Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Methodological Approaches to Literature Review
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 09 May 2023
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Dennis Thomas 2 ,
- Elida Zairina 3 &
- Johnson George 4
862 Accesses
1 Citations
The literature review can serve various functions in the contexts of education and research. It aids in identifying knowledge gaps, informing research methodology, and developing a theoretical framework during the planning stages of a research study or project, as well as reporting of review findings in the context of the existing literature. This chapter discusses the methodological approaches to conducting a literature review and offers an overview of different types of reviews. There are various types of reviews, including narrative reviews, scoping reviews, and systematic reviews with reporting strategies such as meta-analysis and meta-synthesis. Review authors should consider the scope of the literature review when selecting a type and method. Being focused is essential for a successful review; however, this must be balanced against the relevance of the review to a broad audience.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Reviewing Literature for and as Research

Discussion and Conclusion

Systematic Reviews in Educational Research: Methodology, Perspectives and Application
Akobeng AK. Principles of evidence based medicine. Arch Dis Child. 2005;90(8):837–40.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Alharbi A, Stevenson M. Refining Boolean queries to identify relevant studies for systematic review updates. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27(11):1658–66.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Article Google Scholar
Aromataris E MZE. JBI manual for evidence synthesis. 2020.
Google Scholar
Aromataris E, Pearson A. The systematic review: an overview. Am J Nurs. 2014;114(3):53–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Aromataris E, Riitano D. Constructing a search strategy and searching for evidence. A guide to the literature search for a systematic review. Am J Nurs. 2014;114(5):49–56.
Babineau J. Product review: covidence (systematic review software). J Canad Health Libr Assoc Canada. 2014;35(2):68–71.
Baker JD. The purpose, process, and methods of writing a literature review. AORN J. 2016;103(3):265–9.
Bastian H, Glasziou P, Chalmers I. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: how will we ever keep up? PLoS Med. 2010;7(9):e1000326.
Bramer WM, Rethlefsen ML, Kleijnen J, Franco OH. Optimal database combinations for literature searches in systematic reviews: a prospective exploratory study. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):1–12.
Brown D. A review of the PubMed PICO tool: using evidence-based practice in health education. Health Promot Pract. 2020;21(4):496–8.
Cargo M, Harris J, Pantoja T, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 4: methods for assessing evidence on intervention implementation. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:59–69.
Cook DJ, Mulrow CD, Haynes RB. Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126(5):376–80.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Counsell C. Formulating questions and locating primary studies for inclusion in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127(5):380–7.
Cummings SR, Browner WS, Hulley SB. Conceiving the research question and developing the study plan. In: Cummings SR, Browner WS, Hulley SB, editors. Designing Clinical Research: An Epidemiological Approach. 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): P Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 14–22.
Eriksen MB, Frandsen TF. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: a systematic review. JMLA. 2018;106(4):420.
Ferrari R. Writing narrative style literature reviews. Medical Writing. 2015;24(4):230–5.
Flemming K, Booth A, Hannes K, Cargo M, Noyes J. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 6: reporting guidelines for qualitative, implementation, and process evaluation evidence syntheses. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:79–85.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf Libr J. 2009;26(2):91–108.
Green BN, Johnson CD, Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. J Chiropr Med. 2006;5(3):101–17.
Gregory AT, Denniss AR. An introduction to writing narrative and systematic reviews; tasks, tips and traps for aspiring authors. Heart Lung Circ. 2018;27(7):893–8.
Harden A, Thomas J, Cargo M, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 5: methods for integrating qualitative and implementation evidence within intervention effectiveness reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:70–8.
Harris JL, Booth A, Cargo M, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 2: methods for question formulation, searching, and protocol development for qualitative evidence synthesis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:39–48.
Higgins J, Thomas J. In: Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3, updated February 2022). Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.: Cochrane; 2022.
International prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO). Available from https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/ .
Khan KS, Kunz R, Kleijnen J, Antes G. Five steps to conducting a systematic review. J R Soc Med. 2003;96(3):118–21.
Landhuis E. Scientific literature: information overload. Nature. 2016;535(7612):457–8.
Lockwood C, Porritt K, Munn Z, Rittenmeyer L, Salmond S, Bjerrum M, Loveday H, Carrier J, Stannard D. Chapter 2: Systematic reviews of qualitative evidence. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020. Available from https://synthesismanual.jbi.global . https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-03 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Lorenzetti DL, Topfer L-A, Dennett L, Clement F. Value of databases other than medline for rapid health technology assessments. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2014;30(2):173–8.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, the PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for (SR) and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;6:264–9.
Mulrow CD. Systematic reviews: rationale for systematic reviews. BMJ. 1994;309(6954):597–9.
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):143.
Munthe-Kaas HM, Glenton C, Booth A, Noyes J, Lewin S. Systematic mapping of existing tools to appraise methodological strengths and limitations of qualitative research: first stage in the development of the CAMELOT tool. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):1–13.
Murphy CM. Writing an effective review article. J Med Toxicol. 2012;8(2):89–90.
NHMRC. Guidelines for guidelines: assessing risk of bias. Available at https://nhmrc.gov.au/guidelinesforguidelines/develop/assessing-risk-bias . Last published 29 August 2019. Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
Noyes J, Booth A, Cargo M, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 1: introduction. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018b;97:35–8.
Noyes J, Booth A, Flemming K, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 3: methods for assessing methodological limitations, data extraction and synthesis, and confidence in synthesized qualitative findings. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018a;97:49–58.
Noyes J, Booth A, Moore G, Flemming K, Tunçalp Ö, Shakibazadeh E. Synthesising quantitative and qualitative evidence to inform guidelines on complex interventions: clarifying the purposes, designs and outlining some methods. BMJ Glob Health. 2019;4(Suppl 1):e000893.
Peters MD, Godfrey CM, Khalil H, McInerney P, Parker D, Soares CB. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J Evid Healthcare. 2015;13(3):141–6.
Polanin JR, Pigott TD, Espelage DL, Grotpeter JK. Best practice guidelines for abstract screening large-evidence systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Res Synth Methods. 2019;10(3):330–42.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, et al. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7(1):1–7.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. Brit Med J. 2017;358
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. Br Med J. 2016;355
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. JAMA. 2000;283(15):2008–12.
Tawfik GM, Dila KAS, Mohamed MYF, et al. A step by step guide for conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis with simulation data. Trop Med Health. 2019;47(1):1–9.
The Critical Appraisal Program. Critical appraisal skills program. Available at https://casp-uk.net/ . 2022. Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
The University of Melbourne. Writing a literature review in Research Techniques 2022. Available at https://students.unimelb.edu.au/academic-skills/explore-our-resources/research-techniques/reviewing-the-literature . Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison. Learn how to write a literature review in The Writer’s Handbook – Academic Professional Writing. 2022. Available at https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/reviewofliterature/ . Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
Thompson SG, Sharp SJ. Explaining heterogeneity in meta-analysis: a comparison of methods. Stat Med. 1999;18(20):2693–708.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16(1):15.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Yoneoka D, Henmi M. Clinical heterogeneity in random-effect meta-analysis: between-study boundary estimate problem. Stat Med. 2019;38(21):4131–45.
Yuan Y, Hunt RH. Systematic reviews: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(5):1086–92.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre of Excellence in Treatable Traits, College of Health, Medicine and Wellbeing, University of Newcastle, Hunter Medical Research Institute Asthma and Breathing Programme, Newcastle, NSW, Australia
Dennis Thomas
Department of Pharmacy Practice, Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Elida Zairina
Centre for Medicine Use and Safety, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Monash University, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Johnson George
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Johnson George .
Section Editor information
College of Pharmacy, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
Derek Charles Stewart
Department of Pharmacy, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, United Kingdom
Zaheer-Ud-Din Babar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Thomas, D., Zairina, E., George, J. (2023). Methodological Approaches to Literature Review. In: Encyclopedia of Evidence in Pharmaceutical Public Health and Health Services Research in Pharmacy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50247-8_57-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50247-8_57-1
Received : 22 February 2023
Accepted : 22 February 2023
Published : 09 May 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-50247-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-50247-8
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life Sciences Reference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Make your writing flawless in 1 upload
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Upload my document
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.

Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health (m-health) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Jul 15, 2024 10:34 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review, sage campus course: conduct a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
This course guides you through the entire process of preparing a literature review, selecting and analyzing existing literature, and structuring and writing a quality literature review. Most importantly, the course develops skills in using evidence to create and present an engaging and critical argument.
Beginner | 5 hours total for all modules
- What is the Purpose of a Literature Review?
- What to Do Before You Start?
- Selecting and Analyzing the Right Literature
- How Do I Create My Argument?
- How Do I Write My Argument?
- How Should I Structure a Literature Review?

- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Oct 14, 2024 1:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
What is the purpose of literature review , a. habitat loss and species extinction: , b. range shifts and phenological changes: , c. ocean acidification and coral reefs: , d. adaptive strategies and conservation efforts: .
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review .
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.
Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as yo u go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free!
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research | Cite feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface. It also allows you auto-cite references in 10,000+ styles and save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research | Cite” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.

- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references in 10,000+ styles into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.

The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 22+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what are citation styles which citation style to..., what are the types of literature reviews , what are research skills definition, importance, and examples , what is phd dissertation defense and how to..., abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., what is academic integrity, and why is it..., how to make a graphical abstract, academic integrity vs academic dishonesty: types & examples.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
Steps in the literature review process.
- What is a literature review?
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus
- Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy
- Finalize your research question
- Think about relevant dates, geographies (and languages), methods, and conflicting points of view
- Conduct searches in the published literature via the identified databases
- Check to see if this topic has been covered in other discipline's databases
- Examine the citations of on-point articles for keywords, authors, and previous research (via references) and cited reference searching.
- Save your search results in a citation management tool (such as Zotero, Mendeley or EndNote)
- De-duplicate your search results
- Make sure that you've found the seminal pieces -- they have been cited many times, and their work is considered foundational
- Check with your professor or a librarian to make sure your search has been comprehensive
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of individual sources and evaluate for bias, methodologies, and thoroughness
- Group your results in to an organizational structure that will support why your research needs to be done, or that provides the answer to your research question
- Develop your conclusions
- Are there gaps in the literature?
- Where has significant research taken place, and who has done it?
- Is there consensus or debate on this topic?
- Which methodological approaches work best?
- For example: Background, Current Practices, Critics and Proponents, Where/How this study will fit in
- Organize your citations and focus on your research question and pertinent studies
- Compile your bibliography
Note: The first four steps are the best points at which to contact a librarian. Your librarian can help you determine the best databases to use for your topic, assess scope, and formulate a search strategy.
Videos Tutorials about Literature Reviews
This 4.5 minute video from Academic Education Materials has a Creative Commons License and a British narrator.
Recommended Reading
- Last Updated: Oct 23, 2024 11:46 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews


Research Process :: Step by Step
- Introduction
- Select Topic
- Identify Keywords
- Background Information
- Develop Research Questions
- Refine Topic
- Search Strategy
- Popular Databases
- Evaluate Sources
- Types of Periodicals
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Organize / Take Notes
- Writing & Grammar Resources
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Citation Styles
- Paraphrasing
- Privacy / Confidentiality

