Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process.
- © 2023 by Jennifer Janechek - IBM Quantum
Review APA guidelines for the body of an APA-style paper.

Beginning at the top of a new page, the main body of the research paper follows the abstract and precedes the References page. Comprised of the introduction, method, results, and discussion subsections, the main body acts as the third major section of the document and typically begins on the third page of the paper.

General Format
Like the rest of the paper, the pages of the main body should be double-spaced and typed in Times New Roman, 12 pt. The margins are set at 1” on all sides. While the running head is flush with the upper left-hand corner of every page, the page number is flush with the upper right-hand corner of every page. Note that all letters of the running head should be capitalized and should not exceed 50 characters, including punctuation, letters, and spaces.
The full title of the paper is centered directly above the introduction with no extra space between the title and the first paragraph. Avoid formatting the title with bold, italics, underlining, or quotation marks. The first letter of each major word in the title should be capitalized. Unlike other sections of the main body, the introduction does not require a heading or label.
When writing each paragraph, note that the APA recommends using two spaces after sentences that end in a period; however, sentences that end in other punctuation marks may be followed by a single space.

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Body Paragraphs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information
Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more focused on the argument ending with specific, detailed evidence supporting a claim. Lastly, the author explains how and why the information she has just provided connects to and supports her thesis (a brief wrap-up or warrant).

Moving from General to Specific Information
The four elements of a good paragraph (TTEB)
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant ) –TTEB!
- A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
- A T opic sentence that tells the reader what you will be discussing in the paragraph.
- Specific E vidence and analysis that supports one of your claims and that provides a deeper level of detail than your topic sentence.
- A B rief wrap-up sentence that tells the reader how and why this information supports the paper’s thesis. The brief wrap-up is also known as the warrant. The warrant is important to your argument because it connects your reasoning and support to your thesis, and it shows that the information in the paragraph is related to your thesis and helps defend it.
Supporting evidence (induction and deduction)
Induction is the type of reasoning that moves from specific facts to a general conclusion. When you use induction in your paper, you will state your thesis (which is actually the conclusion you have come to after looking at all the facts) and then support your thesis with the facts. The following is an example of induction taken from Dorothy U. Seyler’s Understanding Argument :
There is the dead body of Smith. Smith was shot in his bedroom between the hours of 11:00 p.m. and 2:00 a.m., according to the coroner. Smith was shot with a .32 caliber pistol. The pistol left in the bedroom contains Jones’s fingerprints. Jones was seen, by a neighbor, entering the Smith home at around 11:00 p.m. the night of Smith’s death. A coworker heard Smith and Jones arguing in Smith’s office the morning of the day Smith died.
Conclusion: Jones killed Smith.
Here, then, is the example in bullet form:
- Conclusion: Jones killed Smith
- Support: Smith was shot by Jones’ gun, Jones was seen entering the scene of the crime, Jones and Smith argued earlier in the day Smith died.
- Assumption: The facts are representative, not isolated incidents, and thus reveal a trend, justifying the conclusion drawn.
When you use deduction in an argument, you begin with general premises and move to a specific conclusion. There is a precise pattern you must use when you reason deductively. This pattern is called syllogistic reasoning (the syllogism). Syllogistic reasoning (deduction) is organized in three steps:
- Major premise
- Minor premise
In order for the syllogism (deduction) to work, you must accept that the relationship of the two premises lead, logically, to the conclusion. Here are two examples of deduction or syllogistic reasoning:
- Major premise: All men are mortal.
- Minor premise: Socrates is a man.
- Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
- Major premise: People who perform with courage and clear purpose in a crisis are great leaders.
- Minor premise: Lincoln was a person who performed with courage and a clear purpose in a crisis.
- Conclusion: Lincoln was a great leader.
So in order for deduction to work in the example involving Socrates, you must agree that (1) all men are mortal (they all die); and (2) Socrates is a man. If you disagree with either of these premises, the conclusion is invalid. The example using Socrates isn’t so difficult to validate. But when you move into more murky water (when you use terms such as courage , clear purpose , and great ), the connections get tenuous.
For example, some historians might argue that Lincoln didn’t really shine until a few years into the Civil War, after many Union losses to Southern leaders such as Robert E. Lee.
The following is a clear example of deduction gone awry:
- Major premise: All dogs make good pets.
- Minor premise: Doogle is a dog.
- Conclusion: Doogle will make a good pet.
If you don’t agree that all dogs make good pets, then the conclusion that Doogle will make a good pet is invalid.
When a premise in a syllogism is missing, the syllogism becomes an enthymeme. Enthymemes can be very effective in argument, but they can also be unethical and lead to invalid conclusions. Authors often use enthymemes to persuade audiences. The following is an example of an enthymeme:
If you have a plasma TV, you are not poor.
The first part of the enthymeme (If you have a plasma TV) is the stated premise. The second part of the statement (you are not poor) is the conclusion. Therefore, the unstated premise is “Only rich people have plasma TVs.” The enthymeme above leads us to an invalid conclusion (people who own plasma TVs are not poor) because there are plenty of people who own plasma TVs who are poor. Let’s look at this enthymeme in a syllogistic structure:
- Major premise: People who own plasma TVs are rich (unstated above).
- Minor premise: You own a plasma TV.
- Conclusion: You are not poor.
To help you understand how induction and deduction can work together to form a solid argument, you may want to look at the United States Declaration of Independence. The first section of the Declaration contains a series of syllogisms, while the middle section is an inductive list of examples. The final section brings the first and second sections together in a compelling conclusion.

How to Write a Research Paper: Parts of the Paper
- Choosing Your Topic
- Citation & Style Guides This link opens in a new window
- Critical Thinking
- Evaluating Information
- Parts of the Paper
- Writing Tips from UNC-Chapel Hill
- Librarian Contact
Parts of the Research Paper Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea, and indicate how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas.
1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses. Use keywords that help explain your paper's topic to the reader. Try to avoid abbreviations and jargon. Think about keywords that people would use to search for your paper and include them in your title.
2. The Abstract The abstract is used by readers to get a quick overview of your paper. Typically, they are about 200 words in length (120 words minimum to 250 words maximum). The abstract should introduce the topic and thesis, and should provide a general statement about what you have found in your research. The abstract allows you to mention each major aspect of your topic and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Because it is a summary of the entire research paper, it is often written last.
3. The Introduction The introduction should be designed to attract the reader's attention and explain the focus of the research. You will introduce your overview of the topic, your main points of information, and why this subject is important. You can introduce the current understanding and background information about the topic. Toward the end of the introduction, you add your thesis statement, and explain how you will provide information to support your research questions. This provides the purpose and focus for the rest of the paper.
4. Thesis Statement Most papers will have a thesis statement or main idea and supporting facts/ideas/arguments. State your main idea (something of interest or something to be proven or argued for or against) as your thesis statement, and then provide your supporting facts and arguments. A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. It also points toward the paper's development. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.
Students often learn to write a thesis as a first step in the writing process, but often, after research, a writer's viewpoint may change. Therefore a thesis statement may be one of the final steps in writing.
Examples of Thesis Statements from Purdue OWL
5. The Literature Review The purpose of the literature review is to describe past important research and how it specifically relates to the research thesis. It should be a synthesis of the previous literature and the new idea being researched. The review should examine the major theories related to the topic to date and their contributors. It should include all relevant findings from credible sources, such as academic books and peer-reviewed journal articles. You will want to:
- Explain how the literature helps the researcher understand the topic.
- Try to show connections and any disparities between the literature.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
More about writing a literature review. . .
6. The Discussion The purpose of the discussion is to interpret and describe what you have learned from your research. Make the reader understand why your topic is important. The discussion should always demonstrate what you have learned from your readings (and viewings) and how that learning has made the topic evolve, especially from the short description of main points in the introduction.Explain any new understanding or insights you have had after reading your articles and/or books. Paragraphs should use transitioning sentences to develop how one paragraph idea leads to the next. The discussion will always connect to the introduction, your thesis statement, and the literature you reviewed, but it does not simply repeat or rearrange the introduction. You want to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking, not just reporting back facts that you gathered.
- If possible, tell how the topic has evolved over the past and give it's implications for the future.
- Fully explain your main ideas with supporting information.
- Explain why your thesis is correct giving arguments to counter points.
7. The Conclusion A concluding paragraph is a brief summary of your main ideas and restates the paper's main thesis, giving the reader the sense that the stated goal of the paper has been accomplished. What have you learned by doing this research that you didn't know before? What conclusions have you drawn? You may also want to suggest further areas of study, improvement of research possibilities, etc. to demonstrate your critical thinking regarding your research.
- << Previous: Evaluating Information
- Next: Research >>
- Last Updated: Feb 13, 2024 8:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ucc.edu/research_paper
- Research Guides
Reading for Research: Social Sciences
Structure of a research article.
- Structural Read
Guide Acknowledgements
How to Read a Scholarly Article from the Howard Tilton Memorial Library at Tulane University
Strategic Reading for Research from the Howard Tilton Memorial Library at Tulane University
Bridging the Gap between Faculty Expectation and the Student Experience: Teaching Students toAnnotate and Synthesize Sources
Librarian for Sociology, Environmental Sociology, MHS and Public Policy Studies

Academic writing has features that vary only slightly across the different disciplines. Knowing these elements and the purpose of each serves help you to read and understand academic texts efficiently and effectively, and then apply what you read to your paper or project.
Social Science (and Science) original research articles generally follow IMRD: Introduction- Methods-Results-Discussion
Introduction
- Introduces topic of article
- Presents the "Research Gap"/Statement of Problem article will address
- How research presented in the article will solve the problem presented in research gap.
- Literature Review. presenting and evaluating previous scholarship on a topic. Sometimes, this is separate section of the article.
Method & Results
- How research was done, including analysis and measurements.
- Sometimes labeled as "Research Design"
- What answers were found
- Interpretation of Results (What Does It Mean? Why is it important?)
- Implications for the Field, how the study contributes to the existing field of knowledge
- Suggestions for further research
- Sometimes called Conclusion
You might also see IBC: Introduction - Body - Conclusion
- Identify the subject
- State the thesis
- Describe why thesis is important to the field (this may be in the form of a literature review or general prose)
Body
- Presents Evidence/Counter Evidence
- Integrate other writings (i.e. evidence) to support argument
- Discuss why others may disagree (counter-evidence) and why argument is still valid
- Summary of argument
- Evaluation of argument by pointing out its implications and/or limitations
- Anticipate and address possible counter-claims
- Suggest future directions of research
- Next: Structural Read >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2024 10:44 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.vanderbilt.edu/readingforresearch


