- Join Mind Tools


Cause and Effect Analysis
Identifying the likely causes of problems, (also known as cause and effect diagrams, fishbone diagrams, ishikawa diagrams, herringbone diagrams, and fishikawa diagrams.).
When you have a serious problem, it's important to explore all of the things that could cause it, before you start to think about a solution.
That way you can solve the problem completely, first time round, rather than just addressing part of it and having the problem run on and on.
Cause and Effect Analysis gives you a useful way of doing this. This diagram-based technique, which combines Brainstorming with a type of Mind Map , pushes you to consider all possible causes of a problem, rather than just the ones that are most obvious.
Click here to view a transcript of this video.
About the Tool
Cause and Effect Analysis was devised by professor Kaoru Ishikawa, a pioneer of quality management, in the 1960s. The technique was then published in his 1990 book, " Introduction to Quality Control ."
The diagrams that you create with are known as Ishikawa Diagrams or Fishbone Diagrams (because a completed diagram can look like the skeleton of a fish).
Although it was originally developed as a quality control tool, you can use the technique just as well in other ways. For instance, you can use it to:
- Discover the root cause of a problem.
- Uncover bottlenecks in your processes.
- Identify where and why a process isn't working.
How to Use the Tool
Follow these steps to solve a problem with Cause and Effect Analysis:
Step 1: Identify the Problem
First, write down the exact problem you face. Where appropriate , identify who is involved, what the problem is, and when and where it occurs.
Finding This Article Useful?
You can learn another 44 problem-solving skills, like this, by joining the Mind Tools Club.

Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Receive new career skills every week, plus get our latest offers and a free downloadable Personal Development Plan workbook.
Then, write the problem in a box on the left-hand side of a large sheet of paper, and draw a line across the paper horizontally from the box. This arrangement, looking like the head and spine of a fish, gives you space to develop ideas.
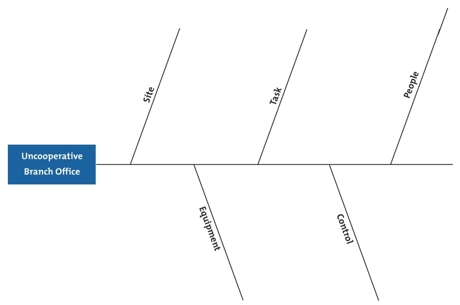
In this simple example, a manager is having problems with an uncooperative branch office.
Figure 1 – Cause and Effect Analysis Example Step 1

(Click image to view full size.)
Some people prefer to write the problem on the right-hand side of the piece of paper, and develop ideas in the space to the left. Use whichever approach you feel most comfortable with.
It's important to define your problem correctly. CATWOE can help you do this – this asks you to look at the problem from the perspective of Customers, Actors in the process, the Transformation process, the overall World view, the process Owner, and Environmental constraints.
By considering all of these, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Work Out the Major Factors Involved
Next, identify the factors that may be part of the problem. These may be systems, equipment, materials, external forces, people involved with the problem, and so on.
Try to draw out as many of these as possible. As a starting point, you can use models such as the McKinsey 7S Framework (which offers you Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared values, Skills, Style and Staff as factors that you can consider) or the 4Ps of Marketing (which offers Product, Place, Price, and Promotion as possible factors).
Brainstorm any other factors that may affect the situation.
Then draw a line off the "spine" of the diagram for each factor, and label each line.
The manager identifies the following factors, and adds these to his diagram:
Figure 2 – Cause and Effect Analysis Example Step 2
Step 3: Identify Possible Causes
Now, for each of the factors you considered in step 2, brainstorm possible causes of the problem that may be related to the factor.
Show these possible causes as shorter lines coming off the "bones" of the diagram. Where a cause is large or complex, then it may be best to break it down into sub-causes. Show these as lines coming off each cause line.
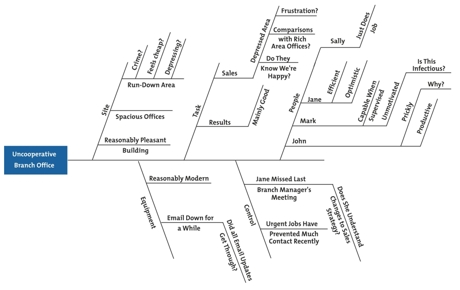
For each of the factors he identified in step 2, the manager brainstorms possible causes of the problem, and adds these to his diagram, as shown in figure 3.
Figure 3 – Cause and Effect Analysis Example Step 3
Step 4: Analyze Your Diagram
By this stage you should have a diagram showing all of the possible causes of the problem that you can think of.
Depending on the complexity and importance of the problem, you can now investigate the most likely causes further. This may involve setting up investigations, carrying out surveys, and so on. These will be designed to test which of these possible causes is actually contributing to the problem.
The manager has now finished his analysis. If he hadn't looked at the problem this way, he might have dealt with it by assuming that people in the branch office were "being difficult."
Instead he thinks that the best approach is to arrange a meeting with the Branch Manager. This would allow him to brief the manager fully on the new strategy, and talk through any problems that she may be experiencing.
