

About Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.
Dr. king jr..

Drawing inspiration from both his Christian faith and the peaceful teachings of Mahatma Gandhi, Dr. King led a nonviolent movement in the late 1950s and ‘ 60s to achieve legal equality for African-Americans in the United States. While others were advocating for freedom by “any means necessary,” including violence, Martin Luther King, Jr. used the power of words and acts of nonviolent resistance, such as protests, grassroots organizing, and civil disobedience to achieve seemingly-impossible goals. He went on to lead similar campaigns against poverty and international conflict, always maintaining fidelity to his principles that men and women everywhere, regardless of color or creed, are equal members of the human family.
Dr. King’s “I Have a Dream” speech, Nobel Peace Prize lecture and “Letter from a Birmingham Jail” are among the most revered orations and writings in the English language. His accomplishments are now taught to American children of all races, and his teachings are studied by scholars and students worldwide. He is the only non-president to have a national holiday dedicated in his honor and is the only non-president memorialized on the Great Mall in the nation’s capital. He is memorialized in hundreds of statues, parks, streets, squares, churches and other public facilities around the world as a leader whose teachings are increasingly-relevant to the progress of humankind.
Some of Dr. King’s Most Important Achievements

In 1957 , Dr. King was elected president of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC), an organization designed to provide new leadership for the now burgeoning civil rights movement. He would serve as head of the SCLC until his assassination in 1968, a period during which he would emerge as the most important social leader of the modern American civil rights movement.
In 1963 , he led a coalition of numerous civil rights groups in a nonviolent campaign aimed at Birmingham, Alabama, which at the time was described as the “most segregated city in America.” The subsequent brutality of the city’s police, illustrated most vividly by television images of young blacks being assaulted by dogs and water hoses, led to a national outrage resulting in a push for unprecedented civil rights legislation. It was during this campaign that Dr. King drafted the “Letter from a Birmingham Jail,” the manifesto of Dr. King’s philosophy and tactics, which is today required-reading in universities worldwide.
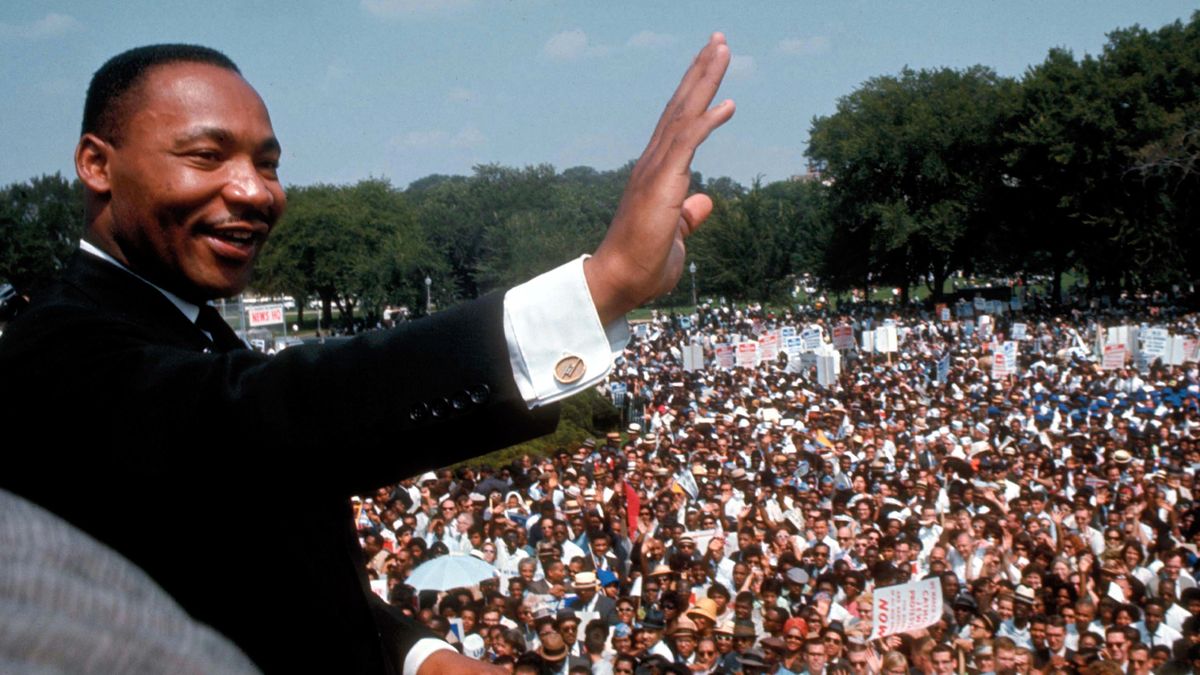
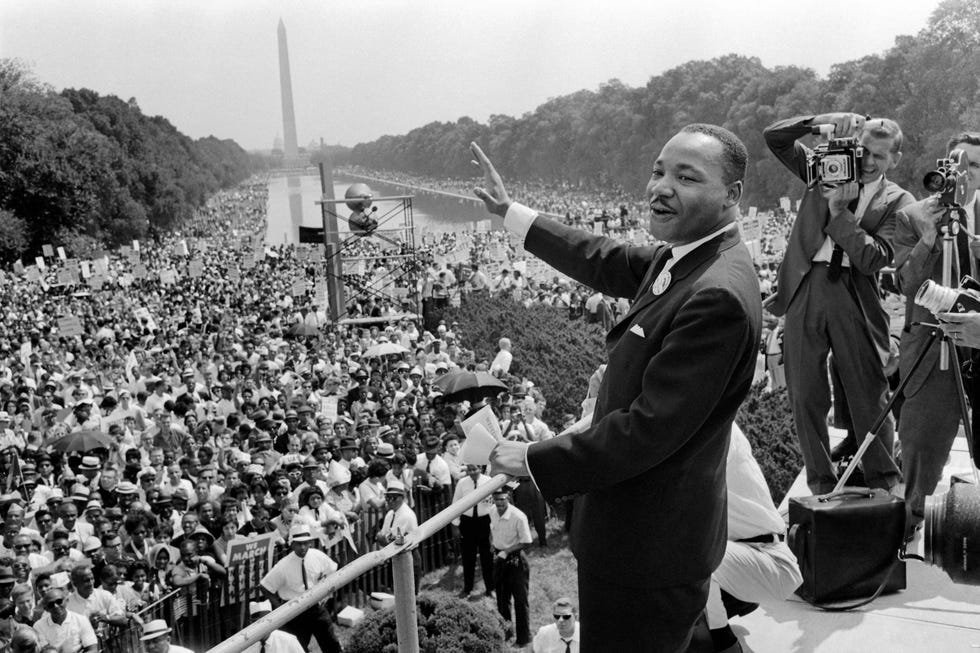
Later in 1963 , Dr. King was one of the driving forces behind the March for Jobs and Freedom, more commonly known as the “March on Washington,” which drew over a quarter-million people to the national mall. It was at this march that Dr. King delivered his famous “I Have a Dream” speech, which cemented his status as a social change leader and helped inspire the nation to act on civil rights. Dr. King was later named Time magazine’s “Man of the Year.”

Also in 1964 , partly due to the March on Washington, Congress passed the landmark Civil Rights Act, essentially eliminating legalized racial segregation in the United States. The legislation made it illegal to discriminate against blacks or other minorities in hiring, public accommodations, education or transportation, areas which at the time were still very segregated in many places.
The next year, 1965 , Congress went on to pass the Voting Rights Act, which was an equally-important set of laws that eliminated the remaining barriers to voting for African-Americans, who in some locales had been almost completely disenfranchised. This legislation resulted directly from the Selma to Montgomery, AL March for Voting Rights lead by Dr. King.
Between 1965 and 1968, Dr. King shifted his focus toward economic justice – which he highlighted by leading several campaigns in Chicago, Illinois – and international peace – which he championed by speaking out strongly against the Vietnam War. His work in these years culminated in the “Poor Peoples Campaign,” which was a broad effort to assemble a multiracial coalition of impoverished Americans who would advocate for economic change.
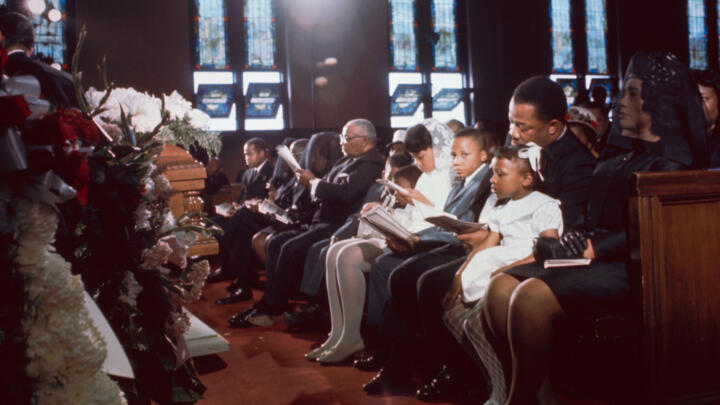
Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.’s less than thirteen years of nonviolent leadership ended abruptly and tragically on April 4th, 1968 , when he was assassinated at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee. Dr. King’s body was returned to his hometown of Atlanta, Georgia, where his funeral ceremony was attended by high-level leaders of all races and political stripes.
- For more information regarding the Transcription of the King Family Press Conference on the MLK Assassination Trial Verdict December 9, 1999, Atlanta, GA. Click Here
- For more information regarding the Civil Case: King family versus Jowers. Click here .
- Later in 1968, Dr. King’s wife, Mrs. Coretta Scott King, officially founded the Martin Luther King, Jr. Center for Nonviolent Social Change, which she dedicated to being a “living memorial” aimed at continuing Dr. King’s work on important social ills around the world.
We envision the Beloved Community where injustice ceases and love prevails.
Contact Info
449 Auburn Avenue, NE Atlanta, Georgia 30312
404.526.8900
Quick Links
- History Timeline
- King Holiday
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Latest News
- Spotlight on Women’s History Month with The King Center
- The King Center Joins the King Family in Mourning the Loss of Naomi Barber King, wife of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr’s Late Brother
Stay Connected
Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and major leader of the Civil Rights Movement. After his assassination, he was memorialized by Martin Luther King Jr. Day.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.
In Focus: Martin Luther King Jr. Day
Days after his 1968 assassination , a campaign for a holiday in King’s honor began. U.S. Representative John Conyers Jr. of Michigan first proposed a bill on April 8, 1968, but the first vote on the legislation didn’t happen until 1979. King’s widow, Coretta Scott King , led the lobbying effort to drum up public support. Fifteen years after its introduction, the bill finally became law.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan ’s signature created Martin Luther King Jr. Day of Service as a federal holiday. It’s celebrated annually on the third Monday in January. The only national day of service, Martin Luther King Jr. Day was first celebrated in 1986. The first time all 50 states recognized the holiday was in 2000.
See Martin Luther King Jr.’s life depicted onscreen in the 2018 documentary I Am MLK Jr. or the Oscar-winning movie Selma .
Quick Facts
Where did martin luther king jr. go to school, philosophy of nonviolence, civil rights accomplishments, "i have a dream" and other famous speeches, wife and kids, fbi surveillance, later activism, assassination, who was martin luther king jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and civil rights activist who had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States, beginning in the mid-1950s. Among his many efforts, King headed the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). Through his nonviolent activism and inspirational speeches , he played a pivotal role in ending legal segregation of Black Americans, as well as the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 . King won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964, among several other honors. He was assassinated by James Earl Ray and died on April 4, 1968, at age 39. King continues to be remembered as one of the most influential and inspirational Black leaders in history.
FULL NAME: Martin Luther King Jr. BIRTHDAY: January 15, 1929 DIED: April 4, 1968 BIRTHPLACE: Atlanta, Georgia SPOUSE: Coretta Scott King (1953-1968) CHILDREN: Yolanda, Martin III, Dexter, and Bernice King ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Capricorn
Martin Luther King Jr. was born as Michael Luther King Jr. in Atlanta. His birthday was January 15, 1929.

His parents were Michael Luther King Sr. and Alberta Williams King. The Williams and King families had roots in rural Georgia. Martin’s maternal grandfather, A.D. Williams, was a rural minister for years and then moved to Atlanta in 1893. He took over the small, struggling Ebenezer Baptist Church with around 13 members and made it into a forceful congregation. He married Jennie Celeste Parks, and they had one child who survived, Alberta.
Michael Sr. came from a family of sharecroppers in a poor farming community. He married Alberta in 1926 after an eight-year courtship. The newlyweds moved to A.D.’s home in Atlanta. Michael stepped in as pastor of Ebenezer Baptist Church upon the death of his father-in-law in 1931. He, too, became a successful minister and adopted the name Martin Luther King Sr. in honor of the German Protestant religious leader Martin Luther . In due time, Michael Jr. followed his father’s lead and adopt the name himself to become Martin Luther King Jr.
A middle child, Martin Jr. had an older sister, Willie, and a younger brother, Alfred. The King children grew up in a secure and loving environment. Martin Sr. was more the disciplinarian, while Alberta’s gentleness easily balanced out their father’s strict hand.
Although they undoubtedly tried, Martin Jr.’s parents couldn’t shield him completely from racism. His father fought against racial prejudice, not just because his race suffered, but also because he considered racism and segregation to be an affront to God’s will. He strongly discouraged any sense of class superiority in his children, which left a lasting impression on Martin Jr.
Growing up in Atlanta, King entered public school at age 5. In May 1936, he was baptized, but the event made little impression on him.
In May 1941, King was 12 years old when his grandmother Jennie died of a heart attack. The event was traumatic for the boy, more so because he was out watching a parade against his parents’ wishes when she died. Distraught at the news, young King jumped from a second-story window at the family home, allegedly attempting suicide.
King attended Booker T. Washington High School, where he was said to be a precocious student. He skipped both the ninth and eleventh grades and, at age 15, entered Morehouse College in Atlanta in 1944. He was a popular student, especially with his female classmates, but largely unmotivated, floating through his first two years.
Influenced by his experiences with racism, King began planting the seeds for a future as a social activist early in his time at Morehouse. “I was at the point where I was deeply interested in political matters and social ills,” he recalled in The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr . “I could envision myself playing a part in breaking down the legal barriers to Negro rights.”
The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr.

At the time, King felt that the best way to serve that purpose was as a lawyer or a doctor. Although his family was deeply involved in the church and worship, King questioned religion in general and felt uncomfortable with overly emotional displays of religious worship. This discomfort had continued through much of his adolescence, initially leading him to decide against entering the ministry, much to his father’s dismay.
But in his junior year, King took a Bible class, renewed his faith, and began to envision a career in the ministry. In the fall of his senior year, he told his father of his decision, and he was ordained at Ebenezer Baptist Church in February 1948.
Later that year, King earned a sociology degree from Morehouse College and began attended the liberal Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania. He thrived in all his studies, was elected student body president, and was valedictorian of his class in 1951. He also earned a fellowship for graduate study.
Even though King was following his father’s footsteps, he rebelled against Martin Sr.’s more conservative influence by drinking beer and playing pool while at college. He became romantically involved with a white woman and went through a difficult time before he could break off the relationship.
During his last year in seminary, King came under the guidance of Morehouse College President Benjamin E. Mays, who influenced King’s spiritual development. Mays was an outspoken advocate for racial equality and encouraged King to view Christianity as a potential force for social change.

After being accepted at several colleges for his doctoral study, King enrolled at Boston University. In 1954, while still working on his dissertation, King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church of Montgomery, Alabama. He completed his doctorate and earned his degree in 1955 at age 25.
Decades after King’s death, in the late 1980s, researchers at Stanford University’s King Papers Project began to note similarities between passages of King’s doctoral dissertation and those of another student’s work. A committee of scholars appointed by Boston University determined that King was guilty of plagiarism in 1991, though it also recommended against the revocation of his degree.

First exposed to the concept of nonviolent resistance while reading Henry David Thoreau ’s On Civil Disobedience at Morehouse, King later discovered a powerful exemplar of the method’s possibilities through his research into the life of Mahatma Gandhi . Fellow civil rights activist Bayard Rustin , who had also studied Gandhi’s teachings, became one of King’s associates in the 1950s and counseled him to dedicate himself to the principles of nonviolence.
As explained in his autobiography , King previously felt that the peaceful teachings of Jesus applied mainly to individual relationships, not large-scale confrontations. But he came to realize: “Love for Gandhi was a potent instrument for social and collective transformation. It was in this Gandhian emphasis on love and nonviolence that I discovered the method for social reform that I had been seeking.”
It led to the formation of King’s six principles of nonviolence :
- Nonviolence is a way of life for courageous people.
- Nonviolence seeks to win friendship and understanding.
- Nonviolence seeks to defeat injustice, not people.
- Nonviolence holds that suffering for a just cause can educate and transform.
- Nonviolence chooses love instead of hate.
- Nonviolence believes that the universe is on the side of justice.
In the years to come, King also frequently cited the “ Beloved Community ”—a world in which a shared spirit of compassion brings an end to the evils of racism, poverty, inequality, and violence—as the end goal of his activist efforts.

