- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring

Social Entrepreneurship, Essay Example
Pages: 10
Words: 2757
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Subject: how can social entrepreneurship contribute to society?
Terms of reference
For a very long time not enough attention has been paid to the importance of social entrepreneurship in bringing about development in our societies. Despite half hearted efforts by the protagonists of this phenomenal to bring into attention of everyone about the importance of this aspect in enhancing our social economic lives, nothing much has really been achieved. The reason for this can be attributed to the slow pace that governments and other stake holders are taking in recognizing the important role that this entities play in our society. This is the major content of this report.
The report begins with a short description of the problem at hand. It gives a brief summary of the history of social entrepreneurship, its recent developments and the possible way forward. This is then followed by an in depth analysis of all the available literature as far as this important subject is concerned. The answer to the problem question (how can social entrepreneurship contribute to society?) is well dealt with in this section. Last but not least I conclude my report with a summary and recommendations of the major findings of the report. It is my hope that this report will form a solid basis for the concerned stakeholders to act so as to full tap the potential of social entrepreneurship in our societies.
Introduction
Before introducing what we mean by social entrepreneurship, let’s define who is a social entrepreneur. There are many ways in which a social entrepreneur has been defined but nevertheless a common agreement exists. Munoz (13) defines a social entrepreneur as an individual who takes his/her time, spirit, and energy to build better communities as opposed to personal businesses for personal gain. On the same note Bornstein (11) also defines a social entrepreneur as someone who look to the world, recognize a problem then uses the principles of entrepreneurship to organize, build and manage such a venture to realize positive social change. A critical look at these two definitions simply shows more or less the same thing. It is only approach that differs. Generally speaking a social entrepreneur is an individual who is set out to bring positive change in the society through the various programs he has decided to undertake. A social entrepreneur is different from a normal entrepreneur in that whereas a normal entrepreneur calculates his success in term of how much profit he has made, a social entrepreneur calculates his success in terms of how much social returns he has achieved. So then what is social entrepreneurship?
Social entrepreneurship is simply the collective work of social entrepreneurs. When done within a country’s borders it is referred to as social entrepreneurship whereas when done outside a country’s borders it is called international social entrepreneurship Bornstein (12). Some of the word’s most recognized social entrepreneurs include the following:
Raul Oscar Abasolo: he operates in Chile and is mostly involved with alleviating youth poverty.
Rafael Alvarez: he is the founder of Genesysworks in America that is involved in expanding youth horizons after high school and college.
Istvan Aba-Horvath: this Hungarian based social entrepreneur involved with promoting child education in his backyard.
Manish Sankila: based in India and also involved with empowering the youth towards self employment for the better of their future life. Manish strongly believes that when the youth are empowered the rest of the society is also empowered because they not only form the majority but also the future of a society.
History of the term social entrepreneurship can be traced back to 1950s and 60s when it first appeared in print literature. This continued to 1980s and 90s with the works of people like Bill Drayton. Bill together with Charles Leadbeater popularized the social movement in Europe, USA and some parts of Asia. They were joined by Michael Young in their endeavors. In fact Harvard professor Daniel Bell describes Michael as “’the world’s most successful entrepreneur of social enterprises’. This was undoubtedly due to his immense work in building about 60 social institutions worldwide (Munoz, 21). The famous among them include school of social entrepreneurs that has branches in Australia, UK, and Canada.
In the contemporary world, whenever the term social entrepreneurship is mentioned, people like Muhammad Yunus come into our mind. He is the founder and proprietor of Grameen Bank and Nobel peace laureate of 2006. Yunus is most recognized for his revolutionary method of making it possible for the word’s poorest people to access credit from banks. Thus he saw a social problem and came up with a strategy to assist his people while at the same time making profits. To some extent also in the contemporary world social entrepreneurship has evolved into organizations like foundations, NGO’s, social enterprise and etc. generally social entrepreneurship remains relevant and appreciated by many societies today as it was in the last century.
The importance of social entrepreneurship
According to modern social entrepreneurship website the first and obvious importance of social entrepreneurship is employment creation. A close look at the objectives of some of the most famous entrepreneurs supports this conclusion. This is why most of them target the society’s most vulnerable groups i.e. the children, the youth, disabled and women. This can be in the form of empowering individuals to start their own businesses or better still starting business ventures and employ them. No human being is totally unemployable, provided one is alive; there is one or two things that he/she can engage in to assist him/her become productive. For instance a cripple can be a shoe shiner in the same way a blind can be a singer. The only thing that such individuals need is empowerment. Thus social entrepreneurship has been seen to be one surest way to end abject poverty especially in less developed economies of the world.
Secondly another direct importance of social entrepreneurship is the ability to bring forth new goods and services in societies. This is due to the innovative nature of social entrepreneurship. The fact that social entrepreneurs target where individuals at the grass root level gives them an upper hand to come with innovative ways to tackle a society’s most pressing problems. A good example is Veronica Khossa; a Brazilian based social entrepreneur who came up a home based care model for people living with aids. It was so innovative and effective that the Brazilian government (through the ministry of health) decided to use it as a government policy!
Next, social entrepreneurship has proved to be a strong pillar in building social capital. Social capital is the communal holding, sharing and managing of a society’s resources. This was historically promoted by the communist ideologies of the eastern block (Bornstein, 33). The protagonist of such ideologies argues that it is better for a society to share the little available resources and every one feels satisfied than just enrich a few individuals while the rest are suffering. Examples of economies that have embraced this model are Japan, Germany and china. Judging from the way such societies have developed, we can comfortably say that social entrepreneurship is the way of the future. With the right approach and tools, social entrepreneurship can easily turn a third word country to be middle earner in a very short time.
Last but not least, the topic of importance of social entrepreneurship can not be complete without mentioning how it promotes societies and individuals achieve (or almost achieve) equality. This point is closely related to the previous one that talked about social capitalism. We can say this is the ultimate achievement of social entrepreneurship. A dream that is dear to almost all protagonists of social entrepreneurship – society where each and every individual is productive and economically able to sustain himself. For instance by supporting the disabled to support themselves is not only beneficial to them but also to the whole society because there will be no need to be looking after them like little children. A good example is professor Yunus’s case of economically empowering disadvantaged women in society. The American social entrepreneur J.B. Schramm’s case of helping financially unable students to attend school also deserves a special mention in such a case (Muhammad, 63).
How social entrepreneurship can contribute to society
The benefits that social entrepreneurship can bring to society are immense and can not be over emphasized if the case of Nobel laureate Yunus is anything to go by. It has demonstrated beyond reasonable doubt that is a strong change agent in societies. Below are some of the contributions that social entrepreneurship can bring to society as supported by (Munoz, 101).
- Charitable institutions
- Welfare program
- New products
- Sponsorship
- Government advisors
Starting with charitable institutions, it can be said that most social entrepreneurs set up institutions that target to improve the living standards of the downtrodden. Such institutions include schools, hospitals, vocational training institutions and etc. All this is meant to serve the societies they are operating in. this is an immense contribution to societies especially where poverty levels are high.
On the same note social entrepreneurs have been known to contribute to society in terms of direct donations they give for various purposes. All these are just aimed at improving the living standards of the less privileged people in society. For instance an entrepreneur like Istvan Aba-Horvath in Hungary donates a lot of funds towards promoting the education of Gypsy children. Therefore this is a great contribution that social enterprises have towards societies in which they are operating (Munoz, 12).
Welfare programs are yet another contribution that social entrepreneurship has to societies. Each and every society has its own unique welfare programs that are aimed at improving the lives of all people. Social entrepreneurship contributes to such programs through funding such organizations, empowering communities or even providing the welfares by themselves. Such welfares programs include helping the disabled, taking care of orphans, feeding the elderly among others.
Social enterprises have earned themselves the tag of being the most innovative and in touch with society’s most pressing needs. Due to this they are able to come up with new products and services that are aimed at addressing the society’s challenges. This is a very great achievement as far as contributions of social enterprises are concerned. The great philosophers once said that necessity is the mother of inventions and this as been demonstrated by man’s endeavor to survive on this planet called earth.
Social entrepreneurship has also demonstrated that it can contribute to the society through sponsorships. Such arrangements are common in educational circles where an entrepreneur can sponsor individuals who have excelled in their academics but are not able to continue with their academic dreams due to their financial inability. In fact there are some social enterprises that have set up foundations and trust funds specifically for this purpose. This is a great way to bring about social quality through empowering individuals using knowledge (Muhammad, 52).
Finally we can say that social enterprises have contributed to society through advising the governments on various issues that affect the society. This is because they have close contact with the people on the ground. A good example is that case of Brazil where a social enterprise devised a model of treating and managing people living with HIV/Aids that was adopted by the government on national scale. What started as a small experimentation on local level became something of national importance. Social enterprises have also been closely working with governments on various social issues affecting societies worldwide.
It is important to note here that whereas I have tried to explore the contributions of social enterprises on society, this is not exhaustive. There are many other contributions that are indirect but equally important. For example we can say that through empowering individuals to fend for themselves, they bring about reduced crime rate in society. Thus providing security to society though in an indirect manner. Thus this is a crucial part of society that should not be overlooked at all costs (social entrepreneurship website).
Expected future developments
Going by the recent developments, we can comfortably say that social entrepreneurship is going to be the thing of the future. For instance there is this instance on international level whereby the wealthy of countries of the world will be measured by how much they contribute to assist the poor nations of the world. This in itself is a great step towards achieving an equal society and even if it is not social entrepreneurship directly, its targets or objectives are the same as those of social entrepreneurship. Going to the future there is likelihood that more states of the world will recognize the role of social entrepreneurship in society and national development and thus support and appreciate it fully (Bornstein, 71).
There is also a likelihood that social entrepreneurship scope will enlarge to involve such entities as community based organizations (CBO), trust funds, governments’ stipends, foundations among others. This is because whereas it is true that all this entities are formed for special objectives, there ultimate aim is societal development which is also the same goal for social entrepreneurship.
Additionally most of the business entrepreneurs that we know today may turn to social entrepreneurship as a way to return to society. This can be seen by the likes of bill gates and bill Clinton. These two individuals have formed foundations that are meant to alleviate human suffering in some of the world’s poorest places on the world like Africa (Bornstein, 73). There is likely hood that more will follow suit and the ultimate result will be an equal society – a good dream indeed or isn’t it?
In conclusion, it can be said that social enterprises remain to be a positive force, change agent and above all an empowerment tool. Social enterprises remain the most effective way to come up with leading edge innovations to meet society’s most challenging needs. The fact that social entrepreneurship emanates from the grass root level should not make it be overlooked as a panacea. This is because it works within the frameworks of economy and society. Therefore it deserves special attention from policy makers, entrepreneurs, scholars and academic theorists. This is very vital to all countries of the world especially those facing high incidence of abject poverty.
Social entrepreneurship should not be looked as fighting the governments and other stakeholders in the provision of services and goods that societies need, but rather they should be seen as contributing to the already existing efforts for the better of society in general. Therefore all the government needs is to regulate them so as to work within the prevailing framework in the most efficient way possible. Wherever possible there is no harm to work hand in hand after all we are all serving the same society.
Summary and Recommendations
From the foregoing discussion, it is very clear that social enterprises have a very critical role to play towards the welfare of societies. In fact it can not be emphasized more than this. Therefore the ball remains on policy makers, entrepreneurs and all of us to fully embrace and appreciate the role it plays in our lives. We can’t ignore it any more. With good policies and right approach to application of social entrepreneurship, societal development and well being is guaranteed. The following are some of the recommendations I have come about in my research.
- There is need for all governments of the world to fully recognize the role that social entrepreneurship plays in developments of society. This then will also be recognized by the state laws.
- Secondly there is urgent need for all entrepreneurs to also set apart some of their resources towards social entrepreneurship. There is no need to focus on enriching oneself while the majority of people are languishing in poverty.
- There is also a need to come up with sound policies to regulate, enhance and develop the works of social entrepreneurship. After all in most if not all the cases they play the same roles that are supposed to be played by governments.
- Third and lastly, the fight against abject poverty and suffering starts with you and me. This is a great war that can not be left to governments and entrepreneurs alone; we should all play our part no matter how small it is to make a difference. Even just sharing information with some one can bring a big difference.
Works cited
Munoz, J.M. (2010). International Social Entrepreneurship: Pathways to Personal and Corporate Impact. New York: Business Expert Press. Available at: http://www.businessexpertpress.com/books/international-social-entrepreneurship .
David Bornstein, (2009). How to Change the World: Social Entrepreneurs and the Power of New Ideas, Oxford University Press.
Yunus, Muhammad; Jolis, Alan. (2007). Banker to the poor : micro-lending and the battle against world poverty . New York: Public Affairs hc. pp. 46–49.
The modern social entrepreneurship available at: http://www.business4good.org/2007/04/importance-of-social-entrepreneurship.html
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Organizational Design, Term Paper Example
Accident Claim Compensation, Thesis Paper Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371

- Arts & Culture
- Civic Engagement
- Economic Development
- Environment
- Human Rights
- Social Services
- Water & Sanitation
- Foundations
- Nonprofits & NGOs
- Social Enterprise
- Collaboration
- Design Thinking
- Impact Investing
- Measurement & Evaluation
- Organizational Development
- Philanthropy & Funding
- Current Issue
- Sponsored Supplements
- Global Editions
- In-Depth Series
- Stanford PACS
- Submission Guidelines
Essentials of Social Innovation
Social entrepreneurship: the case for definition.
Social entrepreneurship is attracting growing amounts of talent, money, and attention, but along with its increasing popularity has come less certainty about what exactly a social entrepreneur is and does.
- download https://ssir.org/images/articles/2007SP_feature_martinosberg.pdf
- order reprints
- related stories
By Roger L. Martin & Sally Osberg Spring 2007

