Module 12: Linear Regression and Correlation
Hypothesis test for correlation, learning outcomes.
- Conduct a linear regression t-test using p-values and critical values and interpret the conclusion in context
The correlation coefficient, r , tells us about the strength and direction of the linear relationship between x and y . However, the reliability of the linear model also depends on how many observed data points are in the sample. We need to look at both the value of the correlation coefficient r and the sample size n , together.
We perform a hypothesis test of the “ significance of the correlation coefficient ” to decide whether the linear relationship in the sample data is strong enough to use to model the relationship in the population.
The sample data are used to compute r , the correlation coefficient for the sample. If we had data for the entire population, we could find the population correlation coefficient. But because we only have sample data, we cannot calculate the population correlation coefficient. The sample correlation coefficient, r , is our estimate of the unknown population correlation coefficient.
- The symbol for the population correlation coefficient is ρ , the Greek letter “rho.”
- ρ = population correlation coefficient (unknown)
- r = sample correlation coefficient (known; calculated from sample data)
The hypothesis test lets us decide whether the value of the population correlation coefficient ρ is “close to zero” or “significantly different from zero.” We decide this based on the sample correlation coefficient r and the sample size n .
If the test concludes that the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero, we say that the correlation coefficient is “significant.”
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero.
- What the conclusion means: There is a significant linear relationship between x and y . We can use the regression line to model the linear relationship between x and y in the population.
If the test concludes that the correlation coefficient is not significantly different from zero (it is close to zero), we say that the correlation coefficient is “not significant.”
- Conclusion: “There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is not significantly different from zero.”
- What the conclusion means: There is not a significant linear relationship between x and y . Therefore, we CANNOT use the regression line to model a linear relationship between x and y in the population.
- If r is significant and the scatter plot shows a linear trend, the line can be used to predict the value of y for values of x that are within the domain of observed x values.
- If r is not significant OR if the scatter plot does not show a linear trend, the line should not be used for prediction.
- If r is significant and if the scatter plot shows a linear trend, the line may NOT be appropriate or reliable for prediction OUTSIDE the domain of observed x values in the data.

Performing the Hypothesis Test
- Null Hypothesis: H 0 : ρ = 0
- Alternate Hypothesis: H a : ρ ≠ 0
What the Hypotheses Mean in Words
- Null Hypothesis H 0 : The population correlation coefficient IS NOT significantly different from zero. There IS NOT a significant linear relationship (correlation) between x and y in the population.
- Alternate Hypothesis H a : The population correlation coefficient IS significantly DIFFERENT FROM zero. There IS A SIGNIFICANT LINEAR RELATIONSHIP (correlation) between x and y in the population.
Drawing a Conclusion
There are two methods of making the decision. The two methods are equivalent and give the same result.
- Method 1: Using the p -value
- Method 2: Using a table of critical values
In this chapter of this textbook, we will always use a significance level of 5%, α = 0.05
Using the p -value method, you could choose any appropriate significance level you want; you are not limited to using α = 0.05. But the table of critical values provided in this textbook assumes that we are using a significance level of 5%, α = 0.05. (If we wanted to use a different significance level than 5% with the critical value method, we would need different tables of critical values that are not provided in this textbook).
Method 1: Using a p -value to make a decision
Using the ti-83, 83+, 84, 84+ calculator.
To calculate the p -value using LinRegTTEST:
- On the LinRegTTEST input screen, on the line prompt for β or ρ , highlight “≠ 0”
- The output screen shows the p-value on the line that reads “p =”.
- (Most computer statistical software can calculate the p -value).
If the p -value is less than the significance level ( α = 0.05)
- Decision: Reject the null hypothesis.
- Conclusion: “There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero.”
If the p -value is NOT less than the significance level ( α = 0.05)
- Decision: DO NOT REJECT the null hypothesis.
- Conclusion: “There is insufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between x and y because the correlation coefficient is NOT significantly different from zero.”
Calculation Notes:
- You will use technology to calculate the p -value. The following describes the calculations to compute the test statistics and the p -value:
- The p -value is calculated using a t -distribution with n – 2 degrees of freedom.
- The formula for the test statistic is [latex]\displaystyle{t}=\dfrac{{{r}\sqrt{{{n}-{2}}}}}{\sqrt{{{1}-{r}^{{2}}}}}[/latex]. The value of the test statistic, t , is shown in the computer or calculator output along with the p -value. The test statistic t has the same sign as the correlation coefficient r .
- The p -value is the combined area in both tails.
Recall: ORDER OF OPERATIONS
| parentheses | exponents | multiplication | division | addition | subtraction |
| [latex]( \ )[/latex] | [latex]x^2[/latex] | [latex]\times \ \mathrm{or} \ \div[/latex] | [latex]+ \ \mathrm{or} \ -[/latex] | ||
1st find the numerator:
Step 1: Find [latex]n-2[/latex], and then take the square root.
Step 2: Multiply the value in Step 1 by [latex]r[/latex].
2nd find the denominator:
Step 3: Find the square of [latex]r[/latex], which is [latex]r[/latex] multiplied by [latex]r[/latex].
Step 4: Subtract this value from 1, [latex]1 -r^2[/latex].
Step 5: Find the square root of Step 4.
3rd take the numerator and divide by the denominator.
An alternative way to calculate the p -value (p) given by LinRegTTest is the command 2*tcdf(abs(t),10^99, n-2) in 2nd DISTR.
THIRD-EXAM vs FINAL-EXAM EXAM: p- value method
- Consider the third exam/final exam example (example 2).
- The line of best fit is: [latex]\hat{y}[/latex] = -173.51 + 4.83 x with r = 0.6631 and there are n = 11 data points.
- Can the regression line be used for prediction? Given a third exam score ( x value), can we use the line to predict the final exam score (predicted y value)?
- H 0 : ρ = 0
- H a : ρ ≠ 0
- The p -value is 0.026 (from LinRegTTest on your calculator or from computer software).
- The p -value, 0.026, is less than the significance level of α = 0.05.
- Decision: Reject the Null Hypothesis H 0
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between the third exam score ( x ) and the final exam score ( y ) because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero.
Because r is significant and the scatter plot shows a linear trend, the regression line can be used to predict final exam scores.
Method 2: Using a table of Critical Values to make a decision
The 95% Critical Values of the Sample Correlation Coefficient Table can be used to give you a good idea of whether the computed value of r is significant or not . Compare r to the appropriate critical value in the table. If r is not between the positive and negative critical values, then the correlation coefficient is significant. If r is significant, then you may want to use the line for prediction.
Suppose you computed r = 0.801 using n = 10 data points. df = n – 2 = 10 – 2 = 8. The critical values associated with df = 8 are -0.632 and + 0.632. If r < negative critical value or r > positive critical value, then r is significant. Since r = 0.801 and 0.801 > 0.632, r is significant and the line may be used for prediction. If you view this example on a number line, it will help you.
