

How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research Papers

Introduction
What is the results section of a research paper, what's the difference between the results section and the discussion section, what's the difference between results and findings, how do you report research findings, strategies for writing the findings section.
The results section of a research paper is where the research audience learns the outcomes of a study and it lays the groundwork for establishing the research's contribution to scientific knowledge. The challenge in qualitative research , however, is comprehensively yet concisely presenting the specific aspects of key findings. When the salient points of your qualitative data analysis cannot be easily reduced to tables and figures alone, how do you present the main findings in a way that persuades your research audience?
This article provides a comprehensive explanation of what constitutes a results or findings section in a paper to offer guidance for those who may be inexperienced writing research papers . This article outlines the place of a findings section in a research paper, and the different strategies employed when writing a findings section to reduce complex information down to a concise overview of a research study.

Most research papers follow a logical sequence to report on the various aspects of a study, from the introduction section to the discussion. This sequence outlines the research problem underpinning the study itself, then the methods employed and data collected, followed by a description of the analysis or organization of that data into a meaningful form that addresses the study's research questions .
From this description, the researcher presents the findings or results of this data analysis . The findings section illustrates and explains the key details or insights that the researcher identifies from the study. It is these findings that form the basis of the discussion that details the main takeaways of the research.
In other words, while other sections of a particular paper discuss the study's theoretical developments and contributions to scientific knowledge, the findings section lays out the evidentiary warrants that support those developments. Without this evidence, a research paper runs the risk of presenting unsupported opinions about theory and research.
The results section should show the key findings that you have identified from your data analysis , while the discussion section highlights how those findings address the research questions in your study. The discussion section is where the key theoretical developments and potential applications to real-world practice are proposed, but the findings provide the evidence that supports the proposals in the research paper .
In this sense, the presentation of your findings should focus primarily, if not exclusively, on what the data means based on the analysis you use to interpret the data . The implications of such data are best left to the discussion section.
As you collect articles for your literature review , you might notice that some papers have a results section while others have a findings section. In broad terms, there is no major difference as both sections typically follow the methods section of a research paper . Essentially, results or findings are what come as a result of analyzing raw data generated from the study in order to answer a research question .
However, the use of one term over another is sometimes field-specific or method-specific. Research results often come from experimental or quantitative data , both of which come with expectations of objective predictability. Such results are presented in tables and figures and then interpreted by the authors in prose to set up the argument for the significance of the research.
Research findings, on the other hand, are associated with phenomena that are observed. In naturalistic inquiry, research methods such as ethnography and document analysis seldom, if ever, produce predictable and ordered results. Rather, they sample what is found in the real world and provide the basis for a report on what occurred in a given research setting.
Imagine a simple experiment where one plant is given water while a similar plant is given fertilizer and water. The results would describe the differences in the rate of growth between these two plants in a manner that guides recommendations about how to grow plants. With rare or unforeseen exceptions, these results are meant to be predictable and suggest a logical sequence that leads to successful plant growth.
In contrast, think about how an education research project, for example, might collect data through observations and interviews . This data might provide findings about how a teacher can be successful in connecting with their students to promote learning. Note that these findings do not guarantee the same results in other settings, given the situated nature of classroom teaching and learning and the potential differences between teachers and students. They only suggest a potential relationship between what a teacher does and how their students might benefit as a result.
Understanding this difference thus makes it easier to see where you will find a results section and where you will find a findings section. The physical and natural sciences, where you are more likely to find experimental studies and statistical analyses, expect results that are ordered and predictable. Researchers in the social sciences and humanities, where ethnographic research, interviews, and focus groups are more common, will opt for findings over results.
What are key findings?
Those who are skilled writing research papers understand the task of choosing the most relevant results from the raw data while presenting the research in a transparent manner. In research disciplines that rely on qualitative research methods, it's impossible to present all of the data collected from even a single study. When interview transcripts or field notes can run into dozens of pages, writers are faced with the challenge of choosing which segments of data should be represented in a findings section.
These segments of data are meant to explain and support the study's key themes or findings. In data coding and data analysis, a successful researcher has the responsibility of sorting through the data and separating the key findings from the whole body of data.

Do more with your data with ATLAS.ti
Cutting-edge artificial intelligence tools support crafting insightful research from your data. Try it out with a free trial.
Reporting research findings in a journal-style scientific paper is a matter of choosing the most relevant results organized in a way that sets up the ensuing discussion. This is a challenge with qualitative data that is unstructured in nature and vast in scope.
