Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals

Genetics research articles from across Nature Portfolio
Genetics research is the scientific discipline concerned with the study of the role of genes in traits such as the development of disease. It has a key role in identifying potential targets for therapeutic intervention and also in understanding genetically based variations in response to therapeutic interventions.
Latest Research and Reviews
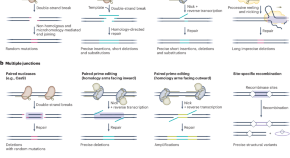
Engineering structural variants to interrogate genome function
Structural variations (SVs) impact gene expression, genome stability and disease susceptibility. This Review discusses recent advances in genome-engineering tools that enable precise SV generation and highlights the challenges that remain.
- Jonas Koeppel
- Juliane Weller
- Leopold Parts
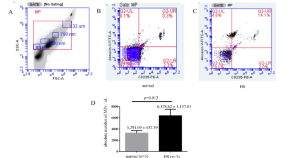
Identification and functional analysis of novel SPTB and ANK1 mutations in hereditary spherocytosis patients
- Charuwan Panarach
- Chaiwat Netsawang
- Kamonlak Leecharoenkiat
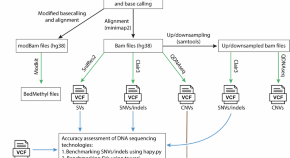
Benchmarking nanopore sequencing and rapid genomics feasibility: validation at a quaternary hospital in New Zealand
- Denis M. Nyaga
- Justin M. O’Sullivan
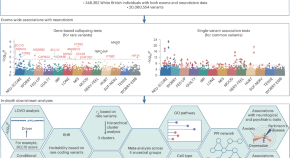
Large-scale exome sequencing identified 18 novel genes for neuroticism in 394,005 UK-based individuals
In 394,005 UK individuals with exome sequencing data, Wu et al. find 56 neuroticism-associated genes (18 novel) and quantify the heritability explained by rare coding variants, highlighting the association of coding variants with neuroticism.
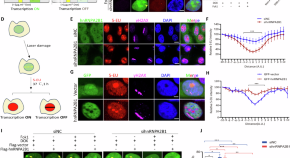
hnRNPA2B1 deacetylation by SIRT6 restrains local transcription and safeguards genome stability
- Wei-Guo Zhu
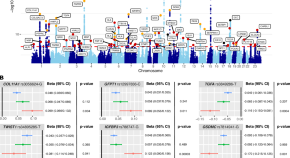
Genome-wide meta-analysis conducted in three large biobanks expands the genetic landscape of lumbar disc herniations
A genome-wide association study suggests 41 previously unreported loci on top of the 23 known loci that influence the disease risk for lumbar disc herniations. Many of these loci harbour genes implicated in disc structure and inflammation, as well as genes related to the nervous system and nerve function.
- Juhani Määttä
- Johannes Kettunen

News and Comment
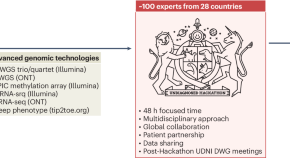
Pushing the boundaries of rare disease diagnostics with the help of the first Undiagnosed Hackathon
In the first-ever Undiagnosed Hackathon, nearly 100 experts from 28 countries combined advanced phenotyping and genomic techniques for 48 hours, ultimately providing diagnoses to 40% of the previously undiagnosed families. This inspiring model demonstrates the power of multidisciplinary collaboration and patient partnership in precision diagnostics.
- Angelica Maria Delgado-Vega
- Helene Cederroth
- Ann Nordgren
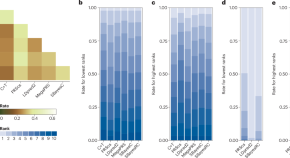
Inconsistent embryo selection across polygenic score methods
Private enterprises offer preimplantation genetic testing with polygenic scores to select embryos with ‘desirable’ potential. In silico simulations using biobank resources show that the selected embryo would rely substantially on the choice of polygenic score method and randomness in score construction, which raises ethical concerns.
- Shinichi Namba
- Masato Akiyama
- Yukinori Okada
SPARCL1 sparkles new insight into corneal dystrophies
- Joni A. Turunen
Systematic decision frameworks for the socially responsible use of precision medicine
Deep learning techniques and whole-genome sequencing promise to increase well-being but also risk perpetuating psychological essentialism, potentially justifying inequality. In this Comment, we offer two much-needed systematic frameworks for clinicians and researchers to avoid essentialist inferences and unfair treatment: (1) a data-driven method for detecting causal fairness in precision health and (2) an ethical framework for determining when it is morally permissible to use racial classifications in population health research.
- Ian S. Peebles
- David B. Kinney
- Emily Foster-Hanson
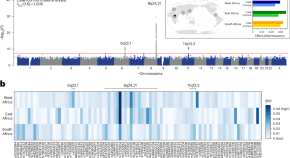
Pan-African analysis identifies genetic differences in prostate cancer risk
To understand the genetic basis of disease, it is essential to study diverse populations. We conducted the largest study to date of African men to evaluate the evolutionary genetics and causes of prostate cancer. Our findings reveal novel genetic associations, including those that were not observed in studies of non-African populations.
Multi-omics analyses of the environMENTAL project provide insights into mental health and disease
Integrative analyses that incorporate different levels of ‘-omics’ data represent a powerful tool for deciphering the biological mechanisms that underlie environmental influences on mental health and disease. This Comment highlights various aspects of such multi-omics approaches, using the example of the EU-funded environMENTAL project.
- Sylvane Desrivières
- Abigail Miller
- George Ogoh
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO