Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Handbook of Technical Writing 9th Edition

Related Papers
Jordi Pique
George Tchobanoglous
Principled Program Management and Team Leadership
Mack McKinney
This handout from a systems engineering course is, itself, a mini-class in writing technical papers. Discusses the importance of deciding upon purpose, audience, content, style and mechanics. Gives examples of clear versus ambiguous writing and discusses fifty-six common mistakes that inexperienced writers (especially engineers) often make. Finally, asks readers of this paper to find the typographic mistake intentionally left in it, and to email that to [email protected] for a neat gift that is provided as a reward.
Ahmed Alkhaldi
dheya al-othmany
This paper has focused on technical writing as a skill for engineers. It has sought to define technical writing and throw light on the content and technique of writing the various components of successful technical reports (for example, articles, papers, or research reports, such as theses and dissertations). Then, it has highlighted other special features and principles of effective technical writing. The material in this paper is divided into seven major parts. Part 1 (Technical writing for engineers) stresses that a successful engineering career requires strong writing skills. Part 2 (How to write the major sections or elements of a report) describes the techniques of writing the abstract, introduction, literature review, procedure/methods & materials, results, discussion, conclusion, and recommendations. Part 3 (Special features of technical writing) brings into focus some of the special features of technical writing such as tables & graphs in the text, graphics in instructions, team writing, ethics (plagiarism), document sources, three citation styles and IEEE reference style. Part 4 (Technical usage) deals with writing abbreviations, initialisms and acronyms, numbers, units of measurement, and equations. Part 5 (Technical style) highlights the imperative writing style and other features of technical writing such as the use of active and passive voices, plain vs. complex syntax, avoiding redundant or superfluous expressions, and vague generalities, using words or expressions with visual impact, the past tense to describe experimental work, the present tense to describe hypotheses, principles, theories and truths, and breaking up the text of the report into short sections. Part 6 (Document specifications) emphasizes the technical writer's need to conform to such document specifications as word count, format, font, number of words per line of text imposed. Finally, part 7 (Reader-friendly technical writing) suggests choosing the varied writing modes (- atterns of organization of information) to suit the technical writing task, checking for technical accuracy and following three levels of editing to help increase the readability of a technical text.
Tchobanoglous, G., Leverenz, H. (2013), A Guidance Manual on the Preparation of Technical Reports, Papers, and Presentations, University of California, Davis, Davis, CA
Sina Khatami
Revista de Sistemas de Informação da FSMA
Armando Vieira
Kevin Karplus
This document contains course notes and exercises for a course in technical writing. The course is intended for third-year computer engineering majors, and emphasizes technical documentation directed to engineers, engineering managers, technical writers, and other specialized audiences.
Norman Fenton
This document describes the basic principles of good writing. It is primarily targeted at students and researchers writing technical and business reports, but the principles are relevant to any form of writing, including letters and memos. Therefore, the document contains valuable lessons for anybody wishing to improve their writing skills. The ideas described here are, apart from fairly minor exceptions, not original. They are drawn from a range of excellent books and have also been influenced by various outstanding authors I have worked with. Thus, the approach represents a kind of modern consensus. This approach is very different to the style that was promoted by the traditional English schools ’ system, which encouraged students to write in an unnecessarily complex and formal way. The approach described here emphasises simplicity (‘plain English’) and informality. For example, it encourages shorter sentences and use of the simplest words and phrases possible. It explains how you...
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Hayden Coombs
Tanguy Wettengel
Fernando Deviente Jr.
International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET)
IJRASET Publication
Ekong Nancy
2004 Annual Conference Proceedings
David Beams
Kazibwe Brian Peter
David Farkas
Oksana Synekop
Tutors India
Eveling Castro
Gayatri Mohanta
Kate Maddalena
Research on humanities and social sciences
M.Sahul Hameed
Cutilioux Rukhshan
TESSIE SANDALAN
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Belen Labrador
Nelson Cheng PhD (H.C.), SRF , Patrick Moe , Nicola Nedev
IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication
Christian F Casper , Elaine Wisniewski
Jonathan Arnett
JUAN ANTONIO PEÑA MARRUFO
Nelson Antony
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8. ORAL AND VISUAL PRESENTATIONS
Suzan Last and Monika Smith
Like any kind of advanced communication skill, the art of giving effective presentations is not in-born; it requires deliberate practice — that is, systematic practice that requires focused attention on improving, and making use of feedback from others to help you do so. An excellent way to learn more about delivering effective presentations is to follow a systematic process:
- Observe others
- Study their strategies and reflect on their effectiveness
- Select and practice strategies that will work for you; reflect and get feedback from others.
Step 1: Observation
You can learn a lot simply by observing how successful public speakers “work the room” and engage their audience. Observe what they do. How do they use their voice as a tool of communication? How do they deploy tone, pausing, pacing, and projection? What do they do with their hands? How do they make use of the physical space around them? Take note of how speakers physically operate, either in person or on media: identify what they do, make note of what you think works well and what doesn’t, then put what you’ve learned into practice.
As a student, you might start by observing your professors. Aim to identify what makes one professor a great lecturer and another less engaging. Compare what they do with their voice, their hands, their gestures, their movements. Pay attention to how they pace their talk to draw you in and create emphasis. Reflect on what they do to convey a sense of enthusiasm for what they’re talking about—or fail to do so. You want to know what kinds of things to avoid—a dull monotonous tone, for example—as well as what kinds of things to adopt to ensure your voice comes across as a powerful tool for communicating your ideas clearly and emphatically.
EXERCISE 8.1: Observation in action
Whether observing your favourite professor give a lecture; watching your favourite podcaster, TV or YouTube presenter; or viewing the videos linked below, turn your observations into an active learning experience: create a list of what the speakers do well as speakers , and then use them as role models. The goal is to create a toolkit of practical tips, approaches, and ideas for building confidence, developing your own “spark” as public speaker, and engaging your audience. In short, watch, observe, and learn.
Here are some public speakers on film that you may enjoy watching and learning from:
- Really achieving your childhood dreams by Randy Pausch, [1] computer scientist (Carnegie Mellon). As you watch the video, make note not simply of what he says, but how he says it.
- “The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout” by Rick Rigsby [2]
- “The Joy of Stats” by Hans Rosling [3] offers an engaging and inspiring description of 250,000 data points from over 200 years for 200 countries—in 4 minutes flat!
Step 2: Study and Reflect
Learning from experts who lay out a set of simple techniques is a confidence builder because it shows that great speakers are made, not born. With deliberate practice, anyone can do this. There are no mysteries, just specific, applicable strategies that anyone can adopt to establish rapport with an audience and make a meaningful impact.
