne suffit pas à définir l'individu particulier dont il est question)
Un chat de mon voisin (Ici, cela suppose que mon voisin a plusieurs chats et du coup, on ne sait pas de quel individu il est question. Comparer ceci avec l'exemple précédant)
Une lune (Ici, on fait référence à un satellite naturel, par exemple une lune de Saturne. On ne sait donc pas de quelle lune il s'agit)
C'est en fait très similaire à l'anglais. Réfléchissez à ce que vous diriez en anglais
- Invariables
- Généralement formés à partir d'adjectifs + « ment »
grand → grandement
4.1.1 Commencer
Premièrement D’abord Tout d'abord Au début Pour commencer
4.1.2 Continuer
Chronologiquement :
Deuxièmement Ensuite Puis Après
En ajoutant :
De plus Ajoutons que En outre Par ailleurs Aussi Egalement
4.1.3 Finir
Enfin Finalement Pour finir Pour terminer Pour conclure En conclusion
4.2.1 Similarités
De la même manière De la même façon Similairement
4.2.2 Différences
En revanche Au contraire Alors que Pourtant D'autre part D'un autre côté Par ailleurs
Du coup En conséquence Par conséquent Il en résulte que De ce fait Donc Ainsi C'est pourquoi
Veuillez noter que ceci ne représente que mon opinion personnelle. Les consignes que vous recevez de vos professeurs sont sans aucun doute plus importantes que les conseils que je présente ici. Si vous avez des doutes, la meilleure chose à faire est toujours de discuter avec le professeur afin d'éliminer toute confusion quant à ses attentes. Il se peut que votre professeur ait une vision différente de la mienne sur la structure d'une dissertation. Il n'y a, de toute façon, aucune règle absolue et ceci ne représente qu'une façon, parmi beaucoup d'autres, de construire un plan.
Ne vous embarquez pas dans l'écriture avant d'avoir un plan! Si vous vous lancez dans l'écriture en aveugle, vous allez perdre énormément de temps à rédiger des choses qui ne fonctionneront probablement pas et que vous devrez réécrire. Assurez vous d'avoir un plan solide avant de commencer à rédiger des phrases. Pour construire ce squelette, des tirets avec vos idées suffisent.
Pour structurer votre plan, imaginez un sablier :

L'introduction , en bleu dans le sablier, commence large et se réduit petit à petit.
Elle peut se construire en trois sous-parties :
- Une introduction du thème qui se veut très ouverte. Vous voulez intéresser un public large. Si vous commencez directement sur le sujet étroit et spécifique de votre dissertation, peu de gens n'auront envie de la lire vu que peu de gens ont un intérêt pour un sujet très pointu.
- Dans une deuxième sous-partie, vous emmenez le lecteur peu à peu vers le sujet de votre dissertation. La problématique se resserre.
- Finalement, dans une troisième partie, vous présentez votre plan. Après avoir lu cette sous-partie, le lecteur doit savoir ce qui l'attend.
Le corps de votre dissertation , en orange dans le sablier, reste ciblé sur votre sujet.
Il comporte deux à quatre parties (souvent trois). C'est là que vous présentez votre analyse. Chaque partie représentant un aspect ou un point différent.
La conclusion , en vert dans le sablier, commence étroite et s'élargit peu à peu.
Vous ne voulez pas laisser le lecteur avec cette vue très pointue d'un sujet. Vous voulez élargir vers une problématique plus large. Là aussi, trois sous-parties est assez classique :
- Une première sous-partie qui conclut votre dissertation,
- Un élargissement de la problématique,
- Une troisième sous-partie peut comporter des questions laissées ouvertes.
Vous avez votre plan et vous en êtes content. Maintenant, il est temps de commencer à rédiger… mais dans quel ordre ? La question peut vous surprendre vu que la plupart des gens commencent… par l'introduction. Erreur ! L'introduction est probablement la partie la plus difficile à écrire. Il est beaucoup plus facile de commencer par le corps de la dissertation car c'est vraiment votre sujet. A partir de là, vous pourrez assez facilement écrire la conclusion. Et finalement, à la fin, après avoir passé tout ce temps avec votre dissertation, vous serez en bien meilleure position pour attaquer cette fameuse introduction qui est si difficile.
Séparez les grandes parties (introduction, corps de la dissertation et conclusion) en sautant une ligne. Les différentes parties du corps central de votre dissertation peuvent aussi être séparées par une ligne blanche. Chaque partie et sous-partie commence typiquement par un alinéa (« indent » en anglais). De cette façon, le lecteur peut, avant même de commencer à lire, voir la structure de votre dissertation.
Les deux à quatre parties du corps de votre dissertation doivent être équilibrées : vous ne voulez pas avoir une partie de plusieurs pages et une autre de quelques lignes. Si tel est le cas, essayez de structurer vos idées différemment en fusionnant certaines parties entre elles ou en revisitant votre plan.
Il est classique de lier les différentes parties ou sous-parties les unes avec les autres grâce à des phrases de transition qui mettent en évidence la cohésion logique de l'ensemble. Vous ne voulez pas que votre essai ressemble à une juxtaposition d'idées sans rapport les unes avec les autres.
En français, comme en anglais, il est important de citer vos sources. Le site de la bibliothèque de SFU a de nombreuses ressources sur le format à suivre : Citation guide: APA .
6. Outil utile : comment faire les caractères français sur n'importe quel clavier ?
La méthode la plus simple est d'utiliser le clavier international américain. Je n'explique pas ici comment l'activer car cela dépend de votre système d'exploitation (OS), mais les instructions sont très simples et disponibles partout sur internet. Une fois activé, le clavier international transforme :
| '' → ' |
|
| `a → à |
|
| ^^ → ^ |
|
| "" → " |
| 'e → é |
|
| `e → è |
|
| ^a → â |
|
| "e → ë |
| 'c → ç |
|
| `u → ù |
|
| ^e → ê |
|
| "i → ï |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ^i → î |
|
| "u → ü |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ^o → ô |
|
| "y → ÿ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ^u → û |
|
|
|
7. Où trouver de l'aide en français ?
Le Student Learning Commons (SLC) offre depuis l'année dernière deux services pour les étudiants écrivant en français :
- des consultations particulières hebdomadaires
- des ateliers
7.1.1 Consultations particulières
Des consultations particulières hebdomadaires sont disponibles. Prenez rendez-vous sur le site du Student Learning Commons : Academic writing resources .
7.1.2 Ateliers
Des ateliers d'écriture en français sont organisés régulièrement. Regardez le programme sur le site du Student Learning Commons: Writing workshops .
Si vous avez des suggestions de nouveaux ateliers d'écriture en français qui vous seraient utiles, n'hésitez pas à nous en faire part en écrivant à l'adresse mail [email protected]
7.2.1 Dictionnaires
7.2.1.1 Français
- Du Centre National de Ressources Textuelles et Lexicales , le meilleur dictionnaire de français en ligne ! Une ressource vraiment excellente.
7.2.1.2 Français/anglais
- WordReference.com
7.2.2 Conjugaison
- Le Conjugueur : un bon site de conjugaison
7.2.3 Plagiat
Toutes les règles que vous avez apprises sur le plagiat dans vos travaux en anglais s'appliquent également en français. Le plagiat est un sujet sérieux que SFU traite avec beaucoup d'attention et si vous n'êtes pas sûrs des règles, je vous encourage vivement à vous familiariser avec elles en lisant les sites suivants. Pour SFU, l'ignorance n'est pas une excuse….
- Voir également: Plagiarism tutorial (SFU Library, anglais)
- Academic honesty
8. S'immerger d'avantage dans le français
8.1.1 meetup français.
- Vancouver French Langage Meetup
8.1.2 Le Centre Culturel Francophone de Vancouver
- Le Centre Culturel Francophone de Vancouver
8.2.1 Histoire et culture
- Radio Canada : Aujourd'hui l'histoire
- France Culture : Les nuits de France Culture
8.2.2 Infos (« Informations » en France ou « Nouvelles » au Canada)
- France Inter : Le journal de 18h
- Radio Canada : Midi info
8.2.3 Sciences et technologie
- France Culture : La marche des sciences
- Radio Canada : Les années lumières
8.3.1 Théâtre en français
Théâtre la Seizième
8.3.2 Internet
Nombreuses options pour voir des films, apprendre de nouveaux mots, améliorer sa prononciation, apprendre à conjuguer…
8.3.3 Films
De nombreux films français sont disponibles gratuitement dans les bibliothèques publiques et de SFU :
- SFU Library movie collection . See How do I find books written in French, Chinese, and other languages? for help narrowing your search to French-language materials.
- Vancouver Public Library
- Burnaby Public Library
This guide was created by Marie-Hélène Burle, December 2016.
Learn How to Write in French Easily
- Everything About
- The alphabet
- Funny phrases
- Common words
- Untranslateable Words
- Reading Hacks
- Writing Tips
- Pronunciation
- Telling time
- Learn FASTER
- More resources
By OptiLingo • 9 minute read

Improve Your Written French Today
Whether you want to pen a love letter or submit an essay in France, you need to know how to write in French. Luckily, learning how to write in French is fairly straightforward. Since French uses the Latin Alphabet, you’re already ahead of the game. Improve your writing in French fast with these easy steps.
The Basics of French Writing for Beginners
When it comes to French writing, it’s a little different than speaking French. But, if you know how to read French well, you shouldn’t have a lot of problems.
Before you read the 8 easy steps of learning to write in French, there’s one important factor in mastering French writing: practice. The only way you can truly improve your French writing skills is with a lot of practice . Make sure you write a little bit in French every day. Soon, you’ll find that writing in French is like second nature.
1. Watch Out for French Spelling
One of the biggest obstacles that throws French learners off is spelling. Unfortunately, those silent letters that you don’t pronounce are very much there in writing. Be careful how you spell certain complicated words. You need to master all parts of French grammar to write French correctly.
2. Genders Influence Grammar in French
You may already know that nouns have genders in French. They can either be masculine or feminine. And depending on the gender, different parts of a French sentence need to be conjugated.
- articles : French articles need to be conjugated to reflect the gender and the number of the noun. These can be ‘le’, ‘la’, ‘l”, and ‘les’ for definite articles, and ‘un’ and ‘une’ for indefinite articles.
- pronouns : Pronouns in French are the words that replace the name of the subject in a sentence. ‘He’, ‘she’, and ‘them’ are some examples of pronouns in English. In French, you need to use different forms of pronouns depending on the gender of the subject.
- adjectives : When you’re describing a noun, you use an adjective. And since the noun is the only reason the adjective’s there in the sentence, you need to make the adjective fit the noun in French. There are various ways to conjugate French adjectives depending on the gender and the number of the noun, so make sure you brush up on that knowledge before you write in French.

