Document Analysis
- First Online: 02 January 2023

Cite this chapter

- Benjamin Kutsyuruba 4
Part of the book series: Springer Texts in Education ((SPTE))
5029 Accesses
2 Citations
This chapter describes the document analysis approach. As a qualitative method, document analysis entails a systematic procedure for reviewing and evaluating documents through finding, selecting, appraising (making sense of), and synthesizing data contained within them. This chapter outlines the brief history, method and use of document analysis, provides an outline of its process, strengths and limitations, and application, and offers further readings, resources, and suggestions for student engagement activities.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Altheide, D. L. (1987). Ethnographic content analysis. Qualitative Sociology, 10 (1), 65–77.
Article Google Scholar
Altheide, D. L. (1996). Qualitative media analysis . SAGE.
Google Scholar
Altheide, D. L. (2000). Tracking discourse and qualitative document analysis. Poetics, 27 , 287–299.
Atkinson, P. A., & Coffey, A. (1997). Analysing documentary realities. In D. Silverman (Ed.), Qualitative research: Theory, method and practice (pp. 45–62). SAGE.
Berg, B. L. (2001). Qualitative research methods for social sciences . Allyn and Bacon.
Bowen, G. A. (2009). Document analysis as a qualitative research method. Qualitative Research Journal, 9 (2), 27–40. https://doi.org/10.3316/qrj0902027
Bryman, A. (2003). Research methods and organization studies . Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Cardno, C. (2018). Policy document analysis: A practical educational leadership tool and a qualitative research method. Educational Administration: Theory and Practice , 24 (4), 623–640. https://doi.org/10.14527/kuey.2018.016
Caulley, D. N. (1983). Document analysis in program evaluation. Evaluation and Program Planning, 6 , 19–29.
Corbin, J., & Strauss, A. (2008). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory (3rd ed.). SAGE.
Derrida, J. (1978). Writing and difference . Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Aldine De Gruyter.
Glesne, C., & Peshkin, A. (1992). Becoming qualitative researchers (2nd ed.). Longman.
Goode, W. J., & Hatt, P. K. (1952). Methods in social research . McGraw-Hill.
Hodder, I. (2000). The interpretation of documents and material culture. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 703–715). SAGE.
Krippendorff, K. (1980). Content analysis: An introduction to its methodology. SAGE.
Lombard, M., Snyder-Duch, J., & Bracken, C. C. (2002). Content analysis in mass communication: Assessment and reporting of intercoder reliability. Human Communication Research, 28 , 587–604.
Lombard, M., Snyder-Duch, J., & Bracken, C. C. (2010). Practical resources for assessing and reporting intercoder reliability in content analysis research projects . Retrieved March 20, 2011, from http://matthewlombard.com/reliability/index_print.html
Mayring, P. (2000). Qualitative content analysis. Forum: Qualitative social research (Vol. 1(2)). Retrieved March 22, 2011, from http://www.qualitative-research.net/index.php/fqs/article/viewArticle/1089/2385
McMillan, J. H., & Schumacher, S. (2010). Research in education: Evidence-based inquiry (7th ed.). Pearson.
Merriam, S. B. (1988a). Case study research in education: A qualitative approach . Jossey-Bass.
Merriam, S. B. (1998b). Case study research in education . Jossey-Bass.
Miller, F. A., & Alvarado, K. (2005). Incorporating documents into qualitative nursing research. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 37 (4), 348–353.
Neuendorf, K. A. (2002). The content analysis guidebook . SAGE.
O’Leary, Z. (2014). The essential guide to doing your research project (2nd ed.). SAGE.
Patton, M. Q. (2002). Qualitative research & evaluation methods (3rd ed.). SAGE.
Prior, L. (2003). Using documents in social research . SAGE.
Prior, L. (2008a). Document analysis. In L. Given (Ed.), The SAGE encyclopaedia of qualitative research methods (pp. 231–232). SAGE. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781412963909
Prior, L. (2008b). Repositioning documents in social research. Sociology, 42 (5), 821–836. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038508094564
Prior, L. (2012). The role of documents in social research. In S. Delamont (Ed.), Handbook of qualitative research in education (pp. 426–438). Edward Elgar.
Salminen, A., Kauppinen, K., & Lehtovaara, M. (1997). Towards a methodology for document analysis. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 48 (7), 644–655.
Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research . SAGE.
Wharton, C. (2006). Document analysis. In V. Jupp (Ed.), The SAGE dictionary of social research methods (pp. 80–81). SAGE. https://doi.org/10.4135/9780857020116
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research, design and methods (4th ed.). SAGE.
Additional Reading
Kutsyuruba, B. (2017). Examining education reforms through document analysis methodology. In I. Silova, A. Korzh, S. Kovalchuk, & N. Sobe (Eds.), Reimagining Utopias: Theory and method for educational research in post-socialist contexts (pp. 199–214). Sense.
Kutsyuruba, B., Christou, T., Heggie, L., Murray, J., & Deluca, C. (2015). Teacher collaborative inquiry in Ontario: An analysis of provincial and school board policies and support documents. Canadian Journal of Educational Administration and Policy, 172 , 1–38.
Kutsyuruba, B., Godden, L., & Tregunna, L. (2014). Curbing the early-career attrition: A pan-Canadian document analysis of teacher induction and mentorship programs. Canadian Journal of Educational Administration and Policy, 161 , 1–42.
Segeren, A., & Kutsyuruba, B. (2012). Twenty years and counting: An examination of the development of equity and inclusive education policy in Ontario (1990–2010). Canadian Journal of Educational Administration and Policy, 136 , 1–38.
Online Resources
Document Analysis: A How To Guide (12:27 min) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vOsE9saR_ck
Document Analysis with Philip Adu (1:16:40 min) https://youtu.be/bLKBffW5JPU
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Queen’s University, Kingston, Canada
Benjamin Kutsyuruba
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Benjamin Kutsyuruba .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Administration, College of Education, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Janet Mola Okoko
Scott Tunison
Department of Educational Administration, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Keith D. Walker
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Kutsyuruba, B. (2023). Document Analysis. In: Okoko, J.M., Tunison, S., Walker, K.D. (eds) Varieties of Qualitative Research Methods. Springer Texts in Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_23
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_23
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-04396-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-04394-9
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Document Analysis - How to Analyze Text Data for Research

Introduction
What is document analysis, where is document analysis used, how to perform document analysis, what is text analysis, atlas.ti as text analysis software.
In qualitative research , you can collect primary data through surveys , observations , or interviews , to name a few examples. In addition, you can rely on document analysis when the data already exists in secondary sources like books, public reports, or other archival records that are relevant to your research inquiry.
In this article, we will look at the role of document analysis, the relationship between document analysis and text analysis, and how text analysis software like ATLAS.ti can help you conduct qualitative research.
Document analysis is a systematic procedure used in qualitative research to review and interpret the information embedded in written materials. These materials, often referred to as “documents,” can encompass a wide range of physical and digital sources, such as newspapers, diaries, letters, policy documents, contracts, reports, transcripts, and many others.
At its core, document analysis involves critically examining these sources to gather insightful data and understand the context in which they were created. Research can perform sentiment analysis , text mining, and text categorization, to name a few methods. The goal is not just to derive facts from the documents, but also to understand the underlying nuances, motivations, and perspectives that they represent. For instance, a historical researcher may examine old letters not just to get a chronological account of events, but also to understand the emotions, beliefs, and values of people during that era.
Benefits of document analysis
There are several advantages to using document analysis in research:
- Authenticity : Since documents are typically created for purposes other than research, they can offer an unobtrusive and genuine insight into the topic at hand, without the potential biases introduced by direct observation or interviews.
- Availability : Documents, especially those in the public domain, are widely accessible, making it easier for researchers to source information.
- Cost-effectiveness : As these documents already exist, researchers can save time and resources compared to other data collection methods.
However, document analysis is not without challenges. One must ensure the documents are authentic and reliable. Furthermore, the researcher must be adept at discerning between objective facts and subjective interpretations present in the document.
Document analysis is a versatile method in qualitative research that offers a lens into the intricate layers of meaning, context, and perspective found within textual materials. Through careful and systematic examination, it unveils the richness and depth of the information housed in documents, providing a unique dimension to research findings.
Document analysis is employed in a myriad of sectors, serving various purposes to generate actionable insights. Whether it's understanding customer sentiments or gleaning insights from historical records, this method offers valuable information. Here are some examples of how document analysis is applied.
Analyzing surveys and their responses
A common use of document analysis in the business world revolves around customer surveys . These surveys are designed to collect data on the customer experience, seeking to understand how products or services meet or fall short of customer expectations.
By analyzing customer survey responses , companies can identify areas of improvement, gauge satisfaction levels, and make informed decisions to enhance the customer experience. Even if customer service teams designed a survey for a specific purpose, text analytics of the responses can focus on different angles to gather insights for new research questions.
Examining customer feedback through social media posts
In today's digital age, social media is a goldmine of customer feedback. Customers frequently share their experiences, both positive and negative, on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.
Through document analysis of social media posts, companies can get a real-time pulse of their customer sentiments. This not only helps in immediate issue resolution but also in shaping product or service strategies to align with customer preferences.
Interpreting customer support tickets
Another rich source of data is customer support tickets. These tickets often contain detailed descriptions of issues faced by customers, their frustrations, or sometimes their appreciation for assistance received.
By employing document analysis on these tickets, businesses can detect patterns, identify recurring issues, and work towards streamlining their support processes. This ensures a smoother and more satisfying customer experience.
Historical research and social studies
Beyond the world of business, document analysis plays a pivotal role in historical and social research. Scholars analyze old manuscripts, letters, and other archival materials to construct a narrative of past events, cultures, and civilizations.
As a result, document analysis is an ideal method for historical research since generating new data is less feasible than turning to existing sources for analysis. Researchers can not only examine historical narratives but also how those narratives were constructed in their own time.
Turn to ATLAS.ti for your data analysis needs
Try out our powerful data analysis tools with a free trial to make the most out of your data today.
Performing document analysis is a structured process that ensures researchers can derive meaningful, qualitative insights by organizing source material into structured data . Here's a brief outline of the process:
- Define the research question
- Choose relevant documents
- Prepare and organize the documents
- Begin initial review and coding
- Analyze and interpret the data
- Present findings and draw conclusions
The process in detail
Before diving into the documents, it's crucial to have a clear research question or objective. This serves as the foundation for the entire analysis and guides the selection and review of documents. A well-defined question will focus the research, ensuring that the document analysis is targeted and relevant.
The next step is to identify and select documents that align with the research question. It's vital to ensure that these documents are credible, reliable, and pertinent to the research inquiry. The chosen materials can vary from official reports, personal diaries, to digital resources like social media data , depending on the nature of the research.
Once the documents are selected, they need to be organized in a manner that facilitates smooth analysis. This could mean categorizing documents by themes, chronology, or source types. Digital tools and data analysis software , such as ATLAS.ti, can assist in this phase, making the organization more efficient and helping researchers locate specific data when needed.
With everything in place, the researcher starts an initial review of the documents. During this phase, the emphasis is on identifying patterns, themes, or specific information relevant to the research question.
Coding involves assigning labels or tags to sections of the text to categorize the information. This step is iterative, and codes can be refined as the researcher delves deeper.
After coding, interesting patterns across codes can be analyzed. Here, researchers seek to draw meaningful connections between codes, identify overarching themes, and interpret the data in the context of the research question .
This is where the hidden insights and deeper understanding emerge, as researchers juxtapose various pieces of information and infer meaning from them.
Finally, after the intensive process of document analysis, the researcher consolidates their findings, crafting a narrative or report that presents the results. This might also involve visual representations like charts or graphs, especially when demonstrating patterns or trends.
Drawing conclusions involves synthesizing the insights gained from the analysis and offering answers or perspectives in relation to the original research question.
Ultimately, document analysis is a meticulous and iterative procedure. But with a clear plan and systematic approach, it becomes a potent tool in the researcher's arsenal, allowing them to uncover profound insights from textual data.
Text analysis, often referenced alongside document analysis, is a method that focuses on extracting meaningful information from textual data. While document analysis revolves around reviewing and interpreting data from various sources, text analysis hones in on the intricate details within these documents, enabling a deeper understanding. Both these methods are vital in fields such as linguistics, literature, social sciences, and business analytics.
In the context of document analysis, text analysis emerges as a nuanced exploration of the textual content. After documents have been sourced, be it from books, articles, social networks, or any other medium, they undergo a preprocessing phase. Here, irrelevant information is eliminated, errors are rectified, and the text may be translated or converted to ensure uniformity.
This cleaned text is then tokenized into smaller units like words or phrases, facilitating a granular review. Techniques specific to text analysis, such as topic modeling to determine discussed subjects or pattern recognition to identify trends, are applied.
The derived insights can be visualized using tools like graphs or charts, offering a clearer understanding of the content's depth. Interpretation follows, allowing researchers to draw actionable insights or theoretical conclusions based on both the broader document context and the specific text analysis.
Merging text analysis with document analysis presents unique challenges. With the proliferation of digital content, managing vast data sets becomes a significant hurdle. The inherent variability of language, laden with cultural nuances, idioms, and sometimes sarcasm, can make precise interpretation elusive.
Many text analysis tools exist that can facilitate the analytical process. ATLAS.ti offers a well-rounded, useful solution as a text analytics software . In this section, we'll highlight some of the tools that can help you conduct document analysis.
Word Frequencies
A word cloud can be a powerful text analytics tool to understand the nature of human language as it pertains to a particular context. Researchers can perform text mining on their unstructured text data to get a sense of what is being discussed. The Word Frequencies tool can also parse out specific parts of speech, facilitating more granular text extraction.
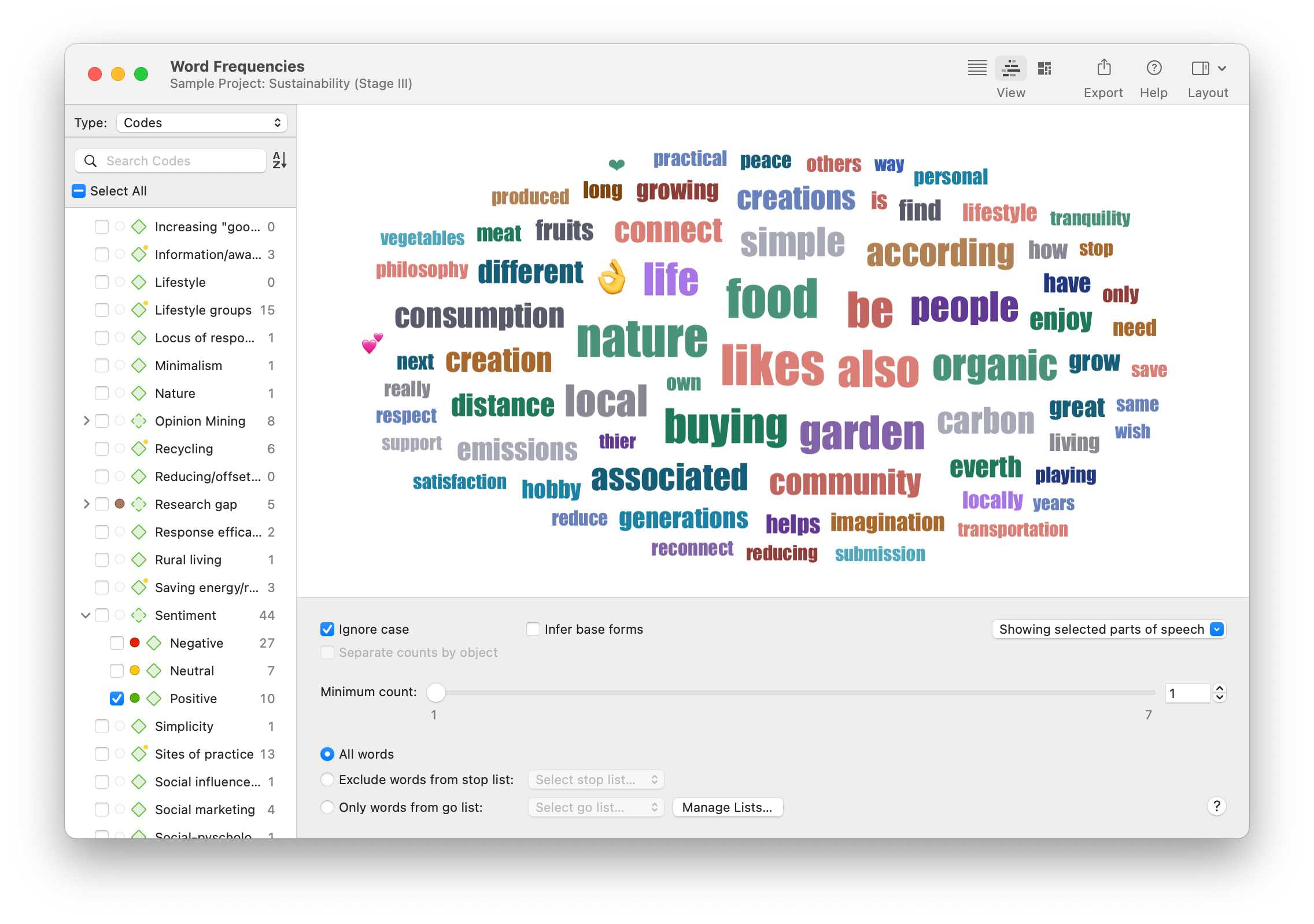
Sentiment Analysis
The Sentiment Analysis tool employs natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to analyze text based on sentiment and facilitate natural language understanding. This is important for tasks such as, for example, analyzing customer reviews and assessing customer satisfaction, because you can quickly categorize large numbers of customer data records by their positive or negative sentiment.
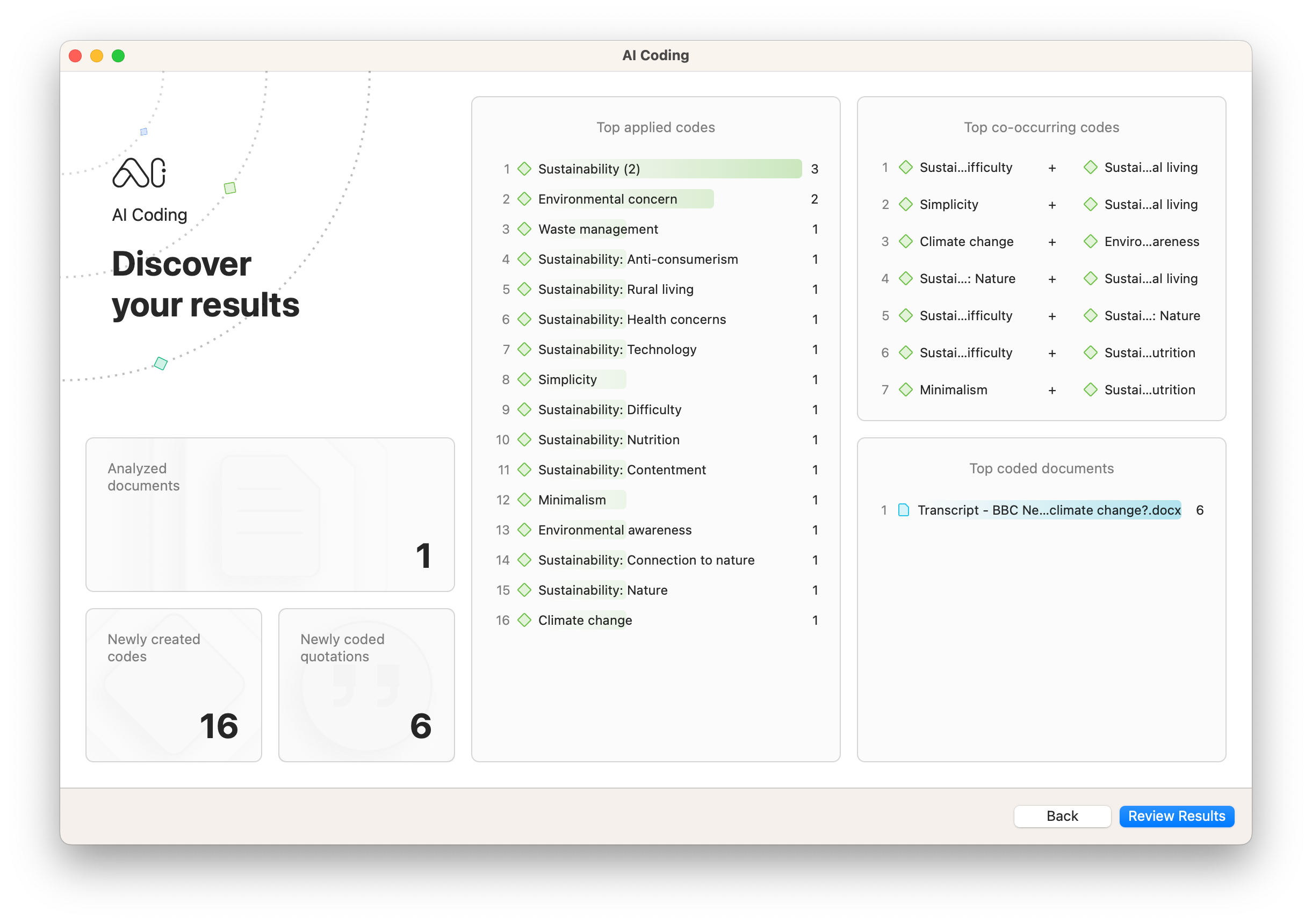
AI Coding relies on massive amounts of training data to interpret text and automatically code large amounts of qualitative data. Rather than read each and every document line by line, you can turn to AI Coding to process your data and devote time to the more essential tasks of analysis such as critical reflection and interpretation.
These text analytics tools can be a powerful complement to research. When you're conducting document analysis to understand the meaning of text, AI Coding can help with providing a code structure or organization of data that helps to identify deeper insights.
AI Summaries
Dealing with large numbers of discrete documents can be a daunting task if done manually, especially if each document in your data set is lengthy and complicated. Simplifying the meaning of documents down to their essential insights can help researchers identify patterns in the data.
AI Summaries fills this role by using natural language processing algorithms to simplify data to its salient points. Text generated by AI Summaries are stored in memos attached to documents to illustrate pathways to coding and analysis or to highlight how the data conveys meaning.
Take advantage of ATLAS.ti's analysis tools with a free trial
Let our powerful data analysis interface make the most out of your data. Download a free trial today.

