- ABBREVIATIONS
- BIOGRAPHIES
- CALCULATORS
- CONVERSIONS
- DEFINITIONS


Grammar Tips & Articles »
Conclusion to the parts of speech, this grammar.com article is about conclusion to the parts of speech — enjoy your reading.
We hope you have enjoyed and profited from Grammar.com’s discussion of the parts of speech in the English language. We’ve tried to cover what you need to know to expand your knowledge of the language. We firmly believe that improving your writing necessarily requires an understanding of the parts of speech. To move to the next level, we urge you to download our eBooks : 1. Understanding the Parts of Speech 2. Common Grammatical Mistakes 3. Developing a Powerful Writing Style 4. Rules on Punctuation And we hope you’ll be a frequent visitor to Grammar.com where you’ll find my blog, complete with comments from others who enjoy a study of the English language.
Email Print
Have a discussion about this article with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe. If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
You need to be logged in to favorite .
Create a new account.
Your name: * Required
Your email address: * Required
Pick a user name: * Required
Username: * Required
Password: * Required
Forgot your password? Retrieve it
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography:
Style: MLA Chicago APA
"Conclusion to the Parts of Speech." Grammar.com. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 27 Apr. 2024. < https://www.grammar.com/conclusion-to-the-parts-of-speech >.
The Web's Largest Resource for
Grammar & spelling, a member of the stands4 network, free, no signup required :, add to chrome.
Two clicks install »
Add to Firefox
Browse grammar.com.

Free Writing Tool :
Instant grammar checker.
Improve your grammar, vocabulary, and writing -- and it's FREE !
Try it now »
Are you a grammar master?
Choose the sentence with correct use of the gerund as the subject:.

Improve your writing now :
Download grammar ebooks.
It’s now more important than ever to develop a powerful writing style. After all, most communication takes place in reports, emails, and instant messages.
- Understanding the Parts of Speech
- Common Grammatical Mistakes
- Developing a Powerful Writing Style
- Rules on Punctuation
- The Top 25 Grammatical Mistakes
- The Awful Like Word
- Build Your Vocabulary
More eBooks »


Conclusions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of conclusions, offer strategies for writing effective ones, help you evaluate conclusions you’ve drafted, and suggest approaches to avoid.
About conclusions
Introductions and conclusions can be difficult to write, but they’re worth investing time in. They can have a significant influence on a reader’s experience of your paper.
Just as your introduction acts as a bridge that transports your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. Such a conclusion will help them see why all your analysis and information should matter to them after they put the paper down.
Your conclusion is your chance to have the last word on the subject. The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
Your conclusion can go beyond the confines of the assignment. The conclusion pushes beyond the boundaries of the prompt and allows you to consider broader issues, make new connections, and elaborate on the significance of your findings.
Your conclusion should make your readers glad they read your paper. Your conclusion gives your reader something to take away that will help them see things differently or appreciate your topic in personally relevant ways. It can suggest broader implications that will not only interest your reader, but also enrich your reader’s life in some way. It is your gift to the reader.
Strategies for writing an effective conclusion
One or more of the following strategies may help you write an effective conclusion:
- Play the “So What” Game. If you’re stuck and feel like your conclusion isn’t saying anything new or interesting, ask a friend to read it with you. Whenever you make a statement from your conclusion, ask the friend to say, “So what?” or “Why should anybody care?” Then ponder that question and answer it. Here’s how it might go: You: Basically, I’m just saying that education was important to Douglass. Friend: So what? You: Well, it was important because it was a key to him feeling like a free and equal citizen. Friend: Why should anybody care? You: That’s important because plantation owners tried to keep slaves from being educated so that they could maintain control. When Douglass obtained an education, he undermined that control personally. You can also use this strategy on your own, asking yourself “So What?” as you develop your ideas or your draft.
- Return to the theme or themes in the introduction. This strategy brings the reader full circle. For example, if you begin by describing a scenario, you can end with the same scenario as proof that your essay is helpful in creating a new understanding. You may also refer to the introductory paragraph by using key words or parallel concepts and images that you also used in the introduction.
- Synthesize, don’t summarize. Include a brief summary of the paper’s main points, but don’t simply repeat things that were in your paper. Instead, show your reader how the points you made and the support and examples you used fit together. Pull it all together.
- Include a provocative insight or quotation from the research or reading you did for your paper.
- Propose a course of action, a solution to an issue, or questions for further study. This can redirect your reader’s thought process and help them to apply your info and ideas to their own life or to see the broader implications.
- Point to broader implications. For example, if your paper examines the Greensboro sit-ins or another event in the Civil Rights Movement, you could point out its impact on the Civil Rights Movement as a whole. A paper about the style of writer Virginia Woolf could point to her influence on other writers or on later feminists.
Strategies to avoid
- Beginning with an unnecessary, overused phrase such as “in conclusion,” “in summary,” or “in closing.” Although these phrases can work in speeches, they come across as wooden and trite in writing.
- Stating the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion.
- Introducing a new idea or subtopic in your conclusion.
- Ending with a rephrased thesis statement without any substantive changes.
- Making sentimental, emotional appeals that are out of character with the rest of an analytical paper.
- Including evidence (quotations, statistics, etc.) that should be in the body of the paper.
Four kinds of ineffective conclusions
- The “That’s My Story and I’m Sticking to It” Conclusion. This conclusion just restates the thesis and is usually painfully short. It does not push the ideas forward. People write this kind of conclusion when they can’t think of anything else to say. Example: In conclusion, Frederick Douglass was, as we have seen, a pioneer in American education, proving that education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
- The “Sherlock Holmes” Conclusion. Sometimes writers will state the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion. You might be tempted to use this strategy if you don’t want to give everything away too early in your paper. You may think it would be more dramatic to keep the reader in the dark until the end and then “wow” them with your main idea, as in a Sherlock Holmes mystery. The reader, however, does not expect a mystery, but an analytical discussion of your topic in an academic style, with the main argument (thesis) stated up front. Example: (After a paper that lists numerous incidents from the book but never says what these incidents reveal about Douglass and his views on education): So, as the evidence above demonstrates, Douglass saw education as a way to undermine the slaveholders’ power and also an important step toward freedom.
- The “America the Beautiful”/”I Am Woman”/”We Shall Overcome” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion usually draws on emotion to make its appeal, but while this emotion and even sentimentality may be very heartfelt, it is usually out of character with the rest of an analytical paper. A more sophisticated commentary, rather than emotional praise, would be a more fitting tribute to the topic. Example: Because of the efforts of fine Americans like Frederick Douglass, countless others have seen the shining beacon of light that is education. His example was a torch that lit the way for others. Frederick Douglass was truly an American hero.
- The “Grab Bag” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion includes extra information that the writer found or thought of but couldn’t integrate into the main paper. You may find it hard to leave out details that you discovered after hours of research and thought, but adding random facts and bits of evidence at the end of an otherwise-well-organized essay can just create confusion. Example: In addition to being an educational pioneer, Frederick Douglass provides an interesting case study for masculinity in the American South. He also offers historians an interesting glimpse into slave resistance when he confronts Covey, the overseer. His relationships with female relatives reveal the importance of family in the slave community.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself. New York: Dover.
Hamilton College. n.d. “Conclusions.” Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://www.hamilton.edu//academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/conclusions .
Holewa, Randa. 2004. “Strategies for Writing a Conclusion.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated February 19, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/acadwrite/conclude.html.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Parts of Speech: The Ultimate Guide for Students and Teachers
This article is part of the ultimate guide to language for teachers and students. Click the buttons below to view these.
What are Parts of Speech ?
Just as a skilled bricklayer must get to grips with the trowel, brick hammer, tape measure, and spirit level, the student-writer must develop a thorough understanding of the tools of their trade too.
In English, words can be categorized according to their common syntactic function in a sentence, i.e. the job they perform.
We call these different categories Parts of Speech . Understanding the various parts of speech and how they work has several compelling benefits for our students.
Without first acquiring a firm grasp of the various parts of speech, students will struggle to fully comprehend how language works. This is essential not only for the development of their reading comprehension but their writing skills too.

Parts of speech are the core building blocks of grammar . To understand how a language works at a sentence and a whole-text level, we must first master parts of speech.
In English, we can identify eight of these individual parts of speech, and these will provide the focus for our Complete Guide to Parts of Speech .
THE EIGHT PARTS OF SPEECH (Click to jump to each section)
A complete unit on teaching figurative language.

FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE is like “SPECIAL EFFECTS FOR AUTHORS.” It is a powerful tool to create VIVID IMAGERY through words. This HUGE UNIT guides you through completely understanding FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE .
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (26 Reviews)

Often the first word a child speaks will be a noun, for example, Mum , Dad , cow , dog , etc.
Nouns are naming words, and, as most school kids can recite, they are the names of people, places, and things . But, what isn’t as widely understood by many of our students is that nouns can be further classified into more specific categories.
These categories are:
Common Nouns
Proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, countable nouns, uncountable nouns.
All nouns can be classified as either common or proper .
Common nouns are the general names of people, places, and things. They are groups or classes on their own, rather than specific types of people, places, or things such as we find in proper nouns.
Common nouns can be further classified as abstract or concrete – more on this shortly!
Some examples of common nouns include:
People: teacher, author, engineer, artist, singer.
Places: country, city, town, house, garden.
Things: language, trophy, magazine, movie, book.
Proper nouns are the specific names for people, places, and things. Unlike common nouns, which are always lowercase, proper nouns are capitalized. This makes them easy to identify in a text.
Where possible, using proper nouns in place of common nouns helps bring precision to a student’s writing.
Some examples of proper nouns include:
People: Mrs Casey, J.K. Rowling, Nikola Tesla, Pablo Picasso, Billie Eilish.
Places: Australia, San Francisco, Llandovery, The White House, Gardens of Versailles.
Things: Bulgarian, The World Cup, Rolling Stone, The Lion King, The Hunger Games.
Nouns Teaching Activity: Common vs Proper Nouns
- Provide students with books suitable for their current reading level.
- Instruct students to go through a page or two and identify all the nouns.
- Ask students to sort these nouns into two lists according to whether they are common nouns or proper nouns.
As mentioned, all common and proper nouns can be further classified as either concrete or abstract .
A concrete noun is any noun that can be experienced through one of the five senses. In other words, if you can see, smell, hear, taste, or touch it, then it’s a concrete noun.
Some examples of concrete nouns include:
Abstract nouns refer to those things that can’t be experienced or identified through the five senses.
They are not physical things we can perceive but intangible concepts and ideas, qualities and states.
Some examples of abstract nouns include:
Nouns Teaching Activity: Concrete Vs. Abstract Nouns
- Provide students with a book suitable for their current reading level.
- Instruct students to go through a page or two and identify all the nouns (the lists from Practice Activity #1 may be suitable).
- This time, ask students to sort these nouns into two lists according to whether they are concrete or abstract nouns.
A collective noun is the name of a group of people or things. That is, a collective noun always refers to more than one of something.
Some examples of collective nouns include:
People: a board of directors, a team of football players, a cast of actors, a band of musicians, a class of students.
Places: a range of mountains, a suite of rooms, a union of states, a chain of islands.
Things: a bale of hay, a constellation of stars, a bag of sweets, a school of fish, a flock of seagulls.
Countable nouns are nouns that refer to things that can be counted. They come in two flavors: singular and plural .
In their singular form, countable nouns are often preceded by the article, e.g. a , an , or the .
In their plural form, countable nouns are often preceded by a number. They can also be used in conjunction with quantifiers such as a few and many .
Some examples of countable nouns include:
COUNTABLE NOUNS EXAMPLES
Also known as mass nouns, uncountable nouns are, as their name suggests, impossible to count. Abstract ideas such as bravery and compassion are uncountable, as are things like liquid and bread .
These types of nouns are always treated in the singular and usually do not have a plural form.
They can stand alone or be used in conjunction with words and phrases such as any , some , a little , a lot of , and much .
Some examples of uncountable nouns include:
UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS EXAMPLES
Nouns teaching activity: how many can you list .
- Organize students into small groups to work collaboratively.
- Challenge students to list as many countable and uncountable nouns as they can in ten minutes.
- To make things more challenging, stipulate that there must be an uncountable noun and a countable noun to gain a point.
- The winning group is the one that scores the most points.

Without a verb, there is no sentence! Verbs are the words we use to represent both internal and external actions or states of being. Without a verb, nothing happens.

There are many different types of verbs. Here, we will look at five important verb forms organised according to the jobs they perform:
Dynamic Verbs
Stative verbs, transitive verbs, intransitive verbs, auxiliary verbs.
Each verb can be classified as being either an action or a stative verb.
Dynamic or action verbs describe the physical activity performed by the subject of a sentence. This type of verb is usually the first we learn as children.
For example, run , hit , throw , hide , eat , sleep , watch , write , etc. are all dynamic verbs, as is any action performed by the body.
Let’s see a few examples in sentences:
- I jogged around the track three times.
- She will dance as if her life depends on it.
- She took a candy from the bag, unwrapped it, and popped it into her mouth.
If a verb doesn’t describe a physical activity, then it is a stative verb.
Stative verbs refer to states of being, conditions, or mental processes. Generally, we can classify stative verbs into four types:
- Emotions/Thoughts
Some examples of stative verbs include:
Senses: hurt, see, smell, taste, hear, etc.
Emotions: love, doubt, desire, remember, believe, etc.
Being: be, have, require, involve, contain, etc.
Possession: want, include, own, have, belong, etc.
Here are some stative verbs at work in sentences:
- That is one thing we can agree on.
- I remember my first day at school like it was yesterday.
- The university requires students to score at least 80%.
- She has only three remaining.
Sometimes verbs can fit into more than one category, e.g., be , have , look , see , e.g.,
- She looks beautiful. (Stative)
- I look through the telescope. (Dynamic)
Each action or stative verb can also be further classified as transitive or intransitive .
A transitive verb takes a direct object after it. The object is the noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that has something done to it by the subject of the sentence.
We see this in the most straightforward English sentences, i.e., the Subject-Verb-Object or SVO sentence.
Here are two examples to illustrate. Note: the subject of each sentence is underlined, and the transitive verbs are in bold.
- The teacher answered the student’s questions.
- She studies languages at university.
- My friend loves cabbage.
Most sentences in English employ transitive verbs.
An intransitive verb does not take a direct object after it. It is important to note that only nouns, noun phrases, and pronouns can be classed as direct objects.
Here are some examples of intransitive verbs – notice how none of these sentences has direct objects after their verbs.
- Jane’s health improved .
- The car ran smoothly.
- The school opens at 9 o’clock.
Auxiliary verbs, also known as ‘helping’ verbs, work with other verbs to affect the meaning of a sentence. They do this by combining with a main verb to alter the sentence’s tense, mood, or voice.
Auxiliary verbs will frequently use not in the negative.
There are relatively few auxiliary verbs in English. Here is a list of the main ones:
- be (am, are, is, was, were, being)
- do (did, does, doing)
- have (had, has, having)
Here are some examples of auxiliary verbs (in bold) in action alongside a main verb (underlined).
She is working as hard as she can.
- You must not eat dinner until after five o’clock.
- The parents may come to the graduation ceremony.
The Subject-Auxiliary Inversion Test
To test whether or not a verb is an auxiliary verb, you can use the Subject-Auxiliary Inversion Test .
- Take the sentence, e.g:
- Now, invert the subject and the suspected auxiliary verb to see if it creates a question.
Is she working as hard as she can?
- Can it take ‘not’ in the negative form?
She is not working as hard as she can.
- If the answer to both of these questions is yes, you have an auxiliary verb. If not, you have a full verb.
Verbs Teaching Activity: Identify the Verbs
- Instruct students to go through an appropriate text length (e.g., paragraph, page, etc.) and compile a list of verbs.
- In groups, students should then discuss and categorize each verb according to whether they think they are dynamic or stative, transitive or intransitive, and/or auxiliary verbs.
The job of an adjective is to modify a noun or a pronoun. It does this by describing, quantifying, or identifying the noun or pronoun. Adjectives help to make writing more interesting and specific. Usually, the adjective is placed before the word it modifies.

