

12 Powerful Creative Problem-Solving Techniques That Work
No one likes the feeling of being stuck.
It creates internal tension. That tension seeks resolution.
Thankfully, there are many creative problem-solving techniques for resolving this tension and revealing new solutions.
In this guide, we’ll explore 12 creative ways to solve problems with a variety of techniques, tools, and methods that be used for personal use and in the workplace.
Let’s dive in…
How to Approach Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
All of the creative problem-solving techniques discussed below work some of the time .
While it’s fine to have a favorite “go-to” creative problem-solving technique, the reality is each problem has some unique elements to it.
The key to is mix and match various techniques and methodologies until you get a workable solution.
When faced with a difficult challenge, try a combination of the problem-solving techniques listed below.
The Power of Divergent Thinking
Creativity is everyone’s birthright.
One study with 1,500 participants, found that 98 percent of children around the age of five qualify as geniuses. 1 George Land and Beth Jarman, Breakpoint and Beyond , 1998.
That is, virtually all children are gifted with divergent thinking— the ability to see many possible answers to a question.
For example, how many uses can you think of for a paper clip?
The average adult might offer 10 to 15 answers. Those skilled in divergent thinking divine closer to 200 answers.
Yet, something happens along the way because by adulthood, how many people score at the genius level? Only 2 percent!
That is, we see a complete inversion: from 98% being geniuses in early childhood to only 2% in adulthood.
What causes this debilitating drop in creativity?
According to creativity researcher Sir Ken Robinson, the answer is our schooling. 2 Sir Ken Robinson, Do schools kill creativity? TED Talk , 2006. Through 13 years of “education” our innate creativity is stripped out of us!
Conditioning Yourself for Creative Solutions
So to improve the efficacy of these creative problem-solving techniques, it helps to re-condition ourselves to use divergent thinking.
The key is to learn how to remove our prior conditioning and restore our natural creative abilities. You’ll notice that many of the creative problem-solving techniques below help us do just that.
Thankfully, divergent thinking is a skill and we can develop it like a muscle. So the more we use divergent thinking, the more second nature it becomes.
For this reason, when you’re presented with personal, professional, or business-related problems, celebrate them as an opportunity to exercise your creative abilities.
12 Powerful Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
Now, we’re going to cover 12 creative problem-solving techniques with examples that you can apply right away to get results.
These creative problem-solving methods are:
- Use “What If” Scenarios
- Focus on Quantity Over Quality
- Switch Roles
- Use the Six Thinking Hats Technique
- Explore Different Contexts
- Take a 30,000-Foot View
- Ask Your Subconscious
- Mind Map Your Problem
- Adopt a Beginner’s Mind
- Alter Your State of Consciousness
- Find Your Center
Then, we’ll quickly review a series of problem-solving tools you can experiment with.
1 – Use “What If” Scenarios
Use “what if?” questions to project different scenarios into the future.
In A Whack on the Side of the Head , Roger Von Oech, says,
“In the imaginative phase, you ask questions such as: What if? Why not? What rules can we break? What assumptions can we drop? How about if we looked at this backwards? Can we borrow a metaphor from another discipline? The motto of the imaginative phase is: Thinking something different.”
Using this creative problem-solving technique challenges you to allow your mind to play out different scenarios without judgment or criticism .
(Judgment always comes after the creative problem-solving process—not before.)
2 – Focus on Quantity Over Quality
Creativity research shows that focusing on generating more ideas or solutions instead of on the quality of the ideas ultimately produces better results. 3 Paulus, Paul & Kohn, Nicholas & ARDITTI, LAUREN. (2011). Effects of Quantity and Quality Instructions on Brainstorming. The Journal of Creative Behavior. 45. 10.1002/j.2162-6057.2011.tb01083.x .
This phenomenon is known as the “Equal-Odds rule.” Nobel laureate Linus Pauling instinctively suggested a similar process: 4 The Evening Sentinel , Priestley Award Winner Says Deployment of ABM’s “Silly”, Start Page 1, Quote Page 6, Column 1, Carlisle, Pennsylvania. March 28, 1969.
I was once asked ‘How do you go about having good ideas?’ and my answer was that you have a lot of ideas and throw away the bad ones.
When I used to facilitate meetings and brainstorming sessions with leadership teams in large organizations, this was an invaluable creative problem-solving technique. By consciously focusing on generating more ideas first instead of evaluating the quality of the ideas, you avoid shifting into a critical mindset that often stops the ideation process.