- Privacy Policy

Home » Documentary Analysis – Methods, Applications and Examples
Documentary Analysis – Methods, Applications and Examples
Table of Contents

Documentary Analysis
Definition:
Documentary analysis, also referred to as document analysis , is a systematic procedure for reviewing or evaluating documents. This method involves a detailed review of the documents to extract themes or patterns relevant to the research topic .
Documents used in this type of analysis can include a wide variety of materials such as text (words) and images that have been recorded without a researcher’s intervention. The domain of document analysis, therefore, includes all kinds of texts – books, newspapers, letters, study reports, diaries, and more, as well as images like maps, photographs, and films.
Documentary analysis provides valuable insight and a unique perspective on the past, contextualizing the present and providing a baseline for future studies. It is also an essential tool in case studies and when direct observation or participant observation is not possible.
The process usually involves several steps:
- Sourcing : This involves identifying the document or source, its origin, and the context in which it was created.
- Contextualizing : This involves understanding the social, economic, political, and cultural circumstances during the time the document was created.
- Interrogating : This involves asking a series of questions to help understand the document better. For example, who is the author? What is the purpose of the document? Who is the intended audience?
- Making inferences : This involves understanding what the document says (either directly or indirectly) about the topic under study.
- Checking for reliability and validity : Just like other research methods, documentary analysis also involves checking for the validity and reliability of the documents being analyzed.
Documentary Analysis Methods
Documentary analysis as a qualitative research method involves a systematic process. Here are the main steps you would generally follow:
Defining the Research Question
Before you start any research , you need a clear and focused research question . This will guide your decision on what documents you need to analyze and what you’re looking for within them.
Selecting the Documents
Once you know what you’re looking for, you can start to select the relevant documents. These can be a wide range of materials – books, newspapers, letters, official reports, diaries, transcripts of speeches, archival materials, websites, social media posts, and more. They can be primary sources (directly from the time/place/person you are studying) or secondary sources (analyses created by others).
Reading and Interpreting the Documents
You need to closely read the selected documents to identify the themes and patterns that relate to your research question. This might involve content analysis (looking at what is explicitly stated) and discourse analysis (looking at what is implicitly stated or implied). You need to understand the context in which the document was created, the author’s purpose, and the audience’s perspective.
Coding and Categorizing the Data
After the initial reading, the data (text) can be broken down into smaller parts or “codes.” These codes can then be categorized based on their similarities and differences. This process of coding helps in organizing the data and identifying patterns or themes.
Analyzing the Data
Once the data is organized, it can be analyzed to make sense of it. This can involve comparing the data with existing theories, examining relationships between categories, or explaining the data in relation to the research question.
Validating the Findings
The researcher needs to ensure that the findings are accurate and credible. This might involve triangulating the data (comparing it with other sources or types of data), considering alternative explanations, or seeking feedback from others.
Reporting the Findings
The final step is to report the findings in a clear, structured way. This should include a description of the methods used, the findings, and the researcher’s interpretations and conclusions.
Applications of Documentary Analysis
Documentary analysis is widely used across a variety of fields and disciplines due to its flexible and comprehensive nature. Here are some specific applications:
Historical Research
Documentary analysis is a fundamental method in historical research. Historians use documents to reconstruct past events, understand historical contexts, and interpret the motivations and actions of historical figures. Documents analyzed may include personal letters, diaries, official records, newspaper articles, photographs, and more.
Social Science Research
Sociologists, anthropologists, and political scientists use documentary analysis to understand social phenomena, cultural practices, political events, and more. This might involve analyzing government policies, organizational records, media reports, social media posts, and other documents.
Legal Research
In law, documentary analysis is used in case analysis and statutory interpretation. Legal practitioners and scholars analyze court decisions, statutes, regulations, and other legal documents.
Business and Market Research
Companies often analyze documents to gather business intelligence, understand market trends, and make strategic decisions. This might involve analyzing competitor reports, industry news, market research studies, and more.
Media and Communication Studies
Scholars in these fields might analyze media content (e.g., news reports, advertisements, social media posts) to understand media narratives, public opinion, and communication practices.
Literary and Film Studies
In these fields, the “documents” might be novels, poems, films, or scripts. Scholars analyze these texts to interpret their meaning, understand their cultural context, and critique their form and content.
Educational Research
Educational researchers may analyze curricula, textbooks, lesson plans, and other educational documents to understand educational practices and policies.
Health Research
Health researchers may analyze medical records, health policies, clinical guidelines, and other documents to study health behaviors, healthcare delivery, and health outcomes.
Examples of Documentary Analysis
Some Examples of Documentary Analysis might be:
- Example 1 : A historian studying the causes of World War I might analyze diplomatic correspondence, government records, newspaper articles, and personal diaries from the period leading up to the war.
- Example 2 : A policy analyst trying to understand the impact of a new public health policy might analyze the policy document itself, as well as related government reports, statements from public health officials, and news media coverage of the policy.
- Example 3 : A market researcher studying consumer trends might analyze social media posts, customer reviews, industry reports, and news articles related to the market they’re studying.
- Example 4 : An education researcher might analyze curriculum documents, textbooks, and lesson plans to understand how a particular subject is being taught in schools. They might also analyze policy documents to understand the broader educational policy context.
- Example 5 : A criminologist studying hate crimes might analyze police reports, court records, news reports, and social media posts to understand patterns in hate crimes, as well as societal and institutional responses to them.
- Example 6 : A journalist writing a feature article on homelessness might analyze government reports on homelessness, policy documents related to housing and social services, news articles on homelessness, and social media posts from people experiencing homelessness.
- Example 7 : A literary critic studying a particular author might analyze their novels, letters, interviews, and reviews of their work to gain insight into their themes, writing style, influences, and reception.
When to use Documentary Analysis
Documentary analysis can be used in a variety of research contexts, including but not limited to:
- When direct access to research subjects is limited : If you are unable to conduct interviews or observations due to geographical, logistical, or ethical constraints, documentary analysis can provide an alternative source of data.
- When studying the past : Documents can provide a valuable window into historical events, cultures, and perspectives. This is particularly useful when the people involved in these events are no longer available for interviews or when physical evidence is lacking.
- When corroborating other sources of data : If you have collected data through interviews, surveys, or observations, analyzing documents can provide additional evidence to support or challenge your findings. This process of triangulation can enhance the validity of your research.
- When seeking to understand the context : Documents can provide background information that helps situate your research within a broader social, cultural, historical, or institutional context. This can be important for interpreting your other data and for making your research relevant to a wider audience.
- When the documents are the focus of the research : In some cases, the documents themselves might be the subject of your research. For example, you might be studying how a particular topic is represented in the media, how an author’s work has evolved over time, or how a government policy was developed.
- When resources are limited : Compared to methods like experiments or large-scale surveys, documentary analysis can often be conducted with relatively limited resources. It can be a particularly useful method for students, independent researchers, and others who are working with tight budgets.
- When providing an audit trail for future researchers : Documents provide a record of events, decisions, or conditions at specific points in time. They can serve as an audit trail for future researchers who want to understand the circumstances surrounding a particular event or period.
Purpose of Documentary Analysis
The purpose of documentary analysis in research can be multifold. Here are some key reasons why a researcher might choose to use this method:
- Understanding Context : Documents can provide rich contextual information about the period, environment, or culture under investigation. This can be especially useful for historical research, where the context is often key to understanding the events or trends being studied.
- Direct Source of Data : Documents can serve as primary sources of data. For instance, a letter from a historical figure can give unique insights into their thoughts, feelings, and motivations. A company’s annual report can offer firsthand information about its performance and strategy.
- Corroboration and Verification : Documentary analysis can be used to validate and cross-verify findings derived from other research methods. For example, if interviews suggest a particular outcome, relevant documents can be reviewed to confirm the accuracy of this finding.
- Substituting for Other Methods : When access to the field or subjects is not possible due to various constraints (geographical, logistical, or ethical), documentary analysis can serve as an alternative to methods like observation or interviews.
- Unobtrusive Method : Unlike some other research methods, documentary analysis doesn’t require interaction with subjects, and therefore doesn’t risk altering the behavior of those subjects.
- Longitudinal Analysis : Documents can be used to study change over time. For example, a researcher might analyze census data from multiple decades to study demographic changes.
- Providing Rich, Qualitative Data : Documents often provide qualitative data that can help researchers understand complex issues in depth. For example, a policy document might reveal not just the details of the policy, but also the underlying beliefs and attitudes that shaped it.
Advantages of Documentary Analysis
Documentary analysis offers several advantages as a research method:
- Unobtrusive : As a non-reactive method, documentary analysis does not require direct interaction with human subjects, which means that the research doesn’t affect or influence the subjects’ behavior.
- Rich Historical and Contextual Data : Documents can provide a wealth of historical and contextual information. They allow researchers to examine events and perspectives from the past, even from periods long before modern research methods were established.
- Efficiency and Accessibility : Many documents are readily accessible, especially with the proliferation of digital archives and databases. This accessibility can often make documentary analysis a more efficient method than others that require data collection from human subjects.
- Cost-Effective : Compared to other methods, documentary analysis can be relatively inexpensive. It generally requires fewer resources than conducting experiments, surveys, or fieldwork.
- Permanent Record : Documents provide a permanent record that can be reviewed multiple times. This allows for repeated analysis and verification of the data.
- Versatility : A wide variety of documents can be analyzed, from historical texts to contemporary digital content, providing flexibility and applicability to a broad range of research questions and fields.
- Ability to Cross-Verify (Triangulate) Data : Documentary analysis can be used alongside other methods as a means of triangulating data, thus adding validity and reliability to the research.
Limitations of Documentary Analysis
While documentary analysis offers several benefits as a research method, it also has its limitations. It’s important to keep these in mind when deciding to use documentary analysis and when interpreting your findings:
- Authenticity : Not all documents are genuine, and sometimes it can be challenging to verify the authenticity of a document, particularly for historical research.
- Bias and Subjectivity : All documents are products of their time and their authors. They may reflect personal, cultural, political, or institutional biases, and these biases can affect the information they contain and how it is presented.
- Incomplete or Missing Information : Documents may not provide all the information you need for your research. There may be gaps in the record, or crucial information may have been omitted, intentionally or unintentionally.
- Access and Availability : Not all documents are readily available for analysis. Some may be restricted due to privacy, confidentiality, or security considerations. Others may be difficult to locate or access, particularly historical documents that haven’t been digitized.
- Interpretation : Interpreting documents, particularly historical ones, can be challenging. You need to understand the context in which the document was created, including the social, cultural, political, and personal factors that might have influenced its content.
- Time-Consuming : While documentary analysis can be cost-effective, it can also be time-consuming, especially if you have a large number of documents to analyze or if the documents are lengthy or complex.
- Lack of Control Over Data : Unlike methods where the researcher collects the data themselves (e.g., through experiments or surveys), with documentary analysis, you have no control over what data is available. You are reliant on what others have chosen to record and preserve.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Cluster Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples

Discriminant Analysis – Methods, Types and...

MANOVA (Multivariate Analysis of Variance) –...

ANOVA (Analysis of variance) – Formulas, Types...

Graphical Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Substantive Framework – Types, Methods and...

No products in the cart.
The Basics of Document Analysis

Document analysis is the process of reviewing or evaluating documents both printed and electronic in a methodical manner. The document analysis method, like many other qualitative research methods, involves examining and interpreting data to uncover meaning, gain understanding, and come to a conclusion.

What is Meant by Document Analysis?
Document analysis pertains to the process of interpreting documents for an assessment topic by the researcher as a means of giving voice and meaning. In Document Analysis as a Qualitative Research Method by Glenn A. Bowen , document analysis is described as, “... a systematic procedure for reviewing or evaluating documents—both printed and electronic (computer-based and Internet-transmitted) material. Like other analytical methods in qualitative research, document analysis requires that data be examined and interpreted in order to elicit meaning, gain understanding, and develop empirical knowledge.”
During the analysis of documents, the content is categorized into distinct themes, similar to the way transcripts from interviews or focus groups are analyzed. The documents may also be graded or scored using a rubric.
Document analysis is a social research method of great value, and it plays a crucial role in most triangulation methods, combining various methods to study a particular phenomenon.
>> View Webinar: How-To’s for Data Analysis
Documents fall into three main categories:
- Personal Documents: A personal account of an individual's beliefs, actions, and experiences. The following are examples: e-mails, calendars, scrapbooks, Facebook posts, incident reports, blogs, duty logs, newspapers, and reflections or journals.
- Public Records: Records of an organization's activities that are maintained continuously over time. These include mission statements, student transcripts, annual reports, student handbooks, policy manuals, syllabus, and strategic plans.
- Physical Evidence: Artifacts or items found within a study setting, also referred to as artifacts. Among these are posters, flyers, agendas, training materials, and handbooks.

The qualitative researcher generally makes use of two or more resources, each using a different data source and methodology, to achieve convergence and corroboration. An important purpose of triangulating evidence is to establish credibility through a convergence of evidence. Corroboration of findings across data sets reduces the possibility of bias, by examining data gathered in different ways.
It is important to note that document analysis differs from content analysis as content analysis refers to more than documents. As part of their definition for content analysis, Columbia Mailman School of Public Health states that, “Sources of data could be from interviews, open-ended questions, field research notes, conversations, or literally any occurrence of communicative language (such as books, essays, discussions, newspaper headlines, speeches, media, historical documents).
How Do You Do Document Analysis?
In order for a researcher to obtain reliable results from document analysis, a detailed planning process must be undertaken. The following is an outline of an eight-step planning process that should be employed in all textual analysis including document analysis techniques.
- Identify the texts you want to analyze such as samples, population, participants, and respondents.
- You should consider how texts will be accessed, paying attention to any cultural or linguistic barriers.
- Acknowledge and resolve biases.
- Acquire appropriate research skills.
- Strategize for ensuring credibility.
- Identify the data that is being sought.
- Take into account ethical issues.
- Keep a backup plan handy.

