

Essay on Fear
Students are often asked to write an essay on Fear in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Fear
Understanding fear.
Fear is a basic human emotion that alerts us to the presence of danger. It is fundamental to our survival, making us respond quickly when we sense a threat.
Fear’s Role
Fear helps us make decisions that protect us from harm. It triggers our ‘fight or flight’ response, preparing our bodies to either confront or escape danger.
Overcoming Fear
Fear can be overcome by understanding and facing it. When we challenge our fears, we learn to control them, reducing their impact on our lives.
The Positive Side of Fear
Fear can also be positive, motivating us to push beyond our comfort zones, leading to personal growth and achievement.
Also check:
- Paragraph on Fear
- Speech on Fear
250 Words Essay on Fear
Fear is an innate emotional response to perceived threats. It is evolutionarily wired into our brains, acting as a survival mechanism that alerts us to danger and prepares our bodies to react. While fear can be a beneficial response, it can also be debilitating when it becomes chronic or irrational.
The Physiology of Fear
Fear triggers a cascade of physiological responses, including the release of adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones prepare the body for the ‘fight or flight’ response by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. This process, while crucial for survival in threatening situations, can lead to health problems if sustained over a long period.
Fear and the Mind
Psychologically, fear can be both a conscious and subconscious experience. It can be based on real threats or imagined ones, leading to anxiety disorders and phobias. Fear can also influence decision-making, often leading to risk-averse behavior. Understanding the psychological aspects of fear is essential for effective mental health treatment.
Overcoming fear involves recognizing and confronting it. Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, exposure therapy, and mindfulness-based stress reduction can be effective. These strategies aim to change the thought patterns that lead to fear and teach coping mechanisms to manage fear responses.
Fear in Society
Fear also plays a significant role in society, influencing politics, economics, and social interactions. It can be used as a tool of manipulation, or it can drive societal change. Recognizing the societal implications of fear is crucial for fostering a more understanding and empathetic society.
In conclusion, fear is a complex emotion with profound impacts on individuals and society. Understanding its mechanisms and implications can help us navigate our fears and use them as catalysts for growth.
500 Words Essay on Fear
Introduction.
Fear is a universal human experience, an essential part of our biological makeup that has evolved over millions of years. It is a complex emotion that can be both protective and paralyzing, serving as a warning signal for danger while also potentially hindering personal growth and exploration. This essay explores the multifaceted nature of fear, its psychological implications, and its role in shaping human behavior and society.
The Biological Basis of Fear
Fear is fundamentally rooted in our biology. It is a response triggered by the amygdala, a small, almond-shaped structure in the brain that processes emotional stimuli. When we perceive a threat, the amygdala activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, leading to physiological changes such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and heightened alertness. This response is adaptive and has been crucial for human survival, allowing us to react quickly to potential threats.
The Psychological Aspect of Fear
Psychologically, fear is a multifaceted emotion with wide-ranging implications. It can be both acute, as in the immediate response to a threat, and chronic, as in the long-term fear associated with anxiety disorders. Fear can also be learned through conditioning or observation, which explains why different individuals may have different fear responses to the same stimulus.
Fear can lead to avoidance behavior, where individuals steer clear of situations that they perceive as threatening. While this can be protective, it can also be limiting, preventing individuals from pursuing opportunities and experiences that could lead to personal growth.
Fear and Society
On a societal level, fear can be both a unifying and a divisive force. It can bring people together in the face of a common threat, but it can also be exploited to manipulate public opinion and justify oppressive policies. Fear can lead to stereotyping and discrimination, as individuals or groups are scapegoated as threats to societal safety and order.
Overcoming fear involves recognizing and understanding it. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one effective method, as it helps individuals reframe their fearful thoughts and gradually expose themselves to feared situations. Mindfulness and meditation can also be beneficial, allowing individuals to stay present and focused rather than getting caught up in fearful thoughts.
In conclusion, fear is an integral part of the human experience, with deep biological roots and far-reaching psychological and societal implications. While it can be protective, it can also be limiting and divisive. Understanding and managing fear is therefore crucial, not just for individual well-being, but also for societal harmony and progress. As we navigate through an increasingly complex and uncertain world, the ability to confront and overcome our fears will be more important than ever.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Family
- Essay on Ethics
- Essay on Equality
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Psychology of Fear
Daniel B. Block, MD, is an award-winning, board-certified psychiatrist who operates a private practice in Pennsylvania.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/block-8924ca72ff94426d940e8f7e639e3942.jpg)
Frederick Bass / Getty Images
What is fear?
Psychologists define fear as a protective, primal emotion that evokes a biochemical and emotional response. Fear alerts us to the presence of danger or the threat of harm, whether that danger is physical or psychological. Whereas the biochemical changes that fear produces are universal, emotional responses are highly individual.
Fear produces biochemical and emotional reactions to a perceived threat, whether that danger is actual or imagined. It's a natural, necessary, protective response, but when the reaction is out of proportion to the actual threat, it can be problematic.
Fear can also be a symptom of some mental health conditions, including panic disorder , social anxiety disorder, phobias , and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Biochemical Reaction
Fear is both a natural emotion and a survival mechanism. When confronted with a perceived threat, the body responds in specific ways. Physical reactions include sweating, increased heart rate, and high adrenaline levels that cause extreme alertness.
This physical response is also known as the fight or flight response , with which your body prepares to confront the danger or run away. This biochemical reaction is likely an evolutionary development—an automatic response that is crucial to survival.
Emotional Response
The emotional response to fear, on the other hand, is highly personalized. Because fear involves some of the same chemical reactions in our brains that positive emotions such as happiness and excitement do, feeling fear under certain circumstances can be perceived as fun—for example, when you watch scary movies .
Some people are adrenaline seekers , thriving on extreme sports and other fear-inducing, thrilling situations. Others have negative reactions to the feeling of fear, avoiding fear-inducing situations at all costs.
Although the physical reaction is the same, the experience of fear can be positive or negative, depending on the person.
Symptoms of Fear
Fear often involves both physical and emotional symptoms. Each person experiences fear differently, but some of the common signs and symptoms include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Upset stomach
In addition to the physical symptoms of fear, people sometimes experience psychological symptoms of being overwhelmed, upset, feeling out of control, or a sense of impending death.
Diagnosing Fear
Talk to your healthcare provider if you are experiencing persistent, excessive feelings of fear. Your doctor may conduct a physical exam and perform lab tests to ensure that your fear and anxiety are not linked to an underlying medical condition.
Your healthcare provider will also ask questions about your symptoms including their duration, intensity, and triggers. Depending on your symptoms, your diagnosis may be related to an anxiety disorder, such as a phobia.
One aspect of anxiety disorders can be a fear of fear. Whereas most people experience fear only during a situation that is perceived as scary or threatening, those who live with anxiety disorders may become afraid that they will experience a fear response. They perceive their fear responses as negative and go out of their way to avoid those responses.
A phobia is a twisting of the normal fear response. The fear is directed toward an object or situation that does not present a real danger. Though you recognize that the fear is unreasonable, you can't help the reaction. Over time, the fear worsens as the fear of fear response takes hold.
Causes of Fear
Fear is incredibly complex, with no single, primary cause. Some fears result from experiences or trauma, whereas others may represent a fear of something else entirely, such as a loss of control. Still, other fears may occur because they cause physical symptoms, such as being afraid of heights because they make you feel dizzy and sick to your stomach.
Some common fear triggers include:
- Certain specific objects or situations (spiders, snakes, heights, flying, etc)
- Future events
- Imagined events
- Real environmental dangers
- The unknown
Certain fears tend to be innate and may be evolutionarily influenced because they aid in survival. Others are learned and are connected to associations or traumatic experiences.
Types of Fear
Some of the anxiety disorders that are characterized by fear include:
- Agoraphobia
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Separation anxiety disorder
- Social anxiety disorder
- Specific phobia
Treatment for Fear
Repeated exposure to similar situations leads to familiarity, which can reduce the fear response dramatically This approach forms the basis of some phobia treatments that depend on slowly minimizing the fear response by making it feel familiar.
Phobia treatments that are based on the psychology of fear focus on techniques such as systematic desensitization and flooding. Both techniques work with the body’s physiological and psychological responses to reduce fear.
Systematic Desensitization
Systematic desensitization involves being led gradually through a series of exposure situations. For example, someone who fears snakes might spend the first session with a therapist talking about snakes.
In subsequent sessions, a therapist might present snake photos, toy snakes, and eventually even a live snake. This is usually accompanied by learning and applying new coping techniques to manage the fear response.
This exposure technique involves flooding, which is based on the premise that a phobia is a learned behavior that can be unlearned.
With flooding, the person is exposed to a vast quantity of the feared object or to a feared situation for a prolonged period in a safe, controlled environment until the fear diminishes. For instance, someone who is afraid of planes might be encouraged to go up anyway.
The point is to get them past the overwhelming anxiety and potential panic to a place where they have to confront their fear and eventually realize that they're OK. This can help reinforce a positive reaction (they're not in danger) with a feared event (being in the sky on a plane), ultimately getting them past the fear.
Although these treatments can be effective, such confrontational approaches should be undertaken only with the guidance of a trained mental health professional.
Coping With Fear
Coping strategies focus on managing fear's physical, emotional, and behavioral effects. Here are a few to consider.
- Get social support. Supportive people in your life can help you manage your feelings of fear.
- Practice mindfulness. You cannot always prevent emotions. Being mindful can help you replace negative thoughts with more helpful ones.
- Use stress management techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation , and visualization.
- Take care of your health. Eat well, get regular exercise, and get adequate sleep each night.
Press Play for Advice on Facing Your Fears
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares a strategy to help you find courage when you need it the most. Click below to listen now.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
The Takeaway
Fear is an important human emotion that can help protect you and prepare you for action, but it also can lead to longer-lasting feelings of anxiety. Finding ways to control your fear can help prevent anxiety from taking hold.
If you or a loved one are experiencing fears, phobias, or anxiety, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for information on support and treatment facilities in your area.
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database .
Kozlowska K, Walker P, McLean L, Carrive P. Fear and the defense cascade: Clinical implications and management . Harv Rev Psychiatry . 2015;23(4):263-287. doi:10.1097/HRP.0000000000000065
Javanbakht A, Saab L. What Happens in the Brain When We Feel Fear . Smithsonian.
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Anxiety Disorders .
Adolphs R. The biology of fear . Curr Biol. 2013;23(2):R79-93. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2012.11.055
Craske MG, Treanor M, Conway CC, Zbozinek T, Vervliet B. Maximizing exposure therapy: An inhibitory learning approach . Behav Res Ther . 2014;58:10–23. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2014.04.006
Samra CK, Abdijadid S. Specific Phobia . StatPearls Publishing.
By Lisa Fritscher Lisa Fritscher is a freelance writer and editor with a deep interest in phobias and other mental health topics.

