- Skip to Content
- Bulletin Home

- Degree Charts >
- Mathematics (PhD)
- Around Campus
- Academic Program
- Administration
- Arts at MIT
- Campus Media
- Fraternities, Sororities, and Independent Living Groups
- Health Services
- Priscilla King Gray Public Service Center
- Religious Organizations
- Student Government
- Work-Life and Family Resources
- Advising and Support
- Digital Learning
- Disability and Access Services
- Information Systems and Technology
- Student Financial Services
- Writing and Communication Center
- Major Course of Study
- General Institute Requirements
- Independent Activites Period
- Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program
- First-Year Advising Seminars
- Interphase EDGE/x
- Edgerton Center
- Grading Options
- Study at Other Universities
- Internships Abroad
- Career Advising and Professional Development
- Teacher Licensure and Education
- ROTC Programs
- Financial Aid
- Medical Requirements
- Graduate Study at MIT
- General Degree Requirements
- Other Institutions
- Registration
- Term Regulations and Examination Policies
- Academic Performance and Grades
- Policies and Procedures
- Privacy of Student Records
- Abdul Latif Jameel Clinic for Machine Learning in Health
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab
- Art, Culture, and Technology Program
- Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard
- Center for Bits and Atoms
- Center for Clinical and Translational Research
- Center for Collective Intelligence
- Center for Computational Science and Engineering
- Center for Constructive Communication
- Center for Energy and Environmental Policy Research
- Center for Environmental Health Sciences
- Center for Global Change Science
- Center for International Studies
- Center for Real Estate
- Center for Transportation & Logistics
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Concrete Sustainability Hub
- D-Lab
- Deshpande Center for Technological Innovation
- Division of Comparative Medicine
- Haystack Observatory
- Initiative on the Digital Economy
- Institute for Medical Engineering and Science
- Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies
- Institute for Work and Employment Research
- Internet Policy Research Initiative
- Joint Program on the Science and Policy of Global Change
- Knight Science Journalism Program
- Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research
- Laboratory for Financial Engineering
- Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems
- Laboratory for Manufacturing and Productivity
- Laboratory for Nuclear Science
- Legatum Center for Development and Entrepreneurship
- Lincoln Laboratory
- Martin Trust Center for MIT Entrepreneurship
- Materials Research Laboratory
- McGovern Institute for Brain Research
- Microsystems Technology Laboratories
- MIT Center for Art, Science & Technology
- MIT Energy Initiative
- MIT Environmental Solutions Initiative
- MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research
- MIT Media Lab
- MIT Office of Innovation
- MIT Open Learning
- MIT Portugal Program
- MIT Professional Education
- MIT Sea Grant College Program
- Nuclear Reactor Laboratory
- Operations Research Center
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Plasma Science and Fusion Center
- Research Laboratory of Electronics
- Simons Center for the Social Brain
- Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology Centre
- Sociotechnical Systems Research Center
- Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
- Women's and Gender Studies Program
- Architecture (SB, Course 4)
- Architecture (MArch)
- Art and Design (SB, Course 4-B)
- Art, Culture, and Technology (SM)
- Architecture Studies (SMArchS)
- Media Arts and Sciences
- Planning (SB, Course 11)
- Urban Science and Planning with Computer Science (SB, Course 11-6)
- Aeronautics and Astronautics Fields (PhD)
- Aerospace Engineering (SB, Course 16)
- Engineering (SB, Course 16-ENG)
- Biological Engineering (SB, Course 20)
- Biological Engineering (PhD)
- Chemical Engineering (Course 10)
- Chemical-Biological Engineering (Course 10-B)
- Chemical Engineering (Course 10-C)
- Engineering (Course 10-ENG)
- Engineering (Course 1-ENG)
- Computation and Cognition (Course 6-9)
- Computer Science and Engineering (Course 6-3)
- Computer Science and Molecular Biology (Course 6-7)
- Electrical Engineering with Computing (Course 6-5)
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (MEng)
- Computer Science and Molecular Biology (MEng)
- Health Sciences and Technology
- Archaeology and Materials (Course 3-C)
- Materials Science and Engineering (Course 3)
- Materials Science and Engineering (Course 3-A)
- Materials Science and Engineering (PhD)
- Mechanical Engineering (Course 2)
- Mechanical and Ocean Engineering (Course 2-OE)
- Engineering (Course 2-A)
- Nuclear Science and Engineering (Course 22)
- Engineering (Course 22-ENG)
- Anthropology (Course 21A)
- Comparative Media Studies (CMS)
- Writing (Course 21W)
- Data, Economics, and Design of Policy (MASc)
- Economics (Course 14-1)
- Economics (PhD)
- Mathematical Economics (Course 14-2)
- Global Studies and Languages (Course 21G)
- History (Course 21H)
- Linguistics and Philosophy (Course 24-2)
- Philosophy (Course 24-1)
- Linguistics (SM)
- Literature (Course 21L)
- Music (Course 21M-1)
- Theater Arts (Course 21M-2)
- Political Science (Course 17)
- Science, Technology, and Society/Second Major (STS)
- Business Analytics (Course 15-2)
- Finance (Course 15-3)
- Management (Course 15-1)
- Biology (Course 7)
- Chemistry and Biology (Course 5-7)
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences (Course 9)
- Chemistry (Course 5)
- Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (Course 12)
- Mathematics (Course 18)
- Mathematics with Computer Science (Course 18-C)
- Physics (Course 8)
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- Institute for Data, Systems, and Society
- Chemistry and Biology
- Climate System Science and Engineering
- Computation and Cognition
- Computer Science and Molecular Biology
- Computer Science, Economics, and Data Science
- Humanities and Engineering
- Humanities and Science
- Urban Science and Planning with Computer Science
- African and African Diaspora Studies
- American Studies
- Ancient and Medieval Studies
- Applied International Studies
- Asian and Asian Diaspora Studies
- Biomedical Engineering
- Energy Studies
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation
- Environment and Sustainability
- Latin American and Latino/a Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Polymers and Soft Matter
- Public Policy
- Russian and Eurasian Studies
- Statistics and Data Science
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Advanced Urbanism
- Computational and Systems Biology
- Computational Science and Engineering
- Design and Management (IDM & SDM)
- Joint Program with Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
- Leaders for Global Operations
- Microbiology
- Music Technology and Computation
- Operations Research
- Real Estate Development
- Social and Engineering Systems
- Supply Chain Management
- Technology and Policy
- Transportation
- School of Architecture and Planning
- School of Engineering
- Artificial Intelligence and Decision Making (Course 6-4)
- Nuclear Science and Engineering (PhD)
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Humanities (Course 21)
- Humanities and Engineering (Course 21E)
- Humanities and Science (Course 21S)
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences (PhD)
- Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences Fields (PhD)
- Interdisciplinary Programs (SB)
- Climate System Science and Engineering (Course 1-12)
- Computer Science, Economics, and Data Science (Course 6-14)
- Interdisciplinary Programs (Graduate)
- Biological Oceanography (PhD)
- Computation and Cognition (MEng)
- Computational Science and Engineering (SM)
- Computational Science and Engineering (PhD)
- Computer Science, Economics, and Data Science (MEng)
- Engineering and Management (SM)
- Leaders for Global Operations (MBA/SM and SM)
- Music Technology and Computation (SM and MASc)
- Real Estate Development (SM)
- Statistics (PhD)
- Supply Chain Management (MEng and MASc)
- Technology and Policy (SM)
- Transportation (SM)
- Aeronautics and Astronautics (Course 16)
- Aerospace Studies (AS)
- Architecture (Course 4)
- Biological Engineering (Course 20)
- Civil and Environmental Engineering (Course 1)
- Comparative Media Studies / Writing (CMS)
- Comparative Media Studies / Writing (Course 21W)
- Computational and Systems Biology (CSB)
- Computational Science and Engineering (CSE)
- Concourse (CC)
- Data, Systems, and Society (IDS)
- Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences (Course 12)
- Economics (Course 14)
- Edgerton Center (EC)
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (Course 6)
- Engineering Management (EM)
- Experimental Study Group (ES)
- Global Languages (Course 21G)
- Health Sciences and Technology (HST)
- Linguistics and Philosophy (Course 24)
- Management (Course 15)
- Media Arts and Sciences (MAS)
- Military Science (MS)
- Music (Course 21M)
- Naval Science (NS)
- Science, Technology, and Society (STS)
- Special Programs
- Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Theater Arts (21T)
- Urban Studies and Planning (Course 11)
- Women's and Gender Studies (WGS)

Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics
Department of Mathematics
| Program Requirements | ||
| Select eight graduate-level subjects in Mathematics | 96 | |
| Classroom Teaching in Mathematics | 12 | |
| Graduate Thesis | 288-360 | |
| Total Units | 396-468 | |
Note: Students in this program can choose to receive the Doctor of Philosophy or the Doctor of Science in Mathematics. Students receiving veterans benefits must select the degree they wish to receive prior to program certification with the Veterans Administration.
| . Either Internship in Mathematics or Research in Mathematics can be counted as one class toward this requirement but can only be taken once. | |

Print this page.
The PDF includes all information on this page and its related tabs. Subject (course) information includes any changes approved for the current academic year.
Natural Sciences and Mathematics
Mathematical sciences.
Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics
The program offers extensive coursework and intensive research experience in theory, methodology, and applications of mathematics (see degree requirements ).
- Faculty members with broad and diverse research interests are available to supervise doctoral dissertations .
- Financial support in the form of assistantships, full tuition support, and scholarships and awards are provided. Additional scholarships are available for US citizens and permanent residents.
- Our students, both domestic and international, have a strong record of starting in full-time jobs right after graduation .
- Students have opportunities to participate in active seminar series in Algebra and Combinatorics ; Computational Science ; Geometry, Topology and Dynamical Systems ; and Nonlinear Analysis and Dynamical Systems ; and the departmental Colloquium series.
- To enhance career prospects, students can pursue Graduate Certificate in Data Science , and possibly use the certificate courses to fulfill the elective requirements.
- NSM Career Success Center is available to support professional development and experiential learning of students.
- GRE test score is not required for admission.
More than 85% of our 45 Mathematics PhD graduates since 2020, both domestic and international, secured full-time employment within a few months of receiving their degrees.