Researchers can use a wide variety of texts as part of their research, but the most common source is likely to be written material. Researchers often ask how many documents they should collect. There is an opinion that a wide selection of documents is preferable, but the issue should probably revolve more around the quality of the document than its quantity.
Why is Document Analysis Useful?
Different types of documents serve different purposes. They provide background information, indicate potential interview questions, serve as a mechanism for monitoring progress and tracking changes within a project, and allow for verification of any claims or progress made.
You can triangulate your claims about the phenomenon being studied using document analysis by using multiple sources and other research gathering methods.
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of document analysis
- Document analysis may assist researchers in determining what questions to ask your interviewees, as well as provide insight into what to watch out for during your participant observation.
- It is particularly useful to researchers who wish to focus on specific case studies
- It is inexpensive and quick in cases where data is easily obtainable.
- Documents provide specific and reliable data, unaffected by researchers' presence unlike with other research methods like participant observation.
Disadvantages
- It is likely that the documents researchers obtain are not complete or written objectively, requiring researchers to adopt a critical approach and not assume their contents are reliable or unbiased.
- There may be a risk of information overload due to the number of documents involved. Researchers often have difficulties determining what parts of each document are relevant to the topic being studied.
- It may be necessary to anonymize documents and compare them with other documents.
How NVivo Can Help with Document Analysis
Analyzing copious amounts of data and information can be a daunting and time-consuming prospect. Luckily, qualitative data analysis tools like NVivo can help!
NVivo’s AI-powered autocoding text analysis tool can help you efficiently analyze data and perform thematic analysis . By automatically detecting, grouping, and tagging noun phrases, you can quickly identify key themes throughout your documents – aiding in your evaluation.
Additionally, once you start coding part of your data, NVivo’s smart coding can take care of the rest for you by using machine learning to match your coding style. After your initial coding, you can run queries and create visualizations to expand on initial findings and gain deeper insights.
These features allow you to conduct data analysis on large amounts of documents – improving the efficiency of this qualitative research method. Learn more about these features in the webinar, NVivo 14: Thematic Analysis Using NVivo.
>> Watch Webinar NVivo 14: Thematic Analysis Using NVivo
Learn More About Document Analysis
Watch Twenty-Five Qualitative Researchers Share How-To's for Data Analysis

Recent Articles
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, document analysis as a qualitative research method.
Qualitative Research Journal
ISSN : 1443-9883
Article publication date: 3 August 2009
This article examines the function of documents as a data source in qualitative research and discusses document analysis procedure in the context of actual research experiences. Targeted to research novices, the article takes a nuts‐and‐bolts approach to document analysis. It describes the nature and forms of documents, outlines the advantages and limitations of document analysis, and offers specific examples of the use of documents in the research process. The application of document analysis to a grounded theory study is illustrated.
- Content analysis
- Grounded theory
- Thematic analysis
- Triangulation
Bowen, G.A. (2009), "Document Analysis as a Qualitative Research Method", Qualitative Research Journal , Vol. 9 No. 2, pp. 27-40. https://doi.org/10.3316/QRJ0902027
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2009, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here

All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Neurol Res Pract

How to use and assess qualitative research methods
Loraine busetto.
1 Department of Neurology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Im Neuenheimer Feld 400, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
Wolfgang Wick
2 Clinical Cooperation Unit Neuro-Oncology, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
Christoph Gumbinger
Associated data.
Not applicable.
This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement. The most common methods of data collection are document study, (non-) participant observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups. For data analysis, field-notes and audio-recordings are transcribed into protocols and transcripts, and coded using qualitative data management software. Criteria such as checklists, reflexivity, sampling strategies, piloting, co-coding, member-checking and stakeholder involvement can be used to enhance and assess the quality of the research conducted. Using qualitative in addition to quantitative designs will equip us with better tools to address a greater range of research problems, and to fill in blind spots in current neurological research and practice.
The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of qualitative research methods, including hands-on information on how they can be used, reported and assessed. This article is intended for beginning qualitative researchers in the health sciences as well as experienced quantitative researchers who wish to broaden their understanding of qualitative research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as “the study of the nature of phenomena”, including “their quality, different manifestations, the context in which they appear or the perspectives from which they can be perceived” , but excluding “their range, frequency and place in an objectively determined chain of cause and effect” [ 1 ]. This formal definition can be complemented with a more pragmatic rule of thumb: qualitative research generally includes data in form of words rather than numbers [ 2 ].
Why conduct qualitative research?
Because some research questions cannot be answered using (only) quantitative methods. For example, one Australian study addressed the issue of why patients from Aboriginal communities often present late or not at all to specialist services offered by tertiary care hospitals. Using qualitative interviews with patients and staff, it found one of the most significant access barriers to be transportation problems, including some towns and communities simply not having a bus service to the hospital [ 3 ]. A quantitative study could have measured the number of patients over time or even looked at possible explanatory factors – but only those previously known or suspected to be of relevance. To discover reasons for observed patterns, especially the invisible or surprising ones, qualitative designs are needed.
While qualitative research is common in other fields, it is still relatively underrepresented in health services research. The latter field is more traditionally rooted in the evidence-based-medicine paradigm, as seen in " research that involves testing the effectiveness of various strategies to achieve changes in clinical practice, preferably applying randomised controlled trial study designs (...) " [ 4 ]. This focus on quantitative research and specifically randomised controlled trials (RCT) is visible in the idea of a hierarchy of research evidence which assumes that some research designs are objectively better than others, and that choosing a "lesser" design is only acceptable when the better ones are not practically or ethically feasible [ 5 , 6 ]. Others, however, argue that an objective hierarchy does not exist, and that, instead, the research design and methods should be chosen to fit the specific research question at hand – "questions before methods" [ 2 , 7 – 9 ]. This means that even when an RCT is possible, some research problems require a different design that is better suited to addressing them. Arguing in JAMA, Berwick uses the example of rapid response teams in hospitals, which he describes as " a complex, multicomponent intervention – essentially a process of social change" susceptible to a range of different context factors including leadership or organisation history. According to him, "[in] such complex terrain, the RCT is an impoverished way to learn. Critics who use it as a truth standard in this context are incorrect" [ 8 ] . Instead of limiting oneself to RCTs, Berwick recommends embracing a wider range of methods , including qualitative ones, which for "these specific applications, (...) are not compromises in learning how to improve; they are superior" [ 8 ].
Research problems that can be approached particularly well using qualitative methods include assessing complex multi-component interventions or systems (of change), addressing questions beyond “what works”, towards “what works for whom when, how and why”, and focussing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation [ 7 , 9 – 12 ]. Using qualitative methods can also help shed light on the “softer” side of medical treatment. For example, while quantitative trials can measure the costs and benefits of neuro-oncological treatment in terms of survival rates or adverse effects, qualitative research can help provide a better understanding of patient or caregiver stress, visibility of illness or out-of-pocket expenses.
How to conduct qualitative research?
Given that qualitative research is characterised by flexibility, openness and responsivity to context, the steps of data collection and analysis are not as separate and consecutive as they tend to be in quantitative research [ 13 , 14 ]. As Fossey puts it : “sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation are related to each other in a cyclical (iterative) manner, rather than following one after another in a stepwise approach” [ 15 ]. The researcher can make educated decisions with regard to the choice of method, how they are implemented, and to which and how many units they are applied [ 13 ]. As shown in Fig. 1 , this can involve several back-and-forth steps between data collection and analysis where new insights and experiences can lead to adaption and expansion of the original plan. Some insights may also necessitate a revision of the research question and/or the research design as a whole. The process ends when saturation is achieved, i.e. when no relevant new information can be found (see also below: sampling and saturation). For reasons of transparency, it is essential for all decisions as well as the underlying reasoning to be well-documented.

Iterative research process
While it is not always explicitly addressed, qualitative methods reflect a different underlying research paradigm than quantitative research (e.g. constructivism or interpretivism as opposed to positivism). The choice of methods can be based on the respective underlying substantive theory or theoretical framework used by the researcher [ 2 ].
Data collection
The methods of qualitative data collection most commonly used in health research are document study, observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups [ 1 , 14 , 16 , 17 ].
Document study
Document study (also called document analysis) refers to the review by the researcher of written materials [ 14 ]. These can include personal and non-personal documents such as archives, annual reports, guidelines, policy documents, diaries or letters.
Observations
Observations are particularly useful to gain insights into a certain setting and actual behaviour – as opposed to reported behaviour or opinions [ 13 ]. Qualitative observations can be either participant or non-participant in nature. In participant observations, the observer is part of the observed setting, for example a nurse working in an intensive care unit [ 18 ]. In non-participant observations, the observer is “on the outside looking in”, i.e. present in but not part of the situation, trying not to influence the setting by their presence. Observations can be planned (e.g. for 3 h during the day or night shift) or ad hoc (e.g. as soon as a stroke patient arrives at the emergency room). During the observation, the observer takes notes on everything or certain pre-determined parts of what is happening around them, for example focusing on physician-patient interactions or communication between different professional groups. Written notes can be taken during or after the observations, depending on feasibility (which is usually lower during participant observations) and acceptability (e.g. when the observer is perceived to be judging the observed). Afterwards, these field notes are transcribed into observation protocols. If more than one observer was involved, field notes are taken independently, but notes can be consolidated into one protocol after discussions. Advantages of conducting observations include minimising the distance between the researcher and the researched, the potential discovery of topics that the researcher did not realise were relevant and gaining deeper insights into the real-world dimensions of the research problem at hand [ 18 ].
Semi-structured interviews
Hijmans & Kuyper describe qualitative interviews as “an exchange with an informal character, a conversation with a goal” [ 19 ]. Interviews are used to gain insights into a person’s subjective experiences, opinions and motivations – as opposed to facts or behaviours [ 13 ]. Interviews can be distinguished by the degree to which they are structured (i.e. a questionnaire), open (e.g. free conversation or autobiographical interviews) or semi-structured [ 2 , 13 ]. Semi-structured interviews are characterized by open-ended questions and the use of an interview guide (or topic guide/list) in which the broad areas of interest, sometimes including sub-questions, are defined [ 19 ]. The pre-defined topics in the interview guide can be derived from the literature, previous research or a preliminary method of data collection, e.g. document study or observations. The topic list is usually adapted and improved at the start of the data collection process as the interviewer learns more about the field [ 20 ]. Across interviews the focus on the different (blocks of) questions may differ and some questions may be skipped altogether (e.g. if the interviewee is not able or willing to answer the questions or for concerns about the total length of the interview) [ 20 ]. Qualitative interviews are usually not conducted in written format as it impedes on the interactive component of the method [ 20 ]. In comparison to written surveys, qualitative interviews have the advantage of being interactive and allowing for unexpected topics to emerge and to be taken up by the researcher. This can also help overcome a provider or researcher-centred bias often found in written surveys, which by nature, can only measure what is already known or expected to be of relevance to the researcher. Interviews can be audio- or video-taped; but sometimes it is only feasible or acceptable for the interviewer to take written notes [ 14 , 16 , 20 ].
Focus groups
Focus groups are group interviews to explore participants’ expertise and experiences, including explorations of how and why people behave in certain ways [ 1 ]. Focus groups usually consist of 6–8 people and are led by an experienced moderator following a topic guide or “script” [ 21 ]. They can involve an observer who takes note of the non-verbal aspects of the situation, possibly using an observation guide [ 21 ]. Depending on researchers’ and participants’ preferences, the discussions can be audio- or video-taped and transcribed afterwards [ 21 ]. Focus groups are useful for bringing together homogeneous (to a lesser extent heterogeneous) groups of participants with relevant expertise and experience on a given topic on which they can share detailed information [ 21 ]. Focus groups are a relatively easy, fast and inexpensive method to gain access to information on interactions in a given group, i.e. “the sharing and comparing” among participants [ 21 ]. Disadvantages include less control over the process and a lesser extent to which each individual may participate. Moreover, focus group moderators need experience, as do those tasked with the analysis of the resulting data. Focus groups can be less appropriate for discussing sensitive topics that participants might be reluctant to disclose in a group setting [ 13 ]. Moreover, attention must be paid to the emergence of “groupthink” as well as possible power dynamics within the group, e.g. when patients are awed or intimidated by health professionals.
Choosing the “right” method
As explained above, the school of thought underlying qualitative research assumes no objective hierarchy of evidence and methods. This means that each choice of single or combined methods has to be based on the research question that needs to be answered and a critical assessment with regard to whether or to what extent the chosen method can accomplish this – i.e. the “fit” between question and method [ 14 ]. It is necessary for these decisions to be documented when they are being made, and to be critically discussed when reporting methods and results.
Let us assume that our research aim is to examine the (clinical) processes around acute endovascular treatment (EVT), from the patient’s arrival at the emergency room to recanalization, with the aim to identify possible causes for delay and/or other causes for sub-optimal treatment outcome. As a first step, we could conduct a document study of the relevant standard operating procedures (SOPs) for this phase of care – are they up-to-date and in line with current guidelines? Do they contain any mistakes, irregularities or uncertainties that could cause delays or other problems? Regardless of the answers to these questions, the results have to be interpreted based on what they are: a written outline of what care processes in this hospital should look like. If we want to know what they actually look like in practice, we can conduct observations of the processes described in the SOPs. These results can (and should) be analysed in themselves, but also in comparison to the results of the document analysis, especially as regards relevant discrepancies. Do the SOPs outline specific tests for which no equipment can be observed or tasks to be performed by specialized nurses who are not present during the observation? It might also be possible that the written SOP is outdated, but the actual care provided is in line with current best practice. In order to find out why these discrepancies exist, it can be useful to conduct interviews. Are the physicians simply not aware of the SOPs (because their existence is limited to the hospital’s intranet) or do they actively disagree with them or does the infrastructure make it impossible to provide the care as described? Another rationale for adding interviews is that some situations (or all of their possible variations for different patient groups or the day, night or weekend shift) cannot practically or ethically be observed. In this case, it is possible to ask those involved to report on their actions – being aware that this is not the same as the actual observation. A senior physician’s or hospital manager’s description of certain situations might differ from a nurse’s or junior physician’s one, maybe because they intentionally misrepresent facts or maybe because different aspects of the process are visible or important to them. In some cases, it can also be relevant to consider to whom the interviewee is disclosing this information – someone they trust, someone they are otherwise not connected to, or someone they suspect or are aware of being in a potentially “dangerous” power relationship to them. Lastly, a focus group could be conducted with representatives of the relevant professional groups to explore how and why exactly they provide care around EVT. The discussion might reveal discrepancies (between SOPs and actual care or between different physicians) and motivations to the researchers as well as to the focus group members that they might not have been aware of themselves. For the focus group to deliver relevant information, attention has to be paid to its composition and conduct, for example, to make sure that all participants feel safe to disclose sensitive or potentially problematic information or that the discussion is not dominated by (senior) physicians only. The resulting combination of data collection methods is shown in Fig. 2 .

Possible combination of data collection methods
Attributions for icons: “Book” by Serhii Smirnov, “Interview” by Adrien Coquet, FR, “Magnifying Glass” by anggun, ID, “Business communication” by Vectors Market; all from the Noun Project
The combination of multiple data source as described for this example can be referred to as “triangulation”, in which multiple measurements are carried out from different angles to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon under study [ 22 , 23 ].
Data analysis
To analyse the data collected through observations, interviews and focus groups these need to be transcribed into protocols and transcripts (see Fig. 3 ). Interviews and focus groups can be transcribed verbatim , with or without annotations for behaviour (e.g. laughing, crying, pausing) and with or without phonetic transcription of dialects and filler words, depending on what is expected or known to be relevant for the analysis. In the next step, the protocols and transcripts are coded , that is, marked (or tagged, labelled) with one or more short descriptors of the content of a sentence or paragraph [ 2 , 15 , 23 ]. Jansen describes coding as “connecting the raw data with “theoretical” terms” [ 20 ]. In a more practical sense, coding makes raw data sortable. This makes it possible to extract and examine all segments describing, say, a tele-neurology consultation from multiple data sources (e.g. SOPs, emergency room observations, staff and patient interview). In a process of synthesis and abstraction, the codes are then grouped, summarised and/or categorised [ 15 , 20 ]. The end product of the coding or analysis process is a descriptive theory of the behavioural pattern under investigation [ 20 ]. The coding process is performed using qualitative data management software, the most common ones being InVivo, MaxQDA and Atlas.ti. It should be noted that these are data management tools which support the analysis performed by the researcher(s) [ 14 ].