As with other parts of speech, not all adjectives are the same. There are many different types of adjectives and, in this article, we will look at:
Descriptive Adjectives
- Degrees of Adjectives
Quantitative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives, possessive adjectives, interrogative adjectives, proper adjectives.
Descriptive adjectives are what most students think of first when asked what an adjective is. Descriptive adjectives tell us something about the quality of the noun or pronoun in question. For this reason, they are sometimes referred to as qualitative adjectives .
Some examples of this type of adjective include:
- hard-working
In sentences, they look like this:
- The pumpkin was enormous .
- It was an impressive feat of athleticism I ever saw.
- Undoubtedly, this was an exquisite vase.
- She faced some tough competition.
Degrees of Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives have three degrees to express varying degrees of intensity and to compare one thing to another. These degrees are referred to as positive , comparative , and superlative .
The positive degree is the regular form of the descriptive adjective when no comparison is being made, e.g., strong .
The comparative degree is used to compare two people, places, or things, e.g., stronger .
There are several ways to form the comparative, methods include:
- Adding more or less before the adjective
- Adding -er to the end of one syllable adjectives
- For two-syllable adjectives ending in y , change the y to an i and add -er to the end.
The superlative degree is typically used when comparing three or more things to denote the upper or lowermost limit of a quality, e.g., strongest .
There are several ways to form the superlative, including:
- Adding most or least before the adjective
- Adding -est to the end of one syllable adjectives
- For two-syllable adjectives ending in y , change the y to an i and add -est to the end.
There are also some irregular adjectives of degree that follow no discernible pattern that must be learned off by students, e.g., good – better – best .
Let’s take a look at these degrees of adjectives in their different forms.
Let’s take a quick look at some sample sentences:
- It was a beautiful example of kindness.
Comparative
- The red is nice, but the green is prettier .
Superlative
- This mango is the most delicious fruit I have ever tastiest.
Quantitive adjectives provide information about how many or how much of the noun or pronoun.
Some quantitive adjectives include:
- She only ate half of her sandwich.
- This is my first time here.
- I would like three slices, please.
- There isn’t a single good reason to go.
- There aren’t many places like it.
- It’s too much of a good thing.
- I gave her a whole box of them.
A demonstrative adjective identifies or emphasizes a noun’s place in time or space. The most common demonstrative adjectives are this , that , these , and those .
Here are some examples of demonstrative adjectives in use:
- This boat is mine.
- That car belongs to her.
- These shoes clash with my dress.
- Those people are from Canada.
Possessive adjectives show ownership, and they are sometimes confused with possessive pronouns.
The most common possessive adjectives are my , your , his , her , our , and their .
Students need to be careful not to confuse these with possessive pronouns such as mine , yours , his (same in both contexts), hers , ours , and theirs .
Here are some examples of possessive adjectives in sentences:
- My favorite food is sushi.
- I would like to read your book when you have finished it.
- I believe her car is the red one.
- This is their way of doing things.
- Our work here is done.
Interrogative adjectives ask questions, and, in common with many types of adjectives, they are always followed by a noun. Basically, these are the question words we use to start questions. Be careful however, interrogative adjectives modify nouns. If the word after the question word is a verb, then you have an interrogative adverb on hand.
Some examples of interrogative adjectives include what , which , and whose .
Let’s take a look at these in action:
- What drink would you like?
- Which car should we take?
- Whose shoes are these?
Please note: Whose can also fit into the possessive adjective category too.
We can think of proper adjectives as the adjective form of proper nouns – remember those? They were the specific names of people, places, and things and need to be capitalized.
Let’s take the proper noun for the place America . If we wanted to make an adjective out of this proper noun to describe something, say, a car we would get ‘ American car’.
Let’s take a look at another few examples:
- Joe enjoyed his cup of Ethiopian coffee.
- My favorite plays are Shakespearean tragedies.
- No doubt about it, Fender guitars are some of the best in the world.
- The Mona Lisa is a fine example of Renaissance art.
Though it may come as a surprise to some, articles are also adjectives as, like all adjectives, they modify nouns. Articles help us determine a noun’s specification.
For example, ‘a’ and ‘an’ are used in front of an unspecific noun, while ‘the’ is used when referring to a specific noun.
Let’s see some articles as adjectives in action!
- You will find an apple inside the cupboard.
- This is a car.
- The recipe is a family secret.
Adjectives Teaching Activity: Types of Adjective Tally
- Choose a suitable book and assign an appropriate number of pages or length of a chapter for students to work with.
- Students work their way through each page, tallying up the number of each type of adjective they can identify using a table like the one below:
- Note how degrees of adjective has been split into comparative and superlative. The positive forms will take care of in the descriptive category.
- You may wish to adapt this table to exclude the easier categories to identify, such as articles and demonstrative, for example.

Traditionally, adverbs are defined as those words that modify verbs, but they do so much more than that. They can be used not only to describe how verbs are performed but also to modify adjectives, other adverbs, clauses, prepositions, or entire sentences.
With such a broad range of tasks at the feet of the humble adverb, it would be impossible to cover every possibility in this article alone. However, there are five main types of adverbs our students should familiarize themselves with. These are:
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of time, adverbs of frequency, adverbs of place, adverbs of degree.
Adverbs of manner describe how or the way in which something happens or is done. This type of adverb is often the first type taught to students. Many of these end with -ly . Some common examples include happily , quickly , sadly , slowly , and fast .
Here are a few taster sentences employing adverbs of manner:
- She cooks Chinese food well .
- The children played happily together.
- The students worked diligently on their projects.
- Her mother taught her to cross the road carefully .
- The date went badly .
Adverbs of time indicate when something happens. Common adverbs of time include before , now , then , after , already , immediately , and soon .
Here are some sentences employing adverbs of time:
- I go to school early on Wednesdays.
- She would like to finish her studies eventually .
- Recently , Sarah moved to Bulgaria.
- I have already finished my homework.
- They have been missing training lately .
While adverbs of time deal with when something happens, adverbs of frequency are concerned with how often something happens. Common adverbs of frequency include always , frequently , sometimes , seldom , and never .
Here’s what they look like in sentences:
- Harry usually goes to bed around ten.
- Rachel rarely eats breakfast in the morning.
- Often , I’ll go home straight after school.
- I occasionally have ketchup on my pizza.
- She seldom goes out with her friends.
Adverbs of place, as the name suggests, describe where something happens or where it is. They can refer to position, distance, or direction. Some common adverbs of place include above , below , beside , inside , and anywhere .
Check out some examples in the sentences below:
- Underneath the bridge, there lived a troll.
- There were pizzerias everywhere in the city.
- We walked around the park in the pouring rain.
- If the door is open, then go inside .
- When I am older, I would like to live nearby .
Adverbs of degree express the degree to which or how much of something is done. They can also be used to describe levels of intensity. Some common adverbs of degree include barely , little , lots , completely , and entirely .
Here are some adverbs of degree at work in sentences:
- I hardly noticed her when she walked into the room.
- The little girl had almost finished her homework.
- The job was completely finished.
- I was so delighted to hear the good news.
- Jack was totally delighted to see Diane after all these years.
Adverb Teaching Activity: The Adverb Generator
- Give students a worksheet containing a table divided into five columns. Each column bears a heading of one of the different types of adverbs ( manner , time , frequency , place , degree ).
- Challenge each group to generate as many different examples of each adverb type and record these in the table.
- The winning group is the one with the most adverbs. As a bonus, or tiebreaker, task the students to make sentences with some of the adverbs.

Pronouns are used in place of a specific noun used earlier in a sentence. They are helpful when the writer wants to avoid repetitive use of a particular noun such as a name. For example, in the following sentences, the pronoun she is used to stand for the girl’s name Mary after it is used in the first sentence.
Mary loved traveling. She had been to France, Thailand, and Taiwan already, but her favorite place in the world was Australia. She had never seen an animal quite as curious-looking as the duck-billed platypus.
We also see her used in place of Mary’s in the above passage. There are many different pronouns and, in this article, we’ll take a look at:
Subject Pronouns
Object pronouns, possessive pronouns, reflexive pronouns, intensive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, interrogative pronouns.
Subject pronouns are the type of pronoun most of us think of when we hear the term pronoun . They operate as the subject of a verb in a sentence. They are also known as personal pronouns.
The subject pronouns are:
Here are a few examples of subject pronouns doing what they do best:
- Sarah and I went to the movies last Thursday night.
- That is my pet dog. It is an Irish Wolfhound.
- My friends are coming over tonight, they will be here at seven.
- We won’t all fit into the same car.
- You have done a fantastic job with your grammar homework!
Object pronouns operate as the object of a verb, or a preposition, in a sentence. They act in the same way as object nouns but are used when it is clear what the object is.
The object pronouns are:
Here are a few examples of object pronouns in sentences:
- I told you , this is a great opportunity for you .
- Give her some more time, please.
- I told her I did not want to do it .
- That is for us .
- Catherine is the girl whom I mentioned in my letter.
Possessive pronouns indicate ownership of a noun. For example, in the sentence:
These books are mine .
The word mine stands for my books . It’s important to note that while possessive pronouns look similar to possessive adjectives, their function in a sentence is different.
The possessive pronouns are:
Let’s take a look at how these are used in sentences:
- Yours is the yellow jacket.
- I hope this ticket is mine .
- The train that leaves at midnight is theirs .
- Ours is the first house on the right.
- She is the person whose opinion I value most.
- I believe that is his .
Reflexive pronouns are used in instances where the object and the subject are the same. For example, in the sentence, she did it herself , the words she and herself refer to the same person.
The reflexive pronoun forms are:
Here are a few more examples of reflexive pronouns at work:
- I told myself that numerous times.
- He got himself a new computer with his wages.
- We will go there ourselves .
- You must do it yourself .
- The only thing to fear is fear itself .
This type of pronoun can be used to indicate emphasis. For example, when we write, I spoke to the manager herself , the point is made that we talked to the person in charge and not someone lower down the hierarchy.
Similar to the reflexive pronouns above, we can easily differentiate between reflexive and intensive pronouns by asking if the pronoun is essential to the sentence’s meaning. If it isn’t, then it is used solely for emphasis, and therefore, it’s an intensive rather than a reflexive pronoun.
Often confused with demonstrative adjectives, demonstrative pronouns can stand alone in a sentence.
When this , that , these , and those are used as demonstrative adjectives they come before the noun they modify. When these same words are used as demonstrative pronouns, they replace a noun rather than modify it.
Here are some examples of demonstrative pronouns in sentences:
- This is delicious.
- That is the most beautiful thing I have ever seen.
- These are not mine.
- Those belong to the driver.
Interrogative pronouns are used to form questions. They are the typical question words that come at the start of questions, with a question mark coming at the end. The interrogative pronouns are:
Putting them into sentences looks like this:
- What is the name of your best friend?
- Which of these is your favourite?
- Who goes to the market with you?
- Whom do you think will win?
- Whose is that?
Pronoun Teaching Activity: Pronoun Review Table
- Provide students with a review table like the one below to revise the various pronoun forms.
- They can use this table to help them produce independent sentences.
- Once students have had a chance to familiarize themselves thoroughly with each of the different types of pronouns, provide the students with the headings and ask them to complete a table from memory.
Prepositions

Prepositions provide extra information showing the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another part of a sentence. These are usually short words that come directly before nouns or pronouns, e.g., in , at , on , etc.
There are, of course, many different types of prepositions, each relating to particular types of information. In this article, we will look at:
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of place, prepositions of movement, prepositions of manner, prepositions of measure.
- Preposition of Agency
- Preposition of Possession
- Preposition of Source
Phrasal Prepositions
It’s worth noting that several prepositional words make an appearance in several different categories of prepositions.
Prepositions of time indicate when something happens. Common prepositions of time include after , at , before , during , in , on .
Let’s see some of these at work:
- I have been here since Thursday.
- My daughter was born on the first of September.
- He went overseas during the war.
- Before you go, can you pay the bill, please?
- We will go out after work.
Sometimes students have difficulty knowing when to use in , on , or at . These little words are often confused. The table below provides helpful guidance to help students use the right preposition in the right context.
The prepositions of place, in , at , on , will be instantly recognisable as they also double as prepositions of time. Again, students can sometimes struggle a little to select the correct one for the situation they are describing. Some guidelines can be helpful.
- If something is contained or confined inside, we use in .
- If something is placed upon a surface, we use on .
- If something is located at a specific point, we use at .
A few example sentences will assist in illustrating these:
- He is in the house.
- I saw it in a magazine.
- In France, we saw many great works of art.
- Put it on the table.
- We sailed on the river.
- Hang that picture on the wall, please.
- We arrived at the airport just after 1 pm.
- I saw her at university.
- The boy stood at the window.
Usually used with verbs of motion, prepositions of movement indicate movement from one place to another. The most commonly used preposition of movement is to .
Some other prepositions of movement include:
Here’s how they look in some sample sentences:
- The ball rolled across the table towards me.
- We looked up into the sky.
- The children ran past the shop on their way home.
- Jackie ran down the road to greet her friend.
- She walked confidently through the curtains and out onto the stage.
Preposition of manner shows us how something is done or how it happens. The most common of these are by , in , like , on , with .
Let’s take a look at how they work in sentences:
- We went to school by bus.
- During the holidays, they traveled across the Rockies on foot.
- Janet went to the airport in a taxi.
- She played soccer like a professional.
- I greeted her with a smile.
Prepositions of measure are used to indicate quantities and specific units of measurement. The two most common of these are by and of .
Check out these sample sentences:
- I’m afraid we only sell that fabric by the meter.
- I will pay you by the hour.
- She only ate half of the ice cream. I ate the other half.
- A kilogram of apples is the same weight as a kilogram of feathers.
Prepositions of Agency
These prepositions indicate the causal relationship between a noun or pronoun and an action. They show the cause of something happening. The most commonly used prepositions of agency are by and with .
Here are some examples of their use in sentences:
- The Harry Potter series was written by J.K. Rowling.
- This bowl was made by a skilled craftsman.
- His heart was filled with love.
- The glass was filled with water.
Prepositions of Possession
Prepositions of possessions indicate who or what something belongs to. The most common of these are of , to , and with .
Let’s take a look:
- He is the husband of my cousin.
- He is a friend of the mayor.
- This once belonged to my grandmother.
- All these lands belong to the Ministry.
- The man with the hat is waiting outside.
- The boy with the big feet tripped and fell.
Prepositions of Source
Prepositions of source indicate where something comes from or its origins. The two most common prepositions of source are from and by . There is some crossover here with prepositions of agency.
Here are some examples:
- He comes from New Zealand.
- These oranges are from our own orchard.
- I was warmed by the heat of the fire.
- She was hugged by her husband.
- The yoghurt is of Bulgarian origin.
Phrasal prepositions are also known as compound prepositions. These are phrases of two or more words that function in the same way as prepositions. That is, they join nouns or pronouns to the rest of the sentence.
Some common phrasal prepositions are:
- According to
- For a change
- In addition to
- In spite of
- Rather than
- With the exception of
Students should be careful of overusing phrasal prepositions as some of them can seem clichéd. Frequently, it’s best to say things in as few words as is necessary.
Preposition Teaching Activity: Pr eposition Sort
- Print out a selection of the different types of prepositions on pieces of paper.
- Organize students into smaller working groups and provide each group with a set of prepositions.
- Using the headings above as categories, challenge students to sort the prepositions into the correct groups. Note that some prepositions will comfortably fit into more than one group.
- The winning group is the one to sort all prepositions correctly first.
- As an extension exercise, students can select a preposition from each category and write a sample sentence for it.
ConjunctionS

Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, and clauses. There are three main types of conjunction that are used to join different parts of sentences. These are:
- Coordinating
- Subordinating
- Correlative
Coordinating Conjunctions
These conjunctions are used to join sentence components that are equal such as two words, two phrases, or two clauses. In English, there are seven of these that can be memorized using the mnemonic FANBOYS:
Here are a few example sentences employing coordinating conjunctions:
- As a writer, he needed only a pen and paper.
- I would describe him as strong but lazy.
- Either we go now or not at all.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to introduce dependent clauses in sentences. Basically, dependent clauses are parts of sentences that cannot stand as complete sentences on their own.
Some of the most common subordinate conjunctions are:
Let’s take a look at some example sentences:
- I will complete it by Tuesday if I have time.
- Although she likes it, she won’t buy it.
- Jack will give it to you after he finds it.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are like shoes; they come in pairs. They work together to make sentences work. Some come correlative conjunctions are:
- either / or
- neither / nor
- Not only / but also
Let’s see how some of these work together:
- If I were you, I would get either the green one or the yellow one.
- John wants neither pity nor help.
- I don’t know whether you prefer horror or romantic movies.
Conjunction Teaching Activity: Conjunction Challenge
- Organize students into Talking Pairs .
- Partner A gives Partner B an example of a conjunction.
- Partner B must state which type of conjunction it is, e.g. coordinating, subordinating, or correlative.
- Partner B must then compose a sentence that uses the conjunction correctly and tell it to Partner A.
- Partners then swap roles.
InterjectionS

Interjections focus on feelings and are generally grammatically unrelated to the rest of the sentence or sentences around them. They convey thoughts and feelings and are common in our speech. They are often followed by exclamation marks in writing. Interjections include expressions such as:
- Eww! That is so gross!
- Oh , I don’t know. I’ve never used one before.
- That’s very… err …generous of you, I suppose.
- Wow! That is fantastic news!
- Uh-Oh! I don’t have any more left.
Interjection Teaching Activity: Create a scenario
- Once students clearly understand what interjections are, brainstorm as a class as many as possible.
- Write a master list of interjections on the whiteboard.
- Partner A suggests an interjection word or phrase to Partner B.
- Partner B must create a fictional scenario where this interjection would be used appropriately.
With a good grasp of the fundamentals of parts of speech, your students will now be equipped to do a deeper dive into the wild waters of English grammar.
To learn more about the twists and turns of English grammar, check out our comprehensive article on English grammar here.
DOWNLOAD THESE 9 FREE CLASSROOM PARTS OF SPEECH POSTERS