- Research guides
Writing an Educational Research Paper
Research paper sections, customary parts of an education research paper.
There is no one right style or manner for writing an education paper. Content aside, the writing style and presentation of papers in different educational fields vary greatly. Nevertheless, certain parts are common to most papers, for example:
Title/Cover Page
Contains the paper's title, the author's name, address, phone number, e-mail, and the day's date.
Not every education paper requires an abstract. However, for longer, more complex papers abstracts are particularly useful. Often only 100 to 300 words, the abstract generally provides a broad overview and is never more than a page. It describes the essence, the main theme of the paper. It includes the research question posed, its significance, the methodology, and the main results or findings. Footnotes or cited works are never listed in an abstract. Remember to take great care in composing the abstract. It's the first part of the paper the instructor reads. It must impress with a strong content, good style, and general aesthetic appeal. Never write it hastily or carelessly.
Introduction and Statement of the Problem
A good introduction states the main research problem and thesis argument. What precisely are you studying and why is it important? How original is it? Will it fill a gap in other studies? Never provide a lengthy justification for your topic before it has been explicitly stated.
Limitations of Study
Indicate as soon as possible what you intend to do, and what you are not going to attempt. You may limit the scope of your paper by any number of factors, for example, time, personnel, gender, age, geographic location, nationality, and so on.
Methodology
Discuss your research methodology. Did you employ qualitative or quantitative research methods? Did you administer a questionnaire or interview people? Any field research conducted? How did you collect data? Did you utilize other libraries or archives? And so on.
Literature Review
The research process uncovers what other writers have written about your topic. Your education paper should include a discussion or review of what is known about the subject and how that knowledge was acquired. Once you provide the general and specific context of the existing knowledge, then you yourself can build on others' research. The guide Writing a Literature Review will be helpful here.
Main Body of Paper/Argument
This is generally the longest part of the paper. It's where the author supports the thesis and builds the argument. It contains most of the citations and analysis. This section should focus on a rational development of the thesis with clear reasoning and solid argumentation at all points. A clear focus, avoiding meaningless digressions, provides the essential unity that characterizes a strong education paper.
After spending a great deal of time and energy introducing and arguing the points in the main body of the paper, the conclusion brings everything together and underscores what it all means. A stimulating and informative conclusion leaves the reader informed and well-satisfied. A conclusion that makes sense, when read independently from the rest of the paper, will win praise.
Works Cited/Bibliography
See the Citation guide .
Education research papers often contain one or more appendices. An appendix contains material that is appropriate for enlarging the reader's understanding, but that does not fit very well into the main body of the paper. Such material might include tables, charts, summaries, questionnaires, interview questions, lengthy statistics, maps, pictures, photographs, lists of terms, glossaries, survey instruments, letters, copies of historical documents, and many other types of supplementary material. A paper may have several appendices. They are usually placed after the main body of the paper but before the bibliography or works cited section. They are usually designated by such headings as Appendix A, Appendix B, and so on.
- << Previous: Choosing a Topic
- Next: Find Books >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2024 6:23 PM
- Subjects: Education
- Tags: education , education_paper , education_research_paper
How to Write a Research Paper
#scribendiinc
The research paper writing process
In the first article of this two part series, we discussed how to research a term paper . In this article, we will discuss how to write a term or research paper.
Write your thesis statement
After you have spent some time finding your sources and absorbing the information, you should then be able to come up with a thesis statement that tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter. This statement is a road map for the research paper, telling the reader what to expect. It usually consists of a single sentence somewhere in your first paragraph and makes a claim that others might later dispute!
For optimal organization, take the time to write an outline that indicates the main aspects to be discussed. This includes deciding on the order of your sub-topics and which key points you will use as evidence to support your position.
Keep the body of your research paper in good shape
The body is the largest part of a research paper; in it you collect and arrange evidence that will persuade the reader of your argument. It should, therefore, have a logical organization. If the paper is long, it is a good idea to partition the body into sections using headings and sub-headings. This includes using parenthetical citations when referencing another author's work in the body of your text.
Sometimes the beginning isn't the best place to start...
Write the introduction and conclusion of your research paper last in order to ensure accuracy. The introduction is the key to letting your readers know where you are headed and what you hope to accomplish. Remember that while the organization of your research paper may be clear to you, it may not necessarily be clear to your readers. Therefore, the introduction should acquaint them with the journey ahead, making it easier for them to understand what follows and helping to improve their evaluation of your work. Tell your readers in concise terms what the subject of the paper is, what it is that you hope to find out, and how you will go about doing so.
Encapsulating your findings in the conclusion is not the only place in the research paper where you make your voice heard. Your analysis should appear throughout. A common ESL mistake is reciting facts in the body of their essay and then waiting until the conclusion to say what they mean. Good research papers bring data, events, and other material together, interpreting the facts throughout. The conclusion should summarize what you have said in the body and should stress the evidence that supports your analysis.
Don't forget your references
Once your research paper is finished, compile your reference list. This is an alphabetical listing of all the sources you referenced in the body of your paper. If you made notes about your sources, this task should be straightforward. Be sure to follow whatever style guide your professor or school recommends. We have an example APA Reference page and an example MLA Works Cited for your reference.
Edit your research paper to ensure clarity
Once you have the pieces of your research paper in place, it's time to polish, polish, polish! Double-check everything. Ensure you have correctly cited your sources, checked your spelling and grammar, and re-read your paper several times, checking for sense, logical structure, and organization. Readers will judge your paper not only on the quality of research, but also on the quality of the writing.
Ta da! You've done it—your research paper is complete! Just think about what you've learned: not just about your subject, but about the whole investigative process.
Image source: Patrik Goethe/Stocksnap.io
Perfect Your Paper Prior to Submission
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing: Traffic Signals for the Reader

How to Research a Term Paper

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Writing a Research Paper
This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper.
Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
Discovering, Narrowing, and Focusing a Researchable Topic
- Try to find a topic that truly interests you
- Try writing your way to a topic
- Talk with your course instructor and classmates about your topic
- Pose your topic as a question to be answered or a problem to be solved
Finding, Selecting, and Reading Sources
You will need to look at the following types of sources:
- library catalog, periodical indexes, bibliographies, suggestions from your instructor
- primary vs. secondary sources
- journals, books, other documents
Grouping, Sequencing, and Documenting Information
The following systems will help keep you organized:
- a system for noting sources on bibliography cards
- a system for organizing material according to its relative importance
- a system for taking notes
Writing an Outline and a Prospectus for Yourself
Consider the following questions:
- What is the topic?
- Why is it significant?
- What background material is relevant?
- What is my thesis or purpose statement?
- What organizational plan will best support my purpose?
Writing the Introduction
In the introduction you will need to do the following things:
- present relevant background or contextual material
- define terms or concepts when necessary
- explain the focus of the paper and your specific purpose
- reveal your plan of organization
Writing the Body
- Use your outline and prospectus as flexible guides
- Build your essay around points you want to make (i.e., don’t let your sources organize your paper)
- Integrate your sources into your discussion
- Summarize, analyze, explain, and evaluate published work rather than merely reporting it
- Move up and down the “ladder of abstraction” from generalization to varying levels of detail back to generalization
Writing the Conclusion
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to add your points up, to explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction.
- Perhaps suggest what about this topic needs further research.
Revising the Final Draft
- Check overall organization : logical flow of introduction, coherence and depth of discussion in body, effectiveness of conclusion.
- Paragraph level concerns : topic sentences, sequence of ideas within paragraphs, use of details to support generalizations, summary sentences where necessary, use of transitions within and between paragraphs.
- Sentence level concerns: sentence structure, word choices, punctuation, spelling.
- Documentation: consistent use of one system, citation of all material not considered common knowledge, appropriate use of endnotes or footnotes, accuracy of list of works cited.

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
How to Write a Research Paper

If you already have a headache trying to understand what research paper is all about, we have created an ultimate guide for you on how to write a research paper. You will find all the answers to your questions regarding structure, planning, doing investigation, finding the topic that appeals to you. Plus, you will find out the secret to an excellent paper. Are you at the edge of your seat? Let us start with the basics then.
- What is a Research Paper
- Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
- Report Papers and Thesis Papers
- How to Start a Research Paper
- How to Choose a Topic for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Plan
- How to Do Research
- How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Rough Draft
- How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Body of a Research Paper
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Revise and Edit a Research Paper
- How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper
- What Makes a Good Research Paper
Research Paper Writing Services
What is a research paper.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
You probably know the saying ‘the devil is not as black as he is painted’. This particular saying is absolutely true when it comes to writing a research paper. Your feet are cold even with the thought of this assignment. You have heard terrifying stories from older students. You have never done this before, so certainly you are scared. What is a research paper? How should I start? What are all these requirements about?
Luckily, you have a friend in need. That is our writing service. First and foremost, let us clarify the definition. A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides information about a particular topic that you’ve researched . In other words, you choose a topic: about historical events, the work of some artist, some social issues etc. Then you collect data on the given topic and analyze it. Finally, you put your analysis on paper. See, it is not as scary as it seems. If you are still having doubts, whether you can handle it yourself, we are here to help you. Our team of writers can help you choose the topic, or give you advice on how to plan your work, or how to start, or craft a paper for you. Just contact us 24/7 and see everything yourself.
5 Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
Why should I spend my time writing some academic paper? What is the use of it? Is not some practical knowledge more important? The list of questions is endless when it comes to a research paper. That is why we have outlined 5 main reasons why writing a research paper is a good thing.
- You will learn how to organize your time
If you want to write a research paper, you will have to learn how to manage your time. This type of assignment cannot be done overnight. It requires careful planning and you will need to learn how to do it. Later, you will be able to use these time-managing skills in your personal life, so why not developing them?
- You will discover your writing skills
You cannot know something before you try it. This rule relates to writing as well. You cannot claim that you cannot write until you try it yourself. It will be really difficult at the beginning, but then the words will come to your head themselves.
- You will improve your analytical skills
Writing a research paper is all about investigation and analysis. You will need to collect data, examine and classify it. These skills are needed in modern life more than anything else is.
- You will gain confidence
Once you do your own research, it gives you the feeling of confidence in yourself. The reason is simple human brain likes solving puzzles and your assignment is just another puzzle to be solved.
- You will learn how to persuade the reader
When you write your paper, you should always remember that you are writing it for someone to read. Moreover, you want this someone to believe in your ideas. For this reason, you will have to learn different convincing methods and techniques. You will learn how to make your writing persuasive. In turns, you will be able to use these methods in real life.
What is the Difference between Report and Thesis Papers?
A common question is ‘what is the difference between a report paper and a thesis paper?’ The difference lies in the aim of these two assignments. While the former aims at presenting the information, the latter aims at providing your opinion on the matter. In other words, in a report paper you have to summarize your findings. In a thesis paper, you choose some issue and defend your point of view by persuading the reader. It is that simple.
A thesis paper is a more common assignment than a report paper. This task will help a professor to evaluate your analytical skills and skills to present your ideas logically. These skills are more important than just the ability to collect and summarize data.
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
Research comes from the French word rechercher , meaning “to seek out.” Writing a research paper requires you to seek out information about a subject, take a stand on it, and back it up with the opinions, ideas, and views of others. What results is a printed paper variously known as a term paper or library paper, usually between five and fifteen pages long—most instructors specify a minimum length—in which you present your views and findings on the chosen subject.