A useful way to use this technique with a team is to write all of the possible causes of the problem down on sticky notes. You can then group similar ones together on the diagram.
This approach is sometimes called CEDAC (Cause and Effect Diagram with Additional Cards) and was developed by Dr. Ryuji Fukuda, a Japanese expert on continuous improvement.
Professor Kaoru Ishikawa created Cause and Effect Analysis in the 1960s. The technique uses a diagram-based approach for thinking through all of the possible causes of a problem. This helps you to carry out a thorough analysis of the situation.
There are four steps to using the tool.
- Identify the problem.
- Work out the major factors involved.
- Identify possible causes.
- Analyze your diagram.
You'll find this method is particularly useful when you're trying to solve complicated problems.
This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter , or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!
Rate this resource
The Mind Tools Club gives you exclusive tips and tools to boost your career - plus a friendly community and support from our career coaches!

Comments (36)
- Over a month ago BillT wrote Hi AnotherFrancis, and Welcome to the Club! As with my response to Alex81, not everyone will find the example the most useful, as is the case with you. We appreciate your feedback. BillT Mind Tools Team
- Over a month ago AnotherFrancis wrote Nice article but, like Alex81, I didn't find the example to be very helpful.
- Over a month ago BillT wrote Hi Alex81, and Welcome to the Club! Thank you for your feedback on the Cause and Effect Analysis. I agree that not everyone may find the example the best way to demonstrate the resource. This diagram has also been known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Fishbone Diagram. You may find additional resources with better examples for you. Also, you may wish to post this in the Forums so that our members can provide their input into the topic. BillT Mind Tools Team
Please wait...
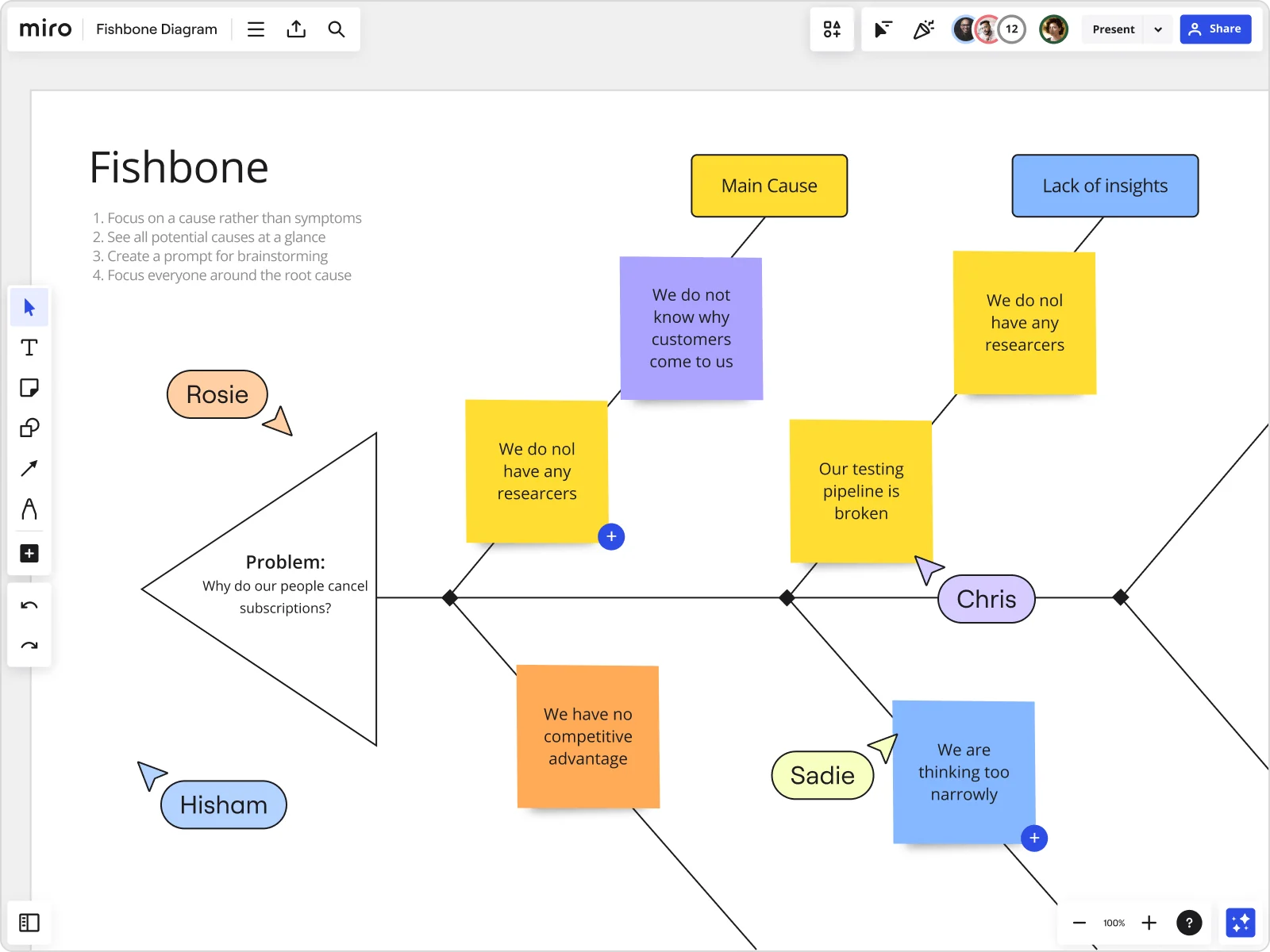
Table of Contents
What is a Fishbone diagram?
