The Benefits of Bilingual Education and Its Impact on Student Learning and Growth
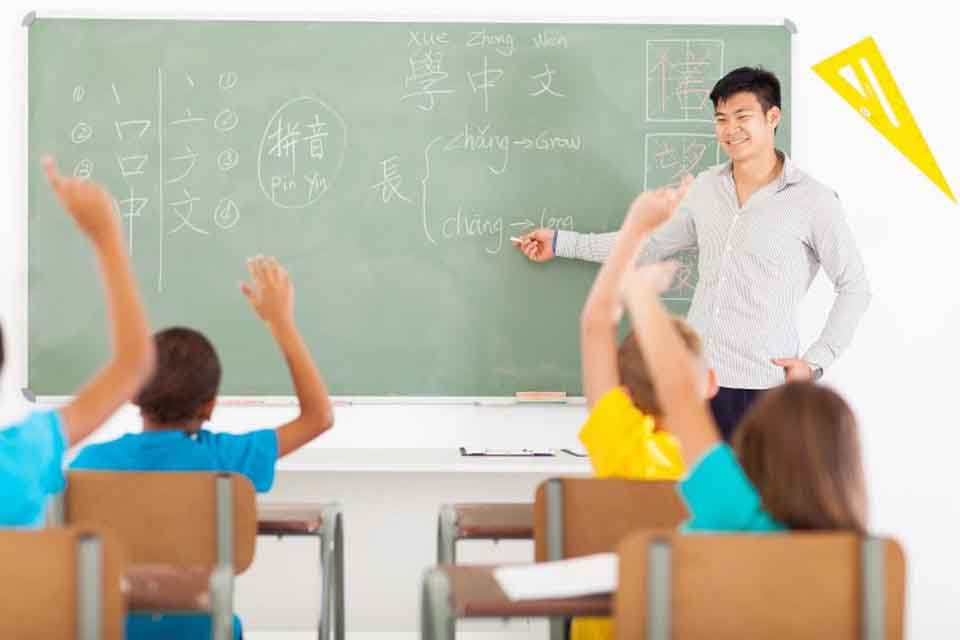

Approximately 5 million students in the United States are English language learners, and the number of English language learners (ELLs) in the US public school system continues to rise steadily, especially in more urbanized school districts.
According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), students who speak English as a second language are more likely to struggle with academics, and only about 67 percent will graduate from public high school in four years—whereas the average for all students is 84 percent. ELL students can better develop their English proficiency and close the gap in achievement by participating in language assistance programs or bilingual education programs, the NCES explains.
The benefits of bilingual education can begin with students in elementary school and follow them throughout their lives. Education’s impact can lead to a variety of outcomes depending on whether ELL students learn English in a monolingual or bilingual environment. Educators in diverse classrooms or working as school leaders should consider the benefits of bilingual education when creating curricula and establishing desired student learning outcomes.

What Is Bilingual Education?
While bilingual education can take many forms, it strives to incorporate multiple languages into the process of teaching. For example, since there is such a large Spanish-speaking population in the United States, many primary and secondary school students can benefit from educational environments where they are learning in both English and Spanish.
Bilingual education can often be the most effective when children are beginning preschool or elementary school. If children grow up speaking Spanish as their primary language, it can be difficult for them to be placed in English-speaking elementary schools and be expected to understand their teachers and classmates. In a bilingual classroom, however, young students can further establish their foundation of Spanish as well as English, better preparing them for the rest of their education.
Of course, this works for students who begin school speaking any language as their primary language. Children whose parents have come to the United States from another country may have limited English skills when they first begin elementary school. Teachers working in bilingual education classrooms will balance their use of two languages when teaching math, science, history, and other subjects to help these students develop a stronger foundation of their first language as well as English as their second language.
Academic Benefits
Students can benefit in many ways from participating in bilingual education programs or classrooms. Some of the benefits of bilingual education relate to intellect. For example, research has shown that students who can speak and write in multiple languages have cognitive advantages over their monolingual peers. Those who learn a second or third language from a young age are able to develop communication skills and a higher degree of literacy. Children who grow up in bilingual environments develop a keen awareness of how language works and have a stronger foundation for learning additional languages in the future.
Students can also benefit academically from bilingual education. Students who pursue higher education are typically required to take a foreign language at the collegiate level, so those who have been exposed to bilingual educational environments before college—and speak two or more languages—have an advantage over their peers. They can advance in their studies and feel comfortable with multiple communities of students on their campuses.
Students who are exposed to multiple languages throughout high school and college can also have long-term career benefits. Their proficiency in multiple languages is an advantage when they graduate and enter the workplace as professionals. Every industry has a need for effective communicators who can speak multiple languages to meet the needs of the growing number of English language learners in the United States. International operations also have a great need for professionals who can speak multiple languages and represent US-based organizations and companies.
Growth beyond Academics
While there are many benefits of bilingual education related to school and work, bilingual education programs also have a huge impact on students’ cultural and social growth. Children who grow up speaking English as a second language often come from culturally diverse backgrounds. Incorporating cultural education in the classroom can help create enriching academic experiences for all students.
Exploring multiple languages in the classroom provides a foundation for cultural education that allows students to learn and grow alongside classmates from a different cultural background. As a result, students learn to become more adaptable and more aware of the world around them.
To encourage the academic and cultural development of students in bilingual education settings, teachers should have a strong foundation in education and leadership. They should demonstrate a passion for teaching as well as an understanding of how language and culture work together in their students’ academic journeys. Educators should be aware of the role that policies play in the educational environments they cultivate and have an understanding of how to best represent their students’ cultural backgrounds.
Pursue a Master of Arts in Teaching or Master of Education in Education Policy and Leadership
To implement the best teaching practices in bilingual education classrooms, teachers should be equipped with a foundation in transformational leadership and cultural awareness. To that end, teachers looking to have a meaningful impact on the lives of their students can further their own education and pursue an advanced degree in education policy and leadership. Through programs like American University’s Master of Arts in Teaching and Master of Education in Education Policy and Leadership , educators can broaden their worldviews, engaging in topics such as education law and policy, quantitative research in education, and educational leadership and organizational change.
Culturally Responsive Teaching Strategies: Importance, Benefits & Tips
EdD vs. PhD in Education: Requirements, Career Outlook, and Salary
Transformational Leadership in Education
Bilingual Kidspot, “5 Amazing Benefits of a Bilingual Education”
Learning English, “Number of English Learners in US Schools Keeps Rising”
National Center for Education Statistics, “Digest of Education Statistics”
National Center for Education Statistics, “English Language Learners in Public Schools”
Pew Research Center, “6 Facts About English Language Learners in U.S. Public Schools”
USA Today, “More US Schools Teach in English and Spanish, But Not Enough to Help Latino Kids”
Request Information

AU Program Helper
This AI chatbot provides automated responses, which may not always be accurate. By continuing with this conversation, you agree that the contents of this chat session may be transcribed and retained. You also consent that this chat session and your interactions, including cookie usage, are subject to our privacy policy .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
5 Million Voices
6 potential brain benefits of bilingual education.
Anya Kamenetz

Part of our ongoing series exploring how the U.S. can educate the nearly 5 million students who are learning English.
Brains, brains, brains. One thing we've learned at NPR Ed is that people are fascinated by brain research. And yet it can be hard to point to places where our education system is really making use of the latest neuroscience findings.
But there is one happy nexus where research is meeting practice: bilingual education. "In the last 20 years or so, there's been a virtual explosion of research on bilingualism," says Judith Kroll, a professor at the University of California, Riverside.
Again and again, researchers have found, "bilingualism is an experience that shapes our brain for a lifetime," in the words of Gigi Luk, an associate professor at Harvard's Graduate School of Education.
At the same time, one of the hottest trends in public schooling is what's often called dual-language or two-way immersion programs.

How We Teach English Learners: 3 Basic Approaches
Traditional programs for English-language learners, or ELLs, focus on assimilating students into English as quickly as possible. Dual-language classrooms, by contrast, provide instruction across subjects to both English natives and English learners, in both English and in a target language.
The goal is functional bilingualism and biliteracy for all students by middle school.
New York City, North Carolina, Delaware, Utah, Oregon and Washington state are among the places expanding dual-language classrooms.
The trend flies in the face of some of the culture wars of two decades ago, when advocates insisted on "English first" education. Most famously, California passed Proposition 227 in 1998. It was intended to sharply reduce the amount of time that English-language learners spent in bilingual settings.
Proposition 58 , passed by California voters on Nov. 8, largely reversed that decision, paving the way for a huge expansion of bilingual education in the state that has the largest population of English-language learners.

Bilingual Education Returns To California. Now What?
Some of the insistence on English-first was founded in research produced decades ago, in which bilingual students underperformed monolingual English speakers and had lower IQ scores.
Today's scholars, like Ellen Bialystok at York University in Toronto, now say that research was "deeply flawed."
"Earlier research looked at socially disadvantaged groups," agrees Antonella Sorace at the University of Edinburgh, in Scotland. "This has been completely contradicted by recent research" that compares more similar groups to each other.
So what does recent research say about the potential benefits of bilingual education? NPR Ed called up seven researchers in three countries — Sorace, Bialystok, Luk, Kroll, Jennifer Steele, and the team of Wayne Thomas and Virginia Collier — to find out.
It turns out that, in many ways, the real trick to speaking two languages consists in managing not to speak one of those languages at a given moment — which is fundamentally a feat of paying attention.
Saying "Goodbye" to mom and then " Guten tag " to your teacher, or managing to ask for a crayola roja instead of a red crayon, requires skills called "inhibition" and "task switching." These skills are subsets of an ability called executive function.
People who speak two languages often outperform monolinguals on general measures of executive function. "[Bilinguals] can pay focused attention without being distracted and also improve in the ability to switch from one task to another," says Sorace.
Do these same advantages accrue to a child who begins learning a second language in kindergarten instead of as a baby? We don't yet know. Patterns of language learning and language use are complex. But Gigi Luk at Harvard cites at least one brain-imaging study on adolescents that shows similar changes in brain structure when compared with those who are bilingual from birth, even when they didn't begin practicing a second language in earnest before late childhood.
Young children being raised bilingual have to follow social cues to figure out which language to use with which person and in what setting. As a result, says Sorace, bilingual children as young as age 3 have demonstrated a head start on tests of perspective-taking and theory of mind — both of which are fundamental social and emotional skills.
Reading (English)
About 10 percent of students in the Portland, Ore., public schools are assigned by lottery to dual-language classrooms that offer instruction in Spanish, Japanese or Mandarin, alongside English.
Jennifer Steele at American University conducted a four-year, randomized trial and found that these dual-language students outperformed their peers in English-reading skills by a full school year's worth of learning by the end of middle school.
Such a large effect in a study this size is unusual, and Steele is currently conducting a flurry of follow-up studies to tease out the causality: Is this about a special program that attracted families who were more engaged? Or about the dual-language instruction itself?
"If it's just about moving the kids around," Steele says, "that's not as exciting as if it's a way of teaching that makes you smarter."

