- Utility Menu

de5f0c5840276572324fc6e2ece1a882

- How to Use This Site
- Core Competencies
Research Presentation Rubric
The format of research presentations can vary across and within disciplines. Use this rubric (PDF) to identify and assess elements of research presentations, including delivery strategies and slide design. This resource focuses on research presentations but may be useful beyond.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- AEM Educ Train
- v.5(4); 2021 Aug

Leveling the field: Development of reliable scoring rubrics for quantitative and qualitative medical education research abstracts
Jaime jordan.
1 Department of Emergency Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles California, USA
2 Department of Emergency Medicine, Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles California, USA
Laura R. Hopson
3 Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Michigan, USA
Caroline Molins
4 AdventHealth Emergency Medicine Residency, Orlando Florida, USA
Suzanne K. Bentley
5 Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York New York, USA
Nicole M. Deiorio
6 Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, Richmond Virginia, USA
Sally A. Santen
7 University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati Ohio, USA
Lalena M. Yarris
8 Department of Emergency Medicine, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland Oregon, USA
Wendy C. Coates
Michael a. gisondi.
9 Department of Emergency Medicine, Stanford University, Palo Alto California, USA
Associated Data
Research abstracts are submitted for presentation at scientific conferences; however, criteria for judging abstracts are variable. We sought to develop two rigorous abstract scoring rubrics for education research submissions reporting (1) quantitative data and (2) qualitative data and then to collect validity evidence to support score interpretation.
We used a modified Delphi method to achieve expert consensus for scoring rubric items to optimize content validity. Eight education research experts participated in two separate modified Delphi processes, one to generate quantitative research items and one for qualitative. Modifications were made between rounds based on item scores and expert feedback. Homogeneity of ratings in the Delphi process was calculated using Cronbach's alpha, with increasing homogeneity considered an indication of consensus. Rubrics were piloted by scoring abstracts from 22 quantitative publications from AEM Education and Training “Critical Appraisal of Emergency Medicine Education Research” (11 highlighted for excellent methodology and 11 that were not) and 10 qualitative publications (five highlighted for excellent methodology and five that were not). Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) estimates of reliability were calculated.
Each rubric required three rounds of a modified Delphi process. The resulting quantitative rubric contained nine items: quality of objectives, appropriateness of methods, outcomes, data analysis, generalizability, importance to medical education, innovation, quality of writing, and strength of conclusions (Cronbach's α for the third round = 0.922, ICC for total scores during piloting = 0.893). The resulting qualitative rubric contained seven items: quality of study aims, general methods, data collection, sampling, data analysis, writing quality, and strength of conclusions (Cronbach's α for the third round = 0.913, ICC for the total scores during piloting = 0.788).
We developed scoring rubrics to assess quality in quantitative and qualitative medical education research abstracts to aid in selection for presentation at scientific meetings. Our tools demonstrated high reliability.
INTRODUCTION
The scientific abstract is the standard method for researchers to communicate brief written summaries of their findings. The written abstract is the gatekeeper for selection for presentation at professional society meetings. 1 A research presentation serves many purposes including dissemination of new knowledge, an opportunity for feedback, and the prospect of fostering an investigator's academic reputation. Beyond the presentation, abstracts, as written evidence of scientific conference proceedings, often endure through publication in peer‐reviewed journals. Because of the above, abstracts may be assessed in a number of potentially high‐stakes situations.
Abstracts are selected for presentation at conferences through a competitive process based on factors such as study rigor, importance of research findings, and relevance to the sponsoring professional society. Prior literature has shown poor observer agreement in the abstract selection process. 2 Scoring rubrics are often used to guide abstract reviewers in an attempt to standardize the process, reduce bias, support equity, and promote quality. 3 There are limited data describing the development and validity evidence of such scoring rubrics but the data available suggest that rubrics may be based on quality scoring tools for full research reports and published guidelines for abstracts. 2 , 4 , 5 Medical conferences often apply rubrics designed for judging clinical or basic science submissions, which reflect standard hypothesis‐testing methods and often use a single subjective Gestalt rating for quality decisions. 6 This may result in the systematic exclusion of studies that employ alternate, but equally rigorous methods, such as research in medical education. Existing scoring systems, commonly designed for biomedical research, may not accurately assess the scope, methods, and types of results commonly reported in medical education research abstracts, which may lead to a disproportionately high rate of rejection of these abstracts. There are additional challenges in reviewing qualitative research abstracts using a standard hypothesis‐testing rubric. In these qualitative studies, word‐count constraints may limit the author's ability to convey the study's outcome appropriately. 7 It is problematic for qualitative studies to be constrained to a standard quantitative abstract template, which may lead to low scores by those applying the rubric and a potential systematic bias against qualitative research.
Prior literature has described tools to assess quality in medical education research manuscripts, such as the Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument (MERSQI) and the Newcastle‐Ottawa Scale–Education (NOS‐E). 8 A limited attempt to utilize the MERSQI tool to retrospectively assess internal medicine medical education abstracts achieving manuscript publication showed increased scores for the journal abstract relative to the conference abstract. 4 However, the MERSQI and similar tools were not developed specifically for judging abstracts, and there is a lack of published validity evidence to support score interpretation based on these tools. To equitably assess the quality of education research abstracts to scholarly venues, which may have downstream effects on researcher scholarship, advancement, and reputation, there is a need for a rigorously developed abstract scoring rubric that is based on a validity evidence framework. 9 , 10
The aim of this paper is to describe the development and pilot testing of a dedicated rubric to assess the quality of both quantitative and qualitative medical education research studies. We describe the development process, which aimed to optimize content and response process validity, and initial internal structure and relation to other variables validity evidence to support score interpretation using these instruments. The rubrics may be of use to researchers developing studies and abstract and paper reviewers and may be applied to medical education research assessment in other specialties.
Study design
We utilized a modified Delphi technique to achieve consensus on items for a scoring rubric to assess quality of emergency medicine (EM) education research abstracts. The modified Delphi technique is a systematic group consensus strategy designed to increase content validity. 11 Through this method we developed individual rubrics to assess quantitative and qualitative EM medical education research abstracts. This study was approved by the institutional review board of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
Study setting and population
The first author identified eight EM education researchers with successful publication records from diverse regions across the United States and invited them to participate in the Delphi panel. Previous work has suggested that six to 10 experts is an appropriate number for obtaining stable results in the modified Delphi method. 12 , 13 , 14 All invited panelists agreed to participate. The panel included one assistant professor, two associate professors, and five professors. All panelists serve as reviewers for medical education journals and four hold editorial positions. We collected data in September and October 2020.