Here are some more great online resources to help you develop further:
- Advanced Public Speaking Institute (Tips )
- Toastmasters 5 tips for public speaking (YouTube)
- 10 Most Common Rookie Mistakes in Public Speaking – Terry Gault (Prezi Blog)
- The Power of your Hands – Allan Pease (TED)
- How to Sound Smart in your TED Talk − Will Stephen (TED)
- How I Overcame my Fear of Public Speaking − Danish Dhamani (TED)
EXERCISE 8.2
Take notes from the sources while you study them. Making written notes about points you want to remember can be an effective way to promote deep learning. As you watch each of the videos, identify 2-3 key tips. If you are doing this activity in class, share your “top two” tips with classmates and make note of their “top two” tips in turn.
Then consider the value of the tips and strategies you’ve compiled. What makes them seem to work so well and, equally important, how could you feasibly incorporate them into your presentations to make them your own?
Step 3: Select, Practice and Assess your Progress
Now that you have identified strategies that you find effective and think might work for you, try putting them into practice. See if they add some extra “oomph” to your presentation style. Afterwards, either by engaging in self-reflection, or by asking for feedback, consider how well these strategies worked for you and whether you need to further hone, adapt, or change the way you used them.
Videos are helpful because they not only provide information, but visually demonstrate the ideas (both showing and telling); however, you can also learn from many books on the subject. Here are four classic books by public speaking experts designed to help you develop your own strong presentation skills. By focusing on aspects such as“voice,” or by getting you to create effective slideshows, they offer a range of practical, “tried and tested” approaches designed to help you build confidence, speak fluently, and hold an audience’s attention with relevant, well designed visuals.
- Lilyan Wilder, 7 Steps to Fearless Speaking offers a lively, straightforward “how to” approach to public speaking, paying special attention to what to do before you even get on stage to deliver your talk. In short, according to Lilyan Wilder, it’s all about preparation. Wilder’s seven steps have been used by many successful public figures, including George H.W. Bush, Oprah Winfrey, Fortune 500 CEO’s, as well as network anchors at CNN, CBS, and more!
- Lee LeFever, The Art of Explanation: Making your Ideas, Products, and Services Easier to Understand invites you to become an “explanation specialist” by using simple elements to motivate your audience and inspire them to say “yes!” to your designs and ideas.
- Garr Reynolds, PresentationZen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery provides a clear, easy-to-read set of tips for cutting through the noise and blather of modern life and reaching an audience through simple, pared-down slides and story-telling: two techniques that can help you connect with and inspire your audience in an authentic, genuine way.
- Nancy Duarte, Slide:ology: T he Art and Science of Creating Great Presentations looks to the role of presentation software in the visualization of ideas and information. Its goal is to turn you into a “visual thinker” so you can design presentation graphics that enable your audience to easily and effectively process data—an especially valuable skill for technical presenters who often have to convey complex data in meaningful ways to non-technical audiences.
EXERCISE 8.3 Build your repertoire
Visual Aids – PowerPoint Basics
Even the most dynamic speakers often make use of visual aids to accompany their presentation and help illustrate their ideas. Having well designed visuals as part of your presentation is one way for beginners and those honing their skills can add interest and audience engagement to their talks. PowerPoint is probably the most common form of visual aid used in presentations, so much discussion has been focused on the pros and cons of this medium. Indeed, a Google search of “death by PowerPoint” brings up over 90 million results!
While there are many other presentation tools out there that you should explore (and perhaps present to your classmates or colleagues in your own presentation!), PowerPoint is a standard workplace tool, so it would be wise to gain proficiency with it. The key concept to remember is that your visual aids should supplement and illustrate what you want to say to your audience. YOU are the presenter; your slides illustrate and amplify what you want to say.
PowerPoint Terminology
When designing a PowerPoint presentation, it is helpful to be familiar with key terminology used to discuss the various elements. Here are a few terms to get started:
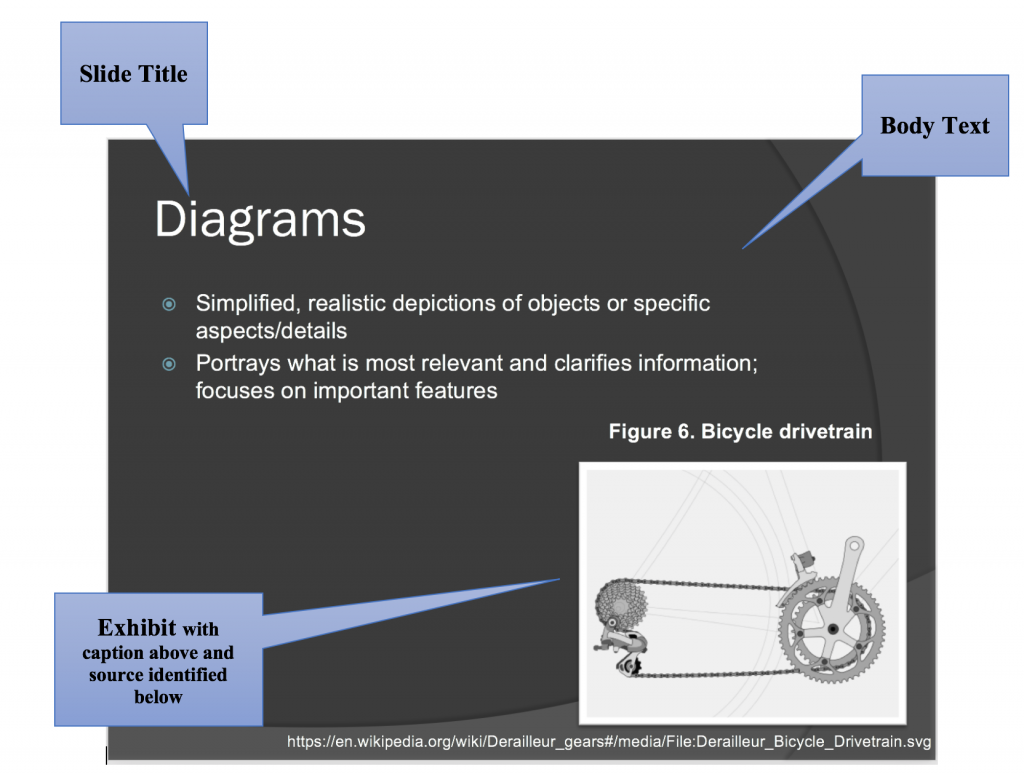
- Deck : the entire presentation (all the slides in the presentation; see Figure 8.2.1) .