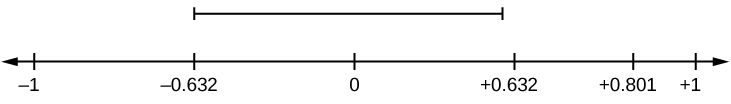
r is not significant between -0.632 and +0.632. r = 0.801 > +0.632. Therefore, r is significant.
For a given line of best fit, you computed that r = 0.6501 using n = 12 data points and the critical value is 0.576. Can the line be used for prediction? Why or why not?
If the scatter plot looks linear then, yes, the line can be used for prediction, because r > the positive critical value.
Suppose you computed r = –0.624 with 14 data points. df = 14 – 2 = 12. The critical values are –0.532 and 0.532. Since –0.624 < –0.532, r is significant and the line can be used for prediction

r = –0.624-0.532. Therefore, r is significant.
For a given line of best fit, you compute that r = 0.5204 using n = 9 data points, and the critical value is 0.666. Can the line be used for prediction? Why or why not?
No, the line cannot be used for prediction, because r < the positive critical value.
Suppose you computed r = 0.776 and n = 6. df = 6 – 2 = 4. The critical values are –0.811 and 0.811. Since –0.811 < 0.776 < 0.811, r is not significant, and the line should not be used for prediction.

–0.811 < r = 0.776 < 0.811. Therefore, r is not significant.
For a given line of best fit, you compute that r = –0.7204 using n = 8 data points, and the critical value is = 0.707. Can the line be used for prediction? Why or why not?
Yes, the line can be used for prediction, because r < the negative critical value.
THIRD-EXAM vs FINAL-EXAM EXAMPLE: critical value method
Consider the third exam/final exam example again. The line of best fit is: [latex]\hat{y}[/latex] = –173.51+4.83 x with r = 0.6631 and there are n = 11 data points. Can the regression line be used for prediction? Given a third-exam score ( x value), can we use the line to predict the final exam score (predicted y value)?
- Use the “95% Critical Value” table for r with df = n – 2 = 11 – 2 = 9.
- The critical values are –0.602 and +0.602
- Since 0.6631 > 0.602, r is significant.
Suppose you computed the following correlation coefficients. Using the table at the end of the chapter, determine if r is significant and the line of best fit associated with each r can be used to predict a y value. If it helps, draw a number line.
- r = –0.567 and the sample size, n , is 19. The df = n – 2 = 17. The critical value is –0.456. –0.567 < –0.456 so r is significant.
- r = 0.708 and the sample size, n , is nine. The df = n – 2 = 7. The critical value is 0.666. 0.708 > 0.666 so r is significant.
- r = 0.134 and the sample size, n , is 14. The df = 14 – 2 = 12. The critical value is 0.532. 0.134 is between –0.532 and 0.532 so r is not significant.
- r = 0 and the sample size, n , is five. No matter what the dfs are, r = 0 is between the two critical values so r is not significant.
For a given line of best fit, you compute that r = 0 using n = 100 data points. Can the line be used for prediction? Why or why not?
No, the line cannot be used for prediction no matter what the sample size is.
Assumptions in Testing the Significance of the Correlation Coefficient
Testing the significance of the correlation coefficient requires that certain assumptions about the data are satisfied. The premise of this test is that the data are a sample of observed points taken from a larger population. We have not examined the entire population because it is not possible or feasible to do so. We are examining the sample to draw a conclusion about whether the linear relationship that we see between x and y in the sample data provides strong enough evidence so that we can conclude that there is a linear relationship between x and y in the population.
The regression line equation that we calculate from the sample data gives the best-fit line for our particular sample. We want to use this best-fit line for the sample as an estimate of the best-fit line for the population. Examining the scatterplot and testing the significance of the correlation coefficient helps us determine if it is appropriate to do this.
The assumptions underlying the test of significance are:
- There is a linear relationship in the population that models the average value of y for varying values of x . In other words, the expected value of y for each particular value lies on a straight line in the population. (We do not know the equation for the line for the population. Our regression line from the sample is our best estimate of this line in the population).
- The y values for any particular x value are normally distributed about the line. This implies that there are more y values scattered closer to the line than are scattered farther away. Assumption (1) implies that these normal distributions are centered on the line: the means of these normal distributions of y values lie on the line.
- The standard deviations of the population y values about the line are equal for each value of x . In other words, each of these normal distributions of y values has the same shape and spread about the line.
- The residual errors are mutually independent (no pattern).
- The data are produced from a well-designed, random sample or randomized experiment.
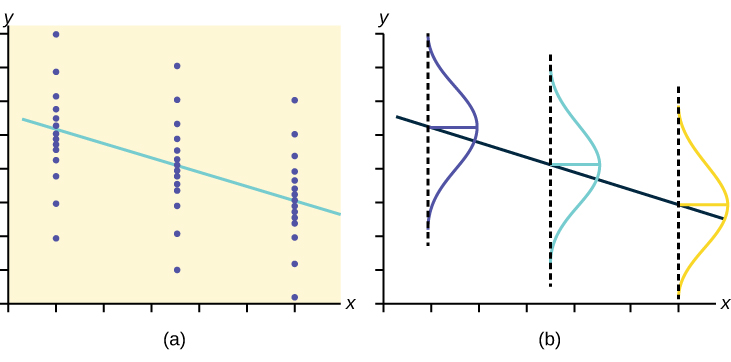
The y values for each x value are normally distributed about the line with the same standard deviation. For each x value, the mean of the y values lies on the regression line. More y values lie near the line than are scattered further away from the line.
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Testing the Significance of the Correlation Coefficient. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/12-4-testing-the-significance-of-the-correlation-coefficient . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Introductory Statistics. Authored by : Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction

Privacy Policy
The Genius Blog
Hypothesis Testing Solved Examples(Questions and Solutions)
Here is a list hypothesis testing exercises and solutions. Try to solve a question by yourself first before you look at the solution.