3. Careful with French Accent Marks
French accent marks also don’t do us any favors. While they’re extremely useful when it comes to French pronunciation, their writing isn’t as straightforward. Try to associate the sound with the written French word. There are only 5 accent marks in French. One is the cedilla (ç), which only works with the letter “c”, and another is the acute accent (é), which only sits on top of the letter “e”. So in practice, there are only 3 different kinds of accents you should look out for in French.
4. Follow the French Sentence Structures
English and French sentence structures are similar in many ways. Both follow the SVO (subject-verb-object) structure, which makes writing in French much easier. And just like in English, the French sentence structure is also flexible. You can switch the words around to emphasize a part of a sentence, but still have the same meaning.
- Tomorrow , I’m going to work. Demain je vais travailler. I’m going to work tomorrow . Je vais travailler demain .
The most important part of the first sentence is the time the speaker goes to work. The second sentence focuses on the subject, the speaker instead. Still, both sentences convey the same meaning of going to work.
If you want to ask a question in French, you can do so by putting a question word at the beginning of the sentence. Common question words are:
- How Comment
- What Que / Qu’est-ce que queue
- What kind Quel genre
- When Quand
- Why Pourquoi
You can also ask a question by switching the order of the verb and the pronoun around, and connecting them with a hyphen:
- Do you speak English? Parlez-vous anglais ?
It’s important to remember these basic rules of French sentence structure before you start writing in French. If you want to learn how to write in French effectively, practice these 4 steps a lot.
Psst! Did you know we have a language learning app?
- It teaches you useful words and phrases.
- Presented in a natural, everyday context.
- Spaced out over time, so you absorb your new language organically.
- It’s kind of like learning the words to your new favorite song!
You’re only one click away!
How to Write in French for Intermediate Students
If you’re an intermediate French learner you’re familiar with basic French grammar, and you’re confident in writing in French. But, there’s always room to improve. Once you know the basic steps of how to write in French, it’s time to make your writing even better. You can start paying attention to style, flow, and structure. The tips below will benefit your French writing practice.
5. Try Nominalization
This useful technique will make your sentences better. Nominalization means that you make nouns in the sentence more dominant. While in English, the dominant words are verbs, in French, you can write with the focus of the noun instead, making them more meaningful. Here’s an example to demonstrate.
- Normal sentence: The ice cream is cold. – La glace est froide.
- Nominalized sentence: The ice cream is cold. – La glace, c’est droid.
6. Use French Conjunctions
Conjunctions are the tools to write complex French sentences. Without them, you’re limited to simple and boring sentence structures. As an intermediate student, you can start connecting two equal or unequal sentences to make an even more interesting phrase. Here are the different kinds of French conjunctions you can use to write better in French:
Coordinating Conjunctions:
You use these kinds of conjunctions to connect two equal sentences. The most common coordinating conjunctions in French are:
Subordinating Conjunctions:
If one of the sentences in unequal or dependent on the other, you need to use subordinating conjunctions. These connectors often show causality. The most common conjunctions in French for this category are:
7. Style and Flow
Now that you wield the power of conjunctions, you have to be careful with it. As fun as it is to write long and complicated sentences in French, it doesn’t sound good. Make sure you use appropriate sentence lengths as you’re writing in French.
Aim for shorter sentences. Make them explain your point well. But, feel free to mix the flow up with the occasional longer sentences. That’s how you write in French with a nice and smooth flow. And that’s how you perfect your French writing too. It will be a pleasure to read your work.
Writing in French for Advanced Learners
Once you mastered all of the French writing rules, you’re officially an advanced French learner. But, there may still be room to improve your French writing. If you’re looking to kick your projects up a notch, you can learn how to write essays and dissertations in French. These pointers will be useful if you ever attend school or university in France, or you want to take a language exam.
8. Get Familiar with French Essay Structure
When you’re writing an essay, you have to structure it for readability. If you want to learn how French high schoolers are taught to write their essays, this is the structure they follow: thèse-antithèse-synthèse (thesis-antithesis-synthesis). Learn how to write French essays using a traditional French essay structure.
- Introduction : You begin your essay by having an introduction, which is a context for argument.
- Thesis : In this section, you present and defend the statement of your thesis. You need to write everything that supports the topic of your essay.
- Antithesis : The antithesis follows the thesis. This is where you state conflicting evidence and explain other potential substitutes for your essay. Including an antithesis doesn’t mean that you disagree with your original thesis. You just need to show that you thought of all possibilities before arriving to your conclusion.
- Synthesis : This is your conclusion. This is where you summarize your arguments, and explain why you still stand by your original thesis despite the antithesis.

9. Use Introduction and Conclusion Vocabulary
Certain words can encourage sentence flow by introducing or concluding some parts of your work.
- tout d’abord (firstly)
- premièrement (firstly)
- deuxièmement (secondly)
- ensuite (then)
- enfin (finally)
- finalement (finally)
- pour conclure (to conclude)
You can use these words when introducing a new idea to your dissertation or essay. These words will signal the readers that they are encountering a new part or thought of your writing process.
10. Writing a Dissertation in French
This is the form of writing you encounter in French higher education. It’s a very complex form of French writing, only the most advanced and fluent French learners should attempt it. It’s also a longer piece of academic writing. It may take you weeks to complete research and write your French dissertation.
The French dissertation is similar to essay structure. But, there’s one main difference: your thesis isn’t a statement, but rather a question. It’s your job in the dissertation to take the reader through your thought process and research to answer your question. This logic is known as “ Cartesian logic .” It comes from Descartes , who was a well known French philosopher.

History of Written French
French was used in Strasbourg Oaths, and it first appeared in writing in 842 AD. Before then, Latin was the only language used for literature in Europe. However, in the 10th and 11th centuries, French appeared in some religious writings and documents but was not used up to the late 12th century or early 13th century. The first greatest French Literature work, the Song of Roland (Chanson de Roland), was published around the year 1200.
Writing in French Alone Won’t Make You Fluent
You need to learn how to write in French to be proficient in the language. But, it won’t make you fluent. The only way to become fluent is to practice speaking French. While it’s crucial to develop every area of your French knowledge, if you want to be fluent in French, you need a reliable language learning method like OptiLingo.
OptiLingo is an app that gets you speaking, not typing a language. It gives you the most common French words and phrases, so you’re guaranteed to learn the most useful vocabulary. Don’t waste time trying to learn French you’ll never use. Complement your French writing practice with fun speaking exercises when you download OptiLingo !
Related posts

Everything About French Adjectives

You Guide to Direct Object Pronouns in French

French Food Culture and Dining Experience

French Accent Marks – Master Typing French Symbols
Many people believe they aren’t capable of learning a language. we believe that if you already know one language, there’s no reason you can’t learn another..
Polyglot Life
Become bilingual – Deviens bilingue
DELF writing exam: how to prepare (DELF, DALF, TEF, TCF)
Summary – French exams: what you are really tested on – How to write a French essay – Why it’s important to structure your texts and use logical connectors – How having structure lowers the stress level – Why work with a coach to prepare an exam – 4 typical outlines to write a French essay
The DELF writing exam and the oral presentation can seem like daunting tasks but with good preparation, you can succeed!
There’s one thing to keep in mind when you’re taking a French test like DELF, DALF, TCF or TEF . You’re evaluated both on the “mechanical” quality of your language (grammar, spelling, pronunciation) AND your ability to express your point of view . The following advice work both for the writing and oral tasks.
As you move further up the levels (B2, C1, C2), the language becomes a tool to express convincing thoughts . You need to showcase a wide range of vocabulary and grammatical structures. You also need to organise your production to showcase your analytical skills and your opinion.
This is “French culture 101”: the French have an opinion about everything and they looooove exchanging views and arguing. In the 17th century the French aristocracy popularized the concept of “ salons ” or discussion circles. There, aristocrats, poets and well-educated guests would gather to talk about anything (grammar, philosophy, current affairs, etc). It’s at that time that French became the language of choice of most European courts (including Russia).
French essays and exposes, like French conversations, are “something like an English garden. It’s highly cultivated to look and feel natural.” The Bonjour Effect, Julie Barlow – Jean-Benoît Nadeau (2016)
And that’s why you should know the rules of the “game” and practice, practice, practice before taking the DELF writing exam.
Watch the video or keep reading
How a French essay differs from an English essay
Many things have changed since then but the education system has perpetuated this tradition for reasoning . As early as middle school, French kids learn how to write formal essays with an introduction, a conclusion and well-organized paragraphs about just about anything (litterature, philosophy, history…). As you enter secondary and post-secondary schools, you’ve acquired the structure so well that, when facing a “ problématique ” (a complex question), you immediately start to envision a 2 or 3-parts essay (see at the end of this post for the detailed breakdown).
In a French essay, you’re supposed to pick a side and clearly state your personal answer to the problematique but not before you’ve examined the pros and cons and explained why we should value some aspects over others.
When I went to Ireland to study for a year, I had to “re-learn” how to write an essay. Over there, I was supposed to pick a side at the beginning and defend my choice. Two or three supporting arguments explained why why my choice was the best option. Although you include some cons or limitations, it wouldn’t take up as much space as in a French essay. It’s possible to use the same patterns to write essays in English and in French. However I think the most common patterns differ from one country to another. I’m not an expert in writing English essays so I could be mistaken…
The importance of signposting in your DELF writing exam
Once aspect that’s common to all good essays is the importance of structuring your thoughts .
The French essay will mix a lot of contradicting ideas and include nuances. In order not to lose your audience, you need to have a very clear structure. You need to take them by the hand at the beginning and constantly let them know where you are , how you got there and where you’re going next .
Think of this as driving… When you’re going from point A to point B , you use a map and sign posts . You also use your signals (turn, headlights, stop) to communicate your intentions to other drivers…
Well it’s exactly what you need to do to get a great score at your test . Be very clear about your map and constantly share your “directions” . That way the reader/audience can understand where you are and the logic of your thoughts.
“Articulateurs logiques”: logical connectors are essentials in your DELF writing exam
To signpost, you’ll need what we call “articulateurs logiques”. They can be adverbs, conjunctions, expressions… So, make sure you learn a few connecting words for each concept (opposition, concession, addition, sequencing…) so that you’re not always using the same ones.
The higher level the exam, the more variety you’ll need . Learn 2-3 connecting words for each concept at B1 level, 4-5 at B2 level . For C1 and C2 try to learn some fancy connectors you’ll only see in the newspapers. Make sure you work with your coach or a qualified tutor to understand all the nuances between these words. Linking words are not always interchangeable.
How signposting keeps the brain calm
Especially in the oral exam , this will have a beneficial effect both on your brain and on the examiner’s . On one hand, you’ll be calmer as you won’t get confused about what to say next. On the other hand, the examiners will follow your train of thoughts clearly. They will be more relaxed as they don’t need to figure out where the heck you’re going with this.
You will provide context and direction . Even though your sentences may not be 100% correct, it will be easier for them to understand . If they don’t, they may ask for clarification after so you’ll get a second chance to get it right.
In the writing exam, you won’t waste precious time while writing the essay. You’ll know what you want to say, your thoughts will flow faster.
And you’ll score points for your ability to organize your thoughts and be convincing. Honestly, these are easy extra points to get if you practice complying with the format .
An exam is already a stressful process. T he last thing you want is to go through it with your brain in “panic mode” .
You might also like to read this post: 3 ways to calm your brain
How to prepare for your French exam
Don’t think you can “wing it” on the day of the exam. It’s not something you can improvise on the day of the exam, you do need to practice .
Some strategies will help and make your training a lot more efficient in the long run.
The principles of the best strategies are:
- Acquire knowledge (read, listen…) about the most frequent exam topics
- Take notes and organize your knowledge into your brain: for example with mindmaps, flashcards, memory palace…
- Practice finding a “ problématique ” (a complex question) on a topic and brainstorm to draft an outline . You can invent one and/or use past exams samples .
If you do that, you’ll accumulate efficient hours of practice thinking about these topics and organizing your thoughts. You’ll already have arguments and examples, therefore you’ll feel more confident on the day of the exam.
Once that’s done, you can focus on the form and produce the best French you can.
A convincing expose or essay for a French proficiency test is roughly 1/3 knowledge, 1/3 methodology and 1/3 language skills* * grammar, vocabulary + enunciation if oral
The benefits of working with a Neurolanguage coach
We understand the necessity of keeping the brain calm and strive to remain in this state during the sessions . We provide tools for you to achieve this state when you study independantly and then when you’re taking the exam.
I find it can be useful to mix working with a tutor or teacher and with a language coach.
With the first one, learn specific aspects of the language, correct some exercises and get extra speaking practice.
When you meet with your coach , you can work on 3 aspects . First, you can fine tune your understanding of a concept. Neurolanguage coaches constantly focus on making grammar “digestible” for your brain. We have in-depth knowledge of the mechanics of the language. We will encourage you to create connections with concepts you already know. Then, we work on your fluency by practicing focused conversation. Finally we’ll draft up together a customized plan to improve.
Your coach will steer the conversation to practice what you need to and facilitate the creation of the connections in your brain . The end goal is that you learn how to think in French naturally.
Instead of lecturing about French essays, we’ll make sure you can embrace the exercise with your own style and your own words .
Types of French outlines (called plans )
Now that you know why it’s important, here are some concrete resources to help you. These are 3 examples of typical French essay or expose outlines.
PATTERN A: it unfolds like a Moliere play – Part 1: Exposition / Facts – Part 2: The action , what problems are we facing because of Part 1 facts – Part 3: The resolution
PATTERN B: everything in life is relative, a philosopher’s reflection – Part 1: “Yes/White” (thèse = thesis, which reflects the direction you’re leaning toward to answer the question) – Part 2: “No/Black” (antithèse = antithesis) – Part 3: “Yes but,/Grey” (synthèse = synthesis, from the arguments in part 1 and 2, find a middle ground or opening to an answer that’s neither of the extremes)
PATTERN C: “YES, BUT…” It’s also acceptable to do 2 parts only: – Part 1: 2 or 3 arguments in favour of your point of view (YES) – Part 2: Limitations of Part 1’s arguments (BUT, why it’s not ideal) Your conclusion would emphasize the upsides of your arguments and how we could overcome the limitations.
PATTERN D: Chronological – Part 1: Phase 1 or Before /The past – Part 2: Phase 2 or Now /The present – Part 3: Phase 3 or After /The future
Which outline should you choose for the DELF writing exam?
There is no “right” pattern, it will depend on what you have to say . The content needs to be divided into balanced parts .
- Pattern A is efficient because there’s tension , your audience wants to know the end of the play.
- On the other hand, pattern B might be the most difficult . You may end up not being convincing enough in conveying your opinion to your audience.
- Pattern C is maybe the most accessible if you’re used to writing English-style essays.
- Pattern D is a rather obvious choice when you’re dealing with a topic spread across a period of time with distinct phases. Make sure you include argumentation, not just facts !
Troubleshooting: If you’ve decided to do 3 parts but end up with 2 long ones and a short one, it means you should do 2 parts only or find more material for your 3rd part. If you were going for a 2-parts outline but have a lot of sub-parts (paragaphs within each section), you should probably divide them up in 3 parts. That’s why it’s important to think and plan before you start writing your DELF exam.
Keep in mind the word count range you’re allowed at the test you’re taking and practice the format.
Watch this video explaining the process leading to writing a good outline
About Cathy
Related post, gifts for learners of french who are afraid of speaking, best resources to immerse yourself in the french language, french conjugation rules: the big picture.
France in the United States
Embassy of France in Washington, D.C.

