
17 Essay Conclusion Examples (Copy and Paste)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Essay conclusions are not just extra filler. They are important because they tie together your arguments, then give you the chance to forcefully drive your point home.
I created the 5 Cs conclusion method to help you write essay conclusions:

I’ve previously produced the video below on how to write a conclusion that goes over the above image.
The video follows the 5 C’s method ( you can read about it in this post ), which doesn’t perfectly match each of the below copy-and-paste conclusion examples, but the principles are similar, and can help you to write your own strong conclusion:
💡 New! Try this AI Prompt to Generate a Sample 5Cs Conclusion This is my essay: [INSERT ESSAY WITHOUT THE CONCLUSION]. I want you to write a conclusion for this essay. In the first sentence of the conclusion, return to a statement I made in the introduction. In the second sentence, reiterate the thesis statement I have used. In the third sentence, clarify how my final position is relevant to the Essay Question, which is [ESSAY QUESTION]. In the fourth sentence, explain who should be interested in my findings. In the fifth sentence, end by noting in one final, engaging sentence why this topic is of such importance.
Remember: The prompt can help you generate samples but you can’t submit AI text for assessment. Make sure you write your conclusion in your own words.
Essay Conclusion Examples
Below is a range of copy-and-paste essay conclusions with gaps for you to fill-in your topic and key arguments. Browse through for one you like (there are 17 for argumentative, expository, compare and contrast, and critical essays). Once you’ve found one you like, copy it and add-in the key points to make it your own.
1. Argumentative Essay Conclusions
The arguments presented in this essay demonstrate the significant importance of _____________. While there are some strong counterarguments, such as ____________, it remains clear that the benefits/merits of _____________ far outweigh the potential downsides. The evidence presented throughout the essay strongly support _____________. In the coming years, _____________ will be increasingly important. Therefore, continual advocacy for the position presented in this essay will be necessary, especially due to its significant implications for _____________.
Version 1 Filled-In
The arguments presented in this essay demonstrate the significant importance of fighting climate change. While there are some strong counterarguments, such as the claim that it is too late to stop catastrophic change, it remains clear that the merits of taking drastic action far outweigh the potential downsides. The evidence presented throughout the essay strongly support the claim that we can at least mitigate the worst effects. In the coming years, intergovernmental worldwide agreements will be increasingly important. Therefore, continual advocacy for the position presented in this essay will be necessary, especially due to its significant implications for humankind.

As this essay has shown, it is clear that the debate surrounding _____________ is multifaceted and highly complex. While there are strong arguments opposing the position that _____________, there remains overwhelming evidence to support the claim that _____________. A careful analysis of the empirical evidence suggests that _____________ not only leads to ____________, but it may also be a necessity for _____________. Moving forward, _____________ should be a priority for all stakeholders involved, as it promises a better future for _____________. The focus should now shift towards how best to integrate _____________ more effectively into society.
Version 2 Filled-In
As this essay has shown, it is clear that the debate surrounding climate change is multifaceted and highly complex. While there are strong arguments opposing the position that we should fight climate change, there remains overwhelming evidence to support the claim that action can mitigate the worst effects. A careful analysis of the empirical evidence suggests that strong action not only leads to better economic outcomes in the long term, but it may also be a necessity for preventing climate-related deaths. Moving forward, carbon emission mitigation should be a priority for all stakeholders involved, as it promises a better future for all. The focus should now shift towards how best to integrate smart climate policies more effectively into society.
Based upon the preponderance of evidence, it is evident that _____________ holds the potential to significantly alter/improve _____________. The counterarguments, while noteworthy, fail to diminish the compelling case for _____________. Following an examination of both sides of the argument, it has become clear that _____________ presents the most effective solution/approach to _____________. Consequently, it is imperative that society acknowledge the value of _____________ for developing a better _____________. Failing to address this topic could lead to negative outcomes, including _____________.
Version 3 Filled-In
Based upon the preponderance of evidence, it is evident that addressing climate change holds the potential to significantly improve the future of society. The counterarguments, while noteworthy, fail to diminish the compelling case for immediate climate action. Following an examination of both sides of the argument, it has become clear that widespread and urgent social action presents the most effective solution to this pressing problem. Consequently, it is imperative that society acknowledge the value of taking immediate action for developing a better environment for future generations. Failing to address this topic could lead to negative outcomes, including more extreme climate events and greater economic externalities.
See Also: Examples of Counterarguments
On the balance of evidence, there is an overwhelming case for _____________. While the counterarguments offer valid points that are worth examining, they do not outweigh or overcome the argument that _____________. An evaluation of both perspectives on this topic concludes that _____________ is the most sufficient option for _____________. The implications of embracing _____________ do not only have immediate benefits, but they also pave the way for a more _____________. Therefore, the solution of _____________ should be actively pursued by _____________.
Version 4 Filled-In
On the balance of evidence, there is an overwhelming case for immediate tax-based action to mitigate the effects of climate change. While the counterarguments offer valid points that are worth examining, they do not outweigh or overcome the argument that action is urgently necessary. An evaluation of both perspectives on this topic concludes that taking societal-wide action is the most sufficient option for achieving the best results. The implications of embracing a society-wide approach like a carbon tax do not only have immediate benefits, but they also pave the way for a more healthy future. Therefore, the solution of a carbon tax or equivalent policy should be actively pursued by governments.
2. Expository Essay Conclusions
Overall, it is evident that _____________ plays a crucial role in _____________. The analysis presented in this essay demonstrates the clear impact of _____________ on _____________. By understanding the key facts about _____________, practitioners/society are better equipped to navigate _____________. Moving forward, further exploration of _____________ will yield additional insights and information about _____________. As such, _____________ should remain a focal point for further discussions and studies on _____________.
Overall, it is evident that social media plays a crucial role in harming teenagers’ mental health. The analysis presented in this essay demonstrates the clear impact of social media on young people. By understanding the key facts about the ways social media cause young people to experience body dysmorphia, teachers and parents are better equipped to help young people navigate online spaces. Moving forward, further exploration of the ways social media cause harm will yield additional insights and information about how it can be more sufficiently regulated. As such, the effects of social media on youth should remain a focal point for further discussions and studies on youth mental health.
To conclude, this essay has explored the multi-faceted aspects of _____________. Through a careful examination of _____________, this essay has illuminated its significant influence on _____________. This understanding allows society to appreciate the idea that _____________. As research continues to emerge, the importance of _____________ will only continue to grow. Therefore, an understanding of _____________ is not merely desirable, but imperative for _____________.
To conclude, this essay has explored the multi-faceted aspects of globalization. Through a careful examination of globalization, this essay has illuminated its significant influence on the economy, cultures, and society. This understanding allows society to appreciate the idea that globalization has both positive and negative effects. As research continues to emerge, the importance of studying globalization will only continue to grow. Therefore, an understanding of globalization’s effects is not merely desirable, but imperative for judging whether it is good or bad.
Reflecting on the discussion, it is clear that _____________ serves a pivotal role in _____________. By delving into the intricacies of _____________, we have gained valuable insights into its impact and significance. This knowledge will undoubtedly serve as a guiding principle in _____________. Moving forward, it is paramount to remain open to further explorations and studies on _____________. In this way, our understanding and appreciation of _____________ can only deepen and expand.
Reflecting on the discussion, it is clear that mass media serves a pivotal role in shaping public opinion. By delving into the intricacies of mass media, we have gained valuable insights into its impact and significance. This knowledge will undoubtedly serve as a guiding principle in shaping the media landscape. Moving forward, it is paramount to remain open to further explorations and studies on how mass media impacts society. In this way, our understanding and appreciation of mass media’s impacts can only deepen and expand.
In conclusion, this essay has shed light on the importance of _____________ in the context of _____________. The evidence and analysis provided underscore the profound effect _____________ has on _____________. The knowledge gained from exploring _____________ will undoubtedly contribute to more informed and effective decisions in _____________. As we continue to progress, the significance of understanding _____________ will remain paramount. Hence, we should strive to deepen our knowledge of _____________ to better navigate and influence _____________.
In conclusion, this essay has shed light on the importance of bedside manner in the context of nursing. The evidence and analysis provided underscore the profound effect compassionate bedside manner has on patient outcome. The knowledge gained from exploring nurses’ bedside manner will undoubtedly contribute to more informed and effective decisions in nursing practice. As we continue to progress, the significance of understanding nurses’ bedside manner will remain paramount. Hence, we should strive to deepen our knowledge of this topic to better navigate and influence patient outcomes.
See More: How to Write an Expository Essay
3. Compare and Contrast Essay Conclusion
While both _____________ and _____________ have similarities such as _____________, they also have some very important differences in areas like _____________. Through this comparative analysis, a broader understanding of _____________ and _____________ has been attained. The choice between the two will largely depend on _____________. For example, as highlighted in the essay, ____________. Despite their differences, both _____________ and _____________ have value in different situations.
While both macrosociology and microsociology have similarities such as their foci on how society is structured, they also have some very important differences in areas like their differing approaches to research methodologies. Through this comparative analysis, a broader understanding of macrosociology and microsociology has been attained. The choice between the two will largely depend on the researcher’s perspective on how society works. For example, as highlighted in the essay, microsociology is much more concerned with individuals’ experiences while macrosociology is more concerned with social structures. Despite their differences, both macrosociology and microsociology have value in different situations.
It is clear that _____________ and _____________, while seeming to be different, have shared characteristics in _____________. On the other hand, their contrasts in _____________ shed light on their unique features. The analysis provides a more nuanced comprehension of these subjects. In choosing between the two, consideration should be given to _____________. Despite their disparities, it’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of both when it comes to _____________.
It is clear that behaviorism and consructivism, while seeming to be different, have shared characteristics in their foci on knowledge acquisition over time. On the other hand, their contrasts in ideas about the role of experience in learning shed light on their unique features. The analysis provides a more nuanced comprehension of these subjects. In choosing between the two, consideration should be given to which approach works best in which situation. Despite their disparities, it’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of both when it comes to student education.
Reflecting on the points discussed, it’s evident that _____________ and _____________ share similarities such as _____________, while also demonstrating unique differences, particularly in _____________. The preference for one over the other would typically depend on factors such as _____________. Yet, regardless of their distinctions, both _____________ and _____________ play integral roles in their respective areas, significantly contributing to _____________.
Reflecting on the points discussed, it’s evident that red and orange share similarities such as the fact they are both ‘hot colors’, while also demonstrating unique differences, particularly in their social meaning (red meaning danger and orange warmth). The preference for one over the other would typically depend on factors such as personal taste. Yet, regardless of their distinctions, both red and orange play integral roles in their respective areas, significantly contributing to color theory.
Ultimately, the comparison and contrast of _____________ and _____________ have revealed intriguing similarities and notable differences. Differences such as _____________ give deeper insights into their unique and shared qualities. When it comes to choosing between them, _____________ will likely be a deciding factor. Despite these differences, it is important to remember that both _____________ and _____________ hold significant value within the context of _____________, and each contributes to _____________ in its own unique way.
Ultimately, the comparison and contrast of driving and flying have revealed intriguing similarities and notable differences. Differences such as their differing speed to destination give deeper insights into their unique and shared qualities. When it comes to choosing between them, urgency to arrive at the destination will likely be a deciding factor. Despite these differences, it is important to remember that both driving and flying hold significant value within the context of air transit, and each contributes to facilitating movement in its own unique way.
See Here for More Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
4. Critical Essay Conclusion
In conclusion, the analysis of _____________ has unveiled critical aspects related to _____________. While there are strengths in _____________, its limitations are equally telling. This critique provides a more informed perspective on _____________, revealing that there is much more beneath the surface. Moving forward, the understanding of _____________ should evolve, considering both its merits and flaws.
In conclusion, the analysis of flow theory has unveiled critical aspects related to motivation and focus. While there are strengths in achieving a flow state, its limitations are equally telling. This critique provides a more informed perspective on how humans achieve motivation, revealing that there is much more beneath the surface. Moving forward, the understanding of flow theory of motivation should evolve, considering both its merits and flaws.
To conclude, this critical examination of _____________ sheds light on its multi-dimensional nature. While _____________ presents notable advantages, it is not without its drawbacks. This in-depth critique offers a comprehensive understanding of _____________. Therefore, future engagements with _____________ should involve a balanced consideration of its strengths and weaknesses.
To conclude, this critical examination of postmodern art sheds light on its multi-dimensional nature. While postmodernism presents notable advantages, it is not without its drawbacks. This in-depth critique offers a comprehensive understanding of how it has contributed to the arts over the past 50 years. Therefore, future engagements with postmodern art should involve a balanced consideration of its strengths and weaknesses.
Upon reflection, the critique of _____________ uncovers profound insights into its underlying intricacies. Despite its positive aspects such as ________, it’s impossible to overlook its shortcomings. This analysis provides a nuanced understanding of _____________, highlighting the necessity for a balanced approach in future interactions. Indeed, both the strengths and weaknesses of _____________ should be taken into account when considering ____________.
Upon reflection, the critique of marxism uncovers profound insights into its underlying intricacies. Despite its positive aspects such as its ability to critique exploitation of labor, it’s impossible to overlook its shortcomings. This analysis provides a nuanced understanding of marxism’s harmful effects when used as an economic theory, highlighting the necessity for a balanced approach in future interactions. Indeed, both the strengths and weaknesses of marxism should be taken into account when considering the use of its ideas in real life.
Ultimately, this critique of _____________ offers a detailed look into its advantages and disadvantages. The strengths of _____________ such as __________ are significant, yet its limitations such as _________ are not insignificant. This balanced analysis not only offers a deeper understanding of _____________ but also underscores the importance of critical evaluation. Hence, it’s crucial that future discussions around _____________ continue to embrace this balanced approach.
Ultimately, this critique of artificial intelligence offers a detailed look into its advantages and disadvantages. The strengths of artificial intelligence, such as its ability to improve productivity are significant, yet its limitations such as the possibility of mass job losses are not insignificant. This balanced analysis not only offers a deeper understanding of artificial intelligence but also underscores the importance of critical evaluation. Hence, it’s crucial that future discussions around the regulation of artificial intelligence continue to embrace this balanced approach.
This article promised 17 essay conclusions, and this one you are reading now is the twenty-first. This last conclusion demonstrates that the very best essay conclusions are written uniquely, from scratch, in order to perfectly cater the conclusion to the topic. A good conclusion will tie together all the key points you made in your essay and forcefully drive home the importance or relevance of your argument, thesis statement, or simply your topic so the reader is left with one strong final point to ponder.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Forums Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Conclude an Essay (with Examples)
Last Updated: July 22, 2024 Fact Checked
Writing a Strong Conclusion
What to avoid, brainstorming tricks.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,230,720 times.
So, you’ve written an outstanding essay and couldn’t be more proud. But now you have to write the final paragraph. The conclusion simply summarizes what you’ve already written, right? Well, not exactly. Your essay’s conclusion should be a bit more finessed than that. Luckily, you’ve come to the perfect place to learn how to write a conclusion. We’ve put together this guide to fill you in on everything you should and shouldn’t do when ending an essay. Follow our advice, and you’ll have a stellar conclusion worthy of an A+ in no time.
Tips for Ending an Essay
- Rephrase your thesis to include in your final paragraph to bring the essay full circle.
- End your essay with a call to action, warning, or image to make your argument meaningful.
- Keep your conclusion concise and to the point, so you don’t lose a reader’s attention.
- Do your best to avoid adding new information to your conclusion and only emphasize points you’ve already made in your essay.