Organize the literature review into sections that present themes or identify trends, including relevant theory. You are not trying to list all the material published, but to synthesize and evaluate it according to the guiding concept of your thesis or research question.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment, but more often it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries
A literature review must do these things:
- be organized around and related directly to the thesis or research question you are developing
- synthesize results into a summary of what is and is not known
- identify areas of controversy in the literature
- formulate questions that need further research
Ask yourself questions like these:
- What is the specific thesis, problem, or research question that my literature review helps to define?
- What type of literature review am I conducting? Am I looking at issues of theory? methodology? policy? quantitative research (e.g. on the effectiveness of a new procedure)? qualitative research (e.g., studies of loneliness among migrant workers)?
- What is the scope of my literature review? What types of publications am I using (e.g., journals, books, government documents, popular media)? What discipline am I working in (e.g., nursing psychology, sociology, medicine)?
- How good was my information seeking? Has my search been wide enough to ensure I've found all the relevant material? Has it been narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material? Is the number of sources I've used appropriate for the length of my paper?
- Have I critically analyzed the literature I use? Do I follow through a set of concepts and questions, comparing items to each other in the ways they deal with them? Instead of just listing and summarizing items, do I assess them, discussing strengths and weaknesses?
- Have I cited and discussed studies contrary to my perspective?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant, appropriate, and useful?
Ask yourself questions like these about each book or article you include:
- Has the author formulated a problem/issue?
- Is it clearly defined? Is its significance (scope, severity, relevance) clearly established?
- Could the problem have been approached more effectively from another perspective?
- What is the author's research orientation (e.g., interpretive, critical science, combination)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g., psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship between the theoretical and research perspectives?
- Has the author evaluated the literature relevant to the problem/issue? Does the author include literature taking positions she or he does not agree with?
- In a research study, how good are the basic components of the study design (e.g., population, intervention, outcome)? How accurate and valid are the measurements? Is the analysis of the data accurate and relevant to the research question? Are the conclusions validly based upon the data and analysis?
- In material written for a popular readership, does the author use appeals to emotion, one-sided examples, or rhetorically-charged language and tone? Is there an objective basis to the reasoning, or is the author merely "proving" what he or she already believes?
- How does the author structure the argument? Can you "deconstruct" the flow of the argument to see whether or where it breaks down logically (e.g., in establishing cause-effect relationships)?
- In what ways does this book or article contribute to our understanding of the problem under study, and in what ways is it useful for practice? What are the strengths and limitations?
- How does this book or article relate to the specific thesis or question I am developing?
Text written by Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, University of Toronto
http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/literature-review
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Step 5: Cite Sources >>
- Last Updated: Oct 18, 2024 11:42 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/researchprocess
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.
- Libraries & Collections
- News & Events
- Process: Literature Reviews
- Literature Review
- Managing Sources
Ask a Librarian

Does your assignment or publication require that you write a literature review? This guide is intended to help you understand what a literature is, why it is worth doing, and some quick tips composing one.
Understanding Literature Reviews
What is a literature review .
Typically, a literature review is a written discussion that examines publications about a particular subject area or topic. Depending on disciplines, publications, or authors a literature review may be:
A summary of sources An organized presentation of sources A synthesis or interpretation of sources An evaluative analysis of sources
A Literature Review may be part of a process or a product. It may be:
A part of your research process A part of your final research publication An independent publication
Why do a literature review?
The Literature Review will place your research in context. It will help you and your readers:
Locate patterns, relationships, connections, agreements, disagreements, & gaps in understanding Identify methodological and theoretical foundations Identify landmark and exemplary works Situate your voice in a broader conversation with other writers, thinkers, and scholars
The Literature Review will aid your research process. It will help you to:
Establish your knowledge Understand what has been said Define your questions Establish a relevant methodology Refine your voice Situate your voice in the conversation
What does a literature review look like?
The Literature Review structure and organization may include sections such as:
An introduction or overview A body or organizational sub-divisions A conclusion or an explanation of significance
The body of a literature review may be organized in several ways, including:
Chronologically: organized by date of publication Methodologically: organized by type of research method used Thematically: organized by concept, trend, or theme Ideologically: organized by belief, ideology, or school of thought

- Find a focus
- Find models
- Review your target publication
- Track citations
- Read critically
- Manage your citations
- Ask friends, faculty, and librarians
Additional Sources
- Reviewing the literature. Project Planner.
- Literature Review: By UNC Writing Center
- PhD on Track
- CU Graduate Students Thesis & Dissertation Guidance
- CU Honors Thesis Guidance

- Next: Managing Sources >>
- University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Research Guides
- Research Strategies
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 3:23 PM
- URL: https://libguides.colorado.edu/strategies/litreview
- © Regents of the University of Colorado

Research Methods: Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Literature Reviews
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Persuasive Arguments
- Subject Specific Methodology
A literature review involves researching, reading, analyzing, evaluating, and summarizing scholarly literature (typically journals and articles) about a specific topic. The results of a literature review may be an entire report or article OR may be part of a article, thesis, dissertation, or grant proposal. A literature review helps the author learn about the history and nature of their topic, and identify research gaps and problems.
Steps & Elements
Problem formulation
- Determine your topic and its components by asking a question
- Research: locate literature related to your topic to identify the gap(s) that can be addressed
- Read: read the articles or other sources of information
- Analyze: assess the findings for relevancy
- Evaluating: determine how the article are relevant to your research and what are the key findings
- Synthesis: write about the key findings and how it is relevant to your research
Elements of a Literature Review
- Summarize subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with objectives of the review
- Divide works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, those offering alternative theories entirely)
- Explain how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
- Conclude which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of an area of research
Writing a Literature Review Resources
- How to Write a Literature Review From the Wesleyan University Library
- Write a Literature Review From the University of California Santa Cruz Library. A Brief overview of a literature review, includes a list of stages for writing a lit review.
- Literature Reviews From the University of North Carolina Writing Center. Detailed information about writing a literature review.
- Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach Cronin, P., Ryan, F., & Coughan, M. (2008). Undertaking a literature review: A step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing, 17(1), p.38-43
Literature Review Tutorial
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Scoping Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Oct 10, 2024 10:30 AM
- URL: https://guides.auraria.edu/researchmethods
1100 Lawrence Street Denver, CO 80204 303-315-7700 Ask Us Directions

Children's Literature and Librarianship
- UMD Discover Overview
- Using eBooks (Guide)
- Database and Journal Finder
- Citing Tools & Citation Managers
Literature Review & Research Methods
- Background Info, Encyclopedias, & Handbooks
- Finding Children's Books in the UMD Libraries
- Professional Organizations
- Award Winning Books
- Internet Resources
- Indexes and Abstracts
- Biographical Sources
- Bibliographies & Guides
What is a literature review?
Research Methods in General
- Research Methods Books
- Search Strategies
- Evidence Based Practices Module
- Qualitative Research
- Quantitative Research
In brief, the lit review is the part of a scholarly paper that discusses the relevant research, theoretical and methodological contributions on the topic. Watch these videos to learn more!
Here are some books that are useful in learning about and improving the research process.
Research Methods in Social Science
Here are some books that discuss researching methods specifically for the social sciences in general, and African American studies in particular.