Led by his religious convictions and philosophy of nonviolence, King became one of the most prominent figures of the Civil Rights Movement . He was a founding member of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference and played key roles in several major demonstrations that transformed society. This included the Montgomery Bus Boycott that integrated Alabama’s public transit, the Greensboro Sit-In movement that desegregated lunch counters across the South, the March on Washington that led to the passage of the 1964 Civil Rights Act, and the Selma-to-Montgomery marches in Alabama that culminated in the 1965 Voting Rights Act.
King’s efforts earned him the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 when he was 35.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
King’s first leadership role within the Civil Rights Movement was during the Montgomery Bus Boycott of 1955–1956. The 381-day protest integrated the Alabama city’s public transit in one of the largest and most successful mass movements against racial segregation in history.
The effort began on December 1, 1955, when 42-year-old Rosa Parks boarded the Cleveland Avenue bus to go home after an exhausting day at work. She sat in the first row of the “colored” section in the middle of the bus. As the bus traveled its route, all the seats in the white section filled up, then several more white passengers boarded the bus.
The bus driver noted that there were several white men standing and demanded that Parks and several other African Americans give up their seats. Three other Black passengers reluctantly gave up their places, but Parks remained seated.
The driver asked her again to give up her seat, and again she refused. Parks was arrested and booked for violating the Montgomery City Code. At her trial a week later, in a 30-minute hearing, Parks was found guilty and fined $10 and assessed $4 court fee.
The local NAACP chapter had been looking to challenge Montgomery’s segregated bus policy and had almost made 15-year-old Claudette Colvin the face of the campaign months earlier. She similarly refused to give up her bus seat to a white man on March 2, 1955, but after organizers learned Colvin was pregnant, they feared it would scandalize the deeply religious Black community and make Colvin, along with the group’s efforts, less credible in the eyes of sympathetic white people. Parks’ experience of discrimination provided another opportunity.
On the night Parks was arrested, E.D. Nixon , head of the local NAACP chapter, met with King and other local civil rights leaders to plan a Montgomery Bus Boycott. King was elected to lead the boycott because he was young, well-trained, and had solid family connections and professional standing. He was also new to the community and had few enemies, so organizers felt he would have strong credibility with the Black community.
In his first speech as the group’s president, King declared:
“We have no alternative but to protest. For many years, we have shown an amazing patience. We have sometimes given our white brothers the feeling that we liked the way we were being treated. But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.”
King’s skillful rhetoric put new energy into the civil rights struggle in Alabama. The Montgomery Bus Boycott began December 5, 1955, and for more than a year, the local Black community walked to work, coordinated ride sharing, and faced harassment, violence, and intimidation. Both King’s and Nixon’s homes were attacked.
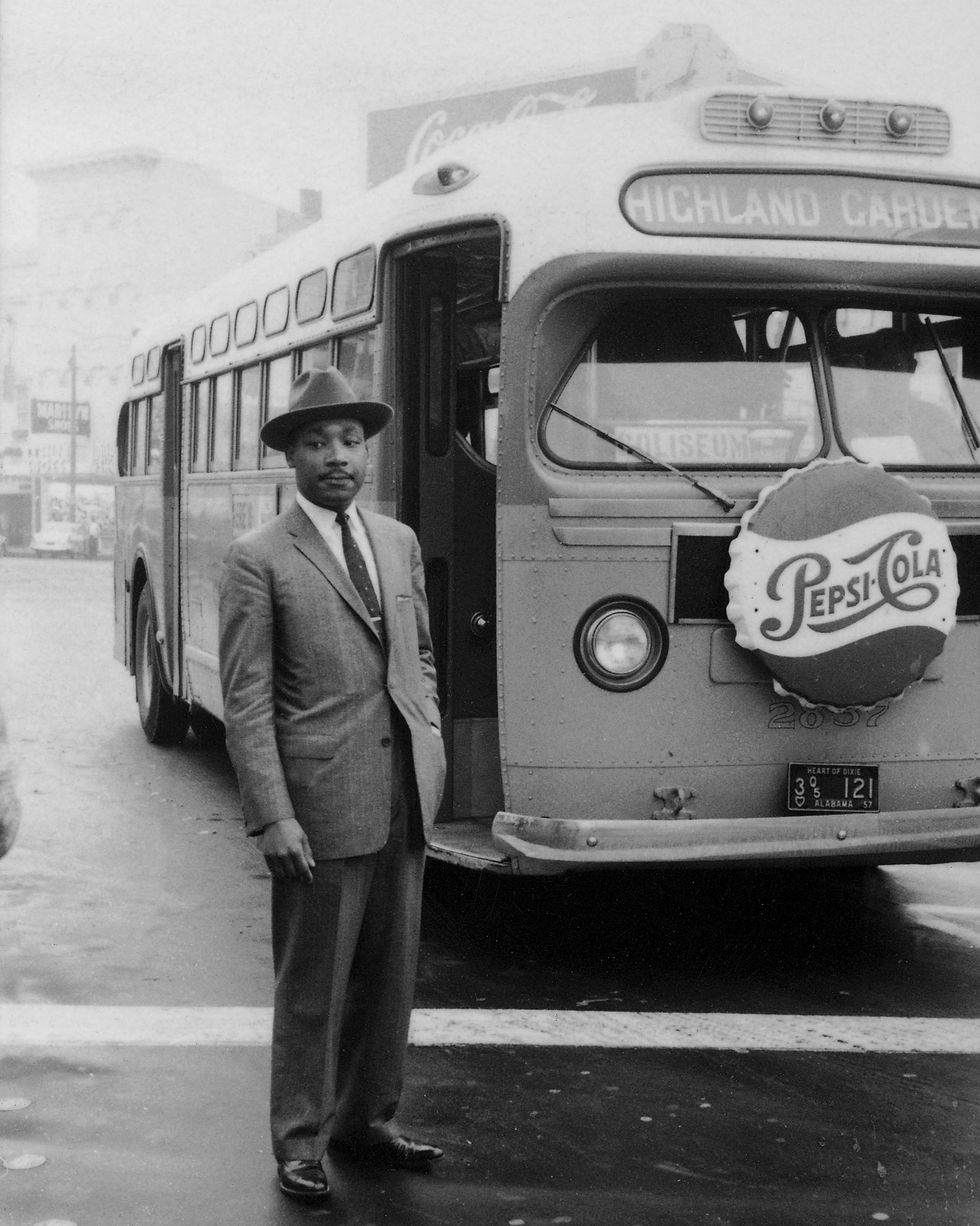
In addition to the boycott, members of the Black community took legal action against the city ordinance that outlined the segregated transit system. They argued it was unconstitutional based on the U.S. Supreme Court ’s “separate is never equal” decision in Brown v. Board of Education (1954). Several lower courts agreed, and the nation’s Supreme Court upheld the ruling in a November 13, 1956, decision that also ruled the state of Alabama’s bus segregation laws were unconstitutional.
After the legal defeats and large financial losses, the city of Montgomery lifted the law that mandated segregated public transportation. The boycott ended on December 20, 1956.
Southern Christian Leadership Conference
Flush with victory, African American civil rights leaders recognized the need for a national organization to help coordinate their efforts. In January 1957, King, Ralph Abernathy , and 60 ministers and civil rights activists founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to harness the moral authority and organizing power of Black churches. The SCLC helped conduct nonviolent protests to promote civil rights reform.
King’s participation in the organization gave him a base of operation throughout the South, as well as a national platform. The SCLC felt the best place to start to give African Americans a voice was to enfranchise them in the voting process. In February 1958, the SCLC sponsored more than 20 mass meetings in key southern cities to register Black voters. King met with religious and civil rights leaders and lectured all over the country on race-related issues.
Stride Toward Freedom: The Montgomery Story

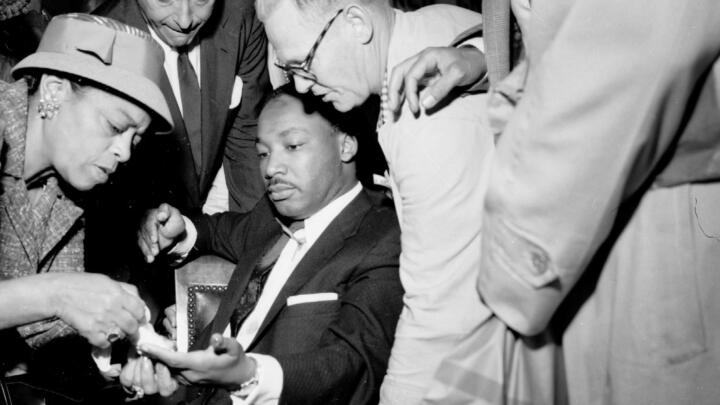
That September, King survived an attempt on his life when a woman with mental illness stabbed him in the chest as he signed copies of his book Stride Toward Freedom in a New York City department store. Saved by quick medical attention, King expressed sympathy for his assailant’s condition in the aftermath .
In 1959, with the help of the American Friends Service Committee, King visited Gandhi ’s birthplace in India. The trip affected him in a profound way, increasing his commitment to America’s civil rights struggle.
Greensboro Sit-In
By 1960, King was gaining national exposure. He returned to Atlanta to become co-pastor with his father at Ebenezer Baptist Church but also continued his civil rights efforts. His next activist campaign was the student-led Greensboro Sit-In movement.
In February 1960, a group of Black students in Greensboro, North Carolina , began sitting at racially segregated lunch counters in the city’s stores. When asked to leave or sit in the “colored” section, they just remained seated, subjecting themselves to verbal and sometimes physical abuse.
The movement quickly gained traction in several other cities. That April, the SCLC held a conference at Shaw University in Raleigh, North Carolina, with local sit-in leaders. King encouraged students to continue to use nonviolent methods during their protests. Out of this meeting, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) formed and, for a time, worked closely with the SCLC. By August 1960, the sit-ins had successfully ended segregation at lunch counters in 27 southern cities. But the movement wasn’t done yet.
On October 19, 1960, King and 75 students entered a local department store and requested lunch-counter service but were denied. When they refused to leave the counter area, King and 36 others were arrested. Realizing the incident would hurt the city’s reputation, Atlanta’s mayor negotiated a truce, and charges were eventually dropped.
Soon after, King was imprisoned for violating his probation on a traffic conviction. The news of his imprisonment entered the 1960 presidential campaign when candidate John F. Kennedy made a phone call to Martin’s wife, Coretta Scott King . Kennedy expressed his concern over the harsh treatment Martin received for the traffic ticket, and political pressure was quickly set in motion. King was soon released.
Letter from Birmingham Jail
In the spring of 1963, King organized a demonstration in downtown Birmingham, Alabama. With entire families in attendance, city police turned dogs and fire hoses on demonstrators. King was jailed, along with large numbers of his supporters.
The event drew nationwide attention. However, King was personally criticized by Black and white clergy alike for taking risks and endangering the children who attended the demonstration.
In his famous Letter from Birmingham Jail , King eloquently spelled out his theory of nonviolence: “Nonviolent direct action seeks to create such a crisis and foster such a tension that a community, which has constantly refused to negotiate, is forced to confront the issue.”
1963 March on Washington
By the end of the Birmingham campaign, King and his supporters were making plans for a massive demonstration on the nation’s capital composed of multiple organizations, all asking for peaceful change. The demonstration was the brainchild of labor leader A. Philip Randolph and King’s one-time mentor Bayard Rustin .
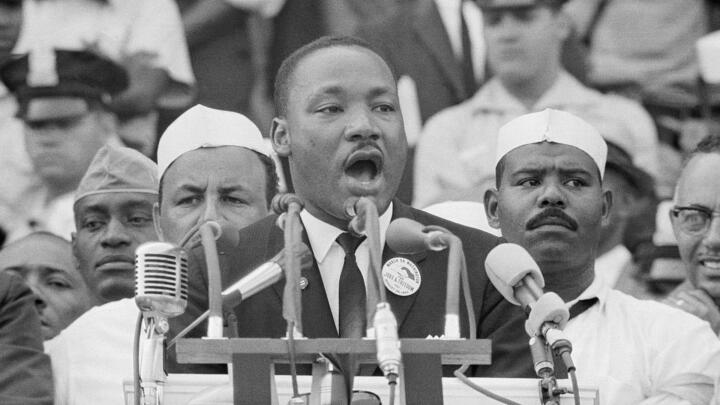
On August 28, 1963, the historic March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom drew an estimated 250,000 people in the shadow of the Lincoln Memorial. It remains one of the largest peaceful demonstrations in American history. During the demonstration, King delivered his famed “I Have a Dream” speech .
The rising tide of civil rights agitation that had culminated in the March on Washington produced a strong effect on public opinion. Many people in cities not experiencing racial tension began to question the nation’s Jim Crow laws and the near-century of second-class treatment of African American citizens since the end of slavery. This resulted in the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 , authorizing the federal government to enforce desegregation of public accommodations and outlawing discrimination in publicly owned facilities.
Selma March
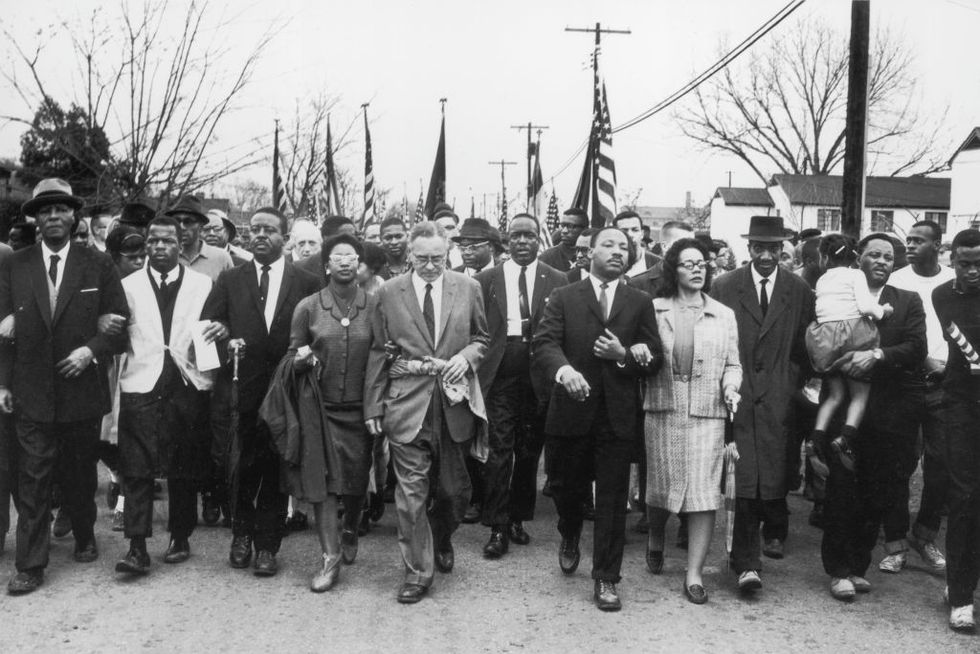

Continuing to focus on voting rights, King, the SCLC, SNCC, and local organizers planned to march peacefully from Selma, Alabama, to the state’s capital, Montgomery.
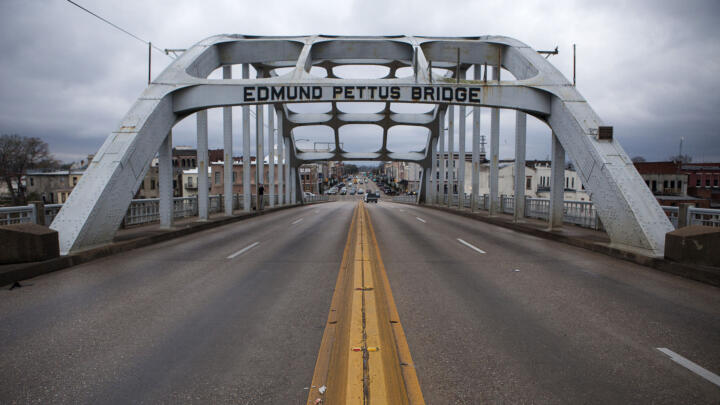
Led by John Lewis and Hosea Williams , demonstrators set out on March 7, 1965. But the Selma march quickly turned violent as police with nightsticks and tear gas met the demonstrators as they tried to cross the Edmund Pettus Bridge in Selma. The attack was televised, broadcasting the horrifying images of marchers being bloodied and severely injured to a wide audience. Of the 600 demonstrators, 58 were hospitalized in a day that became known as “ Bloody Sunday .” King, however, was spared because he was in Atlanta.
Not to be deterred, activists attempted the Selma-to-Montgomery march again. This time, King made sure he was part of it. Because a federal judge had issued a temporary restraining order on another march, a different approach was taken.
On March 9, 1965, a procession of 2,500 marchers, both Black and white, set out once again to cross the Pettus Bridge and confronted barricades and state troopers. Instead of forcing a confrontation, King led his followers to kneel in prayer, then they turned back. This became known as “Turnaround Tuesday.”
Alabama Governor George Wallace continued to try to prevent another march until President Lyndon B. Johnson pledged his support and ordered U.S. Army troops and the Alabama National Guard to protect the protestors.
On March 21, 1965, approximately 2,000 people began a march from Selma to Montgomery. On March 25, the number of marchers, which had grown to an estimated 25,000 gathered in front of the state capitol where King delivered a televised speech. Five months after the historic peaceful protest, President Johnson signed the 1965 Voting Rights Act .