Study protocol
We followed Messick's framework for validity that includes five types of validity evidence; content, response process, internal structure, relation to other variables, and consequential. 15 Our study team drafted initial items for the scoring rubrics after a review of the literature and existing research abstract scoring rubrics to optimize content validity. We created separate items for research abstracts reporting quantitative and qualitative data. We sent the draft items to the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) education committee for review and comment to gather stakeholder feedback and for further content and response process validity evidence. 16 One author (JJ) who was not a member of the Delphi panel then revised the initial lists of items based on committee feedback to create the initial Delphi surveys. We used an electronic survey platform (SurveyMonkey) to administer and collect data from the Delphi surveys. 17 Experts on the Delphi panel rated the importance of including each item in a scoring rubric on a 1 to 9 Likert scale with 1 labeled as “not at all important” and 9 labeled as “extremely important.” The experts were invited to provide additional written comments, edits, and suggestions for each item. They were also encouraged to suggest additional items that they felt were important but not currently listed. We determined a priori that items with a mean score of 7 or greater advanced to the next round and items with a mean score of three or below were eliminated. The Delphi panel moderator (JJ) applied discretion for items scoring between 4 and 6, with the aim of both adhering to the opinions of the experts and creating a comprehensive scoring rubric. For example, if an item received a middle score but had comments supporting inclusion in a revised form, the moderator would make the suggested revisions and include the item in the next round.
Each item consisted of a stem and anchored choices with associated point‐value assignments. Panelists commented on the stems, content, and assigned point value of choices and provided narrative unstructured feedback. The moderator made modifications between rounds based on item scores and expert feedback. After each round, we provided panelists with aggregate mean item scores, written comments, and an edited version of the item list derived from the responses in the previous round. The panelists were then asked to rate the revised items and provide additional edits or suggestions.
We considered homogeneity of ratings in the Delphi process to be an indication of consensus. After consensus was achieved, we created final scoring rubrics for quantitative and qualitative medical education research abstracts. We then piloted the scoring rubrics to gather internal structure and further response process validity evidence. Five raters from the study group (JJ, LH, MG, CM, SB) participated in piloting. We piloted the final quantitative research rubric by scoring abstracts from publications identified in the most recent critical appraisal of EM education research by Academic Emergency Medicine / AEM Education and Training, “Critical Appraisal of Emergency Medicine Education Research: The Best Publications of 2016”. 18 All 11 papers highlighted for excellent methodology in this issue were included in the pilot. 18 Additionally, we included an equal number of randomly selected citations that were included in the issue but not selected as top papers, for a total of 22 quantitative publications. 18 Given the limited number of qualitative studies cited in this issue of the critical appraisal series, we chose to pilot the qualitative rubric on publications from this series from the last 5 years available (2012–2016). 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 We randomly selected one qualitative publication that was highlighted for excellent methodology and one that was not from each year for a total of 10 qualitative publications. 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 The same five raters who performed the quantitative pilot also conducted the qualitative pilot.
Data analysis
We calculated and reported descriptive statistics for item scoring during Delphi rounds. We used Cronbach's alpha to assess homogeneity of ratings in the Delphi process. Increasing homogeneity was considered to be an indication of consensus among the expert panelists. We used intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) estimates to assess reliability among raters during piloting based on a mean rating (κ = 5), absolute agreement, two‐way random‐effects model. We performed all analyses in SPSS (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 27.0).
Quantitative rubric
Three Delphi rounds were completed, each with 100% response rate. Mean item scores for each round are depicted in Table 1 . After the first round, three items were deleted, one item was added, and five items underwent wording changes. After the second round, one item was deleted and eight items underwent wording changes. After the third round items were reordered for flow and ease of use but no further changes were made to content or wording. Cronbach's alpha for the third round was 0.922, indicating high internal consistency. The final rubric contained nine items: quality of objectives, appropriateness of methods, outcomes, data analysis, generalizability, importance to medical education, innovation, quality of writing, and strength of conclusions (Data Supplement S1 , Appendix S1 , available as supporting information in the online version of this paper, which is available at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/aet2.10654/full ). The ICC for the total scores during piloting was 0.893, indicating excellent agreement. ICCs for individual rubric items ranged from 0.406 to 0.878 (Table 3 ).
Items and mean scores of expert review during Delphi process for quantitative scoring rubric
Inter‐rater reliability results during piloting
Qualitative rubric
Three Delphi rounds were completed, each with 100% response rate. Mean item scores for each round are depicted in Table 2 . After the first round 2 items were deleted, one item was added and nine items underwent wording changes. After the second round, three items were deleted and four underwent wording changes. After the third round no further changes were made. The resulting tool contained seven items reflecting the domains of quality of study aims, general methods, data collection, sampling, data analysis, writing quality, and strength of conclusions (Appendix S2 ). Cronbach's alpha for the third round was 0.913, indicating high internal consistency. ICC for the total scores during piloting was 0.788, indicating good agreement. The item on writing quality had an ICC of –0.301, likely due to the small scale of the item and sample size leading to limited variance. ICCs for the remainder of the items ranged from 0.176 to 0.897 (Table 3 ).
Items and mean scores of expert review during Delphi process for qualitative scoring rubric
We developed novel and distinct abstract scoring rubrics for assessing quantitative and qualitative medical education abstract quality through a Delphi process. It is important to evaluate medical education research abstracts that utilize accepted education methods as a distinctly different class than basic, clinical, and translational research. Through our Delphi and piloting processes we have provided multiple types of validity evidence in support of these rubrics aligned with Messick's framework including content, response process, and internal structure. 15 Similar to other tools assessing quality in medical education research, our rubrics assess aspects such as study design, sampling, data analysis, and outcomes that represent the underpinnings of rigorous research. 8 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 Unlike many medical education research assessments published in the literature, our tool was designed specifically for the assessment of abstracts rather than full‐text manuscripts, and therefore the specific item domains and characteristics reflect this unique purpose.
We deliberately created separate rubrics for abstracts reporting quantitative and qualitative data because each has unique methods. When designing a study, education researchers must decide the best method to address their questions. Often, in the exploratory phase of inquiry, a qualitative study is the most appropriate choice to identify key topics that merit further study. These often may be narrow in scope and may employ one or more qualitative methods (e.g., ethnography, focus groups, personal interviews). The careful and rigorous analysis may reveal points that can be studied later via quantitative methods to test a hypothesis gleaned during the qualitative phase. 27 Specific standards for reporting on qualitative research have been widely disseminated and are distinct from standards for reporting quantitative research. 28 Even an impeccably designed and executed qualitative study would fail to meet major criteria for excellent quantitative studies. For example, points may be subtracted for lack of generalizability or conduct of the qualitative study in multiple institutions as well as for the absence of common quantitative statistical analytics. The qualitative abstract itself may necessarily lack the common structure of a quantitative report and lead to a lower score. The obvious problem is that a well‐conducted study might not be shared with the relevant research community if it is judged according to quantitative standards. A similar outcome would occur if quantitative work were judged by qualitative standards; therefore, we advocate for using scoring rubrics specific to the type of research being assessed.