Fishbone diagrams explained.
A fishbone diagram (also known as an Ishikawa fishbone diagram) is an effective problem-solving tool. Instead of focusing on a quick fix, creating a fishbone diagram helps to identify the root cause of a problem and find a long-term solution.
As a type of cause and effect diagram , the “fishbone” name comes from the diagram’s resemblance to a fish skeleton. A fishbone diagram consists of three main categories:
There’s a fish head at the head of the diagram, where you’ll outline the problem you’re trying to solve. The rest of the diagram branches out from here.
The spine stems from the head of the diagram (the problem statement), providing the outline of the fish. At the end of each spinal bone is a category that needs to be considered as part of the problem-solving process.
Branching out from each spinal bone, you’ll see a smaller rib bone. This is where the possible causes will sit to help you pinpoint the potential cause of the problem.
Benefits of fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams are useful tools for improving existing processes and pinpointing causes of issues. Take a look at some benefits of performing a fishbone diagram root cause analysis:
Easily find the root cause of a problem
A fishbone diagram is a visual tool that adds structure and clarity to problem-solving. It indicates the problem and its possible causes in a single location, making it easier for teams to conduct a root cause analysis .
Prevent further problems
By finding the root cause of the problem, you fix the problem at its source and mitigate future issues. As a result, you’re far more likely to prevent the same (or similar) problems from cropping up in the future.
Collaborate with your team
A fishbone diagram is a great way to work with your team to brainstorm solutions . It’s a collaborative diagram, encouraging teams to review all the available information and discuss the best course of action.
If you’re part of a remote or hybrid team, an online platform like Miro allows you to collaborate with your team, no matter where they work. Simply share the diagram and hop on a video chat, and you can perform your root cause analysis virtually.
Example of a fishbone diagram
To see a fishbone diagram in action, look at this CEDAC Template from NEXT LEVEL Partners.
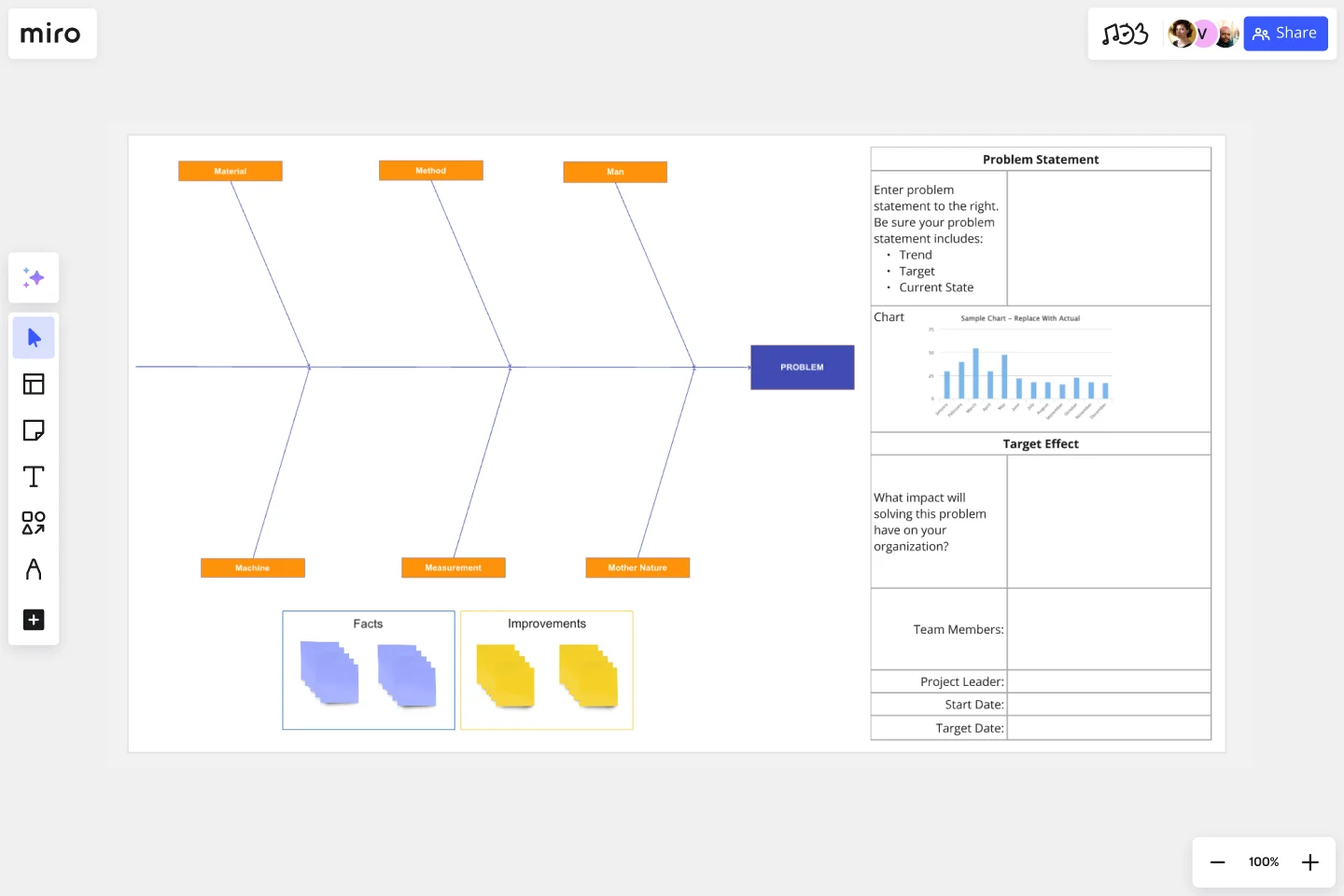
CEDAC is an acronym for Cause and Effect Diagram with the Addition of Cards. The diagram contains issues on the left-hand side of the ribs and solutions on the right-hand side.
Its inventor, Ryuji Fukuda, created CEDAC so that teams can delve deeper into their problem-solving analyses. By adding cards to the diagram, teams have a way of questioning existing information and suggesting new ideas. As a result, they’ll gain a deeper understanding of their problems and how to solve them.
