
Research Topics & Ideas: Education
170+ Research Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project

If you’re just starting out exploring education-related topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of research topics and ideas , including examples from actual dissertations and theses..
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan of action to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .
Overview: Education Research Topics
- How to find a research topic (video)
- List of 50+ education-related research topics/ideas
- List of 120+ level-specific research topics
- Examples of actual dissertation topics in education
- Tips to fast-track your topic ideation (video)
- Free Webinar : Topic Ideation 101
- Where to get extra help
Education-Related Research Topics & Ideas
Below you’ll find a list of education-related research topics and idea kickstarters. These are fairly broad and flexible to various contexts, so keep in mind that you will need to refine them a little. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.
- The impact of school funding on student achievement
- The effects of social and emotional learning on student well-being
- The effects of parental involvement on student behaviour
- The impact of teacher training on student learning
- The impact of classroom design on student learning
- The impact of poverty on education
- The use of student data to inform instruction
- The role of parental involvement in education
- The effects of mindfulness practices in the classroom
- The use of technology in the classroom
- The role of critical thinking in education
- The use of formative and summative assessments in the classroom
- The use of differentiated instruction in the classroom
- The use of gamification in education
- The effects of teacher burnout on student learning
- The impact of school leadership on student achievement
- The effects of teacher diversity on student outcomes
- The role of teacher collaboration in improving student outcomes
- The implementation of blended and online learning
- The effects of teacher accountability on student achievement
- The effects of standardized testing on student learning
- The effects of classroom management on student behaviour
- The effects of school culture on student achievement
- The use of student-centred learning in the classroom
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on student outcomes
- The achievement gap in minority and low-income students
- The use of culturally responsive teaching in the classroom
- The impact of teacher professional development on student learning
- The use of project-based learning in the classroom
- The effects of teacher expectations on student achievement
- The use of adaptive learning technology in the classroom
- The impact of teacher turnover on student learning
- The effects of teacher recruitment and retention on student learning
- The impact of early childhood education on later academic success
- The impact of parental involvement on student engagement
- The use of positive reinforcement in education
- The impact of school climate on student engagement
- The role of STEM education in preparing students for the workforce
- The effects of school choice on student achievement
- The use of technology in the form of online tutoring
Level-Specific Research Topics
Looking for research topics for a specific level of education? We’ve got you covered. Below you can find research topic ideas for primary, secondary and tertiary-level education contexts. Click the relevant level to view the respective list.
Research Topics: Pick An Education Level
Primary education.
- Investigating the effects of peer tutoring on academic achievement in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of mindfulness practices in primary school classrooms
- Examining the effects of different teaching strategies on primary school students’ problem-solving skills
- The use of storytelling as a teaching strategy in primary school literacy instruction
- The role of cultural diversity in promoting tolerance and understanding in primary schools
- The impact of character education programs on moral development in primary school students
- Investigating the use of technology in enhancing primary school mathematics education
- The impact of inclusive curriculum on promoting equity and diversity in primary schools
- The impact of outdoor education programs on environmental awareness in primary school students
- The influence of school climate on student motivation and engagement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of early literacy interventions on reading comprehension in primary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student achievement in primary schools
- Exploring the benefits of inclusive education for students with special needs in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of teacher-student feedback on academic motivation in primary schools
- The role of technology in developing digital literacy skills in primary school students
- Effective strategies for fostering a growth mindset in primary school students
- Investigating the role of parental support in reducing academic stress in primary school children
- The role of arts education in fostering creativity and self-expression in primary school students
- Examining the effects of early childhood education programs on primary school readiness
- Examining the effects of homework on primary school students’ academic performance
- The role of formative assessment in improving learning outcomes in primary school classrooms
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on academic outcomes in primary school
- Investigating the effects of classroom environment on student behavior and learning outcomes in primary schools
- Investigating the role of creativity and imagination in primary school curriculum
- The impact of nutrition and healthy eating programs on academic performance in primary schools
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on primary school students’ well-being and academic performance
- The role of parental involvement in academic achievement of primary school children
- Examining the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior in primary school
- The role of school leadership in creating a positive school climate Exploring the benefits of bilingual education in primary schools
- The effectiveness of project-based learning in developing critical thinking skills in primary school students
- The role of inquiry-based learning in fostering curiosity and critical thinking in primary school students
- The effects of class size on student engagement and achievement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of recess and physical activity breaks on attention and learning in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of outdoor play in developing gross motor skills in primary school children
- The effects of educational field trips on knowledge retention in primary school students
- Examining the effects of inclusive classroom practices on students’ attitudes towards diversity in primary schools
- The impact of parental involvement in homework on primary school students’ academic achievement
- Investigating the effectiveness of different assessment methods in primary school classrooms
- The influence of physical activity and exercise on cognitive development in primary school children
- Exploring the benefits of cooperative learning in promoting social skills in primary school students
Secondary Education
- Investigating the effects of school discipline policies on student behavior and academic success in secondary education
- The role of social media in enhancing communication and collaboration among secondary school students
- The impact of school leadership on teacher effectiveness and student outcomes in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of technology integration on teaching and learning in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of interdisciplinary instruction in promoting critical thinking skills in secondary schools
- The impact of arts education on creativity and self-expression in secondary school students
- The effectiveness of flipped classrooms in promoting student learning in secondary education
- The role of career guidance programs in preparing secondary school students for future employment
- Investigating the effects of student-centered learning approaches on student autonomy and academic success in secondary schools
- The impact of socio-economic factors on educational attainment in secondary education
- Investigating the impact of project-based learning on student engagement and academic achievement in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of multicultural education on cultural understanding and tolerance in secondary schools
- The influence of standardized testing on teaching practices and student learning in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior and academic engagement in secondary education
- The influence of teacher professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of extracurricular activities in promoting holistic development and well-roundedness in secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models on student engagement and achievement in secondary education