When dealing with large amounts of data, along with the word limits found in academic writing, there are a number of accepted practices that qualitative researchers employ to present their findings in a meaningful way.
Most qualitative studies rely on the coding of raw data. By annotating the data with short but descriptive keywords or key phrases, a researcher can provide structure to the data to identify key themes and patterns relevant to the research question at hand. Presenting these codes in your findings is thus a matter of describing those themes and detailing how the data highlights those themes.
Depending on your research questions, detailing your codebook in a findings section can be a matter of, among other things, showing the most prevalent codes or the patterns of codes as applied to the data. After you have coded your data and grouped codes according to themes, you can conduct a thematic analysis to determine the most prevalent themes to describe the aspects of the concept or phenomenon you're analyzing. Methods such as discourse analysis and narrative analysis also look at the combinations or sequences of codes to generate useful findings. In that case, qualitative data analysis software can help researchers determine the prevalence of such patterns, providing evidence for the assertions about the data collected.
Researchers rely on tables and visualizations such as heat maps and Sankey diagrams to summarize an analysis of codes in a findings section. These figures are often followed by a systematic description of the themes and patterns in the data and what meanings they point out to help address the study's research questions.
Data that comes directly from research participants can oftentimes be more powerful than the researcher's descriptions of that data. If your research paper includes data generated from observations or interviews , then excerpts of that data can prove more persuasive as evidence given its authentic nature. For example, in a presentation of an interview study where researchers are given open access, nursing research and its insights can be made more credible when the perspectives and opinions of nursing practitioners are directly presented to the research audience.
Field notes can also be presented in findings as data that supports the critical insights of the study. Ethnographic research can produce useful observations documented at the time of data collection that can provide a basis for reflection in the findings section. In either case, excerpts of qualitative data in a findings section are often followed by the researcher's descriptions of those excerpts and the rationale for why they serve as useful evidence supporting the study's claims.
Anthropological and sociological research often relies on the storytelling aspects of academic writing. It can be a significant challenge to capture an entire culture or social practice in a single segment of data or even a set of separate themes. In such cases, past-tense narratives can convey a holistic sense of the qualitative data to allow readers to immerse themselves in the culture that was observed.
The important point about writing narratives in a paper is that they should describe the salient parts of the data that address the research questions in addition to the context that helps the research audience understand the main findings. When constructing a narrative, it can become easy to lead the audience on a series of tangents that can prove confusing or unhelpful. You can craft a powerful narrative that contributes to scientific knowledge as long as it provides the necessary evidence for your claims while leaving out aspects that can turn out to be irrelevant to your research inquiry.
Figures and tables
To be clear, the findings section in a qualitative research paper cannot easily be reduced to a series of simple data visualizations alone, especially in research fields that depend on narratives to convey the important findings of a study. That said, overlooking the visual elements of a paper, particularly in social science research, can limit opportunities in highlighting evidentiary warrants supporting your claims.
Visualizations include networks, word clouds, heat maps, flowcharts, and Sankey diagrams, among others, all of which can restructure raw data in a form that your research audience can quickly and easily understand. Tables are also included in this discussion as they help to reduce large amounts of qualitative data into compact summaries. Even in social science disciplines that rely heavily on qualitative methods and naturalistic inquiry, statistical analyses and presentations of frequencies can serve a useful purpose in understanding patterns and tendencies. The common thread across all of these visualizations is that they complement the prose or written descriptions of your key findings.
A successful presentation of the main findings should set the stage for an engaging discussion section where readers become convinced of the main takeaways of the research. Where discussion sections are about persuasion, findings provide the necessary evidentiary warrants that ultimately make the arguments in the discussion persuasive.
With this in mind, there are a number of broad strategies to consider when presenting your findings.
Adopt the style of the field
Every research field has their own particular style for highlighting the salient points of a study. Research in economics will focus on statistics, relying on tables and figures to make important assertions about the meaning of the raw data . Cultural anthropology, on the other hand, seldom captures statistical data, opting instead for narratives and artifacts to get at the essence of a culture or community. Other fields have their own unique circumstances that dictate the accepted writing practices among researchers in each discipline.
As a result, you will benefit from reading research similar to the study you want to present, not merely for the findings they highlight but also the style in which they present those findings. Matching the tone and style of similar scholars in your field will resonate with your peer reviewers and eventually your research audience.
Provide the necessary context
Every scientific discipline requires the researcher to describe their research setting, the data or resources they are studying, and the means through which they study them. This task is especially challenging within the social sciences as researchers observe some social phenomenon in some social setting, neither of which is perfectly replicable.