'Invisible' Children: Raised In The U.S., Now Struggling In Mexico
Steele suspects the latter. Because the effects are found in reading, not in math or science where there were few differences, she suggests that learning two languages makes students more aware of how language works in general, aka "metalinguistic awareness."
The research of Gigi Luk at Harvard offers a slightly different explanation. She has recently done a small study looking at a group of 100 fourth-graders in Massachusetts who had similar reading scores on a standard test, but very different language experiences.
Some were foreign-language dominant and others were English natives. Here's what's interesting. The students who were dominant in a foreign language weren't yet comfortably bilingual; they were just starting to learn English. Therefore, by definition, they had much weaker English vocabularies than the native speakers.
Yet they were just as good at decoding a text.
"This is very surprising," Luk says. "You would expect the reading comprehension performance to mirror vocabulary — it's a cornerstone of comprehension."
How did the foreign-language dominant speakers manage this feat? Well, Luk found, they also scored higher on tests of executive functioning. So, even though they didn't have huge mental dictionaries to draw on, they may have been great puzzle-solvers, taking into account higher-level concepts such as whether a single sentence made sense within an overall story line.
They got to the same results as the monolinguals, by a different path.
School performance and engagement.
Wayne Thomas and Virginia Collier, a husband and wife team of professors emeritus at George Mason University in Virginia, have spent the past 30 years collecting evidence on the benefits of bilingual education.
"Wayne came to our research with skepticism, thinking students ought to get instruction all day in English," says Virginia Collier. "Eight million student records later, we're convinced," Wayne Thomas chimes in.
In studies covering six states and 37 districts, they have found that, compared with students in English-only classrooms or in one-way immersion, dual-language students have somewhat higher test scores and also seem to be happier in school. Attendance is better, behavioral problems fewer, parent involvement higher.
Diversity and integration.
American public school classrooms as a whole are becoming more segregated by race and class. Dual-language programs can be an exception. Because they are composed of native English speakers deliberately placed together with recent immigrants, they tend to be more ethnically and socioeconomically balanced. And there is some evidence that this helps kids of all backgrounds gain comfort with diversity and different cultures.
Several of the researchers I talked with also pointed out that, in bilingual education, non-English-dominant students and their families tend to feel that their home language is heard and valued, compared with a classroom where the home language is left at the door in favor of English.
This can improve students' sense of belonging and increase parent involvement in their children's education, including behaviors like reading to children.
"Many parents fear their language is an obstacle, a problem, and if they abandon it their child will integrate better," says Antonella Sorace of the University of Edinburgh. "We tell them they're not doing their child a favor by giving up their language."
Protection against cognitive decline and dementia.
File this away as a very, very long-range payoff. Researchers have found that actively using two languages seems to have a protective effect against age-related dementia — perhaps relating to the changes in brain structure we talked about earlier.
Specifically, among patients with Alzheimer's in a Canadian study, a group of bilingual adults performed on par with a group of monolingual adults in terms of cognitive tests and daily functioning. But when researchers looked at the two groups' brains, they found evidence of brain atrophy that was five to seven years more advanced in the bilingual group. In other words, the adults who spoke two languages were carrying on longer at a higher level despite greater degrees of damage.
The coda, and a caution
One theme that was striking in speaking to all these researchers was just how strongly they advocated for dual-language classrooms.
Thomas and Collier have advised many school systems on how to expand their dual-language programs, and Sorace runs " Bilingualism Matters ," an international network of researchers who promote bilingual education projects.
This type of advocacy among scientists is unusual; even more so because the "bilingual advantage hypothesis" is being challenged once again. A review of studies published last year found that cognitive advantages failed to appear in 83 percent of published studies, though in a separate meta-analysis, the sum of effects was still significantly positive.
One potential explanation offered by the researchers I spoke with is that advantages that are measurable in the very young and very old tend to fade when testing young adults at the peak of their cognitive powers.
And, they countered that no negative effects of bilingual education have been found. So, they argue that even if the advantages are small, they are still worth it.
Not to mention one obvious, outstanding fact underlined by many of these researchers: "Bilingual children can speak two languages! That's amazing," says Bialystok.
- NAEYC Login
- Member Profile
- Hello Community
- Accreditation Portal
- Online Learning
- Online Store
Popular Searches: DAP ; Coping with COVID-19 ; E-books ; Anti-Bias Education ; Online Store
Cultivating Bilingualism: The Benefits of Multilingual Classrooms

You are here
What slows cognitive decline in old age, increases earning potential throughout adulthood, and is best started in early childhood? Learning a second (or third!) language.
For decades, educators, researchers, and policy makers across the United States engaged in heated debates about how to ensure English proficiency. Some thought that learning two languages was somehow confusing to children and detrimental to their education. Far too often, debaters showed little regard for how a child’s home language tied him to his family, community, and culture.
Thanks to new research on the cognitive, social, and economic benefits of bilingualism, that debate has largely ended. Now we can focus our energy on supporting children whose first language is not English by building on their linguistic strengths—and on harnessing those strengths to help their peers who only speak English learn a second language too.
This issue of Young Children takes you inside several multilingual classrooms for in-depth, practical examples of how to enhance social, emotional, scientific, language, and literacy development with children who are learning more than one language.

Because a strong social and emotional foundation supports all other learning, we begin with “ Paired Learning: Strategies for Enhancing Social Competence in Dual Language Classrooms ,” by Iliana Alanís and María G. Arreguín-Anderson. The authors observed teachers in preschool through first grade Spanish-English dual language classrooms; based on their observations, they share detailed accounts of highly effective ways to help children learn to cooperate and collaborate. They emphasize learning in pairs as a way to create many low-pressure opportunities for dual language learners to engage in conversations.

Next, we step inside a dual language Head Start classroom where the teachers alternate the language of instruction (Spanish or English) weekly and offer multilingual supports throughout each day. Wanting to teach more science but not having enough time, the teachers join a professional development collaborative to learn how to incorporate science into their language and literacy activities. The impressive results are captured by Leanne M. Evans in “ The Power of Science: Using Inquiry Thinking to Enhance Learning in a Dual Language Preschool Classroom .” As the teachers’ new lesson plans demonstrate, “science education offers [children] discovery-oriented play, vocabulary-rich content, and abundant opportunities to explore oral and written language.”
Although dual language models are a wonderful way to cultivate bilingualism—along with biliteracy, biculturalism, and a whole new lens on the world—they are not always feasible. Many classrooms are multilingual, so teachers are seeking ways to foster first-, second-, and even third-language development (along with progress in all other domains), even when they don’t speak all of the children’s first languages.
In “ Five Tips for Engaging Multilingual Children in Conversation ,” E. Brook Chapman de Sousa offers research-based and teacher-refined strategies to take on this challenge. With examples from a preschool in which over 30 languages are spoken, Chapman de Sousa demonstrates how children benefit when their teachers “use children’s home languages as a resource; pair conversations with joint activities; coparticipate in activities; use small groups; and respond to children’s contributions.” Active listening and gesturing are key ways teachers can be responsive and communicate caring when they do not speak a child’s first language.
Cristina Gillanders and Lucinda Soltero-González help teachers craft a strengths-based instructional approach in “ Discovering How Writing Works in Different Languages: Lessons from Dual Language Learners .” This article carefully examines children’s emergent writing, with examples from prekindergarten through first grade, asking teachers to consider how a child’s knowledge of and ideas about her first language impact her writing in her second language. Teachers can then build on what the children already know and support children’s progress in both languages.
We close the cluster with “ Can We Talk? Creating Opportunities for Meaningful Academic Discussions with Multilingual Children ,” by Mary E. Bolt, Carmen M. Rodriguez, Christopher J. Wagner, and C. Patrick Proctor. Teachers and researchers together develop a structured approach for building multilingual children’s academic vocabulary, knowledge, oral language skills, and writing as they extend an existing unit on ocean animals to create far more opportunities for meaningful conversations. The authors describe how they helped the children develop the social skills, like turn taking, that are necessary for authentic discussions.
While this cluster focuses on children whose first language is not English, all children benefit from the rich, intentional, language-building instruction described in these articles.
Is your classroom full of children’s artwork?
To feature it in Young Children , see the link at the bottom of the page or email [email protected] for details.
These masterpieces, inspired by van Gogh’s Starry Night and Sunflowers , were created by first and second graders in Ms. Bridget’s class at Plato Academy in Des Plaines, Illinois.
We’d love to hear from you!
Send your thoughts on this issue, as well as topics you’d like to read about in future issues of Young Children , to [email protected] .
Lisa Hansel, EdD, is the editor in chief of NAEYC's peer-reviewed journal, Young Children .

Vol. 74, No. 2
Print this article
Multilingual education: A key to quality and inclusive learning

Language is more than a tool for communication; it’s a very specific human cognitive faculty and the foundation of our shared humanity. It enables the transmission of experiences, traditions, knowledge and identities across generations.
Languages play a crucial role in promoting peace, fostering intercultural dialogue and driving sustainable development. They permeate every facet of our lives—from family and work to education, politics, media, justice, research and technology. Our values, beliefs, knowledge, identities and worldviews are intricately shaped by language, reflecting the richness of the human experience.
Languages are at risk and must be championed
But languages are under significant threat. UNESCO data indicates that around 600 languages have disappeared in the last century. If current trends continue, up to 90 per cent of the world’s languages may become extinct by the end of this century.
International Mother Language Day, observed annually on 21 February, underscores the urgent need to champion linguistic diversity and multilingual education rooted in mother tongues.
For more than seven decades, UNESCO has promoted mother language-based and multilingual education as fundamental to achieving quality, inclusive learning.
Why multilingual education matters
Enhanced learning. First, and most obviously, students learn best in a language they understand. Yet UNESCO data shows that 40 per cent of the world’s population does not have access to an education in a language they speak or understand. Our research documents the benefits of being taught in learners’ native languages: in upper-middle- and high-income countries, children who speak the language they are taught in are 14 per cent more likely to read with understanding at the end of primary, compared to those who do not.
In France, children who speak French at home are 28 per cent more likely to be able to read with understanding at the end of primary than children who do not. This share rises to over 60 per cent more likely in countries such as the Islamic Republic of Iran, Slovakia, South Africa and Türkiye.
At the end of lower secondary, adolescents speaking the language of instruction are over 40 per cent more likely to be able to read with understanding compared to those who did not. This ranges from a 4 per cent gap in Canada to around 40 per cent in Germany and the Kingdom of the Netherlands, and over 60 per cent in Thailand.
Improved access and inclusivity through mother tongue education. Adopting a mother language-based, multilingual education improves access to and inclusion in education, particularly for population groups that speak non-dominant, minority and indigenous languages. Studies have shown that such approaches can boost classroom participation, improve retention rates and encourage family and community involvement in education. They also play a vital role in mitigating the challenges faced by migrant and refugee learners, promoting a sense of safety and resilience. Yet—at a time of record displacement—over 31 million young people who have fled war or crisis situations are learning in a language that differs from the official language of their country of origin.
Contributing to peace and sustainable development. The achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals is intricately linked to linguistic diversity and multilingualism. The Global Action Plan of the International Decade of Indigenous Languages (2022–2032) , spearheaded by UNESCO, underscores the importance of language choice for human dignity, peaceful coexistence and sustainable development. Commitment to these ideals drives UNESCO support for building inclusive and equitable, quality education opportunities in indigenous languages in both formal, non-formal and informal educational settings.
Helping mother language education thrive
The potential of multilingual education is enormous, but realizing its full benefits requires a commitment to lifelong learning and a deeper appreciation of the value of linguistic diversity.
To foster thriving multilingual education, we need robust policy support, advocacy and innovation. This includes adopting policies that promote mother language education from early childhood, as seen in diverse countries such as Ghana, Peru, Singapore and South Africa. It also involves recruiting and training teachers and community members competent in learners’ mother tongues, as well as exploring innovative solutions, such as partnerships with digital platforms, to meet diverse language needs.
Partnerships and cooperation at all levels, including across universities, academic centres and institutions that support language development, can also enhance capacity, and expand access to teaching and learning materials in local languages in both print and digital forms. This must be accompanied by formative and summative assessments that are appropriately designed to monitor the learning outcomes of multilingual learners.
Mother language-based, multilingual education must be part of our efforts to address the learning crisis and learning poverty facing many countries around the world.
In an increasingly globalized world, UNESCO remains committed to promoting multilingual education and cultural and linguistic diversity as cornerstones for the sustainability of our societies.
This article by UNESCO Assistant Director-General for Education, Stefania Giannini, was originally published in the UN Chronicle on 20 February 2024, ahead of International Mother Language Day.
- International Mother Language Day
- Why multilingual education is key to intergenerational learning
Related items
- Mother tongue
- Mother tongue instruction
- Educational trends
- Topics: Display
- See more add

Other recent idea

Products and services
Our innovative products and services for learners, authors and customers are based on world-class research and are relevant, exciting and inspiring.
- Academic Research, Teaching and Learning
- English Language Learning
- English Language Assessment
- International Education
- Educational resources for schools
- Educational Research & Network
- Cambridge CEM
- Partnership for Education
- Cambridge Dictionary
- The Cambridge Mathematics Project
We unlock the potential of millions of people worldwide. Our assessments, publications and research spread knowledge, spark enquiry and aid understanding around the world.
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Environment
- United Nations Global Compact
- Communities
- Diversity and inclusion
- Annual Report 2023
- News and insights
- Anti Slavery and Human Trafficking
- Australia & New Zealand Terms of Trade
- Candidate Privacy Notice
- Conditions of Sale - Consumer
- Conditions of Sale - Goods
- Freedom of Information
- Mobile Apps
- Purchase Terms
- Safeguarding policy
- Security & Vulnerability Disclosure Policy
- Social Media Comments Policy
- Website Terms of Use
- Accessibility
- Rights and permissions
- Media enquiries
- Delivery and returns
- Remittance information
No matter who you are, what you do, or where you come from, you’ll feel proud to work here.
Your bag is empty.
Remove item
Are you sure you want to remove from your bag?
- Learning Passport
- Press coverage
- Our experts
- Needs analysis and policy recommendations
- Curriculum design and development
- Assessment design and development
- Publishing teaching and learning resources
- Teacher professional development
- English language learning and skills
- Case studies
Multilingualism in the classroom: benefits in education and policy recommendations
Michael Evans , Emeritus Reader in Second Language Education at the Faculty of Education, explores research into the relationship between language and learning, to draw out key findings on the advantages of multilingualism and provide policy recommendations.

