- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore

Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- MHT CET Result 2024
- JEE Advanced Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- AP EAMCET Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2024
- CAT 2024 College Predictor
- Top MBA Entrance Exams 2024
- AP ICET Counselling 2024
- GD Topics for MBA
- CAT Exam Date 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET Response Sheet 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET PG Counselling 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Covid 19 Essay in English
Essay on Covid -19: In a very short amount of time, coronavirus has spread globally. It has had an enormous impact on people's lives, economy, and societies all around the world, affecting every country. Governments have had to take severe measures to try and contain the pandemic. The virus has altered our way of life in many ways, including its effects on our health and our economy. Here are a few sample essays on ‘CoronaVirus’.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19
200 words essay on covid 19, 500 words essay on covid 19.

COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very short period of time. It has affected lives, economies and societies across the world, leaving no country untouched. The virus has caused governments to take drastic measures to try and contain it. From health implications to economic and social ramifications, COVID-19 impacted every part of our lives. It has been more than 2 years since the pandemic hit and the world is still recovering from its effects.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the world has been impacted in a number of ways. For one, the global economy has taken a hit as businesses have been forced to close their doors. This has led to widespread job losses and an increase in poverty levels around the world. Additionally, countries have had to impose strict travel restrictions in an attempt to contain the virus, which has resulted in a decrease in tourism and international trade. Furthermore, the pandemic has put immense pressure on healthcare systems globally, as hospitals have been overwhelmed with patients suffering from the virus. Lastly, the outbreak has led to a general feeling of anxiety and uncertainty, as people are fearful of contracting the disease.
My Experience of COVID-19
I still remember how abruptly colleges and schools shut down in March 2020. I was a college student at that time and I was under the impression that everything would go back to normal in a few weeks. I could not have been more wrong. The situation only got worse every week and the government had to impose a lockdown. There were so many restrictions in place. For example, we had to wear face masks whenever we left the house, and we could only go out for essential errands. Restaurants and shops were only allowed to operate at take-out capacity, and many businesses were shut down.
In the current scenario, coronavirus is dominating all aspects of our lives. The coronavirus pandemic has wreaked havoc upon people’s lives, altering the way we live and work in a very short amount of time. It has revolutionised how we think about health care, education, and even social interaction. This virus has had long-term implications on our society, including its impact on mental health, economic stability, and global politics. But we as individuals can help to mitigate these effects by taking personal responsibility to protect themselves and those around them from infection.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Education
The outbreak of coronavirus has had a significant impact on education systems around the world. In China, where the virus originated, all schools and universities were closed for several weeks in an effort to contain the spread of the disease. Many other countries have followed suit, either closing schools altogether or suspending classes for a period of time.
This has resulted in a major disruption to the education of millions of students. Some have been able to continue their studies online, but many have not had access to the internet or have not been able to afford the costs associated with it. This has led to a widening of the digital divide between those who can afford to continue their education online and those who cannot.
The closure of schools has also had a negative impact on the mental health of many students. With no face-to-face contact with friends and teachers, some students have felt isolated and anxious. This has been compounded by the worry and uncertainty surrounding the virus itself.
The situation with coronavirus has improved and schools have been reopened but students are still catching up with the gap of 2 years that the pandemic created. In the meantime, governments and educational institutions are working together to find ways to support students and ensure that they are able to continue their education despite these difficult circumstances.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Economy
The outbreak of the coronavirus has had a significant impact on the global economy. The virus, which originated in China, has spread to over two hundred countries, resulting in widespread panic and a decrease in global trade. As a result of the outbreak, many businesses have been forced to close their doors, leading to a rise in unemployment. In addition, the stock market has taken a severe hit.
Effects of CoronaVirus on Health
The effects that coronavirus has on one's health are still being studied and researched as the virus continues to spread throughout the world. However, some of the potential effects on health that have been observed thus far include respiratory problems, fever, and coughing. In severe cases, pneumonia, kidney failure, and death can occur. It is important for people who think they may have been exposed to the virus to seek medical attention immediately so that they can be treated properly and avoid any serious complications. There is no specific cure or treatment for coronavirus at this time, but there are ways to help ease symptoms and prevent the virus from spreading.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Accepted by more than 11,000 universities in over 150 countries worldwide

PTE Exam 2024 Registrations
Register now for PTE & Save 5% on English Proficiency Tests with ApplyShop Gift Cards
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay On Covid-19: 100, 200 and 300 Words

- Updated on
- Apr 30, 2024

COVID-19, also known as the Coronavirus, is a global pandemic that has affected people all around the world. It first emerged in a lab in Wuhan, China, in late 2019 and quickly spread to countries around the world. This virus was reportedly caused by SARS-CoV-2. Since then, it has spread rapidly to many countries, causing widespread illness and impacting our lives in numerous ways. This blog talks about the details of this virus and also drafts an essay on COVID-19 in 100, 200 and 300 words for students and professionals.

Table of Contents
- 1 Essay On COVID-19 in English 100 Words
- 2 Essay On COVID-19 in 200 Words
- 3 Essay On COVID-19 in 300 Words
- 4 Short Essay on Covid-19
Essay On COVID-19 in English 100 Words
COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, is a global pandemic. It started in late 2019 and has affected people all around the world. The virus spreads very quickly through someone’s sneeze and respiratory issues.
COVID-19 has had a significant impact on our lives, with lockdowns, travel restrictions, and changes in daily routines. To prevent the spread of COVID-19, we should wear masks, practice social distancing, and wash our hands frequently.
People should follow social distancing and other safety guidelines and also learn the tricks to be safe stay healthy and work the whole challenging time.
Also Read: National Safe Motherhood Day 2023
Essay On COVID-19 in 200 Words
COVID-19 also known as coronavirus, became a global health crisis in early 2020 and impacted mankind around the world. This virus is said to have originated in Wuhan, China in late 2019. It belongs to the coronavirus family and causes flu-like symptoms. It impacted the healthcare systems, economies and the daily lives of people all over the world.
The most crucial aspect of COVID-19 is its highly spreadable nature. It is a communicable disease that spreads through various means such as coughs from infected persons, sneezes and communication. Due to its easy transmission leading to its outbreaks, there were many measures taken by the government from all over the world such as Lockdowns, Social Distancing, and wearing masks.
There are many changes throughout the economic systems, and also in daily routines. Other measures such as schools opting for Online schooling, Remote work options available and restrictions on travel throughout the country and internationally. Subsequently, to cure and top its outbreak, the government started its vaccine campaigns, and other preventive measures.
In conclusion, COVID-19 tested the patience and resilience of the mankind. This pandemic has taught people the importance of patience, effort and humbleness.
Also Read : Essay on My Best Friend
Essay On COVID-19 in 300 Words
COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, is a serious and contagious disease that has affected people worldwide. It was first discovered in late 2019 in Cina and then got spread in the whole world. It had a major impact on people’s life, their school, work and daily lives.
COVID-19 is primarily transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets produced and through sneezes, and coughs of an infected person. It can spread to thousands of people because of its highly contagious nature. To cure the widespread of this virus, there are thousands of steps taken by the people and the government.
Wearing masks is one of the essential precautions to prevent the virus from spreading. Social distancing is another vital practice, which involves maintaining a safe distance from others to minimize close contact.
Very frequent handwashing is also very important to stop the spread of this virus. Proper hand hygiene can help remove any potential virus particles from our hands, reducing the risk of infection.
In conclusion, the Coronavirus has changed people’s perspective on living. It has also changed people’s way of interacting and how to live. To deal with this virus, it is very important to follow the important guidelines such as masks, social distancing and techniques to wash your hands. Getting vaccinated is also very important to go back to normal life and cure this virus completely.
Also Read: Essay on Abortion in English in 650 Words
Short Essay on Covid-19
Please find below a sample of a short essay on Covid-19 for school students:
Also Read: Essay on Women’s Day in 200 and 500 words
to write an essay on COVID-19, understand your word limit and make sure to cover all the stages and symptoms of this disease. You need to highlight all the challenges and impacts of COVID-19. Do not forget to conclude your essay with positive precautionary measures.
Writing an essay on COVID-19 in 200 words requires you to cover all the challenges, impacts and precautions of this disease. You don’t need to describe all of these factors in brief, but make sure to add as many options as your word limit allows.
The full form for COVID-19 is Corona Virus Disease of 2019.
Related Reads
Hence, we hope that this blog has assisted you in comprehending with an essay on COVID-19. For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Simran Popli
An avid writer and a creative person. With an experience of 1.5 years content writing, Simran has worked with different areas. From medical to working in a marketing agency with different clients to Ed-tech company, the journey has been diverse. Creative, vivacious and patient are the words that describe her personality.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history.
by Alissa Wilkinson

The world is grappling with an invisible, deadly enemy, trying to understand how to live with the threat posed by a virus . For some writers, the only way forward is to put pen to paper, trying to conceptualize and document what it feels like to continue living as countries are under lockdown and regular life seems to have ground to a halt.
So as the coronavirus pandemic has stretched around the world, it’s sparked a crop of diary entries and essays that describe how life has changed. Novelists, critics, artists, and journalists have put words to the feelings many are experiencing. The result is a first draft of how we’ll someday remember this time, filled with uncertainty and pain and fear as well as small moments of hope and humanity.
- The Vox guide to navigating the coronavirus crisis
At the New York Review of Books, Ali Bhutto writes that in Karachi, Pakistan, the government-imposed curfew due to the virus is “eerily reminiscent of past military clampdowns”:
Beneath the quiet calm lies a sense that society has been unhinged and that the usual rules no longer apply. Small groups of pedestrians look on from the shadows, like an audience watching a spectacle slowly unfolding. People pause on street corners and in the shade of trees, under the watchful gaze of the paramilitary forces and the police.
His essay concludes with the sobering note that “in the minds of many, Covid-19 is just another life-threatening hazard in a city that stumbles from one crisis to another.”
Writing from Chattanooga, novelist Jamie Quatro documents the mixed ways her neighbors have been responding to the threat, and the frustration of conflicting direction, or no direction at all, from local, state, and federal leaders:
Whiplash, trying to keep up with who’s ordering what. We’re already experiencing enough chaos without this back-and-forth. Why didn’t the federal government issue a nationwide shelter-in-place at the get-go, the way other countries did? What happens when one state’s shelter-in-place ends, while others continue? Do states still under quarantine close their borders? We are still one nation, not fifty individual countries. Right?
- A syllabus for the end of the world
Award-winning photojournalist Alessio Mamo, quarantined with his partner Marta in Sicily after she tested positive for the virus, accompanies his photographs in the Guardian of their confinement with a reflection on being confined :
The doctors asked me to take a second test, but again I tested negative. Perhaps I’m immune? The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good news. My mother left hospital, but I won’t be able to see her for weeks. Marta started breathing well again, and so did I. I would have liked to photograph my country in the midst of this emergency, the battles that the doctors wage on the frontline, the hospitals pushed to their limits, Italy on its knees fighting an invisible enemy. That enemy, a day in March, knocked on my door instead.
In the New York Times Magazine, deputy editor Jessica Lustig writes with devastating clarity about her family’s life in Brooklyn while her husband battled the virus, weeks before most people began taking the threat seriously:
At the door of the clinic, we stand looking out at two older women chatting outside the doorway, oblivious. Do I wave them away? Call out that they should get far away, go home, wash their hands, stay inside? Instead we just stand there, awkwardly, until they move on. Only then do we step outside to begin the long three-block walk home. I point out the early magnolia, the forsythia. T says he is cold. The untrimmed hairs on his neck, under his beard, are white. The few people walking past us on the sidewalk don’t know that we are visitors from the future. A vision, a premonition, a walking visitation. This will be them: Either T, in the mask, or — if they’re lucky — me, tending to him.
Essayist Leslie Jamison writes in the New York Review of Books about being shut away alone in her New York City apartment with her 2-year-old daughter since she became sick:
The virus. Its sinewy, intimate name. What does it feel like in my body today? Shivering under blankets. A hot itch behind the eyes. Three sweatshirts in the middle of the day. My daughter trying to pull another blanket over my body with her tiny arms. An ache in the muscles that somehow makes it hard to lie still. This loss of taste has become a kind of sensory quarantine. It’s as if the quarantine keeps inching closer and closer to my insides. First I lost the touch of other bodies; then I lost the air; now I’ve lost the taste of bananas. Nothing about any of these losses is particularly unique. I’ve made a schedule so I won’t go insane with the toddler. Five days ago, I wrote Walk/Adventure! on it, next to a cut-out illustration of a tiger—as if we’d see tigers on our walks. It was good to keep possibility alive.
At Literary Hub, novelist Heidi Pitlor writes about the elastic nature of time during her family’s quarantine in Massachusetts:
During a shutdown, the things that mark our days—commuting to work, sending our kids to school, having a drink with friends—vanish and time takes on a flat, seamless quality. Without some self-imposed structure, it’s easy to feel a little untethered. A friend recently posted on Facebook: “For those who have lost track, today is Blursday the fortyteenth of Maprilay.” ... Giving shape to time is especially important now, when the future is so shapeless. We do not know whether the virus will continue to rage for weeks or months or, lord help us, on and off for years. We do not know when we will feel safe again. And so many of us, minus those who are gifted at compartmentalization or denial, remain largely captive to fear. We may stay this way if we do not create at least the illusion of movement in our lives, our long days spent with ourselves or partners or families.
- What day is it today?
Novelist Lauren Groff writes at the New York Review of Books about trying to escape the prison of her fears while sequestered at home in Gainesville, Florida:
Some people have imaginations sparked only by what they can see; I blame this blinkered empiricism for the parks overwhelmed with people, the bars, until a few nights ago, thickly thronged. My imagination is the opposite. I fear everything invisible to me. From the enclosure of my house, I am afraid of the suffering that isn’t present before me, the people running out of money and food or drowning in the fluid in their lungs, the deaths of health-care workers now growing ill while performing their duties. I fear the federal government, which the right wing has so—intentionally—weakened that not only is it insufficient to help its people, it is actively standing in help’s way. I fear we won’t sufficiently punish the right. I fear leaving the house and spreading the disease. I fear what this time of fear is doing to my children, their imaginations, and their souls.
At ArtForum , Berlin-based critic and writer Kristian Vistrup Madsen reflects on martinis, melancholia, and Finnish artist Jaakko Pallasvuo’s 2018 graphic novel Retreat , in which three young people exile themselves in the woods:
In melancholia, the shape of what is ending, and its temporality, is sprawling and incomprehensible. The ambivalence makes it hard to bear. The world of Retreat is rendered in lush pink and purple watercolors, which dissolve into wild and messy abstractions. In apocalypse, the divisions established in genesis bleed back out. My own Corona-retreat is similarly soft, color-field like, each day a blurred succession of quarantinis, YouTube–yoga, and televized press conferences. As restrictions mount, so does abstraction. For now, I’m still rooting for love to save the world.
At the Paris Review , Matt Levin writes about reading Virginia Woolf’s novel The Waves during quarantine:
A retreat, a quarantine, a sickness—they simultaneously distort and clarify, curtail and expand. It is an ideal state in which to read literature with a reputation for difficulty and inaccessibility, those hermetic books shorn of the handholds of conventional plot or characterization or description. A novel like Virginia Woolf’s The Waves is perfect for the state of interiority induced by quarantine—a story of three men and three women, meeting after the death of a mutual friend, told entirely in the overlapping internal monologues of the six, interspersed only with sections of pure, achingly beautiful descriptions of the natural world, a day’s procession and recession of light and waves. The novel is, in my mind’s eye, a perfectly spherical object. It is translucent and shimmering and infinitely fragile, prone to shatter at the slightest disturbance. It is not a book that can be read in snatches on the subway—it demands total absorption. Though it revels in a stark emotional nakedness, the book remains aloof, remote in its own deep self-absorption.
- Vox is starting a book club. Come read with us!
In an essay for the Financial Times, novelist Arundhati Roy writes with anger about Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s anemic response to the threat, but also offers a glimmer of hope for the future:
Historically, pandemics have forced humans to break with the past and imagine their world anew. This one is no different. It is a portal, a gateway between one world and the next. We can choose to walk through it, dragging the carcasses of our prejudice and hatred, our avarice, our data banks and dead ideas, our dead rivers and smoky skies behind us. Or we can walk through lightly, with little luggage, ready to imagine another world. And ready to fight for it.
From Boston, Nora Caplan-Bricker writes in The Point about the strange contraction of space under quarantine, in which a friend in Beirut is as close as the one around the corner in the same city:
It’s a nice illusion—nice to feel like we’re in it together, even if my real world has shrunk to one person, my husband, who sits with his laptop in the other room. It’s nice in the same way as reading those essays that reframe social distancing as solidarity. “We must begin to see the negative space as clearly as the positive, to know what we don’t do is also brilliant and full of love,” the poet Anne Boyer wrote on March 10th, the day that Massachusetts declared a state of emergency. If you squint, you could almost make sense of this quarantine as an effort to flatten, along with the curve, the distinctions we make between our bonds with others. Right now, I care for my neighbor in the same way I demonstrate love for my mother: in all instances, I stay away. And in moments this month, I have loved strangers with an intensity that is new to me. On March 14th, the Saturday night after the end of life as we knew it, I went out with my dog and found the street silent: no lines for restaurants, no children on bicycles, no couples strolling with little cups of ice cream. It had taken the combined will of thousands of people to deliver such a sudden and complete emptiness. I felt so grateful, and so bereft.
And on his own website, musician and artist David Byrne writes about rediscovering the value of working for collective good , saying that “what is happening now is an opportunity to learn how to change our behavior”:
In emergencies, citizens can suddenly cooperate and collaborate. Change can happen. We’re going to need to work together as the effects of climate change ramp up. In order for capitalism to survive in any form, we will have to be a little more socialist. Here is an opportunity for us to see things differently — to see that we really are all connected — and adjust our behavior accordingly. Are we willing to do this? Is this moment an opportunity to see how truly interdependent we all are? To live in a world that is different and better than the one we live in now? We might be too far down the road to test every asymptomatic person, but a change in our mindsets, in how we view our neighbors, could lay the groundwork for the collective action we’ll need to deal with other global crises. The time to see how connected we all are is now.
The portrait these writers paint of a world under quarantine is multifaceted. Our worlds have contracted to the confines of our homes, and yet in some ways we’re more connected than ever to one another. We feel fear and boredom, anger and gratitude, frustration and strange peace. Uncertainty drives us to find metaphors and images that will let us wrap our minds around what is happening.
Yet there’s no single “what” that is happening. Everyone is contending with the pandemic and its effects from different places and in different ways. Reading others’ experiences — even the most frightening ones — can help alleviate the loneliness and dread, a little, and remind us that what we’re going through is both unique and shared by all.
Most Popular
The frogs of puerto rico have a warning for us, the whole time the boys has been making fun of trumpers the whole time, the supreme court hands an embarrassing defeat to america’s trumpiest court, web3 is the future, or a scam, or both, take a mental break with the newest vox crossword, today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
More in Culture