PARTS OF SPEECH TUTORIAL VIDEOS

MORE ARTICLES RELATED TO PARTS OF SPEECH

The 8 Parts of Speech in English Grammar

Table of Contents
Introduction.
In English grammar, The fundamental components of language that are essential for constructing meaningful and grammatically correct sentences are known as parts of speech. This article will delve into the eight parts of speech, providing definitions, examples, and insights into their distinct roles within sentences.
What are Parts of Speech?
Parts of Speech Defined
In grammar, parts of speech , also referred to as lexical categories, grammatical categories, or word classes, categorize words based on their linguistic functions. These parts play a crucial role in sentence construction by conveying specific meanings and relationships between words.
In English, there are eight parts of speech:
- Adjectives.
- Interjection.
- Conjunction.
Prepositions
Let’s explore these parts of speech in more detail!
A List of 8 Parts of Speech
Definition: Verbs express actions or states of being within a sentence.
- She goes to school every day.
- He writes a diary entry every night.
- The unicorn exists only in myths.
- They are happy together.
English has various types of verbs:
A. Action Verbs : Action verbs denote physical or mental actions and are the most common type of verbs. These verbs can be conjugated in simple and continuous tenses
- She runs in the park every morning. (Simple Present
- He thought deeply about life. (Simple past)
- Look at the students are copying the lesson. (Present Continuous)
B. Stative Verbs: Stative verbs express a state of being or conditions that are not changing or likely to change. In contrast to action verbs, these verbs can’t be conjugated into continuous tenses. It is incorrect to say “The book is belonging to Jane.”
- The necklace belongs to her.
- They love each other deeply.
- He prefers tea to coffee.
C. Linking Verbs: Linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, which describes or identifies the subject.
- She is a teacher.
- The plan seems perfect.
- They become friends quickly.
D. Helping (Auxiliary) Verbs: Helping verbs work in conjunction with the main verb to express nuances such as tense, mood, or voice.
- She has finished her homework.
- They will come to the party.
- He is working on a project.
E. Modal Verbs: Modal verbs express ability, possibility, necessity, or permission.
- She can swim very well.
- You must finish your assignment.
- He may join us later.
F. Transitive Verbs: Transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning.
- She eats an apple.
- They built a sandcastle.
- He reads a book every night.
G. Intransitive Verbs : Intransitive verbs do not require a direct object to convey a complete meaning.
- She runs every morning.
- They laughed loudly.
- He arrived early.
READ MOR ABOUT VERBS
Definition: Nouns represent people, animals, objects, substances, states, events, ideas, and feelings. They function as subjects or objects and can be modified by adjectives.
Here are the major noun characteristics:
- Nouns identify people, places, things, or ideas in a sentence.
- Nouns can serve as subjects, objects, or indirect objects.
- Nouns can be modified by adjectives or possessive pronouns.
- Nouns can be singular or plural.
There are different types of nouns:
- Common Nouns: Refer to general, non-specific entities (e.g., dog, city).
- Proper Nouns: Refer to specific, unique entities and are capitalized (e.g., John, Paris).
- Countable Nouns: Can be counted and have both singular and plural forms (e.g., book, books).
- Uncountable Nouns: Cannot be counted individually and lack a plural form (e.g., water, knowledge).
- Concrete Nouns: Refer to tangible, physical entities (e.g., table, tree).
- Abstract Nouns: Refer to intangible concepts or qualities (e.g., love, courage).
- Collective Nouns: Denote a group or collection of individuals (e.g., team, family).
- Compound Nouns: Comprise two or more words to express a single concept (e.g., toothpaste, basketball).
Example sentences with nouns:
- John is my neighbor.
- lion: The lion roared loudly.
- table: The table is made of oak.
- freedom: Freedom is a precious gift.
- love: Love conquers all.
READ MOR ABOUT NOUNS
Definition: Adjectives describe or specify nouns or pronouns. Examples of adjectives include good, beautiful, nice, my, etc.
- It’s a good day.
- She wears a beautiful dress.
- He has a nice car.
- This is my house.
READ MORE ABOUT ADJECTIVES
Definition: Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Adverbs often end in -ly as in nicely, beautifully, slowly, etc (formed by adding -ly to an adjective). But that’s not always the case.
There are various types of adverbs in English:
- Adverbs of Time: Indicate when an action occurs. ( Today, now, later, etc. )
- Adverbs of Place: Specify the location of an action. ( Here, there, everywhere, etc. )
- Adverbs of Manner: Describe how an action is performed. ( Quickly, softly, well, etc. )
- Adverbs of Frequency: Express how often an action occurs. ( Always, rarely, sometimes, etc. )
- Adverbs of Degree: Modify the intensity or degree of an adjective or adverb. ( Very, too, quite, etc. )
- Adverbs of Certainty: Indicate the level of certainty about an action. ( Surely, certainly, maybe, etc. )
- Adverbs of Purpose: Describe why an action is performed. ( In case, so that, in order to, etc.)
Example sentences with adverbs:
- She is completely unaware.
- I never expected this.
- The book is there on the shelf.
- She speaks slowly .
READ MORE ABOUT ADVERBS
Definition: Pronouns replace nouns or phrases.
Pronouns can be categorized based on their functions:
- Example: She, they, it
- Example: His, hers, theirs
- Example: Himself, herself, themselves
- Example: Who, which, that
- Example: This, these, those
Example sentences with pronouns:
- I love chocolate.
- This is for you.
- He is coming tomorrow.
- She likes ice cream.
- It is on the table.
READ MORE ABOUT PRONOUNS
Definition: Prepositions indicate the relationship between nouns and other words in a sentence. A preposition is positioned before a noun or pronoun, creating a phrase that modifies another word within the sentence.
Consequently, a preposition is an integral component of a prepositional phrase, typically functioning either as an adjective or an adverb.
Below is a compilation of the most frequently used prepositions:
- in, on, under
- with, without, beside
- for, during, after
- between, among, beyond
Example sentences with prepositions:
- The cat is in the basket.
- The plane is above the clouds.
- She went to the market.
- This gift is for you.
READ MORE ABOUT PREPOSITIONS
Conjunctions
Definition: Conjunctions connect clauses, sentences, or words.
There are three types of conjunctions in English:
Coordinating Conjunctions:
- Examples: and, but, or
- Sentence: She likes tea and coffee.
Correlative Conjunctions:
- Examples: not only…but also, either…or
- Sentence: He is not only smart but also diligent.
Subordinating Conjunctions:
- Examples: although, because, since
- Sentence: Although it’s raining, we will go out.
More example sentences:
- She is rich and successful.
- He is intelligent, but he is shy.
- Although it’s raining, we will go out.
- They won because they worked hard.
READ MORE ABOUT CONJUNCTIONS
Interjections
Definition: Interjections express surprise or emotion. Examples of interjections include oh, wow, alas, yippee, etc.
- oh!: Oh! That was unexpected.
- Good Lord: Good Lord, what a mess!
READ MORE ABOUT INTERJECTIONS
Analyzing Sentence Structure (Parts of Speech)
In the following examples, we will analyze the structure of sentences to identify the different parts of speech used.
Sample Sentences:
- My (adjective) friend (noun) speaks (verb) English (noun) fluently (adverb).
- Oh! (interjection) I (pronoun) went (verb) to (preposition) school (noun) and (conjunction) I (pronoun) met (verb) Fred (noun).
In conclusion, parts of speech serve as crucial categories that describe the distinct roles words play within a sentence. A comprehensive grasp of these categories empowers you to discern how words function, fostering a deeper understanding of language nuances.
1. How many parts of speech are used in English? In English, there are traditionally eight parts of speech.
2. Are there 9 parts of speech? No, there are traditionally eight parts of speech in English.
3. Are articles and determiners parts of speech? Yes, articles and determiners are considered parts of speech. They fall under the category of adjectives.
4. How do you identify parts of speech in a sentence? To identify parts of speech in a sentence, analyze the function of each word. Determine whether it expresses an action (verb), describes a noun (adjective), modifies a verb, adjective, or adverb (adverb), replaces a noun (pronoun), connects words or groups of words (conjunction), shows a relationship (preposition), or expresses strong emotion (interjection).
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don’t need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that brings your readers back to your thesis or main idea and reminds your readers where you began and how far you have traveled.
So, for example, in a paper about the relationship between ADHD and rejection sensitivity, Vanessa Roser begins by introducing readers to the fact that researchers have studied the relationship between the two conditions and then provides her explanation of that relationship. Here’s her thesis: “While socialization may indeed be an important factor in RS, I argue that individuals with ADHD may also possess a neurological predisposition to RS that is exacerbated by the differing executive and emotional regulation characteristic of ADHD.”
In her final paragraph, Roser reminds us of where she started by echoing her thesis: “This literature demonstrates that, as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Highlight the “so what”
At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what’s at stake—why they should care about the argument you’re making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put those stakes into a new or broader context.
In the conclusion to her paper about ADHD and RS, Roser echoes the stakes she established in her introduction—that research into connections between ADHD and RS has led to contradictory results, raising questions about the “behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
She writes, “as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Leave your readers with the “now what”
After the “what” and the “so what,” you should leave your reader with some final thoughts. If you have written a strong introduction, your readers will know why you have been arguing what you have been arguing—and why they should care. And if you’ve made a good case for your thesis, then your readers should be in a position to see things in a new way, understand new questions, or be ready for something that they weren’t ready for before they read your paper.
In her conclusion, Roser offers two “now what” statements. First, she explains that it is important to recognize that the flawed behavioral mediation hypothesis “seems to place a degree of fault on the individual. It implies that individuals with ADHD must have elicited such frequent or intense rejection by virtue of their inadequate social skills, erasing the possibility that they may simply possess a natural sensitivity to emotion.” She then highlights the broader implications for treatment of people with ADHD, noting that recognizing the actual connection between rejection sensitivity and ADHD “has profound implications for understanding how individuals with ADHD might best be treated in educational settings, by counselors, family, peers, or even society as a whole.”
To find your own “now what” for your essay’s conclusion, try asking yourself these questions:
- What can my readers now understand, see in a new light, or grapple with that they would not have understood in the same way before reading my paper? Are we a step closer to understanding a larger phenomenon or to understanding why what was at stake is so important?
- What questions can I now raise that would not have made sense at the beginning of my paper? Questions for further research? Other ways that this topic could be approached?
- Are there other applications for my research? Could my questions be asked about different data in a different context? Could I use my methods to answer a different question?
- What action should be taken in light of this argument? What action do I predict will be taken or could lead to a solution?
- What larger context might my argument be a part of?
What to avoid in your conclusion
- a complete restatement of all that you have said in your paper.
- a substantial counterargument that you do not have space to refute; you should introduce counterarguments before your conclusion.
- an apology for what you have not said. If you need to explain the scope of your paper, you should do this sooner—but don’t apologize for what you have not discussed in your paper.
- fake transitions like “in conclusion” that are followed by sentences that aren’t actually conclusions. (“In conclusion, I have now demonstrated that my thesis is correct.”)
- picture_as_pdf Conclusions

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Grammar: Main Parts of Speech
Definitions and examples.
The name of something, like a person, animal, place, thing, or concept. Nouns are typically used as subjects, objects, objects of prepositions, and modifiers of other nouns.
- I = subject
- the dissertation = object
- in Chapter 4 = object of a preposition
- research = modifier
This expresses what the person, animal, place, thing, or concept does. In English, verbs follow the noun.
- It takes a good deal of dedication to complete a doctoral degree.
- She studied hard for the test.
- Writing a dissertation is difficult. (The "be" verb is also sometimes referred to as a copula or a linking verb. It links the subject, in this case "writing a dissertation," to the complement or the predicate of the sentence, in this case, "hard.")
This describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives typically come before a noun or after a stative verb, like the verb "to be."
- Diligent describes the student and appears before the noun student .
- Difficult is placed after the to be verb and describes what it is like to balance time.
Remember that adjectives in English have no plural form. The same form of the adjective is used for both singular and plural nouns.
- A different idea
- Some different ideas
- INCORRECT: some differents ideas
This gives more information about the verb and about how the action was done. Adverbs tells how, where, when, why, etc. Depending on the context, the adverb can come before or after the verb or at the beginning or end of a sentence.
- Enthusiastically describes how he completed the course and answers the how question.
- Recently modifies the verb enroll and answers the when question.
- Then describes and modifies the entire sentence. See this link on transitions for more examples of conjunctive adverbs (adverbs that join one idea to another to improve the cohesion of the writing).
This word substitutes for a noun or a noun phrase (e.g. it, she, he, they, that, those,…).
- they = applicants
- He = Smith; that = ideas; those = those ideas
This word makes the reference of the noun more specific (e.g. his, her, my, their, the, a, an, this, these, … ).
- Jones published her book in 2015.
- The book was very popular.
Preposition
This comes before a noun or a noun phrase and links it to other parts of the sentence. These are usually single words (e.g., on, at, by ,… ) but can be up to four words (e.g., as far as, in addition to, as a result of, …).
- I chose to interview teachers in the district closest to me.
- The recorder was placed next to the interviewee.
- I stopped the recording in the middle of the interview due to a low battery.
Conjunction
A word that joins two clauses. These can be coordinating (an easy way to remember this is memorizing FANBOYS = for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) or subordinating (e.g., because, although, when, …).
- The results were not significant, so the alternative hypothesis was accepted.
- Although the results seem promising, more research must be conducted in this area.
Auxiliary Verbs
Helping verbs. They are used to build up complete verbs.
- Primary auxiliary verbs (be, have, do) show the progressive, passive, perfect, and negative verb tenses .
- Modal auxiliary verbs (can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would) show a variety of meanings. They represent ability, permission, necessity, and degree of certainty. These are always followed by the simple form of the verb.
- Semimodal auxiliary verbs (e.g., be going to, ought to, have to, had better, used to, be able to,…). These are always followed by the simple form of the verb.
- primary: have investigated = present perfect tense; has not been determined = passive, perfect, negative form
- The modal could shows ability, and the verb conduct stays in its simple form; the modal may shows degree of certainty, and the verb lead stays in its simple form.
- These semimodals are followed by the simple form of the verb.
Common Endings
Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs often have unique word endings, called suffixes . Looking at the suffix can help to distinguish the word from other parts of speech and help identify the function of the word in the sentence. It is important to use the correct word form in written sentences so that readers can clearly follow the intended meaning.
Here are some common endings for the basic parts of speech. If ever in doubt, consult the dictionary for the correct word form.
Common Noun Endings
Common verb endings, common adjective endings, common adverb endings, placement and position of adjectives and adverbs, order of adjectives.
If more than one adjective is used in a sentence, they tend to occur in a certain order. In English, two or three adjectives modifying a noun tend to be the limit. However, when writing in APA, not many adjectives should be used (since APA is objective, scientific writing). If adjectives are used, the framework below can be used as guidance in adjective placement.
- Determiner (e.g., this, that, these, those, my, mine, your, yours, him, his, hers they, their, some, our, several,…) or article (a, an, the)
- Opinion, quality, or observation adjective (e.g., lovely, useful, cute, difficult, comfortable)
- Physical description
- (a) size (big, little, tall, short)
- (b) shape (circular, irregular, triangular)
- (c) age (old, new, young, adolescent)
- (d) color (red, green, yellow)
- Origin (e.g., English, Mexican, Japanese)
- Material (e.g., cotton, metal, plastic)
- Qualifier (noun used as an adjective to modify the noun that follows; i.e., campus activities, rocking chair, business suit)
- Head noun that the adjectives are describing (e.g., activities, chair, suit)
For example:
- This (1) lovely (2) new (3) wooden (4) Italian (5) rocking (6) chair (7) is in my office.
- Your (1) beautiful (2) green (3) French (4) silk (5) business (6) suit (7) has a hole in it.
Commas With Multiple Adjectives
A comma is used between two adjectives only if the adjectives belong to the same category (for example, if there are two adjectives describing color or two adjectives describing material). To test this, ask these two questions:
- Does the sentence make sense if the adjectives are written in reverse order?
- Does the sentence make sense if the word “and” is written between them?
If the answer is yes to the above questions, the adjectives are separated with a comma. Also keep in mind a comma is never used before the noun that it modifies.
- This useful big round old green English leather rocking chair is comfortable . (Note that there are no commas here because there is only one adjective from each category.)
- A lovely large yellow, red, and green oil painting was hung on the wall. (Note the commas between yellow, red, and green since these are all in the same category of color.)
Position of Adverbs
Adverbs can appear in different positions in a sentence.
- At the beginning of a sentence: Generally , teachers work more than 40 hours a week.
- After the subject, before the verb: Teachers generally work more than 40 hours a week.
- At the end of a sentence: Teachers work more than 40 hours a week, generally .
- However, an adverb is not placed between a verb and a direct object. INCORRECT: Teachers work generally more than 40 hours a week.
More Detailed Rules for the Position of Adverbs
- Adverbs that modify the whole sentence can move to different positions, such as certainly, recently, fortunately, actually, and obviously.
- Recently , I started a new job.
- I recently started a new job.
- I started a new job recently .
- Many adverbs of frequency modify the entire sentence and not just the verb, such as frequently, usually, always, sometimes, often , and seldom . These adverbs appear in the middle of the sentence, after the subject.
- INCORRECT: Frequently she gets time to herself.
- INCORRECT: She gets time to herself frequently .
- She has frequently exercised during her lunch hour. (The adverb appears after the first auxiliary verb.)
- She is frequently hanging out with old friends. (The adverb appears after the to be verb.)
- Adverbial phrases work best at the end of a sentence.
- He greeted us in a very friendly way .
- I collected data for 2 months .
Main Parts of Speech Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Mastering the Mechanics: Nouns (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Introduction to Verbs (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Articles (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Introduction to Pronouns (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Modifiers (video transcript)
Writing Tools: Dictionary and Thesaurus Refresher Video
Note that this video was created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Writing Tools: Dictionary and Thesaurus Refresher (video transcript)
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Main Parts of Speech
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Grammar
- Next Page: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Discover top guides, trends, tips and expertise from AIO Writers
Exploring English: A Complete Guide to Parts of Speech
Julia McCoy