Our work has several possible applications. The rubrics we developed may be adopted as scoring tools for medical education research studies that are submitted for presentation to scientific conferences. The presence of specific scoring rubrics for medical education research may address disparities in acceptance rates and ensure presentation of rigorously conducted medical education research at scientific conferences. Further, publication of abstract scoring rubrics such as ours sets expectations for certain elements to be included and defines an acceptable level of submission quality. Dissemination and usage of the rubrics may therefore help improve research excellence. The rubrics themselves can serve as educational tools in resident and faculty training. For example, the rubrics could serve as illustrations or practice material in teaching how to prepare a strong abstract for submission. The inclusive wording of the items allows the rubrics to be adapted to medical education work in any medical specialty. Medical educators may also benefit from using the methods described here to create their own scoring rubrics or provide evidence‐based best practice approaches for other venues. Finally, this study provides a tool that could lay the groundwork for future scholarship on assessing the quality of educational research.
LIMITATIONS
Our study has several limitations. First, the modified Delphi technique is a consensus technique that can force agreement of respondents, and the existence of consensus does not denote a correct response. 11 Since the method is implemented electronically, there is limited discussion and elaboration. Second, the team of experts were all researchers in EM; therefore, the rubrics may not generalize to other specialties. The rubrics were intended for quantitative and qualitative education research abstract submission, so it may not perform well for abstracts that include both quantitative and qualitative data or those focused on early work, innovations, instrument development, validity evidence, or program evaluation. Finally, there are two limitations to the pilot testing. An a priori power calculation to determine sample size was not possible since the rubrics were novel. The ICCs of individual items on the scoring rubrics were variable and we chose not to eliminate items with low ICCs given the small sample size during piloting and a desire to create a tool comprehensive of key domains. Future studies of use of these tools incorporating larger samples may provide data for additional refinement. Faculty who piloted the rubrics were familiar with the constructs and rubrics, and it is not known how the rubrics would have performed with general abstract reviewers nor what training might be required. The success of separate rubrics may rely on the expertise of the reviewers in the methodology being assessed.
We offer two medical education abstract scoring rubrics with supporting preliminary reliability and validity evidence. Future studies could add additional validity evidence including use with trained and untrained reviewers and relationship to other variables, e.g., a comparison between rubric scores and expert judgment. Additional studies could be performed to provide consequential validity evidence by comparing the number and quality of accepted medical education abstracts before and after the rubric's implementation or whether the number of abstracts that eventually lead to publication increases.
CONCLUSIONS
Using the modified Delphi technique for consensus building, we developed two scoring rubrics to assess quality in quantitative and qualitative medical education research abstracts with supporting validity evidence. Application of these rubrics demonstrated high reliability.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have no potential conflicts to disclose.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Jaime Jordan and Michael A. Gisondi conceived the study. Jaime Jordan, Michael A. Gisondi, Laura R. Hopson, Caroline Molins, and Suzanne K. Bentley contributed to the design of the study. Jaime Jordan, Laura R. Hopson, Caroline Molins, Suzanne K. Bentley, Nicole M. Deiorio, Sally A. Santen, Lalena M. Yarris, Wendy C. Coates, and Michael A. Gisondi contributed to data collection. Jaime Jordan analyzed the data. Jaime Jordan, Laura R. Hopson, Caroline Molins, Suzanne K. Bentley, Nicole M. Deiorio, Sally A. Santen, Lalena M. Yarris, Wendy C. Coates, and Michael A. Gisondi contributed to drafting of the manuscript and critical revision.
Supporting information
Data Supplement S1 . Supplemental material.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge that this project originated to meet an SAEM Education Committee Objective and thank all the committee members for their support of this work.
Jordan J, Hopson LR, Molins C, et al. Leveling the field: Development of reliable scoring rubrics for quantitative and qualitative medical education research abstracts . AEM Educ Train . 2021; 5 :e10654. 10.1002/aet2.10654 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Presented at Society for Academic Emergency Medicine Virtual Meeting, May 13, 2021.
Supervising Editor: Esther H. Chen, MD.
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, creating and using rubrics.
A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly describes the instructor’s performance expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric identifies:
- criteria: the aspects of performance (e.g., argument, evidence, clarity) that will be assessed
- descriptors: the characteristics associated with each dimension (e.g., argument is demonstrable and original, evidence is diverse and compelling)
- performance levels: a rating scale that identifies students’ level of mastery within each criterion
Rubrics can be used to provide feedback to students on diverse types of assignments, from papers, projects, and oral presentations to artistic performances and group projects.
Benefitting from Rubrics
- reduce the time spent grading by allowing instructors to refer to a substantive description without writing long comments
- help instructors more clearly identify strengths and weaknesses across an entire class and adjust their instruction appropriately
- help to ensure consistency across time and across graders
- reduce the uncertainty which can accompany grading
- discourage complaints about grades
- understand instructors’ expectations and standards
- use instructor feedback to improve their performance
- monitor and assess their progress as they work towards clearly indicated goals
- recognize their strengths and weaknesses and direct their efforts accordingly
Examples of Rubrics
Here we are providing a sample set of rubrics designed by faculty at Carnegie Mellon and other institutions. Although your particular field of study or type of assessment may not be represented, viewing a rubric that is designed for a similar assessment may give you ideas for the kinds of criteria, descriptions, and performance levels you use on your own rubric.
- Example 1: Philosophy Paper This rubric was designed for student papers in a range of courses in philosophy (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Psychology Assignment Short, concept application homework assignment in cognitive psychology (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 3: Anthropology Writing Assignments This rubric was designed for a series of short writing assignments in anthropology (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 4: History Research Paper . This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in history (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 1: Capstone Project in Design This rubric describes the components and standards of performance from the research phase to the final presentation for a senior capstone project in design (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Engineering Design Project This rubric describes performance standards for three aspects of a team project: research and design, communication, and team work.
Oral Presentations
- Example 1: Oral Exam This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam in an upper-division course in history (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Oral Communication This rubric is adapted from Huba and Freed, 2000.
- Example 3: Group Presentations This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing group presentations in history (Carnegie Mellon).
Class Participation/Contributions
- Example 1: Discussion Class This rubric assesses the quality of student contributions to class discussions. This is appropriate for an undergraduate-level course (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Advanced Seminar This rubric is designed for assessing discussion performance in an advanced undergraduate or graduate seminar.
See also " Examples and Tools " section of this site for more rubrics.
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links
Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.
How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Fall 2022)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.

Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper, single-point rubric, more examples:.
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!
15 Helpful Scoring Rubric Examples for All Grades and Subjects
In the end, they actually make grading easier.

