Money is Energy. Learn to Unlock that Energy to Build your Wealth and Abundance. Book Now!


Business Plan vs Business Profile
Do you know the difference between a business plan and a business proposal? These are two very different business documents, each serving a distinct purpose.
A business plan documents your vision for your business and how you intend to achieve that vision. It contains financial projections of what the business will cost to develop and operate plus an estimation of the revenues to be generated. Its purpose is to provide a reasonably detailed explanation of your business for use by potential investors, suppliers, prospective employees, accountants, attorneys and other people who need a quick but comprehensive understanding of what your company does and its potential for success. The primary reason for a business plan is to record and convey information.
You will need a business plan for two reasons. First, your business plan is your blueprint to success — it outlines the steps to move from business idea to business success. If your research reveals that your idea isn’t destined for success, isn’t it better to know it now than a year later when you may have lost thousands of dollars? Spending time to do this provides you with information previously not considered, and gives you a workable strategy to follow for the period covered by the plan.
Secondly, if you are hoping to raise funds through a bank or an angel, don’t even consider approaching them unless you have a thoroughly researched business plan in your hand. Experts estimate that it takes approximately six weeks to develop a business plan, so whipping one up the day before your appointment with your banker won’t work.
A business proposal is a document that you submit to another enterprise proposing a business arrangement. They are limited in scope to a particular project or need. A business proposal also generally has a specific audience. There are two main categories of business proposals: invited and non-invited.
An example of an invited proposal – government and large corporations wanting to purchase services or products from private suppliers often post public tenders inviting contractors to bid. You will be competing against all bidders that noticed the posting and responded.
Similarly, some businesses will send Requests for Proposals (RFPs) to a selection of businesses that they are willing to consider as a potential supplier. In this case, you will be competing against perhaps five businesses that the client has already handpicked as suitable.
In a non-invited proposal, you might have an idea for a product or service that would be of benefit to Company X. You submit a proposal to that Company suggesting a business relationship.
In this case, you don’t know if the company is open to your proposal or whether they will like your proposed idea. However, if they do like the idea, you won’t be competing against numerous other bidders. Your proposal has to sell not only your concept but also your company. It must convince the client that not only is the service/product potentially valuable to them, but you and your company are credible and stable.
Whether invited or non-invited, your proposal must be well researched, well written and contain a reasonable budget. Spend time on this document and you’ll be ahead of the people who threw something together on the maxi.
In conclusion, a business plan and a business proposal have different purposes and goals. A business plan is a factual broad description of a company and its prospects. A business proposal is a focused sales document intended to describe how a company will approach a project. A business plan is a written presentation of fact. A business proposal is a quote and call to action.
Be sure to join our Facebook , Instagram , Tiktok and our Website for more valuable information. Ask about our Business Plan Packages and Business Profile, Business Startup Kit , Retainer Package, Year End Retainer Package , Business Bank Account or learn how manage your finance with our Prerecorded and Live Courses. Book a FREE 15 mins CONSULTATION on Fridays from 1pm to 3 pm.
“A wealthy person is simply someone who has learned how to make money when they’re not working.” – Robert Kiyosaki
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
About the author: destiny planners ltd.
Related Posts

Choosing a colour for your logo…Part 3

Choosing a colour for your logo…Part 2

Choosing a colour for your logo…Part 1

Choosing a Business Name…Part 2

We recognizes the importance of knowledge and learning in achieving financial success. Therefore, we aim to empower entrepreneurs with proper financial structures and strategies with our courses and services from the start.
Contact Info
Phone: 1-868-469-6317
Email: [email protected]

SERVICES & EDUCATION

© Copyright 2012 – 2023 | Destiny Planners – Managing Your Financial Future | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 27, 2023 Updated on December 11, 2023

A business plan and a business proposal are similar documents. In fact, in some cases the terms can be used interchangeably, such as when both aim to attract investment.
But generally speaking, a business proposal tends to have broader scope, and this handy guide lays out precisely how these two common terms differ.
| Feature | Business Plan | Business Proposal |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Outlines a company's mission, vision, and means to achieve its goals. | Proposes a specific project or solution to a client or potential partner. |
| Audience | Investors, stakeholders, financial institutions, and internal team. | Potential clients, partners, or businesses. |
| Content | Executive Summary Company Description/Overview Products/Services Offered Market Analysis Marketing and Sales Strategies Operations and Management Financial Plan Appendices | Introduction Problem Statement Proposed Solution Pricing Timeline Terms and Conditions Conclusion |
| Duration | Generally, long-term. Speaks to the company's overall direction. | Usually short-term, addressing a specific project or need. |
| Focus | Comprehensive view of the business, including strategies, resources, and financial projections. | Focuses on a particular problem or need and the solution the company offers. |
| Use | To guide the company's direction and attract investments or loans. | To secure a contract, partnership, or client engagement. |
| Update Frequency | Periodically, as the company evolves or when significant changes occur in the market or industry. | As needed for different clients or projects. |
| Format | More detailed and structured. May have appendices with additional information. | Typically more concise, tailored to the client or project. |
- What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a detailed document laying out how the business will function and develop in its first few years. The key is the “plan” part of the name, as it will specify how you will launch, gain customers, operate, make money, and, with any luck, expand.
Yet what many first-time business owners seem to forget is that a business plan is not a static document. The initial version is based largely on assumptions, supported by research. But as you run your business you’ll learn what works and what does not and make endless tweaks to your plan.
Thus, creating a business plan is not a one-time action – it’s a dynamic and continuous process of crafting and adapting your vision and strategy.
Components of a Business Plan
A business plan is generally much more detailed and broader than a business proposal, and has several elements :
- Executive Summary
- Company Description/Overview
- Products or Services Offered
- Market Analysis
- Marketing and Sales Strategies
- Operations and Management
- Financial Plan
- What is a Business Proposal?
A business proposal is created in connection to a specific business deal being offered by one party to another. As mentioned, when you take a business plan to an investor, you’re proposing a business relationship, so in this case a business plan and a business proposal are much the same.
But a business proposal could also be for others purposes, including:
- Bringing on a partner
- Proposing a management contract to a person you want to hire
- Proposing a business relationship with a potential customer
- Proposing a partnership with another company
- Suggesting a deal to a member of your board of directors
A business proposal may offer specific terms for the potential relationship, or it may be just about the benefits the relationship will bring, with terms to be negotiated later. Essentially, it’s a sales tool to get people or companies to do business with you in some way.
Business proposals can be structured in various ways, but usually, they’ll include a summary of what your company can offer, a scope of the work to be done together, and sometimes, a price quote or a proposed structure of the business relationship.
Clearly, a business plan and a business proposal are similar – and can even be one and the same. At the same time, they can also serve very different purposes. Unlike a business plan, a business proposal can have a variety of aims and thus does not have a “one size fits all” structure.
Whichever one you need, be sure to take your time with the research and writing so your business has the best chance for success.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
Marketing and Sales
What is a business profile how to make one, highlight your company by making its resume. learn what a business profile is and how to write a great one. plus, read up on some best practices to follow..

Imagine delivering the perfect elevator pitch about your coaching business –– including a concise company description that covers your services, vision, and mission –– and it hits the mark.
And this is only possible through a well-crafted business profile, which summarizes your experience, values, and goals and tells potential clients what sets your coaching practice apart.
Draft a precise piece of write-up you can use on your coaching website and other marketing platforms, and invite a wealth of clients to your practice.
Here’s everything you need to know about what a business profile is and how to create one.
What is a business profile?
A business profile tells a story about the founder(s), what inspired them to build the business, the company’s vision and mission, and more. It should also outline the company’s goals and achievements, such as the number of clients served, retention rate, and awards (if any). It’s typically available on a company website’s “About Us” page.
Your coaching bio may hit many of the same points, but company profiles differ, thanks to their strong focus on values and objectives.
As such, company profiles are not only attractive for clients but also investors. Strong annual metrics and positive testimonials create confidence among the investor community.
How to make a business profile
Organize your thoughts and perfect your coaching business’ marketing message by writing your company profile. Here’s how:
- Determine your profile’s purpose: Perhaps you’re trying to raise money from investors. Or maybe you want to attract new customers. Your profile’s intent can change during your company’s development, but try to pinpoint why you’re writing this document. That said, don’t share it on your website. The purpose should stand to guide you.
- Share your story: Write an honest recap of your history. It’s acceptable to be vulnerable in this section. You’re trying to emotionally connect with your future clients in a company profile, not just share facts about how far you’ve come. Tell them what makes you different and how hard you work. If you’re a solo-prenuer, include your education and training at the beginning of this description.
- Write a tight mission statement: Tell the reader your work, target clientele, and unique selling points (USPs). There’s no need to wax poetic. Keep this section to a sentence or two for maximum impact.
- Tell your business’s story: Include a chronological summary of your coaching business. Talk about how you opened and grew your business. Remember, your business profile differs from a coaching bio and a business plan. In a profile, you’re trying to paint a picture of your company. A bio focuses on personal and professional accomplishments. And a business plan includes strategizing marketing, sales, and operations.
- List your coaching services: Tell the reader about your one-on-one programs, coaching packages, and group programs. Mention your proprietary coaching method (if any).
- Include a good word: If you have testimonials from previous coaching clients, include them. Your words will undoubtedly go far in describing your business and mission, but the feedback from others provides a unique, first-hand perspective on your coaching skills.
Additional ideas for your coaching profile
- Brag a little: Let’s break a myth –– you don’t seem pompous when flexing your accomplishments; rather, it adds value to your profile. Include milestones such as writing a book, starting a successful blog, or receiving awards.
- Include a call to action (CTA): If you post your business profile on your webpage, invite viewers to contact you for more information, follow your social media accounts, or receive a free coaching orientation call.
- Add contact information: If you include a CTA or are using your profile in marketing materials or on your professional site, be sure to provide contact information, such as phone number, email address, physical address, and website link. Give potential customers or investors multiple avenues to reach you.
{{mid-cta}}
Tips for effective profile writing
Take your profile from good to great with the following tips:
- Read business profile examples: Check out the about pages of your favorite brands for business profile inspiration. For instance, Starbucks provides a strong example of a profile that’s exceptionally brief, lists the most essential business details, and represents the company's voice. Nike shows how to break information into unique sections, links to pages that provide more detail, and uses a visually impactful business profile format. If you’re looking for a stellar business description example from the coaching industry, check out Cortney McDermott’s page . She tells her story in a captivating and personal way. Or, take a look at personal trainer and coach Michelle Lavergne’s webpage . She explains her strengths through punchy and encouraging sentences, pushing potential clients to take the first step toward fitness.
- Make the profile easy to digest: Make your business profile readable –– textually and visually. Cut insider terms that only a coach would know and won’t resonate with your clients or investors. Scrape back the language and leave out excess words. Try to be as direct as possible. And when you publish the profile on your website or in marketing or investor materials, use fonts and spacing that are easy on the eyes. Avoid long paragraphs without breaks.
- Keep it relevant: Your business profile is an opportunity to explain your practice thoroughly. While the description doesn’t have to be overly brief, it should be pertinent. Avoid repetition or unnecessary material.
- Update your profile regularly: As your business changes, regularly update your description to reflect shifts, especially costs and packages. This eliminates future conflicts with clients. Also, include information about new certifications, ways your practice has grown, and services you’ve added to your offering.
Take your coaching business to the next level
Writing a business profile is an excellent step toward formalizing and marketing your coaching practice. It instills confidence and trust in clients.
You can also up the professionality of your company by using a customer relationship management (CRM) tool . Practice’s platform , designed with coaches and small business owners in mind, allows you to securely store client data, send messages and documents, and securely receive payment. Try it today .
Give your clients a simple and professional experience
Simple client management designed for teams, free form templates from practice.
Enneagram Coaching Feedback Form Template - get the most out of your coaching sessions with this easy to use feedback form for professionals. Try it now!
Start your executive coaching journey with this helpful onboarding template. Get organized and get the most out of coaching sessions with this easy-to-use form.
Use our Wheel of Life template to help you and your clients reflect on and define their goals and priorities in life. #goal-setting #lifeplanning
More articles from Practice

How to Get on Google Business and Make the Most of It

What Is a Brand Voice? Examples and Tips for Coaches

Guides & Templates
Write an excellent coaching bio.

Nail Your Marketing Game With These 6 Types of Branding Strategies

Create an Amazing Life-Coaching Business Plan

Learn How To Create a Successful Health Coach Business Plan

Professional Development
Here’s how to create an effective virtual assistant resume.

Here’s How to Create a Slogan in 4 Easy Steps

Top 5 Accounting Software for Freelancers

The Ultimate Guide to Becoming a Branding Coach

All You Need to Know About Podcasting for Small Businesses

What’s a Mental Health Coach, and How Can You Become One

Client Success
How to politely ask clients for a deposit (with sample emails).

Best Practices
Measuring success: key metrics for evaluating the performance of coaching subscription models.

The Importance of Coaching Ethics

Coaching Goals Examples for You and Your Clients (with Template)

Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
The terms “business plan” and “business proposal” are sometimes used interchangeably, however, they are very different. The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company, partner with you, etc.).
In this article, we will define a business plan and a business proposal and give you examples of when each is appropriate for you to use.
What is a Business Plan?

Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
Business Plan Structure
Typically, the business plan structure contains the following 10 components:
- Executive Summary
- Business Description & Overview
- Market Research & Analysis
- Customer Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Strategy & Plan
- Operations Plan
- Management Team
- Financial Projections & Plan
It is recommended that a business plan is updated annually to adjust for changes in the industry trends and the business itself.
What is a Business Proposal?

In terms of what you are asking from them, it can be anything that involves funds and time on their end including cash investment, product development assistance, and even employees if they have applicable skill sets.
Business Proposal Structure
An invited business proposal is written in response to an RFP. A request for proposal (RFP) is a document that invites potential suppliers to submit business proposals. How to write a business proposal depends on the format requested and the questions included in the RFP.
The following are the components that usually make up a business proposal:
- Brief description of your company’s services/products as the proposed solution to the goals of the RFP
- Reiteration of the scope of the particular project
- Responses to questions asked in the RFP
- Cost of the project, including drafting services, materials, tools, labor, delivery and other expenses
An unsolicited business proposal is essentially the same format, but it will solicit the client’s business while anticipating the clients’ concerns and issues. A business proposal is more of a marketing document than an offer because it attempts to persuade the potential client to do business by demonstrating your value proposition and a call to action.
So, What’s the Difference Between a Business Proposal vs. a Business Plan?
In a business proposal, company representatives typically work with the customer to tailor a business proposition that is attractive to both parties. This usually comes in the form of a written document detailing the services and cost associated with fulfilling an offer or request but can also include electronic contracts.
In contrast, a business plan is a description of your company on the executive and operational levels aimed at investors for raising financial support or other stakeholders in order to facilitate long-term growth. For example, an investor will want to know about how different departments within your business interact with one another, while somebody who will be implementing your product probably only needs more limited information such as design specs because they are not going into production themselves.
A business proposal may provide you with more details of the project, but it does not include information about your company’s operations or future plans.
Examples of Business Plans vs. Business Proposals
- When you give a potential investor your business plan which includes all sorts of information about how we will achieve your goals together as well as the amount of money it’s going to take. The business proposal is for them to write you a check in return for interest/principal payments or a percentage of your company.
- You might be getting partners involved in your business who will help with product development and distribution. You are offering them a business proposal to work together. However, they may request to see your business plan to better understand your goals, potential profitability, and how you plan to reach these goals before deciding to work with you.
- Your existing business has been so successful that you decide to outsource the social media marketing efforts to a freelancer to free up more of your time. The freelancer would provide a business proposal stating their terms and conditions along with the agreed-upon pay arrangement for their services. This change in organizational structure may be noted in your business plan to demonstrate expansion and financial stability to continue growth.
- In your business plan , one of your goals is to grow your client base by 5% each month. You identify potential clients in need of your services or products and send an unsolicited business proposal to demonstrate how your products or services can benefit them in order to develop a new prospective client list.
The business plan is a roadmap for your company’s present and future, while the business proposal has to do with what you are asking someone else for money. Applying this difference into practice can be difficult at times because business plans are often marketed as business proposals. However, it is important to be able to identify the difference between a business plan and business proposal in order to maximize their effectiveness and importance with potential investors or partners.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


How To Write An Effective Business Profile
Writers Write shares business writing tips and resources. In this post, our guest blogger defines a business profile and gives you steps to write an effective business profile.
In previous posts, we have shared a variety of step-by-step guides for various business correspondence , In this post, we look at writing a business profile.
What Is A Business Profile?
Before we delve into the steps of writing a business profile, let’s try to define what a business profile is? How is it different from a business plan?
A business profile gives a general idea of what a business is about and a glimpse into your organisation’s business plan.
A business profile includes values and objectives. It shows some of the major clients you’re working with, or have worked with in the past. It also gives an idea of where your business is headed. It shows your vision and mission.
Some describe a business profile as “a Curriculum Vitae for your company”. It shows your company’s skills and strengths.
Important to note when writing a business profile:
- Keep it short and engaging. People have busy schedules, and only read through if it captures their attention.
- Study other business profile especially the ones in your industry. Observe the style and tone .
- Use accurate, up-to-date details.
- Use clean and concise words. Don’t use language that requires a dictionary to understand.
- Watch your formatting . Keep it clean.
Depending on your industry and the objectives of the company, most businesses follow these steps.
8 Steps For Writing A Business Profile
Step 1: Put your basic information first. (About Us)
- What is the business about? Are you a clothing designer? Is it a construction company?
- Briefly explain your vision and mission and goal as a company.
Step 2: Who you are.
- 5- 10 lines should suffice. Don’t make it too long.
- Include your company history. How did you start? What drove you to start your company? Make it personal and relatable. What kind of clients do you service?
- Include your experience and expertise. For example, “I have more than 15 years in project management. I have a passion to tackle real challenges.”
Step 3 : Show your company service offering.
- List all your business activities.
- Do you provide services to a specific market, or is it for the general public? What is your target market? Include a sentence explaining your choice of the target market.
- Include the areas you work in. Do you operate locally, regionally, or internationally?
Step 4 : What are your guiding values?
- This is the foundation upon which your company is established. It includes how you run your business, and your company policy.
- They guide your business so that you can manage your internal operations, and how you relate with your customers. Basically, it’s about both internal and external relations.
- Respect and courage.
- Health and safety.
Step 5: Strengths
Mention why your company should be the preferred one. Why should clients choose you over other companies with the same service offering? See the examples below to help you.
- Quality and service offering. Speak about offering high quality service in order to meet client expectations.
- Health and safety policies. For the safety of both your staff and clients.
- Staff development and training. Talk about how you equip your staff with skills and knowledge. Your clients become confident in your company if they know you know what you are doing.
These are just of the few examples of how you can show the strengths of your company, like I mentioned, each business profile should be designed according to your company’s needs. This is just a guideline to help you get started.
Step 6: Your Certification
Why certification?
- You must have some kind of certification relevant to your industry.
- Certification builds credibility, and gives your clients, industry leaders, and potential investors confidence in your business.
- It shows your commitment to your clients
- It demonstrates your dedication to keep abreast with industry standards, innovation, and continuous training/learning.
- It provides recognition of your unique skill set and knowledge of your products and services
Step 7: Show who your current or past projects/clients are.
Clients show what you are able to deliver on.
- Clients can vouch for your integrity, commitment, reliability etc.
- It is easier to trust a company with references.
- If possible, include details such as the size of the project. It gives a better picture of your ability to deliver.
Step 8: The Team
Include a basic company organogram to show the different skills of the core team.
Tailor this according to your purpose and what you want to communicate to your audience.
Put your company contact details (telephone number, email addresses, social media handles, website etc.) and the physical location of the business (unless you run a purely online business).