A starter kit for leaders of social change.
• Collective Impact
• Social Entrepreneurship: The Case for Definition
• The Dawn of System Leadership
• Design Thinking for Social Innovation
• The Nonprofit Starvation Cycle
• Ten Nonprofit Funding Models
• The Science of What Makes People Care
• Stop Raising Awareness Already
• Rediscovering Social Innovation
• Innovation Is Not the Holy Grail
The latest social innovation essentials, delivered to your inbox .
The nascent field of social entrepreneurship is growing rapidly and attracting increased attention from many sectors. The term itself shows up frequently in the media , is referenced by public officials, has become common on university campuses, and informs the strategy of several prominent social sector organizations, including Ashoka and the Schwab and Skoll Foundation foundations.
The reasons behind the popularity of social entrepreneurship are many. On the most basic level, there’s something inherently interesting and appealing about entrepreneurs and the stories of why and how they do what they do. People are attracted to social entrepreneurs like last year’s Nobel Peace Prize laureate Muhammad Yunus for many of the same reasons that they find business entrepreneurs like Steve Jobs so compelling – these extraordinary people come up with brilliant ideas and against all the odds succeed at creating new products and services that dramatically improve people’s lives.
But interest in social entrepreneurship transcends the phenomenon of popularity and fascination with people. Social entrepreneurship signals the imperative to drive social change, and it is that potential payoff, with its lasting, transformational benefit to society, that sets the field and its practitioners apart.
Although the potential benefits offered by social entrepreneurship are clear to many of those promoting and funding these activities, the actual definition of what social entrepreneurs do to produce this order of magnitude return is less clear. In fact, we would argue that the definition of social entrepreneurship today is anything but clear. As a result, social entrepreneurship has become so inclusive that it now has an immense tent into which all manner of socially beneficial activities fit.
In some respects this inclusiveness could be a good thing. If plenty of resources are pouring into the social sector, and if many causes that otherwise would not get sufficient funding now get support because they are regarded as social entrepreneurship, then it may be fine to have a loose definition. We are inclined to argue, however, that this is a flawed assumption and a precarious stance.
Social entrepreneurship is an appealing construct precisely because it holds such high promise. If that promise is not fulfilled because too many “nonentrepreneurial” efforts are included in the definition, then social entrepreneurship will fall into disrepute, and the kernel of true social entrepreneurship will be lost. Because of this danger, we believe that we need a much sharper definition of social entrepreneurship, one that enables us to determine the extent to which an activity is and is not “in the tent.” Our goal is not to make an invidious comparison between the contributions made by traditional social service organizations and the results of social entrepreneurship, but simply to highlight what differentiates them.
If we can achieve a rigorous definition, then those who support social entrepreneurship can focus their resources on building and strengthening a concrete and identifiable field. Absent that discipline, proponents of social entrepreneurship run the risk of giving the skeptics an ever-expanding target to shoot at, and the cynics even more reason to discount social innovation and those who drive it.
Starting With Entrepreneurship
Any definition of the term “social entrepreneurship” must start with the word “entrepreneurship.” The word “social” simply modifies entrepreneurship. If entrepreneurship doesn’t have a clear meaning, then modifying it with social won’t accomplish much, either.
The word entrepreneurship is a mixed blessing. On the positive side, it connotes a special, innate ability to sense and act on opportunity, combining out-of-the-box thinking with a unique brand of determination to create or bring about something new to the world. On the negative side, entrepreneurship is an ex post term, because entrepreneurial activities require a passage of time before their true impact is evident.
Interestingly, we don’t call someone who exhibits all of the personal characteristics of an entrepreneur – opportunity sensing, out-of-the-box thinking, and determination – yet who failed miserably in his or her venture an entrepreneur; we call him or her a business failure. Even someone like Bob Young, of Red Hat Software fame, is called a “serial entrepreneur” only after his first success; i.e., all of his prior failures are dubbed the work of a serial entrepreneur only after the occurrence of his first success. The problem with ex post definitions is that they tend to be ill defined. It’s simply harder to get your arms around what’s unproven. An entrepreneur can certainly claim to be one, but without at least one notch on the belt, the self-proclaimed will have a tough time persuading investors to place bets. Those investors, in turn, must be willing to assume greater risk as they assess the credibility of would-be entrepreneurs and the potential impact of formative ventures.
Even with these considerations, we believe that appropriating entrepreneurship for the term social entrepreneurship requires wrestling with what we actually mean by entrepreneurship. Is it simply alertness to opportunity? Creativity? Determination? Although these and other behavioral characteristics are part of the story and certainly provide important clues for prospective investors, they are not the whole story. Such descriptors are also used to describe inventors, artists, corporate executives, and other societal actors.
Like most students of entrepreneurship, we begin with French economist Jean-Baptiste Say, who in the early 19th century described the entrepreneur as one who “shifts economic resources out of an area of lower and into an area of higher productivity and greater yield,” thereby expanding the literal translation from the French, “one who undertakes,” to encompass the concept of value creation. 1
Writing a century later, Austrian economist Joseph Schumpeter built upon this basic concept of value creation, contributing what is arguably the most influential idea about entrepreneurship. Schumpeter identified in the entrepreneur the force required to drive economic progress, absent which economies would become static, structurally immobilized, and subject to decay. Enter the Unternehmer , Schumpeter’s entrepreneurial spirit, who identifies a commercial opportunity – whether a material, product, service, or business – and organizes a venture to implement it. Successful entrepreneurship, he argues, sets off a chain reaction, encouraging other entrepreneurs to iterate upon and ultimately propagate the innovation to the point of “creative destruction,” a state at which the new venture and all its related ventures effectively render existing products, services, and business models obsolete. 2
Despite casting the dramatis personae in heroic terms, Schumpeter’s analysis grounds entrepreneurship within a system, ascribing to the entrepreneur’s role a paradoxical impact, both disruptive and generative. Schumpeter sees the entrepreneur as an agent of change within the larger economy. Peter Drucker, on the other hand, does not see entrepreneurs as necessarily agents of change themselves, but rather as canny and committed exploiters of change. According to Drucker, “the entrepreneur always searches for change, responds to it, and exploits it as an opportunity,” 3 a premise picked up by Israel Kirzner, who identifies “alertness” as the entrepreneur’s most critical ability. 4
Regardless of whether they cast the entrepreneur as a breakthrough innovator or an early exploiter, theorists universally associate entrepreneurship with opportunity. Entrepreneurs are believed to have an exceptional ability to see and seize upon new opportunities, the commitment and drive required to pursue them, and an unflinching willingness to bear the inherent risks.
Building from this theoretical base, we believe that entrepreneurship describes the combination of a context in which an opportunity is situated, a set of personal characteristics required to identify and pursue this opportunity, and the creation of a particular outcome.
To explore and illustrate our definition of entrepreneurship, we will take a close look at a few contemporary American entrepreneurs (or pairs thereof ): Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak of Apple Computer, Pierre Omidyar and Jeff Skoll of eBay, Ann and Mike Moore of Snugli, and Fred Smith of FedEx.
Entrepreneurial Context
The starting point for entrepreneurship is what we call an entrepreneurial context. For Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, the entrepreneurial context was a computing system in which users were dependent on mainframe computers controlled by a central IT staff who guarded the mainframe like a shrine. Users got their computing tasks done, but only after waiting in line and using the software designed by the IT staff. If users wanted a software program to do something out of the ordinary, they were told to wait six months for the programming to be done.
From the users’ perspective, the experience was inefficient and unsatisfactory. But since the centralized computing model was the only one available, users put up with it and built the delays and inefficiencies into their workflow, resulting in an equilibrium, albeit an unsatisfactory one.
System dynamicists describe this kind of equilibrium as a “balanced feedback loop,” because there isn’t a strong force that has the likely effect of breaking the system out of its particular equilibrium. It is similar to a thermostat on an air conditioner: When the temperature rises, the air conditioner comes on and lowers the temperature, and the thermostat eventually turns the air conditioner off.
The centralized computing system that users had to endure was a particular kind of equilibrium: an unsatisfactory one. It is as if the thermostat were set five degrees too low so that everyone in the room was cold. Knowing they have a stable and predictable temperature, people simply wear extra sweaters, though of course they might wish that they didn’t have to.
Pierre Omidyar and Jeff Skoll identified an unsatisfactory equilibrium in the inability of geographically based markets to optimize the interests of both buyers and sellers. Sellers typically didn’t know who the best buyer was and buyers typically didn’t know who the best (or any) seller was. As a result, the market was not optimal for buyers or sellers. People selling used household goods, for example, held garage sales that attracted physically proximate buyers, but probably not the optimal number or types of buyers. People trying to buy obscure goods had no recourse but to search through Yellow Page directories, phoning and phoning to try to track down what they really wanted, often settling for something less than perfect. Because buyers and sellers couldn’t conceive of a better answer, the stable, yet suboptimal, equilibrium prevailed.
Ann and Mike Moore took note of a subpar equilibrium in parents’ limited options for toting their infants. Parents wishing to keep their babies close while carrying on basic tasks had two options: They could learn to juggle offspring in one arm while managing chores with the other, or they could plop the child in a stroller, buggy, or other container and keep the child nearby. Either option was less than ideal. Everyone knows that newborns benefit from the bonding that takes place because of close physical contact with their mothers and fathers, but even the most attentive and devoted parents can’t hold their babies continuously. With no other options, parents limped along, learning to shift their child from one hip to the other and becoming adept at “one-armed paper hanging,” or attempting to get their tasks accomplished during naptime.
In the case of Fred Smith, the suboptimal equilibrium he saw was the long-distance courier service. Before FedEx came along, sending a package across country was anything but simple. Local courier services picked up the package and transported it to a common carrier, who flew the package to the remote destination city, at which point it was handed over to a third party for final delivery (or perhaps back to the local courier’s operation in that city if it was a national company). This system was logistically complex, it involved a number of handoffs, and the scheduling was dictated by the needs of the common carriers. Often something would go wrong, but no one would take responsibility for solving the problem. Users learned to live with a slow, unreliable, and unsatisfactory service – an unpleasant but stable situation because no user could change it.
Entrepreneurial Characteristics
The entrepreneur is attracted to this suboptimal equilibrium, seeing embedded in it an opportunity to provide a new solution, product, service, or process. The reason that the entrepreneur sees this condition as an opportunity to create something new, while so many others see it as an inconvenience to be tolerated, stems from the unique set of personal characteristics he or she brings to the situation – inspiration, creativity, direct action, courage, and fortitude. These characteristics are fundamental to the process of innovation.
The entrepreneur is inspired to alter the unpleasant equilibrium. Entrepreneurs might be motivated to do this because they are frustrated users or because they empathize with frustrated users. Sometimes entrepreneurs are so gripped by the opportunity to change things that they possess a burning desire to demolish the status quo. In the case of eBay, the frustrated user was Omidyar’s girlfriend, who collected Pez dispensers.
The entrepreneur thinks creatively and develops a new solution that dramatically breaks with the existing one. The entrepreneur doesn’t try to optimize the current system with minor adjustments, but instead finds a wholly new way of approaching the problem. Omidyar and Skoll didn’t develop a better way to promote garage sales. Jobs and Wozniak didn’t develop algorithms to speed custom software development. And Smith didn’t invent a way to make the handoffs between courier companies and common carriers more efficient and error-free. Each found a completely new and utterly creative solution to the problem at hand.
Once inspired by the opportunity and in possession of a creative solution, the entrepreneur takes direct action . Rather than waiting for someone else to intervene or trying to convince somebody else to solve the problem, the entrepreneur takes direct action by creating a new product or service and the venture to advance it. Jobs and Wozniak didn’t campaign against mainframes or encourage users to rise up and overthrow the IT department; they invented a personal computer that allowed users to free themselves from the mainframe. Moore didn’t publish a book telling mothers how to get more done in less time; she developed the Snugli, a frameless front- or backpack that enables parents to carry their babies and still have both hands free. Of course, entrepreneurs do have to influence others: first investors, even if just friends and family; then teammates and employees, to come work with them; and finally customers, to buy into their ideas and their innovations. The point is to differentiate the entrepreneur’s engagement in direct action from other indirect and supportive actions.
Entrepreneurs demonstrate courage throughout the process of innovation, bearing the burden of risk and staring failure squarely if not repeatedly in the face. This often requires entrepreneurs to take big risks and do things that others think are unwise, or even undoable. For example, Smith had to convince himself and the world that it made sense to acquire a fleet of jets and build a gigantic airport and sorting center in Memphis, in order to provide next-day delivery without the package ever leaving FedEx’s possession. He did this at a time when all of his entrenched competitors had only fleets of trucks for local pickup and delivery – they certainly didn’t run airports and maintain huge numbers of aircraft.
Finally, entrepreneurs possess the fortitude to drive their creative solutions through to fruition and market adoption. No entrepreneurial venture proceeds without setbacks or unexpected turns, and the entrepreneur needs to be able to find creative ways around the barriers and challenges that arise. Smith had to figure out how to keep investors confident that FedEx would eventually achieve the requisite scale to pay for the huge fixed infrastructure of trucks, planes, airport, and IT systems required for the new model he was creating. FedEx had to survive hundreds of millions of dollars of losses before it reached a cash-flow positive state, and without a committed entrepreneur at the helm, the company would have been liquidated well before that point.
Entrepreneurial Outcome
What happens when an entrepreneur successfully brings his or her personal characteristics to bear on a suboptimal equilibrium? He or she creates a new stable equilibrium, one that provides a meaningfully higher level of satisfaction for the participants in the system. To elaborate on Say’s original insight, the entrepreneur engineers a permanent shift from a lower-quality equilibrium to a higher-quality one. The new equilibrium is permanent because it first survives and then stabilizes, even though some aspects of the original equilibrium may persist (e.g., expensive and less-efficient courier systems, garage sales, and the like). Its survival and success ultimately move beyond the entrepreneur and the original entrepreneurial venture. It is through mass-market adoption, significant levels of imitation, and the creation of an ecosystem around and within the new equilibrium that it first stabilizes and then securely persists.
When Jobs and Wozniak created the personal computer they didn’t simply attenuate the users’ dependence on the mainframe – they shattered it, shifting control from the “glass house” to the desktop. Once the users saw the new equilibrium appearing before their eyes, they embraced not only Apple but also the many competitors who leaped into the fray. In relatively short order, the founders had created an entire ecosystem with numerous hardware, software, and peripheral suppliers; distribution channels and value-added resellers; PC magazines; trade shows; and so on.
Because of this new ecosystem, Apple could have exited from the market within a few years without destabilizing it. The new equilibrium, in other words, did not depend on the creation of a single venture, in this case Apple, but on the appropriation and replication of the model and the spawning of a host of other related businesses. In Schumpeterian terms, the combined effect firmly established a new computing order and rendered the old mainframe-based system obsolete.
In the case of Omidyar and Skoll, the creation of eBay provided a superior way for buyers and sellers to connect, creating a higher equilibrium. Entire new ways of doing business and new businesses sprang up to create a powerful ecosystem that simply couldn’t be disassembled. Similarly, Smith created a new world of package delivery that raised standards, changed business practices, spawned new competitors, and even created a new verb: “to FedEx.”
In each case, the delta between the quality of the old equilibrium and the new one was huge. The new equilibrium quickly became self-sustaining, and the initial entrepreneurial venture spawned numerous imitators. Together these outcomes ensured that everyone who benefited secured the higher ground.
Shift to Social Entrepreneurship
If these are the key components of entrepreneurship, what distinguishes social entrepreneurship from its for-profit cousin? First, we believe that the most useful and informative way to define social entrepreneurship is to establish its congruence with entrepreneurship, seeing social entrepreneurship as grounded in these same three elements. Anything else is confusing and unhelpful.
To understand what differentiates the two sets of entrepreneurs from one another, it is important to dispel the notion that the difference can be ascribed simply to motivation – with entrepreneurs spurred on by money and social entrepreneurs driven by altruism. The truth is that entrepreneurs are rarely motivated by the prospect of financial gain, because the odds of making lots of money are clearly stacked against them. Instead, both the entrepreneur and the social entrepreneur are strongly motivated by the opportunity they identify, pursuing that vision relentlessly, and deriving considerable psychic reward from the process of realizing their ideas. Regardless of whether they operate within a market or a not-for-profit context, most entrepreneurs are never fully compensated for the time, risk, effort, and capital that they pour into their venture.
We believe that the critical distinction between entrepreneurship and social entrepreneurship lies in the value proposition itself. For the entrepreneur, the value proposition anticipates and is organized to serve markets that can comfortably afford the new product or service, and is thus designed to create financial profit. From the outset, the expectation is that the entrepreneur and his or her investors will derive some personal financial gain. Profit is sine qua non, essential to any venture’s sustainability and the means to its ultimate end in the form of large-scale market adoption and ultimately a new equilibrium.
The social entrepreneur, however, neither anticipates nor organizes to create substantial financial profit for his or her investors – philanthropic and government organizations for the most part – or for himself or herself. Instead, the social entrepreneur aims for value in the form of large-scale, transformational benefit that accrues either to a significant segment of society or to society at large. Unlike the entrepreneurial value proposition that assumes a market that can pay for the innovation, and may even provide substantial upside for investors, the social entrepreneur’s value proposition targets an underserved, neglected, or highly disadvantaged population that lacks the financial means or political clout to achieve the transformative benefit on its own. This does not mean that social entrepreneurs as a hard-and-fast rule shun profitmaking value propositions. Ventures created by social entrepreneurs can certainly generate income, and they can be organized as either not-for- profits or for-profits. What distinguishes social entrepreneurship is the primacy of social benefit, what Duke University professor Greg Dees in his seminal work on the field characterizes as the pursuit of “mission-related impact.” 5
We define social entrepreneurship as having the following three components: (1) identifying a stable but inherently unjust equilibrium that causes the exclusion, marginalization, or suffering of a segment of humanity that lacks the financial means or political clout to achieve any transformative benefit on its own; (2) identifying an opportunity in this unjust equilibrium, developing a social value proposition, and bringing to bear inspiration, creativity, direct action, courage, and fortitude, thereby challenging the stable state’s hegemony; and (3) forging a new, stable equilibrium that releases trapped potential or alleviates the suffering of the targeted group, and through imitation and the creation of a stable ecosystem around the new equilibrium ensuring a better future for the targeted group and even society at large.
Muhammad Yunus, founder of the Grameen Bank and father of microcredit, provides a classic example of social entrepreneurship. The stable but unfortunate equilibrium he identified consisted of poor Bangladeshis’ limited options for securing even the tiniest amounts of credit. Unable to qualify for loans through the formal banking system, they could borrow only by accepting exorbitant interest rates from local moneylenders. More commonly, they simply succumbed to begging on the streets. Here was a stable equilibrium of the most unfortunate sort, one that perpetuated and even exacerbated Bangladesh’s endemic poverty and the misery arising from it.
Yunus confronted the system, proving that the poor were extremely good credit risks by lending the now famous sum of $27 from his own pocket to 42 women from the village of Jobra. The women repaid all of the loan. Yunus found that with even tiny amounts of capital, women invested in their own capacity for generating income. With a sewing machine, for example, women could tailor garments, earning enough to pay back the loan, buy food, educate their children, and lift themselves up from poverty. Grameen Bank sustained itself by charging interest on its loans and then recycling the capital to help other women. Yunus brought inspiration, creativity, direct action, courage, and fortitude to his venture, proved its viability, and over two decades spawned a global network of other organizations that replicated or adapted his model to other countries and cultures, firmly establishing microcredit as a worldwide industry.
The well-known actor, director, and producer Robert Redford offers a less familiar but also illustrative case of social entrepreneurship. In the early 1980s, Redford stepped back from his successful career to reclaim space in the film industry for artists. Redford was struck by a set of opposing forces in play. He identified an inherently oppressive but stable equilibrium in the way Hollywood worked, with its business model increasingly driven by financial interests, its productions gravitating to flashy, frequently violent blockbusters, and its studio-dominated system becoming more and more centralized in controlling the way films were financed, produced, and distributed. At the same time, he noted that new technology was emerging – less cumbersome and less expensive video and digital editing equipment – that gave filmmakers the tools they needed to exert more control over their work.
Seeing opportunity, Redford seized the chance to nurture this new breed of artist. First, he created the Sundance Institute to take “money out of the picture” and provide young filmmakers with space and support for developing their ideas. Next, he created the Sundance Film Festival to showcase independent filmmakers’ work. From the beginning, Redford’s value proposition focused on the emerging independent filmmaker whose talents were neither recognized nor served by the market stranglehold of the Hollywood studio system.
Redford structured Sundance Institute as a nonprofit corporation, tapping his network of directors, actors, writers, and others to contribute their experience as volunteer mentors to fledgling filmmakers. He priced the Sundance Film Festival so that it appealed and was accessible to a broad audience. Twenty-five years later, Sundance is credited with ushering in the independent film movement, which today ensures that “indie” filmmakers can get their work produced and distributed, and that filmgoers have access to a whole host of options – from thought-provoking documentaries to edgy international work and playful animations. A new equilibrium, which even a decade ago felt tenuous, is now firmly established.
Victoria Hale is an example of a social entrepreneur whose venture is still in its early stages and for whom our criteria apply ex ante . Hale is a pharmaceutical scientist who became increasingly frustrated by the market forces dominating her industry. Although big pharmaceutical companies held patents for drugs capable of curing any number of infectious diseases, the drugs went undeveloped for a simple reason: The populations most in need of the drugs were unable to afford them. Driven by the exigency of generating financial profits for its shareholders, the pharmaceutical industry was focusing on creating and marketing drugs for diseases afflicting the well-off, living mostly in developed world markets, who could pay for them.
Hale became determined to challenge this stable equilibrium, which she saw as unjust and intolerable. She created the Institute for OneWorld Health , the first nonprofit pharmaceutical company whose mission is to ensure that drugs targeting infectious diseases in the developing world get to the people who need them, regardless of their ability to pay for the drugs. Hale’s venture has now moved beyond the proof-of-concept stage. It successfully developed, tested, and secured Indian government regulatory approval for its first drug, paromomycin, which provides a cost-effective cure for visceral leishmaniasis, a disease that kills more than 200,000 people each year.
Although it is too early to tell whether Hale will succeed in creating a new equilibrium that assures more equitable treatment of diseases afflicting the poor, she clearly meets the criteria of a social entrepreneur. First, Hale has identified a stable but unjust equilibrium in the pharmaceutical industry; second, she has seen and seized the opportunity to intervene, applying inspiration, creativity, direct action, and courage in launching a new venture to provide options for a disadvantaged population; and third, she is demonstrating fortitude in proving the potential of her model with an early success.
Time will tell whether Hale’s innovation inspires others to replicate her efforts, or whether the Institute for OneWorld Health itself achieves the scale necessary to bring about that permanent equilibrium shift. But the signs are promising. Looking ahead a decade or more, her investors – the Skoll Foundation is one – can imagine the day when Hale’s Institute for OneWorld Health will have created a new pharmaceutical paradigm, one with the same enduring social benefits apparent in the now firmly established microcredit and independent film industries.
Boundaries of Social Entrepreneurship
In defining social entrepreneurship, it is also important to establish boundaries and provide examples of activities that may be highly meritorious but do not fit our definition. Failing to identify boundaries would leave the term social entrepreneurship so wide open as to be essentially meaningless.
There are two primary forms of socially valuable activity that we believe need to be distinguished from social entrepreneurship. The first type of social venture is social service provision. In this case, a courageous and committed individual identifies an unfortunate stable equilibrium – AIDS orphans in Africa, for example – and sets up a program to address it – for example, a school for the children to ensure that they are cared for and educated. The new school would certainly help the children it serves and may very well enable some of them to break free from poverty and transform their lives. But unless it is designed to achieve large scale or is so compelling as to launch legions of imitators and replicators, it is not likely to lead to a new superior equilibrium.
These types of social service ventures never break out of their limited frame: Their impact remains constrained, their service area stays confined to a local population, and their scope is determined by whatever resources they are able to attract. These ventures are inherently vulnerable, which may mean disruption or loss of service to the populations they serve. Millions of such organizations exist around the world – well intended, noble in purpose, and frequently exemplary in execution – but they should not be confused with social entrepreneurship.
It would be possible to reformulate a school for AIDS orphans as social entrepreneurship. But that would require a plan by which the school itself would spawn an entire network of schools and secure the basis for its ongoing support. The outcome would be a stable new equilibrium whereby even if one school closed, there would be a robust system in place through which AIDS orphans would routinely receive an education.
The difference between the two types of ventures – one social entrepreneurship and the other social service – isn’t in the initial entrepreneurial contexts or in many of the personal characteristics of the founders, but rather in the outcomes. Imagine that Andrew Carnegie had built only one library rather than conceiving the public library system that today serves untold millions of American citizens. Carnegie’s single library would have clearly benefited the community it served. But it was his vision of an entire system of libraries creating a permanent new equilibrium – one ensuring access to information and knowledge for all the nation’s citizens – that anchors his reputation as a social entrepreneur.
A second class of social venture is social activism . In this case, the motivator of the activity is the same – an unfortunate and stable equilibrium. And several aspects of the actor’s characteristics are the same – inspiration, creativity, courage, and fortitude. What is different is the nature of the actor’s action orientation. Instead of taking direct action, as the social entrepreneur would, the social activist attempts to create change through indirect action, by influencing others – governments, NGOs, consumers, workers, etc. – to take action. Social activists may or may not create ventures or organizations to advance the changes they seek. Successful activism can yield substantial improvements to existing systems and even result in a new equilibrium, but the strategic nature of the action is distinct in its emphasis on influence rather than on direct action.
Why not call these people social entrepreneurs? It wouldn’t be a tragedy. But such people have long had a name and an exalted tradition: the tradition of Martin Luther King, Mahatma Gandhi, and Vaclav Havel. They are social activists. Calling them something entirely new – i.e., social entrepreneurs – and thereby confusing the general public, who already know what a social activist is, would not be helpful to the cause of either social activists or social entrepreneurs.
Shades of Gray
Having created a definition of social entrepreneurship and distinguished it from social service provision and social activism, we should recognize that in practice, many social actors incorporate strategies associated with these pure forms or create hybrid models. The three definitions can be seen in their pure forms in the diagram to the right.
In the pure form, the successful social entrepreneur takes direct action and generates a new and sustained equilibrium; the social activist influences others to generate a new and sustained equilibrium; and the social service provider takes direct action to improve the outcomes of the current equilibrium.
It is important to distinguish between these types of social ventures in their pure forms, but in the real world there are probably more hybrid models than pure forms. It is arguable that Yunus, for example, used social activism to accelerate and amplify the impact of Grameen Bank, a classic example of social entrepreneurship. By using a sequential hybrid – social entrepreneurship followed by social activism – Yunus turned microcredit into a global force for change.
Other organizations are hybrids using both social entrepreneurship and social activism at the same time. Standards-setting or certification organizations are an example of this. Although the actions of the standards-setting organization itself do not create societal change – those who are encouraged or forced to abide by the standards take the actions that produce the actual societal change – the organization can demonstrate social entrepreneurship in creating a compelling approach to standards-setting and in marketing the standards to regulators and market participants. Fair-trade product certification and marketing is a familiar example of this, with organizations like Cafédirect in the United Kingdom and TransFair USA in the U.S. creating growing niche markets for coffee and other commodities sold at a premium price that guarantees more equitable remuneration for small-scale producers.
Kailash Satyarthi’s RugMark campaign provides a particularly striking example of a hybrid model. Recognizing the inherent limitations of his work to rescue children enslaved in India’s rug-weaving trade, Satyarthi set his sights on the carpet- weaving industry. By creating the RugMark certification program and a public relations campaign designed to educate consumers who unwittingly perpetuate an unjust equilibrium, Satyarthi leveraged his effectiveness as a service provider by embracing the indirect strategy of the activist. Purchasing a carpet that has the RugMark label assures buyers that their carpet has been created without child slavery and under fair labor conditions. Educate enough of those prospective buyers, he reasoned, and one has a shot at transforming the entire carpet-weaving industry.
Satyarthi’s action in creating RugMark lies at the crossroads of entrepreneurship and activism: In itself, the RugMark label represented a creative solution and required direct action, but it is a device meant to educate and influence others, with the ultimate goal of establishing and securing a new and far more satisfactory market-production equilibrium.
Social service provision combined with social activism at a more tactical level can also produce an outcome equivalent to that of social entrepreneurship. Take, for example, a social service provider running a single school for an underprivileged group that creates great outcomes for that small group of students. If the organization uses those outcomes to create a social activist movement that campaigns for broad government support for the wide adoption of similar programs, then the social service provider can produce an overall equilibrium change and have the same effect as a social entrepreneur.
Bill Strickland’s Manchester Bidwell Corporation , a nationally renowned inner-city arts education and job-training program, has launched the National Center for Arts & Technology to advance systematically the replication of his Pittsburgh-based model in other cities. Strickland is spearheading an advocacy campaign designed to leverage federal support to scale up his model. So far, four new centers are operating across the U.S. and several more are in the pipeline. With a sustainable system of centers in cities across the country, Strickland will have succeeded in establishing a new equilibrium. It is because of that campaign that the Skoll Foundation and others are investing in Strickland’s efforts.
Why bother to tease out these distinctions between various pure and hybrid models? Because with such definitions in hand we are all better equipped to assess distinctive types of social activity. Understanding the means by which an endeavor produces its social benefit and the nature of the social benefit it is targeting enables supporters – among whom we count the Skoll Foundation – to predict the sustainability and extent of those benefits, to anticipate how an organization may need to adapt over time, and to make a more reasoned projection of the potential for an entrepreneurial outcome.
Why Should We Care?
Long shunned by economists, whose interests have gravitated toward market-based, price-driven models that submit more readily to data-driven interpretation, entrepreneurship has experienced something of a renaissance of interest in recent years. Building on the foundation laid by Schumpeter, William Baumol and a handful of other scholars have sought to restore the entrepreneur’s rightful place in “production and distribution” theory, demonstrating in that process the seminal role of entrepreneurship. 6 According to Carl Schramm, CEO of the Ewing Marion Kauffman Foundation, entrepreneurs, “despite being overlooked or explicitly written out of our economic drama,” 7 are the free enterprise system’s essential ingredient and absolutely indispensable to market economies.
We are concerned that serious thinkers will also overlook social entrepreneurship, and we fear that the indiscriminate use of the term may undermine its significance and potential importance to those seeking to understand how societies change and progress. Social entrepreneurship, we believe, is as vital to the progress of societies as is entrepreneurship to the progress of economies, and it merits more rigorous, serious attention than it has attracted so far.
Clearly, there is much to be learned and understood about social entrepreneurship, including why its study may not be taken seriously. Our view is that a clearer definition of social entrepreneurship will aid the development of the field. The social entrepreneur should be understood as someone who targets an unfortunate but stable equilibrium that causes the neglect, marginalization, or suffering of a segment of humanity; who brings to bear on this situation his or her inspiration, direct action, creativity, courage, and fortitude; and who aims for and ultimately affects the establishment of a new stable equilibrium that secures permanent benefit for the targeted group and society at large.
This definition helps distinguish social entrepreneurship from social service provision and social activism. That social service providers, social activists, and social entrepreneurs will often adapt one another’s strategies and develop hybrid models is, to our minds, less inherently confusing and more respectful than indiscriminate use of these terms. It’s our hope that our categorization will help clarify the distinctive value each approach brings to society and lead ultimately to a better understanding and more informed decision making among those committed to advancing positive social change.
The authors would like to thank their Skoll Foundation colleagues Richard Fahey, chief operating officer, and Ruth Norris, senior program officer, who read prior drafts of this essay and contributed important ideas to its evolution.
Support SSIR ’s coverage of cross-sector solutions to global challenges. Help us further the reach of innovative ideas. Donate today .
Read more stories by Roger L. Martin & Sally Osberg .
SSIR.org and/or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and to our better understanding of user needs. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to otherwise browse this site, you agree to the use of cookies.
91 Social Entrepreneurship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best social entrepreneurship topic ideas & essay examples, 📃 simple & easy social entrepreneurship essay titles, ⭐ interesting topics to write about social entrepreneurship, ❓ research questions about social entrepreneurship.
- Independent Entrepreneurship, Intrapreneurship, and Social Entrepreneurship This paper examines the similarities and differences of independent entrepreneurship, intrapreneurship, and social entrepreneurship. When it comes to the process, intrapreneurship and entrepreneurship are similar in terms of value creation and undertaking risks.
- IKEA Company’s Social Entrepreneurship One of the potential benefits to IKEA for operating a joint partnership is that it serves to integrate the resources of the partnering business entities, which in turn results in production and cost efficiencies.
- Social and Eco-Entrepreneurship for Environment Social entrepreneurship is a field that deals with the recognition of social problems in society and using entrepreneurial concepts, operations, and processes to achieve a social change.
- Social Entrepreneurship and Social Change The positive externality theory assumes that the allocation of social entrepreneurship is largely for the benefit of the society and not targeted towards the profit analysis.
- The DopePlus Social Entrepreneurship Majeed and Hwang contended that the importance of data-driven decision-making will grow as the world continues to navigate the challenges of the unprecedented crisis.
- Sun Tzu’s Social Entrepreneurship and Organizational Performance Thus, one of the primary reasons to study competition in an attempt to gain a distinctive competence is to log all the successes and failures of the closest rivals.
- Social Entrepreneurship: Khan Academy Project In addition, in the context of the rapid growth of technology and lifestyle changes, entrepreneurship is also dynamically changing depending on the emerging opportunities and threats.
- Social Entrepreneurship Causing Change in Society Therefore, considering the stages of the social problem, it is argued that the appearance of social entrepreneurship belongs to the alternative stage when people attempt to bring change outside of the system.
- Aspects of Social Entrepreneurship Orientation The study conducted by Halberstadt et al.aimed to research the influence of social entrepreneurship orientation on the social entrepreneurial performance of startups and established firms.
- Social Entrepreneurship Definition Such a point of view allows social entrepreneurs to take more active control of the problem, especially if the effect of entrepreneurs trying to solve the problem is more detrimental than its absence.
- Essence and Examples of Social Entrepreneurship In this respect, Saudi social enterprises can contribute to Vision 2030 in the following way. Finally, it is possible for women to be leaders of social entrepreneurship in the Middle East.
- Social Entrepreneurship: Supporting Philanthropic Organizations The program attempts to provide a solution to the needy in underdeveloped countries. The program will be helpful to both the volunteer and the needy children.
- Social Entrepreneurship Propositions Impact on My Career Path Planning Summarizing all the sides and shades of the notion, it should be mentioned that the traits of a social entrepreneur would be useful in any kind of initiative.
- Tjanpi Social Entrepreneurship and Innovation Due to the fact that the aim of the social enterprise is to help the Aboriginal population remain in the locations, they have always lived in and preserve their unique culture, this proposal aims to […]
- Social Entrepreneurship: Al Radda Program for Prisoners The Al Radda program focuses on improving the welfare of prisoners and former prisoners by equipping them with valuable skills and resources that help them to engage in different economic activities.
- Social Entrepreneurship and Corporate Responsibility They evaluated the second half of the 20th century and came to the conclusion that high-growth environments presuppose the presence of structure and strategy.
- Freeplay Radio as a Social Entrepreneurship In the first place, one of the major difficulties was an increase in expenses and the rise of the production costs, as the target audience continued to emerge.
- Social Entrepreneurship Activity in Chautauqua County Social entrepreneurs who have these characteristics such as ethics and morality can be able to identify failed opportunities in the market and use their resources to revert the failed opportunities to successful ventures.
- Social Entrepreneurship Advancement in Chautauqua County We present social entrepreneur activities in Chautauqua County and focus on engagement strategies not-for-profit organizations should employ in solidifying their presence and improvement of the overall economic condition of the county.
- Social Entrepreneurship in the New York City The process of social entrepreneurship and its strategic goals for improving social welfare of the society harnesses a variety of capacities across different sectors which helps facilitate the initiation and maintenance of the activities.
- Social Entrepreneurship and Successful Entrepreneur To access it easily, one has to design the program in a way that compels the legions of imitators and replicators.
- Concept of Social Entrepreneurship in Modern Business Some of the factors that encouraged Gbowee to venture into the forums to fight for peace were triggered by the social injustices that used to happen.
- Social Entrepreneurship Ethical Issues Most social enterprises are geared towards uplifting the poor in society to earn a living that can give them a more decent lifestyle Economists define Bottom of the Pyramid as the lowest level of the […]
- Social entrepreneurship: What Everyone Needs to Know by Bornstein and Davis Social Entrepreneurship is Bornstein’s and Davis’ masterpiece that should interest anyone willing to create a social change in the society. Social entrepreneurship is all about creating a social change in the society.
- Taking Social Entrepreneurship Seriously The current social and environmental conditions in the world demand that the level of social entrepreneurship to be improved as it is yet to get to the desired level.
- Innovation and Profit Motivations for Social Entrepreneurship: A Fuzzy-Set Analysis
- Linking Social Entrepreneurship and Social Change: The Mediating Role of Empowerment
- Corporate Social Entrepreneurship Specific to Knowledge Economy With a Focus on the Romanian Economic Context
- Applying the Social Entrepreneurship Concept of Commerce
- Kicking off Social Entrepreneurship: How a Sustainability Orientation Influences Crowdfunding Success?
- Organizing for Commons-Enabling Decision-Making Under Conflicting Institutional Logics in Social Entrepreneurship
- Chao Guo and Wolfgang Bielefeld: Social Entrepreneurship
- Social Entrepreneurship Competencies of Managers in Social Entrepreneurship Organizations in the Healthcare Sector
- Entrepreneurship Innovation and Uncertainty of Social Entrepreneurship Commerce
- CSR and Social Entrepreneurship: The Role of the European Union
- ‘Changing the System’: Compensatory vs. Transformative Social Entrepreneurship
- The Effect of Social Entrepreneurship, Co-decision, and Co-creation on the Embrace of Good Sustainable Development Practices
- Cultural Leadership Ideals and Social Entrepreneurship: An International Study
- Setting the Stage for Paradigm Development: A ‘Small-Tent’ Approach to Social Entrepreneurship
- How Can Social Entrepreneurship Solve the Problems in New Zealand?
- Academic Leadership and Social Capital in Universities Through Social Entrepreneurship
- Responsible Management Education: Active Learning Approaches Emphasising Sustainability and Social Entrepreneurship
- Boosting Social Entrepreneurship and Social Enterprise Creation in the Republic of Serbia
- Bricolage, Effectuation and Causation Shifts Over Time in the Context of Social Entrepreneurship
- Collective Social Entrepreneurship: Collaboratively Shaping Social Good
- Inequality and Marginalisation: Social Innovation, Social Entrepreneurship, and Business Model Innovation
- Enabling the Original Intent: Catalysts for Social Entrepreneurship
- Organized Chaos: Mapping the Definitions of Social Entrepreneurship
- Social Entrepreneurship and Socio-Economic Development Analysis
- Innovation and Social Entrepreneurship in Tourism: A Potential for Local Business Development
- Indigenous Social Entrepreneurship: The Gumatj Clan Enterprise in East Arnhem Land
- Addressing Development Through Social Entrepreneurship
- Corporate Social Entrepreneurship vs. Social Intrapreneurship: Same Idea, Different Trajectories
- Building Social Capital for Social Entrepreneurship
- Navigating Challenging Fitness Landscapes: Social Entrepreneurship and the Competing Dimensions of Sustainability
- Where Design Thinking Meets Social Media and Creates Civic Engagement and Social Entrepreneurship?
- Connecting the Dots for Social Value: A Review on Social Networks and Social Entrepreneurship
- Measuring Social Entrepreneurship and Social Value With Leakage: Definition, Analysis, and Policies for the Hospitality Industry
- Counting Our Losses: Social Entrepreneurship, Refugees and Urban Transformation in Turkey
- Differences Between Social Entrepreneurship and Traditional Business
- Conceptualizing Social Entrepreneurship: Perspectives From the Literature
- Islamic Gift Economy Vis-à-Vis Waqf (Endowment) As Vehicles for Social Entrepreneurship
- Social Entrepreneurship From an Institutional Perspective
- Full Employment Through Social Entrepreneurship: The Nonprofit Model for Implementing a Job Guarantee
- Can Social Entrepreneurship Researchers Learn From Family Business Scholarship?
- What Is Social Entrepreneurship and Why Is It Important?
- What Are the Benefits of Social Entrepreneurship?
- What Is Social Entrepreneurship in Simple Words?
- What Are Examples of Social Enterprises?
- What Is Social Entrepreneurship Skills?
- What Are the Factors of Social Entrepreneurship?
- What Are the Challenges of Social Entrepreneurship?
- What Are the Risks of Social Entrepreneurship?
- What Are the Opportunities of Social Entrepreneurship?
- Who Is Best Example of Social Entrepreneurship?
- What Is the Vision of Social Entrepreneurship?
- How Do You Identify a Social Entrepreneurship?
- Do Social Entrepreneurship Make Money?
- Why Do Social Entrepreneurship Fail?
- What Are the Disadvantages of Social Entrepreneurship?
- How Can Social Entrepreneurship Change the World?
- What Is the Main Goal of Social Entrepreneurship?
- How Do Social Entrepreneurship Help the Community?
- What Does Social Entrepreneurship Focus On?
- How Do Social Entrepreneurs Identify Opportunities?
- Can Social Entrepreneurship Survive Without Profit?
- What Are the Challenges Social Entrepreneurs Are Facing?
- How Can Social Entrepreneurs Become Successful?
- Can Social Entrepreneurship Solve Social Problems?
- How Does Social Entrepreneur Create Value?
- Macroeconomics Topics
- Intersectionality Research Topics
- Open Innovation Titles
- Problem Solving Essay Ideas
- Innovation Titles
- Franchising Essay Topics
- Workplace Diversity Research Ideas
- Social Change Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 91 Social Entrepreneurship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/social-entrepreneurship-essay-topics/
"91 Social Entrepreneurship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/social-entrepreneurship-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '91 Social Entrepreneurship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "91 Social Entrepreneurship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/social-entrepreneurship-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "91 Social Entrepreneurship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/social-entrepreneurship-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "91 Social Entrepreneurship Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/social-entrepreneurship-essay-topics/.

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
- Business Journal Articles
- Entrepreneurs & Leaders
- Student Essays
Exploring Social Entrepreneurship: ‘My Generation Is Full of Activists and Humanitarians’