From data collection to data analysis
Attributions for icons: see Fig. Fig.2, 2 , also “Speech to text” by Trevor Dsouza, “Field Notes” by Mike O’Brien, US, “Voice Record” by ProSymbols, US, “Inspection” by Made, AU, and “Cloud” by Graphic Tigers; all from the Noun Project
How to report qualitative research?
Protocols of qualitative research can be published separately and in advance of the study results. However, the aim is not the same as in RCT protocols, i.e. to pre-define and set in stone the research questions and primary or secondary endpoints. Rather, it is a way to describe the research methods in detail, which might not be possible in the results paper given journals’ word limits. Qualitative research papers are usually longer than their quantitative counterparts to allow for deep understanding and so-called “thick description”. In the methods section, the focus is on transparency of the methods used, including why, how and by whom they were implemented in the specific study setting, so as to enable a discussion of whether and how this may have influenced data collection, analysis and interpretation. The results section usually starts with a paragraph outlining the main findings, followed by more detailed descriptions of, for example, the commonalities, discrepancies or exceptions per category [ 20 ]. Here it is important to support main findings by relevant quotations, which may add information, context, emphasis or real-life examples [ 20 , 23 ]. It is subject to debate in the field whether it is relevant to state the exact number or percentage of respondents supporting a certain statement (e.g. “Five interviewees expressed negative feelings towards XYZ”) [ 21 ].
How to combine qualitative with quantitative research?
Qualitative methods can be combined with other methods in multi- or mixed methods designs, which “[employ] two or more different methods [ …] within the same study or research program rather than confining the research to one single method” [ 24 ]. Reasons for combining methods can be diverse, including triangulation for corroboration of findings, complementarity for illustration and clarification of results, expansion to extend the breadth and range of the study, explanation of (unexpected) results generated with one method with the help of another, or offsetting the weakness of one method with the strength of another [ 1 , 17 , 24 – 26 ]. The resulting designs can be classified according to when, why and how the different quantitative and/or qualitative data strands are combined. The three most common types of mixed method designs are the convergent parallel design , the explanatory sequential design and the exploratory sequential design. The designs with examples are shown in Fig. 4 .

Three common mixed methods designs
In the convergent parallel design, a qualitative study is conducted in parallel to and independently of a quantitative study, and the results of both studies are compared and combined at the stage of interpretation of results. Using the above example of EVT provision, this could entail setting up a quantitative EVT registry to measure process times and patient outcomes in parallel to conducting the qualitative research outlined above, and then comparing results. Amongst other things, this would make it possible to assess whether interview respondents’ subjective impressions of patients receiving good care match modified Rankin Scores at follow-up, or whether observed delays in care provision are exceptions or the rule when compared to door-to-needle times as documented in the registry. In the explanatory sequential design, a quantitative study is carried out first, followed by a qualitative study to help explain the results from the quantitative study. This would be an appropriate design if the registry alone had revealed relevant delays in door-to-needle times and the qualitative study would be used to understand where and why these occurred, and how they could be improved. In the exploratory design, the qualitative study is carried out first and its results help informing and building the quantitative study in the next step [ 26 ]. If the qualitative study around EVT provision had shown a high level of dissatisfaction among the staff members involved, a quantitative questionnaire investigating staff satisfaction could be set up in the next step, informed by the qualitative study on which topics dissatisfaction had been expressed. Amongst other things, the questionnaire design would make it possible to widen the reach of the research to more respondents from different (types of) hospitals, regions, countries or settings, and to conduct sub-group analyses for different professional groups.
How to assess qualitative research?
A variety of assessment criteria and lists have been developed for qualitative research, ranging in their focus and comprehensiveness [ 14 , 17 , 27 ]. However, none of these has been elevated to the “gold standard” in the field. In the following, we therefore focus on a set of commonly used assessment criteria that, from a practical standpoint, a researcher can look for when assessing a qualitative research report or paper.
Assessors should check the authors’ use of and adherence to the relevant reporting checklists (e.g. Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR)) to make sure all items that are relevant for this type of research are addressed [ 23 , 28 ]. Discussions of quantitative measures in addition to or instead of these qualitative measures can be a sign of lower quality of the research (paper). Providing and adhering to a checklist for qualitative research contributes to an important quality criterion for qualitative research, namely transparency [ 15 , 17 , 23 ].
Reflexivity
While methodological transparency and complete reporting is relevant for all types of research, some additional criteria must be taken into account for qualitative research. This includes what is called reflexivity, i.e. sensitivity to the relationship between the researcher and the researched, including how contact was established and maintained, or the background and experience of the researcher(s) involved in data collection and analysis. Depending on the research question and population to be researched this can be limited to professional experience, but it may also include gender, age or ethnicity [ 17 , 27 ]. These details are relevant because in qualitative research, as opposed to quantitative research, the researcher as a person cannot be isolated from the research process [ 23 ]. It may influence the conversation when an interviewed patient speaks to an interviewer who is a physician, or when an interviewee is asked to discuss a gynaecological procedure with a male interviewer, and therefore the reader must be made aware of these details [ 19 ].
Sampling and saturation
The aim of qualitative sampling is for all variants of the objects of observation that are deemed relevant for the study to be present in the sample “ to see the issue and its meanings from as many angles as possible” [ 1 , 16 , 19 , 20 , 27 ] , and to ensure “information-richness [ 15 ]. An iterative sampling approach is advised, in which data collection (e.g. five interviews) is followed by data analysis, followed by more data collection to find variants that are lacking in the current sample. This process continues until no new (relevant) information can be found and further sampling becomes redundant – which is called saturation [ 1 , 15 ] . In other words: qualitative data collection finds its end point not a priori , but when the research team determines that saturation has been reached [ 29 , 30 ].
This is also the reason why most qualitative studies use deliberate instead of random sampling strategies. This is generally referred to as “ purposive sampling” , in which researchers pre-define which types of participants or cases they need to include so as to cover all variations that are expected to be of relevance, based on the literature, previous experience or theory (i.e. theoretical sampling) [ 14 , 20 ]. Other types of purposive sampling include (but are not limited to) maximum variation sampling, critical case sampling or extreme or deviant case sampling [ 2 ]. In the above EVT example, a purposive sample could include all relevant professional groups and/or all relevant stakeholders (patients, relatives) and/or all relevant times of observation (day, night and weekend shift).
Assessors of qualitative research should check whether the considerations underlying the sampling strategy were sound and whether or how researchers tried to adapt and improve their strategies in stepwise or cyclical approaches between data collection and analysis to achieve saturation [ 14 ].
Good qualitative research is iterative in nature, i.e. it goes back and forth between data collection and analysis, revising and improving the approach where necessary. One example of this are pilot interviews, where different aspects of the interview (especially the interview guide, but also, for example, the site of the interview or whether the interview can be audio-recorded) are tested with a small number of respondents, evaluated and revised [ 19 ]. In doing so, the interviewer learns which wording or types of questions work best, or which is the best length of an interview with patients who have trouble concentrating for an extended time. Of course, the same reasoning applies to observations or focus groups which can also be piloted.
Ideally, coding should be performed by at least two researchers, especially at the beginning of the coding process when a common approach must be defined, including the establishment of a useful coding list (or tree), and when a common meaning of individual codes must be established [ 23 ]. An initial sub-set or all transcripts can be coded independently by the coders and then compared and consolidated after regular discussions in the research team. This is to make sure that codes are applied consistently to the research data.
Member checking
Member checking, also called respondent validation , refers to the practice of checking back with study respondents to see if the research is in line with their views [ 14 , 27 ]. This can happen after data collection or analysis or when first results are available [ 23 ]. For example, interviewees can be provided with (summaries of) their transcripts and asked whether they believe this to be a complete representation of their views or whether they would like to clarify or elaborate on their responses [ 17 ]. Respondents’ feedback on these issues then becomes part of the data collection and analysis [ 27 ].
Stakeholder involvement
In those niches where qualitative approaches have been able to evolve and grow, a new trend has seen the inclusion of patients and their representatives not only as study participants (i.e. “members”, see above) but as consultants to and active participants in the broader research process [ 31 – 33 ]. The underlying assumption is that patients and other stakeholders hold unique perspectives and experiences that add value beyond their own single story, making the research more relevant and beneficial to researchers, study participants and (future) patients alike [ 34 , 35 ]. Using the example of patients on or nearing dialysis, a recent scoping review found that 80% of clinical research did not address the top 10 research priorities identified by patients and caregivers [ 32 , 36 ]. In this sense, the involvement of the relevant stakeholders, especially patients and relatives, is increasingly being seen as a quality indicator in and of itself.
How not to assess qualitative research
The above overview does not include certain items that are routine in assessments of quantitative research. What follows is a non-exhaustive, non-representative, experience-based list of the quantitative criteria often applied to the assessment of qualitative research, as well as an explanation of the limited usefulness of these endeavours.
Protocol adherence
Given the openness and flexibility of qualitative research, it should not be assessed by how well it adheres to pre-determined and fixed strategies – in other words: its rigidity. Instead, the assessor should look for signs of adaptation and refinement based on lessons learned from earlier steps in the research process.
Sample size
For the reasons explained above, qualitative research does not require specific sample sizes, nor does it require that the sample size be determined a priori [ 1 , 14 , 27 , 37 – 39 ]. Sample size can only be a useful quality indicator when related to the research purpose, the chosen methodology and the composition of the sample, i.e. who was included and why.
Randomisation
While some authors argue that randomisation can be used in qualitative research, this is not commonly the case, as neither its feasibility nor its necessity or usefulness has been convincingly established for qualitative research [ 13 , 27 ]. Relevant disadvantages include the negative impact of a too large sample size as well as the possibility (or probability) of selecting “ quiet, uncooperative or inarticulate individuals ” [ 17 ]. Qualitative studies do not use control groups, either.
Interrater reliability, variability and other “objectivity checks”
The concept of “interrater reliability” is sometimes used in qualitative research to assess to which extent the coding approach overlaps between the two co-coders. However, it is not clear what this measure tells us about the quality of the analysis [ 23 ]. This means that these scores can be included in qualitative research reports, preferably with some additional information on what the score means for the analysis, but it is not a requirement. Relatedly, it is not relevant for the quality or “objectivity” of qualitative research to separate those who recruited the study participants and collected and analysed the data. Experiences even show that it might be better to have the same person or team perform all of these tasks [ 20 ]. First, when researchers introduce themselves during recruitment this can enhance trust when the interview takes place days or weeks later with the same researcher. Second, when the audio-recording is transcribed for analysis, the researcher conducting the interviews will usually remember the interviewee and the specific interview situation during data analysis. This might be helpful in providing additional context information for interpretation of data, e.g. on whether something might have been meant as a joke [ 18 ].
Not being quantitative research
Being qualitative research instead of quantitative research should not be used as an assessment criterion if it is used irrespectively of the research problem at hand. Similarly, qualitative research should not be required to be combined with quantitative research per se – unless mixed methods research is judged as inherently better than single-method research. In this case, the same criterion should be applied for quantitative studies without a qualitative component.
The main take-away points of this paper are summarised in Table Table1. 1 . We aimed to show that, if conducted well, qualitative research can answer specific research questions that cannot to be adequately answered using (only) quantitative designs. Seeing qualitative and quantitative methods as equal will help us become more aware and critical of the “fit” between the research problem and our chosen methods: I can conduct an RCT to determine the reasons for transportation delays of acute stroke patients – but should I? It also provides us with a greater range of tools to tackle a greater range of research problems more appropriately and successfully, filling in the blind spots on one half of the methodological spectrum to better address the whole complexity of neurological research and practice.
Take-away-points
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations, authors’ contributions.
LB drafted the manuscript; WW and CG revised the manuscript; all authors approved the final versions.
no external funding.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Find My Rep
You are here
Doing Document Analysis A Practice-Oriented Method
- Kristin Asdal - University of Oslo, Norway
- Hilde Reinertsen - University of Oslo (Norway)
- Description
Uniting methods from disciplines across the social sciences and humanities, this hands-on guide develops a novel approach to doing document analysis. The authors present a framework for studying documents that enables you to conduct a rich and systematic analysis of documents in all their diversity.
Focussing on document analysis both in practice and as practice, the book provides you with an innovative and versatile toolkit for analysing print and digital documents. It also:
- Highlights the impacts of digitalisation on documents themselves and the methods used to study them
- Has a strong focus on research ethics and critical engagement with digital sources
- Offers practical guidance on preparing and doing a document analysis research project.
The book offers insightful perspectives both on the indispensable role of documents in our society and practical advice on how you can best analyse documents and their significance.
Supplements
Social science has increasingly turned to document practices to understand the social processes. But this book actually explains how to do it! Systematic and brimming with insights, this will be an invaluable guide for researchers in fields from history to anthropology and science and technology.
Documents weave through practices. They help to make the world. But how to analyse them? In this beautiful but thoroughly down-to-earth book Asdal and Reinertsen have created an indispensable guide to the ins and outs of analysing documents in practice. Highly recommended.
This is a fascinating, clearly written and much needed guide to the often overlooked world of documents. Ideal for students, researchers and experienced academics, this book will be an invaluable resource to anyone interested in researching the role documents play in the societies in which we live.
Asdal and Reinertsen provide a cutting-edge but also hands-on introduction to analysing documents that is accessible to an interdisciplinary audience. I have never recommended as many students to get a book as soon as it is out.
Preview this book
For instructors.
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
- Electronic Order Options VitalSource Amazon Kindle Google Play eBooks.com Kobo

Related Products

Research Methodology in Education
- Get Edit Link
- The Writing Space
- Welcome Desk

March 9, 2016
- An Introduction to Document Analysis
Introduction
Document analysis is a form of qualitative research in which documents are interpreted by the researcher to give voice and meaning around an assessment topic (Bowen, 2009). Analyzing documents incorporates coding content into themes similar to how focus group or interview transcripts are analyzed (Bowen,2009). A rubric can also be used to grade or score document. There are three primary types of documents (O’Leary, 2014):
- Public Records: The official, ongoing records of an organization’s activities. Examples include student transcripts, mission statements, annual reports, policy manuals, student handbooks, strategic plans, and syllabi.
- Personal Documents: First-person accounts of an individual’s actions, experiences, and beliefs. Examples include calendars, e-mails, scrapbooks, blogs, Facebook posts, duty logs, incident reports, reflections/journals, and newspapers.
- Physical Evidence: Physical objects found within the study setting (often called artifacts). Examples include flyers, posters, agendas, handbooks, and training materials.
Document analysis is a social research method and is an important research tool in its own right, and is an invaluable part of most schemes of triangulation, the combination of methodologies in the study of the same phenomenon (Bowen, 2009). In order to seek convergence and corroboration, qualitative researchers usually use at least two resources through using different data sources and methods. The purpose of triangulating is to provide a confluence of evidence that breeds credibility (Bowen, 2009). Corroborating findings across data sets can reduce the impact of potential bias by examining information collected through different methods. Also, combining qualitative and quantitative sometimes included in document analysis called mixed-methods studies.
Before actual document analysis takes place, the researcher must go through a detailed planning process in order to ensure reliable results. O’Leary outlines an 8-step planning process that should take place not just in document analysis, but all textual analysis (2014):
- Create a list of texts to explore (e.g., population, samples, respondents, participants).
- Consider how texts will be accessed with attention to linguistic or cultural barriers.
- Acknowledge and address biases.
- Develop appropriate skills for research.
- Consider strategies for ensuring credibility.
- Know the data one is searching for.
- Consider ethical issues (e.g., confidential documents).
- Have a backup plan.
A researcher can use a huge plethora of texts for research, although by far the most common is likely to be the use of written documents (O’Leary, 2014). There is the question of how many documents the researcher should gather. Bowen suggests that a wide array of documents is better, although the question should be more about quality of the document rather than quantity (Bowen, 2009). O’Leary also introduces two major issues to consider when beginning document analysis. The first is the issue of bias, both in the author or creator of the document, and the researcher as well (2014). The researcher must consider the subjectivity of the author and also the personal biases he or she may be bringing to the research. Bowen adds that the researcher must evaluate the original purpose of the document, such as the target audience (2009). He or she should also consider whether the author was a firsthand witness or used secondhand sources. Also important is determining whether the document was solicited, edited, and/or anonymous (Bowen, 2009). O’Leary’s second major issue is the “unwitting” evidence, or latent content, of the document. Latent content refers to the style, tone, agenda, facts or opinions that exist in the document. This is a key first step that the researcher must keep in mind (O’Leary, 2014). Bowen adds that documents should be assessed for their completeness; in other words, how selective or comprehensive their data is (2009). Also of paramount importance when evaluating documents is not to consider the data as “necessarily precise, accurate, or complete recordings of events that have occurred” (Bowen, 2009, p. 33). These issues are summed up in another eight-step process offered by O’Leary (2014):
- Gather relevant texts.
- Develop an organization and management scheme.
- Make copies of the originals for annotation.
- Asses authenticity of documents.
- Explore document’s agenda, biases.
- Explore background information (e.g., tone, style, purpose).
- Ask questions about document (e.g., Who produced it? Why? When? Type of data?).
- Explore content.
Step eight refers to the process of exploring the “witting” evidence, or the actual content of the documents, and O’Leary gives two major techniques for accomplishing this (2014). One is the interview technique. In this case, the researcher treats the document like a respondent or informant that provides the researcher with relevant information (O’Leary, 2014). The researcher “asks” questions then highlights the answer within the text. The other technique is noting occurrences, or content analysis, where the researcher quantifies the use of particular words, phrases and concepts (O’Leary, 2014). Essentially, the researcher determines what is being searched for, then documents and organizes the frequency and amount of occurrences within the document. The information is then organized into what is “related to central questions of the research” (Bowen, 2009, p. 32). Bowen notes that some experts object to this kind of analysis, saying that it obscures the interpretive process in the case of interview transcriptions (Bowen, 2009). However, Bowen reminds us that documents include a wide variety of types, and content analysis can be very useful for painting a broad, overall picture (2009). According to Bowen (2009), content analysis, then, is used as a “first-pass document review” (p. 32) that can provide the researcher a means of identifying meaningful and relevant passages.
In addition to content analysis, Bowen also notes thematic analysis, which can be considered a form of pattern recognition with the document’s data (2009). This analysis takes emerging themes and makes them into categories used for further analysis, making it a useful practice for grounded theory. It includes careful, focused reading and re-reading of data, as well as coding and category construction (Bowen, 2009). The emerging codes and themes may also serve to “integrate data gathered by different methods” (Bowen, 2009, p. 32). Bowen sums up the overall concept of document analysis as a process of “evaluating documents in such a way that empirical knowledge is produced and understanding is developed” (2009, p. 33). It is not just a process of lining up a collection of excerpts that convey whatever the researcher desires. The researcher must maintain a high level of objectivity and sensitivity in order for the document analysis results to be credible and valid (Bowen, 2009).
The Advantages of Document Analysis
There are many reasons why researchers choose to use document analysis. Firstly, document analysis is an efficient and effective way of gathering data because documents are manageable and practical resources. Documents are commonplace and come in a variety of forms, making documents a very accessible and reliable source of data. Obtaining and analysing documents is often far more cost efficient and time efficient than conducting your own research or experiments (Bowen, 2009). Also, documents are stable, “non-reactive” data sources, meaning that they can be read and reviewed multiple times and remain unchanged by the researcher’s influence or research process (Bowen, 2009, p. 31).
Document analysis is often used because of the many different ways it can support and strengthen research. Document analysis can be used in many different fields of research, as either a primary method of data collection or as a compliment to other methods. Documents can provide supplementary research data, making document analysis a useful and beneficial method for most research. Documents can provide background information and broad coverage of data, and are therefore helpful in contextualizing one’s research within its subject or field (Bowen, 2009). Documents can also contain data that no longer can be observed, provide details that informants have forgotten, and can track change and development. Document analysis can also point to questions that need to be asked or to situations that need to be observed, making the use of document analysis a way to ensure your research is critical and comprehensive (Bowen, 2009).
Concerns to Keep in Mind When Using Document Analysis
The disadvantages of using document analysis are not so much limitations as they are potential concerns to be aware of before choosing the method or when using it. An initial concern to consider is that documents are not created with data research agendas and therefore require some investigative skills. A document will not perfectly provide all of the necessary information required to answer your research questions. Some documents may only provide a small amount of useful data or sometimes none at all. Other documents may be incomplete, or their data may be inaccurate or inconsistent. Sometimes there are gaps or sparseness of documents, leading to more searching or reliance on additional documents then planned (Bowen, 2009). Also, some documents may not be available or easily accessible. For these reasons, it is important to evaluate the quality of your documents and to be prepared to encounter some challenges or gaps when employing document analysis.
Another concern to be aware of before beginning document analysis, and to keep in mind during, is the potential presence of biases, both in a document and from the researcher. Both Bowen and O’Leary state that it is important to thoroughly evaluate and investigate the subjectivity of documents and your understanding of their data in order to preserve the credibility of your research (2009; 2014).
The reason that the issues surrounding document analysis are concerns and not disadvantages is that they can be easily avoided by having a clear process that incorporates evaluative steps and measures, as previously mentioned above and exemplified by O’Leary’s two eight-step processes. As long as a researcher begins document analysis knowing what the method entails and has a clear process planned, the advantages of document analysis are likely to far outweigh the amount of issues that may arise.
References:
Bowen, G. A. (2009). Document analysis as a qualitative research method. Qualitative Research Journal, 9(2), 27-40. doi:10.3316/QRJ0902027 O’Leary, Z. (2014). The essential guide to doing your research project (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
And So It Was Written