Question 1 In the population, the average IQ is 100 with a standard deviation of 15. A team of scientists want to test a new medication to see if it has either a positive or negative effect on intelligence, or not effect at all. A sample of 30 participants who have taken the medication has a mean of 140. Did the medication affect intelligence? View Solution to Question 1
A professor wants to know if her introductory statistics class has a good grasp of basic math. Six students are chosen at random from the class and given a math proficiency test. The professor wants the class to be able to score above 70 on the test. The six students get the following scores:62, 92, 75, 68, 83, 95. Can the professor have 90% confidence that the mean score for the class on the test would be above 70. Solution to Question 2
Question 3 In a packaging plant, a machine packs cartons with jars. It is supposed that a new machine would pack faster on the average than the machine currently used. To test the hypothesis, the time it takes each machine to pack ten cartons are recorded. The result in seconds is as follows.
| 42.1 | 42.7 |
| 41 | 43.6 |
| 41.3 | 43.8 |
| 41.8 | 43.3 |
| 42.4 | 42.5 |
| 42.8 | 43.5 |
| 43.2 | 43.1 |
| 42.3 | 41.7 |
| 41.8 | 44 |
| 42.7 | 44.1 |
Do the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that, on the average, the new machine packs faster? Perform the required hypothesis test at the 5% level of significance. Solution to Question 3
Question 4 We want to compare the heights in inches of two groups of individuals. Here are the measurements: X: 175, 168, 168, 190, 156, 181, 182, 175, 174, 179 Y: 120, 180, 125, 188, 130, 190, 110, 185, 112, 188 Solution to Question 4
Question 5 A clinic provides a program to help their clients lose weight and asks a consumer agency to investigate the effectiveness of the program. The agency takes a sample of 15 people, weighing each person in the sample before the program begins and 3 months later. The results a tabulated below
Determine is the program is effective. Solution to Question 5
Question 6 A sample of 20 students were selected and given a diagnostic module prior to studying for a test. And then they were given the test again after completing the module. . The result of the students scores in the test before and after the test is tabulated below.
We want to see if there is significant improvement in the student’s performance due to this teaching method Solution to Question 6
Question 7 A study was performed to test wether cars get better mileage on premium gas than on regular gas. Each of 10 cars was first filled with regular or premium gas, decided by a coin toss, and the mileage for the tank was recorded. The mileage was recorded again for the same cars using other kind of gasoline. Determine wether cars get significantly better mileage with premium gas.
Mileage with regular gas: 16,20,21,22,23,22,27,25,27,28 Mileage with premium gas: 19, 22,24,24,25,25,26,26,28,32 Solution to Question 7
Question 8 An automatic cutter machine must cut steel strips of 1200 mm length. From a preliminary data, we checked that the lengths of the pieces produced by the machine can be considered as normal random variables with a 3mm standard deviation. We want to make sure that the machine is set correctly. Therefore 16 pieces of the products are randomly selected and weight. The figures were in mm: 1193,1196,1198,1195,1198,1199,1204,1193,1203,1201,1196,1200,1191,1196,1198,1191 Examine wether there is any significant deviation from the required size Solution to Question 8
Question 9 Blood pressure reading of ten patients before and after medication for reducing the blood pressure are as follows
Patient: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 Before treatment: 86,84,78,90,92,77,89,90,90,86 After treatment: 80,80,92,79,92,82,88,89,92,83
Test the null hypothesis of no effect agains the alternate hypothesis that medication is effective. Execute it with Wilcoxon test Solution to Question 9
Question on ANOVA Sussan Sound predicts that students will learn most effectively with a constant background sound, as opposed to an unpredictable sound or no sound at all. She randomly divides 24 students into three groups of 8 each. All students study a passage of text for 30 minutes. Those in group 1 study with background sound at a constant volume in the background. Those in group 2 study with nose that changes volume periodically. Those in group 3 study with no sound at all. After studying, all students take a 10 point multiple choice test over the material. Their scores are tabulated below.
Group1: Constant sound: 7,4,6,8,6,6,2,9 Group 2: Random sound: 5,5,3,4,4,7,2,2 Group 3: No sound at all: 2,4,7,1,2,1,5,5 Solution to Question 10
Question 11 Using the following three groups of data, perform a one-way analysis of variance using α = 0.05.
| 51 | 23 | 56 |
| 45 | 43 | 76 |
| 33 | 23 | 74 |
| 45 | 43 | 87 |
| 67 | 45 | 56 |
Solution to Question 11
Question 12 In a packaging plant, a machine packs cartons with jars. It is supposed that a new machine would pack faster on the average than the machine currently used. To test the hypothesis, the time it takes each machine to pack ten cartons are recorded. The result in seconds is as follows.
New Machine: 42,41,41.3,41.8,42.4,42.8,43.2,42.3,41.8,42.7 Old Machine: 42.7,43.6,43.8,43.3,42.5,43.5,43.1,41.7,44,44.1
Perform an F-test to determine if the null hypothesis should be accepted. Solution to Question 12
Question 13 A random sample 500 U.S adults are questioned about their political affiliation and opinion on a tax reform bill. We need to test if the political affiliation and their opinon on a tax reform bill are dependent, at 5% level of significance. The observed contingency table is given below.
| total | ||||
| 138 | 83 | 64 | 285 | |
| 64 | 67 | 84 | 215 | |
| total | 202 | 150 | 148 | 500 |
Solution to Question 13
Question 14 Can a dice be considered regular which is showing the following frequency distribution during 1000 throws?
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 182 | 154 | 162 | 175 | 151 | 176 |
Solution to Question 14
Solution to Question 15
Question 16 A newly developed muesli contains five types of seeds (A, B, C, D and E). The percentage of which is 35%, 25%, 20%, 10% and 10% according to the product information. In a randomly selected muesli, the following volume distribution was found.
| Component | A | B | C | D | E |
| Number of Pieces | 184 | 145 | 100 | 63 | 63 |
Lets us decide about the null hypothesis whether the composition of the sample corresponds to the distribution indicated on the packaging at alpha = 0.1 significance level. Solution to Question 16
Question 17 A research team investigated whether there was any significant correlation between the severity of a certain disease runoff and the age of the patients. During the study, data for n = 200 patients were collected and grouped according to the severity of the disease and the age of the patient. The table below shows the result
| 41 | 34 | 9 | ||
| 25 | 25 | 12 | ||
| 6 | 33 | 15 | ||
Let us decided about the correlation between the age of the patients and the severity of disease progression. Solution to Question 17
Question 18 A publisher is interested in determine which of three book cover is most attractive. He interviews 400 people in each of the three states (California, Illinois and New York), and asks each person which of the cover he or she prefers. The number of preference for each cover is as follows:
| 81 | 60 | 182 | 323 | |
| 78 | 93 | 95 | 266 | |
| 241 | 247 | 123 | 611 | |
| 400 | 400 | 400 | 1200 |
Do these data indicate that there are regional differences in people’s preferences concerning these covers? Use the 0.05 level of significance. Solution to Question 18
Question 19 Trees planted along the road were checked for which ones are healthy(H) or diseased (D) and the following arrangement of the trees were obtained:
H H H H D D D H H H H H H H D D H H D D D
Test at the = 0.05 significance wether this arrangement may be regarded as random
Solution to Question 19
Question 20 Suppose we flip a coin n = 15 times and come up with the following arrangements
H T T T H H T T T T H H T H H
(H = head, T = tail)
Test at the alpha = 0.05 significance level whether this arrangement may be regarded as random.