- The role of physical education in promoting physical health and well-being among secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of gender on academic achievement and career aspirations in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of multicultural literature in promoting cultural awareness and empathy among secondary school students
- The impact of school counseling services on student mental health and well-being in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of vocational education and training in preparing secondary school students for the workforce
- The role of digital literacy in preparing secondary school students for the digital age
- The influence of parental involvement on academic success and well-being of secondary school students
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on secondary school students’ well-being and academic success
- The role of character education in fostering ethical and responsible behavior in secondary school students
- Examining the effects of digital citizenship education on responsible and ethical technology use among secondary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of educational technology in promoting personalized learning experiences in secondary schools
- The impact of inclusive education on the social and academic outcomes of students with disabilities in secondary schools
- The influence of parental support on academic motivation and achievement in secondary education
- The role of school climate in promoting positive behavior and well-being among secondary school students
- Examining the effects of peer mentoring programs on academic achievement and social-emotional development in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of teacher-student relationships on student motivation and achievement in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning programs in promoting civic engagement among secondary school students
- The impact of educational policies on educational equity and access in secondary education
- Examining the effects of homework on academic achievement and student well-being in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of different assessment methods on student performance in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of single-sex education on academic performance and gender stereotypes in secondary schools
- The role of mentoring programs in supporting the transition from secondary to post-secondary education
Tertiary Education
- The role of student support services in promoting academic success and well-being in higher education
- The impact of internationalization initiatives on students’ intercultural competence and global perspectives in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of active learning classrooms and learning spaces on student engagement and learning outcomes in tertiary education
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning experiences in fostering civic engagement and social responsibility in higher education
- The influence of learning communities and collaborative learning environments on student academic and social integration in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of undergraduate research experiences in fostering critical thinking and scientific inquiry skills
- Investigating the effects of academic advising and mentoring on student retention and degree completion in higher education
- The role of student engagement and involvement in co-curricular activities on holistic student development in higher education
- The impact of multicultural education on fostering cultural competence and diversity appreciation in higher education
- The role of internships and work-integrated learning experiences in enhancing students’ employability and career outcomes
- Examining the effects of assessment and feedback practices on student learning and academic achievement in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty-student relationships on student success and well-being in tertiary education
- The impact of college transition programs on students’ academic and social adjustment to higher education
- The impact of online learning platforms on student learning outcomes in higher education
- The impact of financial aid and scholarships on access and persistence in higher education
- The influence of student leadership and involvement in extracurricular activities on personal development and campus engagement
- Exploring the benefits of competency-based education in developing job-specific skills in tertiary students
- Examining the effects of flipped classroom models on student learning and retention in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of online collaboration and virtual team projects in developing teamwork skills in tertiary students
- Investigating the effects of diversity and inclusion initiatives on campus climate and student experiences in tertiary education
- The influence of study abroad programs on intercultural competence and global perspectives of college students
- Investigating the effects of peer mentoring and tutoring programs on student retention and academic performance in tertiary education
- Investigating the effectiveness of active learning strategies in promoting student engagement and achievement in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models and hybrid courses on student learning and satisfaction in higher education
- The role of digital literacy and information literacy skills in supporting student success in the digital age
- Investigating the effects of experiential learning opportunities on career readiness and employability of college students
- The impact of e-portfolios on student reflection, self-assessment, and showcasing of learning in higher education
- The role of technology in enhancing collaborative learning experiences in tertiary classrooms
- The impact of research opportunities on undergraduate student engagement and pursuit of advanced degrees
- Examining the effects of competency-based assessment on measuring student learning and achievement in tertiary education
- Examining the effects of interdisciplinary programs and courses on critical thinking and problem-solving skills in college students
- The role of inclusive education and accessibility in promoting equitable learning experiences for diverse student populations
- The role of career counseling and guidance in supporting students’ career decision-making in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty diversity and representation on student success and inclusive learning environments in higher education

Education-Related Dissertations & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic in education, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses in the education space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of education-related research projects to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- From Rural to Urban: Education Conditions of Migrant Children in China (Wang, 2019)
- Energy Renovation While Learning English: A Guidebook for Elementary ESL Teachers (Yang, 2019)
- A Reanalyses of Intercorrelational Matrices of Visual and Verbal Learners’ Abilities, Cognitive Styles, and Learning Preferences (Fox, 2020)
- A study of the elementary math program utilized by a mid-Missouri school district (Barabas, 2020)
- Instructor formative assessment practices in virtual learning environments : a posthumanist sociomaterial perspective (Burcks, 2019)
- Higher education students services: a qualitative study of two mid-size universities’ direct exchange programs (Kinde, 2020)
- Exploring editorial leadership : a qualitative study of scholastic journalism advisers teaching leadership in Missouri secondary schools (Lewis, 2020)
- Selling the virtual university: a multimodal discourse analysis of marketing for online learning (Ludwig, 2020)
- Advocacy and accountability in school counselling: assessing the use of data as related to professional self-efficacy (Matthews, 2020)
- The use of an application screening assessment as a predictor of teaching retention at a midwestern, K-12, public school district (Scarbrough, 2020)
- Core values driving sustained elite performance cultures (Beiner, 2020)
- Educative features of upper elementary Eureka math curriculum (Dwiggins, 2020)
- How female principals nurture adult learning opportunities in successful high schools with challenging student demographics (Woodward, 2020)
- The disproportionality of Black Males in Special Education: A Case Study Analysis of Educator Perceptions in a Southeastern Urban High School (McCrae, 2021)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, in order for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic within education, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

You Might Also Like:

66 Comments
This is an helpful tool 🙏
Special education
Really appreciated by this . It is the best platform for research related items
Research title related to school of students
How are you
I think this platform is actually good enough.