- Gloss : what the speaker says about each slide. The speaker should not simply read what is on the slide. Slides should have minimal text in the form of key words and short bullet points. They might include key quotations. Speakers should elaborate on what is written or shown on the slide in their gloss.
- Slide : one “page” of the presentation ( Figure 8.2.2 shows one slide from the deck above) with the various elements identified.
- Slide Titles : usually at the top of the slide, the title acts as a “heading” indicating the topic to be discussed in each slide.
- Body Text: written text on the slide, often in the form of bullet points or key terms. This text should be kept to a minimum (key words/phrases; quotations you want to read out loud). Don’t write your “script” in the slide’s body text.
- Exhibits : illustrative graphics on the slides that are glossed in the presentation. You should discuss graphics and explain what is important about them.
- Decorative Graphics : Slide motifs, themes, and other non-essential images that add visual appeal to the slides, but do not illustrate substantive ideas.
- Notes : The section underneath the slide where you can write notes you want to cover in your gloss. The audience will not see the “notes” portion.
Click on the Sample PowerPoint Presentations listed below to see detailed examples of PowerPoint decks.
PowerPoint Presentation on PRESENTATIONS (.ppt)
Tuckman’s Model of Team Formation – Sample student presentation (.ppt)
Definitions in Technical Writing – Sample student presentation (.pdf) (Created by Isaac Morton)
Visual Rhetoric
PowerPoint is not the only visual medium you might use. Pamphlets, posters, billboards, and other kinds of displays can also work to effectively convey your message if they are well designed. Considering how to present ideas visually can be as important as determining what to say. Here are some resources to help you design visual information in a rhetorically effective way:
Visual Rhetoric page from the Online Writing Lab (OWL) at Purdue University
Rule of Thirds (Wikipedia)
Color theory (Tiger Color)
Psychology of Font Choices (The Daily Egg)
- R. Pausch, “Really achieving your childhood dreams, Sept. 18, 2007 Youtube [Online]: Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ji5_MqicxSo ↵
- R. Rigsby, “The wisdom of a third grade dropout will change your life,” Oct. 2017, Youtube [Online]. Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bg_Q7KYWG1g ↵
- H. Rosling, “The joy of stats,” Nov. 26, 2010, YouTube [Online]. Available: https://youtu.be/jbkSRLYSojo ↵
- Keithonearth, [Bicycle image embedded in slide]. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derailleur_gears#/media/File:Derailleur_Bicycle_Drivetrain.svg . CC BY-SA 3.0 . ↵
Technical Writing Essentials Copyright © by Suzan Last and Monika Smith is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
We’re fighting to restore access to 500,000+ books in court this week. Join us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Technical writing, presentation skills, and online communication : professional tools and insights
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
46 Previews
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station48.cebu on January 12, 2023
9. PRESENTATION SKILLS
Oral presentations may be one of the most anxiety-inducing prospects for many students and professionals alike. Yet the ability to plan your presentation, use available technologies, and speak clearly and confidently in public is an important competency in the workplace.
Since there is an enormous amount of information on this topic available on the internet, and since “showing” is often more effective than “telling,” links to several online resources are included to help you sort through and find credible and authoritative sources of information and sample presentations to help you learn more and develop your own presentations.
Chapter 8 Learning Objectives
This chapter will help you develop confidence and skills in presenting information orally, both individually and as a team, and in designing visually effective presentations in person and virtually by focusing on the following areas:
9.1 Applying skills and techniques that will help build your confidence as a presenter
9.2 Developing presentation skills by using a systematic process to practice delivery and use visual rhetoric
9.3 Using software features and slide tools to design your presentation
9.4 Using collaboration skills to effectively present as a team
9.5 Extending and applying your skills to present virtually
Technical Writing Essentials Copyright © 2019 by Suzan Last is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8. ORAL AND VISUAL PRESENTATIONS
8.2 Developing Presentation Skills
Suzan Last and Monika Smith
Like any kind of advanced communication skill, the art of giving effective presentations is not in-born; it requires deliberate practice — that is, systematic practice that requires focused attention on improving, and making use of feedback from others to help you do so. An excellent way to learn more about delivering effective presentations is to follow a systematic process:
- Observe others
- Study their strategies and reflect on their effectiveness
- Select and practice strategies that will work for you; reflect and get feedback from others.
Step 1: Observation
You can learn a lot simply by observing how successful public speakers “work the room” and engage their audience. Observe what they do. How do they use their voice as a tool of communication? How do they deploy tone, pausing, pacing, and projection? What do they do with their hands? How do they make use of the physical space around them? Take note of how speakers physically operate, either in person or on media: identify what they do, make note of what you think works well and what doesn’t, then put what you’ve learned into practice.
As a student, you might start by observing your professors. Aim to identify what makes one professor a great lecturer and another less engaging. Compare what they do with their voice, their hands, their gestures, their movements. Pay attention to how they pace their talk to draw you in and create emphasis. Reflect on what they do to convey a sense of enthusiasm for what they’re talking about—or fail to do so. You want to know what kinds of things to avoid—a dull monotonous tone, for example—as well as what kinds of things to adopt to ensure your voice comes across as a powerful tool for communicating your ideas clearly and emphatically.
EXERCISE 8.1: Observation in action
Whether observing your favourite professor give a lecture; watching your favourite podcaster, TV or YouTube presenter; or viewing the videos linked below, turn your observations into an active learning experience: create a list of what the speakers do well as speakers , and then use them as role models. The goal is to create a toolkit of practical tips, approaches, and ideas for building confidence, developing your own “spark” as public speaker, and engaging your audience. In short, watch, observe, and learn.
Here are some public speakers on film that you may enjoy watching and learning from:
- Really achieving your childhood dreams by Randy Pausch, [1] computer scientist (Carnegie Mellon). As you watch the video, make note not simply of what he says, but how he says it.
- “The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout” by Rick Rigsby [2]
- “The Joy of Stats” by Hans Rosling [3] offers an engaging and inspiring description of 250,000 data points from over 200 years for 200 countries—in 4 minutes flat!

Step 2: Study and Reflect
Learning from experts who lay out a set of simple techniques is a confidence builder because it shows that great speakers are made, not born. With deliberate practice, anyone can do this. There are no mysteries, just specific, applicable strategies that anyone can adopt to establish rapport with an audience and make a meaningful impact.