Remember the thrill of creating your first sentence? That magical moment when words danced and played together to express a thought, an idea, or even a story. At that time, you were unknowingly using what we call parts of speech .
Here’s a quick rundown of the eight parts of speech:
- Noun: Names a person, place, thing, or idea (cat, beach, happiness)
- Pronoun: Takes the place of a noun (he, she, it, they)
- Verb: Describes an action or state of being (run, think, is)
- Adjective: Describes or modifies a noun or pronoun (happy, blue, tall)
- Adverb: Describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb (quickly, often, here)
- Preposition: Shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence (on, under, beside)
- Conjunction: Connects words, phrases, and clauses (and, but, or)
- Interjection: Expresses strong emotion (wow, ouch, hooray)
These parts work together to create sentences that make sense.
In English grammar, open and closed word classes are two categories of words that differ in their ability to acquire new members.
Open word classes are constantly expanding, with new words being added regularly. These words typically refer to concepts or objects that are new or have recently become more prominent in society.
For example, “selfie,” “bitcoin,” and “podcast” are all relatively new words that have been added to the English language in recent years.
Closed word classes are relatively static and rarely acquire new members. These words typically provide grammatical structure and function to sentences, such as pronouns, prepositions, and conjunctions.
For example, the pronouns “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” and “they” have been part of the English language for centuries and are unlikely to be replaced with new words.
You’ve been putting these parts of speech into practice since grade school but have you ever wondered how they work behind the scenes? How do word classes and parts of speech make our sentences clear and expressive?
This guide to what is grammar is your backstage pass! It’s about getting up close with nouns and pronouns, making sense of verbs and adjectives, and uncovering the mysteries of adverbs and prepositions while joining conjunctions in harmony.
Let’s explore the different parts of speech in the English language.
Table Of Contents:
Parts of speech overview, prepositions, interjections, and conjunctions.
The English language is composed of eight essential parts. These parts of speech serve as the backbone for constructing meaningful sentences. They include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Nouns represent people or things. They can be either common or proper with options to use them in singular or plural forms.
Pronouns step up when we need substitutes for specific nouns such as possessive pronouns, reflexive pronouns, personal pronouns, and relative pronouns.
Verbs function as action words pulsating at the heart of every sentence while also serving to express states of being.
Adjectives describe attributes about objects or persons in detail while adverbs modify other parts including verbs themselves – adding layers upon layers for richer communication.
Prepositions and conjunctions act as the linguistic glue that binds words, phrases, or clauses together while interjections are used to express strong emotions.
Understanding these basic parts of speech is a crucial step toward becoming an effective communicator. Whether you are composing complex sentences for your latest novel or editing AI-generated content for your company website’s FAQ page, knowing how to use each part will elevate your writing skills significantly.

Source: Your Dictionary
Nouns , the bedrock of the English language, come in many forms and serve various purposes. Understanding their use and variations can significantly enhance your communication skills.
Primarily, nouns are used to name people, places, things, or ideas, they form the subject matter around which our sentences revolve.
For instance: Mary loves apples.
Here ‘Mary’ is a noun denoting a person while ‘apples’ denotes an object.
Proper nouns refer to specific individuals, locations, or organizations. These are always capitalized as they denote unique entities such as ‘John’, ‘New York City’, or ‘Microsoft’.
In contrast to proper nouns, common nouns do not require capitalization unless they begin a sentence. They signify general items like ‘dog’, ‘city’, or ‘company’.
Concrete nouns, another category within this part of speech, represent objects that can be perceived by our senses such as a ‘book’, ‘apple’, or ‘music’.
The opposite of concrete nouns is abstract nouns, which embody concepts or feelings that cannot be touched but experienced like ‘love’, ‘fear’, ‘justice’, and ‘freedom’.
Nouns can denote one item (cat) or more than one (cats), written in singular or plural forms.
Collective nouns describe a group of individuals or things as a single entity, like ‘team’, ‘flock’, or ‘family’.
A solid understanding of how different types of nouns function allows you to construct more meaningful sentences with clarity and precision – crucial for both business writing and creating engaging content for your content marketing strategy.
Pronouns are words used to replace nouns or noun phrases, making sentences less repetitive and more fluid.
For example, instead of saying “John went to John’s house,” we say “John went to his house.”
There are several types of pronouns including personal (I, you), demonstrative (this, those), indefinite (anyone, some), interrogative (who, which), relative (who, that) reflexive/intensive (myself, itself), and possessive (mine, yours).
Using correct pronouns is crucial not only for grammatical accuracy but also for respectful communication. With growing awareness about gender identities and preferences, using an individual’s preferred pronoun has become increasingly important.
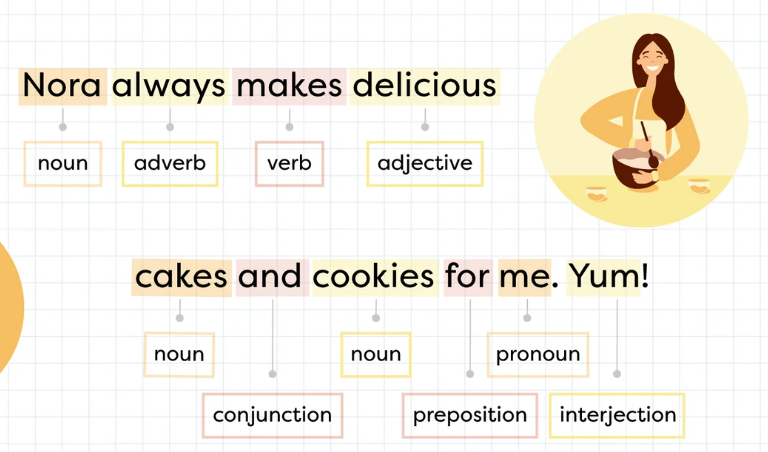
A verb primarily expresses action or state of being. It can tell you what someone or something does, experiences, or exists as.
“She runs every morning.”
“He seems happy.”
‘Runs’ is a verb because it tells us about an action performed, while ‘seems’ describes a state.
Verbs come in several types:
- Action verbs describe physical or mental actions (run, think, build)
- Linking verbs connect subjects to their attributes (seem)
- Auxiliary verbs assist main verbs to express tense or mood (have been running, will go, should study)
An important aspect related to verbs is tense. A verb’s form changes depending on when an event occurs – past (“ran”), present (“run”), and future (“will run”). This helps establish time frames within sentences.
An adjective plays a crucial role in sentences as it describes or modifies nouns and pronouns. It adds detail to your sentences, providing more information about an object’s size, shape, age, color, origin, or material.
For example:
- The brown dog chased its tail.
- I live in a tall , old building.
- Their food tastes incredibly sweet .
In these examples ‘brown’, ‘tall’, ‘old’, and ‘sweet’ are adjectives that give us more information about the noun they’re describing. They make our communication clearer and more interesting by adding depth to our descriptions.
Beyond simply describing things, adjectives have several types based on what they describe. Some common types include descriptive adjectives (e.g., blue), quantitative adjectives (e.g., five), and demonstrative adjectives (this/that).
An adverb describes verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs by providing additional information. They are versatile words capable of indicating manner (how), time (when), place (where), and degree (to what extent). This makes it an indispensable tool for adding detail and color to our language.

Prepositions are the words that link elements within a sentence to express how they relate to each other in terms of time, space, direction, or manner.
- Location or time : in, on, at, above, beneath, nearby
- Position : behind, in front of, between, among
- Direction : towards, past, through
- Manner : by, with
Remember that these categories aren’t rigid; some prepositions may fall under multiple categories based on the context.
If you’ve ever exclaimed “Wow!” in surprise or shouted “Ouch!” when you stubbed your toe, then you’ve used an interjection . This part of English speech is all about expressing strong feelings and emotions. They’re often used to show surprise, excitement, disgust, or other intense feelings.
Unlike other parts of speech such as nouns and verbs which have a grammatical relationship with other words in a sentence, interjections stand alone and often end with an exclamation point.
Conjunctions are essential components of language, binding words, phrases, and clauses together to form coherent and complex sentences. Their primary function is to link different parts of a sentence, contributing to the overall flow and structure of language.
There are three main types of conjunctions: coordinating, subordinating, and correlative.
Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal rank. The most common coordinating conjunctions are “and,” “but,” “or,” “nor,” “for,” “yet,” and “so.”
Each of these has a unique function:
- “And” adds information
- “But” introduces a contrast
- “Or” offers an alternative or choice
- “Nor” adds a negative alternative
- “For” introduces a reason
- “Yet” introduces a contrasting idea
- “So” indicates a cause and effect
Subordinating conjunctions link a dependent clause to an independent clause, helping to establish a relationship between the two. Subordinating conjunctions include words like “although,” “because,” “since,” “unless,” “while,” and “though.”
Correlative conjunctions work in pairs to join various sentence elements that should be considered equal. Examples include “either…or,” “neither…nor,” “not only…but also,” “whether…or,” and “both…and.” They add symmetry and balance to a sentence.
The English language is built around eight fundamental parts of speech, each playing a unique role in sentence structure and meaning. Mastering these elements can greatly enhance your communication skills, whether you’re writing an email or e-book.
Mastering the correct usage of these parts of speech can help you become a better writer. Even if you’re working with an AI assistant, it’s important to know how to navigate the nuances of language and ensure that your message resonates with clarity and impact.
With its vast knowledge and keen understanding of grammar, AI tools like Content at Scale can be a valuable companion for writers seeking precision and finesse in their craft. Through real-time suggestions and feedback from AI, writers can refine their prose — making the journey from an idea to a well-crafted sentence an enriching and error-free experience.
Written by Julia McCoy

UNLOCK YOUR POTENTIAL
Long headline that highlights value proposition of lead magnet.
Grab a front row seat to our video masterclasses, interviews, case studies, tutorials, and guides.
What keyword do you want to rank for?
Discover RankWell ® your SEO best friend
Our proprietary suite of SEO tools, aka RankWell®, offers marketers real-time, deep SEO insights. From keyword ranking difficulty scores to audits on improving your content, our full-service SEO tool suite is your content's best friend.
Get a free topic report that has every insight you need to outrank the competition.
By clicking Sign Up, you agree with our Terms and Conditions.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Parts of Speech Overview

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A noun is a word that denotes a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer the questions who and what.
In the sentence above, there are two nouns, dog and ball . A noun may be concrete (something you can touch, see, etc.), like the nouns in the example above, or a noun may be abstract, as in the sentences below.
The abstract concepts of integrity and love in the sentences above are both nouns. Nouns may also be proper.
Chicago , Thanksgiving , and November are all proper nouns, and they should be capitalized. (For more information on proper nouns and when to capitalize words, see our handout on Capital Letters .)
You may also visit our handout on Count and Noncount Nouns .
Learn how to spot verbs that act as nouns. Visit our handout on Verbals: Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives .
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun in a sentence.
In the sentence above, she is the pronoun. Like nouns, pronouns may be used either as subjects or as objects in a sentence.
In the example above, both she and him are pronouns; she is the subject of the sentence while him is the object. Every subject pronoun has a corresponding object form, as shown in the table below.
For more information on pronouns, go to our handout on Pronouns .
To find out what part of speech are that , which , and whom ? Visit our handout on Relative Pronouns .
Articles include a , an , and the . They precede a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence.
In example 1, the article a precedes the noun house , and a also precedes the noun phrase big porch , which consists of an adjective (big) and the noun it describes (porch). In example 2, the article the precedes the noun phrase blue sweater , in which sweater is the noun and blue, the adjective.
For more information, go to our handouts on Articles: A vs. An and How to Use Articles (a/an/the) .
An adjective is a word that modifies, or describes, a noun or pronoun. Adjectives may precede nouns, or they may appear after a form of the reflexive verb to be (am, are, is, was, etc.).
In example 1, two consecutive adjectives, red and brick , both describe the noun house. In example 2, the adjective tall appears after the reflexive verb is and describes the subject, she .
For more on adjectives, go to our handouts Adjective or Adverb and How to Use Adjectives and Adverbs .
A verb is a word that denotes action, or a state of being, in a sentence.
In example 1, rides is the verb; it describes what the subject, Beth, does. In example 2, was describes Paul’s state of being and is therefore the verb.
There may be multiple verbs in a sentence, or there may be a verb phrase consisting of a verb plus a helping verb.
In example 1, the subject she performs two actions in the sentence, turned and opened . In example 2, the verb phrase is was studying .
Some words in a sentence may look like verbs but act as something else, like a noun; these are called verbals. For more information on verbs that masquerade as other parts of speech, go to our handout on Verbals: Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives .
To learn more about conjugating verbs, visit our handouts on Verb Tenses , Irregular Verbs , and Two-Part (Phrasal) Verbs (Idioms) .
Just as adjectives modify nouns, adverbs modify, or further describe, verbs. Adverbs may also modify adjectives. (Many, though not all, adverbs end in - ly .)
In the first example, the adverb wildly modifies the verb waved . In the second example, the adverb extremely modifies the adjective bright , which describes the noun shirt . While nouns answer the questions who and what , adverbs answer the questions how , when , why , and where .
For a more detailed discussion of adverbs, visit our handout Adjective or Adverb and become an expert.
Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word that joins two independent clauses, or sentences, together.
In the examples above, both but and so are conjunctions. They join two complete sentences with the help of a comma. And, but, for, or, nor, so, and yet can all act as conjunctions.
Prepositions
Prepositions work in combination with a noun or pronoun to create phrases that modify verbs, nouns/pronouns, or adjectives. Prepositional phrases convey a spatial, temporal, or directional meaning.
There are two prepositional phrases in the example above: up the brick wall and of the house . The first prepositional phrase is an adverbial phrase, since it modifies the verb by describing where the ivy climbed. The second phrase further modifies the noun wall (the object of the first prepositional phrase) and describes which wall the ivy climbs.
For a more detailed discussion on this part of speech and its functions, click on Prepositions .
Below is a list of prepositions in the English language:
Aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, onto, out, over, past, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, unto, up, upon, with, within, without.
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement Archive
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback
Parts of Speech: A Guide to Learning English Grammar
By: Author English Study Online
Posted on Last updated: December 27, 2023
Sharing is caring!
In this page, we will break down each part of speech and provide examples to help you understand their usage. We will also discuss how to identify the different parts of speech in a sentence and provide tips on how to use them correctly. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced English learner, this article will provide valuable insights into the parts of speech and improve your language skills. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Overview of Parts of Speech
In this section, we will provide a brief overview of the eight parts of speech in English. Understanding the parts of speech is essential for anyone learning the English language, as it enables them to construct meaningful sentences and communicate effectively.
The eight parts of speech are:
Prepositions
Conjunctions, interjections.
Each part of speech has a specific function in a sentence. For example, nouns are used to name people, places, things, or ideas, while verbs are used to describe an action or state of being. Adjectives are used to describe nouns, while adverbs are used to describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Pronouns are used to replace nouns in a sentence, while prepositions are used to indicate the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, or clauses, while interjections are used to express emotions or feelings.

Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They are one of the most important parts of speech in English and are used in nearly every sentence. In this section, we will explore the different types of nouns and their functions.
Common Nouns
Common nouns are general names for people, places, or things. They are not capitalized unless they appear at the beginning of a sentence.
- Examples of common nouns include “book,” “city,” and “teacher.”
Proper Nouns
Proper nouns are specific names for people, places, or things. They are always capitalized.
- Examples of proper nouns include “Harry Potter,” “New York City,” and “Ms. Johnson.”
Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns are names for ideas, concepts, or emotions. They are intangible and cannot be seen, heard, or touched.
- Examples of abstract nouns include “love,” “happiness,” and “freedom.”
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns are names for groups of people or things. They can be singular or plural, depending on the context.
- Examples of collective nouns include “team,” “family,” and “herd.”
In this section, we will discuss the different types of pronouns used in English grammar. Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help to avoid repetition and make sentences more concise.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things. They can be used as the subject or object of a sentence. Here are the personal pronouns in English:
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are used to point to specific people or things. They can be used to indicate distance or location. Here are the demonstrative pronouns in English:
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. They are typically used at the beginning of a sentence. Here are the interrogative pronouns in English:
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people or things. They can be used as the subject or object of a sentence. Here are the indefinite pronouns in English:
Verbs are one of the most important parts of speech in English. They are used to describe an action, state, or occurrence. In this section, we will cover the three types of verbs: action verbs, linking verbs, and helping verbs.
Action Verbs
Action verbs are used to describe an action that is being performed by the subject of the sentence. They can be used in the present, past, or future tense. Here are a few examples of action verbs:
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs are used to connect the subject of the sentence to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes it. They do not show action. Here are a few examples of linking verbs:
Helping Verbs
Helping verbs are used in conjunction with the main verb to express tense, voice, or mood. They do not have a meaning on their own. Here are a few examples of helping verbs:
In conclusion, verbs are an essential part of English grammar. Understanding the different types of verbs and how they are used in a sentence can help you communicate more effectively in both written and spoken English.
In this section, we will discuss adjectives, which are an important part of speech in English. Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They provide more information about the noun or pronoun, such as its size, shape, color, or quality.
Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives are the most common type of adjectives. They describe the physical or observable characteristics of a noun or pronoun. For example, in the sentence “The red car is fast,” “red” is a descriptive adjective that describes the color of the car, and “fast” is another descriptive adjective that describes its speed.
Here are some examples of descriptive adjectives:
Quantitative Adjectives
Quantitative adjectives are used to describe the quantity or amount of a noun or pronoun. They answer the question “how much” or “how many.” For example, in the sentence “I have two apples,” “two” is a quantitative adjective that describes the number of apples.
Here are some examples of quantitative adjectives:

Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives are used to point out or indicate a specific noun or pronoun. They answer the question “which one” or “whose.” For example, in the sentence “This book is mine,” “this” is a demonstrative adjective that indicates the specific book that belongs to the speaker.
Here are some examples of demonstrative adjectives:
In conclusion, adjectives are an important part of speech in English. They provide more information about nouns and pronouns, and they help to make our language more descriptive and precise. By understanding the different types of adjectives, we can use them effectively in our speaking and writing.
In this section, we will discuss adverbs, which are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Adverbs give more information about the action, manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or intensity of a verb.
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed. They answer the question “how?” and usually end in “-ly”, but not always. Here are some examples:
- She sings beautifully.
- He speaks softly.
- They ran quickly.
- The dog barked loudly.
Adverbs of manner can also be formed by adding “-ly” to some adjectives. For example:
- She is a quick learner. (adjective: quick)
- He is a careful driver. (adjective: careful)
Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of place describe where an action takes place. They answer the question “where?” and usually come after the verb or object. Here are some examples:
- She looked everywhere.
- He lives nearby.
- They went outside.
- The cat hid underneath the bed.
Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time describe when an action takes place. They answer the question “when?” and can come at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence. Here are some examples:
- She wakes up early every day.
- He arrived yesterday.
- They will leave soon.
- The concert starts tonight.
Adverbs of time can also be used to show the duration of an action. For example:
- She studied for hours.
- He worked all day.
- They talked for a long time.
In this section, we will discuss prepositions and their usage in English. Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They usually indicate the position or direction of the noun or pronoun in relation to other elements in the sentence.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time are used to indicate when an action took place. They include words such as “at,” “in,” and “on.”
- “At” is used for specific times, such as “at 2 pm” or “at midnight.”
- “In” is used for longer periods of time, such as “in the morning” or “in October.”
- “On” is used for dates, such as “on Monday” or “on July 4th.”
Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place are used to indicate where something is located. They include words such as “in,” “on,” and “at.”
- “In” is used for enclosed spaces, such as “in the house” or “in the car.”
- “On” is used for surfaces, such as “on the table” or “on the floor.”
- “At” is used for specific locations, such as “at the park” or “at the beach.”
Prepositions of Direction
Prepositions of direction are used to indicate movement. They include words such as “to,” “from,” and “towards.”
- “To” is used to indicate movement towards a specific destination, such as “I am going to the store.”
- “From” is used to indicate movement away from a specific location, such as “I am coming from the park.”
- “Towards” is used to indicate movement in the direction of a specific location, such as “I am walking towards the museum.”
In this section, we will discuss the different types of conjunctions and their functions in English grammar. Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. They are essential in creating complex sentences and conveying relationships between ideas.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses that are of equal importance. They are easy to remember using the mnemonic device FANBOYS: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so. Here are some examples:
- I like pizza and pasta.
- She is neither tall nor short.
- He wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions connect dependent clauses to independent clauses and establish a relationship between them. They are used to show cause and effect, time, condition, and contrast. Some examples of subordinating conjunctions are:
Here are some examples:
- Because it was raining, we stayed inside.
- Although she was tired, she stayed up to finish her work.
- While I was studying, my roommate was watching TV.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of words that work together to connect words, phrases, or clauses. They are used to show a relationship between two elements. Here are some examples:
- both…and
- either…or
- neither…nor
- not only…but also
- Both my sister and I like to read.
- Either you come with us or you stay here.
- Not only was he late, but he also forgot his homework.
In conclusion, conjunctions are important in creating complex sentences and conveying relationships between ideas. By understanding the different types of conjunctions and their functions, you can improve your writing and communication skills.
In English grammar, interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or feelings. They are also known as exclamations and are one of the eight parts of speech in English. Interjections are grammatically independent from the words around them, and they can often be removed from a sentence or context without affecting its basic meaning.
Interjections can be used to express a wide range of emotions, including surprise, joy, anger, frustration, and pain. Some common examples of interjections include “ wow ,” “ ouch ,” “ yay ,” “ oh no ,” and “ oops .” They can be used to add emphasis to a sentence or to convey a particular tone or mood.
It is important to note that interjections do not have any grammatical function in a sentence. They are not nouns, verbs, adjectives, or any other part of speech. Instead, they simply stand alone as a way to express emotion.
When using interjections in writing, it is important to consider the context in which they are being used. While they can be a useful tool for adding emphasis or conveying emotion, they can also be overused or misused, which can detract from the overall effectiveness of the writing.
Articles/Determiners
In English grammar, articles and determiners are words that are used with nouns to provide more information about them. They help us to understand the context and meaning of a sentence.
There are three articles in the English language: “ the ,” “ a, ” and “ an. ” “The” is known as the definite article because it refers to a specific noun that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader. For example, “The cat is sleeping on the sofa.” In this sentence, “the” refers to a specific cat that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader.
“A” and “an” are known as indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a group or class of nouns. “A” is used before words that begin with a consonant sound, while “an” is used before words that begin with a vowel sound. For example, “I need a pen” and “She ate an apple.”
Determiners
Determiners are words that come before a noun to provide more information about it. They can include articles, as well as words like “ this ,” “ that ,” “ these ,” and “ those .”
In addition to these, there are other types of determiners such as possessive determiners (e.g. “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their”), demonstrative determiners (e.g. “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those”), and quantifying determiners (e.g. “some,” “any,” “many,” “few,” “several,” etc.).
Determiners can also be used with adjectives to provide more information about a noun. For example, “She ate the delicious apple” and “I saw that beautiful sunset.”
Understanding articles and determiners is crucial for mastering English grammar. By using them correctly, you can convey your thoughts and ideas more clearly and effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 8 parts of speech in English?
In English, there are eight parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each part of speech serves a different function in a sentence and helps to convey meaning.
What are some examples of different parts of speech?
Here are a few examples of different parts of speech:
- Noun: dog, cat, book, table
- Pronoun: he, she, it, they
- Verb: run, jump, sing, dance
- Adjective: happy, sad, tall, short
- Adverb: quickly, slowly, loudly, softly
- Preposition: in, on, at, under
- Conjunction: and, but, or, so
- Interjection: wow, oh, ouch, hooray
What is the difference between a noun and a verb?
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. A verb is a word that represents an action, occurrence, or state of being. In other words, a noun is a subject or object in a sentence, while a verb is the action or occurrence that takes place.
What are the different types of nouns?
There are several different types of nouns, including:
- Common nouns: refer to general, non-specific people, places, things, or ideas (e.g. dog, city, book)
- Proper nouns: refer to specific people, places, things, or ideas and are always capitalized (e.g. John, Paris, The Great Gatsby )
- Concrete nouns: refer to tangible, physical objects (e.g. table, chair, car)
- Abstract nouns: refer to intangible concepts or ideas (e.g. love, happiness, freedom)
- Recent Posts
- Juridical Process vs. Judicial Process: Understanding the Crucial Differences - December 14, 2023
- Compound Nouns: How to Use Them Effectively in English - November 9, 2023
- English Tenses: A Beginner’s Guide in English - November 6, 2023
EnglishForEveryone.org
Parts of speech worksheets terms of use, prepositions worksheets, below you will find our full list of printable prepositions worksheets to be used by teachers at home or in school. just click on a link to open a printable pdf version of the desired worksheet. we hope you find them useful..
- Identifying Prepositions Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying prepositions in sentences.
- Identifying Prepositions Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Identifying Prepositions worksheet.
- Prepositions of Time Worksheet
This worksheet includes a table outlining the various prepositions of time and their usages. Practice involves using prepositions of time to explain the schedules of color characters in the worksheet.
- Prepositions of Time Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Prepositions of Time Worksheet.
- Prepositions of Place Worksheet 1
The worksheet provides practice using images to explain the positions of people and objects in relation to one another.
- Prepositions of Place Worksheet Answers 1
Answers to the Prepositions of Place Worksheet 1
- Prepositions of Place Worksheet 2
The worksheet includes tables outlining the various prepositions of place (location). Practice involves using prepositions of place to explain the positions of color objects in relation to one another.
- Prepositions of Place Worksheet Answers 2
Answers to the Prepositions of Place Worksheet 2
Nouns worksheets.
- Identifying Nouns Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying nouns in sentences.
- Identifying Nouns Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Nouns Worksheet.
- Identifying Nouns Worksheet - Common vs. Proper
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying common vs. proper nouns in sentences.
- Identifying Nouns Worksheet - Common vs. Proper Answers
Answers to the Identifying Nouns worksheet.
Adjectives worksheets, this section contains printable worksheets on adjectives..
- Identifying Adjectives Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying adjectives in sentences.
- Identifying Adjectives Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Identifying Adjectives worksheet
- Order of Adjectives Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice putting adjectives in the correct order.
- Comparative Adjectives Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice using comparative adjectives in sentences.
- Comparative Adjectives Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Comparative Adjectives worksheet
- Superlative Adjectives Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice using superlative adjectives in sentences.
- Superlative Adjectives Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Superlative Adjectives Worksheet.
Verbs worksheets, this section contains printable worksheets on verbs..
- Identifying Verbs Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying verbs in sentences.
- Identifying Verbs Worksheet Answers
Adverbs Worksheets
This section contains printable worksheets on adverbs..
- Identifying Adverbs Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying adverbs in sentences.
Answers to the identifying adverbs worksheet..
- Frequency Adverbs Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying and using frequency adverbs in sentences. Practice involves rewriting sentences according to percentages labeled on a frequency adverbs chart. This is an excellent worksheet!
- Frequency Adverbs Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Frequency Adverbs worksheet.
Conjunctions worksheets, this section contains printable worksheets on conjunctions..
- Introduction to Conjunctions Worksheet
A brief introduction to conjunctions.
- Introduction to Conjunctions Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Introduction to Conjunctions worksheet.
- Coordinating Conjunctions Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice using coordinating conjunctions.
- Subordinating Conjunctions Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice using subordinating conjunctions.
- Correlative Conjunctions Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice using correlative conjunctions.
Pronouns worksheets, this section contains printable worksheets on pronouns..
- Introduction to Pronouns Worksheet
A brief introduction to pronouns.
- Introduction to Pronouns Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Introduction to Pronouns worksheet.
- Demonstrative Pronouns Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice using demonstrative pronouns.
- Subjective Pronouns Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice using subjective pronouns in sentences.
Interjections worksheets, this section contains printable worksheets on interjections..
- Identifying Interjections Worksheet
Explanation, examples, and practice identifying interjections in sentences.
- Identifying Interjections Worksheet Answers
Answers to the Identifying Interjections worksheet.
Home | About | Privacy Policy | Terms of Use | Contact Us
13 Structure and Format: Outlining the Speech
Rebecca Collier, M.B.A.
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should be able to
- Determine the general and specific purpose of a presentation.
- Create a captivating speech introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Support ideas and arguments through cited research.
- Differentiate between preparation outlines and presentation notes.
Imagine that you are about to enter a building for a job interview. You open the front door and walk straight into the bathroom. A little unsettled, you look around and see that, past the toilet and the shower, there is another door. You walk through that door, and you are now in some type of gymnasium. There is a woman in the room, running on a treadmill, and you approach her to ask for help. “Excuse me,” you say. “I’m here for a job interview. Do you know where I can find the Human Resources Department?” “Sure,” the woman replies. “Just climb through that window and head down the hallway.” She points to the window on the far wall, and you walk over to it. It seems crazy, but the window does overlook a hallway with an office at the end. There doesn’t appear to be any other exit from the room you are in. So, you open the window, lift yourself up, and carefully climb through to the hallway on the other side. At the end of the hallway is a door whose small sign you can now read: “Human Resources.” At last, you’ve made it to your interview, but now you have some grave concerns. What type of company would have their employees work in a building like this? How will you connect with the people and resources you need to do your job in such a crazy setup?