It is not a secret that the majority of students hate writing a research paper. The reason is simple it steals your time and energy. Not to mention, constant anxiety that you will not be able to meet the deadline or that you will forget about some academic requirement.
We will not lie to you; a research paper is a difficult assignment. You will have to spend a lot of time. You will need to read, to analyze, and to search for the material. You will probably be stuck sometimes. However, if you organize your work smart, you will gain something that is worth all the effort – knowledge, experience, and high grades.
The reason why many students fail writing a research paper is that nobody explained them how to start and how to plan their work. Luckily, you have found our writing service and we are ready to shed the light on this dark matter.
We have created a step by step guide for you on how to write a research paper. We will dwell upon the structure, the writing tips, the writing strategies as well as academic requirements. Read this whole article and you will see that you can handle writing this assignment and our team of writers is here to assist you.
How to Start a Research Paper?

It all starts with the assignment. Your professor gives you the task. It may be either some general issue or specific topic to write about. Your assignment is your first guide to success. If you understand what you need to do according to the assignment, you are on the road to high results. Do not be scared to clarify your task if you need to. There is nothing wrong in asking a question if you want to do something right. You can ask your professor or you can ask our writers who know a thing or two in academic writing.
It is essential to understand the assignment. A good beginning makes a good ending, so start smart.
Learn how to start a research paper .
Choosing a Topic for a Research Paper

We have already mentioned that it is not enough to do great research. You need to persuade the reader that you have made some great research. What convinces better that an eye-catching topic? That is why it is important to understand how to choose a topic for a research paper.
First, you need to delimit the general idea to a more specific one. Secondly, you need to find what makes this topic interesting for you and for the academia. Finally, you need to refine you topic. Remember, it is not something you will do in one day. You can be reshaping your topic throughout your whole writing process. Still, reshaping not changing it completely. That is why keep in your head one main idea: your topic should be precise and compelling .
Learn how to choose a topic for a research paper .
How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper?

If you do not know what a proposal is, let us explain it to you. A proposal should answer three main questions:
- What is the main aim of your investigation?
- Why is your investigation important?
- How are you going to achieve the results?
In other words, proposal should show why your topic is interesting and how you are going to prove it. As to writing requirements, they may differ. That is why make sure you find out all the details at your department. You can ask your departmental administrator or find information online at department’s site. It is crucial to follow all the administrative requirements, as it will influence your grade.
Learn how to write a proposal for a research paper .
How to Write a Research Plan?

The next step is writing a plan. You have already decided on the main issues, you have chosen the bibliography, and you have clarified the methods. Here comes the planning. If you want to avoid writer’s block, you have to structure you work. Discuss your strategies and ideas with your instructor. Think thoroughly why you need to present some data and ideas first and others second. Remember that there are basic structure elements that your research paper should include:
- Thesis Statement
- Introduction
- Bibliography
You should keep in mind this skeleton when planning your work. This will keep your mind sharp and your ideas will flow logically.
Learn how to write a research plan .
How to Do Research?

Your research will include three stages: collecting data, reading and analyzing it, and writing itself.
First, you need to collect all the material that you will need for you investigation: films, documents, surveys, interviews, and others. Secondly, you will have to read and analyze. This step is tricky, as you need to do this part smart. It is not enough just to read, as you cannot keep in mind all the information. It is essential that you make notes and write down your ideas while analyzing some data. When you get down to the stage number three, writing itself, you will already have the main ideas written on your notes. Plus, remember to jot down the reference details. You will then appreciate this trick when you will have to write the bibliography.
If you do your research this way, it will be much easier for you to write the paper. You will already have blocks of your ideas written down and you will just need to add some material and refine your paper.
Learn how to do research .
How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper?

To make your paper well organized you need to write an outline. Your outline will serve as your guiding star through the writing process. With a great outline you will not get sidetracked, because you will have a structured plan to follow. Both you and the reader will benefit from your outline. You present your ideas logically and you make your writing coherent according to your plan. As a result, this outline guides the reader through your paper and the reader enjoys the way you demonstrate your ideas.
Learn how to write an outline for a research paper . See research paper outline examples .
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper?

Briefly, the thesis is the main argument of your research paper. It should be precise, convincing and logical. Your thesis statement should include your point of view supported by evidence or logic. Still, remember it should be precise. You should not beat around the bush, or provide all the possible evidence you have found. It is usually a single sentence that shows your argument. In on sentence you should make a claim, explain why it significant and convince the reader that your point of view is important.
Learn how to write a thesis statement for a research paper . See research paper thesis statement examples .
Should I Write a Rough Draft for a Research Paper?

Do you know any writer who put their ideas on paper, then never edited them and just published? Probably, no writer did so. Writing a research paper is no exception. It is impossible to cope with this assignment without writing a rough draft.
Your draft will help you understand what you need to polish to make your paper perfect. All the requirements, academic standards make it difficult to do everything flawlessly at the first attempt. Make sure you know all the formatting requirements: margins, words quantity, reference requirements, formatting styles etc.
Learn how to write a rough draft for a research paper .
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper?

Let us make it more vivid for you. We have narrowed down the tips on writing an introduction to the three main ones:
- Include your thesis in your introduction
Remember to include the thesis statement in your introduction. Usually, it goes at the end of the first paragraph.
- Present the main ideas of the body
You should tell the main topics you are going to discuss in the main body. For this reason, before writing this part of introduction, make sure you know what is your main body is going to be about. It should include your main ideas.
- Polish your thesis and introduction
When you finish the main body of your paper, come back to the thesis statement and introduction. Restate something if needed. Just make it perfect; because introduction is like the trailer to your paper, it should make the reader want to read the whole piece.
Learn how to write an introduction for a research paper . See research paper introduction examples .
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper?

A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument.
It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic. Stay focused and do not be sidetracked. You have your outline, so follow it.
Here are the main tips to keep in head when writing a body of a research paper:
- Let the ideas flow logically
- Include only relevant information
- Provide the evidence
- Structure the paragraphs
- Make the coherent transition from one paragraph to another
See? When it is all structured, it is not as scary as it seemed at the beginning. Still, if you have doubts, you can always ask our writers for help.
Learn how to write a body of a research paper . See research paper transition examples .
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper?

Writing a good conclusion is important as writing any other part of the paper. Remember that conclusion is not a summary of what you have mentioned before. A good conclusion should include your last strong statement.
If you have written everything according to the plan, the reader already knows why your investigation is important. The reader has already seen the evidence. The only thing left is a strong concluding thought that will organize all your findings.
Never include any new information in conclusion. You need to conclude, not to start a new discussion.
Learn how to write a conclusion for a research paper .
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper?

An abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually 100-200 words. You should provide the main gist of your paper in this short summary. An abstract can be informative, descriptive or proposal. Depending on the type of abstract, you need to write, the requirements will differ.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research.
To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery. You should write a short teaser of your paper. That is to say, you need to write an overview of your paper. The aim of a descriptive abstract is to interest the reader.
Finally, to write a proposal abstract you will need to write the basic summary as for the informative abstract. However, the difference is the following: you aim at persuading someone to let you write on the topic. That is why, a proposal abstract should present your topic as the one worth investigating.
Learn how to write an abstract for a research paper .
Should I Revise and Edit a Research Paper?

Revising and editing your paper is essential if you want to get high grades. Let us help you revise your paper smart:
- Check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes
- Sharpen the vocabulary
- Make sure there are no slang words in your paper
- Examine your paper in terms of structure
- Compare your topic, thesis statement to the whole piece
- Check your paper for plagiarism
If you need assistance with proofreading and editing your paper, you can turn to the professional editors at our service. They will help you polish your paper to perfection.
Learn how to revise and edit a research paper .
How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper?

First, let us make it clear that bibliography and works cited are two different things. Works cited are those that you cited in your paper. Bibliography should include all the materials you used to do your research. Still, remember that bibliography requirements differ depending on the formatting style of your paper. For this reason, make sure you ask you professor all the requirements you need to meet to avoid any misunderstanding.
Learn how to write a bibliography for a research paper .
The Key Secret to a Good Research Paper
Now when you know all the stages of writing a research paper, you are ready to find the key to a good research paper:
- Choose the topic that really interests you
- Make the topic interesting for you even if it is not at the beginning
- Follow the step by step guide and do not get sidetracked
- Be persistent and believe in yourself
- Really do research and write your paper from scratch
- Learn the convincing writing techniques and use them
- Follow the requirements of your assignment
- Ask for help if needed from real professionals
Feeling more confident about your paper now? We are sure you do. Still, if you need help, you can always rely on us 24/7.
We hope we have made writing a research paper much easier for you. We realize that it requires lots of time and energy. We believe when you say that you cannot handle it anymore. For this reason, we have been helping students like you for years. Our professional team of writers is ready to tackle any challenge.
All our authors are experienced writers crafting excellent academic papers. We help students meet the deadline and get the top grades they want. You can see everything yourself. All you need to do is to place your order online and we will contact you. Writing a research paper with us is truly easy, so why do not you check it yourself?
Additional Resources for Research Paper Writing:
- Anthropology Research
- Career Research
- Communication Research
- Criminal Justice Research
- Health Research
- Political Science Research
- Psychology Research
- Sociology Research
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources
Writing Research Papers
- Research Paper Structure
Whether you are writing a B.S. Degree Research Paper or completing a research report for a Psychology course, it is highly likely that you will need to organize your research paper in accordance with American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines. Here we discuss the structure of research papers according to APA style.
Major Sections of a Research Paper in APA Style
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in-depth guide, please refer to " How to Write a Research Paper in APA Style ”, a comprehensive guide developed by Prof. Emma Geller). 2
What is this paper called and who wrote it? – the first page of the paper; this includes the name of the paper, a “running head”, authors, and institutional affiliation of the authors. The institutional affiliation is usually listed in an Author Note that is placed towards the bottom of the title page. In some cases, the Author Note also contains an acknowledgment of any funding support and of any individuals that assisted with the research project.
One-paragraph summary of the entire study – typically no more than 250 words in length (and in many cases it is well shorter than that), the Abstract provides an overview of the study.