Here are some more great online resources to help you develop further:
- Advanced Public Speaking Institute (Tips )
- Toastmasters 5 tips for public speaking (YouTube)
- 10 Most Common Rookie Mistakes in Public Speaking – Terry Gault (Prezi Blog)
- The Power of your Hands – Allan Pease (TED)
- How to Sound Smart in your TED Talk − Will Stephen (TED)
- How I Overcame my Fear of Public Speaking − Danish Dhamani (TED)
EXERCISE 8.2
Take notes from the sources while you study them. Making written notes about points you want to remember can be an effective way to promote deep learning. As you watch each of the videos, identify 2-3 key tips. If you are doing this activity in class, share your “top two” tips with classmates and make note of their “top two” tips in turn.
Then consider the value of the tips and strategies you’ve compiled. What makes them seem to work so well and, equally important, how could you feasibly incorporate them into your presentations to make them your own?
Step 3: Select, Practice and Assess your Progress
Now that you have identified strategies that you find effective and think might work for you, try putting them into practice. See if they add some extra “oomph” to your presentation style. Afterwards, either by engaging in self-reflection, or by asking for feedback, consider how well these strategies worked for you and whether you need to further hone, adapt, or change the way you used them.
Videos are helpful because they not only provide information, but visually demonstrate the ideas (both showing and telling); however, you can also learn from many books on the subject. Here are four classic books by public speaking experts designed to help you develop your own strong presentation skills. By focusing on aspects such as“voice,” or by getting you to create effective slideshows, they offer a range of practical, “tried and tested” approaches designed to help you build confidence, speak fluently, and hold an audience’s attention with relevant, well designed visuals.
- Lilyan Wilder, 7 Steps to Fearless Speaking offers a lively, straightforward “how to” approach to public speaking, paying special attention to what to do before you even get on stage to deliver your talk. In short, according to Lilyan Wilder, it’s all about preparation. Wilder’s seven steps have been used by many successful public figures, including George H.W. Bush, Oprah Winfrey, Fortune 500 CEO’s, as well as network anchors at CNN, CBS, and more!
- Lee LeFever, The Art of Explanation: Making your Ideas, Products, and Services Easier to Understand invites you to become an “explanation specialist” by using simple elements to motivate your audience and inspire them to say “yes!” to your designs and ideas.
- Garr Reynolds, PresentationZen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery provides a clear, easy-to-read set of tips for cutting through the noise and blather of modern life and reaching an audience through simple, pared-down slides and story-telling: two techniques that can help you connect with and inspire your audience in an authentic, genuine way.
- Nancy Duarte, Slide:ology: T he Art and Science of Creating Great Presentations looks to the role of presentation software in the visualization of ideas and information. Its goal is to turn you into a “visual thinker” so you can design presentation graphics that enable your audience to easily and effectively process data—an especially valuable skill for technical presenters who often have to convey complex data in meaningful ways to non-technical audiences.
EXERCISE 8.3 Build your repertoire
Visual Aids – PowerPoint Basics
Even the most dynamic speakers often make use of visual aids to accompany their presentation and help illustrate their ideas. Having well designed visuals as part of your presentation is one way for beginners and those honing their skills can add interest and audience engagement to their talks. PowerPoint is probably the most common form of visual aid used in presentations, so much discussion has been focused on the pros and cons of this medium. Indeed, a Google search of “death by PowerPoint” brings up over 90 million results!
While there are many other presentation tools out there that you should explore (and perhaps present to your classmates or colleagues in your own presentation!), PowerPoint is a standard workplace tool, so it would be wise to gain proficiency with it. The key concept to remember is that your visual aids should supplement and illustrate what you want to say to your audience. YOU are the presenter; your slides illustrate and amplify what you want to say.
PowerPoint Terminology
When designing a PowerPoint presentation, it is helpful to be familiar with key terminology used to discuss the various elements. Here are a few terms to get started:
- Deck : the entire presentation (all the slides in the presentation; see Figure 8.2.1) .

- Gloss : what the speaker says about each slide. The speaker should not simply read what is on the slide. Slides should have minimal text in the form of key words and short bullet points. They might include key quotations. Speakers should elaborate on what is written or shown on the slide in their gloss.
- Slide : one “page” of the presentation ( Figure 8.2.2 shows one slide from the deck above) with the various elements identified.

- Slide Titles : usually at the top of the slide, the title acts as a “heading” indicating the topic to be discussed in each slide.
- Body Text: written text on the slide, often in the form of bullet points or key terms. This text should be kept to a minimum (key words/phrases; quotations you want to read out loud). Don’t write your “script” in the slide’s body text.
- Exhibits : illustrative graphics on the slides that are glossed in the presentation. You should discuss graphics and explain what is important about them.
- Decorative Graphics : Slide motifs, themes, and other non-essential images that add visual appeal to the slides, but do not illustrate substantive ideas.
- Notes : The section underneath the slide where you can write notes you want to cover in your gloss. The audience will not see the “notes” portion.
Click on the Sample PowerPoint Presentations listed below to see detailed examples of PowerPoint decks.
PowerPoint Presentation on PRESENTATIONS (.ppt)
Tuckman’s Model of Team Formation – Sample student presentation (.ppt)
Definitions in Technical Writing – Sample student presentation (.pdf) (Created by Isaac Morton)
Visual Rhetoric
PowerPoint is not the only visual medium you might use. Pamphlets, posters, billboards, and other kinds of displays can also work to effectively convey your message if they are well designed. Considering how to present ideas visually can be as important as determining what to say. Here are some resources to help you design visual information in a rhetorically effective way:
Visual Rhetoric page from the Online Writing Lab (OWL) at Purdue University
Rule of Thirds (Wikipedia)
Colour Theory (University of Saskatchewan Pressbooks)
Psychology of Font Choices (The Daily Egg)
- R. Pausch, “Really achieving your childhood dreams, Sept. 18, 2007 Youtube [Online]: Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ji5_MqicxSo ↵
- R. Rigsby, “The wisdom of a third grade dropout will change your life,” Oct. 2017, Youtube [Online]. Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bg_Q7KYWG1g ↵
- H. Rosling, “The joy of stats,” Nov. 26, 2010, YouTube [Online]. Available: https://youtu.be/jbkSRLYSojo ↵
- Keithonearth, [Bicycle image embedded in slide]. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derailleur_gears#/media/File:Derailleur_Bicycle_Drivetrain.svg . CC BY-SA 3.0 . ↵
Technical Writing Essentials Copyright © 2019 by Suzan Last and Monika Smith is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8 8.2 Developing Presentation Skills
Suzan Last and Monika Smith
Like any kind of advanced communication skill, the art of giving effective presentations is not in-born; it requires deliberate practice . An excellent way to learn more about delivering effective presentations is to follow a systematic process:
- Observe others
- Study their strategies and reflect on their effectiveness
- Select and practice strategies that will work for you; reflect and get feedback from others.
