

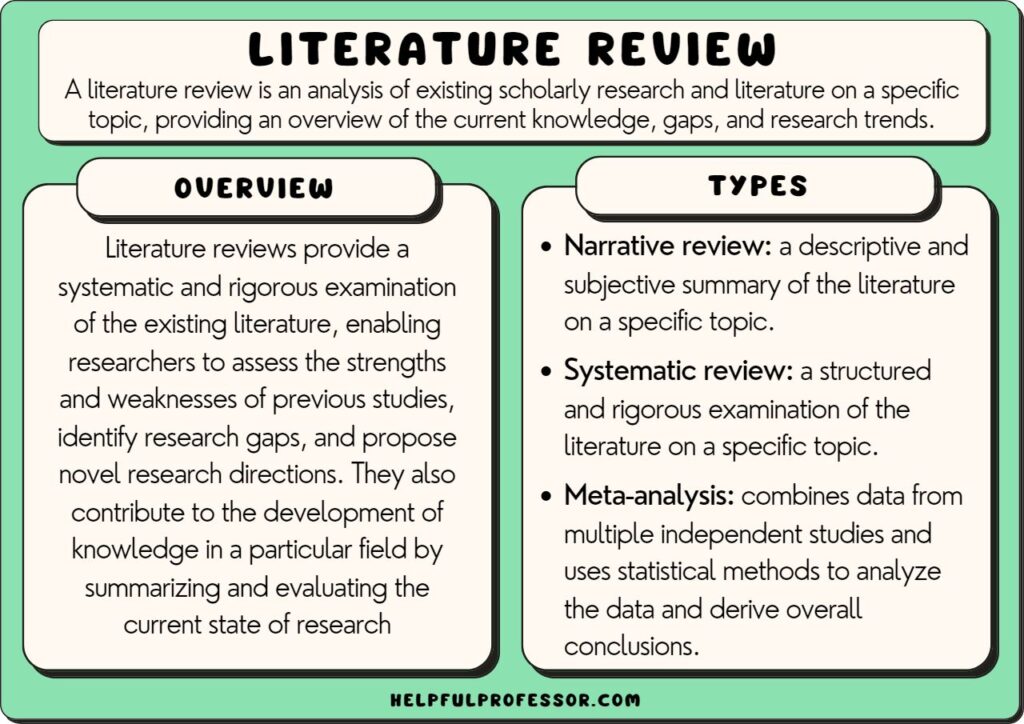
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
What is the purpose of literature review , a. habitat loss and species extinction: , b. range shifts and phenological changes: , c. ocean acidification and coral reefs: , d. adaptive strategies and conservation efforts: .
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review .
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.
Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as yo u go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free!
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research | Cite feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface. It also allows you auto-cite references in 10,000+ styles and save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research | Cite” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.

- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references in 10,000+ styles into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.

The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 22+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what are the types of literature reviews , what are research skills definition, importance, and examples , what is phd dissertation defense and how to..., abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., what is academic integrity, and why is it..., how to make a graphical abstract, academic integrity vs academic dishonesty: types & examples, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is a literature review? [with examples]

What is a literature review?
The purpose of a literature review, how to write a literature review, the format of a literature review, general formatting rules, the length of a literature review, literature review examples, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, related articles.
A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research.
In a literature review, you’re expected to report on the existing scholarly conversation, without adding new contributions.
If you are currently writing one, you've come to the right place. In the following paragraphs, we will explain:
- the objective of a literature review
- how to write a literature review
- the basic format of a literature review
Tip: It’s not always mandatory to add a literature review in a paper. Theses and dissertations often include them, whereas research papers may not. Make sure to consult with your instructor for exact requirements.
The four main objectives of a literature review are:
- Studying the references of your research area
- Summarizing the main arguments
- Identifying current gaps, stances, and issues
- Presenting all of the above in a text
Ultimately, the main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
The format of a literature review is fairly standard. It includes an:
- introduction that briefly introduces the main topic
- body that includes the main discussion of the key arguments
- conclusion that highlights the gaps and issues of the literature
➡️ Take a look at our guide on how to write a literature review to learn more about how to structure a literature review.
First of all, a literature review should have its own labeled section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature can be found, and you should label this section as “Literature Review.”
➡️ For more information on writing a thesis, visit our guide on how to structure a thesis .
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, it will be short.
Take a look at these three theses featuring great literature reviews:
- School-Based Speech-Language Pathologist's Perceptions of Sensory Food Aversions in Children [ PDF , see page 20]
- Who's Writing What We Read: Authorship in Criminological Research [ PDF , see page 4]
- A Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Online Instructors of Theological Reflection at Christian Institutions Accredited by the Association of Theological Schools [ PDF , see page 56]
Literature reviews are most commonly found in theses and dissertations. However, you find them in research papers as well.
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, then it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, then it will be short.
No. A literature review should have its own independent section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature review can be found, and label this section as “Literature Review.”
The main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
A Guide to Literature Reviews
Importance of a good literature review.
- Conducting the Literature Review
- Structure and Writing Style
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Citation Management Software This link opens in a new window
- Acknowledgements
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
- << Previous: Definition
- Next: Conducting the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 3:13 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mcmaster.ca/litreview

Literature Review - what is a Literature Review, why it is important and how it is done
- Strategies to Find Sources
Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
Reading critically, tips to evaluate sources.
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
- Useful Resources
A good literature review evaluates a wide variety of sources (academic articles, scholarly books, government/NGO reports). It also evaluates literature reviews that study similar topics. This page offers you a list of resources and tips on how to evaluate the sources that you may use to write your review.
- A Closer Look at Evaluating Literature Reviews Excerpt from the book chapter, “Evaluating Introductions and Literature Reviews” in Fred Pyrczak’s Evaluating Research in Academic Journals: A Practical Guide to Realistic Evaluation , (Chapter 4 and 5). This PDF discusses and offers great advice on how to evaluate "Introductions" and "Literature Reviews" by listing questions and tips. First part focus on Introductions and in page 10 in the PDF, 37 in the text, it focus on "literature reviews".
- Tips for Evaluating Sources (Print vs. Internet Sources) Excellent page that will guide you on what to ask to determine if your source is a reliable one. Check the other topics in the guide: Evaluating Bibliographic Citations and Evaluation During Reading on the left side menu.
To be able to write a good Literature Review, you need to be able to read critically. Below are some tips that will help you evaluate the sources for your paper.
Reading critically (summary from How to Read Academic Texts Critically)
- Who is the author? What is his/her standing in the field.
- What is the author’s purpose? To offer advice, make practical suggestions, solve a specific problem, to critique or clarify?
- Note the experts in the field: are there specific names/labs that are frequently cited?
- Pay attention to methodology: is it sound? what testing procedures, subjects, materials were used?
- Note conflicting theories, methodologies and results. Are there any assumptions being made by most/some researchers?
- Theories: have they evolved overtime?
- Evaluate and synthesize the findings and conclusions. How does this study contribute to your project?
Useful links:
- How to Read a Paper (University of Waterloo, Canada) This is an excellent paper that teach you how to read an academic paper, how to determine if it is something to set aside, or something to read deeply. Good advice to organize your literature for the Literature Review or just reading for classes.
Criteria to evaluate sources:
- Authority : Who is the author? what is his/her credentials--what university he/she is affliliated? Is his/her area of expertise?
- Usefulness : How this source related to your topic? How current or relevant it is to your topic?
- Reliability : Does the information comes from a reliable, trusted source such as an academic journal?
Useful site - Critically Analyzing Information Sources (Cornell University Library)
- << Previous: Strategies to Find Sources
- Next: Tips for Writing Literature Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/Literature-Review
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Make your writing flawless in 1 upload
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Upload my document
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral

Evidence-Based Practice (EBP)
- The EBP Process
- Forming a Clinical Question
- Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria
- Acquiring Evidence
- Appraising the Quality of the Evidence
- Writing a Literature Review
- Finding Psychological Tests & Assessment Instruments
What Is a Literature Review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis of scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. Put simply, it's a critical evaluation of what's already been written on a particular topic . It represents the literature that provides background information on your topic and shows a connection between those writings and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand-alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
What a Literature Review Is Not:
- A list or summary of sources
- An annotated bibliography
- A grouping of broad, unrelated sources
- A compilation of everything that has been written on a particular topic
- Literary criticism (think English) or a book review
Why Literature Reviews Are Important
- They explain the background of research on a topic
- They demonstrate why a topic is significant to a subject area
- They discover relationships between research studies/ideas
- They identify major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic
- They identify critical gaps and points of disagreement
- They discuss further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies
To Learn More about Conducting and Writing a Lit Review . . .
Monash University (in Australia) has created several extremely helpful, interactive tutorials.
- The Stand-Alone Literature Review, https://www.monash.edu/rlo/assignment-samples/science/stand-alone-literature-review
- Researching for Your Literature Review, https://guides.lib.monash.edu/researching-for-your-literature-review/home
- Writing a Literature Review, https://www.monash.edu/rlo/graduate-research-writing/write-the-thesis/writing-a-literature-review
Keep Track of Your Sources!
A citation manager can be helpful way to work with large numbers of citations. See UMSL Libraries' Citing Sources guide for more information. Personally, I highly recommend Zotero —it's free, easy to use, and versatile. If you need help getting started with Zotero or one of the other citation managers, please contact a librarian.
- << Previous: Appraising the Quality of the Evidence
- Next: Finding Psychological Tests & Assessment Instruments >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 2:44 PM
- URL: https://libguides.umsl.edu/ebp