- “All in all”
- “Ultimately”
- “Furthermore”
- “As a consequence”
- “As a result”

- Make sure to write your main points in a new and unique way to avoid repetition.

- Let’s say this is your original thesis statement: “Allowing students to visit the library during lunch improves campus life and supports academic achievement.”
- Restating your thesis for your conclusion could look like this: “Evidence shows students who have access to their school’s library during lunch check out more books and are more likely to complete their homework.”
- The restated thesis has the same sentiment as the original while also summarizing other points of the essay.

- “When you use plastic water bottles, you pollute the ocean. Switch to using a glass or metal water bottle instead. The planet and sea turtles will thank you.”
- “The average person spends roughly 7 hours on their phone a day, so there’s no wonder cybersickness is plaguing all generations.”
- “Imagine walking on the beach, except the soft sand is made up of cigarette butts. They burn your feet but keep washing in with the tide. If we don’t clean up the ocean, this will be our reality.”
- “ Lost is not only a show that changed the course of television, but it’s also a reflection of humanity as a whole.”
- “If action isn’t taken to end climate change today, the global temperature will dangerously rise from 4.5 to 8 °F (−15.3 to −13.3 °C) by 2100.”

- Focus on your essay's most prevalent or important parts. What key points do you want readers to take away or remember about your essay?

- For instance, instead of writing, “That’s why I think that Abraham Lincoln was the best American President,” write, “That’s why Abraham Lincoln was the best American President.”
- There’s no room for ifs, ands, or buts—your opinion matters and doesn’t need to be apologized for!

- For instance, words like “firstly,” “secondly,” and “thirdly” may be great transition statements for body paragraphs but are unnecessary in a conclusion.

- For instance, say you began your essay with the idea that humanity’s small sense of sense stems from space’s vast size. Try returning to this idea in the conclusion by emphasizing that as human knowledge grows, space becomes smaller.

- For example, you could extend an essay on the television show Orange is the New Black by bringing up the culture of imprisonment in America.
Community Q&A

Reader Videos
Share a quick video tip and help bring articles to life with your friendly advice. Your insights could make a real difference and help millions of people!
- Always review your essay after writing it for proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation, and don’t be afraid to revise. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Have somebody else proofread your essay before turning it in. The other person will often be able to see errors you may have missed!

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.uts.edu.au/current-students/support/helps/self-help-resources/grammar/transition-signals
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/argument_papers/conclusions.html
- ↑ http://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb/conclude.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://www.pittsfordschools.org/site/handlers/filedownload.ashx?moduleinstanceid=542&dataid=4677&FileName=conclusions1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.cuyamaca.edu/student-support/tutoring-center/files/student-resources/how-to-write-a-good-conclusion.pdf
- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185935
About This Article

To end an essay, start your conclusion with a phrase that makes it clear your essay is coming to a close, like "In summary," or "All things considered." Then, use a few sentences to briefly summarize the main points of your essay by rephrasing the topic sentences of your body paragraphs. Finally, end your conclusion with a call to action that encourages your readers to do something or learn more about your topic. In general, try to keep your conclusion between 5 and 7 sentences long. For more tips from our English co-author, like how to avoid common pitfalls when writing an essay conclusion, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Eva Dettling
Jan 23, 2019
Did this article help you?