Along with his “I Have a Dream” and “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” speeches, King delivered several acclaimed addresses over the course of his life in the public eye.
“I Have A Dream” Speech
Date: august 28, 1963.
King gave his famous “I Have a Dream” speech during the 1963 March on Washington. Standing at the Lincoln Memorial, he emphasized his belief that someday all men could be brothers to the 250,000-strong crowd.
Notable Quote: “I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
“Give Us the Ballot” Speech
Date: may 17, 1957.
Six years before he told the world of his dream, King stood at the same Lincoln Memorial steps as the final speaker of the Prayer Pilgrimage for Freedom. Dismayed by the ongoing obstacles to registering Black voters, King urged leaders from various backgrounds—Republican and Democrat, Black and white—to work together in the name of justice.
Notable Quote: “Give us the ballot, and we will no longer have to worry the federal government about our basic rights. Give us the ballot, and we will no longer plead to the federal government for passage of an anti-lynching law... Give us the ballot, and we will transform the salient misdeeds of bloodthirsty mobs into the calculated good deeds of orderly citizens.”
Nobel Peace Prize Acceptance Speech
Date: december 10, 1964.
Speaking at the University of Oslo in Norway, King pondered why he was receiving the Nobel Prize when the battle for racial justice was far from over, before acknowledging that it was in recognition of the power of nonviolent resistance. He then compared the foot soldiers of the Civil Rights Movement to the ground crew at an airport who do the unheralded-yet-necessary work to keep planes running on schedule.
Notable Quote: “I think Alfred Nobel would know what I mean when I say that I accept this award in the spirit of a curator of some precious heirloom which he holds in trust for its true owners—all those to whom beauty is truth and truth, beauty—and in whose eyes the beauty of genuine brotherhood and peace is more precious than diamonds or silver or gold.”
“Our God is Marching On (How Long? Not Long)” Speech
Date: march 25, 1965.
At the end of the bitterly fought Selma-to-Montgomery march, King addressed a crowd of 25,000 supporters from the Alabama State Capitol. Offering a brief history lesson on the roots of segregation, King emphasized that there would be no stopping the effort to secure full voting rights, while suggesting a more expansive agenda to come with a call to march on poverty.
Notable Quote: “I come to say to you this afternoon, however difficult the moment, however frustrating the hour, it will not be long, because ‘truth crushed to earth will rise again.’ How long? Not long, because ‘no lie can live forever.’... How long? Not long, because the arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice.”
“Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence” Speech
Date: april 4, 1967.
One year before his assassination, King delivered a controversial sermon at New York City’s Riverside Church in which he condemned the Vietnam War. Explaining why his conscience had forced him to speak up, King expressed concern for the poor American soldiers pressed into conflict thousands of miles from home, while pointedly faulting the U.S. government’s role in escalating the war.
Notable Quote: “We still have a choice today: nonviolent coexistence or violent co-annihilation. We must move past indecision to action. We must find new ways to speak for peace in Vietnam and justice throughout the developing world, a world that borders on our doors. If we do not act, we shall surely be dragged down the long, dark, and shameful corridors of time reserved for those who possess power without compassion, might without morality, and strength without sight.”
“I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” Speech
Date: april 3, 1968.
The well-known orator delivered his final speech the day before he died at the Mason Temple in Memphis, Tennessee. King reflected on major moments of progress in history and his own life, in addition to encouraging the city’s striking sanitation workers.
Notable Quote: “I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.”
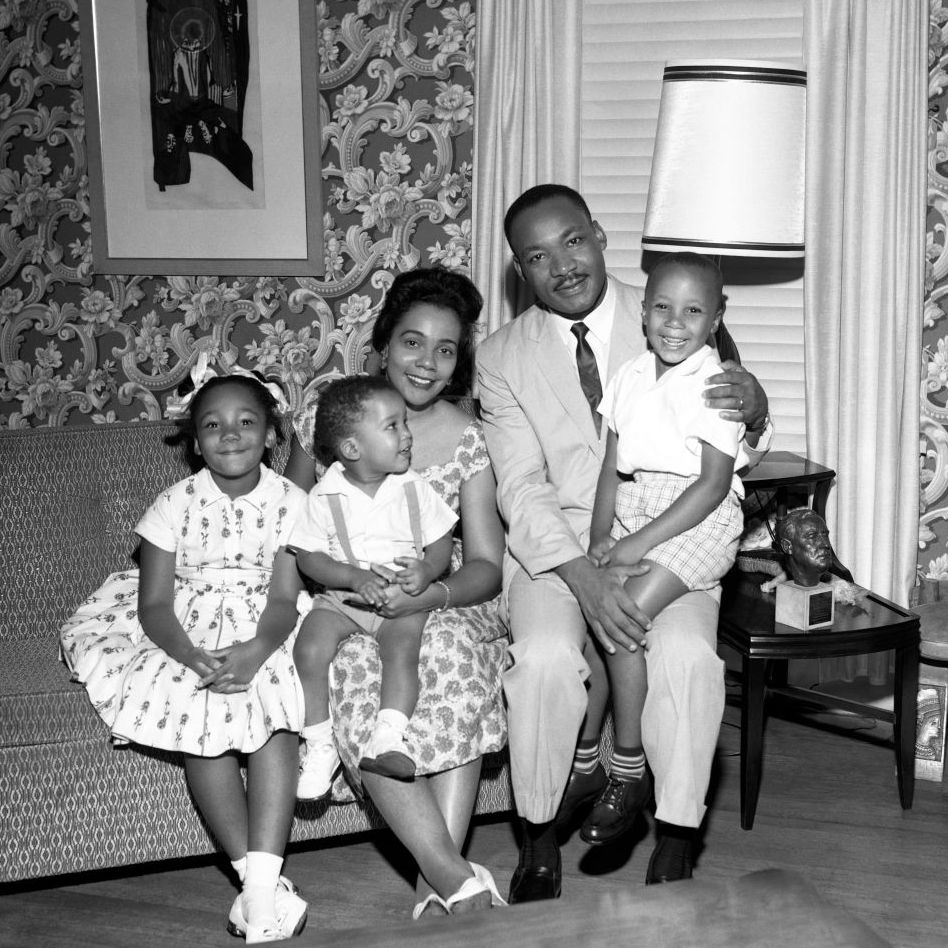
While working on his doctorate at Boston University, King met Coretta Scott , an aspiring singer and musician at the New England Conservatory school in Boston. They were married on June 18, 1953, and had four children—two daughters and two sons—over the next decade. Their oldest, Yolanda, was born in 1955, followed by sons Martin Luther King III in 1957 and Dexter in 1961. The couple welcomed Bernice King in 1963.
Although she accepted the responsibility to raise the children while King travelled the country, Coretta opened their home to organizational meetings and served as an advisor and sounding board for her husband. “I am convinced that if I had not had a wife with the fortitude, strength, and calmness of Corrie, I could not have withstood the ordeals and tensions surrounding the movement,” King wrote in his autobiography.
His lengthy absences became a way of life for their children, but Martin III remembered his father returning from the road to join the kids playing in the yard or bring them to the local YMCA for swimming. King also fostered discussions at mealtimes to make sure everyone understood the important issues he was seeking to resolve.
Leery of accumulating wealth as a high-profile figure, King insisted his family live off his salary as a pastor. However, he was known to splurge on good suits and fine dining, while contrasting his serious public image with a lively sense of humor among friends and family.
Due to his relationships with alleged Communists, King became a target of FBI surveillance and, from late 1963 until his death, a campaign to discredit the civil rights activist. While FBI wiretaps failed to produce evidence of Communist sympathies, they captured the civil rights leader’s engagement in extramarital dalliances. This led to the infamous “suicide letter” of 1964, later confirmed to be from the FBI and authorized by then-Director J. Edgar Hoover , which urged King to kill himself if he wanted to prevent news of his affairs from going public.
In 2019, historian David Garrow wrote of explosive new allegations against King following his review of recently released FBI documents. Among the discoveries was a memo suggesting that King had encouraged the rape of a parishioner in a hotel room, as well as evidence that he might have fathered a daughter with a mistress. Other historians questioned the veracity of the documentation, especially given the FBI’s known attempts to damage King’s reputation. The original surveillance tapes regarding these allegations are under judicial seal until 2027.
From late 1965 through 1967, King expanded his civil rights efforts into other larger American cities, including Chicago and Los Angeles. But he met with increasing criticism and public challenges from young Black power leaders. King’s patient, non-violent approach and appeal to white middle-class citizens alienated many Black militants who considered his methods too weak, too late, and ineffective.
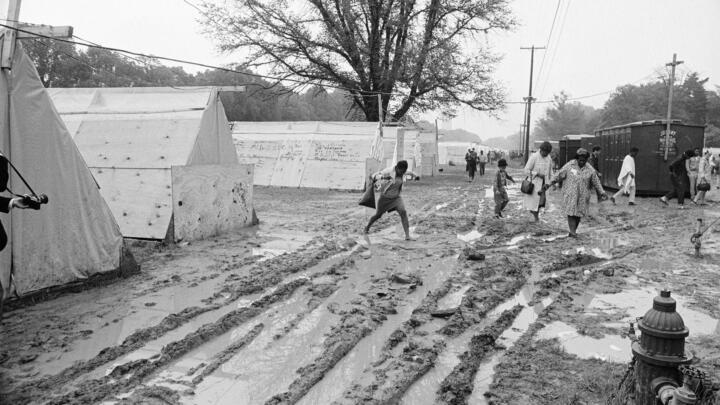
To address this criticism, King began making a link between discrimination and poverty, and he began to speak out against the Vietnam War . He felt America’s involvement in Vietnam was politically untenable and the government’s conduct in the war was discriminatory to the poor. He sought to broaden his base by forming a multiracial coalition to address the economic and unemployment problems of all disadvantaged people. To that end, plans were in the works for another march on Washington to highlight the Poor People’s Campaign, a movement intended to pressure the government into improving living and working conditions for the economically disadvantaged.
By 1968, the years of demonstrations and confrontations were beginning to wear on King. He had grown tired of marches, going to jail, and living under the constant threat of death. He was becoming discouraged at the slow progress of civil rights in America and the increasing criticism from other African American leaders.
In the spring of 1968, a labor strike by Memphis, Tennessee, sanitation workers drew King to one last crusade. On April 3, 1968, he gave his final and what proved to be an eerily prophetic speech, “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop,” in which he told supporters, “Like anybody, I would like to live a long life. Longevity has its place. But I’m not concerned about that now… I’m not worried about anything. I’m not fearing any man. Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord.”

While standing on a balcony outside his room at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, Martin Luther King Jr. was killed by a sniper’s bullet on April 4, 1968. King died at age 39. The shocking assassination sparked riots and demonstrations in more than 100 cities across the country.
The shooter was James Earl Ray , a malcontent drifter and former convict. He initially escaped authorities but was apprehended after a two-month international manhunt. In 1969, Ray pleaded guilty to assassinating King and was sentenced to 99 years in prison.
The identity of King’s assassin has been the source of some controversy. Ray recanted his confession shortly after he was sentenced, and King’s son Dexter publicly defended Ray’s innocence after meeting with the convicted gunman in 1997. Another complicating factor is the 1993 confession of tavern owner Loyd Jowers, who said he contracted a different hit man to kill King. In June 2000, the U.S. Justice Department released a report that dismissed the alternative theories of King’s death. Ray died in prison on April 23, 1998.
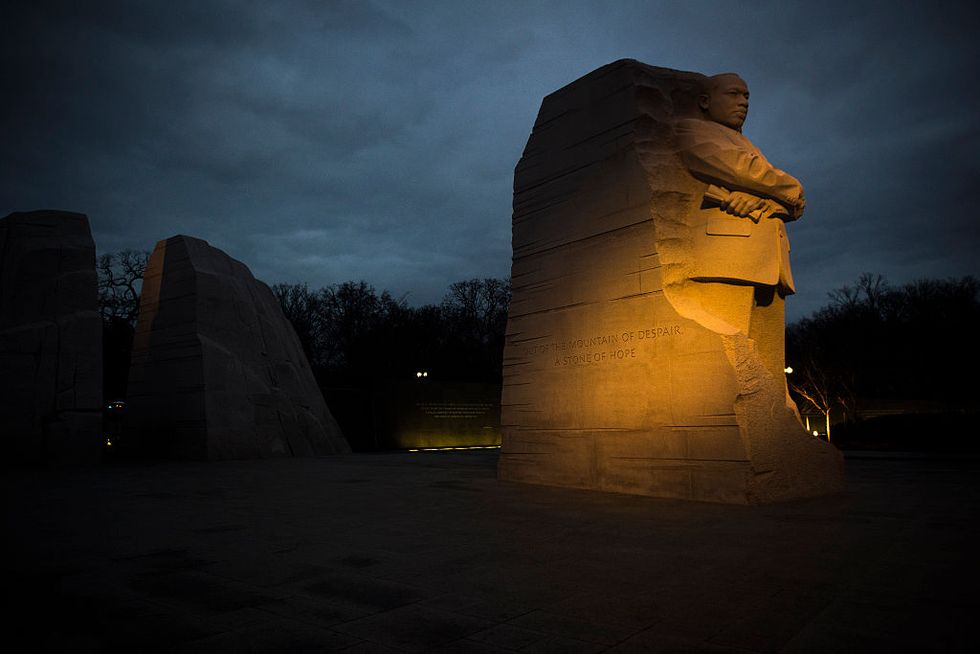

King’s life had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States. Years after his death, he is the most widely known Black leader of his era.
His life and work have been honored with a national holiday, schools and public buildings named after him, and a memorial on Independence Mall in Washington, D.C.
Over the years, extensive archival studies have led to a more balanced and comprehensive assessment of his life, portraying him as a complex figure: flawed, fallible, and limited in his control over the mass movements with which he was associated, yet a visionary leader who was deeply committed to achieving social justice through nonviolent means.
- But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.
- There comes a time when the cup of endurance runs over and men are no longer willing to be plunged into an abyss of injustice where they experience the bleakness of corroding despair.
- Any law that uplifts human personality is just. Any law that degrades human personality is unjust.
- The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.
- Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred.
- Darkness cannot drive out darkness: only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate: only love can do that.
- The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort and convenience, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy. The true neighbor will risk his position, his prestige, and even his life for the welfare of others.
- We must all learn to live together as brothers, or we will all perish together as fools.
- Forgiveness is not an occasional act; it is a permanent attitude.
- I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
- The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. But education which stops with efficiency may prove the greatest menace to society. The most dangerous criminal may be the man gifted with reason but with no morals.
- I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.
- Power at its best is love implementing the demands of justice. Justice at its best is love correcting everything that stands against love.
- A man who won’t die for something is not fit to live.
- At the center of non-violence stands the principle of love.
- Right, temporarily defeated, is stronger than evil triumphant.
- In the end, we will remember not the words of our enemies, but the silence of our friends.
- Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.
- Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Civil Rights Activists

Martin Luther King Jr. Didn’t Criticize Malcolm X

5 Crowning Achievements of Maya Angelou

30 Civil Rights Leaders of the Past and Present

Benjamin Banneker

Marcus Garvey

Madam C.J. Walker

Maya Angelou

17 Inspiring Martin Luther King Quotes

Bayard Rustin

- This Day In History
- History Classics
- HISTORY Podcasts
HISTORY Vault
- Link HISTORY on facebook
- Link HISTORY on twitter
- Link HISTORY on youtube
- Link HISTORY on instagram
- Link HISTORY on tiktok
✯ ✯ ✯ Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. ✯ ✯ ✯ His Life and Legacy
Martin Luther King Jr. dedicated his life to the nonviolent struggle for civil rights in the United States. King's leadership played a pivotal role in ending entrenched segregation for African Americans and to the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, considered a crowning achievement of the civil rights era. King was assassinated in 1968, but his words and legacy continue to resonate for all those seeking justice in the United States and around the world. As King said at the Washington National Cathedral on March 31, 1968, "Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate; only love can do that."

10 Things You May Not Know About Martin Luther King Jr.

An Intimate View of MLK Through the Lens of a Friend

The Fight for Martin Luther King Jr. Day

7 of Martin Luther King Jr.'s Most Notable Speeches

Martin Luther King Jr.

7 Things You May Not Know About MLK’s 'I Have a Dream' Speech

America in Mourning After MLK's Shocking Assassination: Photos

For Martin Luther King Jr., Nonviolent Protest Never Meant ‘Wait and See’

How an Assassination Attempt Affirmed MLK’s Faith in Nonviolence

Jesse Jackson on M.L.K.: One Bullet Couldn’t Kill the Movement

Martin Luther King Jr.’s Final Speech

MLK's Poor People's Campaign Demanded Economic Justice

Martin Luther King Jr.’s Famous Speech Almost Didn’t Have the Phrase 'I Have a Dream'

How Selma's 'Bloody Sunday' Became a Turning Point in the Civil Rights Movement

Playlist: Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.

Watch the Black History collection on HISTORY Vault to look back on the history of African American achievements.
Get instant access to free updates.
Don’t Miss Out on HISTORY news, behind the scenes content, and more.
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
Need help with the site?
Create a profile to add this show to your list.

- HISTORY & CULTURE
- RACE IN AMERICA
How Martin Luther King, Jr.’s multifaceted view on human rights still inspires today
The legendary civil rights activist pushed to ban nuclear weapons, end the Vietnam War, and lift people out of poverty through labor unions and access to healthcare.
The Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr. towers over history as a civil rights legend—known for leading the movement to end segregation and counter prejudice against Black Americans in the 1950s and 1960s, largely through peaceful protests. He helped pass landmark federal civil rights and voting rights legislation that outlawed segregation and enfranchised Americans who had been barred from the polls through intimidation and discriminatory state and local laws.
( How the Voting Rights Act was won—and why it’s under fire today .)
But King knew it would take more to achieve true equality. And so he also worked tirelessly for education, wage equity, peace, housing, and to lift people out of poverty. Some of King’s most iconic speeches and marches were devoted to ending war, dismantling nuclear weapons, and bringing economic justice. As King said after receiving the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 , he believed that any “spiritual and moral lag” in humanity was due to racial injustice, poverty, and war.
His multifaceted view on human rights still inspires today, and on the third Monday in January every year, the United States honors King’s legacy of fighting for equal rights—and standing up for human rights everywhere.
During his lifetime, King’s views often made him unpopular and heralded harsh criticism. At the time of his assassination in 1968, a Harris poll revealed a low approval rating of only about 25 percent among white Americans and 52 percent among Black Americans. But in the decades after he was killed, more Americans came to recognize the enormity of King’s contributions. Communities across the country began to name streets and landmarks after him, and soon a push began to establish a federal holiday in his birth month of January.
( Subscriber exclusive: Where the streets have MLK’s name .)
For Hungry Minds
In 1983 , over objections from Southern lawmakers, President Ronald Reagan finally signed a bill creating the holiday into law and the first celebrations of Martin Luther King, Jr. Day took place in January 1986—although it would take another decade for states such as Arizona and South Carolina to follow suit.
King’s work continues to influence and inspire activism—particularly in the realm of environmental justice, as studies indicate that climate change disproportionately harms marginalized communities. Here are the many layers of King’s work that the U.S. honors on Martin Luther King, Jr. Day.
He advocated against the use of nuclear weapons
King was adamant that peace was inextricably linked to civil rights. Throughout the 1950s and 1960s, major powers like the United States and the U.S.S.R. were aggressively developing and testing nuclear weapons, and several times crept to the brink of warfare that threatened to annihilate the world.
King made clear the connection between the Black freedom struggle and the need for nuclear disarmament, writes nuclear studies and African American history expert Vincent Intondi in the book African Americans Against the Bomb: Nuclear Weapons, Colonialism, and the Black Freedom Movement . King argued that it would be “rather absurd” to integrate schools and lunch counters but not be concerned with world peace and survival.
King spoke out about nuclear warfare as early as 1957, when he signed onto a full-page advertisement in The New York Times that called for all nations to suspend nuclear tests immediately. When asked about his stance later that same year, King tied the weapons to the whole of war, and argued that they should be banned everywhere.
“It cannot be disputed that a full-scale nuclear war would be utterly catastrophic,” he told Ebony magazine in an interview. “The principal objective of all nations must be the total abolition of war.”
As part of King’s advocacy for peace and nuclear disarmament, he condemned the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki the U.S. government had carried out more than a decade earlier to effectively end World War II. Today, Hiroshima is one of the only cities outside North America to celebrate Martin Luther King Day.