Julian Assange’s release is still a lose-lose for press freedom

Why do all the world’s best athletes do Subway commercials?

“Black girl tanning” is the summer’s most radical beauty trend

What this summer’s age-gap escapist fantasies are missing about romance and middle age

Deadpool and Wolverine’s marketing blitz is one long gay joke

The Supreme Court rules that state officials can engage in a little corruption, as a treat

How much can we actually control inflation? Audio

Summertime sadness is real

A new book tackles the splendor and squalor of reality TV

What if quitting your terrible job would help the economy?
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- How to Use AI to Enhance Your Thesis
Guide to Structuring Your Narrative Essay for Success
- How to Hook Your Readers with a Compelling Topic Sentence
- Is a Thesis Writing Format Easy? A Comprehensive Guide to Thesis Writing
- The Complete Guide to Copy Editing: Roles, Rates, Skills, and Process
- How to Write a Paragraph: Successful Essay Writing Strategies
- Everything You Should Know About Academic Writing: Types, Importance, and Structure
- Concise Writing: Tips, Importance, and Exercises for a Clear Writing Style
- How to Write a PhD Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Success
- How to Use AI in Essay Writing: Tips, Tools, and FAQs
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

How to write an essay on coronavirus (COVID-19)
(Last updated: 10 November 2021)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
With the coronavirus pandemic affecting every aspect of our lives for the last 18 months, it is no surprise that it has become a common topic in academic assignments. Writing a COVID-19 essay can be challenging, whether you're studying biology, philosophy, or any course in between.
Your first question might be, how would an essay about a pandemic be any different from a typical academic essay? Well, the answer is that in many ways it is largely similar. The key difference, however, is that this pandemic is much more current than usual academic topics. That means that it may be difficult to rely on past research to demonstrate your argument! As a result, COVID-19 essay writing needs to balance theories of past scholars with very current data (that is constantly changing).
In this post, we are going to give you our top tips on how to write a coronavirus academic essay, so that you are able to approach your writing with confidence and produce a great piece of work.
1. Do background reading
Critical reading is an essential component for any essay, but the question is – what should you be reading for a coronavirus essay? It might seem like a silly question, but the choices that you make during the reading process may determine how well you actually do on the paper. Therefore, we recommend the following steps.
First, read (and re-read) the assignment prompt that you have been given by the instructor. If you write an excellent essay, but it is off topic, you’ll likely be marked down. Make notes on the words that explain what is being asked of you – perhaps the essay asks you to “analyse”, “describe”, “list”, or “evaluate”. Make sure that these same words actually appear in your paper.
Second, look for specific things you have been instructed to do. This might include using themes from your textbook or incorporating assigned readings. Make a note of these things and read them first. Remember to take good notes while you read.
Once you have done your course readings, the question then becomes: what types of external readings are you going to need? Typically, at this point, you are going to be left with newspapers/websites, and a few scholarly articles (books on coronavirus might not be readily available at this stage, but could still be useful!). If it is a research essay, you are likely going to need to rely on a variety of sources as you work through this assignment. This might seem different than other academic writing where you would typically focus on only peer-reviewed articles or books. With coronavirus essays, there is a need for a more diverse set of sources, including;
Newspaper articles and websites
Just like with academic articles, not all newspaper articles and/or websites are created equal. Further, there are likely to be a variety of different statistics released, as the way that countries calculate coronavirus cases, deaths, and other components of the virus are not always the same.
Try to pick sources that are reputable. This might be reports done by key governmental organisations or even the World Health Organisation. If you are reading through an article and can identify obvious areas of bias, you may need to find alternate readings for your paper.
Academic articles
You may be surprised to discover the variety of articles published so far on COVID-19 - a lot can be achieved over multiple lockdowns! The research that has been done has been fairly extensive, covering a broad range of topics. Therefore, when preparing to write your academic essay, make sure to check the literature frequently as new publications are being released all the time.
If you do a search and you cannot find anything on the coronavirus specifically, you will have to widen your search. Think about the topic more widely. Are there theories that you have learned about in your classes that you can link to academic articles? Surely the answer must be yes! Just because there is limited research on this topic does not mean that you should avoid academic articles all together. Relying solely on websites or newspapers can lead you to a biased piece of writing, which usually is not what an academic essay is all about.

2. Plan your essay
Brainstorming.
Taking the time to brainstorm out your ideas can be the first step in a super successful essay. Brainstorming does not have to take a lot of time, and can be done in about 20 minutes if you have already done some background reading on the topic.
First, figure out how many points you need to identify. Each point is likely to equate to one paragraph of your paper, so if you are writing a 1500-word essay (and you use 300 words for the introduction and conclusion) you will be left with 1200 words, which means you will need between 5-6 paragraphs (and 5-6 points).
Start with a blank piece of paper. In the middle of the paper write the question or statement that you are trying to answer. From there, draw 5 or 6 lines out from the centre. At the end of each of these lines will be a point you want to address in your essay. From here, write down any additional ideas that you have.
It might look messy, but that’s OK! This is just the first step in the process and an opportunity for you to get your ideas down on paper. From this messiness, you can easily start to form a logical and linear outline that will soon become the template for your essay.
Creating an outline
Once you have a completed brainstorm, the next step is to put your ideas into a logical format The first step in this process is usually to write out a rough draft of the argument you are attempting to make. In doing this, you are then able to see how your subsequent paragraphs are addressing this topic (and if they are not addressing the topic, now is the time to change this!).
Once you have a position/argument/thesis statement, create space for your body paragraphs, but numbering each section. Then, write a rough draft of the topic sentence that you think will fit well in that section. Once you have done this, pull up the coronavirus articles, data, and other reports that you have read. Determine where each will fit best in your paper (and exclude the ones that do not fit well). Put a citation of the document in each paragraph section (this will make it easier to construct your reference list at the end).
Once every paragraph is organised, double check to make sure they are all still on track to address your main thesis. At this point you are ready to write an excellent and well-organised COVID-19 essay!

3. Structure your paragraphs
When structuring an academic essay on COVID-19, there will be a need to balance the news, evidence from academic articles, and course theory. This adds an extra layer of complexity because there are just so many things to juggle.
One strategy that can be helpful is to structure all your paragraphs in the same way. Now, you might be thinking, how boring! In reality, it is likely that the reader will appreciate the fact that you have carefully thought out your process and how you are going to approach this essay.
How to design your essay paragraphs
- Create a topic sentence. A topic sentence is a sentence that presents the main idea for the paragraph. Usually it links back to your thesis, argument, or position.
- Start to introduce your evidence. Use the next sentence in your introduction as a bridge between the topic sentence and the evidence/data you are going to present.
- Add evidence. Take 2-4 sentences to give the reader some good information that supports your topic sentence. This can be statistics, details from an empirical study, information from a news article, or some other form of information.
- Give some critical thought. It is essential to make a connection for the reader between your evidence and your topic sentence. Tell the reader why the information you have presented is important.
- Provide a concluding sentence. Make sure you wrap up your argument or transition to the next one.
4. Write your essay
Keep it academic.
There is a lot of information available about the coronavirus, but because much of it is coming from newspaper articles, the evidence that you might use for your paper can be skewed. In order to keep your paper academic, it is best to maintain a professional and academic style.
Present statistics from reputable sources (like the World Health Organisation), rather than those that have been selected by third parties. Furthermore, if you are writing a COVID-19 essay that is about a specific region (e.g. the United Kingdom), make sure that your statistics and evidence also come from this region.
Use up-to-date sources
The information on coronavirus is constantly changing. By now, everyone has seen the exponential curve of cases reoccurring all over the world at different times. Therefore, what was true last month may not necessarily be the case now. This can be challenging when you are planning an essay, because your outline from a previous week may need to be modified.
There are a number of ways you can address this. One way is, obviously, to continue going back and refreshing the data. Another way, which can be equally useful, is to outline the scope of the problem in your paper, writing something like, “data on COVID-19 is constantly changing, but the data presented was accurate at the time of writing”.
Avoid personal bias or opinion (unless asked!)
Everybody has an opinion – this opinion can often relate to how you or your family members have been affected by the pandemic (and the government response to this). People have lost jobs, have had to avoid family/friends, or have lost someone as a result of this pandemic. Life, for many, is very different.
While all of this is extremely important, it may not necessarily be relevant for an academic essay. One of the more challenging components of this type of academic paper is to try and remove yourself from the evidence you are providing. Now… there are exceptions. If you are writing a COVID-19 reflective essay, then it is your responsibility to include your opinion; otherwise, do your best to remain objective.
Avoid personal pronouns
Along the same lines as avoiding bias, it is also a good idea to avoid personal pronouns in your academic essay (except in a reflection, of course). This means avoiding words like “I, we, our, my”. While you may agree (or disagree) with the sentiment you are presenting, try and present your information from a distanced perspective.
Proofread carefully
Finally (and this is true of any essay), make sure that you take the time to proofread your essay carefully. Is it free from spelling errors? Have you checked the grammar? Have you made sure that your references are correct and in order? Have you carefully reviewed the submission requirements of your instructor (e.g. font, margins, spacing, etc.)? If the answer is yes, it sounds as if you are finally ready to submit your essay.