Mar 7, 2017
Jul 16, 2021
Gabby Suzuki
Oct 17, 2019
Nicole Murphy
Apr 26, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
On College Life and Writing | Bid4papers Blog
How to write a conclusion of an informative essay.
- Restate a thesis.
- Wrap up subtopics.
- Leave readers with food for thought.
So now you finish the assigned paper and wonder how to write a conclusion of an informative essay. Congrats! You’re at the right place:
This guide will reveal all the details about the process: the elements of an informative essay conclusion, how to connect them to an essay body, and why end on a positive note to leave a reader with food for thought.

What is an Informative Essay Conclusion?
We nailed it a long ago in our super popular article about essay conclusions :
A concluding paragraph of your essay is as critical as its introduction. It summarizes the content, provides closure for readers to remember the main idea of your work, and leaves the audience with food for thought.
Long story short, your essay conclusion needs to answer a “What now?” question, giving the audience something to think about after they’ve read your paper.
A good essay conclusion restates a thesis and main ideas, providing a sense of closure. It concludes the thoughts you covered in the essay body, not presenting new ideas.
Tip: Try to finish your informative essay on a positive note, even if the topic itself wasn’t so. It will influence the final impression of your work. Make your conclusion short and sweet, no longer than 5-7 sentences in length.
Conclusion of an Informative Essay
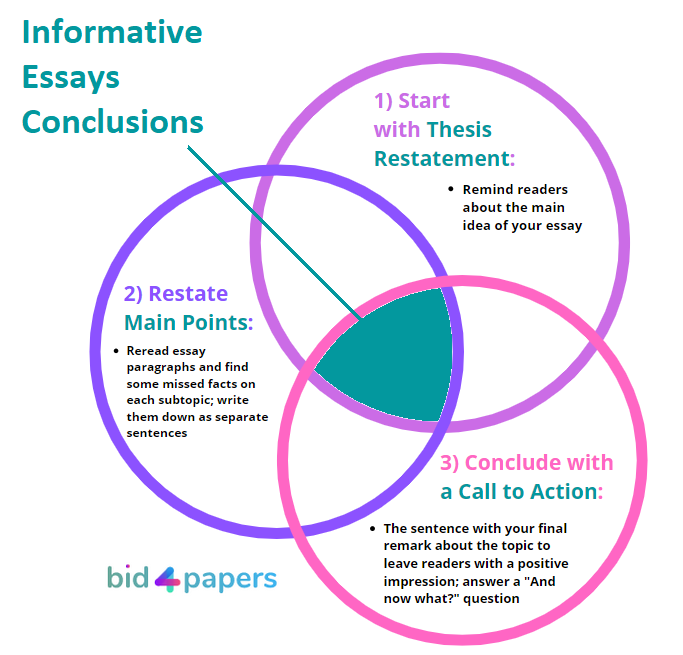
Informative essay conclusions need to relate to the information in your previous paragraphs. As a writer, you have three steps to do that:
- Restate thesis statement
- Restate main ideas
- Finish with a call to action
Let’s reveal more details on each one!
P.S. For better clarity, we’ll use a well-known example with pandas. (Remember we addressed it in other blog posts about informative essays ?
Restate Thesis Statement
A thesis statement should remind readers about the main idea and subtopics of the essay they’ve just read.
We bet you remember the formula for writing a thesis statement in informative essays: main topic + subtopic 1 + subtopic 2 + subtopic 3 , connected in one sentence using correct grammar. When writing about introductions, we used this thesis statement example:
- Giant pandas have special characteristics, live in certain areas of China, and eat food besides just bamboo!
A key aspect to remember when writing a conclusion: Never use the same sentence twice in an essay. What you need to do is take the same ideas but restate your thesis statement in an interesting way yet with the same information.
- Giant pandas are fascinating animals, and there are many interesting facts to remember about their characteristics, their home, and their diet.
Here we have the same subtopics (characteristics, home, and food), and yet they are not the same but rewritten a bit.
Once again, a big thank goes to Mr. S from YouTube for his panda examples!
Restate Main Ideas
Now it’s time to restate your main ideas by using essay body paragraphs.
Your first paragraph was about giant panda’s special characteristics:
Reread it to remind yourself what you’ve already covered because (again!) you don’t want to use the same fact twice in your paper. Then, go back to your informative essay outline and check which fact is missed but still worth using for an essay. Let’s say, you might forget to include the info about giant pandas’ size:
- The bear is only six feet long, not as giant as some people may think.
So, you take this fact and write it down in your essay conclusion.
Then, go to your essay body’s second and third paragraphs to do the same: Reread them and make sure the second and third restatements of your main idea answer the subtopics coved in those paragraphs.
For example, you could mention the following information about giant pandas’ homes and diet:
- Only 2,000 of these black and white bears are left living in the mountains of central China. (To remind readers that many pandas are left, so we need to be careful with what we have left on earth.)
- Though pandas do eat a great deal of bamboo, they also eat eggs and some small animals. (To remind readers that pandas don’t only eat bamboo, which is the most common thing people know about these wonderful creatures.)
Now you’re done with the restatement of the main ideas, and it’s time to move to the last part of your informative essay conclusion.
Finish with a Call to Action
While there are many ways to finish a paper, a compelling call to action works best for informative essays.
If you left a paper just as it is, with a restated thesis and main ideas, it would sound a bit awkward. A concluding sentence of your essay should provide a sense of closure and answer the “And what now?” question the audience might have after reading your work.
A few variants of calls to action for your informative essay about pandas could be as follows:
- Now, go read more about pandas! (Well, this one is super boring and simplistic.)
- Now, it’s time to schedule a visit to a nearby zoo that has one of these amazing animals. (This one is better, providing readers with some thought.)
- Now that you have read some general information about giant pandas, go to your library to find out more information or learn about a different one of your favorite animals! (Let’s stay with this one.)
That said, here’s what your informative essay conclusion would look like if you wrote about giant pandas:

As you’ve probably noticed, we’ve added a few linking words to the conclusion (“furthermore” and “finally”) to give it a natural flow and make the whole paragraph sound better.
Like other essay types, informative papers need a conclusion that would summarize the main points and leave a reader with a positive impression and food for thought. So, when you wonder how to write a conclusion for an informative essay, follow these three steps:
- Restate your thesis statement (the same thoughts with other words)
- Restate main ideas (subtopics you covered in body paragraphs)
- Finish with a call to action (What should the audience do after reading your work? Please think of encouraging them to get involved in something for further knowledge or research.)
Any questions left? You can always contact our writers , or feel free to leave a comment in the section below!
This entry was posted on Monday, July 11th, 2022 at 3:08 pm and is filed under Essays . You can follow any responses to this entry through the RSS 2.0 feed. You can skip to the end and leave a response. Pinging is currently not allowed.
Leave a Reply
Name (required)
Mail (will not be published) (required)
XHTML: You can use these tags: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
On College Life and Writing | Bid4papers Blog is proudly powered by WordPress Entries (RSS) and Comments (RSS) .
How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay

The conclusion is the final paragraph of your writing, and it holds significant weight. It allows you to leave a lasting impression on the reader. But how to write a conclusion that effectively summarizes your points and resonates with your audience?
This article will guide you through the process of crafting a strong conclusion paragraph, step by step. Our term paper writers will break down the key elements and provide clear examples to illustrate each point. By following these steps and referencing the examples, you'll be well on your way to writing impactful conclusions that leave your reader feeling satisfied and informed.
What Is a Conclusion
Conclusion in an essay is the final paragraph or section that wraps up the main points and provides closure to the piece.
Imagine it as the bridge that connects your ideas to a broader significance. A well-crafted conclusion does more than simply summarize; it elevates your points and offers a sense of closure, ensuring the reader leaves with a clear understanding of your argument's impact. In the next section, you will find conclusion ideas that you could use for your essay.