King also used the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962—a 13-day stretch in which the U.S. and Soviet Union stood on the brink of nuclear war over the discovery of Soviet missiles in Cuba—as an opportunity to connect nuclear disarmament to racial and economic justice. King called for the U.S. government to instead turn its attention and funds to education, Medicare, and civil rights, Intondi writes. He then voiced his support for a nuclear test ban treaty , which was signed by President John F. Kennedy in 1963.
He was outspoken against the Vietnam War
King often linked nuclear disarmament with the Vietnam War as it escalated in the 1960s.
King was against the war but initially worried that making his stance public would derail his work to pass the Civil Rights Act and impair his relationship with President Lyndon B. Johnson, according to the Martin Luther King, Jr. Research and Education Institute at Stanford University .
But in 1965, the year the first U.S. ground troops were sent to Vietnam, King issued his first public statement, asserting the war was “accomplishing nothing” and calling for a peace treaty.
He tempered his criticism for the next two years to avoid diminishing the impact of his civil rights work, but by 1967, King was active in the anti-war sphere again, attending a march in Chicago before he went on to make his most notable speech on the matter a few days later on April 4.
It is no longer a choice, my friends, between violence and nonviolence. It is either nonviolence or nonexistence. And the alternative to disarmament… may well be a civilization plunged into the abyss of annihilation , and our earthly habitat would be transformed into an inferno that even the mind of Dante could not imagine. Martin Luther King, Jr.
On that day at the Riverside Church in New York City, King denounced the war for deepening the problems of Black Americans and people living in poverty. He condemned the “madness” of Vietnam as a “symptom of a far deeper malady” that put the U.S. at odds with the aspirations for social justice throughout the world. Just 11 days later, King led 125,000 demonstrators on an anti-war march to the United Nations headquarters in New York as one of the largest peace demonstrations in history.
You May Also Like

Harriet Tubman, the spy: uncovering her secret Civil War missions

MLK and Malcolm X only met once. Here’s the story behind an iconic image.

Why Aboriginal Australians are still fighting for recognition
During the last year of his life , King continued his anti-war work by encouraging grassroots peace activism. On March 31, 1968, five days before he died, King denounced the Vietnam War in his final Sunday sermon at the National Cathedral in Washington, D.C., saying that it was “one of the most unjust wars that has ever been fought in the history of the world.”
King did not live to see the war end. U.S. troops officially pulled out of Vietnam in April 1975 .
He championed union representation and worker’s rights
King's passion for union representation and workers' rights is also an important part of his legacy. Much as he had done with his anti-war speeches, King often tied workers’ rights to the civil rights movement.
“I had also learned that the inseparable twin of racial injustice was economic injustice,” King said in a 1958 speech in New York . “Although I came from a home of economic security and relative comfort, I could never get out of my mind the economic insecurity of many of my playmates and the tragic poverty of those living around me.”
In a 1959 interview with Challenge magazine , King acknowledged that labor unions had historically left out Black Americans, but also could be a key to economic justice. He called for Black Americans to organize their economic and political power in the form of labor unions, and he championed ideas in the labor movement, including better working conditions, adequate housing, guaranteed annual income, and access to healthcare.

For years, King continued to call for economic justice, notably at the August 28, 1963, March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Before a crowd of 250,000 people, he delivered the legendary “I Have A Dream” speech on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial, where he called for an end to poverty, especially targeted poverty and discrimination against Black Americans.
One of King’s last actions before his assassination was in support of the labor movement. King’s final days were spent supporting a group of Black sanitation workers striking in Memphis, Tennessee.
After two workers had been crushed to death by a malfunctioning truck, 1,300 Black workers went on strike for 11 days, seeking an end to a long pattern of neglect and abuse from their management. The strike would’ve ended after the City Council voted to recognize their newly formed union, but the Memphis mayor rejected the vote. King traveled to Memphis to lead a protest march and, on April 3, he spoke to the striking sanitation workers.
“We’ve got to give ourselves to this struggle until the end,” King said . “Nothing would be more tragic than to stop at this point in Memphis. We’ve got to see it through.”
King was gunned down by an assassin on the balcony of his Memphis hotel the next day. On April 16, the sanitation workers’ union was finally recognized and a better wage was promised—the first of many examples of how King’s legacy would continue to reverberate in the work of those whom he inspired.
I have the audacity to believe that peoples everywhere can have three meals a day for their bodies, education and culture for their minds, and dignity, equality and freedom for their spirits. Martin Luther King, Jr.
He’s inspiring a new generation of environmental activists
Although King’s last act supporting the Black sanitation workers in Memphis was not explicitly an act of environmental justice , it has inspired a generation of activists. The working conditions the sanitation workers had endured were polluted and hazardous—much like the conditions many Black Americans endured in their communities and jobs at the time.
Modern environmental activists have drawn on King’s message: Much as segregation and discrimination were inseparable from poverty, they point out that poor communities of color disproportionately face environmental hazards such as pollution. They also bear the brunt of the harmful effects of climate change, including extreme weather events.
( The origins of environmental justice—and why it’s finally getting the attention it deserves .)
Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibits discrimination in the use of federal funds , even gave marginalized people a means to address racial discrimination in environmental matters. As the environmental justice movement grew, King’s work also inspired the Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and the Endangered Species Act.
His advocacy for people of color to have a voice and power has inspired many communities impacted most by climate change to speak up—and take action. Now, the holiday honoring King is typically observed as a national day of service. Organizations and individuals alike volunteer for their communities, often cleaning up roads or river banks in the name of a man who many believe would be on the forefront of the climate fight if he were still alive today.
Related Topics
- CIVIL RIGHTS
- HUMAN RIGHTS
- ENVIRONMENTAL JUSTICE
- NUCLEAR WEAPONS
- VIETNAM WAR

Meet the mom who took on toxic waste—and won

How Emmett Till’s murder catalyzed the U.S. civil rights movement

This is what you need to know about lead and your health

The surprising way that millions of new trees could transform America

How César Chávez changed the labor movement—and became an icon
- Paid Content
- Environment
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

Martin Luther King Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on martin luter king.
Martin Luther King Jr. was an African-American leader in the U.S. He lost his life while performing a peaceful protest for the betterment of blacks in America. His real name was Michael King Jr. He completed his studies and attained a Ph.D. After that, he joined the American Civil Right Movement. He was among one of the great men who dedicated their life for the community.

Reason for Martin Luther King to be famous
There are two reasons for someone to be famous either he is a good man or a very bad person. Martin Luther King was among the good one who dedicated his life to the community. Martin Luther King was also known as MLK Jr. He gained popularity after he became the leader and spokesperson of the Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s and 1960s.
Martin Luther King was an American activist, minister, and humanitarian. Also, he had worked for several other causes and actively participated in many protests and boycotts. He was a peaceful man that has faith in Christian beliefs and non-violence. Also, his inspiration for them was the work of Mahatma Gandhi and Nelson Mandela. For his work in the field of civil rights, the Nobel Committee awarded him the Nobel Peace Prize.
He was a great speaker that motivated the blacks to protest using non-violence. Also, he uses peaceful strategies like a boycott, protest march , and sit-ins, etc. for protests against the government.
Impact of King
King is one of the renowned leaders of the African-American who worked for the welfare of his community throughout his life. He was very famous among the community and is the strongest voice of the community. King and his fellow companies and peaceful protesters forced the government several times to bend their laws. Also, kings’ life made a seismic impact on life and thinking of the blacks. He was among one of the great leaders of the era.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Humanitarian and civil rights work
As we know that King was a civic leader . Also, he has taken part in many civil right campaigns and boycotts like the Bus Boycott, Voting Rights and the most famous March on Washington. In this march along with more than 200,000 people, he marched towards Washington for human right. Also, it’s the largest human right campaign in U.S.A. history. During the protest, he gave a speech named “I Have a Dream” which is history’s one of the renowned speeches.
Death and memorial
During his life working as a leader of the Civil Rights Movement he makes many enemies. Also, the government and plans do everything to hurt his reputation. Martin Luther King was assassinated in 1968. Every year the US celebrates his anniversary as Martin Luther King Jr. day in the US. Also, they honored kings’ memory by naming school and building after him and a Memorial at Independence Mall.
Martin Luther King was a great man who dedicated his whole life for his community. Also, he was an active leader and a great spokesperson that not only served his people but also humanity. It was due to his contribution that the African-American got their civil rights.
Essay Topics on Famous Leaders
- Mahatma Gandhi
- APJ Abdul Kalam
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Swami Vivekananda
- Mother Teresa
- Rabindranath Tagore
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Subhash Chandra Bose
- Abraham Lincoln
- Martin Luther King
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Civil Rights
5 Things Written by Martin Luther King Jr. That Everyone Should Read, According to an Expert

T he words written about Martin Luther King Jr. during his too-short life and in the decades since his assassination on April 4, 1968, would be impossible to count. King himself left a deep archive of writings, speeches and sermons, too. His spoken orations in particular are a powerful reminder of why he was destined to become part of the pantheon of American icons.
Step Into History: Learn how to experience the 1963 March on Washington in virtual reality
“One has to remember that King above all was a preacher,” says Carolyn Calloway-Thomas, chair of African American and African Diaspora Studies at the Indiana University Bloomington and an editor of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. and the Sermonic Power of Public Discourse.
While she notes that he was so prolific that it’s near impossible to choose, Calloway-Thomas spoke to TIME about the pieces of King’s work that everyone should know about. They are:
“The Death of Evil upon the Seashore” (May 17, 1956)
“The death of the Egyptians upon the seashore is a glaring symbol of the ultimate doom of evil in its struggle with good.”
This sermon was delivered to a massive crowd at the Cathedral of St. John the Divine in New York on the occasion of the two-year anniversary of the Supreme Court’s Brown v. Board of Education ruling against school segregation, at an early moment in this phase of the civil rights movement, with the Montgomery bus boycott still ongoing. To Calloway-Thomas, the sermon is noteworthy for the optimistic vision it presented at such a moment. “He had to help African-American people imagine themselves,” she says. “I think the Death of Evil upon the Seashore is that speech.”
It wasn’t the first time King preached on these ideas, and in fact the link he draws between the Biblical exodus and the story of African-American progress toward freedom and equality was an old one, but those present noted that his delivery that day was particularly moving. “He taps into that reservoir, that myth of the Hebrew children in bondage,” Calloway-Thomas says, “and he elevates it and makes it more publicly known.”
Read the full speech here
Letter from a Birmingham Jail (April 16, 1963)
“Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere. We are caught in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny. Whatever affects one directly, affects all indirectly.”
Yes, this is a letter, not a speech or sermon — but Calloway-Thomas says it’s worth including on such a list anyway. After all, the circumstances that created this letter are inherently linked to the fact that he couldn’t deliver a speech in person. At the time, King found himself jailed in Alabama after ignoring an injunction against protests in Birmingham. During that time, a group of clergymen wrote an open letter urging him away from protests. He wanted to respond but, from the jail, his only option if he wanted to answer quickly was to write it down. “Ideas have moments and if those moments aren’t used, you lose that rhetorical moment and it no longer has the force it had,” Calloway-Thomas says.
So, in a format she likens to a spoken call and response, he answers the questions that were posed to him about his methods. While also explaining that he’s on strong biblical footing, he provides the public with a way to understand the work he’s doing. His rhetorical skills are also on display as he uses a story about his 6-year-old daughter’s early perceptions of racism and segregation to underline that the matter is not theoretical. In the years since, this letter has become one of 20th century American history’s most famous documents.
Read the full letter here
“I Have a Dream…” (Aug. 28, 1963)
“I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
The speech that remains Martin Luther King Jr.’s most famous oration — one of the most famous orations in American history, if not world history — is that well-known for a good reason, Calloway-Thomas says. This was the moment when the world as a whole really saw King, and the moment was carefully orchestrated, framed by the Lincoln Memorial. “Think about how dazzling that was!” she says. “Think about the robust visuals and the lovely words echoing from Dr. King. It was an elixir that was made to circulate.”
But, she says, the power of his voice and the impact of the image can sometimes overwhelm the full message of the speech. “Dr. King had some pretty radical statements in that speech,” Calloway-Thomas adds. “Most people gloss over the part in that speech where King says that if we overlook the urgency of now there’ll be a rude awakening. I’ve never seen a student go to that section of the speech; people go right to ‘I have a dream’ and they don’t notice the threat.”
“A Time to Break Silence” (April 4, 1967)
“We still have a choice today: nonviolent coexistence or violent coannihilation. We must move past indecision to action. We must find new ways to speak for peace in Vietnam and justice throughout the developing world, a world that borders on our doors.”
In this speech, King publicly answers his conscience, as Calloway-Thomas puts it, on the matter of the Vietnam War. With an undercurrent of “anguish” about the fact that he feels he must speak, and must criticize the choices of Lyndon Johnson, who had often been an ally , he entered the arena of opposition to the war.
“This is an unsettling moment. People paid attention, but that meant there was backlash,” she says. President Johnson and many others felt that he ought to stay focused on domestic civil-rights issues and leave the foreign policy to them, but in this speech he makes clear why those two topics cannot truly be separated. That idea, Calloway-Thomas says, parallels the experience of earlier fighters for justice, such as Frederick Douglass, who got to the world stage with one kind of story — their personal freedom narratives, in that case — and shocked some of their allies when they showed that their thinking was far more expansive.
“I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” (April 3, 1968)
“I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight, that we, as a people, will get to the Promised Land.”
Start with the date on this one: that’s April 3, 1968, the night before King was assassinated. In this speech, which summons King’s primary background as a preacher, he returns to the story of Moses. Rather than speaking on the joy of the Exodus, though, he turns to the end of Moses’ life, and his death just outside the Promised Land to which he had delivered his people. King casts himself as another leader who may not be there for the end of the journey. “He used Christian values and Democratic traditions to bring people together, so it’s not surprising that he goes to this idea,” Calloway-Thomas says. “What’s significant here is when it occurred. It was almost apocalyptic. Because it occurred at that time it has lingering significance and carries with it an abundance of pathos.”
Of course, as Calloway-Thomas says, we can imagine a scenario in which King gave this speech and then lived. The emotional resonance of his words might be lessened without the seemingly prescient layer of fate, but the story would be there all the same. “Here’s a man talking about longevity, here’s a man talking about god’s Will, here’s a man talking about going up to the mountaintop and looking skyward toward heaven and looking over into the Promised Land,” she says. “It’s a gorgeous story.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- The New Face of Doctor Who
- Putin’s Enemies Are Struggling to Unite
- Women Say They Were Pressured Into Long-Term Birth Control
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- Boredom Makes Us Human
- John Mulaney Has What Late Night Needs
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Lily Rothman at [email protected]

The Purpose of Education
Morehouse College, 1948
As I engage in the so-called “bull sessions” around and about the school, I too often find that most college men have a misconception of the purpose of education. Most of the “brethren” think that education should equip them with the proper instruments of exploitation so that they can forever trample over the masses. Still others think that education should furnish them with noble ends rather than means to an end.
It seems to me that education has a two-fold function to perform in the life of man and in society: the one is utility and the other is culture. Education must enable a man to become more efficient, to achieve with increasing facility the ligitimate goals of his life.
Education must also train one for quick, resolute and effective thinking. To think incisively and to think for one’s self is very difficult. We are prone to let our mental life become invaded by legions of half truths, prejudices, and propaganda. At this point, I often wonder whether or not education is fulfilling its purpose. A great majority of the so-called educated people do not think logically and scientifically. Even the press, the classroom, the platform, and the pulpit in many instances do not give us objective and unbiased truths. To save man from the morass of propaganda, in my opinion, is one of the chief aims of education. Education must enable one to sift and weigh evidence, to discern the true from the false, the real from the unreal, and the facts from the fiction.
The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. But education which stops with efficiency may prove the greatest menace to society. The most dangerous criminal may be the man gifted with reason, but with no morals.
The late Eugene Talmadge, in my opinion, possessed one of the better minds of Georgia, or even America. Moreover, he wore the Phi Beta Kappa key. By all measuring rods, Mr. Talmadge could think critically and intensively; yet he contends that I am an inferior being. Are those the types of men we call educated?
We must remember that intelligence is not enough. Intelligence plus character–that is the goal of true education. The complete education gives one not only power of concentration, but worthy objectives upon which to concentrate. The broad education will, therefore, transmit to one not only the accumulated knowledge of the race but also the accumulated experience of social living.
If we are not careful, our colleges will produce a group of close-minded, unscientific, illogical propagandists, consumed with immoral acts. Be careful, “brethren!” Be careful, teachers!