Step 1: Observation
You can learn a lot simply by observing how successful public speakers “work the room” and engage their audience. Observe what they do. How do they use their voice to make it work as a tool of communication? How do they deploy tone, pausing, pacing, and projection? What do they do with their hands? How do they make use of the physical space around them? Take note of how speakers physically operate, either in person or on media: identify what they do, make note of what you feel works well and what doesn’t, then put what you’ve learned into practice.
As a student, you might start by observing your professors. Aim to identify what makes one professor a great lecturer and another less engaging. Compare what they do with their voice, their hands, their gestures, their movements. Pay attention to how they pace their talk to draw you in and create emphasis. Reflect on what they do to convey a sense of enthusiasm for what they’re talking about—or fail to do so. You want to know what kinds of things to avoid—a dull monotonous tone, for example—as well as what kinds of things to adopt to ensure your voice comes across as a powerful tool for communicating your ideas clearly and emphatically.
EXERCISE 8.1: Observation in action
Whether observing your favourite professor give a lecture; watching your favourite podcaster, TV or YouTube presenter; or viewing the videos linked below, turn your observations into an active learning experience: create a list of what the speakers do well as speakers , and then use them as role models. The goal is to create a toolkit of practical tips, approaches, and ideas for building confidence, developing your own “spark” as public speaker, and engaging your audience. In short, watch, observe, and learn.
Here are some public speakers on film that you may enjoy watching and learning from:
- Really achieving your childhood dreams by Randy Pausch, [1] computer scientist (Carnegie Mellon). As you watch the video, make note not simply of what he says, but how he says it.
- “The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout” by Rick Rigsby [2]
- “The Joy of Stats” by Hans Rosling [3] offers an engaging and inspiring description of 250,000 data points from over 200 years for 200 countries—in 4 minutes flat!
Step 2: Study and Reflect
Learning from experts who lay out a set of simple techniques is a confidence builder because it shows that great speakers are made, not born. With deliberate practice, anyone can do this. There are no mysteries, just specific, applicable strategies that anyone can adopt to establish rapport with an audience and make a meaningful impact.
Here are some more great online resources to help you develop further:
- Advanced Public Speaking Institute (Tips )
- Toastmasters 5 tips for public speaking (YouTube)
- 10 Most Common Rookie Mistakes in Public Speaking – Terry Gault (Prezi Blog)
- The Power of your Hands – Allan Pease (TED)
- How to Sound Smart in your TED Talk − Will Stephen (TED)
- How I Overcame my Fear of Public Speaking − Danish Dhamani (TED)
EXERCISE 8.2
Take notes from the sources while you study them. Making written notes about points you want to remember is an effective way to promote deep learning. As you watch each of the videos, identify 2-3 key tips. If you are doing this activity in class, share your “top two” tips with classmates and make note of their “top two” tips in turn.
Then consider the value of the tips and strategies you’ve compiled. What makes them seem to work so well and, equally important, how could you feasibly incorporate them into your presentations to make them your own?
Step 3: Select, Practice and Assess your Progress
Now that you have identified strategies that you find effective and think might work for you, try putting them into practice. See if they add some extra “oomph” to your presentation style. Afterwards, either by engaging in self-reflection, or by asking for feedback, consider how well these strategies worked for you and whether you need to further hone, adapt, or change the way you used them.
Videos are helpful because they not only provide information, but visually demonstrate the ideas (both showing and telling); however, you can also learn from many books on the subject. Here are four classic books by public speaking experts designed to help you develop your own strong presentation skills. By focusing on aspects such as“voice,” or by getting you to create effective slideshows, they offer a range of practical, “tried and tested” approaches designed to help you build confidence, speak fluently, and hold an audience’s attention with relevant, well designed visuals.
- Lilyan Wilder, 7 Steps to Fearless Speaking offers a lively, straightforward “how to” approach to public speaking, paying special attention to what to do before you even get on stage to deliver your talk. In short, according to Lilyan Wilder, it’s all about preparation. Wilder’s seven steps have been used by many successful public figures, including George H.W. Bush, Oprah Winfrey, Fortune 500 CEO’s, as well as network anchors at CNN, CBS, and more!
- Lee LeFever, The Art of Explanation: Making your Ideas, Products, and Services Easier to Understand invites you to become an “explanation specialist” by using simple elements to motivate your audience and inspire them to say “yes!” to your designs and ideas.
- Garr Reynolds, PresentationZen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery provides a clear, easy-to-read set of tips for cutting through the noise and blather of modern life and reaching an audience through simple, pared-down slides and story-telling: two techniques that can help you connect with and inspire your audience in an authentic, genuine way.
- Nancy Duarte, Slide:ology: T he Art and Science of Creating Great Presentations looks to the role of presentation software in the visualization of ideas and information. Its goal is to turn you into a “visual thinker” so you can design presentation graphics that enable your audience to easily and effectively process data—an especially valuable skill for technical presenters who often have to convey complex data in meaningful ways to non-technical audiences.
EXERCISE 8.3 Build your repertoire
Visual Aids – PowerPoint Basics
Even the most dynamic speakers often make use of visual aids to accompany their presentation and help illustrate their ideas. Having well designed visuals as part of your presentation is one way for beginners and those honing their skills can add interest and audience engagement to their talks. PowerPoint is probably the most common form of visual aid used in presentations, so much discussion has been focused on the pros and cons of this medium. Indeed, a Google search of “death by PowerPoint” brings up over 90 million results!
While there are many other presentation tools out there that you should explore (and perhaps present to your classmates or colleagues in your own presentation!), PowerPoint is a standard workplace tool, so it would be wise to gain proficiency with it. The key concept to remember is that your visual aids should supplement and illustrate what you want to say to your audience.
PowerPoint Terminology
When designing a PowerPoint presentation, it is helpful to be familiar with key terminology used to discuss the various elements.
- Deck : the entire presentation (all the slides in the presentation; see Figure 8.2.1) .

- Gloss : what the speaker says about each slide. The speaker should not simply read what is on the slide. Slides should have minimal text in the form of key words and short bullet points. It might include key quotations. The speaker should elaborate on what is written or shown on the slide.
- Slide : one “page” of the presentation ( Figure 8.2.2 shows one slide from the deck above) with the various elements identified.
- Slide Titles : usually at the top of the slide, the titles acts as “headings” indicating the topic to be discussed in each slide.
- Body Text: written text on the slide, often in the form of bullet points or key terms. This text should be kept to a minimum (key words/phrases; quotations you want to read out loud). Don’t write your “script” in the slide’s body text.