When it comes to student assessment and evaluation, there are a lot of methods to consider. In some cases, testing is the best way to assess a student’s knowledge, and the answers are either right or wrong. But often, assessing a student’s performance is much less clear-cut. In these situations, a scoring rubric is often the way to go, especially if you’re using standards-based grading . Here’s what you need to know about this useful tool, along with lots of rubric examples to get you started.
What is a scoring rubric?
In the United States, a rubric is a guide that lays out the performance expectations for an assignment. It helps students understand what’s required of them, and guides teachers through the evaluation process. (Note that in other countries, the term “rubric” may instead refer to the set of instructions at the beginning of an exam. To avoid confusion, some people use the term “scoring rubric” instead.)
A rubric generally has three parts:
- Performance criteria: These are the various aspects on which the assignment will be evaluated. They should align with the desired learning outcomes for the assignment.
- Rating scale: This could be a number system (often 1 to 4) or words like “exceeds expectations, meets expectations, below expectations,” etc.
- Indicators: These describe the qualities needed to earn a specific rating for each of the performance criteria. The level of detail may vary depending on the assignment and the purpose of the rubric itself.
Rubrics take more time to develop up front, but they help ensure more consistent assessment, especially when the skills being assessed are more subjective. A well-developed rubric can actually save teachers a lot of time when it comes to grading. What’s more, sharing your scoring rubric with students in advance often helps improve performance . This way, students have a clear picture of what’s expected of them and what they need to do to achieve a specific grade or performance rating.
Learn more about why and how to use a rubric here.
Types of Rubric
There are three basic rubric categories, each with its own purpose.
Holistic Rubric

Source: Cambrian College
This type of rubric combines all the scoring criteria in a single scale. They’re quick to create and use, but they have drawbacks. If a student’s work spans different levels, it can be difficult to decide which score to assign. They also make it harder to provide feedback on specific aspects.
Traditional letter grades are a type of holistic rubric. So are the popular “hamburger rubric” and “ cupcake rubric ” examples. Learn more about holistic rubrics here.
Analytic Rubric
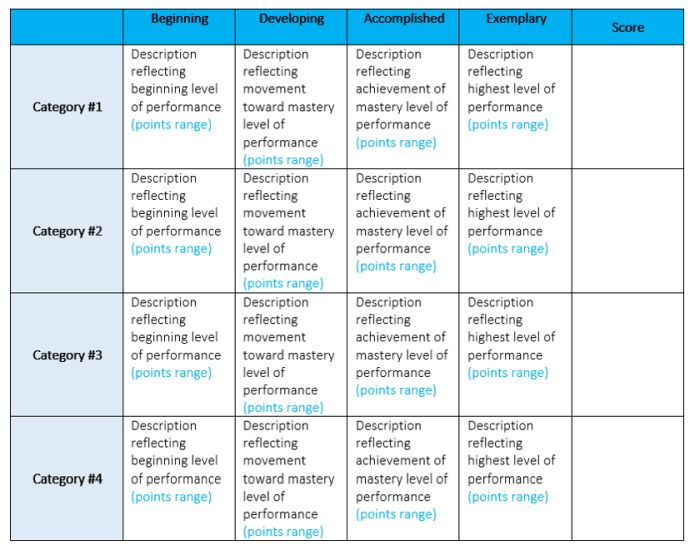
Source: University of Nebraska
Analytic rubrics are much more complex and generally take a great deal more time up front to design. They include specific details of the expected learning outcomes, and descriptions of what criteria are required to meet various performance ratings in each. Each rating is assigned a point value, and the total number of points earned determines the overall grade for the assignment.
Though they’re more time-intensive to create, analytic rubrics actually save time while grading. Teachers can simply circle or highlight any relevant phrases in each rating, and add a comment or two if needed. They also help ensure consistency in grading, and make it much easier for students to understand what’s expected of them.
Learn more about analytic rubrics here.
Developmental Rubric
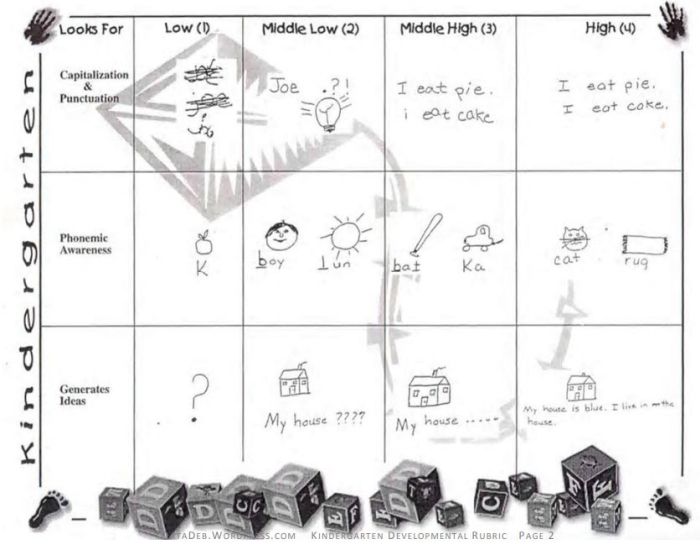
Source: Deb’s Data Digest
A developmental rubric is a type of analytic rubric, but it’s used to assess progress along the way rather than determining a final score on an assignment. The details in these rubrics help students understand their achievements, as well as highlight the specific skills they still need to improve.
Developmental rubrics are essentially a subset of analytic rubrics. They leave off the point values, though, and focus instead on giving feedback using the criteria and indicators of performance.
Learn how to use developmental rubrics here.
Ready to create your own rubrics? Find general tips on designing rubrics here. Then, check out these examples across all grades and subjects to inspire you.
Elementary School Rubric Examples
These elementary school rubric examples come from real teachers who use them with their students. Adapt them to fit your needs and grade level.
Reading Fluency Rubric
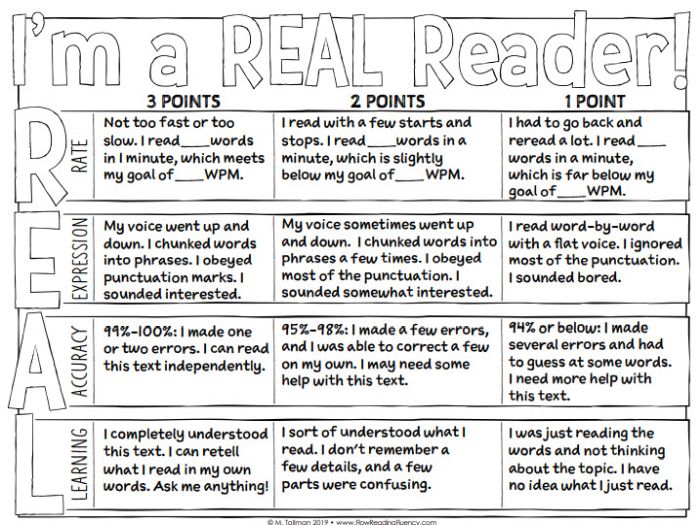
You can use this one as an analytic rubric by counting up points to earn a final score, or just to provide developmental feedback. There’s a second rubric page available specifically to assess prosody (reading with expression).