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
114 Fear Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Fear is a powerful emotion that can have a significant impact on our lives. It can hold us back from pursuing our dreams, trying new things, or taking risks. However, fear can also be a powerful motivator, pushing us to overcome obstacles and achieve our goals.
In this article, we will explore 114 fear essay topic ideas and examples that you can use to explore how fear influences our lives and behaviors.
- The role of fear in decision-making
- How fear can hinder personal growth
- Overcoming the fear of failure
- The fear of rejection and its impact on relationships
- Fear of the unknown: how to navigate uncertainty
- How fear of success can hold you back
- Fear of public speaking and ways to overcome it
- The fear of change and how to embrace it
- The fear of being judged by others
- The fear of death and how it shapes our lives
- Fear of failure in academic settings
- Overcoming the fear of making mistakes
- How fear of the future can paralyze us
- Fear of losing control and ways to manage it
- The fear of being vulnerable and its impact on relationships
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in dating
- Fear of failure in entrepreneurship
- The fear of success and how it can sabotage your goals
- Fear of confrontation and ways to handle conflict
- Fear of being alone and how to overcome it
- The fear of being judged on social media
- Fear of the dark and its impact on mental health
- Overcoming the fear of failure in sports
- The fear of being embarrassed in public
- Fear of failure in the workplace
- The fear of failure in creative endeavors
- Overcoming the fear of failure in relationships
- Fear of failure in parenting
- The fear of missing out (FOMO) and its impact on decision-making
- Fear of rejection in job interviews
- The fear of being vulnerable in friendships
- Fear of failure in starting a new business
- Overcoming the fear of failure in academic settings
- Fear of change in personal relationships
- The fear of being alone in old age
- Fear of rejection in the dating world
- Fear of the unknown in travel
- Overcoming the fear of public speaking in professional settings
- Fear of failure in pursuing your passion
- The fear of being vulnerable in therapy
- Fear of rejection in social situations
- Fear of failure in pursuing your dreams
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in creative pursuits
- Fear of change in career transitions
- The fear of being vulnerable in romantic relationships
- Fear of rejection in networking events
- Fear of failure in starting a new project
- Overcoming the fear of failure in academic pursuits
- Fear of change in personal habits
- The fear of being vulnerable in family relationships
- Fear of rejection in online dating
- Fear of failure in starting a new hobby
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in artistic pursuits
- Fear of change in lifestyle choices
- The fear of being vulnerable in self-expression
- Fear of rejection in job applications
- Fear of failure in pursuing new experiences
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in social settings
- Fear of change in personal beliefs
- The fear of being vulnerable in public speaking
- Fear of rejection in professional settings
- Fear of failure in pursuing personal growth
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in academic settings
- The fear of being vulnerable in leadership roles
- Fear of rejection in creative endeavors
- Fear of failure in starting a new venture
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in romantic relationships
- Fear of change in career advancement
- The fear of being vulnerable in group settings
- Fear of rejection in artistic pursuits
- Fear of failure in pursuing your passions
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in job interviews
- Fear of change in personal goals
- The fear of being vulnerable in social situations
- Fear of failure in starting a new career
- Overcoming the fear of rejection in academic pursuits
- Fear of change in personal challenges
- The fear of being vulnerable in professional settings
- Fear of rejection in social relationships
- Fear of change in personal development
- The fear of being vulnerable in personal growth
- Fear of failure in starting
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
The Psychology of Fear: Definition, Symptoms, Traits, Causes, Treatment
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Florence Yeung
Editor at Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons), Psychology, MSc, Clinical Mental Health Sciences
Florence Yeung is a certified Psychological Wellbeing Practitioner with three years of clinical experience in NHS primary mental health care. She is presently pursuing a ClinPsyD Doctorate in Clinical Psychology at the Hertfordshire Partnership University NHS Foundation Trust (HPFT). In her capacity as a trainee clinical psychologist, she engages in specialist placements, collaborating with diverse borough clinical groups and therapeutic orientations.
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
What Is Fear?
Fear is a natural and primitive emotion that can be experienced by everyone to some degree.
Fear is a basic, emotional response to a perceived threat or danger. It triggers the body’s ‘fight-or-flight’ response, leading to physiological changes like increased heart rate and adrenaline levels.
Fear is an essential survival mechanism, helping individuals react to potentially life-threatening situations. It can respond to immediate, tangible threats and more abstract or future concerns. Fear can also be learned through past experiences or observations.
People may experience fear when in situations such as walking home alone at night, facing animals they perceive as dangerous, or when about to skydive out of a plane.
Fear can also be attributed to feelings of stress and anxiety. It may also contribute to some feelings of disgust, as according to a study investigating those who feared or did not fear snakes, those who experienced this fear reported high feelings of disgust and fear (Rádlová et al., 2020).