Here are some of the common areas where the CEDAC model can be helpful:
Product development
Visualize issues with product development using the CEDAC diagram. Collaborate with the product team to identify the cause of the problem and use cards to identify the best possible solution.
Software features
Effectively allocate resources based on team structures and capabilities. Understand the most critical problems to solve and how they map together.
Product design
Define failures or problems with your product design, and identify effective solutions. Using the diagram’s cards, product designers can generate new and creative solutions to improve the design.
Internal processes
Pinpoint bottlenecks and figure out how to streamline and improve your business processes. Encourage team members to join in the discussion and make suggestions for improving the process going forward.
When to use a fishbone diagram
Take a look at some of the different instances when using a fishbone diagram can be useful for you and your team.
1. To analyze a problem statement
If you have a clear problem statement for your business, a fishbone diagram is a great way to analyze it in detail. You can see the problem’s culprit and decide how to fix the issue.
2. To brainstorm the causes of the problem
Also known as root cause analysis, a fishbone diagram allows you to discuss the potential causes of a problem. It’s the perfect opportunity to host a brainstorming session to identify pressing concerns and work through possible solutions.
3. To analyze a new product design
Use a fishbone diagram to map your new product design and visualize any potential hurdles before they come your way. As a result, you can put preventative measures in place before going live.

4. To improve your processes
If you’re struggling to streamline your processes and inefficiencies, a fishbone diagram can help. Use a fishbone diagram to pinpoint the troublesome areas of your process and find the cause of a problem. From there, you can determine exactly how to fix it.
5. For quality improvement
Use a fishbone diagram to visualize how and where you can improve to offer your customers a higher-quality experience. For example, you might want to improve the quality of your customer service. In this case, you can use the diagram to find areas for improvement in your existing processes.
How to make a fishbone diagram
Follow these simple steps to create an effective fishbone diagram:
1. Select the Fishbone Diagram Template
While you can always build your own diagram from scratch, you can also get a headstart by selecting one of these Fishbone Diagram Templates . It’s free and easy to use, so you can start mapping your diagram immediately.