As a result, reporting background information necessary to understanding a segment of data is important to persuading your research audience of the salience and relevance of your findings. Whether you're presenting narratives or packaging qualitative data in excerpts or tables, you will still need to describe the context surrounding your data in prose to make the findings accessible to your research audience.
Establish research transparency
Beginning researchers may make the mistake of only presenting the good points of their findings, ignoring negative results from their own research while overemphasizing data that demonstrates promising trends but may not show the entire picture of the phenomenon being studied. Because of this, readers of research may be skeptical of unsupported claims. By extension, they may also look for all of the potential aspects that influence a concept or phenomenon which might confound or contextualize the claims made in the findings.
Transparency is thus an important part of the research writing process, demanding that researchers qualify their findings with important caveats worth considering. These caveats will often be found in the discussion section, where limitations of the study are outlined. However, describing contextual details in the findings can help your research audience assess the persuasive power of the evidentiary warrants you are using to support your claims.
Write clearly and consistently
Scientific theory, even in the social sciences, often employs specific jargon and technical terms. The background and discussion sections, where theory is the main focus, will often employ field-specific language that may not be accessible to researchers unfamiliar with the field. A compelling findings section, on the other hand, requires the researcher to make the findings easily understood by their research audience.
Oftentimes, this means using clear language that is accessible to readers of research who may not have a specific expertise but general interest in the topic you are studying. As a result, be sure to limit the technical or theoretical language you employ in the findings section to only what is necessary. Doing so can ground the readers in a clear understanding of the data, making for a more engaging discussion section that is more credible with its claims more readily acceptable as scientific knowledge.

