Biography Online


Nikola Tesla Biography
Nikola Tesla (1856–1943) was one of the greatest and most enigmatic scientists who played a key role in the development of electromagnetism and other scientific discoveries of his time. Despite his breathtaking number of patents and discoveries, his achievements were often underplayed during his lifetime.
Short Biography Nikola Tesla

Tesla was a bright student and in 1875 went to the Austrian Polytechnic in Graz. However, he left to gain employment in Marburg in Slovenia. Evidence of his difficult temperament sometimes manifested and after an estrangement from his family, he suffered a nervous breakdown. He later enrolled in the Charles Ferdinand University in Prague, but again he left before completing his degree.
During his early life, he experienced many periods of illness and periods of startling inspiration. Accompanied by blinding flashes of light, he would often visualise mechanical and theoretical inventions spontaneously. He had a unique capacity to visualise images in his head. When working on projects, he would rarely write down plans or scale drawings, but rely on the images in his mind.
In 1880, he moved to Budapest where he worked for a telegraph company. During this time, he became acquainted with twin turbines and helped develop a device that provided amplification for when using the telephone.
In 1882, he moved to Paris, where he worked for the Continental Edison Company. Here he improved various devices used by the Edison company. He also conceived the induction motor and devices that used rotating magnetic fields.
With a strong letter of recommendation, Tesla went to the United States in 1884 to work for the Edison Machine Works company. Here he became one of the chief engineers and designers. Tesla was given a task to improve the electrical system of direct current generators. Tesla claimed he was offered $50,000 if he could significantly improve the motor generators. However, after completing his task, Tesla received no reward. This was one of several factors that led to a deep rivalry and bitterness between Tesla and Thomas Edison . It was to become a defining feature of Tesla’s life and impacted his financial situation and prestige. This deep rivalry was also seen as a reason why neither Tesla or Edison was awarded a Nobel prize for their electrical discoveries.
Disgusted that he did not ever receive a pay rise, Tesla resigned, and for a short while, found himself having to gain employment digging ditches for the Edison telephone company.
In 1886, Tesla formed his own company, but it wasn’t a success as his backers didn’t support his faith in AC current.
In 1887, Tesla worked on a form of X-Rays. He was able to photograph the bones in his hand; he also became aware of the side-effects of using radiation. However, his work in this area gained little coverage, and much of his research was later lost in a fire at a New York warehouse.
“The scientific man does not aim at an immediate result. He does not expect that his advanced ideas will be readily taken up… His duty is to lay the foundation for those who are to come, and point the way.”
– Nikola Tesla, Modern Mechanics and Inventions (July 1934)
In 1891, Tesla became an American citizen. This was also a period of great advances in electrical knowledge. Tesla demonstrated the potential for wireless energy transfer and the capacity for AC power generation. Tesla’s promotion of AC current placed him in opposition to Edison who sought to promote his Direct Current DC for electric power. Shortly before his death, Edison said his biggest mistake was spending so much time on DC current rather than the AC current Tesla had promoted.
In 1899, Tesla moved to Colorado Springs where he had the space to develop high voltage experiments. This included a variety of radio and electrical transmission experiments. He left after a year in Colorado Springs, and the buildings were later sold to pay off debts.
In 1900, Tesla began planning the Wardenclyffe Tower facility. This was an ambitious project costing $150,000, a fortune at the time.
In 1904, the US patent office reversed his earlier patent for the radio, giving it instead to G. Marconi . This infuriated Tesla who felt he was the rightful inventor. He began a long, expensive and ultimately unsuccessful attempt to fight the decision. Marconi went on to win the Nobel Prize for physics in 1909. This seemed to be a repeating theme in Tesla’s life: a great invention that he failed to personally profit from.
Nikola Tesla also displayed fluorescent lamps and single node bulbs.
Tesla was in many ways an eccentric and genius. His discoveries and inventions were unprecedented. Yet, he was often ostracised for his erratic behaviour (during his later years, he developed a form of obsessive-compulsive behaviour). He was not frightened of suggesting unorthodox ideas such as radio waves from extraterrestrial beings. His ideas, lack of personal finance and unorthodox behaviour put him outside the scientific establishment and because of this, his ideas were sometimes slow to be accepted or used.
“All that was great in the past was ridiculed, condemned, combated, suppressed — only to emerge all the more powerfully, all the more triumphantly from the struggle.”
– Nikola Tesla, A Means for Furthering Peace (1905)
Outside of science, he had many artistic and literary friends; in later life he became friendly with Mark Twain , inviting him to his laboratory. He also took an interest in poetry, literature and modern Vedic thought, in particular being interested in the teachings and vision of the modern Hindu monk, Swami Vivekananda . Tesla was brought up an Orthodox Christian, although he later didn’t consider himself a believer in the true sense. He retained an admiration for Christianity and Buddhism.
“For ages this idea has been proclaimed in the consummately wise teachings of religion, probably not alone as a means of insuring peace and harmony among men, but as a deeply founded truth. The Buddhist expresses it in one way, the Christian in another, but both say the same: We are all one.”
– Nikola Tesla, The Problem of Increasing Human Energy (1900)
As well as considering scientific issues, Tesla was thoughtful about greater problems of war and conflict, and he wrote a book on the subject called A Means for Furthering Peace (1905). This expressed his views on how conflict may be avoided and humanity learn to live in harmony.
“What we now want most is closer contact and better understanding between individuals and communities all over the earth and the elimination of that fanatic devotion to exalted ideals of national egoism and pride, which is always prone to plunge the world into primeval barbarism and strife.”
– Nikola Tesla, My Inventions (1919)
Personal life
Tesla was famous for working hard and throwing himself into his work. He ate alone and rarely slept, sleeping as little as two hours a day. He remained unmarried and claimed that his chastity was helpful to his scientific abilities. In later years, he became a vegetarian, living on only milk, bread, honey, and vegetable juices.
Tesla passed away on 7 January 1943, in a New York hotel room. He was 86 years old.
After his death, in 1960 the General Conference on Weights and Measures named the SI unit of magnetic field strength the Tesla in his honour.
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “ Biography of Nikola Tesla” , Oxford, UK – www.biographyonline.net . Last updated 25th September 2017
Tesla: Inventor of the Electrical Age

Tesla: Inventor of the Electrical Age at Amazon
Tesla: The Man who invented the Twentieth Century

Key Inventions of Nikola Tesla
- Development in electromagnetism
- Theoretical work on Alternating Current (AC)
- Tesla Coil – magnifying transmitter
- Polyphase system of electrical distribution
- Patent for an early form of radio
- Wireless electrical transfer
- Devices for lightning protection
- Concepts for electrical vehicles
Important contributions in
- Early models of radar
- Remote control
- Nuclear physics
Related pages

Inventions that changed the world – Famous inventions that made a great difference to the progress of the world, including aluminium, the telephone and the printing press.