Solution to Question 20
kindsonthegenius
You might also like, chi-square test for independence – question 18 (a publisher is interested…), question 14 – chi-square goodness of fit test problem( can a dice be considered…), welch’s t-test – how and when to use it.
I am really impressed with your writing abilities as well as with the structure to your weblog. Is this a paid subject matter or did you modify it yourself?
Either way stay up the excellent high quality writing, it’s uncommon to look a great blog like this one these days..
Below are given the gain in weights (in lbs.) of pigs fed on two diet A and B Dieta 25 32 30 34 24 14 32 24 30 31 35 25 – – DietB 44 34 22 10 47 31 40 30 32 35 18 21 35 29
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.

AS Level Mechanics and Statistics - Hypothesis Testing
Other Links
Copyright © Maths Genie. Maths Genie Limited is a company registered in England and Wales with company number 14341280. Registered Office: 86-90 Paul Street, London, England, EC2A 4NE.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples
Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples
Published on January 28, 2020 by Rebecca Bevans . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Statistical tests are used in hypothesis testing . They can be used to:
- determine whether a predictor variable has a statistically significant relationship with an outcome variable.
- estimate the difference between two or more groups.
Statistical tests assume a null hypothesis of no relationship or no difference between groups. Then they determine whether the observed data fall outside of the range of values predicted by the null hypothesis.
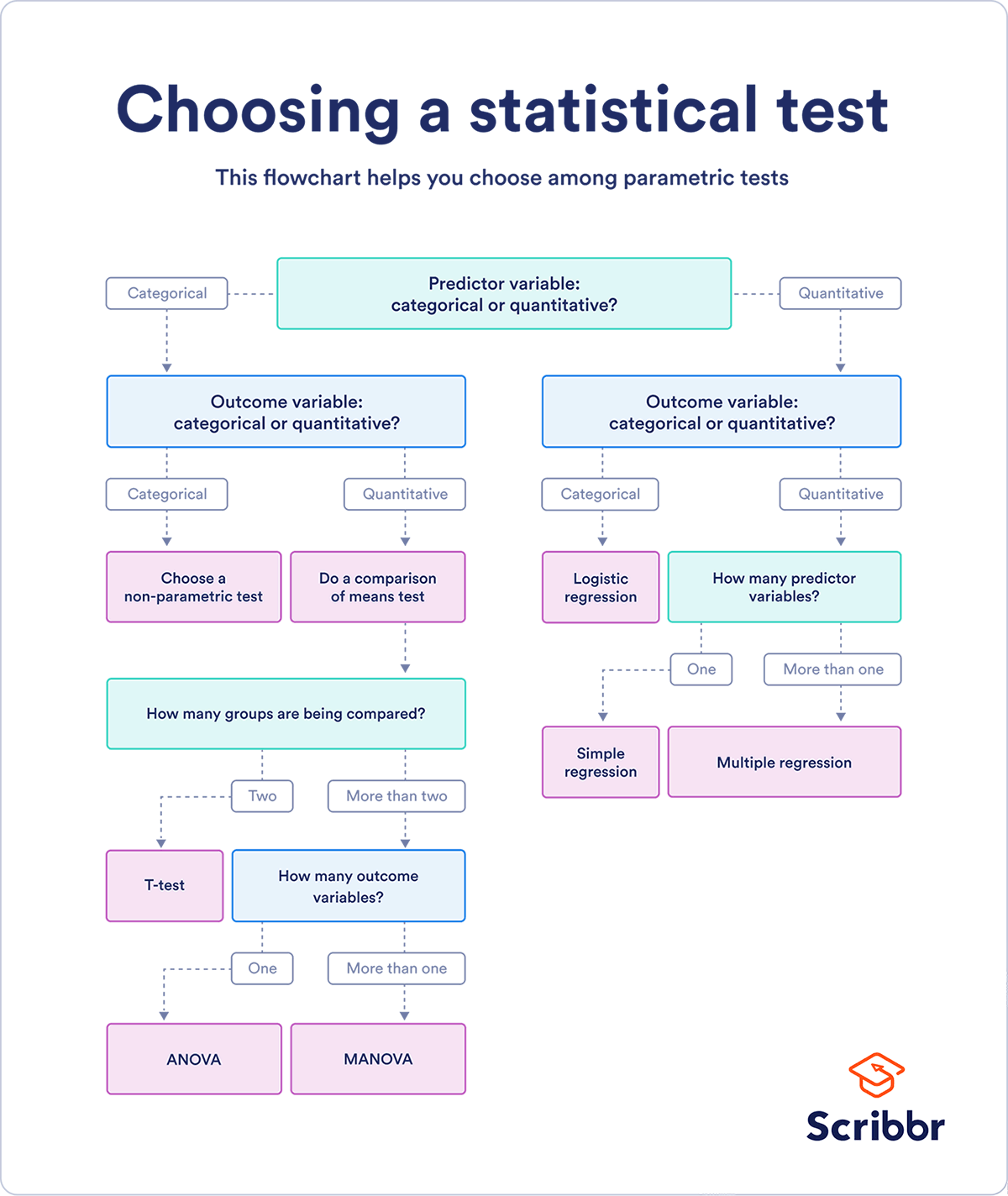
If you already know what types of variables you’re dealing with, you can use the flowchart to choose the right statistical test for your data.
Statistical tests flowchart
Table of contents
What does a statistical test do, when to perform a statistical test, choosing a parametric test: regression, comparison, or correlation, choosing a nonparametric test, flowchart: choosing a statistical test, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about statistical tests.
Statistical tests work by calculating a test statistic – a number that describes how much the relationship between variables in your test differs from the null hypothesis of no relationship.
It then calculates a p value (probability value). The p -value estimates how likely it is that you would see the difference described by the test statistic if the null hypothesis of no relationship were true.
If the value of the test statistic is more extreme than the statistic calculated from the null hypothesis, then you can infer a statistically significant relationship between the predictor and outcome variables.
If the value of the test statistic is less extreme than the one calculated from the null hypothesis, then you can infer no statistically significant relationship between the predictor and outcome variables.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
You can perform statistical tests on data that have been collected in a statistically valid manner – either through an experiment , or through observations made using probability sampling methods .
For a statistical test to be valid , your sample size needs to be large enough to approximate the true distribution of the population being studied.
To determine which statistical test to use, you need to know:
- whether your data meets certain assumptions.
- the types of variables that you’re dealing with.
Statistical assumptions
Statistical tests make some common assumptions about the data they are testing:
- Independence of observations (a.k.a. no autocorrelation): The observations/variables you include in your test are not related (for example, multiple measurements of a single test subject are not independent, while measurements of multiple different test subjects are independent).
- Homogeneity of variance : the variance within each group being compared is similar among all groups. If one group has much more variation than others, it will limit the test’s effectiveness.