Final thoughts
Writing an essay is not easy. Writing an essay on a pandemic while living in that same pandemic is even more difficult.
A good essay is appropriately structured with a clear purpose and is presented according to the recommended guidelines. Unless it is a personal reflection, it attempts to present information as if it were free from bias.
So before you start to panic about having to write an essay about a pandemic, take a breath. You can do this. Take all the same steps as you would in a conventional academic essay, but expand your search to include relevant and up-to-date information that you know will make your essay a success. Once you have done this, make sure to have your university writing centre or an academic at Oxbridge Essays check it over and make suggestions! Now, stop reading and get writing! Good luck.

Essay exams: how to answer ‘To what extent…’

How to write a master’s essay

Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service

Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
More From Forbes
A guide to writing the covid-19 essay for the common app.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Students can use the Common App's new Covid-19 essay to expand on their experiences during the ... [+] pandemic.
Covid-19 has heavily impacted students applying to colleges in this application cycle. High schools have gone virtual, extracurricular activities have been canceled and family situations might have changed. Having recognized this, the Common App added a new optional 250-word essay that will give universities a chance to understand the atypical high school experience students have had. The prompt will be:
“Community disruptions such as COVID-19 and natural disasters can have deep and long-lasting impacts. If you need it, this space is yours to describe those impacts. Colleges care about the effects on your health and well-being, safety, family circumstances, future plans, and education, including access to reliable technology and quiet study spaces.”
Should I Write About The Coronavirus Pandemic?
For many high schoolers, the pandemic will have had a lasting impact on their education and everyday lives. Some students might have had a negative experience: a parent laid off or furloughed, limited access to online classes or a family member (or the student) having fallen ill from the virus.
Other students might have had the opposite experience. Even though they might have undergone a few negative events or stressful times, they might have learned something new, started a new project or gained a new perspective that changed their future major or career choice.
If you fit into either of these categories, writing the optional essay might be a good idea.
Remember, the admission officers have also been dealing with the crisis and understand the situation students are going through. They are well aware that the AP exams were administered remotely, SAT/ACT test dates were canceled and numerous schools transitioned to a virtual learning model. There is likely no need to reiterate this in an essay unless there was a direct impact on an aspect of your application.
Dr. Disrespect Issues Shocking Statement, Finally Revealing Why He Was Banned From Twitch
What time does ‘the bear’ season 3 come out on hulu and disney+, ‘squad’ rep. jamaal bowman unseated by latimer in pricey new york primary, what not to write .
As with every college essay you write, it is important to think about the tone and word choice. You want to remain sensitive to the plight of other students during this global crisis. While every student has likely been affected by the pandemic, the level of impact will vary greatly. For some, classes moved online, but life remained more or less the same. For these types of students, it might not be a strategic move to write about the coronavirus if you don’t have anything meaningful, unique or personal to say. If you only have a limited time to impress the admission officer, you want to ensure that each word is strategically thought out and showcases a new aspect of your personality.
Using this space as a time to complain about how you weren’t able to go to the beach, see friends or eat out could be seen as you flaunting your privilege. Careful consideration of how you portray yourself will be key.
Nearly every student has had an activity or event canceled. It likely won’t be a good use of your word count lamenting on the missed opportunities. Instead, it would be more illuminating to talk about how you remained flexible and pivoted to other learning opportunities.
How To Write The Covid-19 Essay
The Covid-19 essay was introduced so universities could gain a better understanding of how their applicants have had their lives and education disrupted due to the pandemic. You’ll want to give the admission officers context to understand your experiences better.
Here are some examples of how to write this optional essay.
- Outline any extenuating circumstances related to Covid-19. Some students might find themselves crammed in a small apartment or home with their entire family. This disruptive environment might have made it difficult for the student to concentrate on their classes. Some students might be required to care for younger siblings during the day. In many areas of the country, lack of access to high-speed internet or smart devices meant that students couldn’t participate in online learning. Now is the time to share those details.
- Include the impact. Ultimately, this essay is about you. Things likely happened to family members, friends or your community, but you need to show how it altered your life specifically.
- Provide specific details. Give the admission officers a peek into your everyday life. Including specific details can help make your story come alive. For example, don’t just say that it was hard dealing with the emotional trauma of seeing friends and family fall ill. Instead, be specific and talk about how your friend was diagnosed with Covid-19 and had to be hospitalized. Seeing the long-term effects caused you to take the pandemic much more seriously and moved you to take action. Perhaps you were inspired to start a nonprofit that makes masks or to help your neighbors through this difficult time.
Covid-19 Essay for School Counselors
It’s not just students who will get to submit an additional statement regarding the impact of the coronavirus: Counselors will also get a chance to submit a 500-word essay. Their prompt will be:
Your school may have made adjustments due to community disruptions such as COVID–19 or natural disasters. If you have not already addressed those changes in your uploaded school profile or elsewhere, you can elaborate here. Colleges are especially interested in understanding changes to:
- Grading scales and policies
- Graduation requirements
- Instructional methods
- Schedules and course offerings
- Testing requirements
- Your academic calendar
- Other extenuating circumstances
The counselor’s response will populate to all the applications of students from the high school. They will cover any school or district policies that have impacted students. No specific student details will be included.
Students can ask to see a copy of this statement so they know what information has already been shared with colleges. For example, if the school states that classes went virtual starting in March, you don’t need to repeat that in your Covid-19 essay.
Should I Write About The Covid-19 In My Personal Statement?
The world before Covid-19 might seem like a distant memory, but you did spend more than 15 years engaging in a multitude of meaningful activities and developing your passions. It’s important to define yourself from more than just the coronavirus crisis. You likely will want to spend the personal statement distinguishing yourself from other applicants. With the Covid-19 optional essay and the additional information section, you should have plenty of space to talk about how you’ve changed—for better or for worse—due to the pandemic. Use the personal statement to talk about who you were before quarantining.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Writing about COVID-19 in a college admission essay
by: Venkates Swaminathan | Updated: September 14, 2020
Print article

For students applying to college using the CommonApp, there are several different places where students and counselors can address the pandemic’s impact. The different sections have differing goals. You must understand how to use each section for its appropriate use.
The CommonApp COVID-19 question
First, the CommonApp this year has an additional question specifically about COVID-19 :
Community disruptions such as COVID-19 and natural disasters can have deep and long-lasting impacts. If you need it, this space is yours to describe those impacts. Colleges care about the effects on your health and well-being, safety, family circumstances, future plans, and education, including access to reliable technology and quiet study spaces. Please use this space to describe how these events have impacted you.
This question seeks to understand the adversity that students may have had to face due to the pandemic, the move to online education, or the shelter-in-place rules. You don’t have to answer this question if the impact on you wasn’t particularly severe. Some examples of things students should discuss include:
- The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic.
- The candidate had to deal with personal or family issues, such as abusive living situations or other safety concerns
- The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges.
- Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams.
Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions office has a blog about this section. He recommends students ask themselves several questions as they go about answering this section:
- Are my experiences different from others’?
- Are there noticeable changes on my transcript?
- Am I aware of my privilege?
- Am I specific? Am I explaining rather than complaining?
- Is this information being included elsewhere on my application?
If you do answer this section, be brief and to-the-point.
Counselor recommendations and school profiles
Second, counselors will, in their counselor forms and school profiles on the CommonApp, address how the school handled the pandemic and how it might have affected students, specifically as it relates to:
- Grading scales and policies
- Graduation requirements
- Instructional methods
- Schedules and course offerings
- Testing requirements
- Your academic calendar
- Other extenuating circumstances
Students don’t have to mention these matters in their application unless something unusual happened.
Writing about COVID-19 in your main essay
Write about your experiences during the pandemic in your main college essay if your experience is personal, relevant, and the most important thing to discuss in your college admission essay. That you had to stay home and study online isn’t sufficient, as millions of other students faced the same situation. But sometimes, it can be appropriate and helpful to write about something related to the pandemic in your essay. For example:
- One student developed a website for a local comic book store. The store might not have survived without the ability for people to order comic books online. The student had a long-standing relationship with the store, and it was an institution that created a community for students who otherwise felt left out.
- One student started a YouTube channel to help other students with academic subjects he was very familiar with and began tutoring others.
- Some students used their extra time that was the result of the stay-at-home orders to take online courses pursuing topics they are genuinely interested in or developing new interests, like a foreign language or music.
Experiences like this can be good topics for the CommonApp essay as long as they reflect something genuinely important about the student. For many students whose lives have been shaped by this pandemic, it can be a critical part of their college application.
Want more? Read 6 ways to improve a college essay , What the &%$! should I write about in my college essay , and Just how important is a college admissions essay? .

Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race

The truth about homework in America

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
How to Write About the Impact of the Coronavirus in a College Essay
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many -- a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
[ Read: How to Write a College Essay. ]
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.
Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
[ Read: What Colleges Look for: 6 Ways to Stand Out. ]
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them -- and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
[ Read: The Common App: Everything You Need to Know. ]
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic -- and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
I Thought We’d Learned Nothing From the Pandemic. I Wasn’t Seeing the Full Picture
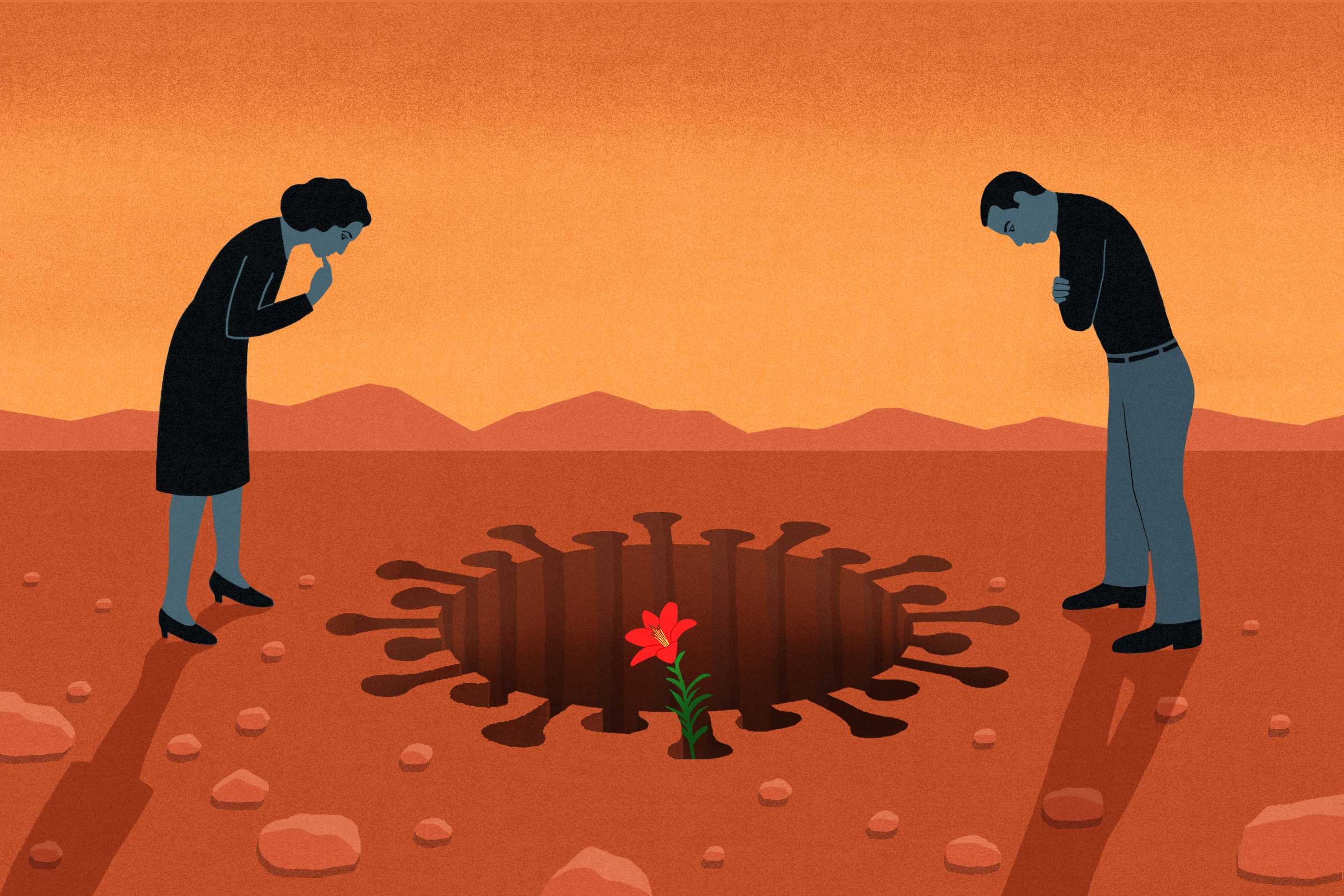