Research title related to students
My field is research measurement and evaluation. Need dissertation topics in the field
Assalam o Alaikum I’m a student Bs educational Resarch and evaluation I’m confused to choose My thesis title please help me in choose the thesis title
Good idea I’m going to teach my colleagues
You can find our list of nursing-related research topic ideas here: https://gradcoach.com/research-topics-nursing/
Write on action research topic, using guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
Thanks a lot
I learned a lot from this site, thank you so much!
Thank you for the information.. I would like to request a topic based on school major in social studies
parental involvement and students academic performance
Science education topics?
plz tell me if you got some good topics, im here for finding research topic for masters degree
How about School management and supervision pls.?
Hi i am an Deputy Principal in a primary school. My wish is to srudy foe Master’s degree in Education.Please advice me on which topic can be relevant for me. Thanks.
Every topic proposed above on primary education is a starting point for me. I appreciate immensely the team that has sat down to make a detail of these selected topics just for beginners like us. Be blessed.
Kindly help me with the research questions on the topic” Effects of workplace conflict on the employees’ job performance”. The effects can be applicable in every institution,enterprise or organisation.
Greetings, I am a student majoring in Sociology and minoring in Public Administration. I’m considering any recommended research topic in the field of Sociology.
I’m a student pursuing Mphil in Basic education and I’m considering any recommended research proposal topic in my field of study
Research Defense for students in senior high
Kindly help me with a research topic in educational psychology. Ph.D level. Thank you.
Project-based learning is a teaching/learning type,if well applied in a classroom setting will yield serious positive impact. What can a teacher do to implement this in a disadvantaged zone like “North West Region of Cameroon ( hinterland) where war has brought about prolonged and untold sufferings on the indegins?
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration PhD level
I am also looking for such type of title
I am a student of undergraduate, doing research on how to use guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
the topics are very good regarding research & education .
Can i request your suggestion topic for my Thesis about Teachers as an OFW. thanx you
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education,PhD level
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education
Hi 👋 I request that you help me with a written research proposal about education the format
Am offering degree in education senior high School Accounting. I want a topic for my project work
l would like to request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
I would to inquire on research topics on Educational psychology, Masters degree
I am PhD student, I am searching my Research topic, It should be innovative,my area of interest is online education,use of technology in education
request suggestion on topic in masters in medical education .
Look at British Library as they keep a copy of all PhDs in the UK Core.ac.uk to access Open University and 6 other university e-archives, pdf downloads mostly available, all free.
May I also ask for a topic based on mathematics education for college teaching, please?
Please I am a masters student of the department of Teacher Education, Faculty of Education Please I am in need of proposed project topics to help with my final year thesis
Am a PhD student in Educational Foundations would like a sociological topic. Thank
please i need a proposed thesis project regardging computer science
Greetings and Regards I am a doctoral student in the field of philosophy of education. I am looking for a new topic for my thesis. Because of my work in the elementary school, I am looking for a topic that is from the field of elementary education and is related to the philosophy of education.
Masters student in the field of curriculum, any ideas of a research topic on low achiever students
In the field of curriculum any ideas of a research topic on deconalization in contextualization of digital teaching and learning through in higher education
Amazing guidelines
I am a graduate with two masters. 1) Master of arts in religious studies and 2) Master in education in foundations of education. I intend to do a Ph.D. on my second master’s, however, I need to bring both masters together through my Ph.D. research. can I do something like, ” The contribution of Philosophy of education for a quality religion education in Kenya”? kindly, assist and be free to suggest a similar topic that will bring together the two masters. thanks in advance
Hi, I am an Early childhood trainer as well as a researcher, I need more support on this topic: The impact of early childhood education on later academic success.
I’m a student in upper level secondary school and I need your support in this research topics: “Impact of incorporating project -based learning in teaching English language skills in secondary schools”.
Although research activities and topics should stem from reflection on one’s practice, I found this site valuable as it effectively addressed many issues we have been experiencing as practitioners.
Your style is unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this site.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
383 Exciting Education Research Topics
Education is vital to every person’s career and life success. People enrolled in higher education programs are 48% less likely to be incarcerated. Moreover, individuals with at least a Bachelor’s degree have the highest employment rates ( 86% ). Thus, investing time and effort in proper education is the best decision you can make in your young years.
Whether you’re interested in studying education or researching this subject for your classes, you will surely benefit from our detailed list of education research topics. Our experts have prepared research suggestions for students of all levels to aid you at every step of your education studies. Read on to find the best pick for your assignment.
- 🔝 Top-15 Research Titles about Education
- #️⃣ Quantitative Research Topics
- ️📋 Qualitative Research Topics
- 🎒 Titles about School Issues in 2024
- 🦼 Research Topics on Special Education
- 👶 Early Childhood Education
- 🧠 Educational Psychology
- 🧸 Child Development Topics
- 👩🏻💼 Educational Management Research Topics
- 📑 Dissertation Topics
🏫 Ideas of a Quantitative Research Title about School Problems
🔗 references, 🔝 top-15 research titles about education for 2024.
If you want to write a compelling paper, select an appropriate topic . You can find a unique research title about education in our list below and simplify your writing process.
- The role of education in eradicating poverty.
- The impact of technology on modern learning.
- The influence of social media on effective learning.
- A comparative analysis of student loans and debt accumulation.
- Effective approaches to student privacy and safety in schools.
- How does the school leadership experience shape a student’s personality?
- Evaluate the significance of assistive technology in special education.
- The role of parents in education.
- The importance of multicultural education.
- Homeschooling vs. regular schooling.
- The role of teachers as moral mediators.
- Approaches to prevent mental health issues among college students.
- The effectiveness of standardized tests in graduate schools.
- Should the government ban boarding schools?
- The importance of preschool education.
️#️⃣ 30 Quantitative Research Topics in Education
Quantitative research topics in education require extensive quantitative analysis and assessment of stats and figures. They involve doing calculations to support the research findings and hypotheses . The following are exciting topics on quantitative research you can use:
- The link between the e-learning environment and students’ social anxiety levels.
- Work hours and academic success relationship.