- Normality of data : the data follows a normal distribution (a.k.a. a bell curve). This assumption applies only to quantitative data .
If your data do not meet the assumptions of normality or homogeneity of variance, you may be able to perform a nonparametric statistical test , which allows you to make comparisons without any assumptions about the data distribution.
If your data do not meet the assumption of independence of observations, you may be able to use a test that accounts for structure in your data (repeated-measures tests or tests that include blocking variables).
Types of variables
The types of variables you have usually determine what type of statistical test you can use.
Quantitative variables represent amounts of things (e.g. the number of trees in a forest). Types of quantitative variables include:
- Continuous (aka ratio variables): represent measures and can usually be divided into units smaller than one (e.g. 0.75 grams).
- Discrete (aka integer variables): represent counts and usually can’t be divided into units smaller than one (e.g. 1 tree).
Categorical variables represent groupings of things (e.g. the different tree species in a forest). Types of categorical variables include:
- Ordinal : represent data with an order (e.g. rankings).
- Nominal : represent group names (e.g. brands or species names).
- Binary : represent data with a yes/no or 1/0 outcome (e.g. win or lose).
Choose the test that fits the types of predictor and outcome variables you have collected (if you are doing an experiment , these are the independent and dependent variables ). Consult the tables below to see which test best matches your variables.
Parametric tests usually have stricter requirements than nonparametric tests, and are able to make stronger inferences from the data. They can only be conducted with data that adheres to the common assumptions of statistical tests.
The most common types of parametric test include regression tests, comparison tests, and correlation tests.
Regression tests
Regression tests look for cause-and-effect relationships . They can be used to estimate the effect of one or more continuous variables on another variable.
| Predictor variable | Outcome variable | Research question example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| What is the effect of income on longevity? | |||
| What is the effect of income and minutes of exercise per day on longevity? | |||
| Logistic regression | What is the effect of drug dosage on the survival of a test subject? |

Comparison tests
Comparison tests look for differences among group means . They can be used to test the effect of a categorical variable on the mean value of some other characteristic.
T-tests are used when comparing the means of precisely two groups (e.g., the average heights of men and women). ANOVA and MANOVA tests are used when comparing the means of more than two groups (e.g., the average heights of children, teenagers, and adults).
| Predictor variable | Outcome variable | Research question example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paired t-test | What is the effect of two different test prep programs on the average exam scores for students from the same class? | ||
| Independent t-test | What is the difference in average exam scores for students from two different schools? | ||
| ANOVA | What is the difference in average pain levels among post-surgical patients given three different painkillers? | ||
| MANOVA | What is the effect of flower species on petal length, petal width, and stem length? |
Correlation tests
Correlation tests check whether variables are related without hypothesizing a cause-and-effect relationship.
These can be used to test whether two variables you want to use in (for example) a multiple regression test are autocorrelated.
| Variables | Research question example | |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson’s | How are latitude and temperature related? |
Non-parametric tests don’t make as many assumptions about the data, and are useful when one or more of the common statistical assumptions are violated. However, the inferences they make aren’t as strong as with parametric tests.
| Predictor variable | Outcome variable | Use in place of… | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman’s | |||
| Pearson’s | |||
| Sign test | One-sample -test | ||
| Kruskal–Wallis | ANOVA | ||
| ANOSIM | MANOVA | ||
| Wilcoxon Rank-Sum test | Independent t-test | ||
| Wilcoxon Signed-rank test | Paired t-test | ||
This flowchart helps you choose among parametric tests. For nonparametric alternatives, check the table above.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
- Null hypothesis
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Statistical tests commonly assume that:
- the data are normally distributed
- the groups that are being compared have similar variance
- the data are independent
If your data does not meet these assumptions you might still be able to use a nonparametric statistical test , which have fewer requirements but also make weaker inferences.
A test statistic is a number calculated by a statistical test . It describes how far your observed data is from the null hypothesis of no relationship between variables or no difference among sample groups.
The test statistic tells you how different two or more groups are from the overall population mean , or how different a linear slope is from the slope predicted by a null hypothesis . Different test statistics are used in different statistical tests.
Statistical significance is a term used by researchers to state that it is unlikely their observations could have occurred under the null hypothesis of a statistical test . Significance is usually denoted by a p -value , or probability value.
Statistical significance is arbitrary – it depends on the threshold, or alpha value, chosen by the researcher. The most common threshold is p < 0.05, which means that the data is likely to occur less than 5% of the time under the null hypothesis .
When the p -value falls below the chosen alpha value, then we say the result of the test is statistically significant.
Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts (e.g. height, weight, or age).
Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups. This includes rankings (e.g. finishing places in a race), classifications (e.g. brands of cereal), and binary outcomes (e.g. coin flips).
You need to know what type of variables you are working with to choose the right statistical test for your data and interpret your results .
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables :
- Discrete variables represent counts (e.g. the number of objects in a collection).
- Continuous variables represent measurable amounts (e.g. water volume or weight).
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bevans, R. (2023, June 22). Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 23, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/statistical-tests/
Is this article helpful?
Rebecca Bevans
Other students also liked, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, test statistics | definition, interpretation, and examples, normal distribution | examples, formulas, & uses, what is your plagiarism score.
Save 10% on All AnalystPrep 2024 Study Packages with Coupon Code BLOG10 .
- Payment Plans
- Product List
- Partnerships

- Try Free Trial
- Study Packages
- Levels I, II & III Lifetime Package
- Video Lessons
- Study Notes
- Practice Questions
- Levels II & III Lifetime Package
- About the Exam
- About your Instructor
- Part I Study Packages
- Part I & Part II Lifetime Package
- Part II Study Packages
- Exams P & FM Lifetime Package
- Quantitative Questions
- Verbal Questions
- Data Insight Questions
- Live Tutoring
- About your Instructors
- EA Practice Questions
- Data Sufficiency Questions
- Integrated Reasoning Questions

Hypothesis Test on Correlation
The correlation between two variables measures the strength of the linear relationship between them. We wish to assess this relationship using the correlation coefficient. The assessment is based on whether the relationship occurs by chance or not.
Intuitively, if the correlation coefficient between two variables is zero, then there is no linear relationship between the variables. Otherwise, if we use the test of significance to determine whether there is a linear relationship, we will be inclined to whether the estimated correlation coefficient is significantly different from 0.
Hypotheses Statements
The null hypothesis is stated as: $$H_0:\rho=0$$ That is, the correlation coefficient in the population is 0.
The alternative hypothesis is stated as: $$H_a:\rho \neq 0$$ That is, the correlation coefficient is not equal to 0. Clearly, the hypothesis test for the correlation is a two-tailed test.
The Test Statistic
Assuming that the two variables are both normally distributed, the test statistic is given by:
$$ t=\frac{r\sqrt{n-2}}{\sqrt{1-r^2}}$$ Where \(r\) = Sample Correlation. \(n\) = Sample size.