M y first home had a back door that opened to a concrete patio with a giant crack down the middle. When my sister and I played, I made sure to stay on the same side of the divide as her, just in case. The 1988 film The Land Before Time was one of the first movies I ever saw, and the image of the earth splintering into pieces planted its roots in my brain. I believed that, even in my own backyard, I could easily become the tiny Triceratops separated from her family, on the other side of the chasm, as everything crumbled into chaos.
Some 30 years later, I marvel at the eerie, unexpected ways that cartoonish nightmare came to life – not just for me and my family, but for all of us. The landscape was already covered in fissures well before COVID-19 made its way across the planet, but the pandemic applied pressure, and the cracks broke wide open, separating us from each other physically and ideologically. Under the weight of the crisis, we scattered and landed on such different patches of earth we could barely see each other’s faces, even when we squinted. We disagreed viciously with each other, about how to respond, but also about what was true.
Recently, someone asked me if we’ve learned anything from the pandemic, and my first thought was a flat no. Nothing. There was a time when I thought it would be the very thing to draw us together and catapult us – as a capital “S” Society – into a kinder future. It’s surreal to remember those early days when people rallied together, sewing masks for health care workers during critical shortages and gathering on balconies in cities from Dallas to New York City to clap and sing songs like “Yellow Submarine.” It felt like a giant lightning bolt shot across the sky, and for one breath, we all saw something that had been hidden in the dark – the inherent vulnerability in being human or maybe our inescapable connectedness .
More from TIME
Read More: The Family Time the Pandemic Stole
But it turns out, it was just a flash. The goodwill vanished as quickly as it appeared. A couple of years later, people feel lied to, abandoned, and all on their own. I’ve felt my own curiosity shrinking, my willingness to reach out waning , my ability to keep my hands open dwindling. I look out across the landscape and see selfishness and rage, burnt earth and so many dead bodies. Game over. We lost. And if we’ve already lost, why try?
Still, the question kept nagging me. I wondered, am I seeing the full picture? What happens when we focus not on the collective society but at one face, one story at a time? I’m not asking for a bow to minimize the suffering – a pretty flourish to put on top and make the whole thing “worth it.” Yuck. That’s not what we need. But I wondered about deep, quiet growth. The kind we feel in our bodies, relationships, homes, places of work, neighborhoods.
Like a walkie-talkie message sent to my allies on the ground, I posted a call on my Instagram. What do you see? What do you hear? What feels possible? Is there life out here? Sprouting up among the rubble? I heard human voices calling back – reports of life, personal and specific. I heard one story at a time – stories of grief and distrust, fury and disappointment. Also gratitude. Discovery. Determination.
Among the most prevalent were the stories of self-revelation. Almost as if machines were given the chance to live as humans, people described blossoming into fuller selves. They listened to their bodies’ cues, recognized their desires and comforts, tuned into their gut instincts, and honored the intuition they hadn’t realized belonged to them. Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. “The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry myself have both shrunk and expanded,” she shared. “I don’t love myself very well with an audience.” Without the daily ritual of trying to pass as “normal” in public, Tamar, a queer mom in the Netherlands, realized she’s autistic. “I think the pandemic helped me to recognize the mask,” she wrote. “Not that unmasking is easy now. But at least I know it’s there.” In a time of widespread suffering that none of us could solve on our own, many tended to our internal wounds and misalignments, large and small, and found clarity.
Read More: A Tool for Staying Grounded in This Era of Constant Uncertainty
I wonder if this flourishing of self-awareness is at least partially responsible for the life alterations people pursued. The pandemic broke open our personal notions of work and pushed us to reevaluate things like time and money. Lucy, a disabled writer in the U.K., made the hard decision to leave her job as a journalist covering Westminster to write freelance about her beloved disability community. “This work feels important in a way nothing else has ever felt,” she wrote. “I don’t think I’d have realized this was what I should be doing without the pandemic.” And she wasn’t alone – many people changed jobs , moved, learned new skills and hobbies, became politically engaged.
Perhaps more than any other shifts, people described a significant reassessment of their relationships. They set boundaries, said no, had challenging conversations. They also reconnected, fell in love, and learned to trust. Jeanne, a quilter in Indiana, got to know relatives she wouldn’t have connected with if lockdowns hadn’t prompted weekly family Zooms. “We are all over the map as regards to our belief systems,” she emphasized, “but it is possible to love people you don’t see eye to eye with on every issue.” Anna, an anti-violence advocate in Maine, learned she could trust her new marriage: “Life was not a honeymoon. But we still chose to turn to each other with kindness and curiosity.” So many bonds forged and broken, strengthened and strained.
Instead of relying on default relationships or institutional structures, widespread recalibrations allowed for going off script and fortifying smaller communities. Mara from Idyllwild, Calif., described the tangible plan for care enacted in her town. “We started a mutual-aid group at the beginning of the pandemic,” she wrote, “and it grew so quickly before we knew it we were feeding 400 of the 4000 residents.” She didn’t pretend the conditions were ideal. In fact, she expressed immense frustration with our collective response to the pandemic. Even so, the local group rallied and continues to offer assistance to their community with help from donations and volunteers (many of whom were originally on the receiving end of support). “I’ve learned that people thrive when they feel their connection to others,” she wrote. Clare, a teacher from the U.K., voiced similar conviction as she described a giant scarf she’s woven out of ribbons, each representing a single person. The scarf is “a collection of stories, moments and wisdom we are sharing with each other,” she wrote. It now stretches well over 1,000 feet.
A few hours into reading the comments, I lay back on my bed, phone held against my chest. The room was quiet, but my internal world was lighting up with firefly flickers. What felt different? Surely part of it was receiving personal accounts of deep-rooted growth. And also, there was something to the mere act of asking and listening. Maybe it connected me to humans before battle cries. Maybe it was the chance to be in conversation with others who were also trying to understand – what is happening to us? Underneath it all, an undeniable thread remained; I saw people peering into the mess and narrating their findings onto the shared frequency. Every comment was like a flare into the sky. I’m here! And if the sky is full of flares, we aren’t alone.
I recognized my own pandemic discoveries – some minor, others massive. Like washing off thick eyeliner and mascara every night is more effort than it’s worth; I can transform the mundane into the magical with a bedsheet, a movie projector, and twinkle lights; my paralyzed body can mother an infant in ways I’d never seen modeled for me. I remembered disappointing, bewildering conversations within my own family of origin and our imperfect attempts to remain close while also seeing things so differently. I realized that every time I get the weekly invite to my virtual “Find the Mumsies” call, with a tiny group of moms living hundreds of miles apart, I’m being welcomed into a pocket of unexpected community. Even though we’ve never been in one room all together, I’ve felt an uncommon kind of solace in their now-familiar faces.
Hope is a slippery thing. I desperately want to hold onto it, but everywhere I look there are real, weighty reasons to despair. The pandemic marks a stretch on the timeline that tangles with a teetering democracy, a deteriorating planet , the loss of human rights that once felt unshakable . When the world is falling apart Land Before Time style, it can feel trite, sniffing out the beauty – useless, firing off flares to anyone looking for signs of life. But, while I’m under no delusions that if we just keep trudging forward we’ll find our own oasis of waterfalls and grassy meadows glistening in the sunshine beneath a heavenly chorus, I wonder if trivializing small acts of beauty, connection, and hope actually cuts us off from resources essential to our survival. The group of abandoned dinosaurs were keeping each other alive and making each other laugh well before they made it to their fantasy ending.
Read More: How Ice Cream Became My Own Personal Act of Resistance
After the monarch butterfly went on the endangered-species list, my friend and fellow writer Hannah Soyer sent me wildflower seeds to plant in my yard. A simple act of big hope – that I will actually plant them, that they will grow, that a monarch butterfly will receive nourishment from whatever blossoms are able to push their way through the dirt. There are so many ways that could fail. But maybe the outcome wasn’t exactly the point. Maybe hope is the dogged insistence – the stubborn defiance – to continue cultivating moments of beauty regardless. There is value in the planting apart from the harvest.
I can’t point out a single collective lesson from the pandemic. It’s hard to see any great “we.” Still, I see the faces in my moms’ group, making pancakes for their kids and popping on between strings of meetings while we try to figure out how to raise these small people in this chaotic world. I think of my friends on Instagram tending to the selves they discovered when no one was watching and the scarf of ribbons stretching the length of more than three football fields. I remember my family of three, holding hands on the way up the ramp to the library. These bits of growth and rings of support might not be loud or right on the surface, but that’s not the same thing as nothing. If we only cared about the bottom-line defeats or sweeping successes of the big picture, we’d never plant flowers at all.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Melinda French Gates Is Going It Alone
- How to Buy Groceries Without Breaking the Bank
- Lai Ching-te Is Standing His Ground
- How to Cool Your Body Down Fast
- Forget Having It All . Let’s Try Having Enough
- 4 Signs Your Body Needs a Break
- The 15 Best Movies to Watch on a Plane
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Editor in Chief's Introduction to Essays on the Impact of COVID-19 on Work and Workers
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared that COVID-19 was a global pandemic, indicating significant global spread of an infectious disease ( World Health Organization, 2020 ). At that point, there were 118,000 confirmed cases of the coronavirus in 110 countries. China had been the first country with a widespread outbreak in January, and South Korea, Iran and Italy following in February with their own outbreaks. Soon, the virus was in all continents and over 177 countries, and as of this writing, the United States has the highest number of confirmed cases and, sadly, the most deaths. The virus was extremely contagious and led to death in the most vulnerable, particularly those older than 60 and those with underlying conditions. The most critical cases led to an overwhelming number being admitted into the intensive care units of hospitals, leading to a concern that the virus would overwhelm local health care systems. Today, in early May 2020, there have been nearly 250,000 deaths worldwide, with over 3,500,000 confirmed cases ( Hopkins, 2020 ). The human toll is staggering, and experts are predicting a second wave in summer or fall.
As the deaths rose from the virus that had no known treatment or vaccine countries shut their borders, banned travel to other countries and began to issue orders for their citizens to stay at home, with no gatherings of more than 10 individuals. Schools and universities closed their physical locations and moved education online. Sporting events were canceled, airlines cut flights, tourism evaporated, restaurants, movie theaters and bars closed, theater productions canceled, manufacturing facilities, services, and retail stores closed. In some businesses and industries, employees have been able to work remotely from home, but in others, workers have been laid off, furloughed, or had their hours cut. The International Labor Organization (ILO) estimates that there was a 4.5% reduction in hours in the first quarter of 2020, and 10.5% reduction is expected in the second quarter ( ILO, 2020a ). The latter is equivalent to 305 million jobs ( ILO, 2020a ).
Globally, over 430 million enterprises are at risk of disruption, with about half of those in the wholesale and retail trades ( ILO, 2020a ). Much focus in the press has been on the impact in Europe and North America, but the effect on developing countries is even more critical. An example of the latter is the Bangladeshi ready-made-garment sector ( Leitheiser et al., 2020 ), a global industry that depends on a supply chain of raw material from a few countries and produces those garments for retail stores throughout North America and Europe. But, in January 2020, raw material from China was delayed by the shutdown in China, creating delays and work stoppages in Bangladesh. By the time Bangladeshi factories had the material to make garments, in March, retailers in Europe and North American began to cancel orders or put them on hold, canceling or delaying payment. Factories shut down and workers were laid off without pay. Nearly a million people lost their jobs. Overall, since February 2020, the factories in Bangladesh have lost nearly 3 billion dollars in revenue. And, the retail stores that would have sold the garments have also closed. This demonstrates the ripple effect of the disruption of one industry that affects multiple countries and sets of workers, because consider that, in turn, there will be less raw material needed from China, and fewer workers needed there. One need only multiply this example by hundreds to consider the global impact of COVID-19 across the world of work.
The ILO (2020b) notes that it is difficult to collect employment statistics from different countries, so a total global unemployment rate is unavailable at this time. However, they predict significant increase in unemployment, and the number of individuals filing for unemployment benefits in the United States may be an indicator of the magnitude of those unemployed. In the United States, over 30 million filed for unemployment between March 11 and April 30 ( Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2020 ), effectively this is an unemployment rate of 18%. By contrast, in February 2020, the US unemployment rate was 3.5% ( Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2020 ).
Clearly, COVID-19 has had an enormous disruption on work and workers, most critically for those who have lost their employment. But, even for those continuing to work, there have been disruptions in where people work, with whom they work, what they do, and how much they earn. And, as of this writing, it is also a time of great uncertainty, as countries are slowly trying to ease restrictions to allow people to go back to work--- in a “new normal”, without the ability to predict if they can prevent further infectious “spikes”. The anxieties about not knowing what is coming, when it will end, or what work will entail led us to develop this set of essays about future research on COVID-19 and its impact on work and workers.
These essays began with an idea by Associate Editor Jos Akkermans, who noted to me that the global pandemic was creating a set of career shocks for workers. He suggested writing an essay for the Journal . The Journal of Vocational Behavior has not traditionally published essays, but these are such unusual times, and COVID-19 is so relevant to our collective research on work that I thought it was a good idea. I issued an invitation to the Associate Editors to submit a brief (3000 word) essay on the implications of COVID-19 on work and/or workers with an emphasis on research in the area. At the same time, a group of international scholars was coming together to consider the effects of COVID-19 on unemployment in several countries, and I invited that group to contribute an essay, as well ( Blustein et al., 2020 ).
The following are a set of nine thoughtful set of papers on how the COVID-19 could (and perhaps will) affect vocational behavior; they all provide suggestions for future research. Akkermans, Richardson, and Kraimer (2020) explore how the pandemic may be a career shock for many, but also how that may not necessarily be a negative experience. Blustein et al. (2020) focus on global unemployment, also acknowledging the privileged status they have as professors studying these phenomena. Cho examines the effect of the pandemic on micro-boundaries (across domains) as well as across national (macro) boundaries ( Cho, 2020 ). Guan, Deng, and Zhou (2020) drawing from cultural psychology, discuss how cultural orientations shape an individual's response to COVID-19, but also how a national cultural perspective influences collective actions. Kantamneni (2020) emphasized the effects on marginalized populations in the United States, as well as the very real effects of racism for Asians and Asian-Americans in the US. Kramer and Kramer (2020) discuss the impact of the pandemic in the perceptions of various occupations, whether perceptions of “good” and “bad” jobs will change and whether working remotely will permanently change where people will want to work. Restubog, Ocampo, and Wang (2020) also focused on individual's responses to the global crisis, concentrating on emotional regulation as a challenge, with suggestions for better managing the stress surrounding the anxiety of uncertainty. Rudolph and Zacher (2020) cautioned against using a generational lens in research, advocating for a lifespan developmental approach. Spurk and Straub (2020) also review issues related to unemployment, but focus on the impact of COVID-19 specifically on “gig” or flexible work arrangements.
I am grateful for the contributions of these groups of scholars, and proud of their ability to write these. They were able to write constructive essays in a short time frame when they were, themselves, dealing with disruptions at work. Some were home-schooling children, some were worried about an absent partner or a vulnerable loved one, some were struggling with the challenges that Restubog et al. (2020) outlined. I hope the thoughts, suggestions, and recommendations in these essays will help to stimulate productive thought on the effect of COVID-19 on work and workers. And, while, I hope this research spurs to better understand the effects of such shocks on work, I really hope we do not have to cope with such a shock again.
- Akkermans J., Richardson J., Kraimer M. The Covid-19 crisis as a career shock: Implications for careers and vocational behavior. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blustein D.L., Duffy R., Ferreira J.A., Cohen-Scali V., Cinamon R.G., Allan B.A. Unemployment in the time of COVID-19: A research agenda. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (2020). Labor Force Statistics from the Current Population Survey. Retrieved May 6, 2020 from https://data.bls.gov/cgi-bin/surveymost .
- Cho E. Examining boundaries to understand the impact of COVID-19 on vocational behaviors. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guan Y., Deng H., Zhou X. Understanding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on career development: Insights from cultural psychology. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johns Hopkins (2020) Coronavirus Outbreak Mapped: Retrieved May 5, 2020 from https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html .
- International Labor Organization ILO monitor: COVID-19 and the world of work. Third edition updated estimates and analysis. 2020. https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/@dgreports/@dcomm/documents/briefingnote/wcms_743146.pdf Retrieved May 5, 2020 from:
- International Labor Organization (2020b) COVID-19 impact on the collection of labour market statistics. Retrieved May 6, 2020 from: https://ilostat.ilo.org .
- Kantamneni, N. (2020). The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on marginalized populations in the United States: A research agenda. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 119 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Kramer A., Kramer K.Z. The potential impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on occupational status, work from home, and occupational mobility. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leitheiser, E., Hossain, S.N., Shuvro, S., Tasnim, G., Moon, J., Knudsen, J.S., & Rahman, S. (2020). Early impacts of coronavirus on Bangladesh apparel supply chains. https://www.cbs.dk/files/cbs.dk/risc_report_-_impacts_of_coronavirus_on_bangladesh_rmg_1.pdf .
- Restubog S.L.D., Ocampo A.C., Wang L. Taking control amidst the Chaos: Emotion regulation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rudolph C.W., Zacher H. COVID-19 and careers: On the futility of generational explanations. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spurk D., Straub C. Flexible employment relationships and careers in times of the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 2020; 119 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization (2020). World Health Organization Coronavirus Update. Retrieved May 5, 2020 from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 .
Essay on COVID-19 Pandemic
As a result of the COVID-19 (Coronavirus) outbreak, daily life has been negatively affected, impacting the worldwide economy. Thousands of individuals have been sickened or died as a result of the outbreak of this disease. When you have the flu or a viral infection, the most common symptoms include fever, cold, coughing up bone fragments, and difficulty breathing, which may progress to pneumonia. It’s important to take major steps like keeping a strict cleaning routine, keeping social distance, and wearing masks, among other things. This virus’s geographic spread is accelerating (Daniel Pg 93). Governments restricted public meetings during the start of the pandemic to prevent the disease from spreading and breaking the exponential distribution curve. In order to avoid the damage caused by this extremely contagious disease, several countries quarantined their citizens. However, this scenario had drastically altered with the discovery of the vaccinations. The research aims to investigate the effect of the Covid-19 epidemic and its impact on the population’s well-being.
There is growing interest in the relationship between social determinants of health and health outcomes. Still, many health care providers and academics have been hesitant to recognize racism as a contributing factor to racial health disparities. Only a few research have examined the health effects of institutional racism, with the majority focusing on interpersonal racial and ethnic prejudice Ciotti et al., Pg 370. The latter comprises historically and culturally connected institutions that are interconnected. Prejudice is being practiced in a variety of contexts as a result of the COVID-19 outbreak. In some ways, the outbreak has exposed pre-existing bias and inequity.
Thousands of businesses are in danger of failure. Around 2.3 billion of the world’s 3.3 billion employees are out of work. These workers are especially susceptible since they lack access to social security and adequate health care, and they’ve also given up ownership of productive assets, which makes them highly vulnerable. Many individuals lose their employment as a result of lockdowns, leaving them unable to support their families. People strapped for cash are often forced to reduce their caloric intake while also eating less nutritiously (Fraser et al, Pg 3). The epidemic has had an impact on the whole food chain, revealing vulnerabilities that were previously hidden. Border closures, trade restrictions, and confinement measures have limited farmer access to markets, while agricultural workers have not gathered crops. As a result, the local and global food supply chain has been disrupted, and people now have less access to healthy foods. As a consequence of the epidemic, many individuals have lost their employment, and millions more are now in danger. When breadwinners lose their jobs, become sick, or die, the food and nutrition of millions of people are endangered. Particularly severely hit are the world’s poorest small farmers and indigenous peoples.
Infectious illness outbreaks and epidemics have become worldwide threats due to globalization, urbanization, and environmental change. In developed countries like Europe and North America, surveillance and health systems monitor and manage the spread of infectious illnesses in real-time. Both low- and high-income countries need to improve their public health capacities (Omer et al., Pg 1767). These improvements should be financed using a mix of national and foreign donor money. In order to speed up research and reaction for new illnesses with pandemic potential, a global collaborative effort including governments and commercial companies has been proposed. When working on a vaccine-like COVID-19, cooperation is critical.
The epidemic has had an impact on the whole food chain, revealing vulnerabilities that were previously hidden. Border closures, trade restrictions, and confinement measures have limited farmer access to markets, while agricultural workers have been unable to gather crops. As a result, the local and global food supply chain has been disrupted, and people now have less access to healthy foods (Daniel et al.,Pg 95) . As a consequence of the epidemic, many individuals have lost their employment, and millions more are now in danger. When breadwinners lose their jobs, the food and nutrition of millions of people are endangered. Particularly severely hit are the world’s poorest small farmers and indigenous peoples.
While helping to feed the world’s population, millions of paid and unpaid agricultural laborers suffer from high levels of poverty, hunger, and bad health, as well as a lack of safety and labor safeguards, as well as other kinds of abuse at work. Poor people, who have no recourse to social assistance, must work longer and harder, sometimes in hazardous occupations, endangering their families in the process (Daniel Pg 96). When faced with a lack of income, people may turn to hazardous financial activities, including asset liquidation, predatory lending, or child labor, to make ends meet. Because of the dangers they encounter while traveling, working, and living abroad; migrant agricultural laborers are especially vulnerable. They also have a difficult time taking advantage of government assistance programs.
The pandemic also has a significant impact on education. Although many educational institutions across the globe have already made the switch to online learning, the extent to which technology is utilized to improve the quality of distance or online learning varies. This level is dependent on several variables, including the different parties engaged in the execution of this learning format and the incorporation of technology into educational institutions before the time of school closure caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. For many years, researchers from all around the globe have worked to determine what variables contribute to effective technology integration in the classroom Ciotti et al., Pg 371. The amount of technology usage and the quality of learning when moving from a classroom to a distant or online format are presumed to be influenced by the same set of variables. Findings from previous research, which sought to determine what affects educational systems ability to integrate technology into teaching, suggest understanding how teachers, students, and technology interact positively in order to achieve positive results in the integration of teaching technology (Honey et al., 2000). Teachers’ views on teaching may affect the chances of successfully incorporating technology into the classroom and making it a part of the learning process.
In conclusion, indeed, Covid 19 pandemic have affected the well being of the people in a significant manner. The economy operation across the globe have been destabilized as most of the people have been rendered jobless while the job operation has been stopped. As most of the people have been rendered jobless the living conditions of the people have also been significantly affected. Besides, the education sector has also been affected as most of the learning institutions prefer the use of online learning which is not effective as compared to the traditional method. With the invention of the vaccines, most of the developed countries have been noted to stabilize slowly, while the developing countries have not been able to vaccinate most of its citizens. However, despite the challenge caused by the pandemic, organizations have been able to adapt the new mode of online trading to be promoted.
Ciotti, Marco, et al. “The COVID-19 pandemic.” Critical reviews in clinical laboratory sciences 57.6 (2020): 365-388.
Daniel, John. “Education and the COVID-19 pandemic.” Prospects 49.1 (2020): 91-96.
Fraser, Nicholas, et al. “Preprinting the COVID-19 pandemic.” BioRxiv (2021): 2020-05.
Omer, Saad B., Preeti Malani, and Carlos Del Rio. “The COVID-19 pandemic in the US: a clinical update.” Jama 323.18 (2020): 1767-1768.
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Practical approach of companies towards CSR and CSI – A study of...
- Analysis of the postal rule and its extension to the private courier s...
- “Broken Men”: Representing Masculinity in Salman Rushdie&#...
- Lifelong Learning Plan
- Essay on the Effects of Incarceration on Pregnancy
- Essay on Effects of Millenium Online Purchase Behavior to Physical Sho...
- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
- Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- HIV and AIDS
- Hypertension
- Mental disorders
- Top 10 causes of death
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- Data collection tools
- Global Health Observatory
- Insights and visualizations
- COVID excess deaths
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment in WHO
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
Impact of COVID-19 on people's livelihoods, their health and our food systems
Joint statement by ilo, fao, ifad and who.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a dramatic loss of human life worldwide and presents an unprecedented challenge to public health, food systems and the world of work. The economic and social disruption caused by the pandemic is devastating: tens of millions of people are at risk of falling into extreme poverty, while the number of undernourished people, currently estimated at nearly 690 million, could increase by up to 132 million by the end of the year.
Millions of enterprises face an existential threat. Nearly half of the world’s 3.3 billion global workforce are at risk of losing their livelihoods. Informal economy workers are particularly vulnerable because the majority lack social protection and access to quality health care and have lost access to productive assets. Without the means to earn an income during lockdowns, many are unable to feed themselves and their families. For most, no income means no food, or, at best, less food and less nutritious food.
The pandemic has been affecting the entire food system and has laid bare its fragility. Border closures, trade restrictions and confinement measures have been preventing farmers from accessing markets, including for buying inputs and selling their produce, and agricultural workers from harvesting crops, thus disrupting domestic and international food supply chains and reducing access to healthy, safe and diverse diets. The pandemic has decimated jobs and placed millions of livelihoods at risk. As breadwinners lose jobs, fall ill and die, the food security and nutrition of millions of women and men are under threat, with those in low-income countries, particularly the most marginalized populations, which include small-scale farmers and indigenous peoples, being hardest hit.
Millions of agricultural workers – waged and self-employed – while feeding the world, regularly face high levels of working poverty, malnutrition and poor health, and suffer from a lack of safety and labour protection as well as other types of abuse. With low and irregular incomes and a lack of social support, many of them are spurred to continue working, often in unsafe conditions, thus exposing themselves and their families to additional risks. Further, when experiencing income losses, they may resort to negative coping strategies, such as distress sale of assets, predatory loans or child labour. Migrant agricultural workers are particularly vulnerable, because they face risks in their transport, working and living conditions and struggle to access support measures put in place by governments. Guaranteeing the safety and health of all agri-food workers – from primary producers to those involved in food processing, transport and retail, including street food vendors – as well as better incomes and protection, will be critical to saving lives and protecting public health, people’s livelihoods and food security.
In the COVID-19 crisis food security, public health, and employment and labour issues, in particular workers’ health and safety, converge. Adhering to workplace safety and health practices and ensuring access to decent work and the protection of labour rights in all industries will be crucial in addressing the human dimension of the crisis. Immediate and purposeful action to save lives and livelihoods should include extending social protection towards universal health coverage and income support for those most affected. These include workers in the informal economy and in poorly protected and low-paid jobs, including youth, older workers, and migrants. Particular attention must be paid to the situation of women, who are over-represented in low-paid jobs and care roles. Different forms of support are key, including cash transfers, child allowances and healthy school meals, shelter and food relief initiatives, support for employment retention and recovery, and financial relief for businesses, including micro, small and medium-sized enterprises. In designing and implementing such measures it is essential that governments work closely with employers and workers.
Countries dealing with existing humanitarian crises or emergencies are particularly exposed to the effects of COVID-19. Responding swiftly to the pandemic, while ensuring that humanitarian and recovery assistance reaches those most in need, is critical.
Now is the time for global solidarity and support, especially with the most vulnerable in our societies, particularly in the emerging and developing world. Only together can we overcome the intertwined health and social and economic impacts of the pandemic and prevent its escalation into a protracted humanitarian and food security catastrophe, with the potential loss of already achieved development gains.
We must recognize this opportunity to build back better, as noted in the Policy Brief issued by the United Nations Secretary-General. We are committed to pooling our expertise and experience to support countries in their crisis response measures and efforts to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. We need to develop long-term sustainable strategies to address the challenges facing the health and agri-food sectors. Priority should be given to addressing underlying food security and malnutrition challenges, tackling rural poverty, in particular through more and better jobs in the rural economy, extending social protection to all, facilitating safe migration pathways and promoting the formalization of the informal economy.
We must rethink the future of our environment and tackle climate change and environmental degradation with ambition and urgency. Only then can we protect the health, livelihoods, food security and nutrition of all people, and ensure that our ‘new normal’ is a better one.
Media Contacts
Kimberly Chriscaden
Communications Officer World Health Organization
Nutrition and Food Safety (NFS) and COVID-19
8 Lessons We Can Learn From the COVID-19 Pandemic
BY KATHY KATELLA May 14, 2021