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Want to Have Better Grades?
Address to our professionals and get your task done asap!
How to Write a Conclusion
A powerful conclusion not only summarizes but also reinforces your message and leaves a lasting impression. Here's a breakdown of how to write a conclusion for an essay:
- Restate Your Thesis: Briefly remind the reader of your central point. Don't simply copy and paste your thesis statement, but rephrase it using different words.
- Summarize Key Points: Revisit the main arguments or evidence you presented throughout your writing. This reminds the reader of the journey you took them on and ensures they grasp the core takeaways.
- Avoid Introducing New Information: The conclusion is not the place to introduce brand new ideas. Stick to summarizing and reinforcing the existing points.
- End on a Strong Note: Go beyond a simple summary. You can add a final thought, pose a question to spark further reflection, or highlight the significance of your topic.
Read more: Persuasive essay outline .
The Purpose of a Conclusion
As you already understand, the conclusion paragraph serves a critical function in your writing. It serves as a final push to solidify your message in your readers’ minds. It's also your opportunity to:
- Remind the reader of your central point (thesis) and the key arguments or evidence used to support it.
- Use this space to offer a final thought, pose a question that prompts further pondering, or emphasize the significance of your topic.
Remember, a concluding paragraph should NOT:
- Introduce New Information: The conclusion is not the place for brand new ideas. Its purpose lies in wrapping up and reinforcing what you've already established.
- Stray from the Thesis: Don't introduce arguments or evidence not discussed earlier in your writing. Maintain focus on the core message you've been building throughout your work.
How Long Should a Conclusion Paragraph Be
Generally, the ideal length depends on the overall length and complexity of your essay. However, it is not the sole factor. A well-written conclusion of 3 sentences can be far more effective than a rambling one that drags on for multiple paragraphs.
Here are some general guidelines can help you achieve a balance when writing a conclusion:
- In most cases, you can effectively summarize your points and leave a lasting impression within 3-5 sentences.
- Prioritize delivering a clear and impactful message over unnecessary elaboration.
- Proportion matters. A lengthy research paper might warrant a slightly longer conclusion (think 5-7 sentences) to adequately address all the main points. Conversely, a shorter piece like a blog post might require a more concise conclusion (2-4 sentences).
Conclusion Transition Words
The right transition word can smoothly bridge the gap between your main body of text and your conclusion. Here are some transition words for conclusion categorized by their purpose:
7 Tips for Writing a Conclusion
Having grasped the core functions and structure of a conclusion paragraph, let's check out some practical tips to elevate your closing statements. Here are 7 effective strategies to consider from our dissertation writer :
.webp)
- Vary Your Sentence Structure: Avoid a monotonous string of simple sentences. Use a mix of sentence structures (short, long, complex) to create a more engaging rhythm.
- Connect to the Introduction: For a cohesive feel, subtly tie your conclusion back to your introduction. You can reference an opening question you posed or revisit a key image you mentioned. Consider this tip especially when unsure how to start a conclusion.
- Embrace Figurative Language (Sparingly): There are different conclusion ideas but a well-placed metaphor or simile can help leave a lasting impression. However, use figurative language strategically and avoid clichés.
- Appeal to the Reader's Emotions: Did your writing highlight a pressing issue? Consider evoking emotions relevant to your topic when you want to know how to write a conclusion paragraph that tugs at the reader's heartstrings.
- Consider a Quote (if Relevant): A powerful quote from a credible source can add authority and depth to your essay conclusion. Ensure the quote aligns with your thesis and enhances your message.
- End with a Strong Call to Action (Optional): If your purpose is to persuade or inspire action, conclude with a clear call to action. Tell your reader exactly what you want them to do next.
- Proofread and Revise: Just like any other part of your writing, proofread your conclusion carefully. Ensure clarity and a smooth flow between your main body of text and the closing statement.
By this time, you already know how to write a conclusion for an essay. However, if you still need further guidance, buy essay from our expert writers anytime!
Do’s and Don’ts of Essay Conclusion
Let's now look at some simple tips from our online paper writing service to help you avoid common mistakes when writing a conclusion.
Conclusion Paragraph Examples
Here are three conclusion paragraph examples showcasing how powerful closings are crafted.
Recommended for reading: Nursing essay examples .
In closing, a strong conclusion is a must-have for any piece of writing. It reminds your reader of your main point and leaves them with a lasting impression. Here are some key things to reflect on how to write a good conclusion:
- Restate your thesis in a fresh way.
- Mention your key arguments.
- Leave a lasting thought or question.
- Consider your audience and tailor your ending to them.
- End with a strong statement.
Remember, a good conclusion is not merely about wrapping things up but rather about making your writing truly impactful.
Need Help with Your Essays?
Our service is the best assistant the money can buy – original and reliable.
How To Write A Conclusion For An Essay?
How to write a good conclusion, how to write a conclusion for a college essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Updated writing tips.
- Added informative tables.
- Added conclusion example.
- Added an article conclusion.
- Essay Conclusions | UMGC. (n.d.). University of Maryland Global Campus. https://www.umgc.edu/current-students/learning-resources/writing-center/writing-resources/writing/essay-conclusions
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay | BestColleges. (n.d.). BestColleges.com. https://www.bestcolleges.com/blog/how-to-write-a-conclusion/
- Ending the Essay: Conclusions | Harvard College Writing Center. (n.d.). https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
%20(1).webp)
Reading Worksheets, Spelling, Grammar, Comprehension, Lesson Plans
How to Write a Conclusion Paragraph
Conclusion paragraphs can be tricky to write, but a clear conclusion can sum up your main points and leave your reader with a clear sense of what to take away from your overall essay. Creating a strong essay means making sure that you have a clear introduction , several body paragraphs, and knowing how to write a conclusion paragraph. Keep reading closely, and you’ll know how to write a conclusion paragraph. Read on for a step-by-step guide on how to write a conclusion paragraph, and then check out our library of conclusion worksheets to get plenty of practice in how to write a conclusion paragraph.
Choose Smooth Conclusion Transition Words

Restate Main Points
Another key aspects of how to write a conclusion paragraph is that you signal that you are drawing your essay to a close, so that you can then restate the main points of your essay. Depending on the length of your essay, this may be done in a single sentence, or it may require a few sentences. Be concise and clear; you should be able to summarize each main point in a simple phrase that avoids restating each detail and piece of evidence related to the point. Simply list off the points as a reminder to your audience about what they’ve just read.
Restate Your Argument
Finally, if you’re writing an argumentative essay, a key component of how to write a conclusion paragraph is that you’ll want to clearly restate your main argument in order to leave readers with one final appeal. If you have provided enough evidence along the way, this restatement should make readers feel as if you’ve persuaded them fully.
Call to Action
For some expository and argumentative essays, a key part of how to write a conclusion paragraph involves a call to action as your last sentence. For example, if you’re writing an informative essay about the sea creatures that live in the very deepest parts of the ocean, you may close with a sentence like this: “It’s clear that today’s scientists should continue to observe and document these mysterious creatures, so we may all learn more about life at the bottom of the ocean.” A call to action like this can make your reader feel inspired and informed after reading your essay.
What to Avoid with Conclusion Transitions
When determining how to write a conclusion paragraph, you want to keep it simple. Use a clear transition word or phrase, restate your main points and argument, and possibly finish with a call to action. Be sure to avoid the following missteps:
- New Information . Your conclusion is not the place to introduce anything new. Simply restate and summarize the main points clearly.
- Personal Opinion . Unless you are writing an opinion piece that includes several “I” statements throughout, avoid ending your essay with a sudden “I think…” or “I feel…” If you haven’t been including your personal opinion throughout the essay, then you shouldn’t insert your opinion into the conclusion.
- Lots of Details . When you restate your main points, don’t worry about restating all the small details that make up your description or evidence. The place for details is in your body paragraphs. The conclusion is simply for summary and a possible call for action or next steps.
Check out our printable conclusion paragraph worksheets too!
Questions? Call us:
Email:
- How it works
- Testimonials
Essay Writing
- Essay service
- Essay writers
- College essay service
- Write my essay
- Pay for essay
- Essay topics
Term Paper Writing
- Term paper service
- Buy term papers
- Term paper help
- Term paper writers
- College term papers
- Write my term paper
- Pay for term paper
- Term paper topic
Research Paper Writing
- Research paper service
- Buy research paper
- Research paper help
- Research paper writers
- College research papers
- Write my research paper
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper topics
Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation service
- Buy dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Dissertation writers
- College thesis
- Write my dissertation
- Pay for dissertation
- Dissertation topics
Other Services
- Custom writing services
- Speech writing service
- Movie review writing
- Editing service
- Assignment writing
- Article writing service
- Book report writing
- Book review writing
Popular request:
Concluding sentence: easy writing guide.
January 21, 2021