External pages
- Tesla Museum
Nikola Tesla
Serbian American scientist Nikola Tesla invented the Tesla coil and alternating-current (AC) electricity, in addition to discovering the rotating magnetic field.
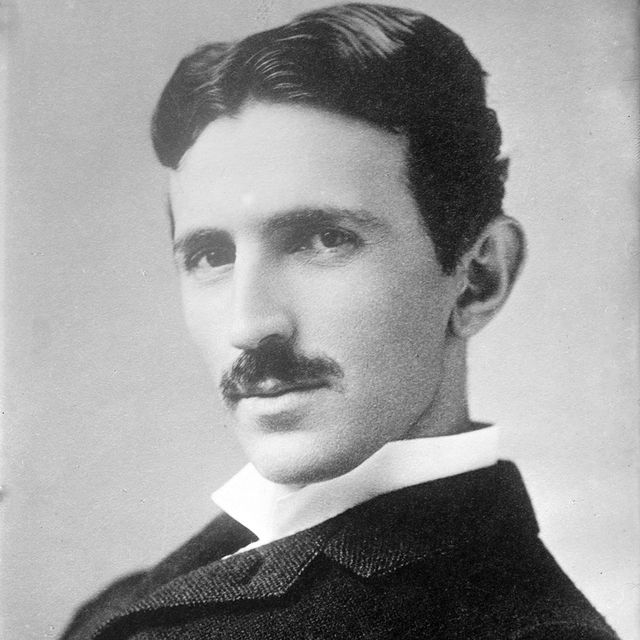

Who Was Nikola Tesla?
Quick facts, when was nikola tesla born, nikola tesla and thomas edison, solo venture, how did nikola tesla die, legacy: movies, electric car, and wardenclyffe tower renovation.
Engineer and inventor Nikola Tesla designed the alternating-current (AC) electric system, which is the predominant electrical system used across the world today. He also created the “Tesla coil” that is still used in radio technology. Born in modern-day Croatia, Tesla immigrated to the United States in 1884 and briefly worked with Thomas Edison before the two parted ways. The Serbian American sold several patent rights, including those to his AC machinery, to George Westinghouse . Tesla died at age 86 in January 1943, but his legacy lives on through his inventions and the electric car company Tesla that’s named in his honor.
FULL NAME: Nikola Tesla BORN: July 10, 1856 DIED: January 7, 1943 BIRTHPLACE: Smiljan, Croatia ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Cancer
Tesla was born on July 10, 1856, in the Austrian Empire town of Smiljan that is now part of Croatia.
He was one of five children, including siblings Dane, Angelina, Milka, and Marica. Nikola’s interest in electrical invention was spurred by his mother, Djuka Mandic, who invented small household appliances in her spare time while her son was growing up.
Tesla’s father, Milutin Tesla, was a Serbian orthodox priest and a writer, and he pushed for his son to join the priesthood. But Nikola’s interests lay squarely in the sciences.
Tesla received quite a bit of education. He studied at the Realschule, Karlstadt (later renamed the Johann-Rudolph-Glauber Realschule Karlstadt) in Germany; the Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria; and the University of Prague during the 1870s.
After university, Tesla moved to Budapest, Hungary, where for a time he worked at the Central Telephone Exchange. It was while in Budapest that the idea for the induction motor first came to Tesla, but after several years of trying to gain interest in his invention, at age 28, Tesla decided to leave Europe for America.
In 1884, Tesla arrived in the United States with little more than the clothes on his back and a letter of introduction to famed inventor and business mogul Thomas Edison , whose DC-based electrical works were fast becoming the standard in the country. Edison hired Tesla, and the two men were soon working tirelessly alongside each other, making improvements to Edison’s inventions.
Several months later, the two parted ways due to a conflicting business-scientific relationship , attributed by historians to their incredibly different personalities. While Edison was a power figure who focused on marketing and financial success, Tesla was commercially out-of-touch and somewhat vulnerable. Their feud would continue to affect Tesla’s career.
In 1885, Tesla received funding for the Tesla Electric Light Company and was tasked by his investors to develop improved arc lighting. After successfully doing so, however, Tesla was forced out of the venture and, for a time, had to work as a manual laborer in order to survive. His luck changed two years later when he received funding for his new Tesla Electric Company.
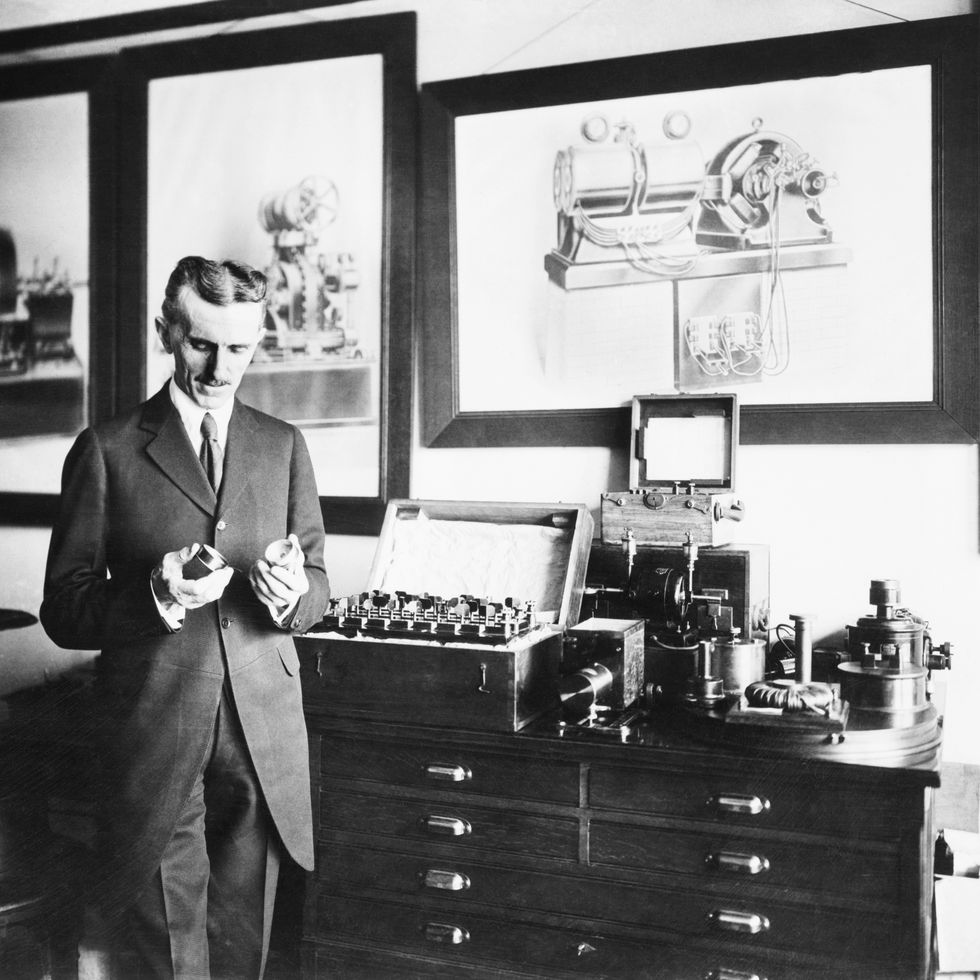