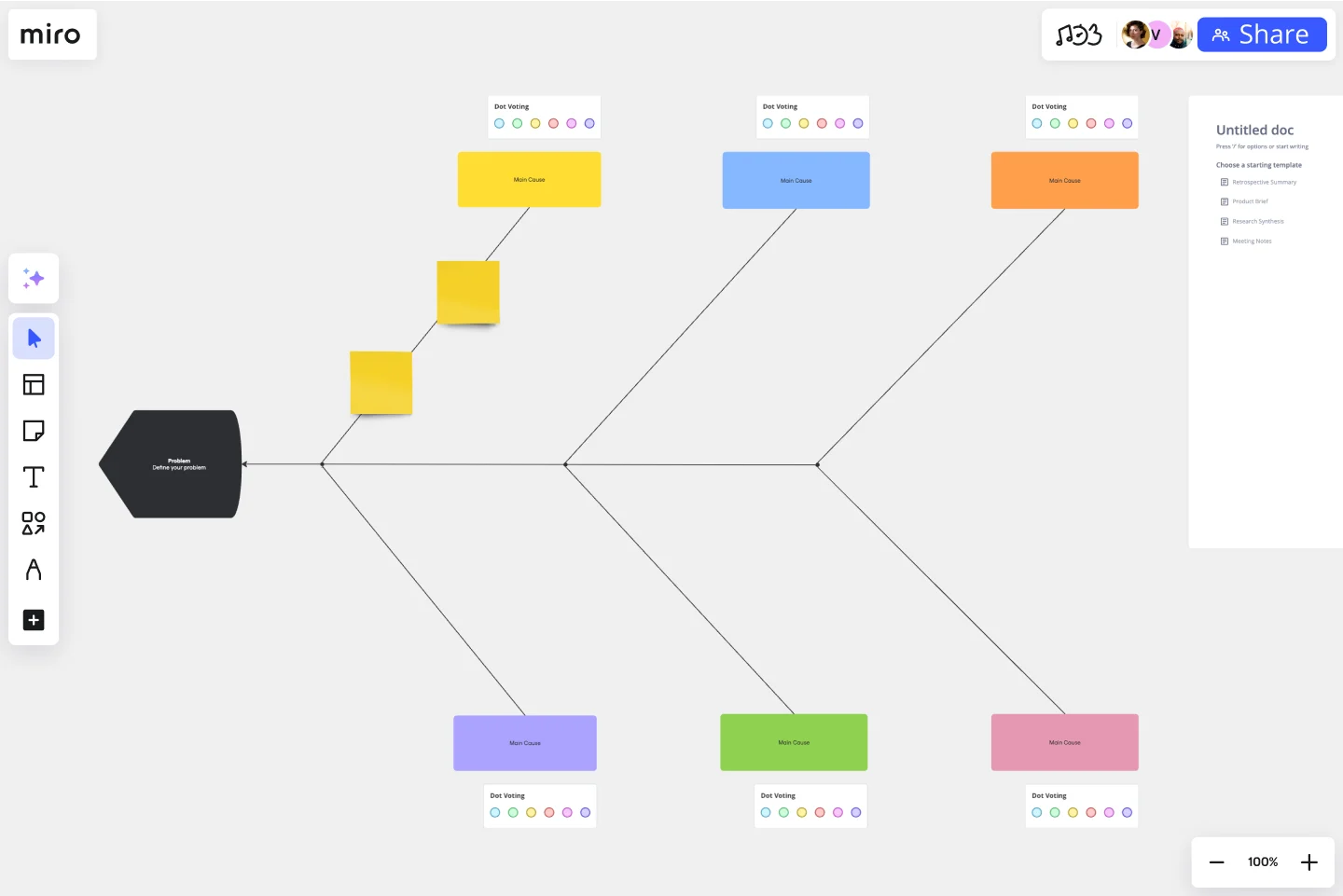
2. Outline your problem statement
When your diagram is ready to use, start by defining the problem. Otherwise known as a problem statement, this will sit at the head of the diagram. This must be as clear and concise as possible to find the right solution.
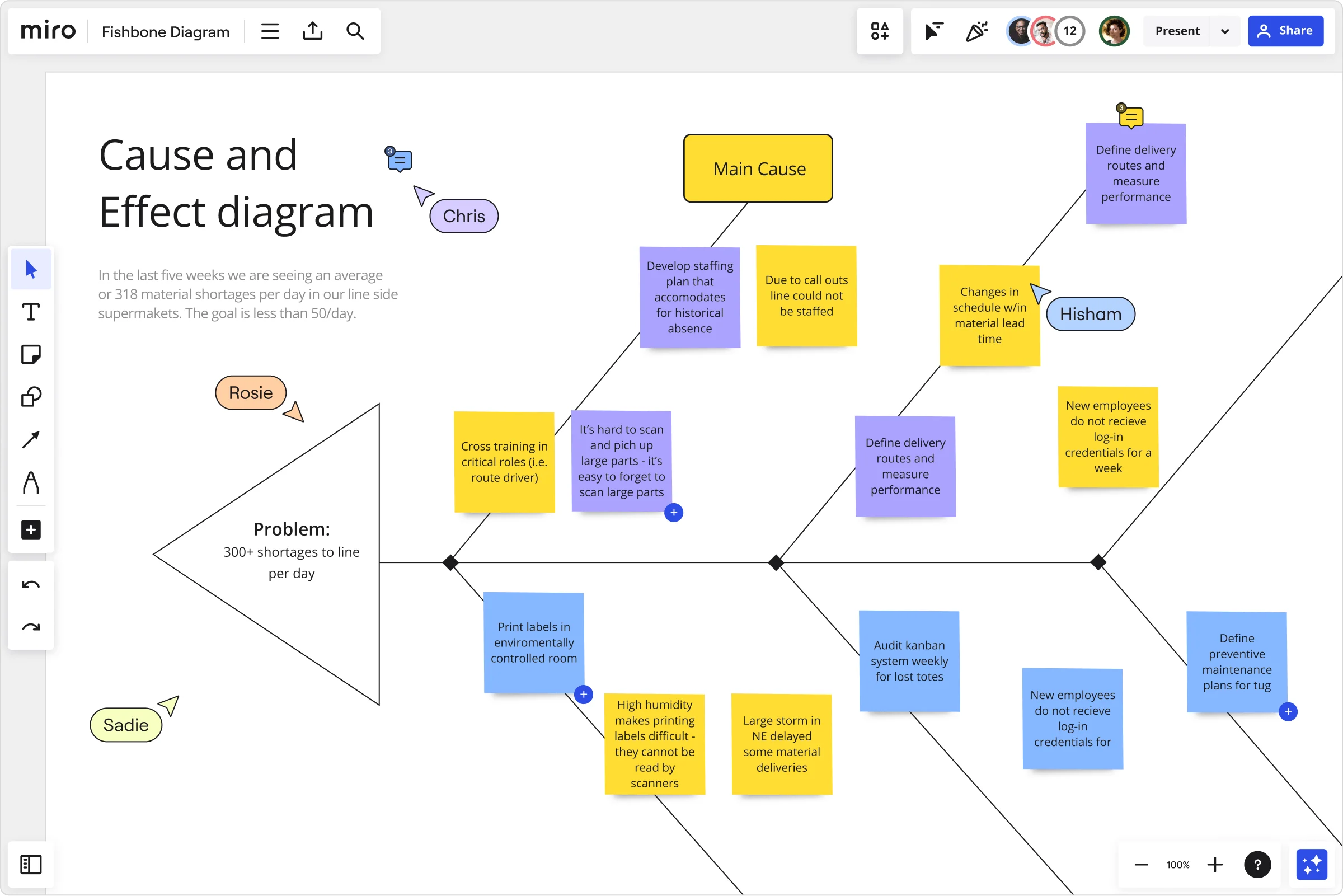
For example, in the diagram below, the main problem is that “40% of users cancel the subscription in the first month.” This statement clearly describes the problem and offers a solid starting point for finding a solution. Now, let’s consider how this would work if the statement were written differently — for example, “to increase customer retention.”
This statement is pretty vague, and there’s a lot of room for interpretation. Instead of focusing specifically on how to keep existing customers after the first month, teams might explore other avenues that won’t necessarily solve the actual problem.
The problem statement doesn’t have to be long and detailed. In fact, you should keep it short — ideally, no longer than a sentence. That way, it’ll be easy for your team to see the problem and won’t overcrowd the diagram. But the problem statement should always be clear and concise, leaving no room for interpretation.
If you’re new to problem statements or want a framework to guide you, look at Prime Motive’s Problem Framing Workshop Template .
3. Pinpoint your root causes
With your problem statement in place, you can now branch out and start to pinpoint the possible causes of the problem.
The specific causes will depend on what your problem statement is. For example, if your problem statement is related to product design, your root causes could include the following:
These are just a few examples. In your diagram, you might find that you have more or fewer root causes. With an intuitive platform like Miro, it’s easy to add or remove boxes based on how many you need.
When adding causes to your diagram, those with the biggest impact should be closest to the problem. The farther away a cause is from the head of the diagram, the less influence it has on the problem.
4. Identify individual causes
You can now identify the individual elements that contribute to the overall cause. These are the bones of the fish.
Let’s use an example to demonstrate how this works. Imagine that one of your root causes is “Equipment.” Here are some of the individual causes that might sit under this area:
You are using outdated and inefficient equipment
It’s expensive to replace existing equipment
There aren’t enough employees who know how to use the equipment
All of these elements could contribute to the problem you’re facing, but it’s up to you and your team to pinpoint the key elements at the root of the problem. Review all this information with your team, and you’ll be able to see which problem is most likely to have a long-term solution.
If you’re unsure how to identify the individual causes, look at the 5 Whys framework . It’s a simple brainstorming tool that helps teams explore the reasons behind a potential problem.
5. Create a plan of action
After working with your team to find the root cause of the problem, you can create an action plan for improvements. This involves mapping out the steps you need to take to solve your problem and how you’ll measure success (we suggest using the SMART Goals framework for this).
During this stage, be sure to focus on how to make lasting improvements. Don’t lose sight of the bigger picture in favor of a quick fix. The purpose of the fishbone diagram is to implement a long-lasting solution to your problem, so keep this in mind when creating your plan of action for the future.
Fishbone diagram categories: the 6Ms of production
The fishbone diagram is used across various industries, but the original diagram was created to improve the manufacturing process. The six methods (6Ms) of production come from this original diagram, and engineers and designers would use this structure to cover all their bases.
The 6Ms of production are as follows:
1. Manpower
The functional activity involved in designing and delivering a product.
The production process and any other processes that contribute to the delivery of the final product.
Any systems, tools, or equipment used in manufacturing.
4. Material
The raw materials and components needed to create the end product.
5. Milieu (or Mother Nature)
Any environmental factors, such as weather, floods, or fire. Although most milieu factors can’t be controlled, there are some instances where businesses can put preventative measures in place to mitigate problems.
6. Measurement
The physical measurements (volume, distance, temperature, and so on) of a product, machine, or workspace.