Introduction
What is the topic and why is it worth studying? – the first major section of text in the paper, the Introduction commonly describes the topic under investigation, summarizes or discusses relevant prior research (for related details, please see the Writing Literature Reviews section of this website), identifies unresolved issues that the current research will address, and provides an overview of the research that is to be described in greater detail in the sections to follow.
What did you do? – a section which details how the research was performed. It typically features a description of the participants/subjects that were involved, the study design, the materials that were used, and the study procedure. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Methods section. A rule of thumb is that the Methods section should be sufficiently detailed for another researcher to duplicate your research.
What did you find? – a section which describes the data that was collected and the results of any statistical tests that were performed. It may also be prefaced by a description of the analysis procedure that was used. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Results section.
What is the significance of your results? – the final major section of text in the paper. The Discussion commonly features a summary of the results that were obtained in the study, describes how those results address the topic under investigation and/or the issues that the research was designed to address, and may expand upon the implications of those findings. Limitations and directions for future research are also commonly addressed.
List of articles and any books cited – an alphabetized list of the sources that are cited in the paper (by last name of the first author of each source). Each reference should follow specific APA guidelines regarding author names, dates, article titles, journal titles, journal volume numbers, page numbers, book publishers, publisher locations, websites, and so on (for more information, please see the Citing References in APA Style page of this website).
Tables and Figures
Graphs and data (optional in some cases) – depending on the type of research being performed, there may be Tables and/or Figures (however, in some cases, there may be neither). In APA style, each Table and each Figure is placed on a separate page and all Tables and Figures are included after the References. Tables are included first, followed by Figures. However, for some journals and undergraduate research papers (such as the B.S. Research Paper or Honors Thesis), Tables and Figures may be embedded in the text (depending on the instructor’s or editor’s policies; for more details, see "Deviations from APA Style" below).
Supplementary information (optional) – in some cases, additional information that is not critical to understanding the research paper, such as a list of experiment stimuli, details of a secondary analysis, or programming code, is provided. This is often placed in an Appendix.
Variations of Research Papers in APA Style
Although the major sections described above are common to most research papers written in APA style, there are variations on that pattern. These variations include:
- Literature reviews – when a paper is reviewing prior published research and not presenting new empirical research itself (such as in a review article, and particularly a qualitative review), then the authors may forgo any Methods and Results sections. Instead, there is a different structure such as an Introduction section followed by sections for each of the different aspects of the body of research being reviewed, and then perhaps a Discussion section.
- Multi-experiment papers – when there are multiple experiments, it is common to follow the Introduction with an Experiment 1 section, itself containing Methods, Results, and Discussion subsections. Then there is an Experiment 2 section with a similar structure, an Experiment 3 section with a similar structure, and so on until all experiments are covered. Towards the end of the paper there is a General Discussion section followed by References. Additionally, in multi-experiment papers, it is common for the Results and Discussion subsections for individual experiments to be combined into single “Results and Discussion” sections.
Departures from APA Style
In some cases, official APA style might not be followed (however, be sure to check with your editor, instructor, or other sources before deviating from standards of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association). Such deviations may include:
- Placement of Tables and Figures – in some cases, to make reading through the paper easier, Tables and/or Figures are embedded in the text (for example, having a bar graph placed in the relevant Results section). The embedding of Tables and/or Figures in the text is one of the most common deviations from APA style (and is commonly allowed in B.S. Degree Research Papers and Honors Theses; however you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first).
- Incomplete research – sometimes a B.S. Degree Research Paper in this department is written about research that is currently being planned or is in progress. In those circumstances, sometimes only an Introduction and Methods section, followed by References, is included (that is, in cases where the research itself has not formally begun). In other cases, preliminary results are presented and noted as such in the Results section (such as in cases where the study is underway but not complete), and the Discussion section includes caveats about the in-progress nature of the research. Again, you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first.
- Class assignments – in some classes in this department, an assignment must be written in APA style but is not exactly a traditional research paper (for instance, a student asked to write about an article that they read, and to write that report in APA style). In that case, the structure of the paper might approximate the typical sections of a research paper in APA style, but not entirely. You should check with your instructor for further guidelines.
Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of the process of writing research papers, please consider attending this department’s “Writing Research Papers” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – empirical research) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
APA Journal Article Reporting Guidelines
- Appelbaum, M., Cooper, H., Kline, R. B., Mayo-Wilson, E., Nezu, A. M., & Rao, S. M. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for quantitative research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 3.
- Levitt, H. M., Bamberg, M., Creswell, J. W., Frost, D. M., Josselson, R., & Suárez-Orozco, C. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for qualitative primary, qualitative meta-analytic, and mixed methods research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 26.
External Resources
- Formatting APA Style Papers in Microsoft Word
- How to Write an APA Style Research Paper from Hamilton University
- WikiHow Guide to Writing APA Research Papers
- Sample APA Formatted Paper with Comments
- Sample APA Formatted Paper
- Tips for Writing a Paper in APA Style
1 VandenBos, G. R. (Ed). (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.) (pp. 41-60). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
2 geller, e. (2018). how to write an apa-style research report . [instructional materials]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing a Literature Review
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Body Paragraph Structure
Introduction.
- Referrences
- Ways to start paragraph
- Step by step guide
- Research paragraph examples

Learning the basics of a paragraph structure
- Title (cover page).
- Introduction.
- Literature review.
- Research methodology.
- Data analysis.
- Conclusion.
- Reference page.
5 winning ways to start a body paragraph
- Topic Sentence : it should provide a clear focus and introduce the specific aspect you will discuss. For example, “One key factor influencing climate change is…”.
- Opening Statement: grab your readers’ attention with a thought-provoking or surprising statement related to your topic. For instance, “The alarming increase in global temperatures has reached a critical point, demanding immediate action.”
- Quotation: find a relevant quote from a reputable source. It won’t only add credibility to your research but will also engage the reader right from the start.
- Anecdote or example: start your academic paragraph with a funny story or a real-world example that illustrates the significance of your research topic.
- Background information : provide a brief background or context for the topic you are about to discuss. For example, “In recent years, the prevalence of cyber-attacks has skyrocketed, posing a severe threat to individuals, organizations, and even national security.”
A step-by-step guide to starting a concise body paragraph
Step 1: introduce the main point or argument., step 2: provide evidence or examples., step 3: explain and analyze., step 4: connect to the main argument., step 5: review and revise., flawless body paragraph example: how does it look.
- Topic Sentence: Rising global temperatures have significant implications for ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Evidence/Example 1: According to a study by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global average temperatures have increased by 1.1 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times (IPCC, 2021). This temperature rise has led to melting polar ice caps and glaciers, rising sea levels, and coastal erosion (Smith et al., 2019).
- Explanation/Analysis 1: The significant increase in global temperatures has caused observable changes in the Earth’s physical environment. The melting of polar ice caps not only contributes to the rise in sea levels but also disrupts marine ecosystems.
- Evidence/Example 2: In addition to the loss of coastal habitats, higher temperatures have also resulted in shifts in the geographical distribution of species. Research by Parmesan and Yohe (2019) indicates that many plant and animal species have altered their ranges and migration patterns in response to changing climate conditions.
- Explanation/Analysis 2: The observed shifts in species distribution highlight the vulnerability of ecosystems to climate change. As temperature zone modification, species that cannot adapt or migrate to suitable habitats may face reduced reproductive success and increased risk of extinction.
- Connect to the main argument: These examples demonstrate that the rising global temperatures associated with climate change have profound implications for ecosystems and biodiversity.
The bottom line

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

- Research Paper >
Parts of a Research Paper
One of the most important aspects of science is ensuring that you get all the parts of the written research paper in the right order.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Outline Examples
- Example of a Paper
- Write a Hypothesis
- Introduction
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Write a Research Paper
- 2 Writing a Paper
- 3.1 Write an Outline
- 3.2 Outline Examples
- 4.1 Thesis Statement
- 4.2 Write a Hypothesis
- 5.2 Abstract
- 5.3 Introduction
- 5.4 Methods
- 5.5 Results
- 5.6 Discussion
- 5.7 Conclusion
- 5.8 Bibliography
- 6.1 Table of Contents
- 6.2 Acknowledgements
- 6.3 Appendix
- 7.1 In Text Citations
- 7.2 Footnotes
- 7.3.1 Floating Blocks
- 7.4 Example of a Paper
- 7.5 Example of a Paper 2
- 7.6.1 Citations
- 7.7.1 Writing Style
- 7.7.2 Citations
- 8.1.1 Sham Peer Review
- 8.1.2 Advantages
- 8.1.3 Disadvantages
- 8.2 Publication Bias
- 8.3.1 Journal Rejection
- 9.1 Article Writing
- 9.2 Ideas for Topics
You may have finished the best research project on earth but, if you do not write an interesting and well laid out paper, then nobody is going to take your findings seriously.
The main thing to remember with any research paper is that it is based on an hourglass structure. It begins with general information and undertaking a literature review , and becomes more specific as you nail down a research problem and hypothesis .
Finally, it again becomes more general as you try to apply your findings to the world at general.
Whilst there are a few differences between the various disciplines, with some fields placing more emphasis on certain parts than others, there is a basic underlying structure.
These steps are the building blocks of constructing a good research paper. This section outline how to lay out the parts of a research paper, including the various experimental methods and designs.
The principles for literature review and essays of all types follow the same basic principles.
Reference List

For many students, writing the introduction is the first part of the process, setting down the direction of the paper and laying out exactly what the research paper is trying to achieve.
For others, the introduction is the last thing written, acting as a quick summary of the paper. As long as you have planned a good structure for the parts of a research paper, both approaches are acceptable and it is a matter of preference.
A good introduction generally consists of three distinct parts:
- You should first give a general presentation of the research problem.
- You should then lay out exactly what you are trying to achieve with this particular research project.
- You should then state your own position.
Ideally, you should try to give each section its own paragraph, but this will vary given the overall length of the paper.
1) General Presentation
Look at the benefits to be gained by the research or why the problem has not been solved yet. Perhaps nobody has thought about it, or maybe previous research threw up some interesting leads that the previous researchers did not follow up.
Another researcher may have uncovered some interesting trends, but did not manage to reach the significance level , due to experimental error or small sample sizes .
2) Purpose of the Paper
The research problem does not have to be a statement, but must at least imply what you are trying to find.
Many writers prefer to place the thesis statement or hypothesis here, which is perfectly acceptable, but most include it in the last sentences of the introduction, to give the reader a fuller picture.
3) A Statement of Intent From the Writer
The idea is that somebody will be able to gain an overall view of the paper without needing to read the whole thing. Literature reviews are time-consuming enough, so give the reader a concise idea of your intention before they commit to wading through pages of background.
In this section, you look to give a context to the research, including any relevant information learned during your literature review. You are also trying to explain why you chose this area of research, attempting to highlight why it is necessary. The second part should state the purpose of the experiment and should include the research problem. The third part should give the reader a quick summary of the form that the parts of the research paper is going to take and should include a condensed version of the discussion.