Search Strategies
1. Use the following keywords to identify qualitative research.
These keywords will search the titles, abstracts and keywords of records held in the databases. Use quotations to search as a phrase:
2. Use controlled vocabulary
Databases use controlled vocabulary to categorize each record stored. The terms they use are known as thesaurus terms or subject headings . The thesaurus terms vary for each database according to their indexing system.
For example, qualitative research is indexed in PubMed as "Qualitative Research" or "Nursing Methodology Research", while in CINAHL their subject heading "Qualitative Studies" is complemented by more detailed terms, including "Phenomenological Research" and "Grounded Theory".
Tutorials for searching subject headings:
3. Use qualitative research filters
Qualitative research filters are pre-formulated search strategies that have been constructed by librarians to help you retrieve articles in databases that deal with qualitative research. You can use the filter and then combine the results with your subject.
- Go to PsychINFO database in Database Finder .
- Enter your topic in the search box.
- In right column, under Methodoly, MATHEMATICAL MODEL , select Qualitative study .
- Under Refine Search section on the left, limit further your search under Methodology drop down menu.
Modify your search strategy accordingly by using thesaurus terms, such as qualitative research, grounded theory, interviews, observation methods, etc.
- Evidence Based Practices Module The IRIS Center at Vanderbilt Peabody College has created a 3 part module to walk you through the theory and application of evidence based practices.
- << Previous: Citing Tools & Citation Managers
- Next: Background Info, Encyclopedias, & Handbooks >>
- Last Updated: Oct 29, 2024 1:36 PM
- URL: https://lib.guides.umd.edu/c.php?g=1425999
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
Usability: An introduction to and literature review of usability testing for educational resources in radiation oncology
Heather l keenan, simon l duke, heather j wharrad, gillian a doody, rakesh s patel.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Corresponding author. [email protected]
Received 2022 Jul 21; Revised 2022 Sep 7; Accepted 2022 Sep 11; Collection date 2022 Dec.
This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Usability, or the ease with which something can be used, is a key aspect in ensuring end-users can achieve the best possible outcomes from a given educational resource. Ideally usability testing should take place iteratively throughout the design of the resource, and there are several approaches for undertaking usability testing described in the wider literature. Within radiation oncology education, the extent to which usability testing occurs remains unclear. This literature review aimed to assess current practice and provide a practical introduction to usability testing for educational resource design within radiation oncology.
Two web databases were searched for articles describing planned or completed usability testing during the design of a radiation oncology educational resource. Fifteen studies were identified. Data was gathered describing the type of usability testing performed, the number of cycles of testing and the number of test subjects. Articles described design of educational resources for both patients and trainees, with the number of test subjects ranging from 8 to 18. Various testing methods were used, including questionnaires, think aloud studies and heuristic evaluation. Usability testing comprised a range of single cycle through to several rounds of testing.
Through illustrative examples identified in the literature review, we demonstrate that usability testing is feasible and beneficial for educational resources varying in size and context. In doing so we hope to encourage radiation oncologists to incorporate usability testing into future educational resource design.
Keywords: Education, Radiotherapy, Usability, Online, Learning, Patient
Introduction
The past two decades have seen a meteoric rise in the use of digital methods and resources within medical education [1] , an increase which has been further fuelled by the Covid-19 pandemic and the accompanying restrictions on face-to-face teaching [2] , [3] , [4] . In parallel, digital educational resources have become an important source of accurate and up-to-date information for patients [5] , [6] .
Usability testing focusses on ensuring the user of any digital tool or information system can navigate and engage with the resource easily and effectively. It is widely performed in system design within the software industry and its importance in design of educational interventions is increasingly recognised [7] . It is not clear to what extent usability is applied within radiation oncology.
The aims of this article are to outline the main ways of testing usability and assess how this has been done already within radiation oncology by means of a literature review. In doing so we aim to provide a practical guide for readers of this special issue in education to incorporate usability testing into design of their own radiation oncology educational resources in future.
Background to Usability
What is usability.
In its simplest terms, usability is “the ease with which a person can use a product in a particular set of circumstances” [8] . Usability has been more formally defined by the International Organization for Standardization as “The extent to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a specified context of use” [9] .
In her introductory book on the subject, Barnum highlights the importance of these specified users, specified goals and specified context when considering usability [10] . To consider these within the realm of medical education:
Users – An online oncology educational resource may be highly usable for a young adult, but relatively unusable to an elderly person (statistically more likely to be diagnosed with cancer and therefore receive radiotherapy) who does not regularly access the internet [11] .
Goals – An educational resource designed to facilitate oncology treatment decisions for patients, which contains detailed information but provides no final summary page, may be highly informative but ultimately unusable for its defined goal as users struggle to remember and assimilate what they have read.
Context – A resource designed to be used on a Safari or Chrome web-browser but released in a hospital where all computers operate a legacy version of Internet Explorer, may be useless in its specified context.
Within this review, we will be considering the assessment of usability of educational resources within radiation oncology. Users are therefore usually either patients or healthcare practitioners and goals range from facilitating treatment decisions to improving communication or radiotherapy contouring skills.
Why is Usability Important?
Usability is relevant in the design of any educational resource, but its importance is never clearer than within e-learning where users may be required to interact with complex systems. These systems can provide new educational opportunities, for example educational contouring software which can provide direct user feedback for trainees [12] . As complexity increases however, so too does the opportunity to lose users due to issues with system design.
Usability has been shown to be a key factor (alongside perceived usefulness) influencing our acceptance of information technology [13] , [14] , which predicts actual use.
E-learning has been extensively studied within the corporate field where e-learning courses increasingly replace traditional instructor-led courses [15] . While e-learning courses are often cheaper and more convenient, they have also been shown to have higher attrition rates than traditional courses; one reason for this could be poor usability of the resources [16] . Sandars agrees with this view, when he argues that poor usability could be an explanation for the findings of a 2008 meta-analysis that demonstrates that while e-learning in healthcare is superior to no intervention, it is no more effective than traditional learning methods [8] , [17] .
It is easy to assume that an educational resource we have created is usable; we have, after all, been carefully developing it for weeks or months and its intricacies are second nature. Barnum observes that “From the moment you know enough to talk about a product […] you know too much to be able to tell if the product would be usable for a person who doesn’t know what you know.” [10] It is therefore essential that we not only consider usability during the design of an educational resource, but that we formally test it.
How to Test Usability