Fear is a very natural human response that arises as a defense mechanism in the face of potential danger or harm. It can manifest in a variety of situations and is a normal part of the human experience.
However, when fear becomes extreme in certain situations, such as in social situations or towards a particular object, it may indicate a more significant issue.
In such cases, seeking professional help and support can be beneficial in managing and overcoming the fear.
Biochemical Reaction
Fear is a normal response to many situations and comprises two primary reactions: biochemical and emotional.
The biochemical reaction to fear causes our bodies to respond to perceived threats in the environment.
This produces automatic physical reactions such as sweating, increased heart rate, breathlessness, and dilated pupils. These bodily reactions prepare the body to either combat the threat or run away from it – this is called the ‘ fight or flight ’ response.
In response to a threat, the sympathetic nervous system , part of the autonomic nervous system, is activated by the sudden release of hormones.
The sympathetic nervous system then stimulates the adrenal glands to trigger the release of hormones, resulting in physical reactions. These hormones are:
- Epinephrine (adrenaline) – Provides energy to the major muscles of the body so they can respond to a perceived threat.
- Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) – increases alertness, arousal, and attention. Connstricts blood vessels that help maintain blood pressure during times of stress.
Emotional Response
The emotional response to fear, however, is personalized to the individual. Since the biology of fear involves some of the same chemical responses to pleasant emotions , such as excitement and happiness, people can experience either pleasant or unpleasant emotions to fear.
For instance, some people may enjoy riding extreme roller coasters, while others may have a negative reaction and will avoid these at all costs.
Although the biochemical reaction for fear may be the same, some people will experience the intensity of fearful situations differently than others.
Symptoms and diagnosis