What Is A Literature Review?
A plain-language explainer (with examples).
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | June 2020 (Updated May 2023)
If you’re faced with writing a dissertation or thesis, chances are you’ve encountered the term “literature review” . If you’re on this page, you’re probably not 100% what the literature review is all about. The good news is that you’ve come to the right place.
Literature Review 101
- What (exactly) is a literature review
- What’s the purpose of the literature review chapter
- How to find high-quality resources
- How to structure your literature review chapter
- Example of an actual literature review
What is a literature review?
The word “literature review” can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature – i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s look at each of them:
Reviewing the literature
The first step of any literature review is to hunt down and read through the existing research that’s relevant to your research topic. To do this, you’ll use a combination of tools (we’ll discuss some of these later) to find journal articles, books, ebooks, research reports, dissertations, theses and any other credible sources of information that relate to your topic. You’ll then summarise and catalogue these for easy reference when you write up your literature review chapter.
The literature review chapter
The second step of the literature review is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or thesis structure ). At the simplest level, the literature review chapter is an overview of the key literature that’s relevant to your research topic. This chapter should provide a smooth-flowing discussion of what research has already been done, what is known, what is unknown and what is contested in relation to your research topic. So, you can think of it as an integrated review of the state of knowledge around your research topic.

What’s the purpose of a literature review?
The literature review chapter has a few important functions within your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s take a look at these:
Purpose #1 – Demonstrate your topic knowledge
The first function of the literature review chapter is, quite simply, to show the reader (or marker) that you know what you’re talking about . In other words, a good literature review chapter demonstrates that you’ve read the relevant existing research and understand what’s going on – who’s said what, what’s agreed upon, disagreed upon and so on. This needs to be more than just a summary of who said what – it needs to integrate the existing research to show how it all fits together and what’s missing (which leads us to purpose #2, next).
Purpose #2 – Reveal the research gap that you’ll fill
The second function of the literature review chapter is to show what’s currently missing from the existing research, to lay the foundation for your own research topic. In other words, your literature review chapter needs to show that there are currently “missing pieces” in terms of the bigger puzzle, and that your study will fill one of those research gaps . By doing this, you are showing that your research topic is original and will help contribute to the body of knowledge. In other words, the literature review helps justify your research topic.
Purpose #3 – Lay the foundation for your conceptual framework
The third function of the literature review is to form the basis for a conceptual framework . Not every research topic will necessarily have a conceptual framework, but if your topic does require one, it needs to be rooted in your literature review.
For example, let’s say your research aims to identify the drivers of a certain outcome – the factors which contribute to burnout in office workers. In this case, you’d likely develop a conceptual framework which details the potential factors (e.g. long hours, excessive stress, etc), as well as the outcome (burnout). Those factors would need to emerge from the literature review chapter – they can’t just come from your gut!
So, in this case, the literature review chapter would uncover each of the potential factors (based on previous studies about burnout), which would then be modelled into a framework.
Purpose #4 – To inform your methodology
The fourth function of the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog , your choice of methodology will be heavily influenced by your research aims, objectives and questions . Given that you’ll be reviewing studies covering a topic close to yours, it makes sense that you could learn a lot from their (well-considered) methodologies.
So, when you’re reviewing the literature, you’ll need to pay close attention to the research design , methodology and methods used in similar studies, and use these to inform your methodology. Quite often, you’ll be able to “borrow” from previous studies . This is especially true for quantitative studies , as you can use previously tried and tested measures and scales.

How do I find articles for my literature review?
Finding quality journal articles is essential to crafting a rock-solid literature review. As you probably already know, not all research is created equally, and so you need to make sure that your literature review is built on credible research .
We could write an entire post on how to find quality literature (actually, we have ), but a good starting point is Google Scholar . Google Scholar is essentially the academic equivalent of Google, using Google’s powerful search capabilities to find relevant journal articles and reports. It certainly doesn’t cover every possible resource, but it’s a very useful way to get started on your literature review journey, as it will very quickly give you a good indication of what the most popular pieces of research are in your field.
One downside of Google Scholar is that it’s merely a search engine – that is, it lists the articles, but oftentimes it doesn’t host the articles . So you’ll often hit a paywall when clicking through to journal websites.
Thankfully, your university should provide you with access to their library, so you can find the article titles using Google Scholar and then search for them by name in your university’s online library. Your university may also provide you with access to ResearchGate , which is another great source for existing research.
Remember, the correct search keywords will be super important to get the right information from the start. So, pay close attention to the keywords used in the journal articles you read and use those keywords to search for more articles. If you can’t find a spoon in the kitchen, you haven’t looked in the right drawer.
Need a helping hand?
How should I structure my literature review?
Unfortunately, there’s no generic universal answer for this one. The structure of your literature review will depend largely on your topic area and your research aims and objectives.
You could potentially structure your literature review chapter according to theme, group, variables , chronologically or per concepts in your field of research. We explain the main approaches to structuring your literature review here . You can also download a copy of our free literature review template to help you establish an initial structure.
In general, it’s also a good idea to start wide (i.e. the big-picture-level) and then narrow down, ending your literature review close to your research questions . However, there’s no universal one “right way” to structure your literature review. The most important thing is not to discuss your sources one after the other like a list – as we touched on earlier, your literature review needs to synthesise the research , not summarise it .
Ultimately, you need to craft your literature review so that it conveys the most important information effectively – it needs to tell a logical story in a digestible way. It’s no use starting off with highly technical terms and then only explaining what these terms mean later. Always assume your reader is not a subject matter expert and hold their hand through a journe y of the literature while keeping the functions of the literature review chapter (which we discussed earlier) front of mind.

Example of a literature review
In the video below, we walk you through a high-quality literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction. This will give you a clearer view of what a strong literature review looks like in practice and hopefully provide some inspiration for your own.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve (hopefully) answered the question, “ what is a literature review? “. We’ve also considered the purpose and functions of the literature review, as well as how to find literature and how to structure the literature review chapter. If you’re keen to learn more, check out the literature review section of the Grad Coach blog , as well as our detailed video post covering how to write a literature review .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
16 Comments
Thanks for this review. It narrates what’s not been taught as tutors are always in a early to finish their classes.
Thanks for the kind words, Becky. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This website is amazing, it really helps break everything down. Thank you, I would have been lost without it.
This is review is amazing. I benefited from it a lot and hope others visiting this website will benefit too.
Timothy T. Chol [email protected]
Thank you very much for the guiding in literature review I learn and benefited a lot this make my journey smooth I’ll recommend this site to my friends
This was so useful. Thank you so much.
Hi, Concept was explained nicely by both of you. Thanks a lot for sharing it. It will surely help research scholars to start their Research Journey.
The review is really helpful to me especially during this period of covid-19 pandemic when most universities in my country only offer online classes. Great stuff
Great Brief Explanation, thanks
So helpful to me as a student
GradCoach is a fantastic site with brilliant and modern minds behind it.. I spent weeks decoding the substantial academic Jargon and grounding my initial steps on the research process, which could be shortened to a couple of days through the Gradcoach. Thanks again!
This is an amazing talk. I paved way for myself as a researcher. Thank you GradCoach!
Well-presented overview of the literature!
This was brilliant. So clear. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
15 Literature Review Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Privacy Policy