Sandars describes four main dimensions that we should consider when assessing usability of e-resources: the learner, technological aspects, instructional design aspects, the context [8] . It is essential that, at least in some stages, a usability assessment involves the intended end-user and that ideally it is assessed in the context in which it will finally be used. ‘Technological aspects’ refers to factors such as the ease of navigation, consistency of layout and clarity of the visual design. Instructional design includes the content itself, the interactivity and judicious use of multimedia.
There are multiple different methods of usability testing described in the literature. Table 1 summarises those most encountered within medical education, briefly describes the benefits and limitations of each and provides an example study which can be consulted for further reference.
Summary of different methods of evaluating usability.
It is relatively straightforward to survey many individuals with a questionnaire; it is considerably more resource intensive to perform multiple think aloud studies, cognitive walkthroughs or heuristic evaluations. Nielson and Landauer analysed 11 usability studies using either heuristic evaluators (i.e. usability experts) or end-user evaluators (e.g. patients or clinicians), compared the number of evaluators with the number of usability problems identified, and developed a model to determine how many testers were required [18] . They showed that for a small project the optimum cost-benefit analysis requires only four evaluators. Five evaluators are generally accepted to be able to identify ∼85% of usability issues [19] . Later authors have however stressed the importance of context and appropriate sampling in defining the numbers to be studied [20] .
Literature review of usability in radiation oncology education
A literature review was carried out to assess the reported use of usability testing in the radiation oncology education literature. PRISMA guidelines were followed [30] . Inclusion criteria were articles which described completed or planned usability assessment of an educational resource within radiation oncology. The search was initially carried out on 25/6/2022 and all results up to this date were included. Fig. 1 outlines the methodology:
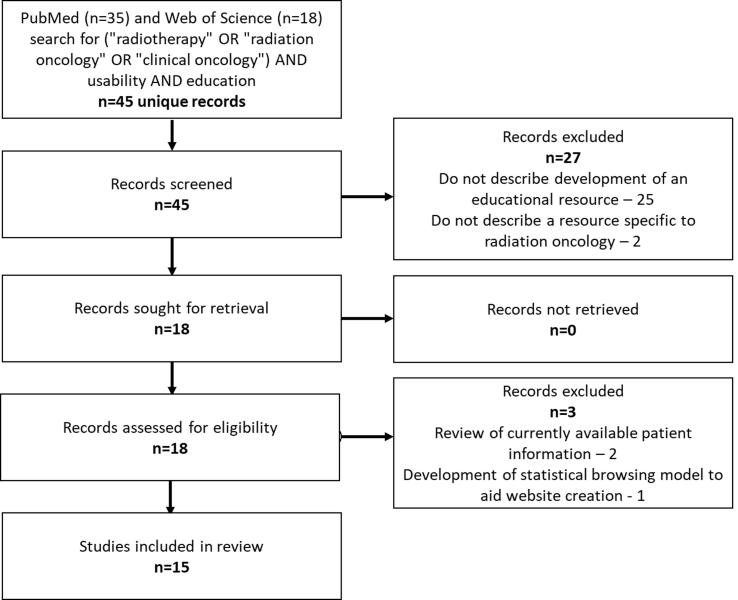
Literature review methodology for identification of relevant articles.
Three articles were identified as relevant from abstract screening and subsequently excluded at review. One was an analysis of pre-existing web resources for patients with prostate cancer [31] . While the tool they used to assess these websites had been previously tested for usability, the websites themselves were not explicitly assessed. A second article addresses usability specifically in the context of patients with lower health literacy levels [32] . They provide recommendations for enhancing usability in a practical sense, e.g. by providing audio material alongside visual, but do not cover how to carry out usability testing. A third study observed browsing patterns of visitors seeking radiology-related information on a hospital website to develop a model which could then by applied elsewhere to improve browsing experience [33] . This was excluded as it is not specifically about the development of an educational resource.
The fifteen items selected for full review were read by two reviewers (HLK, SLD) to identify the educational tool being developed, the intended audience, the usability assessment method used, the number of testers and the point in the design process at which usability was assessed. The results are summarised in Table 2 .
Systematic review of current use of usability testing in the radiation oncology education literature.
SUMI– Software Usability Measurement Inventory [43] .
Most examples of usability testing in the radiation oncology medical education literature describe the design of a patient information resource (13/15, 87%), although there are also examples of usability assessment use in designing resources for healthcare professionals (4/15, 27%). There are two examples of papers which do both: Juraskova et al. [21] describe the design of educational modules for both clinicians and patients/caregivers, and the study by Raith et al. [42] describes two separate augmented reality protocols for patients and radiographers respectively.
Direct observation was used in 8/15 (60%) studies. 3/15 (20%) describe the use of expert heuristic evaluation. Two of these studies are among those which describe more extensive usability testing, including multiple testing modalities and iterative testing throughout the design process. 6/15 (40%) studies describe a think aloud. These involve a range of 8 to 18 participants in any single round of testing, and some studies describe more than one round. The formality of analysis of the think aloud varies; some papers describe extensive transcription and thematic analysis, whereas others describe drawing general learning points.
10/15 (67%) studies use a survey as part of their usability assessment. Of these, 5/10 (50%) were not formally validated usability questionnaires, but asked questions explicitly designed to probe usability. Of those which used validated studies, three (60%) used the SUS (one of which was modified) and one (20%) used SUMI. One study mentions a future plan to use UMUX-LITE but has not yet done so.
6/15 (40%) studies described more than one round of usability testing during the design process and 7/15 (47%) studies use more than one type of usability assessment. Three studies – Juraskova et al., [21] , Ankolekar et al., [29] and Berg et al., [23] – did both.
Although most studies assessed usability on the intended target audience this was not universal; there was one example of a study where clinicians alone were used to assess the usability of a resource being designed for patients. Raith et al., [42] were unable to assess their augmented reality resource on patients due to the restraints of the covid-19 pandemic.
In the introduction to this article, we described five methods of usability testing. These can be divided into ‘expert-led’ testing (heuristic evaluation, cognitive walkthrough) and ‘user-led’ testing (think aloud, semi-structured interview, questionnaire). Examples of all five types of testing exist in the current radiation oncology education literature. There are notably far more cases of user-led testing.
Usability experts may come with a cost - much of the seminal work on usability comes out of software design where usability experts to undertake heuristic evaluations are readily available, which is likely to be a luxury unavailable in healthcare. This scarcity may be addressed by collaboration with computer science departments within or across academic institutions.
In one of only three studies employing expert-led testing, Ankolekar et al. describe the development and validation of a patient-led decision aid for prostate cancer [29] . They detail an extensive process of usability testing involving multiple cycles of testing, re-design and re-testing. Over five rounds of testing, they employ questionnaires, heuristic evaluation and think-aloud methods. They explain that “Our development process spanned over two years and involved 58 participants, resulting in >100 h of interview material and feedback that needed to be processed, analyzed and incorporated in successive rounds.” While such extensive testing clearly has the potential to produce a high-quality educational resource, the time and financial commitment required may prove a disincentive for others to carry out similar work.
Other studies describe less extensive usability testing from which the authors are nevertheless able to make changes to their resource. Bigelow et al. describe two cycles of questionnaire-based testing and demonstrate an improvement in usability between cycle 1 and cycle 2 following changes to the design, language and graphics of their resource [40] . We would therefore argue that current literature suggests that it is both valuable and feasible to carry out usability studies within radiation oncology education on a variety of different scales suited to the specific aims of the resource.
Most of the studies which carry out only one or two rounds of usability testing employ user-led testing. Many of the advantages of this are intuitive; testing on the group that will ultimately be using the resource makes logical sense. Additionally, most healthcare professionals involved in the design of an educational resource will have easy and free (limited by necessary ethical approval) access to the end users, be they trainees or patients.