Placement of 2022 & 2023 Mathematics PhD Graduates
| 2023 | Assistant Professor, Department of Mathematical Sciences, Montana Technological University |
| 2023 | Postdoctoral Researcher, Department of Biophysics, UT Southwestern Medical Center |
| 2023 | Postdoctoral Fellow, School of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, Clemson University |
| 2023 | Senior Software Engineer, Rotor Inc. |
| 2022 | Postdoctoral Researcher, Department of Mathematics, Johns Hopkins University |
| 2022 | Postdoctoral Fellow, Mathematics in Medicine program, Houston Methodist Hospital |
| 2022 | Postdoctoral Research Associate, National Center for Toxicological Research |
| 2022 | Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science and Mathematics, Spring Hill College |
| 2022 | Instructor, Department of Mathematics, Oregon State University |
| 2022 | Lecturer, Department of Mathematics, University of Oklahoma |
| 2022 | Assistant Professor of Instruction, Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Texas at Dallas |
| 2022 | Adjunct Professor, Department of Mathematics, Southern Methodist University |
| 2022 | Actuarial Analyst, Transamerica |
| 2022 | Systems Engineer, Verizon |
| 2022 | Data Analyst, Good Faith Energy |
| 2022 | Senior Data Scientist, Melax Tech |
See a more complete list
Assistantships
Graduate Teaching Assistantships are offered to qualified PhD students on a competitive basis. These assistantships include a monthly stipend (currently set at $2,400) along with a full tuition waiver (covering 9 credit hours per term in the Fall and Spring semesters). The assistantship additionally covers the cost of health insurance purchased through the university and most fees. Graduate Research Assistantships for advanced PhD students are also available on some faculty members’ research grants. Typically, assistantship support is provided for five years and encompasses the Summer semester as well.
All admitted students are considered for assistantships; no separate application is necessary.
Scholarships, Fellowships & Awards
PhD students are additionally supported through the following awards:
- NSM McDermott PhD Admission Fellowship (for highly qualified new students, offered at the time of admission)
- Dean’s Fellowship and EEF Scholarship (for highly qualified new students who are U.S. citizens and permanent residents, offered at the time of admission)
- Julia Williams Van Ness Merit Scholarship and Mei Lein Fellowship
- Outstanding Teaching Assistant of the Year Award
- Dean of Graduate Education Dissertation Research Award
- Best Dissertation Award , David Daniel Thesis Award , and Outstanding Graduate Student Award
Conference Travel Support
NSM Conference Travel Award and Betty and Gifford Johnson Travel Award are available to provide financial support to PhD students to present their research at professional conferences.
- How To Apply
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Scholarships & Awards
- Office of Admissions and Enrollment
Graduate Resources
- Mathematics Research
- Statistics & Actuarial Science Research
- Graduate Advisors
- Mathematics Courses
- Statistics Courses
- Actuarial Science Courses
- Qualifying Exam Archive
- Office of Graduate Education
Ready to start your application?
Before you apply, visit our How to Apply page to get familiar with the admission requirements and application process.
- Department of Mathematics
Graduate Studies
- Mathematics, PhD
Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics (PhD)
Requirements outline.
The Ph.D. degree is a research degree and the principal requirement is that a student writes an original research thesis. The thesis is produced under the supervision of a faculty member and is examined by a committee of three departmental faculty and an outside expert. To qualify to write a thesis, a candidate for a Ph.D. in mathematics first must pass three Preliminary Examinations. It is recommended that Ph.D. candidates discuss possible research opportunities with the Director of Graduate Studies and/or faculty members soon after they enter the Ph.D. Program. Entering students should outline an appropriate sequence of courses to learn the essential material for pursuing their research interests. After a student has passed the Preliminary Examinations they must choose an advisor from the Mathematics Department faculty. A candidate's thesis usually is developed and written with the guidance of this advisor who will later chair the thesis defense committee. The time required to obtain a Ph.D. degree varies a lot. The department does not support graduate students as Teaching Assistants for more than five academic years.
Ph.D. Degree Requirements
The requirements that must be satisfied for a candidate to receive a Ph.D. include:
- The candidate must pass Preliminary Examinations .
- The candidate must obtain a grade of B or better in at least 24 semester credit hours of courses in the Mathematics Ph.D. program. Students should take doctoral research classes MATH 8x98 (where “x” is the number of credit hours) while conducting thesis research. Students must register for. the course MATH 8x99 “Doctoral Dissertation” in the semester when they intend to graduate
- After passing all three Preliminary Examinations the candidate is subject to Annual Performance Review (APR). The APR evaluates research progress of the candidate. The APR is conducted in oral or written form by a committee consisting of at least two faculty members of the Mathematics Department. The APR committee is chaired by the candidate’s advisor. Candidates failing the APR are subject to termination from the Ph.D. program.
- The candidate must be in residence, and take 9 semester credit hours of courses, in two consecutive long semesters, Fall followed by Spring. Alternatively, the candidate must be in residence and take a full load in consecutive Spring, Summer, and Fall terms.
- The candidate must write a Doctoral Dissertation with the guidance of an advisor who is a regular faculty member of the Mathematics Department.
- The candidate must defend their Dissertation in a public examination by a thesis committee consisting of at least 4 members, three of whom are faculty members in the Mathematics Department and at least one member outside UH Mathematics Department.
- NSM Thesis and Dissertation General Guidelines and Instructions
- NSM Thesis and Dissertation Formatting Instructions
- NSM Thesis and Dissertation Submission Instructions
- NSM Checklist for Thesis and Dissertation Review
- NSM Deadlines & Academic Calendar : This link provides deadlines for the submission of Dissertations.
- *The Graduate Record Examination (GRE) is waived for the Ph.D program within the Department of Mathematics.
- International students can not exclusively register for online courses.
Course Selection:
- Information about courses may be found at this link .
- Students can discuss advisor selection process with the Director of Graduate Studies.
- The above is only an outline of the primary requirements for the degree. The Director of Graduate Studies and others can provide more detailed information about conditions. The college and the university may have further requirements as listed at College and websites.
- PhD students can take topics classes at Rice University, UT Health, UTMB, or Baylor College of Medicine. Students must submit the Inter-Institutional Course Registration Form to the Graduate Director for approval. Taking an outside class must be essential for the completion of graduate degree. Thus, students must obtain a prior approval of their PhD avisor (signature on the form).
- Course Selection Requests: Please contact the Director for Instructional Support and Coordination < [email protected] > for more information.
Teaching Opportunities for Ph.D. Students:
As a condition, a student should have experiences of teaching Calculus recitation class with reasonable teaching evaluation. For an international student, by Texas law, the student must pass the English SPEAK test or its equivalence.
All PhD applicants who submit their complete application before the appropriate deadline are automatically considered for Teaching Assistantship.
Please contact the Director for Instructional Support and Coordination for more information about course selection requests .
Preliminary Examinations:
The Preliminary Examination is the final step in assessing the student’s ability and appropriate mathematical background to undertake a program of supervised research and study leading to a Ph.D. in Mathematics. Students who have completed their Master's degree in Mathematics may often be ready to take the Preliminary Examination without further course study.
Preliminary Examinations are three-hour, closed book written examinations that are given in each of the topics listed below. The questions in the examination emphasize problem solving skills and mathematical ability as opposed to rote memorization.
Preliminary Examinations are usually offered twice a year: at the end of the Fall and Spring semesters.
Students who receive support from the Department of Mathematics are expected to pass the Preliminary Examination according to the rules below. For non-supported students, the University rules apply.
All students are supposed to pass three Preliminary Examinations before the beginning of their third year in the Ph.D. program.
The following rules apply:
1. Students must pass three Preliminary Examinations from the different topic groups listed below
2. At least one out of the three Preliminary Examinations must be a core sequence. Core sequences are:
Review information for the preliminary written examinations:
| Sample exam | |||
Additional problems from past preliminary exams:
| Applicable Analysis | |
| Probability | |
| Statistics | Sample Problems |
| Optimization | Sample Problems |
| Numerical Analysis | |
All preliminary exams are based on the content of the corresponding course. Please contact the instructor who taught the corresponding course most recently to obtain the up-to-date information.
MathematicsDoctor of philosophy in mathematics, get your phd in mathematics. The PhD program places a strong emphasis on preparation for research and teaching. Students must earn at least 72 semester hours of graduate credit and spend at least three years in residence at a graduate college, including at least one year at the University of Iowa. They must complete specific courses designated as preparatory for the PhD qualifying examinations; pass the qualifying and comprehensive exams; and write a PhD thesis. For a complete description of these requirements see the graduate student handbook . Graduate student resources
Create your academic pathYou'll find degree overviews, requirements, course lists, academic plans, and more to help you plan your education and explore your possibilities. Current course listThe MyUI Schedule displays registered courses for a particular session and is available to enrolled students. The list view includes course instructors, time and location, and features to drop courses or change sections. University of MissouriCollege of Arts and Science MathematicsMathematics doctor of philosophy (phd). Core and Advanced Graduate Courses: Definitions and Schedules The 8000 level courses appearing in the tables below constitute the current working definition of the term core graduate course. A graduate course not appearing on this list will be called an advanced graduate course. Please refer to the full list of Mathematics courses 4000 and above . To increase the predictability and the enrollment for core graduate courses, we will stay with the prescribed Fall/Spring schedule for core graduate courses. Advanced graduate courses may be offered on a less predictable basis. Advanced graduate courses include three sub-classes:
It is allowable to list a Topics or Seminar course multiple times on your program of study assuming it is not a duplicate course covering the same topic. Topics and Seminar courses generally have subtitles describing the topic, to list two courses on the program of study it is sufficient that the subtitles are (significantly) different even if the course numbers are the same . On your transcript, only the course number and title appear. On your program of study, you should try to list the course number, the abbreviated title and the subtitle. For example:
This is a professional research degree designed to prepare students for various advanced professional careers, including college teaching and research. Year 0 courses include basic advanced undergraduate material, which incoming Ph.D. students are required to master before engaging in graduate coursework. Well prepared incoming students can petition to skip some or all of the Year 0 courses. The Director of Graduate Studies will administer an informal exam to see if the students are sufficiently ready to skip Year 0 courses.
