How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: November 30, 2023
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a struggle. Before you can even begin to expect to earn their business, you need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on what your product or service promises.

Sure, you could say that you're great at X or that you're way ahead of the competition when it comes to Y. But at the end of the day, what you really need to win new business is cold, hard proof.
One of the best ways to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. In fact, HubSpot’s 2020 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so compelling that they are the fifth most commonly used type of content used by marketers.

Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what you need to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic. To jump to different areas of this post, click on the links below to automatically scroll.

Case Study Definition
Case study templates, how to write a case study.
- How to Format a Case Study
Business Case Study Examples
A case study is a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it's common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client. Perhaps the success you're highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers and help you attract new clients.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why write a case study?
I know, you’re thinking “ Okay, but why do I need to write one of these? ” The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples. Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain Complex Topics or Concepts
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies and show how they can be applied in a practical way. You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that shows how your product solved their issue and how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar successful results.
2. Show Expertise
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build Trust and Credibility
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework. They can have confidence in the solutions you’ve presented because they’ve read through as you’ve explained the problem and outlined step-by-step what it took to solve it. All of these elements working together enable you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create Social Proof
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof . People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — putting your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes work together to help you gain more clients. Plus you can even use quotes from customers featured in these studies and repurpose them in other marketing content. Now that you know more about the benefits of producing a case study, let’s check out how long these documents should be.
How long should a case study be?
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved. This may be easier said than done, but it's important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader's interest.
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers. We’ve also seen brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience.
Ultimately, the length of your case study should be determined by the amount of information necessary to convey the story and its impact without becoming too long. Next, let’s look at some templates to take the guesswork out of creating one.
To help you arm your prospects with information they can trust, we've put together a step-by-step guide on how to create effective case studies for your business with free case study templates for creating your own.
Tell us a little about yourself below to gain access today:
And to give you more options, we’ll highlight some useful templates that serve different needs. But remember, there are endless possibilities when it comes to demonstrating the work your business has done.
1. General Case Study Template

Do you have a specific product or service that you’re trying to sell, but not enough reviews or success stories? This Product Specific case study template will help.
This template relies less on metrics, and more on highlighting the customer’s experience and satisfaction. As you follow the template instructions, you’ll be prompted to speak more about the benefits of the specific product, rather than your team’s process for working with the customer.
4. Bold Social Media Business Case Study Template

You can find templates that represent different niches, industries, or strategies that your business has found success in — like a bold social media business case study template.
In this template, you can tell the story of how your social media marketing strategy has helped you or your client through collaboration or sale of your service. Customize it to reflect the different marketing channels used in your business and show off how well your business has been able to boost traffic, engagement, follows, and more.
5. Lead Generation Business Case Study Template

It’s important to note that not every case study has to be the product of a sale or customer story, sometimes they can be informative lessons that your own business has experienced. A great example of this is the Lead Generation Business case study template.
If you’re looking to share operational successes regarding how your team has improved processes or content, you should include the stories of different team members involved, how the solution was found, and how it has made a difference in the work your business does.
Now that we’ve discussed different templates and ideas for how to use them, let’s break down how to create your own case study with one.
- Get started with case study templates.
- Determine the case study's objective.
- Establish a case study medium.
- Find the right case study candidate.
- Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
- Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
- Download a case study email template.
- Define the process you want to follow with the client.
- Ensure you're asking the right questions.
- Layout your case study format.
- Publish and promote your case study.
1. Get started with case study templates.
Telling your customer's story is a delicate process — you need to highlight their success while naturally incorporating your business into their story.
If you're just getting started with case studies, we recommend you download HubSpot's Case Study Templates we mentioned before to kickstart the process.
2. Determine the case study's objective.
All business case studies are designed to demonstrate the value of your services, but they can focus on several different client objectives.
Your first step when writing a case study is to determine the objective or goal of the subject you're featuring. In other words, what will the client have succeeded in doing by the end of the piece?
The client objective you focus on will depend on what you want to prove to your future customers as a result of publishing this case study.
Your case study can focus on one of the following client objectives:
- Complying with government regulation
- Lowering business costs
- Becoming profitable
- Generating more leads
- Closing on more customers
- Generating more revenue
- Expanding into a new market
- Becoming more sustainable or energy-efficient
3. Establish a case study medium.
Next, you'll determine the medium in which you'll create the case study. In other words, how will you tell this story?
Case studies don't have to be simple, written one-pagers. Using different media in your case study can allow you to promote your final piece on different channels. For example, while a written case study might just live on your website and get featured in a Facebook post, you can post an infographic case study on Pinterest and a video case study on your YouTube channel.
Here are some different case study mediums to consider:
Written Case Study
Consider writing this case study in the form of an ebook and converting it to a downloadable PDF. Then, gate the PDF behind a landing page and form for readers to fill out before downloading the piece, allowing this case study to generate leads for your business.
Video Case Study
Plan on meeting with the client and shooting an interview. Seeing the subject, in person, talk about the service you provided them can go a long way in the eyes of your potential customers.
Infographic Case Study
Use the long, vertical format of an infographic to tell your success story from top to bottom. As you progress down the infographic, emphasize major KPIs using bigger text and charts that show the successes your client has had since working with you.
Podcast Case Study
Podcasts are a platform for you to have a candid conversation with your client. This type of case study can sound more real and human to your audience — they'll know the partnership between you and your client was a genuine success.
4. Find the right case study candidate.
Writing about your previous projects requires more than picking a client and telling a story. You need permission, quotes, and a plan. To start, here are a few things to look for in potential candidates.
Product Knowledge
It helps to select a customer who's well-versed in the logistics of your product or service. That way, he or she can better speak to the value of what you offer in a way that makes sense for future customers.
Remarkable Results
Clients that have seen the best results are going to make the strongest case studies. If their own businesses have seen an exemplary ROI from your product or service, they're more likely to convey the enthusiasm that you want prospects to feel, too.
One part of this step is to choose clients who have experienced unexpected success from your product or service. When you've provided non-traditional customers — in industries that you don't usually work with, for example — with positive results, it can help to remove doubts from prospects.
Recognizable Names
While small companies can have powerful stories, bigger or more notable brands tend to lend credibility to your own. In fact, 89% of consumers say they'll buy from a brand they already recognize over a competitor, especially if they already follow them on social media.
Customers that came to you after working with a competitor help highlight your competitive advantage and might even sway decisions in your favor.
5. Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
To get the case study candidate involved, you have to set the stage for clear and open communication. That means outlining expectations and a timeline right away — not having those is one of the biggest culprits in delayed case study creation.
Most importantly at this point, however, is getting your subject's approval. When first reaching out to your case study candidate, provide them with the case study's objective and format — both of which you will have come up with in the first two steps above.
To get this initial permission from your subject, put yourself in their shoes — what would they want out of this case study? Although you're writing this for your own company's benefit, your subject is far more interested in the benefit it has for them.
Benefits to Offer Your Case Study Candidate
Here are four potential benefits you can promise your case study candidate to gain their approval.
Brand Exposure
Explain to your subject to whom this case study will be exposed, and how this exposure can help increase their brand awareness both in and beyond their own industry. In the B2B sector, brand awareness can be hard to collect outside one's own market, making case studies particularly useful to a client looking to expand their name's reach.
Employee Exposure
Allow your subject to provide quotes with credits back to specific employees. When this is an option for them, their brand isn't the only thing expanding its reach — their employees can get their name out there, too. This presents your subject with networking and career development opportunities they might not have otherwise.
Product Discount
This is a more tangible incentive you can offer your case study candidate, especially if they're a current customer of yours. If they agree to be your subject, offer them a product discount — or a free trial of another product — as a thank-you for their help creating your case study.
Backlinks and Website Traffic
Here's a benefit that is sure to resonate with your subject's marketing team: If you publish your case study on your website, and your study links back to your subject's website — known as a "backlink" — this small gesture can give them website traffic from visitors who click through to your subject's website.
Additionally, a backlink from you increases your subject's page authority in the eyes of Google. This helps them rank more highly in search engine results and collect traffic from readers who are already looking for information about their industry.
6. Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
So you know what you’re going to offer your candidate, it’s time that you prepare the resources needed for if and when they agree to participate, like a case study release form and success story letter.
Let's break those two down.
Case Study Release Form
This document can vary, depending on factors like the size of your business, the nature of your work, and what you intend to do with the case studies once they are completed. That said, you should typically aim to include the following in the Case Study Release Form:
- A clear explanation of why you are creating this case study and how it will be used.
- A statement defining the information and potentially trademarked information you expect to include about the company — things like names, logos, job titles, and pictures.
- An explanation of what you expect from the participant, beyond the completion of the case study. For example, is this customer willing to act as a reference or share feedback, and do you have permission to pass contact information along for these purposes?
- A note about compensation.
Success Story Letter
As noted in the sample email, this document serves as an outline for the entire case study process. Other than a brief explanation of how the customer will benefit from case study participation, you'll want to be sure to define the following steps in the Success Story Letter.
7. Download a case study email template.
While you gathered your resources, your candidate has gotten time to read over the proposal. When your candidate approves of your case study, it's time to send them a release form.
A case study release form tells you what you'll need from your chosen subject, like permission to use any brand names and share the project information publicly. Kick-off this process with an email that runs through exactly what they can expect from you, as well as what you need from them. To give you an idea of what that might look like, check out this sample email:
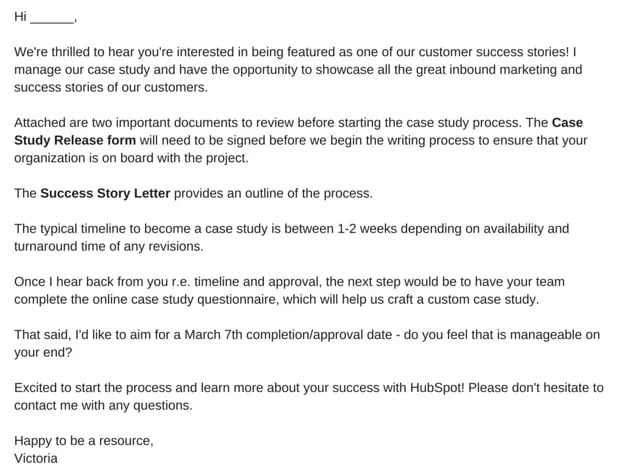
8. Define the process you want to follow with the client.
Before you can begin the case study, you have to have a clear outline of the case study process with your client. An example of an effective outline would include the following information.
The Acceptance
First, you'll need to receive internal approval from the company's marketing team. Once approved, the Release Form should be signed and returned to you. It's also a good time to determine a timeline that meets the needs and capabilities of both teams.
The Questionnaire
To ensure that you have a productive interview — which is one of the best ways to collect information for the case study — you'll want to ask the participant to complete a questionnaire before this conversation. That will provide your team with the necessary foundation to organize the interview, and get the most out of it.
The Interview
Once the questionnaire is completed, someone on your team should reach out to the participant to schedule a 30- to 60-minute interview, which should include a series of custom questions related to the customer's experience with your product or service.
The Draft Review
After the case study is composed, you'll want to send a draft to the customer, allowing an opportunity to give you feedback and edits.
The Final Approval
Once any necessary edits are completed, send a revised copy of the case study to the customer for final approval.
Once the case study goes live — on your website or elsewhere — it's best to contact the customer with a link to the page where the case study lives. Don't be afraid to ask your participants to share these links with their own networks, as it not only demonstrates your ability to deliver positive results and impressive growth, as well.
9. Ensure you're asking the right questions.
Before you execute the questionnaire and actual interview, make sure you're setting yourself up for success. A strong case study results from being prepared to ask the right questions. What do those look like? Here are a few examples to get you started:
- What are your goals?
- What challenges were you experiencing before purchasing our product or service?
- What made our product or service stand out against our competitors?
- What did your decision-making process look like?
- How have you benefited from using our product or service? (Where applicable, always ask for data.)
Keep in mind that the questionnaire is designed to help you gain insights into what sort of strong, success-focused questions to ask during the actual interview. And once you get to that stage, we recommend that you follow the "Golden Rule of Interviewing." Sounds fancy, right? It's actually quite simple — ask open-ended questions.
If you're looking to craft a compelling story, "yes" or "no" answers won't provide the details you need. Focus on questions that invite elaboration, such as, "Can you describe ...?" or, "Tell me about ..."
In terms of the interview structure, we recommend categorizing the questions and flowing them into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, and how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context. That helps match the customer's need with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes. Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you've collected and actually turn it into something, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. Where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
To help you get a handle on this step, it's important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study. They can be very visual, which you'll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated mostly through video or photos, with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections we suggest, which we'll cover in more detail down below:
- Title: Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle: Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary : A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject: An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives: A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped: A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results: A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes: Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans: Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call to Action (CTA): Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible. Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you've completed your case study, it's time to publish and promote it. Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas:
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier in this article, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF. To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client's success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they'd like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people here from your homepage with a "Case Studies" or "Testimonials" button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
Format for a Case Study
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

Image Source
The title is one of the most important parts of your case study. It should draw readers in while succinctly describing the potential benefits of working with your company. To that end, your title should:
- State the name of your custome r. Right away, the reader must learn which company used your products and services. This is especially important if your customer has a recognizable brand. If you work with individuals and not companies, you may omit the name and go with professional titles: “A Marketer…”, “A CFO…”, and so forth.
- State which product your customer used . Even if you only offer one product or service, or if your company name is the same as your product name, you should still include the name of your solution. That way, readers who are not familiar with your business can become aware of what you sell.
- Allude to the results achieved . You don’t necessarily need to provide hard numbers, but the title needs to represent the benefits, quickly. That way, if a reader doesn’t stay to read, they can walk away with the most essential information: Your product works.
The example above, “Crunch Fitness Increases Leads and Signups With HubSpot,” achieves all three — without being wordy. Keeping your title short and sweet is also essential.
2. Subtitle

Your subtitle is another essential part of your case study — don’t skip it, even if you think you’ve done the work with the title. In this section, include a brief summary of the challenges your customer was facing before they began to use your products and services. Then, drive the point home by reiterating the benefits your customer experienced by working with you.
The above example reads:
“Crunch Fitness was franchising rapidly when COVID-19 forced fitness clubs around the world to close their doors. But the company stayed agile by using HubSpot to increase leads and free trial signups.”
We like that the case study team expressed the urgency of the problem — opening more locations in the midst of a pandemic — and placed the focus on the customer’s ability to stay agile.
3. Executive Summary

The executive summary should provide a snapshot of your customer, their challenges, and the benefits they enjoyed from working with you. Think it’s too much? Think again — the purpose of the case study is to emphasize, again and again, how well your product works.
The good news is that depending on your design, the executive summary can be mixed with the subtitle or with the “About the Company” section. Many times, this section doesn’t need an explicit “Executive Summary” subheading. You do need, however, to provide a convenient snapshot for readers to scan.
In the above example, ADP included information about its customer in a scannable bullet-point format, then provided two sections: “Business Challenge” and “How ADP Helped.” We love how simple and easy the format is to follow for those who are unfamiliar with ADP or its typical customer.
4. About the Company

Readers need to know and understand who your customer is. This is important for several reasons: It helps your reader potentially relate to your customer, it defines your ideal client profile (which is essential to deter poor-fit prospects who might have reached out without knowing they were a poor fit), and it gives your customer an indirect boon by subtly promoting their products and services.
Feel free to keep this section as simple as possible. You can simply copy and paste information from the company’s LinkedIn, use a quote directly from your customer, or take a more creative storytelling approach.
In the above example, HubSpot included one paragraph of description for Crunch Fitness and a few bullet points. Below, ADP tells the story of its customer using an engaging, personable technique that effectively draws readers in.

5. Challenges and Objectives

The challenges and objectives section of your case study is the place to lay out, in detail, the difficulties your customer faced prior to working with you — and what they hoped to achieve when they enlisted your help.
In this section, you can be as brief or as descriptive as you’d like, but remember: Stress the urgency of the situation. Don’t understate how much your customer needed your solution (but don’t exaggerate and lie, either). Provide contextual information as necessary. For instance, the pandemic and societal factors may have contributed to the urgency of the need.
Take the above example from design consultancy IDEO:
“Educational opportunities for adults have become difficult to access in the United States, just when they’re needed most. To counter this trend, IDEO helped the city of South Bend and the Drucker Institute launch Bendable, a community-powered platform that connects people with opportunities to learn with and from each other.”
We love how IDEO mentions the difficulties the United States faces at large, the efforts its customer is taking to address these issues, and the steps IDEO took to help.
6. How Product/Service Helped
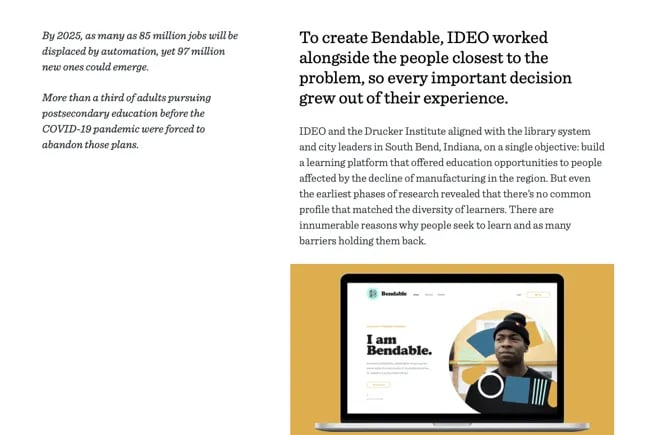
This is where you get your product or service to shine. Cover the specific benefits that your customer enjoyed and the features they gleaned the most use out of. You can also go into detail about how you worked with and for your customer. Maybe you met several times before choosing the right solution, or you consulted with external agencies to create the best package for them.
Whatever the case may be, try to illustrate how easy and pain-free it is to work with the representatives at your company. After all, potential customers aren’t looking to just purchase a product. They’re looking for a dependable provider that will strive to exceed their expectations.
In the above example, IDEO describes how it partnered with research institutes and spoke with learners to create Bendable, a free educational platform. We love how it shows its proactivity and thoroughness. It makes potential customers feel that IDEO might do something similar for them.