Throughout his career, Tesla discovered, designed, and developed ideas for a number of important inventions—most of which were officially patented by other inventors—including dynamos (electrical generators similar to batteries) and the induction motor.
He was also a pioneer in the discovery of radar technology, X-ray technology, remote control, and the rotating magnetic field—the basis of most AC machinery. Tesla is most well-known for his contributions in AC electricity and for the Tesla coil.
AC Electrical System
Tesla designed the alternating-current (AC) electrical system, which quickly became the preeminent power system of the 20 th century and has remained the worldwide standard ever since. In 1887, Tesla found funding for his new Tesla Electric Company, and by the end of the year, he had successfully filed several patents for AC-based inventions.
Tesla’s AC system soon caught the attention of American engineer and businessman George Westinghouse , who was seeking a solution to supplying the nation with long-distance power. Convinced that Tesla’s inventions would help him achieve this, in 1888, he purchased his patents for $60,000 in cash and stock in the Westinghouse Corporation.
As interest in an AC system grew, Tesla and Westinghouse were put in direct competition with Thomas Edison , who was intent on selling his direct-current (DC) system to the nation. A negative press campaign was soon waged by Edison, in an attempt to undermine interest in AC power.
Unfortunately for Edison, the Westinghouse Corporation was chosen to supply the lighting at the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, and Tesla conducted demonstrations of his AC system there.
Hydroelectric Power Plant
In 1895, Tesla designed what was among the first AC hydroelectric power plants in the United States, at Niagara Falls. The following year, it was used to power the city of Buffalo, New York—a feat that was highly publicized throughout the world and helped further AC electricity’s path to becoming the world’s power system.
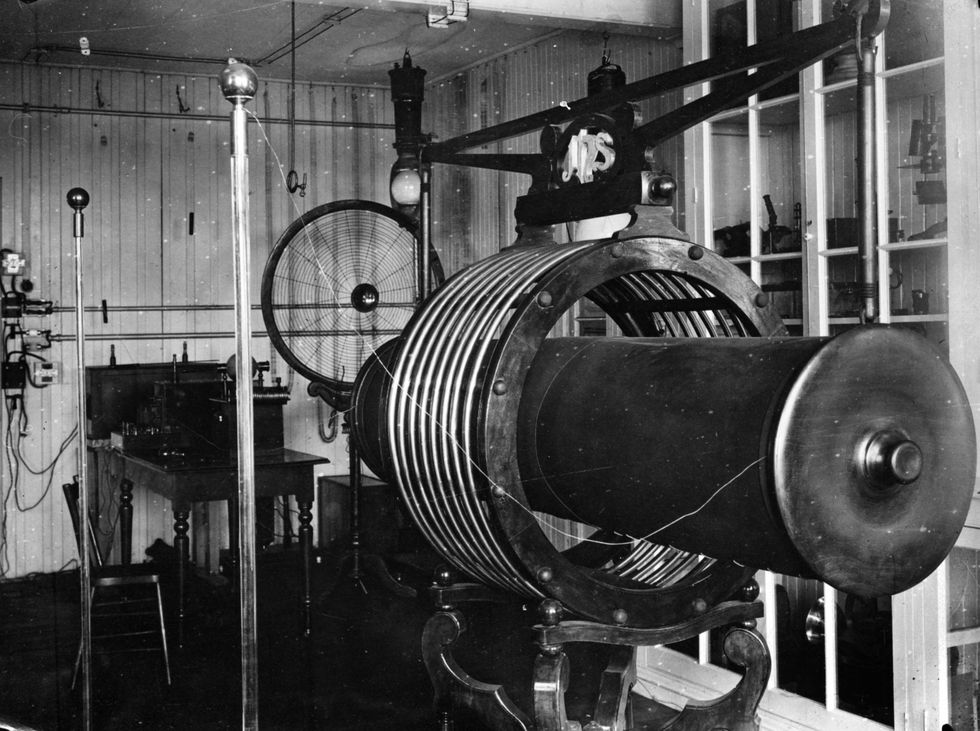
In the late 19 th century, Tesla patented the Tesla coil, which laid the foundation for wireless technologies and is still used in radio technology today. The heart of an electrical circuit, the Tesla coil is an inductor used in many early radio transmission antennas.
The coil works with a capacitor to resonate current and voltage from a power source across the circuit. Tesla used his coil to study fluorescence, x-rays, radio, wireless power, and electromagnetism in the earth and its atmosphere.
Wireless Power and Wardenclyffe Tower
Having become obsessed with the wireless transmission of energy, around 1900, Tesla set to work on his boldest project yet: to build a global, wireless communication system transmitted through a large electrical tower that would enable information sharing and provide free energy throughout the world.
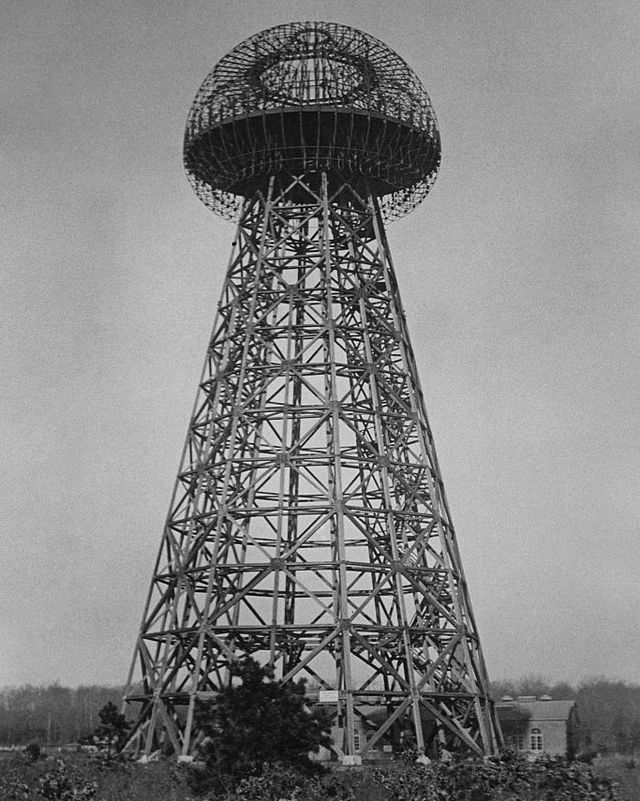

With funding from a group of investors that included financial giant J. P. Morgan , Tesla began work on the free energy project in earnest in 1901. He designed and built a lab with a power plant and a massive transmission tower on a site on Long Island, New York, that became known as Wardenclyffe.
However, doubts arose among his investors about the plausibility of Tesla’s system. As his rival, Guglielmo Marconi —with the financial support of Andrew Carnegie and Thomas Edison —continued to make great advances with his own radio technologies, Tesla had no choice but to abandon the project.
The Wardenclyffe staff was laid off in 1906, and by 1915, the site had fallen into foreclosure. Two years later, Tesla declared bankruptcy, and the tower was dismantled and sold for scrap to help pay the debts he had accrued.
After suffering a nervous breakdown following the closure of his wireless power project, Tesla eventually returned to work, primarily as a consultant. But as time went on, his ideas became progressively more outlandish and impractical. He grew increasingly eccentric, devoting much of his time to the care of wild pigeons in the parks of New York City . Tesla even drew the attention of the FBI with his talk of building a powerful “death ray,” which had received some interest from the Soviet Union during World War II.
Poor and reclusive, Tesla died of coronary thrombosis on January 7, 1943, at the age of 86 in New York City, where he had lived for nearly 60 years.
The legacy of Tesla’s work lives on to this day. In 1994, a street sign identifying “Nikola Tesla Corner” was installed near the site of his former New York City laboratory, at the intersection of 40 th Street and 6 th Avenue.
Several movies have highlighted Tesla’s life and famous works, most notably:
- The Secret of Nikola Tesla , a 1980 biographical film starring Orson Welles as J. P. Morgan .
- Nikola Tesla, The Genius Who Lit the World , a 1994 documentary produced by the Tesla Memorial Society and the Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade, Serbia.
- The Prestige , a 2006 fictional film about two magicians directed by Christopher Nolan , with rock star David Bowie portraying Tesla.
In 2003, a group of engineers founded Tesla Motors, a car company named after Tesla dedicated to building the first fully electric-powered car. Entrepreneur and engineer Elon Musk contributed over $30 million to Tesla in 2004 and serves as the company’s co-founder and CEO.
Tesla Motors unveiled its first electric car, the Roadster, in 2008. A high-performance sports vehicle, the Roadster helped changed the perception of what electric cars could be. In 2014, Tesla launched the Model S, a lower-priced model that, in 2017, set the MotorTrend world record for 0 to 60 miles per hour acceleration at 2.28 seconds. The company’s designs showed that an electric car could have the same performance as gasoline-powered sports car brands like Porsche and Lamborghini.
Tesla Science Center at Wardenclyffe
Since Tesla’s original forfeiture of his free energy project, ownership of the Wardenclyffe property has passed through numerous hands. Several attempts have been made to preserve it, but efforts to declare it a national historic site failed in 1967, 1976, and 1994.
Then, in 2008, a group called the Tesla Science Center (TSC) was formed with the intention of purchasing the property and turning it into a museum dedicated to the inventor’s work. In 2009, the Wardenclyffe site went on the market for nearly $1.6 million, and for the next several years, the TSC worked diligently to raise funds for its purchase. In 2012, public interest in the project peaked when Matthew Inman of TheOatmeal.com collaborated with the TSC in an Internet fundraising effort, ultimately receiving enough contributions to acquire the site in May 2013.
Wardenclyffe Tower finally joined the National Register of Historic Places in 2018. Work on its restoration is still in progress. A $20 million redevelopment broke ground in April 2023, but those efforts were complicated by large fire that November. The site is closed to the public “for the foreseeable future” for reasons of safety and preservation, according to the Tesla Science Center.
- Our virtues and our failings are inseparable, like force and matter. When they separate, man is no more.
- I do not think you can name many great inventions that have been made by married men.
- The scientists of today think deeply instead of clearly. One must be sane to think clearly, but one can think deeply and be quite insane.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us