3 – Switch Roles
Our minds tend to get locked in habitual patterns, leading to what’s called “paradigm blindness.” Another related term is the “curse of knowledge,” a common cognitive bias observed in so-called “experts” in their field. 5 Hinds, Pamela J. (1999). “The curse of expertise: The effects of expertise and debiasing methods on prediction of novice performance”. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied. 5 (2): 205–221. doi:10.1037/1076-898X.5.2.205 . S2CID 1081055
This cognitive bias is another illustration of how divergent thinking was conditioned out of us during our formative years.
Switching roles helps us “wear a different hat” where we momentarily shift away from our conditioning.
For example, if you have a marketing-related problem, try putting on an engineer’s hat—or even a gardener’s hat. If you have a problem as an entrepreneur, put yourself in the customer’s mindset. See the world from their point of view.
The idea is to shift your perspective so you can approach the problem from a new angle. Your ability to shift perspectives quickly—without privileging any one perspective—doesn’t only help you solve problems. It also helps you become a stronger leader .
4 – Use the Six Thinking Hats Technique
Speaking of hats, creativity researcher Edward de Bono developed an effective creative problem-solving technique called the Six Thinking Hats.
The Six Thinking Hats provides you and your team with six different perspectives to utilize when tackling a problem. (You can use these six hats on your own too.)
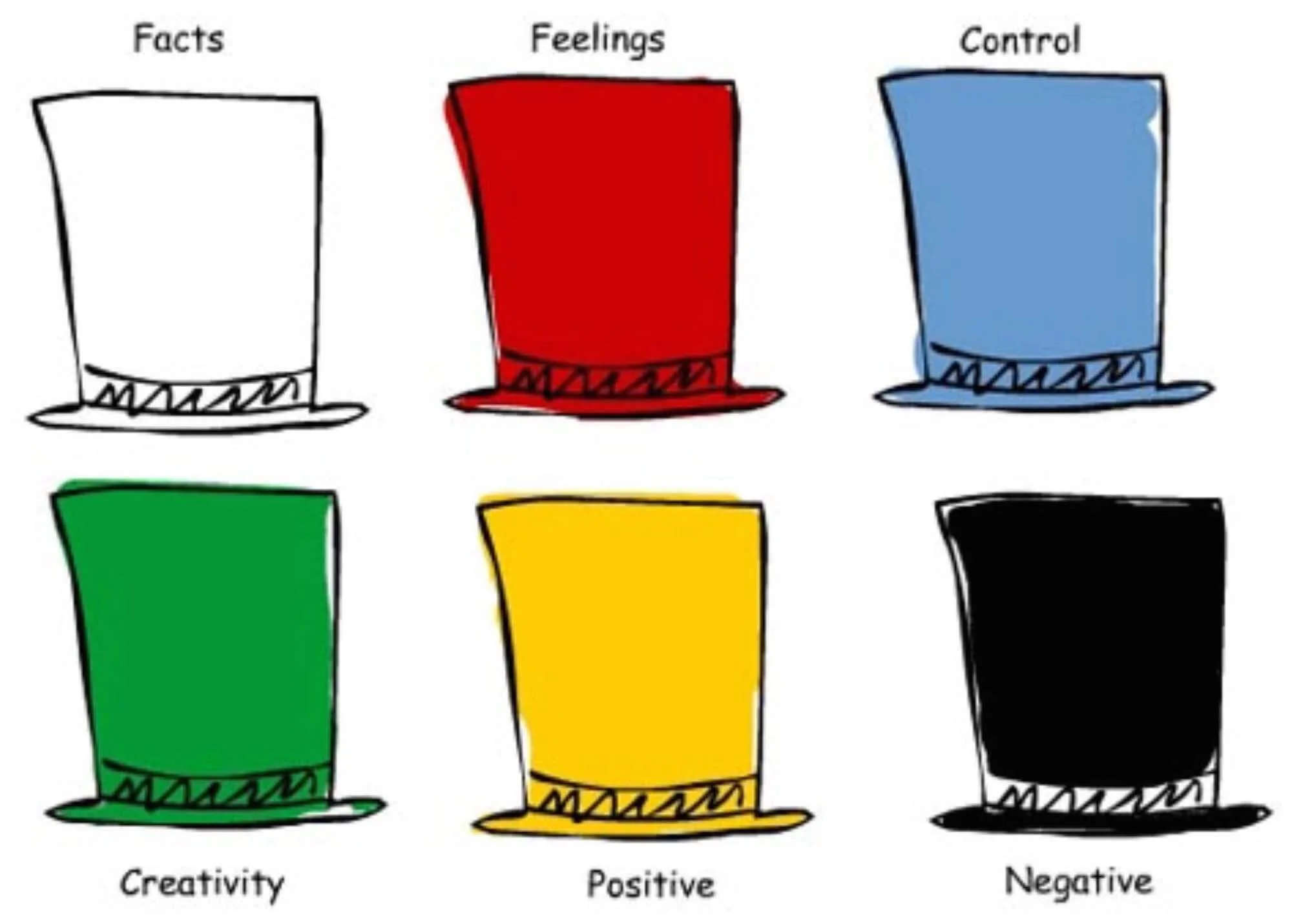
Each hat serves a different function. For creative problem solving, you start with the blue hat to clearly define the problem.