More Guest Posts
- 5 Great Ways To Ruin The Ending Of Your Novel
- How To Add Blogging Experience To Your Resume The Right Way
- 3 Things A Writer’s Journal Isn’t
- The 3 Pillars Of Horror
- Billy Collins’s 6 Elements Of A Poem
- 9 Ways To Write With Literary Flair
- Self-Care For Writers
- Turn Your Dreams Into A Plot Generator
- 7 Reasons Why I Loved The Writers Write Course
- 7 Tips To Remove Distractions While Blogging
- Why All Aspiring Novelists Need A Vision Board
If you want to improve your business writing, buy The Complete Grammar Workbook .
- Business Writing Tips , Featured Post , Guest Post
© Writers Write 2022
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Company Overview for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
When you start a company, you ideally want it to grow. If you’re seeking business funding to scale your business or an initial investment to get your business off the ground, you’re going to need a business plan . Putting together a business plan can be an intimidating process that involves a lot of steps and writing — but breaking it down piece by piece can help you accomplish this seemingly insurmountable task.
One small piece of your business plan is the company overview, so let’s take a look at what that is, exactly, check out some company overview examples and go over how to make a company overview of your very own.

ZenBusiness
What is a company overview?
A company overview provides the reader of your business plan with basic background information about your company so they have an understanding of what you do, who the management team is and what customers your business serves.
The company description is the second piece of a business plan, falling right after the executive summary. Similar to the executive summary, your company overview will be short and succinct. Your reader needs to have a grasp on what your business does and who your customers are, even if they have limited time.

Why do I need a company overview?
The company overview is the part of your business plan that gives the basics and background of your business. It’s the foundation on which you will build the rest of your business plan.
If you’re looking to appeal to investors or potential clients, you need a reader to make an informed decision about your company. Before they can do that, they must know what your company does and who your customer is. Lenders in particular need a reason to keep reading, since they see tons of business plans regularly. The company overview provides those answers, and it will help you get a better sense of your business so you can firm up things like your marketing plan.
Compare cards
How much do you need.
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
What should I include in a company overview?
The exact elements that you need in your company overview will depend upon what details of your business are important, but there are some foundational elements that will be included in every company overview.
Once you’ve covered the basics, you can include any other minor details that will benefit a reader who will need to make an informed decision about your business.
Basic company information
Consider the company overview like an introduction for your business. In the opening paragraph of your company overview, you’ll want to include basic company information. That includes:
Your company name: This should be the official name of your business, exactly as it is written when you registered your business with the state.
Business structure: Your reader will want to know what business entity your company comes in: sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership or corporation.
Location(s): Share where your business is headquartered and other locations the business owns.
Ownership and management team
Break down who owns your business and how each owner is involved with the business. What shares of the company belong to whom? If you have a highly involved management team, share their names and key roles with the company as well.
Company history
Part of what makes your company unique is its history. And, even startups have some history. Don’t put too much focus on this section, but do add some personality and interesting details if possible, especially if they relate to your company culture.
Mission statement
Your company’s mission statement should be included in the company overview. If you don’t yet have a company mission statement, that’s okay. Think of a mission statement as the purpose of your company.
If you don’t have one, you can create one with your team. Or you can simply replace the mission statement with a problem statement. Your business idea should exist to solve a problem or pain point faced by your customers. Share what that problem is and what your business does to solve it. That’s essentially your mission statement.
Product/service and customer
This section of the company overview is where you can share the nitty-gritty details of your business. Talk about what product or service you provide and to whom you provide it. You can share some numbers here, but in general, save the numbers for later in your business plan.
The company overview should give the reader a general understanding of your business, your product or service, and your customer. If they’re interested to know more, they’ll reach out to you for a meeting or take the time to read the rest of your business plan. Keep it simple and straightforward here.
Future goals
While concrete details and facts about your business are important to whoever is reading your company overview, it’s also important to share your dreams and your vision. If you’re writing a business plan for a business that’s already in place, it’s very likely you’re looking for business financing to scale or solve a business problem. If you’re just starting out, though, then it’s likely you’re hoping to find startup funding.
The section on your future business goals should include a brief description of your growth goals for your business. Where you are now tells the reader a lot, but they also want to know where you plan to go.
A company overview is comprised of many small parts. Each part shares just a little bit more about your company with your reader.
Tips for writing a company overview
While a company overview is simply the details of your company written out, it might not be easy to write. Break it down into small steps and use these tips to make putting together your company overview just a little bit easier.
Start with the elevator pitch
If your business is already in operation, then you likely have an elevator pitch. Your company overview can start off with your elevator pitch.
The first paragraph of your company overview should include just a few sentences that explain your business and what you do. The shorter and clearer this is, the more likely your reader will understand and keep reading.
Stick to the basics
It’s tempting to pile on all the details when you’re writing a company overview. Remember, many of the details of your company, including the numbers, will be included in later sections of your business plan.
Your company overview should include only the most basic details about your company that the reader needs to know.
Be passionate
When you share the history, mission statement, and vision for the future of your company, it’s okay to show your passion. You wouldn’t be in business if you didn’t love what you do.
Your excitement for your business could spark interest for the reader and keep them engaged with your company overview and business plan.
Keep it succinct
When you’re passionate about something, it’s easy to get carried away. Remember that you’ve got plenty of space for details in your business plan. The company overview should be just the most basic information someone needs to understand your business.
It’s OK if your first draft of your company overview is long. Simply go through and edit it to be shorter, removing unnecessary details and words each time you read through it. Clear, concise descriptions are more likely to be read and to keep the reader reading to other sections of your business plan.
Have structure
Your company overview is just one piece of a multi-tiered business plan. Creating a clear structure for your business plan makes it easier to read. The same is true for your company overview.
Your business plan should have chapters, one of which is the company overview. Then, you can further break down the content for easy skimming and reading by adding sub-chapters. You can denote these breaks in content with bold headers.
While you can break down each section of the company overview with bold headers based on the above suggestions, you can also interweave some information together, such as the company structure and leadership structure. Each section should be only a few sentences long.
Write it later
If you’re struggling to write your company overview, come back to it. Write the rest of your business plan first and then write your company overview.
While this might seem like the opposite way of doing things, knowing what will be contained in the rest of your business plan can help you to focus in on the very most essential details in the company overview and to leave everything else out.
Get a test reader
If you’re struggling to edit down your company overview, get a test reader. Ideally, you’ll want to ask someone who doesn’t know a lot about your business. They’ll help you understand whether or not you’ve clearly communicated your message.
Proofreading is the final step in editing something you’ve written. This type of editing looks for typos, misspellings and grammatical errors that have been missed. Many of these small errors can be difficult to spot in our own writing, so be sure to ask someone who hasn’t seen multiple drafts of your company overview.
Start Your Dream Business
Company overview examples
If you don’t want to shell out for business planning software, but would still like some company overview examples to get you started, there are many places online you can look to for help getting started, like the Small Business Administration and SCORE.
Many successful companies also have some version of their company overview made public as their company profile page online. There are some variations from the company overview steps we’ve listed above, of course, but you can use the language and style of these company overview examples for inspiration:
Starbucks company profile .
Puma company page .
TaskRabbit About page .
Peloton company page .
Nestlé About page .
If you’re still feeling stuck, or want more company overview examples, try searching the websites of your favorite companies for more information. You might be surprised what you find — the Nestlé page, for example, has more information about their strategy and business principles.