Famous Inventors

The Inventor Connected to the Salem Witch Trials

Louis Braille
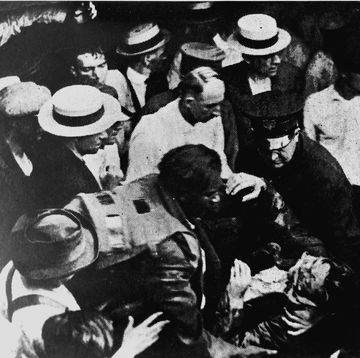
Inventor Garrett Morgan’s Lifesaving 1916 Rescue

Frederick Jones

Lonnie Johnson

11 Famous Black Inventors Who Changed Your Life

Lewis Howard Latimer

Nikola Tesla's Secrets to Longevity

Garrett Morgan
Sarah Boone

Henry Blair

Alfred Nobel
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Nikola Tesla
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 13, 2020 | Original: November 9, 2009

Serbian-American engineer and physicist Nikola Tesla (1856-1943) made dozens of breakthroughs in the production, transmission and application of electric power. He invented the first alternating current (AC) motor and developed AC generation and transmission technology. Though he was famous and respected, he was never able to translate his copious inventions into long-term financial success—unlike his early employer and chief rival, Thomas Edison.
Nikola Tesla’s Early Years
Nikola Tesla was born in 1856 in Smiljan, Croatia, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. His father was a priest in the Serbian Orthodox church and his mother managed the family’s farm. In 1863 Tesla’s brother Daniel was killed in a riding accident. The shock of the loss unsettled the 7-year-old Tesla, who reported seeing visions—the first signs of his lifelong mental illnesses.
Did you know? During the 1890s Mark Twain struck up a friendship with inventor Nikola Tesla. Twain often visited him in his lab, where in 1894 Tesla photographed the great American writer in one of the first pictures ever lit by phosphorescent light.
Tesla studied math and physics at the Technical University of Graz and philosophy at the University of Prague. In 1882, while on a walk, he came up with the idea for a brushless AC motor, making the first sketches of its rotating electromagnets in the sand of the path. Later that year he moved to Paris and got a job repairing direct current (DC) power plants with the Continental Edison Company. Two years later he immigrated to the United States.
Nikola Tesla and Thomas Edison
Tesla arrived in New York in 1884 and was hired as an engineer at Thomas Edison’s Manhattan headquarters. He worked there for a year, impressing Edison with his diligence and ingenuity. At one point Edison told Tesla he would pay $50,000 for an improved design for his DC dynamos. After months of experimentation, Tesla presented a solution and asked for the money. Edison demurred, saying, “Tesla, you don’t understand our American humor.” Tesla quit soon after.
Nikola Tesla and Westinghouse
After an unsuccessful attempt to start his own Tesla Electric Light Company and a stint digging ditches for $2 a day, Tesla found backers to support his research into alternating current. In 1887 and 1888 he was granted more than 30 patents for his inventions and invited to address the American Institute of Electrical Engineers on his work. His lecture caught the attention of George Westinghouse, the inventor who had launched the first AC power system near Boston and was Edison’s major competitor in the “Battle of the Currents.”
Westinghouse hired Tesla, licensed the patents for his AC motor and gave him his own lab. In 1890 Edison arranged for a convicted New York murderer to be put to death in an AC-powered electric chair—a stunt designed to show how dangerous the Westinghouse standard could be.
Buoyed by Westinghouse’s royalties, Tesla struck out on his own again. But Westinghouse was soon forced by his backers to renegotiate their contract, with Tesla relinquishing his royalty rights.
In the 1890s Tesla invented electric oscillators, meters, improved lights and the high-voltage transformer known as the Tesla coil. He also experimented with X-rays, gave short-range demonstrations of radio communication two years before Guglielmo Marconi and piloted a radio-controlled boat around a pool in Madison Square Garden. Together, Tesla and Westinghouse lit the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago and partnered with General Electric to install AC generators at Niagara Falls , creating the first modern power station.
Nikola Tesla’s Failures, Death and Legacy
In 1895 Tesla’s New York lab burned, destroying years’ worth of notes and equipment. Tesla relocated to Colorado Springs for two years, returning to New York in 1900. He secured backing from financier J.P. Morgan and began building a global communications network centered on a giant tower at Wardenclyffe, on Long Island. But funds ran out and Morgan balked at Tesla’s grandiose schemes.
Tesla lived his last decades in a New York hotel, working on new inventions even as his energy and mental health faded. His obsession with the number three and fastidious washing were dismissed as the eccentricities of genius. He spent his final years feeding—and, he claimed, communicating with—the city’s pigeons.
Tesla died in his room on January 7, 1943. Later that year the U.S. Supreme Court voided four of Marconi’s key patents, belatedly acknowledging Tesla’s innovations in radio. The AC system he championed and improved remains the global standard for power transmission.