Powerful data analysis starts with ATLAS.ti
Organize data files and employ powerful tools for critical insights all in one project. See how with a free trial.

- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
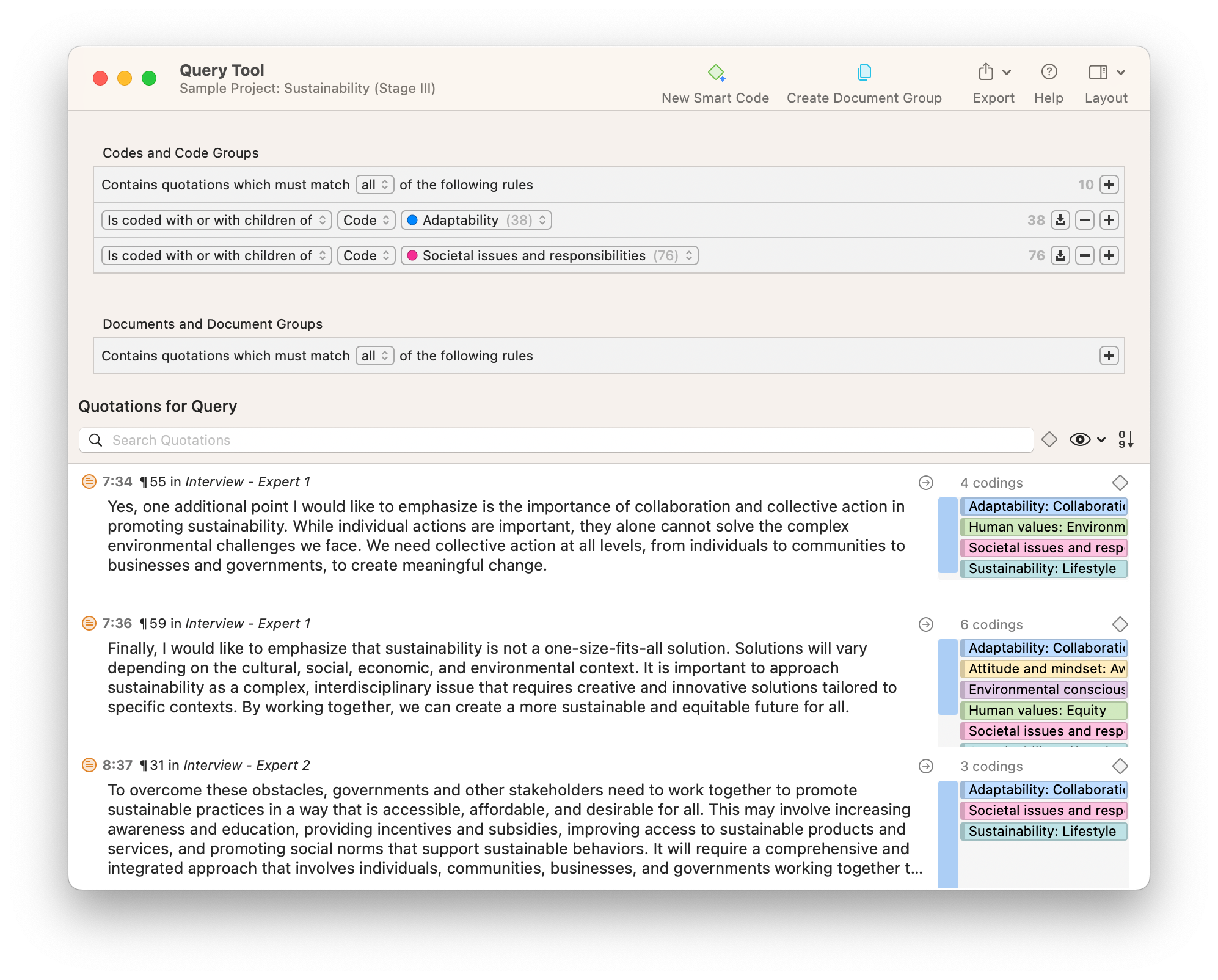
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
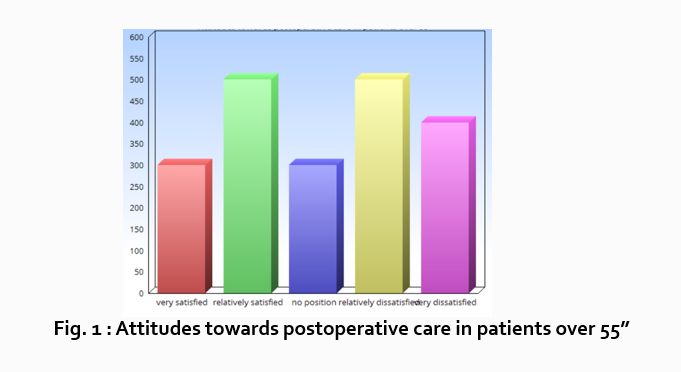
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
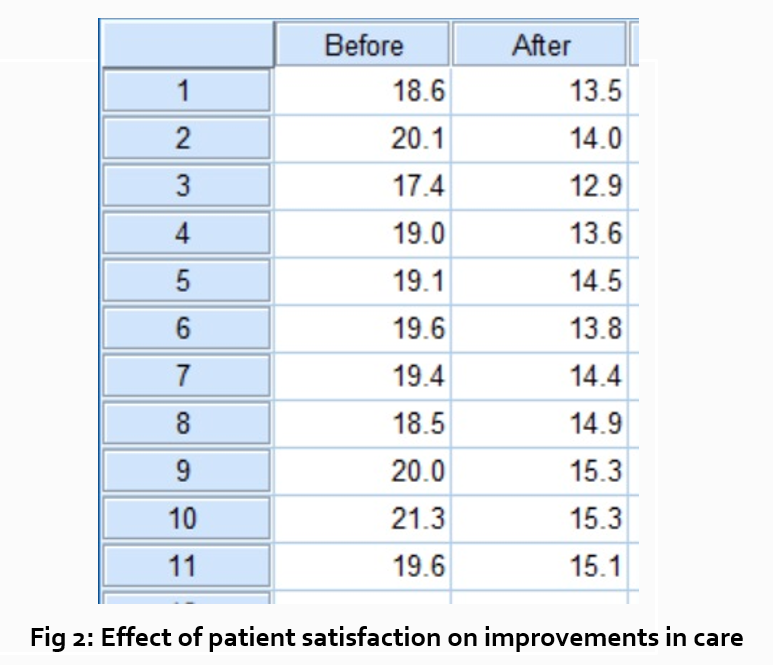
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
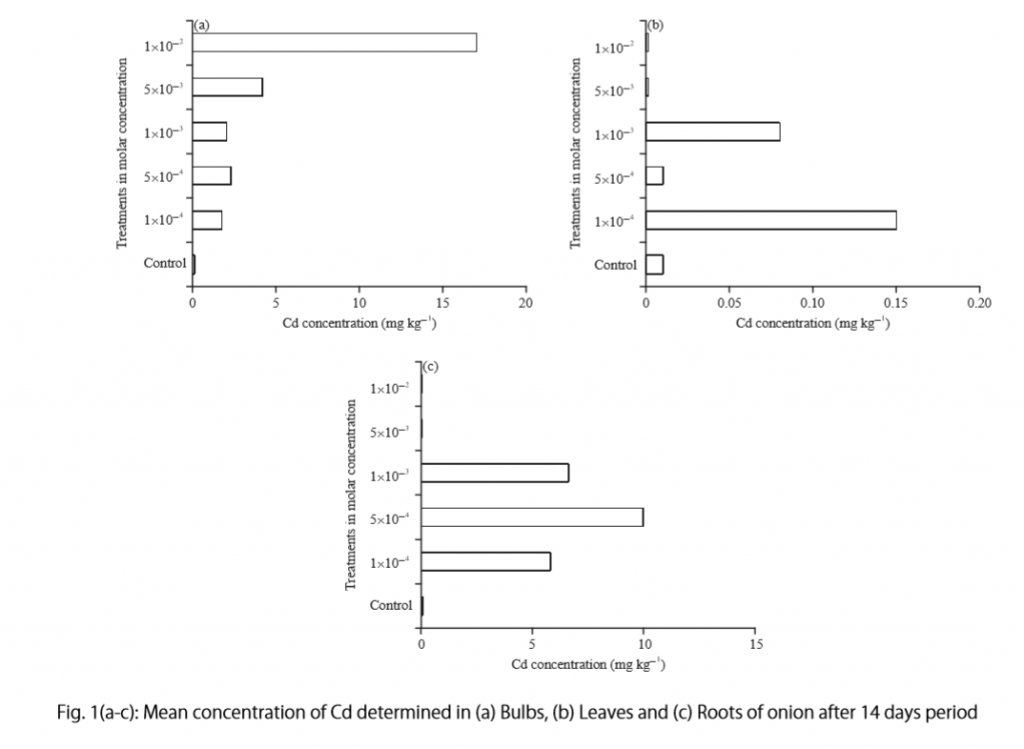
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

How to Write the Results Section: Guide to Structure and Key Points
- 4 minute read
- 86.6K views
Table of Contents
The ‘ Results’ section of a research paper, like the ‘Introduction’ and other key parts, attracts significant attention from editors, reviewers, and readers. The reason lies in its critical role — that of revealing the key findings of a study and demonstrating how your research fills a knowledge gap in your field of study. Given its importance, crafting a clear and logically structured results section is essential.
In this article, we will discuss the key elements of an effective results section and share strategies for making it concise and engaging. We hope this guide will help you quickly grasp ways of writing the results section, avoid common pitfalls, and make your writing process more efficient and effective.
Structure of the results section
Briefly restate the research topic in the introduction : Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to list the notable findings of a study, it is customary to start with a brief repetition of the research question. This helps refocus the reader, allowing them to better appreciate the relevance of the findings. Additionally, restating the research question establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper, creating a smoother flow of information.
Systematically present your research findings : Address the primary research question first, followed by the secondary research questions. If your research addresses multiple questions, mention the findings related to each one individually to ensure clarity and coherence.
Represent your results visually: Graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results. As a rule of thumb, use a visual medium like a graph or a table if you wish to present three or more statistical values simultaneously.