Multilingualism has grown to become a dominant feature of schooling across the world. What is the impact of this development on student learning? What practical steps can we take, so that teaching and learning gain the wide-ranging advantages of multilingualism?
It is challenging to base conclusions and policy recommendations on the few large-scale studies that have researched the link between multilingualism and academic performance. Complex contextual factors tend to influence the findings:
- In most cases the school language of instruction is English, a global language that some immigrant children have already had prior access to; in contrast, identifying the advantages of multilingualism in low-income, developing countries needs more context-sensitive research
- Different countries have varying educational systems and practices (e.g. bilingual schools in North America, or introductory classes in Sweden); these can affect research into the relationship between multilingualism and academic achievement
- The link between multilingualism and academic achievement cannot be separated from other socio-educational goals, such as those of integration
What is the meaning of multilingualism, exactly? The meaning of multilingualism, with regard to national settings, is the use of more than one home or first language by the local population. With regard to an individual, it refers to their ability to speak more than one language.
In terms of the difference between bilingualism and multilingualism - strictly speaking, multilingualism refers to competence in more than two languages. This distinguishes it from bilingualism, which refers to the use of two languages exactly. However in this article, the broader sense of multilingualism is used, as per the definitions in the previous paragraph.
The following is a set of assertions on both the drawbacks and benefits of multilingualism in three broad contexts:
- The migrant context, where the learner’s home language differs from that of the host community
- The indigenous multilingualism context in developing countries, with school learning using a different dominant language to the multiplicity of pupils’ home languages
- The language of instruction context, where schools use a foreign language to teach a range of subjects on the curriculum e.g. English as medium of instruction (EMI)
1. The context of migration in Western developed countries
First generation migrant children with no initial competence in the host country language of instruction require three to five years before acquiring basic interpersonal competence skills (BICS), according to several studies.
They need five to seven years before gaining cognitive academic language proficiency (CALP). BICS and CALP are terms originating from Jim Cummins’ early works, such as Bilingualism and Special Education . Furthermore, proficiency in reading and writing in the home and host languages correlates with academic achievement.
In ‘hyper-diverse’ migrant linguistic environments, such as the UK, the practicality of organising dual-language programs is restricted. Overall it would involve teaching in many of the home (L1) languages represented by the pupil population’s multilingualism.
Statistical studies of the academic performance of English as a second language (EAL) students in England state schools have shown a steady improvement in GCSE and A Level results. However, scores are affected by a number of key variables such as age of arrival in the UK, regional variation and identity of the first language.
2. The context of multilingualism in low-income developing countries
In this context, research shows that at primary school level, proficiency in home language literacy is a predictor of English literacy.
The home language instruction medium in rural primary schools can lead to better academic performance, in comparison to using EMI.
In a 2019 position paper , the British Council stated that primary school learners in low- and medium-income countries “taught in their own or a familiar language, rather than English, […] are more likely to understand what they are learning and be more successful academically”.
Therefore the British Council supports the teaching of English as a subject, rather than as an instruction medium for other subjects, in this age range and context.
In several reports including a recent study in 2016 , UNESCO has also supported promoting a ‘multilingual ethos’ and implementing mother tongue teaching in developing countries.
3. The context of additional language learning
The EMI approach is less effective than using a home language instruction medium for ‘content’ learning at school level, according to several studies.
EMI at secondary school level leads to improved proficiency in the English language, but there is evidence of a negative effect on humanities subjects.
Encouraging multilingualism via Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL) is a different approach - the integration of target language learning and subject teaching. In contrast, EMI has no integrated language learning.
Long-term, a CLIL approach enhances both content learning and competence in the additional language, concludes Pérez Cañado in her study The Effects of CLIL on L1 and Content Learning .
Policy recommendations
Language education policy-making should be guided by the following research-informed principles and practices, based on the advantages of multilingualism:
- A clear rationale for introducing medium of instruction national policies, formed on evidence-based educational judgments rather than strategic considerations
- Evidence-based planning of multilingualism, sensitive to the linguistic needs and repertoires of learners, in different national contexts
- Provision of appropriate training in linguistic competence and language-related pedagogical practice for EMI and CLIL teachers
- Appropriate training and knowledge of the integrated use of the L1 in EMI and CLIL settings
- Knowledge sharing between teachers in different sectors on best practice language use and content learning
- Careful transition planning from L1-based instruction at primary school level, to a staged introduction of teaching selected subjects through the medium of English at secondary school level
- The development of an integrated assessment framework, on language and subject knowledge, appropriate to the socio-cultural context
- The development of dual-language resources and language awareness strategies, for pupils at primary school level
Conclusion: multilingualism in the classroom
Research suggests that competence in multilingualism plays a significant role in students’ academic performance:
- Newcomer migrant students with no initial competence in the host language take up to five years to develop age-appropriate competence in speaking it and up to seven years to reach an appropriate level of academic competence in it
- Literacy in the home language has a positive effect on students’ learning of other languages and other subjects
- Transfer of competence between the languages is also influenced by the nature of the subject matter task (e.g. a maths task, or a text comprehension task)
- Additional language learning has a positive effect on first language literacy, including a greater use of learning strategies
- Students’ socio-economic background affects success of the medium of instruction policy implementation
- EMI is more effective at post-primary school level in non-English speaking countries
- Where students’ home language is other than their school’s medium of instruction, effective integration of home language use and learning leads to improved academic achievement
- CLIL seems a more effective approach for multilingualism in the classroom than EMI
To find out more about research on usage-based approaches to help students learn second languages, read our recent report here .
Cambridge Partnership for Education has partnered with more than 25 governments, with an aim to transform education by implementing evidence-based sustainable solutions.
To find out more about the advantages of multilingualism and other approaches to transform societies through learning, please contact us .
Download Download the full report
Related Posts

Insight - Blog

- Cambridge Assessment English
- Cambridge Assessment International Education
- University of Cambridge Faculty of Education
- Educational Resources for Schools
- Higher Education
What we do What we do
- Author support
- Assessment Research
About us About us
- People and planet
- University of Cambridge
© 2024 Cambridge University Press & Assessment
- Modern slavery
Do you want to continue?
You are about to change your country, but have items in your bag.
Your current bag items may not be available in the new country you wish to view, so we need to empty your bag.
Email verified with restricted access to resources
Your email has been verified. You are now able to request access to teacher restricted resources. If you are a teacher, simply complete the teacher resource request form, and wait for your request to be validated.
Email verified
Your email has been verified.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Gray Matter
Why Bilinguals Are Smarter
By Yudhijit Bhattacharjee
- March 17, 2012

Editor’s Note: We’re resurfacing this story from the archives to show you how learning a second language can improve how you think.
SPEAKING two languages rather than just one has obvious practical benefits in an increasingly globalized world. But in recent years, scientists have begun to show that the advantages of bilingualism are even more fundamental than being able to converse with a wider range of people. Being bilingual, it turns out, makes you smarter. It can have a profound effect on your brain, improving cognitive skills not related to language and even shielding against dementia in old age.
This view of bilingualism is remarkably different from the understanding of bilingualism through much of the 20th century. Researchers, educators and policy makers long considered a second language to be an interference, cognitively speaking, that hindered a child’s academic and intellectual development.
They were not wrong about the interference: there is ample evidence that in a bilingual’s brain both language systems are active even when he is using only one language, thus creating situations in which one system obstructs the other. But this interference, researchers are finding out, isn’t so much a handicap as a blessing in disguise. It forces the brain to resolve internal conflict, giving the mind a workout that strengthens its cognitive muscles.
Bilinguals, for instance, seem to be more adept than monolinguals at solving certain kinds of mental puzzles. In a 2004 study by the psychologists Ellen Bialystok and Michelle Martin-Rhee, bilingual and monolingual preschoolers were asked to sort blue circles and red squares presented on a computer screen into two digital bins — one marked with a blue square and the other marked with a red circle.
In the first task, the children had to sort the shapes by color, placing blue circles in the bin marked with the blue square and red squares in the bin marked with the red circle. Both groups did this with comparable ease. Next, the children were asked to sort by shape, which was more challenging because it required placing the images in a bin marked with a conflicting color. The bilinguals were quicker at performing this task.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades

Benefits of Being Bilingual Essay | Long and Short Essays on Benefits of Being Bilingual for Students and Children
October 1, 2021 by Prasanna
Benefits of Being Bilingual: Language evolution has taken place over the years in different parts of the world. Languages have changed and developed through social needs. To communicate with different groups for trade, travel, and other reasons people have started using more than one language. Many countries also have more than one official language. There are some prominent benefits of being bilingual as revealed through various research and analysis. Let’s discuss some of the cognitive benefits of being bilingual.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
Long Essay on Benefits of Being Bilingual
Develop Brain Power
Learning a second language other than a native language develops a person’s learning aptitude and helps in a great way to keep the brain alert and healthy. It can improve creativity, problem-solving skills, attention control, and confidence. Learning other languages from an early stage can help improve a child’s educational development, social and emotional skills that have positive effects for many years to come. It is also found that people who are conversant with more than one language can process information more efficiently and easily.
Improve Cultural Awareness
Being bilingual gives an individual an opportunity to get exposed to diverse cultures, ideas, and perspectives by way of learning and communication. The children who are born and brought up in different countries get to learn different languages besides the home language. The benefits of being bilingual can be seen in children as they acknowledge the value of other cultures and heritage.
Enhance Social Life
Knowing a second language gives the ability for more social interactions and enhances social skills. The benefits of being bilingual are to connect with a wider range of people; express and interact with more confidence in social situations. This skill often makes you more presentable and attractive while building meaningful relationships. Learning a country’s language when traveling to that country gives a more immersive and authentic experience. It would be easier to communicate with the local language and make more friends. Bilingual skills help individuals to adjust with others from varying cultures and backgrounds. Through this communication skill, one can be more perceptive of others, and be more empathetic.
Better Job Opportunities
One of the benefits of being bilingual is new career and job opportunities. Companies with international offices and client bases consider bilingualism an added advantage. Multilingual consumers constitute a major part of the commercial force and represent a significant opportunity for business. So there are demands for employees who can speak other languages and navigate different cultural expectations. Fields like travel and tourism, healthcare, journalism, and national security give priority to candidates with bilingual language skills.
Improve Learning Aptitude
Researchers established the fact that bilingual adults learn a third language better than monolingual adults. Learning a different language helps one to develop better attention and interest towards other languages in general. The improved understanding of how language works, coupled with the experience already gained, makes it all the easier to learn a third or fourth language. Bilingual experience may help to follow a new language more clearly leading to better learning. The benefits of being bilingual may be rooted in the ability to focus on information while reducing interference from the languages already known.
There are valuable benefits associated with the skill of being bilingual, be it individual or social. It gives the ability to explore a diverse culture, people, and customs. It is really fascinating to interact with someone with whom you might otherwise never be able to communicate. The behavioral changes and social advantages observed are major benefits of being bilingual. It highlights the need to consider how bilingualism shapes the activity and attitude of people in a positive manner.

Short Essay on Benefits of Being Bilingual
Introduction
Language evolution has taken place gradually with advancements of civilization and languages change and develop over time. Different groups of people would have found themselves speaking different languages due to social influence. Learning a second language expands a person’s social circle, improves confidence, and enables them to connect with a growing diverse population of the multilingual community.
Studies have found that being bilingual can improve the ability to focus attention and perform tasks effectively. Bilingual children become more successful in problem-solving and can have a creative approach. Learning a new language helps in a great way to keep the mind focused and sharp.
Bilingual skill can help to interact with different people and understand another culture including music, film, and literature. This means there are more opportunities to make friends, explore different hobbies, and improve social skills. Bilingual people tend to be more open to communication as they can interact through both languages.
Considering the benefits of being bilingual, the educational curriculums in many schools include a compulsory third language to be taught to children. There are private coaching facilities available also to provide learning on a second language. The knowledge of more than one language has several benefits in the long run because of diverse job opportunities. Being in a country without knowing the local language creates a lot of problems, whereas if you can communicate with that language it becomes more convenient to handle any situation. Even one can work as an interpreter to help others to communicate and get appreciation in return which is self-motivating.
Conclusion on Benefits of Being Bilingual
The benefits of being bilingual can be observed through the awareness and the ability to recognize language as a means of building connections and relationships. It brings confidence and motivation to one’s personality which is one of the most important benefits of being bilingual.
FAQ’s on Benefits of Being Bilingual
Question 1. What are the job opportunities for a bilingual person?
Answer: There are job opportunities in the travel and tourism industry, healthcare, Journalism, Teaching, MNCs, and Embassies, etc.
Question 2. Should a foreign language be a part of the educational curriculum for children?
Answer: Yes, learning a foreign language is very important at the school level so that students can capture it quickly and enhance their knowledge about other cultures and heritage.
Question 3. How does bilingualism help people traveling to another country?
Answer: Traveling becomes more convenient and enjoyable when there is no language barrier. With the knowledge of a foreign language, it becomes easier to process information about a new place.
Question 4. What percentages of people speak two languages across the world?
Answer: Around the world, nearly 60%-70% of people speak at least two languages.
Question 5. How do bilingual skills help to improve social life?
Answer: Being bilingual one can get exposed to other cultures and be able to interact in social surroundings building more relationships.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education

We're celebrating 50 years of transforming education across the country!
COVID-19 Updates: Visit our Learning Goes On site for news and resources for supporting educators, families, policymakers and advocates.
- Resource Center
Why Bilingual Education is Important to Me