- Exhibits : illustrative graphics on the slides that are glossed in the presentation. You should discuss graphics and explain what is important about them.
- Decorative Graphics : Slide motifs, themes, and other non-essential images that add visual appeal to the slides, but do not illustrate substantive ideas.
- Notes : The section underneath the slide where you can write notes you want to cover in your gloss. The audience will not see the “notes” portion.
Click on the Sample PowerPoint Presentations listed below to see detailed examples of PowerPoint decks.
PowerPoint Presentation on PRESENTATIONS (.ppt)
Tuckman’s Model of Team Formation – Sample student presentation (.ppt)
Definitions in Technical Writing – Sample student presentation (.pdf) (Created by Isaac Morton)
Visual Rhetoric
PowerPoint is not the only visual medium you might use. Pamphlets, posters, billboards, and other kinds of displays can also work to effectively convey your message if they are well designed. Considering how to present ideas visually can be as important as determining what to say. Here are some resources to help you design visual information in a rhetorically effective way:
Visual Rhetoric page from the Online Writing Lab (OWL) at Purdue University
Rule of Thirds (Wikipedia)
Color theory (Tiger Color)
Psychology of Font Choices (The Daily Egg)
- R. Pausch, “Really achieving your childhood dreams, Sept. 18, 2007 Youtube [Online]: Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ji5_MqicxSo ↵
- R. Rigsby, “The wisdom of a third grade dropout will change your life,” Oct. 2017, Youtube [Online]. Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bg_Q7KYWG1g ↵
- H. Rosling, “The joy of stats,” Nov. 26, 2010, YouTube [Online]. Available: https://youtu.be/jbkSRLYSojo ↵
- Keithonearth, [Bicycle image embedded in slide]. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derailleur_gears#/media/File:Derailleur_Bicycle_Drivetrain.svg . CC BY-SA 3.0 . ↵
Technical Writing Essentials Copyright © 2019 by Suzan Last and Monika Smith is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8.2 Developing Presentation Skills
Suzan Last and Monika Smith
Like any kind of advanced communication skill, the art of giving effective presentations is not in-born; it requires deliberate practice . An excellent way to learn more about delivering effective presentations is to follow a systematic process:
- Observe others
- Study their strategies and reflect on their effectiveness
- Select and practice strategies that will work for you; reflect and get feedback from others.
Step 1: Observation
You can learn a lot simply by observing how successful public speakers “work the room” and engage their audience. Observe what they do. How do they use their voice to make it work as a tool of communication? How do they deploy tone, pausing, pacing, and projection? What do they do with their hands? How do they make use of the physical space around them? Take note of how speakers physically operate, either in person or on media: identify what they do, make note of what you feel works well and what doesn’t, then put what you’ve learned into practice.
As a student, you might start by observing your professors. Aim to identify what makes one professor a great lecturer and another less engaging. Compare what they do with their voice, their hands, their gestures, their movements. Pay attention to how they pace their talk to draw you in and create emphasis. Reflect on what they do to convey a sense of enthusiasm for what they’re talking about—or fail to do so. You want to know what kinds of things to avoid—a dull monotonous tone, for example—as well as what kinds of things to adopt to ensure your voice comes across as a powerful tool for communicating your ideas clearly and emphatically.
EXERCISE 8.1: Observation in action
Whether observing your favourite professor give a lecture; watching your favourite podcaster, TV or YouTube presenter; or viewing the videos linked below, turn your observations into an active learning experience: create a list of what the speakers do well as speakers , and then use them as role models. The goal is to create a toolkit of practical tips, approaches, and ideas for building confidence, developing your own “spark” as public speaker, and engaging your audience. In short, watch, observe, and learn.
Here are some public speakers on film that you may enjoy watching and learning from:
- Really achieving your childhood dreams by Randy Pausch, [1] computer scientist (Carnegie Mellon). As you watch the video, make note not simply of what he says, but how he says it.
- “The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout” by Rick Rigsby [2]
- “The Joy of Stats” by Hans Rosling [3] offers an engaging and inspiring description of 250,000 data points from over 200 years for 200 countries—in 4 minutes flat!
Watch the video of Randy Pausch and note the 13 tips that will help make your presentations better. The video will pause when the tip comes up on the screen, once you have read it, click the play button to continue.
This is a long video but the information and interactions end at approximately the 12 minute mark. You do not need to watch past this point but we encourage you to because it’s a great video. Watch Randy Pausch Last Lecture: Achieving Your Childhood Dream .
Step 2: Study and Reflect
Learning from experts who lay out a set of simple techniques is a confidence builder because it shows that great speakers are made, not born. With deliberate practice, anyone can do this. There are no mysteries, just specific, applicable strategies that anyone can adopt to establish rapport with an audience and make a meaningful impact.
Here are some more great online resources to help you develop further:
- Advanced Public Speaking Institute (Tips )
- Toastmasters 5 tips for public speaking (YouTube)
- 10 Most Common Rookie Mistakes in Public Speaking – Terry Gault (Prezi Blog)
- The Power of your Hands – Allan Pease (TED)
- How to Sound Smart in your TED Talk − Will Stephen (TED)
- How I Overcame my Fear of Public Speaking − Danish Dhamani (TED)
EXERCISE 8.2
Take notes from the sources while you study them. Making written notes about points you want to remember is an effective way to promote deep learning. As you watch each of the videos, identify 2-3 key tips. If you are doing this activity in class, share your “top two” tips with classmates and make note of their “top two” tips in turn.
Then consider the value of the tips and strategies you’ve compiled. What makes them seem to work so well and, equally important, how could you feasibly incorporate them into your presentations to make them your own?
Step 3: Select, Practice and Assess your Progress
Now that you have identified strategies that you find effective and think might work for you, try putting them into practice. See if they add some extra “oomph” to your presentation style. Afterwards, either by engaging in self-reflection, or by asking for feedback, consider how well these strategies worked for you and whether you need to further hone, adapt, or change the way you used them.
Videos are helpful because they not only provide information, but visually demonstrate the ideas (both showing and telling); however, you can also learn from many books on the subject. Here are four classic books by public speaking experts designed to help you develop your own strong presentation skills. By focusing on aspects such as“voice,” or by getting you to create effective slideshows, they offer a range of practical, “tried and tested” approaches designed to help you build confidence, speak fluently, and hold an audience’s attention with relevant, well designed visuals.
- Lilyan Wilder, 7 Steps to Fearless Speaking offers a lively, straightforward “how to” approach to public speaking, paying special attention to what to do before you even get on stage to deliver your talk. In short, according to Lilyan Wilder, it’s all about preparation. Wilder’s seven steps have been used by many successful public figures, including George H.W. Bush, Oprah Winfrey, Fortune 500 CEO’s, as well as network anchors at CNN, CBS, and more!