Share Article:
Google Classroom:
Knowledge@Wharton High School first met Fiorella Riccobono in 2015 when she was a senior in high school. We featured her in a story about a business class project to promote fair trade practices among Haitian coffee farmers. Now Riccobono, who is 19, is a college student studying finance and interdisciplinary social science with concentrations in economics and social entrepreneurship. In this personal essay, Riccobono talks about how and why she is embracing her calling to become a bold and tenacious change maker.
I just completed my freshman year of college at Florida State University (FSU), and in many ways I am feeling transformed. When you first step foot onto your college campus, the feeling is incredible. You have a sense of personal freedom that you have never experienced. In college, you start to explore your major based on your passion and build the necessary classes and curriculum to earn your degree. Now imagine that the major you chose is an emerging field in the business world. Imagine that it is a new program at your school, and imagine just how much room for growth that opportunity means for you.
That chosen field for me is social entrepreneurship. I fell in love with social entrepreneurship a few years ago when Mrs. Zocco, my business teacher at Edward A. McCarthy High School in Florida, showed me a video of the most genuinely happy and grateful man I had ever seen. He was one of the farmers participating in a fair trade coop in Haiti that our class was helping to run, and his smile was amazing. He was thanking us because now, through fair trade – which in this case was helping coffee farmers in Haiti’s poorest region earn a just wage for their very hard work — his children had enough money to go to school. Since that moment, I have been driven to learn all I can about social entrepreneurship and how to make it my life’s work.
Leaving the World a Better Place
Many of us want to be extraordinary, to be change makers and to make positive and influential contributions to society. I have discovered that my generation is full of activists, humanitarians and philanthropists. No matter our passions — education, health, environment, economic development — many of us share a common goal: to leave this world a better place than how we found it. I’ve gathered inspiration from the stories of famous social-justice advocates around the world, like Muhammad Yunus, who created the concept of microfinancing, and Malala Yousafzai, who advocates for women’s education. Both Muhammad and Malala are recipients of the Nobel Peace Prize.
Social entrepreneurship is such an emerging concept that it is still not clearly defined. Most importantly, though, it is not charity. Although social entrepreneurs may need to rely on donations to launch their endeavors, they can’t create a business model based on donations, because charity is not sustainable. How can you build a business when you don’t know where your next dollar is coming from – or when?
In my experience, social entrepreneurs are individuals who draw on innovative business tactics to create solutions to societal issues. Social entrepreneurs combine government, nonprofit and traditional business practices in order to create a sustainable business model that is not only profitable, but also beneficial to the social sector. These innovators create large-scale, systemic and sustainable models by addressing a societal issue at its foundation – poverty, climate change, pollution, whatever it may be. Social entrepreneurs do not have an idea and then apply it. Instead, they go directly to the source of the issue and ask what is needed. Based on that answer, they build their business plans. Social entrepreneurs are often empathetic, bold, open-minded and tenacious.
So, that first day I stepped onto campus, I was more than ready to begin the next phase of my social entrepreneurship journey. The social entrepreneurship culture at Florida Sate University is growing rapidly. Early freshman year, I met Valarie Rodriguez, who wanted to start the Social Entrepreneurs and Innovators Club at FSU. I was the first person to join the team, and since then two of our board members have created social enterprises that are thriving within the Tallahassee community. Ramon started Unhoused Humanity, which uses crowd funding to help working homeless citizens make the down payment to get into a home. Often, the working poor do not have enough money saved up to make the hefty down payment needed for renting living space — typically first and last month rent and security and utility deposits. But they do generate enough income to pay their monthly rent once they are in. Unhoused Humanity helps the homeless get over that initial down-payment hurdle.
Another one of our members, Nikolas, has started Qultur. Qultur’s purpose is to use art to decrease crime in communities. Qultur creates and finds financing for events that bring together local artists, businesses and community members with the premise, “When we support and trust each other, we can live in harmony.”
Launching a social entrepreneurship club feels a bit like starting your own business. You have to find funding, promote your mission, explain the concept, and get people invested in your passion. I recruit local entrepreneurs to come speak at our events, plan those events, find funding and sponsors, and educate people on all aspects of social entrepreneurship.
I am getting hands-on social entrepreneurship experience in other ways, as well. The spring semester of my freshman year, I interned with a local fair trade coffee shop in Tallahassee. During that time, my team of interns created a micro social enterprise using the coffee shop’s food truck. We were trained as baristas and innovators and were responsible for creating a business model that would be profitable, while also maintaining a social mission.
We researched local areas and events and chose where to take our “fair trade” truck, what beverages we should make, and handled the actual food truck operations . We were the first group of interns to ever break even and create profit for this program. Our business model – like many other social enterprises — addressed a triple bottom line: people, planet and profits. The model had three key features: first, the coffee we brewed was purchased from small farmers who were paid a fair price through certified organic cooperatives. The coffee farms were bird-safe and shade-grown to ensure the organic coffee was environmentally sound. (Coffee farmers sometimes take strides to grow coffee in sunnier settings because it is faster; however, this often damages the biodiversity of the region.) And finally, the coffee shop placed all our profits in local and global humanitarian causes, truly addressing the triple bottom line.
Helping the Homeless
It is immensely inspiring to be part of a community where social justice is a priority. It is motivating to be surrounded by young individuals who are not only incentivized by profit, but by creating systemic change. I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making. People are no longer seeing global poverty as a call for charity, but as a place of economic and cultural growth. Young business minds no longer want to exploit our natural resources, rather build business models that protect our environment.
The best advice I can give to incoming freshmen at any school is to be empathetic, bold, open-minded and tenacious. You are about to be exposed to a world of information, opportunity and incredible curiosity. I am as passionate as ever about my social entrepreneurship future. This fall, with the help of my club members, I will be starting a research project at a local homeless shelter. My plan is to speak personally with members of the homeless community in Tallahassee in order to better understand their backgrounds, prior education, work experience and willingness to rejoin the workforce. I want to use this quantitative data to possibly identify a pattern in homelessness. By pinpointing the need, I can create meaningful solutions.
My ultimate goal is to launch a program that rehabilitates the homeless community and reengages homeless people as active, contributing members of society. My heart tells me that many of them want to improve their circumstances, but need the proper channels for lasting change. I’m not sure how this will all play out, but I have little doubt that we are laying the foundation for something truly extraordinary.
Related Links
- RedEye Mobile Cafe
- NY Times: The Rise of the Social Entrepreneur
- K@W Video: Muhammad Yunus: Lifting People Worldwide Out of Poverty
- FSU Social Entrepreneurship
- Unhoused Humanity
Conversation Starters
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What does she mean by this? Why does she make this important distinction?
Using the “Related KWHS Articles” and “Related Links” tabs, find out more about Malala Yousafzai and Muhammad Yunus. How have they made an impact on the world? Can you think of any other social-justice champions whose missions inspire you?
Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” Do you agree? Why or why not?
200 comments on “ Exploring Social Entrepreneurship: ‘My Generation Is Full of Activists and Humanitarians’ ”
Fiorella Riccobono stressed that social entrepreneurship is not charity. She wanted the readers to understand the difference between social entrepreneurship and social services, which I believe readers should give certain importance. As a reader, I feel that I have understood the relation between social entrepreneurship and charity. This distinction plays a role in opening the minds of the readers in defining other facets of social entrepreneurship.
I agree, because many people don’t know the difference between social entrepreneurship and social service. In the social entrepreneurship, you gain money and it is very different than a charity
Social entrepreneurship is where you start companies and develop a fund for some type of environmental issue. Fiorella Riccobono does gain money, but it is for a cause. Fiorella Riccobono donates money to the homeless community because they want to improve their circumstances. I agree as well, that many people don’t know the difference between social service and social entrepreneurship. Unhoused Humanity helps the homeless get over that initial down-payment hurdle. When you are in Social entrepreneurship, you are exposed to a new world of information and technology.
Social entrepreneurship and charity overlap in many fields (helping the homeless, for example); however, charity fosters a feeling of dependence in its recipients. Knowing this, many are scared away from the field. If social entrepreneurs are looking to make a difference, they must set themselves apart from well-established foundations and philanthropy.
1. Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. She is correct. Social Entrepreneurs run a business. While they are more empathetic because their helping the social sector by solving global and humanitarian issues, they ask what is needed and then base their business plan around that. They make a profit while contributing to society. 2. Muhammad Yunus won the Nobel prize for founding the Grameen bank which aided a lot of people with financial structure. Malala Yousafzai fought for women’s education in Pakistan. 3. I agree that social entrepreneurship is the future of business because it builds a good reputation, which is important for an enterprise, while simultaneously making a profit.
1. Fiorella believes that donations are essential, however it can’t create business models because charities are not sustainable. A sustainable business is not only profitable, it has to be beneficial. They want to solve issues and make the business better. Businesses want to fix social issues as well as enviornment issues.
2. Yuman won the noble peace prize and helped people with finances, Malala wanted education for women in Pakistan
3. I agree with social entrepreneuership because it builds a businesses reputation
1. Fiorella Riccobono believes that it is not charity because she is trying to point out to the reader that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, as a charity is not sustainable, because you can’t control the influx of money. She means that social entrepreneurship can last over a long period, and has to be sustainable in order to help the most people possible.
2. Malala and Muhammad inspire the world. Malala inspires women to be educated, even in countries where women are not educated. She wrote a book of her injury, when she was shot by an Islamic group. Muhammad inspires young leaders globally. Also, he won a Nobel Peace Prize for his work on social entrepreneurship. Another social justice champion that I admire is Oprah. She broke barriers by being one of the first black female millionaires in the United States. She also established an empire.
3. I believe that entrepreneurship offers a hopeful way to guide society. This helps people who have less money and in third world countries.
1) Fiorella Riccobonno stresses that it is not charity because she is trying to point out to the reader that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, as a charity is not sustainable, because you cant control the influx of money. She means that social entrepreneurship is different than charity because social entrepreneurship can last over a long period, and has to be sustainable in order to help the most people possible.
2) Malala and Muhammad inspire the world. Malala inspires women to be educated, even in countries where women are not educated. She wrote a book of her injury, when she was shot by an Islamic group. Muhammad inspires young leaders globally. He also won a Nobel Peace Prize for his work on social entrepreneurship. Another social justice champion that I admire is Oprah Winfrey. She broke barriers by being very successful in her field of work, and her work in helping those less fortunate.
3) I believe that social entrepreneurship offers a hopeful way to help rehabilitate the community of people that are less than well off when it comes to their financial situation. Social entrepreneurship is a great way to give back to the less fortunate.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because because charity is not sustainable it cant support. she means that how can you build a buisness not knowing when your next pay is. she makes this important distinction so that she can inform the reader so that she gives a guideline. Malala Yousafzai is a pakastani actavist that emphasizes on women empowerment and how a group of people can make a change.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because although entrepreneurs may rely on donations they cant really create a business model based on it. She makes this important distinction because people may think that entrepreneurship is based on charity and donations when they are basically innovative business tactics to create solutions to social issues.
I Believe Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship isn’t charity so much because of how she wants to impact the world. If Social entrepreneurship was a charity, the problem would only at best get monetarily fixed. However, Social entrepreneurship targets to change the actual problem rather then just throw money at it.
I agree with Fiorella’s statement that social entrepreneurship is the future. Based on the information in this article it appears as though the goal of social entrepreneurship is to help fix the world’s problems. However, instead of simply creating a solution social entrepreneurship also finds ways tranform the issue into an opportunity for economic growth.
Social Entrepreneurship is not a charity because the business still makes money. They do help the community, but making money is a priority. This is an important distinction because she needs to stress the fact that the business still needs to make money. Fiorella does not want people to think that the are a charity that donates all their money.
When Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity she means that its also a business and she makes money off it. This is an important distinction because she needs to stress the fact that its a business and she still needs to make money at same time as helping.
The way in which Fiorella explained how social entrepreneurship is not a charity is very educated and clear to understand. It is easy to agree with her statement on social entrepreneurship not being a charity even though it, in some cases, acts like one. For example when a business receives money from investor, it is similar to a charity receiving money from people to support the business. She makes a very good point in saying that a business cannot operate not knowing where they will get their next dollar. Another good point she makes that not everybody would think of is that if a business is running on donations, and donations alone, the business would not be able to create a business model since charity is not sustainable.
I do agree with her thinking, thanks to our generation of young people getting more interested in social matters and being more open minded. Nowadays, people is more intereste in social, environmental, and economical matters, therefore, making them more eager to get involved with our society . Social entrepreneurs will help in developing abetter society for our people
When Fiorella states that social entrepreneurship is not charity she means that social entrepreneurship is its own thing. She recognizes it as being something that can help many people, in many different places, for many different causes. As opposed to charity which is something that helps one cause, or raises money for something in specific. She makes this important distinction because she also realizes that the topic could be confusing for some who do not necessarily know the exact difference between the two.
Malala Yousafzai is a true hero, a legend, who will be remembered forever. She is a courageous leader who fights for women to be able to get an education. On October 9, 2012 she was shot by the Taliban and left in critical condition. She pushed through and from this tragic event that happened to her, she made her voice heard. Her story is touching and she now has her own foundation that advocates for womens’ rights worldwide. Muhammad Yunus is a social entrepreneur from Bangladesh. He is known for founding the Grameen Bank and developing the concepts of microcredit and microfinance. His objective was to put an end to poverty by giving out loans that were suitable to the people and teaching them some financial principles to help themselves. Not only did these two icons earn a Nobel Peace Prize Award, but they will also have an everlasting legacy for their keen, creative, and unique minds. Some other social-justice champions that I admire are Eleanor Roosevelt and Oprah Winfrey.
Fiorella Riccobono explains that social entrepreneurship is not charity. She goes on to clarify that social entrepreneurship is, in essence, using traditional business practices to create a sustainable business model that is not only profitable, but also beneficial to the social sector. Fiorella makes sure to note that charity is not sustainable and that a business model cannot run on donations alone.
Social entrepreneurship is definitely the future of business and policy making because it is a business enterprise not only focused in profitable gains and societal claims. Its significance is reflected on the demand of customers for business to have grater social objectives.
Fiorella says that social entrepreneurship is not charity because it can’t create a business based on donations. Social entrepreneurship creates solutions to societal issues. This is an important distinct because social entrepreneurship should be it’s own business/its own work. It is not a charity where anyone can help, social entrepreneurship helps other businesses to thrive.
Malala Yousafzai and Muhammad Yunus are both huge figure in the world for what they are and what they accomplished. The impact that they had on the world is different from one to another but both helped the humankind to be better. Another social-justice champion that had a mission that inspire me is Nelson Mandela, for what he forgive and what he accomplished.
3. I do believe social entrepreneurship is the future. It allows to have a business that is self sustainable and driven to help the community/planet without having this motivation for self gain. More and more people will start to realize that if we help the planet as a whole, then we will all benefit from it. Not only does it feel great to know that you’re helping people but also you get the satisfaction of helping the whole entire planet.
Personally, I believe that there is a quote that fits this article.
“If you give a man a fish, you feed him for a day. If you teach a man to fish, you give him an occupation to feed him for his lifetime.”
Charity can be given to someone and yes, it can help them, however it does not provide something long lasting. Giving people jobs, and a way for them to work in just conditions is how you can truly help people. A sustainable company that can support the people, support the environment, and still make a profit for more investment is a company that can help people. That is how you can truly help and make a impact. That’s the difference between social entrepreneurship and charity. One is sustainable and can sustain others.
Malala Yousafzai is Pakistani activguist who publicy campaigned for girls to go to school and won a Nobel YouthPeace Prize. Due to her popularity and exposure, the Taliban were after her. On October 9, 2012, a Taliban masked gunman boarded her school bus, and asked for her by name. The gunman shot her in the head, neck and shoulders. Malala survived the attack and is now a world famous activist for peace and girls in school.
Muhammad Yunus is a Bangladeshi entrepreneur that was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for founding the Grameen Bank and creating microcredit and microfinance. He is working hard to help advocate a world without poverty.
According to “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” as Fiorella said, I agree that social entrepenueurships is the future of bussines annd policy making since entrepeneurs are going up and being more involved in the future policies as well as business
As far as social entrepreneurship being the future of business and policy making, yes, I agree with Fiorella. She has definitely made some interesting and realistic points. She believes that, given our generation and what that all have made a living out of, we all want to leave the world a better place than how we found it. Social entrepreneurship is saving poor regions with solutions such as fair trade and I agree that if you work hard to make that a part of your life work that it can make a difference.
Yes I do agree that, “social is the future of business and policy,” because not only does the entrepreneur make a profit, he or she also supports and helps local, small businesses which in turn helps all the people in a community. Social entrepreneurs need to be smart and innovative to find ways to make money, but still support the community. This benefits the social entrepreneur and the people they are helping. This can build innovative skills and social skills making are world communicate and making our world be together.
I agree with Fiorella when she says “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” because we are moving towards a more socially and environmentally cautious world. More and more companies are starting to deal with environmental issues. I t is likely that most future companies or enterprises will be helping raise money to help solve global problems from the start
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because charity is not sustainable and relies on donations from people. Social entrepreneurship is when individuals use a variety of tactics and strategies to tackle societal problems. She makes this important decision because although they overlap in some areas, social entrepreneurs need to find ways to make their business profitable.
1. Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because in a social entrepreneurship, making money is part of the goal. It does help the community. However, unlike a charity, social entrepreneurship can be sustainable. They don’t base their business plan off of the donations they received but they use innovative ideas and plans. I believe she addressed the difference between the two to clarify that they are separate concepts and emphasize the difference between them.
Throughout the article, Fiorella Riccobono emphasizes on the idea that social entrepreneurship is not charity. Fiorella realizes many young people are willing to help but prevent them self from doing so due to the dependent nature of charity. Through using social entrepreneurship, one is not dependent on others to create a sustainable and reliable network to help those in need. This entices future business students who want to help while still utilizing the skills they have learned.
When Forella says “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making,” I agree with this statement because nowadays the world of business is becoming based off of networking and social elements. It is becoming more common that people want to go out and work on social projects and participate in the community. As this becomes more popular it will begin to become a business. It takes knowledge to turn social work into a business. However if done right, it can make the world a better place.
Social entrepreneurship and charity are two different businesses models. As Fiorella Riccobono says, charity is not a viable business plan that can make money. Social entrepreneurship triple bottom line is people, planet, profits. They want to help the world while making a positive change in the world while making a profit.
I agree with Fiorella’s statement that “social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making” because it gives companies the opportunity to give back to their community while making a profit. The upcoming generation of business owners want to leave the world better than they found it, and social entrepreneurship is the perfect opportunity to make a difference. I believe this is extremely beneficial to society and its members as it will also help shape the future generations to become successful leaders through international connections and job opportunities.
Fiorella, in the article, stated that social entrepreneurship is not charity. By stating this she means that charities will help gain money for a cause, but as a social entrepreneur, you have the opportunity to take your knowledge and make money and business. In the article, Fiorella states that “People are no longer seeing global poverty as a call for charity, but as a place of economic and cultural growth. ” If more people are able to gain that knowledge and share it, many people would be able to help more people at a constant rate. Charity is for one cause while social entrepreneurship can be for many.
Fiorella believes that social entrepreneurship is the future to business and policy, and I agree. Although, I would also argue that it is fundamental to today’s business and policy. This is so important because social entrepreneurship in other words is networking. These skills are important to meet others in the business world and expand upon your knowledge. If you have a wide range of connections you will have more opportunities to get jobs, knowledge in every field of business, and create a supportive business network in your working environment. After all you are not working next to computer all day, but next to people that are similar to you!
Fiorella makes the distinction between social entrepreneurship and charity. This is an important distinction because money in a charity flows in one direction. Conversely, money in a social enterprise flows both ways. Social enterprises cannot be charities because they are businesses, and need money to operate. Compared to traditional businesses, though, social enterprises are conscientious about the environmental and social impacts of their actions.
I agree with Fiorella when she claims that social entrepreneurship is the the future success of business and policy making. It doesn’t only help people who already have good conditions of life but it also financially helps those in need and who can’t afford much money. Entrepreneurs can make a lot of profits and invest their money on themselves and the community on where they which can benefit everyone.
The reason Riccobonno made the distinction between social entrepreneurship and charity is because some people don’t understand that social entrepreneurship is in fact a business and relies on more than just donations. In any business it is important to know where and when your money is coming from. Without the knowledge of when you will have money you can not make financial investments or take risks. If your business is not sustainable and it goes bankrupt it will not be able to help anyone.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because you cannot created a business based off of donations. Social entrepreneurship makes solutions to social issues.
I agree with Fiorella that social entrepreneurship because it will help many people.And to help the environment and the community.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. She focuses about this topic because she wants the reader and society to have the understanding of the difference between entrepreneurship and charity. An entrepreneurship may help and change many people, with different causes or problems, at different situation. A charity is help for a certain person or situation. She wants to make a change not throw money at it and have the problem fixed momentarily.
1. Fiorella Riccobono believes that social entrepreneurship is about making the world a better place. Charity is a completely different subject. Though, they do share a common goal. Malala Yousafzai held a campaign for girls to get an education at school. Muhammad Yunus won the Nobel Peace Prize for social entrepreneurship. They are an inspiration to society. I believe in Fiorella’s point of view. Social entrepreneurship is the future of business. It well help us grow and develop as a person. As well as create opportunities for many in creating a difference.
What Fiorella Riccobono stresses about social entrepreneurship not being charity is that it doesn’t have the ability to launch a business solely based from donations. This is not able to support a fully working business. The charity people give is meant to last a bit, it does not have the ability to make a business work for a long period of time. She makes this important distinction so readers can see the difference between a business that can support itself vs a business that runs on charity.
I agree that social entrepreneurship is the future of business. I believe this because we need to look out for others. There are many people in this world that are self centered and don’t think about others. We need to make sure we take care of others and make sure no one is left behind.
Business entrepreneurship is not charity basically because social entrepreneurs may need to rely on donations to launch their endeavors and making money is part of the goal.
When Fiorella Riccobono states that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she means to create the idea that social entrepreneurship is stable and a dependable new business worth taking part in. She makes this distinction because she wants it to be clear that although it shares a similar idea with charity, it is not only about helping the people but also the planet and business world of the future.
There definitely is a big difference between social entrepreneurship and charity. What Fiorella Riccobono means when she makes this distinction is to not think of social entrepreneurship as the same because of the many differences it has with charity. For example, charity can be looked at as a way to help one specific problem only one time. What she tries to make out of social entrepreneurship is that it helps more than one cause, it is more of a broad way of helping. Also it can shape a better lifestyle for people while charity can only help in one specific way. Giving someone money is not as big of a deal as giving a person a job to consistently earn money. Fiorella makes the distinction so readers know the way that she helps people, by setting a better road for the rest of their lives.
Social entrepreneurship is the future of the business and policy making because it is a way for entrepreneurs to not only make a profit but helps out the community and support their new ideas. And it is a smart way for people to come together as a community and do many great things together.
Fiorella Riccobonno stresses that it is not charity because she wants the reader to be aware that a charity isn’t sustainable because you don’t know where your next dollar comes from, in contrast with social entrepreneurship that is the process to earn profits while helping other people.
[3.] When considering Ms. Riccobono’s statement, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.”, I am reminded of the importance of working with non-profit, government, and traditional business, when working towards startling a successful and innovative business. I agree that social entrepreneurship is an important aspect thats importance will become increasingly apparent as time goes on. Using the policies and beliefs that fall under this category, I believe these thing will change the future of business management and development.
Fiorella Riccobono emphasizes a difference between social entrepreneurship and charity. She highlights that in a social entrepreneurship, the owner cannot solely depend on donations in order to maintain the business plan and model to a profitable amount. She makes this distinction because all social entrepreneurships create profit, whereas charities, specifically non-profit organizations, do not.
Ms. Riccobono had her opinion about the meaning of Social Entrepreneurship, in which she thought that it is not charity at all. She stated that making money is the desired outcome, while as compared to charity it is also stable and/or sustainable. She wanted to clarify the actual difference between the two, explaining it through the expression of her own opinion.
-Fiorella Riccobono believes that it is not charity because, she is trying to tell the reader that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, as a charity is not sustainable, because you can’t control the influx of money. She means that social entrepreneurship can last over a long period, and has to be sustainable in order to help the most people possible.
-Malala and Muhammad inspire the world. Malala inspires women to be educated, even in countries where women are not educated. She wrote a book about the injury that she had injury, when she was shot by an Islamic group. Muhammad inspires young leaders globally. Also, he won a Nobel Peace Prize for his work on social entrepreneurship. Another social justice champion that I admire is Oprah. She broke barriers by being one of the first black female millionaires in the United States. She also established an empire.
-I do believe social entrepreneurship is the future. It allows to have a business that is self sustainable and driven to help the community/planet without having this motivation for self gain.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What does she mean by this? Why does she make this important distinction? She wants the distinction to be clear that social justice in businesses for employees isn’t a charity, and that it’s an obligation for workers to be treated/paid fairly. She strives to make a community where social justice is a priority. Using the “Related KWHS Articles” and “Related Links” tabs, find out more about Malala Yousafzai and Muhammad Yunus. How have they made an impact on the world? Can you think of any other social-justice champions whose missions inspire you? Malala aimed for the education of all women in the world, even in countries where they aren’t educated. Muhammed inspired young entrepreneurs around the world. Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” Do you agree? Why or why not? I agree, social justice calls for fairness in business with helping the homeless, being able to assist those in need, and policy wise making work better/ more efficient for employees/
I agree with Florella in believing that social entrepreneurship is the future. Social entrepreneurship is a useful tool to help the community while still making money in the proccess. Being a social entrepreneur allows said entrepreneur to help the people with less money while being able to maintain profit in the proccess.
Fiorella stresses a good point about social entrepreneurship because the businesses that are focused on being run like this are also making an enormous impact on different societal issues while benefiting as a business as well. That being said, theses businesses are definitely not like charities. She makes the distinction between the two because i’m sure the first thing many people think of when they hear about “social entrepreneurship” is charity. Social entrepreneurship is definitely going to take over in the future because it is a great way for businesses to thrive while also having a positive impact on society and the world.
Fiorella Riccobonno stresses the fact that social entrepreneurship is not charity because she wants the reader to understand the difference between social service and social entrepreneurship. Social entrepreneurs are also businessmen and run a business that also helps others.
Social Entrepreneurship is not a charity. It is not a charity because the business still makes money. They do help the community, but making money is the main/top reason. This is an important because she needs to continue stressing the fact that the business still needs to make money. Fiorella helped the people because she paid them more than what they were getting paid.
When Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she means that the business cannot rely on donations. It would obviously help the business if donations come to them, but the business model cannot be built by just donations. Charity is not sustainable, which means that a certain business can’t survive on donations. Social entrepreneurships are meant to solve societal issues and that is what she is trying to do.
I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making because the world is becoming more and more social. Whether it is through social media or just talking to people, people get ideas from other people who get ideas from other people. Nowadays so many people believe they want to be an entrepreneur and its possible because there are so many places to start a business.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses about social entrepreneurship not being charity and that it is not going to be able to launch a business solely based from donations. This is not able to support a fully working business. The charity people give is meant to last a bit, but it does not have the ability to make a business work or last for a long period of time. She makes this important distinction so readers can see the difference between a business that can support itself vs a business that runs on charity.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What does she mean by this? Why does she make this important distinction? She means that she believes a business is not sustainable by donations. On the other hand, charities are 100% sustained by donations. A business is very costly and it cannot be held by a thread or sustained by chance or luck. Starting a business, one wants to know that his or her business has an opportunity of thriving and growing. When one finds out someone is donating, the donation most of the time arrives that same day. In businesses, one has to know where the next dollar is coming from ahead of time. If a business is failing a backup plan needs to be formed, it cannot just sit around and hope for a miraculous donation.
I agree that social entrepreneurship is the future of business because it is a great way to give back to the people that are struggling financially, and it builds a good reputation which is very important for a business.
When Fiorella stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she means that charity is not sustainable, because the influx of money isn’t not controllable, and a social entrepreneurship has to be sustainable so most involved benefit. I agree with Fiorella that social entrepreneurship is the future of business, and where relationships are built while making profit.
Fiorella stresses the difference between social entrepreneurship and charity. A business model can’t be made in a charity, due to charities not being sustainable. Both of these help the community in many ways but you can make money also in social entrepreneurship as it is sustainable.
Fiorella says,”I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making” I agree with this statement because I believe that people now a days are trying there best to make this world a better place so being a social entrepreneur is not only helping yourself but also helping your community.
I really find this idea of “social entrepreneurship” to be very defining because this allows people with somewhat experience with the business world to get to experience real life. Many people don’t think business is that hard but this thought of having social entrepreneurship I feel will actually make the image of the business world easier to understand. Social Entrepreneurship is the future and is actually happening already, the reason is because being able to interact with customers and consumers will allow the buyers to have more confidence in the product. Interactions also allows the business to have good credit and good credit to a company means that they are worth more and are recognized as a company that has good stuff. Another reason why social entrepreneurship is the future is because it is easier to start than that of an actually big name company, so I predict that there will be more social entrepreneurs than companies trying to sell small products (that is the job of a social entrepreneur).
Fiorela Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship because it is still a business even though it helps people in need. People know the charities are basically just giving money to people and that is not what social entrepreneurship is about. Social entrepreneurship is a business so it still makes a profit but it also helps people. These businesses are all about making a profit while still maintaining a social message. They follow business plans and make a sustainable business while still making an impact with the social sector of the world.
Fiorella Riccobono states that social entrepreneurship it’s not charity. Social entrepreneurs run a business from which they want to take profit while they are contributing to society. She states that they practically show emapthy and use society to make money, which in a way, making money or not, at the end they are still helping people.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. She wants to show that social entrepreneurship isn’t charity because it isn’t to get things for people in need. Social entrepreneurship is to develop, fund and implement solutions to social, cultural, or environmental issues. She makes this important distinction because social entrepreneurship uses techniques and has ideas behind funding solutions to social culture, while charity is to do for the good of the people in need. Also social entrepreneurship looks to find solutions for issues, when charity just helps a certain cause.
I believe strongly in the idea of Social Entrepreneurship and the benefits it can bring to many people. I think that is great for college campuses to have social entrepreneur ship clubs so that college students can be exposed to all of the problems that the world has, I love how the article stresses how its important to be open minded and expose your self to new experiences because the world changes every day and it is key for young people to know that because they are the ones who have the most power to change things for the better
Fiorella strongly stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. This means that it is still business, that means that it is for profit. I think this is a good thing because the best way to support social programs is by money from companies that still have profit. Fiorella also must believe this because she is sure to emphasize the fact that social enterprises are making money and not bankrupting themselves for their programs or relying heavily on inconsistent and unreliable donations like a charity.
Riccobono emphasizes that charity is different from social entrepreneurship by expressing that charity works with donations and social entrepreneurship handles profits. She makes this distinction to help realize that everyone can win; farmers receive just payment for their goods and vendors of these goods can make a profit. This has definitely made an impact on the world by allowing almost any person attain a fair an income at little to no expense. I don’t completely agree with Fiorella’s belief because today many giant corporations, such as Monsanto, benefit greatly at others’ expense and won’t easily change. Yes, it is a great concept and should be adapted all over but it doesn’t seem like something that will truly happen.
What Fiorella Riccobono means by social entrepreneurship not being a charity is that they are totally different concepts. She makes this important distinction because a charity depends on people donating money for their cause. While social entrepreneurship do accept donations, they don’t rely on it. They use a business model to plan it out like a business.
3: I don’t necessarily disagree or agree with the statement that social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making, because there are many other business fields that can have a larger effect on society, for example, the economy keeps the world turning by trading goods to other nations and providing everyone with the funds they earn. The economy also provides storage units known to most as banks, to store any earned money that was not to be spent, this being the opposite of in-wallet or in-pocket money.
But, social entrepreneurship is a very crucial business, and as time goes by, this will get more important. In addition, social entrepreneurship is interconnected with the economics, because with social advantages, one might have a vast connection, thus leading to a higher chance of getting advertised, hired, or partnered with another company.
Firoella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not a charity. Social entrepreneurship is a business that is profitable and is indeed not a charity because then it wouldn’t be sustainable. Instead it is comprised of individuals who want to make the world a better place.These individuals try to make the world a better place by using business tactics to try to create solutions to some of the societal issues that we face today, like poverty, climate change, and pollution. So, not only is it not a charity, it is profitable and at the same time it helps make the world a better place.
1.Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity even though they receive donations, they can’t create a business model, charity is not sustainable. 2.Malala Yousafzai fights for gender equality, and Muhammad Yunus help the poor and poverty worldwide. This inspires me to leave my mark on the world and change the world for the better. 3.I agree when Fiorella said ” I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” Because this will help the poor and raise charity.
Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” I agree with Fiorella because it will help give back to those who do not have the resources that they need. It will not only make provide good reputation to the business, but it will give you such a good feeling to know you are being involved in the community and helping others.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity, because it’s not possible to create a business model based on donations, because charity is not sustainable. Malala inspires the education of all women in the world, even in countries where they are not educated. Muhammed inspires young leaders globally, and he has also won a Nobel Peace Prize. I agree that entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making, because it gives hope to those who need help.
What Fiorella means when she says that entrepreneurship is not a charity is that in the business you have to know when your money is coming not just to wait around for a donation, which is what charity does. I do agree with Fiorella when she says “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making” because it helps keep the community going to a better place.
She means that you still make profit off of social entrepreneurship, as it is what is desired because charity is not sustainable. She makes this important distinction to show that social entrepreneurship is not charity and needs to have a constant influx of cash to help as much people as you can. I do agree because it is a good way to help people who are less fortunate with their situations.
Fiorella Riccobono affirms that all related with social entrepreneurship is not charity, by that you can extract that corporations or business don’t live related with donations or charity. Business must grown from experience, hard working and good ideas and not from donations. Donations can surely help, but a business concept doesn’t not relate to that.
Malala and Muhammad had a big participation with the world. While Malala made the education available for womens she wrote a book that affected the globally society. Muhammad inspired young leaders over the world. He won a Nobel Peace Prize for his social entrepreneurship, which had successful results. I agree with her when saying that the social entrepreneurship is the future of business, because the social entrepreneurship allows a business that self-survive to help the good causes without having this motivation for self gain.
What Fiorella Riccobono means when she says that social entrepreneurship is not a charity is that it does not involve raising money for a cause. Charities also do not have enough money to sustain them for a long period of time without donations. Social entrepreneurship aims to solve problems while still having the ability to make profit, although they do accept donations. It is a business that at the same time makes a huge impact on society.
When Fiorella says that social entrepreneurship is not charity she means that social entrepreneurship is its own thing. She recognizes it as being something that can help many people, in many different places, for many different causes. As opposed to charity which is something that helps one cause, or raises money for something in specific. She makes this important distinction because she also realizes that the topic could be confusing for some who do not necessarily know the exact difference between the two.
When Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she means that social entrepreneurship is not focused on raising or donating money. Social entrepreneurship is a business that benefits when money is used. Of course you are going to need to raise money from somewhere, but the purpose of social entrepreneurship is to run a business not to collect money. Clearly, Fiorella makes this important distinction because she wants to show the readers that social entrepreneurship and charity are two separate things.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. When Fiorella said this, she meant that a social entrepreneurship does not just base solely on donations. Of course, donations can help, but a social entrepreneurship thrives from people working hard to help others. In addition, a charity, unlike a social entrepreneurship, is not sustainable She shows that it is more about creating a work place than a place just collecting money.
When Fiorella Riccobono says it is not charity she means that these companies are not run on donations and not ran by volunteers in their free time. She is saying these companies are real businesses that have to compete in the real world. They too have the goal of making money however, they also make businesses that help a society as well as protect the environment. She mentions this because often times they have no idea where there next check is coming from and when. This is a important distinction because these are people who are interfering with their career or salary to make the world a better place and not doing it on extra time.
Riccobono emphasizes that social entrepreneurship isn’t charity. The difference between a charity and social entrepreneurship is that in a charity, funds received are dependent on the contributions of donors. Profit generated from social entrepreneurship are directly correlated with the economic aspects that entrepreneurs find themselves confronted by, such as competition as well as supply and demand. Because of this, the defining aspect at the core of social entrepreneurship is that success is defined by the financial decisions that entrepreneurs choose to make within the current state of the market in which the entrepreneur operates. Au contraire, running a charity would rely on sporadic donations that prove to be a less reliable source of money than the profits and economic stimulus caused by small businesses and lower-class workers.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because even though some social entrepreneurs do rely on some charity to start their business, social entrepreneurship aims to solve problems and create a sustainable business that doesn’t rely on others to make profit.
1.I believe that Fiorella Riccobono had the need to express that social entrepreneurship is not charity, rather that relies on donations because she felt the need for the individuals that read the article to understand that this project is so innovative and new that the majority of the people don’t really know about it. Charity is defined as an organization that wants to help and raise money for those in need. Instead, what Fiorella Riccobono is doing relies on donations because although she is helping the needed and businesses, she needs resources and wants to improve the ideas she has for individuals to take on their business as soon as she sets them up for success with her unique innovated plan. This makes an important distinction because it may not always be for free that Riccobono may be doing her job, rather to create a change with an imaginative job that helps improve the world.
3. When Fiorella says, “ I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” I somewhat agree with what she said. Due to the fact, that her job might be one of the ones that may help a large amount of people as it has economic and balanced strategies to make a business start or grow exponentially. However, I don’t coincide with it being the essential future of business rather social entrepreneurship taking on a branch. As it will only help an specific business that are in certain conditions. In addition, it may be a good and productive job, but not the overall future.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship isn’t charity to emphasize that it isn’t an organization that runs on donations. Social entrepreneurs create real businesses that make a profit. Although their objective is to improve issues in society and assist people, their goal at the end of the day is also to earn a profit. I think Fiorella makes that important distinction to show that although social entrepreneurs are there to help people in need, they also create thriving business. It shows that there’s a lot more to social entrepreneurship than most people are aware about and how it’s different from any other non-profit organization.
Malala was shot by a takin when she was 14 years old, since then she fought for the rights of young women to study and gender equality. She became the youngest nominee for the Nobel Peace Prize and won it in 2013. Muhammad Yunnus created the Grammen Bank, it researched to study how to design a credit delivery system to provide banking services to the rural poor, he won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2006. Another social-justice champion is Martin Luther King Jr, he is best know for his role in the advancement of civil rights using nonviolent civil disobedience based on his Christian beliefs. On October 24, 1964, King received the Nobel Peace Prize for combating racial inequality through nonviolence.
Malala Yousafzai is a Pakistani women’s right and children’s activist, who is also the youngest-ever Nobel Prize laureate. Muhammad Yunus is a Bangladeshi social entrepreneur ans economist, who was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for founding the Grameen Bank, in which he developed a micro loans and credit system that helped poor Bangladeshis ‘borrow’ small amount of money. Paulette Meyers mission inspired me because she founded and chaired the Women’s Initiative for Self Employment in San Francisco, for 15 years, which helped to train and finance low-income women to start their own businesses.
Fiorella Riccobono is saying that social entrepreneurship is not a charity because they are very different. For instance, charity needs people to donate money to succeed while social entrepreneurship does not rely on donations even though they do accept money to help their concept. Instead, they use innovative business tactics to create solutions to social issues.
Fiorella says “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” I believe this statement is very accurate to the future of the business landscape as large corporations are increasingly searching for ways to give back and help out society. Social entrepreneurship also opens up new possibility to those who enjoy philanthropic work while still utilizing their business skills. Through creating self-sustaining businesses that help out society, more individuals will be open to the idea of entering a field which help people as it eliminates the feeling of charity and volunteer work.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social enterpreneurship is not charity because although enterpreneurs may rely on donations they can’t really create a business model based on it. She makes this important distinction because people may think thet enterpreneurship is based on charity and donations when they really are basically innovactive business tactics to create solutions to social issues.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because charity is giving to those in need with nothing in return, which is similar to social entrepreneurship in the helping side but social entrepreneurs are looking for a profit and the thing that differ them from most of the entrepreneurs is that besides a profit they are looking to help, they are trying to make an impact in their community for the good. Making an impact is clearly really important to her and that’s why she distinct what social entrepreneurship to encourage people to also make an impact and show them they can make a profit out of something that will benefit the social sector.
Social entrepreneurship IS the future of business and policy making. The world is full of hunger, poverty, pollution, etc. What would be more successful than making a profit while helping to make this dirty filthy world a better place?
I agree with Fiorella Riccobono’s statement that social Entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making. Based on the information her article is giving us, the goal of social entrepreneurship is to help fix the world’s issues or problems. To her, instead of a simple solution, social entrepreneurship can also finds ways to transform the conflict into an opportunity for economic growth.
Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” Do you agree? Why or why not? I don’t think it is the future, yes it is helpful to the world and is good and helps people in need, but this can not be the future of business. If a business wants to be successful in the world they can’t be nice, they can’t just go around helping. A business needs to make a profit, needs to be able to pay all its employees, and all its assets. If a business ever hopes of progressing in this world it has to be heartless, or it will be taken advantage of. It cant have a soft spot it it will be open and it will be used. I understand why she would say this but that is in a dream world, but the business world is far from a dream. It is ruthless and has no heart, its all about the money.
Hi Sebastian. Fiorella, the writer of this essay, read your comment and wanted to respond. Here are her thoughts:
Although I do agree that a business needs to make a profit, I disagree with you on the point that the only value a company can generate is revenue. That is an outdated perception of the value modern day corporations and financial institutions are trying to generate. Social entrepreneurship does not exist to be charitable, it exists to create systemic social impact at the core of it’s day- to- day operations, while simultaneously generating profit.
The modern business structure is steering away from a profit-driven model, to a strategy that systemically addresses the triple bottom line. This is not a dream world perception, but rather the new trend and business models of all corporations are trying to adapt in order to stay competitive. But, you do not have to take my word for it, let’s use a modern-day example of investment banking. The young individuals who are entering the banking industry are increasingly making investment decisions that focus on sustainable growth. In order to learn more about impact investing, a form of social entrepreneurship, I have attached an article recently published by Morgan Stanley:
https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/sustainable-socially-responsible-investing-millennials-drive-growth?cid=sm_smsp_LINKEDIN_MorganStanley_20170831
This generation is demanding socially minded products and companies are responding to this in order to stay competitive and relevant.
When Fiorella says that social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making I could not agree more. Many people in this generation are empowered to make a change in there society and around the globe. Social entrepreneurship is a great way for both a way to make a lot of money , and help the change that you want in the world. Also, social entrepreneurship is a great way to gain customers, because people that believe in your platform will want to buy your product and goods. Social entrepreneurship is a great way to not only help yourself succeed but also a great way to help other succeed and get through there struggles.
2- Muhammad Yunnus founded the Grammen Bank and pioneered the concepts of microcredit and microfinance. He gave loans to entrepreneurs too poor to qualify for traditional bank loans. by this Yunus and Grameen Bank have shown that even the poorest of the poor can work to bring about their own development.
Malala Yousafzai is an activist for female education. She is known for human rights advocacy, especially education of women in her native Swat Valley in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Yousafzai opened a school in the Bekaa Valley, Lebanon, near the Syrian border, for Syrian refugees. The school offers education and training to gils aged 14 to 18 years.
A social enterprise is not a charity because is organization that applies commercial strategies to maximize improvements in human and environmental well-being. They basically combine business with social concerns; they ensure that the society can have access to opportunities to grow in the business environment and be able to sustain themselves.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What Fiorella means by this is that entrepreneurship is not runned by money or even sustained by money like a charity is. Although she says that here and there money will be involved but really and truly its not based on donations at all. Her making it a important distinction lets everyone know that its a innovative business.
Fiorella states that social entrepreneurship isn’t a charity. She emphasizes that is not a business that simply runs on donations, which is similar to a charity. Social entrepreneurs create certain businesses to make profit. These businesses do not rely on others to make profit. An important distinction made is that charities are run totally on donations. Real businesses simply can not last on just donations. Social entrepreneurs have actual businesses that make money that is used for social, cultural, or environmental issues. The important distinction is that charities are run on donations while social entrepreneurs create businesses that make money.
When Fiorella says that social entrepreneurship is not charity she means that social entrepreneurship is its own thing. She recognizes it as being something that can help many people in need, in many different places, for many different causes. As opposed to charity which is something that helps one cause, or raises money for something in specific. She makes this important distinction because she also realizes that the topic could be confusing for someone who does not necessarily know the exact difference between the two.
Freshman need to join college already thinking of a way to change the world. By being innovative in the beginning, it opens your mind to greater things in the future. By joining entrepreneurship clubs, you can discover a whole new world of chances to help homeless people and poor communities. These people are in the need of a shelter and income, and if you somehow can manage to help those communities, they may even increase their business, earning well deserved money, and help other communities too.
I agree with Fiorella that, social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making because, to start a business people have to have technics and know how to talk face to face with other company CEO’s or to talk to banks so they know they will get a profit off you if they lend you their money. Those are the reasons why people have to be socially ready.
I agree when Fiorella says that she believes social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making. In a growing age where successful businesses are known for their high rates of pollution, many advocate for business techniques that are more environmentally friendly. Not only does social entrepreneurship promote profit while keeping detrimental environment effects to a minimum, but it also reaches out to the community to aid and improve the lives of those in need. Business thrives off high profit and the ideals behind social entrepreneurship (such as eco-friendly techniques and public aiding) are essential to good policy making and an excellent community of people. Thus, future business and policy making would greatly benefit from this.
Fiorella Riccobon stressed about social entrepreneurship not being a charity so much since the idea of a social entrepreneurship does not want to be labeled as a charity, because their approach to the problem can be very different. Charity solely depends on donations and uses the money the get to first have their business then give back. This distinction is very important since what social entrepreneurship wants to do is give back and make sure their purpose is directly served and is not based off on only donations.
Fiorella stresses about social entrepreneurship not being charity because it is not an organization that runs in donations, social entrepreneurs create real business that make a profit although there goal is to improve the issues in society and help people but at the end of the day there goal is to make a profit out of there business, I think that fiorella makes that important distinction, to show that social entrepreneurship is there to help people in need, and create a working business that are able to create profit at the end of the day.
I think what Fiorella meant by social entrepreneurship not being charity was that people actually have to put a lot of work in to their business and not just rely on donations. She states, ” charity is not sustainable.” Which means that entrepreneurs should not run a business if they do not know who is giving them money; especially off of donations.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. Social entrepreneurship is not charity because you cannot create and run a business in which you, the entrepreneur, do not know when or where the donations to your business are coming from. Social entrepreneurship is also not charity since it is a business, and the entrepreneur and his or her business earns a profit while helping others. Fiorella makes this important distinction so that people do not think that a social entrepreneur’s business is a charity to the homeless, it is a business that earns a profit while helping the community and the homeless.
Social entrepreneurship is indeed not a charity. While a charity is reliant on donations, a social entrepreneurship cannot create a stable business model without having a stable source of income. Instead, a social entrepreneurship finds an underlying problem such as pollution or poverty and then creates a business model that does not only solve the underlying problem, but also makes the business model profitable. Fiorella Riccobono stresses the distinction between a charity and a social entrepreneurship in order to highlight the fact that a charity only helps people, whether it be through financial or material means; while a social entrepreneurship continuously helps people by creating a profitable business model that not only solves a social issues, but also creates a profit. The distinction between a charity and a social entrepreneurship can be seen in the analogy where, “If you give a man a fish he will be fed for one day, if you teach that man how to fish and he’ll never be hungry.” A charity can be seen as simply giving a man a fish, while a social entrepreneurship can be seen as teaching a man how to fish.
Fiorella is right/wrong when she claims that entrepreneurship is not charity even though some business do help our community. Most of the business have a goal of making money and benefiting themselves, that’s the main goal of most entrepreneurship, they are sometimes too ambitious and don’t care about society. On the other hand some do care about our society and help our community by investing on something using their profits that will benefit not only them but everyone else in the community. She makes that important distinction because charity relies on donations and money support for those in need, she is trying encourage more people and other business that thrive in order to be more charity and help those in need.
When Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity she means that you can’t create a business model based on donations, because charity is not sustainable. She says this to make it clear that it is not a charity.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurs is not charity and I agree. She means that social entrepreneurs create a business and make profits. They can’t create a business on donations. Social entrepreneurs create solutions to societal issues. She makes this important distinction because she wants people to understand that social entrepreneurs is not about donations, it’s about assisting and helping ours and your community.
I do not agree with Fiorella when she says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” Although social entrepreneurship will continue to grow and thrive in western businesses, saying it will be the future of all business is impossible. In places like the United States and other similar countries people generally have more money than those in third world countries, so when people start businesses they are more likely to have enough money to use sustained practices to create there products.we have also seen a shift in what consumers want. More and more consumers are looking for ways to make themselves feel like they are helping society in what they buy, so shifting to social enterprise might actually benefit your business more. Although this is true for first world countries in most other second and third world countries this business method would not work. In these countries people make a much smaller income than they would in first world countries so when consumers are looking for products to buy they will most likely pick a cheaper product that does not give back to society rather than spending more money for the same product with the difference this one will give back to society. These business also have less start up money making it harder for them to produce products in a sustainable manner. For reasons like this social enterprises will grown in first world countries or rich people but is no a viable option for people of lesser income. this is why I do not believe social enterprises will be the future business of the world but rather of the first world.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity even though it has some analogous needs and events. For example, social entrepreneurship may need to rely on donations to launch their endeavors. However, like charity is not sustainable, it is futile to create a business model. It is crucial to express that social entrepreneurs try to solve societal issues by combining government, nonprofit, and traditional business practices.
Social Entrepreneurship is an emerging concept and, as any concept that is new, some people don’t really know what it means. Although it relies sometimes on donations, a business can’t sustain itself just by charity. Social Entrepreneurs main purpose is to help needed business to succeed and creating innovative plans in order to do that.
I believe that social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making due to a great deal of social entrepreneurs looking toward the future and building business models that favor our environment. These innovative minds see harsh problems like global poverty and world hunger as a new slate for growth in areas like economy or cultural growth. In the end, the positive minds of social entrepreneurs will be those of the future in business and policy making.
Fiorellla Riccobono is constantly stressing that social entrepreneurship is not similar than charity, because both overlap in many things. But what people don’t realize is that compared to charity social entrepreneurship is a business looking to make profit. Malala Yousafzai is a Pakistani activist for female education and the youngest to ever to receive a Nobel Prize, also survived a shot to the head once and is now a bounty. Muhammad Yunus is a Bangladeshi social entrepreneur who was awarded the Noble Peace Price for founding the Grameen Bank and pioneering the concepts of microcredit and microfinance. I agree seeing the benefit of social entrepreneurship just as many others.
Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” Do you agree? Why or why not?
I disagree with her. I found social entrepreneurship a very respectable cause and i loved the idea, but i don’t think it is the future of business because since now there weren’t social entrepreneurship, so entrepreneurs can create their company without that help.
I agreed with what Fiorella Said about the future or entrepreneurship. I think that these newer generations are more biologically aware of what is going on with our planet and communities, specially with the current science they have more knowledge and a better understanding of the problems on this world. So judging by the way these generations are more aware and having more knowledge they would lean more towards businesses that can help the world and our communities.
“Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What does she mean by this? Why does she make this important distinction?”
She means that its not a charity because a charity is not sustainable. She make the important distinction because a lot of people confuse it for a charity. She wants to make sure that they know the definition of social entrepreneurship is.
Fiorella is making points that social entrepreneurship can make a difference in people’s lives. Social entrepreneurship can help build of jobs and businesses. It also is helping other people that aren’t working in those businesses and improving their community around them. She wants to make a difference in this world I think that this is the key to change the future and what is soon gonna be the next generation of entrepreneurs.
When Fiorella said “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” I agree because social entrepreneurship is very important in the business world. People have to be able to communicate with people face to face. In todays millennials everyone uses phones and in the future could have a hard time communicating with people face to face. So I think that social entrepreneurship will be very important in the future.
Fiorella stresses that using social entrepreneurship isn’t just a charity and it is a way to make money. Even though it isn’t charity way of working it can contribute to the advancement of others or addressing problems injustice in the world. The social side promotes it to which the business can grow off the help of others it needs a source of revenue like any other business to thrive. Though the company’s can take in donations to work and run this helps things and what they need and to do at the same time promoting problems.
I agree with Fiorella. Social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making. As time goes on, more and more people are becoming aware of the state of our world and the people who live in it. Social entrepreneurship finds the source of a problem, and not only fixes it, but helps to make the world a better place in the process. I believe that this generation, as well as generations in the future, will want to help our world and people in need. More people are wanting to leave the world in a better state than we found it, and some people are already trying.
Fiorella Riccobono is saying that the Social Entrepreneurship is not a charity at all. The whole Social Entrepreneurship point is to help fix the worlds problems but making money is still a priority for the Social Entrepreneurship.This idea still finds ways to transform the issues for an economic growth. So Fiorella basically wants us to know that they’re not a charity that donates all their money.
Yes I do agree with Fiorella, social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making and the idea of it, is a great idea to help young entrepreneurs that are lost in the world of business, this would be a very good and helpful tool for them, and we can’t escape from that, because the technology is growing every second of our lives so i wouldn’t be a surprise if technology take over the world of business, many companies are successful and they did it without that help, but now it can be a very good addition for young kids with great ideas this can help them start and i believe they can be very successful with their projects and new businesses
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What does she mean by this? Why does she make this important distinction? she means its not charity because it cant create a business model, based on donations, because charity is not sustainable, because charity is mot sustainable. you cant build a business when you don’t know where your next dollar is coming from or when.
I agree with what Fiorella thinks about social entrepreneurship. The program is related to charity but is not the same thing as she had stated in the article. This program has a potential strong base for jobs in the future. The course deals with societal problems by matching them with economy issues as well as financial issues like a business. This sets it as a powerful candidate for future employments and jobs in my opinion as it has an extravagant amount of potential.
I agree and believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making because one of its main purposes is to make the environment and future businesses successful and better.
I agree with Fiorella because it’s true that in the future we need to socially communicate with different people. Some people are working and are not getting paid enough for the work that they are doing. It’s good that she and other people are making a change to this problem in the world. With the homeless Fiorella and other people are trying to make a difference helping the people that are in a finacial crisis or are in need of help
I agree with Fiorella. I find that social entrepreneurship does a good balance between profit and helping the community. They are not dependent on outside source like charities and are not focused on massive profit like the big enterprises. I believe that more of those kind of business will start to appear and be successful on the near future.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What does she mean by this? Why does she make this important distinction? Fiorella means that social entrepreneurship is forced to donate and charity is your choice to donate money to charity.
Social entrepreneurs can only do so much to help people out. Being a social entrepreneur cannot be anything like a charity because you need to guide yourself and get yourself out there. Like she said, we all want to leave the world a better place than it was before yourself, so yes you can help out but if you just keep helping someone, they are constantly going to keep asking for help. Give a man a fish and he can eat that day but teach a man to fish and he can now provide for himself. She makes this important because people need to understand it, too many people guide others around and can help them for that time but not later on in life. It’s similar to the first 18 to 20 years in your life, your parents provide for you with food and a roof over your head but they cannot support you forever.
I agree with Fiorella. No person, for their entire lifetime, is going to want to be bossed around by someone. Everyone eventually wants to become their own boss and be the founder or CEO of their own company. Everyone can do it, and there are many opportunities down the road, whether you’re getting right out of college (or even high school) or you’re in your later years and have some money to work with and want to make a change in today’s society.
As Fiorella Riccobono said, Social Entrepreneurship is not a charity. It is easy to think that, however it is important to recognize the difference between the two. A Social entrepreneurship is financial and business organization that combines aspects of a running business while helping social problems in the world advance.
I agree with Fiorella because Fiorella wants to make a charity to help homeless people and I think that’s great because she understand that Homeless people needs help and I like to help people that needs help.
Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” I agree with her because as people grow up they are starting to realize the real world and businesses and businesses techniques are changing
The student explained what social entrepreneurship is. She explained that it is not a charity and that it is made to last. In social entrepreneurship you have to think how to make the idea work so the idea doesn’t fall apart and you give money for specific things which will help the idea to develop.
Fiorela has stressed that social enterprise is not at all a charity, it makes money. She means that it is not a charity because then it doesn’t sustain itself well at all. It cannot create a good business model with donations, or nothing at all. She wants people to know that they are not a charity that donated all their profit away.
Fiorella Riccobono is correct because social entrepreneurs is a business. In social entrepeneurs people is more empathetic because of their helping the social sector by solving global and humanitarian issues, they ask what is the problem and then base on that they plan their business around that. They make a money while helping the society.
Social entrepreneurship is truly the future in my opinion because of business and policy making, it is a business enterprise not only with a focus in profitable gains and societal claims. Its meaning is reflected on the demand of clients for business to have grater social goals or targets.
When Riccobono thinks “social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making”, I support her opinion. For me, I think as young adults develop, they establish beliefs on how they can have a positive impact on the Earth. Of course, one of these ways is by social entrepreneurship. With young innovative minds, they can think of things they can create. These people need passion and commitment. They also need to develop skills that persuade other passionate and committed people to join their cause. Social entrepreneurship is about helping the world, and an increasing number of people are constantly trying to do that. As a result, global issues, like poverty, will decrease.
A social entrepreneurship is not a charity because all of the proceeds do not go to other organizations. A part of the revenue goes towards organizations but some goes towards the business to keep it running. A social enterprise is sort of a hybrid between profit business and non-profit charity. What she means to say is that the social enterprise’s goal is not to just give away money but instead to create money for its own needs while giving money to organizations that need it. She has to make this difference clear because many people know about charities and often do not want to donate, but since this is a charity/business in disguise it generates money while also providing a service and good.
Yes I agree that social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making. I believe that social entrepreneurship can do a lot of good in the world and benefit people both the ones being helped and the ones helping. It will open many doors for many people that need help.
1.Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because it makes profit and it is not a situation where someone receives money once, and slips back into trouble. When profit is made, the organization is clearly no longer a charity and social entrepreneurship helps people get back on track. This is an important distinction because it helps people realize that unlike a charity, this organization makes profit and helps people at the same time.
2. Malala Yousafzai has made an impact on the world by advocating for young girls to go to school, and Muhammad Yunus has made an impact on the world by providing small loans to the poorest people in the world. The most inspirational social justice hero to me, is Mahatma Gandhi because he liberated an entire country from England in peace and in friendship.
3.I do not believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making, because there are certain businesses that this won’t work with (Ex: car companies) and there are many people in the corporate world that will not support this type of organization.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because while both aims to aid those in need, social entrepreneurship makes a profit. Charities may give money to those in need, but unless these people are able to regain an income, they will return to their original conditions. It is impossible for charities to keep on giving money to support these people for the rest of their lives since charities relies on donations and the people working in charities also needs an income to support themselves and their own families. Social entrepreneurship tries to address the root of the problem and create a solution. As Fiorella Riccobono has mentioned, instead of giving small coffee farmers money, they bought their coffee for a fair price and sold it at their trucks. This not only helps the farmer, but also helps the people running the business to keep going and continue making contributions to the world.
I do agree that social entrepreneurship will be the future of business and policy making. Social entrepreneurship helps develop, fund, and implement solutions to many different social and environmental issues around us. With different aims and sizes of this concept, it can apply to almost any organization or job. So it can pretty much help out others who work in different industries.
1. Fiorella Riccobono is stressed that entrepreneurship is not charity because they are both different from each other, entrepreneurship helps us make the world a better place by making ideas. Charity is people helping others by giving them money to be successful in life.
2. I agree that entrepreneurship can be helpful in our future because of how helpful it can be for the country and for us living a better and healthy life style. It can also impact others and convince them too work for entrepreneurship to help our grow even bigger then it was suppose to be.
Fiorella Riccobono stress es that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, because charities are not sustainable and can not control the influx of money, in the contrary, social entrepreneurship is a business that is expected to make a profit and relies on more than just donations. Although social entrepreneurship is not a charity, it was also invented in order to help people, businesses and helping make the world a better place. Social entrepreneurship is the future to business and policy making and it is supposed to make enough money to keep the business going, with profits included, and help other businesses that may need financial help.
I think it was very wise for Fiorella Riccobono explain to us that social entrepreneurship is not charity because it makes us understand that you can do the right thing and still get revenue from your work. I think that now I understand way more about social entrepreneurship and I think is a great thing. I feel that It helps the community to improve in many ways. I’m glad she wrote this, I think she may have changed the point of view of a lot of people about entrepreneurship that thought it was like a charity.
Firoella Riccobono explains that social entrepreneurship is not charity because since its just emerging as an idea, she thinks that charity is not sustainable enough to do the job. You can’t build your business on not knowing when or how much money you are gonna receive from charity. They combine government, non-profit, and traditional business in order to create a sustainable business. These innovators create large sustainable models by addressing an issue in the world like poverty, pollution etc.
Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” I agree with her statements beacuse I think that future and presents Entrepreneurs are thinking in ways to make the world a better place. This impacts lots of people by the fact that they are attracted to make the world a safer and healthier place for everyone, especially for the people in need, like the homeless. While lots of people are getting involved in business, the majority will want to start their own social Entrepreneurship campaing which gives a high income and helps the world to be a better place.
I agree with Fiorella because the next generation of Entrepreneurs are trying to find new ways to make the world a better place. This has a huge affect on people today, For example the more unfortunate people.Now a days everyone want their own business where they can do something for money. But Fiorella addressed social entrepreneurship is like a charity where you get a profit from. This is another way we are trying to develop something new to make the world a better enviroment to live in.
I forgot to add that either most or all charities don’t profit, and that this is why she talks about the topic this way.
Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity because for the business to thrive and grow it must have a stable amount of money behind it. The business can use help from donations but it cannot purely be charity. If it were to rely only on donations, it would not be sustainable over a longer period of time. Social entrepreneurship is for the benefit of important causes like the homeless. Having financial support ensures they can do their job.
When Fiorella Riccobono stressed that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she meant that social entrepreneurship although helping people, helps the person who made it generate income, while charity is straight up giving people or organizations money or aide without getting profit. This is an important difference because charities rely on donations and volunteers more than anything, and you never know how much you’ll get over relying on others. In a social entrepreneurship, you are responsible and you make money.
1. Fiorella Riccobono explains that social entrepreneurship and charities are different from one another: A charity is a nonprofit action that is made to see some sort of change in the world, for the better. However, it is made quite clear that social entrepreneurship is a business. Even though it receives donations, it is a business that generates some sort of profit; but, nevertheless, a business with a goal in mind, one that is to make the world better than how we found it. It’s important to make the distinction because a social entrepreneurship is better able to maintain itself without having to purely rely on external sources and donations.
When Fiorella states that social entrepreneurship is not charity work, I attatched that to the fact that it is strictly enterprises for a social change. The business owners in the social enterprise industry understand that they are not being given money for a cause nor are they raising awareness. Social enterprises are not charities because charities are given donations by others. Social enterprises on the other hand can be funded, but can not be donated to. This is a important distinction to make so that other do not get confused and make mistakes when they are starting their own businesses. It is crucial to make this distinction for the sucess of other businesses to come.
When Fiorella says that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she means that if you want to start a business, you have to have stable money behind it to produce it. Social entrepreneurship is a business that makes profit. In charities, you only get money for volunteers, not knowing if you will make lots of profit. Fiorella expresses this because she wants people to know that in entrepreneurship, you have to work or your business and get profit, not getting money from charities.
When Fiorella state that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, she is referring to the fact that charity relies only on founds specific for one cause, which may not be sustainable for a long enough time. Mean while social entrepreneurship, focusses on founding multiple things like homeless, and is not exclusive to one major cause, but is open to a variety of major causes.
What Fiorella means when she says that social entrepreneurship is not charity is that charity is when you raise money or objects for a cause or for a specific person or place. It for people and places that are less fortunate and cant afford a lot fo things. A social entrepreneurship is when you are making a profit out of something. You also focus on many different thing, not just one cause.
i agree because a lot of people don’t know the difference of social entrepreneurship and charity the difference is that in entrepreneurship you gain money in charity you donate money which means you’re losing money.
I agree with Fiorella’s statement on how social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy, I agree with it because it is changing the way by how people see things. For example, the article states, “People are no longer seeing global poverty as a call for charity, but as a place of economic and cultural growth.” New students will exposed to social entrepreneurship and soon enough, there will be plenty of individuals who will use innovative business tactics to create solutions.
Yes, I agree with what Fiorella states. It is the future of business and policy making because you need to “promote your mission” and find funding for it, all while getting other people involved in whatever you may be promoting. These are essential paarts of growing your business.
I do agree that social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making. Many people in the world have the desire to make it a better place for everyone; however, they don’t know how or where to start. With social entrepreneurship, the goal is help and contribute while still making a profit. By doing this, both sides have the ability to grow and prosper. The best part is that you are making the world a better place.
I agree that social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making because companies would have a steady flow of income to them instead of a charity which will have money coming in for one specific cause. Social entrepreneurship will be successful considering how many young minds we have for the future, bringing it to a new level and presenting fresh new ideas into the social entrepreneurship world, changing it completely, allowing success. This is the successful future we have.
I believe that it is stressed that social entrepreneurship is not charity because the organization does not only depend on donations to succeed, they have had a stable amount of money behind them in order to strive as the organization they are. Unlike charities, social entrepreneurship make a profit. This is important and stressed because social entrepreneurship’s need to work for their money and sell instead of relaying on donations and charity events to become a better organization. Social entrepreneurship’s are businesses; they do not depend on donations and they also make a profit. The business also can not be continued if they are not making money on their own.
When Fiorella states that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she means that when you volunteer for charity, you only give. There is no economic balance if you always give, and don’t get anything back. We need to do charity when there is crisis. If not, the economic balance would go down. What Firorella states, makes a lot sense because social entrepreneurship has a economic balance circle that goes around and you make profit in one way or another, but charity does not have a profit if you only give.
When Fiorella states that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, she means that social entrepreneurship is a force used to help people. She states that charity is not a sustainable money flow for a business. Social entrepreneurship, however, is something that people use to (not exclusive to) helping the homeless, sustaining the planet’s resources, and finding ways to make profits for a business. She makes this important distinction because she wants to differentiate between between charity and the work that her and social entrepreneurs do. Charity is an unsustainable source of business, and that is not the goal for social entrepreneurs; social entrepreneurs work to aid people in growing a sustainable economic system.
When Fiorella Ribccobono says that a social enterprise is not charity, she believes that an entrepreneurship that seeks to gain a profit, fails to create a sustainable charity. Therefore, a social enterprise uses specific causes to aid in its operations. For example, rather than giving coffee farmers a percentage of the profits, the coffee food truck buys its coffee beans from farmers who use sustainable methods of farming. This allows the farmers to get a profit and be able to live off their work rather than relying on charity. This distinction helps Fiorella argue the benefits of being a social enterprise for the business and the cause, rather than the charity that does not allow the cause, in this case the farmer, to grow at all. Charity promotes a stagnant, one-way economy that has no advances of any kind. Although charity is important in a crisis or catastrophe, a social enterprise is beneficial in aiding the economic growth of two bodies of work.
when Fiorella says that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she means that if you want to start a business, you have to make stable money behind it to produce it. Social entrepreneurship is a business that makes profit. In charities, you only get money for volunteers, not knowing if you will make lots of profit. Fiorella expresses this because she wants people to know that in entrepreneurship, you have to work or your business and get profit, not getting money from charities.
In the article, the author, Fiorella Riccobon, stresses that social entrepreneurship is not a charity. She uses two important distinctions to explain this. The first is that it’s a more stable business format. Charities rely on donations for their income and funds. Social entrepreneurship sells goods and uses the profit to help others. The second is the way they help. Social entrepreneurship teaches people to support themselves by getting fair wages like the Haitian coffee farmers. Charities give money or food which only helps people when they are there.
It is important, social entrepreneurship is more than just a charity. Even if the businesses your talking about or involved in a nonprofit business, it will sustain its self better than a charity. All charities come to a soon end. you must have a bullishness plan when it comes to whatever your collecting profit for. Charity does not have a foundation like a businesses does. An innovative business will help you make a better profit.
Fiorella is stating the social entrepreneurship is not like charity. Shes saying the for charity it doesn’t last for a long time, entrepreneurship is not on one major thing. Malala has won the Nobel prize inspiring woman and helping the communit
Giancarlo amazing statement
I believe that when Fiorella mentions social entrepreneurship isn’t charity that she is referring to the fact that charity is something that is done for the sake of a devastating event or in other words a single reason but on the opposing side of things , she is saying that social entrepreneurship is for a diversity of necessities including for example as one of the subtitles in the article says “helping the homeless.”
The details given by Fiorella in the article on what a social entrepreneurship does and its functions is truly brilliant. The new level that these social entrepreneurship are achieving is remarkable as they create a business that benefits small businesses, helping in the community, and produce a profit. It’s a truly beneficial business for all aspects included.
As far as the article goes, Fiorella did a really good job distinguishing between charity and social entrepreneurship. Before reading this article, they were both the same thing in my mind. She makes this distinction for exactly this reason, so people are more educated about social entrepreneurship and her business. The way I see it, social entrepreneurship is an equilibrium between charity and the economy. Charity isn’t a sustainable lifestyle, but a social enterprise is. In my opinion, a social enterprise uses the efficiency of the United States economy to benefit the person in charge of the business and others.
When Fiorella said that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, she is stating that charity relies on other founds for only one cause. When you start a business, you need some money to put behind it to support the business. Charity relies on other people to give money. With a business, there is an economic flow of money. Even though donations are involved in a business, its gains some sort of profit. You cannot build your business not knowing where or when your money is coming from. Charity doesn’t generate profit, this is why she said it that way.
I agree with Fiorella, that social entrepreneurship is not charity. What she means by that is charity is when you give to a cause if there is something horrible occurs, such as hurricane Harvey, you would give money to charity to give the people of Houston. But in this case, social entrepreneurship is when you teach someone how to do stuff like make their own food by people teaching them how to farm or raise cattle so they won’t need to be so dependent for others to give them money.
Fiorella stresses that social entrepreneurship is not charity. Even though social entrepreneurs and charity both rely on donations and are similar, social entrepreneurs can’t create a business of it because charity is not sustainable. She wants readers to understand the difference between social entrepreneurship and social services because most people think they are similar.
When Fiorella Riccobono says that social entrepreneurship is not a charity she means that charity is just giving away without gaining any profit out of it. A social entrepreneurship is different because social entrepreneurship makes a profit; it helps a community in some ways but it also benefits the entrepreneur in other ways. There’s a saying that Ms. Zocco said “Give a Man a Fish, and You Feed Him for a Day. Teach a Man To Fish, and You Feed Him for a Lifetime.” This saying explains much about what social entrepreneurship. An example of a social entrepreneurship is, you put a business in a poor town, you teach all the poor people in that town how to do the job and hire them. You pay them a wage that is going to allow them to live comfortably and they are good. An example of a charity is going to a poor town and just give them money. That will only help them for some time. She makes this important distinction because social entrepreneurship is much better than charities. It helps the people, it makes them work, and it helps the entrepreneur make a profit. Charity helps society but it doesn’t improve society as much as social entrepreneurship. This is important to know because the more people make social entrepreneurship, the less poverty will be in the world.
When Fiorella states that social entrepreneurship is not charity, she is referring to the fact that charity relies only on founds and specific for one cause.
It’s not the same because , although social entrepreneurs may need donations to launch their endeavors, they are not going to be able to create a business based on donations. Charity is not continuous. Just imagine building a business when you don’t know where your next dollar is coming from or when, you can’t. This is actually important because social entrepreneurs are individuals who draw on innovative business strategies to create solutions to societal issues. So, this is what I think.
Fiorella stresses that social entrepreneurship isn’t a charity because it isn’t. In order to start a business and have it flourish you need more than just donations to do that. Even though the two have their similarities (meaning they both rely on donations), they are different. You can’t just base your business on a “maybe”, because there’s no 100% that there will be more donations. That’s worry-some for your clients and yourself. Entrepreneurs may use the donations to start off but later own they’re going to have to make better decisions so they gain money instead of receiving it form anonymous or known doners.
When Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not a charity, she’s referring to the fact that a charity is when people give without getting anything out of it. Rather, she wants people to understand that in social entrepreneurship, the entrepreneurs are helping with societal issues but they are building a business not a charity.
When Fiorella said that social entrepreneurship is not charity, charity rely on donations for only one cause but charity isn’t sustainable. All charities will help for some time and come to a soon end. But social entrepreneurship is an equilibrium between charity and economy because makes people work and help the entrepreneur make profit and improve de community. Malala Yousafzi and Muhammad Yunus are positive and influential contributions to de society. Malala advocates for women education and Muhammad created the concept of microfinancing. I agree when Fiorella says, “I believe social entreneurship is the future of business and policy making.” Because the more people who make social entreneurship with innovative business tactics the more solutions to social issues.
When Fiorella Riccobono stresses that social entrepreneurship is not donated, she means that social entrepreneurship is not focused on raising money. Social entrepreneurship is a business that benefits when money is used. Of course you are going to need to donated money from somewhere, but the purpose of social entrepreneurship is to run a business not to collect money. Clearly, Fiorella makes this important distinction because she wants to show the readers that social entrepreneurship and donating are two separate things.
Florella says “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy making”, which I have to totally disagree on. I’m surprised that no one has talked about Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), which is mandatory in many countries, as a % of the net profits made by the firm. Why are firms doing this? Well, if they make a difference (e.g. build a school for a rural place in a country), they gain good publicity. As consumers are getting richer now, they may choose to buy a good or service from a firm with good reputation. By enacting CSR, firms have a better brand image as they are seen to be kind, caring, and giving back to the community. Is this the truth? No. Firms are doing this for more profits and revenue. They can gain more demand and consumer loyalty by CSR.
Now back to social entrepreneurship. This is different from CSR as CSR can be donating money to a major firm. Right now, businesses focus on whether their acts are moral and ethical, as they may be creating lots of external costs e.g. pollution which decreases health of the labour force. Most businesses are for profit – only non-profits will focus on social entrepreneurship. Trust me, it isn’t highly profitable.
I have a social enterprise myself, from the club I created. I’ll talk about the club and distinguish between social entrepreneurship and donating / charities. They are different, but are similar in some respects. Both need money to operate. How do charities get money? They ask people to donate, which is usually tax deductible if they are a 501c3. How do social entrepreneurs get money? They have to get it themselves, which is a very proactive process. Most people get investors. However, I’m only 15, so I gain money by starting a business and profiting. I use those profits to operate my social enterprise.
Florella continues with “Social entrepreneurs do not have an idea and then apply it. Instead, they go directly to the source of the issue and ask what is needed. Based on that answer, they build their business plans. Social entrepreneurs are often empathetic, bold, open-minded and tenacious”. I totally agree on this, but as I am a student, I’m working with a 501c3, and together we are developing a model on how to alleviate poverty and hunger in a part of rural China. We’re working on small ‘life packages’, containing different proportions of food, sanitation, clothing, etc. and we’re finalising the model. Our solution is very meaningful and may bring a whole village out of the absolute poverty line. However, similar to a charity, we need funds to operate and purchase the food packages. I am the social entrepreneur, while the 501c3 is the charity. The charity of course has more funds as they are tax deductible, and a trusted organisation. On the other hand, I have less funds because I’m gathering it myself, but together we make a good group to help fight against the 1st and 2nd UN SDGs!
Finally, I’d like to comment on Malala, a true inspiration. There is a club at my school based off Malala’s vision, providing more education for girls. Although we live in a rich district in the metropolis Shanghai, there are rural places in China (places which need food packages) where girls don’t go to school. Malala’s story has made the whole world realise how inequality still exists, and keeps reminding us to fight against it. I’m so happy that service learning has just been approved at our school as a mandatory academic subject :).
Also, commenting a little more on Malala – her life has a “conveyor belt” image, as she was brought up in an elitist family who trained her to be the voice for many women. Her success would not have been possible without her father. Of course, she was very determined herself as she was stronger than before after being shot and fortunately surviving. Malala wasn’t a social entrepreneur, but more like a political ambassador / representative. Her Noble Peace Prize win raised more awareness of the issue of inequality, to empower women for education.
In the mere chance anyone stumbles by my post nearly 1.5 years ago, I’d like to make a correction after learning much more about impact investing and creating a business with impact. My previous viewpoints still remain the same (well, CSR is mutually beneficial for both the firm’s publicity and those who are supported by the received money/projects – it’s a win win!). However, social enterprises can be for profit. There are many impact investing firms, mostly venture capitals that invest in businesses that will both generate profits and a positive societal impact. Hence, social enterprises can definitely be profitable.
Also, update to the social enterprise I founded. Co-organised event with Rise Against Hunger where 220000 meals were packaged and distributed in Oct 2018!
Great. This article is excellent. I have read many articles with this topic, but I have not liked. I think I have the same opinion with you. ATTITUDE QUOTES
As stressed by Fiorella Riccobono, Social entrepreneurship is different than charity. I feel the same here as charity is merely done for compassion towards humankind and measured by the donations acquired, social entrepreneurship is done for social change and welfare.
When Fiorella says, “I believe social entrepreneurship is the future of business and policy-making”, I completely agree. The concept of innovative thinking is lacking in this world and by social entrepreneurship, such skills are highlighted.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles
The retail rat race: ‘tis the season for shoppers, stores and sales, inside the internet of things.
We inform you that Fundació Esade, as data controller, will process the data for the purpose of managing the registration and sending the DoBetter Newsletter. No data communications will take place The interested party may exercise, if desired, the rights of access, rectification, and deletion of data, as well as request that the processing of personal data be limited, oppose to it, request the portability of their data, not to be subject to automated individual decisions, where appropriate, as well as to withdraw their consent at any time by contacting the Data Protection Officer at [email protected] You can consult additional and detailed information on Data Protection here