People can experience fear differently, but some of the common physical and emotional symptoms are:
- Rapid heart rate
- Upset stomach
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling overwhelmed
- Feeling out of control
- A sense of impending death
For a condition associated with fear and anxiety to be diagnosed, the symptoms must be persistent, interfere with some part of normal functioning, and cannot be better explained by another condition.
If feelings of fear become persistent and excessive, this could be diagnosed as a type of anxiety disorder, depending on the symptoms being experienced.
Common disorders which are associated with fear are: phobias, generalized anxiety disorder, s ocial anxiety disorder , healthy anxiety disorder, panic disorder , and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Is fear useful?
In many situations, fear is normal and healthy in that it can keep us from entering harmful situations and help us decide when to get out of these situations.
The immediate threat of danger and the physical responses that come with it can help focus our attention and mobilize us to cope with the danger, but either fighting against it (fight) or running away from it (flight).
Fear may also help us to react to danger without having to think about it consciously.
For example, if a car is coming towards us, fear can make us jump out of the way and thus save our lives. Also, if humans have the capacity to notice fear in others since we recognize it in ourselves, we can offer compassion and reassurance to others to help them cope.
In contrast, extreme levels of fear could result in the development of mental health conditions such as phobias or other anxiety conditions. A phobia is an intense, persistent, and out of proportional fear of something, an event, or a situation.
Phobias twist the normal fear response into something difficult or impossible to control and can be detrimental to people’s lives. Likewise, other anxiety conditions, such as generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder , involve intense worry or fear of many things and social situations respectively.
The biochemical and emotional response to fear can be so extreme that it can negatively affect people’s lives. If fear gets too extreme, such as in those experiencing anxiety disorders, it can keep us trapped, preventing us from doing things we want.
Disorders That Involve Fear
Phobias may be diagnosed when certain situations, events, or objects create a strong, irrational fear. Some symptoms of phobias include:
A sensation of uncontrollable anxiety when exposed to the source of the fear.
The feeling that the source of the fear needs to be avoided at all costs.
Not being able to function properly when exposed to fear.
They may acknowledge that the fear is irrational and exaggerated, combined with the inability to control feelings of fear.
- Feeling incapable of coping with the fear.
Different types of phobias can be diagnosed: specific phobias, social phobias , and agoraphobia. Specific phobias are intense, irrational fears of a specific trigger.
Some common specific phobias are spiders and snakes. Social phobia is a profound fear of public humiliation or being judged negatively by others in social situations.
Agoraphobia is an intense fear of situations from which escape might be difficult (or embarrassing) or in which help may not be available in the event of having an unexpected panic episode. This could be a fear of enclosed spaces, as well as open or crowded spaces.
Specific phobias are known as simple phobias since they can usually be linked to an identifiable cause and are unlikely to affect daily living as the person can avoid the trigger.
For instance, if someone has a phobia of heights, they are not likely to experience this fear day-to-day, only in situations where they may have to face their fear.
Social phobia (also known as social anxiety disorder) and agoraphobia, however, are known as complex phobias since their triggers are less easily recognizable or avoidable, and the individual is more likely to experience the associated fear more frequently than those with a specific phobia.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
PTSD is a mental health disorder that can develop in people who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event, such as a serious accident, military combat, physical or sexual assault, or natural disaster.
One of the key symptoms of PTSD is experiencing intense fear, anxiety, or distress when confronted with reminders of the traumatic event, even if the present situation is not actually dangerous or threatening (Maren et al., 2013).
This fear response is thought to be related to the way the brain processes and encodes memories of the traumatic event. When someone experiences a traumatic event, the brain’s fear response is activated, causing the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
However, in people with PTSD, the brain’s fear response can become overactive and hyper-vigilant , causing them to perceive even minor cues in their environment as potential threats. For example, a veteran who experienced combat trauma might feel intense fear or panic when they hear a car backfire or fireworks, as these sounds could trigger memories of gunfire or explosions.
In essence, the fear response in people with PTSD is triggered by associations between present experiences and past traumatic events, rather than by a real and present danger.
These associations can be so strong that even subtle reminders of the trauma can trigger a full-blown fear response, leading to symptoms like panic attacks, hypervigilance, and avoidance behaviors.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
Those who experience GAD typically have persistent and excessive worries about everyday life and worry about multiple things. They may be fearful about their health, finances, safety, and relationships, etc. to the point where it can become exhausting.
People with GAD tend to experience the physical symptoms associated with fear but more often and for more reasons.
Panic disorder
Panic disorder is characterized as fear and worries of the panic attacks experienced recurrently, which are sudden and intense feelings of terror.
These feelings could sometimes occur without warning and are associated with physical symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fast heart rate, and trembling.
Panic attacks could become very intense that impairs the individual functioning during the episode.
What Causes fear?
Specific phobias usually develop in childhood and, in some cases, can be pinpointed to an exact moment.
In some cases, specific phobias can result from an early traumatic experience with the feared object, event, or situation, such as a phobia of bicycles caused by a traumatic incident of falling off a bike as a child.
Phobias that start in childhood could also be caused by witnessing the phobia of a family member and developing the same phobia. For instance, if a parent has a phobia of spiders, the child may also learn to have a phobia of spiders.
Evolutionary theory of fear
Seligman (1971) applied his preparedness hypothesis theory to explain why humans fear. The preparedness hypothesis is the belief that humans tend to fear things that were a source of danger to our ancestors.
Seligman proposed that the fears of individuals diagnosed with phobias reflect the evolutionary prepared learning to fear events and situations that have provided survival threats.
He argued these threats would be from an evolutionary rather than a contemporary perspective.
This can explain why phobias such as threatening animals, heights, closed spaces, and social evaluations are very common and appear to be innate fears.
Contemporary fears such as bicycles, broken electrical equipment, and guns are less common as these would not have been survival threats to our ancestors.
The preparedness hypothesis suggests that humans can have innate responses to specific stimuli without any previous environment input.
This has been tested by scientists who found it was easier to train humans to fear snakes and spiders than friendly dogs of pillows, for instance.
This was especially true for very young children who appeared to fear snakes and spiders before encountering or hearing about them.
Fear conditioning
Pavlovian fear conditioning is a state of fear or anxiety that has been demonstrated in animals after repeated pairings of a threatening stimulus with a previously neutral stimulus using classical conditioning.
In experiments, the researchers would pair a neutral stimulus with an unpleasant stimulus – such as a loud noise or shock. After repeated pairing of these two stimuli, the neutral stimulus on its own would eventually elicit a state of fear.
This is another way in which intense fear could be caused. The fear expressed by the animals would be seen as essential for their survival in this instance.
This fear conditioning could be learned in humans who suffer from posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder caused by very distressing, frightening, or traumatic events, causing individuals to relive them through symptoms of intense or prolonged psychological distress when triggered.
This includes marked physiological reactions such as exaggerated and unrelenting unconditioned responses to stimuli (e.g., crowds, flashes of light, or sounds) associated with trauma (e.g., death or injury).
PTSD can bring about feelings of intense fear when something specifically triggers it. Most of the time, the trigger will not be an actual threat to survival but is a conditioned stimulus for the individual.
This means they can experience intense feelings of fear at times when it is not appropriate.
The brain’s fear response
The primary brain region that is responsible for fear is the amygdala. The amygdala is a collection of nuclei in the limbic system.
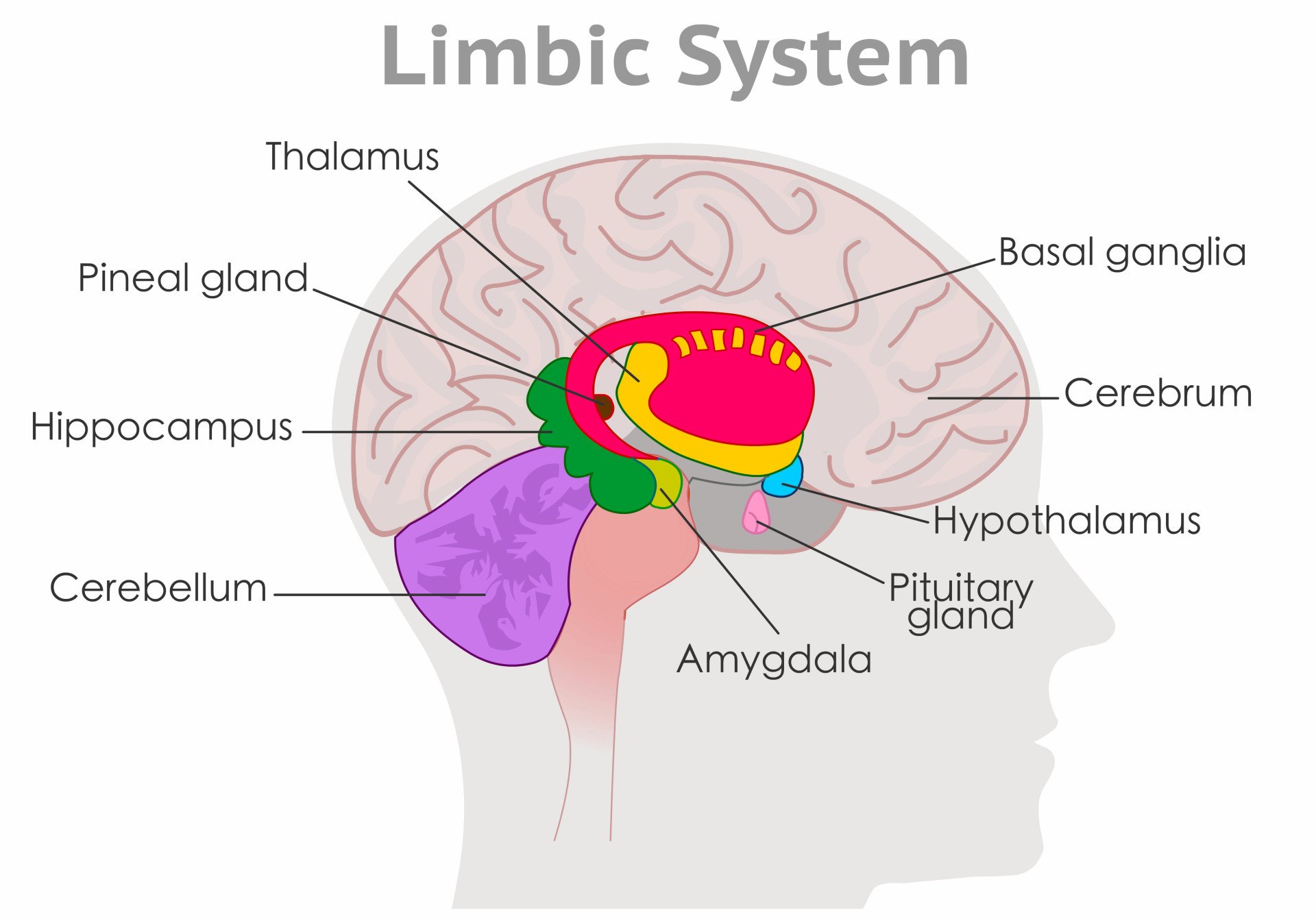
Some main nuclei in the amygdala are the lateral, basal, central lateral, and central medical nuclei. The lateral nucleus is the primary input that receives input from the thalamus and the brain’s cortex, providing it with information about the sensory stimuli being experienced.