Business Plan vs. Business Proposal: Everything You Need to Know
“Ok, so you sell things.”
Well, honestly, I wasn’t surprised or peeved at the half-baked knowledge of my friend’s father when he made a snap judgment and conveniently labeled my marketing profession as sales.
After all, this wasn’t my first time when someone tagged me as a salesperson. So, I took a deep breath and explained to him how sales are different from marketing.
We, humans, dwell in a herd mentality and hone our word skills from our surroundings. Sometimes, we are simply careless, sometimes oblivious, but most of the time, we actually don’t know that the word has a different meaning.
This can be ignored in a casual conversation, but using the wrong words in a business space can change the implied meaning and lead to miscommunication. For example, cost vs. price , digitization vs. digitalization , warranty vs. guarantee , machine learning vs. artificial intelligence , etc.
“Don’t use words too big for the subject. Don’t say ‘infinitely’ when you mean ‘very’; otherwise you’ll have no word left when you want to talk about something really infinite.” – C. S. Lewis
This Process Street guest post untangles the confusion between two crucial terms – business plan and business proposal. These are used interchangeably in the business world, but their meaning and application are pretty different.
Words are the building blocks of communication. There is a French phrase for using the right word – le mot juste .
Let us strive for le mot juste !
Hop on and be a part of this fantabulous journey.
What is a business plan?
What is a business proposal, business plan vs. business proposal: what are the differences.
- Bonus: How to make ‘wow’ business plans and business proposals?
Winding-up: Key takeaways
Here we go!
A business plan is a formal guide that acts as a blueprint, deciphering every root and branch to make a business successful. It is a written document that provides insights to internal and external stakeholders on business vision, goals, and strategies to achieve those goals.
“Without a plan, even the most brilliant business can get lost. You need to have goals, create milestones and have a strategy in place to set yourself up for success.” – Yogi Berra
A business plan, at its core, is an explanation of the below questions –
- Who are we?
- What are our offerings?
- Who are our customers?
- Who are the competitors?
- What is our competitive advantage?
- What are the business projections?
- What is the roadmap to achieve the goals – marketing, operations, research and development, manufacturing, and financial plans?
- What are the funding/investment requirements?
- What is the return on investment?
Why do you need a business plan?
A business plan is not a bag of puffery statements. It is a document with factual information necessary for the survival of a business. You can create a business plan with the right tools or opt for a good business coach to get you started.
Let’s see what Tim Berry , business plan expert, founder and chairman of Palo Alto Softwar and bplans.com , has to say on business plans.
“What I love most about business plans is the business planning: like walking, it’s constant correction and review and revision. Planning, done right, is steering a business, managing growth, aiming the business towards the right future.” – Tim Berry , Small Business Trends
According to a study done by Palo Alto Software, those who create business plans double their chances to succeed in business .
Let us get down to brass tacks and understand why a business plan is super-duper important.
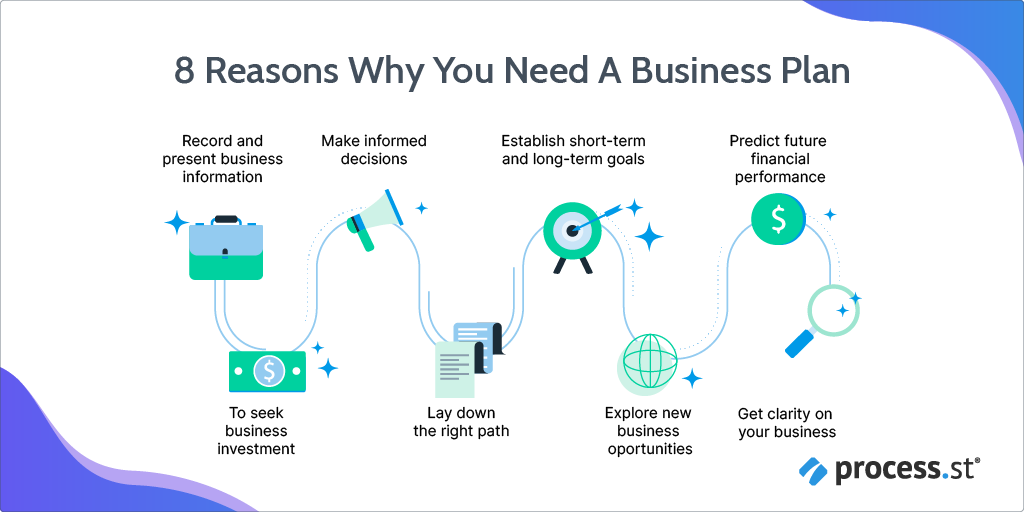
Record and present business information The primary intent of a business plan is to record and communicate information. It must document the business goals and the methods to attain those goals in a structured manner. It keeps businesses on track with their objectives.
A blueprint for seeking business investment ️ Whether you are a fledgling start-up or an established business seeking expansion or diversification, writing a winning business plan acts as a magnet to attract investors. It builds confidence and trust among investors about the lucrativeness of a business idea.
Lay down the right path ✔️ Not everything discussed verbally at an ideation stage transforms into reality in a pragmatic environment. Jotting down a business plan differentiates achievable from impracticable based on market dynamics, opportunities and threats, and company’s strengths and weaknesses. It sets the right track for business growth.
Establish short-term and long-term goals A business plan sets down short-term and long-term goals and the direction to accomplish them, right from baby steps to giant leaps. It becomes a basis to revisit the goals from time-to-time and make iterations depending on the present scenario.
“Any business plan won’t survive its first encounter with reality. The reality will always be different. It will never be the plan.” – Jeff Bezos, CEO of Amazon
Get clarity on your business A frequent question that pops-up in business discussions is: “Are we doing it right?”
A well-articulated business plan brings insightful knowledge on each aspect of a business – from what it has to offer to how to market the offerings.
Make informed decisions A business plan is a reality check to track what is being fruitful and what is causing hindrance. It paves the way to make a business sustainable.
Predict future financial performance Financial projection is the spotlight of a business plan. It’s the carrot that captivates the eyeballs and tickles investors to fund a new business.
A promising business plan talks about the company’s future financial performance – expenditure, profit, revenue, etc.
Explore new business opportunities A business plan is a flexible document that enables learning on the go. It bolsters research and infuses businesses with new and more feasible business opportunities. It gives organizations a fresh outlook and ushers them to be a howling success.
How to prepare for a business plan
Now that we have answered the ‘what’ and ‘why’ of a business plan, let us move forward to solve the next riddle – how do you prepare it?
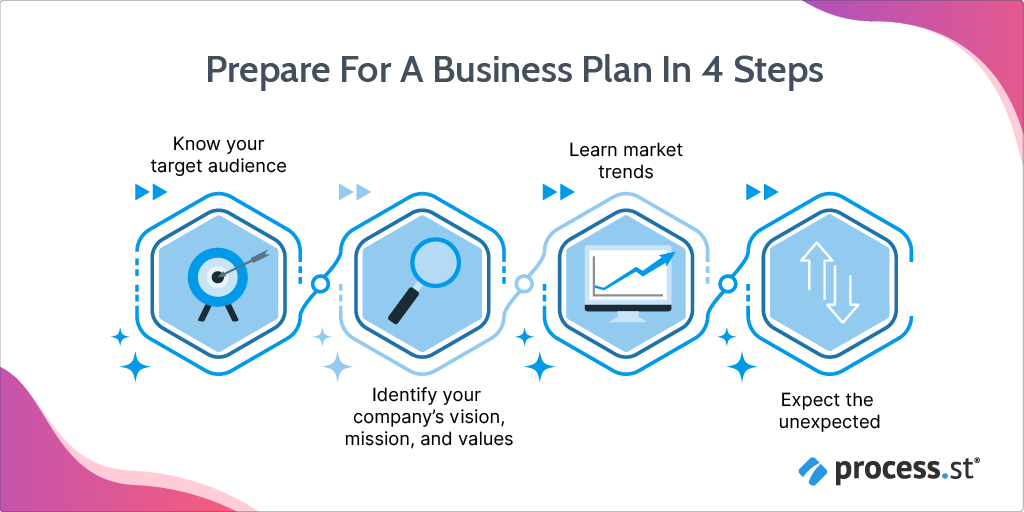
Identify your company’s vision, mission, and values Start by answering and figuring out your business personality:
- What do you desire to be?
- How do you want to be perceived?
- What values put your business in motion?
This is your organization’s compass that acts as a foundation for the succeeding steps.
Know your target audience Dig deep into:
- Whom are you going to cater to?
- What is your target market?
- What is the size and potential of the target market?
- What are the needs of a prospective customer?
- How are the needs addressed presently?
Learn market trends Identifying market trends keeps businesses ahead of the game. Analysis of industry data leads to business growth and profitability in the long run.
Weigh in the impact of unforeseen circumstances From financial turbulence to natural calamities and pandemics – a lot can go wrong in the future and leave a business shaking. Expect the unexpected and gird your loins for these testing times.
How to write a business plan
Creating a winning business plan increases the chances of success and spurs investors to fund your business.
According to a study published in Small Business Economics , entrepreneurs that create a plan are 152% more likely to start their business and appoint a registered agent and 129% more likely to push forward with their business beyond the initial start-up phase and grow it.
Here are the key components of an excellent business plan:
Executive summary First impression is the last impression!
An executive summary is a crucial part of this document. It provides the essence of the whole plan:
- Company details;
- Size and scope of business opportunity;
- A description of your offerings and how it will solve the problem;
- Growth projection;
- Financial requirements.
It should be informative and able to spark readers’ interest to know more about the business plan.
Overview of the business This section lists down information on:
- Your business;
- Your target market;
- Description of your products/services;
- Why and how your offerings are a great fit for prospective customers;
- Your capabilities to handle the demands;
- Your value proposition and competitive advantage.
…and all other related details.
Market analysis and strategies Put forth a strong case built on the solid rock of data analysis and statistics – present data on target market size, industry trends, sales forecasts, and marketing strategy.
Operating plan The operating plan highlights the operational requirements for the smooth functioning of a business. It includes facilities, supply chain management, inventory, manufacturing, shipment, logistics, staff management – everything under the sun that covers capital and expense (CapEx) requirements.
Growth plan This section answers the question: “Where do you see the business going in the next few years?” It provides visibility to investors on the milestones and how you will make money in near future.
Marketing plan Thee marketing plan section describes how to market the offerings to create and fulfill customers’ needs (who are the customers, product positioning, pricing policy, and promotional strategies?)
Management plan This section outlines how your organization is structured and basically how strong you are together. It describes the skills, background, and responsibilities of the management team. It builds conviction that the business is in good hands and has a proficient human capital.
Financial plan and projections This is the part where numbers become the king.
It draws up deets on inflow and outflow of money, sales forecast, profit and loss statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and budget expense. It discloses and forecasts the company’s financial goals, profitability model, and charts a course for the coming years.
Conclusion and appendix Conclude the business plan by succinctly bringing out the key pointers – the business’s vision, mission, goals, strengths, and growth trajectory. Make it compelling and to-the-point. Add relevant appendices to strengthen your business plan.
Pro tip: Use an all-inclusive ready-made business plan template document and Process Street ‘s business plan workflow to create unbeatable business plans.
Business Plan Workflow
Click here to access the Business Plan Checklist!
Types of business plans
There are varying types of business plans depending on the purpose and usage:
- Business plan for start-ups A winning start-up business plan can be a game-changer to attract funding from investors. It should weave all key components to make it a promising investment – company overview, products/services, estimated costs, market evaluation, competition insights, risk analysis, cash flow projections, marketing strategies, and the management team’s strengths.
- Strategic business plan It lays down the details of a company’s strategies to fulfill its goals. It outlines the company’s vision, mission, strategy, and goals, the driving force for success, and the timelines.
- Internal business plan This plan moves the needle and steers focus on in-house planning and growth. It ensures that everyone grasps the company’s overall plan for growth. It prepares organizations to move forward by identifying and removing any blockages and assess and revise the strategies when required.
- Operations business plan It is an internal plan that maps out the nitty-gritties of a company’s operations plans and activities.
- Development business plan This is a development or an expansion plan of a business. It is used for both internal and external purposes. An external growth plan is written to attract investment from external sources. An internal development plan counts on its own business capabilities, revenue, and resources. It works as a guide to provide the right directions.
- Feasibility business plan A company scouts out a feasibility study when it plans to foray into a new venture, new product, or a new market. It articulates: How well will the product or service perform? Is the business promising? What is the expected return on investment (ROI)?
- What-if business plan At a point where you face unordinary conditions, you need a variation on the existing plan. A what-if business plan arranges to fall back on a contingency plan when things go sideways. For example, an unexpected surge in demand, new competition, drop in market size, etc.
A business proposal is the mantra that draws you closer to win a customer or bag a project.
Generally, it is a formal response to a Request for Proposal (RFP) sent by a prospective client looking for the right solution to their problems. It explains the particulars of a seller’s offerings and convinces the buyer that the proposed solution is the gateway to their business’s success and productivity.
“And, after all, winning business is what writing proposals is all about.” ― Tom Sant, Persuasive Business Proposals: Writing to Win More Customers, Clients, and Contracts
A business proposal comprises of four main points :
- What are the challenges of prospective clients?
- How can our solution solve their problems?
- Why should they choose us over others?
- What are the best pricing options available?
Why do you need a business proposal?
A business proposal is a testimony in itself that asserts, “I am the best you can get.”
Here are the reasons why you should and must make a business proposal :
- Create or leverage a business opportunity The prime motive is to win, win, and win! It is a medium to encash a business opportunity by putting forward an I-can’t-say-no-to-this proposal.
- Stand out from the competition It persuades the prospects that you are way ahead of other rivals in the industry in terms of the value you offer.
How to prepare for a business proposal
The heart of preparedness is research and further research. After all, the devil is in the details.
Talk to prospective customers, visit their website(s), read published articles, and be a know-it-all for your prospective clients.
Sort out the ‘who’ First and foremost, dig every possible information about the client:
- Who is the client (its vision, mission, and goals)?
- What does it produce?
- What are its key markets and target customers?
- What are its business growth plans?
- Which markets is it presently serving?
- Also, figure out the kingpins of a proposal approval process. This will help you to create a comprehensive proposal with all the necessary answers expected by the decision-makers.
Understand the challenges Find what’s bothering them and what is causing hindrance to their business success. Learn about their existing solution and its challenges.
Stitch the glitch and offer the best solution After a thorough review of all the points mentioned above, find the best solution to your prospective client’s problems.
List down key differentiators This will help you to beat the competition in the dust. It draws a comparison chart and puts you in a superior position.
According to Gray Mackenzie, founder of GuavaBox ,
“Prior to submitting a proposal, make sure you have clearly defined all the major points verbally with the potential customer. By discussing the scope, cost, timeline, and details prior to submitting a written proposal, you can uncover objections earlier in the process.” – Gray Mackenzie, 10 Sales Experts Share Their Best Business Proposal Tips
How to write a business proposal
Let’s get down to the fundamental elements that form a business proposal. Learn how to create a business proposal that stands out and close sales.
Title page/Cover page The name says it all.
Pretty easy-peasy thing to understand, right? After all, you have been creating the title pages since school days.
Still, make a note: Always write a gripping title that intrigues prospective clients’ interest and urges them to read on.
Other components that should be included on the title page are:
- Your company name and logo;
- Prospective customer’s name;
- Submission date.
Table of contents (TOC) As the name suggests, a TOC is a well-structured layout of the document. It helps to skim and scan and navigate speedily through different sections of a business proposal.
Executive summary It sets the tone for a proposal and makes the reader inquisitive about reading subsequent sections. It sums up the entire business proposal – the purpose of sharing the proposal and why and how your solution is the right fit for the prospective client. Leave no stone unturned to boast about your offerings in the executive summary.
Details of offerings This is an in-depth description of the products or services your company has to offer.
How will the offerings solve the client’s problems? This explains why your products/services are the right fit to address a prospective client’s needs and why it is a better alternative than the competition.
The methodology/implementation of offerings This section is a blanket explanation of how the promised deliverables will be executed. It provides step-by-step clarity on each action along with timelines. It gives the client peace of mind and builds trust and confidence in the offering.
Pricing, payment, and legal matters Here, you talk about the pricing structure, applicable taxes, payment schedule, cancellation policy, and how you plan to solve the legal matters (if any arise in the future).
Here are some tips for this section:
- Ensure that the pricing details are concise and complete.
- Providing a comparison chart with different pricing options helps to make decisions faster.
- Don’t go overboard with pricing, and also, don’t underrate yourself.
- Always refer to the RFP and verify if every request has been fulfilled.
- Separate out and create a new legal section if your business demands an extensive list of legal requirements.
Details about your company This is an exhaustive overview of your company. Don’t forget to add relevant customer testimonials, case studies, or success stories to build your case among prospective customers.
Signatures and Call to action This is the moment that gets butterflies in your stomach; the closure. This is the concluding part of a business proposal. Here (if all your prayers get answered), you and your client sign the proposal and secure the deal. Hurray!
Pro tip: Once you send the business proposal, don’t sit idle in your cocoon day-dreaming of winning the proposal. Always proactively do follow-ups with the prospective clients and clarify their doubts.
For start-ups or small businesses, drafting a business proposal can be an unnerving experience. They work fingers to the bone to write a perfect business proposal. Spending too much time on it might lead to missing the deadline and eventually losing out on a golden opportunity.
According to a report by Better Proposal , sending a business proposal within 24 hours increases the likelihood of winning the deal by 25%.
Here’s the secret sauce to speedily create flawless business proposals :
First, pick a professionally vetted and ready-to-use business proposal template and draft a business proposal like a cakewalk. Such as the Business Proposal Template included below.
Next, always use Process Street ‘s super-powered business proposal template checklist and ensure no step gets missed in the process.
Business Proposal Template Checklist
It even turns out a blessing for big businesses since they have to draft multiple proposals all the time. Templates and checklists save a lot of time, enhance productivity, and increase the chances of success.
Types of business proposals
Majorly, there are two types of business proposals:
Solicited business proposal Also known as an invited business proposal, it comes into play when a buyer, or a company, outlines its requirements and requests suppliers to present an offer. It can be a response to a public tender issued by big corporations or government agencies.
Alternatively, a solicited business proposal can also be submitted as a response to the RFP shared by a prospective client.
The difference between the two is that while the earlier one is open to all bidders, the latter’s scope is limited as it is shared with shortlisted suppliers.
Pro tip: Do a thorough check before submitting an invited business proposal. Missing out on-minute details can kick you out from their consideration list.
Unsolicited business proposal An uninvited or unsolicited business proposal is a proactive attempt to create a business opportunity. This proposal is sent to prospective clients without being asked.
The good news is, there are slim chances of your rival sending a business proposal simultaneously, so less or no competition.
The bad news is, it might breathe in the customer’s inbox for a few days and then, without being read, depart to the heavenly abode -the trash folder.
But still, like a cold call, it leaves some impression on prospective clients and shoots up the chances to cut a deal in the long run.
Pro tip: An unsolicited business proposal is mostly sent through emails. Make certain to write an attention-grabbing headline and a convincing explanation to draw attention.
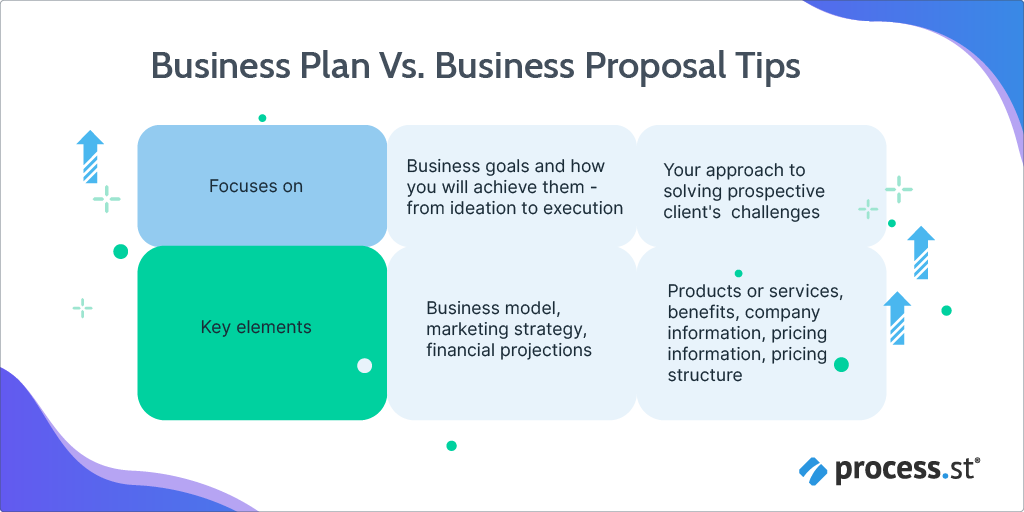
Here’s a comparison chart that distinguishes between business plan and business proposal:
Bonus: How to make ‘wow’ business plans and business proposals
Here are the secret ingredients to make awesome and captivating business plans and proposals:
Follow the principle of KISS (Keep it simple, silly)
This is not the right place to brag about your vocabulary skills. You want the prospective customer to focus on reading rather than wasting time looking up for a word.
Always remember! Communication is the key.
So, go simple and ditch those heavy jargons.
Don’t wear-out the pupils of your prospects with long-winded documents. Capitalize on the multisensorial abilities of humans as well.
Visuals increase people’s desire to read content by 80%.
Leverage the power of visuals and make your document easily graspable by adding graphs, infographics, flowcharts, tables, images, and videos.
Add social proof
Do not forget to add positive feedback or customer testimonials. If similar projects have been delivered in the past, do add relevant links and case studies of that work. It helps to build trust and strengthen your case.
“Make sure you have great success stories that you can share with potential clients. At the end of the day, most, if not all, potential clients want to know you will provide value to them and generate positive ROI.” – Mathew Bivens, Podcast and marketing consultant, 10 Sales Experts Share Their Best Business Proposal Tips
Proofread ️
Ensure the document is free from grammar and spelling errors.
Follow brand guidelines
Your document should reflect your brand. Bring consistency in all your documents and design them as per the brand guidelines.
Use document builder tools ️
Time is money!
The likelihood of getting a ‘yes’ on your business plans and business proposals depends on how fast you can create a flawless document.
Empower your organization with a smart and all-in-one document builder tool like Revv – create, communicate, collaborate, and close your documents in no time.
Business plans and business proposals are two different worlds with distinct purposes and goals. But, both play a prime role in increasing the odds of business success.
People often get the wrong end of the stick and ask for a business plan when they mean business proposal or vice-versa.
But, we don’t need to worry about that since we are now clear on what is what.
Cheers to us!
P.S: Don’t forget to subscribe to the Process Street blog to get notified of our upcoming articles. We also have a podcast “Tech Out Loud” featuring content written by respected industry leaders such as Peep Laja , Sujan Patel , Tomasz Tunguz , and more!
What is your take on business plans and business proposals? Have you ever got your wires crossed with these two terminologies? Don’t forget to post your comments below.
Get our posts & product updates earlier by simply subscribing
Molly Stovold
Hey, I'm Molly, Junior Content Writer at Process Street with a First-Class Honors Degree in Development Studies & Spanish. I love writing so much that I also have my own blog where I write about everything that interests me; from traveling solo to mindful living. Check it out at mollystovold.com .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Take control of your workflows today
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Plans
How to Write a Detailed Company Profile for a Business Plan
If you own a company, the only way for people to have a quick preview of what your company is all about, the products or services you offer, and who are the owners of the company is through your company profile. This section of your business plan will fundamentally answer two important questions:
- Who are you?
- What do you plan to do ?
Answering these questions in a succinct and simple manner would provide an ample introduction of why you are in business, why you are different from the competition, what you have going for you, and why investing in your business would be a good bet.
In essence, if you want to introduce your company to potential clients or to organizations calling for bids and submission of proposals, then you must have a detailed and self-explanatory company profile.
Interestingly, there are several business doors a good company profile can open. For example, an angel investor who is looking to invest in a business would naturally read through the profiles of all the companies he or she is interested in.
The company profile that catches his or her fancy would no doubt be the company he or she would invest in. This is just a bit of what a good company profile can do for a business.
This section of your business plan also offers you the opportunity, if you haven’t done so before, to evaluate and document the intangible facets of your business principles, ideals, and cultural philosophies that will allow you to better grasp your own corporate identity. Here are the necessary components that should go under your company profile:
What is a Company’s Profile?
A company profile is a formal introduction of your business. It usually contains all you would want potential clients, investors, and the general public to know about your business. It is used as a marketing tool and it is your company’s unique selling point.
A complete company profile is expected to contain the vision, mission, and goals of the company, a detailed description of the product and service offering of the company, the profile of the founding members of the company, a brief story of how the company got started and what they intend to achieve. So also, information like company name, address, phone number, website and email et al must be part of your company profile.
Components of your Company’s Profile
- Structure of your business ( sole proprietorship, general partnership, limited partnership, or an incorporated company )
- The date your business was established ( for existing businesses )
- The nature of your business ( what are you selling, or what are you planning to sell ?)
- The industry you are in
- Business vision, mission, and values
- Background information on your business or its history
- Business Objectives ( short and long-term )
- The Business team
Now, let’s discuss tips for tackling some of the more tricky components in the list above:
If you are looking forward to writing a top selling company profile, then the following guide will come in very handy for you.
Study Other Company Profiles
The first step when it comes to writing a good company’s profile is to study other profiles. To better put it, you should go source for companies that are doing the same thing as your do; companies that are selling the same services or products as you do.
If you study their profiles properly, you will be able to have a clear-cut idea of what you should capture in your own profile, and of course, you will be able to improve on it to make yours better.
Please note that you are not expected to plagiarize any company’s profile when writing yours because you can be sued for plagiarism.
Create an Outline
The next step to take after you must have carefully studied several companies’ profiles is to create an outline of your own profile. You can start this by making use of bullet points to highlight the main points you want to make in your company profile.
You should also figure out the angle you want your readers to see your company from, what your company represents, and of course the caliber of people that formed the company et al. This will help you determine what information you need to gather.
Interview Potential Clients
If you truly you want to capture information on your company profile that will resonate with your potential clients, then you will need their inputs. Some of the ways you can get their input is to interview them or via questioners and surveys.
Please make sure that you are prepared with your questions but also be ready to follow the natural flow of the conversation. Ask questions during your meeting that you think readers will want to know.
Pose questions that will encourage your potential clients to give you useful information. Ask them to share anecdotes. Avoid yes or no questions. You want them to open up. Make sure to record and transcribe the entire interview.
As you review their answers on paper or on your computer, highlight the best quotes that can guide you to describe and give reasons why your products or services will better serve them.
Start Writing Your Company Profile
Once you are done with gathering the information that will aid you in writing a fantastic company profile, what is left for you is to start writing. You can settle down in your study, library, hotel room, or any location that will give the concentration that is needed for this all important task.
Although a company profile is not expected to be a large document, but it should capture all that your company represents, the products and services your company offers, and of course all that you want people to know about your company. This information can be captured in a simple and easy to understand format.
Put Your Best Foot Forward
No matter how fantastic your company is especially as it relates to your product and service offering, there will still be some drawbacks that can dissuade potential clients from patronizing your products or services.
For example, if you have someone who has been involved in financial crime in time past as a founding member of your company or a financier of your company, it will not be a wise decision to capture such a person in your profile.
What is expected from you when writing your company profile is to put your best foot forward by projecting people without any controversy around them.
Please note that your company profile is supposed to capture a brief profile of the board of directors, executive members, and key persons that are part of the company.
Edit and Edit
After you have finished writing your profile, you should make sure that it is properly edited. You can contract the editing to a professional. Although it is going to cost you a bit, but trust me, it is worth every cent you will spend.
Please note that you shouldn’t just settle for just one editor, you can give it out to two or more editors to edit until you get a perfect piece. This is important because a good company profile will easily sell your company (products and services) to potential clients with little or no additional effort from your end.
In Conclusion;
A company profile is an essential part of a business plan and a business plan cannot be complete without a company profile. So, when writing your business plan, make sure you come up with a good and highly sellable company profile, and the guide you have here will help you achieve this.
More on Business Plans
What Is a Company Profile? (And How to Write One)
Whether you’re creating content for an established business or a startup, a company profile should be part of your plan. In this post, we’ll discuss what a company profile is, and how to write one.
A company profile can be an effective way to highlight the business to customers or stakeholders. And you’ll quickly find that it is a vital part of business communication.
It’s a way to state what your business stands for, what your goals are, and where you place your focus. As well as featuring all the practical information that anyone might need to know about your company.
2 Million+ Digital Assets, With Unlimited Downloads
Get unlimited downloads of 2 million+ design resources, themes, templates, photos, graphics and more. Envato Elements starts at $16 per month, and is the best creative subscription we've ever seen.
Web Templates
Landing pages & email.