Learn more: Teacher Thrive
Reading Comprehension Rubric
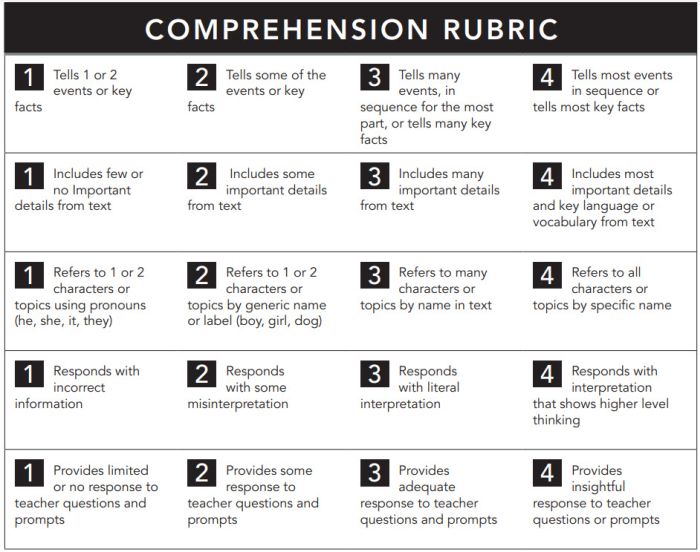
The nice thing about this rubric is that you can use it at any grade level, for any text. If you like this style, you can get a reading fluency rubric here too.
Learn more: Pawprints Resource Center
Written Response Rubric

Rubrics aren’t just for huge projects. They can also help kids work on very specific skills, like this one for improving written responses on assessments.
Learn more: Dianna Radcliffe: Teaching Upper Elementary and More
Interactive Notebook Rubric
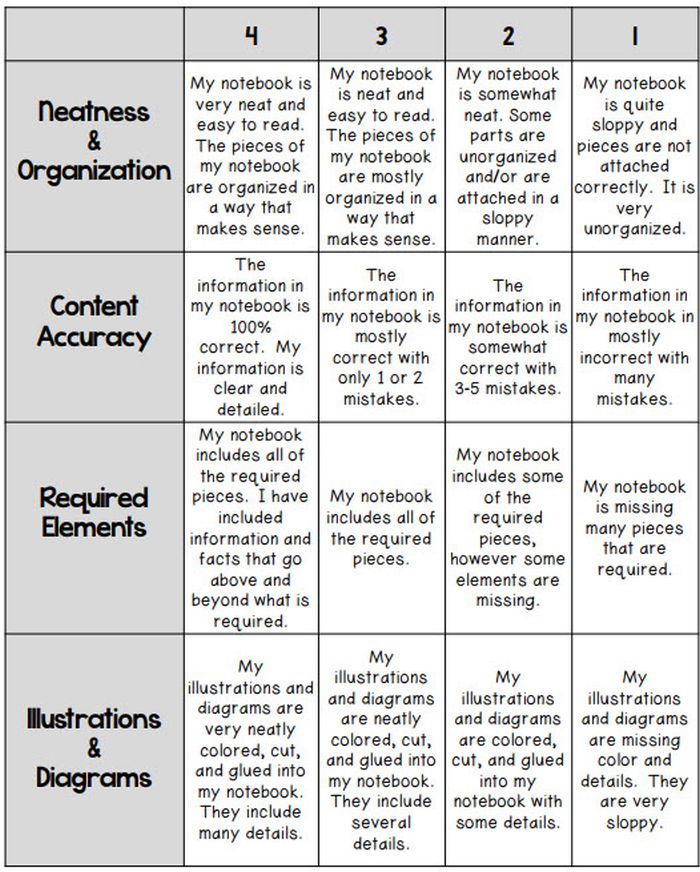
If you use interactive notebooks as a learning tool , this rubric can help kids stay on track and meet your expectations.
Learn more: Classroom Nook
Project Rubric
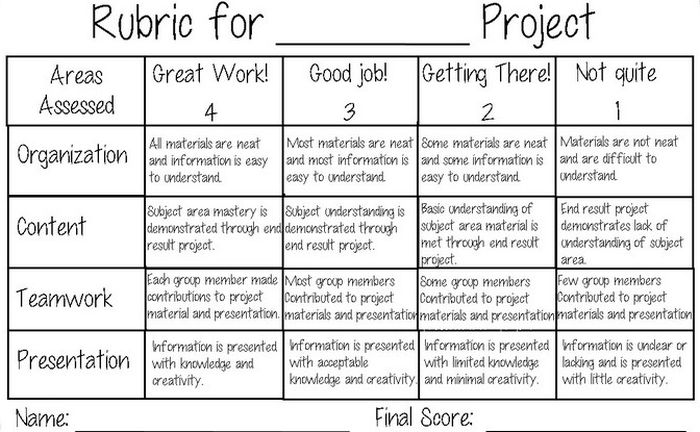
Use this simple rubric as it is, or tweak it to include more specific indicators for the project you have in mind.
Learn more: Tales of a Title One Teacher
Behavior Rubric
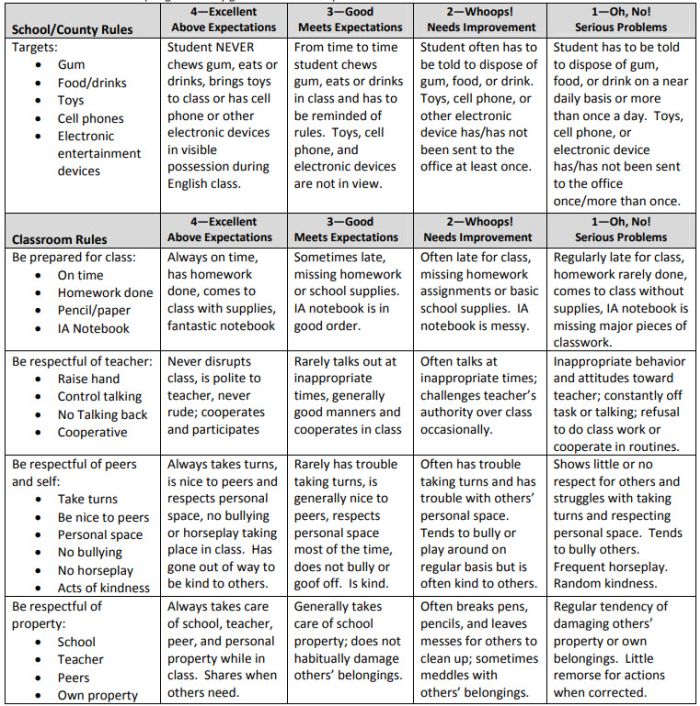
Developmental rubrics are perfect for assessing behavior and helping students identify opportunities for improvement. Send these home regularly to keep parents in the loop.