Author: Triad 3
Published: March 9, 2016
Word Count: 1626

ORGANIZED BY
More to read, add yours →.
I found the document so interesting. Thank you
Dear Triad Your article was very insightful. I am currently researching about document analysis to make it my methodology strategy to analyze a web application. I would be glad if you had any more material regarding this subject to share.
Very helpful.
Thank you for this valuable information. I request for more such information in qualitative analysis.
I benefited from this article so much . thank you for taking your time to write and share it.
This is really helpful for understanding the basic concept of document analysis. Really impressive!
This is one of the good way to remove difficulties during writing the research
Hi, valuable information herein. My research is qualitative and I want to take a number of pictures which I will then use to formulate questions for the interview guide. My question is this, how do I formulate the document analysis checklist?
Regards, Nancy
Comments are closed.
Recently Written
- Observation: Not As Simple As You Thought (ADK)
- RESEARCH TOOLS: INTERVIEWS & QUESTIONNAIRES
- Grounded Theory: A Down-to-Earth Explanation
- Assignment (10)
View by Date Published
Search writings.
A TRU Writer powered SPLOT : Research Methodology in Education
Blame @cogdog — Up ↑
Document analysis in health policy research: the READ approach
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of International Health, Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, 615 N. Wolfe St, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
- 2 Institute for Global Health, University College London, Institute for Global Health 3rd floor, 30 Guilford Street, London WC1N 1EH, UK.
- 3 School of Humanities and Social Sciences, Information Technology University, Arfa Software Technology Park, Ferozepur Road, Lahore 54000, Pakistan.
- 4 Heidelberg Institute of Global Health, Medical Faculty and University Hospital, University of Heidelberg, Im Neuenheimer Feld 130/3, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany.
- PMID: 33175972
- PMCID: PMC7886435
- DOI: 10.1093/heapol/czaa064
Document analysis is one of the most commonly used and powerful methods in health policy research. While existing qualitative research manuals offer direction for conducting document analysis, there has been little specific discussion about how to use this method to understand and analyse health policy. Drawing on guidance from other disciplines and our own research experience, we present a systematic approach for document analysis in health policy research called the READ approach: (1) ready your materials, (2) extract data, (3) analyse data and (4) distil your findings. We provide practical advice on each step, with consideration of epistemological and theoretical issues such as the socially constructed nature of documents and their role in modern bureaucracies. We provide examples of document analysis from two case studies from our work in Pakistan and Niger in which documents provided critical insight and advanced empirical and theoretical understanding of a health policy issue. Coding tools for each case study are included as Supplementary Files to inspire and guide future research. These case studies illustrate the value of rigorous document analysis to understand policy content and processes and discourse around policy, in ways that are either not possible using other methods, or greatly enrich other methods such as in-depth interviews and observation. Given the central nature of documents to health policy research and importance of reading them critically, the READ approach provides practical guidance on gaining the most out of documents and ensuring rigour in document analysis.
Keywords: Health policy; health systems research; interdisciplinary; methods; policy; policy analysis; policy research; qualitative; research methods; social sciences.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press in association with The London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
- Health Policy*
- Policy Making
- Qualitative Research
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- Supplements
- Open Access Articles
- Research Collections
- Review Collections
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access Options
- Self-Archiving Policy
- About Health Policy and Planning
- About the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
- HPP at a glance
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Introduction, what is document analysis, the read approach, supplementary data, acknowledgements.
- < Previous
Document analysis in health policy research: the READ approach
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
Sarah L Dalglish, Hina Khalid, Shannon A McMahon, Document analysis in health policy research: the READ approach, Health Policy and Planning , Volume 35, Issue 10, December 2020, Pages 1424–1431, https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czaa064
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Document analysis is one of the most commonly used and powerful methods in health policy research. While existing qualitative research manuals offer direction for conducting document analysis, there has been little specific discussion about how to use this method to understand and analyse health policy. Drawing on guidance from other disciplines and our own research experience, we present a systematic approach for document analysis in health policy research called the READ approach: (1) ready your materials, (2) extract data, (3) analyse data and (4) distil your findings. We provide practical advice on each step, with consideration of epistemological and theoretical issues such as the socially constructed nature of documents and their role in modern bureaucracies. We provide examples of document analysis from two case studies from our work in Pakistan and Niger in which documents provided critical insight and advanced empirical and theoretical understanding of a health policy issue. Coding tools for each case study are included as Supplementary Files to inspire and guide future research. These case studies illustrate the value of rigorous document analysis to understand policy content and processes and discourse around policy, in ways that are either not possible using other methods, or greatly enrich other methods such as in-depth interviews and observation. Given the central nature of documents to health policy research and importance of reading them critically, the READ approach provides practical guidance on gaining the most out of documents and ensuring rigour in document analysis.
Rigour in qualitative research is judged partly by the use of deliberate, systematic procedures; however, little specific guidance is available for analysing documents, a nonetheless common method in health policy research.
Document analysis is useful for understanding policy content across time and geographies, documenting processes, triangulating with interviews and other sources of data, understanding how information and ideas are presented formally, and understanding issue framing, among other purposes.
The READ (Ready materials, Extract data, Analyse data, Distil) approach provides a step-by-step guide to conducting document analysis for qualitative policy research.
The READ approach can be adapted to different purposes and types of research, two examples of which are presented in this article, with sample tools in the Supplementary Materials .
Document analysis (also called document review) is one of the most commonly used methods in health policy research; it is nearly impossible to conduct policy research without it. Writing in early 20th century, Weber (2015) identified the importance of formal, written documents as a key characteristic of the bureaucracies by which modern societies function, including in public health. Accordingly, critical social research has a long tradition of documentary review: Marx analysed official reports, laws, statues, census reports and newspapers and periodicals over a nearly 50-year period to come to his world-altering conclusions ( Harvey, 1990 ). Yet in much of social science research, ‘documents are placed at the margins of consideration,’ with privilege given to the spoken word via methods such as interviews, possibly due to the fact that many qualitative methods were developed in the anthropological tradition to study mainly pre-literate societies ( Prior, 2003 ). To date, little specific guidance is available to help health policy researchers make the most of these wells of information.
The term ‘documents’ is defined here broadly, following Prior, as physical or virtual artefacts designed by creators, for users, to function within a particular setting ( Prior, 2003 ). Documents exist not as standalone objects of study but must be understood in the social web of meaning within which they are produced and consumed. For example, some analysts distinguish between public documents (produced in the context of public sector activities), private documents (from business and civil society) and personal documents (created by or for individuals, and generally not meant for public consumption) ( Mogalakwe, 2009 ). Documents can be used in a number of ways throughout the research process ( Bowen, 2009 ). In the planning or study design phase, they can be used to gather background information and help refine the research question. Documents can also be used to spark ideas for disseminating research once it is complete, by observing the ways those who will use the research speak to and communicate ideas with one another.
Documents can also be used during data collection and analysis to help answer research questions. Recent health policy research shows that this can be done in at least four ways. Frequently, policy documents are reviewed to describe the content or categorize the approaches to specific health problems in existing policies, as in reviews of the composition of drowning prevention resources in the United States or policy responses to foetal alcohol spectrum disorder in South Africa ( Katchmarchi et al. , 2018 ; Adebiyi et al. , 2019 ). In other cases, non-policy documents are used to examine the implementation of health policies in real-world settings, as in a review of web sources and newspapers analysing the functioning of community health councils in New Zealand ( Gurung et al. , 2020 ). Perhaps less frequently, document analysis is used to analyse policy processes, as in an assessment of multi-sectoral planning process for nutrition in Burkina Faso ( Ouedraogo et al. , 2020 ). Finally, and most broadly, document analysis can be used to inform new policies, as in one study that assessed cigarette sticks as communication and branding ‘documents,’ to suggest avenues for further regulation and tobacco control activities ( Smith et al. , 2017 ).
This practice paper provides an overarching method for conducting document analysis, which can be adapted to a multitude of research questions and topics. Document analysis is used in most or all policy studies; the aim of this article is to provide a systematized method that will enhance procedural rigour. We provide an overview of document analysis, drawing on guidance from disciplines adjacent to public health, introduce the ‘READ’ approach to document analysis and provide two short case studies demonstrating how document analysis can be applied.
Document analysis is a systematic procedure for reviewing or evaluating documents, which can be used to provide context, generate questions, supplement other types of research data, track change over time and corroborate other sources ( Bowen, 2009 ). In one commonly cited approach in social research, Bowen recommends first skimming the documents to get an overview, then reading to identify relevant categories of analysis for the overall set of documents and finally interpreting the body of documents ( Bowen, 2009 ). Document analysis can include both quantitative and qualitative components: the approach presented here can be used with either set of methods, but we emphasize qualitative ones, which are more adapted to the socially constructed meaning-making inherent to collaborative exercises such as policymaking.
The study of documents as a research method is common to a number of social science disciplines—yet in many of these fields, including sociology ( Mogalakwe, 2009 ), anthropology ( Prior, 2003 ) and political science ( Wesley, 2010 ), document-based research is described as ill-considered and underutilized. Unsurprisingly, textual analysis is perhaps most developed in fields such as media studies, cultural studies and literary theory, all disciplines that recognize documents as ‘social facts’ that are created, consumed, shared and utilized in socially organized ways ( Atkinson and Coffey, 1997 ). Documents exist within social ‘fields of action,’ a term used to designate the environments within which individuals and groups interact. Documents are therefore not mere records of social life, but integral parts of it—and indeed can become agents in their own right ( Prior, 2003 ). Powerful entities also manipulate the nature and content of knowledge; therefore, gaps in available information must be understood as reflecting and potentially reinforcing societal power relations ( Bryman and Burgess, 1994 ).
Document analysis, like any research method, can be subject to concerns regarding validity, reliability, authenticity, motivated authorship, lack of representativity and so on. However, these can be mitigated or avoided using standard techniques to enhance qualitative rigour, such as triangulation (within documents and across methods and theoretical perspectives), ensuring adequate sample size or ‘engagement’ with the documents, member checking, peer debriefing and so on ( Maxwell, 2005 ).
Document analysis can be used as a standalone method, e.g. to analyse the contents of specific types of policy as they evolve over time and differ across geographies, but document analysis can also be powerfully combined with other types of methods to cross-validate (i.e. triangulate) and deepen the value of concurrent methods. As one guide to public policy research puts it, ‘almost all likely sources of information, data, and ideas fall into two general types: documents and people’ ( Bardach and Patashnik, 2015 ). Thus, researchers can ask interviewees to address questions that arise from policy documents and point the way to useful new documents. Bardach and Patashnik suggest alternating between documents and interviews as sources as information, as one tends to lead to the other, such as by scanning interviewees’ bookshelves and papers for titles and author names ( Bardach and Patashnik, 2015 ). Depending on your research questions, document analysis can be used in combination with different types of interviews ( Berner-Rodoreda et al. , 2018 ), observation ( Harvey, 2018 ), and quantitative analyses, among other common methods in policy research.
The READ approach to document analysis is a systematic procedure for collecting documents and gaining information from them in the context of health policy studies at any level (global, national, local, etc.). The steps consist of: (1) ready your materials, (2) extract data, (3) analyse data and (4) distil your findings. We describe each of these steps in turn.
Step 1. Ready your materials
At the outset, researchers must set parameters in terms of the nature and number (approximately) of documents they plan to analyse, based on the research question. How much time will you allocate to the document analysis, and what is the scope of your research question? Depending on the answers to these questions, criteria should be established around (1) the topic (a particular policy, programme, or health issue, narrowly defined according to the research question); (2) dates of inclusion (whether taking the long view of several decades, or zooming in on a specific event or period in time); and (3) an indicative list of places to search for documents (possibilities include databases such as Ministry archives; LexisNexis or other databases; online searches; and particularly interview subjects). For difficult-to-obtain working documents or otherwise non-public items, bringing a flash drive to interviews is one of the best ways to gain access to valuable documents.
For research focusing on a single policy or programme, you may review only a handful of documents. However, if you are looking at multiple policies, health issues, or contexts, or reviewing shorter documents (such as newspaper articles), you may look at hundreds, or even thousands of documents. When considering the number of documents you will analyse, you should make notes on the type of information you plan to extract from documents—i.e. what it is you hope to learn, and how this will help answer your research question(s). The initial criteria—and the data you seek to extract from documents—will likely evolve over the course of the research, as it becomes clear whether they will yield too few documents and information (a rare outcome), far too many documents and too much information (a much more common outcome) or documents that fail to address the research question; however, it is important to have a starting point to guide the search. If you find that the documents you need are unavailable, you may need to reassess your research questions or consider other methods of inquiry. If you have too many documents, you can either analyse a subset of these ( Panel 1 ) or adopt more stringent inclusion criteria.
Exploring the framing of diseases in Pakistani media
In Table 1 , we present a non-exhaustive list of the types of documents that can be included in document analyses of health policy issues. In most cases, this will mean written sources (policies, reports, articles). The types of documents to be analysed will vary by study and according to the research question, although in many cases, it will be useful to consult a mix of formal documents (such as official policies, laws or strategies), ‘gray literature’ (organizational materials such as reports, evaluations and white papers produced outside formal publication channels) and, whenever possible, informal or working documents (such as meeting notes, PowerPoint presentations and memoranda). These latter in particular can provide rich veins of insight into how policy actors are thinking through the issues under study, particularly for the lucky researcher who obtains working documents with ‘Track Changes.’ How you prioritize documents will depend on your research question: you may prioritize official policy documents if you are studying policy content, or you may prioritize informal documents if you are studying policy process.
Types of documents that can be consulted in studies of health policy
During this initial preparatory phase, we also recommend devising a file-naming system for your documents (e.g. Author.Date.Topic.Institution.PDF), so that documents can be easily retrieved throughout the research process. After extracting data and processing your documents the first time around, you will likely have additional ‘questions’ to ask your documents and need to consult them again. For this reason, it is important to clearly name source files and link filenames to the data that you are extracting (see sample naming conventions in the Supplementary Materials ).
Step 2. Extract data
Data can be extracted in a number of ways, and the method you select for doing so will depend on your research question and the nature of your documents. One simple way is to use an Excel spreadsheet where each row is a document and each column is a category of information you are seeking to extract, from more basic data such as the document title, author and date, to theoretical or conceptual categories deriving from your research question, operating theory or analytical framework (Panel 2). Documents can also be imported into thematic coding software such as Atlas.ti or NVivo, and data extracted that way. Alternatively, if the research question focuses on process, documents can be used to compile a timeline of events, to trace processes across time. Ask yourself, how can I organize these data in the most coherent manner? What are my priority categories? We have included two different examples of data extraction tools in the Supplementary Materials to this article to spark ideas.
Case study Documents tell part of the story in Niger
Document analyses are first and foremost exercises in close reading: documents should be read thoroughly, from start to finish, including annexes, which may seem tedious but which sometimes produce golden nuggets of information. Read for overall meaning as you extract specific data related to your research question. As you go along, you will begin to have ideas or build working theories about what you are learning and observing in the data. We suggest capturing these emerging theories in extended notes or ‘memos,’ as used in Grounded Theory methodology ( Charmaz, 2006 ); these can be useful analytical units in themselves and can also provide a basis for later report and article writing.
As you read more documents, you may find that your data extraction tool needs to be modified to capture all the relevant information (or to avoid wasting time capturing irrelevant information). This may require you to go back and seek information in documents you have already read and processed, which will be greatly facilitated by a coherent file-naming system. It is also useful to keep notes on other documents that are mentioned that should be tracked down (sometimes you can write the author for help). As a general rule, we suggest being parsimonious when selecting initial categories to extract from data. Simply reading the documents takes significant time in and of itself—make sure you think about how, exactly, the specific data you are extracting will be used and how it goes towards answering your research questions.
Step 3. Analyse data
As in all types of qualitative research, data collection and analysis are iterative and characterized by emergent design, meaning that developing findings continually inform whether and how to obtain and interpret data ( Creswell, 2013 ). In practice, this means that during the data extraction phase, the researcher is already analysing data and forming initial theories—as well as potentially modifying document selection criteria. However, only when data extraction is complete can one see the full picture. For example, are there any documents that you would have expected to find, but did not? Why do you think they might be missing? Are there temporal trends (i.e. similarities, differences or evolutions that stand out when documents are ordered chronologically)? What else do you notice? We provide a list of overarching questions you should think about when viewing your body of document as a whole ( Table 2 ).
Questions to ask your overall body of documents