Graphic Templates
Logos, print & mockups.
Icons, Vectors & More
Presentation Templates
Powerpoint & keynote.

Sans Serif, Script & More
CMS Templates
Shopify, tumblr & more.
Explore Digital Assets
What Is A Company Profile?
A company profile is a professional introduction to your business. It informs potential customers, stakeholders and the general public about your products, services, and business as a whole.
A company profile can be anything from a few sentences to an entire page on your website – most businesses have a long and short version – and is a good way to differentiate yourself from other businesses.
Why Is It Important?
A company profile is important for several reasons. It is a set of guiding words that describe your business.
Use it to shape how employees talk about your company and present a cohesive and consistent vision of the company to people outside of it.
A good company profile will get used frequently. These words can be copy and pasted into all kinds of other documents – grant applications, social media profiles, websites, professional directories and more.
A well-written company profile communicates three key things:
- It persuades others to interact and engage with your company. The profile should entice people to learn more.
- It includes contact information to build business credibility and tell people how to get in touch with your business.
- It tells your company story and sets a vision for the future. It should mention where you’ve been and where you are going.
How to Write a Company Profile
When it comes to actually writing a company profile, start with a plan.
- Outline a purpose. A company profile will get used in a lot of places. Outline what you want each audience to know and tailor the writing to match.
- Pick a style that matches your brand. Your company profile should read like the other elements on your website. Use the same voice so it feels like it belongs to your company.
- Highlight your mission and tell a story. A well-written company profile often has a narrative that makes people want to know more.
- Include plenty of relevant information at a glance. While the company profile might include a few paragraphs of narrative, you can also use bulleted lists to highlight products or services or key company information. Also, make sure to include a block with contact information and links to your website or social media profiles.
- Spellcheck and edit several times. Nothing is worse than a company profile with errors in it.
Once your write a company profile, you’ll likely edit to a couple of versions:
- Long version for applications and business documents
- Short version for quick introductions or descriptions
- About us page on your website version that includes the full company profile
- Tiny version for about lines in social profiles
Where Will You Use a Company Profile?
You will get a lot of mileage out of a company profile. The great thing about having this description written and ready to go is that you can make small tweaks to use it almost anywhere you need to post business information.
Using the company profile as a starting point will ensure that you post consistent business listings everywhere you provide information.
This includes in web and print materials distributed by your company, as boilerplate content for media and press releases, as descriptions for team members when they have speaking engagements, on social media in profiles for Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and LinkedIn, in job descriptions and applications, and anywhere you need to tell people about your business.
A company profile is an important element in your overall brand strategy.
Don’t Be Afraid to Design Your Own
While most of the focus is on writing a company profile, the design matters as well.
While you can’t always dictate what a company profile will look like, you can design it on your website or print pieces.
Don’t overlook this important part of your overall design. Too often, company profile pages are stripped down and look like an afterthought rather than a key element in the design. (Did you know that About pages are some of the most read on the web?)
Stick to trusted design principles when planning how company profile information will look.
- Add visuals that relate to your company. Use images of products or services or team members in action.
- Use white space to your advantage.
- Format intentionally and use the same structure as the rest of the design.
- Show off with testimonials, awards or fun company information.
- Organize content into logical sections that are easy to read at a glance.
Every company – no matter how big or small – can benefit from having a strong company profile. This language will get used everywhere and helps establish consistent messaging for your company or brand.
Having a strong company profile will save you time and effort in the long run because you will have a set of guiding words that you can use time and time again to describe your business, product or service.
Difference Between a Business Plan & a Business Proposal
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Why Create a Business Plan?
How to rescind a business letter, 6 types of business plans.
- How to Create a New Business Plan
- How to Conclude a Business Plan
A business plan and a business proposal are very different documents, with different purposes and goals. A business plan is a factual broad description of a company on the executive and operational level. A business proposal is a focused sales document intended to describe how a company will approach a project, state the value of the project to the client and solicit the client's business. A business plan is a written presentation of fact. A business proposal is a quote and call to action.
Reasons for a Business Plan
A business plan documents your vision for your business and how you intend to achieve that vision. It contains financial projections of what the business will cost to develop and operate plus an estimation of the revenues to be generated. Its purpose is to provide a reasonably detailed explanation of your business for use by potential investors, suppliers, prospective employees, accountants, attorneys and other people who need a quick but comprehensive understanding of what your company does and its potential for success. The primary reason for a business plan is to record and convey information.

Reasons for a Business Proposal
Proposals may be unsolicited business ideas presented to a potential customer or partner, or they may be answers to requests for proposal submitted to your company by a potential client. They are limited in scope to a particular project or need. A business proposal also generally has a specific audience. The primary reason for a business proposal is to solicit or develop a business opportunity.
Business Plan Structure
A business plan has three elements: description of the business model, the marketing model and financial projections. It consists of informative sections, including the executive summary, business description, marketing model, analysis of industry competition, build-out plan, operations plan, introduction of management, and a discussion of financial issues and projection of results. It is introduced by an executive summary, which can be a dense abstract or a longer marketing tool to attract interest in the business plan. The business plan is an informational document designed to factually display your company's operations and potential.
Business Proposal Structure
A business proposal written in response to a Request for Proposal (RFP) should follow the format requested in the RFP. Generally, this involves a quick description of your company's services and products that are relevant to the goals of the RFP, a reiteration of the scope of work, answers to specific questions posed in the RFP and a quote detailing materials, tools, labor, delivery and other elements of the cost of the project.
An unsolicited business proposal intended to create and develop a business opportunity follows essentially the same format but anticipates questions the potential client might have. A proposal is more of a marketing document, designed to convince the audience to do business by presenting a value proposition and a call to action.
- Entrepreneur: An Introduction to Business Plans
- Forbes: The Difference Between a Business Plan and Planning
Victoria Duff specializes in entrepreneurial subjects, drawing on her experience as an acclaimed start-up facilitator, venture catalyst and investor relations manager. Since 1995 she has written many articles for e-zines and was a regular columnist for "Digital Coast Reporter" and "Developments Magazine." She holds a Bachelor of Arts in public administration from the University of California at Berkeley.
Related Articles
5 types of business documents, what does a business plan consist of, the importance of a business plan, what is the relationship between the business plan, marketing plan & sales plan, examples of business feasibility reports, the differences between a business plan & business model, reasons to convert a pdf to microsoft word, what are the six elements of a business plan, mission statement vs. executive summary, most popular.
- 1 5 Types of Business Documents
- 2 What Does a Business Plan Consist Of?
- 3 The Importance of a Business Plan
- 4 What Is the Relationship Between the Business Plan, Marketing Plan & Sales Plan?
Business Plan and Proposal: Everything You Need to Know
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
A business plan and proposal are two different documents with two different purposes and functions. A business plan is a document that clearly spells out how a business intends to realize its objectives and goals, while a business proposal is a sales document that a business entity uses to request a contract from a client.
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
A business plan and a business proposal are different from each other by content, goals, writing style, and structure. The major difference between both is that a business plan is a document that presents facts, while a business proposal is a request for a deal and a quotation of prices.
A Business Plan
You can think of a business plan as the documentation of a company's grand vision. Business plans are naturally tactical. It's like stating where and when you want to start, when you want to get to the next point in view, and how you intend to accomplish that progress. A business plan includes descriptions of how the business is intended to run, the details of financial goals, possible business rivalry, marketing strategy, executive summary, and other factors that affect a company's planned business growth.
A business plan is particularly effective in making potential investors interested in a company (especially a startup company that's yet to make a name in its industry). Additionally, a business plan can provide an idea of what a company requires for professionals such as attorneys, accountants, and potential employees. A business plan distinctly describes the scope of the business, and in so doing, clears your thoughts as a business owner.
The business plan should be honestly made because it's the outline of the company's vision. It indicates whether or not the business goals of the company are realistically achievable. Experts say an effective business plan would take approximately six weeks of thorough research and groundwork to create. In other words, you typically can't create an effective business plan in one day, present it to potential investors the next day, and achieve desired results.
A Business Proposal
A business proposal goes to a prospective client directly from an established business. It's an attempt to sell a business entity's service or product to a client, and not an attempt to sell the business itself. Also, a business proposal isn't an estimate. Though costs and certain other details will be provided in the business proposal, an estimate is a lot more unofficial and simply a provision to skim over the costs. It doesn't present the entire picture.
Basically, business proposals show a particular idea, such as a new, profitable undertaking. The proposal is intended to get investors to support the particular business endeavor being suggested. For instance, a well-known eatery chain may wish to extend its business to a nearby state. Such an eatery would have to compose a business proposal in order to get the financial support of its target investors.
Though the business proposal provides an overview of what the company does (similar to a business plan), its major objective is to provide the details of the suggested business idea, including providing answers in advance for any concerns that could be raised by potential investors.
Components of a Business Plan
Basically, a business plan has three components: business model description, sales tactics, and financial goals. However, more elaborately, it has the following sections of information:
- Executive summary
- Description of products and services
- Industry analysis (analysis of possible business rivalry)
- Marketing strategy
- Operating plan
- Structure of leadership
- Internal analysis
- Built-out plan
- Introduction of management
- Financial goals (deliberations on monetary concerns, and how to address them and achieve expected results).
Solicited vs. Unsolicited Business Proposals
A solicited business proposal, when presented in response to a request for proposal (RFP), should be in the format requested by the client in their RFP. The same format may or may not be used for an unsolicited business proposal. Its purpose is to suggest and develop a business idea. Therefore, it's recommended to use the same format or some other format that's well-known in the field of endeavor.
An unsolicited business proposal offers a business entity the flexibility to choose what structure they deem appropriate. However, the proposal is expected to meet industry standards, no matter what format is used. For instance, it should emphasize major areas of interest, be thoroughly researched, offer a proposition of value, and feature a call to action.
If you need help with a business plan and proposal, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Business Proposal Ideas
- Comparison Between Business Proposal and Business Plan
- Business Contract Proposal
- Business Proposal Introduction
- How To Write A Business Proposal
- Writing A Contract Proposal
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Sample of a Good Business Plan
- Service Business Plan
- How to Contact Companies for Business
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
Quickbooks Sync and compare with your quickbooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how it works →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth and investor readiness
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
- May 15, 2024

When you start a new business or own a young company, you often hear terms like business plan or business proposal. But the question is: do you need a business plan? Or is it a proposal that you need? Or both?
Being new to the game, these terms can seem quite intimidating, and you probably don’t know where to start.
Don’t worry. We’ve created a simple business plan vs. business proposal comparison so you can determine which one to prioritize.
Let’s start by defining them!
What is a business plan?
A business plan documents a company, its business objectives, and how it plans to achieve them. It includes data regarding business goals, marketing strategies, products, services, market research, financial projections, and the dream team.
Pretty much everything a company will use to achieve its intentions.
Okay! And what about the business proposal?
What is a business proposal?
On the other hand, a business proposal is a document that describes your business’s offerings, like a product or service, to help you win potential clients and partners.
It also outlines your business, including its unique value proposition and how your company can help solve customers’ specific problems.
Now that we know the two business documents aren’t the same let’s see how they are different and in what ways.
Business plan vs. business proposal: How are they different?
Even though used interchangeably (and wrongly), a business plan and proposal are poles apart. Here’s how:
Before you ask why you need a business plan , it’s, first and foremost, to legitimize a business idea that you’ve been brewing in your head.
But it’s also to document company strategies, objectives, and operations that help you create a clear idea on how to achieve your company goals. All that data becomes one source of truth that works as a communication tool. That becomes your golden ticket to wooing investors and lenders.
On the other hand, a business proposal’s purpose is entirely about convincing a potential client and partner that your project is worth their time and money.
Unlike a business plan, it only focuses on a specific product, service, or opportunity instead of the entire business.
Create visually appealing business plans with our
AI Business Plan Generator
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Components and Structure
When you write your business plan , it will typically follow a specific structure containing the following components:
- Executive summary: This summary summarizes your entire business plan, highlighting the most important aspects, such as your company’s mission, financial projections, and vision statement.
- Company description: It reveals your company’s history, mission, value proposition, detailed description of products and services, achievements, and target market.
- Industry or market analysis: This is an analysis of the industry landscape to gain statistics about market needs, size, trends, competitors, and target demographics.
- Marketing plan: This includes different marketing strategies and approaches your company will take to market its products and services. It can be your pricing strategy, sales and distribution plan, and unique selling proposition.
- Operations plan: This component reveals how a company’s operations would look on a day-to-day basis.
- Organizational structure and management team: This section provides an overview of your company’s structure and how its management teams will execute the operations plan effectively.
- Financial projections and goals: This section contains a company’s financial performance, including income, sales goals, cash flow projections, and balance sheets.
Similarly, when you write a business proposal , you’ll typically encounter a structure as well. It goes like this:
- Cover or title page: To make a first impression. It can contain aesthetic visuals.
- Introduction: To introduce yourself and your company. Also, briefly explain how your product or service will solve a specific problem.
- Statement of the problem or project: To explain your understanding of the customer’s need, its importance in addressing it, and your right-fit, proposed solution.
- Table of contents: To make your data essay accessible.
- Project details: To communicate essential data, including objective, scope, timeline, key stakeholders, disclaimers, cost, and conclusion.
- Agreement with a signature box: To obtain the client’s signature.
3. Audience
A business plan’s target audience is internal stakeholders, investors, and lenders interested in your company’s long-term goals and path to success.
On the flip side, business proposals go to potential clients from established businesses. They target external or new clients, partners, or funding agencies with a specific focus on:
- Addressing customer needs
- Solving customer problems
- Or seizing opportunities
Do you know how many types of businesses exist today? Two words: Too many!
Now, that implies there are many different types of business plans. But here’s a quick list of the most common types:
- Startup business plan: This plan describes the foundation of a new business with room to adjust as the company grows. It’s given to potential investors to ask for startup funding.
- Internal business plan: In this plan, company leaders communicate business goals, strategy, and performance. The aim is to keep the board and the team in sync regarding business objectives.
- Strategic business plan: This plan documents the framework required to keep long-term goals and company vision intact.
- Growth business plan: Also known as an expansion plan, this plan describes how a company is trying to grow and hence requires greater resources like more employees, funds, materials, etc.
Business proposal types can be broadly divided into two categories:
- Solicited business proposals: In this case, a prospective client requests the informational document from you directly or expects to receive it—implicating their interest in your products or services.
- Unsolicited business proposals: Here, no client requests the documents. Instead, you take the cold email approach and send your unsolicited proposals to people you think are prospective clients or partners.
Business Proposal and Planning Best Practices
It’s already challenging to overcome market entry barriers in saturated markets and persuade potential investors. Creating a compelling business proposal and plan shouldn’t be too!
Here’s how to go about it:
- Clearly define your business goals and objectives.
- Make sure you get your audience right. (Business plans and proposals have different audiences, remember?)
- Conduct in depth research and analysis.
- Use pictures along with words, such as visuals and statistics, to support your claims and projections.
- Pay attention to the writing style, structure, and tone depending on your audience and purpose.
- Use software like an AI business plan generator or proposal templates to save time and effort.
- Review and revise regularly.
Start creating effective business plans and proposals using Upmetrics
It’s okay if you were confused about the difference between a business plan and a proposal before today. You now know the distinction between the two lies in their purpose, components, structure, audience, and type.
While a business plan provides a thorough overview of the entire business and targets internal stakeholders, investors, and lenders, a business proposal focuses on specific projects or opportunities and targets external clients, partners, or funding agencies.
When you understand these differences and employ the best practices in creating both documents, your business can effectively communicate its vision, strategy, and value proposition, securing a solid spot in this competitive world.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a business plan and a business idea.
A business idea is a concept’s initial spark for a product, service, or opportunity. However, a business plan is a detailed document outlining how a business idea will be executed and managed.
How many pages is a business proposal?
A good proposal is 10-20 pages long. However, it can be longer based on the industry, buyer requirements, product or service type, the scale of buyer needs, and other aspects unique to the business.
What comes first, a business plan or business proposal?
The business plan comes first since it legitimizes a business idea. Then comes a proposal because it’s specific to a particular project or opportunity and not the business as a whole.
Do I actually need a business plan?
A business plan is a detailed roadmap for your entire venture. It helps you gain investments, beat competition, make sound decisions, communicate with stakeholders, and identify risks. So, yes, you need a business plan.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Business Profile Layout Example
by Cynthia Clark
Published on 26 Sep 2017
A business profile, also called a company profile or business introduction is written in a narrative form that outlines the key elements regarding the specific business. Although the business profile serves a purpose similar to a resume of the company, it appears more like a summary.
Profile Uses
A business profile provides the public with basic information about the business, and highlights its strengths in the marketplace. The profile is used as one part of a business plan, and can appear on the company website and other marketing literature, and is included in bid or proposal packages. The business profile is also a useful part of a public relations (PR) kit for circulation to the media.
Technical Format
There is no one, single format recommended for use with a business profile. There are however a number of similarities among recommendations. The business profile can be tailored to the industry, size of company and intended purpose of the profile.
Key Information
The business profile includes the legal name of the corporate entity, and full physical address information. The market and industry are mentioned along with the history the company has had in this field. If it is a new company, the experience of key personnel in the industry are highlighted. The profile may mention the number of employees and mention some corporate financial information. Industry certifications and success stories help solidify information regarding the company's abilities.