The results are essential, and the best part is that you don’t need to write the entirety of the case study before sharing them. Like HubSpot, IDEO, and ADP, you can include the results right below the subtitle or executive summary. Use data and numbers to substantiate the success of your efforts, but if you don’t have numbers, you can provide quotes from your customers.
We can’t overstate the importance of the results. In fact, if you wanted to create a short case study, you could include your title, challenge, solution (how your product helped), and result.
8. Supporting Visuals or Quotes

Let your customer speak for themselves by including quotes from the representatives who directly interfaced with your company.
Visuals can also help, even if they’re stock images. On one side, they can help you convey your customer’s industry, and on the other, they can indirectly convey your successes. For instance, a picture of a happy professional — even if they’re not your customer — will communicate that your product can lead to a happy client.
In this example from IDEO, we see a man standing in a boat. IDEO’s customer is neither the man pictured nor the manufacturer of the boat, but rather Conservation International, an environmental organization. This imagery provides a visually pleasing pattern interrupt to the page, while still conveying what the case study is about.
9. Future Plans
This is optional, but including future plans can help you close on a more positive, personable note than if you were to simply include a quote or the results. In this space, you can show that your product will remain in your customer’s tech stack for years to come, or that your services will continue to be instrumental to your customer’s success.
Alternatively, if you work only on time-bound projects, you can allude to the positive impact your customer will continue to see, even after years of the end of the contract.
10. Call to Action (CTA)
Not every case study needs a CTA, but we’d still encourage it. Putting one at the end of your case study will encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
It will also make it easier for them to reach out, if they’re ready to start immediately. You don’t want to lose business just because they have to scroll all the way back up to reach out to your team.
To help you visualize this case study outline, check out the case study template below, which can also be downloaded here .
You drove the results, made the connection, set the expectations, used the questionnaire to conduct a successful interview, and boiled down your findings into a compelling story. And after all of that, you're left with a little piece of sales enabling gold — a case study.
To show you what a well-executed final product looks like, have a look at some of these marketing case study examples.
1. "Shopify Uses HubSpot CRM to Transform High Volume Sales Organization," by HubSpot
What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. This reflects a major HubSpot value, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why Shopify uses HubSpot and is accompanied by a short video and some basic statistics on the company.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the additional text on the page. So, while case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
2. "New England Journal of Medicine," by Corey McPherson Nash
When branding and design studio Corey McPherson Nash showcases its work, it makes sense for it to be visual — after all, that's what they do. So in building the case study for the studio's work on the New England Journal of Medicine's integrated advertising campaign — a project that included the goal of promoting the client's digital presence — Corey McPherson Nash showed its audience what it did, rather than purely telling it.
Notice that the case study does include some light written copy — which includes the major points we've suggested — but lets the visuals do the talking, allowing users to really absorb the studio's services.
3. "Designing the Future of Urban Farming," by IDEO
Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, he or she is greeted with a big, bold photo, and two very simple columns of text — "The Challenge" and "The Outcome."
Immediately, IDEO has communicated two of the case study's major pillars. And while that's great — the company created a solution for vertical farming startup INFARM's challenge — it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, those pillars are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and additional visuals.
4. "Secure Wi-Fi Wins Big for Tournament," by WatchGuard
Then, there are the cases when visuals can tell almost the entire story — when executed correctly. Network security provider WatchGuard can do that through this video, which tells the story of how its services enhanced the attendee and vendor experience at the Windmill Ultimate Frisbee tournament.
5. Rock and Roll Hall of Fame Boosts Social Media Engagement and Brand Awareness with HubSpot
In the case study above , HubSpot uses photos, videos, screenshots, and helpful stats to tell the story of how the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame used the bot, CRM, and social media tools to gain brand awareness.
6. Small Desk Plant Business Ups Sales by 30% With Trello
This case study from Trello is straightforward and easy to understand. It begins by explaining the background of the company that decided to use it, what its goals were, and how it planned to use Trello to help them.
It then goes on to discuss how the software was implemented and what tasks and teams benefited from it. Towards the end, it explains the sales results that came from implementing the software and includes quotes from decision-makers at the company that implemented it.
7. Facebook's Mercedes Benz Success Story
Facebook's Success Stories page hosts a number of well-designed and easy-to-understand case studies that visually and editorially get to the bottom line quickly.
Each study begins with key stats that draw the reader in. Then it's organized by highlighting a problem or goal in the introduction, the process the company took to reach its goals, and the results. Then, in the end, Facebook notes the tools used in the case study.
Showcasing Your Work
You work hard at what you do. Now, it's time to show it to the world — and, perhaps more important, to potential customers. Before you show off the projects that make you the proudest, we hope you follow these important steps that will help you effectively communicate that work and leave all parties feeling good about it.
Editor's Note: This blog post was originally published in February 2017 but was updated for comprehensiveness and freshness in July 2021.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![case study report design 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![case study report design How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![case study report design What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing How to Write a Case Study [+ Design Tips]
How to Write a Case Study [+ Design Tips]
Written by: Ronita Mohan Aug 26, 2021
![case study report design How to Write a Case Study [+ Design Tips] Blog Header](https://venngage-wordpress.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2021/08/How-to-Write-a-Case-Study-Design-Tips-Blog-Header.png)
You need an impactful medium to share your business successes with potential customers and partners. The best way to showcase your brand is by designing a case study.
Case studies are a method of research and storytelling. They help readers gain a better understanding of a subject or process.
In this guide, we’ll explain how to write a case report that markets your business, as well as some design tips.
Don’t know how to start designing case studies? Create a case study with Venngage’s templates. No design experience required.
START CREATING FOR FREE
Click to jump ahead:
Case study defined, what is the purpose of a case study, what is the format of a case study, how do you write a business case study, case study design tips, case study faqs.
A case study is used in business, psychology, epidemiology, as well as the medical and scientific fields. These reports are also used for social and political work.
Case studies are defined as documents that examine a person, groups of people, events, operations and processes.
For marketing purposes, a case analysis can be a document that outlines problems faced by a customer. It also shares the solutions a brand provided to solve them, such as in the case report below.

USE THIS CASE STUDY TEMPLATE
Case studies usually share success stories for a business partnership or client. But case reports can also be used to analyze a process that went wrong.
This type of study will outline the need for improvements and suggest next steps. As a result, these case studies are not shared externally.
You can look at some case study examples for inspiration to design your report. Read on to learn about the importance of case studies and how to write them.
Related: What is a Case Study? [+6 Types of Case Studies]
Return to Table of Contents
Case studies are effective marketing tools that build trust and act as social proof for your brand.
Customers are more likely to choose your company if they know that other businesses like theirs have also benefited.
More importantly, when a customer participates in creating a case report with a brand, they endorse the company and their experience with it.
In other words, a business report , like the example below, acts as a recommendation to anyone on the fence about working with your brand or using your products.

CREATE THIS REPORT TEMPLATE
Related: Report Design Ideas to ENGAGE Readers [10+ Tips & Templates]
A case study can be of varying lengths. It can also take a variety of forms, such as a simple two-page document or a Venngage business infographic like the one below.

Most business case studies feature the following five sections.
Related: What is an Infographic? Examples, Templates & Design Tips
- About the company
When creating a case study for marketing, it is best to include a small section about the company. This section can be short, sharing highlights about the company’s goals and missions.

Venngage’s case study templates offer a variety of options for customizing your report.
Overview of the case study
This is a key section of a case study. What is the study about? What was the reason for conducting it? What are the expected results?
The overview doesn’t have to be very long. Two or three paragraphs that sum up what a reader can expect from the report will suffice.
Case study research
You want to show the kind of research, strategy, and approach adopted for your case study. This is the section where you can showcase your process while conducting the analysis, like in this template.

Results of the case study
By far the most important aspect of a case study is the results section. You can choose to share your findings in a few paragraphs.
Alternatively, go down a more visual route by using data visualizations to showcase your results. You can use different types of charts and graphs or use a single number or donut chart.
This case study template is a great example of how to highlight results.

This is also a good section to include a testimonial or quote from your client as social proof.
Related: How to Choose the Best Types of Charts
Conclusion of the case report
You can choose to add a separate conclusion to your case study following the results section. This is where you sum up the process you used in the analysis.
Also, share why the process or campaign was effective and how your brand achieved these results.
Writing a case study requires research and revision. You should have a single objective decided before you start writing.
Case studies in marketing, like the below example, are meant to highlight your company’s successes. Choosing a client to showcase is also an important step in the writing process.

Below, we share the top steps to complete when writing a case study to promote your business.
Determine your objective
Before you start writing case studies, decide what the main objective for this exercise is. Case reports don’t have the potential to go viral, nor are they shareable on social media.
But a case study is an effective tool for converting prospects into customers. They can also encourage business partners to take that final step and sign on the dotted line.
You need to approach your case analysis differently than all other content. This is why you need to have an objective for undergoing the process of writing a case study.
For example, this report shows how the fictional company Toy Crates used the services of Ad Factory to significantly increase its sales.

The main objective of your case study is to highlight your business processes. You should also show the benefits of using your product. But there needs to be a relatable angle for whoever is reading your study.
Possible angles for a case study can be:
- Audience growth
- Launch of a new type of product
- Entry into a new market
- Improvements in conversion rates
- Increased revenue
- Increased traffic or social media impressions
- Technology or software adoption
This case study focuses on lead generation. The report showcases the efforts behind boosting the client’s lead generation program and the successes achieved.

Once you determine the best objective for your analysis, you can move onto the next step. Look for a client that best showcases positive aspects of your company.
Choose the right client
You need a particular type of client as the subject of your case study. This client will be a loyal customer. They should be willing to participate in the study. The client should also align with the objective of your study.
Pick a customer who knows your product inside and out. They should not be someone who used your product once and had success with it.
You want to showcase consistent and high-quality results over a period of time. In this example, the fictional Ad Factory also showcased Loot Box as a client that had success with their brand.

USE THIS CASE REPORT TEMPLATE
You also want to choose customers who have had success directly from using your product. If a brand has seen overall growth and your product was just part of that success, it won’t make for a compelling case study.
Contacting your client for the case study
The customer you choose for your case study should know what the process entails.
Be open in your communication about what you need to put together the case report. This could be communicated through calls, email conversations, or a project management tool.
Set a deadline and share a project timeline so the client knows what the process will look like. Let them know what documentation or statistics you will need for them before you start writing.
Offer something in exchange for participating in the case study. These could be product discounts, a temporary upgrade, a mention in your newsletter, social media, or increased brand awareness.

USE THIS CASE REPORT TEMPLATE
It is imperative that you let the customer know how their information and data will be used. Tell them if you’re posting the case analysis to your blog, sharing it on YouTube, or with your email subscribers.
Some clients may not want their professional information shared with large audiences, so clarify this step of the process first.
Related: 40+ Timeline Template Examples and Design Tips
Research your case study
Once your client agrees to participate in the case analysis, you can begin researching. Remember the objective of your case study and research the subject accordingly.
For example, we wanted to show how infographics help businesses grow their audience. We contacted our user, ChadSan , who had seen massive growth after adding infographics to their marketing campaigns.
We put our findings into a research infographic along with quotes from the client, charts and graphs.

To do this, we researched the content ChadSan created before and compared their traffic to when they started using infographics.
It’s also important to look at the industry your client is in so you have an idea of what success looks like in that sector.
Client interviews
Conducting interviews with clients is a good way to get information for your case report.
You can hold interviews via video call, which you should record to double-check later or conduct the interview via email.
Email interviews might require follow-ups if you need further clarification on particular questions.
Asking the right questions is crucial during the research phase. You don’t want ‘yes’ or ‘no’ as an answer. You need qualified information and data to build out a case study, like the one below.

USE THIS CASE REPORT TEMPLATE
For example, we asked our contact at ChadSan for her experience using infographics in her marketing. We also asked about her main challenges, why she had chosen Venngage and the benefits of using Venngage.
This is also the stage when you can ask for concrete examples of how your product benefited your client.
We asked ChadSan to share some examples of the infographics they had created using our templates. This helped show our product in use, further social proof of the advantages of using Venngage infographics.
Create the case study outline
With the client interview completed, gather the data you have and start writing the outline for the case report. Remember the case study format we shared earlier when you’re preparing the outline.
This will help you design a case study that is memorable, like this example.

For a case study blog post, you should prepare the following:
- Overview of the study
- The results, with charts
- Call to action
Write a few notes for each point that you can elaborate on in the next writing stage. By following this process, you can build out a case study like this example.

Draft your case report
The outline is your starting point for drafting the case report. Like any other piece of content you create, a case study needs to be engaging. It also needs a beginning, a middle and an end.
Use classic marketing storytelling approaches when writing case studies. Introduce your characters (the client), the conflict (the business problem), the resolution (the benefits of your product).
By using this technique, you can write a case study like this example.

Conclude with an analysis of your success and a testimonial recommending your product and brand.
Finalize your case study
Revise your study and ask one or two colleagues to glance over it to catch any mistakes you may have missed.
You should send the report to the client you’re showcasing for their approval. When you and the client are satisfied with the case study, an infographic study like the one below is ready to be published.

Share a link to the case study with the client to promote on their platforms. You can share the case report on your social channels, with partners and to your email subscribers.
Now that you know how to write your case report, here are some tips on case study design. Improving the aesthetics and usability of your study will make it memorable to read. In the long run, the study will help boost brand awareness.
Use a case study template
Make the case study design process easier by using a template. Venngage offers a variety of customizable case study templates , like this one, to make any study attractive and engaging.
Choose a template from Venngage’s library and edit it to fit your needs. Change the text, upload visuals or choose images from our stock photo integration. Pick icons from the 40,000+ icons available to better reflect your story.
With Venngage for Business , you can get priority support while designing your study.
You can also access real-time collaboration features so you can design your case study with team members.
Incorporate white space
A great way to make your case study engaging is to incorporate one important rule of design: use plenty of white space.
White space is all the blank areas around your text and visuals. This space gives your information room to breathe and makes it easier for readers to absorb your story.
Take a look at this template for inspiration. There is plenty of room around each element. This makes the study easier to navigate.

Write short paragraphs of two or three lines and use bullet points to create more space around your text. Leave room around your visuals, as well, so users can move through the sections easily.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to Design Thinking
Visualize data for your case study
Case studies include a great deal of information but that doesn’t mean they need to be packed full of text. Visuals are a great way to catch the eye and keep users interested in your report.
Statistics are a key element of case reports but numbers on their own can get lost. Instead, visualize your data using Venngage’s chart maker and graph maker .
Design pie charts, bar graphs, donut charts, line and area graphs, or maps to visualize numerous types of data for your case studies, like in this example.

Related: How to Tell a Story With Data: A Guide for Beginners
Add branding to case reports
Branding is an important facet of case reports. Anybody reading the study should know which companies were involved, both the client and your brand.
Add recognizable brand elements such as your logo and the client’s logo. Use your brand colors and brand fonts throughout your case study design.
Ensure that your design adheres to your brand guidelines , including your brand voice.
Take a look at this case study infographic Venngage created with Baptist Care. We incorporated both our logos in the infographic. We also used the brand colors and fonts of both companies.

You can easily add your branding to case report templates using Venngage’s My Brand Kit tool. Input your website and the Autobrand feature will apply your branding across all your designs.
What subjects are covered in a case study?
Depending on the field of study, case reports can examine a variety of subjects, including:
- a group of people
- an organization or business
For example, case studies in psychology may be focused on a person or groups of people. Medical case reports might study events or groups of patients.
Businesses can examine other organizations, as in this example, or events.

What are the characteristics of a case study?
Case studies are characterized by the units or subjects they examine. These units need to be studied in totality. Every aspect of the person, organization or event needs to be included.
Reports should also be qualitative as well as quantitative. This means that case study research describes problems and solutions.
It also backs those assumptions up with data. Both aspects must be included in the analysis, as in this example.

How can you design a case study with Venngage?
Venngage makes it easy to design case studies by offering numerous editable templates. Create an account with Venngage and browse the library for a template.
Customize the template, like the one below, in the easy-to-use drag-and-drop editor. Add text, pick colors , icons, add photos and charts and graphs.

Upload photos with Venngage. Drag and drop images into the Venngage editor and customize your reports in seconds.
Use a case study to highlight your brand’s successes
A case study can be a powerful marketing tool that showcases the advantages of using your product.
By highlighting real clients and their successes, you can provide social proof to potential customers and partners.
Designing case studies has never been easier. Use Venngage’s templates to create engaging reports to impress your audiences and help you grow your client base.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Business growth
Marketing tips
16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;cursor:pointer;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. Ironclad and OpenAI
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . Zoom and Asana
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. NVIDIA and Workday
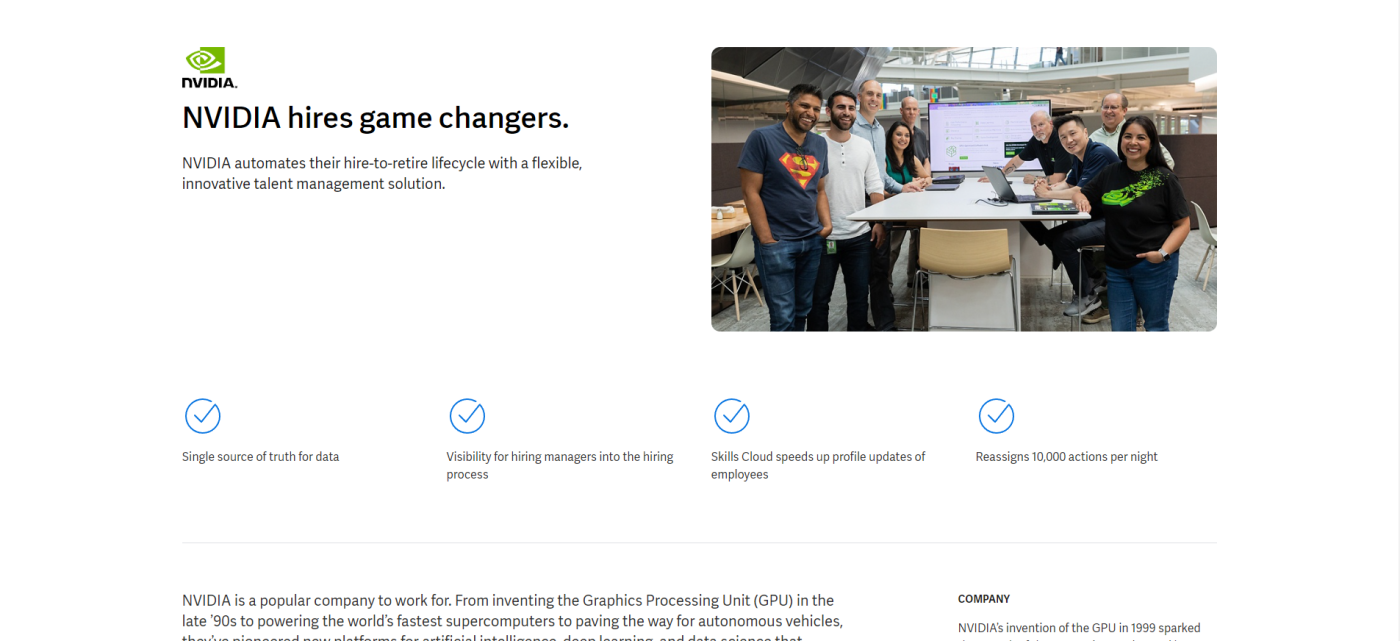
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. KFC and Contentful
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
Takeaway: Invest in videos that capture and promote your partnership with your case study subject. Video content plays a promotional role that extends beyond the case study in social media and marketing initiatives .

14. Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. Hudl and Zapier
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The Zapier format provides nuggets of high-level insights, milestones, and achievements, as well as the challenge, solution, and results. My favorite part of this case study is how it's supplemented with a blog post detailing how Hudl uses Zapier automation to build a seamless user experience.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Writing a good case study comes down to a mix of creativity, branding, and the capacity to invest in the project. With those details in mind, here are some case study tips to follow:
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.
Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
In fact, with the right technology, it can be refined to work better . Explore how Zapier's automation features can help drive results for your case study by making your case study a part of a developed workflow that creates a user journey through your website, your case studies, and into the pipeline.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
How Hudl uses automation to create a seamless user experience
How to make your case studies high-stakes—and why it matters
How experts write case studies that convert, not bore
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles

14 types of email marketing to experiment with
14 types of email marketing to experiment...
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and examples worth celebrating
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and...
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when to try it, and how to get started
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when...

12 Facebook ad copy examples to learn from
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

Limited Time Offer! Save up to 50% Off annual plans.* View Plans
Save up to 50% Now .* View Plans
How To Write A Case Study For Your Design Portfolio
Case studies are an important part of any designer’s portfolio. Read this article to learn everything you need to know to start writing the perfect case study.