The primary output nucleus of the amygdala is the central medial nucleus which projects to different structures, such as the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, which triggers the release of the stress hormone cortisol.
It also projects to the lateral hypothalamus to stimulate the autonomic nervous system , which results in the physiological symptoms associated with the fight or flight, or fear, response.
The amygdala is also thought to be the brain area responsible for fear conditioning. In rats, it was found that an unconditioned stimulus , such as a shock, is picked up by the spinal cord, which sends this signal to the thalamus and the cortex, which then both project to the lateral nucleus of the amygdala.
The synaptic inputs from the unconditioned stimulus are strong enough to excite the lateral amygdala neurons, activating the neurons in the central medial nucleus and thus produces a fear response.
Sensory information from a neutral stimulus (e.g., music) also reaches the thalamus and cortex.
Still, the inputs from this stimulus are not strong enough on their own to excite the lateral amygdala neurons , so the central amygdala neurons remain unstimulated, and there is no fear response.
However, if the neutral stimulus (music) is paired with the unconditioned stimulus (shock), neurons can encode both simultaneously.
This can strengthen the synapse between incoming neurons carrying information about the neutral stimulus and the lateral amygdala neurons.
Eventually, this synapse is strengthened enough to allow them to stimulate the lateral amygdala neurons on their own without the unconditioned stimulus. The lateral nucleus will then excite the central medial nucleus to produce the fear response.
The hippocampus , which plays a role in storing episodic memories, can also interact with the amygdala and be involved in fear.
The neurons from the hippocampus can project to the basal nucleus of the amygdala, which can then stimulate the central medial nucleus.
Because it can do this, the hippocampus allows contextual-related memories to respond to fear. This could be why we can have fearful memories and why they are so strong.
What does the research say?
There are suggested to be sex differences in amygdala activation.
A study that used the brain imaging technique of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) found that when presented with happy facial expressions, there was greater activation in the right amygdala for males but not for females.
Both males and females showed greater left amygdala activation for fearful faces, which supports that the left may be more involved in negative affect (Killgore & Yurgelun-Todd, 2001).
Other researchers have found that the volumes of brain regions involved in fear may differ for those who have experienced more trauma.
Using MRI on children who experienced trauma, research found reduced hippocampal and increased amygdala volume with increasing levels of trauma exposure. Higher exposure to violence was also associated with increased amygdala activation.
Finally, increased functional connectivity between the amygdala and the brain stem was associated with higher levels of exposure to violence (Van Rooij, et al., 2020).
How to Overcome and Manage Fear
Treatment for disorders associated with fear varies depending on the type of disorder and the symptoms experienced.
Often, phobias treatments can be used for disorders associated with extreme fear. Some of these treatment options will be explained below:
Graded Exposure Therapy
A common therapy for people with extreme fears is graded exposure therapy . This involves gradually leading the individual through exposure situations commonly used for those with specific phobias.
The aim is to gradually expose the individual to the fear object or situation in small steps until they feel comfortable and can move on to a higher level of exposure until they eventually can face their fear.
For instance, if someone has a phobia of spiders, the steps may go as follows:
Talking to the therapist about spiders
See pictures of spiders – this could start off as drawings and gradually get more realistic until the patient can manage to view a photo of one.
The patient may be encouraged to watch video footage of a spider
The patient could handle a toy spider
Eventually, the patient should get to a stage where they can face a real spider.
The steps taken to complete the therapy may take a long time, depending on how strong the fear is and the individual’s capability to cope.
Once the individual feels like they can manage their fear at each step, they can move on to the next step until they gradually become desensitized to their fear.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
CBT can help tackle negative and unrealistic thoughts regarding intense fear.
The individual can work with the therapist to work through their fears, form more realistic thoughts, challenge their fearful thoughts, and learn coping strategies.
CBT allows people to learn different ways of understanding and reacting to the source of their fear and can help teach a person to manage their feelings and thoughts.
Some medications can be useful to aid with the symptoms of extreme fear.
Medication should only be used as a short-term treatment for phobias because the medication can become part of safety behaviors for the individual to rely on when facing fearful situations.
This can prevent the individual from fully exposing themselves to the fear and not achieving desensitization eventually.
Below are some medications that can be used for phobias:
Beta-blockers – these work to reduce the physical symptoms of fear by lowering stress on the heart and blood vessels. These block the release of the stress hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine to prevent the fight or flight response from being triggered.
However, these can come with some side effects: insomnia, fatigue, and upset stomach.
Benzodiazepines – tranquilizers are a type of this medication. This helps reduce anxiety symptoms and has a sedative effect on the individual, meaning they slow down the body and brain function.
These medications can be taken when required but have been known to cause a dependency and can have withdrawal effects that could be life-threatening.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) – these medications are a type of antidepressant and are commonly prescribed for phobias.
SSRIs affect serotonin levels in the brain and so can produce better moods in individuals. Side effects of these medications include nausea, sleep problems, and headaches.
Other coping methods
Relaxation techniques can be used to help people calm down. These can include meditation and breath retraining exercises to help treat the symptoms of fear, especially when faced with a fearful situation.
Progressive muscle relaxation is a technique where an individual purposely tenses a muscle group for a few seconds and then releases it. The idea is that the release of the muscles should decrease any build-up tension.
Working through all the muscle groups this way can encourage the whole body to feel relaxed and reduce the fear response. Likewise, yoga can prove a useful method for reducing the fear response.
Combining physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation in yoga can all help people improve their management of anxiety disorders and fear.
Finally, exercise, specifically aerobic exercise, can positively affect stress and anxiety and may decrease the fear response symptoms.
Killgore, W. D., & Yurgelun-Todd, D. A. (2001). Sex differences in amygdala activation during the perception of facial affect. Neuroreport, 12(11), 2543-2547.
Maren, S., Phan, K. L., & Liberzon, I. (2013). The contextual brain: implications for fear conditioning, extinction and psychopathology. Nature reviews neuroscience , 14 (6), 417-428.
Öhman, A. (2009). Of snakes and faces: An evolutionary perspective on the psychology of fear. Scandinavian journal of psychology, 50(6), 543-552.
Rádlová, S., Polák, J., Janovcová, M., Sedláčková, K., Peléšková, Š., Landová, E., & Frynta, D. (2020). Emotional reaction to fear-and disgust-evoking snakes: sensitivity and propensity in snake-fearful respondents. Frontiers in psychology, 11, 31.
Seligman, M. E. (1971). Phobias and preparedness. Behavior therapy, 2(3), 307-320.
Steimer, T. (2002). The biology of fear-and anxiety-related behaviors. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 4(3), 231.
van Rooij, S. J., Smith, R. D., Stenson, A. F., Ely, T. D., Yang, X., Tottenham, N., Stevens, J. S. & Jovanovic, T. (2020). Increased activation of the fear neurocircuitry in children exposed to violence. Depression and anxiety, 37(4), 303-312.
Further Reading
- Kozlowska, K., Walker, P., McLean, L., & Carrive, P. (2015). Fear and the defense cascade: clinical implications and management. Harvard review of psychiatry.
- Adolphs, R. (2013). The biology of fear. Current biology, 23(2), R79-R93.
- LeDoux, J. E. (2014). Coming to terms with fear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(8), 2871-2878.
- LeDoux, J. E., & Pine, D. S. (2016). Using neuroscience to help understand fear and anxiety: a two-system framework. American journal of psychiatry.
Is fear an emotion?
Yes, fear is a basic emotion that is triggered as a response to perceived threats. It is a survival mechanism that prompts action to protect oneself from danger. Fear can cause physiological changes like increased heart rate, and it can also influence thoughts and behaviors.
How do people perceive fear differently?
People perceive fear differently due to personal experiences, genetic predispositions, cultural norms, and mental health conditions. For some, a situation may trigger intense fear, while others may feel excitement or curiosity in the same situation. People’s coping strategies and resilience significantly influence their responses to fear-inducing situations.
What causes fear?
A perceived threat or danger causes fear. This can be a response to something immediate and obvious, such as coming face-to-face with a dangerous animal, or something more abstract, like a fear of losing one’s job. The brain’s amygdala plays a key role in processing fear by sending signals that trigger the fight-or-flight response. Fear can also be learned through personal experiences or by observing others.
Related Articles