- The correlation between homeschooling and GPA.
- The effectiveness of parental involvement in child education: Statistical evidence.
- Motivation and learning relationship analysis.
- An analysis of the divide between tuition rates in private and public universities.
- The relationship between high tuition fees and poor education.
- Intervention strategies addressing six negative emotions.
- The connection between the national debt and student loans.
- Comparing students’ cognitive development scores in boarding and day schools.
- Formative assessments and raising attainment levels.
- The link between student well-being and teacher fulfillment.
- The correlation between students’ academic workload and mental wellness.
- Traditional or online education: which is better?
- The impact of socioeconomic status on academic performance.
- The link between urbanization and education development.
- The impact of school uniforms on school safety .
- The effects of teaching methods on student performance.
- A correlation between higher education attainment rates and unemployment rates.
- The race and class impact on academic performance.
- The impact of government policies on educational quality.
- The correlation between coding courses and a child’s cognitive development score.
- COVID-19 impact on student academic performance.
- Comparing the outcomes of data science programs for students of various specialties.
- The impact of student leadership on academic performance.
- Video games and their impact on students’ motivation.
- The link between social media use and psychological disorders’ incidence among students.
- The effects of students’ educational attainment on their post-graduation economic position.
- Time management: impact on the academic performance.
- The impact of educational field experiences on students’ career preparedness.
📋 30 Qualitative Research Topics in Education
Numerous issues in education need extensive research. Qualitative research is a way to gain an in-depth understanding of problems facing students and teachers. Below are qualitative research topics in education you can use for your academic project:
- Internet use among elementary school children.
- Educational challenges of students with autism.
- Teachers’ perspectives on the best learning strategies for autistic children.
- A case study of the significance of mental health education in schools.
- Inclusive classroom case study.
- The effects of learning conditions in developing countries.
- Early childhood educators’ perspectives on critical preschool classroom experiences.
- A case study examining why new teachers leave the profession.
- Students’ perceptions of their computer literacy skills.
- Coping strategies of schoolchildren’s parents from food-insecure households.
- Case study of a gifted student.
- High school students’ experiences of virtual learning.
- Students’ perceptions of lockdown browsers.
- Case study of learning disabilities: autism.
- The impact of alcoholism on student performance: A case study.
- A qualitative study of adult learners’ self-regulation in a digital learning environment.
- Human resources challenges in the higher education sphere.
- Academic leadership challenges in nursing schools.
- Students’ motivation to learn a rare foreign language.
- Challenges and barriers to equal opportunities in education.
- The role of teachers in improving learning for disabled children.
- Student loans: The effects on student career life.
- Korean Americans’ challenges in education.
- Teachers’ beliefs about their role in shaping the personalities of students.
- How to curb bullying in schools: Educators’ perspectives.
- Challenges and benefits of today’s student life.
- Remote learning: Advantages and disadvantages from students’ perspective.
- Interviews with teachers on the persistence of racism in schools.
- Learning challenges among people of color in public schools.
- Are students from lower social classes stigmatized in schools?
🎒 Research Titles about School Issues in 2024
Education research is vital in explaining and addressing fundamental issues affecting schools. It explores learning approaches, teaching practices , or educational changes after the pandemic. Choose your ideal research title about school issues from this list:
- The importance of standardized tests. Analyze the pros and cons of standardized tests and the consequences for students who fail the test.
- Government policy on education funding. Examine the flaws in the formula for financing schools and assess whether it is constitutional.
- Computer literacy in schools. Conduct a comparative assessment of effective methods to ensure all schools have enough resources to teach computer studies.
- Digital transformation in education. Analyze issues associated with online learning. Talk about the instructional tools that improve remote education.
- The effects of homeschooling. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of homeschooling and its cognitive impact on young children. Examine its sustainability in modern education.
- School safety in the 21st century. Explore the government policies on gun violence and approaches to prevent school shootings.
- Disciplinary policies in schools. Analyze the leading causes of suspensions and expulsions in schools. Examine the impact of reform policies on preventing undisciplined students’ transition into the juvenile system.
- The teaching of evolution. The is an ongoing debate about how to teach students about the origins of life. You can conduct a qualitative study examining parents’ or teachers’ attitudes toward this question.
- Student loans in higher education. Conduct a case study of students who are beneficiaries of student loans. Assess the effects of debt accumulation on their present careers.
- Bullying in schools. Study the causes and effects of bullying on students. Explore viable solutions to prevent bullying and discipline bullies.
🦼 53 Research Topics on Special Education
Special education is vital in modern society since many students have different disabilities and special needs. Teachers adopt accommodative practices to ensure total inclusivity for effective learning. Special education entails attending to students’ special needs using appropriate resources and accessible learning tools.
The following are research topics on special education to inspire your academic paper :
- Government policies on special education. Explore the policy frameworks and implementation guidelines that advocate special needs education. Talk about learning resources, accessibility, and transition rates to higher education and career life.
- Disabled children in early childhood education. Analyze the impact of special education on young children and determine strategies for effective teaching. Identify the challenges and possible solutions for enhancing seamless learning.
- The role of a school principal in improving special education. Discuss the approaches a principal can introduce to support disabled students. Talk about the instructions that teachers should adopt to guarantee inclusivity.
- Global impact of learning disabilities . Evaluate strategic approaches to special education in different countries. Analyze students’ responses to these methods and possible career paths in various countries.
- Coping mechanisms of special needs children. Investigate stress reactions and emotional security among children with disabilities. Explore methods that teachers can adopt to help students cope with new environments.
- The role of workshops on special educators’ mental wellness. Explore the causes and effects of stress and burnout on teachers in special education. Talk about acceptance and commitment therapy in alleviating depressive episodes.
- Social-emotional development in special education. Explain effective ways to promote social and emotional engagement of special needs children. Discuss parent and teacher training interventions and evaluate the results and implications for future research.