- How It Works
- Integrations
The difference between a business plan and a business proposal
Whether you are in business, employment, or college pursuing a degree, understanding the basics of a business proposal is a skill that you must have. Most people use the terms business plan and business proposal interchangeably. These two documents are very different. A business plan is different from a business proposal in terms of content, structure, writing style, goals, and purpose. The most important difference to note is that a business plan is a written presentation of fact while a business proposal is a price quote and a call to action.
According to an article on Entrepreneur.com , a business plan is a document that outlines a detailed description of how a business is set up. It is a 5-year plan of a business showing the company structure, products and services, market findings from research, marketing strategy, planned budget and financial projections. It can be simply defined as the factual and wide description of a business and its projections. A business plan can be drawn by a start-up as well as a going concern.
A business proposal is a purposeful sales document formulated to illustrate how a business will carry out a project, give the value of the project to the prospective client and ask for the client's business. Therefore, it is a document that a business submits to another enterprise or organization putting forward a business arrangement.
A business plan ideally comprises three elements: description of the business model, the marketing strategy and financial projections. It includes informative sections, specifically the executive summary, business description (products and services), marketing plan, industry analysis (competitor analysis), build-out plan, internal analysis, operations plan, leadership structure or introduction of management, and financial projections -- discussion of financial concern and projection of results. The opening page is the executive summary. It can be an intense abstract or a detailed but precise marketing tool to draw interest in the plan. The business plan is an informational document intended to factually showcase the company's operations, goals and potential.
According to Sean Kerner from Tech Republic, the format of a business proposal depends on whether it solicited or unsolicited. A solicited proposal and in response to an RFP should take the format called for in the RFP. Usually, this entails a quick description of the services and products offered by your business and clearly showing their relevance to the goals of the RFP, a replication of the scope of work, response to specific questions raised in the RFP and a quotation detailing materials, equipment, labor, delivery and other basics of the project outlay. An unsolicited business proposal may or may not take the same format. The intention is to create and develop a business opportunity, and so it is advisable to follow the same format or any other that is popular with the industry or business. Be keen to address all the questions that the potential client might have. With an unsolicited proposal, it is up to you to decide the structure. Whichever format you choose, ensure that the proposal is professional, highlights key areas of interest, presents a value proposition, is thoroughly researched and loaded with facts and with a call to action.
A business plan is required for two main reasons. It clearly defines the scope of the business and in the process clarifies your thinking as the proprietor of the business. It offers you information that had not been considered previously. Simply put, it documents the vision of the business and how it will be achieved. This guides the business towards a practical strategy to guide the business for the time-frame enclosed by the plan. It is the blueprint to success of the business. It outlines strategies for converting the ideas into core competencies. It also presents the financial projections of starting and operating the business as well as estimation of revenue generation from business activities. Secondly, it offers comprehensive business information for use by potential investors and employees, suppliers, accountants, attorneys and other stakeholders. The primary function for a business plan is to record and pass on information.
A business plan is also used to raise funds in form of a business loan, venture capitalist, angel investors or incubation. When approaching these money lenders you must present a thoroughly researched and realistic business plan. The investors need to be sure that you are confident and truthful about the market statistics and financial projections indicated in the report. A business plan should be as truthful as possible because it is the blueprint and vision of the company. It provides a checklist of whether the objectives of the business are on track. According to experts, a professional business plan requires about six weeks of in-depth research and preparation. It is not possible to whip one a day before your appointment with investors.
The reason for a business proposal can be well explained based on the type of the proposal. There are two major types of business proposals: invited and non-invited. An invited proposal is submitted in response to an advertisement from the buyer or client. For instance, organization and government agencies wanting to purchases services and products from private suppliers invite contractors to place their bids. Alternatively, some businesses ask for Request for Proposals (RFP) from a selection of suppliers that they willing to consider as a prospective partner. In each case, the business is competing against other bidders. It is in the interest of your business to present a competitive and compelling business proposal.
Non-invited or unsolicited proposals are submitted to potential clients even when they have not requested for one. In this scenario, you give suggestions to the company or organization to purchase services or products in return for funds. For instance, you can tender a proposal to develop an app for an organization or training services for its staff. The most important thing in both cases is to come up with well researched offer to convince buyers. A business proposal is limited to the scope of the specific project or need. In addition, it has a specific audience. The primary function for a proposal is to solicit or grow a business opportunity.
You can look a business plan as more of an internal document. A proposal on the other hand is an external document used for presenting or selling the business to an external player. A business plan guides the activities of the business internally in terms of marketing strategies and revenue projections that should be achieved. A proposal shows the external players such as governments, donors or business partners what the business is all about and how it intends to carry out a project at hand or use the opportunity to generate revue for both partners.
For more information, here is an article on how to write a business proposal .
Entrepreneur.com: An Introduction to Business Plans https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/38290
Win more clients by creating impressive digital business proposals, price quotes, and contracts using ClientPoint Software
If you want your business proposals, price quotes, and contracts to stand out above your competitors and give you the best chance at winning new clients, use ClientPoint's Proposal Software . It makes creating and formatting professional business proposals, price quotes, and contracts fast and easy.
Related Readings
Proposal writing tips, a business proposal checklist to help you win more clients, 8 reasons why paper-based business proposals are dead and digital business proposals are superior, what is a business proposal and how to write it for b2b sales.

Headquarters
6790 Embarcadero Lane Suite 100 Carlsbad, CA 92011
Contact Info
- Privacy Policy
- Master Subscription Agreement
- ClientPoint Brand Style Guide
Difference Between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal

Table of contents
It’s natural to get confused between a business proposal and a business plan if you are planning to turn your idea into reality. While business proposals and plans may sound similar on the surface, they have differences — such as distinct purposes and formats.
A business plan describes your business goals, strategies, and financial projections. A business proposal, on the other hand, proposes a specific solution to a problem or opportunity and helps you persuade the relevant stakeholder to invest in your business.
However, writing a business proposal or a business plan can be challenging, especially if you are confused about their purpose. In this blog, we will explain the difference between a business plan and a business proposal and its major components.
Business Plan
A business plan tells the investors how you plan to ship your product to enough people to clock revenue. It’s about the strategies that will make you the first buck.
A business plan keeps your team on the same page — you can use it as a guiding light. It can help you track the progress of your business, give you a roadmap, and help you make decisions about your business’s future.
Plus, it can be helpful when it comes to pitching your business idea to a third party, for example, when seeking a loan.
Components of a Business Plan
A business plan is majorly divided into three sections, which include an executive summary, a sales and marketing strategy, and a financial plan.
An executive summary is a brief, clear, and compelling overview of your business. It is usually the first section of the document, and it contains the most important information, such as your strengths.
These can be further broken down into the following sections:
- Description of products and services, including mission, vision, and objectives of the business
- Target market
- Competitive advantage
- Industry and Competitor Analysis
- Marketing strategy
- Operating plan
- Team structure and qualifications
- Internal business analysis
- Management introduction
- Financial analysis
- Cash flow statement or sales forecast
- Break-even analysis
Business Proposal
A business proposal is a separate written document that outlines a specific business opportunity, project, or idea and presents it to potential clients.
It intends to persuade them to take action, such as accepting a business deal or entering into a partnership, thereby helping you get new customers or partners.
A business proposal should be customized to the needs and interests of the receiver. A generic proposal will rarely help you meet your business goals.
At the same time, ensure your proposal is well-organized, persuasive, and creative. Check out these free business proposal templates to impress your clients.
Solicited and Unsolicited Business Proposals
Proposals are solicited from you, or you send them on your initiative.
You write a solicited proposal in response to a prospect’s or customer’s request for a product. They may ask you verbally, or they may issue a written request for proposals (RFP). A solicited business proposal contains a detailed description of the product, service, or solution that you offer to solve the customer's problem or need. It’s generally easier to write because you know what the customer wants or expects.
But if you’re writing the proposal on your own, which is the case with unsolicited business proposals, then you’re convincing the receiver to work with you or buy from you. Such proposals are often challenging to write because you have to convince them they have a problem and you have a solution.
Components of a Business Proposal
The following are the key components of a business proposal :
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Problem statement
- Scope of work
- Benefits of Return on Investment (ROI)
- Call to Action (CTA)
Business Plan vs. Business Proposal
While a business plan outlines your goals and explains how you will achieve them, a proposal sells your product to potential customers.
In the following table, we have summarized the main differences between a business plan and a business proposal:

Streamline the proposal creation process
To wrap up, a business proposal is a document that pitches your products or services to a potential client, while a business plan outlines your goals, strategies, and financial projections for your business.
With business management software like Cone, you can easily streamline and automate your proposal creation while ensuring your proposals are bespoke and customized. Sign up for free and experience the seamless proposal creation process for yourself. While you’re at it, check out other business proposals and management resources we have for you.
April 13, 2023
Can't find what you're looking for?
Difference Between Business Plan and Business Proposal
One of the most searched queries on Google is "business proposal vs business plan", and we are here to break the confusion.
What's Inside?
You are starting a new business, and you aren't sure what you need to do. You heard that you needed a business proposal and a business plan, but you weren't sure what's the difference between them.
You did some research and couldn't find what you are looking for... You decided to create both of them, but you need weeks to write and refine them.

Don't worry, we are here to remove this confusing process. Let's see what's the difference between them. You may, and probably do need both of them. But which one should be your priority?
The Difference Between a Business Plan and a Business Proposal
When you're starting a business, one of the most important things you'll need to do is create a business plan . This document will outline your company's goals and strategies for achieving them over the next five years.

A business proposal , on the other hand, is a sales document that you put together to pitch potential projects to clients. It's not the same as a business plan, and it usually includes cost quotes for potential projects.
The main difference between a business proposal and a business plan is that, while a business plan is informative, a business proposal is intended to showcase operations, goals, and potential.
Executive Summary
The executive summary of a business plan will include information about the company leadership structure or the introduction of management. Generally, business plans include an executive summary part while business plans don't.
We have seen some samples that use executive summaries but since the main goal is to close a deal. We suggest keeping them short and clean.
The business proposal format depends on whether the business is solicited or unsolicited . Details of products and services offered, the scope of work and responses to specific questions in an RFP are included in a business proposal.

A business plan documents the vision of a business and how it will be achieved. A business proposal offers comprehensive information for potential investors, suppliers, accountants, etc.
A proposal shows the external player what the company is all about and how it intends to carry out its project. Keep these differences in mind when you're putting together your next business presentation --you'll need to tailor your content accordingly!
What Are Business Plans?
A business plan is a document that outlines the business goals, strategies, and tactics a company will use to achieve those goals. The business plan also includes an overview of the company, its management team, the target market, and the products and services the company plans to offer.
It usually includes information about the company's products and services, target market, marketing plans , financial forecasts, and management team bios.
Here's a sample template to use while creating a detailed business plan.
What Is The Purpose of a Business Plan?
A business plan is a key document for any business. It lays out the goals and strategy of the business and helps to ensure that everyone involved in the business is on the same page. It can also be used as a tool to help secure funding from investors or banks.
A business plan is a document that outlines the strategy and goals of a company. It can be used as a planning tool , to track progress, or as a basis for making decisions . A well-written business plan provides a roadmap for the business , and it can help attract investors or partners.
There are many reasons to create a business plan. Some of the most common reasons include:
- To track progress - A business plan can help you track your progress and ensure that you are on track to achieve your goals.
- To make decisions - A business plan can provide guidance when making decisions about the future of your company.
- As a planning tool - A business plan can help you identify potential problems and solutions, and it can be used to forecast future growth.
- To attract investors or partners - A well-written business plan can help you attract investors or partners who share your vision for the company.
What is a business proposal?
A business proposal is a written document that offers a solution to a problem or a way to achieve a goal. It is often used to sell products or services to a potential customer. A business proposal must be well-written, clear, and concise in order to convince the reader to take the desired action.

A business proposal is a formal response sent to an RFP (request for proposals). It is a way for the seller to convince the buyer that their proposed solution is the right one in order to win business. Business proposals are meant to persuade a prospective client.
A business proposal typically consists of four main points: what are the challenges, how your solution solves the problems, why they should choose you over others, and the best pricing options available. The price is typically stated in the document. If a business is requesting proposals, they should be sent in their format. An RFP response should include specific details about the scope of work and the cost estimate.
Here's a sample template to use while creating a detailed business proposal.
Why do you need a business proposal?
A business proposal is a key part of the business development process . It is a document that outlines the business goals, strategies, and tactics that will be used to achieve those goals. A proposal is used to convince potential clients or partners that your business is the best option for them.
It's typically used to pitch an idea to a potential client or customer. A well-crafted proposal can help you win new business and close deals.

Your company might be expanding into a new market and need to propose a new product or service. Or, you might be approached by another company with an opportunity you'd like to explore. Maybe you've identified a gap in the market and want to propose a new product or service to fill it.
How To Prepare For a Business Proposal?
Well, we do have a comprehensive guide to business proposal creation with templates and examples, but if you need a more brief explanation, keep reading!
When preparing for a business proposal, it is important to do your research and understand the client's needs. You should also have a clear understanding of your own company's capabilities and what you can offer the client. Additionally, it is important to be well-organized and to have a strong pitch.

You should have a clear understanding of your target audience and what will appeal to them. You also need to have a good grasp of the competition and what they are offering. In addition, you should be familiar with the terms and conditions of any potential contracts that may be involved.
Your proposal should be neatly formatted and easy to read. It should also be free of grammatical errors and typos. Be sure to proofread your work carefully before submitting it.
Make sure you provide complete contact information, as well as an outline of your proposed solution or service. If possible, include testimonials from past clients who have been satisfied with your work.
Remember that you are offering a valuable service that can help the reader achieve their goals. Believe in yourself and your ability to succeed, and you will be able to deliver a winning proposal every time
How To Write a Business Proposal?
When writing a business proposal, make sure to follow this brief outline:
- Introduce yourself and your company
- Outline the proposal's purpose
- Explain the problem that you're trying to solve
- Describe your solution
- Explain the benefits of your solution
- List your qualifications
- Request a meeting
It should include an overview of the product or service, information about the company proposing it, financial projections, and terms and conditions. A well-crafted proposal can help your company win new contracts and increase sales.
Here's another sample template you can use while creating a business proposal:
Business Proposal Template Checklist
Here's a story of our customer John who joined the Decktopus community 2 years ago.
John had been working in sales for years, but he had never worked in a company that sold products. When he was hired by a new startup, he was excited about starting making sales and increasing profits. However, he soon realized that there was no one in the company who knew how to sell. The founder of the company told him that he would need to create a presentation template to share with the other reps.

John wasn't sure where to start. He read article after article, trying to gather information about what made a good business proposal. After weeks of research, he finally created a template that he felt confident in sharing with his fellow reps. He was excited to see how it would help them increase sales and profits.
This is the outline we gathered while our support team helped him along the way:
-Executive Summary
-Problem/Opportunity Statement
-Business Plan
- Marketing Plan
-Financial Plan
Types Of Business Proposals
An unsolicited proposal is one in which the company offers a product or service to a potential customer who has not solicited it. Here's an unsolicited proposal template .

A solicited proposal is one in which the company responds to a request for proposal (RFP) from a potential customer. Here's a solicited proposal template .

A proposal to bid is a document that a company submits to a potential customer in response to an RFP.
The purpose of the proposal to bid is to persuade the potential customer that the bidder's product or service is the best option among those being considered.
Here's a proposal to bid template .

Business Plan Structure
A business plan has three main sections: the executive summary, a description of the business model, and financial projections.
The first section is an introduction that should be no more than one or two pages long. It should include a brief overview of your company, its products and services, and how you plan to make money.
The second section, a description of the business model, provides details about your company's competitive landscape, industry trends, and how you plan to reach your target market.
The marketing model is an informative section that should include detailed information about the industry competition and build-out plan. This part of the document can be several pages long and will help investors understand your company's place in the market.

While all three sections are important, remember that potential investors will likely focus on the financial projections most closely when deciding whether to invest in your company. The financial projections section is important because it shows potential investors how you expect your business to grow over time.
A well-crafted business plan can help convince potential investors to put their money into your company.
<cta-section data-ctaTitle="Start Building Your Business Document Now!" data-ctaDescription="Build good looking and functional business proposals and business plans without touching the design, literally in minutes!" data-ctaButtonText="Start Now!" data-ctaButtonURL=" https://www.decktopus.com/ "></cta-section>
100,000+ Ready-Made Designs, Docs & Templates to Start, Run and Grow your Business
Starting and running a business can be difficult, but it doesn't have to be alone. In fact, you're not alone--over 100,000 companies use our design templates, documents, and tools to start, run, and grow their businesses.