- Menu | Content | Site map

- Publications
- News From France
- NFF-2018-10
Essays à la française: la dissertation

Aside from classroom exercises and formal writing assignments, the dissertation is a major part of the BAC exam, which highschool students must pass to enter into university or secondary studies. Introduction Similar to a standard essay introduction, the introduction presents the subject or issue that is to be analyzed and evaluated. The introduction serves as a roadmap for the writer’s upcoming argument and the structure of the remainder of the dissertation.
Thesis Part of what is often referred to as “le développement”, the thesis section outlines the body of the argument chosen for the topic of the dissertation.
Antithesis Unlike the secondary support paragraph often found in an american essay, the anthesis section is dedicated to expressing the limits of one’s argument.
Conclusion Also referred to as the synthesis, provides a brief conclusion of the paper. The conclusion also invites one to go further and put forth questions that the reader can reflect on.
In addition to structural differences, the content of the dissertation can oftentimes be different to that of an american essay.
https://www.etudes-litteraires.com/bac-francais/technique-dissertation.php

French Embassy in the U.S.
TOP STORIES
- THE MOST READ

Support local French businesses!
The French and francophile community's spirit can move mountains! Find and support restaurants, bars, shops and other French businesses in your consular district and across the United States.
Select your consular district:
Atlanta • Chicago • Houston • Los Angeles • New York • San Francisco • Washington, D.C.

- Legal information
Useful Links
- gouvernement.fr
- diplomatie.gouv.fr
- Business France
- Delegation of the EU
- data.gouv.fr
Like puzzles? Check out this daily anagram game: Raganam !
- Your Favourite Cheat Sheets
- Your Messages
- Your Badges
- Your Friends
- Your Comments
- View Profile
- Edit Profile
- Change Password
- New Cheat Sheet
- Live Cheat Sheets
- Draft Cheat Sheets
- Collaborations
- Cheat Sheet Downloads
- Download This Cheat Sheet (PDF)
- Rating: ( )
- Education >
- French Cheat Sheets
Writing essays in French Cheat Sheet by JAM
Useful expressions to help structure your A level French essay.
Introducing the first argument
Adding and listing arguments
Listing arguments - start.
Listing arguments - middle
Listing arguments - end
Indicating the reason for something
Expressing contrast / concession
Introducing one's own point of view.
In conclusion
How's Your Readability?
Cheatography is sponsored by Readable.com . Check out Readable to make your content and copy more engaging and support Cheatography!
Measure Your Readability Now!
Help Us Go Positive!
We offset our carbon usage with Ecologi. Click the link below to help us!
- Languages: English français (French)
- Published: 21st September, 2013
- Last Updated: 26th February, 2020
- Rated: 5 out of 5 stars based on 9 ratings
Favourited By
these are very helpful thank you
Simple et utile, j'aime.
Add a Comment
Please enter your name.
Please enter your email address
Please enter your Comment.
Related Cheat Sheets
Latest Cheat Sheet
Random Cheat Sheet
About Cheatography
Behind the scenes.
Recent Cheat Sheet Activity

The Ultimate List of AP® French Language Tips
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022
If you’re like many foreign language students, the AP® French Language exam has been a worrisome figure on the horizon for quite some time. As you finally begin this AP® course and prepare for the exam next spring, remember that there are many different resources out there to help you along the way. This Ultimate List of the AP® French Language tips will give you a head start over all of the other French students preparing for the exam. Use this list, combined with some hard work and assistance from your AP® teacher, and you’ll ace this exam in no time.
So you want to pass the AP® French Language exam? Well here’s the breakdown. Every year:
– More than 20,000 students take the AP® French Language exam
– About 75% receive a score of 3 or higher
– Only about 38% receive a crucial score of a 4 or 5
– Only 12% score a 5, which can really blow away college admissions staff
Want to be in the top 10% of exam takers? Want to receive even more scholarship money and acceptance letters from top universities? Want to awe and impress your AP® teacher and fellow students? Follow this indispensable list for some tips that will set you on your way. Also, if you’re looking for the best AP® French Language review books, this resource may help .
How to Study for AP® French Language Tips
1. It’s simple – use French! Easier said than done. Unlike Spanish, French doesn’t have a huge presence in the U.S. today. There aren’t French news channels or (many) French radio stations. So how can you start using the language? We’ll offer several ideas in the tips below.
2. Find the culture in your every day . What do you think of when you think Francophone culture? Well, we think of food first and foremost! A fantastic way to incorporate more French into your daily routine – and learn some great new recipes – is to cook French food. Used bookstores typically have foreign language cookbooks on the cheap. Pick one up and highlight some recipes that you’d like to try out. They don’t have to be complicated for you to benefit from the language. Some of the best dishes are simple and require few ingredients – fondue au fromage , anyone?
3. Find a language buddy. This applies to all foreign language students: most high schools have foreign exchange students and teachers. Lucky for you, as a French language student, tons of countries have French as a national language – not just France! French is an official language in all of these places:
France, Canada: Quebec and Ontario, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Mali, Monaco, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Belgium, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Niger, Republic of the Congo, Madagascar, Haiti, Réunion, Martinique, Switzerland, and many more!
Use this to your advantage! Find a language buddy to practice your French. Often times, other students and exchange teachers are willing to do 15 minutes in French for 15 minutes of English practice with you!
4. Find a language exchange. These are more common than you think! Many French speakers in the U.S. are looking to improve their English and are beyond happy to participate in conversational language exchanges with native English speakers. Typically you spend 15-20 minutes speaking in one language and then switch to the other. Where can you find these exchanges? Check out the public library, civic center, or ask around at your school.
5. Get your vocabulary up to par! So you’ve reached AP® French Language. By this time in your foreign language career, you’ve most likely mastered the grammar of the language – at least in written form. You’ve seen all the verb tenses and know your irregular adjective conjugations. Still, you’ll be at a loss communicating in French if you don’t have an extensive vocabulary to express yourself. Get ready, here’s how to start expanding your vocabulary in French today.
6. A new word every day. The easiest way to start studying for AP® French is to introduce a new word into your French vocabulary every day. The Instagram account French Words has a new word (as well as its phonetic pronunciation and grammatical gender) every day! Flip calendars are also great for getting a new word every day. Then, try to use it during class.
7. Bring out your vocabulary cards. Or don’t! We recommend using vocabulary cards – they are a language learner’s best friend. Put a word in French on one side and a description of the word on the other side. Don’t like carrying around a ton of paper? There are so many apps available to make flashcards. Run through the words while you’re on the treadmill. Or every time commercials come on during your favorite show. Or every day before you begin French class to really get your mind churning.
Insider tip : There are good ways to make a vocab card and there are better ways. Which of these looks better for the word la craie ?