• IDRA Newsletter • August 1995
Each of these essays was among the top three winners in the 1994 National Association for Bilingual Education (NABE) nationwide writing contest for bilingual students, sponsored by Coca-Cola USA and Apple Computer, Inc.
By Serana Demientieff Grade 8 Kasigluk, Alaska
Bilingual education is important to me so I can be able to speak in English and Yup’ik. Every child should be taught at least some things about what our ancestors did. Elders of the Yup’ik world worry about losing the Yup’ik language. As for myself, I am very proud of myself because I am a bilingual person.
At our school, in Akula, we have a Yup’ik studies program. The Yup’ik studies program is a program where we can learn or at least remember how to make the things which our ancestors did back then. More and more schools are asking for the curriculum which we are using at our school.
How important do you think it is to keep our language alive? I think it is really important because one we lose it we can not find it ever again. For example, the Eyak language is dying because no one has ever been taught how to read and write in the Eyak way. There is only one elder who knows how to speak and read in the language. If no one has been taught, and that elder dies the Eyak language is gone forever. Would you want that to happen? To keep our language alive we have to teach our future children how to speak in the Yup’ik language and also have to teach them the things we were taught.
It is also important to have the English language too. If we know the English language we can have jobs in the future and be able to speak to non-natives. We also have to know the English language to be able to read things at the store and also in the newspapers and count the money you have to spend.
In the future I plan to teach my children to be bilingual. First, I plan to teach them Yup’ik so they can pass the language onto their children and English so they can be able to communicate with non-natives and also to understand English.
By Huy Nguyen Grade 5 Orlando, Florida
“A person who speaks two languages is worth two persons,” says my bilingual teacher. That is reason enough to make bilingual education important to me. I have a treasure that many people do not have – two worlds of languages and cultures. I would not be writing this essay if there was not a bilingual education program at my school.
My family and I came to the United Sates over two years ago. We came from a war-torn Vietnam, a very small country with a musical language and a millenary old culture. I am so happy to be in this country. My younger sister and I are the unique members in a family of 10 who can go to school in this land of opportunity. That means I will be able to fulfill my dream of becoming a medical doctor. I was not always this hopeful.
Soon after we were enrolled in high school, my hope began to fade away. People around me, teachers and students, all spoke some strange language. I felt like I was enclosed in a box or in a house without windows. I was surrounded by people; yet, I was isolated because communication was impossible.
Fortunately, I was transferred to another school that had a bilingual teacher to help me. My whole world turned around. Suddenly, everything made sense to me. It took my bilingual teacher 15 minutes to explain to me a lesson in my native language, while it took my English speaking teacher an hour to do the same task!
I began to make significant progress in learning English and other subjects. My house now has windows to another world – the world in which I am now living. I have a sense of importance because now I am the link between my family and the world outside of my home.
A Vietnamese adage says: Cây có côi, nuoc có nguon [Trees have roots; springs have sources]. An uprooted tree will die. My tree was not uprooted; it was transplanted to another fertile soil. I am lucky to have my tree deeply and firmly rooted in my family, my language and culture. The branches of my tree reach out and capture new nutrients to feed my hunger for more knowledge. My life becomes richer because it feeds on two sources: one is the world of English, the other Vietnamese.
As the world shrinks, an interdependence among nations becomes more evident. People need the bilingual and bicultural skills to communicate and to avoid conflict. I strongly believe that bilingual education can facilitate cultural understanding as it teaches languages. For that reason, all schools should offer bilingual education to their students.
I am proud to be able to communicate in more than one language. I am confident that I will be able to fulfill my dream and my responsibilities to my family and to this country – thanks to my family who supports me and to my teachers who guide me.
By María Luisa Mijes Grade 6 Houston, Texas
In a society where the bright and the not so bright is given the same opportunity, I address myself to you. First of all, I was born in San Antonio, Texas. My parents were both born in Mexico. I am 11 years old now.
Although I came to school knowing only one language, I was able to impact the new world of English with the wealth of my Spanish heritage. My first teachers at home who were my parents sent me to school fully equipped with concrete concepts which I was able to transfer in my bilingual classes.
Bilingual education begun to formulate my new experiences of success in school. There was never a year in which I was not an honor roll student.
It was in kindergarten where I was able to connect my Spanish culture in the Suzuki Violin classes taught to me in school. The music and Spanish language of my ancestors facilitated the rapid progress in the rich multicultural experience. Bilingual education opened a whole new spectrum of light for me. An array of rainbows through music makes me a leader as an ambassador of my culture to the world through television and personal appearances.
I can tell you with great pride that I have sung the songs of my forefathers and serenaded through mariachi music. Presidents, governors, movie stars, and our unforgettable renown Spanish World Comedian. Streams of tears flowed down his face as he heard me sing and play. This experience will forever be imprinted in the profound depths of my soul. My rich heritage leads me through fields of challenging conquests. To be equipped with the wealth of multicultural experiences through music and academic success is an asset. My serenades are a gift for your enjoyment. Your pay is the song of your soul through the simple clapping of your hands. The molding of my life can never be reproduced, sold, nor bought. My authors are unique bilingual teachers, a one of a kind school, my unique parents and home.
This year, bilingual students throughout the country can submit essays on the topic: Why bilingual education is important to me. Essays are grouped into three categories: elementary, grades three through five; middle/jr. high, grades six through eight; and high school, grades nine through 12. The first place winners for each category will be awarded a $5,000 scholarship and an Apple Macintosh color computer. The winners, with their parents and bilingual teachers, will also win a trip to the next annual NABE conference in Orlando, Florida. Each second place winner will receive a $2,500 scholarship, and each third place winner will receive a $1,000 scholarship. The deadline for submission of essays is November 1, 1995. For contest information in English or Spanish call 1-800-GET-COKE or call NABE at 202/898-1829. Essays printed with permission from the National Association for Bilingual Education (NABE).
Comments and questions may be directed to IDRA via e-mail at [email protected] .
[©1995, IDRA. This article originally appeared in the August 1995 IDRA Newsletter by the Intercultural Development Research Association. Permission to reproduce this article is granted provided the article is reprinted in its entirety and proper credit is given to IDRA and the author.]
- Classnotes Podcast
Explore IDRA
- Data Dashboards & Maps
- Educator & Student Support
- Families & Communities
- IDRA Valued Youth Partnership
- IDRA VisonCoders
- IDRA Youth Leadership Now
- Policy, Advocacy & Community Engagement
- Publications & Tools
- SEEN School Resource Hub
- SEEN - Southern Education Equity Network
- Semillitas de Aprendizaje
- YouTube Channel
- Early Childhood Bilingual Curriculum
- IDRA Newsletter
- IDRA Social Media
- Southern Education Equity Network
- School Resource Hub – Lesson Plans