You then move to the white hat where you outline all of the existing and known data regarding the issue. Next, you put on the green hat and generate as many ideas as you can (similar to the “quantity over quality” technique above).
Then, you put on the yellow hat, which represents what de Bono calls “value sensitivity.” The yellow hat is used to build on the ideas generated from the green hat phase. Finally, you put on the black hat to evaluate your solutions and play Devil’s Advocate.
The Six Thinking Hats is an excellent technique for group brainstorming and creative problem-solving.
5 – Explore Different Contexts
Many problems arise because we neglect to zoom out from the problem and examine the larger context.
For example, long-term investments are often based on an “investment thesis.” This thesis might be based on trends in the market, consumer demands, brand recognition, dominant market share, strength in innovation, or a combination of factors. But sometimes the assumptions you base your thesis on are wrong.
So if you’re facing a problem at home or work, examine your assumptions.
If sales are down, for example, instead of revisiting your sales strategy investigate the context of your overall industry:
- Has your industry changed?
- Is your business disconnected from your customer’s needs?
- Is your product or service becoming obsolete?
We can often find creative solutions to our problems by shifting the context.
6 – Take a 30,000-Foot View
Often, when we’re stuck in a problem, it’s because we’re “missing the forest for the trees.”
Zoom out and take a “30,000-foot view” of the situation. See your problem from above with a detached, neutral mindset. Take an expansive viewpoint before narrowing in on the specific problem.
This problem-solving technique is another variation of changing the context.
Sometimes you’ll find this to be a powerful creative problem-solving technique where the right solution spontaneously presents itself. (You’ll think to yourself: Why didn’t I see this before? )

7 – Walk Away
Most often, the best problem-solving technique is to stop trying to solve it —and walk away.
Yet, our minds often don’t like this technique. The mind likes to be in control. And walking away means letting go of control.
I spent five years researching creative geniuses trying to better understand the source of inspiration for a book I was writing years ago. 6 Scott Jeffrey, Creativity Revealed: Discovering the Source of Inspiration , 2008.
In studying dozens of creative geniuses, from Mozart to William Blake, a clear pattern emerged.
Creative geniuses know when to walk away from the problems they are facing. They instinctively access what can be called the Wanderer archetype.
More recent studies show that deliberate “mind-wandering” supports creativity. 7 Henriksen D, Richardson C, Shack K. Mindfulness and creativity: Implications for thinking and learning. Think Skills Creat. 2020 Sep;37:100689. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100689 . Epub 2020 Aug 1. PMID: 32834868; PMCID: PMC7395604. Great ideas come to use when we’re not trying. 8 Kaplan, M. Why great ideas come when you aren’t trying. Nature (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10678
Wandering and reverie are essential to the creative process because they allow us to hear our Muse. The key is knowing when to let go of trying to solve the problem. Creativity problem-solving can, in this way, become an effortless process.
8 – Ask Your Subconscious
When we’re stuck on a problem and we need a creative solution, it means our conscious mind is stuck.
It does not, however, mean that we don’t already know the answer. The creative solution is often known below our conscious awareness in what can be termed our subconscious mind, or our unconscious.
Psychiatrist Carl Jung realized that dreams are a bridge from the wisdom of our unconscious to our conscious minds. As Jungian analyst Marie-Louise von Franz explains, 9 Fraser Boa, The Way of the Dream: Conversations on Jungian Dream Interpretation With Marie-Louise Von Franz , 1994.