Yup, you guessed it – the one on the right. Why? Because you didn’t need to use English to get to the meaning of the word. This will make you a faster speaker and writer in French. You also included all the relevant information such as the article and the word’s pronunciation.
8. Keep track of unknown words. Successful language learners swear by this technique. Keep a small notepad with you throughout the day. Then, every time you hear or see a word that you don’t know, write it down. Even if you don’t get the spelling right, jotting down these unknown words and looking them up later is one of the best techniques for acquiring new vocabulary items. Why? Because there are so many words that you encounter that you don’t know, even in your AP® class, that you cannot possibly keep track of them all. Write them down. Look them up. Repeat.
9. But don’t forget the important parts. Learning vocabulary is nothing if you don’t know how to use it. This means learning:
1) The pronunciation
How do you say it?
2) If it’s a noun, gender of the word
Is it le or la?
3) If it’s a verb, the conjugation
Is it a regular or irregular verb?
4) Put it in context
How do you use the word in a sentence ?
10. Whip out old practice exams. Reviewing old AP® exams is a technique known to help students prepare for the test. Year after year, AP® teachers say the one thing that sets apart those students who pass from those who don’t, was who completed the practice exams in class. Start getting yourself ready now by reviewing the old exams that your teacher may have available for you.
Insider tip: Know the structure of the exam
There are three main components to the AP® French Language exam: multiple choice, speaking, and writing. In order of appearance on the test they are:
multiple choice
interpersonal writing (e-mail)
presentational writing (persuasive essay)
interpersonal speaking(conversation)
presentational speaking (cultural comparison)
Don’t forget some of the AP® exam basics. Once you complete one section, you can’t go back and change your answers. Instead, simply move on and focus on the section at hand. You also can’t work ahead on the exam. So even if you’re especially nervous for the speaking section, don’t be. There’s nothing you can do during the multiple choice section to ready yourself for it so breathe and focus on the questions in front of you. In a way, it’s relieving. You can’t work ahead anyways, so don’t be anxious about the upcoming sections.
11. Get together to study . Studying can become very tedious. And most AP® French Language students aren’t taking just one AP® test – they’re taking 3, 4, or 5. To get over the boredom of studying alone, form a group that meets once or twice a week. This is a great way to socialize while reviewing but also get fresh ideas and insights on the course material. Split up the culture section and have one person report a new country for every meeting. Already sounds better than reviewing alone, doesn’t it?
12. Look up the guidelines . We’ve talked about a couple other online resources but one you should be especially familiar with is the CollegeBoard itself. The scoring guidelines that AP® French Language exam graders have right in front of them as they grade exams are available on this site. Curious about what graders are looking for? The CollegeBoard is very open with this, so take advantage of it.
13. Incorporate the language into your everyday routine . There are so many ways to incorporate French into your daily life – you’re probably not even thinking of them! Change your social media accounts like Facebook and Twitter to French – even your ads will start to appear in French. Set your browser homepage to Le Monde or Le Journal de Québec and read a news article every morning. Set your cell phone to French to learn new vocabulary. French will be all around you in no time.
14. Utilize your best resource: your teacher . You probably don’t know anyone who is a better resource for you when taking the AP® French Language exam than your AP® French teacher. He/she has seen hundreds of students take the exam and knows what has worked and what hasn’t. This is even more relevant if they are one of the teachers who grades the AP® exam in the summertime. So ask your teacher questions. Be an active learner in class. Learn from previous students’ mistakes. Your teacher will be more than happy to help you in your preparation for the test.
Start your AP® French Language Prep today
Ap® french language multiple choice tips.
1. Ignore instructions. This goes along with practicing for the test like we mentioned earlier. By the time you get to test day, you should be so comfortable with the material and overall structure of the test that you don’t need to read the instructions. While other students waste precious minutes reviewing the directions, you can skip ahead and get cracking on the hefty number of multiple-choice questions you have coming your way.
2. Answer every single question. Remember on the ACT® and SAT® when your teacher constantly stressed not answering questions you didn’t know? You were punished for incorrect answers. Well, not on the AP® French Language exam! In fact, the grading machines just ignore incorrect answers. Can’t figure out a question? Running out of time? Mark an answer anyways – it might be correct.
3. Calculate your time . How many questions do you have on the multiple choice section? 65. How many minutes are you allotted? 95. That means about a minute and half for every question. Don’t go beyond that, even if a question is tripping you up. Mark something down as an answer. Then, circle the question to come back to it later if you have time.
4. Move on from words you don’t know . You will inevitably encounter words that you don’t know in the multiple-choice section. Don’t stress about this or convince yourself that you weren’t sufficiently prepared. Instead, skim past those words and focus on those that you do know. You will be able to figure out the question despite not knowing a word or two. Even looking at the answers can sometimes help. So don’t stress when approached with an unfamiliar word.
5. Read the entire question . AP® tests are notorious for their tough multiple-choice sections. And the College Board thinks they can trip you up by giving a lot of background information and not stating the actual objective until the end of the question. So be one step ahead. Read the entire question, all the way through. Then, select an answer. They anticipate many students not reading the entire question and give wrong answers that correspond appropriately so don’t fall into this trap.
AP® French Language Free Response Tips
1. Sound natural and conversational. This isn’t always so easy for someone who speaks French as a second language. But listening to French radio (try RadioFrance ) or watching television shows ( Fais pas çi, fais pas ça is available on French Netflix and is very popular) can really help you with these elements of your language. What do you hear when you listen to native speakers? Lots of uh , and bon , right? Good. Use this to your advantage. Dot your speech with these native-sounding interjections and give yourself more time to think of the right words.
2. Slow down . For many students, the free response section of the AP® French Language exam is the most anxiety inducing of the test. As a result, too many students speak quickly, stumble over their words, or provide an incoherent argument. Don’t let this be you! Firstly, speak slowly. You have so much time – two whole minutes for the cultural comparison. There is no need to rush through your words. In fact, you’ll make more mistakes and will be less likely to find the words you’re looking if you speak too quickly.
3. Use your transition words . This actually also applies for the written portion. But, French is known to differ a lot stylistically between its written and spoken forms, so we’ll mention it here. There are lots of colloquial words that are used in spoken French to change topic or connect your thoughts. Here are some of them:
Je veux dire…
Comme je disais avant…
Par contre…
D’autre part…
Par exemple…
En même temps…
Insider tip : Sounding native
Par contre and en revanche are often cited in dictionaries as being synonyms in French. And to a certain extent, they are. However, they differ in their context of usage. Whereas you would rarely hear someone say en revanche out loud, you hardly even see par contre written in formal, academic prose. Know when to use which term for your transitions.
4. Use the correct pronouns . You know the difference between vous and tu – or do you? Vous is used for formal contexts, when you’re speaking with a teacher or addressing a grader as you record yourself in the speaking section of the test. Tu , however, is used when speaking with classmates or people you have known for a while. Vous is also used when addressing multiple people. Be very mindful of this distinction when speaking. Register is one thing that AP® graders look for since it’s mentioned explicitly on the scoring guidelines . So you know it’s very important.
5. Try recording yourself and classmates . Still worried about the speaking section of the AP® French Language exam? Not to worry, most students are nervous for this part. An excellent way to prepare is by recording yourself and others. Then, play back what you said. Do you sound rushed? How is your /R/ pronunciation (that guttural sound)? Be sure to get classmates’ help with this. They’d love to exchange tips on this tough section of the test.
AP® French Language Essay Tips & Advice
1. Penmanship matters, so use your best. Maybe it should, maybe it shouldn’t, but penmanship matters. And don’t you want your AP® French Language exam grader to be in a good mood when they’re scoring your exam? Make reading essays simpler for your grader by writing very clearly and unambiguously on the test. Take your time. As we’ll point out below, it isn’t the length of the essay that matters, but the content.
2. No need to fill all the pages! You are given so many pages in the essay booklet on the AP® French Language exam. This is actually an unfortunate part of the test and one that many students fall victim to. Remember: you don’t need to use all the pages! They are there for students who write larger or who made a large mistake and need to start over. Instead, stick to three, maximum four, pages on the presentational writing section. Graders read the essays quickly. And the questions are geared towards shorter essays, not longer. Less is more! (And you have less opportunity to make mistakes.)
Insider tip : French and its punctuation
Did you know that French uses different punctuation than English? Have you ever noticed, for example, that your teacher writes grades not as 92.3% but rather 92,3? Have you ever seen that question marks and exclamation points in French stories always come after a space? Check out the sentence below for some of the common punctuation differences between French and English:
– Le prof t’a donné quelle note sur le partiel ?
– J’ai reçu 13,3 sur 20. Et toi ?
– Moi, j’ai reçu 12,4. Il m’a commenté, « analyse pas suffisante ». Ca veut dire quoi, ça ?
What’s different in the phrases above?
1) space between question mark and end of sentence: partiel?
2) « » Arrows for quotes instead of English high quotes “ ”
3) No accents necessary on uppercase letters, only lowercase: Ca but ça
4) Comma instead of decimal point and vice versa: 1.000.000 instead of 1,000,000 for one million
Does this matter? Absolutely! Impress AP® French Language readers with the depth of your knowledge and detail in French writing. Get all the points that you can!
3. Have an outline and a thesis – before beginning . Before you ever flip the page from the sources to the actual essay, you should have an outline and thesis written. ‘Why?’ you ask. ‘It’s in my mind.’ Not good enough. Stakes are too high and the essay writing time passes by too fast. You must know what you’re writing about from the beginning or you risk wasting precious writing time. By writing down a thesis and having an idea of your structure, you’ll have something to refer back to you if you get lost in the prose of your essay.
4. Use ink on the essays . Pencil is great for writing notes and that all-important outline that we’ve already talked about. But when it comes to the essay itself, stick to ink. Why? Because pencil smudges easily and could render parts of your essay unreadable to the grader – yikes! Also, it simply isn’t as clear as blue or black ink. So stick to pens for the essay itself. Unsure of an idea while you’re writing? Write in pencil first. Then, go back over it in pen once you’ve finished.
5. Proofread. You must, must, must proofread your essay. Even if you’re on the last paragraph and you only have three minutes left, take the time to proofread. You would be amazed how many errors you can make while you’re writing and thinking quickly. When you first construct your essay, you’re likely to be so involved in the material itself and incorporating your sources (we’ll get to those below) that you forget about all-important accents or a consistent verb tense throughout. Proofreading will catch most of those errors. Keep an eye out for the following while you do one last read-through:
1) No passive voice – when in doubt, use on :
This: On peut voir dans la ligne deux que … Not this: La ligne deux est vue par le lecteur comme…
2) A consistent verb tense throughout – don’t switch between past and present
3) Watch out for accents.
There’s a big difference between accent aigu ´ and accent grave ` so don’t get sloppy.
4) Don’t forget subjunctive.
Did the subject change within the clause? Are you expressing doubt or uncertainty? You probably need subjunctive.
6. Use the sources. Hopefully you know this one already! The sources provided for the persuasive essay are not just there for your amusement – you must incorporate them into your essay. In fact, graders are looking to make sure that you include not just one or two of the sources – but all of them. So read the sources carefully and think about how you will incorporate them into the outline before you even begin writing – that way you won’t forget to include one.
7. Weave the sources into the essay . Speaking of sources, if graders are looking to see if you included all three sources – don’t you want to make it very obvious to them that you did? So go ahead and use direct citations from the sources (with quotes and a citation marker). This is better than simply summing up information from the sources because 1) the graders will spot that you used a source right away and 2) you’re less likely to get the information from the sources wrong – a very common mistake that test takers make!
Tips by AP® French Language Teachers
Did you know that teachers grade the AP® French Language exams? And not just any teachers – your teachers. That’s right. Every summer, hundreds of AP® French Language teachers and university professors who teach equivalent courses get together to grade the writing and speaking components of the exam. So who do you think knows best what graders are and aren’t looking for? Teachers themselves, of course!
1. Write neatly. This teacher reinforces one of our writing tips mentioned above! “Just write clearly. We can always tell when you don’t know how to spell a word and you try to fudge your way out of it but writing illegibly. You’d be surprised how few points students lose for orthographic errors so write clearly. If you make a couple of minor mistakes, you won’t lose points for it.”
2. Do full practice exams. On the subject of practice exams , which we have also encouraged, this teacher says, “Unfortunately, we do not have enough time in class to do a full exam run-through of multiple choice, speaking, and writing. Great students will take the initiative and do this on their own or in groups. This is a long exam. It takes stamina. The only way to build that up is to do full run-throughs of the exam. All sections in one sitting – just as it will be on the day of the test.”
3. Re-energizing during the exam . It’s a long exam. How can you prepare yourself to make it all the way through until the writing section? This teacher has some tips: “I hate how the writing comes at the end! I think it’s the hardest part of the exam and takes the most energy out of my students. So I tell them, in addition to eating a large breakfast or lunch on the day of the AP® French Language exam, bring a snack or two with you! Every year my students come back saying how happy they were that I recommended this. The exam will take a lot out of you – get some energy back in return!”
4. Must use sources! Didn’t we tell you that incorporating your sources was important? Here it is again: “Please, please, please use all of your sources! Every year when I’m grading the AP® French Language exams, I feel terrible that I have to dock students points because they forgot a source or forgot to incorporate sources altogether!” How can you remember to do this? Write the sources into your outline from the very beginning. That way, you won’t forget to include them.
Insider tip : What if I forget a source?
Every year, so many students forget a source that the CollegeBoard finally decided that students can still receive a score of a 4 or 5 even without mentioning one of the sources. But the essay has to be exceptionally good to still receive such a high score. So rather than take the chance, follow the directions and use your sources.
5. Be a consistent studier. Studying for the AP® exam doesn’t just happen the few weeks before exam day in May. In fact, many AP® French Language teachers say the best study habits are established from the first week of class. “I try to encourage my students to form study groups outside of class and good learning habits such as learning new vocabulary and exposing themselves to different dialects of French. They should be doing this really from the start of their first semester in AP® French. This is the highest level of French taught at our school and offers them the invaluable opportunity to gain college credit. So students should treat the course as they would a college-level class.”
6. Master the present, including the subjunctive, the past and the future tenses! Thanks for the tip from Debbie M.
7. Challenge yourself daily to do more than you could yesterday. Listen to challenging French news broadcasts. If you don’t understand the background of the topics being discussed, do some further research online. You will enhance your knowledge of current events–a key element of success on the exam–very quickly this way. Thanks for the tip from Stephen O. at West Lafayette Jr./Sr. High.
8. Practice dictation regularly –It may seem old fashioned, but dictation (la dictée) is a great way to hone spelling and grammar and to increase vocabulary. Find a 30-second snip-it online and write out everything you hear. Ask a teacher or native to check it for you. Thanks for the tip from Stephen O. at West Lafayette Jr./Sr. High.
9. Expose yourself to French every day. An easy way to get in 15 minutes is by either listening to the French news (Journal Télévisé) on TF1.fr while getting ready for school in the morning or while getting ready for bed at night. Thanks for the tip from Kerry G. at Greenwich High School.
10. During my study abroad in college, I would listen to the French radio news every morning with my host family or alone. It helped me get used to the pacing of real French while, at the same time, having a general idea of the topic before the report started. Thanks for the tip from Kerry G. at Greenwich High School.
11. I tell my students to watch a French video clip (news or otherwise) daily to get used to hearing different accents and to get their ears used to hearing spoken French. Thanks for the tip from Linda W. at Haddon Township.
12. DON’T PANIC … Breathe and think, what did we talk about. Thanks for the submission by Timothy K. from Apex High.
13. Help the Reader: Assume the reader is tired….it is the end of the day…they have been grading since 8:00am….Help the reader find the answer. Thanks for the submission by Timothy K. from Apex High.
Label your sections
Underline important terms and key parts of your answer
–i.e. if it asks for the definition of nation, underline the word nation…
14. Do Not Dump: You should try to avoid writing “dump” essays where you “dump” or empty your brain of everything you can think of onto the paper. Thanks for the submission by Timothy K. from Apex High.
15. Outline : OUTLINING the questions will help you tremendously! As soon as you get the CRQ’s, spend a couple of minutes outlining the main points for your answer right on the question sheet. This way, when you go to write your full response, you will have a baseline of information and important points to send you on your way. Those who have done this in the past have told me it has really helped them be successful on the exam. Thanks for the submission by Timothy K. from Apex High.
16. Pick On The Weaker Ones First: Answer the question you think is the easiest first; then go onto the next easiest, etc… This way, you leave the hardest one for the end when you have more time to answer. Thanks for the submission by Timothy K. from Apex High.
17. Take your flashcards to another level: When your writing out your flashcards/vocabulary make sure you are not just writing it in your own words… but be able to connect the term/concept to another term/concept. This way when your writing your FRQ you will be able to show the reader that you not only know the information, but can critically connect the material to other units/topics. Thanks for the submission by Timothy K. from Apex High.
18. AP® French Language is vocabulary driven. Study your list of vocabulary terms listed on the CollegeBoard site labeled Martha Sharma’s vocabulary terms. I have my own version as well. Let me know if you want me to send them. Thanks for the tip from David E.
19. READ as many multiple sources as possible to prepare. Thanks for the tip from Anne C.
20. If students make a point to Listen to 10 min of French everyday in the form of news or podcasts – they can make great strides in their listening comprehension which is the most difficult part. Thanks for the tip from Harpreet M.
21. Trouvez un roman qui vous intéresse et lisez-le chaque jour hors de la classe. Thanks for the tip from Rachel D.
22. Try to listen to as much French programming as possible. And talk back to the audio, just to break through the speaking barrier; no one can hear you but you, it will loosen you up! Thanks for the tip from Madame Jean M.
23. To build a good ear for the language, read a script first. Use the CD to listen to what you just read; multiple times. Try to understand it. Then check the script again. Thanks for the tip from Angela W.
24. Listen to AS MUCH FRENCH as possible from authentic sources : videos, vimeos, movies, film trailers, especially clips of films or shows you are already familiar with. Use material which is updated and meaningful to students to keep their interest! Thanks for the tip from Jennifer B.
25. Know real world examples of Vocabulary . Example: What does gerrymandering look like? Thanks for the tip from Sharon R.
26. Read every day about lots of different topics from sources all over the world. News articles, blogs, anything! Thanks for the tip from Danelle C.
Are you a teacher or student? Do you have an awesome tip? Let us know!
Just how tough is the AP® French Language exam? Well we said before that more than 75% of students score a 3 or higher – so this exam is definitely beatable! And this list of the Ultimate Tips will get you started in your preparation for the exam. Here are some of the key points summed up again:
– Start reviewing now – old tests, new vocabulary words, study groups
– Find a language exchange to buff up speaking skills
– On test day, establish an outline and thesis before even approaching your essay
– You can’t work ahead – focus on what’s at hand during the test
– Proofread all written material
But remember that our list of the Ultimate Tips is by no means the last stop on your journey to a great score on this AP® test. Go ahead and check out other sources such as (insert other articles on AP® French prep here) to get even more insider tips and advice from previous test takers and AP® French Language teachers. With these resources in hand, there’s no way you can’t succeed!
– These stats concern “typical” French language learners – those who have not spent considerable time in a country of the target language or do not speak French in the home.
Looking for AP® French Language practice?
Kickstart your AP® French Language prep with Albert. Start your AP® exam prep today .
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
Le petit juriste Site de la revue d'actualité juridique