5815 Callaghan Road, Suite 101 San Antonio, TX 78228
Phone: 210-444-1710 Fax: 210-444-1714

© 2024 Intercultural Development Research Association
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Bilingual education for young children: review of the effects and consequences
Ellen bialystok.
Department of Psychology, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada
Bilingual education has been an educational option in many countries for over 50 years but it remains controversial, especially in terms of its appropriateness for all children. The present review examines research evaluating the outcomes of bilingual education for language and literacy levels, academic achievement, and suitability for children with special challenges. The focus is on early education and the emphasis is on American contexts. Special attention is paid to factors such as socioeconomic status that are often confounded with the outcomes of bilingual education. The conclusion is that there is no evidence for harmful effects of bilingual education and much evidence for net benefits in many domains.
In the US, bilingual education has been a controversial topic almost since the founding of the nation, and from the beginning, the discussions were imbued with political rhetoric (for reviews see Nieto 2009 ; Ovando 2003 ). The Bilingual Education Act of 1968 recognized the situation of minority children with limited proficiency in English and created funding for programs that would assist these children to succeed in American schools and develop their proficiency in both English and their home language. The act was largely focused on Spanish speakers, but subsequent groups, such as Chinese speakers, brought about amendments to the act to expand its scope ( Lau vs. Nichols, 1974 ). Other countries have had a different experience with bilingual education and a different set of political and social associations with these programs. A prime example is Canada, where the social, demographic, and political situations were different from those in the US. Although Canada is officially a bilingual country, there is not a single language that defines most bilinguals as there is in the US, because the majority of bilinguals in Canada speak one of the official languages (English or French) and a heritage language. Surprisingly, few citizens are actually proficient in both official languages. In the 2011 census, about 17% of respondents stated they could conduct a conversation in both English and French, a considerable increase from the estimate of 12% who could achieve this in 1961 ( Lepage and Corbeil 2013 ), although still below what would be expected in a bilingual society. One factor that may be responsible for the growth in French-English bilingualism over the 50-year period is the impact in the past generation of popular French immersion programs in which children who would otherwise have had little exposure to French became very proficient and in many cases, fully bilingual.
In Europe, attitudes to languages, educational systems, and bilingualism in general, to name a few factors, are very different from those in North America. Garcia (2011) makes a strong case for the widespread appropriateness of bilingual education globally, but the context in which education takes place is crucial; there is no universal prescription for bilingual education and no universal outcomes. As Baker (2011) points out, the perspective on bilingual education depends largely on the point of view, and studies conducted in one context may have little relevance for bilingual education in another context. Therefore, this review will focus primarily on North American contexts and address some of the central issues regarding the efficacy of bilingual education for that region, in particular for the US.
Finally, the review will focus on the early school years because they are the foundation for academic outcomes. Education is a long-term process and results continue to influence outcomes throughout life. However, the early years are crucial for establishing basic skills and attitudes toward education, so the examination of bilingual education in the present review will focus on the first three years of schooling. To summarize, the review is restricted in that it selectively reviews studies whose empirical properties are considered sufficiently reliable to form conclusions, with a focus on primary education in the context in the US, and addressing specific questions, namely, language outcomes, cognitive outcomes, and generalized appropriateness of the programs.
Bilingual education is an umbrella terms that encompasses a range of education programs that have been designed for an even wider range of children and a host of special circumstances. Essentially, bilingual education refers to any school program in which more than one language is used in the curriculum to teach non-language academic subject matter or the language of schooling does not match the language of the home or community, but the reasons for incorporating the languages, the specific languages chosen, the structure of the program, and the relation between the school languages and the community vary widely and influence educational outcomes. Over-riding all this is the distinction between ‘bilingual education’ and the ‘education of bilingual children’, concepts that are importantly different from each other. Consider the following two definitions for bilingual education. Genesee (2004 , 548) defined bilingual education as ‘education that aims to promote bilingual (or multilingual) competence by using both (or all) languages as media of instruction for significant portions of the academic curriculum’. In contrast, Rossell and Baker (1996 , 7) defined bilingual education as ‘teaching non-English-speaking students to read and write in their native tongue, teaching them content in their native tongue, and gradually transitioning them to English over a period of several years’. Clearly these definitions are describing different situations and carry different goals.
This distinction between bilingual education and the education of bilingual children is part of the historical difference between the development of bilingual education in the US and elsewhere. For bilingual education of minority language students in the US, the motivation was to create an educational program for children who were at-risk of academic failure because of low proficiency in English, the language of schooling, by engaging them in the education process through the use of their home language (e.g. including Spanish in the education of Hispanic children). The success of these programs was judged primarily by proficiency in English (the majority language), with the main criterion being English language literacy. For bilingual education in Canada, in contrast, the motivation was to offer an educational alternative designed to make majority language children (i.e. English speakers) bilingual. Thus, success of these programs was judged by the extent to which children mastered the minority language while maintaining proficiency in the majority language. Similar immersion programs were developed for children to gain proficiency in both national (e.g. children of Finnish immigrants in Sweden, Troike 1978 ) and heritage languages (e.g. Hawaiian programs in the US, McCarty and Watahomigie 1998 ; Navajo programs in the US, Rosier and Holm 1980 ; Maori programs in New Zealand; Durie 1998 ; May and Hill 2005 ). All these programs fall under the general rubric of bilingual education but are importantly different from each other. A more complete range of the diversity of bilingual education programs is described by Fishman (1976) and more recently by Mehisto and Genesee (2015) .
In spite of substantial differences between them, the two goals of educating bilingual children and creating programs to make children bilingual are interrelated. In the US, there is large overlap between them because the largest number of bilingual education programs was developed to educate bilingual or limited English proficient (EP) students, primarily Spanish-speaking, who were otherwise at-risk for school failure. The present review will focus on bilingual education in general and not on the specific issues involved in the education of this particular group of children (for a detailed discussion of this issue, see August and Shanahan 2006 ). Ultimately, it is important to know if education through two languages is viable, if young children can learn in this kind of an environment, and if the outcomes of these programs meet the needs of all children. The present paper reviews evidence relevant for those judgments.
Development of language and literacy in bilingual education
Evaluation of the effectiveness of bilingual education on language and literacy outcomes requires well-controlled research. The clearest evidence for the unique contribution of bilingual education programs to these outcomes would come from randomized control trials, but such a design is almost impossible to achieve (but see Genesee and Lindholm-Leary 2012 , for discussion). The closest design to this methodological ideal is in studies that investigate bilingual education programs for which spaces are allocated by lottery because of over-demand so that comparisons can be made between children who were admitted to the program and those who were not. Children in this latter group generally enter regular classrooms and may remain on a waiting list. Even here, however, there is the possibility of bias in terms of who enters the lottery. The results of the few studies that have had the opportunity to compare these populations (e.g. Barnett et al. 2007 ) are largely consistent with the majority of the literature in which children in bilingual or single language programs are compared on critical outcome measures.
The primary goal of early schooling is to establish the foundational skills upon which children will build their educational futures. The most important of these abilities are language and literacy competence. Not surprisingly, therefore, the majority of research that has evaluated bilingual education programs has focused on children’s development of these crucial linguistic abilities. The research is complicated because the type of education program is only one of many factors that shape these emerging abilities so clear evidence for the role of the education program as distinct from other sources of variance in the child’s background requires carefully controlled designs. For example, children who are Hispanic but are native speakers of English have education outcomes in terms of dropout rates and academic failure that are similar to Hispanic children who are Spanish-speaking, ruling out English proficiency as the explanation ( Forum for Education and Democracy 2008 ). Just as English proficiency alone cannot explain school outcomes, neither can the educational program.
In part for this reason, conclusions regarding the development of language and literacy through bilingual education in the US is complicated by the confounding of ethnicity and social class with Spanish proficiency and bilingualism (for discussion see Francis, Lesaux, and August 2006 ). Nonetheless, two studies by Lindholm-Leary and colleagues have provided reasonably clear results on these issues. In one study, Lindholm-Leary and Block (2010) assessed the English and mathematics achievement of 659 Hispanic students attending either mainstream English or various types of bilingual programs in California. In the bilingual schools, the proportion of instruction shifted from predominantly Spanish to predominantly English over the period from kindergarten to fourth grade. Students were classified as EP or English Language Learner (ELL) prior to the study. The main result was that standard scores on the English proficiency test were higher for both ELL and EP students who were in the bilingual programs than they were for children in the mainstream English programs. Similar results were found for scores on the mathematics test. Overall, students in the dual language program in this low socioeconomic status (SES) community achieved at least as well and in some cases better in both English and mathematics than did comparable students in a program in which all instruction was in English. Students in the bilingual programs also made more rapid progress across the grades in these tests than did students in the English program and, therefore, were more advanced in their trajectory to close the achievement gap with statewide norms for these tests.
In a similar study that included children in kindergarten through second grade, Lindholm-Leary (2014) assessed 283 low SES Hispanic children in either English or bilingual programs. Children entering the English kindergarten programs had higher language scores than those entering the bilingual programs, but these differences disappeared within one or two years and then reversed, with children in the bilingual program outperforming the English-only instruction group in both English and Spanish test scores by the end of second grade. Not surprisingly, children in the English program showed significant loss of Spanish proficiency, making them in fact less bilingual, a topic that will be discussed below.
Barnett et al. (2007) compared performance of low SES preschool children (3 and 4 years old) in bilingual or English-only programs, but importantly, children were assigned to these programs by lottery, thereby controlling to some extent for pre-existing differences among the children or their families. The programs were in a school district in which 76% of the children qualified for free or reduced-price lunch. The outcome measures were largely experimental tasks that assessed phonological awareness and language knowledge (primarily vocabulary), but the results were consistent with those reported in other studies. Specifically, children in both programs made comparable progress in skill development in English, but children in the bilingual program also developed these skills in Spanish, indicating that dual language instruction did not impede development of English, the L2.
In these examples, bilingual instruction had long-term benefits for children’s language and literacy proficiency in both languages. In a review and meta-analysis of this literature, Francis, Lesaux, and August (2006) concluded that ‘bilingual education has a positive effect on English reading outcomes that are small to moderate in size’ (392). Thus, overall, bilingual education for Hispanic children in the US leads to English outcomes that are equivalent to those found for children in mainstream English programs, with better outcomes for Spanish.
These results are broadly consistent with those found for bilingual education programs serving other communities, with other languages, in other countries, where students are more likely to belong to majority language groups than minority language, as in the US. Thus, the outcomes obtained with children at risk for educational failure produce patterns of results similar to those found for children with entirely different linguistic and demographic backgrounds. The most studied of these programs is Canadian French immersion in which Anglophone children in Canada are educated through French. Results of studies over the past 50 years have shown that English outcomes are equivalent to or better than those found for children in English programs (even though most instruction is in French in the primary grades) and French outcomes are moderate to high, although below levels found for native-speaking French children ( Genesee 1983 , 2004 ; Hermanto, Moreno, and Bialystok 2012 ; Swain and Lapkin 1982 ).
Three further examples with similar results come from bilingual programs operating in Italian and English, Mandarin and English, and Hebrew and Russian. Assessment of the Italian-English program was a small-scale study in which 60 children attending this program in California were evaluated from first through third grades for language and literacy ability in English and Italian ( Montanari 2013 ). Results showed that these children developed strong literacy skills in both Italian and English by first grade, even though instruction was exclusively in Italian. The second program, also implemented in California, provided instruction through Mandarin beginning in kindergarten to children who either had Mandarin exposure at home or were only English speaking ( Padilla et al. 2013 ). Like the Italian-English program, this was a small-scale study. The results showed that all children gained proficiency in both English and Mandarin and importantly achieved at least equivalent and sometimes greater than state levels on standardized tests of English, math, and science in spite of being educated through Mandarin. Finally, two studies investigated language and literacy development in Russian-Hebrew bilingual 4-year-olds who were attending either bilingual Hebrew-Russian or Hebrew schools in Israel, where Hebrew is the majority language. Again, the results showed that children in the bilingual programs developed language proficiency ( Schwartz 2013 ) and narrative skills ( Schwartz and Shaul 2013 ) in Hebrew, the majority language, at least as well as did children in the Hebrew only programs and at the same time maintained higher levels of Russian. Across all these studies, therefore, the majority language of the community was mastered whether or not it was the primary language of instruction, but the minority language required environmental support to reach high proficiency levels.
The studies that compared English-only and bilingual education in Hispanic children were generally conducted with low SES populations, but that is not the case for the non-Spanish programs: children in the Italian-English program were described as ‘middle class’; children in the Mandarin-English program were described as ‘upper middle class’; and children in the Hebrew-Russian program were described as ‘mid-level socioeconomic’. Thus, even though none of the students was at-risk in the manner generally understood for Hispanic children in Spanish-English bilingual programs, the patterns of language and literacy outcomes were similar, even if the absolute levels of achievement were different. Therefore, there is no evidence that education through two languages impedes progress in the development of language and literacy skills in the majority language and has the added benefit of developing and sustaining these skills in the minority language. This generalization about positive outcomes is confirmed by a study in which at-risk low performing children attending bilingual education or majority language English-only programs were compared for their English language and literacy performance ( Lopez and Tashakkori 2004 ). There was no evidence of additional burden on the development of English skills for children in the bilingual program.
Other academic and cognitive achievements
However important language and literacy are for children’s development, they are not the only outcomes that need to be considered in evaluating educational options for children. The impact of education through a weak or non-proficient language on children’s academic success has long been a concern. Dire warnings about harmful effects of these programs were expressed by Macnamara (1967) in his evaluation of children attending an Irish immersion program in Ireland. He reported that children in the Irish program performed more poorly in mathematics than did children in regular English programs, but he neglected to point out that the differences were found only in mathematics ‘word’ problems and not in mathematical operations. Unsurprisingly, children’s knowledge of Irish at that point was weak and interfered with their comprehension of the test questions; in tests of arithmetic calculations, there were no differences between groups. These challenges have been known for a long time (e.g. Cummins and Macnamara 1977 ) but the research remained influential. More recent research demonstrates that even simple arithmetic calculation is faster and easier in the language in which it was taught ( Spelke and Tsivkin 2001 ) and engages different parts of the brain than when the same calculations are performed in the non-school language ( Mondt et al. 2011 ), but the Irish proficiency of the children in Macnamara’s (1967) study may have been too weak to show this effect.
Other studies have generally found no academic cost for children studying in a bilingual program. In the Mandarin-English bilingual education program described above ( Padilla et al. 2013 ), for example, children in the dual language immersion and the English programs performed equivalently on standardized tests of mathematics until third grade, but immersion children began outperforming non-immersion children in fourth grade. Thus, these program effects sometimes take time to demonstrate. For tests of science achievement, there were no differences between children in the two programs.