Note: Information in this article was accurate at the time of original publication. Because information about COVID-19 changes rapidly, we encourage you to visit the websites of the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC), World Health Organization (WHO), and your state and local government for the latest information.
The COVID-19 pandemic changed life as we know it—and it may have changed us individually as well, from our morning routines to our life goals and priorities. Many say the world has changed forever. But this coming year, if the vaccines drive down infections and variants are kept at bay, life could return to some form of normal. At that point, what will we glean from the past year? Are there silver linings or lessons learned?
“Humanity's memory is short, and what is not ever-present fades quickly,” says Manisha Juthani, MD , a Yale Medicine infectious diseases specialist. The bubonic plague, for example, ravaged Europe in the Middle Ages—resurfacing again and again—but once it was under control, people started to forget about it, she says. “So, I would say one major lesson from a public health or infectious disease perspective is that it’s important to remember and recognize our history. This is a period we must remember.”
We asked our Yale Medicine experts to weigh in on what they think are lessons worth remembering, including those that might help us survive a future virus or nurture a resilience that could help with life in general.
Lesson 1: Masks are useful tools
What happened: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) relaxed its masking guidance for those who have been fully vaccinated. But when the pandemic began, it necessitated a global effort to ensure that everyone practiced behaviors to keep themselves healthy and safe—and keep others healthy as well. This included the widespread wearing of masks indoors and outside.
What we’ve learned: Not everyone practiced preventive measures such as mask wearing, maintaining a 6-foot distance, and washing hands frequently. But, Dr. Juthani says, “I do think many people have learned a whole lot about respiratory pathogens and viruses, and how they spread from one person to another, and that sort of old-school common sense—you know, if you don’t feel well—whether it’s COVID-19 or not—you don’t go to the party. You stay home.”
Masks are a case in point. They are a key COVID-19 prevention strategy because they provide a barrier that can keep respiratory droplets from spreading. Mask-wearing became more common across East Asia after the 2003 SARS outbreak in that part of the world. “There are many East Asian cultures where the practice is still that if you have a cold or a runny nose, you put on a mask,” Dr. Juthani says.
She hopes attitudes in the U.S. will shift in that direction after COVID-19. “I have heard from a number of people who are amazed that we've had no flu this year—and they know masks are one of the reasons,” she says. “They’ve told me, ‘When the winter comes around, if I'm going out to the grocery store, I may just put on a mask.’”
Lesson 2: Telehealth might become the new normal
What happened: Doctors and patients who have used telehealth (technology that allows them to conduct medical care remotely), found it can work well for certain appointments, ranging from cardiology check-ups to therapy for a mental health condition. Many patients who needed a medical test have also discovered it may be possible to substitute a home version.
What we’ve learned: While there are still problems for which you need to see a doctor in person, the pandemic introduced a new urgency to what had been a gradual switchover to platforms like Zoom for remote patient visits.
More doctors also encouraged patients to track their blood pressure at home , and to use at-home equipment for such purposes as diagnosing sleep apnea and even testing for colon cancer . Doctors also can fine-tune cochlear implants remotely .
“It happened very quickly,” says Sharon Stoll, DO, a neurologist. One group that has benefitted is patients who live far away, sometimes in other parts of the country—or even the world, she says. “I always like to see my patients at least twice a year. Now, we can see each other in person once a year, and if issues come up, we can schedule a telehealth visit in-between,” Dr. Stoll says. “This way I may hear about an issue before it becomes a problem, because my patients have easier access to me, and I have easier access to them.”
Meanwhile, insurers are becoming more likely to cover telehealth, Dr. Stoll adds. “That is a silver lining that will hopefully continue.”
Lesson 3: Vaccines are powerful tools
What happened: Given the recent positive results from vaccine trials, once again vaccines are proving to be powerful for preventing disease.
What we’ve learned: Vaccines really are worth getting, says Dr. Stoll, who had COVID-19 and experienced lingering symptoms, including chronic headaches . “I have lots of conversations—and sometimes arguments—with people about vaccines,” she says. Some don’t like the idea of side effects. “I had vaccine side effects and I’ve had COVID-19 side effects, and I say nothing compares to the actual illness. Unfortunately, I speak from experience.”
Dr. Juthani hopes the COVID-19 vaccine spotlight will motivate people to keep up with all of their vaccines, including childhood and adult vaccines for such diseases as measles , chicken pox, shingles , and other viruses. She says people have told her they got the flu vaccine this year after skipping it in previous years. (The CDC has reported distributing an exceptionally high number of doses this past season.)
But, she cautions that a vaccine is not a magic bullet—and points out that scientists can’t always produce one that works. “As advanced as science is, there have been multiple failed efforts to develop a vaccine against the HIV virus,” she says. “This time, we were lucky that we were able build on the strengths that we've learned from many other vaccine development strategies to develop multiple vaccines for COVID-19 .”
Lesson 4: Everyone is not treated equally, especially in a pandemic
What happened: COVID-19 magnified disparities that have long been an issue for a variety of people.
What we’ve learned: Racial and ethnic minority groups especially have had disproportionately higher rates of hospitalization for COVID-19 than non-Hispanic white people in every age group, and many other groups faced higher levels of risk or stress. These groups ranged from working mothers who also have primary responsibility for children, to people who have essential jobs, to those who live in rural areas where there is less access to health care.
“One thing that has been recognized is that when people were told to work from home, you needed to have a job that you could do in your house on a computer,” says Dr. Juthani. “Many people who were well off were able do that, but they still needed to have food, which requires grocery store workers and truck drivers. Nursing home residents still needed certified nursing assistants coming to work every day to care for them and to bathe them.”
As far as racial inequities, Dr. Juthani cites President Biden’s appointment of Yale Medicine’s Marcella Nunez-Smith, MD, MHS , as inaugural chair of a federal COVID-19 Health Equity Task Force. “Hopefully the new focus is a first step,” Dr. Juthani says.
Lesson 5: We need to take mental health seriously
What happened: There was a rise in reported mental health problems that have been described as “a second pandemic,” highlighting mental health as an issue that needs to be addressed.
What we’ve learned: Arman Fesharaki-Zadeh, MD, PhD , a behavioral neurologist and neuropsychiatrist, believes the number of mental health disorders that were on the rise before the pandemic is surging as people grapple with such matters as juggling work and childcare, job loss, isolation, and losing a loved one to COVID-19.
The CDC reports that the percentage of adults who reported symptoms of anxiety of depression in the past 7 days increased from 36.4 to 41.5 % from August 2020 to February 2021. Other reports show that having COVID-19 may contribute, too, with its lingering or long COVID symptoms, which can include “foggy mind,” anxiety , depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder .
“We’re seeing these problems in our clinical setting very, very often,” Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh says. “By virtue of necessity, we can no longer ignore this. We're seeing these folks, and we have to take them seriously.”
Lesson 6: We have the capacity for resilience
What happened: While everyone’s situation is different (and some people have experienced tremendous difficulties), many have seen that it’s possible to be resilient in a crisis.
What we’ve learned: People have practiced self-care in a multitude of ways during the pandemic as they were forced to adjust to new work schedules, change their gym routines, and cut back on socializing. Many started seeking out new strategies to counter the stress.
“I absolutely believe in the concept of resilience, because we have this effective reservoir inherent in all of us—be it the product of evolution, or our ancestors going through catastrophes, including wars, famines, and plagues,” Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh says. “I think inherently, we have the means to deal with crisis. The fact that you and I are speaking right now is the result of our ancestors surviving hardship. I think resilience is part of our psyche. It's part of our DNA, essentially.”
Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh believes that even small changes are highly effective tools for creating resilience. The changes he suggests may sound like the same old advice: exercise more, eat healthy food, cut back on alcohol, start a meditation practice, keep up with friends and family. “But this is evidence-based advice—there has been research behind every one of these measures,” he says.
But we have to also be practical, he notes. “If you feel overwhelmed by doing too many things, you can set a modest goal with one new habit—it could be getting organized around your sleep. Once you’ve succeeded, move on to another one. Then you’re building momentum.”
Lesson 7: Community is essential—and technology is too
What happened: People who were part of a community during the pandemic realized the importance of human connection, and those who didn’t have that kind of support realized they need it.
What we’ve learned: Many of us have become aware of how much we need other people—many have managed to maintain their social connections, even if they had to use technology to keep in touch, Dr. Juthani says. “There's no doubt that it's not enough, but even that type of community has helped people.”
Even people who aren’t necessarily friends or family are important. Dr. Juthani recalled how she encouraged her mail carrier to sign up for the vaccine, soon learning that the woman’s mother and husband hadn’t gotten it either. “They are all vaccinated now,” Dr. Juthani says. “So, even by word of mouth, community is a way to make things happen.”
It’s important to note that some people are naturally introverted and may have enjoyed having more solitude when they were forced to stay at home—and they should feel comfortable with that, Dr. Fesharaki-Zadeh says. “I think one has to keep temperamental tendencies like this in mind.”
But loneliness has been found to suppress the immune system and be a precursor to some diseases, he adds. “Even for introverted folks, the smallest circle is preferable to no circle at all,” he says.
Lesson 8: Sometimes you need a dose of humility
What happened: Scientists and nonscientists alike learned that a virus can be more powerful than they are. This was evident in the way knowledge about the virus changed over time in the past year as scientific investigation of it evolved.
What we’ve learned: “As infectious disease doctors, we were resident experts at the beginning of the pandemic because we understand pathogens in general, and based on what we’ve seen in the past, we might say there are certain things that are likely to be true,” Dr. Juthani says. “But we’ve seen that we have to take these pathogens seriously. We know that COVID-19 is not the flu. All these strokes and clots, and the loss of smell and taste that have gone on for months are things that we could have never known or predicted. So, you have to have respect for the unknown and respect science, but also try to give scientists the benefit of the doubt,” she says.
“We have been doing the best we can with the knowledge we have, in the time that we have it,” Dr. Juthani says. “I think most of us have had to have the humility to sometimes say, ‘I don't know. We're learning as we go.’"
Information provided in Yale Medicine articles is for general informational purposes only. No content in the articles should ever be used as a substitute for medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. Always seek the individual advice of your health care provider with any questions you have regarding a medical condition.
More news from Yale Medicine