When you’re putting together your online design portfolio , design case studies are a great way to showcase your experience and skills. They also give potential clients a window into how you work.
By showing off what you can do and your design process, case studies can help you land more clients and freelance design jobs —so it can be smart to dedicate an entire section of your online portfolio website to case studies.
Getting Started
So—what is a design case study and how do they fit in your portfolio.
Let’s get some definitions out of the way first, shall we? A design case study is an example of a successful project you’ve completed. The exact case study format can vary greatly depending on your style and preferences, but typically it should outline the problem or assignment, show off your solution, and explain your approach.
One of the best ways to do that is to use a case study design that’s similar to a magazine article or long-form web article with lots of images throughout. When building your case study portfolio, create a new page for each case study. Then create a listing of all your case studies with an image and link to each of them. Now, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of creating these case studies.
Choose Your Best Projects
To make your online portfolio the best it can be , it’s good to be picky when choosing projects for case studies. Since your portfolio will often act as your first impression with potential clients, you only want it to showcase your best work.
If you have a large collection of completed projects, you may have an urge to do a ton of case studies. There’s an argument to be made in favor of that, since it’s a way to show off your extensive experience. In addition, by including a wide variety of case studies, it’s more likely that potential clients will be able to find one that closely relates to their business or upcoming project.
But don’t let your desire to have many case studies on your portfolio lead you to include projects you’re not as proud of. Keep in mind that your potential clients are probably busy people, so you shouldn’t expect them to wade through a massive list of case studies. If you include too many, you can never be sure which ones potential clients will take a look at. As a result, they may miss out on seeing some of your best work.
There’s no hard-and-fast rule for how many case studies to include. It’ll depend on the amount of experience you have, and how many of your completed projects you consider to be among your best work.
Use Your Design Expertise
When creating the case study section of your portfolio, use your designer’s eye to make everything attractive and easily digestible. One important guideline is to choose a layout that will enable you to include copy and image captions throughout.
Don’t have your portfolio up and running yet and not sure which portfolio platform is best for you? Try one that offers a free trial and a variety of cool templates that you can play around with to best showcase your design case studies.
If you don’t provide context for every image you include, it can end up looking like just a (somewhat confusing) image gallery. Case studies are more than that—they should explain everything that went into what you see in the images.
Check Out Other Case Study Examples for Inspiration
Looking at case study examples from successful designers is a great way to get ideas for making your case study portfolio more effective. Pay special attention to the case study design elements, including the layout, the number of images, and amount of copy. This will give you a better idea of how the designer keeps visitors interested in the story behind their projects.
To see some great case study examples, check out these UX designer portfolios .
Try a Case Study Template
There are plenty of resources online that offer free case study templates . These templates can be helpful, as they include questions that’ll help you ensure you’ve included all the important information.
However, most of them are not tailored to designers. These general case study templates don’t have the formatting you’ll want (i.e. the ability to include lots of images). Even the ones that are aimed at designers aren’t as effective as creating your own design. That’s why case study templates are best used as a starting point to get you thinking, or as a checklist to ensure you’ve included everything.
How to Write Case Studies
Maintain your usual tone.
You should write your case studies in the same personal, authentic (yet still professional!) tone of voice as you would when creating the About Me section of your portfolio . Don’t get bogged down in too much technical detail and jargon—that will make your case studies harder to read.
Since your case studies are part of your online portfolio, changing your usual tone can be jarring to the reader.
Instead, everything on your portfolio should have a consistent style. This will help you with creating brand identity . The result will be potential clients will be more connected to your writing and get the feeling that they’re learning what makes you unique.
Provide Some Context
Case studies are more effective when you include some information at the beginning to set the stage. This can include things like the date of the project, name of the client, and what the client does. Providing some context will make the case study more relatable to potential clients.
Also, by including the date of the project, you can highlight how your work has progressed over time. However, you don’t want to bog down this part of the case study with too much information. So it only really needs to be a sentence or two.
Explain the Client’s Expectations
Another important piece of information to include near the beginning of your case study is what the client wanted to accomplish with the project. Consider the guidelines the client provided, and what they would consider a successful outcome.
Did this project involve unique requirements? Did you tailor the design to suit the client’s brand or target audience? Did you have to balance some conflicting requirements?
Establishing the client’s expectations early on in the case study will help you later when you want to explain how you made the project a success.
Document Your Design Process
As you write your case study, you should take a look at your process from an outsider’s point of view. You already know why you made the decisions you did, so it may feel like you’re explaining the obvious. But by explaining your thought process, the case study will highlight all the consideration you put into the design project.
This can include everything from your initial plan to your inspiration, and the changes you made along the way. Basically, you should think about why you took the approach you did, and then explain it.
At this point, consider mentioning any tricks you use to make your design process more efficient . That can include how you managed your time, how you communicated with clients, and how you kept things on track.
Don’t Be Afraid to Mention Challenges
When writing a case study, it can be tempting to only explain the parts that went flawlessly. But you should consider mentioning any challenges that popped up along the way.
Was this project assigned with an extremely tight deadline? Did you have to ask the client to clarify their desired outcome? Were there revisions requested?
If you have any early drafts or drawings from the project saved, it can be a good idea to include them in the case study as well—even if they show that you initially had a very different design in mind than you ended up with. This can show your flexibility and willingness to go in new directions in order to achieve the best results.
Mentioning these challenges is another opportunity to highlight your value as a designer to potential clients. It will give you a chance to explain how you overcame those challenges and made the project a success.
Show How the Project’s Success Was Measured
Case studies are most engaging when they’re written like stories. If you followed the guidelines in this article, you started by explaining the assignment. Next, you described the process you went through when working on it. Now, conclude by going over how you know the project was a success.
This can include mentioning that all of the client’s guidelines were met, and explaining how the design ended up being used.
Check if you still have any emails or communications with the client about their satisfaction with the completed project. This can help put you in the right mindset for hyping up the results. You may even want to include a quote from the client praising your work.
Start Writing Your Case Studies ASAP
Since case studies involve explaining your process, it’s best to do them while the project is still fresh in your mind. That may sound like a pain; once you put a project to bed, you’re probably not looking forward to doing more work on it. But if you get started on your case study right away, it’s easier to remember everything that went into the design project, and why you made the choices you did.
If you’re just starting writing your case studies for projects you’ve completed in the past, don’t worry. It will just require a couple more steps, as you may need to refresh your memory a bit.
Start by taking a look at any emails or assignment documents that show what the client requested. Reviewing those guidelines will make it easier to know what to include in your case study about how you met all of the client’s expectations.
Another helpful resource is preliminary drafts, drawings, or notes you may have saved. Next, go through the completed project and remind yourself of all the work that went into achieving that final design.
Draw Potential Clients to See Your Case Studies
Having a great portfolio is the key to getting hired . By adding some case studies to your design portfolio, you’ll give potential clients insight into how you work, and the value you can offer them.
But it won’t do you any good if they don’t visit your portfolio in the first place! Luckily, there are many ways you can increase your chances. One way is to add a blog to your portfolio , as that will improve your site’s SEO and draw in visitors from search results. Another is to promote your design business using social media . If you’re looking to extend your reach further, consider investing in a Facebook ad campaign , as its likely easier and less expensive than you think.
Once clients lay eyes on all your well-written, beautifully designed case studies, the work will come roaring in!
Want to learn more about creating the perfect design portfolio? 5 Designers Reveal How to Get Clients With Your Portfolio 20 Design Portfolios You Need to See for Inspiration Study: How Does the Quality of Your Portfolio Site Influence Getting Hired?

A Guide to Improving Your Photography Skills
Elevate your photography with our free resource guide. Gain exclusive access to insider tips, tricks, and tools for perfecting your craft, building your online portfolio, and growing your business.
Get the best of Format Magazine delivered to your inbox.

Top 20 Best Photography Books for Beginners

Beyond the Rule of Thirds: 30 Creative Techniques for Composition

Inspiring Still Life Photography Portfolios: Crafting a Quality Online Presence

10 Inspiring Examples and Expert Tips for Crafting A Powerful Artist Statement

Get Inspired by 10 Fashion Design Portfolios That Capture the Essence of Contemporary Style

Should I Catalog My Art?

Making Your Site Design More Accessible
*Offer must be redeemed by May 31st, 2024 at 11:59 p.m. PST. 50% discount off the subscription price of a new annual Pro Plus plan can be applied at checkout with code PROPLUSANNUAL, 38% discount off the price of a new annual Pro plan can be applied with code PROANNUAL, and 20% discount off the price of a new Basic annual plan can be applied with code BASICANNUAL. The discount applies to the first year only. Cannot be combined with any other promotion.
- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
How to Design Case Studies for Your Clients

Why Case Study Design Matters
Case studies are more than just feel-good success stories for your client’s audience to read.
They’re powerful tools for showcasing your client’s products and services in the very best possible light.
That’s why every aspect of your client’s case study has to count. Not just the information and the statistics and the positive experience of the case study’s subject, but everything that goes into creating the experience of an individual who is reading this case study and thinking hard about whether they should invest in your client’s products or services.
We’re talking about the copywriting, the illustrations and icons, the infographics, everything!
And that’s where you, as a designer, come into play!
Because if your client’s reader isn’t engaged and captivated by the information they’re seeing, they’re not likely to stick around. The layout and design have got to hit their mark every time for your client’s case studies to have the impact they want them to have.
So, what makes for a great case study or report design?
If you’re scratching your head, then this blog is here to help shine some light. Consider today’s blog your handy guide for creating captivating and strategic case study design that showcases your client’s offerings in the best possible way!
How Does a Case Study Tell a Story?

A case study can be an extremely effective marketing tool, even more so than ads, websites, or product demos.
Why? Because a case study isn’t an ad, a case study involves a real-world situation or problem that a real-world business faced and the journey they went through to resolve it, which naturally makes for a great story.
A good case study first introduces the subject, whether it's a business or an individual, and sets the stage for the story by outlining their challenges. It then describes the solution that alleviated this problem (your client’s products and services), the steps it took to implement that solution, and the obstacles it overcame to get there.
The results should show, through the use of data collection, statistics, etc., how your client’s brand was able to help the subject of the case study in whatever way they needed that help. Depending on the type of case study, the results could be increased brand awareness, increased conversions on an ecommerce site , or a boost in revenue due to optimized marketing strategies.
If presented right, this can be huge for a business! It gives real-life context to the pain points their potential customers have and the data analysis to prove that their products or services can get the job done!
And, as a designer, your role in all this is to make sure that the reader of this case study is getting the full effect of this real-life success story. Sure, the copywriter will handle writing a case study, but your job to take those words and enhance them through images, illustrations, layout, and more to present the narrative in the best way possible and guide the reader from beginning to end.
Designing Case Studies: What You Need to Know
Now that you know why case studies are so important, here is what you need to know to design a top-notch case study for your next client!
1. Understand Your Client’s Needs
It’s always a good idea to make sure that you really understand the message your client is looking to display with their case study.
Look through their other content and familiarize yourself with their brand guide so you can be sure that your design aligns with their messaging and their brand. It’s also good to familiarize yourself with the industry your client is in as well as their audience so that you can be sure your design is keeping them engaged.
2. The Right Graphics for the Story
A successful case study is going to need a good number of images and photos to break up all of that text into manageable bites and better explain complex information.
Roll up your sleeves and crank up Adobe Illustrator, because custom graphics is the way to go here. The style will be up to your client and their brand, but common needs for case studies include:
- Illustrations
- Photo treatments
These graphics are extremely handy for not only breaking up big blocks of text but also highlighting important information and making the content easy to navigate and understand.
Refer to your client’s brand guide to get the style right for the custom illustrations and icons you’ll need for their case study. If they don’t have any guidelines for illustrations and icons, then be a pal and kindly refer them here .
3. The Best Way to Visualize Data
Showcasing data effectively in a case study is absolutely crucial to its success. It doesn’t matter how impressive the numbers are if the reader can’t understand them or get a good grasp on their impact.
So, the data you’re working with, whether it's in the form of charts and graphs, statistics, or whatever else your client asks for must be presented in a way that is clear and straightforward. Use colors, type hierarchy, callouts, or whatever you need to best present your information.
Compelling infographics are a great way to do this. Using your client’s brand guide, you can whip up some infographic design templates to use throughout the case study to effectively show the collected data and what it means.
4. A Compelling Color Palette
The right colors not only make a case study visually appealing as readers navigate through the information but can ensure that your client’s case study is on brand, consistent, and a step above the rest of the competition.
Consider also using your colors to strategically highlight key information, such as numbers or data, and to invoke the right emotions as your reader moves through the narrative.
With so much data and information to present, be sure to also use a color palette that works well with your graphics and font. Your headers, captions, and text should be easy to read against whatever color background you’ve chosen.
5. Strategic Layout

The way your case study is laid out is also a crucial component in how readable and user-friendly the final result will be.
Collaborate with the copywriter, if possible, and make sure that the case study has a clear structure. The copy, the data, and your infographics, photos, and images should tell a story: a beginning (before the brand’s product and service), a middle (introducing the product or service), and an end (how the product or service improved the subject’s operations).
Use the power of type hierarchy as well to call out key information, keep text organized, and make the content easier to read.
Conducting a case study involves collecting tons of information, but no matter how much info is presented, you don’t want any portions of your case study to look crowded or busy. Be sure to have enough white space on each page to keep your design looking clean.
Some ways to lay images or photos out neatly are by the use of grids, columns, icons, and by teaming up with the copywriter to insert navigation aids, like clear page numbers, a table of contents, clearly defined sections, an index, or whatever else you think the reader would need to be able to easily follow along.
6. Spotlight Key Information
In addition to using type hierarchy and color scheme to call out the juiciest bits of information, consider also using bullets, lists, quotations, callouts, and even arrows to guide the reader’s eyes to what’s most crucial.
If the specific case study you’re designing for is about complex machinery or products a potential customer might not be familiar with, things might get confusing fast.
Clear it up by adding labels and captions to photos and illustrations to help the reader better understand important technical information and not feel overwhelmed or lost by the data being presented.
Looking for an Outlet for Those Design Skills?
If all of this has you nodding along, then, great! You may already have the design know-how to create visually stunning and easy-to-navigate case studies, reports, or whitepapers.
So, if you’re looking for an outlet for those skills, why not consider joining the Designity community?
Designity is a 100% remote CaaS (creative as a service) platform that is made up of experienced Creative Directors and the top 3% of US-based creative talent, including graphic designers , illustrators, copywriters, video editors, animators, and more.
As part of the Designity community, you’d enjoy competitive pay, a remote work environment, and the freedom to work on your own schedule from wherever you have a good WiFi connection!
You’ll also get to work on a variety of different projects with an even larger variety of clients and industries. And, best of all, you’ll get to team up with that creative talent described earlier and be part of a one-stop shop dream team that creates multiple case studies, whitepapers, brochures, and whatever marketing collateral you want to work on!
Think you have what it takes?
Why not apply today and put your skills to the test?
Share this post:

Creative Directors Make the Difference

- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Quantitative study designs: Case Studies/ Case Report/ Case Series
Quantitative study designs.
- Introduction
- Cohort Studies
- Randomised Controlled Trial
- Case Control
- Cross-Sectional Studies
- Study Designs Home
Case Study / Case Report / Case Series
Some famous examples of case studies are John Martin Marlow’s case study on Phineas Gage (the man who had a railway spike through his head) and Sigmund Freud’s case studies, Little Hans and The Rat Man. Case studies are widely used in psychology to provide insight into unusual conditions.
A case study, also known as a case report, is an in depth or intensive study of a single individual or specific group, while a case series is a grouping of similar case studies / case reports together.
A case study / case report can be used in the following instances:
- where there is atypical or abnormal behaviour or development
- an unexplained outcome to treatment
- an emerging disease or condition
The stages of a Case Study / Case Report / Case Series
Which clinical questions does Case Study / Case Report / Case Series best answer?
Emerging conditions, adverse reactions to treatments, atypical / abnormal behaviour, new programs or methods of treatment – all of these can be answered with case studies /case reports / case series. They are generally descriptive studies based on qualitative data e.g. observations, interviews, questionnaires, diaries, personal notes or clinical notes.
What are the advantages and disadvantages to consider when using Case Studies/ Case Reports and Case Series ?
What are the pitfalls to look for.
One pitfall that has occurred in some case studies is where two common conditions/treatments have been linked together with no comprehensive data backing up the conclusion. A hypothetical example could be where high rates of the common cold were associated with suicide when the cohort also suffered from depression.
Critical appraisal tools
To assist with critically appraising Case studies / Case reports / Case series there are some tools / checklists you can use.
JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Series
JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Reports
Real World Examples
Some Psychology case study / case report / case series examples
Capp, G. (2015). Our community, our schools : A case study of program design for school-based mental health services. Children & Schools, 37(4), 241–248. A pilot program to improve school based mental health services was instigated in one elementary school and one middle / high school. The case study followed the program from development through to implementation, documenting each step of the process.
Cowdrey, F. A. & Walz, L. (2015). Exposure therapy for fear of spiders in an adult with learning disabilities: A case report. British Journal of Learning Disabilities, 43(1), 75–82. One person was studied who had completed a pre- intervention and post- intervention questionnaire. From the results of this data the exposure therapy intervention was found to be effective in reducing the phobia. This case report highlighted a therapy that could be used to assist people with learning disabilities who also suffered from phobias.
Li, H. X., He, L., Zhang, C. C., Eisinger, R., Pan, Y. X., Wang, T., . . . Li, D. Y. (2019). Deep brain stimulation in post‐traumatic dystonia: A case series study. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics. 1-8. Five patients were included in the case series, all with the same condition. They all received deep brain stimulation but not in the same area of the brain. Baseline and last follow up visit were assessed with the same rating scale.
References and Further Reading
Greenhalgh, T. (2014). How to read a paper: the basics of evidence-based medicine. (5th ed.). New York: Wiley.
Heale, R. & Twycross, A. (2018). What is a case study? Evidence Based Nursing, 21(1), 7-8.
Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library. (2019). Study design 101: case report. Retrieved from https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu/tutorials/studydesign101/casereports.cfm
Hoffmann T., Bennett S., Mar C. D. (2017). Evidence-based practice across the health professions. Chatswood, NSW: Elsevier.
Robinson, O. C., & McAdams, D. P. (2015). Four functional roles for case studies in emerging adulthood research. Emerging Adulthood, 3(6), 413-420.
- << Previous: Cross-Sectional Studies
- Next: Study Designs Home >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 4:49 PM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/quantitative-study-designs