Learn more: Teachers.net Gazette
Middle School Rubric Examples
In middle school, use rubrics to offer detailed feedback on projects, presentations, and more. Be sure to share them with students in advance, and encourage them to use them as they work so they’ll know if they’re meeting expectations.
Argumentative Writing Rubric
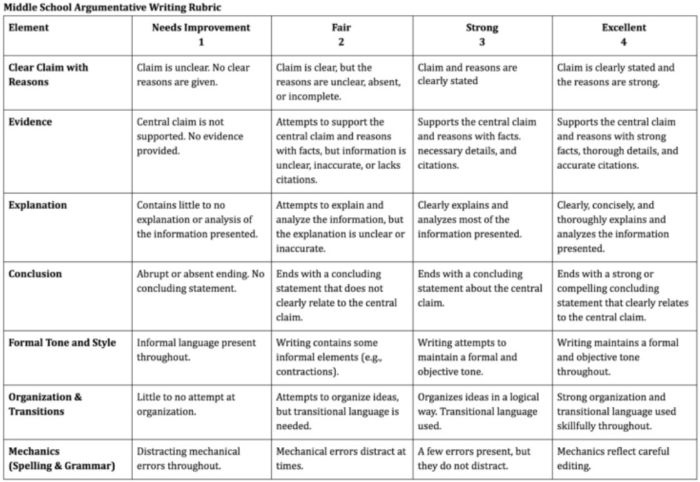
Argumentative writing is a part of language arts, social studies, science, and more. That makes this rubric especially useful.
Learn more: Dr. Caitlyn Tucker
Role-Play Rubric
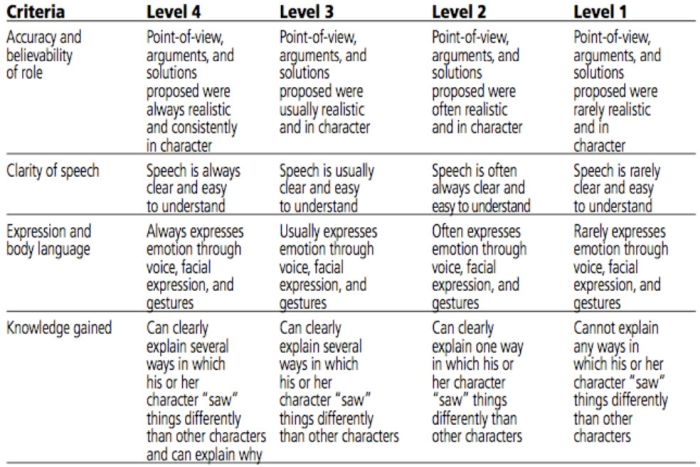
Role-plays can be really useful when teaching social and critical thinking skills, but it’s hard to assess them. Try a rubric like this one to evaluate and provide useful feedback.
Learn more: A Question of Influence
Art Project Rubric
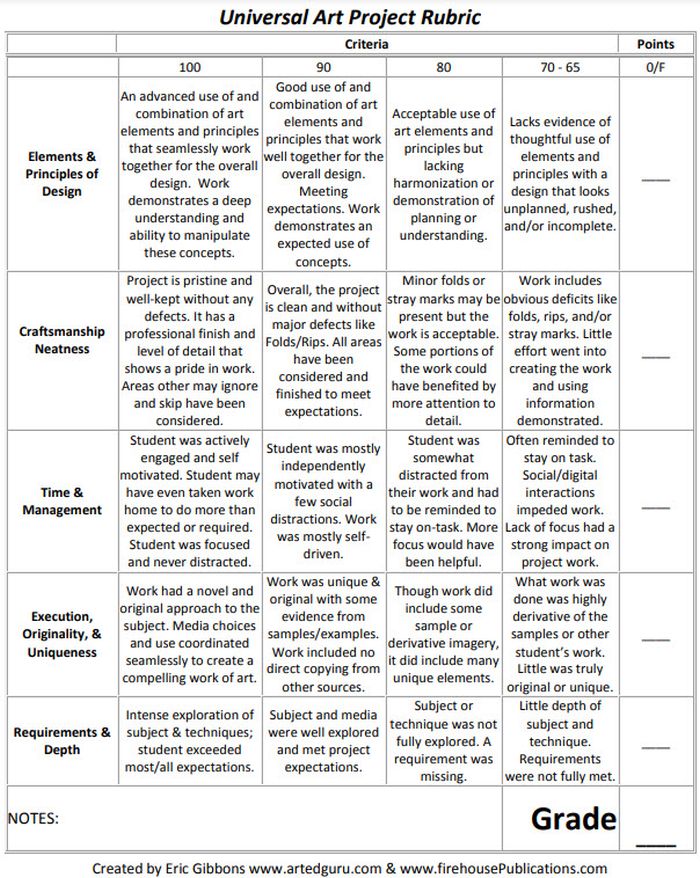
Art is one of those subjects where grading can feel very subjective. Bring some objectivity to the process with a rubric like this.
Source: Art Ed Guru
Diorama Project Rubric
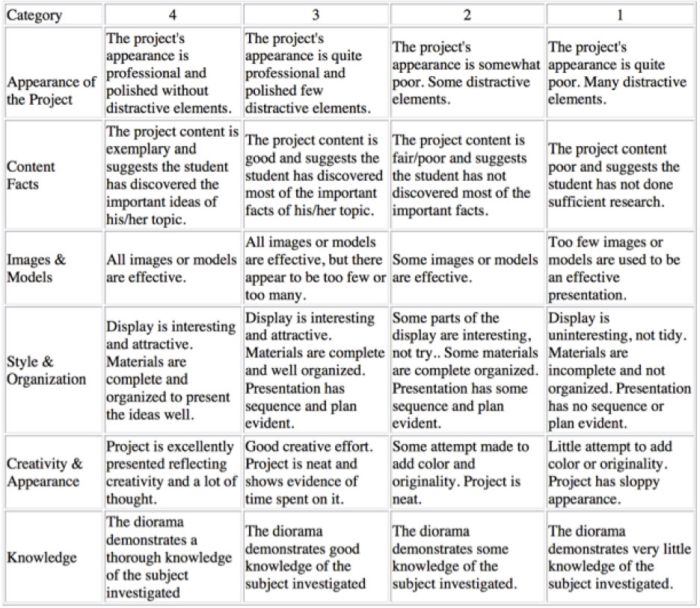
You can use diorama projects in almost any subject, and they’re a great chance to encourage creativity. Simplify the grading process and help kids know how to make their projects shine with this scoring rubric.