The rise and impact of social entrepreneurship
- Innovation & technology
- Compartir en Twitter
- Compartir en Linked in
- Compartir en Facebook
- Compartir en Whatsapp Compartir en Whatsapp
- Compartir en e-Mail
More and more companies are recognizing the importance of generating social and environmental value alongside financial performance.

This article is part of the ‘Inspiring Transformations’ series promoted by Esade Entrepreneur Institute for its 30th anniversary.
The field of social entrepreneurship has grown significantly in the last two decades , with thousands of companies worldwide using entrepreneurial approaches to address social and environmental challenges, a transformation that has been supported by an ecosystem of incubators and accelerators , investors, regulators, and other intermediaries and market actors.
The growth of social entrepreneurship has not only manifested in practice but also in academia . It has become a consolidated field of study in management scholarship, trying to understand, among other issues, the particularities of the profiles of social entrepreneurs, the tensions that appear when blending social and financial logics, the potential of hybrid business models to address societal challenges, and the legitimacy and development of the sector.
Today, Esade Center for Social Impact , Esade Entrepreneurship Institute , and eWorks collaborate to support students and external impact entrepreneurs through courses and acceleration programs, focusing on topics such as developing and managing impact-centric business models, exploring the role of impact tech startups in addressing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) , and effectively supporting new business model exploration and validation through the practice of impact measurement and management.
Towards an impact economy
The current state of the sector is generally positive. Not only are many social enterprises thriving, but an increasing number of conventional companies are also integrating impact considerations into their decision-making processes. In this sense, social entrepreneurship has had a positive influence in promoting what we call the impact economy. More and more companies now recognize the importance of creating social and environmental value alongside financial returns.
Impact measurement, transparency and accountability need to go hand in hand with social innovation
As claimed by the European Social Enterprise Monitor ( ESEM ), a study coordinated in 21 European countries on the state of social entrepreneurship and for which Esade is the country partner in Spain, there has been accelerated growth and spread in the sector : despite many social enterprises being relatively small and young, they are now active in all economic sectors and 91% aim to scale in a sustainable manner.
The challenges ahead
Nonetheless, challenges persist. For example, many social and environmental causes can benefit from business and entrepreneurial approaches, but those organizations might only sometimes be able to produce huge financial returns. Further research is needed to understand the unique challenges and opportunities offered by these hybrid models and explore systemic initiatives that can drive impact across multiple fronts.
With continued support from the ecosystem and ongoing research efforts, social entrepreneurship holds the potential to create a lasting impact that goes beyond individual enterprises and addresses the pressing issues of our time. As with other practices that arise at the intersection of the business and social realms, social entrepreneurship will have to find the proper balance between leveraging business and financial practices that can help organizations scale and be more efficient, and at the same time maintain its strong social purpose.
In other words, impact measurement, transparency and accountability need to go hand in hand with social innovation, new consumer and corporate behaviors, and the objective of systemic change.
Director, Esade Center for Social Impact
Related posts
The emergence of new business models, the crucial role of innovation and entrepreneurship in organizations, protecting and enhancing startup founder wellbeing, do you want to receive the do better newsletter.
Subscribe to receive our featured content in your inbox.
- Business law
- People & talent
- Strategy & business models
- Women in business
- Geopolitics & global risks
- Global governance
- Global markets
- International economy
- Sustainable development
- Data science & behavioural insights
- Entrepreneurship
- Future of education
- Technological change & digital transformation
- Ethics in business
- Managing diversity
- Public purpose
- Social cohesion & inclusiveness
- Technology & people
The impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and its determinants: a systematic review
- Open access
- Published: 04 August 2020
- Volume 71 , pages 553–584, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Thomas Neumann ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7189-8159 1
89k Accesses
52 Citations
Explore all metrics
This paper presents a systematic review of (a) the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and (b) the factors determining this impact. Research over the past 25 years shows that entrepreneurship is one cause of macroeconomic development, but that the relationship between entrepreneurship and welfare is very complex. The literature emphasizes that the generally positive impact of entrepreneurship depends on a variety of associated determinants which affect the degree of this impact. This paper seeks to contribute to the literature in three ways. First, it updates and extends existing literature reviews with the recently emerged research stream on developing countries, and incorporates studies analysing not only the impact of entrepreneurship on economic growth and welfare but also on social and environmental welfare. Second, it identifies and structures the current knowledge on the determinants of this impact. And third, it provides a roadmap for future research which targets the shortcomings of the existing empirical literature on this topic. The review of 102 publications reveals that the literature generally lacks research which (a) goes beyond the common measures of economic welfare, (b) examines the long-term impact of entrepreneurship and (c) focuses on emerging and developing countries. Regarding the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship, the results highlight the need for empirical research which addresses both already investigated determinants which require more attention (e.g. survival, internationalisation, qualifications) and those which are currently only suspected of shaping the impact of entrepreneurship (e.g. firm performance, the entrepreneur’s socio-cultural background and motivations).
Similar content being viewed by others
From economic wealth to well-being: exploring the importance of happiness economy for sustainable development through systematic literature review
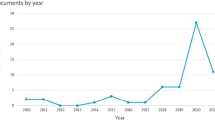
Economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on entrepreneurship and small businesses