Stuart Weitzman School of Design 102 Meyerson Hall 210 South 34th Street Philadelphia, PA 19104
215.898.3425
Get Directions
Get the latest Weitzman news in your Inbox:
Case studies in design: open call to study projects designed in community.
Receive Weitzman Press Announcements
Case Studies in Design is a new effort to create opportunities for community and design leaders to think together about ways to catalyze transformational design, planning, and place-keeping from the ground up. The goals are to learn from ambitious projects designed in community, to share knowledge and experience through dialogue and a public library of case studies, and to train ourselves for new practices of creative, collective action. We hope to build conversation among thinkers and doers in community organizations, movements, public agencies, schools, and the architecture, landscape, planning, heritage and art fields.
Projects designed in community Case Studies in Design will support the development of 5 case studies per year, over 3 years (15 case studies prepared by 15 people in total). The aim is to study projects where design and planning helped build community power, and where community-led processes produced new forms of design agency through:
1. Deep conversation to shape the nature and time horizon of the project 2. Openness and deference to rooted leadership 3. Reciprocal (not extractive) processes, creatively designed 4. Collaboration and resource-sharing 5. New alliances to achieve leverage.
Collective writing and thinking project Case Studies in Design is coordinated by PennPraxis , a center at Weitzman School of Design at the University of Pennsylvania that is dedicated to the translation of theory into praxis (or action). Our aspiration is to bring together people from a wide geography and set of perspectives on diverse change efforts. Case study projects could range from outstanding examples of community- engaged design practice to more radical roles and results of design, planning or place-keeping. To propel this collective writing and thinking project, we are seeking applications from people who would like to research and author a case study.
We will support 5 case study writers in 2024 with a fee and expense allowance of $50,000 per author to research, write, and curate or create illustrations for a case study over a period of 8 months. Fees for community members participating in interviews, travel and other expenses will be managed by authors within the resources of the $50,000 lump sum for fee and expense. (Two people may apply to work together on a case project, sharing the fee.)
Public library and action—oriented summit PennPraxis will publish the case studies and create an online public library to disseminate them. We will organize a variety of forums from the classroom to gatherings with policymakers and funders to propagate strategies that increase community conversation and influence in the built environment. In the third year of the effort, with 15 case studies in print, we will organize a summit for community leaders, policymakers, students, practitioners, and thinkers to probe more deeply into methods and to shape lessons learned for key audiences. The aim of the summit is to create culture-shifting dialogue between disciplines, spheres of action, governments, funders and community leaders, practice and theory.
Case study method of conversation and analysis Most design “case studies” are project descriptions and images that focus on the what, not the how—the built project and perhaps its reception and performance. Designers are skilled at presenting the thesis, appearance and materials of their projects; so much so, that it can be difficult to understand whether the project outcomes and process measure up to the image for those who will live with them. The statement of the designer rarely conveys how the project was made, or the perspectives of community leaders, policymakers, scientists and other participants in the process.
Our case studies will place focus on the process—the many collaborators and contingencies—and offer insight into how communities and interdisciplinary teams have attempted to traverse the “valley of death” between ideas and implementation.
We aim to create a case study method that invites analysis and requires participants to shape their own values and strategies—active learning for would-be activist designers and community leaders interested taking on complex challenges. Similar to teaching case studies developed in policy and business schools, we are interested in supporting the creation of case studies that are intentionally open-ended presentations of a compelling situation that carries some conflict and uncertainty, with many different viewpoints included in the reporting, rather than critical essays that offer the authors’ conclusions or a how-to guide. The purpose is to cultivate the users capacity for critical analysis, bias recognition, collaboration, leadership, decision-making and action on challenging issues and projects. We believe that, done well, case research and discussion can help us develop theory from practice, and apply new theory to practice.
Applying to study and document a project Individuals (or pairs) can apply to develop a case for a fee of $50,000 by submitting the following material via this webform in a single pdf file of no more than 20MB:
1) a writing sample—past work that demonstrates capacity for narrative and analytical writing 2) CV or résumé with current contact information 3 a) 2,000 to 3,000-word description of a project that you think would make an interesting case study in community-engaged design, planning or place-keeping, and why (project images are optional) AND / OR 3 b) 500 to 2,000-word response to our outline of the intent of the case study program, including any critique that you think would make it stronger.
An applicant who does not apply with an interest in a particular project (outlined in response to 3a above) may be invited to document a project suggested by someone else. The length of your résumé is less important than your perspective on projects designed in community and capacity to enrich the knowledge base through the medium of case study writing and illistration.
Suggesting a project if you are not applying to write a case study We also welcome suggestions of exemplary projects worthy of deep analysis from colleagues in community and indigenous organizations, movements, public agencies, design and planning practices, and foundations. You can submit a project suggestion (with or without images) via this webform . Recommendations can be of any length, even just a project name and location or link. We can accept file sizes up to 20MB. Please include your contact information in case we would like to reach out to learn more.
Send any questions to [email protected] .
Timeline Applications will be reviewed as they come in until the deadline at 12pm on June 30, 2024. We aim to award all contracts by July 28, 2024, and may award some contracts for early applicants prior to that date. Authors will have 8 months to submit a completed case study (April 1, 2025), with an interim review at roughly 4 months.
Documentation
Download a PDF version of the Call for Applications
Study Design 101: Case Report
- Case Report
- Case Control Study
- Cohort Study
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Practice Guideline
- Systematic Review
- Meta-Analysis
- Helpful Formulas
- Finding Specific Study Types
- Case Reports
An article that describes and interprets an individual case, often written in the form of a detailed story. Case reports often describe:
- Unique cases that cannot be explained by known diseases or syndromes
- Cases that show an important variation of a disease or condition
- Cases that show unexpected events that may yield new or useful information
- Cases in which one patient has two or more unexpected diseases or disorders
Case reports are considered the lowest level of evidence, but they are also the first line of evidence, because they are where new issues and ideas emerge. This is why they form the base of our pyramid. A good case report will be clear about the importance of the observation being reported.
If multiple case reports show something similar, the next step might be a case-control study to determine if there is a relationship between the relevant variables.
- Can help in the identification of new trends or diseases
- Can help detect new drug side effects and potential uses (adverse or beneficial)
- Educational - a way of sharing lessons learned
- Identifies rare manifestations of a disease
Disadvantages
- Cases may not be generalizable
- Not based on systematic studies
- Causes or associations may have other explanations
- Can be seen as emphasizing the bizarre or focusing on misleading elements
Design pitfalls to look out for
The patient should be described in detail, allowing others to identify patients with similar characteristics.
Does the case report provide information about the patient's age, sex, ethnicity, race, employment status, social situation, medical history, diagnosis, prognosis, previous treatments, past and current diagnostic test results, medications, psychological tests, clinical and functional assessments, and current intervention?
Case reports should include carefully recorded, unbiased observations.
Does the case report include measurements and/or recorded observations of the case? Does it show a bias?
Case reports should explore and infer, not confirm, deduce, or prove. They cannot demonstrate causality or argue for the adoption of a new treatment approach.
Does the case report present a hypothesis that can be confirmed by another type of study?
Fictitious Example
A physician treated a young and otherwise healthy patient who came to her office reporting numbness all over her body. The physician could not determine any reason for this numbness and had never seen anything like it. After taking an extensive history the physician discovered that the patient had recently been to the beach for a vacation and had used a very new type of spray sunscreen. The patient had stored the sunscreen in her cooler at the beach because she liked the feel of the cool spray in the hot sun. The physician suspected that the spray sunscreen had undergone a chemical reaction from the coldness which caused the numbness. She also suspected that because this is a new type of sunscreen other physicians may soon be seeing patients with this numbness.
The physician wrote up a case report describing how the numbness presented, how and why she concluded it was the spray sunscreen, and how she treated the patient. Later, when other doctors began seeing patients with this numbness, they found this case report helpful as a starting point in treating their patients.
Real-life Examples
Hymes KB. Cheung T. Greene JB. Prose NS. Marcus A. Ballard H. William DC. Laubenstein LJ. (1981). Kaposi's sarcoma in homosexual men-a report of eight cases. Lancet. 2 (8247),598-600.
This case report was published by eight physicians in New York city who had unexpectedly seen eight male patients with Kaposi's sarcoma (KS). Prior to this, KS was very rare in the U.S. and occurred primarily in the lower extremities of older patients. These cases were decades younger, had generalized KS, and a much lower rate of survival. This was before the discovery of HIV or the use of the term AIDS and this case report was one of the first published items about AIDS patients.
Wu, E. B., & Sung, J. J. Y. (2003). Haemorrhagic-fever-like changes and normal chest radiograph in a doctor with SARS. Lancet, 361 (9368), 1520-1521.
This case report is written by the patient, a physician who contracted SARS, and his colleague who treated him, during the 2003 outbreak of SARS in Hong Kong. They describe how the disease progressed in Dr. Wu and based on Dr. Wu's case, advised that a chest CT showed hidden pneumonic changes and facilitate a rapid diagnosis.
Related Terms
Case Series
A report about a small group of similar cases.
Preplanned Case-Observation
A case in which symptoms are elicited to study disease mechanisms. (Ex. Having a patient sleep in a lab to do brain imaging for a sleep disorder).
Now test yourself!
1. Case studies are not considered evidence-based even though the authors have studied the case in great depth.
2. When are Case reports most useful?
When you encounter common cases and need more information When new symptoms or outcomes are unidentified When developing practice guidelines When the population being studied is very large
Evidence Pyramid - Navigation
- Meta- Analysis
- << Previous: Welcome to Study Design 101
- Next: Case Control Study >>

- Last Updated: Sep 25, 2023 10:59 AM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/studydesign101

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2850
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
Coordination SUD

Appels d'offres
- Partager sur Facebook
- Partager sur Twitter
- Partager sur LinkedIn
- Partager par Mail
- # Europe
- # Océanie
- # Afrique
- # Amérique du Nord
- # Amérique latine
- # Asie
Terms of Reference – Case studies report & RAAL Guidance Graphic Design – Remote / May-June 2024
Persons with disabilities are disproportionately affected by humanitarian crises and natural disasters. Environmental, institutional, and attitudinal barriers prevent them from accessing humanitarian assistance and participating in decisions on issues affecting their lives.
Continuing gaps in disability-inclusive humanitarian coordination, evidence, and the limited collection and use of quality disability-disaggregated data in the design of response strategies and operational programming have meant persons with disabilities are routinely left behind during humanitarian programming.
The ‘From Guidelines to Action’ project will directly address this by supporting interested humanitarian actors to strengthen their capacity to collect and utilize data information with and on affected people with disabilities, to coordinate effectively on issues of disability-inclusion, and to design and implement interventions which are accessible to persons with disabilities and promote their meaningful engagement and empowerment.
The project will have a specific focus on humanitarian coordination, protection and food security sectors and will work closely with clusters in two pilot countries, implementing partners engaged humanitarian stakeholders in the country and at the global level, and specialist advisors in each area to maintain global quality and technical standards.
2. Overall Objective of the Service
The Consultant will provide graphic design support to produce a Case Study report (containing 8 case studies on disability inclusion) and a RAAL Laboratory Guidance document with annexes.
- Key Deliverables of the Service
In consultation with relevant HI staff, the Consultant is expected to deliver:
- Lay out of 8 case studies reports (between 3-5 pages each, already illustrated, following HI graphic charter)
- Layout of a compiled report of the 8 case studies with a font cover, acknowledgment page, and back cover (following HI graphic charter)
- Layout and design of a RAAL Lab Guidance (10 pages maximum) and relevant annexes (number of pages yet to be defined). Following HI graphic charter. A few simple graphs will need to be designed.
All products should be compliant with the WCAG 2.2 standard for accessibility.
3. Time and Location of the Service
We anticipate that the Consultant will work remotely from end-May to mid-June 2024. The Consultant will provide an estimation of billable hours needed to undertake the Service when submitting an offer / quote. The service is planned to be finalized by mid-June.
The timeline isn’t flexible due to project’s closure.
4. Mechanisms for Communication and Monitoring
For all contractual purposes the primary contact person for the selected Consultant will be the Project Manager. The Consultant will work closely with HI’s Technical Specialists and MEAL and Communications Officer.
At the commencement of the Service there will be an online meeting to between the Consultant and relevant HI team members to agree on a work plan.
5. HI Policies, Procedures and Ethics
The Graphic Designer shall commit to comply with all Protection Policies, Code of Conduct, Good Business Practices, General Purchasing Conditions available for consultation on HI’s website . HI’s data protection policy can be viewed via this link .
In addition the selected Graphic Designer must adhere to:
- Respecting copyright and intellectual property, obtain permissions to use all visual elements;
- Ensure that the final outputs are not used for commercial purposes;
- Ensure the respect of basic accessibility standards for print and digital material.
- Use of Right based approach: a conceptual framework for the process of human development that is normatively based on international human rights standards and operationally directed to promoting and protecting human rights.
- No sub-contracting: we intend to conclude one contract for the service as described
How to apply
Eligibility requirements.
At the time of the closing date for applications, candidates must fulfil all the following conditions:
- Be legally registered as a company / consultant;
- Have fulfilled fiscal obligations;
- At least three years’ experience in a similar role and a proven portfolio of graphic design / recording work
Selection requirements – Essential
- Excellent knowledge of English;
- Training in graphic design, visual arts, or related field.
- A strong portfolio of print and digital design work.
- Excellent command of design software such as Creative Suite (namely Photoshop, Illustrator and InDesign)Excellent time management and organizational skills.
- Excellent communication, interpersonal and diplomatic skills and ability to operate in a multi-national setting;
- Keen eye for detail.
- Understanding of WCAG 2.2 standard for online accessibility
Selection requirements – Desirable
- Experience working with other NGOs as clients
- A university degree or technical diploma in the field of graphic design / recording
8. Application process
Please send your technical and financial offer (including example of your work) to [email protected] before May 24h 2024. We expect the service to start end May.
Vous souhaitez déposer un appel d’offre ?
Déposez vos appels d'offres pour vos recherches de prestations visant à renforcer votre organisation, faciliter vos projets...
Déjà inscrit ?
L’abc des prestataires.
Plus de 50 prestataires référencés dans notre base !
À télécharger
Terms of reference.

3 questions à Emilie Durochat, ancienne membre du Comité de décision FRIO (2020-2023), Déléguée…

3 questions à Géraldine Rippert, ancienne membre du Comité de décision FRIO (2022-2023), Responsable…
![[Webinaire] Capitalisation FRIO - Gouvernance & Sociocratie - 27 mars à 17h webinaire-capitalisation-frio-gouvernance-sociocratie-27-mars-a-17h](https://www.coordinationsud.org/wp-content/uploads/LOGO-FRIO-mention-aspect-ratio-5-3-300x180.png.pagespeed.ce.RpwlZgDqTo.png)
[Webinaire] Capitalisation FRIO – Gouvernance & Sociocratie – 27 mars à 17h
Nous suivre, nous contacter, l’essentiel.
- Qui sommes-nous?
- Nos combats
- Publications
- Newsletters
Accès par profil
- Espace presse
- Espace membre
- Espace annonceur
- Espace prestataire
- Emplois / Job search
- Financements des ONG
- Appels d'offres
- Prestataires
En visitant ce site vous acceptez l'utilisation des cookies. Cliquez sur « Configurer » pour plus d'options.
Réglages des cookies
Nous sommes susceptibles d'enregistrer des cookies sur votre dispositif. Nous utilisons les cookies pour savoir quand vous visitez notre site, comment vous interagissez avec notre site, et pour améliorer votre expérience en tant qu'utilisateur du site.
Cliquez sur les différents intitulés de catégorie pour en savoir plus. Vous pouvez également modifier certaines de vos préférences. Veuillez noter que le blocage de certains types de cookies peut impacter votre expérience sur notre site et les services que nous sommes en mesure d'offrir.
Ces cookies sont strictement nécessaires à la bonne utilisation des services offerts par notre site.
Du fait que ces cookies soient essentiels au fonctionnement de notre site, vous ne pouvez les refuser sans impacter en même temps la manière dont fonctionne le site. Vous pouvez bloquer ou supprimer ces cookies en modifiant vos réglages navigateur et en bloquant tous les cookies sur notre site. Cliquer pour autoriser / refuser les cookies essentiels au site.
Ces cookies collectent des informations utilisées soit de manière agrégée pour nous permettre de mieux comprendre la manière dont est utilisée notre site, soit pour déterminer l'efficacité de nos campagnes, dans le but d'améliorer votre expérience sur le site.
Si vous ne souhaitez pas que nous traquions vos visites sur notre site vous pouvez désactiver le tracking ici: Cliquer pour autoriser / refuser le tracking Google Analytics.
Nous utilisons également différents services externes comme les fournisseurs de service vidéo tiers. Ces fournisseurs de service sont susceptibles de collecter des données personnelles comme votre adresse IP, et nous vous permettons de les bloquer ici. Merci de noter que cela risque d'impacter votre expérience sur notre site et réduire ses fonctionnalités de même que son apparence. Les modifications seront prises en compte une fois la page rechargée.
Réglages Vimeo et Youtube: Cliquez pour activer/désactiver l’incorporation de vidéos.
Vous pouvez lire notre politique de cookies et de vie privée en détail sur notre page de Politique de vie privée
- ISU Navigate
- Faculty & Staff
- Virtual Tour
Common Searches
- Academic Calendar
- Transcripts
- Scholarships
- Event Tickets
- Health Center
- APA Style Guide
- Financial Aid
New technique for case study development published
May 9, 2024
Kevin Parker, ISU professor emeritus, recently published two papers in Communications of the Association for Information Systems (CAIS). Each paper was published by CAIS in their IS Education section, which has a 7% acceptance rate.
Modular Design of Teaching Cases: Reducing Workload While Maximizing Reusability presents a modular case study development concept for better managing the development of case studies. The approach achieves project extensibility through reusable case study modules, while at the same time helping to reduce instructor workload and solution reuse by students. The approach is based on the concept of creating different variations of a case study each semester by adding or replacing existing descriptive modules with new modules.
Wind Riders of the Lost River Range: A Modular Project-Based Case for Software Development focuses on the information technology needs of a simulated specialty sports shop in central Idaho that concentrates on wind sports equipment, like hang gliders, paragliders, and snowkites. The case study consists of a core case that describes both the IT system currently in use and the new system that provides updated business support. Students are tasked with analyzing the system and designing a new system that delivers enhanced functionality. This evolutionary case study is based on the Modular Design of Teaching Cases and consists of the core case and 17 modules that can be swapped in or out of both the current or future system to produce a wide variety of combinations and variations of the case study.
Categories:
Research University News
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Wait Wait...Don't Tell Me!
- Latest Show
- Subscribe to Breaking News Alerts

'Wait Wait' for May 11, 2024: With Not My Job guest Chappell Roan
Recorded at the Studebaker Theater in Chicago, with host Peter Sagal, Not My Job guest Chappell Roan and panelists Brian Babylon, Meredith Scardino and Tom Papa.