A Summary and Analysis of Martin Luther King’s ‘I Have a Dream’ Speech
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
‘I Have a Dream’ is one of the greatest speeches in American history. Delivered by Martin Luther King, Jr. (1929-68) in Washington D.C. in 1963, the speech is a powerful rallying cry for racial equality and for a fairer and equal world in which African Americans will be as free as white Americans.
If you’ve ever stayed up till the small hours working on a presentation you’re due to give the next day, tearing your hair out as you try to find the right words, you can take solace in the fact that as great an orator as Martin Luther King did the same with one of the most memorable speeches ever delivered.
He reportedly stayed up until 4am the night before he was due to give his ‘I Have a Dream’, writing it out in longhand. You can read the speech in full here .
‘I Have a Dream’: background
The occasion for King’s speech was the march on Washington , which saw some 210,000 African American men, women, and children gather at the Washington Monument in August 1963, before marching to the Lincoln Memorial.
They were marching for several reasons, including jobs (many of them were out of work), but the main reason was freedom: King and many other Civil Rights leaders sought to remove segregation of black and white Americans and to ensure black Americans were treated the same as white Americans.
1963 was the centenary of the Emancipation Proclamation , in which then US President Abraham Lincoln (1809-65) had freed the African slaves in the United States in 1863. But a century on from the abolition of slavery, King points out, black Americans still are not free in many respects.
‘I Have a Dream’: summary
King begins his speech by reminding his audience that it’s a century, or ‘five score years’, since that ‘great American’ Abraham Lincoln signed the Emancipation Proclamation. This ensured the freedom of the African slaves, but Black Americans are still not free, King points out, because of racial segregation and discrimination.
America is a wealthy country, and yet many Black Americans live in poverty. It is as if the Black American is an exile in his own land. King likens the gathering in Washington to cashing a cheque: in other words, claiming money that is due to be paid.
Next, King praises the ‘magnificent words’ of the US Constitution and the Declaration of Independence . King compares these documents to a promissory note, because they contain the promise that all men, including Black men, will be guaranteed what the Declaration of Independence calls ‘inalienable rights’: namely, ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness’.
King asserts that America in the 1960s has ‘defaulted’ on this promissory note: in other words, it has refused to pay up. King calls it a ‘sacred obligation’, but America as a nation is like someone who has written someone else a cheque that has bounced and the money owed remains to be paid. But it is not because the money isn’t there: America, being a land of opportunity, has enough ‘funds’ to ensure everyone is prosperous enough.
King urges America to rise out of the ‘valley’ of segregation to the ‘sunlit path of racial justice’. He uses the word ‘brotherhood’ to refer to all Americans, since all men and women are God’s children. He also repeatedly emphasises the urgency of the moment. This is not some brief moment of anger but a necessary new start for America. However, King cautions his audience not to give way to bitterness and hatred, but to fight for justice in the right manner, with dignity and discipline.
Physical violence and militancy are to be avoided. King recognises that many white Americans who are also poor and marginalised feel a kinship with the Civil Rights movement, so all Americans should join together in the cause. Police brutality against Black Americans must be eradicated, as must racial discrimination in hotels and restaurants. States which forbid Black Americans from voting must change their laws.
Martin Luther King then comes to the most famous part of his speech, in which he uses the phrase ‘I have a dream’ to begin successive sentences (a rhetorical device known as anaphora ). King outlines the form that his dream, or ambition or wish for a better America, takes.
His dream, he tells his audience, is ‘deeply rooted’ in the American Dream: that notion that anybody, regardless of their background, can become prosperous and successful in the United States. King once again reminds his listeners of the opening words of the Declaration of Independence: ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.’
In his dream of a better future, King sees the descendants of former Black slaves and the descendants of former slave owners united, sitting and eating together. He has a dream that one day his children will live in a country where they are judged not by the colour of their skin but by the content of their character.
Even in Mississippi and Alabama, states which are riven by racial injustice and hatred, people of all races will live together in harmony. King then broadens his dream out into ‘our hope’: a collective aspiration and endeavour. King then quotes the patriotic American song ‘ My Country, ’Tis of Thee ’, which describes America as a ‘sweet land of liberty’.
King uses anaphora again, repeating the phrase ‘let freedom ring’ several times in succession to suggest how jubilant America will be on the day that such freedoms are ensured. And when this happens, Americans will be able to join together and be closer to the day when they can sing a traditional African-American hymn : ‘Free at last. Free at last. Thank God almighty, we are free at last.’
‘I Have a Dream’: analysis
Although Martin Luther King’s speech has become known by the repeated four-word phrase ‘I Have a Dream’, which emphasises the personal nature of his vision, his speech is actually about a collective dream for a better and more equal America which is not only shared by many Black Americans but by anyone who identifies with their fight against racial injustice, segregation, and discrimination.
Nevertheless, in working from ‘I have a dream’ to a different four-word phrase, ‘this is our hope’. The shift is natural and yet it is a rhetorical masterstroke, since the vision of a better nation which King has set out as a very personal, sincere dream is thus telescoped into a universal and collective struggle for freedom.
What’s more, in moving from ‘dream’ to a different noun, ‘hope’, King suggests that what might be dismissed as an idealistic ambition is actually something that is both possible and achievable. No sooner has the dream gathered momentum than it becomes a more concrete ‘hope’.
In his ‘I Have a Dream’ speech, King was doing more than alluding to Abraham Lincoln’s signing of the Emancipation Proclamation one hundred years earlier. The opening words to his speech, ‘Five score years ago’, allude to a specific speech Lincoln himself had made a century before: the Gettysburg Address .
In that speech, delivered at the Soldiers’ National Cemetery (now known as Gettysburg National Cemetery) in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania in November 1863, Lincoln had urged his listeners to continue in the fight for freedom, envisioning the day when all Americans – including Black slaves – would be free. His speech famously begins with the words: ‘Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.’
‘Four score and seven years’ is eighty-seven years, which takes us back from 1863 to 1776, the year of the signing of the Declaration of Independence. So, Martin Luther King’s allusion to the words of Lincoln’s historic speech do two things: they call back to Lincoln’s speech but also, by extension, to the founding of the United States almost two centuries before. Although Lincoln and the American Civil War represented progress in the cause to make all Americans free regardless of their ethnicity, King makes it clear in ‘I Have a Dream’ that there is still some way to go.
In the last analysis, King’s speech is a rhetorically clever and emotionally powerful call to use non-violent protest to oppose racial injustice, segregation, and discrimination, but also to ensure that all Americans are lifted out of poverty and degradation.
But most of all, King emphasises the collective endeavour that is necessary to bring about the world he wants his children to live in: the togetherness, the linking of hands, which is essential to make the dream a reality.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.
Type your email…
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Racism — Martin Luther King
Essays on Martin Luther King
Hook examples for martin luther king essays, the dream that changed america hook.
Begin your essay by quoting Martin Luther King Jr.'s iconic "I Have a Dream" speech. Explore the impact of this speech on civil rights and its enduring significance in the fight for equality.
The Montgomery Bus Boycott Hook
Introduce the Montgomery Bus Boycott as a pivotal moment in Dr. King's activism. Describe the events leading to the boycott and its role in shaping the civil rights movement.
The Letter from Birmingham Jail Hook
Discuss the powerful "Letter from Birmingham Jail" written by Dr. King during his imprisonment. Examine the letter's arguments for civil disobedience and its impact on the struggle for justice.
The March on Washington Hook
Highlight the significance of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom in 1963. Describe the event, its participants, and Dr. King's historic "I Have a Dream" speech delivered at the Lincoln Memorial.
The Nonviolent Resistance Hook
Explore Martin Luther King Jr.'s philosophy of nonviolent resistance and its influence on the civil rights movement. Discuss the strategies and principles behind nonviolent protest.
The Legacy of Dr. King Hook
Reflect on Dr. King's lasting legacy and his impact on civil rights, social justice, and the quest for equality. Discuss how his work continues to inspire change today.
The Assassination and Mourning Hook
Examine the tragic assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968 and the national mourning that followed. Discuss the immediate aftermath and the long-term effects on the civil rights movement.
The Global Influence Hook
Discuss how Martin Luther King Jr.'s message of equality and justice resonated beyond the United States, inspiring movements for civil rights and social change around the world.
The Continuing Struggle Hook
Connect Dr. King's work to ongoing struggles for racial and social justice. Explore how contemporary movements draw inspiration from his teachings and activism.
The Man Behind the Legend Hook
Offer a glimpse into Martin Luther King Jr.'s personal life, upbringing, and motivations. Explore the man behind the iconic figure and shed light on his character and values.
Rhetorical Analysis of Martin Luther King's Historic Speech
Allusion in i have a dream speech, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Civil Disobedience Rhetorical Analysis
Martin luther king jr: impact on society, martin luther king jr: influential figure in the civil rights movement, different examples of "freedom is never given it must be demanded" in books, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Analysis of Martin Luther King's "I Have a Dream" Speech
Martin luther king's purpose in his speech beyond vietnam: a time to break silence, the life and legacy of martin luther king jr., the impact of martin luther king on american civil rights, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Use of Rhetorical Devices in I Have a Dream Speech by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Impact of martin luther king jr's speech, work to spark the reformation: martin luther king's opposition to the church authority, martin luther king, malcolm x, and rosa parks in the fight against racial inequality, struggle of martin luther king jr. and aneeka pasha, martin luther king jr.: leadership characteristics and legacy, how martin luther king jr's influence shaped american people, the effects of the speech by martin luther king after his death, a personal analysis of i have a dream, a speech by martin luther king jr, the role of martin luther king jr. and malcolm x in civil rights movement, letter from birmingham jail: the rhetorical analysis, analysis of martin luther king jr. as a great leader, 20th-century freedom movements, racism in i have a dream, martin luther king jr.: was everything in vain, analysis of pathos, ethos, and logos in the letter from birmingham jail, martin luther king jr.: life and legacy of a civil rights icon, "i have a dream" by martin luther king, comparison of king’s letter from birmingham jail and lincoln's inaugural address, rhetorical devices, pathos, ethos and logos in 'i have a dream' speech.
January 10, 1957 – April 4, 1968
Martin Luther King Jr. was a prominent leader in the American civil rights movement during the mid-20th century. He dedicated his life to advocating for racial equality and social justice through nonviolent means. King played a crucial role in the advancement of civil rights for African Americans, challenging segregation and discrimination prevalent in American society. King's activism extended beyond racial issues. He spoke out against the Vietnam War, advocating for peace and justice on a global scale. His commitment to nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience inspired millions and earned him international recognition, including the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964.
The American Civil Rights Movement, the Memphis Sanitation Workers’ Strike, the Montgomery Bus Boycott, and the March on Washington
One of King's most notable contributions was his leadership in the Montgomery Bus Boycott in 1955, sparked by Rosa Parks' refusal to give up her bus seat to a white person. The boycott led to a landmark Supreme Court ruling against racial segregation in public transportation. King also organized and participated in numerous peaceful protests, including the famous March on Washington in 1963, where he delivered his iconic "I Have a Dream" speech, calling for racial harmony and equality. King's leadership played a pivotal role in the passage of important legislation, including the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which aimed to dismantle segregation and protect the voting rights of African Americans. His peaceful protests and demonstrations brought attention to the systemic racism and discrimination that plagued American society. Beyond his immediate impact, King's message of equality and justice resonated globally. His philosophy of nonviolence influenced civil rights movements around the world and inspired individuals and communities to stand up against oppression. His emphasis on peaceful resistance demonstrated the power of love, compassion, and unity in the face of hatred and injustice. Martin Luther King Jr.'s legacy extends far beyond his lifetime. His teachings continue to shape social movements, promote equality, and challenge systemic racism.
"Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate; only love can do that." "Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere." "Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter." "Faith is taking the first step even when you don’t see the whole staircase."
Martin Luther King Jr.'s representation and role in media and literature have been significant, with numerous works dedicated to capturing his life, activism, and impact on society. Through various mediums, his story has been shared to inspire and educate generations. In literature, one notable example is the autobiography "The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr." edited by Clayborne Carson. It provides an intimate account of King's life, struggles, and achievements, allowing readers to delve into his personal experiences and motivations. In the realm of media, the film "Selma" directed by Ava DuVernay depicts the historic 1965 voting rights marches from Selma to Montgomery, Alabama, led by Martin Luther King Jr. The movie portrays King's leadership and determination in the face of adversity, highlighting the significance of his efforts in the civil rights movement.
Martin Luther King Jr. is an important figure to write an essay about due to his profound influence on the civil rights movement in the United States and his unwavering commitment to justice, equality, and nonviolent activism. His leadership and tireless efforts were instrumental in advancing the cause of racial equality and challenging systemic racism. By exploring King's life and work in an essay, one can delve into the complexities of his strategies, the impact of his speeches and writings, and the enduring legacy he left behind. King's philosophy of nonviolent resistance and his emphasis on love, peace, and unity continue to inspire and resonate with people around the world. Moreover, examining King's accomplishments within the historical and social context of his time allows for a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by African Americans and the ongoing struggle for civil rights. His contributions to the advancement of human rights and social justice make him a significant figure worth studying and celebrating. Through an essay on Martin Luther King Jr., his remarkable achievements and the lessons he imparted can be explored and shared, contributing to a broader understanding of the quest for equality and social change.
1. King Jr, M. L. (1992). Letter from Birmingham jail. UC Davis L. Rev., 26, 835. (https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/davlr26&div=31&id=&page=) 2. Selby, G. S. (2008). Martin Luther King and the rhetoric of freedom: the Exodus narrative in America's struggle for civil rights. Baylor University Press. (https://muse.jhu.edu/pub/170/book/4075) 3. Wills*, J. S. (2005). ‘Some people even died’: Martin Luther King, Jr, the civil rights movement and the politics of remembrance in elementary classrooms. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, 18(1), 109-131. (https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09518390412331318397) 4. Kirk, J. A. (2004). Martin Luther King, Jr. Journal of American Studies, 38(2), 329-347. (https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-american-studies/article/martin-luther-king-jr/21D5ABE466B6A9BEA01FD61D8671FE5E) 5. Smith, E., & Wilmore, G. S. (1983). The Ethics of Martin Luther King, Jr. (https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/004057368304000218) 6. Nygren, T., & Johnsrud, B. (2018). What would Martin Luther King Jr. say? Teaching the historical and practical past to promote human rights in education. Journal of Human Rights Practice, 10(2), 287-306. (https://academic.oup.com/jhrp/article-abstract/10/2/287/5042965) 7. Fairclough, A. (1983, April). Was Martin Luther King a Marxist?. In History Workshop (pp. 117-125). Editorial Collective, History Workshop, Ruskin College. (https://www.jstor.org/stable/4288462) 8. Berry, M. F. (1996). Vindicating Martin Luther King, Jr.: The road to a color-blind society. The Journal of Negro History, 81(1-4), 137-144. (https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/JNHv81n1-4p137?journalCode=jnh)
Relevant topics
- I Have a Dream
- Black Lives Matter
- Gun Control
- Homelessness
- Pro Choice (Abortion)
- Women's Rights
- Freedom of Speech
- Death Penalty
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
The Birthplace of Martin Luther King: a Look at its Historical Significance and Impact on his Legacy
This essay about the birthplace of Martin Luther King Jr. in Atlanta, Georgia, explores its significance as a symbol of resilience and hope. It highlights the transformative impact of King’s upbringing in the historic Sweet Auburn neighborhood and his enduring legacy of fighting for justice. Through vivid descriptions of the birth home and reflections on King’s influence, the essay underscores the ongoing relevance of his message in today’s world.
How it works
In the vibrant heart of Atlanta, Georgia, an unassuming red-brick house stands as a testament to the transformative journey of one of America’s most revered figures: Martin Luther King Jr. Nestled within the historic Sweet Auburn neighborhood, 501 Auburn Avenue is more than just a birthplace; it is a living symbol of resilience, hope, and the enduring pursuit of justice.
On a crisp January morning in 1929, Martin Luther King Jr. took his first breaths within the walls of this modest home.
Little did the world know that within these humble confines, the seeds of a profound legacy were being sown. Surrounded by the bustling energy of Auburn Avenue, a hub of Black culture and commerce, young Martin was immersed in a community teeming with resilience and determination.
As he grew, so too did the significance of his birthplace. In 1980, the National Park Service bestowed upon the Martin Luther King Jr. Historic Site designation, recognizing the profound impact of King’s legacy and the importance of preserving the spaces that bore witness to his transformative journey. Today, visitors from all walks of life make pilgrimages to this hallowed ground, eager to connect with the spirit of a man who dared to dream of a better world.
Stepping across the threshold of the King birth home, visitors are transported back in time, guided by knowledgeable park rangers who offer insights into the formative years of a civil rights icon. The creaking floorboards and faded wallpaper serve as tangible reminders of the challenges faced by King and countless others in their struggle for equality.
Yet, amidst the relics of the past, there exists a palpable sense of hope—a reminder that King’s legacy is not confined to the annals of history but lives on in the hearts and minds of those who continue to fight for justice today. From the streets of Atlanta to the halls of power in Washington, D.C., King’s message of nonviolent resistance and solidarity resonates with a new generation of activists seeking to dismantle the structures of oppression that persist in society.
Each year, on Martin Luther King Jr. Day, people across the United States pause to reflect on his legacy, honoring his contributions to the ongoing struggle for civil rights and social justice. From commemorative events and marches to educational initiatives aimed at preserving his memory, King’s influence endures as a guiding light in turbulent times.
Yet, even as we celebrate King’s achievements, we are reminded that the work of building a more just and equitable society is far from over. The struggles that King faced—racism, poverty, militarism—persist in new forms, demanding renewed commitment and resolve from those who carry on his legacy.
In this spirit, we honor the birthplace of Martin Luther King Jr. not as a relic of the past, but as a beacon of hope for the future. It is a reminder that change is possible, even in the face of seemingly insurmountable odds, and that the power to effect that change lies within each of us. As we stand on the hallowed ground of 501 Auburn Avenue, let us rededicate ourselves to the unfinished work of justice, inspired by the enduring legacy of a man who dared to dream of a better world.
Cite this page
The Birthplace of Martin Luther King: A Look at Its Historical Significance and Impact on His Legacy. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-birthplace-of-martin-luther-king-a-look-at-its-historical-significance-and-impact-on-his-legacy/
"The Birthplace of Martin Luther King: A Look at Its Historical Significance and Impact on His Legacy." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-birthplace-of-martin-luther-king-a-look-at-its-historical-significance-and-impact-on-his-legacy/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Birthplace of Martin Luther King: A Look at Its Historical Significance and Impact on His Legacy . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-birthplace-of-martin-luther-king-a-look-at-its-historical-significance-and-impact-on-his-legacy/ [Accessed: 21 May. 2024]
"The Birthplace of Martin Luther King: A Look at Its Historical Significance and Impact on His Legacy." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 21, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-birthplace-of-martin-luther-king-a-look-at-its-historical-significance-and-impact-on-his-legacy/
"The Birthplace of Martin Luther King: A Look at Its Historical Significance and Impact on His Legacy," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-birthplace-of-martin-luther-king-a-look-at-its-historical-significance-and-impact-on-his-legacy/. [Accessed: 21-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Birthplace of Martin Luther King: A Look at Its Historical Significance and Impact on His Legacy . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-birthplace-of-martin-luther-king-a-look-at-its-historical-significance-and-impact-on-his-legacy/ [Accessed: 21-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Celebrate the legacy of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. with the University Libraries