This should be the easiest part of the paper to write, as it is a run-down of the exact design and methodology used to perform the research. Obviously, the exact methodology varies depending upon the exact field and type of experiment .
There is a big methodological difference between the apparatus based research of the physical sciences and the methods and observation methods of social sciences. However, the key is to ensure that another researcher would be able to replicate the experiment to match yours as closely as possible, but still keeping the section concise.
You can assume that anybody reading your paper is familiar with the basic methods, so try not to explain every last detail. For example, an organic chemist or biochemist will be familiar with chromatography, so you only need to highlight the type of equipment used rather than explaining the whole process in detail.
In the case of a survey , if you have too many questions to cover in the method, you can always include a copy of the questionnaire in the appendix . In this case, make sure that you refer to it.
This is probably the most variable part of any research paper, and depends on the results and aims of the experiment.
For quantitative research , it is a presentation of the numerical results and data, whereas for qualitative research it should be a broader discussion of trends, without going into too much detail.
For research generating a lot of results , then it is better to include tables or graphs of the analyzed data and leave the raw data in the appendix, so that a researcher can follow up and check your calculations.
A commentary is essential to linking the results together, rather than just displaying isolated and unconnected charts and figures.
It can be quite difficult to find a good balance between the results and the discussion section, because some findings, especially in a quantitative or descriptive experiment , will fall into a grey area. Try to avoid repeating yourself too often.
It is best to try to find a middle path, where you give a general overview of the data and then expand on it in the discussion - you should try to keep your own opinions and interpretations out of the results section, saving that for the discussion later on.
This is where you elaborate on your findings, and explain what you found, adding your own personal interpretations.
Ideally, you should link the discussion back to the introduction, addressing each point individually.
It’s important to make sure that every piece of information in your discussion is directly related to the thesis statement , or you risk cluttering your findings. In keeping with the hourglass principle, you can expand on the topic later in the conclusion .
The conclusion is where you build on your discussion and try to relate your findings to other research and to the world at large.
In a short research paper, it may be a paragraph or two, or even a few lines.
In a dissertation, it may well be the most important part of the entire paper - not only does it describe the results and discussion in detail, it emphasizes the importance of the results in the field, and ties it in with the previous research.
Some research papers require a recommendations section, postulating the further directions of the research, as well as highlighting how any flaws affected the results. In this case, you should suggest any improvements that could be made to the research design .
No paper is complete without a reference list , documenting all the sources that you used for your research. This should be laid out according to APA , MLA or other specified format, allowing any interested researcher to follow up on the research.
One habit that is becoming more common, especially with online papers, is to include a reference to your own paper on the final page. Lay this out in MLA, APA and Chicago format, allowing anybody referencing your paper to copy and paste it.
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Jun 5, 2009). Parts of a Research Paper. Retrieved May 22, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/parts-of-a-research-paper
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Check out the official book.
Learn how to construct, style and format an Academic paper and take your skills to the next level.

(also available as ebook )
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
Google Releases A.I. That Can Predict How the Human Body’s Molecules Behave, Boosting Drug Discovery Research
Called AlphaFold 3, the latest update of the software models the interactions of proteins with DNA, RNA and other molecules for the first time
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/ChristianThorsberg_Headshot.png)
Christian Thorsberg
Daily Correspondent
:focal(960x544:961x545)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f1/c4/f1c4ab29-c6b6-4088-a04a-b804c783b0fb/deepmind.webp)
Last week, Google released a much-anticipated upgrade for its AlphaFold software, which harnesses artificial intelligence to predict the shape and structure of molecules within the human body.
Any given molecule’s shape is indicative of its function and behavior, so biologists have long researched how chains of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, fold into various shapes. The A.I. tool can accelerate and streamline this process, opening new avenues for breakthroughs—notably in vaccine and drug development.
AlphaFold 3, the newest update from Google DeepMind described last week in the journal Nature , builds on its previous two iterations. The software’s initial tease in 2018 offered potential for accurately predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins, while its 2020 update, AlphaFold 2, came with significant improvements. In 2021, Google released an open-source version of AlphaFold, along with the predicted 3D structures of nearly all known proteins in the human body. The next year, two million predicted protein structures were shared.
But despite these leaps forward—which helped researchers map the human heart and better understand extinct birds’ eggs —AlphaFold 2 was limited in scope to modeling proteins.
“The AlphaFold 2 system only knew about amino acids, so it was of very limited utility for biopharma,” Mohammed AlQuraishi , a systems biologist at Columbia University who is not affiliated with Google DeepMind, tells MIT Technology Review ’s James O’Donnell.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/8e/cf/8ecf8233-17b3-47fe-a71c-38637ee9d744/deepmind2.png)
The newest version of the software can predict not only the shape of proteins, but also the structures of DNA, RNA and other molecules, such as ligands. Crucially, this update will allow researchers to better predict and study how different molecules in the human body geometrically interact with each other—and anticipate where a drug might bind to a protein.
This ability can “save months of experimental work and enable research that was previously impossible,” Deniz Kavi , a co-founder and chief executive of Tamarind Bio, a drug discovery start-up, tells the New York Times ’ Cade Metz. “This represents tremendous promise.”
Researchers could use the software update to probe some initial questions, including how proteins respond to DNA damage within the human body.
“It tells us a lot more about how the machines of the cell interact,” John Jumper , the director of Google DeepMind, tells the New York Times . “It tells us how this should work and what happens when we get sick.”

AlphaFold 3 offers researchers a level of confidence, often ranging from 40 percent to 80 percent, with each prediction it models, according to MIT Technology Review . Parts of a structure modeled with high confidence appear in blue, while the more uncertain regions appear in red. In some areas, its inaccuracy is a limitation—for modeling RNA-protein interactions, for example, the system isn’t yet highly exact.
Another potential drawback is the model’s ability to “hallucinate,” or produce false information. The team behind AlphaFold 3, in order to build its molecular library and function, borrowed methods from other A.I. models, such as OpenAI’s DALL-E 2 and Sora, that generate images and video. This improved AlphaFold 3’s capacity to produce large 3D images of molecular shapes, but leaves it liable to hallucinate. The team hopes to alleviate this issue with more training data, and in the paper, they note that hallucinated structures would typically be marked as low confidence.
Unlike its predecessor, the code for AlphaFold 3 will not be made open-source, and only a limited version, the AlphaFold Server , will be released publicly.
“This is a big advance for us,” Demis Hassabis , the CEO of Google DeepMind, tells WIRED ’s Will Knight. “This is exactly what you need for drug discovery: You need to see how a small molecule is going to bind to a drug, how strongly and also what else it might bind to.”
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/ChristianThorsberg_Headshot.png)
Christian Thorsberg | READ MORE
Christian Thorsberg is an environmental writer and photographer from Chicago. His work, which often centers on freshwater issues, climate change and subsistence, has appeared in Circle of Blue , Sierra magazine, Discover magazine and Alaska Sporting Journal .
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Nih research matters.
May 14, 2024
Understanding how exercise affects the body
At a glance.
- A study of endurance training in rats found molecular changes throughout the body that could help explain the beneficial effects of exercise on health.
- Large differences were seen between male and female rats, highlighting the need to include both women and men in exercise studies.