Wait Wait...Don't Tell Me!
- See Wait Wait... Don't Tell Me! sponsors and promo codes
- Open access
- Published: 06 May 2024
Development of a workplace breastfeeding support practice model in South Africa
- Lynette Carmen Daniels 1 ,
- Xikombiso Gertrude Mbhenyane 1 &
- Lisanne Monica Du Plessis 1
International Breastfeeding Journal volume 19 , Article number: 32 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
202 Accesses
Metrics details
Globally, mothers have identified work as one of the main obstacles to exclusive and continued breastfeeding. The support a woman receives in her workplace in terms of workplace arrangements can be critical to enable women to continue breastfeeding. This study aimed to develop and assess the face validity of a practice model to support exclusive and continued breastfeeding in workplaces in the Western Cape, South Africa.
An explanatory, sequential, mixed-method research design, was conducted (June 2017 to March 2019) in three distinct phases. Phase one employed a quantitative, descriptive, cross-sectional study design. Phase 2 used a qualitative, multiple case study. Phase three involved the development and face validity of a practice model to support exclusive breastfeeding in workplaces. The face validity included two Delphi rounds for experts to provide input on the draft practice model. This paper will only report on phase 3 of the study. The practice model was developed, drawing on the analysis of data from phases one and two and using programme theory approaches and a logic model.
The practice model was positively perceived. Participants viewed it as informative, well designed and easy to follow, even for those not knowledgeable about the subject. It was viewed as an ideal tool, if accompanied by some training. Participants were positive that the model would be feasible and most commended the tiered approach to implementation. They felt that workplaces would be more open to a step-by-step approach to implementation and if only a few activities are implemented it would be a start to make the work environment more conducive for breastfeeding employees. There were mixed opinions regarding commitment; a few participants mentioned commitment as a challenge they anticipated in the male-dominant environments in which they worked. The provision of space for breastfeeding at the workplace was also highlighted as a potential challenge.
Conclusions
Advocacy around creating an enabling workplace environment for breastfeeding is needed. The practice model has the potential to be internationally relevant, locally applied and may be of particular use to workplaces that want to initiate and/or strengthen breastfeeding support.
Returning to work is often considered an obstacle to exclusive and continued breastfeeding. It is a major reason for mothers not breastfeeding, or for ceasing to breastfeed early. Several factors may influence the duration of breastfeeding once the mother returns to full time employment. For instance, workplace support in terms of providing breastfeeding time and space, support at home and in the community, the attitudes of employers and colleagues towards breastfeeding employees and employment conditions and workplace arrangements. For many mothers, the lack of workplace support for breastfeeding makes working incompatible with breastfeeding [ 1 ].
The creation of an enabling workplace environment for breastfeeding may assist mothers to continue breastfeeding. Enabling interventions operate to remove structural and societal barriers that interfere with a mother’s ability to breastfeed optimally [ 2 ]. Globally, workplace support for breastfeeding is progressively seen as a cost-effective investment to increase employee morale, minimize absenteeism and reduce staff turnover [ 2 , 3 ]. Workplace interventions like providing lactation rooms and breastfeeding breaks are low-cost strategies [ 2 ] that can improve the duration and continuation of breastfeeding globally and in South Africa.
South Africa is a upper middle income country with low exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) rates. In South Africa only 32% [ 4 ] of infants under the age six months are exclusively breastfed, contrary to the recommendation that children under six months be exclusively breastfed. The percentage of children exclusively breastfed also decreases with age from 44% of infants age 0–1 month to 24% of infants age 4–5 months. Twenty five percent of infants under six months are not breastfed at all [ 4 ]. Mixed feeding before six months is a well-documented social norm in South Africa, closely related to beliefs that breastmilk is insufficient to nourish a child [ 5 ]. Multi-level barriers to EBF exist in South Africa. At an individual level milk insufficiency beliefs and incompatibility of EBF with schooling and employment. At a community level, norms around mix feeding including traditional and cultural beliefs that exist within communities that inform mothers infant feeding decisions [ 5 ]. Mothers face pressure to adhere to family traditions and decisions relating to infant feeding [ 5 ]. Also, with the high level of fathers being absent in many households, buying commercial milk formula is one way that families pressure males to take responsibility [ 6 ]. With this backdrop and the growing number of women in their childbearing years taking up employment, it is essential that support for breastfeeding in the workplace is reinforced and that institutional workplace challenges are addressed.
Workplace breastfeeding support and promotion models, interventions and case studies have been reported in other contexts like Thailand, Indonesia, United States, Bangladesh and Kenya [ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. In South Africa the South African National Department of Health (NDOH) developed a guidance booklet supporting breastfeeding in the workplace a guide for employers and employees [ 11 ]. However, to date, in South Africa there is no practice model to guide employers in supporting breastfeeding in the workplace with a set of comprehensive programme activities to implement, links and access to national and international resources and visually depicting the underlying theory of the programme. Owing to the gap in the literature the objective of this study was to develop and test the face validity of a practice model to support EBF in designated workplaces (employers who employ 50 or more employees) [ 12 ] in the Breede Valley sub-district, Western Cape Province in South Africa.
Providing workplaces with a validated tool to create an enabling workplace environment for the practice of breastfeeding, may ensure that infants are provided with exclusive and prolonged breastfeeding. This, in turn, may contribute to infants receiving the highest, most attainable standard of feeding with numerous health benefits.
To inform the development of the practice model, an explanatory, sequential, mixed-method research study was adopted. The research was conducted in Worcester, Breede Valley sub-district in the Western Cape Province, South Africa. The setting was selected based on designated workplaces being present in Worcester area that represent linkages with various levels, namely local, regional as well as national (retail stores and large commercial food companies).
The research was conducted in three distinct phases (Fig. 1 ). Phase one employed a quantitative, descriptive cross-sectional study design, using an online survey to assess current breastfeeding support practices and has previously been reported [ 13 ]. Phase 2 was a qualitative, multiple case study. Data was collected at nine purposively selected workplaces from the manufacturer, retail and public sector, using focus group discussions (FGDs) with employees and in-depth interviews with managers. FGDs were also conducted with employed breastfeeding mothers from designated workplaces who exclusively or predominantly breastfed their children for any period up to six months. This paper will elaborate only on phase three of the study, the model development and face validation phase. The research received ethical approval (S17/04//089) from the Stellenbosch University Health Research Ethics Committee.
Phases of the research study
Review of the evidence regarding workplace breastfeeding interventions and breastfeeding outcomes
A critical review of the literature in the field of workplace breastfeeding support interventions and breastfeeding outcomes were conducted. A search was conducted on PubMed using the following key words: (breastfeeding OR breast feeding OR lactation) AND (work OR workplace OR employment) AND (intervention OR support) AND (duration OR continuation OR exclusive OR rates). The literature consulted included published articles from 2008 through 2019 listed in PubMed. The PubMed search article titles was assessed. Sixteen selected article abstracts, and full text were further screened of which seven were excluded (two was qualitative studies, three was systematic reviews and two were excluded as the main outcomes measured were not breastfeeding duration, continuation and exclusivity). This yielded a total of nine articles included. Amongst the material a review article [ 14 ] on worksite lactation accommodation was found. The review article was reviewed, and five similar articles as yielded by the selected PubMed search article was found. From the critical review of the literature, it was concluded that workplace breastfeeding interventions and support services are responsive to breastfeeding outcomes and practices in terms of increased rates of breastfeeding duration, continuation and exclusivity [ 7 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ]. There is a lack of randomised control trials relating to breastfeeding support in the workplace as most studies extracted reflected cross-sectional surveys. Not all studies consistently found significant associations with all breastfeeding interventions and breastfeeding outcomes assessed. This can be attributed to possible confounding variables that may have been present e.g. lack of family support, cultural and maternal belief of the mother, the mother`s low self – efficacy for breastfeeding.
Identifying main elements from phase one and two for inclusion in the practice model
Phase one and phase two were analysed, interpreted and the main issues arising were identified for inclusion in the model. Phase one analysis involved statistical analysis of the quantitative data. Phase one findings revealed that provision of a private space for breastmilk expression was uncommon [ 13 ]. Allowing time for breastfeeding and promoting breastfeeding amongst the employees were also not commonly practiced [ 13 ]. The provision of breastfeeding time in South Africa is recommended according to the Basic Conditions of Employment Act, Code of Good Practice on the Protection of Employees during Pregnancy and After the Birth of a Child Sect. 5.13 [ 21 ]. Needs identified by managers related to physical space, a regulatory framework, communication, education and information. From phase one of the study, the following pertinent issues raised were taken up in the practice model: provision of breastfeeding time and private space, education and communication.
Phase two analysis of the FGDs with employees and in-depth interviews with the managers involved content analysis using the Atlas ti programme. Phase two findings revealed the absence of private space and time for expressing breastmilk as major challenges for women returning to work. The lack of communication between employers and employees regarding their needs, policies regulating their return from maternity leave, as well as unsupportive attitudes on the part of staff and co-workers were highlighted. The employed mothers who successfully combined breastfeeding and work had a strong belief in the benefits of breastfeeding and this motivated them to continue breastfeeding with work. Therefore, the provision and promotion of breastfeeding time and space as well as communication (conducting a return-to-work consultation after maternity leave) were included in the practice model. Also included in the model were addressing unsupportive attitudes and increasing belief in breastfeeding among employees by enhancing knowledge of the benefits of breastfeeding and the recommended breastfeeding time through education. Conducting a needs assessment amongst women to assist managers with planning and coordination was also taken up in the practice model.
Integrated programme theory and program logic models to draft the practice model
A programme theory describes how and why a programme is supposed to work [ 22 ]. The process of developing a programme theory promotes evidence-based thinking and provides a clear understanding of how change will occur. It also describes the beliefs and assumptions that underlie the choice of activities, thereby making the results more credible [ 22 ]. By reviewing the literature, the underlying linkages and secure evidence of the mechanism of change that would lead to improved breastfeeding duration and EBF rates amongst employees could be explained. The process involved moving continually between theory and practice to develop the practice model programme theory. A logic model is a commonly used tool for illustrating an underlying programme theory. The logic model was selected for the mentioned reason and also as the logic model would provide stakeholders with an easy-to-follow clear visual representation and clear specific guidance in terms of what needs to be provided (input and responsibilities) and the potential gains it holds. The following components are included in a programme logic model 1) Inputs: any resource or material used by the programme to enable its activities e.g. private hygienic space with resources 2) Activities: any services or treatments provided by the programme e.g. engage in interpersonal communication a return to work consultation 3) Outputs: amount of activity provided, described in quantifiable terms e.g. number of employees aware of breastfeeding space 4) Outcomes: any characteristics of the participants that, according to the programme theory, are expected to change as a result of the participants’ receiving services e.g. improved staff wellness and better work life integration practice 5) Impact: the ultimate intended change e.g. cost saving in terms of retaining staff [ 23 , 24 , 25 ].
Delphi rounds
A list of experts in the fields of infant feeding, breastfeeding, human resources management (private and public sectors), academia, child health and behavioural and organizational development was developed. The experts met the requirements of having knowledge and experience of breastfeeding, infant feeding, or human resource management in an organization. An email was sent to the experts to invite them to take part in the study as an expert panel member. Sixteen experts were invited and 11 (69%) participated in the two modified Delphi rounds. The Delphi process and rounds allowed the researcher to gather the opinions of a panel of experts without having to bring them together physically, thereby saving time, cost and effort. The process is free from social pressure and individual dominance and conducive to independent thinking and the gradual formulation of judgement. Of the 11 expert members, ten were female and one male. Four of the expert members were from the academic/research sector and three were International Board-Certified Lactation Consultants. The remaining expert members comprised a provincial health department official, a UNICEF nutrition specialist, one human resource practitioner from the private sector and one from a provincial organizational development department, industrial psychologist.
A graphic designer assisted with the drafting and refining of the practice model. The first version of the practice model was supported by an additional one-page information sheet providing guidance as to the inputs and activities that the employer must provide and perform. The Delphi round one questionnaire consisted of open-ended questions relating to the elements in the developed practice model: inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, linkages/connections between inputs, activities, outputs and outcomes, strengths, weaknesses, achievability/realistic to implement, challenges, design, use of wording and any recommendations and improvements. Content analysis techniques was used to the open-ended input by grouping similar items together and summarizing the comments received. These were discussed by the research team. Thereafter the practice model was amended. Under the inputs, the identification of a breastfeeding champion, including trade unions, lactation consultants and breastfeeding counsellors as well as other international toolkits was added. Two activities were added to the model: one was maternity leave provision, as this was believed to contribute to the achievement of the stated long-term outcome of increased breastfeeding duration. The provision of antenatal education by the employer was removed and changed to the inclusion of time for pregnant employees to participate in antenatal visits/classes/clinics, which was added under the education heading. Granting pregnant women time off to participate in antenatal preparation is included in Sect. 5.12 of the Code of Good Practice on the protection of employees during pregnancy and after the birth of a child [ 21 ]. Listed activities linked to legislation was highlighted with the text “legal obligation /recommendation to provide”. Also, additional long-term outcomes were added, and more images included under impact.
The improved, second version of the model was sent to the experts. A set of questions mostly using scoring/ranking techniques was used to gain consensus on the amended practice model inputs, activities and outcomes and the connections between them. The round two questionnaire consisted of ten questions relating to the importance of the input and activities used in the model on a one-to-five rating scale of 1 = least importance and 5 = high importance. Also, ten four-point Likert-scale statements and four four-point rated (poor, fair, good, excellent) questions relating to the overall design. To determine the importance of the inputs, a mean score and mean percentage score for each stated input were calculated (Fig. 2 ). Inputs and activities were judged less valid if there was less consensus on their importance. For the input and activity variables, a mean score of 70% (3.5 out of 5) was deemed to be valid for inclusion in the practice model. Therefore, funding for a lactation consultant was removed and a written breastfeeding policy statement as well as the provision of maternity leave benefits were both added to the model, as both scored an overall percentage of 93% (4.65/5).
Score percentage rating for the inputs and activities in the practice model
After the input from the Delphi round two, the final amendments to the model were made. Following on, the practice model face validity was tested by presenting it to the to the nine workplaces that participated in phase two, during four focus group discussions and one in-depth interview. These participants ( n = 16) included human resource practitioners ( n = 5), occupational health nurses ( n = 2), social workers ( n = 2) managers ( n = 6) and personal assistant ( n = 1). The majority of the participants was from the public sector ( n = 8), manufacturing sector ( n = 5) and retail sector ( n = 3). The Atlas ti programme was used to analyse the qualitative data. The analysis was mainly deductive (having a pre-prepared structure), but also partly inductive, in terms of which emerging themes were built and developed.
The practice model (Fig. 3 ) projects a simple logic model flow, making clear connections within the proposed theory of change. The programme theory is based on the Theory of Planned Behaviour [ 25 ] which states that three categories of belief guide human action-oriented behaviours: the outcomes of performing the behaviour (behavioural beliefs – what you feel, think, and the importance of the behaviour = attitude), the expectations of significant others (peers, supervisors) in relation to the behaviour (referent beliefs, how others view the behaviour = subjective norm) and the presence of factors that facilitate or hinder the behaviour (control beliefs = perceived behavioural control).
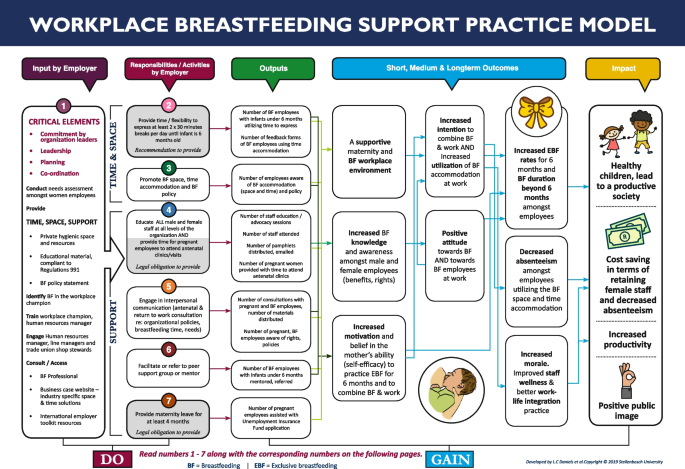
Workplace breastfeeding support practice model
The programme theory in the practice model relies on working mothers’ attitude towards breastfeeding and the uptake of available breastfeeding accommodation (space and time) at the workplace. The uptake of available breastfeeding accommodation depends on a working mother’s intention to combine breastfeeding and work. Intention is influenced by the working mother’s belief in her ability to successfully combine breastfeeding and work (self-efficacy) and her motivation to do so (control belief). It is also influenced by the working mother’s attitude towards breastfeeding and, more specifically, breastfeeding for an extended period (behavioural belief), as well as by the support she receives from workplace supervisors, peers and co-workers (referent belief) [ 25 ].
The theory of change hinges on the following change mechanism as depicted in Fig. 3 short term outcomes, leading to the medium term and long-term outcomes: when workplace breastfeeding support is provided in terms of space, time and support (i.e. education, peer support, communications and policies), employees’ breastfeeding knowledge will increase and foster positive attitudes towards breastfeeding and breastfeeding employees. It will also increase self-efficacy and the motivation to combine breastfeeding and work, which strengthens the intention to combine breastfeeding and work, leading to increased utilization of the available breastfeeding accommodation (space). This may ultimately lead to increased breastfeeding duration and EBF rates among employees. The literature indicates the connection between the implementation of a workplace breastfeeding support programme and significant higher breastfeeding rates after implementation [ 7 ] as well as the positive correlation between the duration of breastfeeding with the level of workplace support, sufficient time and availability of appropriate space at work to express breastmilk [ 18 ]. Organizational support (Odds Ratio = 1.80) increases the odds of EBF by nearly twofold [ 20 ].
Input by employer
The practice model starts off by identifying the critical elements required from the employers. Commitment by organizational leaders, leadership, planning and co-ordination were identified as key elements for the model to succeed.
Responsibilities/activities by employer
The model flows from left to right, starting with the model inputs and responsibilities/ activities that should emanate from the employer. Among the activities and inputs included in the practice model, the elements of time, space and support are paramount. These three elements have been regarded in the literature as the critical elements of a breastfeeding friendly workplace since 1993 [ 26 ]. The activities included in the practice model can be viewed in the below Table 1 . These activities scored more than 70% by the experts in the second Delphi round and meant consensus for inclusion in the practice model.
The model also expands on the expected outcomes, which were based on the literature review and the programme theory of change. The six listed activities included in the practice model are intended to lead to short-term, early changes (i.e. creation of a supportive breastfeeding environment, increased breastfeeding knowledge, increased motivation and self-efficacy to practice EBF and combine breastfeeding and work), which in turn set in motion changes in the medium term (i.e. increased intention to combine breastfeeding and work, increased utilization of breastfeeding accommodation, positive attitudes towards breastfeeding and breastfeeding employees). This is expected to result in the long-term outcomes of increasing breastfeeding duration and exclusivity rates for the first six months of babies’ lives among employees.
Outputs quantify the services provided and describe what the specific activities will produce. The set indicators for each activity were developed by the researcher with inputs form the expert panel members during the two Delphi rounds. The outputs for each activity are portrayed in Fig. 3 , which guides the monitoring aspects of the model. A potential challenge with measuring the outputs and the outcome may include the additional administrative load in monitoring the various aspects.
Impact is the fundamental intended or unintended change occurring in organizations, communities or systems as a result of programme activities within seven to ten years [ 23 ]. The impacts in terms of societal gains (healthy children lead to a productive society) and workplace gains (cost saving in terms of retaining female staff and decrease absenteeism, positive public image) are made explicit in the model.
The model is accompanied by a three-page information sheet providing further explanations on the inputs and activities /responsibilities that needs to be provided by the employer and links to various resources that can assist with the support process.
Qualitative results of the face validity of the practice model
To determine the face validity of the practice model after the two Delphi rounds, four FGDs and one in-depth interview were conducted. Participants ( n = 16) had sufficient opportunity to review the practice model, as the protected document was emailed a few days prior to the discussions to enable participants to engage with the content. The Human Resource practitioners, managers` and occupational health nurses of the nine participating workplaces were invited to attend a focus group discussion in February or March of 2019. Gaining the input of the stakeholders was deemed important in order to gauge the end user’s perception of the model. The input of stakeholders in the development and the face validity of the model serves to improve the quality and also encourage the use of it [ 24 ].
Three main themes were established namely, perceptions of developed practice model, challenges to implementation of the practice model and suggested changes to the model.
The practice model was positively perceived by the majority of the participants. The participants viewed it as informative, well designed and easy to follow ‘ the layout is good’, ‘It`s clearly set out and understandable` . The model was viewed as an ideal tool, if accompanied by some training of how to apply and use it. Participants were positive that implementation of the model was achievable. The model was regarded as informative and insightful, even for someone who are not knowledgeable about the topic. Participants felt the model provided a basic guideline of how to implement breastfeeding support in the workplace.
‘It’s an incredible model … but we know that we must make place for breastfeeding, we know that there are certain laws, but we don’t necessary do it and we don’t know how. So this is actually the how ….` HR manager, manufacturer, male
The tiered approach (selecting a few activities to pilot first) was perceived as the best way to approach implementation. Participants felt that workplaces would be more open to a step-by-step approach.
‘… for management to get into the idea… if it’s in steps then I think they will be more open to the idea.` HR manager, manufacturer, female