Basic Guidelines for Essay Writing
c.anno 4 août 2014 English law , English law
The ability to write well is the cornerstone of one’s legal studies. Being able to express yourself coherently and eloquently whilst analysing a complex point of law is not an easy task but, it can nonetheless be mastered when the right technique is adopted. A logical and well-supported essay is pivotal in order to attain good marks. Indubitably, the French méthodologie en deux partie s is a stark contrast to what the English have in mind when writing a legal essay. The essay in the latter case is assessed on comprehension, critical analysis, structure and presentation . The extent to which each of these components is attained will denote the mark boundary the essay will fall in.
What is expected of you?
Planning the essay:
An essay without a plan is bound to lead to low marks. It is axiomatic to formulate a plan on paper. The reason for this is to first understand what the essay question requires you to do. Breaking the question apart and planning your argument will lead to a more solid approach. The plan could take the form of a mind-map or bullet points in order to facilitate the thought process. When planning the essay it is imperative to look at sources such as Acts of Parliament [1] , Law Reports [2] , journal articles [3] and books . For an adequate analysis, in-depth reading is thus a prerequisite.
Writing the essay:
It is goes without saying that no informal language should be used; instead, technical terminology must be adopted at all times. However, be careful not to use any words you are not too familiar with as this may have the opposite effect. Sometimes simple and clear is best! Every sentence in the essay needs to be relevant and coherent in order to reflect a cohesive and well-represented argument. Each paragraph should lead on to the next and form clear logical steps. It may sometimes be easier to use subheadings to separate large themes or topics in your essay. The paragraphs should be lead by an argument and thus reflect the classic tripartite structure: Introduction , Main Body and Conclusion. A good introduction is fundamental since it will engage the reader and provide them with a brief insight of what the main body of the essay (the bulk of the essay) comprises of. Unlike in France where the conclusion is nonexistent, in England it is a very important element of the essay. Some find it easier to begin by writing the conclusion since it sets a clear response to the question. Furthermore, you must not keep your conclusion for the end in an attempt to surprise the reader; paradoxically, your conclusion must be stated in the beginning. Your essay must be therefore summed up in the introduction. You should be able to read the introduction and immediately know your line of argument; the introduction needs to be a roadmap of the essay . Whilst this may seem like a Herculean task it is nonetheless easier to achieve than it may seem.
When writing the essay, in order to perfect it, one must draft, redraft and redraft again.
Citations in the essay:
Referencing your essays correctly is vital. If you do not cite sources properly then this may be regarded as plagiarism. You must not plagiarise! Law Schools take this matter very seriously since plagiarism is considered to be cheating. All assessed work is checked electronically against sources on the internet including “subscription” based sites which promise to write your essays for you! Referencing is not troublesome when following the Oxford Standard Citation of Legal Authorities (OSCOLA) [4] . This permits you to ensure that everything is cited properly and formatted correctly. OSCOLA is also very helpful with regards to preparing the bibliography. You must continually update the bibliography and not neglect it.
In conclusion, it is evident that the more essays you write and the more feedback you will receive, you will consequently feel more comfortable in your writing skills. However, always remember, as Voltaire says: « Rien ne se fait sans un peu d’enthousiasme »!
Christina AVGOUSTI
Further Reading:
-Finch & Fafinski, Legal Skills , 4e
-Oxford Standard Citation of Legal Authorities (Fourth Edition) <http://www.law.ox.ac.uk/published/OSCOLA_4th_edn.pdf>
[1] <http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga>
[2] Can be accessed on LexisNexis or Westlaw
[4] http://www.law.ox.ac.uk/published/OSCOLA_4th_edn.pdf
Related Articles

An exclusive interview with Lady Hale about British constitutionalism and the role of the Supreme Court
5 juillet 2016