Paragraph Writing on Covid 19
Ai generator.

COVID-19, caused by the coronavirus, significantly impacted global health and daily life. Action plans focused on prevention, treatment, and vaccination. Some sought religious exemptions from mandates. A health thesis statement might explore the pandemic’s effects on mental health. The tone is informative and serious. This paragraph highlights the comprehensive response to COVID-19.
Checkout → Free Paragraph Writer Tool
Short Paragraph on Covid-19
Covid-19 is a global pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus. It has significantly impacted daily life, with governments worldwide implementing lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates to curb the virus’s spread. The pandemic has highlighted the importance of healthcare systems and the need for vaccines. It has also emphasized global cooperation and resilience in facing unprecedented challenges.
Medium Paragraph on Covid-19
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus, has had a profound impact on the world since its outbreak. The pandemic led to widespread lockdowns, social distancing measures, and mandatory mask-wearing to prevent the virus’s spread. Healthcare systems were overwhelmed, emphasizing the need for robust medical infrastructure and preparedness. The development and distribution of vaccines became a global priority, showcasing the importance of scientific research and international cooperation. Economies faced significant challenges, with businesses closing and unemployment rates rising. Despite these hardships, the pandemic also brought communities together, highlighting resilience, adaptability, and the critical role of healthcare workers in combating the crisis.
Long Paragraph on Covid-19
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged in late 2019 and rapidly spread across the globe, leading to an unprecedented pandemic. The virus’s high transmission rate prompted governments worldwide to implement stringent measures such as lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates to control its spread. These measures, while necessary, significantly disrupted daily life, impacting economies, education, and social interactions. Healthcare systems were strained, underscoring the need for better preparedness and robust medical infrastructure. The rapid development and global distribution of vaccines became a beacon of hope, demonstrating the power of scientific collaboration and innovation. The pandemic also highlighted the disparities in healthcare access and the importance of public health initiatives. Despite the immense challenges, communities showed resilience and adaptability, finding new ways to connect and support each other. The dedication of healthcare workers and the collective effort to combat the virus underscored the importance of global solidarity. Covid-19 has reshaped our world, teaching valuable lessons about preparedness, the significance of science, and the strength of human resilience in the face of adversity.
Tone-wise Paragraph Examples on Covid-19
Formal tone.
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, represents an unprecedented global health crisis. The pandemic has led to widespread implementation of public health measures such as lockdowns, social distancing, and mandatory mask usage to mitigate the virus’s transmission. Healthcare systems worldwide faced significant strain, highlighting the critical need for robust medical infrastructure and emergency preparedness. The rapid development and distribution of vaccines have been pivotal in controlling the spread of the virus, underscoring the importance of scientific research and international cooperation. The pandemic has also revealed existing disparities in healthcare access and emphasized the necessity of coordinated global public health strategies to effectively manage such crises.
Informal Tone
Covid-19 has really shaken things up since it started spreading in late 2019. Caused by a new coronavirus, it led to lockdowns, social distancing, and everyone wearing masks. Daily life changed a lot, with schools and businesses shutting down, and everyone trying to stay safe. The healthcare system was hit hard, showing us just how important it is to be prepared. Vaccines were developed super quickly, giving us hope to get back to normal. Even though it was tough, people came together, supported each other, and adapted to the new normal. Covid-19 taught us a lot about resilience and the importance of healthcare.
Persuasive Tone
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus, has highlighted the urgent need for better healthcare systems and global cooperation. The pandemic led to widespread lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates, disrupting daily life and economies. Our healthcare systems were overwhelmed, underscoring the critical need for robust medical infrastructure. The rapid development of vaccines showcased the power of scientific research and international collaboration. Now, more than ever, it is crucial to support and strengthen our healthcare systems, invest in scientific research, and promote global cooperation to ensure we are better prepared for future health crises. Let’s learn from this pandemic and build a stronger, healthier world together.
Reflective Tone
Reflecting on the impact of Covid-19, it’s clear that the pandemic has reshaped our world in profound ways. The novel coronavirus led to unprecedented global lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates, dramatically altering daily life. Our healthcare systems were tested like never before, revealing both strengths and weaknesses. The rapid development and distribution of vaccines highlighted the importance of scientific innovation and international cooperation. Amid the challenges, communities showed remarkable resilience and adaptability, finding new ways to connect and support one another. Covid-19 has taught us valuable lessons about preparedness, the significance of healthcare, and the power of human resilience in the face of adversity.
Inspirational Tone
Covid-19 has been a challenging journey, but it has also shown the incredible strength and resilience of humanity. The novel coronavirus led to global lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates, changing our daily lives dramatically. Despite these hardships, the rapid development and distribution of vaccines brought hope and showcased the power of scientific innovation and global cooperation. Communities came together, supporting each other and adapting to new realities. Healthcare workers became heroes, showing unparalleled dedication and bravery. Covid-19 has taught us the importance of unity, resilience, and the ability to overcome even the toughest challenges. Together, we can build a brighter, healthier future.
Optimistic Tone
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus, brought significant challenges, but it also highlighted the resilience and adaptability of people worldwide. The pandemic led to lockdowns, social distancing, and mask-wearing, changing our daily routines. Despite these difficulties, the rapid development of vaccines brought hope and demonstrated the power of scientific progress. Communities came together, supporting one another and finding new ways to connect. Healthcare workers showed incredible dedication, and the world witnessed the strength of human spirit. Covid-19 has been a tough journey, but it also reinforced our ability to overcome adversity and work towards a healthier, more connected future.
Urgent Tone
The Covid-19 pandemic, caused by the novel coronavirus, demands our immediate attention and action. Since its outbreak, the virus has led to widespread lockdowns, social distancing, and mandatory mask usage, significantly disrupting daily life. Healthcare systems have been overwhelmed, highlighting the urgent need for better preparedness and robust medical infrastructure. The rapid development of vaccines has been crucial, but we must continue to prioritize public health measures and global cooperation to combat this crisis. Now is the time to invest in healthcare, support scientific research, and work together to overcome this pandemic. Immediate action is essential to protect lives and prevent further devastation.
Word Count-wise Paragraph Examples on Covid-19
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus, has had a profound impact on the world since its outbreak. The pandemic led to widespread lockdowns, social distancing measures, and mandatory mask-wearing to prevent the virus’s spread. Healthcare systems were overwhelmed, emphasizing the need for robust medical infrastructure and preparedness. The development and distribution of vaccines became a global priority, showcasing the importance of scientific research and international cooperation. Economies faced significant challenges, with businesses closing and unemployment rates rising. Despite these hardships, the pandemic also brought communities together, highlighting resilience, adaptability, and the critical role of healthcare workers in combating the crisis. The rapid development and distribution of vaccines became a beacon of hope, demonstrating the power of scientific collaboration and innovation.
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged in late 2019 and rapidly spread across the globe, leading to an unprecedented pandemic. The virus’s high transmission rate prompted governments worldwide to implement stringent measures such as lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates to control its spread. These measures, while necessary, significantly disrupted daily life, impacting economies, education, and social interactions. Healthcare systems were strained, underscoring the need for better preparedness and robust medical infrastructure. The rapid development and global distribution of vaccines became a beacon of hope, demonstrating the power of scientific collaboration and innovation. The pandemic also highlighted the disparities in healthcare access and the importance of public health initiatives. Despite the immense challenges, communities showed resilience and adaptability, finding new ways to connect and support each other.
Covid-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged in late 2019 and rapidly spread across the globe, leading to an unprecedented pandemic. The virus’s high transmission rate prompted governments worldwide to implement stringent measures such as lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates to control its spread. These measures, while necessary, significantly disrupted daily life, impacting economies, education, and social interactions. Healthcare systems were strained, underscoring the need for better preparedness and robust medical infrastructure. The rapid development and global distribution of vaccines became a beacon of hope, demonstrating the power of scientific collaboration and innovation. The pandemic also highlighted the disparities in healthcare access and the importance of public health initiatives. Despite the immense challenges, communities showed resilience and adaptability, finding new ways to connect and support each other. The dedication of healthcare workers and the collective effort to combat the virus underscored the importance of global solidarity. Covid-19 has reshaped our world, teaching valuable lessons about preparedness, the significance of science, and the strength of human resilience in the face of adversity. The pandemic emphasized the need for robust healthcare systems, scientific innovation, and global cooperation. Despite the challenges, the collective resilience and adaptability of people worldwide have shown the strength of the human spirit in overcoming adversity.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Imperial College London Imperial College London
Latest news.