Year 1 courses will train students to develop a common solid foundation on basic graduate mathematics. The Ph.D. student is required to pass all 6 courses, and to pass qualifying exams in Algebra and Real Analysis. The qualifying exams will be given in May of each year, shortly after finals week. There will be an opportunity to retake a qualifying exam in August just before the beginning of the Fall semester. The Analysis qualifying exams will be from topics from Real Analysis I and Real Analysis II. The Algebra qualifying exams will be from topics from Algebra I and Algebra II. Extremely well prepared students, with the permission of their initial adviser and the Director of Graduate studies, may take one or both qualifying exams in August before they start their first semester. If they pass, then with the permission of their initial adviser and the Director of Graduate studies they may skip the corresponding courses in Year 1.
Year 2 and above are the post-qual core courses. Every Ph.D. student must complete at least six of the post-qual core courses. (Note that the parity of the year is determined by the beginning of the AY. For example, Spring 2016 occurs in the beginning of AY 2015, and so would be considered to be in an odd year.)
The graduate student must further complete a course of study approved by the doctoral program committee and pass a comprehensive examination. The active areas of research interest of the current members of the staff are: algebraic geometry, commutative algebra, number theory, representation theory, analysis (real, complex, functional and harmonic), analytic functions, applied mathematics, financial mathematics and mathematics of insurance, scattering theory, differential equations (ordinary and partial), differential geometry, dynamical systems, general relativity, mathematical physics, probabilistic analysis and topology. Note: Effective at the start of Winter Semester 2007, there is NO foreign language proficiency requirement for the Mathematics PhD. However, a student's Doctoral Committee still retains the discretion to impose a foreign language proficiency requirement. Ohio State navigation bar
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)The program of studies for a Math Department PhD student is divided into two main parts: Pre- and Post-Candidacy . Before taking the Candidacy Exam , students need to fulfill numerous requirements which ensure solid preparation in core mathematical areas as well in their chosen specialization. These include passing the Qualifying Requirements as well as fulfilling the Breadth and Foreign Language requirements. The Candidacy Exam is usually taken sometime during the third year, marking the end of the preparatory period and the beginning of research leading ultimately to the PhD Dissertation . Time from admission to graduation usually averages around 6 years but may vary greatly depending on many factors such as initial preparation level, individual academic progress, complexity of chosen specializations, and strategic thesis and job decisions. Full program requirements can be found in the OSU Department of Mathematics Graduate Program Handbook [pdf]. The OSU Graduate School has requirements as well, which can be found in the Graduate School Handbook . Headstart TrainingNewly admitted graduate students are required to arrive 4 weeks prior to the beginning of the Autumn semester in order to participate in our Headstart Training teaching preparation program. This is a prerequisite for holding a GTA appointment. Further academic preparation activities are scheduled during this time as well. Exceptions can be made only for students who are offered university fellowships and typically involve a one-year deferment of the teaching portion only. Monetary compensation is provided to all Headstart participants. Qualifying RequirementsFor the Theoretical Track , there are four Qualifying Requirements, corresponding to the content of the four courses Math 6111 , Math 6112 , Math 6211 , and Math 6212 in Abstract Algebra and Real Analysis . Each requirement can be passed by either receiving a grade of A or A- in the respective course, or by receiving a passing grade on a respective (separate) qualifying examination. The Math 6111 and 6211 courses are offered every Autumn Semester and the Math 6112 and 6212 courses are offered every Spring Semester. The four examinations, one for each course, are offered each August (typically in the week before the start of classes) and are open to both incoming and continuing students. Each exam is two hours in length and covers roughly the material of the respective courses. All four requirements need to be fulfilled by the end of the third semester of study (not including summer). Thus a student has four attempts to fulfill, for example, the 6111-requirement (twice by taking the course, and twice by exam) and three attempts to fulfill the 6112-requirement (once by taking the course, and twice by exam). The 6211 and 6212 requirements are analogous. Interested students may substitute one of these four requirements with an approved 6000-level year-long course sequence with A or A- grades. This includes all regular full-year 6000-level sequences, namely, Math 6221-6222, 6251-6252, 6411-6451, 6501-6502, 6601-6602, 6701-6702, and 6801-6802. (For example, the 6112 requirement can be substituted by taking the Math 6411-6451 Differential Equations sequence with A or A- grades in each course). Students should consult the GSC Chair about the use of the 6001-6004 Logic courses. Qualifying requirements for the Applied Track combine a mandatory Scientific Computing ( Math 6601 ) course, one of the algebra or analysis courses, and three additional courses from Math 6602 , Math 6411 , Math 6451 , and the algebra and analysis courses. Passing the Qualifying Requirements also entails an increase in stipend, assuming otherwise satisfactory academic progress (see Financial Support ). The outcome of initial exams and coursework will also inform future advising. Syllabi and exam materials can be viewed at https://math.osu.edu/grad/current/phd/quals . Advisor and Breadth RequirementsUpon attaining Regular PhD status, students are matched with faculty members who guide them to potential dissertation research ideas. The primary task of this Dissertation Advisor is to facilitate their advisee’s development as a mathematician. The course work required for admission to Candidacy is referred to as our Breadth Requirements . The purpose of these requirements is to ensure that graduates master not only their eventual field of specialization, but also develop the breadth, versatility, and maturity expected from mathematicians working in academic professions that traditionally require a PhD . The requirements are as follows:
PhD students are expect to complete their Breadth Requirements within their first two years from admission. Most students fulfill two breadth sequences in their first year through qualifying courses and the third in their second year. Timely completion of breadth requirements may influence stipend level and summer support. All Breadth Requirements must be completed by the time of the Candidacy Exam . Breadth Requirements Chart
Foreign Language RequirementThe foreign language requirement ensures the ability to read (with the aid of a dictionary) one foreign language chosen from among French , German , or Russian. It can be fulfilled in one of the following two ways: Class: Students with little or no prior knowledge of the chosen language can fulfill their language requirement by passing one of the following classes with a grade of B or better:
Exam: Alternatively, a student may pass a translation exam in one of the languages above. To schedule the exam, please start by contacting the Mathematics Department Language Coordinator: Dr. Andrzej Derdzinski ([email protected]) To find out dates and information on the exams, please see below: French Department Translation Exam Coordinator: Matthew Lang [email protected] https://frit.osu.edu/graduate/graduate-reading-proficiency-exam/french-reading-proficiency-exam German Department Translation Exam Coordinator: Natascha Miller [email protected] http://germanic.osu.edu/german-reading-exam Russian Department Translation Exam Coordinator: Larysa Stepanova [email protected] https://slavic.osu.edu/courses/transfer-credit-and-placement Specialization & AdvisorAn important candidacy requirement is the choice of a dissertation specialization and a Dissertation Advisor . The diligent, timely, and careful pursuit of a future research direction is likely the most important responsibility of a prospective PhD candidate . The student should be fully invested in the choice of specialization, which will impact his/her future academic trajectory more than anything else. There are currently 65+ regular mathematics faculty on the Columbus campus, plus over 20 additional faculty on the branch campuses, who can supervise doctoral dissertations. Consult our current Graduate Faculty List for names, contacts and specializations. Under special circumstances, students can also be advised by faculty outside of the department. The advisor pool in our department is thus as large as that of any department in the country. There are numerous opportunities for students to get to know potential advisors. This includes having them as teachers in introductory classes, attending the Invitations to Mathematics lecture series, regular research seminars, and colloquia (see Events ), or self-development through academic advisors, peers, and publicly available research information. After narrowing down possible specializations, students typically sample faculty and topics by taking numerous reading courses ( MATH 6193 ) on special topics with a few prospective advisors. These provide introductions to future research areas that are too specialized to be covered in regular courses. The one-on-one teaching of a reading course may also serve as a preview of the advisor / advisee interaction in future thesis work. The choice of thesis advisor usually evolves out of this process. After student and faculty agree on the thesis advising, the student reports the change from the Preliminary Academic Advisor to the chosen Dissertation Advisor to the Math Graduate Office using the form located outside the Grad Office . Master of Science (MS) DegreeInformation on how students admitted into the PhD program can earn the MS Degree can be found at https://math.osu.edu/grad/current/ms . Candidacy ExaminationFor a graduate student to become an official PhD Candidate, he/she has to pass the Candidacy Exam . The Candidacy Exam evaluates the validity and scope of the dissertation proposal, and serves as a forum for critique and guidance towards the successful completion of dissertation research. This exam is regulated by the university's Graduate School and permission from the department to take the exam is subject to the following requirements (for more detailed information on Candidacy see https://gradsch.osu.edu/handbook/all#7-0 ). These concern the composition of the committee, the written, and the oral portion of the examination: The committee consists of four regular faculty with graduate P-status, including the advisor of the candidate who serves as the chair. Other committee members can be from other Ohio State departments but have to have graduate P-status in their programs. Additional members, beyond these four, can be added by petition and according to Graduate School rules. The written portion consists of a 10-15 page dissertation proposal in which goals, scope, methods, and background of the planned research is outlined. The document has to contain mathematically rigorous statements, needs to be type-set along the usual publishing standards in the field (e.g., LaTeX), and should contain a substantial bibliography that includes all pertinent publications the intended research will be based on. The proposal of the written portion should be submitted to the committee at least ten days before the presentation and oral portion. The candidate is required to describe his/her proposal in a short presentation of approximately 30 minutes to the committee immediately before the start of the oral portion of the examination. The details of the format are determined by the advisor, including whether the presentation should be public and questioning during the presentation. Following the presentation there is a two-hour oral examination by the committee. This time has to be completely dedicated to the questioning by the committee and is not allowed to contain further presentations. The questions can focus on the proposal itself and the validity and relevance of the research questions, but can also include skill and knowledge examination of the needed mathematical background, as well as test familiarity with prior research. An application for candidacy must be submitted via gradforms.osu.edu at least three weeks before the oral examination. The candidacy examination can be taken at any time during business hours when the university is open -- including summer terms and breaks. The final date on which a candidacy exam can be counted as being within any given semester is the day before the first day of the following semester (for example, a "Spring" exam can be scheduled up until the day before Summer Term begins). All committee members' approval signatures must also be submitted in GradForms prior to the first day of the following term. All pre-candidacy requirements of the Mathematics Department, as well as all credit and residency requirements of the Graduate School, have to be fulfilled by the end of the term prior to taking the exam. Candidates also need to be enrolled for at least 3 hours at the graduate level during the term of the exam (note: if you schedule your exam in summer, you will need to enroll in 4 total credit hours in order for your summer tuition waiver to apply). Foreign language classes do not count toward the 3 graduate credits required to take a candidacy examination. Following the exam, the Report on Candidacy form must be approved on GradForms by all committee members. Post-Candidacy & Dissertation ResearchAfter the Candidacy Exam , PhD students spend most of their time on research related to their dissertation, under the close supervision of their Dissertation Advisor . There are some requirements during this time which PhD Candidates must abide by:
Final Defense & GraduationHow long one takes to graduate may vary greatly depending upon initial preparation, chosen specialization, difficulty and scope of the research problem, diligence of the candidate, results required to be competitive in the chosen area or job market, and other factors. Requirements to be eligible for graduation include:
Credit Hours: Students are required to have accumulated 80 graduate credit hours of mathematics courses by the time of graduation. It is possible to substitute some of these with graduate credits from courses outside of the mathematics department, if approved by the advisor and the Graduate Studies Committee . In addition, university rules require that 50 of these credit hours have to be beyond the Master's degree . Once the Dissertation Advisor deems the Dissertation Doctoral Draft complete, the candidate needs to assemble a Final Oral Exam Committee . The committee consists of the Dissertation Advisor and two additional regular category P level faculty members, who will review the draft. The doctoral candidate must submit the Application for Final Exam form via GradForms no later than two weeks prior to the proposed final oral examination date. The approval of the draft is followed by the two-hour Final Oral Examination (dissertation defense) conducted before the dissertation committee members listed, plus a non-Math representative assigned by the Graduate School . See the PhD Dissertations link on the Department website for samples of past approved Dissertations. The department supports the search for academic jobs in several ways. Before graduation, the department provides travel support for students, helps with letters, and circulates job opportunities. After graduation, many former students with can find employment as lecturers with the department while they are looking for permanent jobs, if interim employment is needed. Program Time Expectations
Applied Mathematics - Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Mathematics 3 (M3) Building on Waterloo's Campus Conduct mathematics-based research and generate new knowledge in a multidisciplinary environment with the PhD in Applied Mathematics program. At North America’s only dedicated Faculty of Mathematics and the #1 school in Canada for mathematics and computer science, you’ll connect theoretical advances and innovative mathematics to develop novel solutions to the pressing problems facing today’s world. Through a combination of coursework and original research, you’ll learn cutting-edge applications of mathematical theory in a broad range of fundamental and applied sciences, with five areas of research to choose from including control theory and dynamical systems, fluid mechanics, mathematical medicine and biology, mathematical physics, and scientific computation. With the competitive edge provided by mentorship through the Faculty’s connections around the world, you’ll be prepar ed to pursue a career in academia, government or industry. Research areas and degree options:
Program overviewDepartment/School : Applied Mathematics Faculty : Faculty of Mathematics Admit term(s) : Fall (September - December), Winter (January - April), Spring (May - August) Delivery mode : On-campus Program type : Doctoral, Research Length of program : 48 months (full-time) Registration option(s) : Full-time, Part-time Study option(s) : Thesis Application Deadlines
Key contacts I see all these great scholars around me, like my supervisor Sue Ann Campbell. And like Anita Layton, Ghazal Geshnizjani, my committee members, and so many others in the department. I see their passion for what they do and their dedication to helping us grad students succeed. It’s very heartening. It motivates me to reach that level where I can give back in the same way. Maliha Ahmed, Applied Mathematics, PhD Supervisors
Admission requirements
Degree requirements
Application materials
Tuition and feesVisit the graduate program tuition page on the Finance website to determine the tuition and incidental fees per term for your program Review living costs and housing Review the funding graduate school resources for graduate students
Graduate Studies
Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics (PhD)Requirements outline. The Ph.D. degree is a research degree and the principal requirement is that a student writes an original research thesis. The thesis is produced under the supervision of a faculty member and is examined by a committee of three departmental faculty and an outside expert. To qualify to write a thesis, a candidate for a Ph.D. in mathematics first must pass three Preliminary Examinations. It is recommended that Ph.D. candidates discuss possible research opportunities with the Director of Graduate Studies and/or faculty members soon after they enter the Ph.D. Program. Entering students should outline an appropriate sequence of courses to learn the essential material for pursuing their research interests. After a student has passed the Preliminary Examinations they must choose an advisor from the Mathematics Department faculty. A candidate's thesis usually is developed and written with the guidance of this advisor who will later chair the thesis defense committee. The time required to obtain a Ph.D. degree varies a lot. The department does not support graduate students as Teaching Assistants for more than five academic years. Ph.D. Degree RequirementsThe requirements that must be satisfied for a candidate to receive a Ph.D. include:
Course Selection:
Teaching Opportunities for Ph.D. Students:As a condition, a student should have experiences of teaching Calculus recitation class with reasonable teaching evaluation. For an international student, by Texas law, the student must pass the English SPEAK test or its equivalence. All PhD applicants who submit their complete application before the appropriate deadline are automatically considered for Teaching Assistantship. Please contact the Director for Instructional Support and Coordination for more information about course selection requests . Preliminary Examinations:The Preliminary Examination is the final step in assessing the student’s ability and appropriate mathematical background to undertake a program of supervised research and study leading to a Ph.D. in Mathematics. Students who have completed their Master's degree in Mathematics may often be ready to take the Preliminary Examination without further course study. Preliminary Examinations are three-hour, closed book written examinations that are given in each of the topics listed below. The questions in the examination emphasize problem solving skills and mathematical ability as opposed to rote memorization. Preliminary Examinations are usually offered twice a year: at the end of the Fall and Spring semesters. Students who receive support from the Department of Mathematics are expected to pass the Preliminary Examination according to the rules below. For non-supported students, the University rules apply. All students are supposed to pass three Preliminary Examinations before the beginning of their third year in the Ph.D. program. The following rules apply: 1. Students must pass three Preliminary Examinations from the different topic groups listed below 2. At least one out of the three Preliminary Examinations must be a core sequence. Core sequences are: Review information for the preliminary written examinations:
Additional problems from past preliminary exams:
All preliminary exams are based on the content of the corresponding course. Please contact the instructor who taught the corresponding course most recently to obtain the up-to-date information.  2024-25 Academic CatalogDoctor of philosophy in mathematics, why study mathematics. Because mathematics is a framework upon which humanity builds an understanding of the world. Mission of the Graduate Program:The mission of the Graduate Program of the Department of Mathematics is to prepare students for leadership roles in meeting the mathematical needs of our society and to produce professional mathematicians for positions in universities, colleges, industry, governmental agencies, and research centers. Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics:The Mathematics Department offers the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Mathematics. The Ph.D. program provides broad and deep expertise in mathematics, culminating in a dissertation that includes significant original work. It is intended for students with a strong mathematical background who plan a career in research in academia or industry. A broad range of specialties is possible; research interests of department faculty include algebra, analysis, combinatorics, control theory, dynamical systems, geometry, numerical analysis, partial differential equations, probability, and statistics. There are two tracks: Pure Mathematics and Applied Mathematics. The requirements for each track are listed in the section Degree Requirements. College-wide requirements for graduate students may be found in the Graduate School Catalog . Admission to Graduate StudiesAn applicant seeking to pursue graduate study in the College may be admitted as either a degree-seeking or non-degree seeking student. Policies and procedures of Graduate Studies govern the process of Graduate admission. These may be found in the Graduate Studies section of the online catalog. Please consult the Departments & Programs section of the online catalog for information regarding program-specific admissions criteria and requirements. Special admissions requirements pertain to Interdisciplinary Studies degrees, which may be found in the Graduate Studies section of the online catalog. Admission to the Ph.D. in MathematicsThe minimum prerequisites for admission are:
It is beneficial to have preparation in probability/statistics (comparable to MATH 627 / MATH 628 ) and/or numerical analysis (comparable to MATH 581 ). Although not required, it is also helpful to have taken introductory courses in complex analysis ( comparable to MATH 646 ), partial differential equations (comparable to MATH 647 ), geometry (comparable to MATH 660 / MATH 661 ), and/or topology. The Mathematics Department currently does not require the general or subject Graduate Record Examination (GRE), although applicants may submit scores if they wish. International students whose native language is not English must fulfill English language requirements specified by university policies. Applicants must submit a graduate application online , including the following required materials:
Incomplete applications will not be considered. The minimum admission requirements do not guarantee admission. The Department of Mathematics evaluates candidates and makes recommendations to the Office of Graduate Studies regarding admission. The number of students admitted to the program changes from year to year, and admissions are competitive based on all application materials. There are no additional application forms for financial support. Students are considered for support based on merit. Most Ph.D. students accepted by the program receive an offer of financial support in the form of a Graduate Teaching Assistantship. The number of GTAs available is limited. Further information about applications and admissions is available from the Department of Mathematics . Contact the department: Michelle Morrison Graduate Program Coordinator Department of Mathematics 433 Snow Hall [email protected] Ph.D. Degree RequirementsThe department requires the student to meet the following requirements before taking the comprehensive examination.