This year University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill honors the legacy of Martin Luther King Jr. with the theme “The Time is Now.” To coincide with this celebration, the University Libraries has gathered this list of books, films and other materials to help you learn about King’s impact and engage with his ideals.
E-books and Audiobooks
Throughout January, the University Libraries’ Honoring Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. OverDrive collection will highlight dozens of books on topics related to King’s legacy. From King’s own Where Do We Go from Here to John Lewis’s co-authored graphic novel March , you can engage with the history and impact of King’s work and the movement he helped lead.
Films
The Media & Design Center has created a list of films about King and his legacy, which can be accessed via streaming, DVD or VHS. (The center can also provide devices to play physical media). Films include Selma , Tony Brown’s essay on Martin Luther King Jr. and In Remembrance of Martin .
Selected Materials from the Wilson Special Collections Library
Collections in Wilson Library contain materials related to Martin Luther King Jr., including MLK buttons, a vintage church hand fan bearing King’s image and recordings of King’s speeches.
There are also some materials that you can access online. For example, have you ever wondered how the University reacted to news about the assassination of King? What happened at Carolina’s first MLK celebration in 1982? Blog posts from the University Archives take a look back at these moments in University history.
Wilson Library also holds recordings featuring Dr. King. For example, you can hear him in a 1963 mass meeting along with Ralph Abernathy in this recording from the Guy and Candie Carawan Collection . King discusses the historical significance of the civil rights movement in Birmingham, the importance of perseverance and unity, and jailing of children and other participants in the civil rights movement, among other topics.
The Carawan Collection also includes a press conference from the same year featuring King, Abernathy and Fred Shuttlesworth. The three address questions about the details of negotiations between leaders of the civil rights movement and business leaders and public officials, as well as specific developments in the civil rights movement in the preceding weeks. ( Part 1 ; Part 2 ; Part 3.)
This collection of resources was first published in January of 2023. It was updated in January 2024.
- BROWSE TOPICS X
- Devotionals
- Newsletters
Would Martin Luther King Jr. Be Heard in 2024?
- Dr. James Emery White Mecklenburg Community Church
- Updated Jan 15, 2024
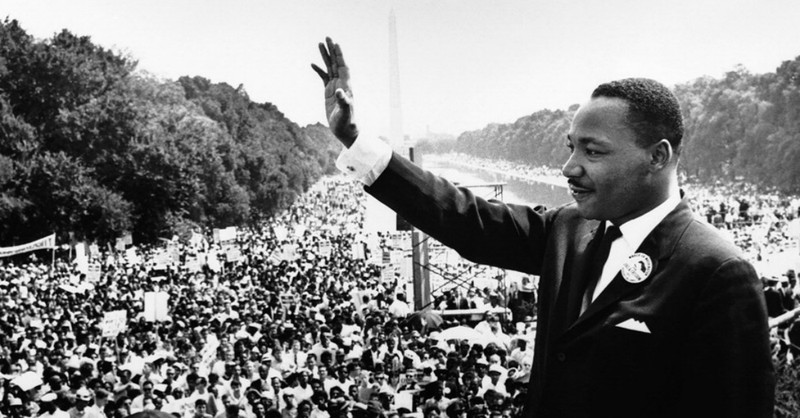

Today, the nation celebrates what would have been Martin Luther King Jr.’s 95th birthday. Sharon Shahid once openly wondered whether King’s famed essay, Letter from Birmingham Jail , “would have made such a lasting impression or had as powerful an impact if today’s instant communication devices existed, and if someone smuggled… a mobile phone into his cell. What would have happened if he texted the famous letter or used Twitter…?”
“Instead of a legacy,” she suggests, “he most likely would have started a conversation.”
And that’s all.
“King’s voice – so poignant and crystal-clear in print – simply would lose its resonance in cyber ink…. A tweet would have faded into ether minutes after it was released, drowned out by a thousand other disparate musings.”
But that is the least of the challenges our current context would bring to King’s words making an impact in our day. Why? It was a prophet’s voice based on a thoroughgoing Christian worldview.
And today, there are few such prophets.
Consider the term itself, “worldview,” from the German Weltanschauung (literally “world perception”), which suggests more than a set of ideas by which you judge other ideas. It is, as Gene Edward Veith has written, “a way to engage constructively the whole range of human expression from a Christian perspective.” Or as Jonathan Edwards, arguably the greatest intellect America has ever produced, once contended that the basic goal of any intellect is to work toward “the consistency and agreement of our ideas with the ideas of God.”
Reflect on the response to the first and most foundational of these questions—where did we come from? There are a limited number of answers at our disposal: We came about by chance (the Naturalist contention), we don’t really exist (the Hindu response), or we were spoken into existence by God.
So for the Christian, the answer to “Where did we come from and who are we?” gives a foundation for thinking that no other answer gives. Because we were created, there is value in each person. There is meaning and purpose to every life. There is Someone above and outside our existence who stands over it authoritatively.
Because of this answer, Martin Luther King, Jr. could write the immortal words found in his jailhouse correspondence:
“... there are two types of law: just and unjust.... A just law is a man-made code that squares with the moral law or the law of God. An unjust law is a code that is out of harmony with the moral law.... Any law that uplifts human personality is just. Any law that degrades human personality is unjust. All segregation statutes are unjust because segregation distorts the soul and damages the personality.”
King’s argument was based on the worth of a human being bestowed upon by God regardless of what other humans might have to say; King laid claim to a law above man’s law. No other worldview would have given King the basis for such a claim.
And from such a worldview, the world was changed.
But would such a worldview get a hearing today?
And there lies the irony: as a culture, we celebrate a man’s Christian convictions that were used to change our culture in the past, while simultaneously rejecting those values as a part of shaping our culture for the future.
Which means the next young leader with passion and conviction may have a dream, but if it’s based on King’s worldview, it will never be heard. Or, if heard, will never spark the cultural revolution it did before.
Not because it would be tweeted instead of written.
But because it would be based on something not of this world that the world no longer recognizes.
James Emery White
Editor ’s Note
Sources
Sharon Shahid, “If MLK Had Tweeted from Jail,” USA Today , Wednesday, January 12, 2011.
Gene Edward Veith, “Reading and Writing Worldviews,” in The Christian Imagination: The Practice of Faith in Literature and Writing , ed. by Leland Ryken, Revised and Expanded Edition (Colorado Springs: Shaw, 2002).
Jonathan Edwards, “Notes on the Mind,” in The Works of Jonathan Edwards: Scientific and Philosophical Writings , edited by Wallace E. Anderson (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1980).
Charles Colson and Nancy Pearcey, How Now Shall We Live (Wheaton: Tyndale, 1999).
Martin Luther King, Jr., Why We Can’t Wait (Letter from Birmingham Jail) (New York: Mentor/New American Library, 1963, 1964).
About the Author
James Emery White is the founding and senior pastor of Mecklenburg Community Church in Charlotte, NC, and a former professor of theology and culture at Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary, where he also served as their fourth president. His latest book, Hybrid Church: Rethinking the Church for a Post-Christian Digital Age , is now available on Amazon or from your favorite bookseller. To enjoy a free subscription to the Church & Culture blog, visit churchandculture.org where you can view past blogs in our archive, read the latest church and culture news from around the world, and listen to the Church & Culture Podcast. Follow Dr. White on X , Facebook and Instagram at @JamesEmeryWhite.
Image credit: Wikimedia Commons
The views expressed in this commentary do not necessarily reflect those of CrosswalkHeadlines .
Recently On Headlines Contributors

Editor's Picks

Trending Headlines

- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Crosswalk App
- California - Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- California - CCPA Notice
- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Sunday at INTA 2024: Why IP was important to Martin Luther King Jr

Highlights from Sunday included judicial insight from across the globe and a keynote address from Martin Luther King Jr’s daughter
Case law analysis from intellectual property judges and insight from the daughter of Martin Luther King Jr on why IP was so important to her father were among the highlights on day two of the INTA Annual Meeting taking place in Atlanta this week.
In between networking and meeting colleagues, Sunday also marked the first time that attendees were able to attend open panel sessions.
One session delved into differing judicial interpretations around the world.
Judicial differences
During that panel, members of the judiciary from Canada, Japan, South Korea, China, Germany, and Kenya analysed notable decisions from their courts and discussed the impact on brand owners.
Judge Justice Jing Yan from the Supreme People’s Court (SPC) of China said that in recent years the court has issued decisions that are “much more favourable to foreign rights owners”.

She referenced a 2023 dispute involving Siemens. The German company was awarded RMB 100 million ($13.8 million) in damages after a Chinese company called Ningbo Qishuai Electrical Appliance used the term ‘Shanghai Siemens Electrical Appliance’. The Chinese company was found liable for unfair competition and trademark infringement.
She also referenced the Panpan door dispute in which Swedish security device company Assa Abloy was awarded RMB100 million in damages after three Chinese companies were found to have infringed its trademarks for ‘Panpan’.
Yan said China, and in particular the SPC, had been issuing more decisions that provided assurances to brand owners.
It was a slightly different story in Kenya, however.
Justice Francis Tuiyott, a judge at the Court of Appeal of Kenya, referenced a decision he handed down in 2020 which he said many brand owners found surprising.
In that ruling, Tuiyott found that Japanese technology company Sony had not provided enough evidence to show that it had a well-known trademark in the country.
Kenyan property developer Sony Holdings had been using the term Sony, but the court found that it was not deceiving the public.
Although the Japanese Sony had registered trademarks in Kenya, it had not demonstrated that it was a well-known brand.
Meanwhile, Judge Naoyuki Iwai from the IP High Court of Japan gave a rundown of disputes concerning colour trademarks.
Colour trademarks, which became available in Japan 2014, have proved to be “rather difficult to protect” he said.
In January 2023, fashion designer Christian Louboutin failed to secure protection for the “red sole” shoe. The Japanese court, contrary to decisions in the EU, US and China, determined that it was not in the public interest to grant protection for a red sole colour.
Further, the colour had not acquired distinctiveness.
In another decision, this time from earlier this year, fashion brand Hermès also failed to secure protection for a shade of orange it uses on product packaging.
The session was moderated by Iris Gunther, director for brand enforcement and sustainability at INTA.
Keynote King
The highlight of the day was hearing from Bernice King, a lawyer and daughter of the late Martin Luther King Jr. Bernice was the keynote speaker for this year’s opening ceremonies.
Auma Reggy, co-chair of the 2024 annual meeting and managing lead IP counsel at health care company McKesson in the US, interviewed King.
King credited her mother, Coretta Scott King, for being the reason why people were still familiar with her father, who she noted was a "great man".
"But if you don't have anyone to carry your legacy, whatever you leave behind – it's going to die. She was very systematic in the way she built his legacy. She built the largest social change brand in the world," King said.
Coretta Scott King founded the Martin Luther King Jr. Center for Nonviolent Social Change, of which Dr Bernice King is now CEO, in 1968.
King went on to explore why IP was important to her father and how it helped maintain his legacy.
She noted that Luther King Jr’s famous "I have a Dream" speech was protected by copyright.
She added that a 1982 ruling from a lawsuit filed by the Center for Nonviolent Social Change was responsible for establishing a post-mortem right of publicity in Georgia.
In the lawsuit, the non-profit sued a defendant who had developed the concept of marketing a plastic bust of Luther King Jr.
King added that the non-profit sought and obtained trademark protection for its initiatives. The organisation was open to licensing its IP, but wanted to understand how it would be used, she said.
"We have to protect the integrity of the brand and the words and teachings of my father," she said.
King's talk ended with a standing ovation from attendees.
Brand Action
For the third year in a row, Brand Action is encouraging attorneys at the INTA Annual Meeting to try to raise money for vital causes.
Managing IP’s editor Max Walters stopped by the charity’s sponsors’ drinks event at the Hard Rock Cafe in Atlanta on Sunday afternoon.
Brand Action is a charity that brings the global trademark community together to help people in crisis.
Efforts this year are focused on supporting the World Central Kitchen's work in Haiti, and on raising funds to donate a second fully-equipped ambulance to provide relief in Ukraine.
Phil Cox, the US-based co-founder of Brand Action (pictured), told Managing IP: “We have an easy way to help people going through unimaginable turmoil. In the last year alone, we have fed people in Turkey, Syria, Ukraine, Mexico, and now Haiti, through our standing charity World Central Kitchen.
“After disasters happen, practitioners have asked Brand Action if we could help the people starving and dying in their countries. And we’ve been able to do it. These are the friends and colleagues our community works with daily. The people you see come and go at the conferences, and you often don’t know what is really going on for them at home.

“It seems that crises are happening everywhere these days, and there is no reason why next time it won’t be you who needs help.
“Brand Action stands as a place where we can collectively help our colleagues in their darkest time of need. These acts of kindness are the things that make a true community. This is more than just giving a few bucks to a good cause.”
You can support Brand Action by purchasing merchandise at the Alt Legal booth in the exhibition hall or via making a donation at BrandAction.org.
The charity will host its annual fundraising event at STATS Brewpub on Monday, May 20.
Question of the day
In addition to attending panels and events, we also caught up with some of our sources and other delegates, put faces to names, and learned more about law firm strategy and the IP issues concerning attorneys.
Today, we asked sources what they hoped to gain from the conference this year.
Saul Perloff, partner at A&O Shearman in Austin, noted that there were very few conferences where attendees have the opportunity to meet so many clients in one place.
“To me, it’s irreplaceable,” he said.
Jennifer Morton , partner at Gowling WLG in Toronto, said she was looking forward to catching up with clients who hadn't been able to attend INTA in the years immediately after the pandemic.
"It hasn't been like this until now. So, it's a great opportunity and the first time we'll be able to meet a lot of our big clients. A lot of corporate America didn't attend INTA before now [post COVID] and they're here at this meeting, which is fantastic."
Morton added that she was also excited to bring a younger associate, who is attending the conference for the first time.
"She's been working with my clients for a year and a bit, and this is the moment where I get her to introduce her to everyone. She's marvelous. And that for me is very fun. I remember being the baby once and how marvelous this conference was, and she's experiencing that."
Looking ahead
Sunday’s receptions included the INTA opening reception at the exhibition centre, a drinks reception at the Omni Hotel with CWB , and an event hosted by Barnes & Thornburg . Law firm Adams & Reece also took delegates to an Atlanta Braves baseball game.
On Monday we’ll report on a panel delving into law firm management concerns, Brand Action’s fundraiser, and much more.
The INTA Annual Meeting runs from May 18 to 23 at the Georgia World Congress Center in Atlanta.

More from across our site

As a premium subscriber, you can gift this article for free
You have reached the limit for gifting for this month
There was an error processing the request. Please try again later.
May 19, 1925 to February 21, 1965
As the nation’s most visible proponent of Black Nationalism , Malcolm X’s challenge to the multiracial, nonviolent approach of Martin Luther King, Jr., helped set the tone for the ideological and tactical conflicts that took place within the black freedom struggle of the 1960s. Given Malcolm X’s abrasive criticism of King and his advocacy of racial separatism, it is not surprising that King rejected the occasional overtures from one of his fiercest critics. However, after Malcolm’s assassination in 1965, King wrote to his widow, Betty Shabazz: “While we did not always see eye to eye on methods to solve the race problem, I always had a deep affection for Malcolm and felt that he had the great ability to put his finger on the existence and root of the problem” (King, 26 February 1965).
Malcolm Little was born to Louise and Earl Little in Omaha, Nebraska, on 19 May 1925. His father died when he was six years old—the victim, he believed, of a white racist group. Following his father’s death, Malcolm recalled, “Some kind of psychological deterioration hit our family circle and began to eat away our pride” (Malcolm X, Autobiography , 14). By the end of the 1930s Malcolm’s mother had been institutionalized, and he became a ward of the court to be raised by white guardians in various reform schools and foster homes.
Malcolm joined the Nation of Islam (NOI) while serving a prison term in Massachusetts on burglary charges. Shortly after his release in 1952, he moved to Chicago and became a minister under Elijah Muhammad, abandoning his “slave name,” and becoming Malcolm X (Malcolm X, “We Are Rising”). By the late 1950s, Malcolm had become the NOI’s leading spokesman.
Although Malcolm rejected King’s message of nonviolence , he respected King as a “fellow-leader of our people,” sending King NOI articles as early as 1957 and inviting him to participate in mass meetings throughout the early 1960s ( Papers 5:491 ). Although Malcolm was particularly interested that King hear Elijah Muhammad’s message, he also sought to create an open forum for black leaders to explore solutions to the “race problem” (Malcolm X, 31 July 1963). King never accepted Malcolm’s invitations, however, leaving communication with him to his secretary, Maude Ballou .
Despite his repeated overtures to King, Malcolm did not refrain from criticizing him publicly. “The only revolution in which the goal is loving your enemy,” Malcolm told an audience in 1963, “is the Negro revolution … That’s no revolution” (Malcolm X, “Message to the Grassroots,” 9).
In the spring of 1964, Malcolm broke away from the NOI and made a pilgrimage to Mecca. When he returned he began following a course that paralleled King’s—combining religious leadership and political action. Although King told reporters that Malcolm’s separation from Elijah Muhammad “holds no particular significance to the present civil rights efforts,” he argued that if “tangible gains are not made soon all across the country, we must honestly face the prospect that some Negroes might be tempted to accept some oblique path [such] as that Malcolm X proposes” (King, 16 March 1964).
Ten days later, during the Senate debate on the Civil Rights Act of 1964 , King and Malcolm met for the first and only time. After holding a press conference in the Capitol on the proceedings, King encountered Malcolm in the hallway. As King recalled in a 3 April letter, “At the end of the conference, he came and spoke to me, and I readily shook his hand.” King defended shaking the hand of an adversary by saying that “my position is that of kindness and reconciliation” (King, 3 April 1965).
Malcolm’s primary concern during the remainder of 1964 was to establish ties with the black activists he saw as more militant than King. He met with a number of workers from the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC), including SNCC chairman John Lewis and Mississippi organizer Fannie Lou Hamer . Malcolm saw his newly created Organization of African American Unity (OAAU) as a potential source of ideological guidance for the more militant veterans of the southern civil rights movement. At the same time, he looked to the southern struggle for inspiration in his effort to revitalize the Black Nationalist movement.
In January 1965, he revealed in an interview that the OAAU would “support fully and without compromise any action by any group that is designed to get meaningful immediate results” (Malcolm X, Two Speeches , 31). Malcolm urged civil rights groups to unite, telling a gathering at a symposium sponsored by the Congress of Racial Equality : “We want freedom now, but we’re not going to get it saying ‘We Shall Overcome.’ We've got to fight to overcome” (Malcolm X, Malcolm X Speaks , 38).
In early 1965, while King was jailed in Selma, Alabama, Malcolm traveled to Selma, where he had a private meeting with Coretta Scott King . “I didn’t come to Selma to make his job difficult,” he assured Coretta. “I really did come thinking that I could make it easier. If the white people realize what the alternative is, perhaps they will be more willing to hear Dr. King” (Scott King, 256).
On 21 February 1965, just a few weeks after his visit to Selma, Malcolm X was assassinated. King called his murder a “great tragedy” and expressed his regret that it “occurred at a time when Malcolm X was … moving toward a greater understanding of the nonviolent movement” (King, 24 February 1965). He asserted that Malcolm’s murder deprived “the world of a potentially great leader” (King, “The Nightmare of Violence”). Malcolm’s death signaled the beginning of bitter battles involving proponents of the ideological alternatives the two men represented.
Maude L. Ballou to Malcolm X, 1 February 1957, in Papers 4:117 .
Goldman, Death and Life of Malcolm X , 1973.
King, “The Nightmare of Violence,” New York Amsterdam News , 13 March 1965.
King, Press conference on Malcolm X’s assassination, 24 February 1965, MLKJP-GAMK .
King, Statement on Malcolm X’s break with Elijah Muhammad, 16 March 1964, MCMLK-RWWL .
King to Abram Eisenman, 3 April 1964, MLKJP-GAMK .
King to Shabazz, 26 February 1965, MCMLK-RWWL .
(Scott) King, My Life with Martin Luther King, Jr. , 1969.
Malcolm X, Interview by Harry Ring over Station WBAI-FM in New York, in Two Speeches by Malcolm X , 1965.
Malcolm X, “Message to the Grassroots,” in Malcolm X Speaks , ed. George Breitman, 1965.
Malcolm X, “We Are Rising From the Dead Since We Heard Messenger Muhammad Speak,” Pittsburgh Courier , 15 December 1956.
Malcolm X to King, 21 July 1960, in Papers 5:491 .
Malcolm X to King, 31 July 1963,
Malcolm X with Haley, Autobiography of Malcolm X , 1965.
Historical Material
Maude L. Ballou to Malcolm X
From Malcolm X
Invoking Struggle and Faith, Biden Reaches Out at Morehouse
Addressing graduates of the historically Black college in Georgia, Mr. Biden spoke to a crucial segment of the electorate and sought to distinguish himself from Donald J. Trump.
- Share full article
Katie Rogers and Maya King
Here’s what to know about Biden’s remarks.
Biden calls on morehouse college graduates to defend democracy, in a commencement speech at morehouse, the historically black men’s college in atlanta, president biden condemned white supremacy and “extremist forces aligned against the meaning and message of morehouse.”.
You started college just as George Floyd was murdered and there was a reckoning on race. It’s natural to wonder if democracy you hear about actually works for you. What is democracy if Black men are being killed in the street? What is democracy if the trail of broken promises still leave Black communities behind? What is democracy if you have to be 10 times better than anyone else to get a fair shot? Well that’s my commitment to you. To show you democracy, democracy, democracy, is still the way. That Black men are being killed in the streets, we bear witness. For me, that means to call out the poison of white supremacy. Graduates, this is what we’re up against: extremist forces aligned against the meaning and message of Morehouse. And they peddle a fiction, a caricature, of what being a man is about — tough talk, abusing power, bigotry. But that’s not you. It’s not us. You all know and demonstrate what it really means to be a man. Being a man is about strength of respect and dignity. It’s about showing up because it’s too late, if you have to ask. It’s about giving hate no safe harbor.