£150,000 study will explore links between breast cancer and breastfeeding

Bezos Centre for Sustainable Protein launches at Imperial with $30m funding

Public Engagement team celebrate six years of sector-leading Academy
- Communications
- Administration and support services
- Communications toolkits

Need support?
Find out how the Brand team can support you .
Email the Brand team at [email protected] .
Imperial is a fantastic institution, delivering world-changing impact. The goal of our brand is to tell our story with greater clarity, confidence and impact.
Building our brand will help us compete on a sustainable basis in the very top tier internationally. It’s at the heart of the ambition and vision we have set through our new institutional strategy , and our own community signaled a clear desire to bolster our reputation and get Imperial the recognition it deserves. This work will deliver multiple benefits, from attracting the best talent, funding and partnerships, to our general reputation and ranking. The initial work on the Brand Project ran from June 2023 to February 2024, and was supported by a Project Board, a Working Group, and a Critical Friends Group.
We worked with the design studio Pentagram on the brand strategy and creative elements, and with the inclusive research agency Open Inclusion to ensure the inclusivity and accessibility of this work.
We now have a new visual and verbal identity that are rooted in our science heritage, modern, confident and expressive. Both elements articulate Imperial's purpose and vision, our strengths – including our London location – and our impact, all while differentiating us in a crowded and competitive landscape.
Brand m anagement p latform
To access the brand guidelines, including our brand strategy, visual and verbal identity and media libraries, templates and r esources please vis it our brand management platform .
Imperial staff and students can access the platform by clicking Sign in via SSO and us ing their Imperial login .
Externals can request access on the login page. If your access request is approved, you will have access for 30 days . If you need access beyond this, please resubmit your access request.
All external suppliers working with the new brand identity are required to attend an Imperial b rand b riefing. The Brand team will follow up with you to book in a briefing session.
As part of our brand hierarchy , we are now able to offer options for faculties, departments, divisions, centres , networks and research groups to include their name alongside the master logo.
If you would like to request a sub- brand logo, the in-house Design team are able to develop this for you, please complete th is form to submit your request.
If you would like to request an exception, where a unique brand identity may be appropriate , please contact the Brand team on [email protected].
Imperial brand briefings
All staff are invited to attend our regular brand briefings to learn more about our brand strategy, verbal and visual identity.
Register your interest in attending one of the upcoming brand briefings
Imperial brand showreel


Making visible the invisible: Supporting long COVID patients and the people caring for them
Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences; Senior Scientist, Pacific Institute on Pathogens, Pandemics and Society, Simon Fraser University
Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences, Simon Fraser University
Master's Student in Communication, Research Assistant for Pacific Institute on Pathogens, Pandemics and Society, Simon Fraser University
Academic Researcher, Director of Knowledge Mobilization, Pacific Institute on Pathogens, Pandemics and Society, Simon Fraser University
Disclosure statement
Kaylee Byers collaborates with and receives funding from the Post-COVID Interdisciplinary Care Network (PC-ICCN). "The MyGuide: Long COVID" is a resource created by the PC-ICCN. The work mentioned in this study is also funded in part by Michael Smith Health Research BC.
Kayli Jamieson collaborates with and receives funding from the B.C. Post-COVID Interdisciplinary Care Network (PC-ICCN). "The MyGuide: Long COVID" is a resource created by the PC-ICCN. The work mentioned in this study is also funded in part by Michael Smith Health Research BC. She also is a patient advisor for Long COVID The Answers.
Rackeb Tesfaye collaborates and receives funding from the PC-ICCN.
Julia Smith does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Simon Fraser University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA.
Simon Fraser University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
View all partners
We are living through a mass-disabling event : Over 200 million people worldwide have long COVID . In Canada, one in nine people have experienced long COVID symptoms, and this is likely an underestimate.
Occurring weeks to months after a COVID-19 infection, this multi-system chronic illness has led to what some have called “ the shadow pandemic .” Although millions are navigating this new illness, four years into the pandemic both patients and their caregivers continue to face challenges accessing the information and care they need.
Most Canadians have had COVID, and at least one in five have been infected more than once . These trends are troubling because evidence suggests that the risk of acquiring long COVID increases with reinfection .
Long COVID is a complex illness that can present with a range of neurological and cardiovascular symptoms, such as post-exertional malaise , heart palpitations, cognitive impairment, fatigue and around 200 other symptoms . Some people with long COVID, often referred to as “longhaulers,” experience other under-researched syndromes, such as myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) — also known as chronic fatigue syndrome.

With a suite of life-altering impacts, it is unsurprising that longhaulers may also experience impacts to their mental health, financial stability and relationships with others. These experiences are further exacerbated by the fact that there remains no cure for long COVID.
Over the past year, our team at Simon Fraser University has been speaking with long COVID patients, unpaid caregivers — such as family and friends who take on caregiving roles — clinicians and long COVID researchers to better understand patient experiences. In a new report , we documented a number of challenges patients and their caregivers face as well as recommendations to reduce these barriers.
Holistic approaches to care
Because symptoms and experiences vary, there is no single approach to care that will support all longhaulers. In British Columbia, post-COVID recovery clinics have been instrumental in creating specialized regional spaces for long COVID care.
These clinics have blended physician care, allied health care — such as physiotherapy and occupational therapy — and patient support groups. The closure of in-person clinics in transition to an online care system , in combination with long wait times, has meant that some patients have difficulty accessing these clinics.

Longhaulers have emphasized the value of specialized clinics and the need for holistic approaches that encompass allied health care to address the multifaceted impacts of long COVID on patients’ lives. Caregivers in particular expressed a need for mental health supports due to additional strains on their ability to work, their relationships and other responsibilities.
Holistic approaches are being embraced by some groups such as the Clinical Post COVID Society in the United Kingdom which brings together a “ diverse multidisciplinary clinical leadership team to reflect the varied expertise needed to care for patients with long COVID .” This example may serve as a helpful model for mobilizing these approaches in Canada.
Information
Access to information about long COVID remains a significant challenge. While longhaulers obtain information from health-care providers ( which can vary and be contradictory ), many are unable to meet with a doctor.
In B.C., approximately one in five people don’t have a family doctor . As a result, many are left to search for information themselves, wading through websites and articles while trying to discern what to trust. This can be especially challenging for people experiencing brain fog and fatigue, or those limited in time and resources due to caregiving, work or other demands on their time.
Patients, caregivers, clinicians and researchers suggest that the federal government create a national long COVID information platform providing details about symptoms, symptom management, a database of health-care practitioners providing long COVID care, and updates on recent research.
This could be modelled off the Post-COVID MyGuide, produced by the Post-COVID Interdisciplinary Clinical Care Network in B.C. . And while such resources are critical to supporting longhaulers, they are only useful if people access them. Therefore, more investment is needed to raise awareness of these platforms, evaluate their usefulness and explore ways to scale them for national use.
Another key outcome for improving care is refocusing preventive efforts to reduce reinfection risk for longhaulers, and future long COVID cases. Prevention measures might include campaigns promoting wearing respirators, regular vaccinations, increasing paid sick days or improving air filtration and ventilation indoors.
Preventing long COVID also involves taking these precautions in the absence of visible illness , as some early estimates suggested that 59 per cent of transmission occurs without symptoms .
Our team put these prevention measures into practice in April when we hosted a hybrid long COVID event with Pulitzer-prize winning journalist Ed Yong and a panel of patients, caregivers, clinicians and researchers. The event included safety measures such as mandatory masking in KN95/N95 respirators, rapid testing of participants and MERV-13 air filters .
Both during and since this event we have received numerous messages from longhaulers speaking to how the event and the safety measures in place were meaningful to them and made them feel seen. In order to do this, collectively (researchers, clinicians, policymakers and the public) can take many steps to create safe spaces as a baseline to reduce transmission risks.
As we continue to grapple with the enduring legacies of the COVID-19 pandemic, we must recognize that many communities have been disproportionately affected by SARS-CoV-2. To address these differential impacts, patients and caregivers advocate for continued investments in patient-centred research and care to create initiatives that resonate and are relevant for those most affected.
To further amplify these stories and raise awareness, our team is developing a long COVID “Day in the Life” photo exhibit in partnership with the Museum of Vancouver, where long COVID patients can share their stories and photos. Activities like this are one more step to making visible the experiences of people with an invisible illness.

Research Fellow – Magnetic Refrigeration

Centre Director, Transformative Media Technologies

Postdoctoral Research Fellowship

Social Media Producer

Dean (Head of School), Indigenous Knowledges
- Health Tech
- Health Insurance
- Medical Devices
- Gene Therapy
- Neuroscience
- H5N1 Bird Flu
- Health Disparities
- Infectious Disease
- Mental Health
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Chronic Disease
- Alzheimer's
- Coercive Care
- The Obesity Revolution
- The War on Recovery
- Adam Feuerstein
- Matthew Herper
- Jennifer Adaeze Okwerekwu
- Ed Silverman
- CRISPR Tracker
- Breakthrough Device Tracker
- Generative AI Tracker
- Obesity Drug Tracker
- 2024 STAT Summit
- Wunderkinds Nomination
- STAT Madness
- STAT Brand Studio
Don't miss out
Subscribe to STAT+ today, for the best life sciences journalism in the industry
Readers respond to essays on long Covid, hypochondria, and more
By Patrick Skerrett June 22, 2024