HISTORY Vault: The Tesla Files
Declassified CIA documents reveal a secret history surrounding Nikola Tesla.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
- Humanities ›
- History & Culture ›
- The 20th Century ›
- People & Events ›
Biography of Nikola Tesla, Serbian-American Inventor
Wikimedia Commons / Public Domain
- People & Events
- Fads & Fashions
- Early 20th Century
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- Women's History
- B.S., Texas A&M University
Nikola Tesla (July 10, 1856–January 7, 1943) was a Serbian-American inventor, electrical engineer, and futurist. As the holder of nearly 300 patents, Tesla is best known for his role in developing the modern three-phase alternating current (AC) electric power supply system and for his invention of the Tesla coil, an early advancement in the field of radio transmission.
During the 1880s, Tesla and Thomas Edison , inventor and champion of direct electrical current (DC), would become embattled in the “War of the Currents” over whether Tesla’s AC or Edison’s DC would become the standard current used in long-distance transmission of electrical power.
Fast Facts: Nikola Tesla
- Known For: Development of alternating current (AC) electrical power
- Born: July 10, 1856 in Smiljan, Austrian Empire (modern-day Croatia)
- Parents: Milutin Tesla and Đuka Tesla
- Died: January 7, 1943 in New York City, New York
- Education: Austrian Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria (1875)
- Patents: US381968A —Electro-magnetic motor, US512,340A —coil for electro-magnets
- Awards and Honors : Edison Medal (1917), Inventor’s Hall of Fame (1975)
- Notable Quote : “If you want to find the secrets of the universe, think in terms of energy, frequency and vibration.”
Early Life and Education
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856, in the village of Smiljan in the Austrian Empire (now Croatia) to his Serbian father Milutin Tesla, an Eastern Orthodox priest, and his mother Đuka Tesla, who invented small household appliances and had the ability to memorize lengthy Serbian epic poems. Tesla credited his mother for his own interest in inventing and photographic memory. He had four siblings, a brother Dane, and sisters Angelina, Milka, and Marica.
In 1870, Tesla started high school at the Higher Real Gymnasium in Karlovac, Austria. He recalled that his physics teacher’s demonstrations of electricity made him want “to know more of this wonderful force.” Able to do integral calculus in his head, Tesla completed high school in just three years, graduating in 1873.
Determined to pursue a career in engineering, Tesla enrolled at the Austrian Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria, in 1875. It was here that Tesla studied a Gramme dynamo, an electrical generator that produces direct current. Observing that the dynamo functioned like an electric motor when the direction of its current was reversed, Tesla began thinking of ways this alternating current could be used in industrial applications. Though he never graduated—as was not uncommon then—Tesla posted excellent grades and was even given a letter from the dean of the technical faculty addressed to his father stating, “Your son is a star of first rank.”
Feeling that chastity would help him focus on his career, Tesla never married or had any known romantic relationships. In her 2001 book, “ Tesla: Man Out of Time ,” biographer Margaret Cheney writes that Tesla felt himself to be unworthy of women, considering them to be superior to him in every way. Later in life, however, he publicly expressed strong dislike what he called the “new woman,” women he felt were abandoning their femininity in an attempt to dominate men.
The Path to Alternating Current
In 1881, Tesla moved to Budapest, Hungary, where he gained practical experience as the chief electrician at the Central Telephone Exchange. In 1882, Tesla was hired by the Continental Edison Company in Paris where he worked in the emerging industry of installing the direct current-powered indoor incandescent lighting system patented by Thomas Edison in 1879. Impressed by Tesla’s mastery of engineering and physics, the company’s management soon had him designing improved versions of generating dynamos and motors and fixing problems at other Edison facilities throughout France and Germany.
When the manager of the Continental Edison facility in Paris was transferred back to the United States in 1884, he asked that Tesla be brought to the U.S. as well. In June 1884, Tesla emigrated to the United States and went to work at the Edison Machine Works in New York City, where Edison’s DC-based electrical lighting system was fast becoming the standard. Just six months later, Tesla quit Edison after a heated dispute over unpaid wages and bonuses. In his diary, Notebook from the Edison Machine Works: 1884-1885 , Tesla marked the end of the amicable relationship between the two great inventors. Across two pages, Tesla wrote in large letters, “Good By to the Edison Machine Works.”
By March 1885, Tesla, with the financial backing of businessmen Robert Lane and Benjamin Vail, started his own lighting utility company, Tesla Electric Light & Manufacturing. Instead of Edison’s incandescent lamp bulbs, Tesla’s company installed a DC-powered arc lighting system he had designed while working at Edison Machine Works. While Tesla’s arc light system was praised for its advanced features, his investors, Lane and Vail, had little interest in his ideas for perfecting and harnessing alternating current. In 1886, they abandoned Tesla’s company to start their own company. The move left Tesla penniless, forcing him to survive by taking electrical repair jobs and digging ditches for $2.00 per day. Of this period of hardship, Tesla would later recall, “My high education in various branches of science, mechanics, and literature seemed to me like a mockery.”
During his time of near destitution, Tesla’s resolve to prove the superiority of alternating current over Edison’s direct current grew even stronger.
Alternating Current and the Induction Motor
In April 1887, Tesla, along with his investors, Western Union telegraph superintendent Alfred S. Brown and attorney Charles F. Peck, founded the Tesla Electric Company in New York City for the purpose of developing new types of electric motors and generators.
Tesla soon developed a new type of electromagnetic induction motor that ran on alternating current. Patented in May 1888, Tesla’s motor proved to be simple, dependable, and not subject to the constant need for repairs that plagued direct current-driven motors at the time.
In July 1888, Tesla sold his patent for AC-powered motors to Westinghouse Electric Corporation, owned by electrical industry pioneer George Westinghouse. In the deal, which proved financially lucrative for Tesla, Westinghouse Electric got the rights to market Tesla’s AC motor and agreed to hire Tesla as a consultant.
With Westinghouse now backing AC and Edison backing DC, the stage was set for what would become known as “The War of the Currents.”
The War of the Currents: Tesla vs. Edison
Recognizing the economic and technical superiority of alternating current to his direct current for long-distance power distribution, Edison undertook an unprecedently aggressive public relations campaign to discredit AC as posing a deadly threat to the public—a force should never allow in their homes. Edison and his associates toured the U.S. presenting grizzly public demonstrations of animals being electrocuted with AC electricity. When New York State sought a faster, “more humane” alternative to hanging for executing condemned prisoners, Edison, though once a vocal opponent of capital punishment, recommended using AC-powered electrocution. In 1890, murderer William Kemmler became the first person to be executed in a Westinghouse AC generator-powered electric chair that had been secretly designed by one of Edison’s salesmen.
Despite his best efforts, Edison failed to discredit alternating current. In 1892, Westinghouse and Edison’s new company General Electric, competed head-to-head for the contract to supply electricity to the 1893 World’s Fair in Chicago. When Westinghouse ultimately won the contract, the fair served as a dazzling public display of Tesla’s AC system.
On the tails of their success at the World’s Fair, Tesla and Westinghouse won a historic contract to build the generators for a new hydroelectric power plant at Niagara Falls. In 1896, the power plant began delivering AC electricity to Buffalo, New York, 26 miles away. In his speech at the opening ceremony of the power plant, Tesla said of the accomplishment, “It signifies the subjugation of natural forces to the service of man, the discontinuance of barbarous methods, the relieving of millions from want and suffering.”
The success of the Niagara Falls power plant firmly established Tesla’s AC as the standard for the electric power industry, effectively ending the War of the Currents.
The Tesla Coil
In 1891, Tesla patented the Tesla coil, an electrical transformer circuit capable of producing high-voltage, low-current AC electricity. Though best-known today for its use in spectacular, lightening-spitting demonstrations of electricity, the Tesla coil was fundamental to the development of wireless communications. Still used in modern radio technology, the Tesla coil inductor was an essential part of many early radio transmission antennas.