Graphical or tabular representations of data can also make your results section more visually appealing. Remember, an appealing and well-organized results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective ‘Results’ section
- Always use simple and plain language. Avoid the use of uncertain or unclear expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings , it is best to avoid over-interpreting the results. In addition, avoid using subjective or emotional words , such as “interestingly” or “unfortunately”, to describe the results as this may cause readers to doubt the objectivity of the paper.
- The content balances simplicity with comprehensiveness . For statistical data, simply describe the relevant tests and explain their results without mentioning raw data. If the study involves multiple hypotheses, describe the results for each one separately to avoid confusion and aid understanding. To enhance credibility, e nsure that negative results , if any, are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to highlight the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey ¹ .
Difference between data, results, and discussion sections
Data , results, and discussion sections all communicate the findings of a study, but each serves a distinct purpose with varying levels of interpretation.
In the results section , one cannot provide data without interpreting its relevance or make statements without citing data ² . In a sense, the results section does not draw connections between different data points. Therefore, there is a certain level of interpretation involved in drawing results out of data.

(The example is intended to showcase how the visual elements and text in the results section complement each other ³ . The academic viewpoints included in the illustrative screenshots should not be used as references.)
The discussion section allows authors even more interpretive freedom compared to the results section. Here, data and patterns within the data are compared with the findings from other studies to make more generalized points. Unlike the results section , which focuses purely on factual data, the discussion section touches upon hypothetical information, drawing conjectures and suggesting future directions for research.