The 6Ms are only relevant if you’re using the fishbone diagram to improve a manufacturing or production process. If you’re using the diagram for any other purpose, there’s no need to follow this structure.
Find solutions faster with a fishbone diagram
When facing a problem, finding the right solution often comes down to understanding its root cause. That’s where a fishbone diagram can make a real difference. By visually breaking down the potential causes of an issue, the diagram helps you and your team stay focused, organized, and on track—leading to quicker and more effective solutions.
The structured layout of a fishbone diagram allows you to systematically explore each factor contributing to the problem. Instead of jumping to conclusions or missing important details, you can see how various causes connect and identify the one that needs the most attention. This logical approach helps reduce wasted time spent on irrelevant areas, allowing you to move more quickly toward the solution.
Miro’s innovation workspace makes the process even faster. With ready-made fishbone diagram templates and automated diagramming tools, you can set up your analysis with just a few clicks. This saves time and ensures that your focus remains on solving the problem rather than the mechanics of building the diagram. Happy diagramming!
Discover more
How to build a fishbone diagram, fishbone diagram examples, what is a cause and effect diagram, what is root cause analysis, what is the 5 whys framework, 5 whys: examples, explanations, and how to find the causes of problems, get on board in seconds, plans and pricing.
Skip to main content
- Contact sales
- Get started Get started for free
Figma Design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Figma Slides
Co-create presentations
Explore all Figma AI features
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Design systems
- Prototyping
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Engineering
- Product managers
Organizations
Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Shortcut: The Figma blog
Stories about how products take shape—and shape our world
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
What is a fishbone diagram—and what can it do for you?
Any bump in the design process can be a learning opportunity. Maybe an unexpected setback is delaying product development, or you're worried your next release may not get rave customer reviews. Whatever issue you’re facing, the fishbone diagram is a simple and effective brainstorming tool that can help you solve problems—and keep them from cropping up in the first place.
Read on to learn more about:
- What a fishbone diagram is
- How a fishbone diagram can help you solve problems
- 5 steps to create a fishbone diagram—and FigJam tools that make it easy
Create your fishbone diagram with FigJam
Get started with FigJam's free fishbone diagram template today.
What’s a fishbone diagram?
A fishbone diagram is also known as the cause-and-effect diagram, because it highlights the causes of a current or potential problem, or any other deviation from your team’s standard workflow. Companies use fishbone diagrams to help streamline processes, boost customer satisfaction, and drive better business outcomes.
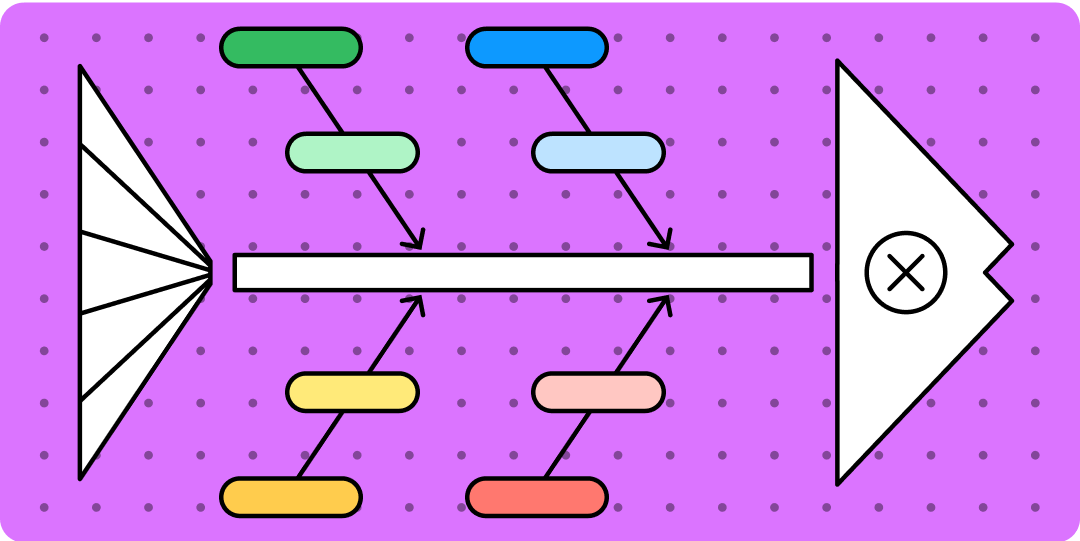
The diagram actually looks like a fish skeleton. A horizontal arrow represents the fish spine and points to the problem (or effect), which is the head of the fish. Shorter arrows act as the fish ribs, branching out to expose the problem’s causes.
How the fishbone method solves problems
The fishbone method of analysis helps teams go deep with their problem-solving, uncovering key factors teams can target and troubleshoot. When used effectively, a fishbone diagram can help you 1 :
- Easily identify and categorize the causes —big and small—of a particular problem in a highly visual way.
- Develop actionable solutions more quickly by providing a structured yet flexible approach to address problems.