HIV and viral hepatitis articles by main frames (%). Note: The percentage of articles is calculated by dividing the number of articles appearing in each frame for viral hepatitis and HIV by the respectivenumber of sampled articles for each disease (N = 137 for HIV; N = 117 for hepatitis). Time frame: 1 January 2006 to 30 September 2016

Representations of progress toward Millennium Development Goal 4 in Nigerien policy documents. Sources: clockwise from upper left: ( WHO 2006 ); ( Institut National de la Statistique 2010 ); ( Ministè re de la Santé Publique 2010 ); ( Unicef 2010 )
In addition to the meaning-making processes you are already engaged in during the data extraction process, in most cases, it will be useful to apply specific analysis methodologies to the overall corpus of your documents, such as policy analysis ( Buse et al. , 2005 ). An array of analysis methodologies can be used, both quantitative and qualitative, including case study methodology, thematic content analysis, discourse analysis, framework analysis and process tracing, which may require differing levels of familiarity and skills to apply (we highlight a few of these in the case studies below). Analysis can also be structured according to theoretical approaches. When it comes to analysing policies, process tracing can be particularly useful to combine multiple sources of information, establish a chronicle of events and reveal political and social processes, so as to create a narrative of the policy cycle ( Yin, 1994 ; Shiffman et al. , 2004 ). Practically, you will also want to take a holistic view of the documents’ ‘answers’ to the questions or analysis categories you applied during the data extraction phase. Overall, what did the documents ‘say’ about these thematic categories? What variation did you find within and between documents, and along which axes? Answers to these questions are best recorded by developing notes or memos, which again will come in handy as you write up your results.
As with all qualitative research, you will want to consider your own positionality towards the documents (and their sources and authors); it may be helpful to keep a ‘reflexivity’ memo documenting how your personal characteristics or pre-standing views might influence your analysis ( Watt, 2007 ).
Step 4. Distil your findings
You will know when you have completed your document review when one of the three things happens: (1) completeness (you feel satisfied you have obtained every document fitting your criteria—this is rare), (2) out of time (this means you should have used more specific criteria), and (3) saturation (you fully or sufficiently understand the phenomenon you are studying). In all cases, you should strive to make the third situation the reason for ending your document review, though this will not always mean you will have read and analysed every document fitting your criteria—just enough documents to feel confident you have found good answers to your research questions.
Now it is time to refine your findings. During the extraction phase, you did the equivalent of walking along the beach, noticing the beautiful shells, driftwood and sea glass, and picking them up along the way. During the analysis phase, you started sorting these items into different buckets (your analysis categories) and building increasingly detailed collections. Now you have returned home from the beach, and it is time to clean your objects, rinse them of sand and preserve only the best specimens for presentation. To do this, you can return to your memos, refine them, illustrate them with graphics and quotes and fill in any incomplete areas. It can also be illuminating to look across different strands of work: e.g. how did the content, style, authorship, or tone of arguments evolve over time? Can you illustrate which words, concepts or phrases were used by authors or author groups?
Results will often first be grouped by theoretical or analytic category, or presented as a policy narrative, interweaving strands from other methods you may have used (interviews, observation, etc.). It can also be helpful to create conceptual charts and graphs, especially as this corresponds to your analytical framework (Panels 1 and 2). If you have been keeping a timeline of events, you can seek out any missing information from other sources. Finally, ask yourself how the validity of your findings checks against what you have learned using other methods. The final products of the distillation process will vary by research study, but they will invariably allow you to state your findings relative to your research questions and to draw policy-relevant conclusions.
Document analysis is an essential component of health policy research—it is also relatively convenient and can be low cost. Using an organized system of analysis enhances the document analysis’s procedural rigour, allows for a fuller understanding of policy process and content and enhances the effectiveness of other methods such as interviews and non-participant observation. We propose the READ approach as a systematic method for interrogating documents and extracting study-relevant data that is flexible enough to accommodate many types of research questions. We hope that this article encourages discussion about how to make best use of data from documents when researching health policy questions.
Supplementary data are available at Health Policy and Planning online.
The data extraction tool in the Supplementary Materials for the iCCM case study (Panel 2) was conceived of by the research team for the multi-country study ‘Policy Analysis of Community Case Management for Childhood and Newborn Illnesses’. The authors thank Sara Bennett and Daniela Rodriguez for granting permission to publish this tool. S.M. was supported by The Olympia-Morata-Programme of Heidelberg University. The funders had no role in the decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The content is the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the views of any funder.
Conflict of interest statement . None declared.
Ethical approval. No ethical approval was required for this study.
Abdelmutti N , Hoffman-Goetz L. 2009 . Risk messages about HPV, cervical cancer, and the HPV vaccine Gardasil: a content analysis of Canadian and U.S. national newspaper articles . Women & Health 49 : 422 – 40 .
Google Scholar
Adebiyi BO , Mukumbang FC , Beytell A-M. 2019 . To what extent is fetal alcohol spectrum disorder considered in policy-related documents in South Africa? A document review . Health Research Policy and Systems 17 :
Atkinson PA , Coffey A. 1997 . Analysing documentary realities. In: Silverman D (ed). Qualitative Research: Theory, Method and Practice . London : SAGE .
Google Preview
Bardach E , Patashnik EM. 2015 . Practical Guide for Policy Analysis: The Eightfold Path to More Effective Problem Solving . Los Angeles : SAGE .
Bennett S , Dalglish SL , Juma PA , Rodríguez DC. 2015 . Altogether now… understanding the role of international organizations in iCCM policy transfer . Health Policy and Planning 30 : ii26 – 35 .
Berner-Rodoreda A , Bärnighausen T , Kennedy C et al. 2018 . From doxastic to epistemic: a typology and critique of qualitative interview styles . Qualitative Inquiry 26 : 291 – 305 . 1077800418810724.
Bowen GA. 2009 . Document analysis as a qualitative research method . Qualitative Research Journal 9 : 27 – 40 .
Bryman A. 1994 . Analyzing Qualitative Data .
Buse K , Mays N , Walt G. 2005 . Making Health Policy . New York : Open University Press .
Charmaz K. 2006 . Constructing Grounded Theory: A Practical Guide through Qualitative Analysis . London : SAGE .
Claassen L , Smid T , Woudenberg F , Timmermans DRM. 2012 . Media coverage on electromagnetic fields and health: content analysis of Dutch newspaper articles and websites . Health, Risk & Society 14 : 681 – 96 .
Creswell JW. 2013 . Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design . Thousand Oaks, CA : SAGE .
Dalglish SL , Rodríguez DC , Harouna A , Surkan PJ. 2017 . Knowledge and power in policy-making for child survival in Niger . Social Science & Medicine 177 : 150 – 7 .
Dalglish SL , Surkan PJ , Diarra A , Harouna A , Bennett S. 2015 . Power and pro-poor policies: the case of iCCM in Niger . Health Policy and Planning 30 : ii84 – 94 .
Entman RM. 1993 . Framing: toward clarification of a fractured paradigm . Journal of Communication 43 : 51 – 8 .
Fournier G , Djermakoye IA. 1975 . Village health teams in Niger (Maradi Department). In: Newell KW (ed). Health by the People . Geneva : WHO .
Gurung G , Derrett S , Gauld R. 2020 . The role and functions of community health councils in New Zealand’s health system: a document analysis . The New Zealand Medical Journal 133 : 70 – 82 .
Harvey L. 1990 . Critical Social Research . London : Unwin Hyman .
Harvey SA. 2018 . Observe before you leap: why observation provides critical insights for formative research and intervention design that you’ll never get from focus groups, interviews, or KAP surveys . Global Health: Science and Practice 6 : 299 – 316 .
Institut National de la Statistique. 2010. Rapport National sur les Progrès vers l'atteinte des Objectifs du Millénaire pour le Développement. Niamey, Niger: INS.
Kamarulzaman A. 2013 . Fighting the HIV epidemic in the Islamic world . Lancet 381 : 2058 – 60 .
Katchmarchi AB , Taliaferro AR , Kipfer HJ. 2018 . A document analysis of drowning prevention education resources in the United States . International Journal of Injury Control and Safety Promotion 25 : 78 – 84 .
Krippendorff K. 2004 . Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology . SAGE .
Marten R. 2019 . How states exerted power to create the Millennium Development Goals and how this shaped the global health agenda: lessons for the sustainable development goals and the future of global health . Global Public Health 14 : 584 – 99 .
Maxwell JA. 2005 . Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach , 2 nd edn. Thousand Oaks, CA : Sage Publications .
Mayring P. 2004 . Qualitative Content Analysis . In: Flick U, von Kardorff E, Steinke I (eds). A Companion to Qualitative Research . SAGE .
Ministère de la Santé Publique. 2010. Enquête nationale sur la survie des enfants de 0 à 59 mois et la mortalité au Niger 2010. Niamey, Niger: MSP.
Mogalakwe M. 2009 . The documentary research method—using documentary sources in social research . Eastern Africa Social Science Research Review 25 : 43 – 58 .
Nelkin D. 1991 . AIDS and the news media . The Milbank Quarterly 69 : 293 – 307 .
Ouedraogo O , Doudou MH , Drabo KM et al. 2020 . Policy overview of the multisectoral nutrition planning process: the progress, challenges, and lessons learned from Burkina Faso . The International Journal of Health Planning and Management 35 : 120 – 39 .
Prior L. 2003 . Using Documents in Social Research . London: SAGE .
Shiffman J , Stanton C , Salazar AP. 2004 . The emergence of political priority for safe motherhood in Honduras . Health Policy and Planning 19 : 380 – 90 .
Smith KC , Washington C , Welding K et al. 2017 . Cigarette stick as valuable communicative real estate: a content analysis of cigarettes from 14 low-income and middle-income countries . Tobacco Control 26 : 604 – 7 .
Strömbäck J , Dimitrova DV. 2011 . Mediatization and media interventionism: a comparative analysis of Sweden and the United States . The International Journal of Press/Politics 16 : 30 – 49 .
UNICEF. 2010. Maternal, Newborn & Child Surival Profile. Niamey, Niger: UNICEF
Watt D. 2007 . On becoming a qualitative researcher: the value of reflexivity . Qualitative Report 12 : 82 – 101 .
Weber M. 2015 . Bureaucracy. In: Waters T , Waters D (eds). Rationalism and Modern Society: New Translations on Politics, Bureaucracy, and Social Stratification . London : Palgrave MacMillan .
Wesley JJ. 2010 . Qualitative Document Analysis in Political Science.
World Health Organization. 2006. Country Health System Fact Sheet 2006: Niger. Niamey, Niger: WHO.
Yin R. 1994 . Case Study Research: Design and Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA : Sage .
Supplementary data
Email alerts, citing articles via.
- Recommend to Your Librarian
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1460-2237
- Copyright © 2024 The London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Application of the DEMATEL method for quantitative analysis of risk factors for railway investments in Poland
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Institute of Civil Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences-SGGW, Warsaw, Poland
Roles Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing
Roles Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Institute of Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences-SGGW, Warsaw, Poland
- Jan Kowalski,
- Marzena Lendo-Siwicka,
- Zdzisław Skutnik,
- Dorota Mirosław-Świątek