Within user-based usability testing a scale of resource and time-intensity exists. Formal think-aloud testing is an extensive process involving scriptwriting, taping of users, transcription of tapes, coding by independent coders and thematic analysis. Hopmans et al. provide an example of how this process can be shortened while still providing valuable insights [36] . In an initial round of think-aloud testing they ask 18 participants to navigate through their website and then ask a series of probing questions. They transcribe all the interviews, then three are selected for independent coding and analysis by two separate researchers; the remainder are analysed by one researcher only. This is one example of how a potentially intensive analysis process can be shortened while still providing useful insights. The article does not describe how the three transcriptions are selected; it would be important to ensure this is done at random.
Finally, questionnaires are a relatively easy method of usability testing. Most frequently used in our review is the SUS, which is a well-validated usability survey that is freely available online. As healthcare practitioners we are generally used to seeking survey style feedback on our educational resources, so it is fairly straightforward to add in some usability-focussed questions. If longer surveys like UTAUT are felt to be too arduous and add excessively to survey burden, then the SUS or UMUX-LITE are shorter alternatives.
Several studies in our review test usability on ‘cancer patients’. We would agree that it is essential in health education to test resources on the target audience, however it is worth considering that unless these testers are at the beginning of their cancer journey, they may in fact have a higher level of knowledge than intended. In this context, healthy volunteers may provide a reasonable alternative, with the caveat that volunteers are likely to be interested and engaged in healthcare and may therefore have a higher level of health literacy than the general population.
Our systematic review identified only two studies describing usability testing on an educational resource for radiation oncology trainees. This might simply represent the fact that there are fewer such resources being regularly created. The two articles identified in our review [26] , [37] both describe design of resources to help with contouring. This is clearly a field where usability is of crucial importance as factors like ease of navigation, ability to concurrently view atlases and contouring software and similarity to trainees’ local contouring software is likely to have a large impact on their engagement with the resource. We would encourage anyone designing such a resource to consider undertaking and reporting usability testing.
As a result of the inclusion criteria, all articles included in our review include a description of planned or completed usability testing. Only a proportion of these articles describe whether and how the results of the usability testing benefited ongoing resource development. An example of this being done well is Nguyen et al.; Table 1 in their paper describes the method, results and insights of serial rounds of usability testing [24] . We would suggest that a description of the changes made (and, if possible, repeat usability testing to demonstrate an improvement), would enhance any paper reporting usability as it would help identify common areas of difficulty.
Limitations and possible future work
A limitation of this review is that due to the search criteria, it only picks up studies which have specifically mentioned ‘usability’. It is possible that usability may be assessed but not formally described, or that usability is being assessed in educational resources that are never formally published (or are published only in abstract form). We would encourage more radiotherapy researchers to publish their usability data and lessons, as these may help prevent others from repeating similar mistakes. The literature search was limited to only two databases, which may also have limited the number of results.
A future review might identify a more specific area of radiation oncology educational material and assess all educational resources published within this field, to determine what proportion of them report usability testing. This would give a better idea of how widespread usability testing is. This is not possible to assess from our review, which does not include educational resources which are not usability tested.
In this article, we have discussed the rationale for carrying out usability testing in the design of educational resources and described the main methods for doing so. We go on to report the results of a literature review of the current use of usability testing within radiation oncology.
Current practice demonstrates that there is a balance to be achieved between the resource intensity of usability testing and the potential improvements to an educational resource. We would encourage all educationalists designing resources for either patients or trainees to consider how usability testing might reasonably be incorporated in their own design process. The ideal method(s) depends on the aim of the resource and certainly anyone aiming to design a durable and far-reaching resource should consider multiple rounds and methodologies of usability testing.
We hope we have also provided the necessary tools and information to show that even in simpler more local projects, it is feasible to carry out some basic usability testing to maximise the impact of a resource.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
- 1. Emanuel E.J. The Inevitable Reimagining of Medical Education. JAMA. 2020;323:1127–1128. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.1227. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Goh P.-S., Sandars J. A vision of the use of technology in medical education after the COVID-19 pandemic. MedEdPublish. 2019;9:49. doi: 10.15694/mep.2020.000049.1. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Khalil R., Mansour A.E., Fadda W.A., Almisnid K., Aldamegh M., Al-Nafeesah A., et al. The sudden transition to synchronized online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: a qualitative study exploring medical students’ perspectives. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1) doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02208-z. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Almarzooq Z.I., Lopes M., Kochar A. Virtual Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:2635–2638. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.015. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Garg S., Williams N.L., Ip A., Dicker A.P. Clinical Integration of Digital Solutions in Health Care: An Overview of the Current Landscape of Digital Technologies in Cancer Care. JCO Clin Cancer Inf. 2018:1–9. doi: 10.1200/CCI.17.00159. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Levine D.M., Lipsitz S.R., Linder J.A. Trends in Seniors’ Use of Digital Health Technology in the United States, 2011–2014. JAMA. 2016;316:538–540. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.9124. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Chen W., Reeves T.C. Twelve tips for conducting educational design research in medical education. Med Teach. 2020;42:980–986. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2019.1657231. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Sandars J. The importance of usability testing to allow e-Learning to reach its potential for medical education. Educ Primary Care. 2010;21:6–8. doi: 10.1080/14739879.2010.11493869. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Iso Ergonomics of human-system interaction – Part 210: Human-centred design for interactive systems. International Standards Organisation. 2010;2010:1–32. doi: 10.1039/c0dt90114h. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Barnum C.M. Usability Testing Essentials. Elsevier; 2011. Establishing the essentials; pp. 9–23. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Jacobs W., Amuta A.O., Jeon K.C., Alvares C. Health information seeking in the digital age: An analysis of health information seeking behavior among US adults. Cogent Social Sci. 2017;3(1):1302785. doi: 10.1080/23311886.2017.1302785. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Duke S.L., Tan L.T., Eminowicz G., Park W.H.E., Wharrad H., Patel R., et al. Rapid Radiotherapy Contouring Practice: Pilot Study of a Novel Web-Based Tool Enabling Automated Individualized Feedback. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;105(1):E147. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.2200. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Dwivedi Y.K., Rana N.P., Jeyaraj A., Clement M., Williams M.D. Re-examining the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT): Towards a Revised Theoretical Model. Inf Syst Front. 2019;21:719–734. doi: 10.1007/s10796-017-9774-y. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Holden R.J., Karsh B.T. The Technology Acceptance Model: Its past and its future in health care. J Biomed Inform. 2010;43:159–172. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2009.07.002. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Clark RC, Mayer RE. E-learning and the science of instruction: proven guidelines for consumers and designers of multimedia learning. 2016.