The test statistic has a t-distribution with n-2 degrees of freedom (only if the null hypothesis is true). Let the critical value from the t-distribution table be \(t_c\). If the test statistic is greater than \(t_c\) or less than \(-t_c\), we reject the null hypothesis and uphold the alternative hypothesis. Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Example: Calculating the t-statistic for Hypothesis Testing on Correlation
A financial analyst wishes to test whether there is a linear relationship in the data used to analyze the stock return for a particular company. The analyst uses a sample size of 32 which has a sample correlation of 0.45. Calculate the test statistic and test the significance at the 5% significance level. Solution We know that the test statistic is given by: $$ t=\frac{r\sqrt{n-2}}{\sqrt{1-r^2}}=\frac{0.45\sqrt{32-2}}{\sqrt{1-0.45^2}}=2.760$$ We need to evaluate the critical value from the t-distribution table. From the information given in the question, the number of degrees of freedom is 32-2=30 so that the crucial value is given by:
$$ t_{\frac{0.05}{2},32-2}= t_{0.025,30}=2.042$$
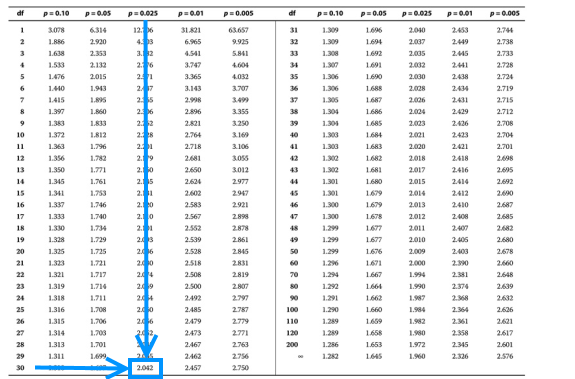
Since the test statistic is greater than the critical value (2.760>2.042), we reject the null hypothesis that the population correlation coefficient is 0, and thus, the correlation coefficient is significantly different from 0.
The Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient
Question The sample correlation between the US dollars (USD) monthly returns to Britain euros (EUR) is estimated to be 0.4565. This estimate is from sample data from January 2015 to December 2019. Assume you are an analyst; would you reject the null hypothesis that the population correlation equals to 0 and 5% significance level? A. Yes. B. No. C. Not enough information to decide. Solution The correct answer is A We need first to determine the sample size, n. From Jan 2015 to Dec 2019, we have five years which is equivalent to 60 months. From here, we can compute the test statistic. $$ t=\frac{r\sqrt{n-2}}{\sqrt{1-r^2}}=\frac{0.4565\sqrt{60-2}}{\sqrt{1-0.4565^2}}=3.908$$ Using the t-distribution table, the critical value is given by: $$ t_{\frac{0.05}{2},60-2}= t_{0.025,58}=2.000$$ Since the test statistic is larger than the critical value, we reject the null hypothesis that the population correlation coefficient is 0.
Quantitative Methods – Learning Sessions
Offered by AnalystPrep

Value at Expiration and Profit for Call and Put Options
Ethics and profession, test for differences between means: pa ..., covariance and correlation, data presentation as a histogram or a ....
Histogram A histogram shows the distribution of numerical data in the form of... Read More
Probability Trees
A tree diagram is a visual representation of all possible future outcomes and... Read More
Stats 2 Ch1 - Regression Correlation and Hypothesis Testing
Home GCSE A-Level Exam Papers
Video Tutorial - coming soon
Exam Questions
Mark Scheme
13.2 Testing the Significance of the Correlation Coefficient
The correlation coefficient, r , tells us about the strength and direction of the linear relationship between X 1 and X 2 .
The sample data are used to compute r , the correlation coefficient for the sample. If we had data for the entire population, we could find the population correlation coefficient. But because we have only sample data, we cannot calculate the population correlation coefficient. The sample correlation coefficient, r , is our estimate of the unknown population correlation coefficient.
- ρ = population correlation coefficient (unknown)
- r = sample correlation coefficient (known; calculated from sample data)
The hypothesis test lets us decide whether the value of the population correlation coefficient ρ is "close to zero" or "significantly different from zero". We decide this based on the sample correlation coefficient r and the sample size n .
If the test concludes that the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero, we say that the correlation coefficient is "significant."
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a significant linear relationship between X 1 and X 2 because the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero.
- What the conclusion means: There is a significant linear relationship X 1 and X 2 . If the test concludes that the correlation coefficient is not significantly different from zero (it is close to zero), we say that correlation coefficient is "not significant".
Performing the Hypothesis Test
- Null Hypothesis: H 0 : ρ = 0
- Alternate Hypothesis: H a : ρ ≠ 0
- Null Hypothesis H 0 : The population correlation coefficient IS NOT significantly different from zero. There IS NOT a significant linear relationship (correlation) between X 1 and X 2 in the population.
- Alternate Hypothesis H a : The population correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero. There is a significant linear relationship (correlation) between X 1 and X 2 in the population.
Drawing a Conclusion There are two methods of making the decision concerning the hypothesis. The test statistic to test this hypothesis is:
Where the second formula is an equivalent form of the test statistic, n is the sample size and the degrees of freedom are n-2. This is a t-statistic and operates in the same way as other t tests. Calculate the t-value and compare that with the critical value from the t-table at the appropriate degrees of freedom and the level of confidence you wish to maintain. If the calculated value is in the tail then cannot accept the null hypothesis that there is no linear relationship between these two independent random variables. If the calculated t-value is NOT in the tailed then cannot reject the null hypothesis that there is no linear relationship between the two variables.
A quick shorthand way to test correlations is the relationship between the sample size and the correlation. If:
then this implies that the correlation between the two variables demonstrates that a linear relationship exists and is statistically significant at approximately the 0.05 level of significance. As the formula indicates, there is an inverse relationship between the sample size and the required correlation for significance of a linear relationship. With only 10 observations, the required correlation for significance is 0.6325, for 30 observations the required correlation for significance decreases to 0.3651 and at 100 observations the required level is only 0.2000.
Correlations may be helpful in visualizing the data, but are not appropriately used to "explain" a relationship between two variables. Perhaps no single statistic is more misused than the correlation coefficient. Citing correlations between health conditions and everything from place of residence to eye color have the effect of implying a cause and effect relationship. This simply cannot be accomplished with a correlation coefficient. The correlation coefficient is, of course, innocent of this misinterpretation. It is the duty of the analyst to use a statistic that is designed to test for cause and effect relationships and report only those results if they are intending to make such a claim. The problem is that passing this more rigorous test is difficult so lazy and/or unscrupulous "researchers" fall back on correlations when they cannot make their case legitimately.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-business-statistics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Alexander Holmes, Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introductory Business Statistics 2e
- Publication date: Dec 13, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-business-statistics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-business-statistics-2e/pages/13-2-testing-the-significance-of-the-correlation-coefficient
© Jul 18, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
6.3 - testing for partial correlation.