Artificial intelligence and big data in entrepreneurship: a new era has begun
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Entrepreneurship and its possible impact on the economy have been studied extensively during the past two decades but the research field still continues to develop and grow. The majority of studies from a variety of scientific disciplines have found empirical evidence for a significant positive macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship (e.g. Atems and Shand 2018 ; Audretsch and Keilbach 2004a ; Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ). However, several empirical studies show that the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship can also be negative under certain conditions (e.g. Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Andersson and Noseleit 2011 ; Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ). Potential explanations for these contradictory results are to be found in the complex relationship between entrepreneurship and economic growth. Already some of the very first empirical studies on the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship showed that factors such as industrial affiliation (Fritsch 1996 ), the country’s level of development and the local density of business owners (Carree et al. 2002 ) significantly determine the impact of entrepreneurship. With more entrepreneurship datasets becoming available, researchers found evidence that only a small number of new firms such as particularly innovative new firms and firms with high-growth expectations create economic value and initiate Schumpeter’s process of ‘creative destruction’ (e.g. Szerb et al. 2018 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; van Oort and Bosma 2013 ; Wong et al. 2005 ). However, over the past decade, researchers have identified a multitude of other relevant determinants (e.g. survival rates of new firms, institutional and cultural settings, motivations and qualifications of the entrepreneur), thereby drawing an increasingly complex web of interrelated determinants around the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship. This complexity combined with the fact that the research on determinants is scattered and mostly based on separate analyses of determinants leads to a number of hitherto unidentified research opportunities. In order to detect these opportunities and to exploit them in a targeted manner, a structured overview of the current knowledge on the determinants of the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship is required. In this context, a structured overview is not only essential for the scientific entrepreneurship community but also for politicians all over the world who need detailed information on the impact of entrepreneurship to promote the right types of entrepreneurship in the right situations.
To ensure that this information prepared for policy makers are truly comprehensive, it is essential that state-of-the-art research considers not only economic outcomes of entrepreneurship but also its social and environmental effects. This demand for a more holistic impact analyses is based on the call of economists who have been emphasizing since the 1970’s that economic development may is a significant part of welfare, but that social and environmental dimensions need to be considered as well (Daly et al. 1994 ; Meadows et al. 1972 ; Nordhaus and Tobin 1972 ). Tietenberg and Lewis ( 2012 , p. 553) summarised the economic, social and environmental effects in a holistic welfare definition and state that a “true measure of development would increase whenever we, as a nation or as a world, were better off and decrease whenever we were worse off”. This understatement is in line with many authors who recently highlighted the importance of entrepreneurship for social and environmental welfare (e.g. Alvarez and Barney 2014 ; Dhahri and Omri 2018 ; McMullen 2011 ). Entrepreneurship research has come to see entrepreneurs as a solution for social inequality and environmental degradation rather than a possible cause of them (Gast et al. 2017 ; Munoz and Cohen 2018 ; Terán-Yépez et al. 2020 ). This scientific consent of the past 50 years clearly illustrates how important it is that econometric research on entrepreneurship incorporates research on the economic as well as on the social and environmental impact of entrepreneurship. Footnote 1
Considering that the research on the macroeconomic impacts of entrepreneurship has been gaining increasing recognition over the last two decades and across a wide range of disciplines (Urbano et al. 2019a ), literature reviews must be conducted periodically to synthesize and reflect recent progress and to stimulate future research. Several high-quality reviews have already summarized the significant amount of research on the impact of entrepreneurship on the economy. Wennekers and Thurik ( 1999 ) were the first who discussed the link between entrepreneurship and economic growth in a narrative literature analysis. With their summary of the theoretical knowledge of that time and the first framework of the entrepreneurial impact the authors laid the groundwork for the following decade of empirical research on that matter. van Praag and Versloot ( 2007 ), extended that first review by systematically reviewing and evaluating the empirical findings of 57 articles published between 1995 and 2007. More precisely, the authors evaluated the various economic contributions of entrepreneurial firms, which have been defined by the authors as either employing fewer than 100 employees, being younger than 7 years or being new entrants into the market, relative to their counterparts. van Praag and Versloot ( 2007 ) thus made the first systematic attempt to distinguish the few new firms which are of economic relevance from the majority of meaningless new firms. Fritsch ( 2013 ), in a non-systematic monograph, exhaustively surveyed and assessed the then available knowledge on how new firms particularly effect regional development over time. Within this review, the author has established the term ‘determinants’ in the field of research on the impact of entrepreneurship and developed first suggestions on which factors may determine the impact of new firms. However, the author has not provided any empirical evidence for the effect of his proposed determinants. In contrast to these three literature reviews, the three most recent reviews also incorporated the latest findings from international studies and on developing countries. However, the three latest reviews all have a narrowly defined research focus. While Block et al. ( 2017 ; systematic literature review of 102 studies published between 2000 and 2015) analysed antecedents, behaviour and consequences of innovative entrepreneurship, Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ; systematic literature review of 28 studies) and Urbano et al. ( 2019a ; systematic literature review of 104 studies published between 1992 and 2016) focused on the relationship between the institutional context, entrepreneurship and economic growth. Accordingly, all the existing reviews are either (1) already outdated, (2) mostly on highly developed countries or (3) focused on specific topics. Furthermore, none of these reviews provided (4) a structured overview on the empirical knowledge on the impact of entrepreneurship on the economy or (5) included research on the social and environmental impact of entrepreneurship.
This paper addresses these five shortcomings through a comprehensive and systematic review of empirical research into the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, Footnote 2 social and environmental welfare. The methodology of the review is based on the current knowledge of systematic reviews (e.g. Fayolle and Wright 2014 ; Fisch and Block 2018 ; Jones and Gatrell 2014 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ), on narrative synthesis (e.g. Dixon-Woods et al. 2005 ; Jones and Gatrell 2014 ; Popay et al. 2006 ) and on recent examples of best practice (e.g. Jones et al. 2011 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ; van Praag and Versloot 2007 ). Using this approach, this paper aims to contribute to the literature on the impact of entrepreneurship on welfare in three ways. First, it updates and extends the existing literature reviews. More specifically, it follows recent research recommendations (e.g. Block et al. 2017 ; Fritsch 2013 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ) by incorporating the recent empirical stream of research on the impact of entrepreneurship in developing countries and research that goes beyond measures of common economic welfare. In practical terms, this means that this review not only considers measures of economic welfare (e.g. GDP, employment rates, innovative capacity), but also for social welfare (e.g. life expectancy, literacy rates, income inequality), for environmental welfare (e.g. CO 2 emissions, water pollution, soil quality) and for indicators which incorporate all three welfare dimensions (e.g. Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare, Genuine Progress Indicator). Second, this paper, as demanded in previous reviews (Fritsch 2013 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ), aims to provide a descriptive analysis of the factors determining the entrepreneurial impact by critically assessing (a) which determinants of the entrepreneurial impact have (b) what impact on (c) which measures of economic welfare. This paper thus represents the first comprehensive attempt to summarize and structure the empirical knowledge on the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship. Finally, to encourage future research, this paper indicates shortcomings in the empirical research not only on the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare, but also on the described and structured determinants of this impact. It concludes with suggestions for future research avenues to close these research gaps.
To achieve these objectives, this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 describes the methodological approach of the review. Sections 3.1 and 3.2 report the available empirical research into the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare. Section 3.3 summarizes the determinants of this impact and Sect. 4 presents a roadmap for future research. Section 5 discusses the limitations of this paper and provides a conclusion.
2 Methodology
In order to clarify not only the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare but also the determinants of this impact, this paper provides a broad-ranging systematic, evidence-based literature review including a narrative synthesis. According to Mulrow ( 1994 ), systematic reviews are particularly useful in identifying and evaluating a large volume of evidence published over a long period of time and have been frequently applied in recent state-of-the-art literature reviews (e.g. Li et al. 2020 ; Mochkabadi and Volkmann 2020 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ). The systematic literature review conducted in this paper employs a rather broad empirical definition of entrepreneurship which covers both the entrepreneur, who creates or discovers new businesses (Kirzner 1973 ; Schumpeter 1942 ) and the entrepreneurial firm itself. Entrepreneurship is understood here as new business activity, which includes entrepreneurs in the process of new firm creation as well as recently founded firms. Furthermore, although not necessarily associated with the formation of new firms, self-employed individuals and owner-managers are defined here as entrepreneurs as well. This general definition is consistent with the majority of empirical studies (e.g. Bosma et al. 2011 ; Fritsch and Schindele 2011 ; Mueller et al. 2008 ). The review process comprises three major steps, namely (1) data collection, (2) the selection of relevant studies and (3) data synthesis.
2.1 Data collection
As a first step, to reduce bias and maintain objectivity in all stages of the review, a review panel was set up. The panel consists of the author, a professor and two doctoral students knowledgeable in this field of research. In order to obtain the most relevant terms for the systematic search, the suggestions of Tranfield et al. ( 2003 ) were followed and a number of scoping studies based on combinations of keywords related to the topic were performed. The insights from this initial search phase were used to further develop relevant search terms resulting in the Boolean search string presented in the online appendix. The number of selected search terms was intentionally rather broad to avoid overlooking potentially valuable studies. It included the most common terms and measures of entrepreneurship and of economic, social and environmental welfare. This search string was subsequently used to scan titles, abstracts, and enclosed keywords of studies in the electronic databases EBSCO Business Source Complete, ProQuest ABI/INFORM Global and Web of Science. These databases were selected, because they allow the application of complex search strings and cover an extensive range of scientific journals from a variety of different disciplines. In order to provide a quality threshold, only peer-reviewed journal articles were scanned, since they are considered as validated knowledge (Podsakoff et al. 2005 ; Ordanini et al. 2008 ). Unpublished papers, books, book chapters, conference papers and dissertations were omitted in the initial search. Furthermore, the search was restricted to studies written in English. The main search was conducted in May 2019 and updated once in December 2019. It yielded, after the removal of duplicates, an initial data set of n = 7533 studies.
In addition to the main search, three more steps were conducted to create an exhaustive sample. First, five journals of particular relevance for the discussion were manually searched. Footnote 3 Second, meta-studies and literature reviews on related topics were screened for additional studies. Footnote 4 And finally, based on the guidelines of Wohlin ( 2014 ), an iterative back- and forward snowballing approach was conducted. The whole process of data collection and selection and its results are summarized in Fig. 1 .
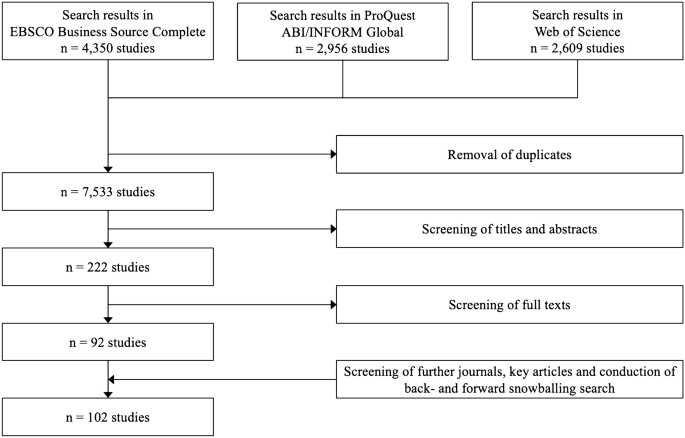
Systematic process of data collection and selection
2.2 Data selection and quality assessment
The studies collected during the main search were carefully reviewed to determine whether they were suitable for the objective of this paper. Titles, abstracts and, in doubtful cases, whole studies were checked against the following set of selection criteria.
Studies must analyse the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship by applying at least one economic, social or environmental welfare measure on an aggregated regional, national or global level.
Studies must employ definitions of entrepreneurship as discussed in the introduction of Sect. 2 . Studies that solely analysed the impact of small firms, intrapreneurship, corporate-entrepreneurship, institutional entrepreneurship, or entrepreneurial capital were excluded.
Studies must apply adequate quantitative methods to measure the impact of entrepreneurship. Studies that only discuss this matter theoretically, that follow a qualitative approach or that do not go beyond simple correlation techniques were excluded.
Studies must analyse spatial units, as they seem to be considerably better suited to analysing the impact of entrepreneurship (Fritsch 2013 ). Studies that are based on the analysis of industry units were excluded.
Studies must analyse long-term panel data or data on an adequately aggregated level to account for demographic, political and economic events. Studies that analysed single spatial units over a short period of time were excluded.
Due to the broadness of the search string, the main search yielded many studies which solely dealt with the microeconomic performance of new firms or which analyse how the local level of development determines the number of new firms. Studies which were not related to the research questions or did not meet all five selection criteria, were manually removed. This process of selection in the main search led to a total of n = 92 studies. The three additional search steps increased this number by n = 10, resulting in a final data set of n = 102 studies, including two high-quality book chapters which present empirical results of particular relevance to the paper’s objective (namely Stam et al. 2011 ; Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). When comparing the sample size with that of related literature reviews, it appears to be appropriate. Hence, even if the selected sample is not exhaustive, it is very likely to be representative of the relevant literature.
2.3 Data analysis
Given that research in this area employs a variety of measures of entrepreneurship and of economic welfare and is methodologically diverse, it was unfeasible to perform a meta-analysis. Instead, an integrative and evidence-driven narrative synthesis based on the guidelines established by Popay et al. ( 2006 ) was chosen to aggregate, combine and summarise the diverse set of studies. Narrative synthesis is considered particularly useful when, as in this case, research area is characterised by heterogeneous methods, samples, theories, etc. (Fayolle and Wright 2014 ).
Once the final set of studies had been identified, the characteristics and study findings were extracted by carefully reading the methods and results sections. To reduce research bias, a review-specific data-extraction form was employed. The extraction-form is based on the suggestions of Tranfield et al. ( 2003 ) and Higgins and Green ( 2008 ) and contains general information, details about the analysed samples, the applied measures of entrepreneurship and economic welfare, the applied econometric techniques as well as short summaries of the relevant findings and the identified microeconomic impact factors.
3 Results of the literature review
The main results of the literature review regarding the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and the determinants of this impact are presented in Table 5 (see online appendix). The large number of gathered studies on impact of entrepreneurship (n = 102) as well as on its determinants (n = 51) attest to the fact that this field of research has already been studied in great detail. Most of the identified studies were published in high-quality management, economics, social science and environmental science journals. Table 1 illustrates that the main part of the cross-disciplinary scientific discussion, however, took place in the Journals Small Business Economics (24%) and Regional Studies (7%). The number of empirical studies published per year has increased over the last decade, indicating the topicality of the research field and the need for an updated review of the new knowledge.
Figure 2 summarizes the statistics of the large amount of data gathered in Table 5 (see appendix) and illustrates the complexity of the research field. The left-hand-side lists the measures of entrepreneurship used in the analysed studies and shows how often they were applied. The most frequently applied measure of entrepreneurship is new firm formations either (a) per work force (labour market approach), (b) per number of existing firms (ecological approach) or (c) per capita. Another frequently applied measure of entrepreneurship is total early-stage entrepreneurial activity (TEA) based on data from the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (Reynolds et al. 2003 ) or its subgroups: necessity-driven entrepreneurial activity (NEA), opportunity-driven entrepreneurial activity (OEA), innovative entrepreneurial activity (IEA) and high-growth expectation entrepreneurial activity (HEA). Other authors estimated regional entrepreneurship using self-employment or business ownership rates. The Kauffman Foundation Index for entrepreneurial activity is used less frequently, as it is a specific measure of entrepreneurship for US regions.
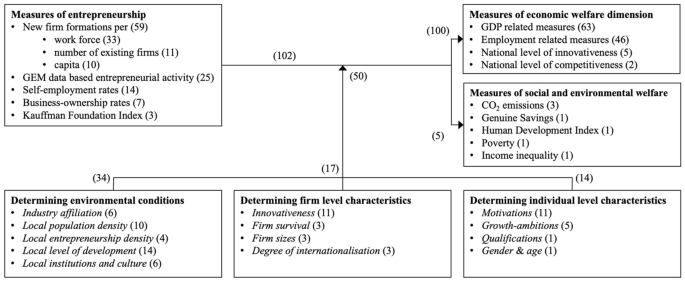
Overview of applied measures of entrepreneurship and welfare, and analysed determinants. Note : the numbers in brackets represent the numbers of associated empirical studies
Regarding the right-hand-side of Fig. 2 , it is noticeable that the majority of authors analysed the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare, primarily on GDP, growth and employment-related measures. Far fewer studies analysed the impact on the economic measures of national competitiveness or innovativeness, e.g. the number of patent applications. In contrast to the clear research focus on economic welfare, only five studies were found which analysed the impact of entrepreneurship on environmental or social welfare. Although many common measures of social and environmental welfare (e.g. crime rates or ecological footprint) were explicitly included in the search string (see online Appendix), no studies could be found that analyse the impact of entrepreneurship on them.
Independent of the measures of entrepreneurship and welfare used, the reviewed studies test their relationship by applying a very heterogenous set of methods. With the availability of more and more cross-sectional data covering longer and high-frequency time-series, authors started to apply new econometric approaches such as pooled and panel data regressions, fixed effect models, and subsequently, dynamic panel data models. Most authors based their analyses on rather straightforward regression techniques.
Sections 3.1 and 3.2 discuss empirical knowledge relating to the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare as well as on social and environmental welfare. Section 3.3 deals with the empirical evidence on the factors which determine this impact of entrepreneurship (see the lower part of Fig. 2 ).
3.1 Impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare
The analysed literature predominantly confirms the results of previous literature reviews and gives empirical evidence that new firm formations have a generally positive effect on regional development and economic performance. The relationship holds for all tested measures of entrepreneurship and is robust across a broad range of spatial and cultural contexts.
The impact does, however, differ over time. Fritsch and Mueller ( 2004 ) studied the time-lag structure of the impact of entrepreneurship by applying an Almon lag model of different polynomial orders in their study of 326 West German regions. Their results revealed that the impact of entrepreneurship follows a typical time-sequence: an S- or wave-shaped pattern which can be structured into three phases. Phase I is defined by a positive immediate increase of employment (direct effects of new capacities). After approximately 1 year, in phase II, this positive short-term impact becomes smaller, insignificant or even negative (displacement effects and market selection). Around year five, this medium-term impact becomes positive again and reaches a peak in year eight (supply-side and spill-over effects). This positive long-term effect of entrepreneurship on employment, which defines phase III, diminishes after a period of 10 years.
Table 2 presents the findings of all reviewed studies which analysed the impact of new firm formations on employment and GDP in one, two or all three phases. It shows that the findings regarding the impact of entrepreneurship on employment are largely consistent with the wave-pattern theory. The existence of the wave-pattern could be confirmed on different regional levels for Great Britain (Mueller et al. 2008 ), for the United States (Acs and Mueller 2008 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ), for Portugal (Baptista et al. 2008 ; Baptista and Preto 2010 , 2011 ), for West Germany (Fritsch and Mueller 2008 ; Fritsch and Noseleit 2013a ), for the Netherlands (van Stel and Suddle 2008 ; Koster 2011 ; Delfmann and Koster 2016 ), for Sweden (Andersson and Noseleit 2011 ), for China (Rho and Gao 2012 ) for Canada (Matejovsky et al. 2014 ) as well as in several cross-country studies on OECD countries (Audretsch et al. 2015 ; Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Koellinger and Thurik 2012 ; Thurik et al. 2008 ). Furthermore, the reviewed studies reveal that this relationship not only holds for new firm formations as a measure of entrepreneurship but also for self-employment (e.g. Matejovsky et al. 2014 ; Rho and Gao 2012 ; Thurik et al. 2008 ) and business ownership (e.g. Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ; Koellinger and Thurik 2012 ). The latter two measures of entrepreneurship, however, seem to have a less pronounced impact (Acs and Armington 2004 ; Rho and Gao 2012 ; Dvouletý 2017 ). Empirical evidence suggests a similar wave-pattern for the impact of entrepreneurship on GDP. Studies on GDP analysing all three phases confirm the positive short- and long-term peaks. However, in contrast to the results on employment, they find the medium-term impact to be less pronounced and positive (Audretsch et al. 2015 ; Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Koellinger and Thurik 2012 ; Matejovsky et al. 2014 ). The few empirical results displayed in Table 2 , which contradict the wave-pattern theory (e.g. findings of a negative short-term impact of entrepreneurship on GDP), can largely be explained by certain determining factors such as a differing impact in developing countries (see Sect. 3.3.4 ) or of necessity-driven entrepreneurship (see Sect. 3.3.9 ).
The results for other measures of economic welfare are scarce and contradictory. Ferreira et al. ( 2017 ) analysed the short-term impact of entrepreneurship on different measures of competitiveness and found that TEA and IEA positively related to competitiveness. However, they found no significant relationship between OEA and competitiveness. On the contrary, a study by Mrozewski and Kratzer ( 2017 ) found a positive relationship between OEA and competitiveness, but not between TEA and competitiveness.
The empirical results regarding the impact of entrepreneurship on innovativeness are also inconclusive. Acs and Varga ( 2005 ) and Draghici and Albulescu ( 2014 ) found that OEA has a positive impact on patent applications and innovation indices, but that TEA and NEA do not have any significant impact on them. Anokhin and Wincent ( 2012 ) found a positive impact of TEA on innovativeness but a more recent study from Albulescu and Draghici ( 2016 ) found that neither TEA nor OEA have a significant relationship to innovativeness. Similarly, Cumming et al. ( 2014 ) found new firm formations based on the labour market approach have a positive short-term impact on patent applications, but new firm formations based on the ecological approach and business ownership rates do not.
3.2 The impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare
Contrary to the well-researched impact of entrepreneurship on employment and GDP, little is known about the impact on social and environmental welfare. Three independent studies recently found empirical evidence that entrepreneurship positively affects measures of social welfare. Rupasingha and Goetz ( 2013 ) found that in the short-term self-employment reduces poverty in rural and urban U.S. counties, Atems and Shand ( 2018 ) found that in the medium-term self-employment decreases income inequality in U.S. states and, finally, Dhahri and Omri ( 2018 ) found new firm formations to increase the national modified Human Development Index (MHDI) in developing countries.
The empirical research on the impact of new firm formations on environmental welfare, however, illustrates that entrepreneurship may also come with major drawbacks. Omri ( 2017 ) as well as Dhahri and Omri ( 2018 ) and Ben Youssef et al. ( 2018 ) found that new firms significantly increase the amount of national CO 2 -emissions. According to Ben Youssef et al. ( 2018 ), this unfortunate impact on CO 2 -emissions is in fact so great that, despite the positive impact on GDP, new firms decrease Genuine Savings (also known as adjusted net saving) in African countries. They also found that the impact is more pronounced for informal new firm formations. This finding matches the results of Omri ( 2017 ), who detected the impact on CO 2 -emissions to be lower in developed countries which generally have lower rates of informal entrepreneurship (Williams and Lansky 2013 ). Furthermore, Omri ( 2017 ) discovered that the relationship between new firm formations and CO 2 -emissions is not linear but can be described as exhibiting an inverted U-shape. Thus, at an already high level of entrepreneurship, new firm formations may result in a decrease in CO 2 -emissions.
3.3 Determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship
So far, the empirical results suggest, in many cases, a clear causal macroeconomic impact of new firm formations on economic measures of welfare. However, this topic is reasonably complex, and the complexity increases further when determining factors of this impact are considered. The lower part of Fig. 2 presents an overview of the empirical knowledge on these determinants. A key finding of this review, namely that all of the found analyses of determinants focus exclusively on the economic effects of entrepreneurship, is, however, not illustrated in Fig. 2 . The review revealed that, although they are strongly interdependent, the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship can generally be categorized into external environmental conditions, firm level characteristics and individual characteristics of the entrepreneurs themselves. Figure 2 illustrates that most empirical research has been conducted on the determining environmental conditions and on the firm level characteristic innovativeness and on the individual level characteristic motivations . In fact, some of the determinants presented have already been thoroughly investigated in highly recommendable earlier literature reviews, namely: industry affiliation (Fritsch 2013 ), regional population - and entrepreneurship density (Fritsch 2013 ), institutions and culture (Bjørnskov and Foss 2016 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ), innovativeness (Block et al. 2017 ). The review for this paper confirms these findings and briefly summarizes the key learnings in the Sects. 3.3.1 to 3.3.3 and 3.3.5 . However, except for a recently emerged empirical research stream on innovativeness , no new insights could be gained on the already reviewed determinants. Therefore, the focus of this section is primarily on the empirical evidence which has not yet been systematically investigated.
3.3.1 Industry affiliation
Fritsch ( 1996 ) was one of the first to analyse how entrepreneurial impact differs between industries. He focused on the impact of new firm formations on employment in West Germany and found it to be significantly higher in the manufacturing sector than in the service sector. Several authors confirmed this finding for the Netherlands (van Stel and Suddle 2008 ), for West-Germany (Fritsch and Mueller 2004 ) and for Sweden (Andersson and Noseleit 2011 ). Other studies, however, found the impact of new firms on economic welfare measures to be higher in the service sector (Bosma et al. 2011 ; Koster and van Stel 2014 ). Fritsch ( 2013 ) reasoned that these contradicting results may be due to considerable differences between the industries in different regions or countries and thus an analysis at the industry level might be not appropriate at all. For more information on the industrial perspective of the entrepreneurial impact on the economy, Fritsch ( 2013 ) provides a comprehensive overview including policy implications and avenues for further research.
3.3.2 Regional population- and entrepreneurship density
In a second wave of literature, researchers analysed how the impact of entrepreneurship differs between regions. They found clear evidence that the magnitude of the entrepreneurial impact is positively related to the population density (Baptista and Preto 2011 ; Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ; Fritsch and Schroeter 2011 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ; Lee 2017 ; Li et al. 2011 ; van Stel and Suddle 2008 ). In urban regions and agglomerations, new firms have a more pronounced and more positive impact on employment (Baptista and Preto 2011 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ; van Stel and Suddle 2008 ) and GDP (Audretsch et al. 2015 ; Belitski and Desai 2016 ) throughout all three previously described phases (see Sect. 3.1 ). On the contrary, in rural and less agglomerated regions, the entrepreneurial impact is weak and often negative (Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ).
While the economic relevance of new firm formations seems to increase with the population density, empirical evidence suggests that this is not the case for the relation between firm formations and regional entrepreneurship density. On the contrary, several authors found that the economic effect of another new firm becomes lower the more entrepreneurs are already on the market and even zero for regions with high entrepreneurship rates close to equilibrium rate (e.g. Carree et al. 2002 , 2007 ; Mueller et al. 2008 ). These empirical insights identify entrepreneurship as a regional phenomenon and illustrate that macroeconomic effects of new firms are shaped by local conditions. An in-depth discussion of regional differences in the macroeconomic impact of new firms can be found in the monograph by Fritsch ( 2013 ).
3.3.3 Institutions and culture
To shed light on the complex interactions between institutions, entrepreneurship and economic growth, Urbano et al. ( 2019a ) and Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ) recently conducted thorough literature reviews. The empirical evidence identified in the present paper (Aparicio et al. 2016 ; Audretsch and Keilbach 2004a , b , c ; Bjørnskov and Foss 2016 ) is in line with the findings of these two reviews which suggest that institutions affect the economy indirectly through endogenous factors like entrepreneurship. This holds true for formal institutions like (academic) support systems for new firms, procedures and costs to create a business, property rights or political structures as well as for informal institutions like social norms, cultures or belief systems (Urbano et al. 2019a ). However, in contrast to Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ), Urbano et al. ( 2019a ) suggest that formal and informal institutions are not of equal importance, but that social norms and cultures have higher and more positive effects on the relation between entrepreneurship and economic growth.
3.3.4 Local level of development
While Sect. 3.1 illustrates that the impact of entrepreneurship in developed countries follows a typical wave-pattern, until now, no studies have analysed this time-pattern in developing countries. In general, the empirical evidence on the impact in developing countries is contradictory: some studies found a positive impact of entrepreneurship (Ben Youssef et al. 2018 ; Dhahri and Omri 2018 ; Feki and Mnif 2016 ; Stam et al. 2011 ), others found no or even a negative impact (Anokhin and Wincent, 2012 ; Ferreira et al. 2017 ; Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). However, studies which compared countries in different development stages found that the magnitude of the impact of entrepreneurship depends on the national welfare level and is generally higher in more developed countries (Anokhin and Wincent 2012 ; Carree et al. 2002 , 2007 ; Crnogaj et al. 2015 ; Hessels and van Stel 2011 ; Urbano and Aparicio 2016 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; van Stel et al. 2005 ; Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). Furthermore, little is known on the mechanisms behind the impact of entrepreneurship in developing countries. Most of the few studies which specifically deal with developing countries (n = 19) analysed the impact on a national level (n = 16) based on GEM data (n = 12), focused on the impact on GDP related measures (n = 17), or solely analysed the short- or medium-term impact (n = 16).
3.3.5 Innovativeness
According to the knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship, new knowledge results in business opportunities and entrepreneurs exploit these opportunities by turning the new knowledge into innovative products (Acs et al. 2009 , 2013 ; Audretsch and Keilbach 2005 ). Recent studies confirm this theory and provide empirical evidence that entrepreneurship moderates the transformation of new knowledge into innovations (Block et al. 2013 ) and that innovative regions with higher levels of entrepreneurship perform economically better (González-Pernía et al. 2012 ). Accordingly, it is reasonable to assume that particularly innovative new firms are more important to economic welfare than their non-innovative counterparts. These considerations coincide with those presented in the literature review on innovative entrepreneurship by Block et al. ( 2017 ). However, the present systematic literature review extends the review of Block et al. ( 2017 ) by including previously unconsidered as well as recently emerged empirical evidence on the macroeconomic impact of innovative entrepreneurship. The identified empirical studies do indeed confirm the presumed positive impact of innovativeness. Crnogaj et al. ( 2015 ) as well as Du and O’Connor ( 2017 ) and Szerb et al. ( 2018 ) used GEM data to compare the impact of founders who stated their products or services to be new or at least unfamiliar to their customers. All of the previously mentioned authors found that innovative founders have a higher impact on GDP, economic efficiency, gross value added (GVA) and employment than less innovative founders. Furthermore, earlier studies attest to new firms which are in innovative, knowledge- or technology-intensive industries a higher than average impact on both GDP (Audretsch and Keilbach 2004a , b , 2005 , Mueller 2007 ) and employment (Baptista and Preto 2010 , 2011 ).
3.3.6 Firm survival
Empirical evidence suggests that a particularly important determinant of the impact of entrepreneurship is whether new firms are able to survive the first years. Falck ( 2007 ) was the first to find empirical evidence of a positive relationship between new firms which survive for at least 5 years and efficiency of the industry in which they are in. On the contrary, he could not find any significant relationship to industry level efficiency growth for firms which did not survive the first 5 years. Brixy ( 2014 ), Fritsch and Noseleit ( 2013b ) and Fritsch and Schindele ( 2011 ) have confirmed that Falck’s ( 2007 ) findings not only hold for the relationship between entrepreneurship and GDP but also for the relationship between entrepreneurship and employment.
3.3.7 Firm size
Baptista and Preto ( 2010 ) found that new firms of a larger than average initial size have a strong impact on employment and that this impact follows a pronounced wave-shaped time-lag structure (see Sect. 3.1 ). New firm formations which are smaller than average, on the other hand, only have a small impact. Acs and Mueller ( 2008 ) confirmed this finding and show that small new firms have a positive but declining direct impact on employment. The impact of medium and large new firms, however, is much higher and increases till it peaks in year five. Very large new firms (> 499 employees), however, decrease employment in the short- and medium-term, probably due to restructuring processes of incumbents. This empirical evidence suggests that up to a threshold, large new firms have a larger impact on employment.
3.3.8 Degree of internationalization
A less studied but yet empirically significant determinant is a firm’s degree of internationalization. Baptista and Preto ( 2010 ) analyzed 30 Portuguese regions and found that new firms which were, at least, partially owned by foreign investors had a much higher and more pronounced medium- and long-term impact on employment. A second measure of the positive impact of internationally active new firms is the export-orientation of new firms. Hessels and van Stel ( 2011 ) compared the impact of total-entrepreneurial activity and export-driven entrepreneurial activity on GDP per capita in 34 developed and developing countries. They found evidence that new firms for which the share of customers living abroad is above 26% have a more positive impact on GDP—but only in developed countries. González-Pernía and Peña-Legazkue ( 2015 ) confirmed their finding on a regional level by comparing OEA and export-oriented OEA in 17 Spanish regions. Besides a generally higher impact of export-oriented new firms, González-Pernía and Peña-Legazkue ( 2015 ) found that the impact increases with higher shares of foreign customers up to a threshold level. An earlier study by Fryges and Wagner ( 2008 ), who found a positive relationship between firm-level productivity and export-sales ratio, supports the evidence for a more positive impact of internationally active new firms.
3.3.9 Motivation
The literature review conducted for this paper provided eleven studies which empirically tested the macroeconomic importance of the entrepreneur’s motivations. All of these studies applied GEM-based data and definitions for opportunity-driven entrepreneurial activity (OEA) and necessity-driven entrepreneurial activity (NEA). Although four of these studies could not find a significant economic impact of OEA or NEA (Albulescu and Draghici 2016 ; Ferreira et al. 2017 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; Wong et al. 2005 ), the other seven studies found evidence that OEA significantly increases national innovativeness (Acs and Varga 2005 ; Draghici and Albulescu 2014 ), competitiveness (Mrozewski and Kratzer 2017 ) and productivity (Du and O’Connor 2017 ; González-Pernía and Peña-Legazkue 2015 ; Ivanovic-Ðukic et al. 2018 ; Urbano and Aparicio 2016 ). Moreover, six of these seven studies confirmed that the impact of OEA is higher compared to NEA and TEA. Mrozewski and Kratzer ( 2017 ) even found NEA to decrease the national competitiveness.
3.3.10 Growth-ambitions
There are some entrepreneurs who not only seek to exploit a business-opportunity but also have high growth - ambitions for their new firms. All five empirical studies selected for this paper take GEM data on high-growth expectation entrepreneurship (HEA) as a measure of the entrepreneur’s growth - ambitions and found that it has a significantly positive impact on GDP-related measures of welfare. Furthermore, the impact of HEA seems to be more positive compared to TEA, to NEA and even to OEA (Ivanović-Đukić et al. 2018 ; Stam et al. 2011 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; Wong et al. 2005 ). Generally, this macroeconomic impact of HEA seems to increase with the level of growth-aspiration (van Oort and Bosma 2013 ). The positive impact of HEA on economic welfare could be confirmed on the regional- and national-level as well as for developed countries. For less-developed countries, however, the empirical evidence is contradicting. On the one hand, Valliere and Peterson ( 2009 ) only found a significant impact of HEA on GDP for 25 developed countries, but not for the 18 emerging countries. On the other hand, Stam et al. ( 2011 ) found the impact of HEA on GDP in eight analysed lower-income to upper-middle-income economies (World Bank 2002 classification) even higher compared to the impact in the 22 analysed high-income economies.
3.3.11 Qualification
While many microeconomic studies have highlighted that an entrepreneur’s qualifications in terms of education (e.g. Kangasharju and Pekkala 2002 ), skills and experience (e.g. Brüderl et al. 1992 ; Baum et al. 2001 ; Unger et al. 2011 ) play a significant part in the success of new firms, only one of the studies empirically investigated the macroeconomic impact of education. This is an analysis of 3702 German firms conducted by Engel and Metzger ( 2006 ). It suggests that new firms founded by people with an academic degree may have a more positive direct employment effect, than firms founded by people without an academic degree. This finding is, however, based on an old dataset (1990–1993) and a simple descriptive comparison and the authors did not apply control variables such as the regional density of more educated people.
3.3.12 Gender and age
Only one study could be found which empirically analysed the economic impact of the entrepreneur’s gender and age . This study was conducted by Verheul and van Stel ( 2010 ) and was based on a dataset of 36 developed and developing countries. Their results show that there is a positive relationship between young opportunity-driven entrepreneurs between the ages of 18 and 24 and national GDP growth in developed countries, while in developing countries there is only a significant positive relationship between entrepreneurs aged between 45 and 64 and GDP growth (Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). Contrary to the microeconomic literature (e.g. Cliff 1998 ; Kalleberg and Leicht 1991 ; Rosa et al. 1996 ), Verheul and van Stel ( 2010 ) could not find any significant gender differences on the macroscale.
4 Roadmap for further research
The major scientific value and contribution of this paper lies in the groundwork for future research. Despite the extant of the reviewed existing research, many questions still remain unanswered. The following two sections therefore highlight the shortcomings of current research and make suggestions on how to address them. Section 4.1 discusses how remaining gaps in empirical research into the impact of entrepreneurship can be addressed and Sect. 4.2 presents fruitful research avenues on the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship.
4.1 Implications for future research on the impact of entrepreneurship
4.1.1 more variety in the measures of entrepreneurship.
A high variety of measures of entrepreneurship is required to test the robustness of results but international comparative studies, in particular, are mainly based on just two entrepreneurship datasets: Comparative Entrepreneurship Data for International Analysis (COMPENDIA) based on OECD statistics and data from the GEM research project. The use of a high variety of entrepreneurship definitions and measures of entrepreneurship across studies makes it difficult to compare the results of these studies. While some studies simply estimate entrepreneurship based on self-employment rates or business-ownership rates, others measure entrepreneurship by counting new firm formations and firm exits or use holistic measures based on, e.g., Schumpeter’s understanding of entrepreneurship.
In order to test the robustness of the results and, at the same time, to allow for comparability between different studies, researchers should employ not one but multiple common measures of entrepreneurship in future studies. To make this possible, policy makers need to encourage the creation of internationally harmonized entrepreneurship databases. Furthermore, due to the limited availability of entrepreneurship data, only a few empirical studies have made a distinction between different types of entrepreneurship. That is why, as recommended by many researchers before (e.g. Baptista and Preto 2011 ; Fritsch and Schroeter 2011 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ), this study calls for more diversity in the application of measures of entrepreneurship.
4.1.2 Implementation of measures of social and environmental welfare