A concluding sentence should tie up an argument in a paragraph, essay, or paper. Unfortunately, many people make a mistake when writing essays and papers by leaving out this sentence. Others don’t even know what a conclusion sentence is and why it is important, leave alone knowing how to write it. So, let’s start by answering, what is a conclusion sentence?
What is a Concluding Sentence?
Every paragraph has a topic sentence, supporting sentences, and a concluding sentence. But, what’s a concluding sentence? Well, this is the sentence that sums up all the information that has been presented in the paragraph. It tells the readers that you’re getting to the closure of the paragraph.
Essentially, this sentence completes a paragraph while restating the main argument or idea. Conclusion sentence starters include words and phrases like “thus”, “therefore”, “resulting”, “in brief”, “hence”, and “to sum up” are often used to start this sentence.
This sentence summarizes the main argument. It also ties the paragraph without rephrasing or your topic sentence. A concluding sentence in a paragraph wraps up the entire argument while guiding the readers regarding the information that you have provided.
How to Write a Concluding Sentence
The concluding sentence definition may vary. However, this sentence should serve its purpose effectively. To achieve this, you should learn how to write a good concluding sentence. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write a conclusion sentence.
- Summarize Start by summarizing the paragraph’s content. Remember that this sentence should not introduce anything new to the paragraph. It should recap what you’ve shared with your readers in simple and few words. Essentially, this sentence should wrap up your main points briefly.
- Make your sentence short The concluding sentence words should be few. However, the length of this sentence should depend on the essay or paragraph size. For instance, two lines could be sufficient for a paragraph that has ten lines. Essentially, summarize everything without losing the meaning.
- Provide a closure In addition to summarizing a paragraph, this sentence should provide a solid closure to your readers. The importance of a solid close is less when composing a cliff-hanger only. Readers should feel at ease after reading your paper or essay. They should not be confused by the last sentence. Therefore, make sure that your sentence wraps up everything nicely.
- Read the sentence Learning how to make a concluding sentence alone is not enough. You should also ensure that this sentence serves its purpose. Therefore, check your sentence to ensure that it mentions the chief points. It should provide a sense of summarization to the paragraph by wrapping up and summarizing all the key points. It should also rephrase the thesis statement to enhance understanding. What’s more, it should restate your topic sentence. It should represent all the findings, data, figures, materials, logic, and facts.
When learning how to write concluding sentence, bear in mind that this is a final word on the topic. As such, it should leave readers with a sense of closure or completion. This should be the clincher instead of a summary. The essential points of your write-up should be presented in your essay conclusion. What’s more, this sentence should compel readers to focus on new views regarding the topic. And most importantly, it should end on a positive note.
How to Start a Concluding Sentence
There are many ways of starting this sentence. You can learn about these ways by checking out well written concluding sentence examples. For instance, you can use these concluding sentence starters:
- In conclusion ,
- In general ,
- Therefore ,
To understand how these starters can be used, check these conclusion sentence examples for essays.
Example 1 : In conclusion, marijuana may become recognized as a healing tool one day because it has more than recreational value.
Example 2 : Lastly, the widespread abuse of marijuana and its profitability should compel lawmakers to decriminalize its use in the U.S
Example 3: Therefore, marijuana should be availed to the general public due to its therapeutic benefits.
Example 4 : Clearly, a significant correlation between health risks and marijuana risks that explain why it should be decriminalized exist.
Example 5 : In general, marijuana should be legalized globally because its use is as old as the history of mankind.
The effective use of starters signals the beginning of this paragraph to the readers. It also ensures a smooth transition from the explanation of the main points to the end of the paragraph.
Concluding Sentence Transitions
You’ve probably read a good concluding sentence example and come across what seems like a transition word. Well, some of these sentences start with transition words. Here are examples of such transitions:
- In other words ,
- All in all ,
A writer can also include their final thought. This is very common in write-ups that do not provide a chance for writers to interject their opinion. Here is a concluding sentence essay sample that includes the final thought and a concluding statement.
In short, you can gain both stamina and muscle by following these steps though all exercise programs take time to achieve the desired results.
In this example, the writer starts the sentence with a transition, then moves on to the concluding statement before giving their opinion about the program’s results.
Useful Tips and Insights
In addition to using conclusion sentence examples, follow these tips:
- Add a summary – Include a summary of your essay or paper in the sentence to serve as the crux of your writing. Your final thought or judgment should be supported by the summary of the main point in this sentence.
- Call for action – This sentence should call readers to take action using an emotional and factual argument to evoke the desired response from the readers.
- Evoke a certain image – Make sure that your sentence has an impact on the readers by painting a vivid picture. You should convey your ideas and transfer your mental image into the mind of the readers.
- Make suggestions – Recommend beneficial changes to the surrounding and the audience.
- Add quotations – Starting or ending your paper or essay with a quotation can create a good impression. It can also leave a lasting effect on the reader. Therefore, consider using a quotation in your conclusion.
By reading a good conclusion sentence example, you will see how the author restates their thesis or topic sentence using the right synonyms. You will also learn to wrap up the paragraph with the right words. What’s more, a good example will show you the best way to use starters and transition words to signal the beginning of this paragraph.
The purpose of the last sentence in a paragraph is to remind the audience about the discussed topic. It also sums up all the information provided in that paragraph. Although you can use a concluding sentence generator, you should learn and practice writing it. This will enable you to give every paragraph that you write a great sense of completion or closure. Writing services may also come in handy here. In short, your readers will feel that you addressed the main point to its conclusion.

Take a break from writing.
Top academic experts are here for you.
- How To Write An Autobiography Guideline And Useful Advice
- 182 Best Classification Essay Topics To Learn And Write About
- How To Manage Stress In College: Top Practical Tips
- How To Write A Narrative Essay: Definition, Tips, And A Step-by-Step Guide
- How To Write Article Review Like Professional
- Great Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Creating Best Stanford Roommate Essay
- Costco Essay – Best Writing Guide
- How To Quote A Dialogue
- Wonderful Expository Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics For 2020
- Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics
Informative Essay — Purpose, Structure, and Examples

What is informative writing?
Informative writing educates the reader about a certain topic. An informative essay may explain new information, describe a process, or clarify a concept. The provided information is objective, meaning the writing focuses on presentation of fact and should not contain personal opinion or bias.
Informative writing includes description, process, cause and effect, comparison, and problems and possible solutions:
Describes a person, place, thing, or event using descriptive language that appeals to readers’ senses
Explains the process to do something or how something was created
Discusses the relationship between two things, determining how one ( cause ) leads to the other ( effect ); the effect needs to be based on fact and not an assumption
Identifies the similarities and differences between two things; does not indicate that one is better than the other
Details a problem and presents various possible solutions ; the writer does not suggest one solution is more effective than the others

Purpose of informative writing
The purpose of an informative essay depends upon the writer’s motivation, but may be to share new information, describe a process, clarify a concept, explain why or how, or detail a topic’s intricacies.
Informative essays may introduce readers to new information .
Summarizing a scientific/technological study
Outlining the various aspects of a religion
Providing information on a historical period
Describe a process or give step-by-step details of a procedure.
How to write an informational essay
How to construct an argument
How to apply for a job
Clarify a concept and offer details about complex ideas.

Explain why or how something works the way that it does.
Describe how the stock market impacts the economy
Illustrate why there are high and low tides
Detail how the heart functions
Offer information on the smaller aspects or intricacies of a larger topic.
Identify the importance of the individual bones in the body
Outlining the Dust Bowl in the context of the Great Depression
Explaining how bees impact the environment
How to write an informative essay
Regardless of the type of information, the informative essay structure typically consists of an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Introduction
Background information
Explanation of evidence
Restated thesis
Review of main ideas
Closing statement

Informative essay introduction
When composing the introductory paragraph(s) of an informative paper, include a hook, introduce the topic, provide background information, and develop a good thesis statement.
If the hook or introduction creates interest in the first paragraph, it will draw the readers’ attention and make them more receptive to the essay writer's ideas. Some of the most common techniques to accomplish this include the following:
Emphasize the topic’s importance by explaining the current interest in the topic or by indicating that the subject is influential.
Use pertinent statistics to give the paper an air of authority.
A surprising statement can be shocking; sometimes it is disgusting; sometimes it is joyful; sometimes it is surprising because of who said it.
An interesting incident or anecdote can act as a teaser to lure the reader into the remainder of the essay. Be sure that the device is appropriate for the informative essay topic and focus on what is to follow.

Directly introduce the topic of the essay.
Provide the reader with the background information necessary to understand the topic. Don’t repeat this information in the body of the essay; it should help the reader understand what follows.
Identify the overall purpose of the essay with the thesis (purpose statement). Writers can also include their support directly in the thesis, which outlines the structure of the essay for the reader.
Informative essay body paragraphs
Each body paragraph should contain a topic sentence, evidence, explanation of evidence, and a transition sentence.

A good topic sentence should identify what information the reader should expect in the paragraph and how it connects to the main purpose identified in the thesis.
Provide evidence that details the main point of the paragraph. This includes paraphrasing, summarizing, and directly quoting facts, statistics, and statements.
Explain how the evidence connects to the main purpose of the essay.
Place transitions at the end of each body paragraph, except the last. There is no need to transition from the last support to the conclusion. A transition should accomplish three goals:
Tell the reader where you were (current support)
Tell the reader where you are going (next support)
Relate the paper’s purpose
Informative essay conclusion
Incorporate a rephrased thesis, summary, and closing statement into the conclusion of an informative essay.
Rephrase the purpose of the essay. Do not just repeat the purpose statement from the thesis.
Summarize the main idea found in each body paragraph by rephrasing each topic sentence.
End with a clincher or closing statement that helps readers answer the question “so what?” What should the reader take away from the information provided in the essay? Why should they care about the topic?
Informative essay example
The following example illustrates a good informative essay format:

- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
- How to Write an Informative Essay: Definition, Structure, Steps & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write an Informative Essay: Definition, Structure, Steps & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
An informative essay is a piece of academic writing that provides clear and balanced information about a specific topic. Its main objective is to educate and inform the reader about a subject, rather than to persuade or argue a point of view.
In this article, we will talk about how to write an informative essay and structure it in an organized way. From introduction to conclusion, we will walk you through each step of informational essay format writing. Keep reading and you will find valuable tips from professional essay writing services and informative essay examples along the way.
But before we dig deeper into details, let’s define what an informative essay is.

What Is an Informative Essay: Definition
An informative essay, as the name suggests, is a type of essay intended to enlighten the reader about a particular subject. The primary purpose of an informative essay is to present information in a clear, concise, and well-structured manner. In this type of writing, students shouldn’t express personal opinions or attempt to persuade their audience.

While informative essays and other academic writing styles may share some structural similarities (e.g., introduction, body, and conclusion), their goals and approaches are distinct.
Unlike other popular forms of academic writing, such as argumentative or persuasive essays , informative essays focus solely on presenting factual information. They do not seek to persuade readers to adopt a particular viewpoint, nor do they provide an analysis, like analytical essays do.
Many students also confuse it with an expository essay . However, unlike expository writing, informational essays do not explore a topic so extensively. Instead, they just offer relevant information.
Informative essay writing deals largely with suggesting well-researched information to expand someone’s knowledge. Teachers assign it to test how well students can educate on a chosen matter without leaving personal biases or emotional appeals. In this sense, an informative essay is more of an educational than a persuasive tool.
Characteristics of Informative Essays
Informative essays have a few peculiar features that set them apart from other forms of writing. Here are the main ones:
- Objective approach to presenting facts
- Balanced coverage of information without redundant details
- Accurate, factual content
- Educational purpose of writing.
Now that you are familiar with the fundamentals, let’s look at how to structure an essay .
Informative Essay Structure
To write informatively, you need to sort things out in a logical order. The structure of an informative essay is typical and comprises 5 paragraphs: an introduction, 3 body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Sometimes, you will need to compose more paragraphs if you feel that information you have provided is insufficient.