From creating a logo and branding your company to writing a business plan and pitching your idea to investors, we have everything you need to get started. And if you need more help along the way, our team of experts is here to support you every step of the way.
Simply select the template or document that's right for you, fill in the blanks, and hit print. It's that easy!
We understand that starting a business can be difficult--but with our help, it doesn't have to be alone. Over 100000+ companies use our design templates & tools every day to start & grow their businesses successfully. You can too!
Other Resources:
Business plan and proposal software solution, business proposal templates, business plan templates, basic business proposal writing guide.

Start Building Your Business Document Now!
Build good looking and functional business proposals and business plans without touching the design, literally in minutes!
Don't waste your time designing your presentations by yourself!
Type your content and let our platform design your presentations automatically. No more wasting time for your presentations. Use hundreds of presentation templates to impress your audience. This is the only tool you need to prepare presentations. Try our Presentation Builder today >>
Don’t waste your time by trying to make a website for all your content
Place your content links and let our platform design your bio link automatically. No more wasting time for your social content distribution. Use hundreds of presentation biolink to impress your audience. This is the only tool you need to prepare good-looking bio links. Try our Bio Link Builder today >>
Do You Want To Create a Presentation?
Latest Articles
.jpg)
June 10, 2024
Top Lead Gen Tools for Marketers: Best Picks for 2024
Lead the pack with superior generation tools! Check out 's best picks for marketers to drive leads.
.jpg)
Best Business Proposal Tools for Founders: 2024 Edition
Founders, streamline your proposal process! Maximize success with top tools for founders to craft best proposable business proposals for perfect impression in no time!
.jpg)
Best Sales Funnel Softwares for Sales People: 2024 Picks
Discover top funnel softwares for sales mastery with best features for sales people. Boost leads with Decktopus, Kajabi, Systeme, Zendesk & more. Elevate your funnels and sales strategy today with the best funnel builders!
Sign up for our newsletter to stay up-to-date on the latest news and tips from Decktopus.
Let’s create a form here to get visitors’ email addresses.
Ready to dive in? Start your free trial today.
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

Business Model vs. Business Plan: Key Differences
A business model is your core framework for operating profitably and providing value to customers; a business plan outlines how you’ll execute your goals.

“A goal without a plan is just a wish,” wrote famed French author and aviator Antoine de Saint-Exupéry. These words ring especially true in modern business planning. As an entrepreneur, planning is a skill that can help ensure your success.
Business models and business plans are both integral aspects of starting a business. But what are the similarities and differences between the two, and when is the right time to think about each for your company? Here’s a breakdown.
Business model vs. business plan: What’s the difference?
A business model is a company’s core framework for operating profitably and providing value to customers. They usually include the customer value proposition and pricing strategy. A business plan outlines your business goals and your strategies for achieving them.
The two documents have a few critical differences, namely their structure and application. But the topics they deal with—such as a company’s finances, goals, and operational framework—are largely the same.
Financial projections
- How they’re similar: Both business models and business plans provide an in-depth description for how a company will generate profits.
- How they’re different: A business plan includes financial performance details relevant to both internal and external stakeholders, such as investors, lenders, or potential business partners. Alternatively, a business model describes your value proposition —what product or service a business will offer and why customers should buy it—as well as the target market .
Operational details
- How they’re similar: Both business models and business plans include overarching information about how a company plans to operate, including components such as distribution channels and management structure.
- How they’re different: Business models explain the fundamental structure of a company, such as how it plans to create and deliver value to customers, while business plans get into the actionable details of how to achieve a company’s operational goals.
- How they’re similar: Business models and business plans are used to outline the goals, strategies, and operations of a business.
- How they’re different: A business plan generally incorporates a business model, explaining how the model should be implemented and executed to achieve the business's goals.
4 examples of business models
- Brick-and-mortar
- Direct to consumer
- Subscription
There are dozens of different templates that you, as a business owner, can draw from when building out your operation. Here are four examples of basic business models:
1. Brick-and-mortar
One of the most common retail business models, brick-and-mortar , includes a traditional physical storefront (or a pop-up shop ) selling either business to business (B2B), in the form of wholesale goods, or business-to-consumer (B2C). Although overhead such as rent is a consideration in this model, physical locations offer the competitive advantage of tapping in-person customers and building brand awareness through exposure.
2. Direct to consumer
Direct to consumer (D2C or DTC) is a retail model that allows your business to sell straight to customers, rather than going through a third-party retailer such as Amazon. There are numerous benefits to D2C, including higher profit margins because you don’t have an intermediary taking a cut. However, the main disadvantage of D2C is that you have to develop your own customer base without the help of an established platform.
3. Subscription
Projections indicate that the subscription ecommerce market has boomed in recent years and is set to hit nearly $900 billion in 2026. The subscription business model includes charging customers a recurring fee for a good or service—anything from home-delivery meal kits to media streaming. Subscription services are dependent on customer relationships and customer loyalty , but they can offer businesses a more predictable revenue stream.
4. Freemium
Under a so-called freemium model, consumers can access part of the business’s goods or services free of charge, but must pay to receive unlimited access to everything the company has to offer. Examples include many media organizations, such as The New York Times, which offers several free articles before requiring a subscription, or audio streaming service Spotify, which has a free version with ads, as well as a paid version without.
What's in a business plan?
A comprehensive business plan details many aspects of your company, including everything from marketing strategies to finances to the legal ownership structure. Here are a few key sections to include when writing your business plan.
- Executive summary . The executive summary includes your mission statement , an explanation of your core values and goals, a brief company history, and descriptions of the products or services you plan to provide to a potential or existing market.
- Organizational structure. Management hierarchy, as well as their roles and responsibilities, would be included in this section.
- Marketing and sales. How do you plan to market your offerings? Who is your target market? What is your pricing strategy and how does it compare to that of your competitors? How do you plan to acquire and retain customers? All these questions should be answered in this section.
- Expected financial performance. This includes projected revenue streams, cash flow management , cost structure, expenses, and anticipated profitability. It typically covers from one to five years in the future.
- Business operations. This section covers everything about the day-to-day running of your business, including your storefront (if you have one), inventory management , supply chain, and production.
Business models vs. business plans FAQ
Which comes first, a business model or business plan.
A business model typically comes before a business plan . Business plans often include the business model, and then explain in detail how you plan to achieve the goals set out in a model.
How can a company test and validate its business model before creating a business plan?
Market research, financial modeling, and even seeking out expert advice or consulting are all ways to review and validate your operation’s business model before developing a business plan.
How often should a company review and update its business plan?
A business should be prepared to update its business plan dynamically, based on changes in the market, shifts within the operation, or new investment or opportunities. Many businesses update their plans annually
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
10 Jun 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
All the marketing tools you need to dominate your local market:
- LocalReviews
- LocalMessages
- LocalResponse
- LocalVisits
- LocalReferrals
- LocalContacts

Real-Life Marketing Experts
Every subscription comes with a dedicated marketing specialist who will help guide your success from day one.
Marketing tools tailored to your industry
- Auto Detailing
- Chiropractors
- Cleaning Services
- Contractors
- Electricians
- Landscapers
- Optometrists
- Pest Control
- Physiotherapists
- Case Studies

The Latest AI Marketing Tools to Fuel Local Business Growth

Why Signature Massage and Facial Spa moved to just one partner

Google Reviews Not Showing Up? Here's How to Fix It
- Bin There Disposal Services
- My Mold Masters
- Signature Massage
- Waterloo Medical Cosmetics
- Why OneLocal
- How We Hire
- Current Openings
- Engineering Careers
Google My Business vs Google Business Profile: Which is Which?
- Rachel Solway
- June 4, 2024

Have you ever tried to keep up with how Google supports businesses online? If you have, you might know that Google My Business (GMB) is now called Google Business Profile (GBP). Things on the internet sure change quickly, don’t they?
Let me break it down for you in easy terms. It’s not as complicated as it might seem. I’ll explain why this is important and how you can benefit from it and give you some easy tips to make your business profile stand out.
I remember feeling completely lost the first time I had to update my business information . But taking things one step at a time helps to manage everything.
Google’s Transition From GMB to GBP
So what’s different now? Before the switch from GMB to GBP, running your business felt a bit clunky: juggling both a separate website and a mobile app was a hassle when I needed to manage things quickly. Now, Google has made things much easier by putting everything right into Google Maps and Search.

For someone like me, that’s a huge plus. You can now easily update your business details on GBP or connect with customers right on platforms that pretty much everyone uses every day.
Here’s how it works in real life – let’s say you need to change your store’s hours or contact info. Before, you had to log into the GMB dashboard to do this. Now, you can make the updates directly through Google Search or Maps. It saves time and makes everything much easier.
And if you’re managing a bigger business, good news. Google has rolled out the Business Profile Manager for businesses with multiple locations. This tool is super helpful for big companies, but it’s also really useful for smaller single-location businesses. It’s like having a tool that grows with you, which is honestly pretty smart.
With the phasing out of the GMB app and new updates in tracking performance metrics and customer interactions, it’s a good idea to get close to these new features. To give you an example, moving from the old Plans section to the new Complete Performance Metrics section has majorly improved my understanding of customer engagement and has helped me make better business decisions directly from GBP.
It might take a bit of time to get used to the term GBP but from what I’ve seen it’s a positive change. The goal here is really to make managing your online presence as easy and useful as possible.
All About Google My Business
As time goes on, Google My Business keeps getting better and better. I remember when they started rolling out new features that really made it easier to connect with customers. You could claim and verify your business profile – use tools like call history messaging and even check when your messages were read. As a business owner, I found these tools super useful for building customer relationships. It felt great to manage my business profile right from Google Search and Google Maps.
Then came 2021, and Google decided to shake things up by renaming GMB to Google Business Profile (GBP) . At first, it seemed like a name change, but they added some cool new features. Now, we have improved messaging options and a performance planner that’s helpful for budgeting local ads . These tools have been awesome for pulling in potential clients and keeping the finances in check.

Switching over to GBP was very easy for me. Those improved messaging options? They’ve been great for keeping a steady flow of talk with customers which is always a good idea. Even though the online interface hasn’t changed much it’s exciting to think about getting new features directly from Google Search and Maps. The main thing is to make our tasks easier and help with our online presence right?
Still you’ll hear some people refer to it as GMB but it’s officially Google Business Profile or GBP for short. I’d love to talk about GBP more with you.
All About Google Business Profile
Talking about Google switching from Google My Business to Google Business Profile feels like tidying up a cluttered desk – so that everything you need is right at your fingertips! Initially, it was known as Google My Business. This helped business owners manage their listings on Google Search and Maps.
They’ve decided to simplify things. Again, all the tools are incorporated directly into Google Search and Maps – where most of us usually go when we need info about businesses. From my experience, I have to say it’s been incredible. It saves so much time since you can manage everything from one close place.
Before this update, managing my business profile felt pretty cumbersome. Imagine having to switch between different apps or websites. It was pretty frustrating. But now, if I need to adjust our opening hours or respond to a customer review , I can just do it straight from Google Search. They’ve cut down on the hassle.
To give you an example, if a customer asks about new safety measures at my shop, instead of jumping through hoops, I update my business details on Google. The process is so much smoother now.
Honestly, the buzz about this update has spread pretty well. It’s kind of like giving your business a steady behind-the-scenes help. Everyone seems to be talking about how these new tools are major. I believe it was a good idea – it makes everything more reachable and user-friendly.
Differences Between GMB and GBP
Let’s talk about the latest updates with Google’s business tools, especially the shift from Google My Business (GMB) to Google Business Profile (GBP) and what stays the same. Do you know how you usually handle important details like your store hours, location, and customer communication methods? All those basics are still the same with the switch from GMB to GBP, which is awesome because it means you don’t have to pick up a new system for these basics.
With the switch to GBP, Google has rolled out some cool new features – one that I’m super excited about is the direct messaging feature. Before, my conversations with customers were pretty much limited to reviews or the Q&A sections – but now I can directly text my customers or talk through the Google Maps app . This has been great as it allows for quicker responses and really strengthens my connection with my customers.
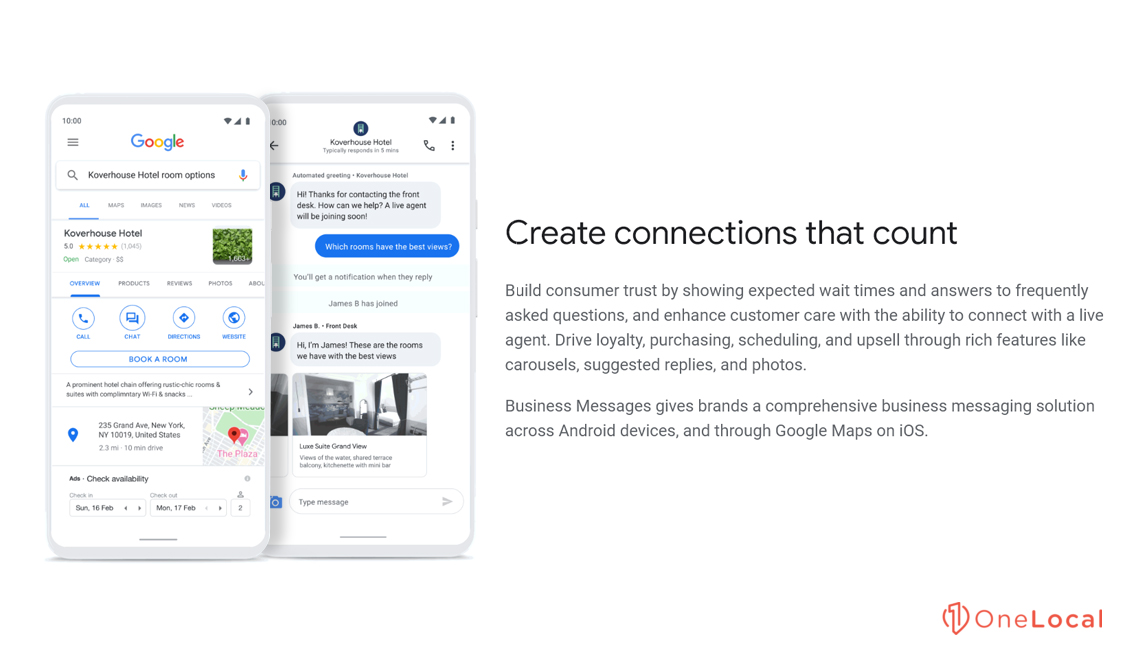
Now let’s talk about the enhanced analytics in GBP. These have deeper plans into how people use my business online – it’s been a good idea for changing my marketing strategies .
Imagine a local cafe that has just made the switch from GMB to GBP. With the new direct messaging, they might see an increase in positive reviews since customers appreciate quick and personalized responses.
Let’s say this cafe owner notices that posts about new menu items are drawing more website visits. In that case, they might choose to update their menu more usually and share those changes now and again. This could seriously help with online engagement and might even bump up in-person visits.
Both GMB and GBP are designed to help with your business’s online presence – yet GBP, with its advanced analytics and new communication features, has even more ways to connect with your online audience and support personal interactions. These tools can completely turn how you engage with people and grow your business.
How to Update Your Business Information
Keeping your business information updated on your Google Business Profile is smart and easy to do. I’ve seen that by staying up to date your visibility on Google Search and Maps goes up – bringing in more customers. And let’s be honest – we all want more customers right?
I’ll show you my easy schedule. When I’m at my desk, I just open Google Search or Google Maps, type in my business name, and click on the profile when it pops up. Pretty easy, right? When I’m on the go, I only need to tap on the Google Maps app on my phone and go right to the “Business” tab. It’s convenient if you’re a desktop or mobile to keep everything up-to-date.
I always log in with the Google Account that’s connected to my business which helps manage everything consistently across all sorts of devices.
When I’m updating my details, I make sure to keep the address, hours, and photos recent and reflective of what’s new at my business. I set aside some time to reply to customer messages and calls, manage reviews, and check on performance metrics. Now and then, I look into advertising options to help with visibility even more, and it’s a good idea.
With Google changing from the Google My Business app to the Google Maps app managing updates on mobile has grown a lot easier. It’s now easier than ever before.
Regular updates make sure that potential customers always get the right information – preventing confusion and building trust. Besides, it’s really interesting to see how small changes like changing business hours or updating a photo can change customer interactions and online metrics. It’s meaningful to put in that effort!
Optimize Your Profile for Local SEO
If you love playing around with SEO to help with your online visibility you’re not alone. I’ve personally seen the benefits while changing my business’s Google Business Profile (GBP). Seriously if you count on local foot traffic – getting the knowledge of your GBP could change the game.
Let’s talk about the basics, okay? Again, make sure your business name, address, and contact info are spot on. It’s surprising how many businesses skip this easy step. Keeping your information consistent avoids confusion for customers and also improves your SEO rankings. Next, it’s a good idea to verify your locations. It makes your presence on Google solid, builds trust, and improves your visibility in important local searches.
You might not think it’s a big deal, but adding quality images can bring about huge changes. Upload some clear, high-resolution photos of your place and products. This helps people get a good feel for what you have before they even drop by.
Picking the right business categories and making a keyword-optimized business description – without cramming it with keywords – can make you stand out. The goal is to make it very easy for potential customers to find and pick your business.
Staying active with GBP features like posting updates and replying to reviews also does wonders. Handling feedback well creates positive relationships and also improves your local SEO . Positive reviews are super valuable. They show off your credibility and commitment to great service, pulling more customers in.
Remember the backend analytics tools too – keeping an eye on your GBP’s performance lets you check out how visible you’re locally, compare yourself to competitors, and spot areas to get better. It’s kind of like making sure your store’s front window is clean and inviting. You’re more likely to draw passersby if they like what they see from the outside.
Remember that keeping up with these features helps you connect more with local customers. It’s kind of like what creates your business and always puts its best foot forward both online and offline.
Need Help Growing Your Local Business?
If you’ve been running a business for years or are just entering this part taking a fresh look at your Google Business Profile can work very well. Ever thought about how some easy adjustments could give your business a big lift?
This reminds me of when I first became serious about my business’s online presence. At first, all the different features and settings on the Google Business Profile seemed overwhelming. But after talking about tools like direct messaging and new performance metrics – I realized just how smart these features are. They help with local SEO and also increase engagement with customers.
Now and then, I update my business profile, and it always helps with my local search rankings and strengthens customer relationships. Honestly, a little change here and there can help a lot – with some businesses more than others.
Looking ahead, it’s a good idea to keep an eye on Google’s updates. They are designed to help with your online strategies. Staying proactive with these changes keeps your business agile: always ready to adapt and excel no matter what new features Google introduces.
Here at OneLocal , we understand that managing these online platforms can be difficult. Why not take a proactive step towards boosting your online visibility by signing up for a free demo with us today? Let us show you how our expertise can help with your local business efforts. Trust me – you’ll find it helpful!