La modernisation de la Chambre des Lords
30 mai 2016

Erin Andrew’s win for women’s rights in the United States
Laisser un commentaire annuler la réponse.
Votre adresse e-mail ne sera pas publiée. Les champs obligatoires sont indiqués avec *
Commentaire *
Ce site utilise Akismet pour réduire les indésirables. En savoir plus sur comment les données de vos commentaires sont utilisées .
French Essay: Topics, Tips, and Examples [2024 Updated]
Nowadays, knowing several foreign languages is no longer surprising. For example, learning French is common for English-speaking countries. So, getting an assignment on this subject won’t be a surprise for a student.
Writing a French essay, you can dwell into:
- the history of the French language;
- various dialects;
- its grammatical features;
- similarities between French and English (or another language);
- the distribution of the language around the globe.
One studying the language may penetrate the rich French culture and comprehend the nation itself. Besides, writing a French essay can develop the author’s writing skills and broaden their outlook. And even if you make mistakes doing so, it’s not the end of the world. The fact that you’re able to recognize them is already good enough, and you can fix complex errors using a free essay rewriter .
Our writers prepared French essay topics and tips for you to nail your task. See the examples below for better understanding.
📯 French Essay Topics
Are you one of those who are assigned to write French essays? Then we suggest you pick out some of the following problems to investigate:
- History of the French language;
- Dialects of the French language;
- French phonology ;
- French orthography;
- French grammar ;
- French alphabet.
The suggested topics are too vague and need narrowing. You may single out some aspects and analyze it in your paper. An excellent French essay topic should be:
- Broad for you to have enough room to develop your arguments;
- Narrow enough for you to be able to concentrate on one or several points;
- It should also be creative and original. You want people to enjoy reading it, right?
- Most importantly, the topic should be interesting for you.
If the essay topics seem too formal to you, study, for example, your progress in analyzing the French language. Alternatively, you can state what attracts you in the language and explain why. You may also do a comparative analysis of French and some other languages. Comparing French with English may turn out to be a fascinating task to cope with. Both languages will benefit from your French essay writing.
Here are some topics and French essay examples you can consider writing about:
- Your progress in learning the French language . Here you can write about your personal experience learning the French language. What techniques do you apply, and what motivates you personally? You can explain why you have to learn how to speak French.
- How are the French language and culture in Southern France different from Parisian? In this essay, you can compare the Southern French dialect and culture with the one in Paris. What are some of the critical phonetic, grammar, and linguistic characteristics of Southern French?
- Parisian dialect as a standard of French. When people think about the French language, the Parisian variant immediately comes to mind. In this essay, you can analyze why Parisian French became the standard version.
- Why do you enjoy learning French? This essay focuses on your personal preferences and likes in the process of learning.
- What makes it fun and enjoyable? Is it French movies, French literature, or understanding French written work documents?
- French influence on English . Although English is a Germanic language, it looks and sounds a lot like French. The influence which French had on English is significant. Look at some historical reasons (the Norman invasion in particular) and why English benefited from it.
- French language in 19th century Russia. Not everyone knows that French was the official language of the Russian elite in the 19th century. Discuss the reasons why and what influence French culture had on Russian literature, music, and language.
- The effect of the French language on the development of English writing . More than 10,000 French words came into the English language. Not only did the vocabulary of English get more prosperous, but the French way of spelling and letter convention influenced English orthography.
- What caused French to become an aristocratic language in Europe? The reasons why the French language became so dominant throughout Europe are broad. In this essay, you can focus on economic grounds, cultural or political reasons.
- An analysis of Canadian French. This essay can be a comparative analysis of Canadian and European French. What are the main differences? What are some similarities between the two variants?
- Is there any similarity between French and German ? All of the languages in the Indo-European language family have some similarities. Therefore, French and German are not exceptions. You can focus on sentence structure, word order, pronunciation, or phonetics.
- The popular strategies in English-French translation .
- Describe the challenges of French language acquisition.
- Analyze the peculiarities of French vowel pronunciation.
- Cultural events and their traditions in French-speaking countries .
- Discuss the advantages of learning French .
- Examine the semantic peculiarities of the French language.
- Explore the role of watching movies in the French language learning process.
- Comparison of language education theories.
- Analyze the impact of French language learning on your personality.
- Describe the methods you’ve used to improve your French language fluency and which turned out to be the most effective.
- Similarities and differences between realism and naturalism in Spanish and French literature .
- What is the role of the French language in the modern world?
- Advantages and disadvantages of knowledge of multiple languages .
- Discuss the role of the French language in the United States.
- The specifics of learning French in early childhood.
- Compare the grammar peculiarities of English and French languages.
- How is the concept of friendship interpreted in American and French cultures?
- Analyze the correlation between the history of France and French language development.
- Explore the origin of the French language.
- Verbal and non-verbal communication in French culture.
- Examine the crucial role of French literature in learning French.
- Describe the relationship between French culture and language.
- Is it a good idea to integrate bilingual programs in early childhood education?
- Discuss the best ways to prepare for the speaking exam in French.
- The role of audiovisual materials in learning French.
- What difficulties did you face when learning to write in French?
- The essential role of sociocultural context when translating from French.
- Compare the customs of French, Chinese, and Hispanic cultures.
- The best methods of learning the second language .
- Describe the best ways of promoting language development for French language learners.
- Analyze the methods of French word formation .
- Would you like to become a French language teacher?
- Analysis of the food words in English and other European languages.
- Examine the specifics of the French language in former French colonies .
Do not treat your French essay as an ordinary task to undertake. Make it as creative as possible!
🖋️ How to Write a French Essay
Note that writing on some language problems requires more than your knowledge of the subject matter. It also tests your abilities to present them in terms of academic writing.
Special care should be taken concerning the following:
- The structural organization of your French essay.
Mostly, it is similar to any other academic essay :
- It should start with a hook . In simple terms, it is the opening sentence or two of your writing. It can be a quote, a short story, or a catchy statement that grabs the reader’s attention.
Here’s an example of from the sample essay:
Every language is a mirror of society, a living organism that exists and changes under the influence of historical, political, and social conditions.
- The next part of your essay is a thesis statement . Typically, it should be placed at the end of the first paragraph. The thesis statement’s purpose is to state the central idea in one or two phrases.
Here is a thesis statement from our French essay example:
Today, it is common to study English as a foreign language, as an international means of communication. However, this does not diminish the importance of learning other foreign language like French.
- After that, the body of the essay should start. This part of the composition usually has three separate paragraphs. These paragraphs can include research, supporting evidence, and arguments that prove the point of view.
- The conclusion brings together all the points of the essay. It goes back to the thesis statement and explains the broader importance of the topic. It is the last chance to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Here is an example form our French essay sample:
To conclude, the above discussion provides evidence and arguments that maintain the position according to which learning French is a necessity nowadays. The crucial points are as follows; first, French has a long tradition of international language; second, French is spoken around the globe; third, it is a language of international relationships. The opposing position that English is sufficient for appropriate global communication was claimed unreasonable – an emphasis in this regard was on the essence of cultural and language diversity.
- The logical organization of your French essay .
There are some ways in which you can coherently write your essay. The following three aspects can guide you when organizing your French essay:
- Topic sentence : you should mind linking elements within the paragraphs and between them. First of all, each section should include a topic sentence. It aims to identify the central idea and express an overall direction in which the writer will develop the paragraph.
The demand for knowledge of a language has changed in recent years.
- Concluding sentence: each paragraph should also include a concluding sentence. It asserts the main idea of the section and sums up all the information said in it.
It may be claimed that in a period of rather an aggressive introduction of the Anglo-American language in the world, the French need to persistently and resolutely defend their language, their national interests, and calls on other nations to preserve linguistic diversity.
- Linking words: it is crucial to use linking words in your essay. Linking words show relationships between ideas. It can be used to build sentences together to develop a cohesive paragraph.
To see the full essay sample, check the link below:
- Grammar, spelling, and vocabulary.
The last step in writing an A+ French essay is proofreading and editing. Before submitting your academic paper, make sure to pay attention to grammar, spelling, and vocabulary mistakes . Without proofreading, your writing can contain typos and errors that will not leave a good impression.
Good luck with your French essay writing! We hope the article was helpful. If so, share it with your peers and leave a comment below to let us know what you think.
This might be interesting for you:
- How to Write an Expository Essay in Simple Steps
- Nursing Reflective Essay Example and Guidelines for Students
- Essay on Dengue Fever: How to Write + Free Examples
- Objective Essay Writing: How to Write, Topics and Examples
- Organizing an Essay: Jerry Plotnick, College Writing Centre, University of Toronto
- Organizing an Essay: Study Guide Zone
- Paragraphs & Topic Sentences: Writing Guides, Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University Bloomington
- Thesis Generator: Ashford Writing Center
- Proofreading: The Writing Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Basic Essay and Paragraph Format: Utah Valley University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Dissertation critique writing develops the students’ critical and logical thinking abilities. When composing, the students learn to analyze the works conducted by other researchers. To critique a dissertation, you should: In this article, we will discuss the aspects of the dissertation critique writing in detail. Our experts gathered essential tips...

An opinion essay is a formal piece of writing which presents the author’s point of view on a particular subject supported by reasoning and examples. The opposing viewpoint is also suggested, but it is followed by arguments that show its inconsistency. Take a look at the guide prepared by Custom-writing experts to...

So, you need to accomplish your discursive essay writing. The typical questions most students ask are: How do you write it? What is discursive essay? A discursive essay is an academic paper that involves a discussion on a particular topic. It is usually assigned to college students. You may be...

How to write a narrative essay? To do that, you need to know what a narrative essay is. It is an academic text usually written as a story and containing all the usual elements of a story. Narrative essays are often personal, experiential, and creative. Still, they should be made...
![french essay style Americanism Essay: Examples, Tips & Topics [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/american-flag-284x153.jpg)
It’s not hard to see why Americanism is one of the most popular essay topics. The concept of Americanism is in the center of the US identity. Writing an essay about it is an excellent way to find out more about this great country.

An art critique paper involves a comprehensive analysis and assessment of an artwork. Though this looks a bit complicated, the task doesn’t require a lot of time if you have sufficient critique writing skills. It’s an interesting assignment for students of art colleges as well as high schoolers. All you...

An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university,...

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

When you hear the phrase “spiritual leadership,” you probably think it’s only associated with religion. But did you know that this form of leadership can also be found in business? The book Spiritual Leadership: Moving People on to God’s Agenda by Henry and Richard Blackaby is a good starting point...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

“If a tree falls in the forest, does it make a sound?” is one of the most debatable philosophical questions regarding observation and perception. Many tried to answer it, including the English philosopher John Locke. Do you need to explore Locke’s perspective on this question in your essay? You are on the right...

The long-standing debate surrounding abortion has many opponents and advocates. Groups known as Pro-Choice and Pro-Life argue which approach is better, with no easy solution in sight. This ethical complexity is what makes abortion a popular topic for argumentative writing. As a student, you need to tackle it appropriately. If...
It is not helpful to me.
Thanks for the help with out this i wouldn’t even know what to do on my essay
Hi, do you also do French powerpoint presentation?
Good advice. Thanks.
This was a very great help. I’m writing a French essay, and I know, thanks to your post and the provided tips on French essay writing, I will pass!
Hi! I just want to thank you for your ideas and tips for writing French essays! Write a French paper in English or write an essay for the French by an American) Funny.
Thanks a lot for the help.

No problem, Sash:) Good luck!
The Dissertation: Writing in French
Dissertation is a very specific way to write what we call a “paper.” In France, this style is used in academics and the professional world alike.
The Necessities
- Personal reaction: Be sincere, though not informal.
- Use examples to affirm your point. Using examples limits verbiage, generalities, and banalities.
- Be clear and coherent : A good paper should resemble a mathematical proof more than a lyrical flood of words. Be understandable and operate by the Law of Occam’s Razor (the simplest explanation tends to be the best one.)
- Outline : Getting your ideas on paper is harder than coming up with them in the first place. In order to convey your ideas effectively to the reader, outline!
The Schema of a Dissertation
In order to write a dissertation, you need a problem or problématique. Situate that problem within your topic or subject. Do not begin to write without these ideas in mind.
Introduction
- The introduction must rapidly situate and introduce the problem. Cite briefly.
- Give an idea of the movement of the paper, but do not announce each step of your work.
- Define key words.
- Attract the reader!
The Body
Separated into parts and paragraphs, where each part is a main point in the problem and each paragraph is one idea or one aspect of an idea.
- Thesis – often the predominant point of view (the most common analysis)
- Synthesis: Establish some nuanced truth in between the two arguments or overcome of the initial contradiction by bringing in additional information.
- “Problem-Cause-Solution” Plan: Introduce and define a problem, pinpoint its causes, and propose a solution.
- Separate your argument into parts (in this case, two: benefits and pleasures)
- Order your arguments within each part
- first element of comparison (one point of view on an issue, for example)
- second element of comparison (an opposing point of view)
- Meditation on the facts presented in the first two parts
- Explanation of the formula (definition, par ex.)
- Commentary on the formula, for example, expansion of a definition, comments on appropriateness
The Conclusion
A conclusion must be written in the spirit of synthesis and with logical rigor. Coming to the end of an argument, a conclusion must be concise and strong. If desired, it can situate the results or thesis a more general sense.
(Desalmand, Paul and Tort, Patrick. Du plan à la dissertation. Paris : 1977)
Mailing Address
Pomona College 333 N. College Way Claremont , CA 91711
Get in touch
Give back to pomona.
Part of The Claremont Colleges
Research Guides
Gould library.
- Quick Links
- Dictionaries
- Sources about Arts & Literature
- Sources about History & Culture
- Sources of Demographics & Statistics
- Have a citation but want to find the actual text?
MLA for French Language essays
What does an annotated bibliography look like.
- Organizing Your Research
- Going Abroad?
MLA Style Guide
- Bibliography
- In-Text Citations
Format your paper so that each item in your bibliography begins with a hanging indent .
More complete information on MLA style is available here .
Lord, Isabelle. Gestionnaires inspirants: les 10 règles de communication des leaders . Éditions Logiques, 2011.
Chapter in a Book
Regazzi, Jean. «Blanc profond: Le Giallo selon Visconti». Cinéma & littérature: Le Grand Jeu , Édité par Jean-Louis Leutrat, De l'incidence, 2011, pp. 401-418.
Journal Article
Aubin, Daniel. «Les facteurs humains: un enjeu d’aujourd’hui pour la sécurité de notre futur». Toutes et transports , vol. 40, no. 2, 2011, pp. 16-18.
Lestringant, Frank. «Rémanence du blanc: à propos d'une réminiscence hugolienne dans l'œuvre de Mallarmé». Revue d'Histoire littéraire de la France , vol. 81, no. 1, jan.-fév. 1981, pp. 64-74. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/40526715.
Newspaper Articles
Goar, Matthieu. «Primaire de la droite : la chasse aux maires est ouverte». Le Monde , France sec., 31 mai 2016, p. 10.
«Maplewood, New Jersey». Google Maps , www.google.com/maps/place/Maplewood,+NJ/@40.7368948,-74.302936,13z/data=!3m1!4b1!4m5!3m4!1s0x89c3ac609613ecb7:0xbfec83fe47282be9!8m2!3d40.7299793!4d-74.271992.
Basse, Nicolas. «Pourquoi la musique des années 60 à 80 cartonne». Le Point, 30 jan 2014. www.lepoint.fr/art-de-vivre/pourquoi-la-musique-des-annees-60-a-80-cartonne-30-01-2014-1786023_4.php
Note that in this example the inclusion of several people in the Other Contributors category. If you were studying a particular person associated with the work, that person could be listed in the Author position followed by a comma and a note about the person's role in the creation of the work, like so: "Jeunet, Jean-Pierre, réalisateur ."
Le Fabuleux Destin d'Amélie Poulain . Réalisé par Jean-Pierre Jeunet, Interprété par Audrey Tautou et Mathieu Kassovitz, TF1 Vidéo, 2001.
Work of art
If you view it first hand, the Location is the physical location of the work. If you view a reproduction, follow the standard rules for Containers.
DaVinci, Leonardo. Mona Lisa . 1503?, Louvre Museum, Paris.
DaVinci, Leonado. Mona Lisa . 1503?, Wikipedia , en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Mona_Lisa,_by_Leonardo_da_Vinci,_from_C2RMF_retouched.jpg.
Parenthetical citations typically go at the end of a sentence that quote, paraphrases, or refers to a source. Closing punctuation for that sentence goes after the citation.
Each item cited in your text should have a corresponding item in your bibliography.
Standard citation
List the author's last name followed by a page number: (Barron 194).
Author has more than one work in your bibliography?
Add a short title to your citation: (Barron, «Redefining» 194).
Source has no author?
Use a short form of the title: ( Reading at Risk 3)
Source has no page numbers?
Exclude page numbers or use a marker that is prominent in the text (like paragraph numbers, section numbers, time stamps, chapter numbers, line numbers, etc): (Chan, par. 41), (sec. 3), «Hush» 00:03:16-17), (ch. 17), («Ode» 1-3), etc.
Citing more than one source in a single sentence?
Separate the citations with a semicolon: (Baron 194; Jacobs 55).
Already mentioned the author's name in the sentence?
Omit the author's name from the citation: (194).
Citing the Bible?
Use the title, followed by abbreviated book name, followed by chapter and verse separated by a period: ( Bible , Ezek. 1.5-10).
Citing Shakespeare?
Use the play's abbreviated title followed by act, scene, and line numbers separated by periods: ( Mac . 1.5.17).
Create a complete citation, ending with a period, and then immediately begin the annotation so that the entire things forms one paragraph. Double space the entire document. Do not include an extra space between entries.