The ‘ Results’ section serves as the core of a research paper, capturing readers’ attention and providing insights into the study’s essence. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section can generate interest in your research. By following the tips outlined here, you can create a results section that effectively communicates your finding and invites further exploration. Remember, clarity is the key, and with the right approach, your results section can guide readers through the intricacies of your research.
Professionals at Elsevier Language Services know the secret to writing a well-balanced results section. With their expert suggestions, you can ensure that your findings come across clearly to the reader. To maximize your chances of publication, reach out to Elsevier Language Services today !
Type in wordcount for Standard Total: USD EUR JPY Follow this link if your manuscript is longer than 12,000 words. Upload
Reference
- Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific manuscript. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2005.07.002
- Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Zadeh-Vakili, A., Hosseinpanah, F., & Ghasemi, A. (2019). The Principles of Biomedical Scientific Writing: Results. International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism/International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism., In Press (In Press). https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.92113
- Guo, J., Wang, J., Zhang, P., Wen, P., Zhang, S., Dong, X., & Dong, J. (2024). TRIM6 promotes glioma malignant progression by enhancing FOXO3A ubiquitination and degradation. Translational Oncology, 46, 101999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2024.101999

Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Submission 101: What format should be used for academic papers?

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!


A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

How to Write the Dissertation Findings or Results – Tips
Published by Grace Graffin at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On August 13, 2024
Each part of the dissertation is unique, and some general and specific rules must be followed. The dissertation’s findings section presents the key results of your research without interpreting their meaning .
Theoretically, this is an exciting section of a dissertation because it involves writing what you have observed and found. However, it can be a little tricky if there is too much information to confuse the readers.
The goal is to include only the essential and relevant findings in this section. The results must be presented in an orderly sequence to provide clarity to the readers.
This section of the dissertation should be easy for the readers to follow, so you should avoid going into a lengthy debate over the interpretation of the results.
It is vitally important to focus only on clear and precise observations. The findings chapter of the dissertation is theoretically the easiest to write.
It includes statistical analysis and a brief write-up about whether or not the results emerging from the analysis are significant. This segment should be written in the past sentence as you describe what you have done in the past.
This article will provide detailed information about how to write the findings of a dissertation .
When to Write Dissertation Findings Chapter
As soon as you have gathered and analysed your data, you can start to write up the findings chapter of your dissertation paper. Remember that it is your chance to report the most notable findings of your research work and relate them to the research hypothesis or research questions set out in the introduction chapter of the dissertation .
You will be required to separately report your study’s findings before moving on to the discussion chapter if your dissertation is based on the collection of primary data or experimental work.
However, you may not be required to have an independent findings chapter if your dissertation is purely descriptive and focuses on the analysis of case studies or interpretation of texts.
- Always report the findings of your research in the past tense.
- The dissertation findings chapter varies from one project to another, depending on the data collected and analyzed.
- Avoid reporting results that are not relevant to your research questions or research hypothesis.
Does your Dissertation Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of the Dissertation strong.

1. Reporting Quantitative Findings
The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or questions you intend to address as part of your dissertation project.
Report the relevant findings for each research question or hypothesis, focusing on how you analyzed them.
Analysis of your findings will help you determine how they relate to the different research questions and whether they support the hypothesis you formulated.
While you must highlight meaningful relationships, variances, and tendencies, it is important not to guess their interpretations and implications because this is something to save for the discussion and conclusion chapters.
Any findings not directly relevant to your research questions or explanations concerning the data collection process should be added to the dissertation paper’s appendix section.
Use of Figures and Tables in Dissertation Findings
Suppose your dissertation is based on quantitative research. In that case, it is important to include charts, graphs, tables, and other visual elements to help your readers understand the emerging trends and relationships in your findings.
Repeating information will give the impression that you are short on ideas. Refer to all charts, illustrations, and tables in your writing but avoid recurrence.
The text should be used only to elaborate and summarize certain parts of your results. On the other hand, illustrations and tables are used to present multifaceted data.
It is recommended to give descriptive labels and captions to all illustrations used so the readers can figure out what each refers to.
How to Report Quantitative Findings
Here is an example of how to report quantitative results in your dissertation findings chapter;
Two hundred seventeen participants completed both the pretest and post-test and a Pairwise T-test was used for the analysis. The quantitative data analysis reveals a statistically significant difference between the mean scores of the pretest and posttest scales from the Teachers Discovering Computers course. The pretest mean was 29.00 with a standard deviation of 7.65, while the posttest mean was 26.50 with a standard deviation of 9.74 (Table 1). These results yield a significance level of .000, indicating a strong treatment effect (see Table 3). With the correlation between the scores being .448, the little relationship is seen between the pretest and posttest scores (Table 2). This leads the researcher to conclude that the impact of the course on the educators’ perception and integration of technology into the curriculum is dramatic.