Tesla would go on to use his Tesla coil in experiments with radio remote control, fluorescent lighting , x-rays , electromagnetism , and universal wireless power transmission.
On July 30, 1891, the same year he patented his coil, the 35-year-old Tesla was sworn in as a naturalized United States citizen.
Radio Remote Control
At the 1898 Electrical Exposition in Boston’s Madison Square Gardens, Tesla demonstrated an invention he called a “telautomaton,” a three-foot-long, radio-controlled boat propelled by a small battery-powered motor and rudder. Members of the amazed crowd accused Tesla of using telepathy, a trained monkey, or pure magic to steer the boat.
Finding little consumer interest in radio-controlled devices, Tesla tried unsuccessfully to sell his “Teleautomatics” idea to the US Navy as a type of radio-controlled torpedo. However, during and after World War I (1914-1918), the militaries of many countries, including the United States incorporated it.
Wireless Power Transmission
From 1901 through 1906, Tesla spent most of his time and savings working on arguably his most ambitious, if a far-fetched, project—an electrical transmission system he believed could provide free energy and communications throughout the world without the need for wires.
In 1901, with the backing of investors headed by financial giant J. P. Morgan, Tesla began building a power plant and massive power transmission tower at his
Wardenclyffe laboratory on Long Island, New York. Seizing on the then commonly-held belief that the Earth’s atmosphere conducted electricity, Tesla envisioned a globe-spanning network of power transmitting and receiving antennas suspended by balloons 30,000 feet (9,100 m) in the air.
However, as Tesla’s project drug on, its sheer enormity caused his investors to doubt its plausibility and withdraw their support. With his rival, Guglielmo Marconi—enjoying the substantial financial support of steel magnate Andrew Carnegie and Thomas Edison—was making great advances in his own radio transmission developments, Tesla was forced to abandon his wireless power project in 1906.
Later Life and Death
In 1922, Tesla, deeply in debt from his failed wireless power project, was forced to leave the Waldorf Astoria hotel in New York City where he had been living since 1900, and move into the more-affordable St. Regis Hotel. While living at the St. Regis, Tesla took to feeding pigeons on the windowsill of his room, often bringing weak or injured birds into his room to nurse them back to health.
Of his love for one particular injured pigeon, Tesla would write, “I have been feeding pigeons, thousands of them for years. But there was one, a beautiful bird, pure white with light grey tips on its wings; that one was different. It was a female. I had only to wish and call her and she would come flying to me. I loved that pigeon as a man loves a woman, and she loved me. As long as I had her, there was a purpose to my life.”
By late 1923, the St. Regis evicted Tesla because of unpaid bills and complaints about the smell from keeping pigeons in his room. For the next decade, he would live in a series of hotels, leaving behind unpaid bills at each. Finally, in 1934, his former employer, Westinghouse Electric Company, began paying Tesla $125 per month as a “consulting fee,” as well as paying his rent at the Hotel New Yorker.
In 1937, at age 81, Tesla was knocked to the ground by a taxicab while crossing a street a few blocks from the New Yorker. Though he suffered a severely wrenched back and broken ribs, Tesla characteristically refused extended medical attention. While he survived the incident, the full extent of his injuries, from which he never fully recovered, was never known.
On January 7, 1943, Tesla died alone in his room at the New Yorker Hotel at the age of 86. The medical examiner listed the cause of death as coronary thrombosis, a heart attack.
On January 10, 1943, New York City mayor Fiorello La Guardia delivered a eulogy to Tesla broadcast live over WNYC radio. On January 12, over 2,000 people attended Tesla’s funeral at the Cathedral of Saint John the Divine. Following the funeral, Tesla’s body was cremated at Ferncliff Cemetery in Ardsley, New York.
With the United States then fully engaged in World War II ., fears that the Austrian-born inventor might have been in possession of devices or designs helpful to Nazi Germany , drove the Federal Bureau of Investigation to seize Tesla’s possessions after his death. However, the FBI reported finding nothing of interest, concluding that since about 1928, Tesla’s work had been “primarily of a speculative, philosophical, and somewhat promotional character often concerned with the production and wireless transmission of power; but did not include new, sound, workable principles or methods for realizing such results.”
In his 1944 book, Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla , journalist, and historian John Joseph O’Neill wrote that Tesla claimed to have never slept more than two hours per night, “dozing” during the day instead to “recharge his batteries.” He was reported to have once spent 84 straight hours without sleep working in his laboratory.
It is believed that Tesla was granted around 300 patents worldwide for his inventions during his lifetime. While several of his patents remain unaccounted for or archived, he holds at least 278 known patents in 26 countries, mostly in the United States, Britain, and Canada. Tesla never attempted to patent many of his other inventions and ideas.
Today, Tesla’s legacy can be seen in multiple forms of popular culture, including movies, TV, video games and several genres of science fiction. For example, in the 2006 movie The Prestige, David Bowie portrays Tesla developing an amazing electro-replicating device for a magician. In Disney’s 2015 film Tomorrowland: A World Beyond, Tesla helps Thomas Edison, Gustave Eiffel , and Jules Verne discover a better future in an alternate dimension. And in the 2019 film The Current War, Tesla, played by Nicholas Hoult, squares off with Thomas Edison, played by Benedict Cumberbatch, in a history-based depiction of the war of the currents.
In 1917, Tesla was awarded the Edison Medal, the most coveted electrical prize in the United States, and in 1975, Tesla was inducted into the Inventor’s Hall of Fame. In 1983, the United States Postal Service issued a commemorative stamp honoring Tesla. Most recently, in 2003, a group of investors headed by engineer and futurist Elon Musk founded Tesla Motors, a company dedicated to producing the first car fittingly powered totally by Tesla’s obsession—electricity.
- Carlson, W. Bernard. “Tesla: Inventor of the Electrical Age.” Princeton University Press, 2015.
- Cheney, Margaret. “Tesla: Man Out of Time.” Simon & Schuster, 2001.
- O'Neill, John J. (1944). “Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla.” Cosimo Classics, 2006.
- Gunderman, Richard. “The Extraordinary Life of Nikola Tesla.” Smithsonian.com , January 5, 2018, https://www.smithsonianmag.com/innovation/extraordinary-life-nikola-tesla-180967758/ .
- Tesla, Nikola. “Notebook from the Edison Machine Works: 1884-1885.” Tesla Universe, https://teslauniverse.com/nikola-tesla/books/nikola-tesla-notebook-edison-machine-works-1884-1885 .
- “The War of the Currents: AC vs. DC Power.” U.S. Department of Energy , https://www.energy.gov/articles/war-currents-ac-vs-dc-power .
- Cheney, Margaret. “Tesla: Master of Lightning.” MetroBooks, 2001.
- Dickerson, Kelly.“Wireless Electricity? How the Tesla Coil Works.” LiveScience , July 10, 2014, https://www.livescience.com/46745-how-tesla-coil-works.html .
- “About Nikola Tesla.” Tesla Society , https://web.archive.org/web/20120525133151/http:/www.teslasociety.org/about.html .
- O’Neill, John J. “Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla.” Cosimo Classics, 2006.
- The Tunguska Event
- Biography of Thomas Edison, American Inventor
- Biography of Dalton Trumbo: Screenwriter on the Hollywood Blacklist
- Biography of Mother Teresa, 'The Saint of the Gutters'
- The Life of Zelda Fitzgerald, the Other Fitzgerald Writer
- Biography of Lenny Bruce
- Life and Work of H.L. Mencken: Writer, Editor, and Critic
- Adlai Stevenson: American Statesman and Presidential Candidate
- Biography of Tom Hayden, Activist and Politician
- Biography of Nikita Khrushchev, Cold War Era Soviet Leader
- Biography of Saddam Hussein, Dictator of Iraq
- Biography of the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., Civil Rights Leader
- Hedy Lamarr
- Edward R. Murrow, Broadcast News Pioneer
- Edward Bernays, Father of Public Relations and Propaganda
- Joe Hill: Poet, Songwriter, and Martyr of the Labor Movement
- Collectibles
Nikola Tesla – The Genius Who Lit the World and Saw the Future
- by history tools
- November 19, 2023
Nikola Tesla was one of the most forward-thinking inventors and engineers in history whose pioneering work with electricity literally lit up the modern world. Though underappreciated in his own time, Tesla created hundreds of groundbreaking innovations that fundamentally advanced technology and changed the course of history. This complete biography explores Tesla’s storied life, brilliant vision, and lasting impact.