Section 3.1 revealed that 95.1% of the examined empirical studies only analysed the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare. Politicians who have no information on the impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare and thus solely rely on this economic information, however, may implement unsustainable development strategies (Tietenberg and Lewis 2012 ). Indeed, the few empirical studies (n = 5) which go beyond a traditional economic analysis indicate that entrepreneurship also has a significant contribution to measures of social and environmental welfare such as HDI, CO 2 emissions or poverty, which must not be neglected by politicians and researchers alike. To fill the immense gap in research on the impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare, two simultaneous approaches are proposed. First, as mentioned before, future research should generally include a variety of dependent welfare variables—social and environmental as well as economic ones. Second, future research should adopt research designs that have already proved effective in the macroeconomic impact analysis to answer novel research questions that address the impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare. The required methods for such analyses have been tested many times and, at least at national level, data availability poses no problem. Most countries have not only been collecting specific social and environmental welfare data for many years, but also established more holistic measures of welfare such as the Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare. Accordingly, it is up to the research community to break with traditions and expand the field of research by analysing social and environmental welfare rather than just economic welfare.
4.1.3 More research on developing countries
Section 3.3.4 illustrated that the local level of development is a relevant determinant of the impact of entrepreneurship. Nevertheless, most of the research reviewed for this paper focused solely on developed countries. This can partly be explained by the fact that most of the authors of these studies are based in Europe and the US, as well as by the lack of adequate long-term data for developing countries. However, this has begun to change. In the past 5 years, the number of empirical studies on developing countries has more than doubled to n = 30. Nevertheless, regional-level studies as well as long-term studies for developing countries remain scarce. Because of the growing importance of developing and particularly BRICS countries, it is important to increase the knowledge on how the impact of entrepreneurship manifests in these countries.
4.1.4 More studies on the lag-structure of the impact of entrepreneurship
Section 3.1 illustrates that although the important indirect impact of entrepreneurship requires 5 or more years to unfold, most empirical research focuses on the direct short-term impact. Neglecting the long-term effects of entrepreneurship therefore results in an incomplete picture. Furthermore, the analysis of longitudinal data is required to conduct relevant causality tests. So far, the bottleneck for national-level long-term studies has been the lack of longitudinal data. But, due to more than 20 years of worldwide data collection for the GEM, there is now at least one sufficiently large entrepreneurship database. In line with other authors who have recognised this issue (e.g. Baptista et al. 2008 ; Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Fritsch 2013 ), this paper recommends that all future research should analyse not only the short-term but also the medium- and long-term impact of entrepreneurship.
4.2 Implications for future research on determinants
Table 3 summarizes key statistics for the determinants in the research reviewed for this paper. Comparing the last two rows, it seems that the studies analysing the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship are a representative share of all reviewed studies. For this reason, the previously presented suggestions for future research also apply to literature on the determinants. On closer examination, however, Table 3 reveals further and more precise research gaps. These include, inter alia, the need to study particularly the environmental and firm level determinants in developing countries, and the analysis of individual level determinants in combination with the lag-structure of the impact of entrepreneurship. The requirement for more long-term studies is further highlighted here. This finding further specifies the previous call for more long-term studies. The following subsections present further research and research implications.
4.2.1 More variety in measures of entrepreneurship
Table 3 shows that research on environmental and firm level determinants are mainly based on new firm formations as a measure of entrepreneurship, and research on individual level determinants almost solely measures entrepreneurship using GEM data.
The only exceptions are studies on the determinants local level of development —which are comparing the entrepreneurial impact across countries and thus are also mostly based on GEM data—and on innovativeness . None of the studies on the determinants apply self-employment (for the sake of clarity not presented in Table 3 ) to estimate entrepreneurship. This illustrates that the research on all individual determinants, except for innovativeness , considerably lacks variety when it comes to the applied measures of entrepreneurship.
4.2.2 More variety in measures of welfare
In addition to the fact that there are no studies examining the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship on social or environmental welfare, there is also a lack of variety in the studies of measures of economic welfare. Studies on all individual level determinants and particularly on the determinant local level of development almost exclusively analyse the impact of entrepreneurship on GDP-related measures of welfare. Studies on the determinants industry affiliation , population density , firm survival and firm size mainly analyse employment effects of entrepreneurship. Other common measures of economic welfare, such as innovativeness or competitiveness, are rarely studied and need further investigation.
4.2.3 Further research on determinants
Table 3 illustrates that the existing research is imbalanced and that it pays varying degrees of attention to individual determinants. Determinants such as innovativeness , motivations and most environmental level determinants have so far received a great deal of attention, while others have only been analysed in very few studies. However, some of these poorly researched factors promise to be relevant determinants. More specific, the few existing empirical results analysing firm survival , degree of internationalisation and growth - ambitions suggest that these determinants have a comparatively high effect on the relationship between entrepreneurship and economic welfare. Furthermore, these determinants as well as the largely unexplored determinant qualifications are of considerable practical and political relevance. More empirical research on these determinants and their moderating role is required to improve incentives and support programs for entrepreneurs.
4.2.4 New research focus on determinants not yet empirically investigated
Table 4 provides a short overview of determinants which are likely to shape the entrepreneurial macroeconomic impact, but which have not yet been empirically investigated. They are a selection of indicators which are believed to determine the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare or which are empirically related to the success and survival of new firms and thus are also likely to be of macroeconomic importance. The overview is based on a non-systematic scan of the microeconomic literature and makes no claim to completeness. Due to their particularly high microeconomic relevance highlighted by the authors listed in Table 4 , this paper specifically proposes additional research on how firm performance, organisational structure and strategies, networking activities and motivations (beyond necessity and opportunity entrepreneurship) determine the impact of entrepreneurship.
4.2.5 Methodological recommendations
Many of the determinants discussed here are highly interdependent, which makes it very difficult to extract and examine their separate effects. Individual level characteristics and environmental conditions are especially likely to affect the impact of entrepreneurship mainly indirectly through firm performance. The complexity is increased further as determinants may be indicators for other macroeconomically relevant effects. For instance, the numbers of highly innovative new firms and of highly qualified entrepreneurs may be positively correlated with the excellence of the regional educational infrastructure. This in turn could mean that the excellence of educational infrastructure is the true reason for economic growth and innovative new firms and highly qualified entrepreneurs have little or no economic impact but are merely indicators for the educational infrastructure. However, little is currently known about such interdependencies and research is required which particularly studies the path dependencies behind the impact of entrepreneurship. This is why future empirical research should examine determinants which are supposed to be interdependent as well as external effects which may be related to the determinants of interest.
5 Limitations and conclusion
This paper has shed light on the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare and the determinants of this impact, but it is not without limitations. First, this paper seeks to give a comprehensive overview of the empirical research, but the search was limited by a variety of in- and exclusion criteria as well as by the terms used in the search string. Although the exclusive focus on peer-reviewed articles is common practice in systematic literature reviews, this may have led to the systematic exclusion of potentially relevant research outcomes, e.g. from dissertation, book chapters, conference contributions or working papers. Furthermore, it is possible that individual studies were not identified by the automated search for the search string in keywords, titles and abstracts. These limitations were necessary to reduce the search results to a manageable level and to ensure a certain quality of the results. The additional screening of key journals, meta-studies and reviews as well as the applied back- and forward snowballing approach, however, weaken the effects of these limitations. Second, this paper only deals with empirical studies. The inclusion of qualitative studies might have revealed further studies dealing with the impact of entrepreneurship on environmental and social welfare. Additionally, the exclusion of qualitative studies limits the analytical depth within the discussion of the determinants. Third, the paper focused on research on a few selected measures of entrepreneurship. In doing so, intrapreneurship, entrepreneurship culture or diverse composed entrepreneurial activity measures of entrepreneurship were excluded. Fourth, it needs to be stated that large parts of the data selection and synthesis were only conducted by the author. Although the chosen procedure and the frequent consultation with the research panel reduced the likelihood of biases, the chance remains that the review is burdened with subjectivity and selection biases. Finally, the scope of this paper was to provide a first descriptive summary of the determinants analysed in the empirical literature and to derive research recommendation. Due to this clear focus this paper does not comprise extensive bibliometric- or meta-analyses that describe in detail the general literature on the impact of entrepreneurship.
The systematic review presented in this paper was conducted for three main reasons. First, to summarize the current state of empirical research on the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare. Second, to identify the determinants of this impact and third, to develop a roadmap for future research. Due to the application of a broad entrepreneurship definition and due to the incorporation of economic, social and environmental welfare, this paper presents the most comprehensive overview, summary and synthesis of empirical research on this topic to date. The results confirm the findings and theories of previous literature reviews on the impact of entrepreneurship, provide an update and extension to the current knowledge and finally, represent a first attempt to structure the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship. The new determinants-driven perspective on the research field reveals several shortcomings that would otherwise have gone unnoticed. The developed roadmap for future research—combined with a higher variety of applied measures of entrepreneurship and with an increased awareness of causality and interdependency issues—will allow future researchers to unravel the complex relationship between entrepreneurship and welfare and therewith to provide politicians the comprehensive information they need to promote the right types of entrepreneurship in the right situations.
For purposes of this study, the three welfare dimensions refer to the widely used definition of the three pillars of sustainable development (economic growth, social equality protection, environmental protection) of the Brundtland Report (World Development Commission on Environment and Development 1987 ). However, the reader should note that later sustainability models like the ‘prism model’ or the ‘concentric circles model’ illustrate that the three pillars of sustainable development (resp. the three welfare dimensions) are interlinked and not always clearly separable from one another.
Although the author is fully aware of their different meanings, for simplicity, the more general term ‘economic welfare’ is used throughout this paper as synonymous with the terms ‘economic growth’ and ‘economic development’.
Namely: Regional Studies , Entrepreneurship & Regional Development , The Annals of Regional Science , Economic Development Quarterly , Technological Forecasting and Social Change .
Namely: Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ), Block et al. ( 2017 ), Fritsch ( 2013 ), Sutter et al. (2018), Urbano et al. ( 2019a ), van Praag and Versloot ( 2007 ), Wennekers and Thurik ( 1999 ).
Abdesselam R, Bonnet J, Renou-Maissant P (2014) Typology of the French regional development: revealing the refugee versus Schumpeter effects in new-firm start-ups. Appl Econ 46:3437–3451. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2014.931920
Article Google Scholar
Acs ZJ, Armington C (2004) Employment growth and entrepreneurial activity in cities. Reg Stud 38:911–927. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280938
Acs ZJ, Mueller P (2008) Employment effects of business dynamics: mice, gazelles and elephants. Small Bus Econ 30:85–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9052-3
Acs ZJ, Varga A (2005) Entrepreneurship, agglomeration and technological change. Small Bus Econ 24:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-1998-4
Acs ZJ, Braunerhjelm P, Audretsch DB, Carlsson B (2009) The knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship. Small Bus Econ 32:15–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-008-9157-3
Acs ZJ, Audretsch DB, Braunerhjelm P, Carlsson B (2012) Growth and entrepreneurship. Small Bus Econ 39:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-010-9307-2
Acs ZJ, Audretsch DB, Lehmann EE (2013) The knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship. Small Bus Econ 41:757–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-013-9505-9
Adusei M (2016) Does entrepreneurship promote economic growth in Africa? Afr Dev Rev 28:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8268.12190
Albulescu CT, Draghici A (2016) Entrepreneurial activity and national innovative capacity in selected European countries. Int J Entrep Innov 17:155–172. https://doi.org/10.1177/1465750316655902
Alvarez SA, Barney JB (2014) Entrepreneurial opportunities and poverty alleviation. Entrep Theory Pract 38:159–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12078
Andersson M, Noseleit F (2011) Start-ups and employment dynamics within and across sectors. Small Bus Econ 36:461–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9252-0
Andersson M, Braunerhjelm P, Thulin P (2012) Creative destruction and productivity: entrepreneurship by type, sector and sequence. J Entrep Public Policy 1:125–146. https://doi.org/10.1108/20452101211261417
Anokhin S, Wincent J (2012) Start-up rates and innovation: a cross-country examination. J Int Bus Stud 43:41–60. https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2011.47
Aparicio S, Urbano D, Audretsch D (2016) Institutional factors, opportunity entrepreneurship and economic growth: panel data evidence. Technol Forecast Soc Change 102:45–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.04.006
Apergis N, Payne JE (2016) An empirical note on entrepreneurship and unemployment: further evidence from U.S. states. J Entrep Public Policy 5:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEPP-10-2015-0029
Arribas I, Vila JE (2007) Human capital determinants of the survival of entrepreneurial service firms in Spain. Int Entrep Manag J 3:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-007-0038-z
Ashcroft B, Love JH (1996) Firm births and employment change in the British counties: 1981–89. Pap Reg Sci 75:483–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1435-5597.1996.tb00675.x
Atems B, Shand G (2018) An empirical analysis of the relationship between entrepreneurship and income inequality. Small Bus Econ 51:905–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-017-9984-1
Audretsch DB, Fritsch M (2003) Linking entrepreneurship to growth: the case of West Germany. Ind Innov 10:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/1366271032000068104
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2004a) Entrepreneurship capital and economic performance. Reg Stud 38:949–959. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280956
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2004b) Entrepreneurship and regional growth: an evolutionary interpretation. J Evol Econ 14:605–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-004-0228-6
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2004c) Does entrepreneurship capital matter? Entrep Theory Pract 28:419–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6520.2004.00055.x
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2005) Entrepreneurship capital and regional growth. Ann Reg Sci 39:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-005-0246-9
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2008) Resolving the knowledge paradox: knowledge-spillover entrepreneurship and economic growth. Res Policy 37:1697–1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2008.08.008
Audretsch DB, Boente W, Keilbach M (2008) Entrepreneurship capital and its impact on knowledge diffusion and economic performance. J Bus Ventur 23:687–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2008.01.006
Audretsch DB, Belitski M, Desai S (2015) Entrepreneurship and economic development in cities. Ann Reg Sci 55:33–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-015-0685-x
Banerji D, Reimer T (2019) Startup founders and their LinkedIn connections: are well-connected entrepreneurs more successful? Comput Hum Behav 90:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.08.033
Baptista R, Preto MT (2010) Long-term effects of new firm formation by type of start-up. Int J Entrep Small Bus 11:382–402. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJESB.2010.036293
Baptista R, Preto MT (2011) New firm formation and employment growth: regional and business dynamics. Small Bus Econ 36:419–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9254-y
Baptista R, Escária V, Madruga P (2008) Entrepreneurship, regional development and job creation: the case of Portugal. Small Bus Econ 30:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9055-0
Bashir S, Gebremedhin T (2011) An analysis of the relationship between new firm formation and economic development in the northeast region of the United States. J Dev Entrep 16:289–306. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1084946711001859
Baum JR, Smith KG, Locke EA (2001) A multidimensional model of venture growth. Acad Manag J 44:292–303. https://doi.org/10.2307/3069456
Belitski M, Desai S (2016) Creativity, entrepreneurship and economic development: city-level evidence on creativity spillover of entrepreneurship. J Technol Transf 41:1354–1376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-015-9446-3
Ben Youssef A, Boubaker S, Omri A (2018) Entrepreneurship and sustainability: the need for innovative and institutional solutions. Technol Forecast Soc Change 129:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.11.003
Bjørnskov C, Foss N (2013) How strategic entrepreneurship and the institutional context drive economic growth. Strateg Entrep J 7:50–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/sej.1148
Bjørnskov C, Foss NJ (2016) Institutions, entrepreneurship, and economic growth: what do we know and what do we still need to know? Acad Manag Perspect 30:292–315
Block J, Thurik R, Zhou H (2013) What turns knowledge into innovative products? The role of entrepreneurship and knowledge spillovers. J Evol Econ 23:693–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-012-0265-5
Block JH, Fisch CO, van Praag M (2017) The Schumpeterian entrepreneur: a review of the empirical evidence on the antecedents, behaviour and consequences of innovative entrepreneurship. Ind Innov 24:61–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/13662716.2016.1216397
Bosma N, Stam E, Schutjens V (2011) Creative destruction and regional productivity growth: evidence from the Dutch manufacturing and services industries. Small Bus Econ 36:401–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9257-8
Braunerhjelm P, Borgman B (2004) Geographical concentration, entrepreneurship and regional growth: evidence from regional data in Sweden, 1975–99. Reg Stud 38:929–947. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280947
Braunerhjelm P, Acs ZJ, Audretsch DB, Carlsson B (2010) The missing link: knowledge diffusion and entrepreneurship in endogenous growth. Small Bus Econ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9235-1
Brixy U (2014) The significance of entry and exit for regional productivity growth. Reg Stud 48:1051–1070. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2014.895804
Brüderl J, Preisendörfer P, Ziegler R (1992) Survival chances of newly founded business organizations. Am Sociological Rev 57:227. https://doi.org/10.2307/2096207
Carree MA, Thurik RA (2008) The lag structure of the impact of business ownership on economic performance in OECD countries. Small Bus Econ 30:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-006-9007-0
Carree M, van Stel A, Thurik R, Wennekers S (2002) Economic development and business ownership: an analysis using data of 23 OECD countries in the period 1976–1996. Small Bus Econ 19:271–290. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019604426387
Carree M, van Stel A, Thurik R, Wennekers S (2007) The relationship between economic development and business ownership revisited. Entrep Reg Dev 19:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985620701296318
Carree M, Congregado E, Golpe A, van Stel A (2015) Self-employment and job generation in metropolitan areas, 1969–2009. Entrep Reg Dev 27:181–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985626.2015.1025860
Chen CC (2014) Entrepreneurship economic growth and employment: a case study of Taiwan. Hitotsubashi J Econ 55:71–88. https://doi.org/10.15057/26817
Chrisman JJ, Bauerschmidt A, Hofer CW (1998) The determinants of new venture performance: an extended model. Entrep Theory Pract 23:5–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/104225879802300101
Cliff JE (1998) Does one size fit all? Exploring the relationship between attitudes towards growth, gender, and business size. J Bus Ventur 13:523–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-9026(97)00071-2
Cole IM (2018) Unemployment and entrepreneurship in the Mid-Atlantic Region of the United States: a spatial panel data analysis. Rev Reg Stud 48:347–375
Google Scholar
Criscuolo C, Gal PN, Menon C (2017) Do micro start-ups fuel job creation? Cross-country evidence from the DynEmp Express database. Small Bus Econ 48:393–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-016-9778-x
Crnogaj K, Rebernik M, Hojnik BB (2015) Supporting economic growth with innovation-oriented entrepreneurship. Ekonomický časopis 63:395–409
Cumming D, Johan S, Zhang M (2014) The economic impact of entrepreneurship: comparing international datasets. Corp Gov Int Rev 22:162–178. https://doi.org/10.1111/corg.12058
Daly HE, Cobb JB, Cobb CW (1994) For the common good: redirecting the economy toward community, the environment, and a sustainable future/Herman E. Daly and John B. Cobb, Jr.; with contributions by Clifford W. Cobb, 2nd ed., updated and expanded. Beacon Press, Boston
Delfmann H, Koster S (2016) The effect of new business creation on employment growth in regions facing population decline. Ann Reg Sci 56:33–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-015-0738-1
Dhahri S, Omri A (2018) Entrepreneurship contribution to the three pillars of sustainable development: what does the evidence really say? World Dev 106:64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.01.008
Dixon-Woods M, Agarwal S, Jones D, Young B, Sutton A (2005) Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. J Health Serv Res Policy 10:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1258/1355819052801804
Doran J, McCarthy N, O’Connor M (2016) Entrepreneurship and employment growth across European regions. Reg Stud Reg Sci 3:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681376.2015.1135406
Draghici A, Albulescu CT (2014) Does the entrepreneurial activity enhance the national innovative capacity? Procedia Soc Behav Sci 124:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.02.500
Du K, O’Connor A (2017) Entrepreneurship and advancing national level economic efficiency. Small Bus Econ 50:91–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-017-9904-4
Dvouletý O (2017) Can policy makers count with positive impact of entrepreneurship on economic development of the Czech regions? J Entrep Emerg Econ 9:286. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEEE-11-2016-0052
Engel D, Metzger G (2006) Direct employment effects of new firms. In: Fritsch M, Schmude J (eds) Entrepreneurship in the region, vol 49. Springer, Boston, pp 75–93
Chapter Google Scholar
Eraydin A, Tasan-Kok T, Vranken J (2010) Diversity matters: immigrant entrepreneurship and contribution of different forms of social integration in economic performance of cities. Eur Plan Stud 18:521–543. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654311003593556
Erken H, Donselaar P, Thurik R (2018) Total factor productivity and the role of entrepreneurship. J Technol Transf 43:1493–1521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9504-5
Falck O (2007) Mayflies and long-distance runners: the effects of new business formation on industry growth. Appl Econ Lett 14:919–922. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504850600705877
Fayolle A, Wright M (2014) How to get published in the best entrepreneurship journals: a guide to steer your academic career/edited by Alain Fayolle and Mike Wright. Edward Elgar, Cheltenham
Book Google Scholar
Feki C, Mnif S (2016) Entrepreneurship, technological innovation, and economic growth: empirical analysis of panel data. J Knowl Econ 7:984–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-016-0413-5
Ferreira JJ, Fayolle A, Fernandes C, Raposo M (2017) Effects of Schumpeterian and Kirznerian entrepreneurship on economic growth: panel data evidence. Entrep Reg Dev 29:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985626.2016.1255431
Fisch C, Block J (2018) Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and management research. Manag Rev Q 68:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-018-0142-x
Fölster S (2000) Do entrepreneurs create jobs? Small Bus Econ 14:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008141516160
Frenken K, Cefis E, Stam E (2014) Industrial dynamics and clusters: a survey. Reg Stud 49:10–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2014.904505
Fritsch M (1996) Turbulence and growth in West Germany: a comparison of evidence by regions and industries. Rev Ind Organ 11:231–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157669
Fritsch M (2013) New business formation and regional development: a survey and assessment of the evidence. Found Trends Entrep 9:249–364. https://doi.org/10.1561/0300000043
Fritsch M, Mueller P (2004) Effects of new business formation on regional development over time. Reg Stud 38:961–975. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280965
Fritsch M, Mueller P (2008) The effect of new business formation on regional development over time: the case of Germany. Small Bus Econ 30:15–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9067-9
Fritsch M, Noseleit F (2013a) Investigating the anatomy of the employment effect of new business formation. Camb J Econ. https://doi.org/10.1093/cje/bes030
Fritsch M, Noseleit F (2013b) Start-ups, long- and short-term survivors, and their contribution to employment growth. J Evol Econ 23:719–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-012-0301-5
Fritsch M, Schindele Y (2011) The contribution of new businesses to regional employment—an empirical analysis. Econ Geogr 87:153–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1944-8287.2011.01113.x
Fritsch M, Schroeter A (2011) Why does the effect of new business formation differ across regions? Small Bus Econ 36:383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9256-9
Fryges H, Wagner J (2008) Exports and productivity growth: first evidence from a continuous treatment approach. Rev World Econ 144:695–722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10290-008-0166-8
Gast J, Gundolf K, Cesinger B (2017) Doing business in a green way: a systematic review of the ecological sustainability entrepreneurship literature and future research directions. J Clean Prod 147:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.065
Gilbert BA, McDougall PP, Audretsch DB (2006) New venture growth: a review and extension. J Manag 32:926–950. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206306293860
Gilbert BA, McDougall PP, Audretsch DB (2008) Clusters, knowledge spillovers and new venture performance: an empirical examination. J Bus Ventur 23:405–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2007.04.003
Gittell R, Sohl J, Tebaldi E (2014) Do entrepreneurship and high-tech concentration create jobs? Exploring the growth in employment in U.S. metropolitan areas from 1991 to 2007. Econ Dev Q 28:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891242414530467
González-Pernía J, Peña-Legazkue I (2015) Export-oriented entrepreneurship and regional economic growth. Small Bus Econ 45:505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-015-9657-x
González-Pernía J, Peña-Legazkue I, Vendrell-Herrero F (2012) Innovation, entrepreneurial activity and competitiveness at a sub-national level. Small Bus Econ 39:561–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-011-9330-y
Hafer RW (2013) Entrepreneurship and state economic growth. J Entrep Public Policy. https://doi.org/10.1108/20452101311318684
Hamdan AMM (2019) Entrepreneurship and economic growth: an Emirati perspective. J Dev Areas 53:65–78. https://doi.org/10.1353/jda.2019.0004
Harmina A (2016) The role of entrepreneurship in explaining the real gross domestic product per capita: regression model selection. Croat Rev Econ Bus Soc Stat 2:297. https://doi.org/10.1515/crebss-2016-0007
Henderson J, Weiler S (2009) Entrepreneurs and job growth: probing the boundaries of time and space. Econ Dev Q 24:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891242409350917
Hessels J, van Stel A (2011) Entrepreneurship, export orientation, and economic growth. Small Bus Econ 37:255–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9233-3
Higgins JPT, Green S (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley, Chichester
Hoang H, Yi A (2015) Network-based Research in entrepreneurship: a decade in review. Found Trends Entrep 11:1–54. https://doi.org/10.1561/0300000052
Irastorza N, Pena-Legazkue I (2018) Immigrant entrepreneurship and business survival during recession: evidence from a local economy. J Entrep 27:243–257. https://doi.org/10.1177/0971355718781248
Ivanović-Đukić M, Lepojevi V, Stefanovic S, van Stel A, Petrovic J (2018) Contribution of entrepreneurship to economic growth: a comparative analysis of south-east transition and developed European countries. Int Rev Entrep 16:257–276
Jones O, Gatrell C (2014) Editorial: The future of writing and reviewing for IJMR. Int J Manag Rev 16:249–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12038
Jones MV, Coviello N, Tang YK (2011) International entrepreneurship research (1989–2009): a domain ontology and thematic analysis. J Bus Ventur 26:632–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2011.04.001
Kalleberg AL, Leicht KT (1991) Gender and organizational performance: determinants of small business survival and success. Acad Manag J 34:136–161. https://doi.org/10.5465/256305
Kangasharju A, Pekkala S (2002) The role of education in self-employment success in Finland. Growth Change 33:216–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/0017-4815.00188
Kasseeah H (2016) Investigating the impact of entrepreneurship on economic development: a regional analysis. J Small Bus Enterp Dev. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-09-2015-0130
Kessler A, Korunka C, Frank H, Lueger M (2012) Predicting founding success and new venture survival: a longitudinal nascent entrepreneurship approach. J Enterp Cult 20:25–55. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218495812500021
Kirzner IM (1973) Competition and entrepreneurship. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Koellinger PD, Thurik RA (2012) Entrepreneurship and the business cycle. Rev Econ Stat 94:1143–1156. https://doi.org/10.1162/REST_a_00224
Koster S (2011) Individual foundings and organizational foundings: their effect on employment growth in The Netherlands. Small Bus Econ 36:485–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9253-z
Koster S, van Stel A (2014) The relationship between start-ups, market mobility and employment growth: an empirical analysis for Dutch regions. Pap Reg Sci 93:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12000
Lee YS (2017) Entrepreneurship, small businesses and economic growth in cities. J Econ Geogr 17:311–343. https://doi.org/10.1093/jeg/lbw021
Li H, Cheng S, Haynes KE (2011) The employment effects of new business formation: a regional perspective. Econ Dev Q 25:282–292. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891242411407310
Li H, Yang Z, Yao X, Zhang H, Zhang J (2012) Entrepreneurship, private economy and growth: evidence from China. China Econ Rev 23:948–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2012.04.015
Li H, Terjesen S, Umans T (2020) Corporate governance in entrepreneurial firms: a systematic review and research agenda. Small Bus Econ 54:43–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-018-0118-1
Liargovas P, Repousis S (2013) Development paths in the knowledge economy: innovation and entrepreneurship in Greece. J Knowl Econ 6:1063–1077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-013-0176-1
Matejovsky L, Mohapatra S, Steiner B (2014) The dynamic effects of entrepreneurship on regional economic growth: evidence from Canada. Growth Change 45:611–639. https://doi.org/10.1111/grow.12055
McMullen JS (2011) Delineating the domain of development entrepreneurship: a market-based approach to facilitating inclusive economic growth: ET&P ET&P. Entrep Theory Pract 35:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6520.2010.00428.x
Meadows DH, Meadows DL, Randers J, Behrens WW III (1972) The limits to growth: a report for the Club of Rome’s project on the predicament of mankind/Donella H. Meadows … [et al.]. Universe Books, New York
Meyer N, Meyer DF (2017) An econometric analysis of entrepreneurial activity, economic growth and employment: the case of the BRICS countries. Int J Econ Perspect 11:429–441
Mochkabadi K, Volkmann CK (2020) Equity crowdfunding: a systematic review of the literature. Small Bus Econ 54:75–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-018-0081-x
Mrozewski M, Kratzer J (2017) Entrepreneurship and country-level innovation: investigating the role of entrepreneurial opportunities. J Technol Transf 42:1125–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9479-2
Mueller P (2007) Exploiting entrepreneurial opportunities: the impact of entrepreneurship on growth. Small Bus Econ 28:355–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-006-9035-9
Mueller P, van Stel A, Storey DJ (2008) The effects of new firm formation on regional development over time: the case of Great Britain. Small Bus Econ 30:59–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11187-007-9056-Z
Mulrow CD (1994) Rationale for systematic reviews. BMJ 309:597–599. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.309.6954.597
Munoz P, Cohen B (2018) Sustainable entrepreneurship research: taking stock and looking ahead. Bus Strateg Environ 27:300–322. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2000
Nafziger EW, Terrell D (1996) Entrepreneurial human capital and the long-run survival of firms in India. World Dev 24:689–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(95)00161-5
Naudé W, Siegel M, Marchand K (2017) Migration, entrepreneurship and development: critical questions. IZA J Migration 6:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40176-016-0077-8
Nissan E, Galindo Martin M-A, Mendez Picazo M-T (2011) Relationship between organizations, institutions, entrepreneurship and economic growth process. Int Entrep Manag J 7:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-011-0191-2
Nordhaus W, Tobin J (1972) Is growth obsolete? Econ Res 5:1–80
North DC (2012) Institutions, institutional change and economic performance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Noseleit F (2013) Entrepreneurship, structural change, and economic growth. J Evol Econ 23:735–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-012-0291-3
Omri A (2017) Entrepreneurship, sectoral outputs and environmental improvement: international evidence. Technol Forecast Soc Change. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.10.016
Ordanini A, Rubera G, DeFillippi R (2008) The many moods of inter-organizational imitation: a critical review. Int J Manag Rev 10:375–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2370.2008.00233.x
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Bachrach DG, Podsakoff NP (2005) The influence of management journals in the 1980s and 1990s. Strateg Manag J 26:473–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.454
Popay J, Roberts H, Sowden A, Petticrew M, Arai L, Rodgers M, Britten N, Roen K, Duffy S (2006) Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews: a product from the ESRC Methods Programme. Lancaster University, Lancaster
Prieger JE, Bampoky C, Blanco LR, Liu A (2016) Economic growth and the optimal level of entrepreneurship. World Dev 82:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2016.01.013
Raz O, Gloor PA (2007) Size really matters-new insights for start-ups’ survival. Manag Sci 53:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1060.0609
Reynolds PD, Bygrave WD, Autio E (2003) Global entrepreneurship Monitor: 2003 executive report. http://www.gemconsortium.org/report/47102 . Accessed 27 Dec 2017
Rho S, Gao J (2012) Employment effect of entrepreneurial activity in China’s private economy. Seoul J Econ 25:177–206
Rosa P, Carter S, Hamilton D (1996) Gender as a determinant of small business performance: insights from a British study. Small Bus Econ 8:463–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390031
Rupasingha A, Goetz SJ (2013) Self-employment and local economic performance: evidence from US counties. Pap Reg Sci 92:141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1435-5957.2011.00396.x
Sabella A, Farraj W, Burbar M, Qaimary D (2014) Entrepreneurship and economic growth in West Bank, Palestine. J Dev Entrep 19:1. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1084946714500034
Salgado Banda H (2007) Entrepreneurship and economic growth: an empirical analysis. J Dev Entrep 12:3–29. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1084946707000538
Schumpeter JA (1942) Capitalism, socialism and democracy, [Reprint]. Harper colophon, Harper Perennial, New York
Semrau T, Werner A (2014) How exactly do network relationships pay off? The effects of network size and relationship quality on access to start-up resources. Entrep Theory Pract 38:501–525. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12011
Stam E, Hartog C, van Stel A, Thurik R (2011) Ambitious entrepreneurship, high-growth firms, and macroeconomic growth. In: Minniti M (ed) The dynamics of entrepreneurship. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Szerb L, Lafuente E, Horváth K, Páger B (2018) The relevance of quantity and quality entrepreneurship for regional performance: the moderating role of the entrepreneurial ecosystem. Reg Stud. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2018.1510481
Tang J, Tang Z (2007) The relationship of achievement motivation and risk-taking propensity to new venture performance: a test of the moderating effect of entrepreneurial munificence. Int J Entrep Small Bus 4:450. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJESB.2007.013691
Terán-Yépez E, Marín-Carrillo GM, Casado-Belmonte MP, Capobianco-Uriarte MM (2020) Sustainable entrepreneurship: review of its evolution and new trends. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119742
Thurik RA, Carree MA, van Stel A, Audretsch DB (2008) Does self-employment reduce unemployment? J Bus Ventur 23:673–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2008.01.007
Tietenberg TH, Lewis L (2012) Environmental & natural resource economics. Pearson series in economics, 9th edn. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14:207–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Unger JM, Rauch A, Frese M, Rosenbusch N (2011) Human capital and entrepreneurial success: a meta-analytical review. J Bus Ventur 26:341–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2009.09.004
Urbano D, Aparicio S (2016) Entrepreneurship capital types and economic growth: International evidence. Technol Forecast Soc Change 102:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.02.018
Urbano D, Aparicio S, Audretsch D (2019a) Twenty-five years of research on institutions, entrepreneurship, and economic growth: what has been learned? Small Bus Econ 53:21–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-018-0038-0
Urbano D, Audretsch D, Aparicio S, Noguera M (2019b) Does entrepreneurial activity matter for economic growth in developing countries? The role of the institutional environment. Int Entrep Manag J 6:875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-019-00621-5
Valliere D, Peterson R (2009) Entrepreneurship and economic growth: evidence from emerging and developed countries. Entrep Reg Dev 21:459–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985620802332723
van Oort FG, Bosma NS (2013) Agglomeration economies, inventors and entrepreneurs as engines of European regional economic development. Ann Reg Sci 51:213–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-012-0547-8
van Praag CM, Versloot PH (2007) What is the value of entrepreneurship? A review of recent research. Small Bus Econ 29:351–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9074-x
van Praag CM, Wit GD, Bosma N (2005) Initial capital constraints hinder entrepreneurial venture performance. J Priv Equity 9:36–44. https://doi.org/10.3905/jpe.2005.605369
van Stel A, Storey D (2004) The link between firm births and job creation: is there a Upas Tree effect? Reg Stud 38:893–909. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280929
van Stel A, Suddle K (2008) The impact of new firm formation on regional development in the Netherlands. Small Bus Econ 30:31–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9054-1
van Stel A, Carree M, Thurik R (2005) The effect of entrepreneurial activity on national economic growth. Small Bus Econ 24:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-1996-6
Vázquez-Rozas E, Gómes S, Viera E (2010) Entrepreneurship and economic growth in Spanish and Portuguese regions. Reg Sect Econ Stud 10:109–126
Verheul I, van Stel A (2010) Entrepreneurial diversity and economic growth. In: van Auken H, Bonnet J, García Pérez De Lima D (eds) The entrepreneurial society. Edward Elgar Publishing, Cheltenham
Watson J (2007) Modeling the relationship between networking and firm performance. J Bus Ventur 22:852–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2006.08.001
Wennberg K, Lindqvist G (2010) The effect of clusters on the survival and performance of new firms. Small Bus Econ 34:221–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-008-9123-0
Wennekers S, Thurik R (1999) Linking entrepreneurship and economic growth. Small Bus Econ 13:27. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008063200484
Williams CC, Lansky MA (2013) Informal employment in developed and developing economies: perspectives and policy responses. Int Labour Rev 152:355–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1564-913X.2013.00196.x
Wohlin C (2014) Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In: Shepperd M, Hall T, Myrtveit I (eds) Proceedings of the 18th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering—EASE ‘14. ACM Press, New York, pp 1–10
Wong PK, Ho YP, Autio E (2005) Entrepreneurship, innovation and economic growth: evidence from GEM data. Small Bus Econ 24:335–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-2000-1
World Commission on Environment and Development (1987) Brundtland report: our common future. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Zhao S (2018) Entrepreneurship and economic growth during china’s economic transformation, 1978–2008. Seoul J Econ 31:307–331
Download references
Acknowledgements
Open Access funding provided by Projekt DEAL. I like to thank Dirk Ludewig, of the Flensburg University of Applied Sciences and Olav Hohmeyer, of the Europa-Universität Flensburg, for their useful and valuable feedback on previous versions of this paper. Furthermore, I would like to express my appreciation to the participants of the G-Forum conference in Wien, Austria (September, 2019) and of the paper development workshop of the FGF e.V. working group on sustainable entrepreneurship in Flensburg, Germany (March, 2020), where earlier versions of the paper were discussed.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of economics, Flensburg University of Applied Sciences, Kanzleistraße 91-93, Flensburg, Germany
Thomas Neumann
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Thomas Neumann .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 109 kb)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Neumann, T. The impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and its determinants: a systematic review. Manag Rev Q 71 , 553–584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00193-7
Download citation
Received : 21 May 2020
Accepted : 19 July 2020
Published : 04 August 2020
Issue Date : July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00193-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Entrepreneurship
- Economic development
- Sustainable development
- Developing countries
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Social entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurship
- Business plans
- Entrepreneurial business strategy
- Entrepreneurial exit strategy
- Entrepreneurial finance
Innovating for Shared Value
- Marc Pfitzer
- Valerie Bockstette
- From the September 2013 Issue