- Impact of technology on special education. Analyze the benefits of assistive technology in improving learning and give examples of tools used in special education. Talk about the barriers faced by special needs children, which result in learning exclusion.
- Discrimination and stigmatization. Conduct a case study of physically disabled children attending regular schools. Explore the psychological impact and trauma faced by special needs children. Present possible recommendations for better learning conditions.
- Effects of parenting style on special needs children. Analyze how different parenting styles can affect the behavior of special needs children. Explore a group of high school students with various disabilities.
- Behavioral issues in early childhood special education. Explore the influence of negative parent-child interactions on the behavior of children with disabilities. Discuss problem-solving models for correcting behavior and creating a positive learning environment.
- Patterns of language acquisition in children with disabilities. Compare language development in healthy and special needs children. Discuss the significance of communication skills in the early years and their effects on future learning.
- Social participation barriers. Compare the barriers to social participation in school faced by students with hearing and visual impairment. Talk about the assistive technologies that offer solutions and prevent social obstacles.
- Teaching strategies for special needs children. Analyze the effectiveness of various teaching approaches regarding their impact on the academic performance of special needs children.
- Disciplining students with disabilities. Explore appropriate methods of enforcing discipline among special needs students without raising controversies. Address the rights of students and ways of encouraging good behavior.
Here are other themes you can consider when writing on a special education topic:
- Discuss collaborative teaching strategies for special educators.
- Special education and teacher burnout.
- Speech-language therapists: The benefits of working in an inclusive environment.
- Discuss the challenges faced by special needs children.
- Special education disability categories.
- Why should special needs children learn in a special school, not a mainstream one?
- Effects of positive social interactions on children with disabilities.
- Teaching strategies for pupils with special educational needs.
- How to prevent bullying of special children?
- Analyze the history of early childhood education for special needs children.
- The inclusion of learners with special educational needs.
- Should the government make special education free for all students?
- The role of parents in instilling self-confidence in their children with disabilities.
- Exceptional children: introduction to special education.
- Why do students with autism face bullying more often than regular students?
- Should teachers be trained in handling special needs children?
- Field experience report and reflection: special education.
- Discuss effective teaching practices in special schools.
- Inclusive learning environment: Does it hinder or promote academic performance?
- Learning disability: special education strategies.
- Government policies on special education.
- A comparative analysis of special education in different countries.
- American special education and early intervention.
- Why are parents of children with disabilities prone to stress?
- Standardized tests for evaluating special needs children in early childhood education.
- Technology integration in special education.
- How to identify gifted children with different disabilities?
- An analysis of education equality for children with disabilities.
- The effect of training employees to work with special education children.
- The effects of teachers’ attitudes on students with dyslexia.
- Special needs children should have equal access to education.
- Special education: parent–professional collaboration.
- Is distance learning effective in special education?
- Evaluate digital literacy in special schools.
- Teacher leadership in special education.
- The importance of peer support in special education.
- Discuss strategies to motivate and retain special educators.
- Autism spectrum disorder and special education issues.
👶 53 Research Topics for Early Childhood Education
Early childhood education is a vital phase that sets the proper academic foundation for students. The early years of a child are essential since education provides a base for future learning abilities and social development .
Below are research topics for early childhood education to inspire your thesis:
- Child development stages. Compare different theories of child development. Analyze the role of the environment and genetics or explain the changes that occur from conception until a child is fully developed.
- The role of parents in early childhood education. Explore parents’ contribution to a child’s cognitive development and behavioral patterns . Discuss the importance of consistent communication with children for their proper development.
- The significance of field activities in preschool. Evaluate the effects of singing, dancing, drawing, painting, and physical exercise on cognitive development. Discuss the teachers’ attitudes toward child performance.
- The history of early childhood theorists. Assess the contribution of Maria Montessori to early childhood education. Describe her approach and explain why multi-sensory learning is essential.
- Computer literacy in young learners. Explore the reasons for introducing computer lessons in preschools. Discuss why young learners need to embrace technology but with strict limitations. Talk about the pros and cons of screen time for young children.
- Development of cognitive abilities in the early years. Analyze how children acquire knowledge, develop skills, and learn to solve problems. You can also focus on the brain development in the early years.
- The importance of play in child development. Explain how playing stimulates the brain and encourages social and emotional development. Give examples of child play and toys and discuss their impact.
- Early detection of special needs children. Explain how preschool educators can detect signs of learning disabilities. Talk about the symptoms of autism, ADHD, and other conditions affecting young learners.
- Teaching strategies in early childhood education. Explore the different teaching approaches used by educators for effective learning. Discuss play-based , inquiry, direct instruction, and project methods and assess their impact on young learners.
- Diversity in preschool. Compare opportunities to learn about cultural differences in homeschooling and regular schooling. Highlight the benefits of diversity for a child’s cognitive development.
- Child trauma. Explain how educators are trained to detect trauma in preschool kids. Talk about the signs of traumatic stress and its impact on a child’s development.
- Legal regulations in early childhood education. Explore the objective of public regulation of education. Discuss children’s rights to education and the regulatory bodies that ensure their protection.
- Contribution of Friedrich Froebel. Explore Froebel’s advocacy of an activity-based approach to early childhood education. Talk about the importance of creative and structured learning for developing minds.
- Effects of social interaction. Discuss the significance of socializing on a child’s cognitive development. Explain why educators should incorporate social activities in preschool to boost a child’s confidence.
- Importance of childcare centers. Evaluate their significance in developing emotional, social, and communication skills. Talk about the safety and health of children in preschool.
Here are some more exciting topics about early childhood education:
- The significance of physical books for preschool children.
- Best practices in early childhood education.
- The effects of divorce on the cognitive development of a preschool child.
- The influence of parents on young children’s moral development .
- Interview with an early childhood professional.
- Teachers’ attitudes toward children with ADHD in preschool.
- Effects of technology in an early childhood class.
- Impact of early childhood experience on the development of the personality .