Home » Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Literature Review
Definition:
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
Types of Literature Review
Types of Literature Review are as follows:
- Narrative literature review : This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper.
- Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and structured review that follows a pre-defined protocol to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all relevant studies on a specific research question. It is often used in evidence-based practice and systematic reviews.
- Meta-analysis: This is a quantitative review that uses statistical methods to combine data from multiple studies to derive a summary effect size. It provides a more precise estimate of the overall effect than any individual study.
- Scoping review: This is a preliminary review that aims to map the existing literature on a broad topic area to identify research gaps and areas for further investigation.
- Critical literature review : This type of review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a critical analysis of the literature and identify areas where further research is needed.
- Conceptual literature review: This review synthesizes and integrates theories and concepts from multiple sources to provide a new perspective on a particular topic. It aims to provide a theoretical framework for understanding a particular research question.
- Rapid literature review: This is a quick review that provides a snapshot of the current state of knowledge on a specific research question or topic. It is often used when time and resources are limited.
- Thematic literature review : This review identifies and analyzes common themes and patterns across a body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the literature and identify key themes and concepts.
- Realist literature review: This review is often used in social science research and aims to identify how and why certain interventions work in certain contexts. It takes into account the context and complexities of real-world situations.
- State-of-the-art literature review : This type of review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field, highlighting the most recent and relevant research. It is often used in fields where knowledge is rapidly evolving, such as technology or medicine.
- Integrative literature review: This type of review synthesizes and integrates findings from multiple studies on a particular topic to identify patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Umbrella literature review : This review is used to provide a broad overview of a large and diverse body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to identify common themes and patterns across different areas of research.
- Historical literature review: This type of review examines the historical development of research on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a historical context for understanding the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Problem-oriented literature review : This review focuses on a specific problem or issue and examines the literature to identify potential solutions or interventions. It aims to provide practical recommendations for addressing a particular problem or issue.
- Mixed-methods literature review : This type of review combines quantitative and qualitative methods to synthesize and analyze the available literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research question by combining different types of evidence.
Parts of Literature Review
Parts of a literature review are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction of a literature review typically provides background information on the research topic and why it is important. It outlines the objectives of the review, the research question or hypothesis, and the scope of the review.
Literature Search
This section outlines the search strategy and databases used to identify relevant literature. The search terms used, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and any limitations of the search are described.
Literature Analysis
The literature analysis is the main body of the literature review. This section summarizes and synthesizes the literature that is relevant to the research question or hypothesis. The review should be organized thematically, chronologically, or by methodology, depending on the research objectives.
Critical Evaluation
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and validity of the literature. This includes evaluating the reliability and validity of the studies reviewed, the methodology used, and the strength of the evidence.
The conclusion of the literature review should summarize the main findings, identify any gaps in the literature, and suggest areas for future research. It should also reiterate the importance of the research question or hypothesis and the contribution of the literature review to the overall research project.
The references list includes all the sources cited in the literature review, and follows a specific referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard).
How to write Literature Review
Here are some steps to follow when writing a literature review:
- Define your research question or topic : Before starting your literature review, it is essential to define your research question or topic. This will help you identify relevant literature and determine the scope of your review.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: Use databases and search engines to find relevant literature. Look for peer-reviewed articles, books, and other academic sources that are relevant to your research question or topic.
- Evaluate the sources: Once you have found potential sources, evaluate them critically to determine their relevance, credibility, and quality. Look for recent publications, reputable authors, and reliable sources of data and evidence.
- Organize your sources: Group the sources by theme, method, or research question. This will help you identify similarities and differences among the literature, and provide a structure for your literature review.
- Analyze and synthesize the literature : Analyze each source in depth, identifying the key findings, methodologies, and conclusions. Then, synthesize the information from the sources, identifying patterns and themes in the literature.
- Write the literature review : Start with an introduction that provides an overview of the topic and the purpose of the literature review. Then, organize the literature according to your chosen structure, and analyze and synthesize the sources. Finally, provide a conclusion that summarizes the key findings of the literature review, identifies gaps in knowledge, and suggests areas for future research.
- Edit and proofread: Once you have written your literature review, edit and proofread it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and concise.
Examples of Literature Review
Here’s an example of how a literature review can be conducted for a thesis on the topic of “ The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers’ Mental Health”:
- Start by identifying the key terms related to your research topic. In this case, the key terms are “social media,” “teenagers,” and “mental health.”
- Use academic databases like Google Scholar, JSTOR, or PubMed to search for relevant articles, books, and other publications. Use these keywords in your search to narrow down your results.
- Evaluate the sources you find to determine if they are relevant to your research question. You may want to consider the publication date, author’s credentials, and the journal or book publisher.
- Begin reading and taking notes on each source, paying attention to key findings, methodologies used, and any gaps in the research.
- Organize your findings into themes or categories. For example, you might categorize your sources into those that examine the impact of social media on self-esteem, those that explore the effects of cyberbullying, and those that investigate the relationship between social media use and depression.
- Synthesize your findings by summarizing the key themes and highlighting any gaps or inconsistencies in the research. Identify areas where further research is needed.
- Use your literature review to inform your research questions and hypotheses for your thesis.
For example, after conducting a literature review on the impact of social media on teenagers’ mental health, a thesis might look like this:
“Using a mixed-methods approach, this study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in teenagers. Specifically, the study will examine the effects of cyberbullying, social comparison, and excessive social media use on self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. Through an analysis of survey data and qualitative interviews with teenagers, the study will provide insight into the complex relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes, and identify strategies for promoting positive mental health outcomes in young people.”
Reference: Smith, J., Jones, M., & Lee, S. (2019). The effects of social media use on adolescent mental health: A systematic review. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65(2), 154-165. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.03.024
Reference Example: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range. doi:0000000/000000000000 or URL
Applications of Literature Review
some applications of literature review in different fields:
- Social Sciences: In social sciences, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing research, to develop research questions, and to provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and political science.
- Natural Sciences: In natural sciences, literature reviews are used to summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in a particular field or subfield. Literature reviews can help researchers identify areas where more research is needed and provide insights into the latest developments in a particular field. Fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics commonly use literature reviews.
- Health Sciences: In health sciences, literature reviews are used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, identify best practices, and determine areas where more research is needed. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as medicine, nursing, and public health.
- Humanities: In humanities, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing knowledge, develop new interpretations of texts or cultural artifacts, and provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as history, literary studies, and philosophy.
Role of Literature Review in Research
Here are some applications of literature review in research:
- Identifying Research Gaps : Literature review helps researchers identify gaps in existing research and literature related to their research question. This allows them to develop new research questions and hypotheses to fill those gaps.
- Developing Theoretical Framework: Literature review helps researchers develop a theoretical framework for their research. By analyzing and synthesizing existing literature, researchers can identify the key concepts, theories, and models that are relevant to their research.
- Selecting Research Methods : Literature review helps researchers select appropriate research methods and techniques based on previous research. It also helps researchers to identify potential biases or limitations of certain methods and techniques.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Literature review helps researchers in data collection and analysis by providing a foundation for the development of data collection instruments and methods. It also helps researchers to identify relevant data sources and identify potential data analysis techniques.
- Communicating Results: Literature review helps researchers to communicate their results effectively by providing a context for their research. It also helps to justify the significance of their findings in relation to existing research and literature.
Purpose of Literature Review
Some of the specific purposes of a literature review are as follows:
- To provide context: A literature review helps to provide context for your research by situating it within the broader body of literature on the topic.
- To identify gaps and inconsistencies: A literature review helps to identify areas where further research is needed or where there are inconsistencies in the existing literature.
- To synthesize information: A literature review helps to synthesize the information from multiple sources and present a coherent and comprehensive picture of the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- To identify key concepts and theories : A literature review helps to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to your research question and provide a theoretical framework for your study.
- To inform research design: A literature review can inform the design of your research study by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
Characteristics of Literature Review
Some Characteristics of Literature Review are as follows:
- Identifying gaps in knowledge: A literature review helps to identify gaps in the existing knowledge and research on a specific topic or research question. By analyzing and synthesizing the literature, you can identify areas where further research is needed and where new insights can be gained.
- Establishing the significance of your research: A literature review helps to establish the significance of your own research by placing it in the context of existing research. By demonstrating the relevance of your research to the existing literature, you can establish its importance and value.
- Informing research design and methodology : A literature review helps to inform research design and methodology by identifying the most appropriate research methods, techniques, and instruments. By reviewing the literature, you can identify the strengths and limitations of different research methods and techniques, and select the most appropriate ones for your own research.
- Supporting arguments and claims: A literature review provides evidence to support arguments and claims made in academic writing. By citing and analyzing the literature, you can provide a solid foundation for your own arguments and claims.
- I dentifying potential collaborators and mentors: A literature review can help identify potential collaborators and mentors by identifying researchers and practitioners who are working on related topics or using similar methods. By building relationships with these individuals, you can gain valuable insights and support for your own research and practice.
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest research : A literature review helps to keep you up-to-date with the latest research on a specific topic or research question. By regularly reviewing the literature, you can stay informed about the latest findings and developments in your field.
Advantages of Literature Review
There are several advantages to conducting a literature review as part of a research project, including:
- Establishing the significance of the research : A literature review helps to establish the significance of the research by demonstrating the gap or problem in the existing literature that the study aims to address.
- Identifying key concepts and theories: A literature review can help to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to the research question, and provide a theoretical framework for the study.
- Supporting the research methodology : A literature review can inform the research methodology by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
- Providing a comprehensive overview of the literature : A literature review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic, allowing the researcher to identify key themes, debates, and areas of agreement or disagreement.
- Identifying potential research questions: A literature review can help to identify potential research questions and areas for further investigation.
- Avoiding duplication of research: A literature review can help to avoid duplication of research by identifying what has already been done on a topic, and what remains to be done.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : A literature review helps to enhance the credibility of the research by demonstrating the researcher’s knowledge of the existing literature and their ability to situate their research within a broader context.
Limitations of Literature Review
Limitations of Literature Review are as follows:
- Limited scope : Literature reviews can only cover the existing literature on a particular topic, which may be limited in scope or depth.
- Publication bias : Literature reviews may be influenced by publication bias, which occurs when researchers are more likely to publish positive results than negative ones. This can lead to an incomplete or biased picture of the literature.
- Quality of sources : The quality of the literature reviewed can vary widely, and not all sources may be reliable or valid.
- Time-limited: Literature reviews can become quickly outdated as new research is published, making it difficult to keep up with the latest developments in a field.
- Subjective interpretation : Literature reviews can be subjective, and the interpretation of the findings can vary depending on the researcher’s perspective or bias.
- Lack of original data : Literature reviews do not generate new data, but rather rely on the analysis of existing studies.
- Risk of plagiarism: It is important to ensure that literature reviews do not inadvertently contain plagiarism, which can occur when researchers use the work of others without proper attribution.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Research Project – Definition, Writing Guide and...