Rachel Solway is a seasoned marketing professional dedicated to empowering small businesses through innovative marketing strategies. With extensive experience at OneLocal, a leading marketing solutions provider, Rachel’s insights are helping thousands of local businesses navigate the digital landscape.

Do Mobile Carriers Use SMS Spam Filters to Stop Marketing?
You’ve probably been hit with marketing texts you never signed up for – it’s annoying. Mobile carriers understand this annoyance and have been working hard

How Much Does a Local Business Site Redesign Cost in 2024?
You might be wondering about the cost of refreshing your local business website with a new look in 2024. Giving your site a fresh design
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Push vs. Pull Marketing
Have you ever noticed that some brands stay in your mind? It seems as if they’ve figured out how to talk in a way that
545 King Street West
Toronto, Ontario M5V 1M1 Canada
Our Company
- Terms of Use
- Web Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Careers NOW HIRING
- Affiliate Program
- Get a Free Analysis
- Request a Demo
- Call Us: 1 (855) 428-2669
- Email us: [email protected]
Copyright © 2023 OneLocal. All Rights Reserved.
- Yes, please contact me for more information
Enter your details below to set-up your no-obligation demo. All fields are required.*
- +8801997310000
- [email protected]

What is the Difference Between a Business Profile and a Company Profile?
When you start a business, you are required to make an investment of time, money, and resources. All these things are required to create a strong brand that can help you to grow your business. But all these things will be useless if your brand is not strong and attractive.
So, to start your business you need to have a business profile. A business profile will include basic information about your business. This profile will be your first step to building your brand.
A business profile is also known as a company profile or a business entity profile. When we talk about company profile it means that you have the right to trade and sell the products in a particular area. A company profile is also used to create a business license. You need to apply for the company profile once you have started your business.
In the business profile, there are various sections that are mentioned as follows:
Basic Information: In this section, you need to mention all the information about your business. Your name, address, contact number, email, and website are some of the information that should be mentioned. It is the basic information that is required to create a business license. You need to make sure that you mention all the required information about your business.
Company Information: In this section, you need to mention the complete information about your company. The legal documents, employees, addresses, and other information will help you to create a strong brand.
Management Information: In this section, you need to mention the management information of your business. In this section, you need to mention the details of the management team and also mention their information.
Financial Information: In this section, you need to mention the complete financial information of your company. This section will help you to calculate the profit and loss of your company.
In conclusion, the above information about a business profile will help you to get a clear idea about your business. If you are starting a new business, then you need to make sure that you are providing complete information in this section. So, if you want to make sure that you have provided all the required information, then you can use the free online business profile generator.
Your Comment: Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
ColourBangla © 2023. All rights reserved.
How to Use Instagram for Business and Drive Results in 2024
Everything you need to know about using Instagram for business — from setting up your account to creating a winning strategy.

Table of Contents
Is your business still “like”-ing the idea of using Instagram, rather than confidently sliding into the DMs of the platform’s full potential? It’s high time to stop scrolling and start strategizing.
If you’re wondering how to use Instagram for business in 2024 , we’ve got you covered. In this guide, we’ll share the top strategies to help your brand thrive on the ever-evolving platform.
Bonus: Claim your free pack of 15 creative Instagram post templates made by Hootsuite’s professional graphic designers. Easily customize them in Canva, and start getting more engagement today.
How to set up Instagram for business in 4 steps
Using Instagram for business is a bit different than using a personal account. But don’t worry, it’s not rocket science! Follow these 4 simple steps to get your brand up and running on Instagram.
1. Switch to an Instagram business account
Before you start using Instagram for business, you need to create an Instagram account for business. It’s free and anyone can do it.
Here’s how to switch your existing Instagram account to a business account:
- From your profile, tap the hamburger (three lines) menu icon in the upper-right corner.
- Tap Settings and privacy . Then, scroll down until you see the Account type and tools menu.
- Next, click Switch to a professional account to change the account you’re logged into into an Instagram business account.
- Tap Continue (you may need to tap it multiple times as Instagram previews the available features of a professional account).
- Select a Category and use the slider to choose whether to show it on your profile, then tap Done .
- Choose Business (unless it makes sense for you to choose Creator ), and tap Next .
- Use the slider to opt in or out of promotional emails from Instagram for professional accounts, then tap Next .
- Add or edit relevant contact details, then use the slider to choose whether to show your contact information on your profile, then tap Next (or tap Don’t use my contact info to skip this step).
- If you plan to connect your Instagram business account with a Facebook business page, follow the prompts to connect your account to your Facebook Page. This is technically optional, but it’s necessary in order to use Instagram shopping features or run ads on Instagram .
- Next, you’ll be prompted to add additional features to your account, like telling Instagram your goals, adding details to your portfolio, and growing your audience. If you want to save this for later, tap the X in the top left corner to close this window and return to your profile.
If you’re interested in making an Instagram account for business simply sign up for a new Instagram account , and convert it to an Instagram business account.
You can have up to five Instagram accounts , so go ahead and keep your personal Instagram account personal if that’s what you prefer. Learn more about the difference between Instagram business and creator accounts .
2. Add business information to your bio
In 150 characters or less, your Instagram bio should describe your brand and showcase your brand voice . We’ve got a full guide to creating an effective Instagram bio for business (complete with templates), but here’s a quick video to walk you through the basics:
Also be sure to make the most of the other components of your Instagram business profile:
- Profile pic: Most brands use their logo. Your profile photo displays as 110 x 110 pixels (cropped to a circle), but it’s stored at 320 x 320, so that’s the size you should upload.
- Link in bio: Link to your website, your latest blog post, a current campaign or a Link Tree .
- Contact information: If you didn’t add contact info during your account creation, you can do so at any time by tapping Edit profile . Instagram will then add a Contact button to your profile.
- Action buttons: If relevant, you can add a button that allows customers to book or reserve appointments or to order food. To use this feature, you need an account with one of Instagram’s partners . Tap Edit profile , then scroll down to Action Buttons.
- Story highlights and covers: Instagram Story highlights are another way to maximize your profile real estate by providing more information about your brand, products, or services. Organize Stories into saved collections, then add some polish with Highlight covers.
Create. Schedule. Publish. Engage. Measure. Win.
3. Connect your product catalog
To tag products in Instagram content, or to run certain kinds of Instagram ads, you need to create a product catalog. You can do this in Meta’s Commerce Manager.
- Head to Commerce Manager and click Start Now , then select Create a catalog and click Get started again.
- Select Ecommerce , then click Next.
- If you have a shop on an ecommerce platform like Shopify or BigCommerce, click Connect to an ecommerce platform and follow the prompts to create your catalog. Otherwise, click Upload product info , name your catalog and click Next.
- Click View catalog to open your catalog, then Add items to start adding products.
We’ve got a whole post on using Commerce Manager if you’d like more details on how this tool works.
4. Turn on Instagram shopping
Once your catalog is full of products, it’s time to turn on Instagram’s shopping features.
- Go to the Get started page.
- Select Get started .’
- Click Create a shop , then Get started , then Next.
- Review the pre-selected sales channels and add or subtract accounts as needed.
- Choose the account/sales channel you want to connect your shop to. If you’re already selling on Shopify or another partner platform, change your Checkout method to reflect this . When everything is set up, click Next.
- Next, choose the countries you want to ship your products to. Note that Instagram Shopping is not available everywhere. You can choose from available countries in the drop-down menu.
- Add in your business email . This is where you’ll get any communication about your Instagram Shop.
- Select your business portfolio or create a new one. Click Next .
- Select the catalog you want to use for your shop and click Next . To select a catalog, it must meet catalog eligibility requirements for shops. You can’t switch this catalog later. Note: If you don’t have a catalog already, you won’t see this step.
- Look over your shop details, review and agree to the Seller Agreement and click Finish setup to complete creating your shop.
We’ve got a full blog post explaining everything you need to know about Instagram Shopping if you want to focus on this particular aspect of using Instagram for business.
How to use Instagram for business: 8 strategies
Standing out as a business on Instagram can be, well, tough. Use these Instagram for business tips to make it easier.
1. Research your audience
A good social media strategy starts with a sound understanding of your audience.
Instagram’s audience demographics give you an overall picture of who uses the platform. For example, 18-34-year-olds represent the largest ad audience on the site.
However, that doesn’t mean your specific audience on Instagram will be made up of 18-to-34-year-olds. For example, looking at the audience insights for my own Instagram account, I can see that my audience skews older than the Instagram average:
You can find demographic information on your existing audience using Instagram Insights , Meta Business Suite , or Hootsuite Analytics . But, if you’re just getting started using Instagram for business, you might not have a large enough following to gain meaningful insights here yet.
In that case, take a look at the demographics of your audience on other social channels and of your existing customer base. While this won’t translate exactly to Instagram, it should give you a sense of who’s interested in your business and what you have to say.
Understanding your audience puts you in a better position to create targeted content and business captions for Instagram that resonate. Since audience research is an important foundation for your content strategy, we’ve got a whole post dedicated to helping you find your target market .
2. Figure out your content mix
Now that you know who your audience is, you need to determine what to share with them. Rather than posting random content whenever the mood strikes, you need to develop a content strategy that speaks to your audience and keeps them engaged, all while contributing to real business goals .
While you should certainly post some promotional content to get people excited about your products and drive sales, you also need to provide content that builds community and sparks engagement.
That might mean including user-generated content or other curated resources , sharing insider expertise about your industry, or joining in on a trending meme. (But tread carefully here—only join in on trends that are appropriate for your brand voice.)
i am wearing a disguise pic.twitter.com/HlWFQb8P22 — no name (@nonamebrands) October 31, 2022
Look for opportunities to develop themes or regular installments that you can build into a series. “Content buckets” allow you to check certain boxes without having to overthink creation. The more planning you do upfront, the better you’ll be able to produce regular content and respond to last-minute or unplanned events.
3. Schedule your content in advance
From Reels to Stories to posts, there are many options when it comes to Instagram content.
The best way to create a unified strategy is to schedule your content across all Instagram surfaces (and other social platforms) using a content calendar . Or, take it up a level and schedule all your content to publish automatically at the right time using a tool like the Hootsuite Publisher . Yes, you can even schedule Stories and Reels in advance.
The added advantage here is that you can create your content in dedicated blocks of time and schedule it to post at the best time for your audience . Even if that time is outside business hours, on the weekend, or in the middle of the night.
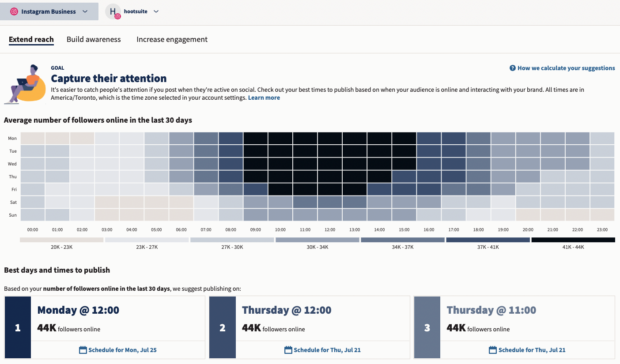
4. Tag products
When you share content about your products on Instagram, tagging makes it much easier for people to learn more or buy. You can tag up to 20 products in a photo feed post.
Source: Tory Burch
To tag products, create your Instagram post or Reel as usual. Then, on the final screen before posting, tap Tag products . You can tag products from your own shop or someone else’s, which creates great opportunities for collaboration and cross-promotion.
In Stories, you can tag products using the Product link sticker.

Source: Pat McGrath
5. Track your results (and learn from wins and losses)
With an Instagram for business account, you have access to the platform’s built-in analytics tools to help you understand how well different types of content perform.
There are several other analytics tools available, including Hootsuite’s , that can track longer time frames, automate reporting and make it easier to compare Instagram metrics across other social media platforms.
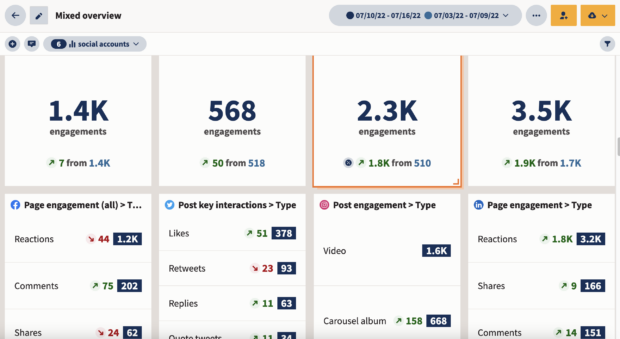
No matter which social media marketing tools you use, the important thing is to check in regularly to learn what kind of content resonates best with your target audience. You’ll start to see patterns about what generates the most engagement, as well as what kinds of social media content increase views beyond your existing follower base. ( Hint: Try Instagram Reels .)
Use these lessons to hone your content strategy over time.
6. Treat Instagram as a customer service channel
Success on Instagram requires you to engage with your followers rather than just blast content out and hope someone likes it. One important component of this two-way communication is monitoring your DMs for questions, comments, and customer service requests.
Instagram business accounts have access to a couple of DM features that make managing customer service easier on the platform. First, your inbox is divided into Primary and General tabs to make it easier to keep track of your messages. And second, you can create saved replies to commonly asked questions that you can access via keyboard shortcuts.
Hootsuite Inbox makes it even easier to manage your DMs by allowing you to assign messages to the appropriate team members . Or, create templated replies to common questions to save your team time and effort.
Manage all your messages stress-free with easy routing, saved replies, and friendly chatbots. Try Hootsuite’s Inbox today.
7. Automate content creation
The average Instagram business account posts 1.55 times per day on the main feed.
That’s a lot of content!
Luckily, manual content creation is now a thing of the past. These days, it’s easy to speed up content creation processes like copywriting and graphic design with the help of generative AI tools .
OwlyWriter AI is Hootsuite’s latest generative AI tool, free to all Hootsuite users. Use OwlyWriter to generate quick social media captions , and get inspiration for your posts across platforms.
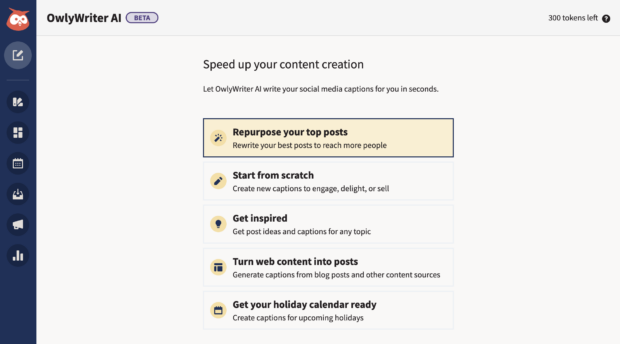
You can also leverage outside tools like ChatGPT, Dall-E, Midjourney, and more. But, because OwlyWriter is oh-so convenient in your Hootsuite dashboard, we recommend starting there. Check out our blog on the best AI content creation tools here .
Always remember, content generated by AI should always be seen as a starting point, not a finished product . Be sure to check over any AI generated content for accuracy, brand voice, style, and tone before posting.

OwlyWriter AI instantly generates captions and content ideas for every social media network. It’s seriously easy.
8. Elevate your grid aesthetics
Looking to make your Instagram grid stand out from the crowd? With Hootsuite’s Instagram Grid integration , you can make a totally aesthetic Instagram grid in just a few clicks.
Here’s how it works:
- Seamless planning: Planning your grid layout has never been easier. With Instagram Grid, you can visualize how your posts will look together , ensuring a cohesive and visually appealing grid.
- Drag-and-drop simplicity: Want to rearrange your grid? No problem. With easy-to-use drag-and-drop functionality , you can experiment with different layouts until you find the perfect arrangement.
- Scheduled posts: Say goodbye to last-minute scrambling. With Hootsuite, you can schedule your grid posts in advance , ensuring that your grid remains active and engaging even when you’re busy.
- Curate like a pro: Discover and curate high-quality content right from the Hootsuite dashboard. Whether it’s user-generated content, AI hashtag suggestions , or trending topics, we’ve got the tools you need to keep your grid fresh and relevant.
- Track your success: With Hootsuite’s analytics dashboard, you can track engagement metrics and understand what resonates with your audience. Use these insights to refine your grid strategy and drive even more engagement.
FAQs about using Instagram for business
Is instagram for business free.
It’s free to set up an Instagram business account, promote your business, and even set up an Instagram shop.
The only fees for Instagram business accounts are ad costs if you choose to run Instagram ads , and selling fees if you use Commerce Manager to allow your customers to check out and complete their purchase within the Meta platform.
There is also no fee to use Instagram Shopping to tag products and direct users to your website to buy them.
What is the difference between personal and business Instagram?
The difference between personal and business Instagram accounts is pretty straightforward. Personal accounts are great for sharing your daily life and connecting with friends and family. But, if you’re running a business or want to promote or sell a product, a business account on Instagram offers tools like analytics, shopping, and advertising to help you reach your goals.
What is the best time to post on Instagram for business?
The best time to post on Instagram for your business depends on who you’re trying to reach and what you’re sharing. Mornings generally bring the most engagement for brand accounts, though certain industries, like real estate, retail, or entertainment accounts, may see more success posting in the evening.
Check out our comprehensive guide on the best times to post on every social network to learn more.
How does Instagram work for business?
By switching your personal profile to a business account, you unlock a treasure trove of tools to boost your business. Get free access to features like Instagram Insights, which lets you peek into who’s engaging with your business on Instagram, or Commerce Manager, which lets you tag and sell products directly on Instagram. It’s like having your own personal business assistant right at your fingertips!
What are the disadvantages of using Instagram for business?
While business Instagram accounts are a great way to sell products and be seen, there are a few drawbacks to consider.
First, increased competition among businesses on the platform can make it tough to secure organic reach. Second, managing a business account requires consistent effort, and eventually you may want to consider hiring a social media manager . Third, unlike personal accounts, where updates are more flexible, business profiles carry the weight of reputation and customer perception. Be sure to read up on managing social media crises before you get started.
Save time managing Instagram for business using Hootsuite. From a single dashboard, you can schedule and publish posts, carousels, Stories, Reels, and ads directly to Instagram — and engage your audience, measure performance, and handle all your other social media profiles. Try it free today.
Easily create, analyze, and schedule Instagram posts, Stories, Reels, and Threads with Hootsuite. Save time and get results.
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
Hannah Macready is a freelance writer with 12 years of experience in social media and digital marketing. Her work has appeared in publications such as Fast Company and The Globe & Mail, and has been used in global social media campaigns for brands like Grosvenor Americas and Intuit Mailchimp. In her spare time, Hannah likes exploring the outdoors with her two dogs, Soup and Salad.
Related Articles

35 Instagram Statistics That Matter to Marketers in 2024
Are you marketing on the world’s third most-used social platform? These Instagram statistics can help you shape your strategy.