- The significance of kindergarten in children’s development.
- How does unlimited screen time affect a child’s brain?
- Arts and play in early childhood development.
- Discuss the environmental factors that influence a child’s development.
- What is the observational strategy in early childhood training?
- Early childhood education: leadership and management.
- Significance of outdoor play in kindergarten learners.
- The role of vision therapy in young autistic children.
- Teaching philosophy in early childhood development.
- The influence of video games on young children’s learning outcomes.
- Discuss Vygotsky’s theory of socio-cultural learning.
- Early childhood profession in Australia.
- An analysis of the practical implications of early childhood learning.
- Discuss the objectives of international agreements on early childhood education.
- Environment in early childhood education.
- The barriers and challenges hindering young children’s effective learning.
- Genetic influences on a child’s behavior.
- Curricular issues in early childhood education.
- The significance of play in enhancing social skills.
- How does storytelling improve cognitive development?
- Early childhood safety considerations.
- Does early childhood development affect an individual’s personality?
- The effect of green classroom environment on young children.
- Early childhood education standards and practices.
- The role of diet on child development.
- The influence of culture on a child’s behavior.
- Overcoming stereotypes in early childhood education.
- The impact of bullying on young children.
- Emotional development in early childhood education.
- Stress in early childhood education.
🧠 53 Educational Psychology Research Topics
Educational psychology studies human learning processes, such as memory, conceptual understanding, and social-emotional skills. It covers both cognitive and behavioral aspects. Below are interesting educational psychology research topics to inspire your academic project:
- History of educational psychology. Explore the origin of educational psychology and the contributions made by its founders. Discuss the formal learning steps according to Johann Herbart.
- Young learners vs. adult learners. Explain the difference between learning as a child and an adult. Describe the challenges encountered and problem-solving skills demonstrated by children and adults in different situations.
- Significance of inspirational teaching. Explore the gender differences in teaching strategies. Discuss the pros and cons of incorporating emotions when teaching. Present the findings and implications for student performance.
- Emotion-based learning. Conduct a comparative study among autistic children and regular children in preschool. Explain how emotion-based teaching influences cognitive development and corrects learning impairments in autistic children.
- Importance of discipline models. Construct a case study of high-school students engaging in extra-curricular activities. Establish a connection between discipline models and high achievements. Talk about the psychological impact of a strict routine on shaping an individual’s personality.
- Effects of language challenges. Explore how language impacts the learning abilities of young children and how it may affect a student’s personality and performance later.
- Philosophers of education. Present a comparative evaluation of the history of education philosophers. Talk about the approaches of Juan Vives, Johann Herbart, and Johann Pestalozzi and their contribution to educational psychology.
- Impact of culture on education. Explore how culture can strongly influence an individual’s perception of education. Discuss the positive and negative aspects of culture from modern and historical angles.
- Educational psychology in rural schools. Evaluate the ethical, professional, and legal frameworks of education in rural contexts. Talk about the challenges faced by educators in rural areas.
- Effects of motivation on student performance. Explain the importance of motivation in students. You can focus on high-school learners and assess the effectiveness of a particular system of rewards for good performance.
- Language and literacy in education. Identify and define language issues during early years and the implications for future achievements. Talk about reading and language barriers affecting young children.
- Bell curve approach. Explore the fairness of the bell curve system of grading. Discuss the history of this method and its pros and cons. Explain its educational relevance and role in motivating students.
- Positive psychology in education. Evaluate the role of positive psychology in encouraging student performance. Analyze how schools can integrate mental health education into teaching achievement and accomplishment.
- Stress management techniques. Suggest the best approach to managing academic stress and preventing depression among students. Talk about the leading causes and effects of stress among college students and effective coping techniques.
- Impact of peer pressure. Explain the upsides and downsides of peer groups in school-going children. Discuss the effects of peer pressure on the moral conduct of students.
Here are some more examples of educational psychology topics for your research writing:
- The importance of educational psychology.
- Educational psychology: theory and practice.
- How does a child’s brain develop during learning?
- The risk factors and outcomes of bullying.
- Educational psychology: changing students’ behavior.
- The significance of peer interaction in adolescents.
- Effects of substance abuse on student performance.
- Using educational psychology in teaching.
- The influence of cartoons on a child’s mental state.
- Discuss teenage rebellion against parents.
- Reinforcers in classrooms: educational psychology in teaching.
- The relationship between speech disorders and cognitive development.
- An analysis of psychological theories in education.
- Educational psychology: behaviorism.
- The impact of media violence on child development.
- Explore the trends in educational psychology.
- School facilities in educational psychology.
- The effect of gender stereotyping in schools.
- Autism spectrum : the perspectives of parents and teachers.
- Psychology of learning and memory .
- The influence of the authoritarian parenting style on student performance.
- The impact of single parenting on children’s cognitive development.
- Cognitive learning and IQ tests.
- Discuss major challenges in mathematical thinking.
- An analysis of social-emotional development in children.
- Pathways of adult learning.
- The influence of modern technology on educational psychology.
- The importance of critical thinking in learners.
- Learning styles and their importance .
- Should schools teach moral behavior?
- A comparative study of psychological disorders.
- Anxiety causes and effects on language learning.
- Leading causes of mental health issues among students.
- The significance of professional educators.
- Student motivation and ways to enhance it.
- Discipline approaches for moral development.
- The mechanism of character development in young children.
- Learning and memory relations.
🧸 53 Child Development Topics to Explore
Child development is an important field of study since it investigates the changes a person undergoes from conception to adolescence. Finding a unique topic on child development may be challenging. We offer a comprehensive list of child development topics to simplify your research project:
- Child development theories. Explore significant theories and their importance in explaining children’s social and emotional development. For example, talk about the contributions of Jean Piaget to understanding children’s cognition.
- The significance of social interaction. Evaluate the importance of socialization in a child’s behavior. Present the outcomes of interacting with peers and its influence on a child’s personality.