Dreams are the letters of the Self that the Self writes us every night.
One of the most powerful creative problem-solving techniques is to ask your subconscious mind to solve the problem you’re facing before you go to sleep. Then, keep a journal and pen on your nightstand and when you awaken, record whatever comes to mind.
This is a powerful technique that will improve with practice. It’s used by many geniuses and inventors.
Another variation of this creative problem-solving technique that doesn’t require sleeping is to ask your inner guide. I provide a step-by-step creative technique to access your inner guide here .
9 – Mind Map Your Problem
Another way to get unstuck in solving problems is to access the visual side of our brain. In left/right hemisphere parlance, the left brain is dominated by logic, reason, and language while the right brain is dominated by images, symbols, and feelings. (I realize that the “science” behind this distinction is now questionable, however, the concept is still useful.)
Our problems arise largely in our “thinking brain” as we tend to favor our thoughts over other modes of processing information. In the language of Jung’s Psychological Types , most of us have a dominant thinking function that rules over our feelings, intuition, and sensing functions.
Mind mapping is a powerful creative problem-solving technique that deploys visual brainstorming.
I learned about mind mapping in the 1990s from Tony Buzan’s The Mind Map Book and used this method for many years.
In the context of problem-solving, you draw the problem in the center of the page and then start ideating and connecting ideas from the center. Think of mind mapping as a visual outline.
You don’t need to be a skilled artist to use mind mapping. Nowadays, there are also numerous apps for mind mapping including Mind Meister and Miro, but I would still recommend using a blank piece of paper and some colored pencils or markers.
10 – Adopt a Beginner’s Mind
Our early “education” conditions us with what psychologists call functional fixedness where we look at problems from a familiar viewpoint.
Numerous creative problem-solving techniques we discussed above—like switching the context, changing our roles, wearing the Six Thinking Hats, and taking a 30,000-foot view—are designed to overcome functional fixedness.
Another technique is found in Zen philosophy called a Beginner’s Mind .
With a beginner’s mind, we empty our minds and forget what we think we know. In doing so, we enter a more playful, childlike state. Instead of being serious and “attacking the problem,” we can tinker and play with different ideas and scenarios without any fears of “getting it wrong.”
It can be a liberating experience. Psychologist Abraham Maslow found that self-actualizing individuals enter a state like the Beginner’s Mind where they get fully absorbed in whatever they are doing.
11 – Alter Your State of Consciousness
Another thing I noticed in my examination of artists and creative geniuses is that virtually all of them used various substances to alter their state of consciousness when producing creative work and solving intellectual problems .
The substances vary widely including stimulants like coffee and/or cigarettes, alcohol (like absinthe), and all manner of psychedelic substances like LSD, psilocybin mushrooms, and peyote.
I’m not suggesting you should “take drugs” to solve your problems. The point is that it’s incredibly useful to alter your state of consciousness to help find creative solutions.
While using various substances is one way to accomplish this, there are many other methods like:
- Stanislav Grof’s Holotropic Breathing Technique (similar to pranayama breathing)
- The WIM Hof Method (ice cold showers)
- Brainwave entrainment programs (binaural beats and isochronic tones)
- The Silva Method (also uses brainwave entrainment)
- Kasina Mind Media System by Mindplace (light stimulation and binaural beats)
Many of these types of programs shift your brain from a beta-dominant state to an alpha-dominated state which is more conducive for creativity. See, for example, Brain Awake by iAwake Technologies.
12 – Access Your Center
Perhaps the easiest and safest way of altering your state of consciousness is via meditation . Studies show that people experience improved brainstorming and higher creativity after only twenty minutes of meditation—even if they’re inexperienced meditators. 10 Colzato, L.S., Szapora, A., Lippelt, D. et al. Prior Meditation Practice Modulates Performance and Strategy Use in Convergent- and Divergent-Thinking Problems. Mindfulness 8, 10–16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-014-0352-9
When we’re stuck on a problem, or feeling confused about what we should do, we’re usually experiencing internal resistance. Different parts of us called archetypes hijack our minds and give us conflicting wants, beliefs, attitudes, and perspectives. These parts keep us from thinking clearly to find workable solutions.
As such, when you’re stuck, it helps to find your center first . It can also be highly beneficial to ground yourself on the earth . Both of these methods can help you quiet your mind chatter and shift into a more alpha-dominant brain pattern.