There is evidence that bilingualism alone, aside from bilingual education, may be beneficial for aspects of academic achievement. Han (2012) conducted a longitudinal study in the US of a national cohort of over 16,000 children in kindergarten and followed their academic progress until fifth grade. Because of national education policies requiring standardized testing on English literacy and math scores, large data bases are available for such investigations. In the study by Han (2012) , the children included in the analyses were Hispanic, Asian, or non-Hispanic native-born White and outcome variables were results on standardized reading and math achievement scores. Although the analyses did not explicitly control for the effect of education program, the quality of education was defined in terms of the resources and interventions for English support available in the school program, quality of the teachers, and other such factors and included in the analyses. The results were based on a complex classification of children according to their language abilities. Most relevant is a group called ‘mixed bilingual’, referring to children who spoke a non-English language at home to a high degree of fluency. Although these children entered kindergarten with limited English proficiency and obtained initial scores on both English and math tests that were lower than native English-speaking children, they fully closed the math gap by fifth grade, an achievement that the Han attributes to bilingualism. Nonetheless, English scores still lagged by fifth grade. The focus of the analyses were on quality of school programs, availability of resources, and quality of school personnel, all of which contributed significantly to children’s success. The study was not designed to evaluate the effectiveness of bilingual education but the results are consistent with the conclusion that children’s bilingualism can be a positive factor in school achievement.
Much of this research has focused on children in low SES environments, but Marian, Shook, and Schroeder (2013) extended the question to investigate whether these results would be similar for Spanish-speaking low SES children and monolingual English-speaking middle-class children who were in Spanish-English bilingual programs and were instructed through Spanish from kindergarten. The numbers of children in each of the relevant groups defined by language and social background, grade, and education program were vastly different (ranging from 6 to 624), so non-parametric analyses were used and results need to be interpreted cautiously. The analyses of children’s performance on standardized tests of reading and mathematics showed better outcomes for children in bilingual programs than monolingual programs for both minority Spanish and majority English-speaking children, although there were differences in the size and timing of these effects for children from the two language backgrounds. Thus, all children profited from the bilingual education program, although not surprisingly their progress depended as well on other factors known to affect education outcomes.
One explanation that Marian and colleagues offer for the better mathematics outcomes for children in the bilingual programs is that the bilingualism achieved in these programs led to higher levels of executive function and that better executive function was the mechanism for the improvement in math performance. Several studies of young children in the early grades have demonstrated a direct relationship between children’s executive functioning and mathematics achievement ( Blair and Razza 2007 ; Bull, Espy, and Wiebe 2008 ) and a large body of research has established that bilingualism promotes the development of executive function in young children (see Barac et al. 2014 for review; Adesope et al. 2010 for meta-analysis). Importantly, children’s level of executive functioning predicts academic success ( Best, Miller, and Naglieri 2011 ; McClelland, Morrison, and Holmes 2000 ), and academic success predicts long-term health and well-being ( Duncan, Ziol-Guest, and Kalil 2010 ). Therefore, bilingual education may have a serendipitous effect in that it not only promotes bilingualism but also enhances a crucial aspect of cognitive performance.
There is a large and growing literature investigating the relation between bilingualism and executive functioning in young children, but three studies are particularly relevant. The first study is interesting because the results were unexpected. Mezzacappa (2004) used the children’s Attention Network Task ( Fan et al. 2002 ) to assess executive functioning in 6-year-old children who varied in SES (middle-class or low) and ethnicity (White, African-American, or Hispanic). In addition to expected effects of SES, he found that Hispanic children outperformed the other groups, particularly on the most difficult condition. Although he did not collect information about children’s language proficiency or level of bilingualism, he noted that 69% of the Hispanic children spoke Spanish at home, making them at least somewhat bilingual. Mezzacappa proposed that this bilingualism was responsible for the superior executive function performance by children in that group.
The second study was a relatively small-scale study that examined children from low SES communities in which about 90% of children received free or reduced-price lunch. Esposito and Baker-Ward (2013) administered two executive function tasks to children in kindergarten, second grade and fourth grade who were in a bilingual education or English-only program. Their results showed that children in second and fourth grades in the bilingual program outperformed children in the English program on the trail-making task, an executive function task that has previously been shown to be performed better by bilingual than monolingual 8-year-olds ( Bialystok 2010 ). There were no differences between children in the two kindergarten programs, but all these children found the task to be difficult. Because of the small sample size, the results need to be considered more suggestive than definitive, but they point to the possibility that even limited exposure to bilingual education improves children’s executive function.
Another small-scale study conducted with a population of middle-class children from kindergarten through second grade produced somewhat different results. Kaushanskaya, Gross, and Buac (2014) examined the effects of classroom bilingualism on executive functioning as measured by task shifting as well as measures of verbal memory and word learning. For task switching, they used the Dimensional Change Card Sorting Task ( Frye, Zelazo, and Palfai 1995 ), a task previously found to be performed better by bilingual than monolingual preschool children ( Bialystok 1999 ). There were no performance differences between children in the two programs on the executive function shifting task, but the task was arguably too easy for the children since it is typically used with younger children, or on a test of verbal short-term memory. However, tests of verbal working memory and word learning were performed better by the children in the bilingual education program.
In these three examples, children who were assigned to groups either because of ethnicity ( Mezzacappa 2004 ) or education program ( Esposito and Baker-Ward 2013 ; Kaushanskaya, Gross, and Buac 2014 ) were compared to controls for their performance on executive function tasks. A different approach is to use exposure to bilingual education as a scaled variable to determine if it is associated with executive function performance and thereby avoid between-groups comparisons. Two studies by Bialystok and Barac (2012) investigated the relation between the amount of time young children had spent in an immersion program and performance on executive function tasks. Children from monolingual English-speaking homes who were attending schools in which instruction was either in Hebrew (Study 1) or French (Study 2) were administered executive function and metalinguistic tasks. The tasks were different in both studies, but the results were the same: performance on the metalinguistic task was related to children’s verbal ability and intelligence but performance on the executive function task was related to the length of time children had spent in the bilingual program and their degree of bilingualism. Similar results were reported in two studies by Nicolay and Poncelet (2013 , 2015 ) showing better performance on executive function tasks for children in French immersion programs. In these studies, children were followed longitudinally, ruling out initial differences in ability. Thus, the results show that children’s level of executive function performance is related to their degree of bilingualism and experience with bilingual education.
Is bilingual education for everyone?
There have always been questions about whether bilingual education programs were appropriate for all children or whether they were an exclusive option best suited for high-achieving students with strong family support (see review and discussion in Cummins and Swain 1986 ). Equally, some have argued that bilingualism itself is difficult and should be reserved as a ‘privilege’ for children who face no additional burdens from linguistic or other cognitive challenges, a position strongly disputed by Kohnert (2007) . Unsurprisingly, the answer is not simple, but the evidence that exists supports Kohnert’s view that bilingualism adds no further cost to children’s achievement regardless of their initial levels of language and cognitive ability.
Consider first the role of intelligence, a variable on which all children differ. In one of the first studies on this issue, Genesee (1976) examined the role of IQ as measured by a standardized test on the development of French second-language abilities for children who were learning French either through immersion or foreign language instruction in school. The main result was that IQ was related to reading ability and language use for all children, but there was no association between IQ and overall communication ability; children at all levels of intelligence communicated with similar effectiveness. Importantly, there were no interactions with the type of program in which children were learning French: low IQ children in the immersion and foreign language program performed similarly to each other on all language and cognitive measures, in both cases performing more poorly than children with higher IQ scores in both programs. Thus, there was no evidence of any negative effect of participation in an immersion program for children whose measured intelligence was below average.
More serious than low IQ, however, is the possible role that a learning disability, such as specific language impairment (SLI), might play in children’s response to bilingual education. The limited evidence for this question is similar to that found for IQ, namely, that the deficit associated with SLI is not further exacerbated by bilingual education and has the additional consequence of imparting at least some measure of proficiency in another language. Few studies have investigated this question in the context of bilingual education, perhaps because children with language impairment are widely discouraged from attending bilingual education programs, but an early study by Bruck (1982) assessed language and cognitive outcomes for children in kindergarten and first grade in French immersion programs, some of whom had been diagnosed with language impairment. These were Anglophone children being educated through French, and linguistic measures for both French and English were included. The crucial comparison was the progress found for language-impaired children in the French immersion program and similar children in a mainstream English instruction program. There were no significant differences between these groups. Even though these children struggled, they did not struggle more than they would if they were in the bilingual program. This issue of selecting the appropriate comparison is central to the debate. Trites (1978) , for example, argued against placing children with learning disabilities in French immersion programs, but his comparison was based on children without learning disabilities in those programs rather than children with learning disabilities in monolingual English programs.
Aside from the role of bilingual education in children’s language development, it is difficult to compare skills in the two languages for children with SLI because the areas of linguistic difficulty associated with this disorder vary across languages ( Kohnert, Windsor, and Ebert 2009 ). With this caveat in mind, a few studies have examined the effect of SLI on language development for children who grow up bilingually. Korkman et al. (2012) compared monolingual Swedish speakers and Swedish-Finnish bilingual children who were 5–7 years old on a range of language assessments in Swedish. About half of the children in each language group were typically developing and half had been diagnosed with SLI. As expected, children with SLI performed more poorly than typically developing children on these linguistic measures, an outcome required by definition, but there was no added burden from bilingualism and no interaction of bilingualism and language impairment. Bilingual children also obtained lower scores on some vocabulary measures, but this occurred equally for bilingual children in the typically developing and SLI groups and is consistent with large-scale studies comparing the vocabulary of monolingual and bilingual children ( Bialystok et al. 2010 ).
Paradis et al. (2003) took a different approach to investigating syntactic proficiency in children with SLI. Rather than comparing children with SLI to typically developing children, they compared three groups of 7-year-old children, all of whom had been diagnosed with SLI: monolingual English speakers, monolingual French speakers, and English-French bilinguals. The sample was small and consisted of only 8 bilingual children, 21 English monolingual children, and 10 French monolingual children, so data were analyzed with non-parametric tests and results must be interpreted cautiously. The results showed no significant differences between the three groups of children in their mastery of morphosyntax; in other words, no additional delay to language acquisition could be attributed to bilingualism for children with SLI.
The most salient risk factor generally considered in this literature is not individual differences in children’s ability to become bilingual but rather low SES, a situation that applies to many bilingual Hispanic children in the US. Although it was discussed above in the context of testing outcomes of bilingual education, the issue is sufficiently important to warrant further consideration.
The main concern for Hispanic children from Spanish-speaking homes in the US is whether they will acquire adequate levels of English language proficiency and literacy to function in school and beyond. Although there is some controversy over this question, the majority of studies have shown improved outcomes with bilingual education ( Genesee and Lindholm-Leary 2012 ). This conclusion is supported by two major reviews and meta-analyses conducted first by Willig (1985) and then by Rolstad, Mahoney, and Glass (2005) for papers published after the Willig review. In a later review and meta-analysis, Francis, Lesaux, and August (2006) came to a broader and more emphatic conclusion: ‘there is no indication that bilingual instruction impedes academic achievement in either the native language or English, whether for language-minority students, students receiving heritage language instruction, or those enrolled in French immersion programs’ (397). The most persuasive evidence on this point comes from the large-scale longitudinal study and review conducted by Collier and Thomas (2004) that included every variety of bilingual education; the authors decide unequivocally for the superiority of bilingual education in developing the skills and knowledge of Hispanic and other at-risk children.
Contrary to this conclusion, Rossell and Baker (1996) argued that the effectiveness of bilingual education is inconclusive. As stated earlier, Rossell and Baker defined bilingual education narrowly and considered only programs that provided instruction through the first language for limited EP children, in other words, Spanish-speaking children in the US (although curiously they included some studies of Canadian French immersion in their analyses). However, this is only one of the many incarnations of bilingual education so while an evaluation of its effectiveness is important, that evaluation does not necessarily generalize to the broader concept, a point that Rossell and Baker acknowledge. Their review began with a list of 300 studies and then excluded 228 of them for a variety of methodological reasons, so the final sample of 72 studies that entered the meta-analysis may not be representative of this literature. However, Greene (1997) conducted a follow-up study from the same database using different inclusion criteria and reported that a meta-analysis found positive outcomes for bilingual education. The decision about inclusion or exclusion of specific studies is obviously crucial to the outcome; Rossell and Baker acknowledge that Willig’s (1985) positive conclusion can be traced to her choices on this important decision. However, it is impossible to adjudicate between these two conclusions regarding whether bilingual education is the most effective way to promote English language skills in limited English proficiency children ( Willig 1985 ) or not ( Rossell and Baker 1996 ) because the conclusions were based on different evidence. Yet, whether or not there are advantages, the evidence is clear that there is no cost to the development of English language skills in bilingual programs. What is completely uncontroversial is that bilingual education additionally maintains and develops Spanish skills in these children, an outcome that Rossell and Baker note but dismiss as irrelevant.
A different way of considering the impact of bilingual education on school outcomes for low SES Hispanic children in the US is to use data on the reclassification of children from ELL to EP, a decision made on the basis of English language and literacy test scores. In that sense, reclassification is an indication that adequate levels of English proficiency have been achieved. Lindholm-Leary and Block (2010) note that the probability of these children being designated as EP after 10 years of essentially mainstream English classrooms is only 40%, so the standard is low. However, Umansky and Reardon (2014) compared this reclassification rate for Hispanic students enrolled in either bilingual or English-only classrooms and found that these rates were lower in elementary school for children in bilingual programs than in English classrooms, but that the pattern reversed by the end of high school at which time children in bilingual programs had an overall higher rate of reclassification and better academic outcomes. As with some of the studies based on test scores, English proficiency takes several years to develop, but according to the reclassification data, it developed sooner in the bilingual programs.
In a review of studies that have examined the effect of various risk factors on children’s response to bilingual education, Genesee and Fortune (2014) found no case in which the bilingual education program contributed to lower academic outcomes for these children than for similar children in monolingual programs. Children with language disability, for example, will always find language tasks to be difficult; the important outcome of this research is that they do not find such tasks to be any more difficult in two languages than they are in one.
Evaluation of bilingual education for young children
In most evaluation research for educational programs, the conclusion tends to converge on a binary answer in which the program is considered to be either effective or not, or more or less effective than a control or alternative program. Given the complexity of bilingual education, such binary conclusions are inadequate. One reason is that independently of the quality of the program, bilingual education to some extent will almost inevitably help children to become bilingual or maintain bilingualism, an outcome that in itself is valuable but rarely considered in strict program evaluations. Some research has shown that even at early stages of bilingual education the cognitive advantages of bilingualism can be detected. Therefore, beyond the possible cognitive benefits of bilingualism described above are the intangible benefits of bilingual education such as potential to connect to extended family, increased opportunity for employment in a global economy, facilitation of travel and broadening of social spheres, and enrichment from widened horizons from language, arts, and culture. When successful, bilingual education offers a unique opportunity to impart the resources to sustain a valuable lifestyle asset. As one example, recent research has shown that lifelong bilingualism contributes to cognitive reserve and delays the onset of symptoms of dementia (reviews in Bak and Alladi 2014 ; Bialystok et al. 2016 ).
These consequences of bilingualism, however, should not bias the interpretation of the evidence regarding the educational efficacy of bilingual education. To undertake that assessment, it is necessary to return to the distinction between bilingual education and the education of bilingual children. The first is a general question about the feasibility of educating children through a language in which they may not be fully proficient; the second is a specific question about the appropriateness of this option for children whose circumstances and abilities may mitigate those educational outcomes.