(Example from the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th edition, section 5.3.1. Click here for a larger version of the image above .)
Entries may be ordered alphabetically, thematically, or chronologically, depending on your rhetorical intent.
- << Previous: Have a citation but want to find the actual text?
- Next: Organizing Your Research >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 8:51 AM
- URL: https://gouldguides.carleton.edu/fren
Questions? Contact [email protected]

Powered by Springshare.
- Free Resources
- 1-800-567-9619
- Subscribe to the blog Thank you! Please check your inbox for your confirmation email. You must click the link in the email to verify your request.
- Explore Archive
- Explore Language & Culture Blogs
What’s The Problem? – Writing A Thesis In French Posted by John Bauer on Aug 31, 2016 in Culture , Vocabulary
These past few weeks I’ve been hard at work on mon mémoire (my thesis). The last big project for un diplôme (a degree) is always hard, and writing un mémoire in another language makes the whole process even more of un casse-tête (a headache).

“ Place de la Sorbonne ” by Alan on Flickr. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
I came to France to do mon master (my Master’s), and it has been an interesting exeprience learning how nobody’s perfect and what a CM and TD are . Now hard at work on mon mémoire , I’m struggling to find enough café (coffee) to keep me going.
Writing more than cinquante pages (fifty pages) en français has been tough. I can’t tell you how many times I’ve mixed up the words une mémoire (a memory) and un mémoire (a thesis). Not to mention all the other dual gender nouns .
To make things easier, le mémoire should follow le plan (the outline), but sometimes il est difficile de savoir par où commencer (it’s hard to know where to start).

“ Plan de dissertation ” by dicophilo on Flickr. Licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0.
Figuring out une problématique is a big part of writing un mémoire . Once you have une idée (an idea) you have to fix not just le grammaire (the grammar), but le raisonnement et la logique (the reasoning and logic) as well.
C’est quoi une problématique ? What is une problématique?
Une problématique is a thesis statement to some people. In my experience, they are used in the same general educational contexts. Cependant (however), they do not mean exactly the same thing.
The word for a thesis statement is une thèse principale or un énoncé de la thèse .
It’s a subtle difference, but la problématique is more about defining the research problem or outlining the research problem rather than a summary of the main point or presenting un point de vue (a point of view) and making a claim.
It can be difficult to understand how to succeed in the French education system without understanding this difference. Surtout (especially) because in the classroom you’ll hear le professeur (the professor) talk about the importance of la problématique in the same way you would hear le professeur talk about the thesis statement in aux États-Unis (in the United States).
There is also a lot to learn about les travaux universitaires (academic writing). All the nuances of specific wordings can easily get lost in translation. The main ideas of writing clearly, citing your sources, creating a bibliography, and proper formatting are all the same, but the details can be different enough that figuring out how to write correctly is un casse-tête .
De plus (what’s more), if you went to school in the US, you are probably familiar with MLA or APA formatting and it’s hard to realize that those are American guidelines.
Ne vous inquiétez pas ! Don’t worry!
In France, all the information you need is in le guide de mise en page (the style guide) provided by le professeur .
Maintenant (now), the biggest problem I have is that with la canicule it’s too hot to drink du café !

Build vocabulary, practice pronunciation, and more with Transparent Language Online. Available anytime, anywhere, on any device.

About the Author: John Bauer
John Bauer is an enthusiast for all things language and travel. He currently lives in France where he's doing his Master's. John came to France four years ago knowing nothing about the language or the country, but through all the mistakes over the years, he's started figuring things out.
A Level French Essay Vocab

Students also viewed

Trinity College Dublin, The University of Dublin

Trinity Search
Trinity menu.
- Faculties and Schools
- Trinity Courses
- Trinity Research
- The Library of Trinity College Dublin
- Library Guides
- Reference Styles (or, Citation Styles)
- Databases for students
- Tutorials & Guides
- Blackboard - embedding Library resources
- Reading Lists & Book Orders
- RSS - Keep your Research Profile and Publications' record up-to-date
- TARA - Deposit Your Research in TARA
- E-Books and E-Book Databases
- Print Books
- Databases for French
- Film Studies databases
- Other TCD databases
- Dictionaries
- Journals and Journal Articles
- Reference Management - EndNote
TCD Library catalogue search
Research and citation resources / purdue university online writing lab.
Research and Citation Resources from Purdue University Online Writing Lab
(For help with formatting your references when citing someone's work.)
About Citation Styles
There are thousands of citation styles in use. Your lecturer, course director or supervisor may tell you to use a particular one, or allow you to choose one on your own.
Guides for each style will tell you how to format the references:
- Details on which order to present the bibliographic information.
- Grammar instructions such as how to use punctuation and capitalisation - what is emboldened , underlined , italicised … where the full stops and commas go…
- Different rules will apply to different formats of sources (journal articles, book with one author, books with several authors, edited books, chapters in edited books, webpages, reports, films, etc. etc…)
Many different styles are in use in Trinity College Dublin - for definitive answers you should use the full style manual for each system.
We are going to see what a reference looks like using using different citation styles. Here's the information we want to reference:
- Reference Type: Journal Article
- Authors: Adrian Stagg, Lindy Kimmins, and Nicholas Pavlovski
- Article Title: Academic style with substance: A collaborative screencasting project to support referencing skills
- Journal Title: The Electronic Library
- Pages: 452-464
- DOI: 10.1108/el-01-2012-0005
We demonstrate how this appears in a variety of different referencing systems, namely the APA 7th Edition, MLA 8th Edition, Vancouver; and Chicago 17th Edition.
About Inline Styles
Inline citations use a brief summary of the reference in the text (such as listing the author and date, or the author and title, or author and page) with the full reference stated at the end of the chapter or work.
This final list is called a reference list or bibliography.
Generally the full list of references will be in alphabetical order by the first author’s surname.
Inline styles are sometimes called the “Harvard” style as they were first used at Harvard in the 1880s. They are also called “Parenthetical” styles as they enclose the partial information in brackets.
Two of the most popular Harvard-type styles are the APA 7th Edition, and the MLA 8th Edition. Our example is used to show the similarities and differences below.
The Library has books on these (and other) styles available to guide students on how to reference correctly.
- Compared - Text
- Compared - Reference List
In the text:
"Referencing, like research and other academic learning skills, has often not been taught explicitly, or within a discipline context prior to tertiary education" (Stagg et al., 2013).
Reference list:
Stagg, A., Kimmins, L., & Pavlovski, N. (2013). Academic style with substance: A collaborative screencasting project to support referencing skills. The Electronic Library, 31 (4), 452-464. doi:10.1108/el-01-2012-0005
"As the global information landscape increasingly facilitates the sharing, re-purposing and dissemination of information, the ways in which students are accustomed to interacting with information resources are also changing" (Stagg et al.).
Stagg, Adrian et al. "Academic Style with Substance: A Collaborative Screencasting Project to Support Referencing Skills." The Electronic Library , vol. 31, no. 4, 2013, pp. 452-464, doi:10.1108/el-01-2012-0005.
"Referencing, like research and other academic learning skills, has often not been taught explicitly, or within a discipline context prior to tertiary education" (Stagg et al.).
Stagg, A., Kimmins, L., & Pavlovski, N. (2013). Academic style with substance. The Electronic Library, 31 (4), 452-464. doi:10.1108/el-01-2012-0005
Stagg, Adrian et al. "Academic Style with Substance." The Electronic Library , vol. 31, no. 4, 2013, pp. 452-464, doi:10.1108/el-01-2012-0005.
About Numbered Styles
Numbered styles list references in the order they are mentioned, using a digit in the text to refer to the fuller citation at the end.
If a reference is mentioned again later, it reuses the same number.
The most common numbered style is Vancouver - while this style has its own particular rules, numbered styles in general are often referred to as Vancouver styles.
Here's our example in the Vancouver style, using the "official" rules given by the NLM/PubMed.
"As the global information landscape increasingly facilitates the sharing, re-purposing and dissemination of information, the ways in which students are accustomed to interacting with information resources are also changing" (1).
1. Stagg A, Kimmins L, Pavlovski N. Academic style with substance: A collaborative screencasting project to support referencing skills. The Electronic Library. 2013;31(4):452-64.
About Footnote Styles
Like numbered styles, footnote styles give the reference an ascending number in the text and the full references are listed in that order at the bottom of the page in a footnote. A full list at the end of the work or chapter may also be required - although unlike with numbered styles, this may be in alphabetical order by surname, rather than in order of mention.
The Chicago style is the most well-known footnote style. In Chicago and other footnote styles there are rules that apply if you use a work again in another footnote. Up until the Chicago 16th Edition, If you mention the citation again as the next footnote, then the term “ ibid ” (“in the same place”) is used instead of the reference. If it is used again after referring to a different citation, then a short form of the reference is used in the footnotes - the manual for the style will tell you what this should look like. However, this was changed in the Chicago 17th Edition, with the short form now favoured over ibid even if mentioned immediately afterwards.
- Chicago Manual of Style Online This link opens in a new window Used to document sources for papers and assignments in the Humanities (e.g., history, fine arts, and political science). more... less... This 16th edition of the CMOS provides recommendations on editorial style and publishing practices in the digital age. The database incorporates tools such as, sample correspondence, proofreaders' marks, and a quick guide to citation and also the Chicago Style Q & A. This edition also includes an introduction to Unicode, tips for citing blogs, podcasts and other electronic resources.
Chicago 17th
"As the global information landscape increasingly facilitates the sharing, re-purposing and dissemination of information, the ways in which students are accustomed to interacting with information resources are also changing" 1 .
As a footnote at the bottom of the page:
1 Adrian Stagg, Lindy Kimmins, and Nicholas Pavlovski, "Academic Style with Substance," The Electronic Library 31, no. 4 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1108/el-01-2012-0005.
(elements are separated by commas)
2 Stagg, Kimmins, and Pavlovski, "Academic style with substance."
Stagg, Adrian, Lindy Kimmins, and Nicholas Pavlovski. "Academic Style with Substance." The Electronic Library 31, no. 4 (2013): 452-64. https://doi.org/10.1108/el-01-2012-0005 .
(first author’s name inverted, elements are separated by full stops)
Subject Librarian