When discussing ordinary correlations we looked at tests for the null hypothesis that the ordinary correlation is equal to zero, against the alternative that it is not equal to zero. If that null hypothesis is rejected, then we look at confidence intervals for the ordinary correlation. Similar objectives can be considered for the partial correlation.
First, consider testing the null hypothesis that a partial correlation is equal to zero against the alternative that it is not equal to zero. This is expressed below:
\(H_0\colon \rho_{jk\textbf{.x}}=0\) against \(H_a\colon \rho_{jk\textbf{.x}}\ne 0\)
Here we will use a test statistic that is similar to the one we used for an ordinary correlation. This test statistic is shown below:
\(t = r_{jk\textbf{.x}}\sqrt{\frac{n-2-c}{1-r^2_{jk\textbf{.x}}}}\) \(\dot{\sim}\) \(t_{n-2-c}\)
The only difference between this and the previous one is what appears in the numerator of the radical. Before we just took n - 2. Here we take n - 2 - c , where c is the number of variables upon which we are conditioning. In our Adult Intelligence data, we conditioned on two variables so c would be equal to 2 in this case.
Under the null hypothesis, this test statistic will be approximately t -distributed, also with n - 2 - c degrees of freedom.
We would reject \(H_{o}\colon\) if the absolute value of the test statistic exceeded the critical value from the t -table evaluated at \(\alpha\) over 2:
\(|t| > t_{n-2-c, \alpha/2}\)
Example 6-3: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Data Section
For the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Data, we found a partial correlation of 0.711879, which we enter into the expression for the test statistic as shown below:
\(t = 0.711879 \sqrt{\dfrac{37-2-2}{1-0.711879^2}}=5.82\)
The sample size is 37, along with the 2 variables upon which we are conditioning is also substituted in. Carry out the math and we get a test statistic of 5.82 as shown above.
Here we want to compare this value to a t -distribution with 33 degrees of freedom for an \(\alpha\) = 0.01 level test. Therefore, we are going to look at the critical value for 0.005 in the table (because 33 does not appear to use the closest df that does not exceed 33 which is 30). In this case it is 2.75, meaning that \(t _ { ( d f , 1 - \alpha / 2 ) } = t _ { ( 33,0.995 ) } \) is 2.75.
Because \(5.82 > 2.75 = t _ { ( 33,0.995 ) }\), we can reject the null hypothesis, \(H_{o}\) at the \(\alpha = 0.01\) level and conclude that there is a significant partial correlation between these two variables. In particular, we would include that this partial correlation is positive indicating that even after taking into account Arithmetic and Picture Completion, there is a positive association between Information and Similarities.
Confidence Interval for the partial correlation, \(\rho_{jk\textbf{.x}}\) Section
The procedure here is very similar to the procedure we used for ordinary correlation.
Compute Fisher's transformation of the partial correlation using the same formula as before.
\(z_{jk} = \dfrac{1}{2}\log \left( \dfrac{1+r_{jk\textbf{.X}}}{1-r_{jk\textbf{.X}}}\right) \)
In this case, for a large n , this Fisher transform variable will be possibly normally distributed. The mean is equal to the Fisher transform for the population value for this partial correlation, and the variance is equal to 1 over n-3-c .
\(z_{jk}\) \(\dot{\sim}\) \(N \left( \dfrac{1}{2}\log \dfrac{1+\rho_{jk\textbf{.X}}}{1-\rho_{jk\textbf{.X}}}, \dfrac{1}{n-3-c}\right)\)
Compute a \((1 - \alpha) × 100\%\) confidence interval for the Fisher transform correlation. This expression is shown below:
\( \dfrac{1}{2}\log \dfrac{1+\rho_{jk\textbf{.X}}}{1-\rho_{jk\textbf{.X}}}\)
This yields the bounds \(Z_{l}\) and \(Z_{u}\) as before.
\(\left(\underset{Z_l}{\underbrace{Z_{jk}-\dfrac{Z_{\alpha/2}}{\sqrt{n-3-c}}}}, \underset{Z_U}{\underbrace{Z_{jk}+\dfrac{Z_{\alpha/2}}{\sqrt{n-3-c}}}}\right)\)
Back transform to obtain the desired confidence interval for the partial correlation - \(\rho_{jk\textbf{.X}}\)
\(\left(\dfrac{e^{2Z_l}-1}{e^{2Z_l}+1}, \dfrac{e^{2Z_U}-1}{e^{2Z_U}+1}\right)\)
Example 6-3: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Data (Steps Shown) Section
The confidence interval is calculated by substituting the results from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Data into the appropriate steps below:
Step 1 : Compute the Fisher transform:
\begin{align} Z_{12} &= \dfrac{1}{2}\log \frac{1+r_{12.34}}{1-r_{12.34}}\\[5pt] &= \dfrac{1}{2} \log \frac{1+0.711879}{1-0.711879}\\[5pt] &= 0.89098 \end{align}
Step 2 : Compute the 95% confidence interval for \( \frac{1}{2}\log \frac{1+\rho_{12.34}}{1-\rho_{12.34}}\) :
\begin{align} Z_l &= Z_{12}-Z_{0.025}/\sqrt{n-3-c}\\[5pt] & = 0.89098 - \dfrac{1.96}{\sqrt{37-3-2}}\\[5pt] &= 0.5445 \end{align}
\begin{align} Z_U &= Z_{12}+Z_{0.025}/\sqrt{n-3-c}\\[5pt] &= 0.89098 + \dfrac{1.96}{\sqrt{37-3-2}} \\[5pt] &= 1.2375 \end{align}
Step 3 : Back-transform to obtain the 95% confidence interval for \(\rho_{12.34}\) :
\(\left(\dfrac{\exp\{2Z_l\}-1}{\exp\{2Z_l\}+1}, \dfrac{\exp\{2Z_U\}-1}{\exp\{2Z_U\}+1}\right)\)
\(\left(\dfrac{\exp\{2\times 0.5445\}-1}{\exp\{2\times 0.5445\}+1}, \dfrac{\exp\{2\times 1.2375\}-1}{\exp\{2\times 1.2375\}+1}\right)\)
\((0.4964, 0.8447)\)
Based on this result, we can conclude that we are 95% confident that the interval (0.4964, 0.8447) contains the partial correlation between Information and Similarities scores given scores on Arithmetic and Picture Completion.

COMMENTS
11.2: Correlation Hypothesis Test. The correlation coefficient, r, tells us about the strength and direction of the linear relationship between x and y. However, the reliability of the linear model also depends on how many observed data points are in the sample.