- 16. Zaharias P., Poylymenakou A. Developing a Usability Evaluation Method for e-Learning Applications: Beyond Functional Usability. Int J Hum-Comput Interact. 2009;25:75–98. doi: 10.1080/10447310802546716. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 17. Cook D.A., Levinson A.J., Garside S., Dupras D.M., Erwin P.J., Montori V.M. Internet-Based Learning in the Health Professions: A Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2008;300:1181. doi: 10.1001/jama.300.10.1181. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 18. Nielsen J., Landauer T.K. Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems - CHI ’93. ACM Press; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1993. A mathematical model of the finding of usability problems; pp. 206–213. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 19. Jaspers M.W.M. A comparison of usability methods for testing interactive health technologies: Methodological aspects and empirical evidence. Int J Med Inf. 2009;78:340–353. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.10.002. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 20. Usability L.JR. Lessons Learned. and Yet to Be Learned. Int J Hum Comput Interact. 2014;30:663–684. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2014.930311. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 21. Juraskova I., Laidsaar-Powell R., Keast R., Schofield P., Costa D.SJ., Kay J., et al. eTRIO trial: study protocol of a randomised controlled trial of online education modules to facilitate effective family caregiver involvement in oncology. BMJ Open. 2021;11(5):e043224. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043224. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 22. Jabbour J., Dhillon H.M., Shepherd H.L., Sundaresan P., Milross C., Clark J.R. A web-based comprehensive head and neck cancer patient education and support needs program: Usability testing. Health Inf J. 2022;28 doi: 10.1177/14604582221087128. 146045822210871. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 23. van den Berg M., van der Meij E., Bos A.M.E., Boshuizen M.C.S., Determann D., van Eekeren R.R.J.P., et al. Development and testing of a tailored online fertility preservation decision aid for female cancer patients. Cancer Med. 2021;10(5):1576–1588. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3711. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 24. Nguyen M.H., Bol N., van Weert J.C.M., Loos E.F., Tytgat K.M.A.J., Geijsen D., et al. Optimising eHealth tools for older patients: Collaborative redesign of a hospital website. Eur J Cancer Care. 2019;28(1):e12882. doi: 10.1111/ecc.12882. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 25. Lewis J.R. The System Usability Scale: Past, Present, and Future. Int J Hum-Comput Interact. 2018;34:577–590. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2018.1455307. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 26. Gillespie E.F., Panjwani N., Golden D.W., Gunther J., Chapman T.R., Brower J.V., et al. Multi-institutional Randomized Trial Testing the Utility of an Interactive Three-dimensional Contouring Atlas Among Radiation Oncology Residents. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;98(3):547–554. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.11.050. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 27. Lewis JR, Utesch BS, Maher DE. UMUX-LITE: when there’s no time for the SUS. Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Paris France: ACM; 2013, p. 2099–102. 10.1145/2470654.2481287. [ DOI ]
- 28. Venkatesh, Morris, Davis, Davis User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Quarter. 2003;27(3):425. [ Google Scholar ]
- 29. Ankolekar A., Vanneste B.G.L., Bloemen-van Gurp E., van Roermund J.G., van Limbergen E.J., van de Beek K., et al. Development and validation of a patient decision aid for prostate Cancer therapy: from paternalistic towards participative shared decision making. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019;19(1) doi: 10.1186/s12911-019-0862-4. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 30. Page M.J., McKenzie J.E., Bossuyt P.M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T.C., Mulrow C.D., et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021 doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 31. Kobes K., Harris I.B., Regehr G., Tekian A., Ingledew P.-A. Malignant websites? Analyzing the quality of prostate cancer education web resources. CUAJ. 2018;12 doi: 10.5489/cuaj.5084. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 32. Garcia S.F., Hahn E.A., Jacobs E.A. Addressing low literacy and health literacy in clinical oncology practice. J Support Oncol. 2010;8:64–69. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 33. Suzuki R., Suzuki T., Tsuji S., Fujiwara K., Yamashina H., Endoh A., et al. A Bayesian Network-Based Browsing Model for Patients Seeking Radiology-Related Information on Hospital Websites: Development and Usability Study. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23:e14794. doi: 10.2196/14794. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 34. Tran C., Szumacher E., Di Prospero L. A Pilot Study Evaluating the Usability and Usefulness of a Multi-language Online Patient Education Tool for Patients Undergoing Radiation Treatment: Findings from a Student Project. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2012;43:181–186. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2011.11.002. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 35. Buzaglo J.S., Miller S.M., Kendall J., Stanton A.L., Wen K.-Y., Scarpato J., et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and usability of NCI’s Facing Forward booklet in the cancer community setting. J Cancer Surviv. 2013;7(1):63–73. doi: 10.1007/s11764-012-0245-7. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 36. Hopmans W., Damman O.C., Timmermans D.R.M., Haasbeek C.J.A., Slotman B.J., Senan S. Communicating cancer treatment information using the Web: utilizing the patient’s perspective in website development. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2014;14:116. doi: 10.1186/s12911-014-0116-4. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 37. Deraniyagala R., Amdur R.J., Boyer A.L., Kaylor S. Usability study of the EduMod eLearning Program for contouring nodal stations of the head and neck. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2015;5:169–175. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2014.10.008. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 38. Shinn E.H., Jensen K., McLaughlin J., Garden A.S., Fellman B.M., Liang L.i., et al. Interactive website for head and neck cancer patients: Adherence and coping program to prevent dysphagia after radiation. Internet Intervent. 2019;18:100289. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2019.100289. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 39. Arya R., Ichikawa T., Callender B., Schultz O., DePablo M., Novak K., et al. Communicating the External Beam Radiation Experience (CEBRE): Perceived Benefits of a Graphic Narrative Patient Education Tool. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2020;10(4):e219–e226. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2019.09.001. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 40. Bigelow E.O., Windon M.J., Fakhry C., Kiess A.P., Seiwert T., D’Souza G. Development of a web-based, patient-centered decision aid for oropharyngeal cancer treatment. Oral Oncol. 2021;123:105618. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105618. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 41. Cruz FO de AM da, Faria ET, Ghobad PC, Alves LYM, Reis PEDD. A Mobile App (AMOR Mama) for Women With Breast Cancer Undergoing Radiation Therapy: Functionality and Usability Study. J Med Internet Res 2021;23:e24865. 10.2196/24865. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- 42. Raith A., Kamp C., Stoiber C., Jakl A., Wagner M. Augmented Reality in Radiology for Education and Training—A Design Study. Healthcare. 2022;10:672. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10040672. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 43. Kirakowski J., Corbett M. SUMI: the Software Usability Measurement Inventory. Br J Educ Technol. 1993;24:210–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8535.1993.tb00076.x. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (595.2 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