- << Previous: References: Citing and EndNote
- Next: Reference Management - EndNote >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 12:18 PM
- URL: https://libguides.tcd.ie/french/guide
- Share full article

fashion review
Before the Olympics, the Fabulous French Fashion Flex
Christian Dior, Balenciaga, Chanel, Hermès and Louis Vuitton have turned cruise shows into diplomatic currency.
The Christian Dior cruise show at Drummond Castle in Perthshire, Scotland. Credit... Lesley Martin/Reuters
Supported by

By Vanessa Friedman
- June 7, 2024
When is a fashion show not just a fashion show? When it is a vehicle for cultural diplomacy.
At least this appears to be the case with the cruise (or resort or pre-spring or whatever you want to call them) destination extravaganzas that have taken place over the last month. These events increasingly serve to position the big five brands that hold them less as mere fashion houses and more as national ambassadors to the world: billion-euro avatars of influence on unofficial state visits.
Once upon a time, back when this interstitial season was invented to bridge the gap between the fall and spring runway shows, cruise collections seemed to contain clothes that were more wearable or practical than designs shown during the regular seasons. Now, at least in the hands of the mega-brands, the clothes (or at least their wearability) are almost besides the point. The point is the spectacle, access and power they represent — of all kinds, including that of celebrity and social media. Indeed, the front-row stars are as much an attention-grabbing part of the shows as the shows themselves.
In a world of fashion micro-trends, that may be the biggest trend of all.
This was especially true this season, as the shows of the five big heritage French brands — Chanel, Louis Vuitton, Hermès, Dior and Balenciaga — served as de facto calling cards for the Paris Olympics, which is being touted as the most “fashion” Olympics ever.
It is no coincidence that two of those brands, Louis Vuitton and Dior, are owned by LVMH, which is a top-line sponsor of the Olympics. Nor is the fact that Bernard Arnault , the mastermind of LVMH, has explicitly stated that he sees his mega-brands not as selling luxury, but selling “culture.” And it is worth noting that this was the first time Balenciaga had shown in China, and, for Hermès, the first new collection show held outside of France.
“Hermès has always had a strong connection with New York, ” said the brand’s designer Nadège Vanhee, before her New York debut, held on Pier 36 and complete with hanging yellow traffic lights and a Gallic cocktail boîte.
- Simbarashe Cha/The New York Times
- Filippo Fior
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
LOOK OF THE DAY
The summer 2024 imagemakers issue, what to buy, trending celebrities, celebrity style, more latest news, latest issues.
- Search the site Please fill out this field.
- Saved Recipes & Collections
- Add a Recipe
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Food News and Trends
I Asked 4 Chefs To Pick the Best Fast-Food French Fries, and Their Pick Was Unanimous (And Shocking!)
Sorry, Ronald. McDonald’s didn’t come out on top!
Adobe Stock
While the Golden Arches gets a lot of glory for its secret sauce , Coke , and even ketchup , McDonald's might be most lauded for its incredibly popular French fries . Despite this fact, the chain actually finished second in our fast-food French fry taste test last year, inspiring us to ask another highly-qualified group of experts for their opinion. Here is where four top chefs stand on the piping-hot side dish debate.
Ahead, we’re dishing up the qualities that chefs from coast to coast look for in a French fry, and then we’ll reveal their unanimous choice for the best fast-food French fry—and the best sauces to dip them in.
Our Panel of Fast Food Fry-Judging Chefs
- Matt Ayala, executive chef at Francois Frankie in Chicago, Illinois
- Elliot Bell, chef-owner of Charlie’s in St. Helena, California
- Dominic Iannarelli, chef-owner of Prime & Providence in West Des Moines, Iowa
- Vivek Surti, founder and owner of Tailor in Nashville, Tennessee
Qualities of the Best Fast-Food French Fries
From how thick the potatoes are sliced to whether they consist of potatoes-only or a blend of potatoes with seasonings and preservatives, to the cut (crinkle, waffle, steak, etc.), the fast-food French fry landscape is vast and varied.
Admittedly, a fair amount of the choice of which is “best” boils down to personal preference, but bland and soggy fries are out of the running. These three qualities qualify a French fry to be considered for the best in fast food :
- Crispiness. “Texture is the biggest quality that I look for in fast-food French fries. The best fries are crispy on the outside, soft on the inside, and seasoned to perfection,” Bell says.
- Seasoning. As our recipe for the Best Potatoes You'll Ever Taste proves, potatoes are a blank slate for whatever flavors you add, and enough salt is key when it comes to the fried variety.
- Temperature. At his American brasserie, Francois Frankie, Ayala serves fries alongside menu items including a Lobster Roll, Le Cheeseburger Royale, a Prime Steak Burger, and Braised Short Rib Dip. “Even though the fries are secondary, I make sure they are always served hot and crispy to balance the integrity of the entire dish,” Ayala says. Lukewarm or cold fries simply can’t compare. “A lot of people love McDonald's fries, but if they are cold, they’re a huge letdown,” Ayala adds. For the ultimate experience, fries should be savored hot.
Related: I Tested 5 Different Frozen French Fries and This Is the Brand I’ll Buy From Now On
The Best Fast-Food French Fries, According to Chefs
With runner-up honors going to both McDonald’s and Rally’s/Checkers , our four chefs unanimously selected Arby’s curly fries as the best fast-food French fries.
“Arby's is the best,” Surti says. “First, they’re curly, so they’re automatically more fun. The seasoning they add to the curly fries is more than just salt, so there’s more flavor. Arby’s also puts their curly fries through a batter, which results in more texture and bits that get crispy.”
The curly quality isn’t just fun, though. It increases the surface area of the fries, which leads to more real estate to crunchify—and coat in seasonings.
Part of the pleasure comes from the novelty, according to Iannarelli. “Arby’s seasoned curly fries are my favorite because so few places have them.” While the chain is in 48 states, it’s not as prolific as some other fast-food fry slingers like McDonald’s, Burger Kind, and Wendy's.
But it’s also about the quality. Bell and Ayala agree that they deliver on that “fast-food French fry trifecta” of texture, seasoning, and temperature. “They always come out hot and crispy,” Ayala says. “This is a must.”
The Best Dipping Sauces for Arby’s Curly Fries
While they’re good on their own, curly fries are even better dunked in any of Arby’s sauces . Here are the top five dips to grab, according to our chefs:
- Horsey Sauce. For the uninitiated, this is horseradish-flavored.
- Ketchup. “I like fries and ketchup,” Surti says. “It’s a classic.”.
- Ranch. Arby’s recipe is a buttermilk ranch, and it ranks high in our restaurant ranch taste test thanks to its comforting flavor, “pleasant, well-rounded tang, and excellent dips-cocity.”
- Cheddar Cheese Sauce. This costs an extra 50 cents, but is more than worth it, Iannarelli says.
- Arby’s Sauce. This recipe reminds us of a mash-up of ketchup and barbecue sauce.
You’ll Also Love

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Discover how to write an essay in French with four types of academic essays and essential phrases. Learn from FluentU, the best online resource for French learning.
The first paragraph of your French essay should briefly introduce the topic and engage the reader. Here are some examples to help you write your essay: In recent years, the [topic] has become a hotly debated issue, with [brief outline of arguments]. The [subject] has been the subject of controversy for several decades, with [brief overview of ...
Tips to Write an Excellent French Essay. Writing essays is challenging enough, but when you are asked to write a French essay, you are not only being asked to write in a foreign language, but to follow the conventions of another linguistic and literary tradition.
30 Useful French Essay Phrases and Transition Words in French
Tips to help you write a great French essay with exam requirements in mind (VCE French exam or any other exam). French essay proofreading checklist.
Analyzing essays written by experienced writers can prove invaluable in grasping the authentic style required to compose a captivating essay. 3. Use Transition Words: Crafting a Smooth Flow of Ideas. In French essays, the use of transition words and phrases plays a pivotal role in connecting ideas seamlessly.
This document offers resources to students writing in French at the undergraduate and postgraduate levels. It has been inspired by the recurring questions and issues encountered during consultations with students and it includes: Grammatical and vocabulary help. Advice on dissertation structure and dissertation writing.
Whether you're a beginner or an advanced learner, you can always improve your writing in French. Learn how to write in French effectively with 8 easy steps.
Summary- French exams: what you are really tested on- How to write a French essay- Why it's important to structure your texts and use logical connectors- How having structure lowers the stress level- Why work with a coach to prepare an exam- 4 typical outlines to write a French essay The DELF writing exam and
#frenchwriting Improve your French essay-writing for French CAPE, French A' Level and DELF B2 by working on your style to get a top grade in your French e...
France's equivalent to the American standard five-paragraph essay, 'la dissertation' adheres to a structure unfamiliar to most. The format for the dissertation is as follows: introductory paragraph, thesis paragraph, antithesis paragraph, and concluding paragraph. However, depending on the subject, the format is subject to change. Aside from classroom exercises and formal writing assignments ...
Useful expressions to help structure your A level French essay.
Got the AP® French exam woes? Find out how to conquer the exam with these AP® French Language tips, written by exam graders and teachers themselves.
Indubitably, the French méthodologie en deux parties is a stark contrast to what the English have in mind when writing a legal essay. The essay in the latter case is assessed on comprehension, critical analysis, structure and presentation .
Looking for French essay topics? 🥇 You've found the right article! See the tips and ideas for a French essay with examples. ★ Learn how to write a French composition!
When writing an academic essay in French, it is important to avoid repetition and Anglicisms. Often, the temptation is to literally translate what you want to say in English into French but this can often cause mistakes.
All writing exercises are made by our qualified native French teachers to help you improve your writing skills and confidence. Kwizbot will give you a series of prompts to translate to French. He'll show you where you make mistakes as you go along and will suggest related lessons for you. Boost your French writing skills by adding the lessons ...
Dissertation is a very specific way to write what we call a "paper." In France, this style is used in academics and the professional world alike.
What does an Annotated Bibliography look like? Create a complete citation, ending with a period, and then immediately begin the annotation so that the entire things forms one paragraph. Double space the entire document. Do not include an extra space between entries. (Example from the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, 7th edition ...
These past few weeks I've been hard at work on my thesis. The last big project for a degree is always hard, and writing a thesis in another language makes the whole process even more of a headache.
Useful words and phrases for writing essays in French Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
The Chicago style is the most well-known footnote style. In Chicago and other footnote styles there are rules that apply if you use a work again in another footnote. Up until the Chicago 16th Edition, If you mention the citation again as the next footnote, then the term " ibid " ("in the same place") is used instead of the reference. If ...
Melinda French Gates is a philanthropist and the founder of Pivotal, a charitable, investment and advocacy organization. Source photographs by Bryan Bedder, filipfoto, and Westend61, via Getty Images.
In a world of fashion micro-trends, that may be the biggest trend of all. This was especially true this season, as the shows of the five big heritage French brands — Chanel, Louis Vuitton ...
InStyle offers the latest beauty tips, celebrity style insights, and fashion advice.
Ben, the French artist best known for his irreverent approach to modern art, has died aged 88, taking his own life hours after the death of his wife, his family said in a statement Wednesday.
Nigel Farage has said the NHS "isn't working" and he suggested the UK adopt a French-style healthcare system. In a call to "change the model" of healthcare in the country, Mr Farage said ...
Four top chefs from across the country reveal their favorite fast-food French fry brand, and the unanimous results surprised us! Plus, what makes a great fast-food fry and the best dipping sauces for them, ranked.
French country style embraces rustic and elegant design to create a timeless yet homely scheme. Here's how to achieve the look according to designers.