Introduction to the Master of Electricity
Nikola Tesla was born in 1856 in Smiljan, Croatia and displayed astonishing mental abilities and imagination from an early age. His lifelong passion for energy and electricity was evident even as a child when he created his own tiny waterwheels and turbines. Tesla went on to study math, physics, and mechanics in his teen years at advanced schools in Austria and Germany, showing great promise. After graduating, he worked with Thomas Edison on DC power projects for a period but soon struck out on his own to champion AC electricity instead.
Tesla constructed his first AC motors in the late 1880s and partnered with George Westinghouse to commercialize AC power. This set the stage for an epic technology battle against Edison called the “War of the Currents” which Tesla and Westinghouse ultimately won, ensuring AC became the global standard. Throughout his life, Tesla discovered groundbreaking electrical innovations that form the basis of modern power and communication systems. Though he died in obscurity, Tesla‘s inventionsUNDOUBTEDLY constituted some of the most important technological advances in history.
Early Life and Education – The Making of a Genius
Childhood of creativity and tragedy.
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10th, 1856 in Smiljan, Croatia. His father, Milutin Tesla, was a priest in the Serbian Orthodox church and his mother Djuka Mandic was a homemaker and amateur inventor who created household appliances to help with daily tasks. Tesla inherited much of his inventive spirit from his mother. Tesla was one of five children, though his older brother died tragically in an accident when Nikola was five years old. The loss deeply impacted him and shaped his obsessive and eccentric personality later in life.
As a child, Tesla displayed astonishing creativity and visualization abilities. He could supposedly perform complex mathematical equations entirely in his mind without writing them down. Young Tesla was also captivated by thunderstorms and lightning. He made sketches of inventions like turbines and engines, even constructing a tiny waterwheel as a boy by observing the local river. His interests foreshadowed his future passion for electricity and engineering.
Immersive Education Shapes a Visionary Mind
In 1870, Tesla attended the Austrian Polytechnic School in Graz on an academic scholarship where he studied physics, mechanics, and mathematics. There, Tesla became fascinated with the Gramme dynamo which generated direct current electricity while also exploring fields like electrical engineering before they were widely taught. In his second year, Tesla stopped attending lectures and studied independently instead, astonishing professors with his brilliance but also worrying them with his unusual study habits and solitary nature.
After leaving Graz without a degree in 1878, Tesla contracted cholera and seemingly had intense visions during his recovery where he claimed to have unlocked the secrets of alternating current in a moment of insight. The following year, he attended the Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague deepening his education even further and receiving a degree in physics in 1882. Tesla’s academic efforts clearly shaped his boundary-pushing innovations down the line.
Early Career – Harnessing the Magic of Electricity
Fresh out of school in 1882, Tesla began working for the Continental Edison Company in Paris. He focused on improving direct current generators and motors. At the time, Edison’s DC system was the only existing power system. After two years, Tesla departed for America to meet Edison himself and share his ideas.
Working With his Hero-turned-Rival, Edison
In 1884, Tesla arrived in New York and was hired to work directly for Thomas Edison. The two inventors got along well initially, and Edison was impressed by Tesla‘s skill. But things began deteriorating as Tesla pushed for more pay and Edison denied him. Edison reportedly offered $50,000 if Tesla could improve his inefficient direct current dynamos. Tesla succeeded but Edison dismissed the offer as a joke, causing bad blood between them.
Tesla left Edison‘s company after just one year of service. But this marked the start of Tesla’s pioneering research into alternating current electricity which would become his claim to fame. The messy split also sparked an intense rivalry with Edison that would culminate in the War of the Currents.
Discovering Alternating Current
In 1885, Tesla secured funding for his own startup focused on arc lighting systems and began developing his own AC motors and transformers. While working with high frequency alternators, he rediscovered the rotating magnetic field principle that essentially forms the basis of AC machinery today.
Tesla acquired several patents for AC motors, generators, and transformers in 1887-1888. His innovations relied on polyphase alternating currents rather than direct currents to distribute power more efficiently over long distances. Tesla gave acclaimed lectures to engineers describing the advantages of AC over DC. His ideas quickly caught the attention of American entrepreneur George Westinghouse.
Winning the War of the Currents – AC vs DC
George Westinghouse recognized the merits of Tesla’s AC approach and purchased his polyphase system patents in 1888 which included AC motors and transformers. This decision set the stage for a battle over the future of electricity between Westinghouse backing AC and Thomas Edison promoting DC. The stakes were enormous given the two incompatible electrical standards.
Edison wielded his broad patents and influence to block adoption of AC as much as possible, even staging public stunts to portray AC as dangerous. But thanks to Tesla’s innovations, Westinghouse prevailed when AC was chosen to power the Chicago World Fair of 1893 illuminating over 200,000 lightbulbs. Niagara Falls also chose AC to generate their groundbreaking hydroelectric plant in 1895. AC proved capable of transmitting power over vastly greater distances than DC which required power stations every mile.
This victory by Westinghouse demonstrated the superiority of AC power which was quickly adopted as the standard. To this day, our homes and cities are powered by Tesla‘s polyphase AC system showing its profound impact. Tesla‘s innovations literally electrified the modern world.
Trailblazing Inventions – Fueling the Future
In addition to revolutionizing electric power, Tesla discovered countless groundbreaking inventions over his lifetime that changed the future of technology and paved the way for modern wireless communication.
Radio and Wireless Communication
Tesla is credited by many to have been the first person to transmit and receive radio signals when he demonstrated a radio-controlled boat in 1898. While Guglielmo Marconi won the Nobel Prize for radio in 1909, Tesla had developed the underlying principles two years earlier. Tesla predicted the coming age of wireless communication, stating:
“As I review the events of my past life I realize how subtle are the influences that shape our destinies…we can never fathom the marvellous complexity of the causes behind the daily incidents that pass before our eyes and their altered relationships.” (Tesla 1926)
Tesla also patented various fundamental radio circuits between 1896-1900 that formed the basis for modern radio engineering. Though Marconi is often viewed as the inventor of radio, clearly Tesla‘s groundwork was pivotal.
Remote Control
In 1898 at Madison Square Garden, Tesla demonstrated a boat controlled wirelessly using radio-like technology to the amazement of crowds. This was one of the earliest implementations of remote control technology. Tesla described the system as being wireless like “invisible waves” and foresaw remote control being used in all kinds of mechanical devices and vehicles in the future.
Working with high voltage electricity and vacuum tubes, Tesla created some of the first X-ray images in 1895. They were produced earlier than Wilhelm Röntgen’s discovery of X-rays which garnered him the first Nobel Prize in Physics. Though Tesla did not win that prize, his innovations contributed to the field.
Electric Motors
Tesla invented the first AC induction motor in 1883 exploiting rotating magnetic fields generated by alternating current. Induction motors are brushless motors that provide high efficiency and operational speeds. They are the most common type of AC motors in use today powering appliances, tools, conveyors, and more.
Neon Lights
While investigating gases, Tesla created fluorescent light bulbs that lit up when electricity passed through them. This discovery led to the development of neon signs and lighting. Tesla‘s innovations literally brightened up the world.
Laser Vision
Tesla proposed using high voltage electricity and tiny metal particles to produce beams of concentrated light. Essentially, he had envisioned laser technology before the first working laser was invented in 1960. This showed Tesla’s thinking was decades ahead of his time.
A Futurist Stalled by Business Failures
In addition to his AC system and visionary inventions, Tesla conceived of even more ambitious plans that were simply impossible with the technology of his era. He envisioned worldwide wireless transmission of electricity essentially turning the earth into a giant conductor. In 1901, he began constructing his Wardenclyffe Tower facility on Long Island to demonstrate wireless power transmission on a large scale and provide telecommunications. But unable to secure adequate funding from industrialists like J.P Morgan, Tesla had to abandon the unfinished project in 1905.
Tesla articulated many forward-thinking concepts like wireless networks, self-driving vehicles, smart homes, and AI. But his poor business skills and inability to gain investors meant many of these revolutionary technologies could only be realized later by others. While a brilliant scientist, Tesla lacked the entrepreneurial abilities of businessmen like Edison or Westinghouse to commercialize his ideas. Tesla lived the final decade of his life in poverty relying on the kindness of friends until passing in 1943.
Legacy – Illuminating the Modern Age
Though Tesla‘s pioneering technologies were not always recognized during his lifetime, his inventions legitimately transformed the world and remain integral to our electrical infrastructure today. He was a pivotal figure whose work ranks among the most important innovations in history. Tesla undisputably provided the key infrastructure enabling modern society to flourish. He electrified the world and saw the future more clearly than almost anyone.
Related posts:
- Who is Ben Horowitz, Silicon Valley‘s Billionaire Rainmaker?
- Robert Noyce – Complete Biography, History and Inventions
- What Does RGB Stand For? – A Complete History
- John Patterson — Complete Biography, History and Inventions
- Hello There! Let‘s Explore How Jabez Burns‘ Addometer Paved the Way for Modern Computing
- Samuel Kelso: Complete Biography, History, and Inventions
- Friedrich Kaufmann and the Trumpet Player: A Complete History
- The Integrated Circuit Revolution – How Jack Kilby‘s Microchip Changed the World
The fascinating life of Nikola Tesla, the genius who electrified the world and dreamed up death rays
July 10 is the birthday of Nikola Tesla, who would have been 161 years old today.
It's a good time to celebrate the life of the Serbian-American engineer and physicist: Without Tesla, you might not be able to affordably power your home, let alone read this sentence.
Tesla filed more than 300 patents during his 86 years of life, and his inventions helped pave the way for alternating current (AC), electric motors, radios, fluorescent lights, lasers, and remote controls, among many other things.
Some of his ideas later in life, however, seem strange even now. He once described plans for a death ray, for example, and alluded to another idea for an impenetrable "wall of force" to block and destroy foreign invasions.
Here's a glimpse into the remarkable life of one of history's most important — and eccentric — geniuses.
Tanya Lewis wrote a previous version of this story.
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856 in Smiljan in the Austo-Hungarian Empire (modern-day Croatia).
His father, Milutin Tesla, was a Serbian Orthodox Priest and his mother, Djuka Mandic, was an inventor of household appliances.
Source: Tesla Society
In college, Tesla was initially interested in studying physics and mathematics, but soon became fascinated by electricity.
He attended the Realschule, Karlstadt in 1873, the Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria and the University of Prague. He took a job as an electrical engineer at a telephone company in Budapest in 1881.
He developed the concept of an induction motor while walking in a park with a friend.
Later, while he was in Strasbourg, France in 1883, he built a prototype of the induction motor (an AC motor powered by electromagnetic induction) and tested it successfully. Since he couldn't get anyone in Europe interested in it, Tesla came to the United States to work for Thomas Edison in New York.
Tesla's childhood dream was to harness the power of Niagara Falls.
In 1895, he designed the first hydroelectric power plant in the Falls, a major victory for alternating current. A statue was later erected on Goat Island in Tesla's honor.
For all his brilliance, Tesla was pretty eccentric. At one point, he stopped eating solid foods.
He ate honey, drank bowls of warm milk, and made a potion from vegetables like artichokes and celery.
Source: " The Life and Times of Nikola Tesla - Biography of a Genius "
He claimed he never slept for more than two hours at a time.
However, Tesla did admit to dozing off sometimes to "recharge his batteries." According to one report, he once worked for 84 hours without sleeping.
Source: " Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla "
In 1882, Tesla discovered the rotating magnetic field, a principle of physics that forms the basis for nearly all devices that use AC power.
He used this principle to construct the AC induction motor and polyphase system for the generation, transmission, distribution and use of electric power.
While Tesla was working in Thomas Edison’s lab in New Jersey, the two fought a 'war' with over the best form of electrical current.
Edison favored direct current or DC (which flows in one direction), while Tesla favored alternating current or AC (which changes direction periodically). This led to the "war of the currents," which Tesla eventually won because of AC's greater efficiency.
Tesla also worked closely with industrialist and inventor George Westinghouse, and their partnership helped establish electricity across America.
Tesla wrote a classic paper called "A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers," in 1888, in which he introduced the concept of his motors and electrical systems. The work caught Westinghouse's attention, and they ended up partnering to work on bringing electricity to the rest of the country.
Tesla's AC-driven system remains the world standard for delivering electricity today.
He also invented the Tesla coil, a device that is widely used today in radios, TV sets, and other electronics.
In 1891, Tesla developed an induction coil that produced high-frequency alternating currents, now known as the Tesla coil. He used it in experiments to produce electric lighting, X-rays, and wireless power, and it became the basis of radio and TV. Today, the coils are mostly used in educational displays and entertainment.
Source: PBS.org
Tesla patented the basic system of radio in 1896.
The invention of radio is often credited to Guglielmo Marconi, who made the first transatlantic radio transmission in 1901. But Tesla developed patents for the basic elements of a radio transmitter that were later used by Marconi — a point that led the two into a court battle.
Source: Earlyradiohistory.us
Tesla also dreamed up two concepts that remained purely theoretical: the 'death ray' and an 'impenetrable wall of force' that'd ward off foreign invasions.
T he FBI kept a dossier on Tesla throughout his life in the US, but kept it classified until 2011, when the bureau publicly released 250 pages .
In 1943, when Tesla died, electrical engineer and military technology researcher John G. Trump — who an April 2016 New Yorker article dubbed President Trump's "nuclear" uncle — examined Tesla's effects for the FBI and reported his findings.
John Trump reportedly told the Bureau: "Tesla's 'thoughts and efforts during at least the past 15 years were primarily of a speculative, philosophical, and somewhat promotional character,' but 'did not include new, sound, workable principles or methods for realizing such results.'"
Source: Business Insider
Through his life, Tesla never married, but he once claimed to love a pigeon.
Tesla used to take walks to the park to feed the pigeons. He developed an unusual relationship with a white pigeon that used to visit him every day.
" I loved that pigeon as a man loves a women, and she loved me. As long as I had her, there was a purpose to my life," Tesla reportedly said.
Source: Tesla Society and Tesla Universe