In terms of the three-page information sheet some participants felt at first glance that there was a lot of information to process. Others considered the information sufficient. Most participants appreciated the degree of detail in the information sheet and described it as informative, clearly set out and reader friendly.
‘So I think that it’s good that the explanations is there. Because we are being told: “consult people”, but then you are, where should I begin, who must I look for, who else must I approach?` HR manager, retail, female
Commitment on the part of organization leaders, an important element mentioned in the model, was viewed as critical for the model to succeed. There were mixed opinions regarding commitment; a few participants mentioned commitment as a challenge they anticipated in the male-dominant environments in which they worked.
‘You need the commitment from the leaders or the management team to buy into this model, to have things in the workplace like that. So, I think that is aimed …. Most of them at our company are men so they don’t usually understand the importance of breastfeeding and things like that. So, I think that to me will be a challenge.’ HR manager, manufacturer, female
Others stated that their workplace would commit to something like that, as it stands to benefit both employees and the employer. It is therefore essential that organizational commitment be developed for successful breastfeeding support. Other challenges that workplaces may experience with implementation of the model was voiced as the provision of space within their work environments.
This study aimed to develop and assess the face validity of a practice model to support EBF in designated workplaces at district level. A similar Australian-based study also developed a good practice model to evaluate the effectiveness of comprehensive primary health care in local communities [ 27 ]. This research employed a similar methodology of combining programme logic and theory-based approaches, drawing on the literature and conducting interviews to draft the practice model. Another study set out to develop a generic community health worker (CHW) logic model, proposed a theoretical causal pathway to improved performance [ 28 ]. The researchers described their model as a practical tool that offers guidance for continuous learning about what works. The value of the logic model for CHWs was that it can aid planning, draw attention to certain elements of design that are sometimes overlooked, contribute to consensus building to facilitate communication and a shared understanding of what is needed, and it can be used as a guide for improving programme implementation [ 28 ]. The reported value of the logic model for CHWs can similarly apply to the value of the practice model developed in this study, which is also based on a programme logic model.
The six activities included in the practice were providing the recommended breastfeeding time and flexibility (allow 2 × 30 min breaks per day until infant is 6 months old), promotion of breastfeeding space, time accommodation and breastfeeding policy, education of all male and female staff at all levels of the organization and providing pregnant women time to attend antenatal clinic visits, interpersonal communication (antenatal and return-to-work consultation) regarding organizational policies, breastfeeding time, and the mother’s needs, facilitation or referral to peer support group or mentor and provision of the legislated four months maternity leave. The implementation of these selected activities and workplace interventions and the impact on breastfeeding outcomes are well documented. Research reveals that women with access to breaks and space are 2.3 times more likely to EBF at 6 months [ 29 ] and women with an independent breastfeeding room in the workplace are less likely to discontinue breastfeeding [ 30 ]. Qualitative research found interpersonal communication as important to enhance workplace breastfeeding support [ 31 ]. A review article highlights the positive relationship between providing maternity leave and breastfeeding duration [ 32 ]. Furthermore, the literature reveals that a workplace environment that included supervisor and peer support, quiet space other than a bathroom and the frequency of breastfeeding in the workplace showed significant positive correlations ( r = 0.26, p = 0.01) with a longer duration of EBF [ 12 ].
Also, the literature shows that a combination of different interventions physical resources (e.g. space) organizational resources (e.g. flexible breaks) education resources and workplace support (e.g. by establishing policy and encourage support from managers and co-workers) leads to more comprehensive breastfeeding support programmes [ 33 ]. However, the comprehensive approach is still uncommon [ 34 ]. The practice model suggests a comprehensive set of activities to be implemented.
To achieve equitable work environments, interventions should focus at the three ecological layers namely individual, interpersonal, and organizational [ 34 ]. The workplace is an organizational level in which institutional support for breastfeeding mothers can be fostered. This support interacts with individual level factors linked to breastfeeding intentions and self-efficacy. Organizational support in terms of promoting lactation rooms and flexible time to express breastmilk, is associated with longer breastfeeding duration [ 34 ]. Interpersonal factors are also important and includes support from co-workers. An effective way to promote organizational support is imparting knowledge among coworkers [ 34 ]. When evaluating the activities in the practice model it addresses these three ecological layers through education of all staff, institutional support in terms of space, time and policies which links to individual factors of intention and self-efficacy.
The practice model is distinctive as it showcases the activities and their potential pathways of change. A systematic review highlighted that interventions and their impact pathways need to be better understood and documented [ 34 ]. The systematic review suggested further studies on the adaption of workplace interventions for firms of different types and size. The practice model addresses this, as it was mainly developed for workplaces with more than 50 employees from the manufacturing, retail and public sectors.
A participatory action research study was conducted in Thailand to develop a workplace breastfeeding support model for employed lactating mothers [ 7 ]. This study compared breastfeeding rates before and after implementation of the breastfeeding support campaign. The Thailand model was also based on the three core elements of time, space and support. The process undertaken to develop the Thailand model included the creation of a breastfeeding support committee, breastfeeding support activities and educational materials for breastfeeding support campaigns in the workplace. Similarly, this practice model incorporates engagement with trade unions, human resources managers, line managers and consulting breastfeeding professionals. The implementation of the Thailand model consisted of breastfeeding education and support by nurses, midwives and/or lactation consultants as part of the breastfeeding support campaign at the workplace. Breastfeeding education and support from health professionals started from the third trimester of pregnancy and continued during hospitalisation, after giving birth, during the four- to six-week post-partum follow-up visit, one-two weeks before resuming employment, and continued after the mother’s resuming employment through at least six months. Similarly in the current study, the aspect of breastfeeding education for all levels of male and female staff was included as an activity in the practice model. The practice model additionally included facilitation and/or referral to peer support groups as part of the support. The Thailand model proved to be effective, as the breastfeeding rates after implementation were significantly higher for both EBF and any breastfeeding at six months, at levels of 0.004 and 0.033 respectively. The employed lactating mothers had a positive psychological experience from combining breastfeeding with work, and members of the committee reported positive attitudes towards breastfeeding and themselves felt good about supporting lactating workers [ 7 ].
A study by Basrowi et al. (2018) in Indonesia similarly to the current study, used the aspect of expert consensus on developing a workplace-based lactation promotion model. A three-round online survey using Delphi approach was conducted. The seven dimensions, i.e. policy and regulation, facility, education material, target participants, promotion approach, human resources, and time was highlighted as the most important actions to promote lactation in the workplace. In the final round, “maternity leave of 3–6 months” and “employees have the right to breast-pumping every 3 h” ranked as the two most important indicators regarding policy and regulation. Having a dedicated lactation room was the highest ranked indicator regarding facility dimension. Regarding education materials, benefits of breastmilk for babies ranked as the highest indicator. The top management in the company and lactation counsellor are the two highest-ranked indicators in human resources dimension. For the delivering methods dimensions, social media and interactive counselling were the two highest ranked indicators [ 8 ]. The dimensions highlighted in this study has several links with the developed practice model. The links relates to importance of breastfeeding time, providing the maternity leave period, space/facility, involvement of education, using interactive communication and the importance of top management and lactation counsellors.
A study by Garvin et al. (2013) in Southeastern Virginia aimed to assist workplaces in developing lactation support using the business case for breastfeeding resource toolkit [ 9 ]. This one-year project educated 20 businesses about breastfeeding support in the workplace and engaged 10 businesses to implement the business case for breastfeeding. The aim was to assess sustainability via documented policy and environmental changes as well as integration of the lactation support programme into the businesses infrastructure. The results indicated out of 17 businesses that engaged with the project 14 significantly increased their stage of change, development of a lactation support programme, written policies and physical and social environment changes ( p < 0.001). A brief follow-up also indicated that all 14 businesses sustained the programme eight months after the program ended with increased stages of change, policy enforcement and physical environment ( p < 0.05). This resource toolkit provided an effective approach in assisting and maintaining lactation support programmes in workplaces across several cities in Virginia. Similar to the Garvin et al. study there is also potential to conduct similar research in the South African context. By providing workplaces with education and training relating to the developed practice model and assessing the progression of the stages of change, physical and social environment with the aim to determine if the approach would be effective in establishing support in the workplace.
The United Nations Childrens Fund (UNICEF) Bangladesh and Kenya workplace breastfeeding case study, similar to the practice model activities of the current study, included interpersonal communication, pre-maternity leave and a back-to-work preparatory consultation. Workplace dialogue was included to sensitize employees and promote available breastfeeding breaks and space accommodation. The lessons learned from the Bangladesh case study were about the importance of involvement from leadership as well as commitment from the business to initiate the programme [ 10 ]. The practice model starts off by identifying the critical elements, with leadership and commitment considered important elements for the practice model to succeed.
A report by World Health Organization and UNICEF relating to breastfeeding family-friendly policies sets out a call for action: advocacy within business is needed and workplace policies must be adapted and strengthened. The report mentions that technical assistance is needed to build workplace capacities to implement such policies [ 35 ]. The practice model addresses these aspects through providing workplaces with practical guidance in how to build workplace capacities to support breastfeeding.
A recommendation is for a campaign for the endorsement of the practice model by all government departments in the Western Cape. The South African NDOH should consider recognition for workplaces that support breastfeeding. Government could for example provide tax breaks as an incentive for employers to create breastfeeding facilities. Furthermore, the NDOH should ensure the distribution, awareness and marketing of the breastfeeding in the workplace toolkit and guide for employers and employees. Much more advocacy around this aspect is needed.
In terms of the results and outcomes of this research, using a sequential mixed-method approach proved to be helpful in bridging the gap between research knowledge and the creation of an action-orientated model to help create a supportive workplace environment for breastfeeding. Limitations in terms of the model development process relates to the extensive logistical arrangements to set up a suitable date and time for the FGDs for the participants with high-ranking positions. The Delphi experts also held high ranking positions and were employed in occupations that are very demanding. The two Delphi rounds took three months of periodic interaction to complete. Participant fatigue was sensed, and no further rounds were therefore conducted. Another limitation can be that the research did not engage organizational change theory to develop the model in conjunction with the programme theory used. A challenge of the model may be that it may be too ambitious for some workplaces to implement. Other potential barriers to implementing the model may be the commitment from leaders may be lacking due to breastfeeding not being a priority in the organization, the male dominant work environments that do not prioritize female needs and breastfeeding. Also not able to identify a breastfeeding champion to drive the process in the workplace and providing the space for breastfeeding and the associated infrastructure. To overcome these potential challenges advocacy in workplaces around the importance and benefits of workplace breastfeeding support is needed.
The practice model was positively perceived. Participants viewed it as informative, well designed and easy to follow, even for those not knowledgeable about the subject. It was viewed as an ideal tool, if accompanied by some training. Participants were positive that the model would be feasible and commended the tiered step by step approach to implementation. Challenges related to commitment from management, especially in the male dominant environments as well as the provision of a breastfeeding space. There is a need for greater advocacy around creating an enabling workplace environment for breastfeeding. If employers implement concerted activities according to the practice model, it may go a long way to assist employed mothers with EBF and longer breastfeeding duration. It additionally holds the potential outcomes for the employee in terms of increased morale, improved staff wellness and better work life integration, which benefits the workplace in terms of cost saving relating to retaining skilled female staff, decreased absenteeism and increased productivity. The practice model has the potential to be applicable nationally and relevant internationally. The model can be locally applied and may be of particular use to workplaces that want to initiate and/or strengthen breastfeeding support. Future research should explore the piloting of the practice model within the three workplace categories (i.e. retail, manufacturing and public) and exploring the perceptions of employees and employers before and after the implementation of the intervention and to evaluate the effect on breastfeeding outcomes. Research on the impact of the recommended breastfeeding time on organizational workplace practices and policies is also needed. Exploring the experiences of breastfeeding mothers employed in the informal sector is also recommended, as these mothers presumably face similar but unique challenges.
Availability of data and materials
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
Exclusive breastfeeding
Focus group discussions
National Department of Health
United Nations Children Fund
International Labor Organization. Module 10: Breastfeeding arrangements at work. Maternity protection resource package: From aspiration to reality for all. Geneva; 2012. http://mprp.itcilo.org/allegati/en/m10.pdf . Accessed 7 Dec 2023.
Rollins NC, Bhandari N, Hajeebhoy N, Horton S, Lutter CK, Martines JC, et al. Why invest, and what it will take to improve breastfeeding practices? Lancet. 2016;387(10017):491–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)01044-2 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
International Labour Organization. Maternity and paternity leave. Law and practice across the world. Geneva; 2014. https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---dgreports/---dcomm/---publ/documents/publication/wcms_242615.pdf . Accessed 7 Dec 2023.
Statistics South Africa. South Africa Demographic and Health Survey key indicator report 2016. https://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/Report%2003-00-09/Report%2003-00-092016.pdf . Accessed 7 Dec 2023.
Nieuwoudt SJ, Ngandu CB, Manderson L, Norris SA. Exclusive breastfeeding policy, practice and influences in South Africa, 1980 to 2018: A mixed-methods systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2019; https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224029
Ijumba P, Doherty T, Jackson D, Tomlinson M, Sanders D, Persson LA. Social circumstances that drive early introduction of formula milk: An exploratory qualitative study in a peri-urban South African community. Matern Child Nutr. 2014;10(1):102–11.
Yimyam S, Hanpa W. Developing a workplace breast feeding support model for employed lactating mothers. Midwifery. 2014;30(6):720–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2014.01.007 .
Basrowi RW, Sastroasmoro S, Sulistomo AW, Bardosono S, Hendarto A, Soemarko DS, et al. Developing a workplace lactation promotion model in Indonesia using Delphi technique. Arch Public Health. 2018;5(76):70.
Article Google Scholar
Garvin CC, Sriraman NK, Paulson A, Wallace E, Martin CE, Marshall L. The business case for breastfeeding: A successful regional implementation, evaluation, and follow-up. Breastfeed Med. 2013;8(4):413–7.
United Nations Children`s Fund. Let’s make it work ! Breastfeeding in the workplace - Using communication for development to make breastfeeding possible among working mothers. New York; 2018. https://www.healthynewbornnetwork.org/hnn-content/uploads/Mother_BabyFriendlyWorkplaceInitiativeC4D_web1_002_.pdf . Accessed 8 Dec 2023.
Department of Health. Supporting breastfeeding in the workplace. A guide to employers and employees. https://sidebyside.co.za/booklets/ . Accessed 14 Mar 2024
Republic of South Africa. Employment Equity Act, No. 55 of 1998 Pretoria, South Africa: Government Gazette; 1998. https://www.labour.gov.za/DocumentCenter/Acts/Employment%20Equity/Act%20-%20Employment%20Equity%201998.pdf . Accessed 7 Dec 2023.
Daniels L, Du Plessis LM, Mbhenyane X. Breastfeeding support practices in designated workplaces in the breede Valley sub-district, Western Cape, South Africa. South African J Chid Health. 2020;14(2):94–8.
Hilliard ED. A review of worksite lactation accommodations. Workplace Health Saf. 2017;65(1):33–44.
Balkam JAJ, Cadwell K, Fein SB. Effect of components of a workplace lactation program on breastfeeding duration among employees of a public-sector employer. Matern Child Health J. 2011;15(5):677–83.
Tsai SY. Impact of a breastfeeding-friendly workplace on an employed mother’s intention to continue breastfeeding after returning to work. Breastfeed Med. 2013;8(2):210–6.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bai Y, Wunderlich SM. Lactation accommodation in the workplace and duration of exclusive breastfeeding. J Midwifery Women’s Health. 2013;58(6):690–6.
Alvarez R, Serwint JR, Levine DM, Bertram A, Sattari M. Lawyer mothers: infant-feeding intentions and behavior. Southern Med J. 2015;108(5):262–7.
Basrowi RW, Sulistimo AB, Adi NP, Vandenplas Y. Benefits of a dedicated breastfeeding facility and support in Indonesia. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2015;18(2):94–9.
Scott VC, Taylor YJ, Basquin C, Venkitsubramanian K. Impact of key workplace reastfeeding support characteristics on job satisfaction, breastfeeding duration, and exclusive breastfeeding among health care employees. Breastfeed Med. 2019;14(6):6–8.
South African Department of Labour. Basic Conditions of Employment Act, 1998. Code of Good Practice on protection of employees during pregnancy and during child birth. Government Gazette. https://www.gov.za/sites/default/files/gcis_document/201409/a75-97.pdf . Accessed 8 Dec 2023.
Wilder Research. Program theory and logic models. Evaluation resources from Wilder Research. 2009. http://www.evaluatod.org/assets/resources/evaluation-guides/logicmodel-8-09.pdf . Accessed 8 Dec 2023.
WK Kellogg Foundation. W.K. Kellogg foundation logic model development guide. 2004. http://www.wkkf.org . Accessed 8 Dec 2023.
Knowlton LW, Phillips CC. Creating program logic models. In: The logic model guidebook: Better strategies for great results. Second edition. California: Sage Publication Inc; 2013. p. 4–47.
Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 1991;50:179–21.
World Alliance for Breastfeeding Action. World Breastfeeding Week - 1993. http://worldbreastfeedingweek.net/webpages/1993.html . Accessed 8 Dec 2023.
Lawless A, Freeman T, Bentley M, Baum F, Jolley G. Developing a good practice model to evaluate the effectiveness of comprehensive primary health care in local communities. BMC Fam Pract. 2014;15:99.
Naimoli JF, Frymus DE, Wuliji T, Franco LM, Newsome MH. A community health worker “logic model” : Towards a theory of enhanced performance in low- and middle-income countries. Hum Res Health. 2014;12(1):1–16.
Kozhimannil K, Jou J, Gjerdingen D, McGovern PM. Access to workplace accommodations to support breastfeeding after passage of the Affordable Care Act. Women’s Health Issues. 2016;26(1):6–13.
Mao ZY, Lin XH, Tai XJ, Wang J. Breastfeeding supports for two-child professional women: A case study of Beijing China. Asian Women. 2018;34(2):111–34.
Anderson J, Kuehl RA, Drury SA, Tschetter L, Schwaegerl M, Hildreth M, et al. Policies aren’t enough: The importance of interpersonal communication about workplace breastfeeding support. J Hum Lact. 2015;31(2):260–6.
Navarro-Rosenblatt D, Garmendia ML. Maternity leave and its impact on breastfeeding: A review of the literature. Breastfeed Med. 2018;13(9):589–97.
United States Department of Health and human services office on women`s health. (2018). Business case for breastfeeding. https://www.womenshealth.gov/breastfeeding/breastfeeding-home-work-and-public/breastfeeding-and-going-back-work/business-case Accessed 22 Mar 2024.
Vilar-Compte M, Hernández-Cordero S, Ancira-Moreno M, Burrola-Méndez S, Ferre-Eguiluz I, Omaña I, et al. Breastfeeding at the workplace: a systematic review of interventions to improve workplace environments to facilitate breastfeeding among working women. International Journal for Equity in Health. 2021;20:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-021-01432-3 .
UNICEF/WHO. Breastfeeding and family- friendly policies: Advocacy brief. 2019. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NMH-NHD-19.23 . Accessed 8 Dec. 2023.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants and expert panel members who participated in the study.
This work was supported by National Research Foundation, Thuthuka Funding for author L Daniels (Reference number TTK170419227683). The co-authors have no financial support to disclose.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Human Nutrition, Department of Global Health, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa
Lynette Carmen Daniels, Xikombiso Gertrude Mbhenyane & Lisanne Monica Du Plessis
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LD developed the protocol for the research study, undertook data collection with the assistance of a research assistant and a fieldworker, captured the data, analysed the data with the assistance of a statistician, interpreted the data, developed and finalized the practice model and drafted the article. Co-authors, XM and LDP, provided input at all stages of the research, revised the protocol, provided input on analysis and interpretation and reviewed the article. All authors contributed to critically reviewing the article and gave final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lynette Carmen Daniels .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was approved by the Health Research Ethics Committee of Stellenbosch University (S17/04//089). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Daniels, L.C., Mbhenyane, X.G. & Du Plessis, L.M. Development of a workplace breastfeeding support practice model in South Africa. Int Breastfeed J 19 , 32 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-024-00638-9
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2023
Accepted : 19 April 2024
Published : 06 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13006-024-00638-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Breastfeeding
- Practice model
International Breastfeeding Journal
ISSN: 1746-4358
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Analysis of distribution method of designed air quantity in coal mine ventilation—a case study
- Yongyin Wang 1 , 2 ,
- Qizhi Pan 1 , 2 ,
- Lin Gao 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Yunqin Cao 1 , 2 ,
- Ping Liu 1 , 2 ,
- Hanhua Yi 1 , 2 &
- Changsi Gao 1 , 2
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 10917 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Energy science and technology
- Engineering
In a coal mine, air leakage exists in some roadways through doors and other ventilation structures inevitably. Based on this opinion, there are different views on whether these roadways must be assigned airflow in coal mine ventilation design. This paper analyses some relevant regulations and criteria on the designed air quantity of coal mines. Then, based on the ventilation design of the Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine, through the study of the calculation of needed air quantity of every working place and its distribution method in coal mine ventilation design, this paper puts forward that explosion-proof door, safety exit, and other short distance roadways with ventilation structures need not assign airflow in coal mine ventilation design, while some long-distance roadways need. Additionally, it presents the main reason to support this opinion, gives the distribution method of inner air leakage quantity, which comes with the calculation of the designed mine total air quantity, puts forward the remedy method for the air leakage through ventilation structures in a coal mine ventilation system, then offers the mine operator with the basic opinions for the day-to-day planning and effective operation of a coal mine ventilation system.
Similar content being viewed by others