Exercise is one of the most beneficial activities that people can engage in. Regular exercise reduces the risk of heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and other health problems. It can even help people with many mental health conditions feel better.
But exactly how exercise exerts its positive effects hasn’t been well understood. And different people’s bodies can respond very differently to certain types of exercise, such as aerobic exercise or strength training.
Understanding how exercise impacts different organs at the molecular level could help health care providers better personalize exercise recommendations. It might also lead to drug therapies that could stimulate some of the beneficial effects of a workout for people who are physically unable to exercise.
To this end, researchers in the large, NIH-funded Molecular Transducers of Physical Activity Consortium (MoTrPAC) have been studying how endurance exercise and strength training affect both people and animals. The team is examining gene activity, protein alterations, immune cell function, metabolite levels, and numerous other measures of cell and tissue function. The first results, from rat studies of endurance exercise, were published on May 2, 2024, in Nature and several related journals.
Both male and female rats underwent progressive exercise training on a treadmill over an 8-week period. By the end of training, male rats had increased their aerobic capacity by 18%, and females by 16%. Tissue samples were collected from 18 different organs, plus the blood, during the training period and two days after the final bout of exercise. This let the researchers study the longer-term adaptations of the body to exercise.
Changes in gene activity, immune cell function, metabolism, and other cellular processes were seen in all the tissues studied, including those not previously known to be affected by exercise. The types of changes differed from tissue to tissue.
Many of the observed changes hinted at how exercise might protect certain organs against disease. For example, in the small intestines, exercise decreased the activity of certain genes associated with inflammatory bowel disease and reduced signs of inflammation in the gut. In the liver, exercise boosted molecular changes associated with improved tissue health and regeneration.
Some of the effects differed substantially between male and female rats. For example, in male rats, the eight weeks of endurance training reduced the amount of a type of body fat called subcutaneous white adipose tissue (scWAT). The same amount of exercise didn’t reduce the amount of scWAT in female rats. Instead, endurance exercise caused scWAT in female rats to alter its energy usage in ways that are beneficial to health. These and other results highlight the importance of including both women and men in exercise studies.
The researchers also compared gene activity changes in the rat studies with those from human samples taken from previous studies and found substantial overlap. They identified thousands of genes tied to human disease that were affected by endurance exercise. These analyses show how the MoTrPAC results from rats can be used to help guide future research in people.
“This is the first whole-organism map looking at the effects of training in multiple different organs,” says Dr. Steve Carr, a MoTrPAC investigator from the Broad Institute. “The resource produced will be enormously valuable, and has already produced many potentially novel biological insights for further exploration.”
Human trials are expected in the next few years. Information on participating can be found here .
—by Sharon Reynolds
Related Links
- Gut Microbes May Affect Motivation to Exercise
- Exercise-Induced Molecule Reduces Obesity in Mice
- Testing Ways to Encourage Exercise
- Hormone Links Exercise with Cognitive Benefits
- Exercise-Induced Protein May Reverse Age-Related Cognitive Decline
- Getting Active Later in Life Brings Benefits
- Get Active Together: Social Support Can Help Keep You Moving
- Personalized Exercise? How Biology Influences Fitness
- Maintain Your Muscle: Strength Training at Any Age
- Molecular Transducers of Physical Activity Consortium (MoTrPAC)
- Participating in MoTrPAC
References: Temporal dynamics of the multi-omic response to endurance exercise training. MoTrPAC Study Group; Lead Analysts; MoTrPAC Study Group. Nature . 2024 May;629(8010):174-183. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06877-w. Epub 2024 May 1. PMID: 38693412. Sexual dimorphism and the multi-omic response to exercise training in rat subcutaneous white adipose tissue. Many GM, Sanford JA, Sagendorf TJ, Hou Z, Nigro P, Whytock KL, Amar D, Caputo T, Gay NR, Gaul DA, Hirshman MF, Jimenez-Morales D, Lindholm ME, Muehlbauer MJ, Vamvini M, Bergman BC, Fernández FM, Goodyear LJ, Hevener AL, Ortlund EA, Sparks LM, Xia A, Adkins JN, Bodine SC, Newgard CB, Schenk S; MoTrPAC Study Group. Nat Metab . 2024 May 1. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00959-9. Online ahead of print. PMID: 38693320. The impact of exercise on gene regulation in association with complex trait genetics. Vetr NG, Gay NR; MoTrPAC Study Group; Montgomery SB. Nat Commun . 2024 May 1;15(1):3346. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45966-w. PMID: 38693125.
Funding: NIH’s Office of the Director (OD), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), National Institute on Aging (NIA), National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), and National Library of Medicine (NLM); Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation; National Science Foundation (NSF).
Enhancing research accessibility and reuse: new study outlines strategic measures
Today, the European Commission published a study aimed at improving access to and reuse of research results, including publications and data for scientific purposes. This marks a significant step under the European Research Area Policy Agenda 2022-2024 on an EU copyright and data legislative and regulatory framework fit for research.
The study has identified barriers and challenges to access and reuse of publicly funded research results, evaluated effects of the EU copyright framework on research, and identified relevant provisions for research in EU data and digital legislation. On this basis, it presents options for legislative and non-legislative measures to strengthen the free circulation of knowledge and thereby contribute to reinforce the European Research Area .
Iliana Ivanova , Commissioner for Innovation, Research, Culture, Education and Youth, said:
“The European Union has been pioneering open science policies and actions for over a decade. At the heart of our ambitious open science policy lies a simple but powerful belief: Publicly funded research should be a public resource. In our ongoing efforts under the European Research Area and its Policy Agenda, we collaborate closely with Member States, Associated Countries and stakeholders to create an environment where knowledge flows freely to benefit the society”.
The most common barriers encountered by researchers include lack of subscriptions by their organisations, inability to get permissions from the copyright owner, and fear of copyright infringement. Research performing organisations report challenges emerging from copyright law, not only in accessing and re-using publicly funded research results, but also in making results available in open access.
Special focus has been placed in investigating the situation in EU Member States that had introduced a Secondary Publication Right (SPR), including Germany, France, Netherlands, Belgium and Austria. SPR grants authors the right to freely share their published articles under certain conditions, alongside the initial publication in scientific journals. The study found that most research performing organisations in these Member States consider SPR to have at least a moderate impact on their research activities, including the share of research publications in open access. However, the study indicates that many researchers remain unaware of this right and a majority of research performing organisations consider certain provisions of national SPR legislation to be limiting factors. For example, the need to respect embargo periods and the fact that SPR is applicable only to the author-accepted manuscript, not the version of record, for publication.
The study presents options for legislative and non-legislative measures. It also outlines a diversity of stakeholders’ perspectives on the options proposed, indicating the need for further analysis and discussions. Measures explored encompass the introduction of an EU-wide Secondary Publication Right and provisions that could be included in such legislation, spanning from the type of scientific output to the embargo period to be allowed. Other proposed measures focus on strengthening open-ended and flexible research exceptions. This could be achieved by introducing a fully harmonised, mandatory, and general exemption for scientific research, by clarifying lawful forms of access, and by removing excessive barriers posed by technological protection measures. Lastly, options explored also include giving guidance on current text and data mining provisions, to raise awareness and facilitate implementation by the research community.
Finally, the study provides an analysis of provisions relevant to researchers and research organisations in EU data and digital legislation, examine the interplay against different legislative instruments, and present the main opportunities and challenges. The findings identify a growing entanglement of provisions relating to research activities and put forward recommendations.
The study was commissioned as part of Action 2 of the ERA Policy Agenda 2022-2024 . It has been carried out by a consortium led by PPMI Group, and including as partners the Institute for Information Law of the University of Amsterdam, the Centre for IT & IP Law at KU Leuven, and the Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies.
It also responds to the Council Conclusions of May 2023 on ‘High-quality, transparent, open, trustworthy and equitable scholarly publishing’, which encouraged the Commission to examine and propose measures at EU level.
More information
Study: Improving access to and reuse of research results, publications and data for scientific purposes
Executive Summary
European Research Area Platform
EU open science policy
Press contact:
EC Spokesperson for Research, Science and Innovation
Share this page
Cookie Acceptance Needed
This website would like to use cookies to collect information to improve your browsing experience. Please review our Privacy Statement for more information. Do you accept?
Accept Deny
- News |
- Articles |
- Body image research to practice
Customized care: Auburn University body image research sets new standard for person-centered treatment
From research to treatment, students and faculty at Auburn University are leading the charge to dispel stereotypes about eating disorders. Their work lays a foundation for a new clinical model, one that understands that eating disorders can happen to anyone, and through that understanding, prepares clinicians to better help everyone.
Assistant Professor of Psychological Sciences Tiffany Brown leads the Appearance Concerns, Eating, Prevention and Treatment (ACCEPT) Lab and co-directs the Auburn Eating Disorders Clinic (AEDC). Through both, she leads a cyclical effort to investigate, test and improve eating disorders treatment.
"The really exciting thing for me as both a clinician and then also a researcher, an academic, is being able to integrate what we're finding out in research about risk for eating disorder behaviors within diverse groups," Brown said. "We can then actually apply that or target some of those factors in treatment."
Culturally informed research
The ACCEPT Lab researches the factors behind negative body image and eating disorders across traditionally underserved populations. Recent psychology graduate and research assistant Minh Le's '24 work focused on how identity-related stress affects body dissatisfaction, including in populations across racial groups and the LGBTQ+ community.
Le said Brown helped him translate his hope for positive change into deliverable results that will benefit future researchers and clinicians. For example, Le's study revealed that stress around hiding sexual identity can predict body dissatisfaction in Asian individuals.
"My initial process of wanting to do this project was me being a part of a minority group and also the LGBTQ+ community. I really saw a difference between individuals that I have met in my life, and I wanted to see if there was an impact on body dissatisfaction," Le said. "I saw in my experiences that there is a sense of shame and dishonor whenever you are seen outside of the 'normal' group within Asian cultures. So, I see why it makes sense that sexual orientation concealment would be the highest predictor for it."
Graduate research assistant and clinical psychology student Marley Billman Miller also studies body dissatisfaction with an intersectional lens. Her latest work studied how race, gender and sexuality interacts with body image and eating disorders.
She found that while BIPOC (Black, Indigenous or other people of color) men have low rates of body dissatisfaction, they reported higher rates of eating disorder behavior. Those behaviors included purging and excessive exercise, which may be considered atypical if research is only limited to body dissatisfaction as the driving force behind eating disorders.
Billman Miller said these findings are important because while stereotypes around eating disorders are changing, treatment is slower to develop.
"My hope for the future is that more representation is seen in clinical trials and better adaptations are made to the existing, evidence-based treatments," Billman Miller said. "What we know is even our best treatments are only meeting the needs of about 50% of our patients, so if we incorporate more representation within our clinical trials or adapt our existing evidence-based treatments for those groups, we'll see better outcomes for everybody."
Evidence backed treatment
Research from the ACCEPT Lab applies directly to developing informed treatments for AEDC patients. The AEDC, co-directed by Brown and Associate Professor April Smith , treats a variety of eating disorders across the lifespan.
Billman Miller, who came to Auburn after serving as a clinical research coordinator at the Penn State College of Medicine, said that direct link between research and treatment drew her to Auburn's doctoral program.
"Knowing that we had an in-house training clinic, where I could work directly with individuals who were struggling with eating disorders, was a huge draw, as well as the ample opportunities to get involved with both research and clinical work," Billman Miller said. "Auburn does a great job of balancing the two, so I knew I'd come out a very well-rounded researcher and clinician at the end of my training."
Graduate students both conduct research and serve as clinicians in the AEDC. They also help undergraduate researchers address the gap between body image literature and treatment.
Brown said undergraduate and graduate students bring a variety of perspectives to challenging the one-size-fits-all approach to eating disorder treatment.
"One of the things we're trying to do with both the ACCEPT Lab and then also the AEDC is to help provide affirmative care for LGBTQ folks. Specifically, our research is currently focused on developing more specific treatments that target unique risk factors for LGBTQ individuals with an eating disorder," Brown said. "For men, both in the ACCEPT Lab and at the AEDC, we're really trying to develop and deliver prevention and treatment programs that focus on both traditional and male-specific body image and eating disorder concerns."
Lifesaving results
Research and treatment for eating disorders, which are the deadliest among mental health conditions, is underfunded compared to other psychological disorders. While Auburn faculty and students treat as many people as possible, their efforts also contribute to preventative measures.
Through the research collected in the ACCEPT Lab and the AEDC, Auburn has developed and delivered programs to prevent body dissatisfaction and eating disorders before they start. One of those interventions focused on improving body image concerns for young men.
Le served as an interventionist during the program and said his work around body image has completely changed the trajectory of his psychology career.
"Initially I didn't really know where I wanted to go or what I had to do for it, but joining this lab has set so many foundations for me to know what my path is, what my goal is at the end," Le said. "I really hope to see a bigger understanding of how to accommodate each person's need, depending on their backgrounds, depending on their identities, that we do focus on what is the most important part of helping these individuals rather than just finding out what's wrong."
The demand for high-quality, research-informed eating disorders treatment in Alabama is high. The AEDC is uniquely positioned to deliver specialized care, but currently has a waitlist to manage its patient load. Further, it follows a sliding scale model for treatment cost, meaning patients can receive treatment at a more affordable rate than other clinics.
Brown said the self-funded clinic hopes to expand services to care for even more patients in the future.
"We had a waitlist basically within a week of opening, which both shows a huge need in the community here for eating disorder treatment, but also shows that we weren't able to fully care for everybody who was coming in and needing treatment," Brown said. "One of the really great things with having increased support from the university and donors is we've been able to expand our services further."
Since the AEDC opened in 2022, support from the Auburn Family has helped the clinic double its patient capacity by hiring two full-time graduate clinicians and assisting its low-income patients by covering treatment costs.
To give or learn more about how your support makes a difference, visit the AEDC website .
Tags: Students Faculty Research Community and Outreach Psychological Sciences

