
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 4 Minutes
Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals.
Case Study Questions
Question 1:
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow-
For the continuity of life, all living things produce organisms of their own kind. This is called reproduction. A special organ system called the reproductive system is responsible for carrying out the process of reproduction in a living body. Although all living things reproduce they do so by different means. There are two types of Reproduction-Asexual and Sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction requires one parent while Sexual reproduction requires two parents to produce a baby. Asexual reproduction is the simplest form of reproduction and is commonly found in plants and lower animals like starfish, sponges and worms. Most plants and mammals, including human beings, reproduce sexually.
a) What is reproduction? i) Producing fruits ii) Producing young ones of its own kind iii) Producing food iv) All of these
b) What are the two types of reproduction? i) Budding ii) Fragmentation iii) Asexual reproduction iv) Sexual reproduction a. i) b. ii) c. ii&iv d. iii &iv
c) Which type of reproduction involves only one parent? i) Sexual reproduction ii) Asexual reproduction iii) Both of these iv) None of these
d) How do mammals reproduce? i) By sexual reproduction ii) By asexual reproduction iii) By budding iv) All of these
e)Identify the organism which reproduces asexually. i) Shark ii) Sponges iii) Snake iv) Snail
b) iii & iv (Option c)
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Reproduction in Animals
Case study questions class 8 science chapter 8 reproduction in animals, cbse case study questions class 8 science reproduction in animals, case study 1.
Do you recall the processes ofdigestion, circulation andrespiration which you havestudied in your previous classes? Theseprocesses are essential for the survivalof every individual. You have also learntabout the process of reproduction inplants. Reproduction is essential for thecontinuation of a species. Imagine whatwould have happened if organisms hadnot reproduced. You will realise thatreproduction is very important as itensures the continuation of similarkinds of individuals, generation aftergeneration.Modes of Reproduction:Have you seen the young onesof different animals? Try to name someof the young ones by completing shown in examples at S. No.1 and 5.You must have seen the youngones of various animals being born.Can you tell how chicks andcaterpillars are born? How are kittensand puppies born? Do you think thatthese young ones looked the samebefore they were born as they do now?Let us find out.Just as in plants, there are two modesby which animals reproduce. These are:(i) Sexual reproduction, and(ii) Asexual reproduction.Sexual ReproductionTry to recall reproduction in plantswhich you studied in Class VII. You willremember that plants that reproducesexually have male and femalereproductive parts. Can you name theseparts? In animals also, males andfemales have different reproductive partsor organs. Like plants, the reproductiveparts in animals also produce gametesthat fuse to form a zygote. It is the zygotewhich develops into a new individual.This type of reproduction beginningfrom the fusion of male and femalegametes is called sexual reproduction.Let us find out the reproductive partsin humans and study the process ofreproduction in them.
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
|
Case study 2
Case study 3, case study 4.
Que. 5) Answer: Cloning is the production of the exact copy of the cell, any other living part or a complete organism. The first successfully cloned animal is a sheep named Dolly.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, up scert solutions class 7 english chapter 14 – florence nightingale, telangana scert class 5 evs chapter 7 forests – tribals solution, ncert solutions class 6 sanskrit deepakam chapter 6 स: एव महान् चित्रकार:, tribals, dikus and the vision of a golden age class 8 quiz.
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6

Last Updated on September 12, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 8 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 8 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 8 science chapter 6 Reproduction in Animals.
| Reproduction in Animals | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 8 | |
| Science | |
| Class 8 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Reproduction in Animals
Question 1:
Read the given passage below and answer the question:
All plants and animals go through life cycles. Just think about all the growing and changing human children do as they grow up. Children grow in height and get heavier until they reach adulthood. Children also change as their body matures. Although we grow lots from the time we are born to adulthood, humans never transform. Unlike us, butterflies go through a metamorphosis, or transformation. A butterfly looks very different as it changes through all four stages of its life cycle. A butterfly transforms through the first stage egg to the last stage adult butterfly. Similarly, frogs go through the same transformation from egg to an adult.
Q. 1. Frog and butterfly comes under: (a) Oviparous animals (b) Viviparous animals (c) Ovoviviparous (d) None of the above
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Animals lay eggs which later develop into young ones. They are called oviparous animals. So, it is easier to observe the eggs of oviparous animals as they are outside the body.
Q. 2. What is another name of the pupa stage of butterfly? (a) Caterpillar (b) Adult (c) Chrysalis (d) None of the above.
Ans. Option(c) is correct. Explanation: The transformation of a caterpillar (larva) to a butterfly takes place in the chrysalis (pupa). Butterflies go through a life cycle of 4 stages: egg, larva, pupa and an adult.
Q.3. Define the term metamorphosis.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. The process of transformation of a larva to an adult through a series of drastic changes, for example, frog, silkworm, butterfly, etc., undergo metamorphosis.
Q. 4. What are the stages of life cycle of a frog? (Medium)
Ans. Unlike mammals, frogs lay eggs. To increase the chances of survival, many eggs are laid in masses by the frog. Frog eggs can usually be found in calm or static waters. Stages of life cycle of a frog are: Egg → Tadpole → Froglet (young frog) → Adult frog.
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Sound Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
- Friction Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 9
- Force and Pressure Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 5
- Combustion and Flame Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
- Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Crop production and management class 8 case study questions science chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Learning the modes of reproduction in animals.
- Learning process of asexual reproduction in microscopic organisms.
- Knowing various parts of the male and female reproductive system.
- Understanding the process of sexual reproduction.
- Understanding the process of fertilisation and development of embryo.
- Discussing the difference between viviparous and oviparous animals.
The process through which living beings produce new young ones of their own kind is called reproduction. Reproduction is necessary for the continuation of species, the transfer of variations from one generation to another and also for the addition of new species. This chapter deals with reproductive systems and various modes of reproduction in animals.
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 8 Science Preparation
- Download Latest Sample Papers for CBSE Class 8 Science
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Reproduction in Animals Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 8 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of reproduction in animals, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 8 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on reproduction in animals for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Reproduction in Animals class 8 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of reproduction in animals.
Q7: Which is the largest cell and smallest cell in the human body?
A7: Human reproductive system contains the largest cell (ovum) and smallest cell (sperm) in the human body.
Q8: Why the gametes have only half the number of chromosomes?
A8: Gametes are produced as a result of meiosis. In meiosis, a single cell divides into four haploid cells. The numbers of chromosomes are halved in meiosis and produces haploid gametes. Thus, the gametes have only half the number of chromosomes.
Q9: Define the term cloning.
A9: An artificial method invented by human beings to produce organ cell or part of living organisms without sexual or asexual reproduction. For example, sheep named Dolly was a clone.
Q10: Name the primary male and female sex hormones
A10: Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone produced by the testes and Estrogen or oestrogen is the primary female sex hormone secreted by ovaries.

Related Posts

Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions with Answers are provided here. We prepared these extra questions based on the latest NCERT Class 8 Science Book. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals Extra Questions will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals Extra Questions
Very short answer type question.
Question 1: Name two animals which reproduce sexually.
Answer: Cow, Elephant
Question 2: Name two animals which reproduce asexually.
Answer: Hydra, Amoeba
Question 3: Which type of reproduction involves gametes?
Answer: Sexual reproduction
Question 4: Which type of reproduction does not involve gametes?
Answer: Asexual reproduction
Question 5: What is another term for a fertilised egg?
Answer: Zygote
Question 6: Name the reproductive process which involves two parents.
Question 7: Name the reproductive process which involves one parent.
Question 8: What type of fertilization takes place in hen?
Answer: Internal fertilization takes place in hen.
Question 9: Name the organs which produce sperms in human.
Answer: The testes produce sperms in human.
Question 10: What are the male gametes in humans called?
Answer: The male gametes in humans are called sperms.
Question 11: What are the female gametes in humans called?
Ans. Female gametes in humans are called ova (eggs).
Question 12: Name the organs which produce female gametes.
Answer: Ovaries produce female gametes.
Question 13: Name the parent sheep of which dolly was a clone.
Answer: Finn Dorsett sheep
Question 14: Where does a fertilized egg (or zygote) develop into a baby?
Answer: A fertilized egg (or zygote) develops into a baby in the uterus.
Question 15: What are the reproductive organs of male?
Answer: The reproductive organs in male include testes, sperm ducts and penis.
Question 16: What term is used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of hydra?
Answer: Buds
Question 17: What is the name given to the fusion of male and female gametes?
Answer: Fertilization is the name given to the fusion of male and female gametes.
Question 18: What are the reproductive organs of female?
Answer: The reproductive organs in the female include ovaries, oviducts and uterus.
Question 19: What is foetus?
Answer: The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus.
Question 20: In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
Ans. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What type of asexual reproduction take place in amoeba?
Answer: Amoeba reproduces by the common asexual reproduction method called binary fission.
Question 2: Who cloned Dolly the sheep?
Answer: Dolly was cloned by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland.
Question 3: What purpose does the tail in a sperm serve?
Answer: Tail allows the sperm to become motile, hence helps the sperm to reach female gametes for fusion.
Question 4: What is cloning?
Answer: Cloning is the production of an exact copy of a cell, any other living part, or a complete organism.
Question 5: What are the two modes of reproduction in animals?
Answer: There are two modes by which animals reproduce. These are: (i) Sexual reproduction, and (ii) Asexual reproduction.
Question 6: What are the reproductive organs in humans which produce the gametes?
Answer: The ovary produces female gametes called ova and the testes produce male gametes called sperms.
Question 7: Which life process ensures that a plant or animal species will not disappear from the earth?
Answer: Reproduction is the life process ensures that a plant or animal species will not disappear from the earth.
Question 8: Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
Answer: Reproduction is essential for the continuation of a species. It ensures the continuation of similar kinds of individuals, generation after generation.
Question 9: What is an embryo?
Answer: The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells. The cells then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is termed as an embryo.
Question 10: Name the technique which is used to help a woman with blocked oviducts to have a baby.
Answer: . IVF or in vitro fertilization (fertilization outside the body) is the technique which is used to help a woman with blocked oviducts to have a baby.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: Describe the process of fertilization in human beings.
Answer: The first step in the process of reproduction is the fusion of a sperm and an ovum. When sperms come in contact with an egg, one of the sperms may fuse with the egg. Such fusion of the egg and the sperm is called fertilization. During fertilization, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus. This results in the formation of a fertilized egg or zygote.
Question 2: How does a hydra reproduce?
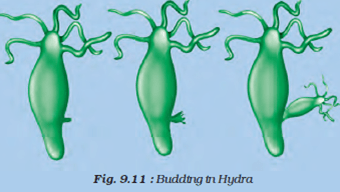
Answer: Hydra reproduces asexually by the process of budding. A small outgrowth called ‘bud’ is formed on the side of its body. This bud then grows gradually to form a small hydra. And finally the tiny new hydra detaches itself from the body of parent hydra and lives as a separate organism.
Question 3: Give two differences between a zygote and a foetus.
Answer: Differences between a zygote and a foetus
| 1. The fusion of ovum and sperm is called fertilization. The fertilized egg is called a zygote. | 1. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts are identifiable is called foetus. |
| 2. A zygote is a single cellular. | 2. A foetus is a multicellular. |
Question 4: Give two differences between zygote and embryo.
Answer: Differences between zygote and embryo
| 1. The fusion of ovum and sperm is called fertilization. The fertilized egg is called a zygote. | 1. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to an embryo. |
| 2. A zygote is a single cellular. | 2. An embryo is a multicellular. |
Question 5: Why do fish and frogs lay eggs in hundreds?
Answer: Though these animals lay hundreds of eggs and release millions of sperms, all the eggs do not get fertilized and develop into new individuals. This is because the eggs and sperms get exposed to water movement, wind and rainfall. Also, there are other animals in the pond which may feed on eggs. Thus, production of large number of eggs and sperms is necessary to ensure fertilization of at least a few of them.
Question 6: Explain how chicks are born.
Answer: Internal fertilization takes place in hens also. Soon after fertilization, the zygote divides repeatedly and travels down the oviduct. As it travels down, many protective layers are formed around it. The hard shell that we see in a hen’s egg is one such protective layer. After the hard shell is formed around the developing embryo, the hen finally lays the egg. The embryo takes about 3 weeks to develop into a chick.
Question 7: Define asexual reproduction. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
Answer: The type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction. The two methods of asexual reproduction in animals are:
Budding – In this type of asexual reproduction, a small part of the body of the parent organism grows as a ‘bud’ which then detaches and becomes a new organism. Example- hydra
Binary fission – In this type of asexual reproduction, the parent organism splits (or divides) to form two new organisms. Example – Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing itself into two parts.
Question 8: Differentiate between Viviparous and Oviparous Animals.
Answer: Difference between Viviparous and Oviparous Animals
| The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals. | Those animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. |
| Examples of viviparous animals are cow, dog, cat, lion, tiger, horse, rabbit etc. | Examples of oviparous animals are butterfly, frog, fish, crow, sparrow, snake, lizard, ostrich etc. |
Question 9: What is the basic difference between asexual and sexual reproduction?
Answer: Difference between asexual and sexual reproduction
| 1. The type of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction. | 1. Reproduction resulting from the fusion of male and female gametes is called sexual reproduction. |
| 2. No formation or fusion of gametes occurs. | 2. Gametes are always formed, and fusion also occurs. |
| 3. No fertilization takes place. | 3. Fertilization takes place. |
Question 10: Differentiate between internal fertilization and external fertilization.
Answer: Difference between internal fertilization and external fertilization
| 1. Fertilization which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilization. | 1. Fertilization that takes place outside the female body is called external fertilization. |
| 2. This is observed in human beings and other animals such as hens, cows and dogs. | 2. This is observed in frogs, fish, starfish, etc. |
Question 11: What is metamorphosis? Give examples.
Answer: The transformation of the larva into adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis. Commonly known examples of metamorphosis include the process undergone by most insects and the transformation of tadpoles into frogs. The diagram below shows the stages of this change, wherein the small fish-like tadpoles transform into what seems a completely different animal:
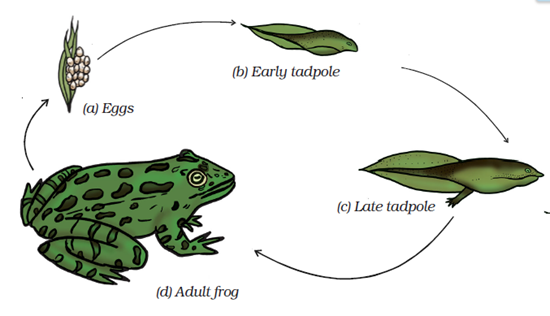
Question 12: How does fertilization take place in frog? Or How do frog eggs get fertilized? Or How does fertilization occur in frog?
Answer: During spring or rainy season, frogs and toads move to ponds and slow flowing streams. When the male and female come together in water, the female lays hundreds of eggs. Frog’s egg is not covered by a shell and it is comparatively very delicate. A layer of jelly holds the eggs together and provides protection to the eggs. As the eggs are laid, the male deposits sperms over them. Each sperm swims randomly in water with the help of its long tail. The sperms come in contact with the eggs. This results in fertilization.
Question 13: What is ‘in vitro fertilization’ technique of reproduction? Or What are test-tube babies?
Answer: In some women oviducts are blocked. These women are unable to bear babies because sperms cannot reach the egg for fertilization. In such cases, doctors collect freshly released egg and sperms and keep them together for a few hours for IVF or in vitro fertilization (fertilization outside the body). In case fertilization occurs, the zygote is allowed to develop for about a week and then it is placed in the mother’s uterus. Complete development takes place in the uterus and the baby is born like any other baby. Babies born through this technique are called test-tube babies.
Question 14: How could a single cell become such a big individual?
Answer: Fertilization results in the formation of zygote. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells. The cells then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is termed an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development. The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops the body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, ears, etc. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus. When the development of the foetus is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
Question 15: What are the steps involved in sexual reproduction in animals?
Answer: Steps involved in sexual reproduction in animals are:
- The male parent produces male gametes called sperms. Sperm is a single cell with all the usual cell components.
- The female parent produces female gametes called eggs (or ova). Like the sperm, an egg is also a single cell.
- The sperm enters into the egg. The nucleus of sperm fuses with the nucleus of egg cell to form a new cell called zygote.
- The zygote divides repeatedly to form a hollow ball of hundreds of cells which is called embryo.
- Embryo grows and becomes a foetus in which all main body features of the baby animal have formed.
- Foetus grows and develops to form a new baby animal.
At Study Path, you can also learn more about Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Notes, Important Questions, and MCQ.
Book a Trial With Our Experts
Hey there! We receieved your request
Stay Tuned as we are going to contact you within 1 Hour
Thank you for registering.
One of our academic counsellors will contact you within 1 working day.