Let's perform the hypothesis test on the husband's age and wife's age data in which the sample correlation based on n = 170 couples is r = 0.939. To test H 0: ρ = 0 against the alternative H A: ρ ≠ 0, we obtain the following test statistic: t ∗ = r n − 2 1 − R 2 = 0.939 170 − 2 1 − 0.939 2 = 35.39. To obtain the P -value, we need ...
The t-test is a statistical test for the correlation coefficient. It can be used when x x and y y are linearly related, the variables are random variables, and when the population of the variable y y is normally distributed. The formula for the t-test statistic is t = r (n − 2 1 −r2)− −−−−−−−√ t = r (n − 2 1 − r 2).
Past Papers. CIE. Spanish Language & Literature. Past Papers. Other Subjects. Revision notes on 2.5.2 Hypothesis Testing for Correlation for the Edexcel A Level Maths: Statistics syllabus, written by the Maths experts at Save My Exams.
The test statistic is: t ∗ = r n − 2 1 − r 2 = (0.711) 28 − 2 1 − 0.711 2 = 5.1556. Next, we need to find the p-value. The p-value for the two-sided test is: p-value = 2 P (T> 5.1556) <0.0001. Therefore, for any reasonable α level, we can reject the hypothesis that the population correlation coefficient is 0 and conclude that it is ...
s a correlation between temperature and rainfall. (2)The product moment. correlation coefficient is calculated to be r = 0.37.(. ) Test your hypotheses at the 10% sig. e level. (2) (Total for question 2 is 4 marks)3 The temperature and t. e number of hours of sunshine on 12 days is recorded. The product moment.
It should be noted that the three hypothesis tests we learned for testing the existence of a linear relationship — the t-test for H 0: β 1 = 0, the ANOVA F-test for H 0: β 1 = 0, and the t-test for H 0: ρ = 0 — will always yield the same results. For example, if we treat the husband's age ("HAge") as the response and the wife's age ("WAge") as the predictor, each test yields a P-value ...
the product moment correlation coefficient between: (i) x and y; (ii) x and z. (5 marks) Carry out hypothesis tests, at the 5% level of significance, to determine whether the values of the two product moment correlation coefficie. rt (a) indicate a positive association between each of the. ables. (4 marks) Summarise, in context, your findings ...
The hypothesis test lets us decide whether the value of the population correlation coefficient ρ is "close to zero" or "significantly different from zero.". We decide this based on the sample correlation coefficient r and the sample size n. If the test concludes that the correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero, we ...
View Solution to Question 1. Question 2. A professor wants to know if her introductory statistics class has a good grasp of basic math. Six students are chosen at random from the class and given a math proficiency test. The professor wants the class to be able to score above 70 on the test. The six students get the following scores:62, 92, 75 ...
We perform a hypothesis test of the "significance of the correlation coefficient" to decide whether the linear relationship in the sample data is strong enough to use to model the relationship in the population. The hypothesis test lets us decide whether the value of the population correlation coefficient. \rho ρ.
The correlation coefficient, r, tells us about the strength and direction of the linear relationship between x and y.However, the reliability of the linear model also depends on how many observed data points are in the sample. We need to look at both the value of the correlation coefficient r and the sample size n, together.. We perform a hypothesis test of the "significance of the correlation ...
Maths Genie Limited is a company registered in England and Wales with company number 14341280. Registered Office: 86-90 Paul Street, London, England, EC2A 4NE. Maths revision videos and notes on the topics of hypothesis testing, correlation hypothesis testing, mean of normal distribution hypothesis testing and non linear regression.
The course begins with basic descriptive statistics and ends with correlation analysis, but there are a few lectures dedicated to hypothesis testing. This resource also provides instruction on how to use StatKey and Minitab to analyze data and actually conduct these hypothesis tests. The first video on hypothesis testing is available here. 4.
Choosing a parametric test: regression, comparison, or correlation. Parametric tests usually have stricter requirements than nonparametric tests, and are able to make stronger inferences from the data. ... Research question example; Paired t-test: Categorical; 1 predictor; Quantitative; ... Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for ...
Clearly, the hypothesis test for the correlation is a two-tailed test. The Test Statistic. Assuming that the two variables are both normally distributed, the test statistic is given by: $$ t=\frac{r\sqrt{n-2}}{\sqrt{1-r^2}}$$ ... Question. The sample correlation between the US dollars (USD) monthly returns to Britain euros (EUR) is estimated to ...
MrModoniMaths - Stats 2 Ch1 - Regression Correlation and Hypothesis Testing. Density mass Volume Compound Measure - Multiplicative Reasoning. Histograms (harder) Using Graph - Multiplicative Reasoning. Pure 1 Ch10 - Trigonometric Identities and Equations. Pure 1 Ch12 - Differentiation from First Principles and Standard Result.
Alternate Hypothesis H a: The population correlation coefficient is significantly different from zero. There is a significant linear relationship (correlation) between X 1 and X 2 in the population. Drawing a Conclusion There are two methods of making the decision concerning the hypothesis.
The p-value is calculated using a t -distribution with n − 2 degrees of freedom. The formula for the test statistic is t = r√n − 2 √1 − r2. The value of the test statistic, t, is shown in the computer or calculator output along with the p-value. The test statistic t has the same sign as the correlation coefficient r.
The hypotheses are: Find the critical value using dfE = n − p − 1 = 13 for a two-tailed test α = 0.05 inverse t-distribution to get the critical values ± 2.160. Draw the sampling distribution and label the critical values, as shown in Figure 12-14. Figure 12-14: Graph of t-distribution with labeled critical values.
If p-value < 0.05, you will Reject the null hypothesis H0 Fail to reject the null hypothesis H0 Reject the alternative hypothesis H1 Question 6: When the pretest criterion for a paired t- test is not satisfied, you must instead use The Mann-Whitney U test The Kruskal-Wallis test The Wilcoxon test Question 7: Exercise 7.1; This question is ...
The p-value is calculated using a t -distribution with n − 2 degrees of freedom. The formula for the test statistic is t = r√n − 2 √1 − r2. The value of the test statistic, t, is shown in the computer or calculator output along with the p-value. The test statistic t has the same sign as the correlation coefficient r.
First, consider testing the null hypothesis that a partial correlation is equal to zero against the alternative that it is not equal to zero. This is expressed below: H 0: ρ j k.x = 0 against H a: ρ j k.x ≠ 0. Here we will use a test statistic that is similar to the one we used for an ordinary correlation. This test statistic is shown below:
The Null hypothesis \(\left(H_{O}\right)\) is a statement about the comparisons, e.g., between a sample statistic and the population, or between two treatment groups. The former is referred to as a one-tailed test whereas the latter is called a two-tailed test. The null hypothesis is typically "no statistical difference" between the ...