Related Articles

Medina awarded a prestigious NYT Fellowship

Werner receives two distinguished AU awards

Chiafele's book receives 2022 Italian Prose in Translation Award

Department of Psychological Sciences SCOPE program featured in national publication

Island Press publishes Retzlaff's 'Justice and the Interstates: The Racist Truth about Urban Highways'

Acclaimed composer Andrew Lynch to design sound, music for Shakespeare’s return to the Auburn mainstage
Newsletter signup.
share this!
May 13, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
Researchers develop algorithms to understand how humans form body part vocabularies
by Kathrin Haimerl, Universität Passau
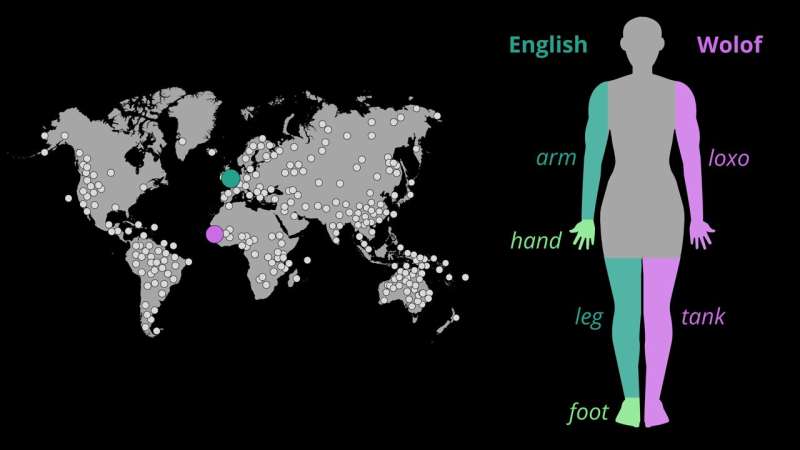
Human bodies have similar designs. However, languages differ in the way they divide the body into parts and name them. For example, English speakers have two words for foot and leg, whereas other languages express the concepts foot and leg in one word.
The study of the variation in body part vocabularies across diverse languages has attracted the attention of researchers in linguistics, anthropology and psychology for many years. Similar to the principles developed for the semantic domain of color, universal tendencies have been identified and contrasted with culture-specific variations.
The emergence of new methods in network analysis has made it possible to conduct large-scale comparisons of vocabulary in specific semantic domains to study universal and cultural structures.
Professor Johann-Mattis List, who leads the chair of Multilingual Computational Linguistics at the University of Passau, is one of the researchers who developed algorithms in order to shed light on the question of how humans form their vocabulary in different languages.
He joined researchers from the Department of Linguistic and Cultural Evolution at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, in their study comparing the vocabulary of body parts in 1,028 languages.
The study , titled "Universal and cultural factors shape body part vocabularies," has now been published in Scientific Reports .
Languages differ in how they name body parts
"Although our bodies follow similar designs, languages differ in how they divide the body into parts and name them," says Annika Tjuka, a former doctoral student with Professor List and now postdoctoral researcher at MPI-EVA, who initiated and conducted the study.
"In English, we have one word for arm and another for hand, but Wolof, a language spoken in Senegal in West Africa, uses one word, loxo, to refer to both body parts. Speakers of both languages have a human body. So why do they differ in which parts are given unique names?"
The results confirm the principle that if a separate word exists for foot, then there will also be one for hand. But the results also show that a body part that is adjacent to another is more likely to have the same name. One reason for this pattern is that languages like Wolof focus on and emphasize the functional features that connect two parts.
Speakers recognize that we throw a ball with our hand and arm, or that we walk with our leg and foot. Languages like English, on the other hand, focus on visual cues like the wrist or ankle to separate parts.
Body part vocabularies vary from language to language. However, general tendencies emerge within this diversity. "To understand the factors that shape linguistic diversity , we need more data. We need to document the languages spoken in linguistically diverse areas. And we need to collect data on the sociological context in which the languages are spoken," says Dr. Tjuka.
Large collection of wordlists across the world's languages
For the current study, the team of linguists used an existing database, Lexibank , which is developed by researchers at the MPI-EVA in Leipzig and the Chair of Multilingual Computational Linguistics in Passau. It is a large collection of wordlists across the world's languages.
With a computational approach, the Passau and Leipzig researchers extracted the words for 36 body parts in all these languages and analyzed the relationships between the words in a network analysis .
"It took us several years to assemble the data in the Lexibank collection," says Professor List, who used to work as a senior researcher at the MPI-EVA in Leipzig. "Now we can start to analyze the data in various ways."
Professor List heads the research group "ProduSemy" at the University of Passau. Together with his research team he also uses the data base in order to understand how word families are formed across languages.
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Universität Passau
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Nuclear physicists make first precision measurements of radium monofluoride
8 hours ago
Many microplastics in the world's oceans have likely escaped detection, researchers say

Community science volunteers can set scientific world abuzz with new bumble bee sightings

Kenyan fishers face increased drowning risk from climate change
A merger of microbes: Study shows low-nutrient conditions alter viral infection
9 hours ago

Study finds sea-level rise and weather-related shocks caused Louisiana marsh to die back

Repurposed protease controls important signaling molecule-activating protein
11 hours ago

Escaped GMO canola plants persist long-term, but may be losing their engineered resistance to pesticides

Ancient people hunted now extinct elephants at Tagua Tagua Lake in Chile 12,000 years ago, study finds

Ancient Mycenaean armor tested by Marines and pronounced suitable for extended combat
Relevant physicsforums posts, cover songs versus the original track, which ones are better, metal, rock, instrumental rock and fusion.
May 20, 2024
Today's Fusion Music: T Square, Cassiopeia, Rei & Kanade Sato
May 19, 2024
Bach, Bach, and more Bach please
May 18, 2024
What are your favorite Disco "Classics"?
May 17, 2024
Who is your favorite Jazz musician and what is your favorite song?
More from Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
Related Stories

Tracing the evolution of sign languages using computer modeling
Feb 2, 2024
Public database of standardized linguistic features
Jun 16, 2022
How AI can help map sign languages
Apr 15, 2024

Why all languages have words for 'this' and 'that'
Oct 30, 2023
First languages of North America traced back to two very different language groups from Siberia
Apr 9, 2024

Database shows the diversity of the world's languages
Apr 19, 2023
Recommended for you

Gender gaps remain for many women scientists, study finds

Military rank affects medical care, offering societal insights: Study
May 16, 2024

Study finds saying 'please' may not be so polite in everyday requests

Singing researchers find cross-cultural patterns in music and language
May 15, 2024

Mechanistic model shows how much gossip is needed to foster social cooperation

Study finds avoiding social media before an election has little to no effect on people's political views
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
China should hike tariffs on large cars to 25%, says research body
- Medium Text

- Company Bayerische Motoren Werke AG Follow
- Company Carparts.Com Inc Follow
- Company China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co., Ltd. Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Philip Blenkinsop, additional reporting by Sarah Wu and Zoey Zhang in Beijing; Editing by Elaine Hardcastle
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Asia stocks ease as central banks play game of patience
Several Asian share benchmarks fell on Thursday as markets digested the implications of policymakers in major economies preferring to take a patient approach to monetary easing amid sticky inflation.

Unique brain circuit is linked to Body Mass Index
Newly discovered connection between two brain regions may help regulate how much we eat.
Why can some people easily stop eating when they are full and others can't, which can lead to obesity?
A Northwestern Medicine study has found one reason may be a newly discovered structural connection between two regions in the brain that appears to be involved in regulating feeding behavior. These regions involve the sense of smell and behavior motivation.
The weaker the connection between these two brain regions, the higher a person's Body Mass Index (BMI), the Northwestern scientists report.
The investigators discovered this connection between the olfactory tubercle, an olfactory cortical region, which is part of the brain's reward system, and a midbrain region called the periaqueductal gray (PAG), involved in motivated behavior in response to negative feelings like pain and threat and potentially in suppression of eating.
The study will be published May 16 in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Previous research at Northwestern by co-author Thorsten Kahnt, now at the National Institutes of Health, has shown the smell of food is appetizing when you're hungry. But the smell is less appealing when you eat that food until you are full.
Odors play an important role in guiding motivated behaviors such as food intake, and -- in turn -- olfactory perception is modulated by how hungry we are.
Scientists have not fully understood the neural underpinnings of how the sense of smell contributes to how much we eat.
"The desire to eat is related to how appealing the smell of food is -- food smells better when you are hungry than when you are full," said corresponding author Guangyu Zhou, research assistant professor of neurology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. "But if the brain circuits that help guide this behavior are disrupted, these signals may get confused, leading to food being rewarding even when you are full. If this happens, a person's BMI could increase. And that is what we found. When the structural connection between these two brain regions is weaker, a person's BMI is higher, on average."
Though this study does not directly show it, the study authors hypothesize that healthy brain networks connecting reward areas with behavior areas could regulate eating behavior by sending messages telling the individual that eating doesn't feel good anymore when they're full. In fact, it feels bad to overeat. It's like a switch in the brain that turns off the desire to eat.
But people with weak or disrupted circuits connecting these areas may not get these stop signals, and may keep eating even when they aren't hungry, the scientists said.
"Understanding how these basic processes work in the brain is an important prerequisite to future work that can lead to treatments for overeating," said senior author Christina Zelano, associate professor of neurology at Feinberg.
How the study worked
This study used MRI brain data -- neurological imaging -- from the Human Connectome Project, a large multi-center NIH project designed to build a network map of the human brain.
Northwestern's Zhou found correlations to BMI in the circuit between the olfactory tubercle and the midbrain region, the periaqueductal gray. For the first time in humans, Zhou also mapped the strength of the circuit across the olfactory tubercle, then replicated these findings in a smaller MRI brain dataset that scientists collected in their lab at Northwestern.
"Future studies will be needed to uncover the exact mechanisms in the brain that regulate eating behavior," Zelano said.
The research reported in this press release was supported by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Diseases grants R01-DC-016364, R01-DC-018539, R01-DC-015426 and the Intramural Research Program at the National Institute on Drug Abuse grant ZIA DA000642, all of the National Institutes of Health. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
- Nervous System
- Brain Tumor
- Psychology Research
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Neuroscience
- Brain Injury
- West Nile virus
- Human skin color
- Limbic system
Story Source:
Materials provided by Northwestern University . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Guangyu Zhou, Gregory Lane, Thorsten Kahnt, Christina Zelano. Structural connectivity between olfactory tubercle and ventrolateral periaqueductal gray implicated in human feeding behavior . The Journal of Neuroscience , 2024; e2342232024 DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2342-23.2024
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- 'Major' Ancient Migration to Timor Island
- Ancient Viral DNA: Psychiatric Disorders
- New AI Accurately Predicts Fly Behavior
- Extreme Impacts: Metals Stronger When Heated
- Rare Earth Element's Secrets Exposed
- Origin of Sun's Magnetic Field
- Measuring Spin of Supermassive Black Hole
- 'Cell Cannibalism' Across Tree of Life
- Very Low Emission Concrete at Scale
- Kangaroos: Fearing Human 'Super Predator'
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

UC study uses health factors to predict kidney function recovery
Age, race, heart health, body mass among key factors in kidney care with dialysis-dependent aki.