Note: Contact your department or program for more information about the qualifying exam coursework requirement, the research skills and responsible scholarship, and the current requirements for doctoral students. Current policies on Doctoral Research Skills and Responsible Scholarship are listed in the Graduate Studies section of the online catalog and in the KU Policy Library. Pure MathematicsThis track requires:
In addition, the pure-track student must complete four additional MATH courses at the 800 level or above before the final examination. MATH 896 , MATH 899 , MATH 993 and MATH 999 may not be used to satisfy this requirement. MATH 990 may be used to satisfy this requirement only with Graduate Committee approval. Courses outside Mathematics may be used to satisfy this requirement only with Graduate Committee approval. Applied Mathematics
In addition, the applied-track student must complete four additional MATH courses at the 800 level or above before the final examination. MATH 896 , MATH 899 , MATH 993 and MATH 999 may not be used to satisfy this requirement. MATH 990 may be used to satisfy this requirement only with Graduate Committee approval. Courses outside Mathematics may be used to satisfy this requirement only with Graduate Committee approval. Examination PreparationNormally the work required to prepare a student for the oral comprehensive examination (and to do research) includes one or more semesters of advanced courses, directed readings, and seminars. In the oral comprehensive examination, a student must show proficiency in the chosen area of mathematics. Precise areas of responsibility on this examination are discussed in detail with the advisory committee (the student’s advisor and two other members of the department’s Graduate Faculty). In addition to meeting general requirements, the Ph.D. candidate in mathematics must complete a minimum of 28 credit hours of mathematics coursework (this number includes 1 credit hour of MATH 999 ). The minimum amount of credit hours is possible only if a student passes all Ph.D. qualifying exams in lieu of the preparatory coursework ( MATH 727 , MATH 765 , MATH 781 , MATH 791 ). The program routinely takes 12 semesters to complete when factoring in research and milestone exams. A typical student completes 72 or more credit hours when enrolled full-time. Print OptionsSend Page to Printer Print this page. Download Page (PDF) The PDF will include all information unique to this page. 2024-25 Entire Catalog All pages in the Academic Catalog University of Notre Dame Department of Mathematics College of Science Math/Philosophy Math Graduate Programs
MSIM PROGRAM FOR PHILOSOPHY PhD STUDENTS, MAMP PROGRAM FOR MATHEMATICS PhD STUDENTS, AND JOINT MATH/PHILOSOPHY PhD PROGRAMIn collaboration with the Philosophy Department, the Mathematics Department at Notre Dame offers several joint programs for students interested in Mathematical Logic as well as Philosophy. The acronym MSIM stands for Master of Science in Interdisciplinary Mathematics, and this degree is given by the Mathematics Department. The program is available also to students from fields besides Philosophy. See this link: https://math.nd.edu/graduate/msim-degree/ for more information about joint Mathematics/Philosophy graduate degrees at Notre Dame. If you are a PhD student at Notre Dame interested in the MSIM degree with your primary area of interest not in Mathematical logic and Philosophy, the MAMP (Master of the Arts in Mathematical Philosophy) program may be of interest. See https://philosophy.nd.edu/graduate-program/mathematical-philosophy-minor/ for additional information about MAMP. This page gives instructions for how to apply for the MSIM, MAMP, or the joint PhD program in Mathematical Logic and Philosophy. Please contact the Math or Philosophy DGS if you have additional questions. Admission to either of these degree programs requires the approval of both the Mathematics and Philosophy Departments. Similarly, any extension of the deadlines discussed below need the approval of the Mathematics and Philosophy Departments. Approval by the Philosophy Department requires primary approval by the Logic Group within that department, and final certification by the Philosophy DGS. Approval by the Math department requires approval by the Logic Group within that department in consultation with the Math DGS and if necessary, the graduate committee. As these degrees are additional degrees beyond the student’s Ph.D. program, they are not funded separately. We expect that the students earning these degrees will be exceptional. A student in the joint PhD program will have to find a Mathematics adviser and a Philosophy adviser. The student will write a single PhD thesis, but it may have separate parts with a Math or Philosophy focus. Philosophy PrimaryAn essential criterion for admission to the MSIM or Joint Degree for a Philosophy graduate student by the mathematics department is the approval of a mathematics department faculty member who agrees to oversee the student’s work. This will normally require that the student has become integrated into that faculty member’s research group, and has proposed a viable area for research. It is the student’s responsibility to find their own advisor. Given that, the path towards admission to the MSIM or Joint Degree is as follows:
Mathematics PrimaryAn essential criterion for admission to the MAMP or Joint PhD for a mathematics graduate student by the Philosophy Department is the recommendation of a Philosophy Department faculty member who agrees to oversee the student’s work. This will normally require that the student has articulated a viable area for research and demonstrated to the satisfaction of the faculty member relevant competence to undertake a research project in the area. It is the student’s responsibility to find their own advisor. The joing PhD program for graduate students in the Department of Mathematics is called the PdD in Mathematics and Philosophy.
Latest News2024 richard sady dissertation prize. April 23, 2024 2024 Eli J. and Helen Shaheen Graduate School Award in ScienceApril 15, 2024 
Go to programs search Mathematicians use theoretical and computational methods to solve a wide range of problems from the most abstract to the very applied. UBC's mathematics graduate students work in many branches of pure and applied mathematics. The PhD program trains students to operate as research mathematicians. The focus of the program is on substantial mathematical research leading to the PhD dissertation. Students also develop their skills in presenting and teaching mathematics and its applications. For specific program requirements, please refer to the departmental program website What makes the program unique?UBC has one of the largest and most vigorous departments of mathematics in Canada. Our faculty routinely win national and international awards for their research and teaching achievements. We have an engaged and sociable cohort of graduate students who are essential members of a broad selection of active research groups. Each group holds a variety of seminars and events that allow graduate students, postdoctoral fellows, visitors and faculty to enjoy regular interaction. UBC is the headquarters for the Pacific Institute of Mathematical Sciences (PIMS). PIMS hosts a plethora of mathematical events such as conferences and summer schools, greatly enriching the scientific environment in the quantitative sciences at UBC. Our mathematics students are also regular participants at the nearby Banff International Research Station for Mathematical Innovation and Discovery. Finally, our Institute for Applied Mathematics provides options for interdisciplinary studies for PhD students who wish to work in applied and computational mathematics. UBC's math program has a high reputation and there are many renowned professors in the department. This was a selling point of the UBC math graduate program for me.  Pardis Semnani Quick FactsProgram enquiries, admission information & requirements, 1) check eligibility, minimum academic requirements. The Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies establishes the minimum admission requirements common to all applicants, usually a minimum overall average in the B+ range (76% at UBC). The graduate program that you are applying to may have additional requirements. Please review the specific requirements for applicants with credentials from institutions in:
Each program may set higher academic minimum requirements. Please review the program website carefully to understand the program requirements. Meeting the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission as it is a competitive process. English Language TestApplicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application. Minimum requirements for the two most common English language proficiency tests to apply to this program are listed below: TOEFL: Test of English as a Foreign Language - internet-basedOverall score requirement : 100 IELTS: International English Language Testing SystemOverall score requirement : 7.0 Other Test ScoresSome programs require additional test scores such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Test (GMAT). The requirements for this program are: The GRE is not required. 2) Meet Deadlines3) prepare application, transcripts. All applicants have to submit transcripts from all past post-secondary study. Document submission requirements depend on whether your institution of study is within Canada or outside of Canada. Letters of ReferenceA minimum of three references are required for application to graduate programs at UBC. References should be requested from individuals who are prepared to provide a report on your academic ability and qualifications. Statement of InterestMany programs require a statement of interest , sometimes called a "statement of intent", "description of research interests" or something similar.
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.  Instructions regarding thesis supervisor contact for Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics (PhD)Citizenship verification. Permanent Residents of Canada must provide a clear photocopy of both sides of the Permanent Resident card. 4) Apply OnlineAll applicants must complete an online application form and pay the application fee to be considered for admission to UBC. Tuition & Financial Support
Financial SupportApplicants to UBC have access to a variety of funding options, including merit-based (i.e. based on your academic performance) and need-based (i.e. based on your financial situation) opportunities. Program Funding PackagesAll full-time students who begin a UBC-Vancouver PhD Mathematics program in September 2018 or later will be provided with a funding package of at least $24,256 for each of the first four years of their PhD. The funding package may consist of any combination of internal or external awards, teaching-related work, research assistantships, and graduate academic assistantships. Average Funding
Scholarships & awards (merit-based funding)All applicants are encouraged to review the awards listing to identify potential opportunities to fund their graduate education. The database lists merit-based scholarships and awards and allows for filtering by various criteria, such as domestic vs. international or degree level. Graduate Research Assistantships (GRA)Many professors are able to provide Research Assistantships (GRA) from their research grants to support full-time graduate students studying under their supervision. The duties constitute part of the student's graduate degree requirements. A Graduate Research Assistantship is considered a form of fellowship for a period of graduate study and is therefore not covered by a collective agreement. Stipends vary widely, and are dependent on the field of study and the type of research grant from which the assistantship is being funded. Graduate Teaching Assistantships (GTA)Graduate programs may have Teaching Assistantships available for registered full-time graduate students. Full teaching assistantships involve 12 hours work per week in preparation, lecturing, or laboratory instruction although many graduate programs offer partial TA appointments at less than 12 hours per week. Teaching assistantship rates are set by collective bargaining between the University and the Teaching Assistants' Union . Graduate Academic Assistantships (GAA)Academic Assistantships are employment opportunities to perform work that is relevant to the university or to an individual faculty member, but not to support the student’s graduate research and thesis. Wages are considered regular earnings and when paid monthly, include vacation pay. Financial aid (need-based funding)Canadian and US applicants may qualify for governmental loans to finance their studies. Please review eligibility and types of loans . All students may be able to access private sector or bank loans. Foreign government scholarshipsMany foreign governments provide support to their citizens in pursuing education abroad. International applicants should check the various governmental resources in their home country, such as the Department of Education, for available scholarships. Working while studyingThe possibility to pursue work to supplement income may depend on the demands the program has on students. It should be carefully weighed if work leads to prolonged program durations or whether work placements can be meaningfully embedded into a program. International students enrolled as full-time students with a valid study permit can work on campus for unlimited hours and work off-campus for no more than 20 hours a week. A good starting point to explore student jobs is the UBC Work Learn program or a Co-Op placement . Tax credits and RRSP withdrawalsStudents with taxable income in Canada may be able to claim federal or provincial tax credits. Canadian residents with RRSP accounts may be able to use the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) which allows students to withdraw amounts from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSPs) to finance full-time training or education for themselves or their partner. Please review Filing taxes in Canada on the student services website for more information. Cost EstimatorApplicants have access to the cost estimator to develop a financial plan that takes into account various income sources and expenses. Career Outcomes88 students graduated between 2005 and 2013: 1 is in a non-salaried situation; for 19 we have no data (based on research conducted between Feb-May 2016). For the remaining 68 graduates: 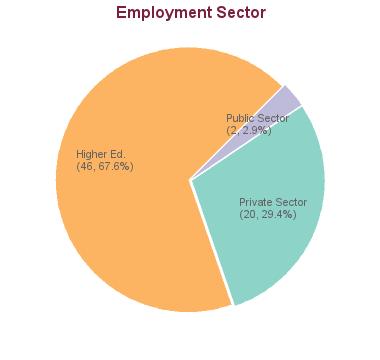 Sample Employers in Higher EducationSample employers outside higher education, sample job titles outside higher education, phd career outcome survey, career options. A great majority of our PhD graduates move on to postdoctoral fellowships and faculty positions at universities and research institutes in North America and around the world. However, a significant fraction of students move into careers in industry. Students considering non-academic careers are encouraged to complete an industrial internship (for instance through the Mitacs Accelerate program - headquartered at UBC) during their studies. Enrolment, Duration & Other StatsThese statistics show data for the Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics (PhD). Data are separated for each degree program combination. You may view data for other degree options in the respective program profile. ENROLMENT DATA
Completion Rates & TimesUpcoming doctoral exams, tuesday, 17 september 2024 - 2:00pm - room 203.