2024 Instagram Demographics: Top User Stats for Your Strategy
Who are the people using Instagram every day? Understanding Instagram demographics will help you build a strategy that works — and reach your social marketing goals.

What is Social Media Marketing? The Short and the Long of It
This complete guide will help you get started with social media marketing and follow the right best practices from day one.

Social Media Marketing Tools: The Complete Guide
Automate your work, save time, and build better relationships with your audience by using the right social media marketing tools.
Published: 22 December 2023 Contributors: Amanda McGrath, Alexandra Jonker
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the idea that businesses should operate according to principles and policies that make a positive impact on society and the environment.
Through CSR, companies make decisions driven by financial gain and profitability, and the impact of their actions on their communities and the world at large. CSR goes beyond legal obligations: by voluntarily adopting ethical, sustainable and responsible business practices, companies seek to deliver benefits to consumers, shareholders, employees and society.
Learn about the processes used to manage environmental performance data and the steps required to account for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
Register for the playbook on smarter asset management
Often, a company’s business model and practices are built around financial goals. However, CSR programs encourage business leaders to consider corporate citizenship or the larger impact of the business on society when making decisions. Corporate social responsibility helps companies ensure that their operations are ethical, safe and delivering positive impact wherever possible. Through CSR initiatives, companies work to limit environmental impact, contribute to solving societal problems (such as poverty and inequality) and ensure their brand identity reflects their values.
The theory of the “ triple bottom line ” can help organizations as they pursue corporate social responsibility. As a financial framework, the triple bottom line refers to the idea that a company’s business model should revolve around the three P’s: people, planet and profit. By maximizing all three, a company aims to make a positive impact on the world and remove barriers to growth.
Corporate social responsibility initiatives generally fall into four categories: environmental, ethical, philanthropic and economic. Each type of CSR contributes to a company’s overall CSR strategy.
More companies are assessing their overall environmental impact and engaging in CSR efforts that aim to protect natural resources and minimize any contribution to climate change. CSR encourages sustainability in business through eco-friendly practices, such as by reducing energy consumption, using renewable resources and minimizing waste.
Environmental responsibility hinges on eliminating negative impacts of business operations (primarily through limiting pollution-causing activities) as well as offsetting them through actions such as planting trees and engaging in programs that support biodiversity.
CSR initiatives often focus on social impact and human rights concerns, such as ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions and proper treatment of employees and suppliers. They also encourage accountability both internally and externally. Ethical CSR may include abiding by fair labor practices, ending workplace discrimination and ensuring supply chain transparency.
CSR practices include donating money, resources or time to positive causes and organizations, such as local and national charities, educational programs, disaster relief and more. Businesses who adopt philanthropic CSR engage with the communities where they operate, offering support through volunteer work, sponsoring local events, making contributions to local nonprofits or supporting skills training programs.
Corporate social responsibility involves ensuring that money is not a company’s sole motivator. To demonstrate this, companies enact policies and procedures to make sure their choices align with values, even if the alternatives may save money or boost profitability. Economic CSR also includes efforts to support the economic development and growth of the communities in which a business operates—for example, supporting job training and job creation efforts and forging local partnerships.
The benefits of CSR include:
CSR can have a positive impact on an organization’s brand identity as well as its bottom line. Some CSR efforts, such as improving energy efficiency, can reduce operating costs and might lead to savings in the end. Consumers increasingly prefer brands that share their values, and CSR policies offer ways for organizations to demonstrate those values, building trust and loyalty to fuel a competitive advantage.
CSR can also help attract top talent and drive employee engagement and retention, as more workers seek employers whose values align with their own. Additionally, a proactive approach to ethical and social issues has the potential to prevent legal problems, fines and reputational damage.
CSR initiatives can help people become more responsible consumers, making it easier for them to access products and services that align with their values and educating them on issues of sustainability and ethical consumption. It can encourage companies to prioritize and invest in testing, quality control and safety measures. CSR can also minimize the likelihood of defective or harmful products reaching consumers.
CSR can have a positive impact on the overall health of the planet, as it encourages environmental responsibility and sustainable practices. CSR initiatives can help companies reduce their greenhouse gas emissions or pursue net-zero emissions goals that are key to slowing climate change. They might also help conserve natural resources, reduce pollution and limit disruption of ecosystems. Additionally, a focus on CSR can support investment in research and development of eco-friendly products and practices.
Corporate social responsibility can help support local communities and address societal issues, such as poverty, inequality and environmental concerns. CSR initiatives can fuel economic growth by creating jobs. They can also shape public opinion as companies leading the way inspire others to follow suit, creating a positive ripple effect. A focus on ethical behavior at the corporate level reinforces a broader norm of ethical behavior across other parts of society.
Consumers are increasingly seeking products and services from socially responsible companies. Meanwhile, many investors are prioritizing companies whose values are clear and aligned with their own. To meet these demands, businesses are integrating CSR into their operations. In addition, global expansion and the increasingly interconnected nature of supply chains pushes companies to comply with a growing web of regulatory environments and to better confront the impact of their business on communities around the world.
With increased awareness of environmental issues, labor practices and ethical concerns, combined with better research and communication, CSR is now more central to business strategies. Some companies even have dedicated CSR departments.
Examples of CSR include:
- Donating a percentage of profits to environmental or social causes
- Committing to using recycled and eco-friendly materials
- Sourcing fair-trade materials and ingredients
- Engaging in social activism or fundraising on behalf of social causes
- Using technology such as artificial intelligence (AI) to drive energy efficiency and reduce carbon footprints
- Creating programs for the ethical use and disposal of products, such as electronics recycling programs
- Instituting diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) programs that support efforts to diversify and grow the workforce in new ways
- Supporting programs that replenish the natural resources, such as water or timber, used for production
- Turning to renewable energy sources and other strategies that help in the pursuit of net-zero or carbon-neutral goals
- Establishing employee well-being programs that support their physical and mental health
Corporate social responsibility is the overall ethos that drives a company to adopt policies and practices that support sustainability, societal and other ethical ends. Environmental, social and governance (ESG) is about the ways in which their impact is measured or quantified. While both CSR and ESG are about reflecting the company’s values, CSR is typically seen as more of an internal framework, while ESG frameworks are often used externally as a way of demonstrating real-world impact.
Because the parameters of corporate social responsibility are continually evolving, there is no single standard by which CSR initiatives are measured or governed. Companies that embrace CSR are guided by local and international laws, including environmental regulations, labor rules and consumer protection standards.
Some efforts are also held to industry-specific standards; for example, the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) provides reporting standards for sustainability. Organizations like the United Nations have introduced global guidance, such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
Many companies that embrace CSR will also engage in CSR reporting , through which they document performance of non-financial metrics and provide transparency on social and environmental impact. CSR reporting is typically voluntary; however, some jurisdictions mandate that large organizations disclose social and environmental performance, so that investors and consumers can assess CSR efforts.
Some organizations have designated corporate social responsibility teams that oversee a company's CSR activities. People on these teams plan and run the social and environmental programs that align with the company's values and goals. They work with company leadership to devise the overall CSR strategy and engage stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors and community partners, to help them succeed. They also typically track and report on their progress by using metrics and other methods of assessment, deal with compliance and regulatory issues and manage communication about the company’s CSR efforts both internally and externally.
Simplify the capture, consolidation, management, analysis and reporting of your environmental, social and governance (ESG) data.
CSR reporting is the practice of reporting an organization’s performance of non-financial metrics, providing transparency on the organization’s impact on society and the environment.
Net zero is the point at which greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere are balanced by an equivalent amount removed from the atmosphere.
The goal of the CRSD is to provide transparency that will help stakeholders better evaluate EU companies’ sustainability performance as well as the related business impacts and risks.
The triple bottom line (TBL) is a sustainability framework that revolves around the three P’s: people, planet and profit.
Sustainability in business refers to a company's strategy and actions to eliminate the adverse environmental and social impacts caused by business operations.
Decarbonization is a method of climate change mitigation that reduces greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, as well as removes them from the atmosphere.
Simplify the capture, consolidation, management, analysis and reporting of your environmental, social and governance (ESG) data with IBM Envizi ESG Suite.
3 former 'Love is Blind' contestants say being on 'Perfect Match' was harder because of one key difference between the shows
- "Perfect Match" season 2 stars four former contestants from "Love Is Blind."
- Micah Lussier, Izzy Zapata, and Jessica Vestal spoke to Business Insider about their "Perfect Match" experience.
- They said the dating competition was harder than the marriage-focused series.

Warning: Spoilers ahead for the first two episodes of "Perfect Match" season two.
Three " Love Is Blind " stars told Business Insider that competing in "Perfect Match" was harder than their original marriage-focused series.
" Perfect Match " season two features four former contestants from "Love Is Blind" — Jessica Vestal , Micah Lussier , Izzy Zapata, and Trevor Sova.
Though they had already been on Netflix's biggest dating show , Jessica, Micah, and Izzy told Business Insider that filming "Perfect Match" was tougher.
Jessica described "Love Is Blind" as "definitely more my element."
"I've always dated with the marriage mindset with just not the tools as far as how to get there," she said. "So I mean, 'Love is Blind' just prepared me to be able to be vulnerable and date in a place where you kind of just give it your all."
The contestants who make it through the " Love Is Blind " process get married at the show's end. "Perfect Match" is competition-based, not marriage-focused, and has not produced lasting relationships so far.
Related stories
In the show, contestants from different Netflix reality shows date each other and cast votes for a winning couple at the end of the season.
Micah also acknowledged the differences between the two shows and told BI that "Love Is Blind" helped her gain the confidence to appear on another reality TV show.
"I think it did allow me to be able to gain a confidence that I probably wouldn't have had going into the 'Perfect Match' house without being on 'Love Is Blind,'" Micah said. "So maybe it was a nice little starter."
Izzy similarly told BI that he found "Perfect Match" difficult because he went into the show with the idea that he would find his wife.
"It was definitely harder," he said. "I went in with the 'Love Is Blind' mentality and learned very quickly, it ain't no 'Love Is Blind.'"
Izzy was eliminated from the cast in "Perfect Match" season two, episode two, when his original partner, Tolú Ekundare, dumped him for another man.
Despite his early elimination, Izzy told BI that he was happy to leave the house because there wasn't anyone he was interested in.
"We had to leave the house, and when I came back, it was a whole different game plan," Izzy said. "Honestly, at that point, I realized there was no one there for me, which I didn't mind just because I was hopeful there was an opportunity down the road to come back into the house and hopefully land on a date."
New episodes of " Perfect Match " season two premiere on June 14.
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the difference between a business plan and a business proposal, two distinct documents with different purposes and audiences. A business plan is a comprehensive vision and strategy for your company, while a business proposal is a focused sales pitch for a project.
In Closing. Clearly, a business plan and a business proposal are similar - and can even be one and the same. At the same time, they can also serve very different purposes. Unlike a business plan, a business proposal can have a variety of aims and thus does not have a "one size fits all" structure.
Tell your business's story: Include a chronological summary of your coaching business. Talk about how you opened and grew your business. Remember, your business profile differs from a coaching bio and a business plan. In a profile, you're trying to paint a picture of your company. A bio focuses on personal and professional accomplishments.
The main difference between a business plan and a business proposal is that a business plan documents your growth strategy while a business proposal is a specific ask for someone to take an action you desire (e.g., buy your product/service, invest in your company, partner with you, etc.). In this article, we will define a business plan and a ...
Updated November 12, 2020: Conducting a comparison between a business proposal and a business plan enables you to highlight the differences between the two. Business plans are documents detailing how owners want to set up their business, their goals and objectives, and the processes and methods required to achieve these goals.
A business profile gives a general idea of what a business is about and a glimpse into your organisation's business plan. Learn the difference between a business profile and a business plan, and follow the 8 steps to write an effective business profile.
That includes: Your company name: This should be the official name of your business, exactly as it is written when you registered your business with the state. Business structure: Your reader will ...
A promising business plan talks about the company's future financial performance - expenditure, profit, revenue, etc. Explore new business opportunities. A business plan is a flexible document that enables learning on the go. It bolsters research and infuses businesses with new and more feasible business opportunities.
A company profile is an essential part of a business plan and a business plan cannot be complete without a company profile. So, when writing your business plan, make sure you come up with a good and highly sellable company profile, and the guide you have here will help you achieve this.
A company profile is a professional introduction to your business. It informs potential customers, stakeholders and the general public about your products, services, and business as a whole. A company profile can be anything from a few sentences to an entire page on your website - most businesses have a long and short version - and is a ...
A business plan is a factual broad description of a company on the executive and operational level. A business proposal is a focused sales document intended to describe how a company will approach ...
A business plan and a business proposal are different from each other by content, goals, writing style, and structure. The major difference between both is that a business plan is a document that presents facts, while a business proposal is a request for a deal and a quotation of prices. A Business Plan. You can think of a business plan as the ...
You now know the distinction between the two lies in their purpose, components, structure, audience, and type. While a business plan provides a thorough overview of the entire business and targets internal stakeholders, investors, and lenders, a business proposal focuses on specific projects or opportunities and targets external clients ...
The business profile includes the legal name of the corporate entity, and full physical address information. The market and industry are mentioned along with the history the company has had in this field. If it is a new company, the experience of key personnel in the industry are highlighted. The profile may mention the number of employees and ...
The most important difference to note is that a business plan is a written presentation of fact while a business proposal is a price quote and a call to action. Definition. According to an article on Entrepreneur.com, a business plan is a document that outlines a detailed description of how a business is set up.
A business plan describes your business goals, strategies, and financial projections. A business proposal, on the other hand, proposes a specific solution to a problem or opportunity and helps you persuade the relevant stakeholder to invest in your business. However, writing a business proposal or a business plan can be challenging, especially ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
A business proposal, on the other hand, is a sales document that you put together to pitch potential projects to clients.It's not the same as a business plan, and it usually includes cost quotes for potential projects. The main difference between a business proposal and a business plan is that, while a business plan is informative, a business proposal is intended to showcase operations, goals ...
A business model is a company's core framework for operating profitably and providing value to customers. They usually include the customer value proposition and pricing strategy. A business plan outlines your business goals and your strategies for achieving them. The two documents have a few critical differences, namely their structure and ...
A business plan is a living document that's subject to change in order to keep up with the business' needs. On the contrary, a business proposal is a persuasive document that's used to bring more money into the business through business deals and sales. Promoting existing goods and services characterise a business proposal, which in turn ...
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's reasoning for being in business, strategy for earning revenue and predictions of financial performance for the foreseeable future. Business plans are often used as a way to give investors, lenders, shareholders and other interested parties an overview of a company.
All About Google Business Profile. Talking about Google switching from Google My Business to Google Business Profile feels like tidying up a cluttered desk - so that everything you need is right at your fingertips! Initially, it was known as Google My Business. This helped business owners manage their listings on Google Search and Maps.
This profile will be your first step to building your brand. A business profile is also known as a company profile or a business entity profile. When we talk about company profile it means that you have the right to trade and sell the products in a particular area. A company profile is also used to create a business license.
CEOs in the S&P 500 made almost 200 times what their average worker did in 2023. CEO compensation had been trending downward before a 12.6% increase in 2023. Broadcom CEO Hock Tan was the highest ...
Deciding on a plan can depend on your specific business needs. The Microsoft 365 plan chooser is designed to help you with this. The chooser will make recommendations based on your answers to questions such as the size of your business, your field of work, the devices you use, and what kind of features, IT support, and security you're looking for.
Other subscription plans. Besides Microsoft 365 Family or Personal, there are other Microsoft 365 plans which include additional benefits and features designed specifically for small and mid-size businesses, enterprises, schools, or non-profits. You also get 5 GB of OneDrive online cloud storage with your free Microsoft account so you can access your files from anywhere.
Microsoft Edge for Business, the new, dedicated work experience for the Microsoft Edge browser, is now available in Microsoft Edge stable version 116 . ... is enabled so users with a personal profile can separate their work and personal browsing and take advantage of the full feature set of Edge for personal use. This will also enable automatic ...
The difference between personal and business Instagram accounts is pretty straightforward. Personal accounts are great for sharing your daily life and connecting with friends and family. But, if you're running a business or want to promote or sell a product, a business account on Instagram offers tools like analytics, shopping, and ...
People on these teams plan and run the social and environmental programs that align with the company's values and goals. They work with company leadership to devise the overall CSR strategy and engage stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors and community partners, to help them succeed.
Micah also acknowledged the differences between the two shows and told BI that "Love Is Blind" helped her gain the confidence to appear on another reality TV show.