What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Research Approach – Types Methods and Examples

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Librarian Assistance
For help, please contact the librarian for your subject area. We have a guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 2 2, 2024
- Last Updated: Oct 23, 2024 11:46 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

Literature Review in Research Writing
- 4 minute read
- 429.5K views
Table of Contents
Research on research? If you find this idea rather peculiar, know that nowadays, with the huge amount of information produced daily all around the world, it is becoming more and more difficult to keep up to date with all of it. In addition to the sheer amount of research, there is also its origin. We are witnessing the economic and intellectual emergence of countries like China, Brazil, Turkey, and United Arab Emirates, for example, that are producing scholarly literature in their own languages. So, apart from the effort of gathering information, there must also be translators prepared to unify all of it in a single language to be the object of the literature survey. At Elsevier, our team of translators is ready to support researchers by delivering high-quality scientific translations , in several languages, to serve their research – no matter the topic.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a study – or, more accurately, a survey – involving scholarly material, with the aim to discuss published information about a specific topic or research question. Therefore, to write a literature review, it is compulsory that you are a real expert in the object of study. The results and findings will be published and made available to the public, namely scientists working in the same area of research.
How to Write a Literature Review
First of all, don’t forget that writing a literature review is a great responsibility. It’s a document that is expected to be highly reliable, especially concerning its sources and findings. You have to feel intellectually comfortable in the area of study and highly proficient in the target language; misconceptions and errors do not have a place in a document as important as a literature review. In fact, you might want to consider text editing services, like those offered at Elsevier, to make sure your literature is following the highest standards of text quality. You want to make sure your literature review is memorable by its novelty and quality rather than language errors.
Writing a literature review requires expertise but also organization. We cannot teach you about your topic of research, but we can provide a few steps to guide you through conducting a literature review:
- Choose your topic or research question: It should not be too comprehensive or too limited. You have to complete your task within a feasible time frame.
- Set the scope: Define boundaries concerning the number of sources, time frame to be covered, geographical area, etc.
- Decide which databases you will use for your searches: In order to search the best viable sources for your literature review, use highly regarded, comprehensive databases to get a big picture of the literature related to your topic.
- Search, search, and search: Now you’ll start to investigate the research on your topic. It’s critical that you keep track of all the sources. Start by looking at research abstracts in detail to see if their respective studies relate to or are useful for your own work. Next, search for bibliographies and references that can help you broaden your list of resources. Choose the most relevant literature and remember to keep notes of their bibliographic references to be used later on.
- Review all the literature, appraising carefully it’s content: After reading the study’s abstract, pay attention to the rest of the content of the articles you deem the “most relevant.” Identify methodologies, the most important questions they address, if they are well-designed and executed, and if they are cited enough, etc.
If it’s the first time you’ve published a literature review, note that it is important to follow a special structure. Just like in a thesis, for example, it is expected that you have an introduction – giving the general idea of the central topic and organizational pattern – a body – which contains the actual discussion of the sources – and finally the conclusion or recommendations – where you bring forward whatever you have drawn from the reviewed literature. The conclusion may even suggest there are no agreeable findings and that the discussion should be continued.
Why are literature reviews important?
Literature reviews constantly feed new research, that constantly feeds literature reviews…and we could go on and on. The fact is, one acts like a force over the other and this is what makes science, as a global discipline, constantly develop and evolve. As a scientist, writing a literature review can be very beneficial to your career, and set you apart from the expert elite in your field of interest. But it also can be an overwhelming task, so don’t hesitate in contacting Elsevier for text editing services, either for profound edition or just a last revision. We guarantee the very highest standards. You can also save time by letting us suggest and make the necessary amendments to your manuscript, so that it fits the structural pattern of a literature review. Who knows how many worldwide researchers you will impact with your next perfectly written literature review.
Know more: How to Find a Gap in Research .
Language Editing Services by Elsevier Author Services:

What is a Research Gap

Types of Scientific Articles
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Article Review
Ai generator.