Advice and insights from UBC Faculty on reaching out to supervisorsThese videos contain some general advice from faculty across UBC on finding and reaching out to a supervisor. They are not program specific.  This list shows faculty members with full supervisory privileges who are affiliated with this program. It is not a comprehensive list of all potential supervisors as faculty from other programs or faculty members without full supervisory privileges can request approvals to supervise graduate students in this program.
Doctoral Citations
Sample Thesis Submissions
Related ProgramsSame specialization.
At the UBC Okanagan CampusFurther information, specialization. Mathematicians use theoretical and computational methods to solve a wide range of problems from the most abstract to the very applied. UBC's mathematics graduate students work in many branches of pure and applied mathematics. UBC CalendarProgram website, faculty overview, academic unit, program identifier, classification, social media channels, supervisor search. Departments/Programs may update graduate degree program details through the Faculty & Staff portal. To update contact details for application inquiries, please use this form .  Nicholas RichardsonHaving grown up outside of Toronto and completed my undergrad and master's degree at the University of Waterloo, I was ready to change the scenery and go study somewhere else. I joke that is it the farthest I could move without leaving Canada, but more truthfully it was the campus that felt "right...  Gabriel CurrierI quite like the kind of math that people do here, and enjoy working with my supervisors. The campus is also a beautiful place and the graduate student community is pretty laid back and friendly.  Nathan LawrenceMany factors contributed to my choice of UBC for graduate school. I was attracted to Vancouver’s geographical similarities to Portland in the pacific northwest. Also, I have family in the area. However, most importantly, I was intrigued and inspired by my professors and advisors to take on the...  Considering Vancouver as your next home?This city won’t disappoint. It has it all: sea, parks, mountains, beaches and all four seasons, including beautiful summers and mild, wet winters with snow.
Strategic Priorities
Initiatives
Doctor of Philosophy ProgramBesides satisfying the general regulations of the Graduate School for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, the student must comply with the requirements briefly outlined below. For complete details about these requirements see section IV of the Graduate Handbook . Pass four Qualifying Examinations . The exams are based on material that is covered in the courses listed and on material from undergraduate prerequisites. Credit for passing a similar examination at another university cannot be transferred. See sections IV and VI of the Graduate Handbook for more information. Advanced Topics Examinations. A student becomes eligible to take the Advanced Topics Examination after passing the Qualifying Examinations. Plan of Study. The plan of study should be submitted electronically to the Graduate School through myPurdue by each student preparing to hold their Advanced Topics. Preliminary Examination. The preliminary examination for most students will only require the completion of a form for the Graduate School. An oral or written examination may be required by the student's advisory committee for admission to candidacy. Graduate School regulations require that at least two sessions (including summer sessions) must elapse between the preliminary examination and the thesis defense. Admission to Candidacy. To be admitted to candidacy for the Ph.D. degree, the student must have fulfilled the requirements above which are detailed in section IV of the Graduate Handbook . Dissertation. A thesis must be submitted in final form presenting new results of sufficient importance to merit publication. Recommendation for the Ph.D. Degree. If the requirements are met within the time limits detailed in section IV of the Graduate Handbook , the candidate will be recommended to the faculty to receive the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. For information about financial support and research in absentia see section IV of the Graduate Handbook .
Department of Mathematics, Purdue University, 150 N. University Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907-2067 Phone: (765) 494-1901 - FAX: (765) 494-0548 Contact Us © 2024 Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Copyright Complaints | DOE Degree Scorecards Trouble with this page? Accessibility issues ? Please contact the College of Science . Maintained by Science IT  Search form
Research Groups
 Doctor of Philosophy (DPhil)What is a dphil. A DPhil is Oxford's name for a PhD - a higher research degree which allows you to make an original contribution to mathematics in the form of a thesis. A DPhil takes three to four years to complete. During your DPhil, you will be supervised by at least one academic, although some students will have more than one supervisor (particularly if they are working across disciplines). Unlike CDT courses (and PhDs in other countries), you will begin to do research straight away and there is no prescribed taught component. As part of your study toward a DPhil in Mathematics at Oxford, you will also be required to complete broadening and skills training and deliver class teaching to undergraduates, to enhance your broader mathematical knowledge and develop your career. You are very welcome to attend seminars and there may also be journal clubs or seminar series specific to your area of study. If you enjoy doing mathematics, and would like to be part of a lively and world-class research institute, take a look at our research groups to see if they align with your own interests. How to applyAll applications should be submitted online through the University's Graduate Application Form . Before you apply, check that you can meet the entry requirements , and read the University of Oxford's graduate application guide . Key DeadlinesApplication deadlines for the DPhil in Mathematics:
Please apply by the 8th January deadline to be considered for available University-administered or Departmental scholarships. Martingale Foundation Postgraduate ScholarshipsThe Martingale Foundation awards fully funded Scholarships for postgraduate degrees in the mathematical sciences at research universities in the UK. Tuition fees and research expenses are fully covered, and Scholars receive a tax free living wage stipend. Martingale Scholars also receive access to leadership and career develop through a multi-year programme of training and support. Visit the Martingale website for more information. Applications for the 2025 academic year are open until 27 October 2024. Why do a PhD?Research interests: group theory, representation theory and algebraic aspects of geometry. Who's who in Algebra Find out more about the group Combinatorics Research interests: extremal combinatorics, graph theory, and combinatorial number theory. Who's who in Combinatorics Functional Analysis Research interests: operator theory, including unbounded operators, and abstract differential equations. Who's who in functional analysis  Research interests: algebraic geometry, geometric representation theory , and differential geometry. Who's who in Geometry History of Mathematics Research interests: history of algebra (19th and 20th century), history of modern algebra, and Soviet mathematics.  Research interests: analytic topology, geometric stability theory, and the model theory of p-adic fields and diophantine geometry. Who's who in Logic Machine Learning and Data Science Machine Learning and Data science are being developed using wide ranging mathematical techniques. Our particular research expertise include: applied and computational harmonic analysis, networks, optimisation, random matrix theory, rough paths, topological data analysis, and the application of these methods. Who's who in machine learning and data science Mathematical & Computational Finance Research interests: behavioural finance, financial big data, high dimensional numerical methods, stochastic analysis. Who's who in Mathematical and Computational Finance Mathematical Biology Research interests: cancer modelling, collective behaviour, gene regulatory networks, multiscale modelling, pattern formation, and sperm dynamics. Who's who in Mathematical Biology Mathematical Physics Research interests: gauge and gravity theories (quantum field theories), string theory, twistor theory, Calabi-Yau manifolds, quantum computation and cryptography. Who's who in Mathematical Physics Number TheoryResearch interests: analytic number theory, arithmetic geometry, prime number distribution, and Diophantine geometry. Who's who in Number Theory Numerical Analysis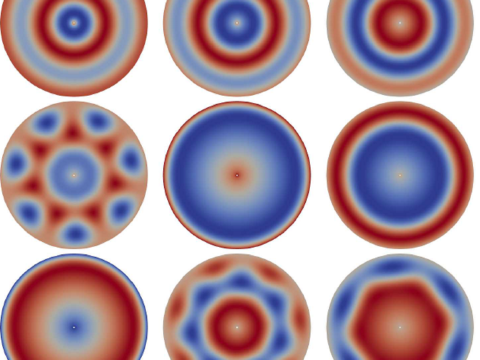 Research interests: complexity in optimisation, symmetric cone programming, numerical solutions of PDEs. Who's who in Numerical Analysis Oxford Centre for Industrial and Applied Mathematics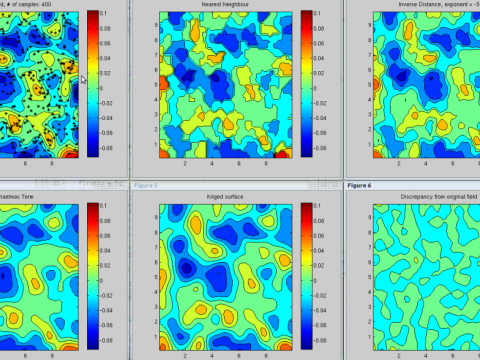 Research interests: energy, industry, geoscience, networks, finance, methodologies. Who's who in OCIAM Oxford Centre for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations Research interests: geometric analysis, inverse problems, nonlinear hyperbolic systems, specific PDE systems. Who's who in OxPDE Stochastic Analysis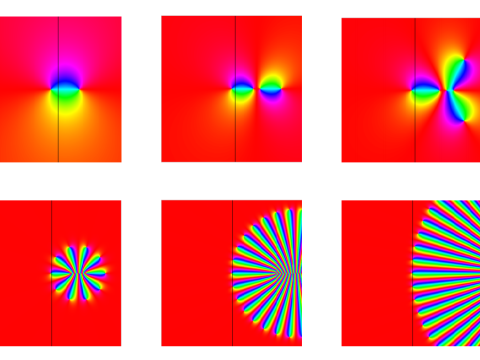 Research interests: rough path theory, Schramm-Loewner evolution, mathematical population genetics, financial mathematics, self-interacting random processes. 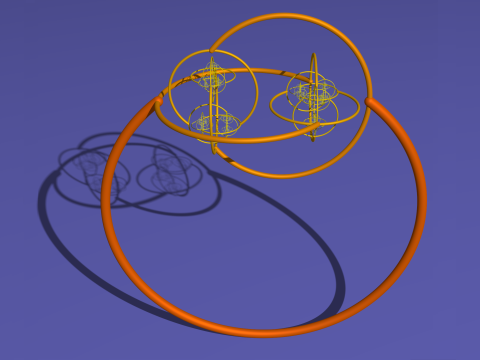 Research interests: geometric group theory, 3-manifold topology and knot theory, K-theory, algebraic topology. Who's who in Topology Ph.D. ProgramDegree requirements. In outline, to earn the PhD in either Mathematics or Applied Mathematics, the candidate must meet the following requirements.