Click to Chat
- 1800-5470-145
- +91 7353221155
- Login | Register
- My Classroom
- My Self Study Packages
- Batch Discussion
- My Forum Activity
- Refer a Friend
- Edit Profile
- Add Question
- Add Paragraph
- Search Coupon
Use Coupon: CART20 and get 20% off on all online Study Material
Complete Your Registration (Step 2 of 2 )

Register Now and Win Upto 25% Scholorship for a Full Academic Year !
Enter your details.

Registration done!
Sit and relax as our customer representative will contact you within 1 business day
Mobile Verification
OTP to be sent to Change
- Junior Hacker
- Junior Hacker New
- Self Study Packages
- JEE Advanced Coaching
- 1 Year Study Plan
- Rank Predictor
- Paper Pattern
- Important Books
- Sample Papers
- Past Papers
- Preparation Tips
- Latest News
- JEE Main Exams
- Online Coaching
- Branch Predictor
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Past Year Papers
- Math Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Exam Details
- JEE Syllabus
- IIT JEE Toppers Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 11
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 9
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 8
- IIT JEE Preparation Time Table
- IIT JEE Online Coaching
- Correspondence Course For IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Coaching after 10th
- IIT JEE Coaching For Foundation Classes
- JEE Coaching Institutes
- IIT JEE Coaching in Kota
- IIT JEE Coaching Institutes In Kota
- BITSAT Examination
- View complete IIT JEE Section
- View All Engineering Exams
- Top Engineering Colleges
- Top Engineering Branches
- Engineering Exam Calendar
- NEET Entrance Exam
- NEET Online Coaching
- NEET Preparation Tips
- Participating States
- AIIMS Examination
- AIIMS Online Coaching
- View all Medical Exams
- Top Medical Colleges
- Medical Exam Coaching
- Best Medical Coaching In Kota
- Medical Exam Calendar
- NTSE Examination
- Notifications
- Application
- Important Dates
- Eligibility
- Study Material
- KVPY Examination
- Olympiads Examination
- Indian National Mathematics Olympiad
- Physics Olympiad
- Chemistry Olympiad
- Biology Olympiad
- Olympiads Sample Papers
- INMO Papers
- CBSE School Exams
- Solutions for Board Exam
- JEE Advanced
- Karnataka CET
- Manipal UGET
- NCERT Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Class 10 Solutions
- NCERT Class 9 Solutions
- NCERT Class 8 Solutions
- NCERT Class 7 Solutions
- NCERT Class 6 Solutions
- List of JEE Main & JEE Advanced Books
- R.D. Sharma Solutions PDFâ
- Concepts of Physics by HC Verma for JEE
- HC Verma Solutions Part 1
- HC Verma Solutions Part 2
- Most Scoring Topics in IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Entrance Exam
- Discuss with Colleagues and IITians
- Engineering Entrance Exams
- Branch Ranking of IIT
- Discuss with Askiitians Tutors
- NEET (AIPMT)
- Marks and Rank in IIT JEE
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- AIEEE Entrance Exam
- Electric Current
- Wave Motion
- Modern Physics
- Thermal Physics
- Electromagnetic Induction
- General Physics
- Electrostatics
- Wave Optics
- Physical Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Trigonometry
- Analytical Geometry
- Differential Calculus
- Integral Calculus
- Magical Mathematics
- Online Tutoring
- View complete NRI Section
- View Complete Study Material
- View Complete Revision Notes
- Ahmadi (FAIPS)
- Khaitan (Carmel School)
IIT JEE Courses

One Year IIT Programme
- Super Premium LIVE Classes
- Top IITian Faculties
- 955+ hrs of Prep
- Test Series & Analysis

Two Year IIT Programme
- 1,835+ hrs of Prep

Crash Course
- LIVE + Pre Recorded Sessions
- 300+ hrs of Prep
NEET Courses

One Year NEET Programme
- Top IITian & Medical Faculties
- 900+ hrs of Prep

Two Year NEET Programme
- 1,820+ hrs of Prep

- LIVE 1-1 Classes
- Personalized Sessions
- Design your own Courses
- Personalized Study Materials
School Board
Live online classes, class 11 & 12.
- Class 11 Engineering
- Class 11 Medical
Class 9 & 10
Class 6, 7 & 8, test series, jee test series.
- 2 Year Jee Test Series
- 1 Year Jee Test Series
NEET test series
- 2 Year NEET Test Series
- 1 Year NEET Test Series
C.B.S.E test series
- 11 Engineering
- 12 Engineering
Complete Self Study Packages
Full course.
- 2 year NEET
- Chemistry 11th & 12th
- Maths 11th & 12th
- Physics 11th & 12th
- Biology 11th & 12th
- View Complete List
For class 12th
- Chemistry class 12th
- Maths class 12th
- Physics class 12th
- Biology class 12 th
For class 11th
- Chemistry class 11th
- Maths class 11th
- Physics class 11th
- Biology class 11th
Revision Notes on Reproduction in Animals
Quick revision.
Several processes such as circulation of blood, digestion and respiration are essential for the survival of human beings and other animals.
Similarly, reproduction is essential to maintain the continuity in the species.
If reproduction in animals does not take place, no similar kind of organisms will be present on the earth generation of the generation.
Modes of Reproduction in Animals
There are two modes of reproduction in animals:
Sexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Similarities between Reproduction in Plants and Animals
Plants and animals can both undergo the sexual and asexual process of reproduction.
Just like plants, in animals, the males and females have different reproductive organs.
In both the plants and animals, the zygote is formed when the male and female gametes fuse together and hence the zygote develops into a new individual.
The type of reproduction that begins with the fusion of male and female gametes is called Sexual Reproduction .
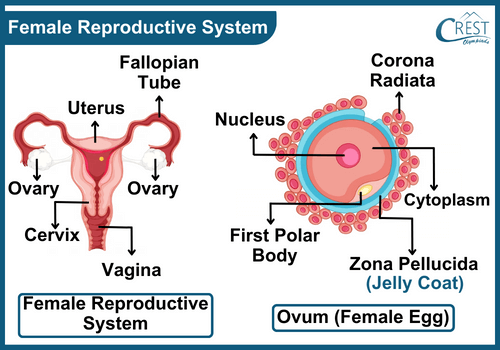
Reproductive Parts in Humans
Male Reproductive Organs

Figure 1: Male reproductive organs
The male reproductive system provides the sperm (male gametes) for fertilization. The male reproductive organs include the following:
It is a cylinder-shaped organ containing a small opening at its top. It secretes semen which contains the male gametes or sperms.
It is a sac-like structure present behind the penis. The testicles or testes are present in this organ. It provides them the right temperature so that they can produce sperms.
Most males have a pair of testis (testes) or testicles. The testes consist of coiled tube-like structures that produce sperms. The testes also generate the male sex hormone or the testosterone that causes puberty in males.
It is a tube-like structure that allows the flow of semen that contains sperms outside the body. The urethra and penis both are also a part of the male urinary system.
Vas Deferens
It is a tube that carries the sperms from the testicles to the urethra.
Prostate Gland
It a gland located under the urinary bladder. It secretes prostate fluid which makes the one third content of semen. This fluid contains some enzymes, zinc and citric acid.
Seminal Vesicles
They have a pouch-like structure. They are located above the prostate gland and connect with the vas deferens. They also secrete a fluid that provides nourishment to the sperms.
Male Sex Hormone or Testosterone
The testes produce testosterone and the pituitary gland controls how much testosterone will be produced. This hormone is responsible for the development of male sex organs and development of secondary sexual characters in males during puberty such as deepening of voice and growth of facial and body hair.
The Sperm Cell

Figure 2: Sperm Cell
The testes secrete millions of sperm cells together. A sperm comprises of a single cell and has a specific structure with three main parts as given below:
Head: It consists of the nucleus which contains the DNA information of the cell.
Middle Part: It is packed with cell organelles called Mitochondria . The mitochondria are responsible for producing energy in the cell. Hence, sperm uses this energy to move.
Tail: It allows the sperm cell to travel at a fast pace.
Female Reproductive Ogans

Figure 3: Female Reproductive Organs
The female reproductive system provides the eggs (female gametes) for fertilization. The female reproductive organs are:
The female reproductive system comprises of a pair of ovaries. These are the main female sex organs and are responsible for the production of female gametes called Eggs or Ova (ovum – singular) and female hormones. The ova or female eggs also consist of a single cell.
Estrogen and Progesterone
These are hormones or chemical substances produced by the ovaries. These hormones are responsible for the development of the female reproductive organs and the secondary sexual characteristics in women such as development of breasts and body hair.

Figure 4: Ovum or Female Egg
2. Oviduct or Fallopian Tubes
These are two funnel-shaped structures that extent from the superior right and left corners of the uterus to the edge of the ovaries. The ovaries release one egg every month into the oviducts. The oviducts consist of cilia that carry the ovum from the oviduct to uterus.
It is an inverted pear-shaped organ that allows the development of the fertilized egg into a human baby. The uterus connects with an opening called Cervix that connects it to the vagina.
It is a muscular tube-like structure that connects with the cervix. It acts as the receptor of the penis and allows the movement of sperms to the fallopian tubes and uterus. It also allows delivery of the foetus during the birth of the child.
Menstrual Cycle
When females hit puberty, they start producing mature eggs every month indicating the ability to reproduce. This process is called menstrual cycle. In this cycle, the ovaries produce an egg every month that travels to the uterus and attaches to its lining. If the egg is not fertilized, the uterus sheds its lining and the egg which result in bleeding in the females. On an average the duration of the menstrual cycle is 28 days. The cycle starts at puberty, around the age of 10 or 11 years and lasts until the age of 45 to 55 years.
Gametogenesis
It is the process of production of gametes by the male and female primary reproductive organs. It ocuurs in three phase in both males and females:
Multiplication Phase
Growth or maturation phase
Meiotic Phase
Gametogenesis in males is called Spermatogenesis . It occurs in the testes and results in formation of sperm cells.
Gametogenesis in females is called Oogenesis . It occurs in the ovaries and results in production of female eggs or ova.
Fertilization
Firstly, reproduction in animals begins when the sperm fuses with an ovum. This process is called Fertilization .
The nuclei of the sperm and egg combine together and form a single nucleus.
As a result, the zygote is formed.
Since the zygote is formed with the fusion of male and female gametes the new individual possesses the characteristics of both the parents.

Figure 4: Fertilization and Zygote
Fertilization can be of two types:
| The fertilization process takes place inside the female body | The fertilization process takes place outside the body of the females. |
| Less number of eggs are produced by such females as there are high chances of the survival of the offspring. | A large number of eggs are produced by such females as the chances of survival of the offspring are very low. |
| For Example, Cows, Human beings and hens undergo internal fertilization. | For Example, Aquatic animals like fishes and amphibians like frogs undergo external fertilization. |
External Fertilization in Frogs and Toads
The frogs and toads reproduce by laying eggs in a slow stream or ponds.
The female frogs first lay hundreds of eggs together in the water.
These eggs are not covered with any hard shell instead there is a jelly-like substance that guards them all and holds them together.
As the female frogs lay their eggs, the male frogs deposit the sperms over them.
This results in external fertilization when the sperms come in contact with the eggs in the water.
Though the eggs are large in numbers only a few of them manage to survive.
There are several factors which may hinder the fertilization process such as exposing to water movement, rainfall, winds and other animals.
Internal Fertilization in Hens
Hens reproduce by laying eggs.
After the formation of the zygote, it keeps on dividing itself and then travels through the oviduct.
In this process, different layers are formed over the egg that then turns into a hard shell or covering of the egg.
When this hard shell is formed the hen lays the egg.
Then it takes almost 3 weeks for the embryo to develop into a chick.
In this time period, the hen often sits over the egg to provide it with warmth.
What are test tube babies?
In some women, the oviducts are blocked and hence they are unable to hold the eggs. This means that these women are not able to bear babies because of blocked oviducts. However, due to the process of Vitro Fertilization or IVF , the freshly released eggs of females and the male sperms can be fertilized externally.
The zygote thus formed is allowed to develop for a week outside the female body in safe conditions and is then placed in the woman's uterus.
In this way, these women can bear babies.
The babies that are born with the IVF process are called Test Tube Babies .
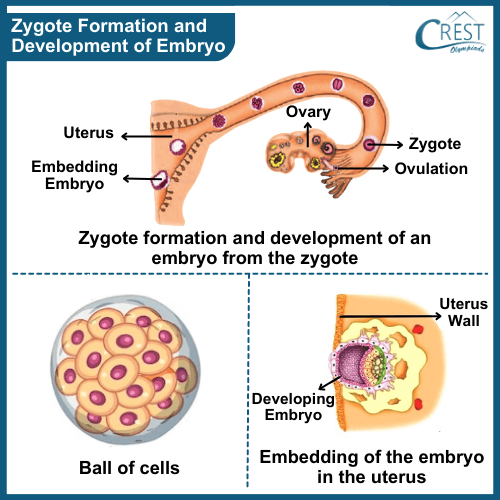
Development of the Embryo
The zygote formed after the fertilization process divides itself in a repeated manner and forms a ball of cells.
These cells then form different groups and each group then starts developing into different tissues and organs. This structure is called an Embryo .
The embryo embeds itself into the uterus wall and continues to develop and grow.
Soon the body parts such as hands, legs, feet, eyes and ears start developing.
The embryo whose parts can be identified individually is called a Foetus .
The foetus then completely develops and takes birth as a baby.

How is an embryo different from a zygote?
| A zygote consists of a single cell. | An embryo consists of more than one cell. |
| It is formed as the fertilization process occurs. | It is formed after the fertilization process. |
| It has no well-defined organs or tissues. | The body parts and tissues are well defined in an embryo. |
Based on the way how the organisms give birth to their offspring, they are classified into two categories:
| These are the organisms that give birth to their young ones directly. | These are the organisms that reproduce by laying eggs. |
| For Example, Human beings, Dogs, Cattle, Cats | For Example, Fishes, Reptiles Amphibians |
Turning into adults from young ones
As individuals are born they continue to grow until they turn into adults.
The young ones may or may not look like the same when they become adults. For instance, in the case of frogs and silkworms, the adults and young ones are completely different.

Figure 6: Life cycle of a frog
What is metamorphosis?
The process in which the young ones undergo drastic changes as they develop into an adult is called Metamorphosis .
Human beings do not undergo metamorphosis. This is because their body parts remain the same from the childhood to adulthood.

Figure 7: Metamorphosis in Silk moth
Asexual Reproduction in Animals
This type of reproduction involves only one parent. It takes place in microscopic animals like Amoeba and small animals like the hydra.
Budding in Hydra
Just like yeast, reproduction in hydra takes place through the process called Budding .
The Hydra possesses different bulges on itself called Buds .
These buds develop into individual Hydra. Each Hydra can possess a different number of buds.

Figure 8: Budding in Hydra
Binary Fission in Amoeba
The Amoeba divides itself into two individuals and the reproduction takes place in this way. It is called Binary Fission .
Amoeba consists of only one cell.
As it reproduces the nucleus of the Amoeba divides itself and forms two different nuclei.
Then the division of the body of the Amoeba takes place and each part receives one nucleus.
In this way, two Amoebas are produced from a single parent.

Figure 9: Binary fission in Amoeba
Fragmentation and Regeneration
In some organisms, the parent organism divides itself into different fragments where each fragment then regenerates and develops into a new organism. This type of asexual reproduction takes place in Planaria and Starfish. Although, starfishes are capable of sexual reproduction as well but many times they also reproduce asexually with the process of fragmentation.

Figure 11: Fragmentation and Regeneration in Planaria
Parthenogenesis
In this type of asexual reproduction, the female organisms are capable of producing eggs without fertilization. These eggs develop into a new organism. This type of reproduction can be seen in some fishes like sharks, some birds, reptiles like lizards and a few insects. However it cannot be seen in mammals.
You Might Like to Refer:
CBSE online class 9 | online study 11th class | CBSE online coaching
TOP Your EXAMS!
Upto 50% scholarship on live classes, course features.
- Video Lectures
- Revision Notes
- Previous Year Papers
- Study Planner
- NCERT Solutions
- Discussion Forum
- Test paper with Video Solution
Book Free demo of askIITians Live class
View courses by askiitians.

Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Ask question.
Get your questions answered by the expert for free

Your Question has been posted!
You will get reply from our expert in sometime.
We will notify you when Our expert answers your question. To View your Question
POST QUESTION
Select the tag for question.

Metals and Non-Metals CBSE Class 8 Science...
Coal and Petroleum CBSE Class 8 Science Revision...
Revision Notes on Pollution of Air and Water What...
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics CBSE Class 8 Science...
Reaching the Age of Adolescence CBSE Class 8...
Friction CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 12...
Revision Notes on Stars and the Solar System...
Revision Notes on Light What makes things visible?...
Conservation of Plants and Animals CBSE Class 8...
Revision Notes on Chemical Effects of Electric...
Revision Notes on Force and Pressure What is a...
Sound CBSE Class 8 Science Revision Notes Chapter...
Revision Notes on Combustion and Flame Quick...
Revision Notes on Cell – Structure and...
Revision Notes on Crop Production and Management...
Microorganisms CBSE Class 8 Science Revision Notes...
Some Natural Phenomena CBSE Class 8 Science...
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 9 Class 8 - Reproduction In Animals
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Get Notes, NCERT Solutions and Extra Questions of Chapter 9 Class 8 NCERT - Reproduction in Animals. Teachoo provides the best content to learn about Reproduction with NCERT questions, worksheets, extra questions and revision notes.
In this chapter, we will learn
What is Reproduction
Different Modes of Reproduction
What are Gametes
Reproduction in Human Beings
What is a Test Tube Baby ?
Internal and External Fertilization
Viviparous and Oviparous Animals
What is Metamorphosis
What is asexual reproduction ?
What purpose does the tail in a sperm serve ?
Why do fish and frogs lay eggs in hundreds whereas a hen lays only one egg at a time?
Here, we have divided this chapter into parts - Concepts, NCERT Questions and Extra Questions.
In Concepts , we explain the concept and then questions related to the concept are solved. In NCERT Questions , we have solved each and every question of the NCERT Book - you will find the best solutions at teachoo. And in Extra Questions , we provide Worksheets, practice questions for better understanding of the chapter... and to get more marks!
Click on a link below to start with the first concept.
NCERT Questions
Teachoo questions.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- Toggle navigation

- CREST Mathematics Olympiad (CMO)
- CREST Science Olympiad (CSO)
- CREST English Olympiad (CEO)
- CREST Reasoning Olympiad (CRO)
- CREST Cyber Olympiad (CCO)
- CREST Mental Maths Olympiad (CMMO)
- International Green Warrior Olympiad (IGWO)
- CREST International Drawing Olympiad (CIDO)
- CREST International Spell Bee Summer (CSB)
- CREST International Spell Bee Winter (CSBW)
- International Teacher Olympiads
- Teacher Mathematics Olympiad
- Teacher Science Olympiad
- Teacher English Olympiad
- Exam Syllabus
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Papers
- Marking Scheme
- Cut-Offs & Ranking Criteria
- Awards & Recognition
- Subject Rankers
- Subject Cut-Off
- Zone Definition
- Green Warrior Initiatives
- Rankholder's Gallery
- Testimonials
- Olympiad Exam Blog
- WhatsApp Channel
- Olympiad Books
- Live Classes
- Mental Mathematics Olympiad (CMMO)
- Green Warrior Olympiad (IGWO)
- School Registration
- Become a Coordinator
- Country Wise Olympiads
- Student Registration
- Teacher Registration
- Special Needs Kids
- CMO arrow_drop_down
- CSO arrow_drop_down
- CEO arrow_drop_down
- CRO arrow_drop_down
- CCO arrow_drop_down
- CMMO arrow_drop_down
- IGWO arrow_drop_down
- CIDO arrow_drop_down
- CSB arrow_drop_down
- CSBW arrow_drop_down
- Individual Registration
- Register Your School
- Exam Schedule
- Ranking Criteria
- Become a Co-ordinator
- assignment_ind
- account_balance
Reproduction in Animals for Class 8
- Topic Description
Quick Video Recap
Curio - ai doubt solver.
- Practice Questions
- More Topics
- Other Subjects
- Register for CREST Olympiads
- Online Classes
Table of Content
Reproduction in animals, asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction, sexual reproduction in humans, viviparous, oviparous and ovoviviparous animals, young ones to adults.
- Solved Questions on Reproduction in Animals
a) Reproduction in animals is the biological process through which new offspring are produced to ensure the continuation of the species. b) There are two main modes of reproduction in animals: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which only one parent is involved in producing offspring. In this process, offspring are generated without the need for the fusion of specialised reproductive cells (gametes) from two parents. As a result, the offspring produced are genetically identical to the parent and to each other, creating clones. Asexual reproduction is common in many unicellular organisms and some higher plants and animals.

Methods of Asexual Reproduction
Some methods of asexual reproduction in animals include budding in hydra, binary fission in amoeba, and fragmentation and regeneration in planaria and starfish.
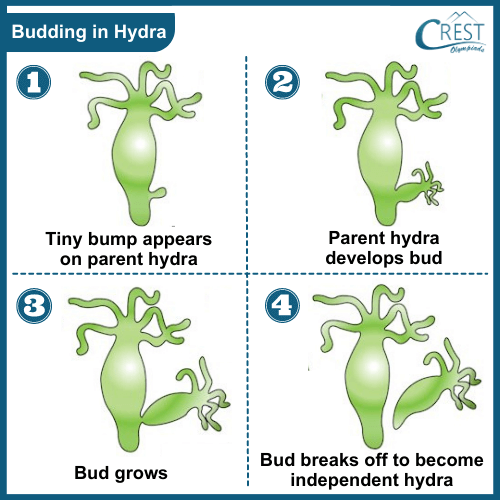
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction commonly observed in organisms like hydra, coral, and sponges. The process of budding involves the following steps:
a) A bud appears on the parent's body: A small outgrowth, or bud, forms on the body of the parent organism. This bud contains a portion of the parent's body cells. b) The bud grows into a full organism: The bud continues to grow and develop, eventually becoming a complete and independent organism. During this process, the bud receives nourishment and energy from the parent organism. c) Separation from the parent: Once the bud reaches a sufficient size and matures into a fully functional organism, it separates from the parent's body. This separation can occur in different ways, depending on the organism. In some cases, the bud breaks off entirely, becoming a new, individual organism. In other cases, like in certain corals and sponges, the bud remains attached to the parent's body, forming colonies of interconnected individuals.
Budding allows these organisms to reproduce rapidly and efficiently. It results in the production of genetically identical offspring, as the new organism originates from a portion of the parent's body. This form of reproduction is advantageous in stable and favourable environments where conditions support the growth and survival of the offspring.
2. Binary Fission
a) Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction commonly observed in single-celled organisms like bacteria and protozoa. In this process, a single parent cell divides into two daughter cells, each identical to the parent. It is a simple and efficient way for these organisms to reproduce and increase their population rapidly. b) Amoeba, a common microscopic organism, reproduces through binary fission.
During binary fission in amoeba:
- The nucleus of the parent amoeba divides into two nuclei.
- The other cell organelles in the cytoplasm also undergo division.
- Finally, the cytoplasm splits, resulting in the formation of two separate amoeba cells.
- Each newly formed amoeba is genetically identical to the parent cell, and they continue to grow and function as independent organisms.
Binary fission allows amoebas to rapidly reproduce and populate their surroundings, ensuring their survival and spread in various environments.
3. Fragmentation
a) Fragmentation is a mode of asexual reproduction where the parent organism breaks itself into multiple fragments or pieces. b) Each fragment has the potential to develop into a new, complete organism. c) This process is common in organisms like planaria, which are flatworms found in freshwater. d) When a planaria divides itself into fragments, each fragment can regenerate the missing body parts and form a new planaria individual.
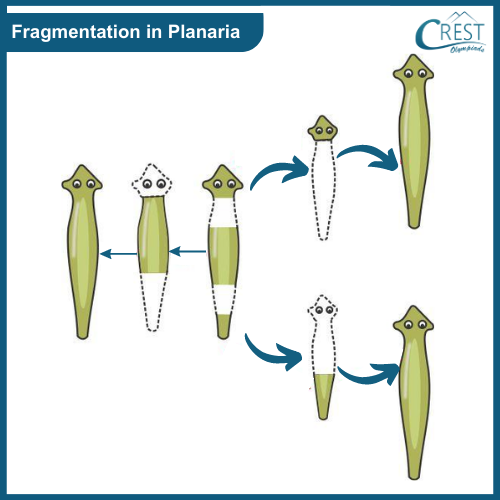
4. Regeneration
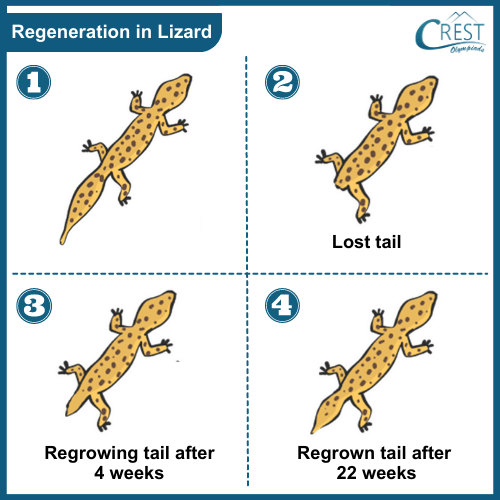
a) Regeneration is the ability of an organism to regrow or replace lost or damaged body parts. b) In some organisms, like lizards, certain body parts can be lost due to predation or accidents. c) Unlike fragmentation, where the entire organism breaks into fragments, in regeneration, only specific body parts or tissues are lost or damaged. d) The organism then regrows these lost body parts over time. For example, lizards can regrow their tails if they lose them in a predator attack.
Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which two parents, typically one male and one female, are involved in producing offspring. This process involves the fusion of specialized reproductive cells called gametes from each parent, resulting in the formation of genetically diverse offspring. Sexual reproduction is the most common mode of reproduction in higher animals, including humans, and many plants.
I. Male Reproductive System
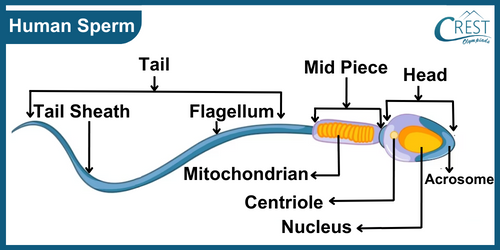
a) The male reproductive system is responsible for producing and delivering sperm, the male gametes required for sexual reproduction. The main male reproductive organs are the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands, and urethra. b) Sperm from the testes move through the sperm ducts and mix with the secretions from the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands to form semen. The semen is then ejaculated through the penis during sexual intercourse. c) Each sperm cell is unicellular and consists of a head, a middle piece, and a tail. The head contains the genetic material (DNA), the middle piece is rich in mitochondria for energy production, and the tail allows the sperm to swim towards the egg for fertilisation.
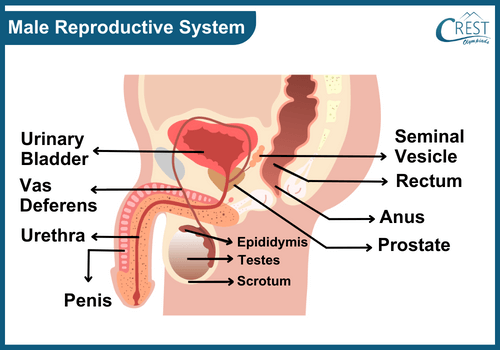
Male Reproductive Organs
Testes: The testes are located in the scrotum and produce sperm and male sex hormones, such as testosterone.
Epididymis: The epididymis is a coiled tube attached to each testis where sperm mature and are stored.
Vas Deferens: The vas deferens is a muscular tube that carries mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
Seminal Vesicles: The seminal vesicles secrete a fluid rich in nutrients that mix with sperm to form seminal fluid.
Prostate Gland: The prostate gland produces a milky fluid that helps neutralize acidity in the urethra and female reproductive tract.
Bulbourethral Glands: These glands secrete a lubricating fluid that aids in the passage of semen during ejaculation.
Urethra: The urethra is a tube that carries semen from the reproductive system and urine from the bladder out through the penis.
II. Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system is a complex and intricate system responsible for the production of female gametes (ova or eggs), the nurturing and development of the embryo during pregnancy, and the production of female sex hormones. It consists of several organs and structures working together to facilitate reproduction. The ovum, or egg cell, is the female gamete. It is a single cell containing a nucleus and cytoplasm. Once released from the ovary during ovulation, the ovum can be fertilized by sperm if sexual intercourse occurs around the same time.
Female Reproductive Organs
The female reproductive system consists of the following organs and structures:
Ovaries: A pair of ovaries are located in the lower abdomen on either side of the uterus. They are the primary female reproductive organs and are responsible for producing female gametes called ova (eggs). Ovaries also secrete the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, which play crucial roles in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts): There are two fallopian tubes, one on each side, that extend from near the ovaries to the upper part of the uterus. These tubes serve as a pathway for the ova to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. fertilisation of the egg by sperm usually occurs in the fallopian tubes.
Uterus: The uterus, commonly known as the womb, is a hollow, muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity. It provides the environment for the developing embryo or fetus during pregnancy. If fertilisation occurs, the fertilised egg (zygote) implants itself into the lining of the uterus and begins to grow into a baby. If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining is shed.
III. Fertilisation and Development of the Embryo
Fertilisation is the process of fusing the male and female gametes (sperm and egg) to form a zygote, which is the first cell of the new organism. Here's a summary of the subsequent events:
Fusion of Nuclei: During fertilisation, the nuclei of the sperm and egg come together, combining their genetic material to form a single nucleus in the zygote.
Cell Division: After fertilisation, the zygote undergoes multiple rounds of cell division through a process called mitosis. These divisions produce a cluster of cells, which eventually forms an embryo.
Embryo Development: As cell division continues, the embryo starts taking shape, and its cells differentiate into different types to form the basis of various tissues and organs.
Implantation: The developing embryo, now called a blastocyst, travels down the fallopian tube and reaches the uterus. It attaches itself to the uterine wall and starts embedding itself in the uterine lining through a process called implantation.
Growth and Development: Once implanted, the embryo continues to grow and develop inside the uterus. It receives nourishment and oxygen from the mother's bloodstream through the placenta, a structure that develops from the tissues of both the embryo and the mother.
Foetus Formation: At a certain stage of development, typically around the eighth week after fertilisation, the embryo is recognizable as a human, and it is then termed a foetus. During this foetal stage, all major organs and body systems form, and the foetus goes through various growth phases.
Birth: After a gestation period of around nine months, the fetus is fully developed and ready for birth. The process of childbirth, also known as delivery, occurs when the fetus passes through the birth canal (vagina) and is born into the world.
Types of Fertilisation
Fertilisation can be classified into two main types based on where it takes place: internal and external fertilisation.
|
|
|
| In internal fertilisation, the fusion of male and female gametes occurs inside the body of the female. | In external fertilisation, the fusion of male and female gametes occurs outside the body of the female, typically in water. |
| This process is common in most terrestrial animals, including mammals like cows, humans, and dogs. | This method is common among many aquatic animals, especially fish and amphibians like frogs. |
| During internal fertilisation, the male delivers the sperm directly into the female's reproductive tract, where it meets the egg. This ensures that the sperm is protected and has a higher chance of reaching the egg for fertilisation. | During external fertilisation, both the eggs and sperm are released into the surrounding water, where fertilisation takes place. However, this method poses some challenges as the gametes need to meet and fuse in the water, and many eggs may go unfertilised. |
Viviparous, oviparous, and ovoviviparous are terms used to classify animals based on their method of giving birth or reproduction. They refer to how the offspring are developed and born.
Viviparous Animals
a) Viviparous animals are those that give birth to live young ones. b) In this reproductive strategy, the embryo develops and grows inside the mother's body, receiving nourishment directly from her through a specialized placenta or other means. c) When the offspring have completed their development, they are born as live and fully-formed individuals. d) The term "viviparous" comes from Latin and means "to give live birth." e) Examples of viviparous animals:
- Most mammals, including humans, dogs, cats, elephants, and whales.
- Some reptiles, such as certain species of snakes and lizards.
- Certain fish, such as some sharks and rays.
Oviparous Animals
a) Oviparous animals are those that lay eggs as part of their reproductive process. The embryo develops and grows within the protective environment of the egg outside the mother's body. The egg contains all the necessary nutrients and materials needed for the embryo's development. After a period of incubation, the egg hatches, and the young offspring emerge. b) Examples of oviparous animals:
- Birds are classic examples of oviparous animals, laying eggs in nests or suitable locations.
- Many reptiles, including snakes, lizards, turtles, and crocodiles, lay eggs.
- Amphibians, such as frogs, toads, and salamanders, typically lay eggs in water or damp environments.
Ovoviviparous Animals
a) There are also ovoviviparous animals, which produce eggs that are retained and hatch within the mother's body. b) These animals give birth to live young, similar to viviparous species, but the live young result from hatched eggs inside the mother rather than direct internal development. c) Great white sharks, rattlesnakes, and sea horses are a few examples of ovoviviparous animals.
| Explore more about |
The journey from young ones to adults is a process known as growth and development. It is a fundamental aspect of the life cycle of most organisms, including animals. Throughout this process, individuals undergo significant changes in their physical structure, behaviour, and reproductive capabilities. Below are some examples that illustrate this remarkable transformation.
Life Cycle of a Frog
In the life cycle of certain animals like frogs, there are distinct stages of growth and development, starting from the egg to the adult stage. In the case of frogs, the life cycle consists of three main stages: egg, tadpole (larva), and adult.
Egg: The life cycle begins with the laying of eggs by adult female frogs in water bodies like ponds or lakes. The eggs are usually laid in clusters and are protected by a jelly-like substance.
Tadpole (Larva): Once the eggs hatch, they give rise to tadpoles, which look very different from adult frogs. Tadpoles are aquatic, have long tails, and breathe through gills. During this stage, tadpoles feed on algae and other aquatic plants.
Adult: As the tadpoles grow and undergo a process called metamorphosis, they gradually transform into adult frogs. Metamorphosis is a series of drastic changes in the body structure and function, leading to the development of legs, lungs, and a more suitable body form for terrestrial life. Eventually, the tadpoles develop into fully-formed frogs capable of jumping and swimming on land.
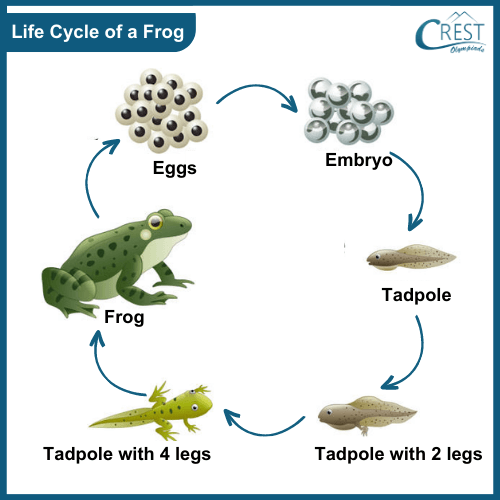
Life Cycle of Insects
Insects, a diverse group of animals, also undergo remarkable transformations during their life cycle. This process is known as metamorphosis and can take two primary forms: incomplete metamorphosis and complete metamorphosis.
Incomplete Metamorphosis: In insects such as grasshoppers and cockroaches, the life cycle includes three stages – egg, nymph, and adult. Nymphs resemble miniature adults but lack certain mature features. As they grow, nymphs moult several times, each time resembling the adult form more closely. Eventually, they reach full maturity.
Complete Metamorphosis: Many insects, like butterflies and beetles, undergo complete metamorphosis with four distinct stages – egg, larva (caterpillar or grub), pupa (cocoon or chrysalis), and adult. The larval stage is markedly different from the adult and serves for feeding and growth. The pupal stage involves a transformation within a protective case, leading to the emergence of the adult insect with wings and reproductive capabilities.
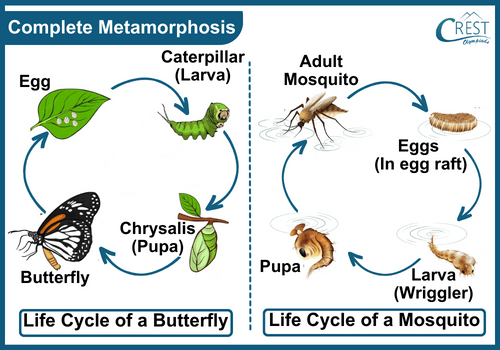
Life Cycle of Humans
In contrast, human beings do not undergo the same type of metamorphosis as frogs or insects. Humans have a relatively gradual growth and development process, and their body parts, such as limbs and vital organs, are present from birth. Human growth involves a combination of cell division, tissue differentiation, and hormonal changes that lead to the development of various body systems over time.
While there are no drastic transformations like metamorphosis in humans, the process of growth and development is still critical for reaching adulthood and achieving the full potential of an individual's physical and mental capabilities. The human life cycle involves stages such as infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood, each marked by specific milestones and changes in physical appearance, behaviour, and cognitive abilities.