F irst Opinion is STAT’s platform for interesting, illuminating, and maybe even provocative articles about the life sciences writ large, written by biotech insiders, health care workers, researchers, and others.
To encourage robust, good-faith discussion about issues raised in First Opinion essays, STAT publishes selected Letters to the Editor received in response to them. You can submit a Letter to the Editor here , or find the submission form at the end of any First Opinion essay.
advertisement
“Long Covid feels like a gun to my head,” by Rachel Hall-Clifford
Thank you for this. I’m a 65-year-old woman who’s Covid cautious and wears a mask in public places (yes, in 2024). I’ve never had Covid as far as I know, and I try to keep up with the research. I feel like everybody would be more cautious if they read this article on long Covid, because it helps to really understand the horrible ways that a mild case of Covid can affect your life in ways that are unimaginable.
— Hildy Hogate
“I’m a hypochondriac. Here’s how the health care system needs to deal with people like me,” by Hal Rosenbluth
Health anxiety is the less biased term, rather than hypochondria with all its comic baggage.
Though the writer likes full body scans for himself and they suit his particular fears, many, many people with health anxiety, including me, wouldn’t get within 10 feet of a full body scan. It would be the opposite of reassuring.
Even if it did reassure for the moment, anyone with health anxiety knows reassurance is short-lived. A scan done in, say, January, might reassure a non-anxious person for the next six months. But it would be the rare person with health anxiety who would feel reassured for more than a couple of weeks.
And why on earth would you want to create a separate billing code for this, which would, without question, be used to pick out, stigmatize, and limit access to medical care? That doesn’t help patients, it soothes and enriches insurers, who would undoubtedly limit access to care based on a scan. How long would it take before you called to make an appointment with your doctor and were told sorry, your insurance won’t cover an office visit — your scan said you have no problems?
The writer’s personal experience, psychology, and taste for scans are just that, personal. They don’t generalize to most, or even many, of those who suffer from health anxiety.
— Maria Perry
“NIH needs reform and restructuring, key Republicans committee chairs say,” by Cathy McMorris Rodgers and Robert B. Aderholt
I agree with the authors that NIH needs reform. I was an athletic, otherwise healthy person who was struck down and disabled by long Covid in January 2022. For over two years, I’ve watched life pass me by as NIH has fumbled the $1.15 billion allocated to it by Congress to study and treat long Covid. This initiative, known as RECOVER, has failed to publish any research that furthers our understanding of the underlying cause of long Covid and the vast majority of clinical trials they’ve launched are for drugs that people have already tried and found unhelpful.
Perhaps NIH would not have bungled the long Covid funding had it not completely ignored other post viral diseases, namely myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) for the past 40 years. ME receives only $15 million a year — the most underfunded disease per patient burden at the NIH.
NIH should reevaluate how it allocates funding to diseases and base allocations on objective patient burdens. HIV, a disease with treatments that allow people with it to live mostly normal lives, receives $3.3 billion annually through NIH. Meanwhile, ME patients are disabled, have no approved treatments, and suffer a higher patient burden. Covid long haulers are suffering the same fate, many struck down as first wavers in March of 2020 are still disabled and sick as ever over four years later. Despite this, there is still no yearly allocation for long Covid in NIH’s baseline budget, as funding has only ever come from one time appropriations. NIH should right-size funding for ME and long Covid and start taking these diseases seriously.
— John Bolecek, long Covid patient
“Addressing health care workers’ trauma can help fight burnout,” by Sadie Elisseou
Thank you for writing this essay on the trauma and burnout that are all too common among today’s health care workforce. I applaud you for underscoring the importance of trauma-informed organizations and the critical value of workplaces that are safe, supportive, and flexible.
As a nurse educator and researcher, I have come to understand the important role of resilience in the work that nurses do. Considering two-thirds of nurses (65%) experience burnout, resilience-building skills are critical to mitigating nurse exhaustion and preserving our nation’s nursing pipeline. If actions are not taken to better protect the physical and mental health of our healthcare workforce, patient care will suffer. Lawmakers must take notice.
Some efforts in Congress have been successful. Congress has introduced legislation to reauthorize the Dr. Lorna Breen Provider Protection Act , bipartisan legislation that recognizes the need for mental health resources and support programs for healthcare professionals. Since its original enactment, this act has been instrumental in funding grant programs for mental health training, education, peer support, and crisis intervention services.
The reauthorization of this measure would expand grants to more than 200,000 other types of health care settings as well as renew the focus on reducing administrative burden for health care workers. While this bill is not a perfect solution, it does provide needed to support for a workforce that is understaffed, overworked, and in need to relief.
I urge Congress to finish the job and fully reauthorize the Dr. Lorna Breen Provider Protection Act this year.
— Stephanie Turner, R.N., Ed.D., M.S.N., ATI Nursing Education
About the Author Reprints
Patrick skerrett.
Acting First Opinion Editor
Patrick Skerrett is filling in as editor of First Opinion , STAT's platform for perspective and opinion on the life sciences writ large, and host of the First Opinion Podcast .
STAT encourages you to share your voice. We welcome your commentary, criticism, and expertise on our subscriber-only platform, STAT+ Connect
To submit a correction request, please visit our Contact Us page .

Recommended

Recommended Stories

AI and rural health care: A paradigm shift in America’s heartland

FDA: Don’t rush publishing your diversity guidance plan. Take your time and do it right

STAT Plus: A primer on HELIOS-B, an enormous stock-moving event for Alnylam Pharmaceuticals

STAT Plus: Top FDA official Peter Marks overruled staff, review team to approve Sarepta gene therapy

STAT Plus: What the Sarepta decision means for Duchenne patients, the company, and the FDA
- Share full article

Opinion Zeynep Tufekci
An Object Lesson From Covid on How to Destroy Public Trust
Credit... Nicole Natri
Supported by

By Zeynep Tufekci
Opinion Columnist
- June 8, 2024
Big chunks of the history of the Covid pandemic were rewritten over the last month or so in a way that will have terrible consequences for many years to come.
Under questioning by a congressional subcommittee, top officials from the National Institutes of Health, along with Dr. Anthony Fauci, acknowledged that some key parts of the public health guidance their agencies promoted during the first year of the Covid-19 pandemic were not backed up by solid science. What’s more, inconvenient information was kept from the public — suppressed, denied or disparaged as crackpot nonsense.
Remember the rule that we should all stay at least six feet apart? “It sort of just appeared,” Fauci said during a preliminary interview for the subcommittee hearing, adding that he “was not aware of any studies” that supported it. Remember the insistence that the virus was primarily spread by droplets that quickly fell to the floor? During his recent public hearing, he acknowledged that to the contrary, the virus is airborne.
As for the repeated assertion that Covid originated in a “wet market” in Wuhan, China, not in an infectious diseases laboratory there, N.I.H. officials were privately expressing alarm over that lab’s lax biosafety practices and risky research. In his public testimony, Fauci conceded that even now there “has not been definitive proof one way or the other” of Covid-19’s origins.
Officials didn’t just spread these dubious ideas, they also demeaned anyone who dared to question them . “ Dr. Fauci Throws Cold Water on Conspiracy Theory That Coronavirus Was Created in a Chinese Lab ” was one typical headline. At the hearings, it emerged that Dr. David Morens, a senior N.I.H. figure, was deleting emails that discussed pandemic origins and using his personal account so as to avoid public oversight . “We’re all smart enough to know to never have smoking guns, and if we did we wouldn’t put them in emails and if we found them we’d delete them,” he wrote to the head of a nonprofit involved in research at the Wuhan lab.
I wish I could say these were all just examples of the science evolving in real time, but they actually demonstrate obstinacy, arrogance and cowardice. Instead of circling the wagons, these officials should have been responsibly and transparently informing the public to the best of their knowledge and abilities.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement
By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies and similar tracking technologies described in our privacy policy .
Voice of the Discipline
News and publications.
Access AHA news and publications supporting the work of historians.
Stay up-to-date with the AHA

June 25, 2024
AHA Members Co-author Article on SCOTUS and Gun Control
AHA members Holly Brewer (Univ. of Maryland) and Laura F. Edwards (Princeton Univ.) have co-authored an article for Washington Monthly…

June 24, 2024
Action Alert Opposing Ohio SB 83

June 21, 2024
AHA Signs On to CIE Letter Urging HEA-Title VI Funding for FY 2025

June 18, 2024
Welcome to the AHA’s New Website
The American Historical Review is the flagship journal of the AHA and the journal of record for the historical discipline in the United States, bringing together scholarship from every major field of historical study.
Perspectives on History is the newsmagazine of the AHA and is the principal source for news and information about the discipline of history. Since 1962, Perspectives has promoted our work by publishing articles and commentary on all aspects of the historical discipline.
History in Focus Podcast

Environmental Crisis and Recovery
Collaborative history + revisiting marion thompson wright, aha booklets.
The AHA publishes booklets that address a diversity of topics to serve the needs of history students and historians in all professions. Our publications include career advice for history graduates, overviews and syntheses of current historical topics and fields, and guides to teaching and learning in history.
For the Press
The AHA is pleased to provide resources for journalists and press. If you are a member of the media and would like to submit a request for a referral or interview, please email [email protected] . Please provide any pertinent deadlines and we will do our best to accommodate your request. The AHA can find you a historian for any topic, and assists with dozens of inquiries each year.
The AHA encourages the reading of history with periodic reading challenges.
Permission to Use AHA Copyrighted Material
All material published by the American Historical Association in any medium is protected by copyright.
Join the AHA
The AHA brings together historians from all specializations and all work contexts, embracing the breadth and variety of activity in history today.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write About Coronavirus Using the Special COVID-19 (250-Word) Section on the Common App. Option 1: The Straightforward Way. Option 2: The Slightly More Creative Way. How to Write About Coronavirus Using the (650-Word) Additional Information Section.
100 Words Essay on Covid 19. COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very ...
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays. Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic. The global impact of COVID-19, the disease ...
This essay is an opportunity to share your pandemic experience and the lessons learned. The college admissions process has experienced significant changes as a result of COVID-19, creating new challenges for high school students. Since the onset of the pandemic, admissions officers have strongly emphasized a more holistic review process.
In conclusion, COVID-19 tested the patience and resilience of the mankind. This pandemic has taught people the importance of patience, effort and humbleness. Also Read: Essay on My Best Friend. Essay On COVID-19 in 300 Words. COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, is a serious and contagious disease that has affected people worldwide.
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus. Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history. A woman wearing a face mask in Miami. Alissa Wilkinson ...
Start with a blank piece of paper. In the middle of the paper write the question or statement that you are trying to answer. From there, draw 5 or 6 lines out from the centre. At the end of each of these lines will be a point you want to address in your essay. From here, write down any additional ideas that you have.
A Guide To Writing The Covid-19 Essay For The Common App. I write about the strategy leading to successful college admissions. This article is more than 3 years old. Students can use the Common ...
A novel coronavirus (CoV) named '2019-nCoV' or '2019 novel coronavirus' or 'COVID-19' by the World Health Organization (WHO) is in charge of the current outbreak of pneumonia that began at the beginning of December 2019 near in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China [1-4]. COVID-19 is a pathogenic virus. From the phylogenetic analysis ...
Writing about COVID-19 in your main essay. Write about your experiences during the pandemic in your main college essay if your experience is personal, relevant, and the most important thing to discuss in your college admission essay. That you had to stay home and study online isn't sufficient, as millions of other students faced the same ...
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays. Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on individuals, societies, and economies worldwide. Its multifaceted nature presents a wealth of topics suitable for academic exploration. This essay provides guidance on developing engaging and insightful essay topics related to COVID-19, offering a comprehensive range of perspectives to choose from.
Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. "The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry ...
He suggested writing an essay for the Journal. The Journal of Vocational Behavior has not traditionally published essays, but these are such unusual times, and COVID-19 is so relevant to our collective research on work that I thought it was a good idea. I issued an invitation to the Associate Editors to submit a brief (3000 word) essay on the ...
Essay on COVID-19 Pandemic. Published: 2021/11/08. Number of words: 1220. As a result of the COVID-19 (Coronavirus) outbreak, daily life has been negatively affected, impacting the worldwide economy. Thousands of individuals have been sickened or died as a result of the outbreak of this disease. When you have the flu or a viral infection, the ...
Reading time: 3 min (864 words) The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a dramatic loss of human life worldwide and presents an unprecedented challenge to public health, food systems and the world of work. The economic and social disruption caused by the pandemic is devastating: tens of millions of people are at risk of falling into extreme poverty ...
Future historians may look back on the journals, essays and art that ordinary people are creating now to tell the story of life during the coronavirus. But writing can also be deeply therapeutic.
The CDC reports that the percentage of adults who reported symptoms of anxiety of depression in the past 7 days increased from 36.4 to 41.5 % from August 2020 to February 2021. Other reports show that having COVID-19 may contribute, too, with its lingering or long COVID symptoms, which can include "foggy mind," anxiety, depression, and post ...
Short Paragraph on Covid-19. Covid-19 is a global pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus. It has significantly impacted daily life, with governments worldwide implementing lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates to curb the virus's spread. The pandemic has highlighted the importance of healthcare systems and the need for vaccines.
iCal. AACOMAS, AADSAS, and OPTCOMCAS have all added a new prompt that asks you how your path to medical, dental, or optometry school has been impacted by COVID-19. This seminar is specifically designed to assist applicants in writing a strong response to this essay that is authentic, compelling, and reflective.
COVID-19 Coronavirus. Abstract. First appearing in China in late 2019, the novel Coronavirus COVID-19 has become the most significant global pandemic event in a century. As of October 28, 2020 the total number of cases worldwide was 44 million with 1.17 million deaths. The United States has had an extremely politicized response to the virus ...
COVID-19 or Covid-19. Our preference is to use 'COVID-19' when writing about the coronavirus, rather than 'Covid-19' or 'covid-19'. This is consistent with the World Health Organization's (WHO) use of the abbreviation and its use in scientific papers, for example: 'As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, much of Imperial's teaching moved online.'.
Occurring weeks to months after a COVID-19 infection, ... Write an article and join a growing community of more than 185,900 academics and researchers from 4,984 institutions.
How to Write Your COVID-19 Essay. Whether you have decided to write about COVID-19 in a supplement or in the main personal statement, there are several guidelines to make your essay more impactful.
You can submit a Letter to the Editor here, or find the submission form at the end of any First Opinion essay. "Long Covid feels like a gun to my head," by Rachel Hall-Clifford. Thank you for ...
June 8, 2024. Big chunks of the history of the Covid pandemic were rewritten over the last month or so in a way that will have terrible consequences for many years to come. Under questioning by a ...
AMCAS has not added a specific new essay prompt about COVID-19 but there will be other places in your application where you will be able to inform medical schools about how your path to medical school was impacted by the pandemic. This workshop is strongly recommended for 2020-2021 and 2021-2022 applicants to medical, dental, and optometry schools.
Stay up-to-date with the AHA View All News The American Historical Review is the flagship journal of the AHA and the journal of record for the historical discipline in the United States, bringing together scholarship from every major field of historical study. Learn More Perspectives on History is the newsmagazine…