How To Support Someone With Social Anxiety: 9 Tips

How To Stop Worrying About Things You Can’t Control (+PDFs)

Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Anxiety

How to Practice Exposure Therapy for Social Anxiety & Worksheets (PDF)

Does Pure O Exist?

Reduce Anxiety Now: How To Calm Down Quickly
Fear: Definition, Effects, and Overcoming Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Effects of fear
How to overcome fear.
Webster’s dictionary defines fear as “an unpleasant, sometimes strong emotion caused by an anticipation or awareness of danger” or “anxious concern” Fear is a feeling that causes agitation and anxiety mostly caused by presence or imminence of danger. It is a state or condition marked by feeling of agitation or anxiety. It can also be described as a feeling of disquiet. Fear is an abstract concept and may have different meanings. Holder (2007) adds that fear is more pervasive when there is lack of faith that we have greater significance in the universe than what we own or how others perceive us.
Fear is manifested in many ways in human beings. It may manifest as showing signs of withdrawing or by cowering. But the most profound manifestation of fear is anger and hatred. People acts out their insecurity as anger which shows that they are the most fearful people.
Effects of fear have been documented in many studies. Fear has been documented to case mind paralyses, heart attacks and closure of fallopian tube due to fear of pain during child birth (Jim Rohn, 2004), describes fear, indifference, indecision, doubt, worry and timidness as the five greatest enemies within us which can destroy our lives completely. Fear may manifest itself in physical short term effects or affect your whole life. It will affect both he physiology of the body and the brain. Fear generates stress which manifests itself physically in many signs physically and emotionally. It causes judgmental errors and affects our reasoning that most of time when we are in a fearful situation; we tend to take the wrong action.
According to Sidney B., (1988), fear is a great paralyzer. It will keep you from making positive changes in your life and thus retard your recovery from depression. He continues to argue that fear persuades you to set easier goals and do less than your capability. It will also cause internal defense system fooling you that you have good reasons not to change. Fear of failure reduces the available alternatives you can pursue because you cannot stand by the outcome of what you do. You always feel that you cannot succeed in anything you try. It will keep you away from seeking help because you don’t want others to see you as a failure. Fear has been identified by psychologist as what causes people to give up when they are one step short to their goal. It will keep you stuck or make you develop unhealthy habits and behavior problems. Most of all fear keeps many people from taking risks.
Rim Rohn, (2004), argues that we are not born with courage, neither are we born with fear. He argues that some of our fears are brought on by our own experiences by what someone has told us or what we read in papers and books. Sri Swami Sivananda, (2007), describes fear as an illusion that cannot live. He suggests that to overcome fear we should always feel the presence of a Supreme Being watching us, by meditating and developing positive thoughts all the time. We should devote ourselves to eradicating fear. Since we have seen that fear is developed within our minds, it can also be eradicated within our mind and hence it is just a matter of reconditioning our minds that will help us overcome fear. It is also suggesting that we should share with others our fears. In this way they will help us find solutions to the cause of fears. President Roosevelt said, “We have nothing to fear but the fear itself” hence fearing fear starts and ends with us.
Holder P. (2007): FEAR… YOUR WORST ENEMY . Web.
Rohn, J., (2004). Build courage to face the enemies within. Web.
Sidney S., (1998). Getting Unstuck: Breaking through Your Barriers to Change . Web.
Sri Sivanand, S. (2007). The Divine Life Society: How to overcome fear. Web.
- Management of Police Department
- The Using Phrase "Retardation"
- RIM and IBM Companies Environmental Scanning
- Personality Theory of Abraham Maslow Critique
- Postmodern Psychology and Counseling
- Philosophy: The Most Ancient Discipline of Knowledge
- Ethical Dilemma in the Psychologists Career
- Grief Counseling With Multicultural Clients
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, September 3). Fear: Definition, Effects, and Overcoming. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fear-definition-effects-and-overcoming/
"Fear: Definition, Effects, and Overcoming." IvyPanda , 3 Sept. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/fear-definition-effects-and-overcoming/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Fear: Definition, Effects, and Overcoming'. 3 September.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Fear: Definition, Effects, and Overcoming." September 3, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fear-definition-effects-and-overcoming/.
1. IvyPanda . "Fear: Definition, Effects, and Overcoming." September 3, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fear-definition-effects-and-overcoming/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Fear: Definition, Effects, and Overcoming." September 3, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fear-definition-effects-and-overcoming/.

- Micro Expressions Training Tools
- Facial Action Coding System
- Micro Expressions

What is Fear?
Fear is one of the seven universal emotions experienced by everyone around the world. Fear arises with the threat of harm, either physical , emotional, or psychological, real or imagined. While traditionally considered a “negative” emotion, fear actually serves an important role in keeping us safe as it mobilizes us to cope with potential danger.
Feeling fear
The family of fearful experiences can be distinguished in terms of three factors:
- Intensity: How severe is the harm that is threatened?
- Timing: Is the harm immediate or impending?
- Coping: What, if any, actions can be taken to reduce or eliminate the threat?
When we are able to cope with the threat, this lessens or removes the fear. Alternatively, when we are helpless to decrease the threat of harm, this intensifies the fear.