In this section, you will find interesting and well-explained topic-wise video summary of the topic, perfect for quick revision before your Olympiad exams.

>> Join CREST Olympiads WhatsApp Channel for latest updates.
This is Curio, your AI Doubt Solver. Here to help you with any educational doubts you encounter while preparing for your Olympiad exams. Feel free to ask questions and learn!

Share Your Feedback
CREST Olympiads has launched this initiative to provide free reading and practice material. In order to make this content more useful, we solicit your feedback.
Do share improvements at [email protected]. Please mention the URL of the page and topic name with improvements needed. You may include screenshots, URLs of other sites, etc. which can help our Subject Experts to understand your suggestions easily.
Other Science Related Topics for Class 8
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Combustion and Flame
- Coal and Petroleum
- Metals and Non-metals
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Micro-organisms
- Crop Production and Management
- Force and Pressure
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Some Natural Phenomena
- Stars and Solar System
- Pollution of Air and Water
Other Subjects for Class 8
- Maths Reading Material for Class 8
- English Reading Material for Class 8

Register For CREST Olympiads
Important Questions for Class 8 Science - Reproduction in Animals
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Q1: What are the two modes of reproduction in animals, and how do they differ from each other? Ans: The two modes of reproduction in animals are sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, while asexual reproduction only involves a single parent. Q2: Explain the male reproductive organs in humans, and what is their role in reproduction? Ans: Male reproductive organs in humans include testes, sperm ducts, and the penis. Testes produce sperm, which are male gametes. The sperm's role is to fertilize the female egg during sexual reproduction. Q3: Describe the female reproductive organs in humans and their functions. Ans: Female reproductive organs in humans consist of ovaries, oviducts (fallopian tubes), and the uterus. Ovaries produce eggs (ova). The oviducts transport the egg to the uterus, where fertilization can occur. The uterus is where the embryo develops during pregnancy. Q4: What is fertilization, and how does it occur in humans? Ans: Fertilization is the fusion of a sperm cell from a male with an egg cell from a female. In humans, fertilization takes place in the oviduct when a sperm cell meets an egg cell. Q5: Explain the difference between internal and external fertilization with examples. Ans: Internal fertilization occurs inside the female's body, as in humans and some other animals like dogs and cows. External fertilization occurs outside the female's body, often in water, as in frogs and fish. Q6: What is the significance of producing a large number of eggs and sperm in animals that undergo external fertilization? Ans: Producing a large number of eggs and sperm increases the chances of successful fertilization because many eggs and sperm may not survive due to exposure to external factors like water movement or predation. Q7: How does the zygote develop into an embryo in animals? Ans: The zygote undergoes repeated cell divisions to form a ball of cells, which eventually differentiate into different tissues and organs. This developing structure is called an embryo. Q8: What is metamorphosis, and provide an example of an animal that undergoes metamorphosis. Ans: Metamorphosis is a process in which an animal undergoes drastic changes in its body structure during its life cycle. Frogs are an example; they start as eggs, then become tadpoles (larvae), and finally develop into adult frogs. Q9: Differentiate between viviparous and oviparous animals, and provide examples of each. Ans: Viviparous animals give birth to live young ones, while oviparous animals lay eggs. Examples of viviparous animals include humans and dogs, while examples of oviparous animals include birds and reptiles. Q10: How does asexual reproduction differ from sexual reproduction, and what are the methods of asexual reproduction mentioned in the chapter? Ans: Asexual reproduction involves a single parent and does not involve the fusion of gametes. Methods of asexual reproduction mentioned in the chapter include budding (as seen in hydra) and binary fission (as seen in amoeba). Q11: Explain the process of budding in hydra and its significance. Ans: Budding in hydra involves the development of new individuals as outgrowths from a single parent. This allows hydra to reproduce asexually and increase its population rapidly. Q12: Describe the process of binary fission in amoeba and its significance. Ans: Binary fission in amoeba begins with the division of the nucleus, followed by the division of the body into two, resulting in two new amoebae. This method allows amoeba to reproduce asexually and increase its numbers. Q13: Why is it important for animals to reproduce, and what role does reproduction play in the continuation of a species? Ans: Reproduction is crucial for the continuation of a species as it ensures the production of new individuals that carry the genetic information of the species. Without reproduction, a species would become extinct. Q14: How do the reproductive organs in male and female animals contribute to sexual reproduction? Ans: Male reproductive organs produce gametes (sperm), while female reproductive organs produce gametes (eggs) and provide a suitable environment for fertilization and embryo development. Q15: Can you provide examples of animals that reproduce asexually other than those mentioned in the chapter, and explain the method they use for asexual reproduction? Ans: Students may research and provide examples of other animals that reproduce asexually, such as starfish (regeneration) or planarians (fission). They should explain the specific methods these animals use for asexual reproduction.
| |273 docs|44 tests |
Top Courses for Class 8
FAQs on Important Questions for Class 8 Science - Reproduction in Animals
| 1. How do animals reproduce? |
| 2. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction in animals? |
| 3. How do animals mate? |
| 4. What is internal fertilization? |
| 5. How do animals reproduce without a mate? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
past year papers
Objective type questions, sample paper, important questions, semester notes, shortcuts and tricks, mock tests for examination, viva questions, study material, video lectures, extra questions, practice quizzes, previous year questions with solutions.