- Published: May 23, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606
- Reader Comments
The paper presents the results of research on the influence of risk factors on the implementation of railway investments in Poland (build stage) and deals with a detailed diagnosis of relation between factors. The application of DEcision MAking Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) method for the analyses allowed to develop a cause-and-effect model of key factors and analyse the importance of the factors. Eleven factors identified in eariel studies as the most important risk factors were examined. It was found that the factors: errors in the preparation of tender documents (10.38%), errors in project documentation (10.02%), improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer (9.82%), internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts (9.51%) have the highest degree of importance. Factors: too many external institutions involved in the investment process and internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts, have the greatest net impact on the other factors. The relations between the factors and factors importance are valuable knowledge for engineers, enabling the project to be implemented according to the planned schedule and investment cost.
Citation: Kowalski J, Lendo-Siwicka M, Skutnik Z, Mirosław-Świątek D (2024) Application of the DEMATEL method for quantitative analysis of risk factors for railway investments in Poland. PLoS ONE 19(5): e0303606. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606
Editor: Abel C.H. Chen, Chunghwa Telecom Co. Ltd., TAIWAN
Received: November 22, 2023; Accepted: April 26, 2024; Published: May 23, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Kowalski et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper.
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Soon, funds from the European Union intended for improving the infrastructure of member countries will no longer be directed to Poland. They will be sent to other countries, e.g. Ukraine and the Balkan countries. Therefore, if we want to effectively use the financial resources currently allocated to Poland, we must be able to predict the causes of threats that may occur during the implementation of railway investments and prepare appropriately to counteract emerging risk factors. Experience from the first tranches of financing for Polish investments shows that during the implementation of railway investments, domestic and foreign contractors encountered several problems that had not been taken into account before. Therefore, all possible remedial measures should be taken immediately to ensure that the allocated funds are spent in accordance with the adopted plan. The knowledge gathered in this area can be used when implementing similar investments in other countries.
Most rail projects are major engineering projects with complex construction technology, variable construction environments, which generate various hazard during construction process. There are a lot of example in the literature where the authors analyse different types of risk associated with railway projects and present varius methods for assessing them. In general, risk is estimated as the outcome of the probability of an adverse event and a measure of the consequences of such an event. The International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) (2018) defined risk as the impact of uncertainty on objectives. In terms of a construction project, risk is described as any action or event that will impact the achievement of project objectives [ 1 ].
Wang et al. [ 2 ] developed a new safety risk identification method based on the on the grid–time–work breakdown structure–risk breakdown structure (G–T–WBS–RBS) matrix by integrating the methods of WBS, RBS, and risk management grid. This study proposed to move away from identifying risk factors from a static perspective to considering the dynamic process of risk factor change. Based on the spatial and temporal distribution and interaction of risk factors, the causes of risks can be examined to form more oriented risk control measures according to the characteristics of safety risks. Kowalski and Polonski [ 3 ] developed a risk estimation method (the Railway Matrix of Risk Factors (RMRF)) on Polish railway investments, based on a risk matrix which is developed at the design and construction works. Risk factors were analysed in the context of delays in investment realisation and investment costs. Risk matrix elements are represented by the calculated weight of individual risk factors. Leśniak and Janowiec used Bayesian Belief Network (BBN) for risk assessment of additional works in railway construction investment [ 4 ]. The nodes of the network are the identified risk factors. The use of BBN allows not only to estimate the risks, but also to manage them. Using the network makes it possible to compare different ways of reducing risks, to check the effect of risk factor reduction and to determine a satisfactory level of financial and time effects as a result of additional work.
Regardless of the adopted risk estimation method, a key element of the analysis is the identification of risk factors [ 5 ]. Issues related to the identification of risk factors occurring in construction are discussed broadly in literature [ 6 ]. There are several types of risk in a construction project, which can be categorised into the following types: environmental, financial, logistical, managerial, socio-political and technical [ 7 ]. In the literature there is a number of studies that identified risk factors associated with safety, delays in construction completion dates and increases in investment costs [ 8 , 9 ]. The most common group of factors irrespective of the country are problems related to contract management [ 10 – 16 ] financial problems [ 17 ] and employee performance [ 18 ]. Competent management deficiencies affect both the investor and the contractor [ 19 , 20 ].
Regarding railway projects as in construction, the identification of risk factors depends on the type of effects considered in the analysis (safety, costs, construction completion date delays) and the stage of the investment (design, construction) [ 2 , 4 , 21 ].
Attempts to eliminate potential risks are a key issue of construction projects at the risk management stage. In recent years, researchers and practitioners have made numerous efforts to count the assessment of the impact of potential risk factors when forecasting the implementation time of construction projects. Knowing the links between the risk factors, the strength of their interaction and their impact on the risk analysed is the basis for taking more targeted measures to decrease the level of risk. Multi-criteria analysis is an adequate method to evaluate factors and rank them by defining their weights. Most methods only specify weights on the basis of direct assessments by experts without examining the mutual influence between the factors [ 22 ]. A multi-criteria analysis method allows to consider the interaction of factors is the DEcision MAking Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL). This methods, based on the relationship between effective factors, allows to determine the strength of influence and the scale of dependence for each factor and to visualize this structure using an influence matrix or appropriate directed graphs. This method not only transforms the interdependence relationships into a cause-and-effect group through the matrix, but also finds the critical factors of the complex system through the influence relationship diagram. DEMATEL is used in solving problems in areas such as: business management, shaping products and services, transport, energy, medicine, finance, banking, education, information systems, environmental engineering and construction. [ 23 , 24 ]. In issues related to risk analysis in construction, this method was successfully applied in the work of Dytczak et al. [ 25 ] to identify the causes of building structure failure. It was also used as an effective tool of the risk analysis of tunnel engineering construction [ 26 ]. In the work of Mirosław-Swiatek et al. [ 27 ] it was used in the analysis of factors affecting the safety of flood embankments. The DEMATEL method was applied by Stoilova [ 28 ] to analyse the importance and the relations between the criteria and to establish the weights of the criteria for assesing the transport technology for passenger transport by railway and road. Farooq et al. [ 29 ] used DEMATEL to determine weights for smart urban mobility evaluation criteria in Beijing. Farooq’s research demonstrates the congruence between the evaluation of weights from DEMATEL and the Analityc Hierarchy Process (AHP) method, which is often used in multi-criteria analysis. There is research in which the two methods are combined by using DEMATEL to determine weights [ 30 ].
As mentioned above, railway investments, depending on the stage of implementation, are characterized by various risk factors. In this research we analyse the factors associated with the construction stage. While the risk factors themselves are widely discussed in the literature [ 3 ], there are no studies that analyse the relationship, importance, influence and impact of factors on each other.
The cause-and-effect model of factors influencing the risks associated with railway investments in Poland described in this publication, is based on factors identified in previous studies [ 22 ]. The risk factors were determined as a result of the study carried out with the participation of experts implementing one of the most complex railway investments in Poland. The DEMATEL method was applied to build this model, and the ranking of factors was performed on the basis of weights, and their estimation is an element of this method. The estimated weights for the risk factors were compared with the weights that were directly determined by the expert group and used in Kowalski’s research [ 3 , 22 ].
The novelty in this study is the assignment of weights (ranks) to the analysed risk factors and investigation of mutual influences of these factors. This research attempts to fill the gap in this area and can be used in other countries with similar risk factors for railway investments. This is extremely important in order to optimise the use of funds allocated for rail investment in Poland.
Due to the deficiencies in the literature of similar studies Thus, taking into account only factors typical of railway investments, the paper does not perform analyses indicating how the used in the study factors align or differ from those in other studies on railway investments in poland.
Materials and methods
Risk factors for railway investment (build stage).
The risk factors that pose the greatest threat to railway investment implementation for the build stage are listed in Table 1 and are consistent with the factors identified in the work of Kowalski [ 22 ]. Eleven key factors were identified by a group of experts with many years of successful experience in the implementation of railway investments, including scientists, contractors and investors.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.t001
a1: Errors in the preparation of tender documents result primarily from errors in the tender documents. In the Functional and Utility Program (FFU) itself, as well as in the Specification of Essential Terms of the Procurement (SIWZ), it is possible to identify probable causes of threats that may occur at the design and implementation stages. Examples include missing documents confirming the Employer’s legal title to use the land for construction purposes, outdated arrangements with external stakeholders or errors in the conceptual design.
a2: Improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer is a consequence of incorrect analyzes at the initiation stage of a given contract. Problems with incorrect estimation of implementation deadlines may be related to the lack of sufficient technical knowledge of the team preparing application documents for funding from the European Union.
a3: Too many external institutions involved in the investment process is a risk factor whose scale of impact cannot always be determined at the stage of the tender procedure. It happens that external institutions, whose participation is identified only after the design documentation has been developed, have unclear maximum deadlines within which they should make arrangements for the submitted design documentation. In Poland, an example may be companies belonging to the PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) capital group.
a4: Terms of the contract not adapted to the contract specificity . An example of failure to adapt contract provisions to the conditions prevailing in a given project is the need to construct engineering facilities located partly outside the Employer’s premises (railway area), where the manager of such area, who is not also a party to the contract, has a direct impact on the technical implementation and completion dates. Another major concern may be the incorrect selection of FIDIC (Federation Internationale des Ingenieurs-Conseils) Contract Conditions for a given investment. Not in all cases, implementing investments in accordance with the FIDIC Yellow Book procedures is the right solution.
a5: Investment costs incorrectly estimated by the Contractor result primarily from inappropriate internal procedures of the Contractor, regulating the process of preparing the investment for implementation.
a6: Difficulties in the preparation, in terms of formal, legal and technical areas for investment are mainly related to formal errors occurring during the preparation of the tender procedure. An example may be negligence towards further stakeholders, where the temporary occupation of their areas is necessary for the implementation of works.
a7: Internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts . They are related to the role and possibility of significant influence on the process of agreeing project documentation of the Ordering Party’s internal organizational unit, i.e. the Investment Project Assessment Team (ZOPI). According to general knowledge, ZOPI has the obligation and authority to agree and adopt solutions for design studies regarding railway investments. On the other hand, it is not one of the parties to the contract, especially one implemented on the basis of the FIDIC Code. Moreover, arrangements with ZOPI, which consist of members without appropriate construction licenses and who are not directly responsible for and related to the implementation of the contract, may result in the need for constant detailing of the conceptual design and endless explanations, which should be resolved at the stage of the detailed design.
a8: Errors in project documentation may in particular refer to errors in the conceptual design documentation from the tender stage, which should be the starting material for the development of architectural and construction documentation by the designer. Unfortunately, the solutions indicated in the documentation in question (conceptual) often become outdated after signing the contract.
a9: Problems with the supply of materials and other resources may result from situations beyond the control of the parties to the contract, e.g. the War in Ukraine and/or from the Contractor’s organizational errors.
a10: Awarding shorter track closures to the contractor. Most railway investments are carried out under pain of maintaining train traffic at all rebuilt railway stations. In order to carry out the works, the Contractor to submit a request to the relevant units of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) for temporary track closures. These closures enable performance of works that must be coordinated across industries. Unfortunately, approvals for track closures are largely withdrawn, sometimes several hours before the start of works.
a11: Problems with outdated geodetic materials (numerous collisions with uninventoried underground infrastructure) result primarily from the lack of documents in the PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) archives confirming the inventory of underground infrastructure from the 19 th and 20 th centuries.
DEMATEL method
DEMATEL is a comprehensive a multi-criteria analysis method that allows to analyze complex dependencies in the system. This method transforms the interrelationships between factors into an understandable structural model of the system and divides them into a group of causes and a group of effects [ 31 ]. The developed cause and effect model can be presented in the form of a diagram. It allows for the description of the interrelationships between factors, determining the key factors considering the causal relationships and interrelationship degree between the factors and calculating the weights of factors by considering the interrelationships and factors impact levels. The basis of the DEMATEL method is the comparison of events (in this case the risk factors listed in Table 1 ) in pairs in terms of causality (direct impact). A rating scale of 0–3 is most often used to express the intensity of direct influence relationships. Its individual levels correspond to a gradual increase in the intensity of the influence relationship, where: 0 –no influence of the first event on the second event; 1 –low influence of the first event on the second event; 2 –significant influence of the first event on the second event; 3 –very high influence of the first event on the second event. The set of assessments of direct impact relationships allows, in mathematical transformations, the construction of a direct influence matrix A . From this, a matrix T of the total (both direct and indirect) influence is calculated. Its elements allow the values of two characteristic indicators to be determined: Prominace and Relations , identifying the nature of the factors under consideration in terms of their role in the process of determining the structure of influence of the factors (causes group) and their influence on other factors (effects group), respectively. A visual demonstration of cause-and-effect model is the Impact-Relations Map (IRM). As a result of the T matrix transformations, a net influence matrix— NeT —is developed, the graphical representation of which is the map of the total net influence, showing the strength of influence of one factor on another factor. Building the classic DEMATEL model can be formulated as follows [ 23 , 28 ].
- Step 1—Generate the direct-influence matrix A . In this step, a direct influence matrix A = [ a ij ] n × n is generated. Elements of matrix A indicate the direct influence that factor a has on factor a j ( Table 1 ), using an integer scale (0–3). Its individual rows are dedicated to the events that appear first in the comparison, and the columns to the events that appear second in the comparison. When determining matrix A , it is assumed that each factor can directly influence the other elements, but cannot influence itself, which means that all principal diagonal elements of matrix A are equal to zero. The values of the elements of the direct-influence matrix can be agreed jointly by experts or calculated as an average value from their opinions.
- Step 6—Development of the influential relation map (IRM). The influential relation map (IRM) is created by mapping the set of two indexes ( R+C , R-C ; Eqs: 4 , 5 , 6 and 7 ), that are calculated from the T matrix. IRM enables the visualization of complex causal relationships among factors. The resulting structure of total influence is often very complex because it represents all the connections between the elements of the system. To simplify it, a reduction is used, which involves filtering out irrelevant connections by eliminating from the T matrix connections with values lower than the assumed positive threshold of the total influence θ . Only those elements from the T matrix whose values are greater than θ are selected to represent their correlations in the IRM diagram. In the literature, the threshold value θ is usually determined by experts’ methods [ 23 ] or the average of all elements in the matrix T [ 32 ]. Usually, the factors in the complicated system are grouped, depending on the value of R+C and R-C , into four quadrants according to their locations in the IRM diagram [ 33 – 35 ]. Due to their location in a specific quadrant, factors are classified as: most important ( R i - C i is positive; R i +C i is large), important ( R i -C i is positive; R i +C i is small), independent ( R i -C i is negative; R i +C i is small), indirect ( R i -C i is negative; R i +C i is large).
- Step 8—Drawing the map of the total net influence Based on the total net influence matrix, an acyclic and asymmetric directed graph can be developed, called the total net influence map, showing the impact relationships between individual factors. The arcs of the graph indicate the factor under the influence of the other factor, and the type of line represents the intensity of the total influence, estimated from the values of the elements of the NeT matrix.
Expert grup
The selection of experts resulted from their competences and experience in the field of risk analyzes occurring in railway investments. These were people implementing and supervising railway investments in Poland, and scientists involved in research and teaching in the field of engineering construction projects. Nine experts took part in the evaluation of pairwise comparisons in terms of influence between the factors. Among them four experts are from academia. The condition for the selection of the remaining experts was appropriate seniority (at a minimum 10 years) and a broad view of railroad investments, taking into account the risk factors involved and their consequences. In the end, fife experts were selected who, in addition to their technical knowledge and experience, have general administrative and economic experience. All respondents were Polish citizens. At the time of the survey, the surveyed experts were directly involved in the implementation of one of the most difficult railroad investments in the Mazowieckie Voivodeship, which ensured a high level of quality of the data obtained.
In the presented study, each of the nine experts conducted pairwise comparisons in terms of influence between factors (according to a 0–3 scale) and independently presented an individual direct influence matrix. The elements of direct influence matrix A were determined as an average value based on the experts’ opinions.
In order to identify the relationships between the studied risk factors using the DEMATEL method, the computational model described above was used. Risk factors were identified as presented in Table 1 . The direct infuence matrix A was determined using the expert method. In the presented study, each of the nine experts conducted pairwise comparisons in terms of influence between factors (according to a 0–3 scale) and independently presented an individual direct influence matrix. The final form of matrix A was estimated by taking the arithmetic mean of the values given by each expert. As a result of calculations using the DEMATEL method, direct influence matrix A ( Table 2 ), total influence matrix T ( Table 3 ) were obtained.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.t002
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.t003
The threshold of the total influence θ was calculated as the average of all elements in the matrix T .
Based on the T matrix, the influential power ( R i ), dependency ( C i ), Promineance ( R i +C i ), Relation ( R i -C i ) and weighs of factor ( w i ) indicators were calculated (Eqs 4 – 8 ), which are summarized in Table 4 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.t004
The factor with the greatest direct and indirect impact ( R index) on other factors is a3 –Too many external institutions involved in the investment process. The smallest effect on other factors is a5 –Investment costs incoretly estimated by the Contractor and a9 –Problems with the supply of materials and other resources. Values above the average for the total impact indicator ( R index) are: a7 –Internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts, a8 –Errors in project documentation, a1 –Errors in the preparation of tender documents (SIWZ, OPZ, PFU), a2—Improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer, a6—Difficulties in the preparation, in terms of formal, legal and technical areas for investment, a11—Problems with outdated geodetic materials (numerous collisions with uninventoried underground infrastructure). The factor most dependent on the others (index C ) is a5 –Investment costs incorretly estimated by the Contractor, and the most independent is a3 –Too many external institutions involved in the investment process. Values above the average are: a1 –Errors in the preparation of tender documents (SIWZ, OPZ, PFU), a8 –Errors in project documentation, a2 –Improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer, a7—Internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts, a6 –Difficulties in the preparation, in terms of formal, legal and technical areas for investment.
The analysis of Table 4 and Fig 1 shows that the highest value of Prominence is achieved by factor a1 ‒ Errors in the preparation of tender documents (SIWZ, OPZ, PFU), which proves its central role in the process of determining the total impact of the factors. Factors a8 ‒ Errors in project documentation and a2 ‒ Improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer are also highly influential. The following factors also achieve values above the average: a7 ‒ Internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts, a6 ‒ Difficulties in the preparation, in terms of formal, legal and technical areas for investment. The factors with the lowest impact are: a10 ‒ Awarding shorter track closures to the contractor, a9 ‒ Problems with the supply of materials and other resources.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.g001
The importance of the factors in terms of the Relation index is shown in Fig 2 . The group of causes ( R i -C i > 0) includes the following five factors: a3, a7, a11, a8, a10, a6. By far the highest Relation value is a3, which proves that it has the greatest influence on other factors. Next comes the a7. The remaining 4 factors have a much smaller impact on the other factors. Factors a4, a9, a1, a2, a5 belong to the group of effects ( R i -C i < 0) and are influenced by causal factors. In this group, the factor with the greatest influence is a5. Factor a4 is the nearest to the center, it means that it is least influenced by the identified causal factors.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.g002
The weights ( Eq 8 ) calculated in the DEMATEL method for the individual risk factors are summarised in Table 4 . They range from 7.45% to 10.38%. The factors of great importance are a1 (10.38%) and a8 (10.02%). The factors with the lowest impact are a9 (7.45%) and a10 (7.91%). Calculated with DEMATEL weights were compared ( Fig 3 ) with the weights that, for the eleven risk factors analysed, were directly determined by the experts [ 22 ]. In Kowalski’s research [ 22 ], the experts assigned importance on a scale from 1 to 10, and the calculated weights range from 6.75% to 11.49%. The lowest percentage difference in weight values is 0.50% and is reached for a6. The greatest difference of 38.19% is found for a9. For four factors (a4, a5, a6, a8), the differences do not exceed 1.44%. In the 10–30% range, percentage differences occur for factors a1, a2, a10, a3 and a7. Only for factors a11 and a9 are the percentage differences greater than 30%.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.g003