- Mental health in early childhood development. Explain why mental health is often overlooked in young children. Discuss the signs of psychological problems in children.
- Jean Piaget’s perspective on child development. Explore the history of Piaget’s philosophy and the importance of child psychology in the modern world. Talk about the relevance of each developmental stage.
- Early childhood personality. Study personality development at a young age. Discuss how childhood shapes an individual’s personality throughout their life.
- The impact of gender roles in child development. Explore what part parents and educators play in teaching children about gender roles. Discuss the possible effects of learning gender roles on shaping a child’s perception and actions as an adult.
- The significance of the environment. Explain the role of the environment in developing the human mind during childhood. Consider such environmental factors as friends, housing, climate, and access to basic needs.
- Communication skills in language development. Explain the importance of consistent communication with a child from conception to the early years. Talk about parent-child bonding through communication and how it influences language development.
- The influence of culture on child development. Conduct a comprehensive study of how cultural differences impact a child’s development. Talk about the cultural norms that children are trained to accept as they grow from infancy to adulthood.
- Importance of child observation . Explain why observing a child during the early years is crucial to identify issues in achieving developmental milestones. Discuss the role of parents and educators in child development.
- Attachment theory by John Bowlby. Explore the attachment theory and why interpersonal relationships are essential among humans. Talk about the significance of an emotional bond between a child and a parent to facilitate normal development.
- Erickson’s stages of development. Analyze the eight phases of human development. Discuss the importance of each stage and how it affects an individual’s future behavior and personality.
- Asynchronous development. Explore the challenges of asynchronous development to parents, educators, and the child. Talk about the possible causes and effects of asynchronous development.
- Child research methods. Conduct a comparative analysis of infant research methods. Discuss the key challenges when studying infants. Talk about such approaches as eye tracking, the sucking technique, or brain imaging technology.
- Ethical considerations in child research. Explore the ethical dilemmas when conducting studies on children. Describe the verbal and non-verbal indicators that researchers can use as a child’s consent to participation.
Here are more exciting topics on child development:
- Discuss Piaget’s theory of child development.
- Child development from birth to three wears and the role of adults.
- Importance of play in improving gross motor skills.
- Why do parents need to understand child development theories?
- Attachment and its role in child development.
- The role of music in increasing focus in children.
- Discuss the five steps of cognitive development.
- Child development and education: physical exercise.
- Ego formation in a child.
- Discuss positive parenting styles.
- Cognitive domain of child development: activity plan.
- Effects of food insecurity on child development.
- Explore Vygotsky’s social-cultural theory.
- Gifted students: child development.
- Child development: The role of a mother .
- Importance of language stimulation in young children.
- Physical education: impact on child development.
- Significance of movement in child development.
- An analysis of effective parenting styles.
- Child development theories.
- The influence of genetics on child development.
- The role of a balanced diet in child development.
- Educative toys’ role in child development.
- Why are children more creative than adults?
- The importance of pretend-play on development.
- Connection between screen time and child development.
- Discuss social development theory in relation to children.
- A comparative analysis of Vygotsky’s and Piaget’s theories.
- Child development: ages one through three.
- Discuss the impact of literate communities on child development.
- How can parents deal with stress in children and teenagers?
- Child development and environmental influences.
- The environmental influences on a child’s behavior.
- Pros and cons of imaginary friends.
- The impact of dyslexia on child development.
- Effective approaches in language development.
- The role of books in child development.
- Child development during the COVID-19 pandemic.
👩🏻💼 53 Educational Management Research Topics
Educational management is a collection of various components of education. Research topics cover multiple concepts ranging from administrative to financial aspects of education. Here are inspiring educational management research topics for your perusal:
- Higher education leadership. Explore the qualifications of higher education leaders in developed countries. Discuss their implications for pursuing a career in educational management.
- A review of the educational ecosystem. Explore the governing bodies in education. Talk about the government ministries, statutory bodies, principals, administrative personnel, educators, and non-teaching staff. Explain why management is vital at all levels.
- Significance of extra-curricular activities. Explore the role of co-curricular activities in maintaining a holistic education approach. Discuss the types of activities and their benefits for student performance.
- Curriculum planning. Explore the strategies used in curriculum planning and the factors affecting its development, evaluation, and implementation. Discuss the three stages involved in this process.
- Friedrich Frobel’s approach to curriculum development. Explore the key educational components at the preschool level and describe the forms of knowledge. Explain Frobel’s focus on life, knowledge, and beauty.
- The impact of technology. Explore the significance of technology in education management. Investigate such issues as budget limitations, data security concerns, and poor network infrastructure.
- Importance of financial policies in schools. Explain how economic policies offer administrative support to ensure seamless operations. Talk about the revenue streams, school funds, government subsidies, grants, and allowances.
- Health and physical development. Explain why institutions need a health and physical education department. Talk about healthy living and the importance of exercise.
- Significance of human resources. Discuss the role of the HR department in educational institutions. Present the benefits of specific organizational structures and operational policies in ensuring smooth functioning.
- The objectives of educators. Explore the strategies for planning and implementing lessons. Talk about the importance of pedagogical practices in educational management. Discuss the effects of the classroom-management approach.
- National examples of educational management. Conduct a comparative study on Australia, Finland, and Singapore. Discuss the school structure, curriculum, and government policies and involvement.
- Parents’ perception of educational administrative policies. Discuss the parents’ attitudes toward policies from preschool to the university level. Explore both private and public institutions.
- The goals of education ministries. Explore the objectives of the education ministry, such as designing, implementing, monitoring, and evaluating educational legislation. Discuss the leadership roles in ensuring smooth operations of learning institutions.
- Challenges of educators. Explore the leadership styles of educators in high school. Talk about the discipline strategies for dealing with rebellious teenagers and cases of indiscipline.
- Special education. Analyze the features of education management in special schools. Discuss the process of developing individual education plans and dealing with special education issues, such as budgeting or parent education.