Both questions can be considered in terms of two factors that permeate many of these studies: the type of outcome measured and the demographic profile of the children in the program. Regarding the first, the main distinction is whether the studies assessed language proficiency or some other cognitive or academic outcome. Most studies included an evaluation of language proficiency in the majority language (English for Hispanic children in the US, French immersion children in Canada, community language for indigenous language programs in the US and elsewhere) and some included assessments of proficiency in the minority language, which is often the language of instruction (e.g. Spanish in the US, French in Canada, Maori in New Zealand). Fewer studies examined assessments of other educational outcomes, such as mathematics, subject curricula, cognitive ability, retention rates, attitudes, or enrollment in higher education. The second factor is whether the children assessed in these studies were at risk of academic failure for any number of reasons, such as low SES, poor language proficiency, or individual difficulty from learning, language, or social challenges. This combination of factors creates four categories for which there are three possible outcomes: (a) no measurable difference between bilingual and standard programs, (b) some advantage for participation in a bilingual program, or (c) hardship for students in bilingual programs that leads to poorer outcomes than would be obtained in traditional programs. If we consider that all bilingual programs additionally support some degree of bilingualism, then the only negative outcome would be (c).
Regarding language assessments, most studies show that proficiency in the majority language is comparable for children in bilingual and mainstream classes, providing that an appropriate comparison group is used and sufficient time is allowed. Children in Canadian French immersion programs develop English language skills that are at least comparable to those of other middle-class children in English programs (and sometimes higher but there may be other factors involved because of the selectivity of French immersion, see Hutchins 2015 ), and Hispanic children in US bilingual education programs eventually develop English language skills that are comparable to those of similar Hispanic children in English programs, although it takes several years to reach that level. Proficiency in the minority language is inevitably lower than is found for a native speaker of those languages, even when it is the language of instruction, but is invariably higher than levels obtained by children in English programs who have had little exposure to that language. For language proficiency, therefore, there is no evidence of a cost to the development of either language, although it may take several years to establish desired levels.
For other subject material, outcomes depend in part on the language of testing. As Macnamara (1967) showed long ago, the extent to which a weak language is used to conduct achievement tests can make the test equally a test of language proficiency, impeding children’s demonstration of proficiency in the tested content. In many cases, studies that assess academic achievement provide inadequate information about the potential involvement of language proficiency so the test results are sometimes indeterminate. At the same time, Mondt and colleagues (2011) demonstrated that simply by teaching a subject through a particular language makes proficiency in that subject more fluent when tested in the language of schooling. Thus, there are reciprocal relationships between academic achievement and the language of school instruction, and these relationships are flexible.
The second factor is the characteristics of the children themselves. Children entering school with any learning or language disability or social disadvantage will struggle to succeed, so an evaluation of bilingual education needs to hold constant these abilities and select the appropriate comparison group. Thus, the relevant question is whether children struggle disproportionately more if they are in a bilingual education program. Here, too, the evidence seems clear: there is no additional burden for children with specific challenges in bilingual programs than in single language programs if the appropriate comparison is made. But even if there were additional effort required by bilingual education, it needs to be evaluated in terms of the potential benefits for that child – the possibility of acquiring a heritage language, the opportunity to develop at least some proficiency in another language, and the potential for attaining the cognitive benefits of bilingualism.
Bilingual education is not perfect and it is not one thing. At the same time, the quality of the research is uneven and it is difficult to determine how much weight should be assigned to contradictory outcomes. The research generally pays inadequate attention to the social context in which these complex processes play out, such as home literacy, parental education, children’s levels of language proficiency, ability of parents to support children’s education in that language, and numerous other factors. Rossell and Baker (1996) claim that the research is inconclusive, and although there is still much to be learned, the weight of evidence is firmly on the side of bilingual education. In this brief review of a small portion of bilingual education programs in different countries and aimed at educating different kinds of children, there is no evidence that it creates measurable obstacles to children’s school achievement. Some studies show no advantage of bilingual education over other programs, but those need to be interpreted in terms of the benefits of learning another language and gaining access to the cognitive advantages of bilingualism. Ultimately, a proper evaluation of bilingual education requires detailed description of the structure of the program, the quality of the teaching, and the match between children’s needs and abilities and the specific educational program being offered.
There is no single factor that can override the deep complexity of children’s development and prescribe a solution for an individual child, let alone a solution for all children. For both gifted children who are certain to excel and children who face challenges, the education program they follow, including participation in a bilingual program, may not fundamentally change their school experience. There is no credible evidence that bilingual education adds or creates burden for children, yet it is incontrovertible that it provides the advantage of learning another language and possibly the cognitive benefits of bilingualism. The over-riding conclusion from the available evidence is that bilingual education is a net benefit for all children in the early school years.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the US National Institutes of Health [grant number R01HD052523].
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author.
Notes on contributor
- Adesope OO, Lavin T, Thompson T, Ungerleider C. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Cognitive Correlates of Bilingualism. Review of Educational Research. 2010; 80 :207–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- August D, Shanahan T. Developing Literacy in Second-language Learners: Report of the National Literacy Panel on Language Minority Children and Youth. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bak TH, Alladi S. Can Being Bilingual Affect the Onset of Dementia? Future Neurology. 2014; 9 :101–103. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baker C. Foundations of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. Stroud: Multilingual Matters; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barac R, Bialystok E, Castro DC, Sanchez M. The Cognitive Development of Young Dual Language Learners: A Critical Review. Early Childhood Research Quarterly. 2014; 29 :699–714. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barnett WS, Yarosz DJ, Thomas J, Jung K, Blanco D. Two-way and Monolingual English Immersion in Preschool Education: An Experimental Comparison. Early Childhood Research Quarterly. 2007; 22 :277–293. [ Google Scholar ]
- Best JR, Miller PH, Naglieri JA. Relations Between Executive Function and Academic Achievement from Ages 5 to 17 in a Large, Representative National Sample. Learning and Individual Differences. 2011; 21 :327–336. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bialystok E. Cognitive Complexity and Attentional Control in the Bilingual Mind. Child Development. 1999; 70 :636–644. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bialystok E. Global-local and Trail-making Tasks by Monolingual and Bilingual Children: Beyond Inhibition. Developmental Psychology. 2010; 46 :93–105. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bialystok E, Abutalebi J, Bak TH, Burke DM, Kroll JF. Aging in Two Languages: Implications for Public Health. Ageing Research Reviews. 2016; 27 :56–60. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bialystok E, Barac R. Emerging Bilingualism: Dissociating Advantages for Metalinguistic Awareness and Executive Control. Cognition. 2012; 122 :67–73. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bialystok E, Luk G, Peets KF, Yang S. Receptive Vocabulary Differences in Monolingual and Bilingual Children. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition. 2010; 13 :525–531. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blair C, Razza RP. Relating Effortful Control, Executive Function, and False Belief Understanding to Emerging Math and Literacy Ability in Kindergarten. Child Development. 2007; 78 :647–663. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bruck M. Language Impaired Children’s Performance in an Additive Bilingual Education Program. Applied Psycholinguistics. 1982; 3 :45–60. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bull R, Espy KA, Wiebe SA. Short-term Memory, Working Memory, and Executive Functioning in Preschoolers: Longitudinal Predictors of Mathematical Achievement at age 7 Years. Developmental Neuropsychology. 2008; 33 :205–228. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Collier VP, Thomas WP. The Astounding Effectiveness of Dual Language Education for All. NABE Journal of Research and Practice. 2004; 2 :1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cummins James, John Macnamara. Working Papers on Bilingualism, No. 13. Washington, DC: Distributed by ERIC Clearinghouse; 1977. Immersion Education in Ireland: A Critical Review of Macnamara’s Findings. Reply to Dr. Cummins. Reply to the Reply. http://www.eric.ed.gov/contentdelivery/servlet/ERICServlet?accno=ED140666 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Cummins J, Swain M. Bilingualism in Education: Aspects of Theory, Research, and Practice. Abingdon: Routledge; 1986. [ Google Scholar ]
- Duncan GJ, Ziol-Guest KM, Kalil A. Early-childhood Poverty and Adult Attainment, Behavior, and Health. Child Development. 2010; 81 :306–325. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Durie A. Emancipatory Maori Education: Speaking from the Heart. Language, Culture and Curriculum. 1998; 11 :297–308. [ Google Scholar ]
- Esposito AG, Baker-Ward L. Dual-language Education for Low-income Children: Preliminary Evidence of Benefits for Executive Function. Bilingual Research Journal. 2013; 36 :295–310. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fan J, McCandliss BD, Sommer T, Raz A, Posner MI. Testing the Efficiency and Independence of Attentional Networks. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2002; 14 :340–347. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fishman J. Bilingual Education: An International Sociological Perspective. Rowley, MA: Newbury House; 1976. [ Google Scholar ]
- Forum for Education and Democracy. Democracy at Risk: The Need for a New Federal Policy in Education. Washington, DC: The Forum for Education and Democracy; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Francis DJ, Lesaux N, August D. Language of Instruction. In: August D, Shanahan L, editors. Developing Literacy in Second-language Learners. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 2006. pp. 365–413. [ Google Scholar ]
- Frye D, Zelazo PD, Palfai T. Theory of Mind and Rule-based Reasoning. Cognitive Development. 1995; 10 :483–527. [ Google Scholar ]
- Garcia O. Bilingual Education in the 21st Century: A Global Perspective. New York: Wiley-Blackwell; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Genesee F. The Role of Intelligence in Second Language Learning. Language Learning. 1976; 26 :267–280. [ Google Scholar ]
- Genesee F. Bilingual Education of Majority-language Children: The Immersion Experiments in Review. Applied Psycholinguistics. 1983; 4 :1–46. [ Google Scholar ]
- Genesee F. What Do We Know About Bilingual Education for Majority Language Students. In: Bhatia TK, Ritchie W, editors. Handbook of Bilingualism and Multiculturalism. Malden, MA: Blackwell; 2004. pp. 547–576. [ Google Scholar ]
- Genesee F, Fortune T. Bilingual Education and at-risk Students. Journal of Immersion and Content-Based Language Education. 2014; 2 :165–180. [ Google Scholar ]
- Genesee F, Lindholm-Leary K. The Education of English Language Learners. In: Harris K, Graham S, Urdan T, editors. APA Handbook of Educational Psychology. Washington, DC: APA Books; 2012. pp. 499–526. [ Google Scholar ]
- Greene JP. A Meta-analysis of the Rossell and Baker Review of Bilingual Education Research. Bilingual Research Journal. 1997; 21 :103–122. [ Google Scholar ]
- Han WJ. Bilingualism and Academic Achievement. Child Development. 2012; 83 :300–321. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hermanto N, Moreno S, Bialystok E. Linguistic and Metalinguistic Outcomes of Intense Immersion Education: How Bilingual? International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. 2012; 15 :131–145. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hutchins A. Just Say ‘Non’: The Problem with French Immersion. Macleans Magazine. 2015 http://www.macleans.ca/education/just-say-non-the-problem-with-french-immersion/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaushanskaya M, Gross M, Buac M. Effects of Classroom Bilingualism on Task-shifting, Verbal Memory, and Word Learning in Children. Developmental Science. 2014; 17 :564–583. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohnert K. Language Disorders in Bilingual Children and Adults. San Diego, CA: Plural Publishing; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohnert K, Windsor J, Ebert KD. Primary or ‘Specific’ Language Impairment and Children Learning a Second Language. Brain and Language. 2009; 109 :101–111. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Korkman M, Stenroos M, Mickos A, Westman M, Ekholm P, Byring R. Does Simultaneous Bilingualism Aggravate Children’s Specific Language Problems? Acta Paediatrica. 2012; 101 :946–952. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lau v. Nichols, 414 U.S. 563. 1974 [ Google Scholar ]
- Lepage JF, Corbeil JP. The Evolution of English–French Bilingualism in Canada from 1961 to 2011. Statistics Canada; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lindholm-Leary K. Bilingual and Biliteracy Skills in Young Spanish-speaking Low-SES Children: Impact of Instructional Language and Primary Language Proficiency. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. 2014; 17 :144–159. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lindholm-Leary K, Block N. Achievement in Predominantly Low SES/Hispanic Dual Language Schools. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. 2010; 13 :43–60. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lopez MG, Tashakkori A. Narrowing the Gap: Effects of a Two-way Bilingual Education Program on the Literacy Development of at-risk Primary Students. Journal of Education For Students Placed At Risk. 2004; 9 :325–336. [ Google Scholar ]
- Macnamara J. The Effects of Instruction in a Weaker Language. Journal of Social Issues. 1967; 23 :121–135. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marian V, Shook A, Schroeder SR. Bilingual Two-way Immersion Programs Benefit Academic Achievement. Bilingual Research Journal. 2013; 36 :167–186. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- May S, Hill R. Maori-medium Education: Current Issues and Challenges. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. 2005; 8 :377–403. [ Google Scholar ]
- McCarty TL, Watahomigie LJ. Indigenous Community-based Language Education in the USA. Language, Culture and Curriculum. 1998; 11 :309–324. [ Google Scholar ]
- McClelland MM, Morrison FJ, Holmes DL. Children at Risk for Early Academic Problems: The Role of Learning-related Social Skills. Early Childhood Research Quarterly. 2000; 15 :307–329. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mehisto P, Genesee F, editors. Building Bilingual Education Systems: Forces, Mechanisms and Counterweights. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mezzacappa E. Alerting, Orienting, and Executive Attention: Developmental Properties and Sociodemographic Correlates in an Epidemiological Sample of Young, Urban Children. Child Development. 2004; 75 :1373–1386. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mondt K, Struys E, Van den Noort M, Baleriaux D, Metens T, Paquier P, Van de Craen P, Bosch P, Denolin V. Neural Differences in Bilingual Children’s Arithmetic Processing Depending on Language of Instruction. Mind, Brain, and Education. 2011; 5 :79–88. [ Google Scholar ]
- Montanari S. A Case Study of Bi-literacy Development among Children Enrolled in an Italian–English Dual Language Program in Southern California. International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism. 2013; 17 :509–525. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nicolay A-C, Poncelet M. Cognitive Advantage in Children Enrolled in a Second-language Immersion Elementary School Program for Three Years. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition. 2013; 16 :597–607. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nicolay A-C, Poncelet M. Cognitive Benefits in Children Enrolled in an Early Bilingual Immersion School: A Follow Up Study. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition. 2015; 18 :789–795. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nieto D. A Brief History of Bilingual Education in the United States. Perspectives on Urban Education. 2009; 6 :61–72. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ovando CJ. Bilingual Education in the United States: Historical Development and Current Issues. Bilingual Education in the United States. 2003; 27 :1–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Padilla AM, Fan L, Xu X, Silva D. A Mandarin/English Two-way Immersion Program: Language Proficiency and Academic Achievement. Foreign Language Annals. 2013; 46 :661–679. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paradis J, Crago M, Genesee F, Rice M. French-English Bilinguals with SLI: How Do They Compare with Their Monolingual Peers? Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 2003; 46 :113–127. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rolstad K, Mahoney K, Glass GV. The Big Picture: A Meta-analysis of Program Effectiveness Research on English Language Learners. Educational Policy. 2005; 19 :572–594. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosier P, Holm W. The Rock Point Experience: A Longitudinal Study of a Navajo School Program. Washington, DC: Center for Applied Linguistics; 1980. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rossell CH, Baker K. The Educational Effectiveness of Bilingual Education. Research in the Teaching of English. 1996; 30 :7–74. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwartz M. The Impact of the First Language First Model on Vocabulary Development among Preschool Bilingual Children. Reading and Writing. 2013; 27 :709–732. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwartz M, Shaul Y. Narrative Development among Language-minority Children: The Role of Bilingual Versus Monolingual Preschool Education. Language, Culture and Curriculum. 2013; 26 :36–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Spelke ES, Tsivkin S. Language and Number: A Bilingual Training Study. Cognition. 2001; 78 :45–88. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Swain M, Lapkin S. Evaluating Bilingual Education: A Canadian Case Study. Clevedon: Multilingual Matters; 1982. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trites R. Learning Disabilities in Immersion. Canadian Modern Language Review. 1978; 5 :888–889. [ Google Scholar ]
- Troike RC. Research Evidence for the Effectiveness of Bilingual Education. NABE Journal. 1978; 3 :13–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Umansky IM, Reardon SF. Reclassification Patterns among Latino English Learner Students in Bilingual, Dual Immersion, and English Immersion Classrooms. American Educational Research Journal. 2014; 51 :879–912. [ Google Scholar ]
- Willig A. A Meta-analysis of Selected Studies on the Effectiveness of Bilingual Education. Review of Educational Research. 1985; 55 :269–317. [ Google Scholar ]
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Multiculturalism — Importance Of Being Bilingual
Importance of Being Bilingual
- Categories: Effective Communication Globalization Multiculturalism
About this sample