Learn more: Historyourstory.com
Oral Presentation Rubric
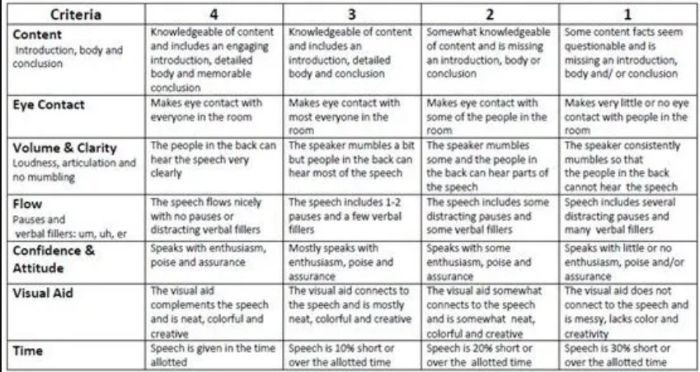
Rubrics are terrific for grading presentations, since you can include a variety of skills and other criteria. Consider letting students use a rubric like this to offer peer feedback too.
Learn more: Bright Hub Education
High School Rubric Examples
In high school, it’s important to include your grading rubrics when you give assignments like presentations, research projects, or essays. Kids who go on to college will definitely encounter rubrics, so helping them become familiar with them now will help in the future.
Presentation Rubric
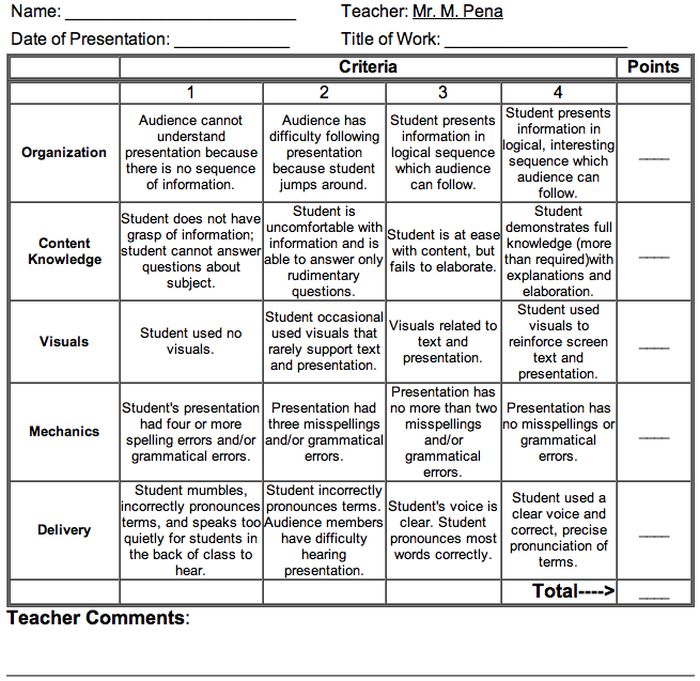
Analyze a student’s presentation both for content and communication skills with a rubric like this one. If needed, create a separate one for content knowledge with even more criteria and indicators.
Learn more: Michael A. Pena Jr.
Debate Rubric
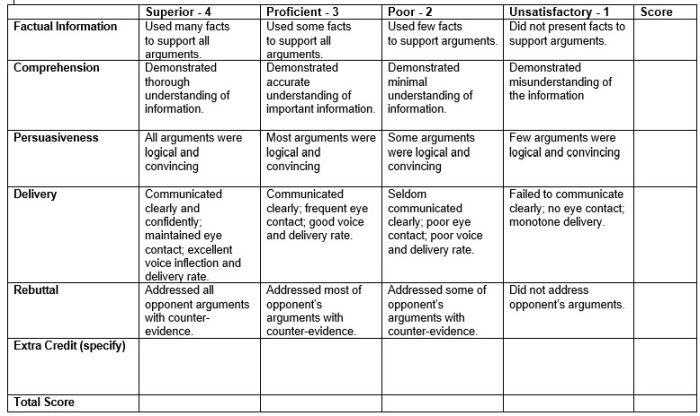
Debate is a valuable learning tool that encourages critical thinking and oral communication skills. This rubric can help you assess those skills objectively.
Learn more: Education World
Project-Based Learning Rubric
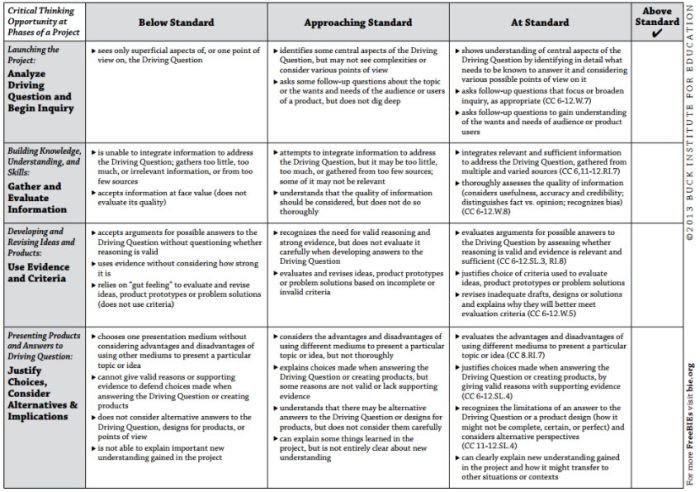
Implementing project-based learning can be time-intensive, but the payoffs are worth it. Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier.
Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers
100-Point Essay Rubric
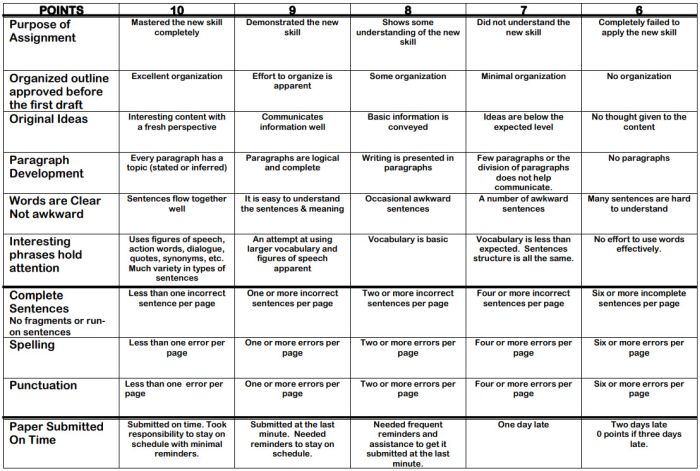
Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points.