Let’s take a closer look at each part individually.
Informative Essay Introduction
An informative essay introduction paragraph is a perfect place to capture your reader's attention. It should include such components:
- Background information
- Thesis statement.
Your opening will start with a compelling "hook" – a staggering statistic, an interesting anecdote, or a provocative question. This is followed by a brief transition to the topic, which provides some context. You may include essential facts, historical background, or why the theme is important. Remember to keep it concise and don’t overdo with details.
Your introductory paragraph should end with a thesis statement. And we will talk about it right below.
>> Read more: How to Write a Hook for an Essay
Informative Essay Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is arguably the most crucial sentence in your paper. It establishes your ruther direction by framing the main points you will cover. Thesis for an informative essay should be neutral and objective. Here, you should focus on presenting facts rather than asserting an opinion. A thesis statement is brief and usually takes no more than 1-2 sentences.
Informative Essay Body Part
The body part is where you delve into the details of your topic. Here are the things you should cover in each section:
- Topic sentence
- Supporting details
Each paragraph begins with a topic sentence, which introduces the main point of that section. But this shouldn’t be a bold statement. Integrate supporting details, which may include facts, statistics, examples, or explanations that elaborate on the topic sentence. Use transition words for essay to build links between your sentences.
Every paragraph should stick to one main idea and shouldn't change the subject. Additionally, your body part should systematically address the key point mentioned in your thesis statement. For instance, if you are talking solely about the origin of art, you can’t suddenly change the direction and discuss its use in modern society.
>> Learn more: How to Write a Body Paragraph
Informative Essay Conclusion
The conclusion of an informative essay serves to bring about the key points presented in your paper. This is the last paragraph and it should bring a sense of closure. Keep in mind this structure:
- Rewritten thesis statement
- Succinct summary
- Prediction or implication.
While an informative essay doesn't typically require a call-to-action, you might end with a thought-provoking question or a relevant implication for further consideration.
How to Write an Informative Essay Step-by-Step?
At this point, you should be equipped with all necessary knowledge, and we finally can discuss how to write an informative essay. This guide will walk you through each phase of your essay writing process .
In the steps below, you'll learn how to select a captivating topic, retrieve necessary information and weave those facts into your paper. From penning a powerful thesis statement to rounding it all off with a succinct conclusion, we will cover each essential stage. Without further ado, let’s see how to write an informational essay together!
1. Choose a Proper Topic
Choosing a topic is a critical first step in writing an informative essay.
Before you pick any title, ensure you understand your assignment and its requirements thoroughly. Only when all instructions are clear, start brainstorming all potential informative essay topics . Remember to include subjects that pique your interest, as writing about something you love can make the process enjoyable.
Once you've got your list, it's time to narrow it down. Select topics that are relevant to your audience and have ample information available for research. Also, consider the scope – it shouldn't be too broad or too narrow. After all, you don’t want to end up writing about a subject that has limited information.
After evaluating based on all criteria described above, select the idea that ticks all the boxes.
2. Conduct Research and Collect Information
The integral part of academic essay writing is a thorough investigation. When you're ready to start gathering facts for your informative essay, the first thing to remember is to truly understand the concept. Look it up online and read a few general articles to get a handle on the subject.
When it comes to research sources, variety is your friend. Try to explore a mix of resources like books, academic articles, reliable websites, and documentaries. It is better to exclude sources that provide an opinion on the matter (for example, article review , book review or critical analysis ). Pay attention to the date of publishing and avoid outdated sources older than 5 years.
While researching, be critical. Not all information you'll find, especially on the internet, is accurate or reliable. Check the author's credentials and the source's reputation. Always aim for information from authoritative and trustworthy sources.
3. Write Down Crucial Facts
As you carry out your research, remember to take notes. There are 2 things you should keep in mind at this stage:
- Important facts Write down key points, interesting facts, or quotes that you think will support your essay. Organize them based on the main points of your essay. This will make the writing process smoother.
- Source referencing details When it's time to reference sources in your informative essay, you'll need accurate information about where you found your data. It's much easier to do this as you go along, rather than trying to find it again later.
Now let’s figure out how to write a thesis statement for an informative essay.
4. Prepare a Thesis Statement
Writing a thesis statement for an informative essay is like drawing a map for your reader. Usually, it’s a 1-2 sentences statement that highlights the major focus of your paper. This is your opportunity to tell your audience exactly what information you will be presenting.
Avoid being vague or overly general. For instance, if your essay is about the impacts of climate change on agriculture, your thesis statement could be:
Climate change has profound effects on agriculture, with potential consequences for food security globally.
As you can see, this statement is informative, but neutral. In this case, a college essay writer isn’t trying to take any particular stance on climate change. Instead, they are just saying that climate change affects agriculture. Let’s consider another example of a thesis statement for informative essay on the history of the Internet:
The history of the Internet showcases a remarkable evolution, from its humble beginning as a military project to the widespread global network today.
5. Build an Outline
By having a clear plan of action, you will be able to write an informative essay without taking unexpected turns. Much like a compass, an outline serves as a vital tool during the writing process helping students to stay on track.
In most cases, instructions may not explicitly require the preparation of an outline. However, we still suggest that you create a basic plan listing the main ideas of each section. By having a layout, students can easily refer to it whenever they veer off topic. This ensures that your thoughts remain aligned with the central theme of your writing.
6. Write the First Draft
Writing an informative essay is all about breaking down complex information into digestible chunks of information. There are 2 ways to go about creating an informative essay:
- Start writing a polished version right after building a plan.
- Compose a rough draft and revise it later.
You may think that skipping the draft will save you time, and opt for the first way. We highly recommend preparing a draft instead. This way, you'll see your thoughts on paper and be able to rearrange them if needed. Ultimately, it takes less time and allows you to craft a well-organized paper.
Your draft shouldn’t be perfect. It's a starting point that you'll polish later. At this stage, just focus on transforming your ideas and research into a structured form. You can try essay typer free right now instead of doing the task yourself.
How to Write an Informative Essay Introduction?
Next, let’s explore how to start an informative essay in an engaging manner. Our professionals shared some valuable tips on composing a truly effective opening paragraph.
Your task in the introduction for informative essay is to get your readers interested and present them with a preview of what's to come.
To begin, create a hook. This could be a striking fact or an intriguing question. Another nice option is adding a simile or metaphor. The purpose of the hook is to entice your readers right from the beginning. For instance, if you're writing about recycling, your hook could be something like this:
Did you know that only 9% of the world's plastic waste has been recycled?
Your next move is to prepare your audience for the major point of your informative writing. This is where you need to contextualize your subject matter. You can briefly touch on its history, why it's relevant, or its implications. Using our recycling example, you might mention when the concept of recycling was introduced and its significance in environmental conservation.
Finally, finish your informative essay introduction paragraph with your thesis statement. Simply state what you will talk about in your piece. Using the recycling topic, your thesis might be:
This essay will explore the different types of recycling processes, their effectiveness, and their impact on the environment.
Let’s see how to put all these guidelines into practice.
Informative Essay Introduction Example
As the world becomes increasingly digitized, impacting many aspects of our lives. A key area where this change is apparent is education. In the past, classrooms were defined by physical boundaries and face-to-face interaction. Today, however, the landscape of education is increasingly blending with technology. In fact, it's estimated that about 95% of classrooms now have access to computers, a far cry from a few decades ago. In the context of this technological evolution, it's important to understand how the integration of technology is reshaping the way we teach and learn. In this essay, we will explore the various ways technology is changing the face of education, from the rise of online learning and digital literacy to the use of augmented reality in classrooms. We'll also discuss the challenges these changes present and how educators can navigate them to enhance education.
>> Learn more: How to Start an Introduction for an Essay
How to Write an Informative Essay Body Paragraphs?
A body section is where you demonstrate all your research and provide your readers with the information you've promised in your thesis statement. Generally, you will need to come up with 3 distinct points and cover them in each body paragraph. You can extend your paper to more paragraphs if there is a lot to say about your subject.
As a rule, the body paragraphs of an informative essay should include these parts:
- The main aspect – your topic sentence
- Supporting details – your research and facts
- A closing line that wraps up your point or smoothly transitions to the next paragraph.
Always make sure your information is clear and your points are well organized. You want your reader to easily follow your line of thought. Use simple, straightforward language to explain complex ideas or concepts.
Informative Essay Body Paragraph Example
One significant way technology has transformed education is through the advent of online learning platforms. These platforms have expanded the boundaries of education beyond the traditional classroom. Students from all over the world can now access courses offered by prestigious universities, right from the comfort of their homes. Websites like Coursera host thousands of courses across a wide range of subjects. This widespread availability of knowledge has democratized education to a great extent. No longer are learning opportunities restricted by geography or socio-economic status. Indeed, with a stable Internet connection and a willingness to learn, anyone can pursue a course in a field of their interest. This shift towards digital learning is one of the most profound changes brought about by the integration of technology in education.
How to Write a Conclusion for an Informative Essay?
We are approaching the finish line and it’s time to learn how to end an informative essay and make it memorable.
A useful approach is to round out your critical points. But avoid simply repeating them. Aim to synthesize information, showing your reader how the pieces fit together to build a clear picture.
Then, revisit your thesis statement. Has your essay successfully conveyed the information you intended? If so, rephrase your thesis statement in a way that shows its significance.
Finally, close out your essay with a statement that leaves your reader with something to think about. It is a good idea to finish your informative essay with an implication, forecast or a final thought.
Example of an Informative Essay Conclusion Paragraph
It is clear that technology has impacted education, drastically transforming its landscape. From online learning platforms broadening access to education, to digital literacy becoming a vital skill in today's world, the intersection of technology and education is rich. This exploration of the topic has demonstrated how the classroom's physical boundaries have extended into the digital realm, opening up opportunities for learning beyond what was previously imaginable. The integration of technology, as we've discussed, isn't without its challenges. However, the benefits it brings, like making education more accessible and fostering digital citizenship, are significant strides towards a future-ready society. The ongoing evolution of this relationship invites further study, promising many more enlightening revelations.
7. Revise and Edit
When you're satisfied with the organization and content of your essay, it's time to add the final touches. Essay revision is a crucial step in the writing process since it helps ensure that you've created an informative and accurate piece of work.
To make sure that your informational essay is error-free, read through the text several times and pay attention to spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Make sure you’ve applied the right style, and that citations are properly formatted. Also, check if your sources are credible and are correctly referenced in your paper.
Informative Essay Format
It is time to say several words about the format of an informative essay. Most instructions will have this point among the rest, so do not overlook these requirements. When formatting your writing, you will deal with 2 essential aspects:
- Direct/indirect in-text citations inserted in the body text
- List of references, which appears at the end of the informative essay after the concluding paragraph.
The format of each citation varies depending on the paper style you are using. Most likely you will apply one of these popular formats:
- APA style format
- Chicago style .
Stick to the chosen format and use the corresponding manual for specific guidelines.
Informative Essay Examples
One more thing that a student might lack after reading the article is a decent informative essay example. Fortunately, we have rendered some good sample informative essay examples that you may use as a template.
Informative Essay Writing Checklist
As a writer, your role is much like that of a tour guide, leading your readers through the landscape of your chosen subject. Your ultimate goal is to ensure your audience finishes the tour more knowledgeable than when they started. Use this handy checklist and tips on how to write a good informative essay to compose your own piece.
- checkbox I gathered sufficient information about my subject from reliable sources.
- checkbox I brainstormed and organized my thoughts in an outline.
- checkbox My informative essay is written following the structure I've set up.
- checkbox The introductory paragraph contains background information and ends with a thesis statement.
- checkbox I did fact-checking to offer accurate details.
- checkbox My essay educates the audience and doesn’t try to persuade or support any viewpoint.
- checkbox I cited all sources and formatted quotations properly.
Bottom Line on How to Write an Informative Essay
Now that you have a full grasp of how to write an informative essay, all that's left to do is sit down and start creating your own paper. Remember to be unbiased and carefully plan each section. Above all, strive to enlighten your readers with valuable insights, helping them sharpen their knowledge.
Our professional team of experienced writers is here to assist you with your essays, ensuring high-quality and timely submissions. Take the stress out of essay writing and get straight As effort-free. Order essays online now for personalized assistance!
FAQ About Informative Essays
1. what is the main purpose in writing an informative essay.
The main purpose of writing an informative essay is to educate and provide information. Writer's task is to present facts, details, and explanations about a subject without convincing the audience.
2. How to start an informative essay?
To start an informative essay, you can begin with an attention-grabbing introduction that creates context and engages the reader's interest. You can use a relevant anecdote or a shocking fact to make your opening section intriguing. Then, introduce your topic and provide a brief thesis statement communicating your main focus.
3. How many paragraphs are there in an informative essay?
The number of paragraphs in an informative essay can vary depending on the essay length and its complexity. However, a typical informative essay includes 5 paragraphs. You can always adjust the number of sections based on how much you want to tell.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like