Just as a building has structure and an overall plan to guide people through the space in a logical way, you will need an outline for your speech to provide a framework for your ideas and to help your audience see how these ideas connect to create your overall message. Additionally, similar to the way people have expectations for what they will experience when walking into a building, your audience will have some expectations about how your speech will unfold. When these expectations are not met, such as in the example earlier, when you entered the door expecting to see a receptionist and were instead met with a toilet, your audience may find it jarring or uncomfortable if your speech does not have a recognizable introduction or conclusion, or if you abruptly jump from subtopic to subtopic without notice.
In this chapter, we’ll look at how to create an outline to guide your audience through your points in an organized format for a well-structured speech. In a professional setting, most speakers outline their speeches far enough in advance of their presentation date so that they have time to practice their performance and become comfortable with the material. Creating an outline will help you feel confident during your speech, because you took the time to carefully plan out what you desired to say. This leaves you free to focus on your delivery—how you say it—during your speech.
This chapter will first walk you through all the different parts of a speech outline, and it will then show you how a formal outline can be translated into less cumbersome speaking notes.
The Speech Topic
One of the hardest parts of the speech assignment for students is choosing a topic with which to work with. Oftentimes, as soon as you begin drafting an outline for a chosen topic, other topics will start to look more and more appealing, and you will want to change to a new topic. Resist this impulse, if you can! Many speech students have lost points on late assignments because they kept changing their mind about what to speak about. Once you begin working with a topic (approved by your instructor, when applicable), commit to it. Your instructor can help you navigate through the challenges of a topic with which that you are struggling with. Remember, your research and your speech delivery can make almost any topic engaging for the audience.
The Speech Purpose
Before you begin preparing your speech, your instructor will let you know what kind of speech you are working on. Is it a speech intended to inform your audience? Is it a speech where you will be persuading the audience? Or, is the speech designed for entertainment purposes? You will need to know what kind of speech you are giving before you do any other work on this assignment. To make sure that you are aware of the overall goal of the speech, your instructor may ask you to include the general purpose on your outline. There are three basic general purposes that apply to speech presentations: to inform, persuade, or entertain. An informative speech requires you to give a neutral, unbiased perspective to the audience, while a persuasive speech attempts to change an audience’s beliefs, feelings, or actions. An entertainment speech is used to celebrate or commemorate something or as part of a ceremony.
In addition to the general purpose, each speech will also have a corresponding specific purpose. The specific purpose identifies what you would like to leave the audience with after your speech. For example, the specific purpose for an i nformative speech about the pyramids of Giza, Egypt might read: To inform my audience about when and how the pyramids of Giza were built and what they look like today . A specific purpose for a persuasive speech about organ donation might read: To persuade my audience to register as organ donors.
Some professors might prefer that you submit a purpose statement in lieu of a specific purpose. The purpose statement identifies your goal for the audience. Using the example informative speech topic above on the pyramids of Giza, Egypt, your purpose statement might read: At the end of my speech, my audience will know when and how the pyramids of Giza were built and what they look like today. The organ donation speech might have the following purpose statement: At the end of my speech, my audience members will register as organ donors .
The Central Idea
Once you know your topic and your purpose, it’s time to brainstorm the key message of your speech. This message is known as the central idea, and it serves as a thesis for your presentation. Your instructor may ask you to include a central idea on your outline. Creating a central idea is good practice, because it shows that you can state the main ideas of the speech in one sentence. A central idea elaborates on the speech purpose.
For a persuasive speech, the central idea includes what we’re persuading the audience about, and why our viewpoint is correct. For example: Everyone should register as an organ donor because it’s easy to do, and it could save or drastically improve someone’s life at no cost to the donor.
For an informative speech, the central idea is a summary thesis, and it gives the main ideas of the speech in one strong statement. For example: The pyramids of Giza, Egypt, were built by hand over six thousand years ago, and their outer structures and inner chambers are mostly intact today.
A strong central idea should have the following three characteristics:
- It should be a complete sentence.
- It should make a statement, not ask a question.
- It should encapsulate each main idea.
The Speech Introduction
Although your instructor may ask you to include the topic, general purpose, specific purpose, and central idea on your speech outline, you actually won’t share these with your audience as part of your speech. Instead, your presentation to the class should begin with your introduction. The introduction and the conclusion are the most important parts of your speech, because they are the parts that your audience is most likely to remember. Thus, the structure and development of these two parts is crucial to the success of your speech. Your speech introduction should do the following five things:
- Begin with an attention-getter.
- Introduce yourself and your topic.
- Include a statement of credibility/interest.
- Relate the topic to your audience.
- Preview your main ideas.
The Attention-Getter
The first—and most important—thing you can do in a speech introduction is to captivate your audience and interest them in your speech topic. It is much easier to keep someone’s attention than to fight to regain it, so the attention-getter is the first part of your speech that your audience will hear.
There are lots of ways you can help your topic appeal to your listeners. One classic example is to tell a short story. This can either be a personal story, or you can recount a story you heard or read somewhere that leads into your topic. A story can help personalize your topic for the audience and bring in a human connection.
Another way to draw attention to your topic is to startle your audience with a shocking statistic or example that they won’t be expecting. Be careful with this technique. If the audience is already familiar with your “shocking” material, your attention-getter could backfire, and you may end up losing the attention of your audience instead of gaining it.
Many students like to begin their speeches by asking a series of rhetorical questions. This requires the audience to think about the speech topic and make personal applications. If you start your speech in this way, make sure that you ask a few questions. One is rarely enough to generate interest in the topic. Also, the questions should make the audience ponder something. Suppose I began my speech with, “How many of you like lemons? Well, today I’m going to inform you about Miracle Berries.” Did that get your attention? Not likely. Are you excited to hear more about my topic? It’s doubtful. Let’s try that again. “By show of hands, who here likes drinking lemonade? Okay, now who likes having a slice or two of lemons in their drinking water? Now, how many of you would enjoy snacking on slices of lemon—no sugar added? Well, what if I told you there was a way to make lemons taste intensely sweet, without adding any sugar? Today, I’m going to tell you about Miracle Berries. . . .” When using questions as an attention-getter, you might consider incorporating a silent survey. This is where you have your audience answer your questions in a physical way, such as by raising a hand. If students answer your questions vocally, the attention-getter will likely go on for far too long. A silent survey keeps the entire audience involved, without letting the audience take over your speech.
Additionally, you could begin with a powerful quote that ties into your topic. Make sure that you tell the audience where the quote comes from. If the source of the quote is someone that your audience is not likely to be familiar with, you may need to contextualize the source and explain why the words of this person are relevant. For example, if I began my speech, “‘Taxes are the price we pay for civilized society,’ as Oliver Wendell Holmes Junior said . . . ,” your audience might wonder, Who is this person? Nobody knows, so nobody cares. I should contextualize this source, by saying something like, “According to U.S. Supreme Court Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes Junior . . .” Now my audience will understand why the person who spoke these words is relevant.
You might also try to get the audience’s attention by making them curious about your topic. Give them some clues, and see if they can guess what your topic will be from these clues. Be sure to take a moment and celebrate with them when they finally guess correctly!
Finally, you can begin your speech with some audience participation. Just make sure this is carefully planned and not too complicated. You don’t want the attention-getter to take up all the allotted time for your speech. One student began her informative presentation by having everyone write down five numbers, between zero and nine, in any order, with no repeats. She then held a mini lottery for the class by randomly drawing numbers from a hat and giving a small prize to the student whose written-down numbers were the closest to the drawn ones. This was an exciting way to begin a speech on the New York Lottery.
The attention-getter of the speech is arguably the most important part of the presentation. If you don’t capture the audience’s attention, they are less likely to take in the rest of your speech. Thus, it is worthwhile to spend some time developing an engaging attention-getter that you are comfortable delivering.
Introducing Yourself and Your Topic
Now that your audience is focused and interested in what you have to say, you should share with them who you are, and what you will be speaking to them about. This is especially important if you have used a detailed or complex attention-getter, where it may be necessary to clarify your actual topic for the audience.
Statement of Credibility/Interest
Once you have piqued the interest of your audience, and they know who you are and what you’ll be speaking about, it’s time to gain their trust. What makes you a credible speaker on this topic? Share with the audience why you chose this particular subject, and any personal experience you have with it. For example, if I were giving an informative speech on lacrosse, I might say, “I was first exposed to lacrosse in middle school, and I went on to play the sport for all four years of high school. Our team was very successful, and we won several championships.”
However, you might give a speech on a topic with which you have had no direct experience. Never fear! You can also tell the audience about the kinds of research you have done to prepare yourself to speak on this subject. For example: “Although I’ve never actually played lacrosse, I’ve always been curious about it. I began preparing for this speech by watching videos online to understand how the sport is played, and I found some great articles to help me understand its history and development.”
Sharing your interest in this topic, along with your experience with it, or an explanation of your research process will show the audience that you are a credible speaker on this topic and someone worth listening to.
Relating the Topic to Your Audience
The next step is to help the audience see how they can relate to the topic you have chosen. Be creative! This can be a challenging step, and it requires some critical thinking. Suppose you are giving a speech where you are persuading your audience that college students shouldn’t have to buy textbooks for their classes. Well, this is an easy one, because almost everyone in your audience will be a college student, and most people like to save money. Now, imagine that you are giving a speech to inform your audience about conjoined twins. It is unlikely that you will have many pairs of conjoined twins in your audience, so how can you make this topic relatable? You might start with the idea that many audience members may want to have children (or more children) someday, or they may know people who plan to have children. It’s important to be informed about a condition that could affect these future children. Also, you could take the angle that we live in a complex world, and we have to deal with lots of different kinds of people. Understanding more about the conditions of people different from ourselves can help us develop empathy. Almost any topic can relate to your audience, but some will take more work than others.
Previewing your Main Ideas
For the final part of the speech introduction, you’ll give your audience a summary of what you’ll specifically be talking about in this speech. This is different from introducing yourself and your topic. There, you might tell the audience that you’ll be informing them about the axolotl. In the preview, you’ll let them know that this speech will describe the physical appearance of the axolotl, where it lives, and how it regenerates different parts of its body. The preview is given at the end of the introduction to help the audience pace the speech. For the example above, when you come to the part about the axolotl regenerating, the audience will know that the speech is almost done. It also helps your audience to know what they should be focusing on during your speech, and what the takeaway will be.
The speech introduction is the foundation of your presentation, and it’s important to ensure that this foundation is sturdy. If the foundation of a building is unstable, the building may crumble and fall apart. Similarly, the speech introduction prepares the audience for the body of the speech. If the introduction is underdeveloped, the rest of the speech will be weakened by association. It is worth taking some extra time to make sure your speech introduction covers each of the five steps.
The Body of the Speech
The body of the speech is where you elaborate on your main ideas, providing information to support the ideas and using transitions to show the relationships between ideas. The body of your speech might begin with a transition from the introduction.
Transitioning from Point to Point
Suppose you were driving a car down the highway, and the driver in front of you kept switching lanes abruptly without using a turn signal. Wouldn’t that be frustrating? Well, when a speaker doesn’t use transitions, it creates a similarly jarring experience for the audience. Using a transition phrase prepares the audience for a new topic and helps your speech flow logically from point to point.
Transitions in a speech are a little bit different from transitions used in written work. When you are writing an essay, you can use a word such as “also” or “however” to move on to your next point. In a speech, you need to be more specific. The audience needs a clear signal that you are about to begin a new point. In order to transition to your first main point, you might say, “Let’s begin by,” “I’d like to start with,” “First of all, ” “To commence,” etc. For additional main ideas, you could transition with, “Moving on,” “My next point will be,” “Now that we’ve looked at _____, I’ll tell you about _____,” etc. Transitions are especially helpful in separating out your main ideas for your audience so that the body of the speech has distinct sections.
The Main Ideas
The main ideas are the major subtopics of your speech, each serving as a topic sentence in your speech. As a general rule, you should have at least two main ideas. If you only have one main idea, your speech has nowhere to go, and it may feel repetitive for the audience. That being said, you generally shouldn’t have more than five main ideas in your speech. Once you get past the fifth main idea, the audience may have trouble remembering the first one! It’s often a good idea to plan on having three main ideas for your speech. Think about how often the number three comes up in life: three strikes in baseball; three wishes; first, second, and third place, etc. In writing, this is known as the “Rule of Three.” How many bears does Goldilocks encounter? How many musketeers are there? People are used to hearing things come up in sets of three, and so having three main points may make it easier for your audience to remember them. In the end, though, you will need to decide on the appropriate number of points you need to develop your speech topic for your audience.
The Supporting Material
After you have your main ideas planned out, it’s time to start researching material to support these points. For each point, you’ll need some things to talk about. Depending on how you have chosen to organize your speech, you may need to look up some facts to share. This includes definitions, descriptions, and explanations. If you have too many facts, your speech may come across as dry and lacking in depth. Facts are generally used to lay the foundation for your main idea, and you will use other supporting materials to illustrate your point or defend your argument.
As you continue to research your topic, you should look for examples to share. Examples help your audience to understand and relate to your main idea. If I were giving an informative speech on the solar eclipses, I might share a brief example with my audience: “On Monday, August 17th, 2017, a rare, full solar eclipse crossed the North American continent.” A brief example takes an abstract idea from your speech and quickly translates it into a real-life situation. This can help make your topic clearer for your audience.
In that same speech on solar eclipses, you could also use an extended example. In this situation, you would fill in all the details to create a story for your audience. “It was a day to be remembered. Hotels across North America had been booked over a year in advance, and millions of people traveled to find a spot in the path of totality—the area, about 70 miles wide, that would experience a total eclipse of the sun. As the time of the eclipse drew near, the air felt noticeably colder, and there were strange shadows on the ground. Then, for a little over a minute in most cities, the sky was plunged into darkness and the beautiful, white corona of the sun could be seen, along with a few stars. People gasped and screamed with delight. It was over all too soon, but those who witnessed this event would never forget it.” Extended examples add a personal touch to your speech and can help ensure that you have enough content to reach the timing parameters of your assignment.
Additionally, you may decide to use a hypothetical example, beginning with phrases like, “What if you…,” “Suppose you…,” or “Imagine that you….” When used in a speech, a hypothetical example puts the audience into your speech. These types of examples work well as attention-getters in the introduction, and you can use them throughout your speech to grab the attention of your audience and refocus them on your topic. As the audience members think about how they would respond to the imagined scenario, they are directly engaging with your speech concepts.
If you are looking to build credibility with your audience on your main idea, you should include testimonies as part of your supporting material. In the court of law, a person who has experience with the subject of the trial is called upon to give their opinion or relate their direct experience. This is similar to how testimonies are used in a speech, where you will include quotations from people who are experienced with your topic. These quotations fall into two categories: expert and peer. An expert testimony comes from someone who has professional experience with the topic, or some other publicly recognized form of expertise. A peer testimony is someone who has personal experience with your topic, but this experience is not from a professional or academic standpoint. Now, which is better for your speech, expert or peer testimonies? It depends. People tend to trust expert testimony about scientific and medical points; however, people relate to a peer testimony more when the speech point has to do with everyday life. Sometimes expert testimony can feel out of touch with how the average person lives.
Another way to come across as a credible speaker on your topic is to include statistics in your speech. Any numerical data in your speech, except, perhaps, a date or time, would be considered a statistic. When people hear numbers, they are more likely to believe that what you are telling them is backed up by research. However, you need to make sure you are using statistics appropriately. Here are some guidelines to follow when using this type of supporting material.
- Cite: If you use a statistic in your speech, you need to tell us where that number came from. Otherwise, we’ll think you made it up!
- Be sparing: Don’t use too many statistics in your speech! Remember, statistics are like spices. If you use the right ones, they will bring out the flavors of your meal, but if you use too many, they will overwhelm your meal.
- Round: It can be difficult to process complex numbers unless we see them written out. While it’s fine to read that “New York City covers 300.36 miles,” in a speech, it’s better to say that “New York City has just over 300 miles.” It’s okay to be a little less accurate, if it helps you to be understood. Words like “approximately,” “close to,” “almost,” and “nearly” will come in handy here.
- Explain: Help your audience to understand the numbers you are using. For example: “How much is a billion dollars? You could spend $100,000 a day for 25 years before you’d run out of cash.” During your speech, help us grasp complicated numbers in terms we can relate to.
No matter what materials you decide to use in your speech to support your main ideas, you’ll want to include citations in your outline to show where you found this information. Unlike writing, which has several formal citation styles, there is no specific way to cite your sources in your speech body. Your professor may require you to use a particular writing citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, Associated Press). If not, note that speech citations should include at least the source where you found the information and the date the information was published. You may also include the author of the information, but you may need to contextualize this for us. For example, if I said during my speech, “According to Bob Smith…,” who is Bob Smith? No one knows, and no one cares. However, if I said, “According to the financial journalist Bob Smith, in an article published by The New York Times last month…,” people may care more about Bob’s point of view. The date is important here because the recency of your information can affect its relevance. Unlike a citation in a paper, you don’t need to cite your source every time you use information from it. This would become tedious for the audience to listen to. Instead, you should add your citation at the beginning or end of the portion of your speech in which you are sharing information from that source. For example: “All of the statistics I’ve shared today come from the Red Cross website, updated in 2019.” Or, “The examples you’ll be hearing in my speech all come from the Mermaid documentary published on Animal Planet in 2011.” These oral citations give your audience enough information about your sources to be able to find a complete reference on your outline, if they need to verify something.
The Speech Conclusion
Once you have finished taking your audience on a journey through the main ideas of your speech, it’s time to draw things to a close. However, you need to give your audience a hint that the end is coming. We call this a signal . If you forget to signal the end of your speech, you may finish speaking and find that your audience does not break into applause. They didn’t realize you were on your way to the finish line. Giving your audience a signal alerts them that your speech will be over soon and helps them emotionally prepare for the end of your speech. The signal can be given a specific phrase, such as, “I’d like to end by…” or “to wrap things up….” Pay attention, and you may notice that your college professors will often use a verbal signal near the end of the class session, such as, “and last of all…” or “before we go….” Try using a signal phrase in your next presentation, and see if you can spot your audience visibly perking up when they hear it. More advanced signals can also signal the end of the speech by changing the rate, pitch, or volume of their remarks. However, if you are using this technique, be sure to practice in front of someone before your actual presentation in class. You may think that you’re effecting a great change in the way you are speaking, but those changes might need to be exaggerated to be noticeable by your audience. The only way you’ll know for sure is to get some live feedback.
The signal of the conclusion leads into a brief summary of your main ideas. Simply restate an overview of the main ideas you just covered to help your audience retain the message of your speech. You may notice that your professors will also do this near the end of a class session. “Today we have covered…” is a common way for this to begin.
You’ll want to cap off your conclusion with a strong statement . It’s a good idea to actually plan out, word for word, what you would like to say for the last line of your speech. The audience is most likely to remember the first thing you said, and the last thing you said, so these words are the most important part of your speech. As much as you are able, commit them to memory. This will help you to make eye contact with your audience as you speak to help the words land with maximum effect. A strong statement can be a quote, or it can refer back to something you said in your introduction. In a persuasive speech, this statement will usually contain a call to action, or it will reinforce what you want your audience to believe, feel or do after hearing your presentation. For an informative speech, the strong statement should reinforce the importance of knowing about your topic, or what makes it so interesting.
It may be useful to think of the Three S’s of the speech conclusion as you work on this part of your presentation. Using a signal, summary, and strong statement will provide closure for the audience and help them to remember the ideas that you shared.
Creating a List of References
The last piece of your outline will generally be a list of references that you have used to provide source material for your speech. There should be at least one citation in the body of your speech from each reference. A reference is not just a website link to your research, but it shares details about your source in an organized format. You will generally need to provide the author’s name and the title of the piece, along with the name of the source you got this information from, and the date it was published. If you found the source online, you will also include the URL for the web page where this source can be found. There are standardized ways to organize all this information, and your professor may ask you to use a specific format. The two most common styles for formatting references are MLA and APA. You can find many resources, both online, and in your college’s library, to help you apply the correct formatting of the style your professor has requested. Carefully following these guidelines will add a professional polish to your speech outline and help you develop attention to detail in your written work, which is a valuable skill in the workforce, and in daily life.
Practicing with the Outline
As you are preparing to present your speech, it may be helpful to highlight key words and phrases so that you can quickly find the information you need in a single glance. This way you can have consistent eye contact with your audience. You want to avoid bobbing your head up and down as you speak, alternating between reading and seeing your audience. Remember, the outline is merely there to keep you on track. You don’t have to say all the words exactly as you have written them. In fact, your words will have much greater impact with the audience if you can create the impression that you are speaking spontaneously. Don’t be afraid to check in with your outline to make sure you have included all your ideas, and in the correct order, but also don’t rely so much on the outline that you are not connected to the audience.
If your instructor has asked you to include a speech topic, general purpose, specific purpose, purpose statement, and/or central idea on your outline, do not include these as part of your speech presentation. They belong on the outline to show your professor that you understood the topic and the goals for the assignment, and that you had a clear thesis for the speech, but you don’t share these out loud with your audience. Likewise, you also won’t read off the references to the audience at the end. These are part of the written assignment, but your oral citations are sufficient to establish your credibility in your presentation. For each speech assignment, you’ll begin with the introduction and finish up with the conclusion.
To help you prepare for your in-class presentation, you should plan on practicing your speech out loud, with a timer, in front of at least one other person. The first time you run through your speech in this way, you’ll find out what you’ve got, and you will likely need to make some adjustments to your outline. You can also get some feedback on your speech delivery, so that you can begin to refine your presentation skills. Continue this process of making changes and then practicing again in front of someone. In general, by the fifth time you’ve gone through the speech, you have it loosely committed to memory. You will know the overall flow of your topics and supporting material, and you can focus on connecting with your audience.
Remember the example of the disjointed building at the beginning of this chapter? The building had important rooms, but it was very difficult to navigate between them and make use of them. This concept also applies to your speech. You might find interesting examples and compelling arguments, but if they are not organized well, your audience may miss them. A well-organized speech will help your audience process and remember your message and will give you greater confidence as a speaker. Spending a little extra time polishing your outline will pay off in dividends towards a speech performance that you can be proud of.
Review Questions
- Why is it important to create an outline for a presentation?
- What are the three general purposes of speech presentations?
- What is the difference between a specific purpose, or purpose statement, of a speech and its central idea?
- What are the five parts of a speech introduction?
- How do transitions in a speech help the audience?
- What is an example of a type of effective attention-getter for a speech?
- Why should we use statistics sparingly in our presentations?
- When would a peer testimony be more credible with the audience than an expert testimony?
- How does oral citation differ from the type of citation you would use for an essay?
- What could you say to signal the end of your speech?
- What information might you include in your outline that you would speak aloud as part of your speech?
Class Activities
- Read aloud a series of specific purposes or purpose statements, and have the students classify each as having the general purpose of informing, persuading, or entertaining.
- Write down different types of attention-getters on small pieces of paper, such as “Telling a story,” “Startling the audience,” “Asking rhetorical questions,” “Using a powerful quote,” “Making the audience curious,” “Having the audience participate,” etc. Break up the class into small groups and have each group blindly choose an attention-getter from the pile. Then, give the entire class a topic, such as “Chewing gum.” Each group has to come up with an attention-getter for this topic in the type they selected.
- Have students help you come up with a list of 10–14 totally random, but specific, people, places, or things. Give a few examples, such as: mustaches, black widow spiders, North Dakota, etc. Once you have a list, pair the students up and have them share how they would establish credibility on this topic. Do they have personal experience with this topic? Will they need to do research?
- Using the same list as above, have students work with their partner to decide how they would relate this topic to their diverse classroom audience.
- Create an abbreviated preparation outline for students that includes the general purpose, specific purpose, central Idea, and a list of main points. Break up the class into small groups and give each group either the introduction or a main point. Ask each group to prepare 1–2 minutes of content for their section of the speech and elect a spokesperson to present their section to the class. Once the students are prepared, start a timer and do the presentation. Provide transitions between main ideas and a conclusion.
- Have the students find a quotation from their favorite celebrity in an article (not a from a website that simply lists quotations). Break up the class into small groups, have students share their quotation with their group, and let each group pick the best one to present to the class. The elected spokesperson for each group will share the quotation beginning with an oral citation as follows: “According to [the celebrity’s name], as reported by [the source of the quotation] on [the date] . . .”
- Make 5–10 enlarged copies of both an APA reference and an MLA reference. Cut the copies up so that the author, article title, publication date, URL, and other elements of the reference each appear on a different slip of paper. Divide the class into groups and give each group an APA “puzzle” to assemble. The first group to assemble its reference correctly wins! Repeat with the MLA reference.
- Pass out a lined index card to each student. Give students an easy topic, and have them freewrite in complete sentences on this topic until either the time is up or the card is filled. Next, have students choose 10 key words that will help them remember what they wrote and list those words on the blank side of the card. Then, pair the students up and tell them to decide who will be “Person A” and who will be “Person B.” “Person A” holds their card so that they can see only the key words and their partner can see the freewriting. “Person A” then attempts to share what they wrote with “Person B,” using only the key words as a prompt. At the end, “Person B” will let them know if anything was left out. Next, the partners will switch roles, so that “Person B” can present. Have a discussion with the class about the difference between presentation notes and preparation outlines.
Works Consulted
Gallo, Carmine. Talk Like TED: The 9 Public-Speaking Secrets of the World’s Top Minds . St. Martin’s Press, 2014.
Hemmert, Nancy Grass. Public Speaking in American English: A Guide for Non-Native Speakers . Pearson, 2007.
Lucas, Stephen E. The Art of Public Speaking . 12th ed., McGraw Hill, 2014.
Powell, Susanna, et al. Stand and Deliver: High Impact Presentations . 4th ed., Pearson, 2014.
the general reason or intention of the speech, such as to inform, persuade, or entertain
the reason or intention that is specific to a particular speech
a statement that identifies the goal for the audience of a speech
references to the sources of information
references to the sources of information given verbally during a speech
a hint that the conclusion of a speech is coming soon
a brief restatement of the main ideas
a statement that leaves a lasting impression on the audience
Start Here, Speak Anywhere! Second Edition Copyright © by Rebecca Collier, M.B.A. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Writing the Conclusion of a Speech