Getting in the habit of centering yourself before approaching a problem is perhaps the most powerful creative problem-solving technique. It can greatly assist you in taking a 30,000-foot view of our problem as well.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
We referenced numerous problem-solving tools in the above examples including:
- Roger von Oech’s Creative Whack Pack (a deck of cards with 64 creative strategies)
- Edward de Bono’s Six Thinking Hats method
- Mind mapping (see Tony Buzan’s How to Mind Map or research online)
- Brainwave entrainment (download free samples on iAwake or try your luck online)
- All of the mind-altering methods under “Alter Your State of Consciousness”
If you’re looking for problem-solving tools for a business/group context, in addition to the Six Thinking Hats, you might also try:
SWOT Analysis
Brainwriting.
Let’s have a quick look at each of these tools.
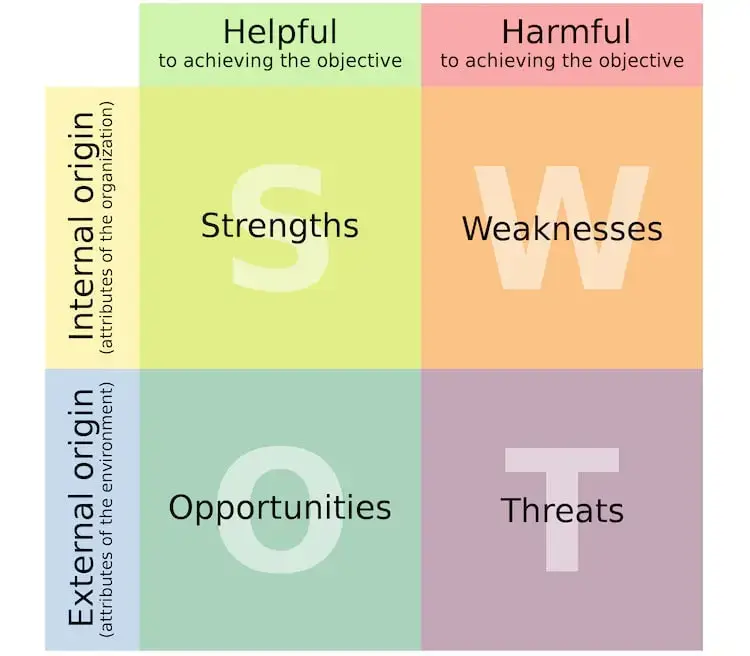
SWOT analysis is an excellent tool for business owners to help them understand their competitive landscape and make important business decisions. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. SWOT analysis is a practical strategic planning tool for businesses and it can be an effective problem-solving tool for your business.
Five Whys sometimes helps identify the root cause of the problem when it’s not clearly understood. You start by stating the problem as you understand it. Then you ask, “Why?” (For example, why is this occurring? ) As the tool’s name implies, you ask Why questions five times in total.
Brainwriting is a form of brainstorming where individuals generate ideas on their own before meeting to discuss them as a group. For a host of psychological reasons, this is often a superior way of approaching problem-solving in the workplace. Combining brainwriting with the Six Thinking Hats method can be even more powerful.

Using These Creative Problem-Solving Tools
All of the techniques and tools above represent creative problem-solving methods.
These examples illustrate that there are numerous pathways to get the answers we seek.
Some pathways, however, are more effective than others. The key is to experiment with various methods to uncover which ones work best for you .
Different methods will be more effective in different contexts.
Here, wisdom and intuition come into play. Over time, your connection with your inner guide improves and creative problem-solving becomes a more spontaneous process.
Recap: Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
Creative problem-solving is a skill based on the development of divergent thinking combined with altering our state of consciousness.
Due to our early conditioning, our “normal” waking state of consciousness is often filled with biases, limitations, blind spots, and negativity. This causes us to perceive problems rigidly.
When we get “stuck” it’s because our minds are fixed on a limited number of options.
To get “unstuck,” we just need to alter our state of consciousness and examine our problems from various perspectives, which is what the above creative problem-solving techniques are designed to do.
The more you play with these techniques, the more they become second nature to you.
You may find that each technique begins to play off the other. Then, the art and subtleties of the discovery process begin to emerge.
Enjoy solving your next problem!