Writing Under Pressure: Strategies for Excelling in Timed Essay Exams
- Posted on October 24, 2024
Writing under time constraints often brings out the best—or the most challenging—aspects of academic performance. In environments where essays and exams dictate success, mastering the skill of timed writing is crucial.
Whether you’re a seasoned essayist or a newcomer to this type of test, you’ll need valuable tips on preparation, time management, and effective writing techniques to handle the timed essays. The goal of this guide is to empower you to deliver your best work within strict time limits.
Understanding Timed Essay Exams
Timed essay exams require candidates to draft essays within a specified, limited time frame, typically seen in educational assessments and some professional tests.
These exams test not only your knowledge and understanding of the subject matter but also your ability to organize thoughts, argue effectively, and write succinctly under pressure. However, strict time limits can induce significant stress, impacting clarity of thought and writing quality.
Managing to formulate coherent arguments and structuring essays efficiently within the given time is another common issue.
Additionally, the inability to revise thoroughly due to time constraints often leads to mistakes that could have been easily corrected under normal circumstances. Thus, addressing these challenges is key to improving performance in timed writing tasks.
Preparation Strategies for Essay Exams
Understanding the format of your essay exams is the first step toward success. Different exams require unique approaches. Some might ask for persuasive essays, others for analytical responses.
Knowing the format helps you anticipate the kind of questions you might face and the best strategies to answer them.
Master the Material: Effective Study Techniques
Effective study habits are crucial for excelling in essay exams. Begin by organizing your study materials based on topics likely to be covered.
Use active learning techniques such as summarizing information , teaching the material to someone else, and using flashcards.
Regular review sessions increase retention and understanding, ensuring you’re prepared to apply your knowledge under exam conditions. Prioritize understanding over memorization to adapt your knowledge to any question in the exam.
Developing a Writing Strategy
An effective outline is your roadmap during a timed essay. Start with a clear thesis statement that defines the direction of your essay. List the main points that support your thesis, ensuring they are logical and compelling.
Under each point, jot down a few subpoints or evidence that bolster your argument. This method not only organizes your thoughts but also speeds up your writing process, as you have a clear framework to follow during the exam.
Practice Essays
Practicing under conditions that simulate the actual exam is one of the best ways to prepare for essay exams. Set a timer and write essays within the allotted time. This practice helps you gauge how well you can organize and express your thoughts under pressure.
After each session, review your essay to identify areas for improvement. Adjust your strategy accordingly to manage your time better and enhance the quality of your writing. This repetitive practice builds confidence and skills, greatly improving your performance when it counts.
Time Management During the Exam
Effective time management is essential during timed essay exams. It helps you allocate enough time for planning, writing, and revising your essay.
Allocating Time: Breaking Down the Exam
Begin by reading all the questions carefully and noting how much time you can allocate to each based on their point value. Spend the first few minutes planning your answers.
For example, if you have one hour, allocate 5-10 minutes to outline your essays, 40-45 minutes to write, and the remaining time to review and make necessary edits. This strategy ensures you can cover all required sections without rushing through any part.
Techniques to Accelerate Your Writing
By applying these techniques, you can improve your efficiency and ensure that you use your exam time optimally, allowing for better-structured and more compelling essays.
- Outline First: Quickly jot down a basic outline for each essay. This guide keeps you on track and prevents you from veering off-topic.
- Write Clear, Concise Sentences: Avoid complex sentence structures that could slow down your writing speed. Keep sentences short and to the point.
- Focus on Main Ideas: Spend less time on elaborate details. Concentrate on developing strong main points to support your thesis.
- Use Keywords: Integrate keywords from the question into your essay to ensure it remains relevant and focused.
- Skip Difficult Sections: If you’re stuck, move on to other sections of your essay. Return to difficult parts later if time permits.
Writing Techniques for Essay Exams
Proper structuring of essays enhances both clarity and persuasive power, particularly under time constraints. It is important to know the essential strategies for crafting impactful introductions, developing coherent paragraphs, and concluding essays memorably.
Starting Strong
The introduction of your essay sets the tone and establishes the scope of your argument. Begin with a strong thesis statement that clearly outlines your main point. This statement should be concise and assertive, directly addressing the essay prompt.
To engage the reader, introduce your key points briefly, providing a roadmap of your essay’s structure.
Consider opening with a compelling hook, such as a surprising statistic, a relevant quote, or a provocative question, to grab the reader’s attention. This approach ensures that your introduction is not only informative but also interesting.
Maintaining Focus
Coherence in paragraphs is crucial for maintaining the flow of your argument. Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that ties directly back to your thesis. This sentence should introduce the main idea of the paragraph.
Follow this with supporting sentences that include evidence, examples, or explanations that validate your point. Use logical connectors and transitional phrases to link your ideas smoothly from one to the next, ensuring that your argument builds logically throughout the essay.
Keep your writing concise and focused, avoiding digressions or extraneous information that could distract from the main topic.
Concluding Effectively
Your conclusion should serve as a powerful closure for your essay, synthesizing your main points and reinforcing your thesis. Begin by summarizing the key arguments discussed, highlighting how they collectively support your central claim.
Then, restate your thesis, reflecting on the evidence and showing a deeper understanding or a broader implication of your argument. Consider ending with a call to action or a forward-looking statement that challenges the reader to think beyond the essay.
Reviewing and Revising Under Time Constraints
Writing essays under time constraints often feels daunting. Efficient review and revision within such limits can dramatically improve the quality of your work. By adopting a strategic approach, you can refine your essays effectively, even during timed exams.
Quick Review Techniques
Before diving into revisions, a quick review of your essay ensures that it aligns with the prompt and flows logically. Here are several techniques to implement:
- Skim your introduction and conclusion first: Confirm that both sections mirror each other in terms of the thesis and main points. This alignment sets a coherent framework for your essay.
- Read the first sentences of each paragraph: This helps you gauge whether each paragraph’s topic is clear and contributes directly to your thesis. Adjust as necessary to maintain focus.
- Check for common errors: Quickly scan for grammatical mistakes that are often repeated, such as subject-verb agreement or incorrect pronoun usage. Correcting these can significantly clean up your text.
- Use shorthand comments: While reviewing, jot down quick notes or symbols in the margins to indicate areas needing refinement, such as unclear statements or examples that don’t quite fit.
- Time your review sessions: Allocate a specific amount of time for review, usually a third of the total time given for the essay. This ensures you leave enough time for actual revisions without feeling rushed.
Prioritizing Revisions: What to Focus On
Once you’ve reviewed your essay, deciding what to revise is the next step. Prioritize clarity and coherence. Start by strengthening your thesis statement if it feels vague; this acts as the foundation of your essay.
Next, ensure that each paragraph’s main idea supports your thesis. If any paragraph strays from the topic, refocus it or remove it. Additionally, improving transitions between paragraphs can help your essay flow more smoothly.
Lastly, cut redundant words or phrases to tighten your arguments. These revisions make your essay more persuasive and easier to read under the scrutiny of exam conditions.
Coping with Exam Stress and Anxiety
Handling stress and anxiety effectively is crucial when writing essays during exams. Mastering relaxation and focus techniques can significantly enhance your performance and well-being.
Pre-Exam Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques can dramatically reduce stress before exams, setting a positive tone for your performance. With these key relaxation strategies, you will be better prepared to write your exam or essay.
- Deep breathing exercises: Spend a few minutes taking deep, controlled breaths to slow your heart rate and promote calmness.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Tense and then relax each muscle group, starting from your toes and working up to your shoulders and neck.
- Visualization: Close your eyes and imagine a place where you feel at peace. Visualize yourself succeeding and writing confidently during the exam.
- Mindful meditation: Focus on being present in the moment. Concentrate on your breathing or a single object to clear your mind of anxieties.
- Brief physical activity: Engage in a short walk or do some light stretching. Physical activity can reduce stress hormones and increase endorphins.
Staying Calm and Focused During the Exam
Once the exam begins, maintaining calm and focus is essential for writing effectively. Start by organizing your thoughts and sketching a brief outline of your essay. This outline should clearly state your thesis and the main points you plan to discuss.
Refer to this outline throughout the exam to keep your essay on track and ensure that every paragraph serves a purpose in your argument. If you feel panic setting in, pause for a moment, close your eyes, and take a few deep breaths to reset.
Keep your focus on the question at hand and avoid worrying about the ticking clock. Concentrate solely on one section at a time, which helps manage overwhelming feelings and sharpens your concentration.
By staying methodical and calm, you can improve your performance under pressure and produce a well-structured essay.
Leveraging Feedback and Learning from Mistakes
Utilizing feedback and learning from past mistakes is pivotal in improving your essay writing skills for exams. This approach not only boosts your performance but also builds your confidence.
Analyzing Feedback from Past Exams
Reviewing feedback from previous exams provides crucial insights into your writing strengths and weaknesses. Start by reading comments carefully and noting recurring themes or criticisms.
If instructors consistently point out issues with your thesis clarity or argument structure, prioritize these areas in your next preparations. Also, look for positive feedback to understand what aspects of your writing resonate well.
It’s beneficial to discuss this feedback with your instructors or peers to gain further clarity and advice on how to address the criticisms effectively.
Strategies for Continuous Improvement in Essay Writing
Improving essay writing, especially under exam conditions, requires a systematic approach. By implementing these strategies, you can continuously enhance your essay-writing skills.
- Practice regularly: Write essays frequently to hone your skills. Timed practice sessions simulate exam conditions and help you write more efficiently.
- Expand your vocabulary: A richer vocabulary allows for more precise and impactful writing. Learn new words daily and practice incorporating them into your essays.
- Seek feedback actively: Regularly ask teachers, tutors, or peers for feedback on your essays. Constructive criticism is invaluable for improvement.
- Analyze top-scoring essays: Study essays that scored highly to identify effective strategies and techniques. Emulate these in your writing.
- Focus on essay structure: Ensure every essay has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. A strong structure helps convey your arguments more effectively.
- Refine your editing skills: Develop your ability to spot and correct errors during the revision phase. This skill is crucial for producing polished and concise essays under time constraints.
Mastering Timed Essays: Key Takeaways and Final Thoughts
Mastering timed essay exams hinges on preparation, effective time management, and strong writing skills. By familiarizing yourself with the exam format, mastering the material, and practicing under timed conditions, you can significantly improve your performance.
Writing succinctly and coherently within set time limits not only boosts your exam scores but also enhances your overall academic and professional communication skills. Now, take these strategies, apply them in your study routine, and witness the improvement in your next timed essay exam. Start practicing today and transform your approach to essay exams!
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