Article reviews are an essential part of academic article writing , providing an opportunity to evaluate and analyze published research . A well-written review can help readers understand the simple subject matter and determine the value of the article . In this article, we’ll cover what is an article review, provide step-by-step guidance on how to write one, and answer some common questions.
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical assessment of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves analyzing the content, methodology, and findings of the article and providing an evaluation of its strengths and weaknesses. The review typically includes a summary of the article’s main points, an evaluation of its contribution to the subject, and suggestions for improvement.
Examples of Article Review
1. literary analysis of “the great gatsby”.
Title : “The American Dream in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s ‘The Great Gatsby'” Summary : This article delves into the theme of the American Dream in “The Great Gatsby”. It explores how the characters of Jay Gatsby, Daisy Buchanan, and Tom Buchanan each represent different facets of this dream. The review highlights the contrast between Gatsby’s idealistic pursuit of wealth and love, and the moral decay of society depicted in the novel. Evaluation : The article offers a thorough and insightful analysis, drawing on specific passages to support its claims. However, it occasionally lacks depth in exploring secondary characters. Recommendation : Overall, this article is a valuable resource for understanding the complexities of the American Dream in Fitzgerald’s work. It is recommended for students and literary enthusiasts.
2. Scientific Study on Climate Change
Title : “Impact of Global Warming on Arctic Ice Melting Rates” Summary : This article examines recent research on the accelerated melting of Arctic ice due to global warming. The study uses satellite data and climate models to project future ice loss and its implications for global sea levels. Evaluation : The article presents data in a clear and accessible manner, making complex scientific concepts understandable for a general audience. The visual aids, such as graphs and maps, effectively complement the text. Recommendation : This article is highly recommended for anyone interested in climate science and environmental studies. It provides a comprehensive overview of current research and its global significance.
3. Technology Review of the Latest iPhone
Title : “A Comprehensive Review of the iPhone 14 Pro” Summary : The article provides an in-depth review of the iPhone 14 Pro, covering its design, performance, camera capabilities, and new features. It compares the latest model with previous versions and other smartphones on the market. Evaluation : The review is detailed and well-organized, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses of the device. However, it could benefit from more user testimonials to provide a broader perspective. Recommendation : This review is a must-read for potential buyers considering the iPhone 14 Pro. It offers valuable insights into the device’s capabilities and overall performance.
4. Health and Wellness Article on Yoga Benefits
Title : “The Health Benefits of Practicing Yoga Daily” Summary : This article explores the various physical and mental health benefits of incorporating yoga into a daily routine. It discusses how yoga can improve flexibility, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being. Evaluation : The article is informative and engaging, backed by scientific research and expert opinions. It includes practical tips for beginners and links to additional resources. Recommendation : This article is highly recommended for individuals seeking to improve their health through yoga. It provides a comprehensive guide to the benefits and practice of yoga.
5. Historical Analysis of World War II
Title : “The Role of Codebreakers in World War II” Summary : The article examines the critical role that codebreakers played in the Allied victory during World War II. It focuses on the efforts at Bletchley Park and the breaking of the Enigma code. Evaluation : The article is well-researched and presents a compelling narrative of the contributions of codebreakers. It includes firsthand accounts and historical documents to support its analysis. Recommendation : This article is recommended for history buffs and students. It offers a fascinating insight into a lesser-known aspect of World War II and highlights the importance of intelligence work in warfare.
Examples of Article Review for Students
Review of “the effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance”.
Title : The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance: A Detailed Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s investigation into how lack of sleep affects cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Summary : The article explores various studies showing that sleep deprivation significantly impairs cognitive performance, leading to reduced attention spans, poor memory retention, and slower reaction times. Critique : The article is thorough in its examination of the negative effects of sleep deprivation. However, it could include more information on the long-term consequences and potential mitigation strategies. Some studies cited have small sample sizes, which could limit the findings’ reliability. Conclusion : Overall, the article effectively highlights the critical impact of sleep on cognitive functions, though it would benefit from more comprehensive data and solutions to counteract sleep deprivation.
Review of “Renewable Energy Sources and Their Impact on the Environment”
Title : Renewable Energy Sources and Their Impact on the Environment: An In-Depth Review Introduction : This review analyzes the article discussing the environmental impacts of various renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Summary : The article covers the benefits of renewable energy in reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. It also examines potential environmental concerns such as habitat disruption and resource consumption. Critique : The article provides a balanced view of renewable energy’s benefits and challenges. However, it lacks detailed case studies and comparative analysis with non-renewable energy sources. The discussion on environmental impacts could be more nuanced. Conclusion : The article is informative and highlights the importance of renewable energy, though it would be stronger with more specific examples and a deeper environmental impact analysis.
Review of “The Influence of Advertising on Consumer Behavior”
Title : The Influence of Advertising on Consumer Behavior: A Comprehensive Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s exploration of how advertising affects consumer purchasing decisions and behavior. Summary : The article examines various advertising techniques and their psychological effects on consumers, including the use of emotional appeal, repetition, and celebrity endorsements. Critique : The article effectively discusses different advertising strategies and their impact on consumers. However, it could include more recent examples and data to reflect current trends. Additionally, it would benefit from a broader range of perspectives, including consumer psychology. Conclusion : The article provides a solid overview of advertising’s influence on consumer behavior, but it needs more up-to-date examples and a wider scope of analysis.
Review of “The Role of Nutrition in Child Development”
Title : The Role of Nutrition in Child Development: An Analytical Review Introduction : This review analyzes the article’s discussion on the critical role of nutrition in children’s physical and cognitive development. Summary : The article highlights the importance of a balanced diet for children’s growth, emphasizing nutrients such as proteins, vitamins, and minerals. It also examines the consequences of malnutrition and dietary deficiencies. Critique : The article is well-researched and presents a comprehensive view of the subject. However, it could benefit from more practical dietary recommendations and a discussion on the challenges faced by different socioeconomic groups. Conclusion : The article effectively underscores the importance of nutrition in child development, though it would be improved by including practical advice and addressing socioeconomic disparities.
Review of “Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges”
Title : Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges: A Detailed Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s exploration of the potential benefits and obstacles of implementing artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare. Summary : The article discusses various AI applications in healthcare, such as diagnostic tools, personalized medicine, and administrative support. It also addresses ethical concerns, data privacy issues, and the need for regulatory frameworks. Critique : The article provides a balanced and insightful analysis of AI in healthcare. However, it could include more case studies and examples of successful AI implementations. The discussion on ethical concerns is somewhat limited and could be expanded. Conclusion : The article offers a thorough overview of AI’s potential in healthcare, but it would benefit from more real-world examples and a deeper exploration of ethical issues.
Examples of Article Review for Research
Review of “the impact of remote work on employee productivity”.
Title : The Impact of Remote Work on Employee Productivity: A Research Review Introduction : This review assesses the research article’s investigation into how remote work influences employee productivity, examining both positive and negative aspects. Summary : The research article explores various factors affecting productivity in remote work settings, such as flexible schedules, work-life balance, and the use of digital communication tools. It presents data from surveys and case studies to support its findings. Critique : The article provides a comprehensive analysis backed by empirical data. However, it could benefit from a more detailed exploration of the long-term impacts of remote work and potential industry-specific variations. Additionally, the research could include a larger, more diverse sample size. Conclusion : The research article effectively highlights the key factors influencing productivity in remote work environments, though it would be strengthened by broader data and long-term impact analysis.
Review of “Climate Change and Agricultural Sustainability”
Title : Climate Change and Agricultural Sustainability: A Review of Current Research Introduction : This review evaluates the research article’s examination of the relationship between climate change and agricultural sustainability, focusing on crop yields and farming practices. Summary : The article discusses the effects of changing weather patterns, increased CO2 levels, and extreme weather events on agricultural productivity. It includes case studies and statistical models to illustrate potential future scenarios. Critique : The research is thorough and well-supported by data. However, it could include more practical recommendations for farmers and policymakers. The article would also benefit from a more detailed discussion of regional differences and adaptation strategies. Conclusion : The research article provides valuable insights into the challenges posed by climate change to agriculture, though it would be improved by offering actionable solutions and considering regional variations.
Review of “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Healthcare”
Title : The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Healthcare: A Comprehensive Research Review Introduction : This review analyzes the research article’s exploration of AI’s applications in healthcare, including diagnostic tools, patient care, and administrative efficiency. Summary : The article outlines various AI technologies used in healthcare, such as machine learning algorithms for diagnostics, robotic surgeries, and AI-driven patient management systems. It presents data from clinical trials and expert opinions to support its claims. Critique : The research is well-rounded and provides a clear overview of AI’s potential in healthcare. However, it could address more of the ethical considerations and data privacy issues associated with AI implementation. Additionally, more real-world examples of AI applications would enhance the article’s relevance. Conclusion : The research article effectively showcases AI’s transformative potential in healthcare, though it could be strengthened by a deeper exploration of ethical issues and more practical examples.
Review of “The Psychological Effects of Social Media Use on Adolescents”
Title : The Psychological Effects of Social Media Use on Adolescents: A Research-Based Review Introduction : This review evaluates the research article’s examination of how social media affects adolescents’ mental health, focusing on anxiety, depression, and self-esteem. Summary : The article presents data from longitudinal studies and surveys to show the correlation between social media use and various psychological issues. It discusses the impact of online interactions, cyberbullying, and the pressure to conform to social norms. Critique : The research is detailed and presents significant findings. However, it could benefit from a more balanced view that includes positive aspects of social media, such as support networks and educational content. Additionally, the sample sizes in some studies are limited, which may affect the generalizability of the results. Conclusion : The research article provides a comprehensive overview of the negative psychological effects of social media on adolescents, though it would be improved by a more balanced perspective and larger sample sizes.