Important Questions: Reproduction in Animals Free PDF Download
Importance of important questions: reproduction in animals, important questions: reproduction in animals notes, important questions: reproduction in animals class 8, study important questions: reproduction in animals on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
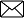
Forgot Password
Change country.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9
Home » CBSE » Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9 – Reproduction in Animals
Science Chapter 9 of Class 8 is about reproduction in animals. This chapter is about learning the different modes of reproduction, like sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. In the sexual reproduction part, the students will learn about the male reproductive organs, female reproductive organs, and fertilisation. In the asexual reproduction part, the students will learn about budding and binary fission.
Quick Links
Extramarks is one of the best and the most trusted online platforms for students to get comprehensive NCERT based study solutions. Teachers and students across the country use our study materials because they have complete faith in Extramarks. To enjoy the maximum benefit of these resources, students just need to register themselves at Extramarks’ official website and stay ahead of the competition.
Our Science subject experts understand the importance of frequently solving questions to gain a better understanding of different Science chapters. Our team has carefully chosen questions from different sources including NCERT textbook, NCERT exemplars, past year question papers, and other reference books. Students can refer to our question bank of Chapter 9 Class 8 Science Important Questions to get access to these questions and their answers.
For each question, there is a step-by-step self-explainable answer that helps students to revise the chapter concepts. The question bank of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9 is accessible to students after registering on our website.
Apart from the questions and answers, students can find a lot of additional study resources on our website including NCERT chapter-wise solutions, CBSE revision notes, previous year test questions, etc.
Get Access to CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions 2022-23 with Chapter-Wise Solutions
You can also find CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter-by-Chapter Important Questions here:
| 1 | Chapter 1 | |
| 2 | Chapter 2 | |
| 3 | Chapter 3 | |
| 4 | Chapter 4 | |
| 5 | Chapter 5 | |
| 6 | Chapter 6 | |
| 7 | Chapter 7 | |
| 8 | Chapter 8 | |
| 9 | Chapter 9 | Reproduction in Animals |
| 10 | Chapter 10 | |
| 11 | Chapter 11 | |
| 12 | Chapter 12 | |
| 13 | Chapter 13 | |
| 14 | Chapter 14 | |
| 15 | Chapter 15 | |
| 16 | Chapter 16 | |
| 17 | Chapter 17 | |
| 18 | Chapter 18 | |
Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9 – With Solutions
By referring to Extramarks chapter-wise notes students will gain good knowledge about the chapter. After completing the NCERT textbook students can start solving questions from our question bank of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9 .
We at Extramarks take our role seriously to provide the best resources to the students and help them get excellent grades. The question bank has a variety of question formats including MCQs, short answers, long answers, etc. They represent exam-pattern questions and help students to be more confident while answering the actual exam questions.
Given below are a set of few questions and their answers from our question bank of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9. Students after solving these questions will also get to revise the entire chapter.
Question 1. Sets of reproductive terms are given below. Choose the set that has an incorrect combination.
- sperm, testis, sperm duct, penis
- menstruation, egg, oviduct, uterus
- sperm, oviduct, egg, uterus
- ovulation, egg, oviduct, uterus
- C) Sperm → oviduct, egg → uterus
Reproduction is a process in which organisms make more organisms similar to themselves. Millions of these sperm are in this small amount of semen, and they swim up from the vagina through the cervix following the uterus to meet the egg present in the fallopian tube. It takes sperm to fertilise the egg.
- Around 5 to 6 days after the sperm fertilises the egg, the fertilised egg becomes a multicelled blastocyst.
- A blastocyst is the size of a pinhead, a hollow ball of cells with fluid inside. The blastocyst burrows itself into the uterus lining, called the endometrium.
- The oestrogen hormone causes the endometrium to become thick and rich in blood.
- Progesterone hormone, released by each of the ovaries, keeps the endometrium thick with blood through which the blastocyst may attach to the uterus and absorb nutrients.
- This process is called implantation.
Question 2. Explain the embryo’s future development after it gets embedded in the uterus.
The developing embryo gets embedded in the uterus wall for further development. The embryo continues to develop inside the uterus. It eventually develops body parts such as hands, legs, eyes, head, ears etc. The stage of an embryo in which all the parts of the body can be identified is known as a foetus. When the development of the foetus is completed, the mother gives birth to the baby.
Question 3. How is reproduction in hydra different from that in Amoeba?
Amoeba is a unicellular organism that can change its shape. It is generally found in water bodies like ponds, lakes and slow-moving rivers.
Binary fission in Amoeba
- Initially, the pseudopodia are retrieved. The body of an amoeba is coiled and becomes round.
- Amitosis is observed, and the nucleus’s division occurs, followed by the cytoplasm’s splitting.
- Constriction starts to develop at the point of fission in the amoeba body.
- The furrow or constriction turns deeper, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
Budding in Hydra
- Hydra is a freshwater organism, having different species.
- Hydra uses regenerative cells for reproduction, where a bud expands as an outgrowth because of repeated cell division at one specific location.
- These buds then develop into new small individuals who, when completely matured, detach from the parent body.
Question 4. Define asexual reproduction. Explain one method of asexual reproduction in animals.
The continuity of generation in society is a common process. Everyone wants to see the next generation. This process is termed reproduction. The process through which organisms give birth to young, new organisms of the same kind is known as reproduction. There are two main types of reproduction. Sexual and asexual are two types of reproduction. This article will read about asexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction is the mode of reproduction involved in producing offspring by a single parent. Asexual reproduction is the mode of reproduction in which a single parent produces new offspring. The new individuals produced are physically and genetically identical to each other.
The following are the important features of asexual reproduction:
- A single parent is involved.
- This process of reproduction occurs in a short time.
- No fertilisation or gamete formation takes place.
- The offspring is genetically similar.
- The organisms multiply and grow rapidly.
Types of asexual reproduction
There are various types of asexual reproduction:
- Binary Fission
- Fragmentation
- Vegetative Propagation
- Sporogenesis
Binary fission
The term “fission” indicates “to divide”. Through binary fission, the parent cell gets divided into two cells. The cell division patterns vary in various organisms, i.e., some are directional while others are non-directional.
Example: Amoeba and euglena show binary fission.
It is one of the most simplest and uncomplicated methods of asexual reproduction. The parent cell gets divided into two, each daughter cell containing a nucleus of its own that is genetically identical to its parent. The cytoplasm also takes part in division, leading to two equal-sized genetically identical daughter cells. The process repeats itself, and these daughter cells grow and further divide.
Question 5. The hen is odd in the list of animals given below. (human beings, cows, dogs, hens). The reason for it is
- it undergoes internal fertilisation.
- It is oviparous.
- It is viviparous.
- It undergoes external fertilisation.
- B) It is oviparous
Here, the hen is the odd one out because it is oviparous, i.e. it lays an egg from which young ones are hatched later. Viviparous animals undergo internal fertilisation, and the embryo develops inside the mother until a young one is born. The ovoviviparous animals produce eggs, but the eggs develop inside the mother, and a live organism is born. However, unlike viviparous animals, ovoviviparous animals do not have a placenta. Ovoviviparous animals are born alive.
- Examples of oviparous are birds and reptiles.
- Examples of viviparous species are snakes and sharks.
Question 6. Although two cells called gametes fuse, the product formed is a single cell called the zygote. Justify.
During the process of fertilisation, the sperm gets fused with the egg cell. The content of the sperm cell gets transferred into the egg to form the zygote. Hence, the product formed is a single-celled zygote. A zygote is the first diploid cell formed by the fusion of female and male gametes resulting in the formation of an embryo.
The zygote rapidly divides in the initial 12-24 hours of formation.
The cell mass forms a hollow ball during the process of blastulation.
Cells start differentiating and forming cavities.
The three germ layers form during gastrulation.
Formation of primitive streak is followed by notochord formation
Tubes get formed, making a neurula.
The notochord forms into the neural plate.
The neural plate folds to form a neural tube and crest.
The mesoderm gets divided into axial, paraxial, intermediate and lateral plate mesoderm, which gives rise to different organs.
Question 7. Why do only male gametes have a tail?
Male gametes or sperms are motile. The tail of the sperm helps the sperm swim through the female’s reproductive tract to reach the oviduct. The male gametes, i.e., sperms, are produced within the male reproductive system. Sperms are small unicellular structures with a head, middle piece, and tail.
- The tip of the sperm head is a portion called the acrosome that enables the sperm to penetrate the egg.
- The midpiece has the mitochondria that supply the energy the tail needs to move and swim.
- The tail moves in whip-like movements back and forth to propel the sperm toward the egg.
Question 8. How can we say that fish exhibit external fertilisation?
External fertilisation in fish:
- External fertilisation is the process where the fusion of male and female gametes occurs in the outside environment.
- The female fish lays its eggs in the surrounding water environment, and the male sperm travels towards the egg randomly in the water.
- The nucleus of sperm moves into the egg and fuses with it.
- Due to water as the external environment, the female eggs do not dry out in case of external fertilisation.
- Since fertilisation occurs in water, outside the female body, it is external fertilisation.
- Hence, we can say that fish exhibit external fertilisation.
Question 9. In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
The embryo gets embedded in the uterus of the female reproductive system. The female reproductive organ is where the embryo gets embedded in the uterus wall. It is here that the embryo continues its development.
Question 10. What is the uterus?
The uterus is a hollow muscular structure seen in the pelvic region of females between the rectum and the bladder. The uterus’s main function is to nourish the developing foetus until birth.
Over the gestation period which is 9 months in humans, the embryo develops its body parts such as hands, ears, eyes, nose, legs, etc. There is an embryonic stage wherein all body parts can be distinguished, and the embryo has then termed the foetus.
Question 11. Aquatic animals where fertilisation occurs in water are said to be:
- Viviparous without fertilisation.
- Oviparous with external fertilisation.
- Ovoviviparous with internal fertilisation.
- Oviparous with internal fertilisation.
- b) oviparous with external fertilisation.
Fertilisation that occurs on the outside of the body of an organism is known as external fertilisation. It normally requires a water body for successful fertilisation.
- It results in increased genetic variations.
- It produces a larger number of offspring.
- The gametes released can drift, making it easy to find mates.
The female releases its eggs in the water. The male also releases the sperm in the water for fertilising them. The larval life of frogs is in water, whereas the adult life is on land.
Question 12. The eggs of frogs do not have shells for protection, yet they are safe in the water. How?
Answer 12.
Frog’s eggs are present without any external covering or shell, but a layer of jelly holds the eggs together, thus providing them protection. This jelly or thick covering also protects them from drying up and prevents them from being eaten by other predators or animals.
- In a female frog, the pair of ovaries produce an ovum and pass it to the oviduct, which opens into the cloaca. The cloaca is a common pathway for the process of excretion and reproduction. At a time, 2500 to 3000 eggs are laid and fertilised externally.
Question 13. Hens and frogs are both oviparous exhibiting different types of fertilisation. Explain.
Hens are oviparous in nature, in which internal fertilisation takes place. The fertilised egg develops into an embryo inside the body. Frogs are oviparous, in which fertilisation and development of zygote to the embryo and young ones occur outside the body.
- Internal fertilisation occurs in hens. The fertilised egg is enclosed in a protective shell covering the hen’s body and is laid outside for development.
- In frogs, fertilisation and development of zygotes occur outside their body, that is, external fertilisation.
Question 14. The term metamorphosis is not used while describing human development. Why?
In human beings, the body parts of an adult are present from the time of birth. In the metamorphosis process, the parts of the adult are different from those at the time of birth. Metamorphosis does not occur in humans and other viviparous animals because their offspring are entirely formed inside their mother’s womb. They do not require any further differentiation of their body parts. However, the body parts grow and develop to reach maturity after birth.
Question 15. Explain the importance of reproduction in living organisms.
Reproduction is the process of producing or giving birth to an offspring. There are generally two forms of reproduction – Asexual and sexual reproduction.
Here are some points highlighting the importance of reproducing in living organisms:
- It’s very critical for any species to reproduce to continue their species. Else that species would become extinct.
- Reproduction plays a crucial role in organisms evolution as it creates small variations via genetic recombinations over generations.
- Having a healthy balance is very important for any ecosystem. Reproduction helps to increase the number of species ensuring a good ecosystem balance.
Question 16. Which of the following statements about reproduction in humans is correct?
- Fertilisation takes place externally.
- Fertilisation takes place in the testes.
- During fertilisation, the egg moves towards the sperm.
- Fertilisation takes place in the human female.
- D) Fertilisation takes place in the human female (oviduct).
The female reproductive system is framed in such a way to perform different functions. It makes egg cells that are essential for reproduction, called ova. The system is organised for delivering the ova to the region of fertilisation. The egg fertilisation takes place in the fallopian tubes along with the sperm. Implanting in the uterus’s walls and initiating the pregnancy stages is the next step for fertilised eggs. Once sperm enter the vagina, they can move through the cervix, into the uterus, and to the end of a fallopian tube. If sperm can fuse with an egg, fertilisation takes place.
Question 17. A mother gives birth to a baby, but the baby has the characteristics of both parents. How is this possible?
Though the mother gives rise to a baby, fertilisation involves the fusion of gametes from both parents. Hence, the character is obtained by both parents. The zygote, therefore, has both father’s and mother’s contributions. Since the zygote develops into the baby, it has the characteristics of both parents.
- The term used for describing the fusion of the female and male gametes is fertilisation.
- Fertilisation can also be described as the fusion of the male gametes with the female gametes to form a diploid zygote.
- It is a process that occurs after the process of pollination of the carpel. The complete sequence of the process takes place in the zygote to develop into a seed.
Question 18. In markets, birds’ eggs are available but never dogs’ eggs. Why?
Dogs are viviparous. Dogs do not lay eggs, and it gives birth to puppies. Hence, dog eggs are not available in the market. Birds lay their eggs, Birds are oviparous, hence, their eggs are easily available in the market,
- Oviparity refers to a mode of reproduction in which animals lay eggs. These eggs are released into the external environment. Thus, these embryos develop on the outside of the mother’s body. Here, egg yolk nourishes the developing embryo.
- Viviparity refers to the mode of reproduction through which animals directly give birth to their young ones. Therefore, viviparous animals give birth to their young ones without laying eggs. Fertilisation takes place internally inside the female organism.
Question 19. What is metamorphosis? Give examples.
In many living species, the young one or the offspring does not resemble the adult. This is known as indirect development and such a young one is known as a larva or nymph. The process of changing from a nymph or larva to an adult body is known as metamorphosis. This transformation of a larva or nymph into an adult is characterised by a series of morphological, behavioural and physiological changes.
Examples include frogs, butterflies, etc.
- State two differences between a zygote and a foetus.
- It is the earliest stage of development
- It is a single cell
- It is formed by the fusion of male and female gametes
- The zygote usually lasts a week and then develops into its next stage.
- The zygote gets divided several times to form an embryo
- It is the last developmental stage of an organism
- The embryo stage shows all a mature organism’s main recognizable body parts.
- The foetus stage usually occurs after the embryo stage.
- Foetus mainly undergoes internal development.
Question 20. Differentiate between internal fertilisation and external fertilisation.
Fertilisation is generally defined as the fusion of a male and a female gamete.
Internal fertilisation occurs inside the female body.
There are higher chances of survival of the offspring.
Internal fertilisation protects fertilised eggs or embryos from harsh environments.
Examples are cows, humans, dogs, monkeys, etc.
External fertilisation
It occurs on the outside of the female body.
There are low chances of survival of the offspring.
Most aquatic animals use this type of fertilisation, and the advantage of external fertilisation is that it produces many offspring due to external hazards. Examples are fish, frogs, organisms etc.
Question 21. Reproduction by budding takes place in
- paramecium
Reproduction in all the given organisms takes place through asexual methods. Hydra reproduces by forming buds on its body surface, which develops into a new organism. Amoeba, paramecium and bacteria multiply by dividing themselves into two parts, i.e. by binary fission method. Budding is an asexual mode of producing new organisms. In this process, an organism is developed from a small part of the parent’s body.
Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9
Students must first read through the entire chapter to understand the new themes presented in the chapter. It also helps to identify the crucial concepts necessary from an examination point of view.
Regularly solving questions will further enhance the exam preparation for any student. Students can rely on Extramarks question bank of Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Important Questions to get a full set of questions from different sources at one place. The question bank comes with simplified and clear answers to each question. The list of questionnaires cover the entire chapter. All the questions covered in our question bank are quite important and expected in the exams.
At Extramarks, we understand the importance of solving important questions and we take our role seriously to provide the best resource to the students and help them excel in life. Given below are a few benefits of solving Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9:
- Students will receive a fair idea about the important topics they must study for their examinations. By solving these questions they would be able to understand their weak areas. Based on it they can properly revise these areas and become stronger with overall concepts of the chapter.
- Due to the written practice while solving questions, students will understand how to frame answers according to the question and will be able to handle tricky questions with ease . Also the solutions are given by our expert faculty members, so by referring to these answers students will be able to learn how to prepare exam specific answers.This encourages the students to master the topic and increases their confidence in achieving a high grade
- The questions and answers are based on the latest CBSE syllabus and as per CBSE guidelines. So students can rely on them completely. . So we recommend students to refer to our Science Class 8 Chapter 9 Important Questions during their exams and come out with flying colours. .
Extramarks leaves no stone unturned when it comes to providing the best learning material with unmatchable speed and accuracy for students irrespective of the class and subject. We have all the answers to your queries. Besides important questions and solutions, students can access an abundance of other study materials on our website. Few of these links are given below:
- NCERT books
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity while molten sodium chloride conducts. Explain why?
Marks: 2 Ans
Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity because the particles (ions) are held together by strong forces of electrostatic attraction. In molten state the ions become free and move to conduct electricity, since on heating the bonds between ions become weak.
Q.2 Why is an acid or an ionic salt added to water in the electrolysis of water?
Pure water or distilled water is a bad conductor of electricity whereas acids and bases are good conductors of electricity. When an acid or ionic salts are dissolved in distilled water then the resulting solution conducts electricity.
Q.3 Define electrolysis.
Marks: 1 Ans
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 8 science important questions, chapter 1 - crop production and management.

Chapter 2 - Microorganisms : Friend and Foe
Chapter 3 - synthetic fibres and plastics, chapter 4 - materials : metals and non-metals, chapter 5 - coal and petroleum, chapter 6 - combustion and flame, chapter 7 - conservation of plants and animals, chapter 8 - cell - structure and functions, chapter 10 - reaching the age of adolescence, chapter 11 - force and pressure, chapter 12 - friction, chapter 13 - sound, chapter 14 - chemical effects of electric current, chapter 15 - some natural phenomena, chapter 16 - light, chapter 17 - stars and the solar system, chapter 18 - pollution of air and water, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. apart from the ncert textbook, where can i find good study resources for class 8 science.
You can find the important study materials for Class 8 Science on the Extramarks official website. Our study materials cover all important topics from sources like NCERT textbooks, NCERT exemplar and other reference sources related to the CBSE curriculum. You can build your confidence and improve your scores by practising and revising from our study resources. The important questions and their solutions will help you to clarify your concepts which will come handy while answering difficult questions in the exams..
Extramarks credibility lies in providing reliable and trusted study material for all Classes from 1 to 12. To enjoy the maximum benefit of these resources, students just need to register themselves at Extramarks official website and stay ahead of the competition.
2. How many chapters are there in CBSE Class 8 Science syllabus?
Many important chapters that form the base of Class 9 and Class 10 Science are covered in CBSE Class 8 Science syllabus. Here is a complete list of these eighteen chapters:
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System
Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 - Reproduction in Animals
- NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 6 Reproduction In Animals

NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 Reproduction in Animals Class 8 - FREE PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 delves into the fascinating world of how animals reproduce. From tiny insects to large mammals, reproduction is essential for species' survival. This Chapter explores the various methods animals use to reproduce, from simple processes like budding and fission to more complex ones like sexual reproduction. Through easy-to-understand explanations and examples, Class 8 Reproduction In Animals helps students learn about the different reproductive organs and cycles in animals. Class 8 Science Chapter 6 PDF helps students thoroughly understand the main concepts presented in the curriculum.