Act Bigger than You Are
- Rosabeth Moss Kanter
- July 17, 2012
Deviating from the Business Plan
- Steven S. Rogers
- June 22, 2015
The $300 House: Businesses Take Up the Challenge
- Vijay Govindarajan
- July 18, 2011

Key Traits of Social Entrepreneurs
- John Elkington
- June 15, 2008


Nurturing Innovation
- Anne-Laure Fayard
- Jess Majekodunmi
- Martina Mendola
- Rachel Kenny
- From the March–April 2024 Issue

How Low and Middle-Income Countries Are Innovating to Combat Covid
- Ben Ramalingam
- Benjamin Kumpf
- Rahul Malhotra
- Merrick Schaefer
- June 09, 2021

It's Time to Invest in Climate Adaptation
- Ravi Chidambaram
- Parag Khanna
- July 31, 2022

Design an Organization that Makes a Difference
- Christian Busch
- January 12, 2013

Two Keys to Sustainable Social Enterprise
- Roger Martin
- Sally Osberg
- From the May 2015 Issue
An Innovative Approach to Funding CSR Projects
- Theo Vermaelen
- From the June 2011 Issue
An Apollo Program for American Philanthropy and the Nonprofit Sector
- Dan Pallotta
- September 05, 2012

Getting Serious About Stakeholder Capitalism
- Hubert Joly
- Julie Battilana
- Tiziana Casciaro
- Mary Johnstone-Louis
- Charmian Love
- Ranjay Gulati
- Thomas Dudley
- Ethan Rouen
- Auden Schendler
- May 24, 2021
A New Approach to Funding Social Enterprises
- Antony Bugg-Levine
- Bruce Kogut
- Nalin Kulatilaka
- From the January–February 2012 Issue

The 3-Stage Process That Makes Universities Prime Innovators
- April 19, 2024

How Cities Are Using Analytics to Improve Public Health
- Bechara Choucair
- Raed Mansour
- September 15, 2014

Accountants Will Save the World
- Peter Bakker
- March 05, 2013

Put the "and" Back in "Sales and Marketing"
- Jenny Cermak
- Roland John
- Homayoun Hatami
- Maryanne Hancock
- October 30, 2014

Why Social Ventures Need Systems Thinking
- Vanessa Kirsch
- Jeff Walker
- Jim Bildner
- July 25, 2016

For Start-Ups Seeking Talent, a Lofty Purpose Can Backfire

OnStar: Not Your Father's General Motors
- Clayton M. Christensen
- September 01, 2009
Hope for Special Hope? (C)
- G. Paul Matherne
- Rebecca Goldberg
- March 17, 2020
A Community for Change: B Lab and Certified B Corps
- Mary Margaret Frank
- Elena Loutskina
- Gerry Yemen
- August 27, 2019
Kathy Giusti and the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation
- Richard G. Hamermesh
- Joshua D. Margolis
- Matthew Preble
- June 25, 2014
Saahas Zero Waste Solutions: Getting to a Product Market Fit While Cleaning Up India
- Suresh Bhagavatula
- July 01, 2019
James Chen's Entrepreneurial Odyssey (A): Adlens
- Randel Carlock
- Elin Williams
- October 28, 2016
Roxbury Technology Corporation
- Richard S. Ruback
- Royce Yudkoff
- September 24, 2012
Just Arrived: Integrating Refugees in Sweden
- Brian Trelstad
- Emilie Billaud
- Mette Fuglsang Hjortshoej
- August 20, 2020
Eco Femme Cloth Pads: Reaching Rural Women
- Sreeram Sivaramakrishnan
- Subhasis Ray
- Paromita Goswami
- November 23, 2020
Safecast: Bootstrapping Human Capital to Big Data
- Ethan S. Bernstein
- Stephanie Marton
- October 24, 2018
Givewith: Harnessing Social Impact from Everyday Business Activities
- David Y. Choi
- Darlene M. Fukuji
- December 31, 2021
Serengeti Eyewear: Entrepreneurship Within Corning, Inc.
- David A. Garvin
- Jonathan West
- September 13, 1993
NOW PT (B): Should We Invest?
- George A. Riedel
- Amy Klopfenstein
- August 08, 2022
Wellington Global Impact
- Lynn Schenk
- February 27, 2018
Ferrero Group: Achieving Sustainability Through Supply Chain Integration
- Wiboon Kittilaksanawong
- Ottavia Curcuraci
- June 19, 2017
The Robin Hood Army
- Susanna Gallani
- July 05, 2018
Intrapreneurship @ Nokia Software: Instilling Culture Change
- Yossi Feinberg
- Sheila Melvin
- March 04, 2019
Narayana Hrudayalaya Heart Hospital: Cardiac Care for the Poor (A)
- Tarun Khanna
- V. Kasturi Rangan
- June 22, 2005
Hero MotoCorp: Championing a Cause
- Utkarsh Majmudar
- Namrata Rana
- June 29, 2018
Harry Susilo: Moral Leadership and Family Business Succession

Junko Yoda and Her Collaboration to Address Sex Trafficking in Asia, Teaching Note
- Ai-Ling Jamila Malone
- Tessa Natanay Hamilton
- April 05, 2016
Measuring Impact at the Los Angeles Cleantech Incubator, Teaching Note
- Jill Kickul
- Zephyr James
- December 05, 2022
Dalmia Bharat: Social Return on Investment, Instructor Spreadsheet
- November 08, 2017

The VC Fund Closing Equity Gaps — and Making Money
- August 08, 2023
Popular Topics
Partner center.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
The Power of Purpose-Driven Entrepreneurship — How Social Entrepreneurs Are Changing the World Social entrepreneurs are the torchbearers of hope and progress, redefining the role of business in society.
By Taiwo Sotikare Edited by Chelsea Brown Aug 1, 2023
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
In a rapidly evolving world facing an array of pressing challenges, the rise of purpose-driven entrepreneurship has emerged as a beacon of hope.
Social entrepreneurs are individuals who use entrepreneurial principles, innovative thinking and business acumen to create positive and sustainable social or environmental impact. They are driven by a strong sense of purpose to address pressing societal challenges and improve the well-being of communities and the planet.
Social entrepreneurs apply the same entrepreneurial mindset used in traditional business ventures to develop innovative solutions to complex social problems. Their primary goal is to generate positive outcomes rather than solely seeking financial profit. They often work to empower marginalized groups, improve access to essential services, address environmental issues and promote social justice.
This article delves into the transformative force of purpose-driven ventures, exploring their sustainable impact and the supportive ecosystem propelling their success.
Related: 3 Steps to Forge Your Company's Purpose-Driven Path
The emergence of purpose-driven ventures
Traditionally, entrepreneurship has been associated with profit-driven motives, but a paradigm shift is underway. Social entrepreneurs have recognized that addressing societal and environmental challenges requires more than just good intentions; it demands a sustainable approach that integrates purpose into business strategies. These visionary leaders view challenges as opportunities and harness the power of innovation and empathy to create lasting impact.
For example, Patagonia, founded by Yvon Chouinard , is a renowned outdoor apparel company that embraces sustainability and environmental responsibility as part of its core mission. They prioritize eco-friendly materials, minimize waste and actively support environmental causes through campaigns like "1% for the Planet," where they donate a portion of their revenue to environmental initiatives.
The power of profit and purpose alignment
Contrary to the notion that profit and purpose are conflicting concepts, social entrepreneurs have unlocked the potential of aligning the two forces for the greater good. By imbuing their ventures with a meaningful mission , they attract a loyal customer base and engage employees who are deeply committed to the cause. This alignment fuels passion, creativity and dedication, propelling these purpose-driven ventures towards remarkable success.
A good example is Warby Parker, an eyewear company co-founded by four friends (Neil Blumenthal, Dave Gilboa, Andrew Hunt and Jeffrey Raider), which has a "Buy a Pair, Give a Pair" business model. For every pair of glasses sold, they provide a pair to someone in need through partnerships with nonprofit organizations. This alignment of profit and purpose has resulted in both business success and significant social impact.
Related: How to Build a Business that Makes a Positive Impact
Driving sustainable impact
One defining characteristic of purpose-driven entrepreneurship is its commitment to sustainable impact . Social entrepreneurs look beyond short-term gains, focusing on solutions that create lasting change. Whether it's tackling environmental issues, empowering marginalized communities or improving healthcare access, these ventures invest in projects with far-reaching and enduring effects, leaving behind a positive legacy for generations to come.
Green School, for example, founded by John and Cynthia Hardy, is an innovative, eco-focused school in Bali that integrates sustainability, environmental education and holistic learning into its curriculum. The school's unique approach empowers students to become changemakers, fostering a generation of environmentally conscious leaders.
Inspiring stories of social entrepreneurs
Tony Elumelu is a visionary entrepreneur and philanthropist who has become a leading example of purpose-driven entrepreneurship. As the founder of The Tony Elumelu Foundation, he is empowering African entrepreneurs to drive sustainable economic growth and social development on the continent. Through his foundation's flagship initiative, the Tony Elumelu Foundation Entrepreneurship Programme (TEEP), Tony Elumelu has provided mentorship and training to 1,500,000 and seed funding to 18,000 young African entrepreneurs .
There's also Kiva, an online micro-lending platform, co-founded by Jessica Jackley and Matt Flannery. It connects individuals looking to lend small amounts of money (as little as $25) to entrepreneurs in developing countries. This peer-to-peer lending model empowers entrepreneurs to start or grow their businesses, with the goal of lifting them out of poverty.
The support ecosystem
Behind every successful social entrepreneur stands a supportive ecosystem that nourishes their vision. Impact investors, philanthropic organizations and government initiatives play a pivotal role in nurturing purpose-driven ventures. The collective effort of these stakeholders provides access to capital, mentorship and networks that amplify the ventures' reach and potential.
Related: 3 Steps for Making a Positive Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Impact
Spreading the movement
The rise of purpose-driven entrepreneurship is not an isolated phenomenon. It is part of a global movement towards a more sustainable and equitable world. As these social entrepreneurs blaze a trail, they inspire others to follow suit, creating a ripple effect that catalyzes positive change across industries and borders.
B Corporations , also known as B Corps, are businesses that meet rigorous standards of social and environmental performance, accountability and transparency. These Save & Send for Review companies include Patagonia, Ben & Jerry's and Seventh Generation, among others. The B Corp movement is spreading globally, inspiring businesses to pursue not just profit but also purpose and positive impact.
CEO of Insight.ng
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This Former Tesla Employee Started a Side Hustle to Save Gen Z Time — Now It's Raised Over $40 Million From the CEOs of Salesforce, Uber and More
- Lock 20 Things Emotionally Intelligent People Don't Say
- Lock A CEO Who Runs a Fully Remote Company Has an Unusual Take on Employees Starting Side Hustles: 'We Have to Be Honest With Ourselves'
- How an Idea and a Facebook Post Led to a $49 Million Tiny Home Business
- Lock I Thought I Was Resilient , Until a Devastating Loss Showed Me Resilience Is Not Something You Just 'Have'
- Bill Gates Recommends These Books for Your Summer Reading List
Most Popular Red Arrow
Is one company to blame for soaring rental prices in the u.s..
The FBI recently raided a major corporate landlord while investigating a rent price-fixing scheme. Here's what we know.
This Former Starbucks Employee Started a Side Hustle That's Making More Than $70,000 a Month — and He's Not Done Yet
When Tom Saar moved to New York City, he spotted a lucrative business opportunity.
Microsoft Reportedly Lays Off Over 1,500 Employees in Cloud Sector as Partnership with OpenAI Strengthens
Alphabet also reportedly laid off employees from several teams in Google's cloud unit last week.
Why You Need a Contribution Mindset to Thrive in 2024 and Beyond
How to set yourself and your business up for long-term success.
10 Online Side Hustles Proven to Boost Your Bank Account
Even the busiest schedules can accommodate finding a precious few hours to create a profitable online venture — something that many are already mastering.
How to Start a Passive Income Side Hustle That Uses Assets You Already Own, From 3 People Who Make Thousands of Dollars Doing It
You could be sitting on a major money-maker.
Successfully copied link

Essay on Social Entrepreneurship
Students are often asked to write an essay on Social Entrepreneurship in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Social Entrepreneurship
What is social entrepreneurship.
Social entrepreneurship is a way of solving social problems by starting a business. Social entrepreneurs are people who see a problem in the world and use their business skills to solve it. They want to make a difference in the world and are willing to take risks to do it.
How Social Entrepreneurship Works
Social entrepreneurs start businesses that sell products or services that help people. These businesses can be for-profit or non-profit. The profits from the business are used to fund the social mission of the company. For example, a social entrepreneur might start a business that sells fair-trade coffee. The profits from the business are used to pay the farmers who grow the coffee a fair price.
Importance of Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship is important because it can help solve some of the world’s most pressing problems. Social entrepreneurs are often able to find creative solutions to problems that governments and large corporations cannot. They can also raise awareness about important social issues.
Challenges Faced by Social Entrepreneurs
Social entrepreneurs face many challenges. They often have difficulty raising money, and they may face resistance from people who are opposed to their ideas. However, social entrepreneurs are often very passionate about their work, and they are willing to overcome these challenges to make a difference in the world.
250 Words Essay on Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship is when someone starts a project or business not just to make money, but to help solve social problems. Imagine seeing a lot of people in your town don’t have clean water to drink, and you start a company that finds a cheap way to clean water. That’s being a social entrepreneur. You’re making a difference by solving a big problem.
Why It Matters
This kind of work is important because it looks at big problems in the world like hunger, pollution, or people not having homes, and tries to fix them. It’s not just about the person doing it getting rich; it’s about making life better for everyone. This way, businesses can help make the world a nicer place for all of us.
Examples of Social Entrepreneurship
There are many people and companies out there doing great things. For example, some companies make shoes, and for every pair they sell, they give a pair to a child who doesn’t have shoes. Others might create apps that help people learn new things for free. These are all ways of using business to help others.
In short, social entrepreneurship is a powerful way to help solve some of the world’s big problems. By starting businesses that focus on helping others, social entrepreneurs can make a real difference. It’s about using creativity and business skills for a good cause, and anyone can do it if they really want to help make the world a better place.
500 Words Essay on Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship: a force for good.
Social entrepreneurship is a way of using business strategies to address social problems. This means that social entrepreneurs are not only looking to make a profit, but they want to make a positive impact on the world.
Characteristics of a Social Entrepreneur
Social entrepreneurs are often driven by a passion to make a difference in the world. They’re usually creative and innovative thinkers, always looking for new ways to solve social problems.
How Social Entrepreneurs Make a Difference
Social entrepreneurs can make a difference in many ways. They can create new products or services that help people, or they can come up with innovative solutions to social problems. For example, some social entrepreneurs have developed affordable housing for people who are homeless, while others have created programs to help people get jobs.
Social entrepreneurs often face challenges in their work. They may have trouble getting funding. Social entrepreneurs may also face resistance from people who want to keep things that way, or who believe that government is the only one that can solve social problems.
Social entrepreneurs are making a difference in the world. They are using their skills and business acumen to address social problems and create a better world for all. They may face challenges, but they don’t give up. They are determined to make a difference, and they won’t stop until they succeed.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Social Discrimination
- Essay on Social Development In Physical Education
- Essay on Social Determinants Of Health
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Understanding social entrepreneurship

Checked : Grayson N. , Abigail C.
Latest Update 20 Jan, 2024
Table of content
Why is it important to study social entrepreneurship?
The social enterprise spectrum.
The aspiration to do good and make work sustainable is among the significant features of a social enterprise. For the past several years, social enterprise has seen tremendous growth with more and more companies recognizing their value. There are several not-for-profit organizations seeking opportunities to expand their ventures that fulfill their missions besides earning them revenues. A social enterprise is an organization that provides avenues through both aspects. Since nonprofit organizations of not have many sources funding, approaching their business from such a perspective could be most functional.
We can define social entrepreneurship as a process of identifying and acknowledging social problems and creating social change through entrepreneurial principals, processes, and operations. In other words, it is the identification of a particular social issue, then designing, organizing, and managing a social approach to change the situation. Many social problems in the world demand a specific approach to try and resolve. Strategies employed may not solve the completely, but offers a lifetime process with a focus on improving the existing environment. It is not about changing the situation but changing the approach to finding a lasting solution, and this does not eliminate the problem.
Entrepreneurship is defined as the process of identifying new ventures and creating a way to gain opportunities therein. It is all about taking up risks in a certain area where others cannot, to make a profit.
In general and common business terms, entrepreneurship means taking the lead to start a new business. It may also mean diversifying an existing business to create more opportunities. Social entrepreneurship, on the other hand, focuses on building social capital. It does not measure how a profile performs or returns on investment. This is a field majorly influenced by non-profit organizations and sectors. Note, however, that social entrepreneurship does not eliminate the possibility of making a profit. To succeed as an entrepreneur , one needs capital to run their businesses, and so do nonprofits if they must bring change in society.
Another vital issue social entrepreneurship seeks to address, apart from social problems, is environmental issues. Organizations that deal with child rights, plants for treatment, and waste product and women empowerment seek to empower the society on the importance of these aspects. They identify issues in a particular societal setting and bring together individuals with similar interests to try resolving the issue.
Social entrepreneurship involves social entrepreneurs. These are individuals who are affiliated with non-profit and non-government organizations. They run fundraisers through community events and activities to invest in people.
Today, several social entrepreneurs have changed society and inspire many others to do so. The founder and manager of Grameen Bank, Muhammad Yunus, is an excellent example of such entrepreneurs. He was awarded a Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts in creating an organization that benefits a large section of society.
Another great example is Rang De, a social enterprise established in 2008 by Ramakshina and Smita Ram. This is an online platform that gives rural and poor urban Indian people access to micro-credits. They offer loans with interest rates of as low as 2 percent annually.
The George Foundation is a well recognized social enterprise. It is a program for empowering women by offering them education, vocational training, cooperative farming, business development, and saving plans. These organizations employ the principles and approaches of social enterprise to impact society.
A social enterprise is a field that has been growing steadily over the past few years. It has attracted the attention of different volunteers, all interested in giving back to society. It allows individuals to do what they have always wanted to do for long. It comprises of extraordinary and innovative people with brilliant ideas to change society in many issues.
Studying social entrepreneurship is vital both in the general business realm as well as social well being. It equips students with skills to change their society as well as use innovative ways to create living for themselves. Many social enterprises, like the ones mentioned above, have played a vital role in shaping society. Anyone can be a social entrepreneur. All you need is some motivation and reason to help others.

We Will Write an Essay for You Quickly
The social enterprise realm contains three significant sectors, social enterprise, the private sector, and charities. In many states, ‘social enterprise’ is not a legal term. The social enterprise as an entity is founded on a spectrum with organizations interested in undertaking activities that benefit other people. It may or may not benefit themselves, but they are willing to go ahead anyway. Such entities rely on grants on one side and self-financing on the other.
The best way set venture into social entrepreneurship is through the following means:
- Charities and voluntary organizations. These are organizations whose aim is purely to help those in need. They rely on fundraising to raise money for the same.
- Charities with a trading arm. They are the most recognized charities that operate by selling products and services through a shop. They can include a charity shop.
- Social enterprise. Different from the ones mentioned above, social enterprise trades for profit but has a measurable social impact.
- Commercial businesses with a social imperative. These are businesses set to gain profit but founded on strong values.
- Private sector. These are entities that seek profit, with a focus on making money. They trade to maximize the value of stakeholders.
Social entrepreneurship is a wide term used to refer to business processes with a social purpose. In some countries, like Ireland, you cannot register a business legally on this basis. One can use different forms mentioned above to incorporate social enterprises. Generally, however, a social enterprise is described as such if it adopts and meets a set of principles. It must show impact, through a clear mission, it displays finance/profit characteristics, and there is a sense of ownership. These features make such an organization entrepreneurial. Though sometimes them benefits may not be purely monetary, there is always the aspect of finances.
Looking for a Skilled Essay Writer?

- Castleton University Master of Education (MEd)
No reviews yet, be the first to write your comment
Write your review
Thanks for review.
It will be published after moderation
Latest News

What happens in the brain when learning?
10 min read
20 Jan, 2024

How Relativism Promotes Pluralism and Tolerance

Everything you need to know about short-term memory
Discover more with our Mobile App!
Login to epale.

To log into your EPALE account, please choose one of the registration options below:
Epale - electronic platform for adult learning in europe, what is social entrepreneurship.
The SocEnter project supports individuals at risk of social exclusion in establishing social enterprises. Read an excerpt from our handbook

I’d like to share with you an exciting initiative from the Zofia Zamenhof Foundation. The SocEnter project aims to support individuals at risk of social exclusion and those looking to establish social enterprises collaboratively.
As part of this project, we have created a comprehensive guide that provides essential information and tips on how to successfully start and manage a social enterprise. Below, you’ll find an excerpt from our handbook.
Chapter 1: Social Entrepreneurship
What is social entrepreneurship.
Nowadays, social entrepreneurship is a broad umbrella term that encompasses activities and processes aimed at giving effective and sustainable solutions to social problems. Social entrepreneurship has developed as a distinctive form of the third sector’s enterprises in the 21st century (Nicholls, 2008). It represents a part of the contemporary economy, especially in many developing countries and involves different figures of changemakers who act as entrepreneurs. The aim of these entrepreneurs is to create opportunities for their communities, build multiplier partnerships, and develop policy changes and market system changes.
The research, More in Common: The Global State of Social Enterprise (British Council, June 2022), has estimated that the number of social enterprises in developed countries is very wide. Hundreds of thousands social enterprises have been estimated in the United States, 20,000 in Australia, 102,000 in Italy, 18,000 in Belgium, 96,603 in France, 15,855 in Hungary, 29,535 in Poland, 205,000 in Japan.

Event SocEnter, May 2023
The term social entrepreneur was first mentioned in 1972 by Joseph Banks in his book The Sociology of Social Movements. The author used this term to describe the need to use managerial skills to address social problems as well as to address business challenges. According to Raghda El Ebrashi (El Ebrashi, 2013), the founder and chairperson of Alashanek ya Balady Association for Sustainable Development (AYB-SD), which is one of the biggest youth NGOs in Egypt, social entrepreneurship practices emerged in the 1980s with the establishment of Ashoka, which was the first organization to support social entrepreneurs in the world (Sen, 2007).
Social entrepreneurship can been considered as entrepreneurship with a social goal while social entrepreneurs should be deemed as change agents or changemakers. Accordingly, one expects that the primary aim of social entrepreneurship is to obtain social returns from social economical activity.
In this perspective, social entrepreneurship operates in the conventional economic system but with a different primary objective. Conventional entrepreneurs aim at creating value for themselves while social entrepreneurs aim at creating value for the community in which they operate.
Social entrepreneurship shares with conventional entrepreneurship innovation, risk-taking, and proactivity but its objective is to offer concrete and valuable solutions to real social problems. Indeed, in social entrepreneurship, innovation is at the service of the community while risk-taking and proactivity are finalized to solve a social problem. It has been observed that social entrepreneurship can be moved by the intrinsic and extrinsic motivations of social entrepreneurs.
In this regard, the behavioural theory of social entrepreneurship examines the relevant variables that lead to social endeavour creation, the basic association elements and structures, and how these typologies measure the social effect, activate assets and realize effective and sustainable social change. Human behaviour can have a fundamental role in fostering or hindering social and economic development (Huggins & Thompson, 2021). The motivation to become a social entrepreneur is an individual choice although social problems, political and situational factors can influence this choice.

Project meeting
The full handbook is available on the SocEnter project website in English, Polish, Italian, Portuguese, and Greek. We invite you to explore the guide and learn more about the entire project. We believe our initiative will help people create stable and meaningful social enterprises.
For more information, please visit our project website: https://socenter.eu/
Fundacja im. Zofii Zamenhof

Ciekawe spojrzenie
Przed przeczytaniem całości artykułu, w mojej głowie pojawiła się tylko pierwsza część definicji przedsiębiorstwa społecznego - takiego które działa na rzecz swoich członków i wspiera ich rozwój. Dziękuję za to nowe spojrzenie które też pokazuje, że cel działania przedsiębiorstwa powinien być powiązany ze zmianą dla społeczności czy grup marginalizowanych.
- Log in or register to post comments
Login or Sign up to join the conversation.
Want another language?
Want to write a blog post .
Don't hesitate to do so! Click the link below and start posting a new article!
Latest Discussions
What do adults want? (What are their expectations?)
Adult education principles recognize that adults learn in different ways. So are the expectations the same for all adults?
Creative drama process can provide several benefits to individuals with disabilities and their families:
Language Learning in Adult Education: A Discussion
Related articles
Ecowork + audiovisual materials, highlights from the national skills council business brunch, cgc-digitrans training, digital skills and the world of work, potential sectors for harnessing the power of 3d printing for deaf entrepreneurs and how to navigate them, "we stand out in the profession 2023-1-rs01-ka121-vet-000115651, latest news.

EPALE NSS Conference 2024
National Support Services (NSSs) EPALE from 35 European countries gathered on May 29 and 30, 2024 in...
PROJECT “DIGI-MENTOR” – TOWARDS NEW POSSIBILITIES
Project Digi-Mentor to empower Ukrainian refugees in Germany and Estonia with digital skills, remote...
Intergenerational learning requires tolerance and mutual respect
Upcoming Events
Erasmus+ courses in split (8 - 14 june), ace: colonialism: as seen, we see, epale is europe's biggest multilingual, open membership community of adult learning professionals..
Accessibility
Get the Mobile App
Get in touch.

COMMENTS
A good example is professor Yunus's case of economically empowering disadvantaged women in society. The American social entrepreneur J.B. Schramm's case of helping financially unable students to attend school also deserves a special mention in such a case (Muhammad, 63).
Her essay on philanthropy's changing landscape is included in Social Entrepreneurship: New Models of Sustainable Social Change, published in 2006 by Oxford University Press. DOI: 10.48558/tsav-fg11. Tags Activism, Muhammad Yunus, Poverty, Social Entrepreneurship. Cite
Independent Entrepreneurship, Intrapreneurship, and Social Entrepreneurship. This paper examines the similarities and differences of independent entrepreneurship, intrapreneurship, and social entrepreneurship. When it comes to the process, intrapreneurship and entrepreneurship are similar in terms of value creation and undertaking risks.
The contested concept of social entrepreneurship has gained particular prominence in academic literature over the last few decades. To explore how patterns of understandings relating to social entrepreneurship have emerged and shifted over time, we undertook a critical historical review focusing on the most highly cited social entrepreneurship articles in each of five time periods over the ...
Knowledge@Wharton High School first met Fiorella Riccobono in 2015 when she was a senior in high school. We featured her in a story about a business class project to promote fair trade practices among Haitian coffee farmers. Now Riccobono, who is 19, is a college student studying finance and interdisciplinary social science with concentrations in economics and social entrepreneurship.
Although the notion of social entrepreneurship (SE) has been around since the 1950s (Bowen, 1953), it is only within the past decade that SE research has become a major and influential literature stream.For example, SE has been identified as a powerful mechanism to confront poverty (Bloom, 2009; Ghauri, Tasavori, & Zaefarian, 2014), empower women (Datta & Gailey, 2012), catalyze social ...
Social Entrepreneurship (SE) is a popular area of research and practice. An analysis of the existing literature reviews on SE reveals a dearth of studies classifying the existing SE literature into multiple research themes and further presenting popular and less popular research themes. With the aim of bridging this gap, this study presents a ...
The essays in the present article argue for a reconceptualization of entrepreneurship to account for the social effects of entrepreneurship on society. Each essay presents a pathway of how such a reimagination of entrepreneurship can look and as such opens a new, broader research agenda.
This essay describes the challenges of Social Entrepreneurship and Social Innovation as a field and explores how it could contribute to transforming business education. The first suggestion is to think about System Change as a much needed shift in perspective away from focusing on the lone individual hero entrepreneur. Current problems often defy the market based approach to entrepreneurship ...
The field of social entrepreneurship has grown significantly in the last two decades, with thousands of companies worldwide using entrepreneurial approaches to address social and environmental challenges, a transformation that has been supported by an ecosystem of incubators and accelerators, investors, regulators, and other intermediaries and market actors.
This paper presents a systematic review of (a) the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and (b) the factors determining this impact. Research over the past 25 years shows that entrepreneurship is one cause of macroeconomic development, but that the relationship between entrepreneurship and welfare is very complex. The literature emphasizes that the generally ...
Innovation & Entrepreneurship Magazine Article. Roger Martin. Sally Osberg. Social entrepreneurship has emerged over the past several decades as a way to identify and bring about potentially ...
Social entrepreneurs look beyond short-term gains, focusing on solutions that create lasting change. Whether it's tackling environmental issues, empowering marginalized communities or improving ...
Social entrepreneurship. Student organizers from the Green Club at Newcomb College Institute formed a social entrepreneurship organization in 2010 that aimed to encourage people to reduce waste and live in a more environmentally conscious way. Social entrepreneurship is an approach by individuals, groups, start-up companies or entrepreneurs, in ...
500 Words Essay on Social Entrepreneurship Social Entrepreneurship: A Force for Good. Social entrepreneurship is a way of using business strategies to address social problems. This means that social entrepreneurs are not only looking to make a profit, but they want to make a positive impact on the world. Characteristics of a Social Entrepreneur
the genus entrepreneur. They are entrepreneurs with a social mission. However, because of this mission, they face some distinctive challenges and any definition ought to reflect this. For social entrepreneurs, the social mission is explicit and central. This obviously affects how social entrepreneurs perceive and assess opportunities.
One-year plan. Social entrepreneurship is used by the startup companies and other potential businesses in order to strategize, find a source of financing with the sole aim of providing desirable solutions to the social, environmental and cultural issues that affect the population (Zahra, S. A., Newey, L. R., & Li, Y. 2014).
In this journal, social entrepreneurship is defined as having four key components - sociality, innovation, market orientation, and hybridity. First, sociality is a focus on a defined social purpose or benefit to society that is carefully measured. This could be identifiable by organization type such as co-operatives or charities, or sectors ...
Social Entrepreneurship the Nuba Water. PAGES 3 WORDS 825. Western sanitation facilities, for example, are expected to be white, clean, and indoors. In the United States, for example, we expect every home to have its own faucet and running water. In Sudan, however, the expectations for design and infrastructure are different.
Social entrepreneurship, on the other hand, focuses on building social capital. It does not measure how a profile performs or returns on investment. This is a field majorly influenced by non-profit organizations and sectors. Note, however, that social entrepreneurship does not eliminate the possibility of making a profit.
Social entrepreneurship has developed as a distinctive form of the third sector's enterprises in the 21st century (Nicholls, 2008). It represents a part of the contemporary economy, especially in many developing countries and involves different figures of changemakers who act as entrepreneurs. The aim of these entrepreneurs is to create ...
Entrepreneurs may also be motivated primarily by their desire to make a positive impact on the world by creating a new business. This type of leader is known as a social entrepreneur. They see a problem facing their communities, or the world at large, and they strive to create and implement new solutions that drive change.
The purpose of this paper is to provide an overview of existing literature in this emerging area, and to examine social entrepreneurship in light of growing expectations that it will generate and support radically new and effective ways of dealing with pressing social problems. The first part of this paper will briefly examine the contextual ...
Although we know a great deal about creating ventures that can generate financial wealth for entrepreneurs, we have largely excluded, ignored, or "danced around" the creation of nonprofit ventures (with some important exceptions). We propose research to explore how initiating, engaging, and performing nonprofit venturing may differ from for-profit venturing and how some nonprofit ...