Review of “The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Programs”
Title : The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Programs: A Research Review Introduction : This review analyzes the research article’s evaluation of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) programs and their impact on mental health and well-being. Summary : The article reviews various studies on MBSR, highlighting its benefits for reducing stress, anxiety, and depression. It includes meta-analyses and randomized controlled trials to provide a robust evidence base. Critique : The research is comprehensive and well-supported by empirical data. However, it could explore more on the long-term benefits and potential limitations of MBSR programs. The article would also benefit from discussing the accessibility and applicability of these programs across different populations. Conclusion : The research article effectively demonstrates the benefits of MBSR programs for mental health, though it could be enhanced by addressing long-term effects and broader applicability.
Journal Article Review Examples
Review of “the impact of social media on academic performance”.
Title : The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance: A Comprehensive Review Introduction : This review evaluates the journal article’s investigation into the relationship between social media usage and academic performance among students. Summary : The article discusses various studies that explore how social media affects students’ academic outcomes. It highlights both positive effects, such as improved communication and resource sharing, and negative impacts like distraction and reduced study time. Critique : The article is thorough, providing a balanced view supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from more longitudinal studies to understand long-term effects. Additionally, the article does not address differences in impact based on the type of social media platform used. Conclusion : The journal article effectively highlights the dual impact of social media on academic performance. To strengthen the research, including more long-term studies and platform-specific analyses would be beneficial.
Review of “Climate Change Adaptation in Urban Areas”
Title : Climate Change Adaptation in Urban Areas: An Analytical Review Introduction : This review analyzes the journal article’s discussion on how urban areas are adapting to climate change, focusing on infrastructure and policy changes. Summary : The article examines various adaptation strategies employed by cities worldwide, such as green infrastructure, zoning laws, and disaster preparedness programs. It presents case studies from different regions to illustrate successful adaptation efforts. Critique : The article is well-researched and provides a comprehensive overview of adaptation strategies. However, it could include more data on the effectiveness of these strategies over time. Additionally, the article would benefit from a discussion on the socio-economic challenges that hinder adaptation in less developed areas. Conclusion : The journal article provides valuable insights into urban climate change adaptation strategies. It would be strengthened by including long-term effectiveness data and addressing socio-economic barriers.
Review of “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Medicine”
Title : The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Medicine: A Detailed Review Introduction : This review evaluates the journal article’s exploration of AI applications in personalized medicine, including diagnostics and treatment plans. Summary : The article discusses how AI technologies, such as machine learning and data analytics, are revolutionizing personalized medicine. It highlights examples where AI has improved diagnostic accuracy and tailored treatment plans to individual patient needs. Critique : The article is insightful and well-supported by clinical data. However, it could delve deeper into the ethical considerations and potential biases in AI algorithms. Additionally, more real-world examples of AI implementation in diverse healthcare settings would enhance the article’s applicability. Conclusion : The journal article effectively demonstrates the transformative potential of AI in personalized medicine. To improve, it should include a more detailed discussion on ethics and practical applications across different healthcare systems.
Review of “The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 on Healthcare Workers”
Title : The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 on Healthcare Workers: A Research Review Introduction : This review analyzes the journal article’s investigation into the mental health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare workers. Summary : The article presents data from surveys and interviews with healthcare professionals, highlighting increased levels of stress, anxiety, and burnout due to the pandemic. It discusses the factors contributing to these psychological impacts, such as workload, exposure risk, and lack of support. Critique : The article provides a comprehensive analysis of the psychological challenges faced by healthcare workers during the pandemic. However, it could benefit from more longitudinal studies to understand long-term mental health outcomes. Additionally, the article would be improved by offering more detailed recommendations for institutional support and intervention strategies. Conclusion : The journal article effectively sheds light on the mental health struggles of healthcare workers during COVID-19. To strengthen the research, including long-term studies and detailed support recommendations would be beneficial.
Review of “Sustainable Agriculture Practices and Food Security”
Title : Sustainable Agriculture Practices and Food Security: An In-Depth Review Introduction : This review evaluates the journal article’s discussion on the role of sustainable agriculture practices in enhancing food security. Summary : The article explores various sustainable agriculture techniques, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and agroforestry, and their impact on food security. It presents case studies demonstrating how these practices can increase crop yields and improve resilience to climate change. Critique : The article is well-researched and provides a detailed analysis of sustainable agriculture practices. However, it could include more quantitative data on the economic viability of these practices for small-scale farmers. Additionally, the article would benefit from discussing the policy frameworks needed to support widespread adoption of sustainable agriculture. Conclusion : The journal article effectively highlights the importance of sustainable agriculture for food security. It would be enhanced by including more economic data and policy recommendations to support these practices.
College Article Review Examples
Review of “the effects of sleep deprivation on academic performance”.
Title : The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Academic Performance: A Detailed Review Introduction : This review assesses the article’s exploration of how sleep deprivation impacts college students’ academic performance, focusing on cognitive functions and overall well-being. Summary : The article examines studies showing that insufficient sleep negatively affects memory, concentration, and problem-solving skills, leading to lower grades and academic achievement. It also discusses the role of stress and lifestyle factors contributing to sleep deprivation. Critique : The article provides a thorough analysis supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from a broader range of studies, including different demographic groups. Additionally, practical solutions for improving sleep habits among students are not adequately addressed. Conclusion : The article effectively highlights the critical relationship between sleep and academic performance but would be strengthened by more diverse studies and practical recommendations for students.
Review of “The Impact of Technology on Modern Education”
Title : The Impact of Technology on Modern Education: A Comprehensive Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s discussion on the integration of technology in higher education and its effects on teaching and learning processes. Summary : The article explores various technological tools used in education, such as online learning platforms, interactive simulations, and digital resources. It discusses the benefits, including increased accessibility and personalized learning, as well as challenges like digital divide and technological distractions. Critique : The article is well-researched and balanced, highlighting both positive and negative aspects of technology in education. However, it could include more recent data and specific examples of successful technology implementations in colleges. Additionally, the article should address potential long-term impacts on traditional teaching methods. Conclusion : The article provides valuable insights into the role of technology in education, though it would be enhanced by including more up-to-date examples and long-term impact analysis.
Review of “Mental Health Awareness Among College Students”
Title : Mental Health Awareness Among College Students: An Analytical Review Introduction : This review analyzes the article’s exploration of mental health awareness programs in colleges and their effectiveness in addressing student mental health issues. Summary : The article examines various initiatives aimed at improving mental health awareness, such as workshops, counseling services, and peer support groups. It highlights the importance of early intervention and the role of campus resources in supporting student well-being. Critique : The article provides a comprehensive overview of mental health awareness programs and their benefits. However, it could benefit from more quantitative data on program effectiveness and student outcomes. Additionally, the article should discuss the barriers to accessing mental health services, such as stigma and resource limitations. Conclusion : The article effectively underscores the significance of mental health awareness in colleges, but it would be improved by including more data on program effectiveness and addressing access barriers.
Review of “The Role of Extracurricular Activities in Student Development”
Title : The Role of Extracurricular Activities in Student Development: A Detailed Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s discussion on how participation in extracurricular activities impacts college students’ personal and academic development. Summary : The article explores various benefits of extracurricular activities, such as improved social skills, leadership development, and enhanced academic performance. It includes case studies and survey data to support its findings. Critique : The article is well-rounded and provides clear evidence of the positive impacts of extracurricular activities. However, it could include more diverse examples from different types of colleges and regions. Additionally, the article should address potential negative aspects, such as time management challenges and academic pressure. Conclusion : The article effectively highlights the importance of extracurricular activities in student development, though it would benefit from a more diverse range of examples and a balanced discussion of potential drawbacks.
Review of “The Influence of Social Media on College Students’ Mental Health”
Title : The Influence of Social Media on College Students’ Mental Health: A Research Review Introduction : This review analyzes the article’s investigation into how social media usage affects the mental health of college students, focusing on both positive and negative impacts. Summary : The article discusses various studies showing that social media can lead to increased anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation among students. It also highlights positive aspects, such as enhanced communication, social support, and access to mental health resources. Critique : The article provides a balanced view, supported by empirical data and real-world examples. However, it could benefit from more recent studies and a deeper exploration of how different social media platforms uniquely impact mental health. Additionally, the article should include practical advice for students on managing social media use. Conclusion : The article effectively addresses the complex relationship between social media and mental health among college students, but it would be strengthened by including more recent research and practical recommendations.
Scientific Article Review Examples
Review of “the effects of microplastics on marine life”.
Title : The Effects of Microplastics on Marine Life: A Comprehensive Review Introduction : This review assesses the scientific article’s investigation into the impact of microplastics on marine organisms, focusing on ingestion, toxicity, and ecological consequences. Summary : The article presents various studies showing that microplastics are ingested by a wide range of marine species, leading to physical harm and chemical toxicity. It discusses how microplastics affect growth, reproduction, and survival rates of marine life. Critique : The article is well-researched, providing detailed evidence of the harmful effects of microplastics. However, it could benefit from a broader geographic scope, including more diverse marine environments. Additionally, the article lacks a discussion on potential mitigation strategies to reduce microplastic pollution. Conclusion : The article effectively highlights the detrimental impact of microplastics on marine life, but it would be strengthened by including a wider range of environments and discussing mitigation measures.
Review of “The Role of CRISPR-Cas9 in Gene Editing”