Download the FREE PDF of Reproduction In Animals Class 8 Questions And Answers These NCERT Solutions are prepared by the Vedantu Experts and are updated according to the Class 8 Science syllabus . Start with Vedantu to pursue a path of academic excellence!
Quick Insights for NCERT Class 8 Science Reproduction in Animals Question Answer
Class 8 Science Reproduction In Animals covers various reproductive methods observed in the animal kingdom, including asexual and sexual reproduction.
Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Question Answer helps students learn about the structural adaptations of different animals for reproduction, such as the reproductive organs and their functions.
Through examples and diagrams, learners gain insights into the lifecycle of various animals.
Reproduction In Animals Class 8 PDF delves into the process of sexual reproduction, explaining the roles of male and female reproductive organs and fertilisation.
The concepts covered in this chapter are crucial for academic learning and offer insights into real-world phenomena and the diversity of life on Earth.
By engaging with NCERT Solutions for Reproduction In Animals Class 8, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the mechanisms through which life is sustained and propagated in the animal world.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 – Reproduction in Animals
1. Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
Ans: Importance of reproduction:
Human reproduction is essential for the continuance of the human species.
It is the process of producing new individuals from the living organisms.
Reproduction ensures the passage of traits and habitats from generation to generation.
Without reproduction the species will be vanished from the earth and there is no world without species.
2. Describe the process of fertilization in human beings.
Ans: Process of fertilization in human beings:
Human reproduction is brought about by formation and fusion of the male and female gametes. The male gametes, i.e. the sperms are produced by the testis and the female gametes, i.e. the ovum is produced by the ovary.
During copulation, the male releases sperm into the female reproductive tract. Since the sperm is a motile gamete, it will swim up the female reproductive tract to reach the ovum in the fallopian tube.
The process of fertilization happens when the male and female gametes fuse together in the fallopian tube. The end product of fertilization is called a zygote, which will develop further and become a foetus in the womb.
3. Choose the most appropriate answer.
a. Internal fertilisation occurs
In the female body.
Outside female body.
In male body.
Outside male body
Ans:
I. In a female body
Internal fertilization takes place inside the female body and external fertilization takes place outside the female body.
b. A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of
Fertilisation.
Metamorphosis
Embedding
Budding
Ans: (II) Metamorphosis
Fertilization takes place in human beings by the fusion of gametes and budding is a type of asexual reproduction takes place in parents in forming the buds.
c. The number of nuclei present in a zygote is
Ans: (II) one
Only one nuclei is present in a zygote.
4. Indicate whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F).
Oviparous animals give birth to young one.
Oviparous animals lay eggs and the young ones develop inside it.
Each sperm is a single cell.
Ans: T
External fertilisation takes place in frogs.
A new human individual develops from a cell called gamete.
Egg laid after fertilisation is made up of a single cell.
Amoeba reproduces by budding.
Amoeba reproduces asexually through binary fission.
Fertilisation is necessary even in asexual reproduction.
Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction.
A zygote is formed as a result of fertilisation.
An embryo is made up of a single cell.
Embryo is a multicellular structure.
4. Give two differences between a zygote and Foetus.
Ans: Difference between zygote and foetus:
Zygote | Foetus |
Zygote is the single cell resulting from fusion of ovum and sperm. | Foetus is the much-developed form of zygote which has body parts and body organs. |
It is generally observed in the fallopian tube of the female | The foetus is a much-developed version of a baby present in the uterus. |
5. Define asexual reproduction. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
Ans: Asexual Reproduction:
It is a mode of reproduction that does not entails the union of sex cells or gametes.
There are different types of asexual reproduction, they are binary fission, budding vegetative propagation, spore formation, fragmentation. There is no gamete formation in this type of reproduction. Animals like Hydra, Amoeba undergo asexual mode of reproduction.
Two types of Asexual reproduction are:
Budding: It is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. These buds develop into tiny individuals and when fully they mature and detach from the parets body and become a new independent individual. Example: Hydra.
Binary Fission: In this type of asexual reproduction the body of the organism mainly unicellular organism divides into two. Each of the two daughter cells are alike. Example: Amoeba.
6. In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
Ans: The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development.
7. What is metamorphosis? Give examples.
Ans: Metamorphosis:
It means sudden change which happens while developing.
The animals that undergoes metamorphosis are
Butterfly (egg🡪larva🡪pupa🡪adult)
Frog (egg🡪tadpole🡪adult)
8. Difference between internal fertilisation and external fertilisation.
Ans: Difference between internal fertilization and external fertilization:
Internal Fertilisation | External Fertilisation |
The fertilisation takes place inside the female body. Union of male and female gametes occur in the female body after copulation. Example- human beings, reptiles, birds. | The fertilisation takes place outside the body of the female. Union of male and female gametes occur outside the female body. Example- frog, fish and some of the algae etc. |
9. Complete the crossword puzzle using the hints given below. Across
1. The process of the fusion of the zygotes.
6. The type of fertilisation in hen.
7. Term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here.
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for the fertilized egg.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission in amoeba.

1. The process of the fusion of the zygotes - FERTILIZATION
6. The type of fertilisation in hen - INTERNAL
7. Term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of hydra - BUDS
8. Eggs are produced here - OVARY
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs - TESTES
3. Another term for the fertilized egg - ZYGOTE
4. These animals lay eggs - OVIPAROUS
5. A type of fission in amoeba – BINARY