- Lee LeFever, The Art of Explanation: Making your Ideas, Products, and Services Easier to Understand invites you to become an “explanation specialist” by using simple elements to motivate your audience and inspire them to say “yes!” to your designs and ideas.
- Garr Reynolds, PresentationZen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery provides a clear, easy-to-read set of tips for cutting through the noise and blather of modern life and reaching an audience through simple, pared-down slides and story-telling: two techniques that can help you connect with and inspire your audience in an authentic, genuine way.
- Nancy Duarte, Slide:ology: T he Art and Science of Creating Great Presentations looks to the role of presentation software in the visualization of ideas and information. Its goal is to turn you into a “visual thinker” so you can design presentation graphics that enable your audience to easily and effectively process data—an especially valuable skill for technical presenters who often have to convey complex data in meaningful ways to non-technical audiences.
EXERCISE 8.3 Build your repertoire
Visual Aids – PowerPoint Basics
Even the most dynamic speakers often make use of visual aids to accompany their presentation and help illustrate their ideas. Having well designed visuals as part of your presentation is one way for beginners and those honing their skills can add interest and audience engagement to their talks. PowerPoint is probably the most common form of visual aid used in presentations, so much discussion has been focused on the pros and cons of this medium. Indeed, a Google search of “death by PowerPoint” brings up over 90 million results!
While there are many other presentation tools out there that you should explore (and perhaps present to your classmates or colleagues in your own presentation!), PowerPoint is a standard workplace tool, so it would be wise to gain proficiency with it. The key concept to remember is that your visual aids should supplement and illustrate what you want to say to your audience.
PowerPoint Terminology
When designing a PowerPoint presentation, it is helpful to be familiar with key terminology used to discuss the various elements.
- Deck : the entire presentation (all the slides in the presentation; see Figure 8.2.1) .

- Gloss : what the speaker says about each slide. The speaker should not simply read what is on the slide. Slides should have minimal text in the form of key words and short bullet points. It might include key quotations. The speaker should elaborate on what is written or shown on the slide.
- Slide : one “page” of the presentation ( Figure 8.2.2 shows one slide from the deck above) with the various elements identified.
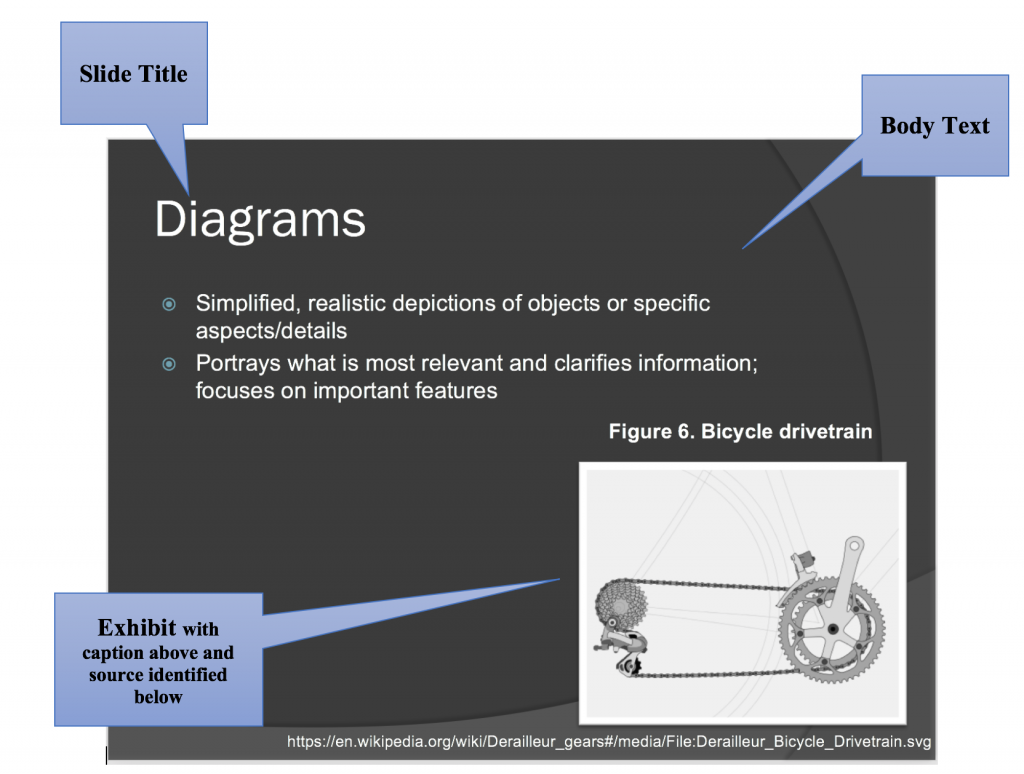
- Slide Titles : usually at the top of the slide, the titles acts as “headings” indicating the topic to be discussed in each slide.
- Body Text: written text on the slide, often in the form of bullet points or key terms. This text should be kept to a minimum (key words/phrases; quotations you want to read out loud). Don’t write your “script” in the slide’s body text.
- Exhibits : illustrative graphics on the slides that are glossed in the presentation. You should discuss graphics and explain what is important about them.
- Decorative Graphics : Slide motifs, themes, and other non-essential images that add visual appeal to the slides, but do not illustrate substantive ideas.
- Notes : The section underneath the slide where you can write notes you want to cover in your gloss. The audience will not see the “notes” portion.
Click on the Sample PowerPoint Presentations listed below to see detailed examples of PowerPoint decks.
Sample PowerPoint Presentations
PowerPoint Presentation on PRESENTATIONS [PPTX]
Tuckman’s Model of Team Formation – Sample student presentation [PPTX]
Definitions in Technical Writing – Sample student presentation [PPTX] (Created by Isaac Morton)
Visual Rhetoric
PowerPoint is not the only visual medium you might use. Pamphlets, posters, billboards, and other kinds of displays can also work to effectively convey your message if they are well designed. Considering how to present ideas visually can be as important as determining what to say. Here are some resources to help you design visual information in a rhetorically effective way:
- Visual Rhetoric page from the Online Writing Lab (OWL) at Purdue University
- Rule of Thirds (Wikipedia)
- Color theory (Tiger Color)
- Psychology of Font Choices (The Daily Egg)
Media Attributions
- Figure 8.2.1 PowerPoint Deck by Suzan Last is licensed under a CC BY 4.0 licence .