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

One of the best ways to conclude a speech is to tie the conclusion into the introduction. For example, you might begin your speech by telling a suspenseful story that relates to your topic, but save the end of the story for the very end of your speech. Or refer back to the same quotation. Or refer to the joke that you told. Any of these strategies will give your speech a sense of connection and closure, and will leave the audience with a great final impression.
If you are delivering a persuasive speech, you might try a slightly different ending because your goal is not just to be remembered, it’s to inspire people to take action. One way to do this is to issue a call-to-action. This means that you specifically tell your audience what actions you expect them to take related to your speech. Another way to inspire action with the conclusion of your speech is to appeal to their emotions. If you create a desired emotion within your audience, and then leave them with that emotion, they will take that emotion with them. For example: If you leave them feeling guilty about not-recycling by painting a bleak picture about the state of the Earth that their grandchildren will live in, then they might recall that emotion the next time they choose not to recycle and alter their behavior.
Leaving a strong final impression is the most important aspect of the conclusion, but their are some other necessary steps as well:
- Making a smooth transition from the body of the speech to the conclusion is crucial. To do this, use a signpost known as a concluding statement. The most common concluding statements include: “in conclusion”, “I leave you with”, “finally today”, and other similarly obvious endings.
- Just as it is important to preview a speech in the introduction, it is important to summarize the speech in the conclusion. The more the audience hears your main points, the more likely they are to remember them. By previewing, discussing, and summarizing your main points your audience will be exposed to them at least three times during your speech.
A good conclusion should be about 5-10% of the total speech length. Anything shorter that 5% means that the ending has come too abruptly. Anything more that 10%, and the audience may become restless. This brings up another point: If it sounds like a conclusion, you need to finish your speech in a reasonable amount of time. The conclusion is not the place to add new material.
Effective ways to end a speech
- Summarize the main speech topics or main points.
- Repeat a few keywords or phrases by using the rhetorical figure of speech repetition.
- State how your points prove your general and specific goal.
- Restate and reinforce the central idea.
- Repeat the tie between the needs and interests of the listeners, and your thesis.
- Refer back to an anecdote or quotation in the introduction text.
- Offer a so-called moral of the story.
- Call them to act and offer them how-to-do-it steps.
- List the benefits or available applications; very effective ways to end a speech.
- Restate the problem and provide your solution in two sentences.
- Visualize the outcome of your call to action with a prop or visual aid.
- Transform your central idea or even the discourse title into an easy to remember slogan.
- Recite a couple of lines from songs, poems or citations and quotes from a historical presentation.
- End with a heart-felt human interest story in which all comes together.
- Finish with a clinching personal anecdote.
- Close with an illustrative design example.
- End with a joke or funny remark. Must say that only choose these ways to end a speech if it’s really funny.
- Connect your speech topics with the common grounds and thoughts of the public speaking audience. This way to end a speech brings the overall speech topic in their hearts and minds.
- Ask a rhetorical question and answer with an easy to remember oneliner.
- Give the ultimate answer on an important question you proposed earlier in your introduction.
- Surprise with a shocking fact or figure that empahizes the need for change.
- Draw the contours of the ideal situation you propose. Visualize that they will see paradise if they do, think or act as you want.
Speech Anxiety
Writing a Speech
2 thoughts on “Writing the Conclusion of a Speech”
Great information,but need samples to further help us understand
I want to have and example of conclusion please
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
- English Grammar
- Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech - Definition, 8 Types and Examples
In the English language , every word is called a part of speech. The role a word plays in a sentence denotes what part of speech it belongs to. Explore the definition of parts of speech, the different parts of speech and examples in this article.
Table of Contents
Parts of speech definition, different parts of speech with examples.
- Sentences Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
A Small Exercise to Check Your Understanding of Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech, what is a part of speech.
Parts of speech are among the first grammar topics we learn when we are in school or when we start our English language learning process. Parts of speech can be defined as words that perform different roles in a sentence. Some parts of speech can perform the functions of other parts of speech too.
- The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines parts of speech as “one of the classes into which words are divided according to their grammar, such as noun, verb, adjective, etc.”
- The Cambridge Dictionary also gives a similar definition – “One of the grammatical groups into which words are divided, such as noun, verb, and adjective”.
Parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns . Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
Examples of nouns used in sentences:
- She bought a pair of shoes . (thing)
- I have a pet. (animal)
- Is this your book ? (object)
- Many people have a fear of darkness . (ideas/abstract nouns)
- He is my brother . (person)
- This is my school . (place)
Also, explore Singular Nouns and Plural Nouns .
2. Pronouns are words that are used to substitute a noun in a sentence. There are different types of pronouns. Some of them are reflexive pronouns, possessive pronouns , relative pronouns and indefinite pronouns . I, he, she, it, them, his, yours, anyone, nobody, who, etc., are some of the pronouns.
Examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- I reached home at six in the evening. (1st person singular pronoun)
- Did someone see a red bag on the counter? (Indefinite pronoun)
- Is this the boy who won the first prize? (Relative pronoun)
- That is my mom. (Possessive pronoun)
- I hurt myself yesterday when we were playing cricket. (Reflexive pronoun)
3. Verbs are words that denote an action that is being performed by the noun or the subject in a sentence. They are also called action words. Some examples of verbs are read, sit, run, pick, garnish, come, pitch, etc.
Examples of verbs used in sentences:
- She plays cricket every day.
- Darshana and Arul are going to the movies.
- My friends visited me last week.
- Did you have your breakfast?
- My name is Meenakshi Kishore.
4. Adverbs are words that are used to provide more information about verbs, adjectives and other adverbs used in a sentence. There are five main types of adverbs namely, adverbs of manner , adverbs of degree , adverbs of frequency , adverbs of time and adverbs of place . Some examples of adverbs are today, quickly, randomly, early, 10 a.m. etc.
Examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- Did you come here to buy an umbrella? (Adverb of place)
- I did not go to school yesterday as I was sick. (Adverb of time)
- Savio reads the newspaper everyday . (Adverb of frequency)
- Can you please come quickly ? (Adverb of manner)
- Tony was so sleepy that he could hardly keep his eyes open during the meeting. (Adverb of degree)
5. Adjectives are words that are used to describe or provide more information about the noun or the subject in a sentence. Some examples of adjectives include good, ugly, quick, beautiful, late, etc.
Examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- The place we visited yesterday was serene .
- Did you see how big that dog was?
- The weather is pleasant today.
- The red dress you wore on your birthday was lovely.
- My brother had only one chapati for breakfast.
6. Prepositions are words that are used to link one part of the sentence to another. Prepositions show the position of the object or subject in a sentence. Some examples of prepositions are in, out, besides, in front of, below, opposite, etc.
Examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The teacher asked the students to draw lines on the paper so that they could write in straight lines.
- The child hid his birthday presents under his bed.
- Mom asked me to go to the store near my school.
- The thieves jumped over the wall and escaped before we could reach home.
7. Conjunctions are a part of speech that is used to connect two different parts of a sentence, phrases and clauses . Some examples of conjunctions are and, or, for, yet, although, because, not only, etc.
Examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- Meera and Jasmine had come to my birthday party.
- Jane did not go to work as she was sick.
- Unless you work hard, you cannot score good marks.
- I have not finished my project, yet I went out with my friends.
8. Interjections are words that are used to convey strong emotions or feelings. Some examples of interjections are oh, wow, alas, yippee, etc. It is always followed by an exclamation mark.
Examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow ! What a wonderful work of art.
- Alas ! That is really sad.
- Yippee ! We won the match.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Noun – Tom lives in New York .
- Pronoun – Did she find the book she was looking for?
- Verb – I reached home.
- Adverb – The tea is too hot.
- Adjective – The movie was amazing .
- Preposition – The candle was kept under the table.
- Conjunction – I was at home all day, but I am feeling very tired.
- Interjection – Oh ! I forgot to turn off the stove.
Let us find out if you have understood the different parts of speech and their functions. Try identifying which part of speech the highlighted words belong to.
- My brother came home late .
- I am a good girl.
- This is the book I was looking for.
- Whoa ! This is amazing .
- The climate in Kodaikanal is very pleasant.
- Can you please pick up Dan and me on your way home?
Now, let us see if you got it right. Check your answers.
- My – Pronoun, Home – Noun, Late – Adverb
- Am – Verb, Good – Adjective
- I – Pronoun, Was looking – Verb
- Whoa – Interjection, Amazing – Adjective
- Climate – Noun, In – Preposition, Kodaikanal – Noun, Very – Adverb
- And – Conjunction, On – Preposition, Your – Pronoun
What are parts of speech?
The term ‘parts of speech’ refers to words that perform different functions in a sentence in order to give the sentence a proper meaning and structure.
How many parts of speech are there?
There are 8 parts of speech in total.
What are the 8 parts of speech?
Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections are the 8 parts of speech.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Module 4: Organizing and Outlining
Outlining your speech.
Most speakers and audience members would agree that an organized speech is both easier to present as well as more persuasive. Public speaking teachers especially believe in the power of organizing your speech, which is why they encourage (and often require) that you create an outline for your speech. Outlines , or textual arrangements of all the various elements of a speech, are a very common way of organizing a speech before it is delivered. Most extemporaneous speakers keep their outlines with them during the speech as a way to ensure that they do not leave out any important elements and to keep them on track. Writing an outline is also important to the speechwriting process since doing so forces the speakers to think about the main points and sub-points, the examples they wish to include, and the ways in which these elements correspond to one another. In short, the outline functions both as an organization tool and as a reference for delivering a speech.
Outline Types

“Alpena Mayor Carol Shafto Speaks at 2011 Michigan Municipal League Convention” by Michigan Municipal League. CC-BY-ND .
There are two types of outlines. The first outline you will write is called the preparation outline . Also called a working, practice, or rough outline, the preparation outline is used to work through the various components of your speech in an inventive format. Stephen E. Lucas [1] put it simply: “The preparation outline is just what its name implies—an outline that helps you prepare the speech” (p. 248). When writing the preparation outline, you should focus on finalizing the purpose and thesis statements, logically ordering your main points, deciding where supporting material should be included, and refining the overall organizational pattern of your speech. As you write the preparation outline, you may find it necessary to rearrange your points or to add or subtract supporting material. You may also realize that some of your main points are sufficiently supported while others are lacking. The final draft of your preparation outline should include full sentences, making up a complete script of your entire speech. In most cases, however, the preparation outline is reserved for planning purposes only and is translated into a speaking outline before you deliver the speech.
A speaking outline is the outline you will prepare for use when delivering the speech. The speaking outline is much more succinct than the preparation outline and includes brief phrases or words that remind the speakers of the points they need to make, plus supporting material and signposts. [2] The words or phrases used on the speaking outline should briefly encapsulate all of the information needed to prompt the speaker to accurately deliver the speech. Although some cases call for reading a speech verbatim from the full-sentence outline, in most cases speakers will simply refer to their speaking outline for quick reminders and to ensure that they do not omit any important information. Because it uses just words or short phrases, and not full sentences, the speaking outline can easily be transferred to index cards that can be referenced during a speech.
Outline Structure
Because an outline is used to arrange all of the elements of your speech, it makes sense that the outline itself has an organizational hierarchy and a common format. Although there are a variety of outline styles, generally they follow the same pattern. Main ideas are preceded by Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc.). Sub-points are preceded by capital letters (A, B, C, etc.), then Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.), and finally lowercase letters (a, b, c, etc.). Each level of subordination is also differentiated from its predecessor by indenting a few spaces. Indenting makes it easy to find your main points, sub-points, and the supporting points and examples below them. Since there are three sections to your speech— introduction, body, and conclusion— your outline needs to include all of them. Each of these sections is titled and the main points start with Roman numeral I.
Outline Formatting Guide
Title: Organizing Your Public Speech
Topic: Organizing public speeches
Specific Purpose Statement: To inform listeners about the various ways in which they can organize their public speeches.
Thesis Statement: A variety of organizational styles can used to organize public speeches.
Introduction Paragraph that gets the attention of the audience, establishes goodwill with the audience, states the purpose of the speech, and previews the speech and its structure.
(Transition)
I. Main point
A. Sub-point B. Sub-point C. Sub-point
1. Supporting point 2. Supporting point
Conclusion Paragraph that prepares the audience for the end of the speech, presents any final appeals, and summarizes and wraps up the speech.
Bibliography
In addition to these formatting suggestions, there are some additional elements that should be included at the beginning of your outline: the title, topic, specific purpose statement, and thesis statement. These elements are helpful to you, the speechwriter, since they remind you what, specifically, you are trying to accomplish in your speech. They are also helpful to anyone reading and assessing your outline since knowing what you want to accomplish will determine how they perceive the elements included in your outline. Additionally, you should write out the transitional statements that you will use to alert audiences that you are moving from one point to another. These are included in parentheses between main points. At the end of the outlines, you should include bibliographic information for any outside resources you mention during the speech. These should be cited using whatever citations style your professor requires. The textbox entitled “Outline Formatting Guide” provides an example of the appropriate outline format.
If you do not change direction, you may end up where you are heading. – Lao Tzu
Preparation Outline
This chapter contains the preparation and speaking outlines for a short speech the author of this chapter gave about how small organizations can work on issues related to climate change (see appendices). In this example, the title, specific purpose, thesis, and list of visual aids precedes the speech. Depending on your instructor’s requirements, you may need to include these details plus additional information. It is also a good idea to keep these details at the top of your document as you write the speech since they will help keep you on track to developing an organized speech that is in line with your specific purpose and helps prove your thesis. At the end of the chapter, in Appendix A, you can find a full length example of a Preparation (Full Sentence) Outline.
Speaking Outline
In Appendix B, the Preparation Outline is condensed into just a few short key words or phrases that will remind speakers to include all of their main points and supporting information. The introduction and conclusion are not included since they will simply be inserted from the Preparation Outline. It is easy to forget your catchy attention-getter or final thoughts you have prepared for your audience, so it is best to include the full sentence versions even in your speaking outline.
Using the Speaking Outline