Fear can sometimes take place immediately following surprise and often oscillates with the experience of anger .
What makes us fearful
The universal trigger for fear is the threat of harm, real or imagined. This threat can be for our physical, emotional or psychological well-being. While there are certain things that trigger fear in most of us, we can learn to become afraid of nearly anything.
Common fear triggers:
- Darkness or loss of visibility of surroundings
- Heights and flying
- Social interaction and/or rejection
- Snakes, rodents, spiders and other animals
- Death and dying
Moods and disorders
Persistent fear can sometimes be referred to as anxiety if we feel constantly worried without knowing why. The inability to identify the trigger prevents us from being able to remove ourselves, or the actual threat, from the situation.
While anxiety is a common experience for many people, it can be considered a disorder when it is recurrent, persistent, intense, and interferes with basic life tasks such as work and sleep.
For more information about anxiety and phobias, read here .
Recognizing fear
Facial expression of fear.
The facial expression of fear is often confused with surprise . While both expressions show distinctly raised eyebrows, a fear expression's eyebrows are straighter and more horizontal whereas in surprise they are raised and curved. The upper eyelid is also lifted higher in fear than in surprise, exposing more sclera (white of the eye). Finally, the lips are tensed and stretched in fear but more open and slack in surprise.

Vocal expression of fear
When experiencing fear, one’s voice often has a higher pitch and more strained tone. One may also scream.
Sensations of fear
Common sensations include feeling cold and shortness of breath. It also may include sweating and trembling or tightening of muscles in the arms and legs.
Posture of fear
The posture of fear can either be one of mobilizing or immobilizing- freezing or moving away.
The function of fear
The universal function of fear is to avoid or reduce harm. Depending on what we have learned in the past about what can protect us in dangerous situations, we are capable of doing many things we wouldn’t typically be able, or willing, to do in order to stop the threat.
The immediate threat of harm focuses our attention, mobilizing us to cope with the danger. In this way, fear can actually save our lives by forcing us to react without having to think about it (e.g., jumping out of the way of a car coming at us). The evolutionary preset actions of fear include fight, flight and freezing.
Responding to fear in ourselves
While traditionally considered a “negative” emotion, fear actually serves an important role in keeping us safe. It can, however, also keep us feeling trapped and prevent us from doing things we’d like to. Whereas some people find fear nearly intolerable and avoid the emotion at all costs, others experience pleasure from feeling fear and seek it out (i.e., watching a horror film).
Responding to fear in others
It takes a well-developed capacity for compassion to respect, feel sympathetic toward, and patiently reassure someone who is afraid of something we are not afraid of (most of us dismiss such fears). We do not need to feel another person's fear to accept it and help them cope.
Additional Resources
Learn to recognize and respond to the emotional expressions of others with our online micro expressions training tools to increase your ability to detect deception and catch subtle emotional cues.
Expand your knowledge of emotional skills and competencies with in-person workshops offered through Paul Ekman International.
Delve into personal exploration and transformation with Cultivating Emotional Balance .
Build your emotional vocabulary with the Atlas of Emotions , a free, interactive learning tool created by Drs. Paul and Eve Ekman at the request of the Dalai Lama.
Read Dr. Ekman’s guide to emotions, the best-seller Emotions Revealed .
Introduce the world of emotions to children in a fun way with Dr. Ekman's official guide to Disney•Pixar's Inside Out .
- Training Tools
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Life
Essay Samples on Fear
Is fear always a harmful emotion: the complex nature of fear.
Is fear always a harmful emotion? Fear is a primal human emotion that has evolved to protect us from danger. While fear is often associated with negative outcomes, it is essential to recognize that fear serves an important purpose in our lives. In this essay,...
The Pervasive and Paralyzing Power of Fear in The Crucible
Introduction In Arthur Miller's seminal play "The Crucible," fear operates as a lethal and pervasive force that drives the action and defines the lives of key characters. Set against the backdrop of the Salem witch trials, the play is not merely a recounting of historical...
- The Crucible
Overcoming the Fear Of Failure and Reaching Goals
Fear of failure is when we let that fear to stop us from achieving our goals and objectives, but is very important to learn how to overcome it. This kind of fear is most of the time irrational and continuous. People should find a way...
- Fear of Failure
Coping With Loss: Kubler-Ross And Mitford'S Articles
The moral of Jessica Mitford's article, “Behind the Formaldehyde Curtain”, is to expose the process of what occurs have someone dies. She also exposes all of the procedures that undergo the deceased body in order to be displayed at the funeral. In comparison to Ross’s...
- On The Fear of Death
Attitudes Towards Death In Mitford'S And Kubler-Ross'S Articles
Death is inevitable and unexplainable which is why people fear death. Nobody wants to die leaving behind all the memories of family and friends behind. “Behind the formaldehyde curtains” by Mitford and “On the fear of death” by Ross both share the same view on...
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
The Variation of Horror Genre and Its Examples
When I was a kid, I used to hate horror films, as the matter of fact, I refuse to watch them as I didn’t fathom why would anyone purposely scare themselves. For many people, horror movies are a horrendous experience. They hate to see graphic...
The Debate About the Horror Genre as Appropriate to Children
Beetlejuice, Beetlejuice, Beetlejuice! Everyone remembers the iconic 1980s movie Beetlejuice. This classic horror movie has been enjoyed by many kids and adults for years now. Beetlejuice is not the only iconic horror movie that is enjoyed by all age ranges. Gremlins another class favorite is...
Edgar Allan Poe's Horror Works: The Pit and The Pendulum
Edgar Allan Poe is an expert when it comes to writing horror. He holds over 60 short stories to his name. Poe has a very distinct style of writing. Because of his uniqueness, his stories share many attributes. Poe is obsessed with the macabre and...
- The Pit and The Pendulum
Conquering Personal Fear of Roller Coaster
As I sit at the front seat of the roller coaster train, fear and anxiety infiltrate my mind. The red color of the train makes me think of the rushing blood in my body. The tension in my mind causes me to think that I...
- Roller Coaster
The Atomic Age Feasted On Fear
The unknown outcome of the Atomic Age plagued American society with fear. The public was influenced by the use of what some may call propaganda and tales of doom. Sources such as Duck and Cover by the Office of Civil Defence, Atomic War! by Ace...
- Nuclear War
Reality of Fighting With Fear In 'A Separate Peace'
Everyone experiences the reality of internal and external conflicts at one time or another (and often create their own psychological enemies). Internal conflicts refer to one’s inner struggles, feelings like doubt, guilt or shame become the source of someone’s actions. Whereas external conflicts are created...
- A Separate Peace
Fear Conditioning Under Social Stress
Introduction In the study of psychology, research has always looked at emotions and the role they play in everyday behaviour as well as in pathological behaviour. Several studies have shown that emotionally charged stimuli attract human attention quicker and have an advantage in information processing....
What Is Courage And Why Need It In Our Life
The ability to do something that frightens you, having strength while facing grief or pain, and the ability to act on your beliefs despite danger or disapproval are all definitions of courage. Courage is something that isn't always easy to have, but those who are...
Struggle of Persistance and Overcoming the Fear of Religious Faith
Faith can be influenced by the people we surround ourselves with, the religions we grew up with, particular things we believe in, and all of them define us based on the degree of our confidence in faith. Founded on all these fragments of our life...
Dealing with the Fear of Failure
If failure does not lead to a new product, process, or discovery, it should lead to some type of learning. Leaders with developed character regarding failure have the poise to accept it without condemning themselves. Like a good football coach looking at the game films...
An Account of Fear of Failure: Fear of Driving
As a young teen, one of our greatest moments growing up is learning how to drive. Driving is a rite of passage that signifies freedom through the ability of being able to maneuver a vehicle and get from one point to another. Learning to drive...
The Value of Failure and Challenging the Fear of It
Failure is like a puzzle, you cannot see the bigger and beautiful picture until every piece is put in place. Puzzles are time-consuming and often leave one in a state of tedium as to where they believe their task of completing the puzzle cannot be...
Understanding and Breaking Down the Fear of Public Speaking
Communicating your ideas publicly is an essential part of many aspects of life. Weather your doing a school presentation, or presenting your ideas to your fellow co-workers, public speaking is an important aspect that many people are afraid of. Public speaking can lead to many...
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
You Should Define Your Fears Instead Of Your Goals
What we most fear doing, asking, saying are very often exactly what we most need to do. How can we overcome self-paralysis and take action? We all know goal setting exercise. What about Fear setting exercise? What should we define our FEAR or our GOALS?...