COMMENTS
A Review of the Theoretical Literature" (Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.) Example literature review #2: "Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines" ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and ...
the literature review involves activities such as identi-fying, recording, understanding, meaning-making, and transmitting information. Indeed, the literature review process is actualized through data collection. In its opti-mal form, the literature review represents a formal data collection process wherein information is gathered in a
The literature review can serve various functions in the contexts of education and research. It aids in identifying knowledge gaps, informing research methodology, and developing a theoretical framework during the planning stages of a research study or project, as well as reporting of review findings in the context of the existing literature.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
What kinds of literature reviews are written? Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
The "literature" of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. "Literature" could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL.
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works. Also, we can define a literature review as the ...
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it ...
This paper draws input from a study that employed a systematic literature review as its main source of data. A systematic review can be explained as a research method and process for identifying ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Literature Review and Research Design by Dave Harris This book looks at literature review in the process of research design, and how to develop a research practice that will build skills in reading and writing about research literature--skills that remain valuable in both academic and professional careers. Literature review is approached as a process of engaging with the discourse of scholarly ...
The process of undertaking a literature review is an integral part of doing research. While this may be considered to be its primary function, the literature review is also an important tool that serves to inform and develop practice and invite dis-cussion in academic work. Whatever its purpose, the task of doing a literature
A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment, but more often it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis.
Typically, a literature review is a written discussion that examines publications about a particular subject area or topic. Depending on disciplines, publications, or authors a literature review may be: A summary of sources. An organized presentation of sources. A synthesis or interpretation of sources. An evaluative analysis of sources.
A literature review involves researching, reading, analyzing, evaluating, and summarizing scholarly literature (typically journals and articles) about a specific topic. The results of a literature review may be an entire report or article OR may be part of a article, thesis, dissertation, or grant proposal.
Research Design by John W. Creswell; J. David Creswell This best-selling text pioneered the comparison of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research design. For all three approaches, John W. Creswell and new co-author J. David Creswell include a preliminary consideration of philosophical assumptions, key elements of the research process, a review of the literature, an assessment of ...
Literature review methodology for identification of relevant articles. Results. Three articles were identified as relevant from abstract screening and subsequently excluded at review. One was an analysis of pre-existing web resources for patients with prostate cancer . While the tool they used to assess these websites had been previously tested ...
Purpose: Our study aims to understand what is known about happiness at work (HAW) in terms of publication, citations, dimensions and characteristics, as well as how knowledge about HAW is generated regarding theoretical frameworks, context and methods. Additionally, it explores future directions for HAW research. Design/methodology/approach: This paper conducts a systematic literature review ...