“TAG speaks of others first” by Texas Military Forces. CC-BY-ND .
Once you have prepared the outline and are almost ready to give your speech, you should decide how you want to format your outline for presentation. Many speakers like to carry a stack of papers with them when they speak, but others are more comfortable with a smaller stack of index cards with the outline copied onto them. Moreover, speaking instructors often have requirements for how you should format the speaking outline. Whether you decide to use index cards or the printed outline, here are a few tips. First, write large enough so that you do not have to bring the cards or pages close to your eyes to read them. Second, make sure you have the cards/pages in the correct order and bound together in some way so that they do not get out of order. Third, just in case the cards/pages do get out of order (this happens too often!), be sure that you number each in the top right corner so you can quickly and easily get things organized. Fourth, try not to fiddle with the cards/pages when you are speaking. It is best to lay them down if you have a podium or table in front of you. If not, practice reading from them in front of a mirror. You should be able to look down quickly, read the text, and then return to your gaze to the audience.
Any intelligent fool can make things bigger and more complex… It takes a touch of genius – and a lot of courage to move in the opposite direction. – Albert Einstein
- Lucas, Stephen E. (2004). The art of public speaking (8th edition). New York: McGraw-Hill. ↵
- Beebe, S. A. & Beebe, S. J. (2003). The public speaking handbook (5th edition). Boston: Pearson. ↵
- Chapter 8 Outlining Your Speech. Authored by : Joshua Trey Barnett. Provided by : University of Indiana, Bloomington, IN. Located at : http://publicspeakingproject.org/psvirtualtext.html . Project : The Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Alpena Mayor Carol Shafto Speaks at 2011 Michigan Municipal League Convention. Authored by : Michigan Municipal League. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/aunJMR . License : CC BY-ND: Attribution-NoDerivatives
- TAG speaks of others first. Authored by : Texas Military Forces. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/texasmilitaryforces/5560449970/ . License : CC BY-ND: Attribution-NoDerivatives

Privacy Policy

20 Analyzing a Sample Conclusion
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate parts of a conclusion.

Theilr – blank dossier – CC BY-SA 2.0.
So far this chapter has focused on how to go about creating a clear conclusion. We discussed why conclusions are important, the three steps of effective conclusions, and ten different ways to conclude a speech. In this section, we’re going to examine an actual conclusion to a speech. Please read the sample conclusion paragraph for the smart dust speech.
Sample Conclusion: Smart Dust
Today, we’ve explored how smart dust may impact all of our lives in the near future by examining what smart dust is, how smart dust could be utilized by the US military, and how smart dust could impact all of our lives sooner rather than later. While smart dust is quickly transforming from science fiction to science fact, experts agree that the full potential of smart dust will probably not occur until 2025. While smart dust is definitely coming, swarms of smart dust eating people as was depicted in Michael Crichton’s 2002 novel, Prey , aren’t reality. However, as with any technological advance, there are definite ethical considerations and worries to consider. Even Dr. Kris Pister’s Smart Dust Project website admits that as smart dust becomes more readily available, one of the trade-offs will be privacy. Pister responds to these critiques by saying, “As an engineer, or a scientist, or a hair stylist, everyone needs to evaluate what they do in terms of its positive and negative effect. If I thought that the negatives of working on this project were larger than or even comparable to the positives, I wouldn’t be working on it. As it turns out, I think that the potential benefits of this technology far outweigh the risks to personal privacy.”
Now that you’ve had a chance to read the conclusion to the speech on smart dust, read it a second time and try to find the three parts of an introduction as discussed earlier in this chapter. Once you’re finished analyzing this conclusion, take a look at the example below which shows you how the speech was broken down into the various parts of a conclusion.
Key Takeaways
A solid conclusion will leave a lasting impression on an audience.
- To ensure you have a strong conclusion, you might consider comparing your work to that of the Smart Dust conclusion.
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Learning Object — Clip
Rate conclusion, clip: conclusion.
A brief review of the eight parts of speech
Student Application
Find out why it helps to know the different kinds of words and the reason for knowing parts of speech.
Learning Objectives
- Students will understand that learning the eight parts of speech helps people to know the function of words and how they are joined together to make coherent sentences.
Supporting Activities
Related content.

Introduction Clip

Pronoun Clip

Adjective Clip

Adverb Clip

Preposition Clip

Conjunction Clip

Interjections Clip

Conclusion Clip

Eight Parts Of Speech Lesson
Eight Parts Of Speech Video
Welcome back, sign in to your classorbit dashboard., oops please sign in to access this content..

Advertisement
Supported by
Student Protest Movement Could Cause a Tumultuous End to School Year
Protesters were arrested at the University of Minnesota and Yale, and the House speaker, Mike Johnson, said he would come to Columbia to speak to Jewish students about antisemitism on campuses.
- Share full article

By Troy Closson
As a wave of pro-Palestinian activism on college campuses showed few signs of abating on Tuesday, the demonstrations have raised new questions about what shape the end of the semester may take for thousands of students across the United States.
At Columbia University, where the arrests of more than 100 protesters unleashed a flurry of national protests, students will have the option to attend their last week of lectures remotely for safety reasons. At the University of Texas at Austin, protesters announced plans to occupy a campus plaza and said that, at least for them, “class is canceled.”
And at the University of Michigan, administrators were already looking ahead and bracing for graduation. They set up designated areas for demonstrations, and agreed to “generally be patient with lawful disruptions.”
“Commencement ceremonies have been the site of free expression and peaceful protest for decades,” the university said in an online message, adding, “And they will likely continue to be.”
The steps are an acknowledgment that the last weeks of the spring could be among the most difficult for administrators at some of the nation’s most prestigious universities. On Tuesday, the campus police at the University of Minnesota took nine people into custody after they erected a protest encampment, following dozens of arrests at Yale and New York University.
Other demonstrations continue to emerge from coast to coast, including at the University of New Mexico and Emerson College. At California State Polytechnic University, Humboldt, students took over a campus building, and barricaded the exits with chairs and trash bins.
The pro-Palestinian student movement has disrupted campus life, especially for Jewish students. Many have said they no longer feel safe in their classrooms or on university quads as the tone of protests at times has become threatening. Speaker Mike Johnson said he would meet with Jewish students at Columbia University on Wednesday and give remarks about the “troubling rise of virulent antisemitism on America’s college campuses,” according to a news release.
At the same time, many school leaders may face the possibility of graduation ceremonies transforming into high-profile stages of protest over the war in Gaza.
No matter how administrators approach these final weeks, the stakes are uniquely high for students who are graduating. Many graduated from high school in the first months of the coronavirus pandemic, and never walked across the stage or celebrated alongside their classmates.
The tumult on campuses escalated after Columbia’s administration called in the police last week to arrest student protesters who had organized a large encampment on a school lawn and refused to leave.
At the New School in Manhattan, where protesters have set up tents inside a school lobby, a couple dozen students formed a picket line on Tuesday as they chanted to the beat of a drum. When one student was asked how long protesters intended to continue the demonstrations, she said there was no immediate end in sight.
“We’re demanding something,” said the student, Skylar Schiltz-Rouse, a freshman who joined the protest on Monday. “So if it doesn’t happen, we’re going to have to keep going.”
It was not yet apparent whether the turmoil at schools would prompt additional arrests, or whether college leaders would adopt a less aggressive playbook as the semester winds down.
Many administrators, watching the uproar at Columbia, seem to be choosing other strategies to handle the protests. Several universities, including Harvard and schools in the California State University system, have shut down parts of their campuses in an effort to avoid major clashes and conclude the school year quietly.
“What you’re seeing is an inability to find spaces for dialogue and conversation and understanding,” said Benjie Kaplan, the executive director of Minnesota Hillel, a Jewish student group.
After school leaders often inflamed unrest with their initial responses, some have begun to hit the brakes.
At Barnard College, Columbia’s affiliate school, many student protesters had received interim suspensions for last week’s tent demonstration. But in a Monday night email, the school’s president, Laura Ann Rosenbury, extended an olive branch.
The school would lift most of the suspensions and restore students’ access to campus, she said, as long as they promised to follow the rules. Those who still face discipline would have access to hot meals, mental health counseling and academic support. And with a professor’s permission, they could also finish out the semester virtually.
“I strongly believe that exposure to uncomfortable ideas is a vital component of education, and I applaud the boldness of all of our students who speak out,” Ms. Rosenbury said in the email, her first message since the arrests of protesters on Columbia’s campus last week, several of whom were Barnard students.
“But,” she said, “no student should fear for their safety while at Barnard.”
She added: “In these last few weeks together before our seniors graduate, let’s be good to one another.”
Some pro-Palestinian students, though, may regard commencement as an opportunity.
Protesters at many schools have vowed to press on until their universities divest from companies with ties to Israel, often chanting “We will not stop. We will not rest.” Administrators are on high alert for demonstrations or threats, as tens of thousands of families travel to campuses in May and June to attend graduations.
Dagmar Michelson, a senior at the New School, was unsure if protests were planned for the university’s May 17 ceremonies. But if they are, she added, she would not be upset.
“It’ll be nice for those who haven’t recognized their privilege,” she said.
Earlier this month, the University of Southern California cited security concerns when it canceled a speech by its valedictorian , a first-generation Muslim student who questioned the university’s explanation. The school later said it would also not host outside honorees.
Already, students have organized demonstrations meant to disrupt cherished college traditions.
At Michigan, several dozen protesters took over a celebration for honors students last month, waving signs that read “Divest Now” and interrupting a speech by the university’s president, Santa J. Ono, according to The Michigan Daily .
“Protest is valued and protected,” Dr. Ono said in a statement after the event. “Disruptions are not.”
Shira Goodman, the senior director of advocacy at the Anti-Defamation League, said the disturbance at Michigan “may unfortunately be a harbinger for what’s to come.”
The group is concerned about the potential of harassment or “identity-based hostility” toward Jewish families at graduation ceremonies. “We remain deeply concerned,” Ms. Goodman said in a statement.
Some colleges are now stepping in to promise Jewish students a safe haven. Brandeis, a historically Jewish university in Massachusetts, said this week that it would extend its deadline for transfer applications in response to campus protests.
The president, Ronald D. Liebowitz, said the school would provide an environment “free of harassment and Jew-hatred.”
Other schools have had little time to look ahead to the future as they reel from the last few days.
At N.Y.U., where at least 120 people were arrested on Monday night after refusing to vacate a plaza, several students said on Tuesday that they would continue to voice support for Palestinians, and were unconcerned that their protest activities might upend final essays and assignments.
The university had said it turned to the police because “disorderly, disruptive and antagonizing behavior” of protesters created safety concerns. But on Tuesday, a professional faculty organization shot back.
The school’s chapter of the American Association of University Professors called “much of their account” false, referring to the administration, and criticized the decision to call the police as an “egregious overstep.”
And at Columbia, the university’s president, Nemat Shafik, is facing the threat of a formal censure resolution from the school’s faculty for her handling of demonstrations. Many Republican lawmakers are also still calling for her resignation, arguing that the school has failed to safeguard its Jewish students.
The decision to offer hybrid classes at Columbia seemed to be a tacit acknowledgment that many students were, at the very least, uncomfortable there. Many are expected to log on from their dorms and apartments. Others might attend from a large protest encampment that remained in the center of campus.
Along with the demonstration, occasional outbursts at rallies have occurred outside the campus’s gates over the past several days. But otherwise, Columbia has been quiet during what is typically a bustling final week of the semester.
Angela V. Olinto, the university provost, said in an email on Monday night that if even one student wanted to finish out the year online, professors should offer hybrid classes — or move to fully remote if that was not an option.
“Safety is our highest priority,” Dr. Olinto said.
Maia Coleman , Eliza Fawcett , Colbi Edmonds , Jose Quezada , Ernesto Londoño , Kaja Andric , Coral Murphy Marcos , Dana Goldstein , Karla Marie Sanford and Stephanie Saul contributed reporting.
Troy Closson reports on K-12 schools in New York City for The Times. More about Troy Closson

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We firmly believe that improving your writing necessarily requires an understanding of the parts of speech. 1. Understanding the Parts of Speech 2. Common Grammatical Mistakes 3. Developing a Powerful Writing Style 4.
The conclusion pushes beyond the boundaries of the prompt and allows you to consider broader issues, make new connections, and elaborate on the significance of your findings. Your conclusion should make your readers glad they read your paper. Your conclusion gives your reader something to take away that will help them see things differently or ...
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
Parts of Speech: The Ultimate Guide for Students and Teachers. By Shane Mac Donnchaidh September 11, 2021March 5, 2024 March 5, 2024. This article is part of the ultimate guide to language for teachers and students. Click the buttons below to view these.
You must finish your assignment. He may join us later. F. Transitive Verbs: Transitive verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning. Examples: ... Conclusion. In conclusion, parts of speech serve as crucial categories that describe the distinct roles words play within a sentence. A comprehensive grasp of these categories empowers you ...
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don't need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that brings ...
This comes before a noun or a noun phrase and links it to other parts of the sentence. These are usually single words (e.g., on, at, by ,…) but can be up to four words (e.g., as far as, in addition to, as a result of, …). I chose to interview teachers in the district closest to me. The recorder was placed next to the interviewee.
One of the hardest parts of the speech assignment for students is choosing a topic with which to work with. Oftentimes, as soon as you begin drafting an outline for a chosen topic, other topics will start to look more and more appealing, and you will want to change to a new topic. ... The Speech Conclusion. Once you have finished taking your ...
Conclusion. The English language is built around eight fundamental parts of speech, each playing a unique role in sentence structure and meaning. Mastering these elements can greatly enhance your communication skills, whether you're writing an email or e-book. Mastering the correct usage of these parts of speech can help you become a better ...
Prepositional phrases convey a spatial, temporal, or directional meaning. Example 1: Ivy climbed up the brick wall of the house. There are two prepositional phrases in the example above: up the brick wall and of the house. The first prepositional phrase is an adverbial phrase, since it modifies the verb by describing where the ivy climbed.
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
Parts of Speech. You're probably quite familiar with the "grammar police"—those people who find it necessary to correct any grammar mistake you make. You, in fact, may be a member of the "grammar police" squad yourself, but if you're not, you probably get a little tired of the corrections.
Overview of Parts of Speech. In this section, we will provide a brief overview of the eight parts of speech in English. Understanding the parts of speech is essential for anyone learning the English language, as it enables them to construct meaningful sentences and communicate effectively. The eight parts of speech are: Nouns. Verbs.
Below you'll find printable parts of speech worksheets. On these worksheets, students learn to identify the part of speech of a word according to how it is used in a given sentence. Then, they are given opportunity to practice writing sentences using the specified part of speech. All eight parts of speech are covered in this section: Nouns ...
The introduction and the conclusion are the most important parts of your speech, because they are the parts that your audience is most likely to remember. Thus, the structure and development of these two parts is crucial to the success of your speech. Your speech introduction should do the following five things: Begin with an attention-getter.
By previewing, discussing, and summarizing your main points your audience will be exposed to them at least three times during your speech. A good conclusion should be about 5-10% of the total speech length. Anything shorter that 5% means that the ending has come too abruptly. Anything more that 10%, and the audience may become restless.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples: 1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns. Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
A speaking outline is the outline you will prepare for use when delivering the speech. The speaking outline is much more succinct than the preparation outline and includes brief phrases or words that remind the speakers of the points they need to make, plus supporting material and signposts. [2] The words or phrases used on the speaking outline ...
The first part of the conclusion is a restatement of the thesis statement. examining what smart dust is, how smart dust could be utilized by the US military, and how smart dust could impact all of our lives in the near future. Following the thesis statement, the speech briefly reiterates the three main points discussed in the speech.
Conclusion Learning Object — Clip. Rate Conclusion. 5 4 3 2 1 Clip: Conclusion. A brief review of the eight parts of speech. Student Application. Find out why it helps to know the different kinds of words and the reason for knowing parts of speech. Learning Objectives. Students will understand that learning the eight parts of speech helps ...
Protesters were arrested at the University of Minnesota and Yale, and the House speaker, Mike Johnson, said he would come to Columbia to speak to Jewish students about antisemitism on campuses.