The Path to Success: How Failure Is A Blessing In Disguise
Failure, a single word that strikes fear into the hearts of many. We all know failure as not being able to achieve that one thing you’ve been dreaming of for so many years. Failure, reaching for success but falling hard, hitting the ground hard, having...
My Relationship with Water: a Journey of Triumph Over Aquaphobia
Since I was a little girl I’d been afraid of the ocean, hair prickling all over my body, afraid. I could feel the sensation of my heart palpitating. I stood paralyzed, traumatized for life as the dolphin passed by the small circled window to greet...
Public Speaking as My Biggest Fear
As a student one of my biggest fears is public speaking. Fear in public speaking or glosopobia is frequently but incorrectly cited as a people's biggest fear, and it is very common in students like us,it happens when reporting,roleplaying, and reciting. This is not just...
- Personal Life
You Should Never Let Fear Overcome You
The story starts with a picture that was taken in a classroom with three of my friends in my high school during our Christmas program. It was taken to memorialize the first time that we, as performers, attended the school’s program by performing a Christian...
The Need For Investigation Of The Fear Relation To Anxiety Disorders
Fear has been characterized as separate from Anxiety. Fear is “a basic emotion that is an adaptive response to threat marked by quick, automatic onset, brief duration, and sympathetic arousal” whereas Anxiety is a “future-focused cognitive association that connects basic emotions (such as fear) to...
- Anxiety Disorder
A Prerequisite to Growth: Why People Fear Change
Different situations have different effect on us. Changes are the reason for thrill in our lives, but many people fear CHANGE. No matter how small a change is, sometimes it is hard for people to accept. Change in a relation due to distance can be...
Best topics on Fear
1. Is Fear Always a Harmful Emotion: The Complex Nature of Fear
2. The Pervasive and Paralyzing Power of Fear in The Crucible
3. Overcoming the Fear Of Failure and Reaching Goals
4. Coping With Loss: Kubler-Ross And Mitford’S Articles
5. Attitudes Towards Death In Mitford’S And Kubler-Ross’S Articles
6. The Variation of Horror Genre and Its Examples
7. The Debate About the Horror Genre as Appropriate to Children
8. Edgar Allan Poe’s Horror Works: The Pit and The Pendulum
9. Conquering Personal Fear of Roller Coaster
10. The Atomic Age Feasted On Fear
11. Reality of Fighting With Fear In ‘A Separate Peace’
12. Fear Conditioning Under Social Stress
13. What Is Courage And Why Need It In Our Life
14. Struggle of Persistance and Overcoming the Fear of Religious Faith
15. Dealing with the Fear of Failure
- Personality
- Career Goals
- Clinical Experience
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Home / Essay Samples / Life / Emotion / Fear
Fear Essay Examples
The moment of fear i will remember forever.
I will never forget that moment in time. It had occurred on a Sunday like any other. The birds had been chirping, the sky was a luminous blue. I had been up on my roof cleaning the gutter. Scrape, brush I did in a regular...
The Role of Fears and Phobias in Our Life
Fear is an emotion or feeling which is felt by humans due to any types of frightening or scary behavior. Fearing for a certain long period of time may cause damage to a person and leads to depression or anxiety perhaps death too. Fear is...
Facing Fear to Overcome It
Fear is a strong negative emotion that keeps a person from doing something and also a signal of danger and weakness. It is considered as one of most powerful emotion where it can change the course of action or make a situation seem more unfortunate....
How I Overcome My Fear of Flying
Sitting rather uncomfortably in my seat while facing the painfully bright light piercing from the window, I fidgeted nervously, desperately trying to ignore the gloominess of the situation. I attempted to focus on staying warm in the bitterly frigid row, but as thoughts of certain...
Fear and Fhobias in My Life
Fear is an unpleasant emotion and it is an emotional response induced by a perceived threat, which causes change in human’s brain and as well as in behavior. Fear can lead to a danger zone were people commits suicide in order to avoid fear. Fear...
Overcoming the Fear of Public Speaking
Fears can be one’s worst enemy, and it hinders you from progressing. But for those who are willing to fight it, it can serve as a gateway to greatness. If you are able to overcome your fears, it will not only help you to grow...
The Theme of Embarrassment in the Things They Carried by Tim O’brien
“All external expectations, all pride, all fear of embarrassment or failure- these things just fall away in the face of death.” This quote by Steve Jobs parallels the ideas depicted by Tim O'Brien about embarrassment in his novel. Not only do most literary characters struggle...
Unpacking the Influence of Fear on Our Daily Lives
In today’s society, fear plays a huge role and influences many decisions of many people. We see this everywhere, politics, media and even our daily lives. In the article, “3 Roles Fear Plays In Our Lives”, written by Donna Labermeier, fear is talked about as...
The Effect of Fear on Communities in Year of Wonders
Fear is a constant reminder that we are human although it can make us believe we’re not. Both Geraldine Brooks the author of ‘Year of Wonders’ and Arthur Miller author of ‘The Crucible’, explore the effect of fear on the seventeenth century communities. While both...
Man Versus Fear in the Red Badge of Courage
Fear is a powerful motivator. A naïve, young man named Henry Fleming decides to join the Union army simply for the glory of becoming a Civil War hero. He quickly realizes that war is terrible and struggles with his conscious as to whether-or-not he can...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
You may also like
- Inspiration
- Professionalism
- Betrayal Essays
- Compassion Essays
- Gratitude Essays
- Forgiveness Essays
- Regret Essays
- Nostalgia Essays
- Ambition Essays
- Kindness Essays
- Happiness Essays
- Respect Essays
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->