NCERT Class 8 Reproduction in Animals- Quick Overview of Detailed Structure of Topics
S. No | Topics of Reproduction in Animals Class 8 | |
1. | Modes of Reproduction | |
2. | Sexual Reproduction | |
3. | Asexual Reproduction | |
Important Points from Class 8 Science Chapter 6 PDF
Types of Reproduction:
Asexual Reproduction: Involves one parent; offspring are genetically identical to the parent. Methods include budding, fission, regeneration, and fragmentation.
Sexual Reproduction: Involves the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg) to form a zygote, leading to genetic variation.
Male Reproductive System:
Organs: Testes, vas deferens, penis.
Function: Testes produce sperm, which is transported through the vas deferens and released through the penis.
Female Reproductive System:
Organs: Ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina.
Function: Ovaries produce eggs; fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tubes, and the fertilised egg implants in the uterus.
Fertilisation:
Process: Sperm fuses with an egg to form a zygote, usually in the female reproductive tract.
Viviparous Animals:
Give birth to live young.
Examples: Humans, dogs, whales.
Oviparous Animals:
Lay eggs that hatch into offspring.
Examples: Birds, reptiles, amphibians, and most fish.
Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Question Answer
Vedantu’s Class 8 Science Reproduction In Animals Question Answer comprehensively explains each topic in Chapter 6, ensuring a thorough understanding of animal reproduction concepts.
Reproduction In Animals Class 8 PDF follows a structured approach, breaking down complex topics like types of reproduction.
The topics like the reproductive systems of animals, fertilisation, and life cycle into small sections, making it easier for students to grasp the content.
Concepts are explained in a clear and simple language, making it accessible for students of all learning levels.
Class 8 Science Reproduction In Animals includes diagrams, illustrations, and charts to help visual learners understand complex concepts more easily.
Class 8 Reproduction In Animals Question Answer helps students learn about the structural adaptations of different animals for reproduction, such as the reproductive organs and their functions.
Vedantu offers supplementary resources such as video lectures, quizzes, and study materials to complement the chapter solutions, providing a holistic learning experience.
Important Study Materials for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 - Reproduction in Animals
S. No | Study Material Links for Class 8 Science Chapter 6- Reproduction in Animals |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6: Reproduction in Animals is an excellent resource for understanding key concepts like modes of reproduction, fertilisation, and development of embryos. Students should focus on these areas to grasp the essentials of animal reproduction. The solutions simplify complex topics, making them easy to understand and apply. Additionally, practice is crucial as the previous year's question papers often include around 10 questions from this chapter. By studying these solutions, students can confidently prepare for exams and improve their understanding of the subject.
Links for Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
S. No | NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter-wise List |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
12 |
|
Other Important Links for Class 8 Science
S. No | Important Resources for Class 8 Science |
1. |
|
3. |
|
4. |
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 - Reproduction in Animals
1. Explain the difference between a Zygote and a Foetus?
The difference between a zygote and a foetus is
Zygote– Zygote is the first stage of development. It is developed by the fusion of male and female gametes. It is a single cell. The zygote is divided to form an embryo. It lasts for a few weeks and then develops into the next stage.
Foetus– Foetus is the last stage of the development of an organism. Foetus usually undergoes an internal development. The stage of an embryo that shows all the main body parts of a mature organism.
2. Explain two methods of Asexual reproduction in animals?
The two modes of asexual reproduction are:
Binary Fission in Amoeba– It is asexual reproduction in which one cell is divided into two equal parts. It is a unicellular organism that consists of a cell membrane, cell wall and cytoplasm. In this process, the nucleus of amoeba is first divided into two parts to form daughter nuclei.
Budding in Hydra– Organisms like hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction by the process of budding. The first step in this process is the formation of buds and then it develops as a small outgrowth on the parent’s body. As the bud develops, it receives the characteristics of the parent organism.
3. List out the important topics covered in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 8 Science?
The following topics have been covered in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 8 Science:
Modes of Reproduction (Sexual and Asexual)
Male and Female Reproductive Organs
Fertilization
Development of an Embryo
Viviparous and Oviparous animals
Asexual Reproduction (Budding and Binary Fission)
With the help of NCERT Solutions, you will learn all about these concepts so that acing your exams becomes a cakewalk.
4. What is the advantage of using the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 8 Science provided by Vedantu?
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 8 Science provided by Vedantu are the best choice to understand the Chapter ‘Reproduction in Animals’. The experts curate these solutions at Vedantu to provide the most accurate, high-quality answers to clarify all their doubts and answer the questions in the exams with ease. Solutions at Vedantu are curated by experts and are available free of cost.
5. What is Reproduction? Why is Reproduction an important topic of Chapter 6 of Class 8 Science?
Reproduction is the procedure through which a living organism produces more of its kind. Reproduction helps to continue their generation. It is important to study and understand in Class 8 that if there is no reproduction, no living thing can continue to survive. To understand the concepts related to Reproduction and its importance, you must know the basic points as included in the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 8 Science by Vedantu. These are guaranteed to help you to clear your concepts easily and effectively.
6. What is reproduction in animals? Short answer.
Reproduction in animals is the process used by organisms to produce offspring like them. For a better idea of the concept of reproduction and how to write short answers on that topic, refer to NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 Reproduction in Animals of Class 8 Science at free of cost on the Vedantu website and on the Vedantu app. This will help you to understand the concepts easily and clearly. With the help of the NCERT solutions by Vedantu, you can write down the answers effectively for the exams.
7. What is fertilization, according to Chapter 6 of Class 8 NCERT?
The fusing of the male gamete with the female gamete to form a zygote with the process of sexual reproduction is referred to as fertilization.
Fertilization has been explained in depth in the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 8 Science by Vedantu. If you want to get a good grip of the topics and score well in the exam, it is advisable to download these solutions for quick reference.
8. Why is studying reproduction in animals in class 8 important?
Understanding animal reproduction is essential as it explains how species propagate and ensure their survival. It also helps in understanding the biological processes involved in the continuity of life and genetic variation.
Vedantu’s Class 8 Reproduction In Animals Question Answer offers step-by-step explanations for all the topics covered in the Chapter, helping students understand the process and logic behind each concept.
9. What are the key differences between viviparous and oviparous animals discussed in Reproduction In Animals Class 8 Questions and Answers?
Viviparous animals give birth to live young, and the embryo develops inside the mother's body. Oviparous animals lay eggs, and the embryo develops outside the mother's body within the egg.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Science Chapter 9
October 11, 2019 by Sastry CBSE
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1. What is reproduction? Answer: Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced from their parents.
Question 2. What is sexual reproduction? Answer: Reproduction which involves the fusion of male and female gametes is known as sexual reproduction.
Question 3. What is fertilisation? Answer: The fusion of ova and sperm is called fertilisation.
Question 4. What is a fertilised egg called? Answer: Zygote
Question 5. What is asexual reproduction? Answer: The mode of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved.
Question 6. Which mode of reproduction does take place in human beings? Answer: Sexual reproduction
Question 7. How many partners involve in sexual reproduction? Answer: Two (Parents)
Question 8. Name two animals in which asexual reproduction takes place. Answer: Hydra and yeast
Question 9. Name the reproductive organs of male. Answer: A pair of testes, two spermducts and a penis.
Question 10. Name the reproductive organs of female. Answer: A pair of ovaries, oviducts and uterus.
Question 11. Name the modes of reproduction. Answer:
- Sexual reproduction
- Asexual reproduction.
Question 12. What is male gamete or sperm? Answer: The reproductive cell produced by male reproductive organs is called male gamete or sperm.
Question 13. What is female gamete or ova? Answer: The reproductive cell produced by female reproductive organs is called female gamete or ova.
Question 14. Which organ produces eggs or ovum? Answer: A pair of ovary.
Question 15. Name the male gamete. Answer: Sperm
Question 16. Name the female gamete. Answer: Ova or egg
Question 17. Which male reproductive organ produces sperm? Answer: A pair of testes.
Question 18. In which organ fertilisation take place in female? Answer: Fallopian tube
Question 19. What are the two methods of asexual reproduction? Answer:
- Binary fission
Question 20. Name two animals which undergo external fertilisation. Answer: Frog and fish
Question 21. Name two animals which undergo internal fertilisation. Answer: Human being and cow
Question 22. Which type of reproduction takes place in Amoeba? Answer: Asexual reproduction through binary fission.
Question 23. What type of reproduction is cloning? Answer: Asexual reproduction
Question 24. What is foetus? Answer: Foetus is a well developed embryo.
Question 25. What is IVF technique of reproduction? Answer: It is fertilisation outside the body.
Question 26. Give the full form of IVF. Answer: In vitro Fertilisation.
Question 27. How are test tube babies born? Answer: Test tube babies are born through IVF technique.
Question 28. What is cloning? Answer: Cloning is the production of exact copy of a part of or whole living body.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Explain two modes of reproduction with examples. Answer: There are two modes of reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction: This type of reproduction takes place by fusion of male and female gametes; e.g., Human beings, mammals like cow, buffalo, etc.
- Asexual reproduction: This mode of reproduction involves only a single parent; e.g., Hydra, Amoeba, yeast, etc.
Question 2. Explain the process of fertilisation in brief. Answer: Fusion of the male and female gamete, i.e., sperm and egg is called fertilisation. During fertilisation, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus resulting in the formation of a fertilised egg or zygote.
Question 3. What is internal fertilisation? Explain briefly. Answer: Fertilisation which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation. In this a smaller number of ova or eggs are produced. Offsprings have high chance of survival. It occurs mostly in mam¬mals; e.g., in human being, cow, buffalo, etc.
Question 4. Explain briefly the external fertilisation. Answer: In external fertilisation, fusion of male and female gametes take place outside the female body. The female discharge many eggs in the water and the male discharge sperms. The sperms swim to the eggs and fertilise them. It occurs in most of the aquatic animals like frog, fish, starfish, etc.
Question 5. How is an embryo developed? Answer: Fertilisation results in the formation of zygote. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells which then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is called an embryo. It gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development.
Question 6. Explain what is foetus. Answer: The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops different body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, etc. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus. After its development is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
Question 7. What are viviparous and oviparous animals? Answer: The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals and those which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. For example, Mammals including human beings are viviparous animals and hen, lizards, all birds, etc., are oviparous animals.
Question 8. What are sperm and ovum? Explain. Answer: The male gamete is called sperm. It is produced by male reproductive organ, testes. Structurally, it consists of a head attached to a long tail. The tail helps the sperm to move around. The head bears the small nucleus.
Ovum are the female gamete. They are also called egg. They are produced by the female reproductive organ. They consist of larger nucleus. Both sperm and ovum are reproductive cells and contain single cell.
Question 9. Explain briefly the life cycle of a frog. Answer: There are mainly three distinct stages in the life cycle of a frog, i.e., egg → tadpole (larva) → adult. Tadpoles look different from the adults. After sometime tadpoles are converted into an adult frog.
Question 10. Explain in short life cycle of silkworm. Answer: The life cycle of silkworm is completed in four stages. Egg → Larva or Caterpillar → Pupa → Adult In silkworm the caterpillar or pupa looks very different from the adult moth.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1. What do you mean by reproduction? Describe various modes of reproduction. Answer: Reproduction is an important process which is responsible for the continuity of life on the planet earth. In this process, an individual produces young ones of the same species. It helps in increasing the population of the same species on the earth, generation after generation. This is the fundamental feature which ensures the existence of all life forms on the earth. There are two modes of reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction: In this type of reproduction, both male and female parents are involved and they produce different gametes called male gametes or sperms and female gametes or ova (egg) respectively. Both fuse to form zygote which finally develops into foetus. For example, mammals including human beings higher invertebrates and all vertebrates undergo sexual reproduction.
- Asexual reproduction: In this type of reproduction, only single parent is involved and gametes or sex cells are not produced. Budding, binary fission, etc., are different methods of asexual reproduc¬tion. Lower organisms like Hydra, Amoeba, yeast, etc., undergo asexual reproduction.
Question 2. What do you mean by metamorphosis? How does metamorphosis take place in frog? Explain with a diagram. Answer: The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic (sudden or abrupt) changes is called metamorphosis. For example, a moth emerging out of the cocoon, an adult frog from a tadpole, etc., undergo metamorphosis.
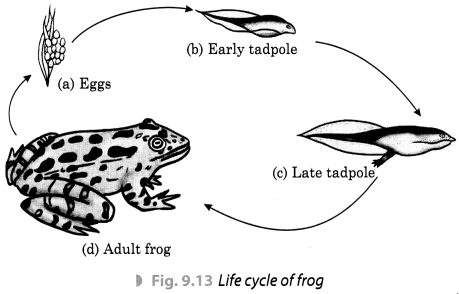
The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cell (Refer Fig. 9.7(b)) which further begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is called an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development [Refer Fig. 9.7(c)]. The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops different body parts. This developing stage of embryo is called foetu (Fig. 9.16).
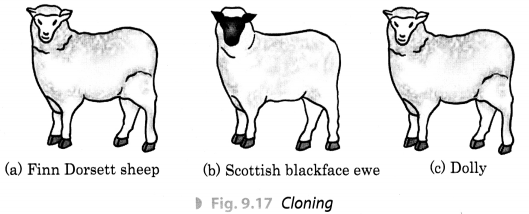
Question 7. What is budding? Explain. Answer: Budding is type of asexual reproduction in which an organism or new individual develops from an outgrowth from a single parent. This outgrowth is called bud. On maturation this bud get separated from the parent’s body to grow into new individual. This process of reproduction is known as budding. For example, Hydra, yeast and sponges produce their young ones through the process of budding. In some organisms, like sponges, buds are not separated from their parent’s body and form a colony. They remain attached to parent’s body.
Question 8. Explain how Amoeba reproduce? or Explain in brief the process of binary fission. Answer: Amoeba reproduces through the process of binary fission. Binary fission is another method of asexual reproduction. Amoeba is a single-celled organism. It begins the process of reproduction by the division of its nucleus into two nuclei followed by division of its body into two, each part receiving a nucleus. Finally two daughter cells are produced from one parent Amoeba. This type of asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals is known as binary fission.
Question 9. What is metamorphosis? Explain. Answer: Some insects and animals undergo a series of changes after birth. Their young ones look quite different from them. The features of these young ones are completely different from the adults. A biological process in which larva transforms into an adult through drastic changes (sudden and abrupt changes) in the body of the animal during the life cycle of an invertebrate or amphibian is called metamorphosis. For example, frog, butterfly, etc., undergo metamorphosis.
Question 10. How are babies produced through IVF technique? What are such babies called? Answer: IVF (In Vitro Fertilisation), is an artificial type of fertilisation. Some women’s oviducts are blocked and so they cannot bear babies because sperms cannot reach the egg for fertilisation. In such cases, freshly released eggs and sperms are kept together for a few hours for IVF (fertilisation outside the body). In case fertilisation occurs, zygote thus formed is allowed to develop for a week and then it is placed in the mother’s uterus. Complete development of baby occurs in uterus and is born like any other baby. Babies born through this technique are called test tube babies.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1. Although two cells called gamete fuse, the product formed is a single cell called zygote. Justify. Answer: During fertilisation, only the male nucleus moves into the egg cell and fuses to the egg nucleus to form zygote which is thus a single cell. The sperm remain outside the egg cell and degenerates after some time.
Question 2. The eggs of frogs do not have shells for protection, yet they are safe in water. How? Answer: A layer of jelly covers the eggs of frog and provides protection. Water help them to float and retain moisture. If eggs are laid in land then they will dry up and die.
Question 3. Mother gives birth to a baby but the baby has characters of both parents. How? Answer: Human beings show sexual reproduction. During fertilisation, two gametes, one from the mother and the other from father, fuse together to form zygote. Therefore baby developed from zygote has characters of both parents though mother gives birth to a baby.
Question 4. Why do only male gametes have a tail? Answer: Male gametes have to reach non-motile female gamete in oviduct from the vagina. So they have a tail to reach the egg cell.
Question 5. Though hen and frog both are oviparous but they have different types of fertilisation. Justify. Answer: In hen, internal fertilisation takes place. The fertilised egg develops into an embryo inside the body. But development of chick from the embryo takes place outside the body. On the other hand, frog shows external fertilisation. The female frog discharge many eggs in the water and the male frog discharge sperms. The sperms swim to the eggs and fertilise them.
Question 6. How does twinning occurs during sexual reproduction? Answer: Twins are two offspring produced by same pregnancy. Non-identical twins results from two fertilised eggs when get implanted in the uterus wall at the same time. Identical twins occur when a single egg is fertilised to form one zygote which then divides into two separate embryos.
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Extra Questions Value-Based Questions
Question 1. Ram with his family went to a picnic spot near a pond. He saw some jelly-like mass floating on the sides of the pond. He asked about this to his father. His father explained him that these are frog’s egg and are millions in number. Ram wondered if all of them get hatched, what will happen to other aquatic animals?
- What type of fertilisation is shown by frog?
- Why do frog lay eggs in large amount?
- Is Ram’s concern about hatching of too many eggs at a time will affect the aquatic animals correct? Why?
- What Value of Ram is shown here?
- Frog shows external fertilisation.
- Mortality rate is very high for tadpoles as their predators are more. Many of the eggs do not develop due to being not get fertilised. So for continuation of their species, they lay egg in large amount.
- No, his concern is not correct because most of the eggs either never develops or are preyed by other animals. So survival chance of a frog from its egg to an adult frog is very low.
- Ram is inquisitive, future thinker and eco-concerned.
Activities and Projects Question 1. Visit a poultry farm. Talk to the manager of the farm and try to find out the answers to the following.
- What are layers and broilers in a poultry farm?
- Do hens lay unfertilised eggs?
- How can you obtain fertilised and unfertilised eggs?
- Are the eggs that we get in the stores fertilised or unfertilised?
- Can you consume fertilised eggs?
- Is there any difference in the nutritional value of fertilised and unfertilised eggs?
Answer: Visit a poultry farm, you can get answers to these questions. However, answers are given here for your help.
- Hens which lay eggs are layers and broilers are the hens used to get meat.
- Yes. Though hens lay fertilised eggs but in the poultry farms, the unfertilised eggs are obtained by induced ovulation.
- We can obtain fertilised eggs by normal procedure whereas unfertilised eggs can be obtained by induced ovulation in a poultry farm.
- Both types of eggs are available at stores.
- Yes, fertilised eggs have more nutritional value.
Question 2. Observe live Hydra yourself and learn how they reproduce by doing the following activity: During the summer months collect water weeds from ponds or ditches along with the pond water and put them in a glass jar. After a day or so you may see several Hydra clinging to the sides of the jar. Hydra is transparent, jelly-like and with tentacles. It clings to the jar with the base of its body. If the jar is shaken, the Hydra will contract instantly into a small blob, at the same time drawing its tentacles in. Now take out few Hydras from the jar and put them on a watch glass. Using a hand lens or a binocular or dissection microscope, observe the changes that are taking place in their body. Note down your observations. Answer: Do it yourself.
Question 3. The eggs we get from the market are generally the unfertilised ones. In case you wish to observe a developing chick embryo, get a fertilised egg from the poultry or hatchery which has been incubated for 36 hours or more. You may then be able to see a white disc-like struc¬ture on the yolk. This is the developing embryo. Sometimes if the heart and blood vessels have developed you may even see a red spot. Answer: Do it yourself at home.
Question 4. Talk to a doctor. Find out how twinning occurs. Look for any twins in your neighbourhood, or among your friends. Find out if the twins are identical or non-identical. Also find out why identical twins are always of the same sex? If you know of any story about twins, write it in your own words. You could visit the following websites for information on twins: www. keepkidshealthy.com/twins/expecting_twins.html. For more information on animal reproduction, you can visit: www.saburchill.com/chapters/chap0031.html Answer: Twinning means producing two offspring at a time. It occurs in two ways:
- Two ova or eggs (female gametes) are released during ovulation and get fertilised.
- Single fertilised egg or ovum undergoes fission giving rise to two foetus.
In first case, twins are unidentical or unsimilar whereas in second case, they are identical or similar. Since identical twins are born from same egg (ova) and sperm, i.e., same female and male gametes, they always have same sex. Students are advised to find out all these practically in their neighbourhood with friends.
I. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) Choose the correct option. Question 1. The number of modes by which animals reproduce are (a) two (b) three (c) four (d) none of these
Question 2. Binary fission is observed in (a) Hydra (b) yeast (c) Amoeba (d) human being
Question 3. Asexual reproduction is observed in (a) cow (b) buffalo (c) sponge (d) hen
Question 4. In Hydra, the mode of reproduction is (a) asexual (b) sexual (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Question 5. The animals that produce new young ones are called (a) viviparous (b) oviparous (c) both (d) none of these
Question 6. The male gamete or sperm consists of (a) three parts (b) two parts (c) four parts (d) none of these
Question 7. Ovum or eggs are formed in (a) ovary (b) testes (c) penis (d) ovident
Question 8. Internal fertilisation takes place (a) inside male body (b) inside female body (c) outside female body (d) outside male body
Question 9. In humans, the development of fertilised egg takes place in the (a) ovary (b) oviduct (c) testis (d) uterus
Question 10. The cell formed after fertilisation is called (a) embryo (b) foetus (c) zygote (d) egg
Question 11. The fusion of sperm and ova usually occur in the (a) ovary (b) uterus (c) testes (d) oviduct
Question 12. Sets of reproductive terms are given below. Choose the set that has an incorrect combination. (a) Sperm, testis, sperm duct, penis (b) Menstruation, egg, oviduct, uterus (c) Sperm, oviduct, egg, uterus (d) Ovulation, egg, oviduct, uterus
Question 13. Which of the following shows external fertilisation? (a) Frog (b) Human being (c) Cow (d) Hen
Question 14. Which one of the following is not a part of female reproductive organs? (a) Uterus (b) Ovary (c) Oviduct (d) Penis
Question 15. In the list of animals given below, hen is the odd one out. ‘human being, cow, dog, hen’ The reason for this is (a) it undergoes internal fertilisation (b) it is oviparous (c) it is viviparous (d) it undergoes external fertilisation
Question 16. Animals exhibiting external fertilisation produce a large number of gametes. Pick the appropriate reason from the following (a) The animals are small in size and want to produce more offsprings. (b) Food is available in plenty in water. (c) To ensure better chance of fertilisation. (d) Water promotes production of large number of gametes.
Question 17. Which is not a viviparous animal? (a) Human being (b) Cow (c) Dog (d) Butterfly
Question 18. Budding occurs in (a) Amoeba (b) dog (c) Paramecium (d) yeast
Question 19. The female gamete is called (a) ova (b) sperm (c) zygote (d) uterus
Question 20. The male gamete is called (a) sperm (b) ova (c) embryo (d) zygote Answer: 1. (a) 2. (c) 3. (c) 4. (c) 5. (a) 6. (a) 7. (a) 8. (b) 9. (d) 10. (c) 11. (d) 12. (c) 13. (a) 14. (d) 15. (b) 16. (c) 17. (d) 18. (d) 19. (a) 20. (a)
II. Fill in the Blanks Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s. 1. __________ is the process that ensures continuity of life on earth. 2. __________ are the cells involved in sexual reproduction. 3. The animals which lay eggs are called __________. 4. The animals which give birth to young ones are called __________. 5. __________ is the process of fusion of gametes. 6. The process of reproduction involving fusion of male and female gametes is called __________ reproduction. 7. The testes produce the male gametes called __________. 8. Sperms are __________ in size. 9. Sperm is a __________ cell. 10. The female reproductive organ consists of __________, __________ and __________. 11. The ovary produces female gamete called __________. 12. An ova or egg is a __________ cell. 13. __________ is a fertilised egg. 14. Internal fertilisation takes place inside __________. 15. Babies born through __________ technique are called test tube babies. 16. __________ fertilisation takes place outside the female body. 17. Fertilisation results in the formation of __________ and __________. 18. All living organisms have the power to __________. 19. __________ produces sperm in male. 20. In __________ reproduction only a single parent is involved. Answer: 1. Reproduction 2. Gametes 3. oviparous 4. viviparous 5. Fertilisation 6. sexual 7. sperms 8. very small 9. single 10. ovaries, oviduct, uterus 11. ova (egg) 12. single 13. Zygote 14. female body 15. IVF 16. External 17. zygote, embryo 18. reproduce 19. Testes 20. asexual
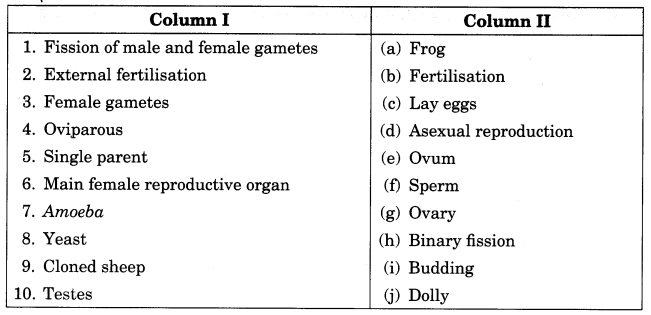
IV. True or False State whether the given statements are true or false. 1. Zygote is an unfertilised egg. 2. External fertilisation occurs in frog. 3. An embryo is made up of multicells. 4. Amoeba reproduces by budding. 5. Fertilisation is not necessary in asexual reproduction. 6. Each sperm is multicellular. 7. A new young one is developed from a cell called gamete. 8. Cloning is a sexual reproduction method in any living organisms. 9. Viviparous animals give birth to young ones. 10. Male gametes are sperms. 11. Female gametes are ovum. 12. Starfish reproduces by external fertilisation. 13. Two individuals are needed for sexual reproduction. 14. Internal fertilisation occurs in dogs and cats. 15. An embryo grows in uterus. Answer: 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True 6. False 7. False 8. False 9. True 10. True 11. True 12. True 13. True 14. True 15. True
Extra Questions for Class 8 Science
Free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- CBSE- Reproduction in Animals
Reproduction in Animals-Notes
- STUDY MATERIAL FOR CBSE CLASS 8 SCIENCE
- Chapter 1 - Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 2 - Chemical Effects of Electrical Current
- Chapter 3 - Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 4 - Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 5 - Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 6 - Force and Pressure
- Chapter 7 - Friction
- Chapter 8 - Light
- Chapter 9 - Microorganisms - Friend and Foe
- Chapter 10 - Pollution of Air and Water
- Chapter 11 - Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Chapter 12 - Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 13 - Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 14 - Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 15 - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 16 - Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 17 - Materials-metals and non-metals
- Chapter 18 - Sound

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Class 8th /
Reproduction in Animals Class 8
- Updated on
- Apr 21, 2021

Class 8 Science chapter on Reproduction in Animals elaborates on the major forms of reproduction in different animals. The mechanism of reproducing individuals of the same species is known as reproduction. A bulk of species replicate by mating, which increases genetic diversity. Males and females have gonads, which are independent sex organs. These gonads contain gametes, which combine together to form the zygote, a single cell. Earthworms, snails, slugs, and a few other species are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs in the same body. Read this blog to find important study notes on Reproduction in Animals Class 10.
Must Read: Some Natural Phenomena Class 8
Table of contents
Modes of reproduction in animals, male reproductive organs, female reproductive organs, internal fertilization, external fertilization, embryo development, types of asexual reproduction.
The first section of Reproduction in Animals Class 10 talks about the forms of animal reproduction. There are various forms of reproduction depending on the number of parents involved. There are two forms of reproduction in animals:
- Sexual Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction in Animals
Sexual reproduction is the result of male and female gametes fusing together to create a new organism. Let’s take a look at the human reproductive organs and how they help in fertility as per Class 8 chapter on Reproduction in Animals.
A pair of testes, two sperm ducts, and a penis are among the male reproductive organs. Sperm are male gametes formed by the testes. The testes contain millions of sperm, as shown in the illustration below of a sperm. Despite their tiny scale, sperm have a head, a middle section, and a tail. Each sperm is, in fact, a single cell with all of the normal cell components.

Moving to the next topic in Class 8 Reproduction in Animals, the female reproductive organs constitute a pair of ovaries, oviducts, and the uterus. Ovary creates ova, which are feminine gametes. Per month, one of the ovaries releases a single matured egg into the oviduct in humans. The uterus is the area of the body where the baby develops. An egg is a single cell, much like sperm.