Paired Samples
Paired samples correlation, paired samples test.
Also Read: How to Write the Abstract for the Dissertation.
2. Reporting Qualitative Findings
A notable issue with reporting qualitative findings is that not all results directly relate to your research questions or hypothesis.
The best way to present the results of qualitative research is to frame your findings around the most critical areas or themes you obtained after you examined the data.
In-depth data analysis will help you observe what the data shows for each theme. Any developments, relationships, patterns, and independent responses directly relevant to your research question or hypothesis should be mentioned to the readers.
Additional information not directly relevant to your research can be included in the appendix .
How to Report Qualitative Findings
Here is an example of how to report qualitative results in your dissertation findings chapter;
The last question of the interview focused on the need for improvement in Thai ready-to-eat products and the industry at large, emphasizing the need for enhancement in the current products being offered in the market. When asked if there was any particular need for Thai ready-to-eat meals to be improved and how to improve them in case of ‘yes,’ the males replied mainly by saying that the current products need improvement in terms of the use of healthier raw materials and preservatives or additives. There was an agreement amongst all males concerning the need to improve the industry for ready-to-eat meals and the use of more healthy items to prepare such meals. The females were also of the opinion that the fast-food items needed to be improved in the sense that more healthy raw materials such as vegetable oil and unsaturated fats, including whole-wheat products, to overcome risks associated with trans fat leading to obesity and hypertension should be used for the production of RTE products. The frozen RTE meals and packaged snacks included many preservatives and chemical-based flavouring enhancers that harmed human health and needed to be reduced. The industry is said to be aware of this fact and should try to produce RTE products that benefit the community in terms of healthy consumption.
Looking for dissertation help?
Research prospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

What to Avoid in Dissertation Findings Chapter
- Avoid using interpretive and subjective phrases and terms such as “confirms,” “reveals,” “suggests,” or “validates.” These terms are more suitable for the discussion chapter , where you will be expected to interpret the results in detail.
- Only briefly explain findings in relation to the key themes, hypothesis, and research questions. You don’t want to write a detailed subjective explanation for any research questions at this stage.
The Do’s of Writing the Findings or Results Section
- Ensure you are not presenting results from other research studies in your findings.
- Observe whether or not your hypothesis is tested or research questions answered.
- Illustrations and tables present data and are labelled to help your readers understand what they relate to.
- Use software such as Excel, STATA, and SPSS to analyse results and important trends.
Essential Guidelines on How to Write Dissertation Findings
The dissertation findings chapter should provide the context for understanding the results. The research problem should be repeated, and the research goals should be stated briefly.
This approach helps to gain the reader’s attention toward the research problem. The first step towards writing the findings is identifying which results will be presented in this section.
The results relevant to the questions must be presented, considering whether the results support the hypothesis. You do not need to include every result in the findings section. The next step is ensuring the data can be appropriately organized and accurate.
You will need to have a basic idea about writing the findings of a dissertation because this will provide you with the knowledge to arrange the data chronologically.
Start each paragraph by writing about the most important results and concluding the section with the most negligible actual results.
A short paragraph can conclude the findings section, summarising the findings so readers will remember as they transition to the next chapter. This is essential if findings are unexpected or unfamiliar or impact the study.
Our writers can help you with all parts of your dissertation, including statistical analysis of your results . To obtain free non-binding quotes, please complete our online quote form here .
Be Impartial in your Writing
When crafting your findings, knowing how you will organize the work is important. The findings are the story that needs to be told in response to the research questions that have been answered.
Therefore, the story needs to be organized to make sense to you and the reader. The findings must be compelling and responsive to be linked to the research questions being answered.
Always ensure that the size and direction of any changes, including percentage change, can be mentioned in the section. The details of p values or confidence intervals and limits should be included.
The findings sections only have the relevant parts of the primary evidence mentioned. Still, it is a good practice to include all the primary evidence in an appendix that can be referred to later.
The results should always be written neutrally without speculation or implication. The statement of the results mustn’t have any form of evaluation or interpretation.
Negative results should be added in the findings section because they validate the results and provide high neutrality levels.
The length of the dissertation findings chapter is an important question that must be addressed. It should be noted that the length of the section is directly related to the total word count of your dissertation paper.