Research on controlling gas overrun in a working face based on gob-side entry retaining by utilizing ventilation type “Y”

Influences of ventilation parameters on flow field and dust migration in an underground coal mine heading
Distribution of H2S in the 10103 excavation working face of the Baozigou coal mine
Introduction.
Safety Regulations of Coal Mine (China) 1 and other regulations and criteria 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 all stipulate the calculation method of the designed mine total air quantity and its distribution method.
The calculation method of air quantity is as follows 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 .
Firstly, calculate the needed air quantity according to the maximum number of workers who work underground simultaneously. Secondly, calculate the required air quantity of each working face, developing face, chamber, and other roadways which need airflow according to gas emission rate, air absorption volume of the auxiliary fans, explosive consumption, and others. Especially, the air quantity of other roadways in a newly designed coal mine can be calculated as 3–5% of the total air quantity of the calculated working face, developing face, and chambers. Thirdly, the maximum value of the first two steps multiplied by the mine ventilation coefficient is the total mine air quantity of the designed coal mine. Mine ventilation coefficient includes the inner air leakage and the uneven air quantity distribution within the mine. It is a comprehensive index reflecting the underground ventilation structures and ventilation management level.
The air distribution method on needs in coal mine design is as follows 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 .
Firstly, distribute airflow to every working face, developing face, chamber, and other roadways according to calculated air quantity. The remaining airflow is allocated to other air-demand sites according to a certain proportion to ensure the safety of pedestrians and roadways.
It’s essential to calculate the required air quantity and to distribute airflow on needs in underground coal mine ventilation design, because the calculation of mine ventilation resistance is based on the distributed airflow and the coefficient of frictional resistance of the mine.
The main fan is selected according to the calculated mine ventilation resistance and the required air quantity, which further affects mine production, mine safety, fan efficiency, and electricity consumption 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 .
Different opinions about the distribution of designed total mine air quantity
A coal mine ventilation system consists of interconnected roadways, working locations, chambers, and ventilation structures. According to airflow distribution method on needs, the designed total mine air quantity must distribute to every air-demand location.
There are two different understandings of air-demand locations, especially for some roadways with ventilation structures. A focus of the discussion was on whether these roadways with ventilation structures need to be assigned airflow in mine ventilation design. The traditional distribution method of designed air quantity adheres that due to air leakage existing through ventilation structures, all underground roadways with ventilation structures, including explosion-proof doors, safety exits, short cross-cut, and others, all need to be distributed with airflow 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 . According to this opinion, not only the working face, developing face, and chamber need to be distributed with airflow; other roadways with ventilation structures also need to be distributed with airflow. The new opinion on distribution method of designed air quantity adheres that most of the underground roadways with ventilation structures, including explosion-proof doors, safety exits, short cross-cut, and others, do not need to be distributed with airflow 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , 11 ; if some of them need to be distributed with airflow should set up regulators. According to the different opinions of the air-needed locations, there are considerable differences in the calculated air quantity requirement and the distribution method of air quantity, which further influence the selection of main fan and fan efficiency, and finally affect mine production, mine safety, and the power consumption of coal mine ventilation.
The suitable mine design of ventilation plays a vital role in mine productivity, profit, and safety. Purpose of this paper is to analyze which roadway is required to be distributed with air quantity, put forward a reasonable method to distribute air quantity in coal mine ventilation design, and then provide the mine operator with the essential opinions and effective operations for day-to-day management in a coal mine ventilation system.
Literature survey
Currently, many regulations and criteria of coal mine stipulate the calculation and distribution method of mine air quantity. For example, the Safety Regulations of Coal Mine 1 provide the calculation method of air quantity, the distribution method of air quantity in coal mine design, and the acceptable maximum and minimum air velocity of each roadway and working place. The other regulations and criteria 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 stipulate the calculation and distribution methods of mine air quantity, provide technical requirements about air quantity and air velocity also. Professional technical books 8 , 9 , 15 about coal mines provided mine air quantity calculation methods and distribution methods also. However, these regulations, criteria, and professional books are not clearly stated which roadway needs airflow in coal mine design, and which need not, especially for short-distance roadways with ventilation structures.
Ventilation system analysis for underground coal mines has remained mostly unchanged since the Atkinson method was made famous by McElroy in 1935 10 , 16 . Data available to ventilation technicians and engineers are typically limited to in-situ 10 , 11 , 16 , 17 . Thus, there are few papers on mine ventilation design, except for some papers on mine ventilation safety. For example, Wang et al. 11 , 18 analyzed the distribution method of designed air quantity in mine ventilation design. They provided the idea that some-short distance roadways need not be distributed with airflow, but didn’t analyze it in detail to support this idea. Watson et al. and Hartman et al. 16 , 19 presented a new technique for estimating underground drift friction factors that work by processing 3D point cloud data obtained by a mobile LiDAR. Develo et al. 20 optimized the ventilation system of a zinc mine by replacing the existing western orefield fans with more giant fans from the inactive southern orefield workings to increase the airflow of the western orefield and to reduce the ventilation cost according to simulation results of the Wentsim™ software. Pach et al. 21 introduced a new method for lowering ventilation costs based on an algorithm that allows the determination of the resistance of stopping, the head of the fans, and the air quantity for which air distribution is optimal. As a result, the total power output of the fans is at the lowest level, which yields a reduction in ventilation costs using this new method. To reduce the operating expenses of ventilating and cooling underground mines permanently, Du Plessis et al. 22 discussed some strategies to reduce energy consumption by using optimizing cooling and ventilation network simulation models. Heriyadi et al. 23 examined the importance of evaluating and analyzing the need for ventilation systems in underground coal mines with a case study of several mines operating in Sawahlunto. These papers mainly focus on mine friction factors and ventilation costs, rarely discuss the calculation and distribution of mine air quantity during coal mine design. Particularly, they didn’t give further discussion of whether these roadways with ventilation structures need to be distributed with airflow, such as short crossheading, ventilation bypass, and so on.
A case study: ventilation design of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine
Overview of the safety conditions of guizhou yizhong coal mine.
The designed mine capacity of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine is 0.6 Mt/a. Coal seams in the minefield are roughly in east–west direction with strike length of 4.5 km, incline width of 2.5 km in the west, and 1.2 km in the east. Coal seams No.9, No.11, No.12, No.14, and No.17 are minable with spacing ranging from 2 to 44 m. The thickness of minable coal seams varies from 0.81 to 3.18 m. The Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine is mining the close spacing coal seam group, mainly thin and medium thick coal seams in which coal dust is explosive, and coal seam is not easy to spontaneous combustion. It’s a coal (rock) and gas outburst mine.
Overview of the mine design of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine
The design of the Yizhong Coal Mine adopts inclined shaft development, equipped with a main inclined shaft, a service inclined shaft, and an air-return inclined shaft. The main inclined shaft adopts a large dip angle belt conveyor to transport coal and also serves as an intake airway. The service inclined shaft is used for pedestrian, material transport, gangue transport, water supply pipeline laying, drainage pipeline laying, compressed air pipeline laying, and also services as an intake airway. The air-return inclined shaft is used for air-return roadway and gas drainage pipeline laying. The air-return inclined shaft is equipped with two air ducts and a safety exit near the ground.
The minefield is divided into a mining level. The horizontal elevation of the mining level is + 1400 m. Above + 1400 m in the west of the minefield is named 11 rise district. Below + 1400 m in the west of the minefield is designated as 21 dip district. The east of the minefield is quoted as 12 dip district. The district rise or district dip is located in the floor of No.17. It adopts cross-cuts to contact each coal seam. The first mining district is 11 rise district using the downward mining method between sections and between coal seams in the same section. Coal seam No.9 is the first mined coal seam, which thickness varies from 0.59 to 2.88 m.
There is one fully-mechanized longwall face, 2 gate developing faces, and one driving place in the floor of No.17 used as a gas drainage laneway for the designed commissioning period of the coal mine. Predicted relative gas emission rate is 93.84 m 3 /t, and the absolute gas emission rate is 118.48 m 3 /min during mining coal seam No.9.
The designed ventilation system is a centralized exhausting system. The working face, developing face, and district substation adopt separate airflow. The working face adopts a "U" ventilation system. The developing face is equipped with auxiliary fans using a blowing ventilation system.
The roadway layout of the designed commissioning period is shown in Fig. 1 .
Roadway layout and air distribution of the designed commissioning period of 11 district.
According to the ventilation design of the Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine, the calculated air quantity of the designed commissioning period is shown in Table 1 .
The total air quantity of the working face, gate developing faces, driving face, gas drainage roadways, and chambers is 61 m 3 /s. According to Zhang 5 , the air requirement of other locations shall be calculated by a factor of 3–5% of the total of working face, developing face, and chamber in the ventilation design of a new mine. The calculated air quantity of other locations is 3.0 m 3 /s. If the central ventilation system is adopted, the mine ventilation coefficient is between 1.2 and 1.25. Thus, the total air quantity of the mine is 77 m 3 /s, increased by 13 m 3 /s. In other words, after considering other roadways and the mine ventilation coefficient, the total mine air quantity is increased by 16 m 3 /s.
The characteristic of the design for air distribution
The designed air distribution is based on the opinion that all underground roadways must be distributed with airflow. The distribution of air quantity for every working place and chamber is shown in Table 1 and Fig. 1 . The distribution of the increased airflow after considering other roadways and the mine ventilation coefficient is shown in Table 2 and Fig. 1 .
The characteristic of the design for air distribution is as follows:
Firstly, for roadways of the same cross-sectional area with doors, the designed air quantity is different. For example, the cross-sectional area of the 111 medium station and the 112 air-return cross-cut is 11.9 m 2 , but the designed airflow is 2 m 3 /s and 1 m 3 /s, respectively.
Secondly, most air velocity in roadways distributed with air quantity is lower than the acceptable minimum air velocity. For example, the air velocity in 112 air-return cross-cut and 11,902 haulage roadway is lower than 0.15 m/s, which is the allowable minimum air velocity of roadways in rock.
Thirdly, some of the roadways with ventilation structures are not equipped with air quantity, such as the safety exit of the air-return inclined shaft, the explosion-proof door of the air-return inclined shaft, the alternative air duct of the air-return inclined shaft, and the connecting lane between the 11,902 tailgate and 11,901 tailgate. Some of the roadway with flexible tubing through ventilation doors is distributed with air quantity while the others not. For example, the 111 medium station and the 113 haulage cross-cut is distributed with 2 m 3 /s air quantity, while the 11,902 bypass is not distributed with air quantity.
The problem of the design for air distribution
The main reasons for the design of air quantity distribution of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine are as follows: firstly, all underground roadways must be equipped with airflow because air leakage through doors is inevitable. Secondly, the mine ventilation coefficient is taken into account in the calculation of the mine total air quantity. Thus, the increased air quantity must be distributed to each leakage site. Based on this opinion, it caused some questions about the designed air quantity distribution of the Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine.
The increased air quantity calculated by other locations and mine ventilation coefficient is insufficient for all these different locations and roadways with ventilation structures. The designer of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine has to distribute 2 m 3 /s or 1 m 3 /s to some roadways with doors, even some of the roadways are not equipped with air quantity because there is no more air quantity. It is contrary to the opinion that all underground roadways must be distributed with air quantity, especially for some roadways with doors that are not distributed with air quantity.
The air velocity in some roadways with doors will not meet the acceptable minimum air velocity. Regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 stipulate that the allowable minimum air velocity of roadway in rock is 0.15 m/s and roadway in coal is 0.25 m/s. According to Table 2 , the air velocity of most roadways distributed with air quantity is lower than the allowable minimum air velocity. The reason for this still is no more air quantity for all these roadways. Currently, the cross-sectional area of underground roadways is usually above 12 m 2 in a fully mechanized coal mine, and the acceptable minimum air quantity is 2 m 3 /s (roadway in rock) or 3 m 3 /s (roadway in coal).
Roadway with doors is distributed with air quantity, which does not meet the tightness requirements of the building standards of doors. According to the building standards of doors, qualified doors should tighten enough to ensure no air leakage.
Based on the analysis above, on the one hand, it can be concluded that the increased air quantity calculated by other roadways and mine ventilation coefficient are insufficient for all roadways with doors; on the other hand, it breaks the tighten requirements of doors if roadway with doors is distributed with air quantity.
In the ventilation design of a coal mine, every working face, developing face, and chamber is distributed with the calculated air quantity, the remaining air quantity shall distribute to each district according to output, number of working faces, number of developing faces, chambers, and other airflow needed roadways according to a certain proportion.
Auxiliary roadway of the air-return inclined shaft shall not be equipped with air quantity in design
Firstly, the safety exit, the explosion-proof door, and the alternative air duct of the air-return inclined shaft shall not be equipped with air quantity in coal mine design. According to regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , the total mine air quantity multiplied by the external air leakage coefficient (k = 1.05–1.15) 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 is the calculated air quantity of the main fan. In other words, air leakage through the explosion-proof door, safety exit, and alternative air duct are external air leakage, which is calculated in the process of the choice of main fan. So external air leakage can be compensated by the air quantity produced by the external air leakage coefficient in the main fan selection. In addition, not only is the calculated air quantity of main fan larger than the total mine air quantity, but also the main fan’s operating point is higher than the designed point, therefore, the excess air quantity is sufficient to compensate for the external air leakage.
Secondly, referring to the requirements of diffusion ventilation, the safety exit, the explosion-proof door, and the alternative air duct of the air-return inclined shaft shall not be distributed with air quantity. According to regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , the requirements for underground workplaces using diffusion ventilation must not be more than 6 m long, the inlet width must not be less than 1.5 m, and where haven’t gas emission. Based on this, it can be concluded that the safety exit, the explosion-proof door, and the alternative air duct of the air-return inclined shaft shall not be distributed with air quantity. Because, on the one hand, these roadways are located near the surface where is no gas emission; on the other hand, these roadways are no more than 6 m long on every side of doors and the inlet width is generally wider than 5 m.
Thus, these roadways shall not be distributed with air quantity in coal mine design.
Short-distance roadways with doors underground shall not be equipped with air quantity in design
Firstly, referring to the requirements of diffusion ventilation, short-distance roadways with doors shall not be distributed with air quantity. According to regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , the requirements for underground workplaces that use diffusion ventilation must not be more than 6 m long, the inlet width must not be less than 1.5 m, and where haven’t gas emission. Based on this, it can be concluded that short-distance roadways with doors should not be distributed with air quantity where is no gas emission and no more than 6 m long on every side of doors. If a short-distance roadway or a long-distance roadway for transportation where need ventilation structures to control airflow does not meet the requirements of diffusion ventilation, the ventilation structure of the roadway should be regulators, rather than doors. In addition, according to regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 , the operator of an underground mine must ensure that sheets or ducts used to direct the ventilation in a working place in any part of the mine are erected and maintained so as to minimize any leakage of air 5 , 7 .
Secondly, no air leakage is an essential requirement for the construction of air doors. On the one hand, doors with 1–2 m 3 /s or even with more significant air leakage are impossible to construct except for regulators; on the other hand, the basic requirements for the design and construction of doors are no leakage also. Due to the influence of structure and other factors, air leakage through doors or locks exists actually, but it is improper to consciously let doors leakage in coal mine design, though the mine ventilation coefficient (k m = 1.15–1.25) 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 has taken into account these factors such as inner air leakage, uneven air distribution, and the management level of the mine. If it is necessary to pass a certain airflow through a long-distance or gas-emission roadway, regulators should be designed to ensure reasonable air quantity and velocity in the roadway.
The distribution of air quantity caused by mine ventilation coefficient
During the design of a coal mine, if there has gas emission data of a roadway, the needed air quantity of the roadway shall be calculated according to gas emission and meet the requirement of air velocity. In this case, the air quantity caused by mine ventilation coefficient k m = 1.15–1.25 shall allocate to the other roadway according to a certain proportion 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 .
During the design of a coal mine, if there hasn’t gas emission data of a roadway, the needed air quantity of the roadway shall calculate according to 3–5% of the total air quantity of the calculated working faces, developing faces, and chambers. In this case, the air quantity caused by 3–5% of the total air quantity of the calculated working faces, developing faces, and chambers, and caused by mine ventilation coefficient k m = 1.15–1.25 shall distribute to the other roadway according to a certain proportion all 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 .
Usually, regulators should be designed in long-distance or gas-emission roadways to ensure reasonable air quantity and velocity.
Compensation for air leakage of doors or locks
The air quantity of the main fan is larger than the designed mine total air quantity, which can compensate for air leakage of doors or locks.
Selection of the main fan is as follows 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 .
Firstly, the needed air quantity of the main fan is determined by the equation:
where k is the external air leakage coefficient of mine (k = 1.05–1.15); Q m is the total mine air quantity (m 3 ).
Secondly, the needed static pressure of the axial main fan is determined by the equation:
where h m is the mine total resistance of the ventilation system (Pa), h d is the exit resistance of accessory equipment of the main fan, including fan drift and diffusion tower (Pa), H N is natural air pressure (Pa).
Thirdly, according to the result of Eqs. ( 1 ) and ( 2 ), a main fan is selected, and the main fan’s designed point is determined. Still, the main fan’s designed point is not possible precisely on one of the actual characteristic curves of the fan chosen, because the main fan’s operating point is determined by the suitable fan blade installation angle and its working resistance.
The working resistance curve is drawn in the characteristic curves of the main fan. The intersection of the active resistance curve with the static pressure curve R sd = H sd /Q f 2 of the axial main fan is the main fan’s operating point. The operational air quantity of the main fan can determine according to the main fan’s operating point.
For example, Table 3 lists the total mine air quantity Q m , the needed air quantity of the main fan Q f , and the needed static pressure of the axial main fan H sd . It is in the designed ventilation easy period and the designed ventilation difficult period of the Guizhou Yizhong coal mine, respectively. According to Q f and H sd , the designed main fan is shown in Fig. 2 , and its operating point (Q 0 and H 0 ) is shown in Fig. 2 and Table 3 .
The designed main fan and its operating point of Guizhou Yizhong coal mine.
According to Fig. 2 and Table 3 , it can be seen that the operating air quantity of the main fan is 3.2 m 3 /s larger than the needed air quantity of the main fan in the ventilation easy period, and it is 2.6 m 3 /s larger than the needed air quantity of the main fan in the ventilation difficult period. It also can be seen that the operating air quantity of the main fan is 7.1 m 3 /s larger than the total mine air quantity in the ventilation easy period, and it is 13.8 m 3 /s larger than the total mine air quantity in the ventilation difficult period. The increased air quantity here plus 16 m 3 /s produced by mine ventilation coefficient are sufficient to make up air leakage of various ventilation structures.
Once the main fan is selected, the auxiliary facilities such as the air duct and diffusion tower shall be determined according to the main fan.
Mine ventilation management can adjust the mine airflow dynamically
The mine ventilation system is a dynamic system according to the status of production. Thus, the operators of mine ventilation management should adjust the air quantity of every air-needed working place effectively. In addition, coal mine safety regulations stipulate 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 : an airflow measurement system must be established in every coal mine, and a comprehensive air measurement should be conducted once every 10 days. An airflow measurement should be performed when the production status is changed, such as relocation of the working face, developing face, and other air-needed place. Based on this, measures shall carry out to adjust the air quantity of each air-needed place. So, air leakage shall not be considered in the design of coal mine ventilation.
Comparison between the different distribution methods of designed air quantity
The different results of distributed air quantity according to the different opinions about the distribution of designed air quantity.
The focus of the different distribution methods of designed air quantity was on whether underground roadways with ventilation structures need to be assigned airflow. According to the different opinions, air distribution of these roadways for the designed commissioning period of Yizhong Coal Mine is shown in Table 4 .
According to Table 4 , the air velocity of the underground roadways with regulators distributed with air quantity is higher than the allowable minimum air velocity which meets the requirements of Regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 . While the other short-distance roadways use diffusion ventilation which meets the requirements of Regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 also. According to regulations 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , the inner air leakage of underground roadways with ventilation structures is included in the mine ventilation coefficient (k m = 1.15–1.25); the external air leakage, such as leakage of air duct is included in the external air leakage coefficient of mine (k = 1.05–1.15); therefore, this new distribution method of designed air quantity meets the requirements of Regulations.
The different results of the selection of main fan
Due to the different air distribution method, the mine total resistance of the ventilation system (h m ) is different, thus the needed static pressure (H sd ) of the axial main fan is different. The selection of main fan according to the traditional technology and the new technology for Yizhong Coal Mine is shown in Table 5 .
Based on Table 5 , it can be concluded that the main fan guided by the new technology has less power consumption.
Conclusions
Through the theoretical analysis of the distribution method of designed air quantity, and through the practice of ventilation design in Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine, a reasonable method of air quantity distribution in coal mine ventilation design is provide. Using this new technology, it can reduce the cost of mine ventilation, improve the efficiency of mine ventilation, and reduce the ineffective air leakage of coal mine. In addition, this new technology can provide the mine operator with basic opinions for the day-to-day planning and effective operation of a coal mine ventilation system.
In the design of coal mine ventilation, every working face, developing face, chamber, and roadway with gas emission shall be distributed with the calculated air quantity. The remaining air quantity shall distribute to each district according to output, and the number of working places, then to other air-needed roadways with regulators according to a certain proportion.
The safety exit of the air-return inclined shaft, the explosion-proof door of the air-return inclined shaft, and the alternative air duct shall not be equipped with air quantity in coal mine design. The air leakage of these roadways can be compensated by the air quantity calculated by the external air leakage coefficient of coal mine.
Short-distance roadways shall not be equipped with air quantity in coal mine design, though the internal air leakage is included in the mine ventilation coefficient (k m = 1.15–1.25). To facilitate the construction of ventilation structures with no air leakage, it is not suitable to consciously distribute air leakage for doors and other ventilation structures. The inevitable air leakage in underground coal mines can be compensated by the actual air quantity produced by the main fan.
Mine ventilation management can effectively adjust the air quantity of every air-needed working place, and reduce invalid air leakage.
Regulators shall be constructed in long-distance or gas-emission roadways to ensure reasonable air quantity and air velocity.
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available from the first author and the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
NMSA. Safety Regulations of Coal Mine (China) (Press of Emergency Management, Beijing, 2022).
MHURD. Guide for Design of Mine of Coal Industry (GB 50215–2015) (China Plans Press, Beijing, 2022).
Dou, Y. S. & Dou, Q. F. Explanation of “Safety Regulation of Coal Mine” (Coal Industry Press, 2005).
Google Scholar
NMSD. Technical Requirements for Ventilation in Coal Mine (AQ 1028–2006) (Coal Industry Press, Beijing, 2016).
MMR. Coal Mine Health and Safety Regulation 2006-New South Wales. Published in Gazette No. 189 of 22 December 2006: Minister for Mineral Resources (2006).
PCQ. Coal Mining Safety and Health Act 1999-Queensland. www.legislation.qld.gov.au . the Office of the Queensland Parliamentary Counsel (2014).
PCQ. Coal Mining Safety and Health Regulation 2001-Queensland. www.legislation.qld.gov.au . The Office of the Queensland Parliamentary Counsel (2015).
Zhang, R. L., He, G. W. & Li, D. Manual of Mining Engineering Design (Coal Industry Press, 2003).
Zhang, G. S. Ventilation safety (China University of Mining and Technology Press, 2007).
Mcelroy, G. E. Engineering Factors in the Ventilation of Metal Mines (United States Department of the Interior, 1935).
Wang, Y. Y., Jiang, Z. B. & Liu, Y. Analysis on distribution method of designed air quantity in mine ventilation. Coal Eng. 45 (5), 14–16 (2013).
CAS Google Scholar
Akande, J. M. & Moshood, O. Modelling of Okaba underground coal mine ventilation system. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 3 (7), 766–772 (2013).
Singh, A. K., Ahmad, I., Sahay, N., Varma, N. K. & Singh, V. K. Air leakage through underground ventilation stoppings and in situ assessment of air leakage characteristics of remote filled cement concrete plug by tracer gas technique. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 104 (2), 101–106 (2004).
Acua, E. I., Alvarez, R. A., & Hardcastle, S. G. A theoretical comparison of ventilation on demand strategies for auxiliary mine ventilation systems. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Mine Ventilation Congress. South Africa: Sun City pp. 2–7 (2014).
Kingery, D. S. Introduction to Mine Ventilating Principles and Practices (United State Government Printing Office, 1960).
Watson, C. & Marshall, J. Estimating underground mine ventilation friction factors from low density 3D data acquired by a moving LiDAR. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 28 (4), 650–655 (2018).
Article Google Scholar
Zhong, D. Y., Wang, L. G., Bi, L., Wang, J. M. & Zhu, Z. H. Algorithm of complex ventilation network solution based on circuit air-quantity method. J. China Coal Soc. 40 (2), 365–370 (2015).
Yongyin, W., Abbas, T. & Xianbi, X. Application of coal mine roof rating (CMRR) in Chinese coal mines [J]. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 28 (3), 491–497 (2018).
Hartman, H., Mutmansky, J., Ramani, R. & Wang, Y. Mine Ventilation and Air Conditioning (John Wiley &Sons, 2012).
Develo, E., Pillalamarry, M. & Garab, E. Improving the ventilation system at Rosh Pinah Zinc Mine. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 116 (4), 301–305 (2016).
Pach, G., Sułkowski, J., Różański, Z. & Wrona, P. Costs reduction of main fans operation according to safety ventilation in mines—a case study. Arch. Min. Sci. 63 (1), 43–60 (2018).
DuPlessis, J. J. L., Marx, W. M. & Nell, C. Efficient use of energy in the ventilation and cooling of mines. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 114 (12), 1033–1037 (2014).
Heriyadi, B. & Zakri, R. S. Evaluation and analysis of needs for air ventilation systems in underground coal mine (case study in underground coal mine, Sawahlunto City). J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1940 (1), 1–12 (2021).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The data collection support provided by Guizhou Coal Mine Design & Research Institute is thankfully acknowledged. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 52004073, 52264008); The Science and Technology Support Plan of Guizhou Province (Grant number: Qian Ke He Zhi Cheng [2021] General 400, Qian Ke He Zhi Cheng [2023] General 288).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mining College of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025, China
Yongyin Wang, Qizhi Pan, Lin Gao, Yunqin Cao, Ping Liu, Hanhua Yi & Changsi Gao
National and Local Joint Laboratory of Engineering for Effective Utilization of Regional Mineral Resources from Karst Areas, Guiyang, 550025, China
Coal Mine Roadway Support and Disaster Prevention Engineering Research Center, Beijing, 100083, China
Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control, Qingdao, 266590, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Y.W.: conceptualization, methodology, Supervision, Project administration, Data curation, Formal analysis. Q.P.: writing-original draft, conceptualization, methodology, validation, funding acquisition. L.G.: conceptualization, investigation, data curation. Y.C.: methodology, resources, review and editing. P.L.: software, resources, data curation. H.Y.: methodology, resources, review and editing. C.G.: visualization, investigation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Qizhi Pan .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wang, Y., Pan, Q., Gao, L. et al. Analysis of distribution method of designed air quantity in coal mine ventilation—a case study. Sci Rep 14 , 10917 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61787-9
Download citation
Received : 27 January 2024
Accepted : 09 May 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61787-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Press Herald
Account Subscription: ACTIVE
Questions about your account? Our customer service team can be reached at [email protected] during business hours at (207) 791-6000 .
9 places to nosh on bagels in southern Maine
From old-school spots to foodie favorites, there's a 'hole' lot to try.