Writing with Confidence: Strategies for Overcoming Self-Doubt and Imposter Syndrome
- Posted on October 18, 2024 October 22, 2024

Best AI Detector Tools for Content, Images & Videos
- Posted on October 9, 2024

7 Best AI Detectors for Teachers & Professors (+ How To Choose)
- Posted on September 25, 2024 October 9, 2024

How Professors Check for Plagiarism (+Tips for Plagiarism Prevention)
- Posted on September 18, 2024 October 9, 2024

How Accurate Are AI Content Detectors? (+ How They Work)
- Posted on September 6, 2024 October 18, 2024

Best Chat GPT Detector
- Posted on August 22, 2024 October 9, 2024

- Tips & Guides
The Importance of Proofreading: Techniques for Catching Errors and Polishing Your Writing
- Posted on August 16, 2024 August 19, 2024

The Benefits of Peer Review: How to Give and Receive Constructive Feedback on Your Writing
- Posted on August 9, 2024 October 18, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to write a conclusion for an informative essay that summarizes the content and restates the thesis in an interesting way. Find tips, examples and strategies to improve your writing skills and tackle essays with confidence.
Writing an effective conclusion is one of the most important aspects of essay writing. The reason is that a conclusion does a lot of things all at once: It ties together the main ideas of the essay; Reiterates the thesis without sounding repetitious; Offers a compelling final thought for the reader to take home
Learn how to write a conclusion for an essay by restating your thesis, reiterating your supporting points, adding perspective, and ending with a clincher. Avoid common mistakes and follow the 5 key details for writing a conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Learn how to write effective essay conclusions with the 5 Cs method and 17 copy-and-paste examples. Find out how to summarize your arguments, restate your thesis, and end with a strong statement for argumentative, expository, compare and contrast, and critical essays.
Learn the definition, structure, and steps of an informative essay, a type of academic writing that explains a topic objectively. See an example of an informative essay on troubleshooting common Wi-Fi problems.
Learn how to write a strong conclusion for different types of essays with 20 examples. Find out why a conclusion is important, what it should include, and how to avoid common mistakes.
Learn how to write a strong conclusion for your essay by returning to your thesis, reviewing your main points, and showing why your argument matters. See examples of effective conclusions for different types of essays and avoid common mistakes.
Learn how to write a conclusion for different types of papers, such as essays, reports, and theses. See examples of professional and student conclusions that summarize, restate, and reflect on the main points and arguments.
Learn how to use transition signals to mark your conclusion and summarize your key points. See 5 examples of concluding words and phrases for different types of essays, such as argumentative, research, or narrative.
Learn how to write a strong conclusion for your essays by returning to your thesis, reviewing your main points, and showing the significance of your argument. Avoid common mistakes such as presenting new evidence, undermining your argument, or using generic statements.
To end an essay, start your conclusion with a phrase that makes it clear your essay is coming to a close, like "In summary," or "All things considered." Then, use a few sentences to briefly summarize the main points of your essay by rephrasing the topic sentences of your body paragraphs.
It will influence the final impression of your work. Make your conclusion short and sweet, no longer than 5-7 sentences in length. Conclusion of an Informative Essay. Informative essay conclusions need to relate to the information in your previous paragraphs. As a writer, you have three steps to do that: Restate thesis statement; Restate main ideas
In this video, you'll learn how to write a strong essay conclusion paragraph that ties together the essay's main points, shows why your argument matters, and...
Learn how to write a conclusion that summarizes your points and leaves a lasting impression. Find out the key elements, tips, and examples of a conclusion paragraph for different types of essays.
For example, if you're writing an informative essay about the sea creatures that live in the very deepest parts of the ocean, you may close with a sentence like this: "It's clear that today's scientists should continue to observe and document these mysterious creatures, so we may all learn more about life at the bottom of the ocean."
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write a conclusion sentence. ... To understand how these starters can be used, check these conclusion sentence examples for essays. Example 1: In conclusion, marijuana may become recognized as a healing tool one day because it has more than recreational value.
Learn how to write an informative essay that educates the reader about a certain topic. Follow the steps to create an introduction, body, and conclusion that present objective facts and evidence.
Learn how to write an informative essay that engages readers with new, interesting, and often surprising facts and details about a subject. Follow the five steps to get started, including choosing a topic, writing a question, finding sources, creating a thesis, and outlining your paper.
Learn how to write an informative essay that provides clear and balanced information about a specific topic. Follow the 7 steps and see the examples of informative essay structure and format.
Analyze top-scoring essays: Study essays that scored highly to identify effective strategies and techniques. Emulate these in your writing. Focus on essay structure: Ensure every essay has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. A strong structure helps convey your arguments more effectively.
Learn how to write an informative essay that educates and informs the reader on a given subject matter objectively. Follow the steps to select a topic, research, create an outline, and write the introduction, body, and conclusion of your paper.