How to Access Your Imagination
Peak Experiences: A Complete Guide
A Grounded Guide to Spiritual Guidance
About the Author
Scott Jeffrey is the founder of CEOsage, a self-leadership resource publishing in-depth guides read by millions of self-actualizing individuals. He writes about self-development, practical psychology, Eastern philosophy, and integrated practices. For 25 years, Scott was a business coach to high-performing entrepreneurs, CEOs, and best-selling authors. He's the author of four books including Creativity Revealed .
Learn more >
Some great ideas here. I am particularly intrigued by the "walk away" idea fulfilling the wanderer archetype. While counter intuitive, in my experience, walking away lets my mind develop subconcious connections that are sometimes the best. Sort of like letting my brain do the work instead of me! Bravo!
Todd Alexander
Thanks for your comments, Todd. It seems as though he need to train and remind ourselves to "walk away" because the mind thinks it can push its way through the problem.
How many times does it take for us to "absolutely know" that answers answer themselves when we take a break from forceful problem-solving and walk into the creative nature zone?! ;) The solution presents itself when we let go.
Great Post, Scott!
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips

- 01 Mar 2022
The importance of creativity in the workplace—particularly when problem-solving—is undeniable. Business leaders can’t approach new problems with old solutions and expect the same result.
This is where innovation-based processes need to guide problem-solving. Here’s an overview of what creative problem-solving is, along with tips on how to use it in conjunction with design thinking.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Encountering problems with no clear cause can be frustrating. This occurs when there’s disagreement around a defined problem or research yields unclear results. In such situations, creative problem-solving helps develop solutions, despite a lack of clarity.
While creative problem-solving is less structured than other forms of innovation, it encourages exploring open-ended ideas and shifting perspectives—thereby fostering innovation and easier adaptation in the workplace. It also works best when paired with other innovation-based processes, such as design thinking .
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Design thinking is a solutions-based mentality that encourages innovation and problem-solving. It’s guided by an iterative process that Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar outlines in four stages in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation :

- Clarify: This stage involves researching a problem through empathic observation and insights.
- Ideate: This stage focuses on generating ideas and asking open-ended questions based on observations made during the clarification stage.
- Develop: The development stage involves exploring possible solutions based on the ideas you generate. Experimentation and prototyping are both encouraged.
- Implement: The final stage is a culmination of the previous three. It involves finalizing a solution’s development and communicating its value to stakeholders.
Although user research is an essential first step in the design thinking process, there are times when it can’t identify a problem’s root cause. Creative problem-solving addresses this challenge by promoting the development of new perspectives.
Leveraging tools like design thinking and creativity at work can further your problem-solving abilities. Here are eight tips for doing so.

8 Creative Problem-Solving Tips
1. empathize with your audience.
A fundamental practice of design thinking’s clarify stage is empathy. Understanding your target audience can help you find creative and relevant solutions for their pain points through observing them and asking questions.
Practice empathy by paying attention to others’ needs and avoiding personal comparisons. The more you understand your audience, the more effective your solutions will be.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
If a problem is difficult to define, reframe it as a question rather than a statement. For example, instead of saying, "The problem is," try framing around a question like, "How might we?" Think creatively by shifting your focus from the problem to potential solutions.
Consider this hypothetical case study: You’re the owner of a local coffee shop trying to fill your tip jar. Approaching the situation with a problem-focused mindset frames this as: "We need to find a way to get customers to tip more." If you reframe this as a question, however, you can explore: "How might we make it easier for customers to tip?" When you shift your focus from the shop to the customer, you empathize with your audience. You can take this train of thought one step further and consider questions such as: "How might we provide a tipping method for customers who don't carry cash?"
Whether you work at a coffee shop, a startup, or a Fortune 500 company, reframing can help surface creative solutions to problems that are difficult to define.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
If you encounter an idea that seems outlandish or unreasonable, a natural response would be to reject it. This instant judgment impedes creativity. Even if ideas seem implausible, they can play a huge part in ideation. It's important to permit the exploration of original ideas.
While judgment can be perceived as negative, it’s crucial to avoid accepting ideas too quickly. If you love an idea, don’t immediately pursue it. Give equal consideration to each proposal and build on different concepts instead of acting on them immediately.
4. Overcome Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind that prevents you from recognizing a situation’s alternative solutions or interpretations instead of considering every situation through the lens of past experiences.
Although it's efficient in the short-term, cognitive fixedness interferes with creative thinking because it prevents you from approaching situations unbiased. It's important to be aware of this tendency so you can avoid it.
5. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
One of the key principles of creative problem-solving is the balance of divergent and convergent thinking. Divergent thinking is the process of brainstorming multiple ideas without limitation; open-ended creativity is encouraged. It’s an effective tool for generating ideas, but not every idea can be explored. Divergent thinking eventually needs to be grounded in reality.
Convergent thinking, on the other hand, is the process of narrowing ideas down into a few options. While converging ideas too quickly stifles creativity, it’s an important step that bridges the gap between ideation and development. It's important to strike a healthy balance between both to allow for the ideation and exploration of creative ideas.
6. Use Creative Tools
Using creative tools is another way to foster innovation. Without a clear cause for a problem, such tools can help you avoid cognitive fixedness and abrupt decision-making. Here are several examples:
Problem Stories
Creating a problem story requires identifying undesired phenomena (UDP) and taking note of events that precede and result from them. The goal is to reframe the situations to visualize their cause and effect.
To start, identify a UDP. Then, discover what events led to it. Observe and ask questions of your consumer base to determine the UDP’s cause.
Next, identify why the UDP is a problem. What effect does the UDP have that necessitates changing the status quo? It's helpful to visualize each event in boxes adjacent to one another when answering such questions.
The problem story can be extended in either direction, as long as there are additional cause-and-effect relationships. Once complete, focus on breaking the chains connecting two subsequent events by disrupting the cause-and-effect relationship between them.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool encourages you to consider how people from different backgrounds would approach similar situations. For instance, how would someone in hospitality versus manufacturing approach the same problem? This tool isn't intended to instantly solve problems but, rather, to encourage idea generation and creativity.
7. Use Positive Language
It's vital to maintain a positive mindset when problem-solving and avoid negative words that interfere with creativity. Positive language prevents quick judgments and overcomes cognitive fixedness. Instead of "no, but," use words like "yes, and."
Positive language makes others feel heard and valued rather than shut down. This practice doesn’t necessitate agreeing with every idea but instead approaching each from a positive perspective.
Using “yes, and” as a tool for further idea exploration is also effective. If someone presents an idea, build upon it using “yes, and.” What additional features could improve it? How could it benefit consumers beyond its intended purpose?
While it may not seem essential, this small adjustment can make a big difference in encouraging creativity.
8. Practice Design Thinking
Practicing design thinking can make you a more creative problem-solver. While commonly associated with the workplace, adopting a design thinking mentality can also improve your everyday life. Here are several ways you can practice design thinking:
- Learn from others: There are many examples of design thinking in business . Review case studies to learn from others’ successes, research problems companies haven't addressed, and consider alternative solutions using the design thinking process.
- Approach everyday problems with a design thinking mentality: One of the best ways to practice design thinking is to apply it to your daily life. Approach everyday problems using design thinking’s four-stage framework to uncover what solutions it yields.
- Study design thinking: While learning design thinking independently is a great place to start, taking an online course can offer more insight and practical experience. The right course can teach you important skills , increase your marketability, and provide valuable networking opportunities.

Ready to Become a Creative Problem-Solver?
Though creativity comes naturally to some, it's an acquired skill for many. Regardless of which category you're in, improving your ability to innovate is a valuable endeavor. Whether you want to bolster your creativity or expand your professional skill set, taking an innovation-based course can enhance your problem-solving.
If you're ready to become a more creative problem-solver, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses . If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist.
Thankfully, there are many creative problem-solving techniques for resolving this tension and revealing new solutions. In this guide, we’ll explore 12 creative ways to solve problems with a variety of techniques, tools, and methods that be used for personal use and in the workplace.
Creative problem-solving techniques can help you to overcome difficult challenges and unlock your inner genius. By exploring a variety of different techniques, such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and the SCAMPER method, you can approach problems from new angles and discover innovative solutions.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving? Encountering problems with no clear cause can be frustrating. This occurs when there’s disagreement around a defined problem or research yields unclear results. In such situations, creative problem-solving helps develop solutions, despite a lack of clarity.
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of solving problems or identifying opportunities when conventional thinking has failed. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals.
Creative Problem Solving is a proven method for approaching a problem or. challenge in an imaginative and innovative way. It’s a process that helps people re-define the problems they think they face, come up with breakthrough ideas and then take action on these new ideas all with the same innovative spirit.