Detailed RegulationsThe detailed regulations of the Ph.D. program are the following: Course RequirementsDuring the first year of the Ph.D. program, the student must enroll in at least 4 courses. At least 2 of these must be graduate courses offered by the Department of Mathematics. Exceptions can be granted by the Vice-Chair for Graduate Studies. Preliminary ExaminationThe Preliminary Examination consists of 6 hours (total) of written work given over a two-day period (3 hours/day). Exam questions are given in calculus, real analysis, complex analysis, linear algebra, and abstract algebra. The Preliminary Examination is offered twice a year during the first week of the fall and spring semesters. Qualifying ExaminationTo arrange the Qualifying Examination, a student must first settle on an area of concentration, and a prospective Dissertation Advisor (Dissertation Chair), someone who agrees to supervise the dissertation if the examination is passed. With the aid of the prospective advisor, the student forms an examination committee of 4 members. All committee members can be faculty in the Mathematics Department and the chair must be in the Mathematics Department. The QE chair and Dissertation Chair cannot be the same person; therefore, t he Math member least likely to serve as the dissertation advisor should be selected as chair of the qualifying exam committee . The syllabus of the examination is to be worked out jointly by the committee and the student, but before final approval, it is to be circulated to all faculty members of the appropriate research sections. The Qualifying Examination must cover material falling in at least 3 subject areas and these must be listed on the application to take the examination. Moreover, the material covered must fall within more than one section of the department. Sample syllabi can be reviewed online or in 910 Evans Hall. The student must attempt the Qualifying Examination within twenty-five months of entering the PhD program. If a student does not pass on the first attempt, then, on the recommendation of the student's examining committee, and subject to the approval of the Graduate Division, the student may repeat the examination once. The examining committee must be the same, and the re-examination must be held within thirty months of the student's entrance into the PhD program. For a student to pass the Qualifying Examination, at least one identified member of the subject area group must be willing to accept the candidate as a dissertation student. Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics
International students may need to surpass the Graduate School’s minimum English language proficiency exam scores for this program. If the graduate program has unique score requirements, they will be detailed below. Otherwise, please refer to the Graduate School’s minimum score guidelines.
Degree Description:PhD in Mathematics This degree is awarded in recognition of distinctive scholarship and original contributions to knowledge in Mathematics. The PhD program is especially designed to prepare the student for teaching at the graduate level and doing mathematical research in academic, industrial and business settings. Students studying various fields within the realm of pure mathematics would be included in this PhD program. PhD in Mathematics (Applied Mathematics Option) The specialization of modern academic disciplines provides both a challenge to those who wish to do research at the interface of mathematics and its areas of application and many opportunities to make valuable contributions. The Applied Mathematics Option allows students from a range of backgrounds to pursue a traditional applied mathematics program, while retaining the option to thoroughly learn an area of application. Entering students may not necessarily have a bachelor’s degree in Mathematics. However, they will be required to demonstrate a grasp of the core areas of advanced calculus and linear algebra at the level of a bachelor’s degree in Mathematics. They will then be given great latitude to take specialized courses in Mathematics and their area of application. PhD in Mathematics with Education Emphasis The degree of PhD in Mathematics with Education Emphasis is awarded in recognition of scholarship and original contributions to the teaching and learning of mathematics. The main difference from the other PhD choices is in the research focus. The requirements for this PhD include competence in core mathematics, as well as study in the research methodologies applicable to research in mathematics education. Admission Requirements:Students should have taken upper-level analysis and linear algebra courses before applying, and have the equivalent of an undergraduate degree in mathematics, statistics, or a related field. Additional upper-level courses like abstract algebra, functional or complex analysis, optimization, applied mathematics, topology, etc. will be taken into account. For international students, either a TOEFL, IETLS or Duolingo score is required. The minimum score for admission is listed above. The minimum score required for assistantship consideration is TOEFL score of 100, IELTS of 7, or Duolingo of 130. Exceptions can be found here: https://gradschool.wsu.edu/international-requirements/ Students applying to the PhD Mathematics program will be automatically considered for an assistantship position. The application will require:
Career Opportunities:Academia (tenure-track positions at universities and colleges worldwide), Bio-statistics (health and pharmaceutical companies), Risk analysis (financial and insurance companies, investment management), Research (state or federal government, software development), Mathematics education (publishing, consulting and developing of educational software). Career Placements:Graduates from the Mathematics PhD program begin careers in both academia and government or industry. A few examples of career placements in academia from the past few years include:
A few examples of career placements in government and industry from the past few years include:
Contact Information:
Department of Philosophy
Philosophy and MathematicsThe Departments of Philosophy and of Mathematics together offer a joint Ph.D. degree in Philosophy and Mathematics. Students in this program submit a single dissertation prepared under the supervision of members of both departments. Students enrolled in the Philosophy PhD program at Notre Dame can apply to the joint-degree program (typically during their third year of study). The joint-degree program does not accept applications from students outside of Notre Dame or admit students to the University. The joint Ph.D. program continues a long tradition of the advanced study of formal logic at the University of Notre Dame. Tim Bays (Philosophy) Jc Beall (Philosophy) Patricia Blanchette (Philosophy) Peter Cholak (Mathematics) Natasha Dobrinen (Mathematics) Curtis Franks (Philosophy) Joel David Hamkins (Philosophy and Mathematics) Julia Knight (Mathematics) Anand Pillay (Mathematics and Philosophy) Nicholas Ramsey (Mathematics) Sergei Starchenko (Mathematics) Philosophy students interested in the joint program begin preparing to apply immediately upon beginning their studies at Notre Dame. In addition to philosophy coursework, they take at least the two semester logic sequence, and sometimes other courses, in the Mathematics Department in their first year. They also take part in the Mathematics Department's research seminars. By the second year, they have taken several courses in the Mathematics Department and become integrated into the research group of a Mathematics faculty member whom they intend to be their mathematics supervisor. Most students will then choose to apply to the Master of Science in Interdisciplinary Mathematics (MSIM). This application describes a list of courses and a research project that the student and his or her mathematics supervisor propose. While working towards the MSIM, the student decides either to complete the degree as initially described or to expand the project into a joint program dissertation. In the latter case, the student applies to the joint-degree program. RequirementsStudents in the joint program are required to take only 27 credits in Philosophy. Joint Program students need to take only two of the three seminars in the history of philosophy that are required for the regular Philosophy PhD. program, and the 3 credit seminar "Intermediate Logic" is not required. Students are required to take the two course logic sequence, the two course algebra sequence, and 9 additional credits in the Mathematics Department. Joint program students take the Mathematics Department's oral candidacy exam instead of the Philosophy Department's oral exam. This consists of both the basic and advanced exams in logic and the basic exam in one other area. Matteo Bianchetti, MSIM: "Infinite Time Computation: Strong and Weak Infinite Time Turing Machines" (C. Franks, J. Knight); Ph.D. in Philosophy: "Geometric representations in mathematical problem-solving. Intuition and creativity" (C. Franks), Current Placement: non-academic Paul Trần-Hoàng , MSIM: "Model-Theoretic Galois Cohomology" (A. Pillay, C. Franks); Ph.D. in Philosophy: "Model-Theoretic Approaches to Theoretical Equivalence and Reduction" (T. Bays, C. Franks). Current placement: Visiting Assistant Professor, Vassar College Graham Leach-Krouse , Joint Ph.D.: "Conceptions of Absolute Provability" (T. Bays, M. Detlefsen, P. Larson). Current placement: Associate Professor, Department of Philosophy, Kansas State University. Chris Porter , Joint Ph.D.: "Mathematical and Philosophical Perspectives on Algorithmic Randomness" (P. Cholak, M. Detlefsen, C. Franks). Current placement: Assistant Professor, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Drake University. Sean Walsh , Joint Ph.D.: "Arithmetical Knowledge and Arithmetical Definability: Four Studies" (P. Cholak, M. Detlefsen). Current placement: Associate Professor, Logic and Philosophy of Science, UCLA Andy Arana , Joint PhD: "Arithmetical Investigations: A Study of Models of Arithmetic and Purity of Methods" (M. Detlefsen, J. Knight). Current placement: Professor of Philosophy, University of Lorraine and Archives Henri-Poincaré.
 Home / Programs / Doctor of Philosophy (Mathematics) Doctor of Philosophy (Mathematics)The Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics Program is intended to encourage the development of mathematics in the Philippines through the production of highly trained mathematicians whose research works contribute to the development of new knowledge. Corollary to this main objective is the upgrading of mathematics teaching in colleges and universities. The PhD Math program is a research-oriented program that
Applications for admission to the program are processed by the College of Science (more information here ). Students can apply for admission during the 1st semester or 2nd semester. Aside from the general requirements for admission set forth by the College of Science, applicants of the PhD Math program must have either a BS or MS degree in mathematics, or its equivalent from a recognized institution of higher learning, and a high degree of intellectual capacity and aptitude for advanced study and research in mathematics. For more inquiries, please send an email to [email protected] . Students are required to accomplish the following:
The maximum residence of student under the PhD Math program is six (6) years for those with MS degrees and eight (8) years for those with BS degrees only. Core Courses
Other Required Courses
* courses in mathematics and allied fields, with at least twelve (12) of the fifteen (15) units chosen from advanced mathematics courses. Registration ProcessRefer to the Graduate Student Guide from the UPD College of Science website. Program AdvisersFor students admitted to the PhD Math program, please contact your program advisers listed below for your registration concerns.
Affiliations
Department of PhilosophyDietrich college of humanities and social sciences.  Philosophy and History of MathematicsLogic and mathematics are tools for almost all members of the Department, but they are also objects of investigation. As tools they provide means of rigorously capturing aspects of experience; as objects of investigation they are examined as to their internal coherence, their philosophical justification, and their adequacy for particular purposes. Since ancient times, there has been an intimate connection between philosophical and mathematical thought, a relationship that can be seen in the philosophical reflections of Plato, Descartes, Leibniz, and Kant. Subtle interactions between philosophy and mathematics can also be seen in the development of mathematics in the 19th century, i.e., in the revolutionary conceptual advances made by Dirichlet, Riemann, Dedekind and others, as well as in the similarly dramatic changes in logic, brought about in large part by Boole, Frege, Peano, Peirce, and Schröder. Complemented by the continuing evolution of the sciences, for example in the work of Hertz, Mach, and Einstein, these developments form the background for the emergence of early analytic philosophy and modern mathematical logic. This historical background reshapes in significant ways the contemporary discussion in the philosophy of mathematics. The subject is deeply influenced by results of meta-mathematical investigations, but most importantly, for the work in this department, also by mathematical practice. The incompleteness theorems are considered, rightly, to be gems of work in mathematical logic of the last century. They are also viewed as having an enormous philosophical significance; that seems to be right, but only relative to a precise concept of "formal system". The latter is defined using the notion of computability. On the one hand, one can understand then the seemingly conflicting views of Gödel and Turing on mathematical knowledge and the capacities of the human mind. On the other hand, one can go back and see what was supposed to be captured by "formal theories" and uncover the dramatic transformation of mathematics in the 19th century. The "structuralist" view of mathematics one finds in Dedekind's "foundational" work really emerged out of his concrete work in algebraic number theory. His broad perspective on mathematics impacted that view, which was of course also influenced by Gauss, Dirichlet, and Riemann. Sieg has taken that view as a starting-point and joined it with a quasi-constructive perspective of accessible domains to arrive at an articulation of a "reductive structuralism". This position resolves a number of traditional epistemological and ontological problems. With Awodey and a number of other colleagues, Sieg is editing and translating the marvelous and most significant philosophical essays of Hilbert’s collaborator in the proof theoretic enterprise, Paul Bernays. Sieg's own perspective is developed in his book Hilbert’s Programs and Beyond that was published by Oxford University Press. The philosophy of mathematics has traditionally been concerned with questions of justification and correctness. But as of late a number of researchers have aimed to characterize more general methodological goals and values that influence the decisions that mathematicians make in their everyday practice, for example, when posing questions, formulating definitions, writing proofs, and structuring theories. Using insights from proof theory, formal verification, and the history of mathematics, Avigad has worked to develop more robust accounts of mathematical concepts, methods, and understanding. Awodey is exploring connections between category theory and structuralism, especially in light of the new Univalent Foundations program. Univalent Foundations includes a new foundational axiom, the Univalence Axiom, according to which isomorphic structures can be identified. This new principle has obvious philosophical consequences, and will doubtless challenge philosophers of mathematics to adjust their views. Philosophers interested in structuralism have begun to recognize the importance of these recent developments, with e.g. several leading philosophers of physics including Ladymann (Bristol) and Halvorson (Princeton) actively engaged in philosophical research on Univalent Foundations. In addition to the comprehensive book Homotopy Type Theory , Awodey has written a survey article on the topic of Univalence and structuralism to be published in the journal Philosophia Mathematica which will serve to introduce the subject to a wider audience of philosophers of mathematics. The history of mathematics can be a useful aid in developing a robust and informative philosophy of mathematics. Sieg has explored the logicist and structuralist perspectives that are found in the seminal foundational writings of Dedekind. These perspectives emerged out of the concrete mathematical work Dedekind did in algebraic number theory, and they stand in sharp contrast with those of his contemporary Leopold Kronecker. In work with Rebecca Morris, respectively with Dirk Schlimm, Sieg has analyzed as central features in Dedekind’s work the introduction of abstract concepts (structures) and the use of structure preserving mappings between different structures (of the same kind). The concept of abstraction involved here is not the classical one, found for example in Kant’s "Logik", but rather one that is exposed in the writings on logic of the contemporaneous and very influential Göttingen philosopher Hermann Lotze. Avigad has explored methodological aspects of Dedekind's work, especially the development of his theory of ideal divisors, in an effort to understand the way that such methodological considerations interact with philosophical views. With Rebecca Morris, he has studied the history of Dirichlet's seminal theorem on primes in an arithmetic progression, which illuminates the methodological forces that shaped the development of the modern function concept, as well as some of the issues that Frege had to address with his treatment of functions. Avigad has also considered the philosophical views of Kurt Gödel vis-a-vis the meta-mathematical tradition, and has tried to characterize and explain an uneasy tension between Gödel's views and Carnap's. This concrete work on the dramatic shift in the evolution of mathematics during the 19th century, where some speak of a "transformation of the subject" others of a "revolution," has deep impact on the philosophy of mathematics - a subject that as recently as twenty years ago was pre-occupied with the "Grundlagenstreit" between Brouwer and Hilbert in the 1920s. Both Hilbert and Brouwer are deeply connected to the broad issues alluded to above. Sieg, with colleagues W. Ewald, M. Hallett, and U. Majer, has been working on editing unpublished lecture notes of Hilbert's from the 1890s to the 1930s. They open up a completely novel and fresh perspective on the evolution of Hilbert's foundational thinking and the emergence of proof theory, but that means also on the origins of analytic philosophy.
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in mathematics is the highest degree offered by our program. Graduates will have demonstrated their ability to conduct independent scientific research and contribute new mathematical knowledge and scholarship in their area of specialization. They will be well-supported and well prepared for research and faculty positions at academic institutions anywhere in the ...
Graduate Thesis 2. 288-360. Total Units. 396-468. Note: Students in this program can choose to receive the Doctor of Philosophy or the Doctor of Science in Mathematics. Students receiving veterans benefits must select the degree they wish to receive prior to program certification with the Veterans Administration. 1. Select subjects in Mathematics.
Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics. The program offers extensive coursework and intensive research experience in theory, methodology, and applications of mathematics (see degree requirements ). Faculty members with broad and diverse research interests are available to supervise doctoral dissertations.
The requirements that must be satisfied for a candidate to receive a Ph.D. include: The candidate must pass Preliminary Examinations. The candidate must obtain a grade of B or better in at least 24 semester credit hours of courses in the Mathematics Ph.D. program. Students should take doctoral research classes MATH 8x98 (where "x" is the ...
The Department of Mathematics offers a program leading to the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. The PhD program is an intensive course of study designed for the full-time student planning a career in research and teaching at the university level or in quantitative research and development in industry or government.
Get your PhD in Mathematics The PhD program places a strong emphasis on preparation for research and teaching. Students must earn at least 72 semester hours of graduate credit and spend at least three years in residence at a graduate college, including at least one year at the University of Iowa.
The graduate student must further complete a course of study approved by the doctoral program committee and pass a comprehensive examination. The active areas of research interest of the current members of the staff are: algebraic geometry, commutative algebra, number theory, representation theory, analysis (real, complex, functional and harmonic), analytic functions, applied mathematics ...
The program of studies for a Math Department PhD student is divided into two main parts: Pre- and Post-Candidacy. Before taking the Candidacy Exam, students need to fulfill numerous requirements which ensure solid preparation in core mathematical areas as well in their chosen specialization. These include passing the Qualifying Requirements as ...
Conduct mathematics-based research and generate new knowledge in a multidisciplinary environment with the PhD in Applied Mathematics program. At North America's only dedicated Faculty of Mathematics and the #1 school in Canada for mathematics and computer science, you'll connect theoretical advances and innovative mathematics to develop ...
Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics (PhD) Requirements Outline. The PhD degree is a research degree and the principal requirement is that a student writes an original research thesis (also referred to as their doctoral dissertation). The thesis is produced using research conducted under the supervision of a faculty member, and it is examined by ...
The Mathematics Department offers the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Mathematics. The Ph.D. program provides broad and deep expertise in mathematics, culminating in a dissertation that includes significant original work. It is intended for students with a strong mathematical background who plan a career in research in academia or ...
Applications for the Joint PhD in Mathematics and Philosophy. will only be considered for students in their first four years of graduate study, and admission to the Joint PhD must happen before the start of the student's 5th year. A student applying to the Joint PhD program need not complete their MAMP thesis; in many cases the work going ...
The Department of Mathematics offers a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Program that prepares students to pursue successful research careers as professional mathematicians in academia, industry, government labs, or the financial sector. It provides a rigorous and thorough education, under a very dynamic and interactive environment, aimed at preparing ...
Mathematicians use theoretical and computational methods to solve a wide range of problems from the most abstract to the very applied. UBC's mathematics graduate students work in many branches of pure and applied mathematics. The PhD program trains students to operate as research mathematicians. The focus of the program is on substantial mathematical research leading to the PhD dissertation ...
Doctor of Philosophy Program. Besides satisfying the general regulations of the Graduate School for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, the student must comply with the requirements briefly outlined below. For complete details about these requirements see section IV of the Graduate Handbook. Pass four Qualifying Examinations.
A DPhil is Oxford's name for a PhD - a higher research degree which allows you to make an original contribution to mathematics in the form of a thesis. A DPhil takes three to four years to complete. During your DPhil, you will be supervised by at least one academic, although some students will have more than one supervisor (particularly if they ...
In outline, to earn the PhD in either Mathematics or Applied Mathematics, the candidate must meet the following requirements. During the first year of the Ph.D. program: Take at least 4 courses, 2 or more of which are graduate courses offered by the Department of Mathematics. Pass the six-hour written Preliminary Examination covering calculus ...
Each mathematics graduate student must maintain a cumulative grade point average of 3.0 or better. First Year, Qualifying and Language Exams ... The Departments of Mathematics and Statistics jointly offer a Doctor of Philosophy degree with a comajor in mathematics and statistics for graduate students who wish to combine the strengths of both ...
Degree Description: PhD in Mathematics. This degree is awarded in recognition of distinctive scholarship and original contributions to knowledge in Mathematics. The PhD program is especially designed to prepare the student for teaching at the graduate level and doing mathematical research in academic, industrial and business settings.
The Departments of Philosophy and of Mathematics together offer a joint Ph.D. degree in Philosophy and Mathematics. Students in this program submit a single dissertation prepared under the supervision of members of both departments. Students enrolled in the Philosophy PhD program at Notre Dame can apply to the joint-degree program (typically ...
The Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics Program is intended to encourage the development of mathematics in the Philippines through the production of highly trained mathematicians whose research works contribute to the development of new knowledge. ... The PhD Math program is a research-oriented program that. prepares students for careers in the ...
Graduate Students Not in Residence Research Research Areas Logic and Philosophy of Mathematics Categorical Logic Computability & Automated Proof Search Homotopy Type Theory Philosophy and History of Mathematics Philosophy of Language and Linguistics Philosophical Logic Proof Theory
Subtle interactions between philosophy and mathematics can also be seen in the development of mathematics in the 19th century, i.e., in the revolutionary conceptual advances made by Dirichlet, Riemann, Dedekind and others, as well as in the similarly dramatic changes in logic, brought about in large part by Boole, Frege, Peano, Peirce, and ...