The writer should use their discretion in deciding the length of the findings section or refer to the dissertation handbook or structure guidelines.
It should neither belong nor be short nor concise and comprehensive to highlight the reader’s main findings.
Ethically, you should be confident in the findings and provide counter-evidence. Anything that does not have sufficient evidence should be discarded. The findings should respond to the problem presented and provide a solution to those questions.
Structure of the Findings Chapter
The chapter should use appropriate words and phrases to present the results to the readers. Logical sentences should be used, while paragraphs should be linked to produce cohesive work.
You must ensure all the significant results have been added in the section. Recheck after completing the section to ensure no mistakes have been made.
The structure of the findings section is something you may have to be sure of primarily because it will provide the basis for your research work and ensure that the discussions section can be written clearly and proficiently.
One way to arrange the results is to provide a brief synopsis and then explain the essential findings. However, there should be no speculation or explanation of the results, as this will be done in the discussion section.
Another way to arrange the section is to present and explain a result. This can be done for all the results while the section is concluded with an overall synopsis.
This is the preferred method when you are writing more extended dissertations. It can be helpful when multiple results are equally significant. A brief conclusion should be written to link all the results and transition to the discussion section.
Numerous data analysis dissertation examples are available on the Internet, which will help you improve your understanding of writing the dissertation’s findings.
Problems to Avoid When Writing Dissertation Findings
One of the problems to avoid while writing the dissertation findings is reporting background information or explaining the findings. This should be done in the introduction section .
You can always revise the introduction chapter based on the data you have collected if that seems an appropriate thing to do.
Raw data or intermediate calculations should not be added in the findings section. Always ask your professor if raw data needs to be included.
If the data is to be included, then use an appendix or a set of appendices referred to in the text of the findings chapter.
Do not use vague or non-specific phrases in the findings section. It is important to be factual and concise for the reader’s benefit.
The findings section presents the crucial data collected during the research process. It should be presented concisely and clearly to the reader. There should be no interpretation, speculation, or analysis of the data.
The significant results should be categorized systematically with the text used with charts, figures, and tables. Furthermore, avoiding using vague and non-specific words in this section is essential.
It is essential to label the tables and visual material properly. You should also check and proofread the section to avoid mistakes.
The dissertation findings chapter is a critical part of your overall dissertation paper. If you struggle with presenting your results and statistical analysis, our expert dissertation writers can help you get things right. Whether you need help with the entire dissertation paper or individual chapters, our dissertation experts can provide customized dissertation support .
FAQs About Findings of a Dissertation
How do i report quantitative findings.
The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or research questions you intended to address as part of your dissertation project. Report the relevant findings for each of the research questions or hypotheses, focusing on how you analyzed them.
How do I report qualitative findings?
The best way to present the qualitative research results is to frame your findings around the most important areas or themes that you obtained after examining the data.
An in-depth analysis of the data will help you observe what the data is showing for each theme. Any developments, relationships, patterns, and independent responses that are directly relevant to your research question or hypothesis should be clearly mentioned for the readers.
Can I use interpretive phrases like ‘it confirms’ in the finding chapter?
No, It is highly advisable to avoid using interpretive and subjective phrases in the finding chapter. These terms are more suitable for the discussion chapter , where you will be expected to provide your interpretation of the results in detail.
Can I report the results from other research papers in my findings chapter?
NO, you must not be presenting results from other research studies in your findings.
You May Also Like
Anyone who supports you in your research should be acknowledged in dissertation acknowledgments. Learn more on how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
Dissertation conclusion is perhaps the most underrated part of a dissertation or thesis paper. Learn how to write a dissertation conclusion.
When writing your dissertation, an abstract serves as a deal maker or breaker. It can either motivate your readers to continue reading or discourage them.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself …
Research findings refer to the results obtained from a study or investigation conducted through a systematic and scientific approach. These findings are the outcomes of …
The results section should show the key findings that you have identified from your data analysis, while the discussion section highlights how those findings address the research questions in …
The Results/Findings section of a scientific research paper presents the core findings of a study derived from the methods. Examples & tips.
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are …
Technically or academically speaking, ‘findings’ seems to be used more for qualitative studies whereas ‘results’ seems to be used more for quantitative studies. For example, in a behavioral study, you may say ‘ It was …
Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section can generate interest in your research. By following the tips outlined here, you can create a results section that effectively communicates your finding and …
The dissertation’s findings section presents the key results of your research without interpreting their meaning. Theoretically, this is an exciting section of a dissertation because it involves writing what you have observed …