Fig 4 shows the IRM diagram, which was developed on the basis of the Prominence ( R+C ) and Relation indicators ( R-C ) ( Table 4 ). Factors a7, a8, a6 belong to group I (the most important factors) because they influence ( R i -C i > 0 ) the remaining factors (they are the causes) and at the same time significantly related to them R i + C i >( R+C ) mean ). Factors a3, a11, a10 belong to group II (important factors), they significantly influence the other factors ( R i -C i > 0), but weakly related to them ( R i + C i < ( R+C ) mean ), so they can be treated in the system as autonomous causes. Group III (independent factors) includes three factors a9, a5 and a4. They are effects ( R i -C i < 0) and at the same time weakly related to other factors ( R i +C i < (R+C) mean ). The remaining three factors a1, a2 belong to group IV (Indirectly factors). They are effects ( R i -C i < 0) and, at the same time, strongly related ( R i +C i >( R+C ) mean ) to other factors affecting the risk of failure of railway investments. IRM diagram maps the correlations between the risk factors by using solid lines and broken lines for two-way and one way significant relationships, respectivley. Only those relationships for which the elements of the T matrix ( Table 3 ) are greater than the threshold value ( θ = 0 . 295 ) are considered. Significant bi-directional relationship with the other factors occur for a7, a8 and a6. These factors are characterised by Prominence values above average and belong to the group of causes.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.g004
Table 5 shows the net influence between the studied risk factors. This relationship is used to assess the strength of the influence of one factor on another ( Eq 9 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.t005
The analysis of the values listed in the table above shows that, for example, factors a3 and a7 influence remaining factors to a greatest extent. Factors a5 and a9 practically does not influence any other factor, it is practically always the effect of other factors ( Fig 4 ). Based on the NeT matrix, the total net influence map was developed ( Fig 5 ). The strength of the influence of one factor on another is shown in four classes (0 < Net ij ≤ 0.03 weak influence; 0.03 < NeT ij ≤ 0.06 average influence; 0.06 < NeT ij ≤ 0.09 strong influence; NeT ij > 0.09 very strong influence). The developed map of the total influence of factors confirms the strongly causal nature of factors a3 and a7, which are located in the upper part of the map, and strongly consequential nature of factor a5, which is located at the bottom. Factor a3 has a very strong net impact on related factors. Five of the eight impacts exceed the lower limit (0.09) of the strongest net influence. The second factor a7 only exceeds 0.09 for two of the links NetT 75 and NetT 79 . All eleven factors intensively influence a5, eight of them feature a very strong net influence.
Graph arcs indicate a factor under the influence of another factor and the type of line -total influence intensity—the value range for element n ij in the NeT matrix.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0303606.g005
An analysis of Figs 3 and 4 shows that the ranking of factors based on the value of the calculated weights is as follows: a1>a8>a2>a7>a6>a4>a3>a5>a11>a10>a9. According to Eq 8 , the weights are estimated based on the value of Prominence . It shows the degree of being influenced by other factors and influences them as well. Fig 4 presents the cause and effect diagram and IRM for the factors. It shows that a8 is a key factor for risk problems. Factors a7, a6 have also high importance. All 3 factors are characterized by high Relation and Prominence . They are related to each other and to the other factors. This is particularly evident in Fig 5 , where the significant influence of factor a7 on the others is shown. Among the cause group factors that are autonomous in the system (factors: a3, a11, a10) ( Fig 4 ), factor a3 has the highest Relation . Its autonomy and strong influence on other factors is evidenced by Fig 5 . In the group of independent factors (factors: a4, a5, a9) ( Fig 4 ). factor a5 has the lowest Relation value. Its character, as an autonomous receiver, can be seen in Fig 5 . It is very strongly influenced by all other factors. The Fig 4 demonstrates that factors a1, a2 have an indirect impact on the system. They are interpreted as intertwined receivers (low Relation but high Prominence ) cannot be enhanced directly and must be influenced by other ones. This is confirmed by Fig 5 , where they are located in the middle of the diagram and more factors have a net influence on them than they do on the others.
The basis of the DEMATEL method, like other methods used in multi-criteria analysis, is the subjective assessment of experts. In most applications of this method in its classic approach (Fontela et al., 1972), experts evaluate the direct influence between any two criteria by using a five-point scale (0—no influence; 1—low influence; 2—medium influence; 3—high influence; 4—very high influence). In our study, experts used a scale of 0–3, in which intermediate levels 1 and 2 describe a gradual transition (low influence, significant influence) from no influence to very high influence of one factor on another. According to experts, the use of a 0–3 scale significantly simplifies a clear pairwise comparison of the analyzed 11 risk factors. A four-point scale for comparisons between criteria is often used in various studies that use the DEMATEL method [ 24 , 25 , 27 ].
The assessment of the importance of risk factors on railway investment implementation for the build stage was made on the basis of factor weights, calculated using the classical DEMATEL technique, in which the weights are determined based on normalized prominence ( R+C ) ( Eq 8 ). Despite various modifications introduced by some authors in calculating criteria weights in DEMATEL [ 24 , 38 , 39 ], the classic method of estimating them is widely used [ 28 , 29 ]. The calculated criteria weights are characterized by little variability. Their average value is 9.09% ( Fig 3 ) and the standard deviation is 0.87%. This distribution of weights, which vary in the range from 7.45% to 10.38%, indicates that the factors are characterized by similar importance weights for factors.
Due to the lack of research in the literature related to the construction of a cause-and-effect model of risk factors for railway investment implementation, it is difficult to compare our results against the background of other studies. The results of previous research conducted by Kowalski [ 22 ] were used to validate the importance calculated by the DEMATEL ( Eq 8 ) for individual risk factors. The weights determined in accordance with Eq 8 were compared with the weights calculated on the basis of direct opinions of experts. The weights assigned by experts are one of the core issues of the Railway Matrix of Risk Factors (RMRF) method, developed by Kowalski to analyze risk for railway investment [ 3 , 22 ]. In Kowalski’s research, experts directly answered on a scale from 1 to 10 the question of what influence a specific factor has on the investment time and cost. Questionairre involved large groups of 85 experts with extensive professional experience. The average percentage difference between the scales is 16.60% and proves that the results of both methods are close ( Fig 3 ). In the DEMATEL method, factors a1, a2, a3, and a7 were more important than in the opinion of experts. The opposite situation occurs in the case of factors a9, a10, a11. The remaining factors (a4, a5, a6) have similar weights in both methods. In the DEMATEL method, the weights change to a lesser extent (7.45%–10.38%) than the weights determined directly by experts (6.75% -11.49%). Experts significantly overestimate the role of the a11 factor, which they give the greatest importance in their assessment. Perhaps this is due to the fact that it is hard for the experts to detect indirect connections between the factors that the DEMATEL method determines analytically, based on the computational algorithm. In our opinion, experts also overestimate the importance of factors that have a high probability of occurring. According to Leśniak and Janowiec [ 4 ], the probability of a11 occurrence is 76%, and experts attach the greatest importance to this factor.
Taking into account the very wide scope of research conducted by Kowalski [ 22 ], in our analysis we used the 11 factors he identified that influence the risk for railway investment implementation for the build stage. The ranking of factors a1>a8>a2>a7>a6>a4>a3>a5>a11>a10>a9 obtained in the DEMATEL method differs from the ranking determined on the basis of direct expert opinions in the RMRF method (a11>a9>a8>a10>a1>a6>a4>a5>a2>a7>). However, most importantly, the weights assigned to the factors are close in both methods. Despite the fact that there are different groups of experts in both methods (both in terms of their composition and number), the similar weight values (DEMATEL vs. RMRF) prove the great application potential of DEMATEL, in which a much simpler task was set for a smaller number of experts, based on direct pairwise comparison of factors. This is one advantage of the DEMATAL method. It can be combined subjectively and objectively to make a comprehensive assessment. Another advantage of the DEMATEL method is the fact that experts estimate the direct impact for each pair of factors only once, and any indirect connections are the result of computational analyzes used in this method. This approach eliminates potential errors resulting from engaging experts on a broader scale. In our future studies, we will combine both methods by using DEMATEL to determine the weights for risk factors in the RMRF method. This will reduce the impact of experts’ subjectivity in assessing the importance of factors on risk. Combining DEMATEL with other multi-criteria analysis methods to determine weights for criteria is often used in the literature [ 29 , 40 ].
The obtained cause-and-effect model of connections between factors presented using IRM and Map of the total net influence (Figs 4 and 5 ) indicates the dominant nature of factors a7—Internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts and a8 ‒ Errors in project documentation. They are the causes strongly related to many factors and have a large net influence on other factors. Errors in design documentation are among the most common events. Leśniak and Janowiec [ 4 ] state that the probability of their occurrence is 97%. The Map of the total net influence shows that factor a3—Too many external institutions involved in the investment process (located in the upper part of the diagram), has the greatest net influence on other factors, and its location in IRM ( R+C = 6.481 close to the average value of 6.486) indicates that it belongs to the transitional group between important factors and the most important factors in the structure of connections. Factors a2, a1, a4, a6 have a double role (partly effect—partly cause) and their R-C value is close to zero and varies in the range from -0.15 to 0.09 ( Fig 2 ). This is particularly visible in the Map of the total net influence, where these factors are located in the middle part of the diagram. Factors a10 and a11 are causes ( Fig 4 ) that have a small net effect on the associated factors ( Fig 5 ). The definite effects are factors a5 and a9 ( Fig 4 ). Due to the value of R+C = 6.377 located close to the average value of 6.486 ( Fig 4 ), factor a5 is related to many factors that have a very high influence on it. It can also be defined as a dual factor, which is partly independent and partly an indirect factor. The conducted research fills the knowledge gap in terms of quantitative description of the importance of risk factors for railway investments in Poland and investigation of factors mutual influences. This is a very important issue and in the last few years, numerous legal regulations have been introduced (European standards, national instructions) aimed at unifying the requirements for research and design calculations, as well as the scope and format of design documentation (factor a7). Such standardization is also intended to limit (to the most professional and competent) the number of institutions involved in the investment process (factor a3). These activities can speed up the investment process, and shortening it may be crucial in determining the most likely investment cost (factor a5). Eliminating problems with the supply of materials is possible by implementing alternative design solutions that provide for the use of replacement building materials that meet the technical requirements (a5). This is of great importance for both accelerating and eliminating delays in ongoing railway investments. Identifying factors a3, a7 and errors in project documentation (factor a8), as the most important factors is crucial for practice. Previously mentioned activities like standardizing research and design (introduced regulations) unifying the requirements for the design documentation can also improve the quality of the documentation by minimizing or eliminating errors in project documentation (factor a8).
The weights of the individual factors, determined by the DEMATEL method, are the result of mathematical transformations of the direct influence matrix, which is derived on the assumption that the relative weights of experts are equally important. In practice, each expert has unique characteristics in terms of knowledge, skills, experience and personality, which means that different weights of experts should be assigned to their influence on the final results. In the interrelationship evaluation process, some experts may assign unduly high or unduly low values depending on their preferences. Therefore, advanced DEMATEL methods should be developed in the future to mitigate the impact of unfair arguments on the decision results. It is crucial to propose more objective and efficient methods to establish key parameters in DEMATEL, such as the threshold value considered in the causality diagram in IRM and to correctly account for the influence of both the prominence and relation index in the method of calculating weights.
The proposed DEMATEL model for determining weights for risk factors may be used in the future in the Railway Matrix of Risk Factors method, intended for estimating risk for railway investment. The identified structure of connections between factors can be the basis for the development of applications of risk models for railway investments, the basis of which is the identification of cause-effect connections (for example, models based on Bayesian Belief Network [ 4 ]).
Regardless of the method used, the analysis of 11 factors by experts seems to be quite a complex issue, so it may be worth using the method of grouping factors, which leads to reducing the size of the issue, and then conducting a DEMATEL analysis for the groups and within them. This type of approach was successfully used in other studies [ 28 , 41 ].
The results of the analysis indicate that recommendations or strategies should be developed in the future in order to minimise the negative effects of factors a8, a7, a6 or a3. This could be achieved through introducing additional studies and analyses at the pre-design stage, changing the form of documentation—introducing uniform documentation formats across various branches. Creation of databases that will enable the application of artificial intelligence for certain decisions.
Conclusions
The analysis of cause and effect relationships of risk factors for failure of railway investments presented in the article, performed using the DEMATEL technique, allowed to classify them as cause or effect factors. The group of cause factors includes in decreasing order: errors in project documentation (a8), internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts (a7), difficulties in the preparation, in terms of formal, legal and technical areas for investment (a6), too many external institutions involved in the investment process (a3), problems with outdated geodetic materials (a11) and awarding shorter track closures to the contractor (a10).
Other factors ranked in decreasing order: errors in the preparation of tender documents (SIWZ, OPZ, PFU) (a1), improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer (a2), terms of the contract not adapted to the contract specificity (a4), investment costs incorrectly estimated by the Contractor (a5), problems with the supply of materials and other resources (a9) belong to groups of effects and are influenced by causal factors. Among this group of factors, investment costs incorrectly estimated by the Contractor (a5) is the least influencing factor among all identified factors.
Due to the value of the Relation indicator close to zero, factors a2, a1, a4, a6 play a double role (partly the effect—partly the cause).
The highest value of the prominence index (causes group) for the errors in project documentation factor (a8) indicates that it is the most important for the implementation of railway investments. Important factors are: problems with outdated geodetic materials (a11) and awarding shorter track closures to the contractor (a10).
Problems with the supply of materials and other resources (a9) belongs and to the group of independent factors that have little impact on the others factors.
Factors strongly related to the remaining factors but being an effect of the influence of the remaining factors are: errors in the preparation of tender documents (SIWZ, OPZ, PFU) (a1), investment costs incorrectly estimated by the Contractor (a5) and improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer (a2).
The application of the DEMATEL method made it possible not only to identify the relations between the factors, but also, by calculating the weights, to determine the importance of the factor. It was found that the factors errors in the preparation of tender documents (SIWZ, OPZ, PFU) (10.38%), errors in project documentation (10.02%), improperly estimated time of completion of the investment by the Employer (9.82%), internal regulations of PKP Polskie Koleje Państwowe S.A. (Polish State Railways) not coordinated with the provisions of contracts (9.51%) have the highest degree of importance. The weights calculated in DEMATEL were validated by the importance of factors, which in earlier studies were determined directly by experts. The weights assigned to the factors are close in both methods, the percentage difference not exceeding 16.60%.
The manuscript addresses the practical implications of the research for risk management in railway projects. It is therefore important to develop specific guidelines in the future for combating negative effects or preventing individual risk factors. The proposed DEMATEL model for determining weightts for risk factors may be used in the future in the Railway Matrix of Risk Factors method, intended for estimating the risk of railway investments. The identified structure of connections between factors may be the basis for the development of applications of railway investment risk models based on the identification of cause-effect connections (for example, models based on Bayesian Belief Network).
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 12. Skorupka D. Method of construction risk assessment. [Warsaw]: Military University of Technology; 2007.
- 13. Skorupka D, Kuchta D, Górski M. Risk management. In: Malara Z. & Trzaskalik T., editor. Risk management in the project. Warsaw: Military University of Technology; 2012. p. 53–69.
- 15. Niazai GA, Gidado K. Causes of Project Delay in the Construction Industry in Afghanistan. In 2012.
- 16. Anysz H. Ussing ANN to assess the possibility of delays in the implementation of construction contracts. [Warsaw]: Warsaw University of Technology; 2017.
- 21. Kowalski J, Połoński M, Lendo–Siwicka M. Risk factors for delays in rail investments implemented in the Design & Build contracts. MATEC Web of Conferences. 2019;262.
- 22. Kowalski J. Harmonogramowanie inwestycji kolejowych w Polsce z uwzględnieniem ryzyka w trakcie ich realizacji. [Warsaw]: Warsaw University of Life Sciences; 2021.
- 26. Guo W, Deng Q, Pan XD. Risk evaluation of highway tunnel construction based on DEMATEL method. In: Applied Mechanics and Materials. 2013.
- PubMed/NCBI
- 41. Dytczak M. Selected Methods for Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis in Civil Engineering. [Opole]: Opole University of Technology; 2010.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The origins of document analysis as a social science research method can be traced back to Goode and Hatt (), who recommended that scholars screen, count, and code documents content and use it as appropriate evidence.Later, Glaser and Strauss argued that documents should be considered in social investigation similar to "anthropologist's informant or a sociologist's interviewee" (p. 163).
This article examines the function of documents as a data source in qualitative research and discusses document analysis procedure in the context of actual research experiences. Targeted to ...
Document analysis is a versatile method in qualitative research that offers a lens into the intricate layers of meaning, context, and perspective found within textual materials. Through careful and systematic examination, it unveils the richness and depth of the information housed in documents, providing a unique dimension to research findings.
document analysis is a valuable research method, one would expect to find a wide variety of literature on this topic. Unfortunately, the literature on documentary research is scant. This paper is designed to close the gap in the literature on conducting a qualitative document analysis by focusing on the
Documentary Analysis. Definition: Documentary analysis, also referred to as document analysis, is a systematic procedure for reviewing or evaluating documents.This method involves a detailed review of the documents to extract themes or patterns relevant to the research topic.. Documents used in this type of analysis can include a wide variety of materials such as text (words) and images that ...
Published: Dec. 12, 2023. Document analysis is the process of reviewing or evaluating documents both printed and electronic in a methodical manner. The document analysis method, like many other qualitative research methods, involves examining and interpreting data to uncover meaning, gain understanding, and come to a conclusion.
Conducting a document analysis can also reduce some of the ethical concerns associated with other qualitative methods. Since document analysis is a valuable research method, one would expect to find a wide variety of literature on this topic. Unfortunately, the literature on documentary research is scant.
Document analysis (also called document review) is one of the most commonly used methods in health policy research; it is nearly impossible to conduct policy research without it. Writing in early 20th century, Weber (2015) identified the importance of formal, written documents as a key characteristic of the bureaucracies by which modern ...
This article examines the function of documents as a data source in qualitative research and discusses document analysis procedure in the context of actual research experiences. Targeted to research novices, the article takes a nuts‐and‐bolts approach to document analysis. It describes the nature and forms of documents, outlines the ...
Morgan (2022) states that document analysis is a research method for analyzing written documents such as books, newspapers, journals, and visual documents such as photos, videos, and films. In ...
Document study (also called document analysis) refers to the review by the researcher of written materials . These can include personal and non-personal documents such as archives, annual reports, guidelines, policy documents, diaries or letters. ... Rather, it is a way to describe the research methods in detail, which might not be possible in ...
In relation to other qualitative research methods, document analysis has both advantages and limitations. Let us look first at the advantages. Efficient method: Document analysis is less time-consuming and therefore more efficient than other research methods. It requires data selection, instead of data collection.
Document analysis is a qualitative research technique used by researchers. The process involves evaluating electronic and physical documents to interpret them, gain an understanding of their meaning and develop upon the information they provide. ... Researchers may also use document analysis as a part of mixed-method studies, which combine ...
Conducting a document analysis can also reduce some of the ethical concerns associated with other qualitative methods. Since document analysis is a valuable research method, one would expect to find a wide variety of literature on this topic. Unfortunately, the literature on documentary research is scant.
Preview. Uniting methods from disciplines across the social sciences and humanities, this hands-on guide develops a novel approach to doing document analysis. The authors present a framework for studying documents that enables you to conduct a rich and systematic analysis of documents in all their diversity. Focussing on document analysis both ...
Document analysis is a topical method used in health and nursing sciences. Written, audio, and visual healthcare documents are constantly being produced (Bowen, 2009; Coffey, 2014; Gibson & Brown, 2011) and the number of documents is increasing (Olivares Bøgeskov & Grimshaw-Aagaard, 2019), because of wider healthcare regulations and the need to evaluate the effectiveness of care and services.
The nature and forms of documents are described, the advantages and limitations of document analysis are outlined, and specific examples of the use of documents in the research process are offered. This article examines the function of documents as a data source in qualitative research and discusses document analysis procedure in the context of actual research experiences. Targeted to research ...
In relation to other qualitative research methods, document analysis has both advantages and limitations. Let us look first at the advantages. Efficient method: Document analysis is less time ...
Document analysis is a social research method and is an important research tool in its own right, and is an invaluable part of most schemes of triangulation, the combination of methodologies in the study of the same phenomenon (Bowen, 2009). In order to seek convergence and corroboration, qualitative researchers usually use at least two ...
Document analysis is one of the most commonly used and powerful methods in health policy research. While existing qualitative research manuals offer direction for conducting document analysis, there has been little specific discussion about how to use this method to understand and analyse health pol …
Document analysis (also called document review) is one of the most commonly used methods in health policy research; it is nearly impossible to conduct policy research without it. Writing in early 20th century, Weber (2015) identified the importance of formal, written documents as a key characteristic of the bureaucracies by which modern ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
Psychology document from Capella University, 7 pages, Facial Recognition Angela Collier PSYC-FPX4600: Research Methods in Psychology Data Analysis and Interpretation Capella University May, 2024 2 Facial Recognition This literature review takes an integrative approach to assess the current state of research
The paper presents the results of research on the influence of risk factors on the implementation of railway investments in Poland (build stage) and deals with a detailed diagnosis of relation between factors. The application of DEcision MAking Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) method for the analyses allowed to develop a cause-and-effect model of key factors and analyse the importance ...