Title : The Role of CRISPR-Cas9 in Gene Editing: A Detailed Review Introduction : This review evaluates the scientific article’s exploration of the CRISPR-Cas9 technology and its applications in gene editing, focusing on its potential and ethical considerations. Summary : The article discusses the mechanism of CRISPR-Cas9 and its use in various fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. It highlights successful case studies, including the treatment of genetic disorders and the development of disease-resistant crops. Critique : The article is insightful and provides a comprehensive overview of CRISPR-Cas9. However, it could delve deeper into the ethical issues and potential unintended consequences of gene editing. Additionally, the article would benefit from more recent examples of CRISPR applications. Conclusion : The article effectively demonstrates the potential of CRISPR-Cas9 in gene editing, though it could be enhanced by addressing ethical considerations and providing more up-to-date examples.
Review of “Climate Change and Its Impact on Global Food Security”
Title : Climate Change and Its Impact on Global Food Security: An Analytical Review Introduction : This review analyzes the scientific article’s examination of how climate change affects global food security, focusing on crop yields, food supply, and nutrition. Summary : The article explores various factors influenced by climate change, including temperature changes, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events. It discusses how these factors affect agricultural productivity and food availability. Critique : The article is thorough and supported by extensive data. However, it could include more case studies from different regions to provide a global perspective. Additionally, the article would benefit from discussing adaptation strategies and policy recommendations to mitigate the impact of climate change on food security. Conclusion : The article provides valuable insights into the effects of climate change on food security, but it would be improved by including more regional case studies and discussing mitigation strategies.
Review of “The Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies”
Title : The Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies: A Research Review Introduction : This review evaluates the scientific article’s discussion on the latest advancements in renewable energy technologies, including solar, wind, and bioenergy. Summary : The article highlights recent innovations in renewable energy, such as improved solar panel efficiency, advanced wind turbine designs, and sustainable bioenergy production methods. It presents data on the cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits of these technologies. Critique : The article is well-researched and presents a clear overview of advancements in renewable energy. However, it could benefit from a more detailed analysis of the challenges and limitations associated with each technology. Additionally, the article should include projections on the future adoption of these technologies. Conclusion : The article effectively showcases the progress in renewable energy technologies, though it would be enhanced by addressing challenges and providing future adoption projections.
Review of “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare”
Title : The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare: A Comprehensive Review Introduction : This review analyzes the scientific article’s exploration of AI’s impact on healthcare, focusing on diagnostic tools, patient care, and administrative efficiency. Summary : The article discusses various AI applications in healthcare, such as machine learning algorithms for disease diagnosis, robotic surgeries, and AI-driven patient management systems. It highlights the potential benefits and challenges of AI integration in healthcare. Critique : The article is insightful and supported by clinical data. However, it could delve deeper into the ethical considerations and data privacy issues associated with AI in healthcare. Additionally, more real-world examples and case studies would enhance the article’s relevance. Conclusion : The article effectively demonstrates AI’s transformative potential in healthcare, but it would be strengthened by addressing ethical concerns and including more practical examples.
Examples of Article Review for Psychology
Review of “the influence of parenting styles on child development”.
Title : The Influence of Parenting Styles on Child Development: A Comprehensive Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s investigation into how different parenting styles affect children’s psychological and emotional development. Summary : The article explores various parenting styles—authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and neglectful—and their impacts on children’s behavior, self-esteem, academic performance, and social skills. It presents data from longitudinal studies and surveys. Critique : The article is thorough and well-supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from more recent studies and a broader demographic scope. Additionally, practical recommendations for parents based on the findings are not adequately addressed. Conclusion : The article effectively highlights the significant role of parenting styles in child development. It would be strengthened by including more up-to-date research and practical advice for parents.
Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health”
Title : The Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health: A Detailed Review Introduction : This review analyzes the article’s exploration of the psychological effects of social media use on adolescents, focusing on issues like anxiety, depression, and self-esteem. Summary : The article discusses various studies that show a correlation between social media use and increased rates of mental health issues among adolescents. It examines factors such as cyberbullying, social comparison, and screen time. Critique : The article provides a balanced view supported by empirical data. However, it could include more recent studies and a deeper exploration of positive aspects of social media, such as support networks and educational content. Additionally, practical strategies for managing social media use are not sufficiently addressed. Conclusion : The article effectively discusses the negative impacts of social media on adolescent mental health but would benefit from more recent research and practical recommendations.
Review of “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Treating Depression”
Title : Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Treating Depression: An Analytical Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s discussion on the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating depression, focusing on clinical outcomes and patient experiences. Summary : The article reviews various studies demonstrating CBT’s effectiveness in reducing depressive symptoms and preventing relapse. It discusses CBT’s core components, including cognitive restructuring and behavioral activation. Critique : The article is well-researched and provides a comprehensive overview of CBT’s effectiveness. However, it could benefit from more detailed comparisons with other therapeutic approaches and a discussion on the accessibility and scalability of CBT. Additionally, the article should address potential limitations and criticisms of CBT. Conclusion : The article effectively showcases CBT’s effectiveness in treating depression, though it would be enhanced by including comparisons with other therapies and addressing accessibility issues.
Review of “The Role of Mindfulness Meditation in Stress Reduction”
Title : The Role of Mindfulness Meditation in Stress Reduction: A Research Review Introduction : This review analyzes the article’s examination of mindfulness meditation as a technique for reducing stress and improving mental health. Summary : The article discusses various studies that show how mindfulness meditation can reduce stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms. It explains the underlying mechanisms, such as increased self-awareness and emotional regulation. Critique : The article is insightful and supported by empirical data. However, it could include more longitudinal studies to understand the long-term effects of mindfulness meditation. Additionally, the article should address potential barriers to practicing mindfulness, such as time constraints and individual differences in response to meditation. Conclusion : The article effectively highlights the benefits of mindfulness meditation for stress reduction but would be improved by including long-term studies and discussing barriers to practice.
Review of “The Impact of Sleep on Cognitive Function”
Title : The Impact of Sleep on Cognitive Function: A Comprehensive Review Introduction : This review evaluates the article’s investigation into the relationship between sleep and cognitive function, focusing on memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Summary : The article presents various studies demonstrating that adequate sleep is crucial for optimal cognitive performance. It discusses how sleep deprivation negatively affects cognitive functions and the underlying biological mechanisms involved. Critique : The article is thorough and well-supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from a more detailed exploration of the differences in sleep needs across different age groups and a discussion on strategies to improve sleep quality. Additionally, practical recommendations for individuals suffering from sleep disorders are not adequately addressed. Conclusion : The article effectively highlights the critical role of sleep in cognitive function but would be strengthened by including more age-specific research and practical advice for improving sleep quality.
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews are critical assessments of scholarly articles, often used to evaluate the quality, relevance, and significance of the research. Understanding the different types of article reviews helps in identifying the purpose and approach suitable for various academic and professional needs. Here are the main types of article reviews:
1. Narrative Review
A narrative review provides a comprehensive summary of literature on a specific topic. It focuses on discussing the findings of the research studies and offers a narrative explanation of the trends and themes.
Characteristics:
- Summarizes and synthesizes a body of literature.
- Identifies gaps in current research.
- Provides a background for understanding the topic.
- Less structured compared to systematic reviews.
Example: Reviewing literature on the impact of social media on mental health.
2. Systematic Review
A systematic review is a methodical and comprehensive literature review that aims to answer a specific research question. It uses systematic methods to collect secondary data, critically appraise research studies, and synthesize findings.
- Uses explicit, systematic methods.
- Pre-defined criteria for selecting studies.
- Often includes meta-analysis.
- Highly structured and replicable.
Example: Evaluating the effectiveness of different interventions for reducing hypertension.
3. Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical technique that combines the results of multiple studies to identify overall trends and determine the effectiveness of interventions.
- Integrates quantitative data from multiple studies.
- Provides a higher statistical power.
- Often included in systematic reviews.
- Focuses on effect sizes and statistical significance.
Example: Combining data from various studies on the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy for anxiety.
4. Critical Review
A critical review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of a scholarly article. It involves analyzing the methodology, arguments, evidence, and contributions of the article.
- In-depth critique of a single article.
- Focuses on the validity and reliability of the research.
- Discusses the implications and limitations.
- Offers suggestions for improvement.
Example: Critiquing the research design and conclusions of a study on climate change impacts on agriculture.
5. Literature Review
A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, providing a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works.
- Broad overview of existing research.
- Identifies patterns and trends.
- Highlights gaps in current knowledge.
- Provides a foundation for new research.
Example: Reviewing literature on renewable energy sources and their environmental impacts.
6. Scoping Review
A scoping review maps the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It aims to provide an overview of the range of research activity.
- Identifies the scope of literature on a topic.
- Useful for emerging areas of research.
- Highlights areas for future research.
- Less detailed than systematic reviews.
Example: Exploring the range of studies on artificial intelligence applications in healthcare.
7. Integrative Review
An integrative review synthesizes theoretical and empirical literature to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a specific phenomenon or healthcare problem.
- Combines qualitative and quantitative research.
- Generates new frameworks and perspectives.
- Addresses mature topics with substantial research.
- Useful for policy and practice implications.
Example: Integrating research on patient-centered care models in nursing.
8. Conceptual Review
A conceptual review focuses on theories and concepts in a particular field. It examines how these concepts are defined, measured, and applied in the literature.
- Emphasizes theoretical frameworks.
- Analyzes the development of concepts over time.
- Identifies theoretical gaps.
- Proposes new conceptual models.
Example: Reviewing the evolution of the concept of resilience in psycholog
More Article Review Examples & Samples in PDF
1. formal article review.