Also Read: Class 8 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Fertilization

Fertilisation is another important topic you will study in Class 8 Reproduction in Animals. There are millions of sperm in the sperm. During fertilisation, a single sperm fuses with the ova. The egg and sperm nuclei join together to create a new nucleus. As a result, a zygote is formed.
There are two methods of fertilisation:
Internal fertilisation is the process of fertilisation that takes place within the female’s body. People, pigs, dogs, and other species are examples. In terrestrial animals, this approach is more common. Some marine species, however, also use this technique. This may happen either by the male directly injecting sperm into the female reproductive tract or by the male depositing sperm in the area, which the female picks up and injects into her reproductive tract.
They are three ways by which babies are produced by internal fertilization:
- Oviparity– The fertilised eggs are laid outdoors, where the yolk provides nutrition.
- Ovoviviparity– The fertilised eggs are stored in the female’s shell, where the yolk provides nourishment. Before the eggs are hatched, they are laid.
- Viviparity– Instead of hatching from the eggs, the offspring are born alive. The mother provides them with food. Mammals are examples of this.
External fertilisation refers to fertilisation that happens outside of the person. Frogs and fish, for example. The majority of fertilisation occurs during the spawning period. Spawning is triggered by environmental signals such as water temperature.
Oviparous and viviparous animals are two separate classes of animals categorised according to how they fertilise their offspring. The main difference between oviparous and viviparous animals are listed below:
| Basis | ||
| Definition | Egg-laying animals are called Oviparous. | Animals that give birth to the young ones are called Viviparous. |
| Fertilization | Fertilization can be either internal or external. | Fertilization can only be internal. |
| Development of embryo | Nutrient is provided by the egg yolk. | Nutrient is provided by the mother through the placenta |
| Development of zygote | The embryo develops very little or not at all inside the mother. | The embryo grows completely inside the mother’s womb. |
| Chances of Survival | Since the eggs are laid outside the womb, there are less chances of survival. | Since the young one is safe within the mother, it has a better chance of surviving. |
| Examples | Insects, hens, fish, amphibians, etc. | Humans, dogs, cats, horses, etc. |
The zygote separates into a ball of cells after repeated divisions. This is known as the developing embryo. These cells differentiate into respective tissues and organs. The embryo gets implanted in the uterine wall. This process is known as implantation.
A foetus is formed when all of the embryo’s body parts become apparent. In humans, the foetus develops after nine months.
Must Read: Cell Structure and Function Class 8
Asexual Reproduction in Animals:
Asexual reproduction is the second most common form of reproduction in animals, after sexual reproduction. Lower species and unicellular microbes are the most common examples of this form of reproduction.
It is the mechanism by which a new entity is created without the presence of the gamete formation by a single parent. Genetically and morphologically, the individuals produced are alike. It’s found in single-celled species. There is no fertilisation and the cells separate by mitotic division. The separation happens very fast.
Let’s take a look at the types of asexual reproduction as elaborated in Class 8 Reproduction in Animals:
Binary Fission Amoeba and euglena are examples of Binary Fission. The parent cell goes through mitosis and grows in size. The nucleus separates as well. Two equivalent daughter cells, each with a nucleus, are obtained. Binary fission is the most common form of reproduction for prokaryotes including bacteria.
Budding In this situation, the offspring emerges from the parent’s womb. When it matures, it stays bound to the parent. It separates from the parent after maturation and survives as a separate entity. Hydras use this method of reproduction the most.
Fragmentation When the body of an entity, such as a Planarian, splits into many parts, each piece develops into an independent offspring. Fragmentation is the term for this. It may happen as a result of predator-caused harm or as a natural form of reproduction. A fractured arm develops into a full organism in a few species, such as the sea star.
Regeneration It is a form of fragmentation that is found mainly in Echinoderms. When a part of an individual, such as an arm, splits from its parent body, it transforms into a different entity. This is referred to as regeneration.
Parthenogenesis This is an asexual reproduction method in which the egg forms without being fertilised. Bees, wasps, ants, aphids, rotifers, and other insects engage in this process. Hemiploid males are produced by ants, wasps, and bees. When females were separated from males, parthenogenesis was found in a few vertebrates such as hammerhead sharks, Komodo dragons, and blacktop sharks.
We hope that this blog has provided you with a deeper understanding of Class 8 Reproduction in Animals. Check out our Class 8 study notes section to find similar material for Class 8 subjects! Don’t forget to follow Leverage Edu on Instagram , Facebook and Twitter to stay updated with the latest educational news!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2025
September 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ Test (Online Available)
Free mcq test, table of content, reproduction in animals test - 20.
Duration: 10 Mins
Maximum Marks: 10
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. The test contains 10 total questions.
2. Each question has 4 options out of which only one is correct .
3. You have to finish the test in 10 minutes.
4. You will be awarded 1 mark for each correct answer.
5. You can view your Score & Rank after submitting the test.
6. Check detailed Solution with explanation after submitting the test.
7. Rank is calculated on the basis of Marks Scored & Time
Reproduction in Animals Test - 19
Reproduction in animals test - 18, reproduction in animals test - 17, reproduction in animals test - 16, reproduction in animals test - 15, reproduction in animals test - 14, reproduction in animals test - 13, reproduction in animals test - 12, reproduction in animals test - 11, reproduction in animals test - 10, reproduction in animals test - 9, reproduction in animals test - 8, reproduction in animals test - 7, reproduction in animals test - 6, reproduction in animals test - 5, reproduction in animals test - 4, reproduction in animals test - 3, reproduction in animals test - 2, reproduction in animals test - 1.
The chapter Reproduction in Animals is one of the important chapters in class 8. The highly qualified experts of Selfstudys developed these Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ to test what students have learnt and also helps them to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
These MCQ on Reproduction in Animals history class 8 are developed as per the latest pattern of CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education). If a student wants to secure good marks in their exams, then they should attempt Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ.
The MCQ on Reproduction in Animals history class 8 is created with detailed explanation of concepts which can help students understand the concepts better and also increases their objective knowledge.
Format of Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ
By regularly practising the MCQ on Reproduction in Animals History class 8, the students will get to know about the most common repeated questions. They will also get to know about the HOTS Questions (High Order Thinking Skills). The Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ also helps the students to do a thorough revision for their final examinations.
The Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ is developed as per the question papers of the last 5 years to help the students to give an idea about the most repeated questions and also about the pattern of the examination.
Steps To Attempt The Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ
If students want to attempt Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ, they need to follow the following steps:
- The first step is to go to the official website of selfstudys i.e. selfstudys.com.
- Click on the three lines on the upper left side, and then tap on the ‘CBSE’ Option, scroll down and click on the option stating ‘MCQ Tests’.
- A page will appear in which there will be options for choosing classes.
- Choose class 8.
- Now, you have to choose the subject and the chapter.
- Now, you can attempt Reproduction in Animals History Class 8 MCQ.
Instructions To Attempt Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ
Before starting the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ, it is advisable for all the students to go through the instructions to attempt the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ;
- The total number of questions in the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ is 10.
- Out of 4 options in the MCQ on Reproduction in Animals history class 8, only 1 is correct.
- The duration in the Reproduction in Animals history class 8 MCQ will be 10 minutes to ensure time management among the students.
- For each correct answer, the students will be given 1 mark.
- After submitting the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ, all the students can have a look at the answers with detailed information.
- On the basis of the marks scored in the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ test and time taken by the student to complete the test, the rank will be calculated.
How To Prepare for The Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ?
All the students should prepare for Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ in the following way to secure good marks in their examination:
- Start by memorising the important notes: The first step is to brush up all the important notes to create a strong base for the learning if a student is preparing for Reproduction in Animals history class 8 MCQ. Multiple choice questions is one of the most effective methods to test the skills of students and also it helps to know how well prepared a student is for the exam.
- Make Acronyms: Another effective method which is advisable for all the students is to make acronyms to prepare for Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ. The procedure for that will be taking the first alphabet of the word and relating it with a word so that it becomes easy for you to remember.
- Make flashcards: Making flashcards is also an effective way to prepare for the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ which can help you to explain and relate key terms and names. Flashcards are a great tool if a student wants to do revision after the completion of their preparation. It also helps to recall all the important concepts which is a very important skill in the case of MCQ tests.
- Put important information into a song which you like: Take a musical tune that is easy to memorise and replace the words with important dates, names and other important things.
- Quiz yourself: Develop your own questions after going through the CBSE Class 8 syllabus and important notes. After creating 10 questions, test your knowledge to see how well you know the topic and also to identify your strengths and weaknesses.
How Regular Practice of Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ Can Help Students Improve Their Scores
The first thing which a student wants to know after completing the preparation of Reproduction in Animals history class 8 MCQ, they want to know how well are they actually prepared for the exam
The benefits of Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ are huge, a student can get to know about their strengths and weaknesses and also the areas where they lack.
Benefits of The Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ
There are numerous benefits of Reproduction in Animals history class 8 MCQ can help students to improve their marks in examinations. Some of them are:
- Flexible Questioning Technique: Flexible questioning technique is used in the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ which can promote effective learning among the students and as MCQ questions are versatile, students can learn them with critical thinking.
- Time Management: The Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ helps the students to manage their time effectively. Time management reduces the chance of procrastination which can increase the chances for scoring well in the examination for all the students. As the time duration of the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ will only be 10 minutes, it can be helpful for students as they will have more time for other important study materials.
- Fast: The Reproduction in Animals history class 8 MCQ is fast as compared to other modes of exam available. Examples include offline (pen and paper) etc. This can be beneficial for students as they will get the status of their exam preparation fast.
- Developed by the Subject Matter Experts: These Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ are developed by the subject matter experts of selfstudys.com who have years of experience in the educational field and are aware of the most common questions which can be asked in examinations.
- Give the idea of the pattern of the exam: The Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ gives the idea of the pattern of the exam to the students which can make them confident and also help them to score well in the exam.
- Improve the skills of the students: The Reproduction in Animals history class 8 MCQ can significantly improve critical thinking, management skills and time management skills.
Hacks to Score Well in the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ
If a student want to score well in the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ, they can try the following hacks:
- Read the complete question: It is advisable for students to read the entire question of the MCQ on Reproduction in Animals history class 8 completely as it helps them to understand the requirement of the question. Students often feel that they know the answer by looking at the question and without reading the complete question, they choose the most logical answer. This mistake is very common among the students.
- Answer it in your mind first: Answer the question in your mind after reading the Reproduction in Animals history class 8 MCQ without looking at the options. Try to answer it without looking at the options as it will help you to be completely sure about the answer.
- Attempt the questions you know first: Students are advised to attempt the questions for which they are completely sure that they know the answer whereas if a student doesn’t know the particular answer, they can skip it. By doing this, no unnecessary time will be wasted and time management will be ensured.
- Make a guess: Students should make a guess while attempting the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ because there is no negative marking. So, there is no need to skip any questions.
How To Select The Correct Answers To The Reproduction in Animals History Class 8 MCQ?
- Use the process of elimination: After reading the entire questions and all the four options, students can use the process of elimination for the options for which they are 100% sure that they are incorrect. Even if they know the correct option, students are advised to use the elimination process.
- “All of the above” and “None of the above”: While attempting the Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ, if you see options like “All of the above” and “none of the above”, prefer not to choose them unless you are 100% sure as students think that this is the correct option.
- Find the answers hidden in the Question: A lot of times, the answers are hidden in the given questions so, try to find the answers hidden in Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ. Try decoding the questions by rereading them as you can find them in the questions itself.
- True or False Test: Doing a true or false test in Reproduction in Animals Science Class 8 MCQ can be very beneficial as it can be easier for a student to not consider all the false answer options and choose the correct answer.
- Possibility of two correct answers: If in case, two answers look correct with all of the above options while attempting the Class 8 Reproduction in Animals of History MCQ, then there is a strong possibility that it is the correct answer option.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction Animals
Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 – Reproduction in Animals
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 6 in NCERT Class 8 Science Textbook.
Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals – Download Free PDF

CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 9 MCQ Type Questions
1. Where are the ovum or the eggs formed?
(a) testes (b) penis (c) ovary (d) ovident
2. Where do the fusion of the sperm and the ova usually take place?
(a) uterus (b) testes (c) ovary (d) oviduct
3. Animals exhibiting external fertilisation produce numerous gametes. Justify with a reason from the one given below:
(a) The animals are small and want to produce more offspring (b) Food is available in plenty of water (c) To ensure a better chance of fertilisation (d) Water promotes the production of numerous gametes
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals. Case Study Questions. Question 1: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow-. For the continuity of life, all living things produce organisms of their own kind.
Que. 2) (a) Caterpillar. Que. 3) (d) Cow. Que. 4) Answer:In sexual reproduction, the reproductive parts produce gametes that fuse to form a zygote. The zygote develops into a new individual. Que. 5) Answer: The two modes of reproduction in animals include: i) Sexual reproduction ii) Asexual reproduction.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Reproduction in Animals class 8 science into classroom teaching? A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of ...
The Case Study Based Questions: Reproduction in Animals is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 8 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
The NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 will benefit you immensely, as the solutions help you understand the topics in-depth. Besides, this will aid in learning advanced topics. This exemplar has a variety of questions and answers which you can rely on for your exam preparation. The chapter Reproduction in Animals is about learning the ...
Long Answer Type Questions. Question 1: Describe the process of fertilization in human beings. Answer: The first step in the process of reproduction is the fusion of a sperm and an ovum. When sperms come in contact with an egg, one of the sperms may fuse with the egg. Such fusion of the egg and the sperm is called fertilization.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 9 - 5 Mark Questions and Answers. Question 1. Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F). [NCERT] Oviparous animals give birth to young ones. ( ) Each sperm is a single cell. ( ) External fertilisation takes place in frog.
It includes Multiple Choice Questions, Case-based Questions, Assertion-Reasoning Questions, and even Source-Based Questions to help the students undergo an intelligent preparation process. The intent of these questions is to facilitate self-practice. They will test your ability to apply what you have learned rather than testing your memory.
There are two modes of reproduction in animals: Sexual Reproduction. Asexual Reproduction. Similarities between Reproduction in Plants and Animals. Plants and animals can both undergo the sexual and asexual process of reproduction. Just like plants, in animals, the males and females have different reproductive organs.
Get Notes, NCERT Solutions and Extra Questions of Chapter 9 Class 8 NCERT - Reproduction in Animals. Teachoo provides the best content to learn about Reproduction with NCERT questions, worksheets, extra questions and revision notes. In this chapter, we will learn. What is Reproduction. Different Modes of Reproduction.
Answer. (a) In human beings, sexual reproduction takes place by the combination of gametes, i.e. sperm and egg, formed in male and female, respectively. The fusion of gametes is called fertilisation. The fusion forms a zygote, which divides repeatedly to form the embryo.
2. Binary Fission. a) Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction commonly observed in single-celled organisms like bacteria and protozoa. In this process, a single parent cell divides into two daughter cells, each identical to the parent. It is a simple and efficient way for these organisms to reproduce and increase their population rapidly.
The PPT: Reproduction in Animals is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 8 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
The "Important Questions: Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the Class 8 exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to help students gauge their understanding of the exam topics.
Sexual reproduction. The type of reproduction, which involves two parents to give rise to an offspring is called sexual reproduction. The males and females have different reproductive parts or organs. These organs produce the male and female gametes, which fuse together to form the offspring.
Answer 1. C) Sperm → oviduct, egg → uterus. Reproduction is a process in which organisms make more organisms similar to themselves. Millions of these sperm are in this small amount of semen, and they swim up from the vagina through the cervix following the uterus to meet the egg present in the fallopian tube.
Class 8 Reproduction In Animals Question Answer helps students learn about the structural adaptations of different animals for reproduction, such as the reproductive organs and their functions. Vedantu offers supplementary resources such as video lectures, quizzes, and study materials to complement the chapter solutions, providing a holistic ...
Question 8. Name two animals in which asexual reproduction takes place. Answer: Hydra and yeast. Question 9. Name the reproductive organs of male. Answer: A pair of testes, two spermducts and a penis. Question 10. Name the reproductive organs of female. Answer: A pair of ovaries, oviducts and uterus.
Visit the Selfstudys website. Bring the arrow towards the CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar/ button. Select New Revision notes from the given list. A new page will appear, select Class 8th from the list of classes. Again a new page will appear, select the Reproduction in Animals to access the Notes.
Class VIII Science. Notes for Reproduction in Aniamals. Facts the Matter. • The process of reproduction is not essential for the survival of an individual but reproduction is essential for the continuation of a species. • Modes of Reproduction: Like plants, animal also reproduce by (i) Sexual reproduction and (ii) Asexual reproduction.
Class 8 Science chapter on Reproduction in Animals elaborates on the major forms of reproduction in different animals. The mechanism of reproducing individuals of the same species is known as reproduction. A bulk of species replicate by mating, which increases genetic diversity. Males and females have gonads, which are independent sex organs.
Steps To Attempt The Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ. If students want to attempt Reproduction in Animals class 8 MCQ, they need to follow the following steps: The first step is to go to the official website of selfstudys i.e. selfstudys.com. Click on the three lines on the upper left side, and then tap on the 'CBSE' Option, scroll down ...
1. Where are the ovum or the eggs formed? 2. Where do the fusion of the sperm and the ova usually take place? 3. Animals exhibiting external fertilisation produce numerous gametes. Justify with a reason from the one given below: Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Reproduction Animals are provided here which can help the students to ...