President Biden invoked scripture and lessons from his own tragic past on Sunday in a commencement address to hundreds of young Black men at Morehouse College, saying he believes there are “extremist forces aligned against the meaning and message” of the prestigious institution.
Mr. Biden’s speech, delivered at the historically Black men’s college in Atlanta, put him directly in front of hundreds who represent a slice of the electorate that is drifting away from him over the war in Gaza and growing apathy about their choices ahead of the election. Mr. Biden used the moment to say that manhood was not about “tough talk” and “bigotry” but about calling out hate.
“Their idea of being a man is toxic,” Mr. Biden told the graduates, a reference to adversaries he did not name — but, given that his other events this weekend were focused on attacking his Republican competitor, Donald J. Trump, it was little mystery who he was talking about. “That is not you. That is not us. Being a man is about strength and respect and dignity.”
Those who stormed the Capitol with Confederate flags “are called patriots by some,” he said — a clear reference to Mr. Trump. “Not in my house.”
Mr. Biden’s speech was his first significant appearance before college students since protests over the war in Gaza began roiling campuses. For a ceremony in which students are discouraged even from decorating their caps, the signs of protest were respectful but noticeable: A small group of graduates turned to sit with their backs to Mr. Biden as he spoke, and several graduates wore the kaffiyeh, a traditional scarf associated with the Palestinians, draped over their shoulders. Some parents urged their graduating sons not to protest.
Mr. Biden also called for an immediate cease-fire and said that his administration was working to secure one. He said that members of his family had been upset by the war, a group that includes Jill Biden, the first lady, who has urged her husband in private to bring a stop to it.
“What’s happening in Gaza, in Israel, is heartbreaking,” Mr. Biden said. “It’s a humanitarian crisis in Gaza.”
In a statement, Morehouse said that discussions between White House officials and students, faculty and alumni had helped shape Mr. Biden’s speech and his calls for a cease-fire in Gaza. The school also praised its graduates. “It is fitting that a moment of organized, peaceful activism would occur on our campus while the world is watching to continue a critical conversation,” the statement read.
During his 27-minute speech, Mr. Biden tried to stress to the graduates — none of whom stood for him as he took the lectern — that throughout his life he had respected and espoused the same ideas they care about.
He said he had worked throughout his life, as a public defender, senator and president, to correct inequalities. He outlined the work his administration has done that he and his advisers believe deserves more credit than it receives, including the forgiveness of large amounts of student loan debt and reducing the poverty rate for Black children.
“We know Black history is American history,” Mr. Biden said at one point, urging the crowd to “check my record,” which includes choosing the first Black female Supreme Court justice, Ketanji Brown Jackson, and the first Black woman to hold the vice presidency, Kamala Harris.
By focusing on matters of adversity and strength, Mr. Biden also sought to strike a contrast with Mr. Trump not on the grounds of politics or policy but through the lessons of keeping faith in moments of hopelessness. He spoke of the death of his first wife and daughter as well as his eldest son, Beau, from brain cancer.
He told the Morehouse graduates, a class that weathered the chaos of the pandemic and the tumult of widespread protests over the police killings of Black men, that it was natural for them to question whether there was a place for them in democracy at all.
“What is democracy when Black men are being killed in the streets?” he said. “What is democracy when a trail of broken promises still leave Black communities behind? What is democracy when you have to be 10 times better than anyone else to get a fair shot?”
Repeatedly, Mr. Biden reached for religious inspiration, recalling that Jesus was buried on Friday and resurrected on Sunday, leaving Saturday as a day of hopelessness. He suggested that 2020 — the year he was elected, with its twin traumas of the Covid-19 pandemic and the police killing of George Floyd — had been one such Saturday.
At one point, Mr. Biden said, “I’ve learned there was no easy optimism but by faith, by faith you can find redemption.”
Mr. Biden, who has a bust of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. in the Oval Office — and who is old enough to have shared his memories of Dr. King’s assassination in his speech — walked into commencement on Sunday unsure of how the crowd would receive him.
Morehouse, which was established in Atlanta in 1867, is a school whose culture is steeped in tradition. Students spend their years working toward becoming the embodiment of the Morehouse man: well traveled, well read and civically engaged. As the alma mater of Dr. King, there is also a proud history of protesting for social justice.
Mr. Biden’s visit to Morehouse drew the objections of some faculty members, alumni and students, who have voiced anger over the war in Gaza and the American government’s support for Israel. The tension drew so much attention that the school’s president, David A. Thomas, publicly warned that he would stop the commencement if graduates shouted at the president or disrupted the event.
The men of Morehouse found ways to work their opposition to the war into the ceremony. DeAngelo Jeremiah Fletcher, the class valedictorian, took the stage with the Palestinian flag pinned on his stole and on his cap.
“It is my stance as a Morehouse man, nay, as a human being, to call for an immediate and permanent cease-fire, in the Gaza Strip,” Mr. Fletcher said. Mr. Biden joined the crowd in standing up and clapping when Mr. Fletcher finished, and he shook the graduate’s hand.
But by the end of Mr. Biden’s speech, signs of support were visible, too. As Mr. Biden received an honorary doctorate of law, Mr. Thomas praised the president for listening to the concerns of the graduating class. And some people chanted “four more years” as Mr. Biden left the stage.
After addressing Morehouse, Mr. Biden was set to travel to Detroit to speak at a dinner hosted by the N.A.A.C.P.
Hitting two battleground states in eight hours was the clearest sign yet that Mr. Biden is serious about reintroducing himself to voters who carried him to the White House in 2020 and whose support he will need to win to stay in office for a second term.
In 2020 , 95 percent of Black women and 87 percent of Black men voted for Mr. Biden, according to the Pew Research Center. But in April, only 55 percent of Black voters told Pew that they approved of his job performance. A recent poll by Ipsos and The Washington Post showed that 62 percent of Black Americans planned to vote in 2024, down from 74 percent in 2020.
In recent days, both Mr. Biden and Ms. Harris have traveled outside of Washington to host events geared toward bringing those voters back into the fold.
Mr. Biden’s trip to Detroit comes as the latest New York Times/Siena College poll shows him winning support from less than half of Black voters in Michigan in a five-way race. In 2020, he won more than 90 percent of Black voters in the state, exit polls show.
The war in Gaza and concerns about the economy are driving factors behind what analysts say is an increase in apathy. In Michigan, nearly nine in 10 Black voters rated the economy as being in “fair” or “poor” condition, a higher rate than white voters, the Times/Siena poll found.
Alexis Wiley, the founder of a strategic communications firm in Detroit and a former member of the Democratic National Committee, said the Biden administration had to do more to communicate its victories.
“I think that they’re finally catching up to the fact that people aren’t feeling great,” Ms. Wiley said, “and now there’s this mad dash to try to correct it.”
Reporting was contributed by Nicholas Nehamas in Washington and Chevaz Clarke-Williams , Alan Blinder and Sean Keenan in Atlanta.
Biden asks Black voters to align with him in defending democracy.
President Biden on Sunday appealed to the graduating men of Morehouse College, and Black voters by extension, to align themselves with him on the side of democracy and against the forces of white supremacy that have coursed through American politics.
“It’s natural to wonder if the democracy you hear about actually works for you,” he said in a half-hour commencement speech. “What is democracy when Black men are being killed in the streets? What is democracy when a trail of broken promises still leave Black communities behind? What is democracy when you have to be 10 times better than anyone else to get a fair shot?”
He condemned both the “extremist forces aligned against the meaning and message of Morehouse” and what he called false notions of what “manhood” really is.
Repeatedly, Mr. Biden reached for religious inspiration, recalling that Jesus was buried on Friday and resurrected on Sunday, leaving Saturday as a day of hopelessness. He suggested that 2020 — the year he was elected, with its twin traumas of the Covid-19 pandemic and the police killing of George Floyd and the protests that it ignited — had been one such Saturday.
“In our lives, in our nation, we have those Saturdays to bear witness to the day before glory,” he said to the graduating class, largely made up of students who were barred from in-person high school graduations because of the pandemic. “What work is done on Saturday can move pain to purpose.”
Left unsaid was how Mr. Biden’s administration and the current political moment fit into that metaphor.
Mr. Biden highlighted policies that he said had disproportionately harmed Black voters, like a law enacted in Georgia in 2021 that placed more restrictions on ballot access. One provision outlawed giving voters water or snacks while they wait in line and has drawn the ire of Democrats nationwide.
“What the hell is that all about?” Mr. Biden asked.
He also underlined the policies his administration has championed that he said were meant to improve Black communities, like increased funding to historically Black colleges and reconnecting Black neighborhoods decimated by highway construction. “Instead of forcing you to be 10 times better,” he said, “we’re breaking down doors to save 100 more opportunities.”
Advertisement
Sean Keenan
After spending most of the morning marching on sidewalks outside campus, as police requested, a group of about 100 pro-Palestinian demonstrators has taken to the street. The march, which includes some Morehouse students and faculty members, is now blocking southbound traffic on Joseph E. Lowery Boulevard, a road named for the late minister and civil rights leader.
Chevaz Clarke
As Biden concluded his speech, guests seated in the V.I.P. section chanted “four more years.”
As Biden was being presented with his honorary degree, several students walked out .

This moment, where Biden is receiving an honorary degree, was more protested than his speech itself in some circles. Now that he’s received the recognition, Biden could technically be considered a “Morehouse man” — something many students and alumni disagreed with.
1 00:00:00,000 —> 00:00:05,178 I confer upon you, Joseph R. Biden Jr., 2 00:00:05,178 —> 00:00:07,490 the honorary doctor of laws, 3 00:00:07,490 —> 00:00:10,310 honoris causa, with all the rights, 4 00:00:10,310 —> 00:00:13,940 privileges and responsibilities appertaining 5 00:00:13,940 —> 00:00:15,450 thereunto. 6 00:00:15,450 —> 00:00:19,064 Congratulations, Dr. Joseph Biden. 7 00:00:19,064 —> 00:00:21,421 [cheering]

Katie Rogers
Biden makes a bit of a show for the cameras, smiling and pointing to his stole, after receiving his honorary degree.
That was a difficult needle to thread for the president, who went into this speech aware that there was a protest movement against his appearance here. But the president of Morehouse just praised him for “listening” to the concerns of the graduating class.
Alan Blinder
The president is finished. I clocked Biden’s speech at roughly 27 minutes, a bit shorter than Barack Obama’s 33-minute commencement address at Morehouse in 2013.
Black leaders and Democratic strategists have long warned that the biggest challenge this November will not be Black voters’ drift to voting for Trump or other Republican candidates but that they may stay home altogether. This speech — with its heavy allusions to democracy, manhood and the rich history of Black institutions like Morehouse — is meant to inspire groups like this to vote. And, even more, to get others in their communities to do the same.
Shane Goldmacher
When Biden puts it in such quick succession, his links to the Black community’s top political leaders are fairly remarkable. He was vice president to the first Black president; he named the first Black woman to serve as vice president; he appointed the first Black woman to the Supreme Court. Yet early polls show him winning a smaller share of Black voters that most Democrats.
It was not a foregone conclusion that Biden’s address would continue without protests. But he spoke largely uninterrupted.
Zolan Kanno-Youngs
“Whether you’re young or old, I know what endures. The strength and wisdom of faith endures,” Biden says, acknowledging a concern among many young voters who I have talked to: the president’s age.
“I know I don’t look like I’ve been around very long,” Biden jokes, crossing himself.
“She’s tough, guys,” he adds.
Biden said that a Morehouse Man would become president one day, right after an “A.K.A. from Howard,” all but name-checking the vice president, Kamala Harris.
1 00:00:00,000 —> 00:00:02,570 I’ve been vice president of the first Black president 2 00:00:02,570 —> 00:00:04,863 and become my close friend 3 00:00:04,863 —> 00:00:07,925 and president of the first woman vice president. 4 00:00:08,652 —> 00:00:10,247 [cheers] 5 00:00:12,160 —> 00:00:13,810 Well, I have no idea — 6 00:00:13,810 —> 00:00:18,348 no doubt that a Morehouse man will be president one day — 7 00:00:18,348 —> 00:00:21,834 just after an A.K.A. from Howard. 8 00:00:21,834 —> 00:00:23,276 [laughs]

Biden lays out the stakes of 2024 for this crowd, saying there are “extremist forces aligned against the meaning and message of Morehouse.”
Biden says those who stormed the Capitol with Confederate flags “are called patriots by some” — a clear reference to Donald Trump. “Not in my house,” he says.
President Biden also makes mention of Georgia’s stringent election laws. One provision that outlaws giving water or snacks to those waiting in line at the polls drew outrage nationwide.
The invoking of his own family’s frustration was very revealing.
Biden said that his family was angry and affected by what is happening in Gaza. We reported recently that Jill Biden, the first lady, has urged him to find a way to stop it .
Biden seems to be spending more time talking about Israel and Gaza than he spent discussing, say, student loan debt or education policy.
“What’s happening in Gaza in Israel is heartbreaking,” Biden says. “It’s a humanitarian crisis in Gaza.” Biden says he’s been “working around the clock” for an immediate ceasefire. Jake Sullivan, his national security adviser, is Saudi Arabia and Israel this weekend for talks with top leaders.

This Biden speech shows a president torn between the frustrated feelings of many voters of his and the nation’s shortcomings, and the economic statistics that he hopes take hold in their view of his presidency this fall. “Record numbers of Black Americans have jobs,” he says, while acknowledging that is not enough.
As much as Biden is talking to this class of mostly 20-something men, he’s also talking to the hundreds of family members in the crowd. There are scores of Black voters here who eagerly wanted to hear from the president.
Biden makes specific his efforts to nix student loan debt to this crowd. “I’m relieving the burden of student debt — many of you have already had the benefit of it,” he said.
At first, Biden was not really using politics or policy to draw a comparison with his challenger, Donald J. Trump. He did it instead by focusing on scripture and talking at length about what faith had taught him. I’ve covered dozens of Trump rallies and can’t say that was ever much of a theme. Now Biden is transitioning to his agenda.
About 15 minutes into the speech, we hear Biden starting to trumpet his policy agenda, including on student debt.
“Instead of forcing you to prove you’re 10 times better, we’re breaking down doors so you can have 100 times more opportunities,” Biden says.
President Biden is framing an understanding of democratic norms around how this class of young, Black men might view it: through racial prejudice and inequality. Many students I spoke to this week echoed this theme and said they felt that in light of the crises they face, political leaders don’t listen to them.
Yes, it’s notable to me too, Zolan, that he is going with such a personal approach, trying to show his character and empathy. “Faith asked me to hold on to hope,” he says. “That’s my commitment to you to show you democracy, democracy, democracy is still the way.”
This speech so far has been mostly about Biden’s upbringing — one of a law student, public defender and single father — rather than promoting the economic achievements of the Biden administration. The White House has been focused on promoting such policy achievements to galvanize a crucial constituency of Black voters frustrated with the Biden White House.
Biden is trying to turn his broad pitch about the centrality of democracy to the 2024 campaign to the realities of being Black in America in 2024. After invoking the death of George Floyd, he says, “What is democracy, if Black men are being killed in the street?”