You are able to gift 5 more articles this month.
Anyone can access the link you share with no account required. Learn more .
With a Press Herald subscription, you can gift 5 articles each month.
It looks like you do not have any active subscriptions. To get one, go to the subscriptions page .
Loading....

Bread and bagels at The Works Cafe in downtown Portland. Photo by Aimsel Ponti
From New York-style boiled bagels to Montreal-inspired wood-fired ones, there’s lots of great bagels in southern Maine and several shops have the accolades to back that up.
In 2023, Bon Appetit named bagels from Rose Foods and Rover Bagel among the best in the country.
Two years before that, Food & Wine Magazine put Rover, Forage and Scratch Baking Co. on its list of best bagels in the U.S.
Whether you like yours toasted with cream cheese or as the bread for your breakfast sandwich, you can find plenty of styles and flavors from Biddeford to Brunswick.
BEACH BAGELS
The offerings at Beach Bagels include a French toast and marble bagel, and the cream cheese menu comprises spreads like strawberry, olive and honey walnut. Along with breakfast sandwiches, Beach Bagels has hearty breakfast options like omelets and pancakes. Best of all, you’re steps away from a beach stroll. Just don’t let the seagulls steal your bagel. Advertisement
WHEN: 7 a.m. to 3 p.m. daily WHERE: 34 Old Orchard St., Old Orchard Beach. beachbagels.yolasite.com ______________
Dutchman’s opened in 2022 as a pop-up housed at Nomad pizza in Brunswick’s Fort Andross building. It’s since become a permanent fixture there and uses the pizzeria’s wood-fired ovens to bake its bagels. The hand-shaped, honey-boiled bagels come in plain, roasted garlic, poppy and a bagel-of-the-day flavor.
WHEN: 8 a.m. to 1 p.m. Thursday to Sunday WHERE: Fort Andross, 14 Maine St., Brunswick. dutchmans.me ______________
FORAGE MARKET
Making bagels at Forage Market involves a two-day aging process. The bagels are naturally leavened with wild yeast starter and baked next to a hardwood fire. There are usually five flavors available, including sesame and garlic. Breakfast sandwiches (including vegan options) are available. Forage also has a location in Lewiston. Advertisement
WHEN: 7 a.m. to 1 p.m. Monday to Friday, 8 a.m. to 1 p.m. Saturday and Sunday WHERE: 123 Washington Ave., Portland. foragemarket.com _____________
MISTER BAGEL
There are 10 or so Mister Bagel locations in Maine, including South Portland and Falmouth. It all began with the Portland location, which was the first bagel shop to open in Maine. The late Rick Hartglass started Mister Bagel in 1977, and it is still a family business. Music fans will appreciate the breakfast sandwich menu, which includes The David Bowie (bacon, egg and American cheese), the Jimmy Buffett (egg with roast beef and cheddar) and The Lady Gaga (avocado, salt and pepper, with or without egg).
WHEN: 6:30 a.m. to noon Monday to Friday, 7 a.m. to noon Saturday and Sunday WHERE: 599 Forest Ave., Portland. misterbagelforestave.com ______________
At Rose Foods, the menu varies depending on the day, but there are usually six to eight flavors available. For example, should you pop in on a Friday, you’ll find a poppy and onion bialy (a cousin of the bagel that is not boiled). Rose Foods also makes a number of bagel sandwiches, including the Classic Nova with Nova lox and the Classic Whitefish. Advertisement
WHEN: 7 a.m. to 2 p.m. daily WHERE: 428 Forest Ave., Portland. rosefoods.me
______________
ROVER BAGEL
At Rover Bagel, you’ll find wood-fired plain, poppy, sea salt, sesame and everything bagels available most of the time, and the spread game here is strong with cream cheese options like lemon-thyme-honey cream and chili-garlic.
WHEN: 7 a.m. to 1 p.m. Wednesday to Friday, 8 a.m. to 1 p.m. Saturday, 8 a.m. to noon Sunday WHERE: 10 West Point Lane Suite 10-204, Biddeford (Pepperell Mill). roverbagel.com
______________ Advertisement
SCRATCH BAKING CO.
You haven’t lived until you’ve experienced the line of devoted fans waiting for Scratch Baking Co. to open, especially on weekend mornings. Along with the popular Maine sea salt, plain and other everyday flavors, Scratch has a daily special bagel. There’s honeyed rosemary on Wednesday and jalapeno cheddar on Thursday. Scratch is also famous, at least to locals, for its P-Cheese spread. It’s a pimento cheese recipe made with cheddar, mayo, roasted red peppers and seasoning and was passed down to co-owner and head baker Allison Reid by her grandmother, Mern.
WHEN: 7 a.m. to 1 p.m. Wednesday to Saturday, 7 a.m. to noon Sunday WHERE: 416 Preble St., South Portland. scratchbakingco.com ___________
THE MAINE BAGEL
The Maine Bagel is a drive-thru with several breakfast and other kinds of sandwiches available. With a bagel list that features egg and bialy among the standards, the family-owned spot is the perfect place to stop on your way to Pine Point Beach. The Maine Bagel really shines with a dozen kinds of cream cheese spreads, including raisin-walnut, lox, strawberry, cranberry-nut and bacon-chive.
WHEN: 6:30 a.m. to 2 p.m. Tuesday to Friday, 7 a.m. to 1 p.m. Saturday. WHERE: 117 Route 1, Scarborough. themainebagel.com Advertisement
THE WORKS CAFE
The Works Cafe is an institution on the edge of the Portland’s Old Port. It opened in 1990 as Bagel Works before it changed its name in 2002. The original shop in this regional chain opened in Manchester, Vermont, in 1988, and there are 11 locations around New England, though just the one in Maine. Gone are the ’90s-era banana-walnut bagels and cold pizza cream cheese, but The Works Cafe is still a reliable place to grab a salt, multigrain or cinnamon raisin bagel, among others. The menu also has bowls, sandwiches and smoothies.
WHEN: 6 a.m. to 7 p.m. daily WHERE: 15 Temple St., Portland. workscafe.com
Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Forgot Password?
Don't have a commenting profile? Create one.
Hi, to comment on stories you must create a commenting profile . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login. Already have a commenting profile? Login .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Create a commenting profile by providing an email address, password and display name. You will receive an email to complete the registration. Please note the display name will appear on screen when you participate.
Already registered? Log in to join the discussion.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why .
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.
Send questions/comments to the editors.
Member Log In
Please enter your username and password below. Already a subscriber but don't have one? Click here .
Not a subscriber? Click here to see your options

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
This means the normal rules of design apply. Use fonts, colors, and icons to create an interesting and visually appealing case study. In this case study example, we can see how multiple fonts have been used to help differentiate between the headers and content, as well as complementary colors and eye-catching icons.
2. Determine the case study's objective. All business case studies are designed to demonstrate the value of your services, but they can focus on several different client objectives. Your first step when writing a case study is to determine the objective or goal of the subject you're featuring.
A case study is a detailed analysis of a specific topic in a real-world context. It can pertain to a person, place, event, group, or phenomenon, among others. The purpose is to derive generalizations about the topic, as well as other insights. Case studies find application in academic, business, political, or scientific research.
The main elements of case study design include the research question, propositions, units of analysis, ... The final step is writing the case study report. This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the ...
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case. ... How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing.
2. Intel Case Study. This simple light-red template is perfect for tech companies looking to quickly present their case study with an overview of its background, goals, and strategy. It ends the presentation by going through the study's figures and data. Customize this template and make it your own!
Case study design tips. Now that you know how to write your case report, here are some tips on case study design. Improving the aesthetics and usability of your study will make it memorable to read. In the long run, the study will help boost brand awareness. Use a case study template. Make the case study design process easier by using a template.
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
14 Case Study Templates. Now that we have explored some of the high level strategies you can use to create a business case study, we will transition to 14 case study design templates you can use with Visme. 1. Fuji Xerox Australia Case Study Template. Customize this template and make it your own!
Provide Some Context. Case studies are more effective when you include some information at the beginning to set the stage. This can include things like the date of the project, name of the client, and what the client does. Providing some context will make the case study more relatable to potential clients.
The way your case study is laid out is also a crucial component in how readable and user-friendly the final result will be. Collaborate with the copywriter, if possible, and make sure that the case study has a clear structure. The copy, the data, and your infographics, photos, and images should tell a story: a beginning (before the brand's product and service), a middle (introducing the ...
An article that describes and interprets an individual case, often written in the form of a detailed story. Case reports often describe: Unique cases that cannot be explained by known diseases or syndromes. Cases that show an important variation of a disease or condition. Cases that show unexpected events that may yield new or useful information.
Some scientist classifies case reports as a qualitative study design, others might consider it a quantitative approach or even a mixed method design. This polarization of the case report is unfair. However, if we have to categorize it; when we consider all research approaches in medicine, it can be classified into exploratory or confirmatory ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemolo...
A case study, also known as a case report, is an in depth or intensive study of a single individual or specific group, while a case series is a grouping of similar case studies / case reports together. A case study / case report can be used in the following instances: where there is atypical or abnormal behaviour or development.
Skip to start of list. 25,784 templates. Green Minimalist Company Case Study Flyer Portrait. Flyer by Epitomi. Blue and White Clean Corporate Company Case Study. Document by Rongbaaz. Brown Modern Company Case Study Flyer Portrait. Flyer by Ruang Kreasi. White Green Professional Gradients Business Case Study and Report Business Presentation.
Projects designed in community. Case Studies in Design will support the development of 5 case studies per year, over 3 years (15 case studies prepared by 15 people in total). The aim is to study projects where design and planning helped build community power, and where community-led processes produced new forms of design agency through: 1.
Lancet. 2 (8247),598-600. This case report was published by eight physicians in New York city who had unexpectedly seen eight male patients with Kaposi's sarcoma (KS). Prior to this, KS was very rare in the U.S. and occurred primarily in the lower extremities of older patients. These cases were decades younger, had generalized KS, and a much ...
The Consultant will provide graphic design support to produce a Case Study report (containing 8 case studies on disability inclusion) and a RAAL Laboratory Guidance document with annexes. ... Lay out of 8 case studies reports (between 3-5 pages each, already illustrated, following HI graphic charter) Layout of a compiled report of the 8 case ...
Modular Design of Teaching Cases: Reducing Workload While Maximizing Reusability presents a modular case study development concept for better managing the development of case studies. The approach achieves project extensibility through reusable case study modules, while at the same time helping to reduce instructor workload and solution reuse ...
Recorded at the Studebaker Theater in Chicago, with host Peter Sagal, Not My Job guest Chappell Roan and panelists Brian Babylon, Meredith Scardino and Tom Papa.
Phase 2 used a qualitative, multiple case study. Phase three involved the development and face validity of a practice model to support exclusive breastfeeding in workplaces. The face validity included two Delphi rounds for experts to provide input on the draft practice model. This paper will only report on phase 3 of the study.
A case study: ventilation design of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine Overview of the safety conditions of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine The designed mine capacity of Guizhou Yizhong Coal Mine is 0.6 Mt/a.
Gone are the '90s-era banana-walnut bagels and cold pizza cream cheese, but The Works Cafe is still a reliable place to grab a salt, multigrain or cinnamon raisin bagel, among others. The menu ...