Learn more: Learn for Your Life
Drama Performance Rubric
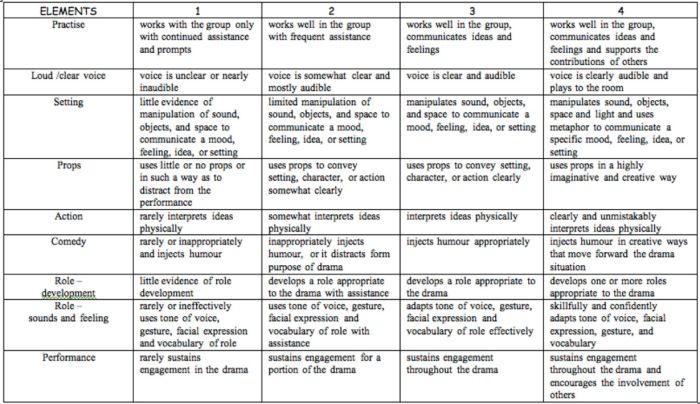
If you’re unsure how to grade a student’s participation and performance in drama class, consider this example. It offers lots of objective criteria and indicators to evaluate.
Learn more: Chase March
How do you use rubrics in your classroom? Come share your thoughts and exchange ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, 25 of the best alternative assessment ideas ..

You Might Also Like

How To Get Started With Interactive Notebooks (Plus 25 Terrific Examples)
It's so much more than a place to take notes during class. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Center for Excellence in Teaching
Home > Resources > Group presentation rubric
Group presentation rubric
This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students’ work on this type of assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a particular assignment. Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before submitting their assignment.
Download this file
Download this file [63.74 KB]
Back to Resources Page

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The goal of this rubric is to identify and assess elements of research presentations, including delivery strategies and slide design. • Self-assessment: Record yourself presenting your talk using your computer's pre-downloaded recording software or by using the coach in Microsoft PowerPoint. Then review your recording, fill in the rubric ...
presentation. 10 Information is presented in a logical sequence. 5 Conclusion succinctly summarizes the presentation to reiterate how the main points support the purpose/central thesis. 10 Content (30 points) Technical terms are well-defined in language appropriate for the target audience 5 Presentation demonstrates substance and depth. 10
Audience members have difficulty hearing presentation. Presenter mumbles, talks very fast, and speaks too quietly for a majority of students to hear & understand. Timing 4 - Exceptional 3 - Admirable 2 - Acceptable 1 - Poor. Length of Presentation Within two minutes of allotted time +/-. Within four minutes of allotted time +/-.
AP® Research — Presentation and Oral Defense 2021 Scoring Guidelines. NOTE: To receive the highest performance level presumes that the student also achieved the preceding performance levels in that row. ADDITIONAL SCORES: In addition to the scores represented on the rubric, teachers can also assign scores of 0 (zero). A score of. A score of.
Grading rubric for research proposals - oral presentation (15%) Grade component Mostly not true Partly true Mostly true Completely true Background (15%) 0-6% 9% 12% 15% • The literature review is comprehensive and describes relevant material. • The purpose of the study is clearly described. Specific aims (10%) 0-4% 6% 8% 10%
Oral Presentation Rubric 4—Excellent 3—Good 2—Fair 1—Needs Improvement Delivery • Holds attention of entire audience with the use of direct eye contact, seldom looking at notes • Speaks with fluctuation in volume and inflection to maintain audience interest and emphasize key points • Consistent use of direct eye contact with ...
Oral Presentation: Scoring Guide. 4 points - Clear organization, reinforced by media. Stays focused throughout. 3 points - Mostly organized, but loses focus once or twice. 2 points - Somewhat organized, but loses focus 3 or more times. 1 point - No clear organization to the presentation. 3 points - Incorporates several course concepts ...
Title: Scoring Rubric for Oral Presentations: Example #1 Author: Testing and Evaluation Services Created Date: 8/10/2017 9:45:03 AM
The format of research presentations can vary across and within disciplines. Use this rubric (PDF) to identify and assess elements of research presentations, including delivery strategies and slide design. This resource focuses on research presentations but may be useful beyond.
Art History 153 Presentations Grading Rubric. Research question is clear and relevant. Working thesis is clear, creative, and fits the evidence presented. Research question and thesis are mostly clear. Thesis is somewhat creative and mostly fits the evidence. Research question and thesis are articulated. Thesis is not creative or does not fit ...
Organization. Logical, interesting, clearly delineated themes and ideas. Generally clear, overall easy for audience to follow. Overall organized but sequence is difficult to follow. Difficult to follow, confusing sequence of information. No clear organization to material, themes and ideas are disjointed. Evaluation.
Scoring Rubric for Oral Scientific Presentations. Level of Achievement. Excellent 16-20 points. Good 11-15 points. Marginal 6-10 points. Inadequate 0-5 points. Organization. Well thought out with logical progression. Use of proper language.
Scoring Rubric for Oral Presentation/Written Summary of Scientific Research Papers (for written omit Style/Delivery column) Adapted from Brewer, C.A., and D. Ebert-May. 1998. Hearing the case for genetic engineering: breaking down the barriers of anonymity through student hearings in the large lecture hall.
The rubrics we developed may be adopted as scoring tools for medical education research studies that are submitted for presentation to scientific conferences. The presence of specific scoring rubrics for medical education research may address disparities in acceptance rates and ensure presentation of rigorously conducted medical education ...
Example 4: History Research Paper. This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in history (Carnegie Mellon). Projects. Example 1: Capstone Project in Design This rubric describes the components and standards of performance from the research phase to the final presentation for a senior capstone project in design (Carnegie Mellon).
presentation contains multiple fact errors Topic would benefit from more focus; presentation contains some fact errors or omissions Topic is adequately focused and relevant; major facts are accurate and generally complete Topic is tightly focused and relevant; presentation contains accurate information with no fact errors
Step 7: Create your rubric. Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle.
GRADING RUBRIC FOR A RESEARCH PAPER—ANY DISCIPLINE. *exceptional introduction that grabs interest of reader and states topic. **thesis is exceptionally clear, arguable, well-developed, and a definitive statement. *paper is exceptionally researched, extremely detailed, and historically accurate. **information clearly relates to the thesis.
Oral Presentation Rubric. Rubrics are terrific for grading presentations, since you can include a variety of skills and other criteria. ... In high school, it's important to include your grading rubrics when you give assignments like presentations, research projects, or essays. Kids who go on to college will definitely encounter rubrics, so ...
Group presentation rubric. This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students' work on this type of assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a particular assignment. Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before submitting their assignment.
Research Paper Scoring Rubric Ideas Points 1-10 Has a well-developed thesis that conveys a perspective on the subject Poses relevant and tightly drawn questions about the topic; excludes extraneous details and inappropriate information Records important ideas, concepts, and direct quotations from a variety of reliable