Words: 513 |
Published: Mar 14, 2024
Words: 513 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 475 words
4 pages / 1935 words
2 pages / 1131 words
2 pages / 801 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Multiculturalism
The world is becoming increasingly interconnected, bringing people from diverse cultural backgrounds closer together. The ability to form friendships with individuals from different cultures is a valuable skill that fosters [...]
Our culture molds us, molds our behavior, and our sense of self. Our way of life is defined by the shared language, ideas, values, conventions, behaviors, and material items that are passed down from generation to generation. We [...]
Within the realm of contemporary educational discourse, the concept of multicultural education stands as an indelible cornerstone, profoundly shaping the educational landscape. This essay undertakes an extensive exploration of [...]
The term "hyphenated American" has been used for over a century to describe individuals in the United States who identify with both their ancestral or ethnic heritage and their American nationality. It's a label that has [...]
Culture, unlike biology, should allow us to seek liberation from cruel and uncomfortable practices. But instead culture wraps us in a suffocating embrace. ... re cultures discrete or bounded? ...Who defines the boundaries of [...]
This article considers the factors associated with faculty multicultural teaching competence. Mena and Rogers (2017) state that most research surrounding the teaching of multicultural courses focus on instructional strategies, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Varsity Athletes
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
The Benefits of Being Bilingual
- Share This: Share The Benefits of Being Bilingual on Facebook Share The Benefits of Being Bilingual on LinkedIn Share The Benefits of Being Bilingual on X
The Benefits of Being Bilingual was originally published on Idealist Careers .
Bilingualism, or the ability to speak two or more languages fluently, can be a huge asset for job seekers. As a 2017 report by New American Economy discovered, the need for bilingual workers in the United States more than doubled in the previous five years. This trend is projected to increase, especially for Spanish, Mandarin Chinese, and Arabic speakers.
But even if you don’t speak one of these languages—or don’t use a second language on the job at all—bilingualism makes you a more adaptable thinker, according to a report by the Language Institute . Quick and flexible thinkers with broad perspectives will benefit any employer.
Here are some of the benefits of being bilingual, from the job hunt to personal and professional development.
The benefits of being bilingual in social-impact careers
The New American Economy report also reveals bilingual jobs are common in fields with a high degree of person-to-person interaction. Employers in fields like education, health care, and social work actively seek bilingual workers. Dozens of languages may be represented among students at a school, clients at a housing or health facility, and residents of a neighborhood—especially in urban areas. A staff member who can serve as an interpreter or translator is invaluable. Language skills are also applicable in many advocacy jobs; immigration lawyers, for instance, often need to communicate with clients who may not speak English.
So where can your language skills be best put to use? The most in-demand bilingual skill depends on where you live. In a place where many people speak a certain language—be it Spanish in Miami, French in Louisiana, or Vietnamese in the Bay Area of California—many jobs strongly encourage bilingual candidates.
Benefits of being bilingual beyond language
Your bilingual skill set can give you an edge whether you speak your second language in the workplace or not. Knowing two languages makes your brain more flexible ; switching between two sets of grammar rules, vocabulary, tones, and nuances is a lot of work! In fact, even if you’re only speaking one language, your brain activates both language systems and requires you to focus on one—making you a natural at complex mental tasks.
This adaptability can make you quicker at thinking on your feet, better at workplace problem solving, and a whiz at multitasking. When it comes to working with people, bilingual thinkers can be more adept at “reading” and communicating with others.
Bilingualism versus biculturalism
Linguistic fluency comes in many varieties. If you learned a second language in school, you’ve probably mastered reading, speaking, and listening. But if you spoke two languages at home or learned a second language specific to your ethnic background, you may also be bicultural—someone with insider knowledge of two different cultures. This includes the dominant culture of the country you’re in; for example, the English-speaking culture in many areas of the United States.
Each culture has its own rituals, values, and behaviors that go far beyond language. A bicultural candidate will be able to navigate between the complex aspects of both cultures. While this perspective is key when working with diverse cultural groups, it also gives you a skill you can apply in any job—the ability to understand and combine multiple perspectives at once, known as integrative complexity. Your aptitudes count as a bonus in many ways, from interpersonal skills like mediation and conflict resolution to brainstorming big ideas for an organizational mission.
Promote your skills
If you’re bilingual, remember that you’re a standout candidate! Mention your second language on your resume , even if you don’t consider yourself fully fluent. A little ability can be just the boost you need to bring something extra to the table.
In an interview , you can emphasize your:
- Ability to understand diverse perspectives;
- Creativity and inventiveness;
- Problem-solving expertise;
- Skill at different modes of communication; and
- Any other benefits you think bilingualism has given you, since each person’s experience will be different.
Ready to start searching? Check out job, internship, and volunteer opportunities requiring or encouraging a specific second language skill .
Bilingual Education: Benefit in Today’s World Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
U.s. residents have the legal right to learn and speak any, works cited.
Richard Rodriguez wrote an article under the title of “Bilingual Education: Outdated and Unrealistic” in which he criticizes bilingual education. He considers bilingual education a form of separation in the society. He also sees it as a negative result of “the civil rights movement of the 1960s”. In his opinion, all U.S. residents must learn and speak one language only which is English. And that’s because (in his opinion) it is the language of the United States.
The author claims that English is the only language that can ensure better chances in life and also better jobs. He totally disagrees with any form of “Bilingualism” in life (Rodriguez 457-60). Those opinions don’t fit with the laws and the values of the United States of America. Also, bilingual education can be useful in many fields in life. Studies have proved that bilingual education enhances mental abilities and improves the skills of students in schools.
Language They Want
“The First Amendment to the Constitution of the United States has guaranteed freedom of religion and required that Congress shall pass no law abridging the freedom of speech” (Reyhner). Fighting bilingual education is a serious violation to the freedom of speech. In most cases, the language is a part of any culture in the world, and preventing bilingual education can have a negative effect on many cultures in the United States.
Thus, the United States will become a country with only one language and one culture. In the federal Constitution, there is no specific official language, and that makes it legal for everyone to learn and speak any language he/she wants. European colonists who arrived to America never focused on deciding an official language. Forcing American citizens to use one language is a new way of slavery. The reasons that made English the mainstream language in the United States were the “forces of the marketplace and mass communication” (Reyhner).
The Language Diversity Inside One Country Is Beneficial
Many “multi-national corporations” inside the United States demand employees who have the ability to speak more than one language. And this means that Bilingual education is a priority for getting better chances in employment (Reyhner).
Interestingly, there are some countries in the world that have multiple major languages, but they have no problems about that. Switzerland is an example. Switzerland’s major languages are German, French and Italian (Reyhner).
Bilingual Education Enhances Mental Abilities and Improves Students’ Skills
According to many researches, it was found that people who study with bilingual education programs show better mental abilities than people who study with “monolingual” education programs. The results can be noticed with children and older people. Bilingual education enhances mental abilities in many ways. Some of those ways are:
- “Bilingualism Enhances Attention”: A research done by Dr. Ellen Bialystok from York University in Canada proved that fact. The participants in this research were a group of older people. Some of them were bilingual students and some others were monolingual students. The research team assigned some mental tasks to the participants. The participants performed these tasks during the “Simon Task”. The Simon Task is “an experimental procedure that deliberately distracts the test takers. The Simon Task measures reaction time and cognitive processing that decline with age” (Desaulniers). It was found that bilingual participants were more able to focus on tasks and ignore distractions than monolingual participants (Desaulniers).
- “Bilingualism Builds Cognitive Reserve”: With aging, 2 mental abilities become weaker, attention and memory. Bilingual education protects the human brain through aging. Bilingual education creates something called “cognitive reserve”. Cognitive reserve is “the ability of the brain to be more flexible than normal because the demands made on it at an early age (through bilingualism) have enhanced its ability to rewire and compensate for aging and dysfunctional neurons” (Desaulniers). If any organ in the human body (including brain) gets used to perform more unusual tasks, its abilities will be improved. And this means that bilingual education programs are more beneficial for the human brain than monolingual education programs because they give the brain more mental tasks to perform (Desaulniers).
Foreign-speaking students who are registered in bilingual education programs do better in school than their counterparts who are registered in monolingual education programs. In 2000, there was a study that examined the performance of 952 students in various schools in Date County, Florida. Some of those students were registered in bilingual education programs and some others were registered in monolingual education programs. It was found that students in bilingual education got higher marks in “English literacy”. The difference started to appear by 2 nd grade, but it became notable by the 5 th grade (National Association for Bilingual Education).
Richard Rodriguez’s opinions about bilingual education clash with the American values that ensure the diversity in society. Bilingual education is a right, not just a demand. Bilingual education offers better chances for people in life. It maintains the mental abilities through all age levels. Bilingual education improves the performance of students in schools and that can bring more positive results in the future.
Desaulniers, Mary. “Why Bilingualism Slows Aging: Delays Dementia, Enhances Attention, Builds Cognitive Reserve.” Suite. 2009. Web.
National Association for Bilingual Education. “Does Bilingual Education Really Work?” National Association for Bilingual Education . 2004. Web.
Reyhner, Jon. “Linguicism in America.” Teaching Indigenous Languages . 2007. Northern Arizona University. Web.
Rodriguez, Richard. “Bilingual Education: Outdated and Unrealistic.” Connections: A Multicultural Reader for Writers. 2nd ed. Ed. Judith A. Stanford. Mountain View: Mayfield Publishing, 1993. 457-60.
- Comparing the Education Systems of Italy and America
- What Are the Causes of Poor Educational Standards in the Chicago Public Schools?
- Bilingual Neurodivergent Students
- Bilingualism Resistance and Receptivity Explained
- Bilingualism and Multilingualism
- Educational Systems from a Sociological Perspective
- “Mobile Learning in Developing Nations” by Scott Motlik
- Reforms in the Singaporean Education System
- Key Objectives and Ideas in Brazil’s National Education Plan
- The Structure of Learning Systems in Schools
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, November 13). Bilingual Education: Benefit in Today’s World. https://ivypanda.com/essays/bilingual-education-benefit-in-todays-world/
"Bilingual Education: Benefit in Today’s World." IvyPanda , 13 Nov. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/bilingual-education-benefit-in-todays-world/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Bilingual Education: Benefit in Today’s World'. 13 November.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Bilingual Education: Benefit in Today’s World." November 13, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/bilingual-education-benefit-in-todays-world/.
1. IvyPanda . "Bilingual Education: Benefit in Today’s World." November 13, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/bilingual-education-benefit-in-todays-world/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Bilingual Education: Benefit in Today’s World." November 13, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/bilingual-education-benefit-in-todays-world/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
Home / Essay Samples / Science / Bilingualism / The Benefits Of Bilingual Education
The Benefits Of Bilingual Education
- Category: Science
- Topic: Bilingualism , Second Language
Pages: 5 (2497 words)
Views: 3109
- Downloads: -->
--> ⚠️ Remember: This essay was written and uploaded by an--> click here.
Found a great essay sample but want a unique one?
are ready to help you with your essay
You won’t be charged yet!
Black Hole Essays
Brain Essays
Mountains Essays
Hindi Essays
Related Essays
We are glad that you like it, but you cannot copy from our website. Just insert your email and this sample will be sent to you.
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Your essay sample has been sent.
In fact, there is a way to get an original essay! Turn to our writers and order a plagiarism-free paper.
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->