- Main content

COMMENTS
Nikola Tesla (born July 9/10, 1856, Smiljan, Austrian Empire [now in Croatia]—died January 7, 1943, New York, New York, U.S.) was a Serbian American inventor and engineer who discovered and patented the rotating magnetic field, the basis of most alternating-current machinery. He also developed the three-phase system of electric power transmission. He immigrated to the United States in 1884 ...
Nikola Tesla (1856-1943) was one of the greatest and most enigmatic scientists who played a key role in the development of electromagnetism and other scientific discoveries of his time. Despite his breathtaking number of patents and discoveries, his achievements were often underplayed during his lifetime. Short Biography Nikola Tesla Nikola Tesla was born 10 July […]
Serbian American scientist Nikola Tesla invented the Tesla coil and alternating-current (AC) electricity, in addition to discovering the rotating magnetic field. By Biography.com Editors Updated ...
Nikola Tesla (/ ˈ n ɪ k ə l ə ˈ t ɛ s l ə /; [2] Serbian Cyrillic: Никола Тесла, [nǐkola têsla]; 10 July 1856 - 7 January 1943) was a Serbian-American [3] [4] engineer, futurist, and inventor.He is known for his contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system. [5]Born and raised in the Austrian Empire, Tesla first studied ...
Nikola Tesla was born on July 9 or 10, 1856, in Smiljan, Austria-Hungary (now Croatia). His parents were Serbian. Nikola was an excellent student who easily memorized books and solved math problems. He studied electricity in college. Career. In 1880 Tesla graduated from the University of Prague. In 1882 Tesla discovered a type of current, or ...
In the 1890s Tesla invented electric oscillators, meters, improved lights and the high-voltage transformer known as the Tesla coil. He also experimented with X-rays, gave short-range ...
Nikola Tesla (July 10, 1856-January 7, 1943) was a Serbian-American inventor, electrical engineer, and futurist. As the holder of nearly 300 patents, Tesla is best known for his role in developing the modern three-phase alternating current (AC) electric power supply system and for his invention of the Tesla coil, an early advancement in the field of radio transmission.
November 19, 2023. Nikola Tesla was one of the most forward-thinking inventors and engineers in history whose pioneering work with electricity literally lit up the modern world. Though underappreciated in his own time, Tesla created hundreds of groundbreaking innovations that fundamentally advanced technology and changed the course of history.
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856 in Smiljan in the Austo-Hungarian Empire (modern-day Croatia). His father, Milutin Tesla, was a Serbian Orthodox Priest and his mother, Djuka Mandic, was an ...
Nikola Tesla continued his research work on electricity generation and turbine design in his later life. Even at 81, he claimed to have completed a "dynamic theory of gravity" - something which was never published. He died in New York City of a heart thrombus on 7 January 1943. He was 86 years old. Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American ...