2. Article Review Guideline

3. Format for Review Article

4. Scientific Article Review

5. Research Experience Article Review

6. Review of Research Articles

Components of Article Review
An article review involves evaluating and summarizing a scholarly article, presenting critical insights, and reflecting on its implications. Understanding the essential components helps in crafting a thorough and insightful review. Here are the key components:
- Clearly indicates the focus of the review.
- Should include the article’s title and author(s).
Example: “Review of ‘The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health’ by John Smith”
2. Introduction
- Provides context for the review.
- Introduces the article’s main topic and objectives.
- States the purpose of the review.
The article “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health” by John Smith explores the relationship between social media usage and mental health outcomes. This review aims to critically evaluate the article’s findings and discuss its implications for future research.
3. Summary of the Article
- Concisely summarizes the article’s main points.
- Includes the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
The article investigates both positive and negative effects of social media on mental health. Using a mixed-methods approach, the study finds that while social media can enhance social support and community building, it also contributes to anxiety, depression, and cyberbullying.
4. Critical Analysis
- Evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the article.
- Discusses the validity and reliability of the research.
- Analyzes the methodologies used and the evidence provided.
- Considers the implications of the findings.
The article provides a balanced view of social media’s impact, effectively synthesizing current research. However, it lacks in-depth analysis of the methodologies used, which could affect the validity of the findings. Future research should include longitudinal studies to better understand causal relationships.
5. Conclusion
- Summarizes the key points of the review.
- Restates the significance of the article.
- Provides final thoughts and suggestions for future research.
In conclusion, Smith’s article offers valuable insights into the complex relationship between social media and mental health. While the study is comprehensive, addressing methodological limitations in future research would enhance our understanding of this important issue.
6. Personal Reflection
- Discusses the reviewer’s personal perspective on the article.
- Explains how the article’s findings relate to the reviewer’s own experiences or studies.
- Offers insights on how the article influenced their understanding of the topic.
As a student, I find the article’s discussion on the negative impacts of social media particularly relevant. It underscores the importance of mindful social media use to maintain mental well-being. This review has deepened my understanding of the subject and will inform my future research.
7. References
- Lists all the sources cited in the review.
- Follows a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
Example: Smith, J. (2023). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychological Studies, 45(2), 123-145.
How to write an Article Review?
Writing an article review involves summarizing and critically evaluating a scholarly article. This process helps in understanding the article’s contributions and limitations, and it enhances critical thinking skills. Follow these steps to write an effective article review:
1. Read and Understand the Article
- Read the Article Thoroughly : Start with a quick overview to understand the main idea, then read in detail.
- Identify Key Points : Note the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Understand the Context : Research the background information and the article’s significance in its field.
2. Plan Your Review
- Outline the Structure : Plan the sections of your review: Introduction, Summary, Critical Analysis, Conclusion, Personal Reflection, and References.
- Determine the Focus : Decide what aspects of the article you will highlight and critique.
3. Write the Introduction
- Provide Context : Introduce the topic of the article and its relevance.
- State the Purpose : Explain the purpose of your review.
- Mention the Article : Include the title of the article and the author’s name.
The article “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health” by John Smith explores the relationship between social media usage and mental health outcomes. This review aims to critically evaluate Smith’s findings and discuss their implications for future research.
4. Summarize the Article
- Concise Summary : Summarize the main points of the article without inserting personal opinions.
- Include Key Elements : Mention the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Smith’s article investigates both positive and negative effects of social media on mental health. Using a mixed-methods approach, the study finds that social media can enhance social support and community building but also contributes to anxiety, depression, and cyberbullying.
5. Critical Analysis
- Evaluate Strengths and Weaknesses : Discuss the strengths of the article, such as comprehensive literature review or innovative methodology. Point out weaknesses, such as limited sample size or potential biases.
- Analyze Methodology and Evidence : Critically assess the research methods and the evidence provided.
- Discuss Implications : Consider the significance of the findings and how they contribute to the field.
The article provides a balanced view of social media’s impact, effectively synthesizing current research. However, it lacks an in-depth analysis of the methodologies used, which could affect the validity of the findings. Future research should include longitudinal studies to better understand causal relationships.
6. Write the Conclusion
- Summarize Key Points : Briefly restate the main points of your review.
- Restate the Article’s Significance : Emphasize the importance of the article’s contributions.
- Provide Final Thoughts : Offer any concluding thoughts and suggestions for future research.
7. Personal Reflection
- Discuss Personal Insights : Share how the article relates to your own experiences or studies.
- Explain Impact on Understanding : Describe how the article influenced your understanding of the topic.
8. Include References
- Cite the Article : Include a full citation of the article you reviewed.
- Follow Citation Style : Use the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
Smith, J. (2023). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychological Studies, 45(2), 123-145.
How do I start an article review?
Begin with a brief introduction that provides context, states the purpose of your review, and mentions the article’s title and author.
What should be included in the summary?
Summarize the main points of the article, including the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions without inserting personal opinions.
How do I write a critical analysis?
Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the article, analyze the methodology and evidence, and discuss the significance and implications of the findings.
How long should an article review be?
The length varies, but typically an article review is 2-4 pages, balancing summary, critical analysis, and personal reflection.
How do I conclude an article review?
Summarize the key points of your review, restate the article’s significance, and provide final thoughts and suggestions for future research.
What is the difference between a summary and a critique?
A summary restates the article’s main points objectively, while a critique evaluates the article’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution.
How do I incorporate personal reflection?
Discuss how the article relates to your own experiences or studies and describe how it influenced your understanding of the topic.
Should I include direct quotes from the article?
Use direct quotes sparingly, only when they enhance your analysis. Always explain their relevance to your critique.
How do I properly cite the article in my review?
Follow the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) to include a full citation of the article at the end of your review.
Can I express my opinion in an article review?
Yes, but primarily in the critical analysis and personal reflection sections. Ensure your opinions are supported by evidence from the article.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. Learn the purpose, structure, and tips of writing a literature review, with an example on climate change impacts on biodiversity.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic that provides an overview of current knowledge. Learn the five key steps to write a literature review, with examples, templates, and tips.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects and discusses key sources on a topic in a given field. Learn about the purposes, parts, and strategies of writing a literature review in different disciplines and situations.
Learn the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review, and see examples from three theses. A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research that reports on the existing scholarly conversation.
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem.
When writing a literature review it is important to start with a brief introduction, followed by the text broken up into subsections and conclude with a summary to bring everything together. A summary table including title, author, publication date and key findings is a useful feature to present in your review (see Table 1 for an example). This ...
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. ... For example, your study may show that your research ...
A good literature review evaluates a wide variety of sources (academic articles, scholarly books, government/NGO reports). It also evaluates literature reviews that study similar topics. This page offers you a list of resources and tips on how to evaluate the sources that you may use to write your review.
This paper discusses different types of literature reviews, such as systematic, semi-systematic and integrative reviews, and how to conduct and evaluate them in business research. It also provides practical tips and common pitfalls for writing and publishing literature review papers.
Learn how to write a literature review for your dissertation or research paper with this step-by-step guide. Find out how to search, evaluate, and synthesise sources, and see examples of different types of literature reviews.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
begin by clearing up some misconceptions about what a literature review is and what it is not. Then, I will break the process down into a series of simple steps, looking at examples along the way. In the end, I hope you will have a simple, practical strategy to write an effective literature review.
A literature review is a comprehensive overview of scholarly sources on a topic that helps you create rapport, avoid plagiarism, and sharpen your research focus. Learn what a literature review is, why it is important, and how to write different types of literature reviews for your research paper.
A literature review is an integrated analysis of scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. Put simply, it's a critical evaluation of what's already been written on a particular topic.It represents the literature that provides background information on your topic and shows a connection between those writings and your research question.
A literature review is a chapter in a dissertation or thesis that summarises and evaluates the existing research on a topic. It serves several purposes, such as demonstrating topic knowledge, revealing research gaps, laying the foundation for a conceptual framework and informing the methodology.
Literature Review Examples. For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics. ... Example Study. Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review . Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M ...
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field. A literature review should: Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature; Explain why this review has taken place;
Review all the literature, appraising carefully it's content: After reading the study's abstract, pay attention to the rest of the content of the articles you deem the "most relevant." Identify methodologies, the most important questions they address, if they are well-designed and executed, and if they are cited enough, etc.
Learn what an article review is, how to write one, and see 30+ examples from various fields. An article review is a critical assessment of a scholarly article or research paper that involves analyzing the content, methodology, and findings.