Researchers at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine have created a scoring model that uses key health indicators to accurately predict recovery for patients who experience kidney failure due to acute kidney injury (AKI), which occurs when kidneys stop working properly and can range from minor loss of kidney function to complete failure.
AKI is a major contributor to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). About a third of patients with ESKD due to AKI recover kidney function.
Their findings, published in the Clinical Kidney Journal , predict kidney recovery within 90 days and 12 months after the start of dialysis for kidney failure patients due to AKI. The study looked at the health outcomes of 22,922 patients from the U.S. Renal Data System from 2005 to 2014 to offer predictions.
Lead author Silvi Shah, MD, associate professor in the Division of Nephrology at UC, explains that researchers examined several factors used in logistic regression models to analyze the effect of various covariates on a patient’s health outcome and found that 24% and 34% of patients with kidney failure due to AKI recovered kidney function within 90 days and 12 months, respectively.
Patient factors such as age, race or ethnicity, body mass index, congestive heart failure, cancer, amputation, functional status, hemoglobin and prior nephrology care are used in the regression model.
“One of the significant comorbidities was a history of heart failure,” Shah says. “If you had heart failure, you were at a lower chance of recovering as well. If you had a lower body mass index, you had a lower chance of recovery; if you had amputation or poor functional status, you had a low chance of recovery. These were some of the significant predictors of the score.”
Dr. Charuhas Thakar and Dr. Silvi Shah are shown in the UC College of Medicine. Photo by Colleen Kelley/UC Marketing + Brand.
Shah notes that younger people got more points in her prediction model because older age was also associated with a likelihood of lower recovery for kidney failure patients due to AKI.
The scoring model was developed as a way to help staff providing clinical care in a dialysis unit quickly triage patients based on characteristics that would be easily available in their medical history, explains Charuhas Thakar, MD, a senior author in the study, professor at Queen’s University Belfast in the United Kingdom and former division chief of nephrology at the University of Cincinnati.
“Patients who develop dialysis dependent AKI typically receive care in dialysis facilities amongst other patients with end stage kidney disease,” says Thakar. “Our goal was to quickly triage and determine who has the higher, medium or low prospect of recovery based on clinical characteristics the patient had in their medical history.”
“That was our broad approach. If your score is high, you have the best chance of recovery,” adds Thakar. “Patients who are more likely to recover can be monitored closely for that prospect, and we can focus our energies on preserving renal function. At the same time, those who are unlikely to recover should be allowed to undergo long term planning including transplantation. In summary, our study paves the way to individualize care as well as facilitate efficient use of treatment and resources.”
Shah says it’s important to understand that patients who have kidney failure due to AKI can recover.
“Around one-fourth of those patients will recover in 90 days, and around one-third of those patients will recover in 12 months,” says Shah. “There are several factors which can predict the recovery rate. If you have lower body mass index, if you are Black, have congestive heart failure or a history of amputation, you have lower chances of recovery.
“It helps us to do a risk prediction score and at the same time helps us to tell patients and healthcare providers what is the percentage recovery that may be expected,” adds Shah. “If you fall in the high score category, they have a 57% chance of recovery in 90 days. This is very encouraging for both patients and physicians."
She emphasizes that researchers included the largest data in the U.S. — using the United States Renal Data System — and captured all patients on dialysis in the country, including information for women, men and different races and ethnicities.
“One of the biggest strengths of the paper was that it was inclusive, and the score was individualized,” Shah says. “It can help in counseling and risk prediction and tailoring treatment specifically for patients that have dialysis-dependent AKI, and based on the score, we can tell patients what’s the chance of their recovery.”
Other co-authors of the research at the University of Cincinnati are Department of Environmental and Public Health Sciences professors Anthony Leonard, PhD; Karthikeyan Meganathan, PhD; and Annette Christianson; along with Kathleen Harrison from the Division of Nephrology. Jia Ng, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Hofstra University, is also a co-author of the study.
Both Silvi Shah and Jia Ng had career development awards from the National Institutes of Health. Ng also received support from the Breslin Family Foundation. Shah received intramural funds from the UC Division of Nephrology.
Disclosures: Jia Ng received consultancy fees from Vifor Pharmaceuticals. She is a founder of PublishedMD Consulting LLC.
Read the research study online .
Impact Lives Here
The University of Cincinnati is leading public urban universities into a new era of innovation and impact. Our faculty, staff and students are saving lives, changing outcomes and bending the future in our city's direction. Next Lives Here.
- College of Medicine
- Public Health
- Environmental Health
- Academic Health Center
Related Stories
May 21, 2024
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine have created a scoring model that uses key health indicators to accurately predict recovery for patients who suffer kidney failure due to acute kidney injury (AKI).
U.S. News & World Report: Metformin may help young patients with bipolar disorder avoid weight gain
October 31, 2023
U.S. News & World Report highlighted recent research led by the University of Cincinnati and Northwell Health that found the drug metformin can help prevent or reduce weight gain in youth taking medication to treat bipolar disorder.
UC research examines the impact of maternal stress during pregnancy on child’s health
April 20, 2023
New research out of the University of Cincinnati examines the impact that maternal stress during pregnancy has on the neurodevelopment of babies. The study was published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.

COMMENTS
The main part of your research paper is called "the body.". To write this important part of your paper, include only relevant information, or information that gets to the point. Organize your ideas in a logical order—one that makes sense—and provide enough details—facts and examples—to support the points you want to make.
The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order. Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper. Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
Placement Beginning at the top of a new page, the main body of the research paper follows the abstract and precedes the References page. Comprised of the introduction, method, results, and discussion subsections, the main body acts as the third major section of the document and typically begins on the third page of the paper.
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant) -TTEB! A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
Table of contents. Step 1: Identify the paragraph's purpose. Step 2: Show why the paragraph is relevant. Step 3: Give evidence. Step 4: Explain or interpret the evidence. Step 5: Conclude the paragraph. Step 6: Read through the whole paragraph. When to start a new paragraph.
The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas. 1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses.
Knowing these elements and the purpose of each serves help you to read and understand academic texts efficiently and effectively, and then apply what you read to your paper or project. Social Science (and Science) original research articles generally follow IMRD: Introduction- Methods-Results-Discussion. Introduction. Introduces topic of article.
It describes the essence, the main theme of the paper. It includes the research question posed, its significance, the methodology, and the main results or findings. Footnotes or cited works are never listed in an abstract. Remember to take great care in composing the abstract. It's the first part of the paper the instructor reads.
The Anatomy of a Body Paragraph When you write strong, clear paragraphs, you are guiding your readers through your argument by showing them how your points fit together to support your thesis. The number of paragraphs in your essay should be determined by the number of steps you need to take to build your argument.
The body is the largest part of a research paper; in it you collect and arrange evidence that will persuade the reader of your argument. It should, therefore, have a logical organization. If the paper is long, it is a good idea to partition the body into sections using headings and sub-headings. This includes using parenthetical citations when ...
Writing a Research Paper. This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper. Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper? A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument. It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic.
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in ...
A primary research paper involves writing body paragraphs to effectively communicate the study's purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. While there may be some variations depending on the discipline and journal guidelines, the following paragraph structure is commonly used: Introduction. The body of research paper sets the stage.
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
Method. This should be the easiest part of the paper to write, as it is a run-down of the exact design and methodology used to perform the research. Obviously, the exact methodology varies depending upon the exact field and type of experiment.. There is a big methodological difference between the apparatus based research of the physical sciences and the methods and observation methods of ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
Her research focuses on the creation and negotiation of contradiction, specifically within the topics of organizational socialization, midwifery, and birth, and the body in the workplace. Kristen M. Norwood (PhD, University of Iowa, 2010) is an assistant professor in the Department of English and Communication at Fontbonne University.
The human body is the physical substance of the human organism. Characteristic of the vertebrate form, the human body has an internal skeleton with a backbone, and, as with the mammalian form, it has hair and mammary glands. Learn more about the composition, form, and physical adaptations of the human body.
That Can Predict How the Human Body's Molecules Behave, Boosting Drug Discovery Research. Called AlphaFold 3, the latest update of the software models the interactions of proteins with DNA, RNA ...
Changes in gene activity, immune cell function, metabolism, and other cellular processes were seen in all the tissues studied, including those not previously known to be affected by exercise. The types of changes differed from tissue to tissue. Many of the observed changes hinted at how exercise might protect certain organs against disease.
The cells generated by the very first division of the fertilized egg make a lopsided contribution to the body's organs and tissues. A living human embryo (left) is shown at the eight-cell stage ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Today, the European Commission published a study aimed at improving access to and reuse of research results, including publications and data for scientific purposes. This marks a significant step under the European Research Area Policy Agenda 2022-2024 on an EU copyright and data legislative and regulatory framework fit for research.
Customized care: Auburn University body image research sets new standard for person-centered treatment. From research to treatment, students and faculty at Auburn University are leading the charge to dispel stereotypes about eating disorders. Their work lays a foundation for a new clinical model, one that understands that eating disorders can ...
With a computational approach, the Passau and Leipzig researchers extracted the words for 36 body parts in all these languages and analyzed the relationships between the words in a network ...
China should raise its import tariffs on large gasoline-powered cars to 25%, a government-affiliated auto research body expert told China's Global Times newspaper as the country faces sharply ...
The research reported in this press release was supported by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Diseases grants R01-DC-016364, R01-DC-018539, R01-DC-015426 and the ...
Age, race, heart health, body mass among key factors in kidney care with dialysis-dependent AKI. By Cedric Ricks Email Cedric Email Cedric 260-415-8554. ... Read the research study online. Impact Lives Here. The University of Cincinnati is leading public urban universities into a new era of innovation and impact. Our faculty, staff and students ...