- Figure 8.2.2 PowerPoint slide. A modern road bicycle drivetrain with front and rear derailleurs embedded in slide by Keithonearth is licensed under a CC BY-SA 3.0 licence .
- R. Pausch, “Really achieving your childhood dreams, Sept. 18, 2007 Youtube [Online]: Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ji5_MqicxSo ↵
- R. Rigsby, “The wisdom of a third grade dropout will change your life,” Oct. 2017, Youtube [Online]. Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bg_Q7KYWG1g ↵
- H. Rosling, “The joy of stats,” Nov. 26, 2010, YouTube [Online]. Available: https://youtu.be/jbkSRLYSojo ↵
Technical Writing Essentials - H5P Edition Copyright © 2022 by Suzan Last and Monika Smith is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Know your stuff; do not read slides; time yourself and be ready to skip slides if time is short. Dress for success; speak clearly, loud enough and not too quickly; maintain eye contact with audience. Ask questions and stimulate thinking. Presentation is a story telling; be positive and keep it simple.
Introduction. Technical writing is a critical skill in the field of engineering, playing a pivotal role in effective. communication and knowledge dissemination. As engineers, the ability to convey complex ideas, procedures, and project details clearly and concisely is paramount. The Introduction section of the.
Part 5 (Technical style) highlights the imperative writing style and other features of technical writing such as the use of active and passive voices, plain vs. complex syntax, avoiding redundant or superfluous expressions, and vague generalities, using words or expressions with visual impact, the past tense to describe experimental work, the ...
This open textbook offers students of technical writing an introduction to the processes and products involved in professional, workplace, and technical writing. The text is broken up into sections reflecting key components of researching, developing, and producing a technical report. Readers will also learn about other professional communication, designing documents, and creating and ...
Clear& prompt interest. Provide an overview of the talk. Clearly express the purpose of the talk (and the project) •. •. •. Body of the talk: Follow the order established in the introduction Provide clear "road signs" Stay focused and on-message. Conclusion. Briefly summarize important points/results.
Body Text: written text on the slide, often in the form of bullet points or key terms. This text should be kept to a minimum (key words/phrases; quotations you want to read out loud). Don't write your "script" in the slide's body text. Exhibits : illustrative graphics on the slides that are glossed in the presentation.
Department of Computer Science Center for Visual Computing. How to Improve Technical Writing. • Practice, practice, practice, etc. • Read good articles and take notes (write down good words, sentences and memorize good structures) • Have people with better writing skills modify your draft or or help in different aspects • Fully ...
ENGL-2111 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document outlines a 16-week course on technical writing and presentation skills. It includes topics such as the concepts of written and verbal communication, styles of writing for different contexts, paragraph structure, revision, technical writing as an ...
Technical writing, presentation skills, and online communication : professional tools and insights Bookreader Item Preview ... Pdf_module_version 0.0.20 Ppi 360 Rcs_key 24143 Republisher_date 20230117163927 Republisher_operator [email protected] ...
1 Elements of Technical Writing The ability to communicate clearly is the most impor-tant skill engineers and scientists can have. Their best work will be lost if it is not communicated effec-tively. In this chapter, elements of the technical style of writing are examined. Technical writing differs in presentation and tone from other styles of ...
3. Adapt the technical report writing to the type of audience and objectives set. 4. Correctly present technical work in front of an audience of experts. 4. CONTEXT, TARGETS AND PRE-REQUISITES This course offers the basic concepts of technical communication in engineering, and is not currently taught in any of the bachelor degrees at the
This book addresses four main topics: professional ethics, technical writing, presentation skills, and online writing. These topics are woven throughout the book and some of them are the main subjects of one or more chapters. The overarching theme of this book is to provide well-tested, best-practice techniques and strategies for main topic areas while focusing on information that can be ...
When designing a PowerPoint presentation, it is helpful to be familiar with the key terminology used to discuss the various elements. Deck : The deck is the entire presentation (all the slides in the presentation; see Figure 9.2.1). Gloss : Gloss is what the speaker says about each slide.
9.1 Applying skills and techniques that will help build your confidence as a presenter. 9.2 Developing presentation skills by using a systematic process to practice delivery and use visual rhetoric. 9.3 Using software features and slide tools to design your presentation. 9.4 Using collaboration skills to effectively present as a team.
Course Title: Technical Writing and Presentation Skills Course Code: HSS-320 Pre-Requisites: Credit Hours Theory: 3 Credit Hours Lab (If Applicable): 0 Course Objectives: The main objective of this course is to develop effective writing and presentation skills in students. After learning effective data gathering, interpreting and presentation ...
8.2 Developing Presentation Skills Suzan Last and Monika Smith. Like any kind of advanced communication skill, the art of giving effective presentations is not in-born; it requires deliberate practice — that is, systematic practice that requires focused attention on improving, and making use of feedback from others to help you do so. An excellent way to learn more about delivering effective ...
The document discusses technical writing and presentation skills, defining technical writing as writing that conveys complex technical processes through various documents and formats. It outlines the purpose, objectives, characteristics, and skills needed for technical writing, including researching information, understanding audience perception, and having strong communication and technical ...
17. Technical Presentations and Demonstrations 141 Technical presentations 141 Setting demonstration objectives 144 Demonstrations 147 The sales cycle 151 18. Controlling the Audience 155 Handling interruptions 157 19. Handling the Media 158 Just before an interview - taking control 162 Preparing for an interview - the five-step preparation ...
This document outlines the objectives and skills covered in a technical writing and presentation skills course. The course aims to enhance language skills, develop critical thinking, and teach various types of writing including essays, reports, research papers, and proposals. It also focuses on developing strong presentation abilities. The document recommends textbooks on essay writing ...
8 8.2 Developing Presentation Skills Suzan Last and Monika Smith. Like any kind of advanced communication skill, the art of giving effective presentations is not in-born; it requires deliberate practice. An excellent way to learn more about delivering effective presentations is to follow a systematic process: Observe others
Slides should have minimal text in the form of key words and short bullet points. It might include key quotations. The speaker should elaborate on what is written or shown on the slide. Slide : one "page" of the presentation ( Figure 8.2.2 shows one slide from the deck above) with the various elements identified.
TECHNICAL WRITING AND. COMMUNICA TION SKILLS. Pr of G N PUROHIT. Head, Department of V eterinary. Gynecology an d Obstetrics, V eterinary College, B ikaner.
9. Suzan Last and Monika Smith. Like any kind of advanced communication skill, the art of giving effective presentations is not in-born; it requires deliberate practice — that is, systematic practice that requires focused attention on improving, and making use of feedback from others to help you do so. An excellent way to learn more about delivering effective presentations is to follow a ...