- Promote a more effective work environment by fostering better collaboration and communication across teams.
- Continuously improve your product or process by documenting root causes to avoid repeating the same mistakes in the future.
5 steps to create a fishbone diagram
Build your own fishbone diagram in five steps 2 :
Step 1: Define the problem.
Create a clear, concise problem statement. This should address a known issue or one you’re trying to prevent, such as “customer satisfaction rate for our app has fallen 20%.” Use FigJam’s online whiteboard to brainstorm and agree on a problem statement. Or try FigJam’s fishbone diagram template .
Step 2: Label potential issues.
You can use the six labels in the classic fishbone diagram (see sidebar), or create your own set of categories to suit the product and problem facing your team. For example, Mazda chose styling, touch, cornering, driving, listening, and braking as key issues to address in developing the MX5 Miata sports car.
Step 3: Brainstorm all possible causes.
Ask why this problem occurred, and organize possible causes by category. For example, under the people category, you might list causes for a drop in customer satisfaction as staff burnout, lack of training, or employee turnover. Some causes may fit under more than one category.
Step 4: Add more detail to your fishbone analysis.
Keep asking why to further identify sub-causes that contribute to the problem. FigJam’s 5 whys template will help you dig deeper.
Step 5: Review each cause and develop action items.
Work with your team to create a list of action items that will help solve the problem. Invite your team to check the finished diagram, making sure no detail has been overlooked (see sidebar).
Creative examples of fishbone diagrams
Popularized in Japan’s manufacturing industry in the 1960s, the fishbone or Ishikawa diagram is now industry-standard in multiple fields. From healthcare and higher education to retail and high tech, fishbone diagrams help teams improve and innovate.
For inspiration, consider these creative examples from a range of industries:
- Product defects fishbone diagram , Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering
- Carver County Public Health fishbone diagram , Minnesota Department of Health
- Cause and effect of blurry photos , Michigan State University Extension
- Bad coffee fishbone diagram , Kaizen Consulting Group
The classic 6-rib fishbone diagram
A typical fishbone diagram includes six ribs , each labeled with a potential issue to address. This could include:
- People. Evaluate everyone involved in the process, including their skill level, training, and performance.
- Machines. Examine equipment and any maintenance or upgrades required to solve a problem.
- Materials. Assess the raw and finished materials used. Do they meet expectations?
- Environment. Consider external factors such as bad weather or safety issues that can affect the development cycle.
- Method. Audit your team’s process—the number of steps, their complexity, and any potential bottlenecks.
- Measurement. Review the way your process is measured, controlled, and monitored.
Fishbone analysis pitfalls to avoid
The simplicity of a fishbone diagram makes it easy to use and understand, but it can also make it harder to prioritize tasks. Of all the causes identified in a fishbone diagram, a problem’s main causes aren’t necessarily ranked ahead of minor ones. It’s up to you and your team to prioritize issues that will have the most impact versus those that won’t.
Fishbone diagrams can sometimes reflect human biases, so you'll need to work to maintain objectivity. Gather input from key players across your company to ensure your fishbone analysis is valid and complete.
Bone up on your fishbone diagrams with FigJam
Problem-solving is a team sport. Work together to zero in on root causes using FigJam’s online collaborative whiteboard , then organize them with FigJam’s ready-made fishbone diagram template . If you’d rather make one from scratch, use FigJam’s free diagramming tools to:
- Produce an easy-to-understand visual that clearly shows cause-and-effect relationships.
- Collaborate in real time with key stakeholders to make sure the causes included are accurate and actionable.
- Construct a polished diagram that supports your brand and is presentation-ready.
Want to see an example of a fishbone diagram created in FigJam? Check out these inspiring fishbone diagrams shared by the Figma community .
Now you’ve got what you need to solve problems—and prevent them, too.
Go to next section
[1] https://6sigma.com/benefits-of-using-the-fishbone-diagram/
[2] https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/ncepcr/resources/job-aid-5-whys.pdf
Keep reading
How to create a swimlane diagram
Swimlane diagrams give flowcharts an extra-informative superpower.
How to create a flow chart
Having a flow chart can help visually represent actions or people in a complex situation.
What is a UML diagram
UML diagrams can help you plan complex systems and processes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
October 25, 2024. Lean Basics. Ishikawa fishbone diagrams, also known as cause-and-effect diagrams or fishbone charts, are powerful tools for problem-solving and quality …
Follow these steps to solve a problem with Cause and Effect Analysis: Step 1: Identify the Problem. First, write down the exact problem you face. Where appropriate, identify who is involved, what the problem is, and when and where …
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving tool that helps to identify the root cause of a problem and find a long-term solution. Learn what a fishbone diagram is, how to use it, and see examples of different applications and …
Use a fishbone diagram to help you solve problems by understanding what’s causing them. Learn how to make one using FigJam’s fishbone diagram template.
The Fishbone Diagram is a visual tool used in Lean Six Sigma to identify root causes of problems. It resembles a fish skeleton, with the main problem at the head and potential causes branching off the spine into …