And he’s trying to express that he understands why these graduates might question the promise of democracy.
Biden is essentially retelling the story of his personal life and how he learned the lessons of optimism and compassion. The importance of family and keeping the faith. It’s a way of acknowledging the difficulties this Covid class has faced in reaching this moment, their education upended by the pandemic and killing of George Floyd.
Indeed, one of Biden’s touchstones was a memory of Martin Luther King Jr. still alive.
Biden is recounting his college years, early career and the death of his first wife and daughter after being elected to the Senate. These are events that occurred more than a half-century before this graduation.
When describing his upbringing, Biden has increasingly mentioned his time as a public defender in Delaware. After the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., Biden left a private firm that specialized in representing big companies to work as a public defender.
A march of more than 100 pro-Palestinian demonstrators has stopped in front of a police blockade outside the school’s entrance on Atlanta Student Movement Boulevard. Multiple Atlanta Police prisoner transport vans just pulled up. Activists are continuing speeches and chants decrying Biden, Israel and law enforcement.

Biden pokes fun at Morehouse, calling Delaware State, a historically Black college in his home state, the nation’s “best.” This Howard alumna would beg to differ.
Morehouse parents to their graduating seniors considering protests: Don’t.
After it became clear that some students at Morehouse, the all-male historically Black institution in Atlanta, would protest President Biden’s commencement address on Sunday, Davida Morgan Washington and her husband offered some gentle-but-firm advice to the graduate in their family: Don’t engage.
“I do not expect you to participate” in the protests, she said she told her son, Kollin Washington, who is receiving his bachelor’s degree in cinematography on Sunday. He, in turn, guaranteed her that he would steer clear of the fray.
Another parent, Chiara King, warned her son against demonstrating. Though she was upset by the images of destruction in the Gaza Strip and saw valid reasons for students’ demonstrations against the war, she said she felt Mr. Biden’s visit to the storied campus was a huge honor and wanted to hear what a sitting president would say to the Class of 2024.
“He does have compassion for the children that have been lost in this,” she said of her son. “But this day is truly about him enjoying the moments that he has studied so hard for.”
Her son, Christian Shields, agreed. In an interview Friday, he said his reasons for avoiding protests were largely familial — he wanted his loved ones to enjoy the ceremony.
“The commencement, it isn’t for us, it’s for them,” said Mr. Shields, who earned a bachelor’s degree in physics. He added a practical caveat: “We want to keep the commencement to a nice, short and sweet hour and a half, two hours. We don’t want anything to happen.”
In the days and hours before Mr. Biden’s address, the style and scale of protests against his visit were both an open question and widely-discussed topic in parent group forums. Across the country, colleges and universities have been roiled by protests against the war between Israel and Hamas. Multiple — including Emory University, another Atlanta-area institution — moved their graduation ceremonies to off-campus locations to avoid major demonstrations.
But Morehouse has seen few signs of sustained protest — students did not establish encampments on campus or hold long-term demonstrations. Tensions around the president’s visit have largely played out in classrooms and auditoriums. Students and a group of alumni expressed their disdain in a handful of letters to Morehouse’s president, David Thomas, asking him to rescind the invitation to Mr. Biden. Some faculty members threatened to boycott the ceremony altogether.
In response, campus leaders and a handful of White House officials held meetings with students to ease tensions and encourage peaceful protest. Mr. Thomas said that he would stop the ceremony if demonstrations became too disruptive.
And parents have taken their own precautions, too. Ms. King said that she had a safety plan in place for her family members attending commencement, including both of her octogenarian parents. They aimed to arrive at the university’s campus near downtown Atlanta around 4 a.m. on Sunday, five hours before the ceremony. On Thursday, they shot graduation pictures on campus to avoid doing so in crowds when the ceremony ended.
The thoughts of many Black parents were even captured in popular culture. In a Saturday Night Live episode that aired in early May, cast member Kenan Thompson, who played a parent of a Columbia University student, said he supported student protesters — as long as those students were not his children. His daughter, he added, “better have her butt in class.”
“I’m in support of y’all’s kids protesting. Not mine,” his character said in the cold open skit. “My kids know better.”
Kaelyn Jones, council leader of the Morehouse Parents’ Council’s Georgia and Alabama region, said she has spent the better part of the last few weeks fielding concerns from parents across the country who were concerned about protests that could disrupt their day. Though her son is a junior at Morehouse, she said she is concerned for all of the students who are graduating — and their parents.
“These are my sons,” Ms. Jones said. “Regardless of how many kids you have there.”
An earlier version of this article misstated on second reference the last name of a member of the Morehouse Parents’ Council leadership, as well as her title. She is Kaelyn Jones, not Johnson, and she is council leader of the Morehouse Parents’ Council’s Georgia and Alabama region, not president.
How we handle corrections
Erica L. Green
Reporting from Washington
Biden has been working to shore up support among Black voters.
President Biden has been trying to shore up support among Black Americans, who helped deliver him the White House in 2020.
His outreach culminates on Sunday with a highly anticipated commencement address at prestigious Morehouse College, one of the nation’s oldest historically Black colleges.
Mr. Biden plans to underscore past victories for Black Americans while also heralding the achievements he has delivered, White House officials said, citing a 60 percent increase in Black household wealth and the lowest Black unemployment rate ever last year.
“We’re not just talking about history, like we are doing today with the Brown and related cases, but how indeed the president’s making history every single day,” said Stephen K. Benjamin, a senior adviser to Mr. Biden and the director of public engagement, referring to Brown v. Board of Education, which the president commemorated last week .
But it is not clear that Mr. Biden’s efforts are resonating. A new set of polls in five crucial battleground states found deep frustration among young, Black and Hispanic voters that threatens to unravel the president’s Democratic coalition.
His speech at Morehouse comes as discontent over the war in Gaza has broken out on campuses nationwide. But at Morehouse, which has a legacy of civil rights protests and is the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s alma mater, such debates have not played out quite so publicly .
Representative James E. Clyburn, the South Carolina Democrat whose 2020 endorsement helped resurrect Mr. Biden’s campaign, said he believed the erosion of Black support for Mr. Biden had been overblown.
Mr. Biden’s policies, Mr. Clyburn said, are meaningful — particularly his efforts to eliminate lead pipes that have poisoned Black children for decades and lowering insulin costs for a population that has a higher rate of death from diabetes. And he said measures like wiping out billions in student loan debt would resonate at a school like Morehouse.
“Joe Biden’s relationship with Black people is really solid,” Mr. Clyburn said. “Black people see in Joe Biden the kind of presidency that they would like to have.”
Last week, Mr. Biden’s efforts to connect with Black voters included meeting on Thursday with plaintiffs and their families to commemorate the 70th anniversary of the Brown case, a landmark decision that ruled that racial segregation in schools was unconstitutional. On Friday, he spoke at the National Museum of African American History and Culture and met with the leaders of the Divine Nine, a group of historically Black sororities and fraternities.
Zach Montague contributed reporting.
Other graduation ceremonies where protests occurred are happening today.
Aside from Morehouse College, several other universities are holding commencement ceremonies on Sunday, some with increased safety and security measures in case of protests or disruptions.
Over the past several weeks, some ceremonies have been disrupted by protests over the war in Gaza. Since mid-April, protesters have filled campuses across the country and formed encampments, demanding that their universities divest from Israel. More than 2,900 protesters have been arrested .
Many encampments have since been cleared out, as several schools reached agreements with protesters to remove them, including Harvard; Rutgers; the University of California, Berkeley; and Wesleyan University.
Among the schools honoring their graduates today are George Washington University in Washington, D.C.; Tufts University in Massachusetts; and the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee — all universities that have dealt with protesters on campus in recent weeks.
Here’s what has happened at those schools.
George Washington University
This month, the police broke up an encampment and arrested more than 30 protesters. Days later, protesters briefly occupied a street in front of the university president’s residence .
The main graduation ceremony is at 10:30 a.m. at the National Mall. The school said that it has taken additional safety and security measures. Jen Psaki, former press secretary to President Biden, will give the commencement address .
University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Unlike many other universities, the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee allowed an encampment on its campus to stand, though officials had signaled that their patience was running out. Two weeks after the encampment was set up, the university announced that protesters had agreed to remove it. In return, the university pledged to join calls for a cease-fire and hear protesters’ concerns regarding university investments, among other things. The protesters also agreed to not disrupt the university’s commencement events.
Commencement ceremonies are scheduled for 9 a.m. and 2 p.m. at the school’s Panther Arena. The university is prohibiting items including large banners, flag signs and poles from the ceremonies.
Tufts University
At Tufts University, protesters had set up a brief encampment in late April . It was taken down in early May, according to CBS News, and school officials stated that the protest ended voluntarily.
The school’s commencement ceremony was scheduled for 9 a.m. on campus. The school has increased security measures and prohibited items such as signs, banners and flags.
Barack Obama spoke at Morehouse’s commencement 11 years ago.
With his appearance in Atlanta on Sunday, President Biden will become the second sitting president to deliver Morehouse College’s commencement address in 11 years.
President Barack Obama, speaking almost 50 years after the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. gave his “I Have a Dream” speech in Washington, invoked King and his own life’s story during the college’s 2013 commencement .
Morehouse’s most celebrated alumnus, King “learned to be unafraid, and he, in turn, taught others to be unafraid, and over time, he taught a nation to be unafraid,” Mr. Obama said.
“And over the last 50 years, thanks to the moral force of Dr. King and a Moses generation that overcame their fear and their cynicism and their despair, barriers have come tumbling down, and new doors of opportunity have swung open, and laws and hearts and minds have been changed to the point where someone who looks just like you can somehow come to serve as president of these United States of America,” Mr. Obama continued to applause. “So the history we share should give you hope. The future we share should give you hope.”
Mr. Obama, whose speech touched on his own childhood and upbringing with bracing candor, also directly challenged the graduating class.
“Nobody cares how tough your upbringing was,” he said moments after referring to ascendant economies in other countries and their legions of young people. “Nobody cares if you suffered some discrimination. And moreover, you have to remember that whatever you’ve gone through, it pales in comparison to the hardships previous generations endured — and they overcame them. And if they overcame them, you can overcome them, too.”
Mr. Obama returned to Morehouse in 2018, after he had left the White House, to campaign for Democratic candidates in Georgia.
Maya King and Reid J. Epstein
Maya King reported from Atlanta, and Reid J. Epstein from Washington.
Here’s why antiwar protests haven’t flared up at Black colleges like Morehouse.
Ahead of President Biden’s graduation remarks on Sunday at Morehouse College in Atlanta, a prestigious historically Black institution, the White House signaled some anxiety about the potential for protests over the war in Gaza.
During a recent visit to Atlanta, Vice President Kamala Harris stopped to ask the Morehouse student government president about the sentiment on campus about the conflict, how students felt about Mr. Biden’s visit and what the graduating class wanted to hear from him. Later, the leader of the administration’s public engagement office and one of its most senior Black officials, Stephen K. Benjamin, visited to take the temperature of students, faculty members and administrators.
The reasons for concern are clear: Nationwide demonstrations over the war and Mr. Biden’s approach to it have inflamed more than 60 colleges and universities , stoked tensions within the Democratic Party and created new headaches for his re-election bid.
Yet Mr. Biden appears to be entering a different type of scene at Morehouse.
While anger over the war remains palpable at Morehouse and other historically Black colleges and universities, these campuses have been largely free of turmoil, and tensions are far less evident: no encampments, few loud protests and little sign of Palestinian flags flying from dorm windows.
The reasons stem from political, cultural and socioeconomic differences with other institutions of higher learning. While H.B.C.U.s host a range of political views, domestic concerns tend to outweigh foreign policy in the minds of most students. Many started lower on the economic ladder and are more intently focused on their education and their job prospects after graduation.
At Morehouse — which has a legacy of civil rights protests and is the alma mater of the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. — discontent over the Gaza war has played out in classrooms and auditoriums rather than on campus lawns.
“This should not be a place that cancels people regardless of if we agree with them,” David Thomas, the Morehouse president, said in an interview earlier this month. Of Mr. Biden’s visit, he said, “Whether people support the decision or not, they are committed to having it happen on our campus in a way that doesn’t undermine the integrity or dignity of the school.”
Some students have held contentious meetings with university leaders and urged them to rescind Mr. Biden’s invitation, and a small group of faculty members has vowed not to attend commencement. Some alumni wrote a letter expressing worries that student protesters could be punished, noting Morehouse’s history of “celebrating student activists long after they have graduated.”
But the college might appear politically safer for the president to visit than many others. Morehouse is a custom-bound place where undergraduates traditionally do not step on the grass in the heart of campus until they receive their degrees. Alumni view commencement as a distinguished event not only for students but also for scores of family and community members — making it a less likely venue for a major disruption.
Kitty Bennett contributed research.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Martin Luther King, Jr., Day was established as an annual observance in the United States in 1983. The King holiday campaign overcame forceful opposition, with critics citing FBI surveillance files suggesting that King was an adulterous radical influenced by communists. Although the release of these files during the 1970s under the Freedom of ...
Martin Luther King Jr. Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his assassination in ...
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 - April 4, 1968) was an American Christian minister, activist, and political philosopher who was one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968. A black church leader and a son of early civil rights activist and minister Martin Luther King Sr., King advanced civil rights ...
During the less than 13 years of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.'s leadership of the modern American Civil Rights Movement, from December 1955 until April 4, 1968, African Americans achieved more genuine progress toward racial equality in America than the previous 350 years had produced. Dr. King is widely regarded as America's pre-eminent advocate of nonviolence and one of the greatest ...
Martin Luther King, Jr., (born Jan. 15, 1929, Atlanta, Ga., U.S.—died April 4, 1968, Memphis, Tenn.), U.S. civil rights leader. The son and grandson of Baptist preachers, King became an adherent of nonviolence while in college. Ordained a Baptist minister himself in 1954, he became pastor of a church in Montgomery, Ala.; the following year he received a doctorate from Boston University.
Introduction. Martin Luther King, Jr., made history, but he was also transformed by his deep family roots in the African-American Baptist church, his formative experiences in his hometown of Atlanta, his theological studies, his varied models of religious and political leadership, and his extensive network of contacts in the peace and social ...
This year's Martin Luther King Jr. Day, on January 15, coincides with the late civil rights leader 's birthday. Had he lived, King would be turning 95 years old. Days after his 1968 ...
Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his assassination in 1968. Explore his life ...
The Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr. towers over history as a civil rights legend—known for leading the movement to end segregation and counter prejudice against Black Americans in the 1950s and ...
August 28, 1963. Martin Luther King's famous "I Have a Dream" speech, delivered at the 28 August 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, synthesized portions of his previous sermons and speeches, with selected statements by other prominent public figures.. King had been drawing on material he used in the "I Have a Dream" speech in his other speeches and sermons for many years.
500+ Words Essay on Martin Luter King. Martin Luther King Jr. was an African-American leader in the U.S. He lost his life while performing a peaceful protest for the betterment of blacks in America. His real name was Michael King Jr. He completed his studies and attained a Ph.D.
Author: King, Martin Luther, Jr. (Morehouse College) Date: January 1, 1947 to February 28, 1947 Location: Atlanta, Ga. Genre: Published Article Topic: Martin Luther King, Jr. - Political and Social Views Details. Writing in the campus newspaper, the Maroon Tiger, King argues that education has both a utilitarian and a moral function. 1 Citing the example of Georgia's former governor Eugene ...
Dr. Martin Luther King addresses some 2,000 people on the eve of his death—April 3, 1968—giving the speech "I've been to the mountaintop." Bettmann/Getty Images. T he words written about ...
To save man from the morass of propaganda, in my opinion, is one of the chief aims of education. Education must enable one to sift and weigh evidence, to discern the true from the false, the real from the unreal, and the facts from the fiction. The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically.
Martin Luther King then comes to the most famous part of his speech, in which he uses the phrase 'I have a dream' to begin successive sentences (a rhetorical device known as anaphora ). King outlines the form that his dream, or ambition or wish for a better America, takes. His dream, he tells his audience, is 'deeply rooted' in the ...
Introduction Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech is one of the most iconic and powerful orations in American history. Delivered on August 28, 1963, during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, King's speech called for racial equality and justice, and... Martin Luther King I Have a Dream. 4.
Essay Example: In the vibrant heart of Atlanta, Georgia, an unassuming red-brick house stands as a testament to the transformative journey of one of America's most revered figures: Martin Luther King Jr. Nestled within the historic Sweet Auburn neighborhood, 501 Auburn Avenue is more than just
For Martin Luther King, the concept of agape stood at the center of both his spiritual belief in a knowable God and his assertion that love and nonviolence were essential to remedying America's race problems. He defined agape as "purely spontaneous, unmotivated, groundless, and creative.It is the love of God operating in the human heart" (Papers 6:325)
That Lives Large In Jazz. In 1964, Martin Luther King, Jr. penned an essay concerning the significance of jazz. The essay was written at the request of the organizers of the 1964 Berlin Jazz Festival. While one of Dr. King's lesser known speeches, it remains as one of the most profound essays about jazz in modern times.
The Media & Design Center has created a list of films about King and his legacy, which can be accessed via streaming, DVD or VHS. (The center can also provide devices to play physical media). Films include Selma, Tony Brown's essay on Martin Luther King Jr. and In Remembrance of Martin. Selected Materials from the Wilson Special Collections ...
Martin Luther King, Jr., was a religious leader and social activist who led the civil rights movement in the United States from the mid-1950s until his assassination in 1968. His leadership was fundamental to that movement's success in ending the legal segregation of African Americans in the South and other parts of the United States.
Today, the nation celebrates what would have been Martin Luther King Jr.'s 95th birthday. Sharon Shahid once openly wondered whether King's famed essay, Letter from Birmingham Jail, "would ...
Keynote King. The highlight of the day was hearing from Bernice King, a lawyer and daughter of the late Dr Martin Luther King Jr. Bernice was the keynote speaker for this year's opening ceremonies. Auma Reggy, co-chair of the 2024 annual meeting and managing lead IP counsel at health care company McKesson in the US, interviewed King.
May 19, 1925 to February 21, 1965. As the nation's most visible proponent of Black Nationalism, Malcolm X's challenge to the multiracial, nonviolent approach of Martin Luther King, Jr., helped set the tone for the ideological and tactical conflicts that took place within the black freedom struggle of the 1960s.Given Malcolm X's abrasive criticism of King and his advocacy of racial ...
President Barack Obama, speaking almost 50 years after the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. gave his "I Have a Dream" speech in Washington, invoked King and his own life's story during the ...