Here are some more engaging topics in educational management you can check out to get inspiration:
- Discuss the critical issues of classroom management.
- Why is the UK education system successful?
- Effects of guidance on student performance.
- The effectiveness of standardized tests for measuring student performance.
- Corruption in the education sector: Democratic Republic of Congo.
- The features of managing distance learning systems.
- The role of a principal in school functioning.
- The financial issues in the secondary education area in the US.
- The relationship between a principal’s leadership style and teachers’ satisfaction.
- The link between classroom management and student behavior.
- School principals as agents of change.
- Effects on instructional-based learning on academic performance.
- An analysis of interactive teaching methods.
- School-community partnership and its benefits.
- The influence of government policies in educational administration.
- Discuss educational leadership in the digital age.
- Program quality assessment: teaching and learning.
- The role of educators in moral discipline.
- The impact of a poor educational system.
- The lack of sex education in the Thai educational system.
- An analysis of Montessori education.
- Importance of curriculum planning.
- Teachers’ certification: is it necessary?
- The effects of progressive education.
- The influence of the environment on academic performance.
- How can a principal improve the quality of special education?
- Discuss the impact of teacher motivation.
- Does strict school supervision translate to high academic performance?
- Effectiveness of educational leadership management skills.
- Can poor management of schools result in increased student indiscipline?
- The influence of good administrative leadership in education.
- Educational leadership and instruction differentiation.
- Factors preventing effective school management.
- Explore biases in educational administration.
- The use of standardized tests in college admissions.
- The link between academic performance and school accountability.
- Gender equality in educational management.
- Financial issues facing US higher education.
📑 15 Dissertation Topics in Education
Dissertation research is more complex than usual research for college or university assignments. It requires more originality and extends over a longer period. Here are some dissertation topics in education you can consider for your forthcoming dissertation project:
- Examine the impact of COVID-19 social isolation on students of your university.
- Social media impact on English language learning.
- Cross-cultural communication and conflict management at your chosen online study course.
- Principals’ concerns and attitudes toward social distancing policies in Texas schools.
- Formative assessment: impact on student achievement.
- A case study of children’s first and second language use in play-based interactions in a private kindergarten.
- The impact of present-day economic pressures on the K-12 curriculum development in the US: Teachers’ and policymakers’ perspectives.
- How does inclusion impact autistic children?
- Collaborative inquiry and video documentation to facilitate school teachers’ critical thinking competencies: Analysis of the INSIGHT project at a public school.
- Using computer-based reading interventions for at-risk preschoolers: Teachers’ perspectives.
- Homeschooling and its impact on learners.
- Relationship between the Math assessment method and student self-esteem.
- Parents’ attitudes toward the use of technology in elementary school.
- Impact of classroom technology on learner attitudes.
- Impact of teacher training on student attainment: An EU study.
- The link between homework load and student stress levels.
- How common are shootings in American schools?
- The impact of classroom size on academic performance in elementary schools.
- The relationship between school safety measures and student psychological well-being.
- How effective is an inclusive school environment in fostering better academic outcomes?
- The impact of socioeconomic factors on school dropout rates.
- What is the role of school policies in addressing cyberbullying among students?
- The influence of socioeconomic aspects on the quality of education in public schools.
- How prevalent is bullying in public schools?
- The influence of standardized testing on student success.
- How important is parent involvement in the learning process?
- The effect of extracurricular overload on student anxiety development.
- How does peer pressure affect student decision-making?
- The influence of inclusive education on the performance of students with learning disabilities.
- How can AI technology in education engage students in more active learning?
- The link between socioeconomic background and access to educational resources.
- The impact of government funding on the education system.
- How limited is access to mental health support in high schools?
Now that you have a comprehensive list of educational research topics of all complexity levels, you can easily ace any assignment for your Pedagogy course. Don’t hesitate to share this article with your peers and post a commentary if any topic has been helpful to you.
❓ Education Research Topics FAQ
What are some good research topics in education.
Well-chosen topics for educational research should be carefully scoped and relevant to your academic level and context. It’s vital to cover hot issues by linking theory and practice, thus ensuring that your study is valuable and related to present-day education.
What is an example of educational research?
Educational research covers many subjects and subdisciplines, so you may focus on any area important to you. It may be a special education class where you can approach teachers or observe students with special needs . Or it can be educational leadership research, where you will search for new, efficient ways of school administration for principals.
What topics should be addressed in sex education?
Sex education is a pressing issue in many schools worldwide, as teenage pregnancy rates are increasing. You may approach this subject by examining the attitudes to sex education among parents with different religious affiliations. Or you can compare the rates of teenage abortion and pregnancies in states with and without sex education in the formal curriculum.
What is action research in education?
Action research is a combination of practice and research in one endeavor. You should first study theory, develop an assumption that can be applied in practice, and then implement that method in your educational setting. After the intervention, you measure the outcomes and present findings in your research paper, thus concluding whether your assumption was valid.
- Child Development Basics | CDC
- Issues and Challenges in Special Education | Southeast Asia Early Childhood Journal
- Social Issues That Special Education Teachers Face | Chron
- Problems in Educational Administration | Classroom
- Early Childhood Development: The Promise, the Problem, and the Path Forward | Brookings
- Educational Psychology and Research | University of South Carolina
- 5 Big Challenges for Schools in 2023 | EducationWeek
- Quantitative Methods in Education | University of Minnesota
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | American University
414 Proposal Essay Topics for Projects, Research, & Proposal Arguments
725 research proposal topics & title ideas in education, psychology, business, & more.
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
100+ Quantitative Research Topics For Students

Quantitative research is a research strategy focusing on quantified data collection and analysis processes. This research strategy emphasizes testing theories on various subjects. It also includes collecting and analyzing non-numerical data.
Quantitative research is a common approach in the natural and social sciences , like marketing, business, sociology, chemistry, biology, economics, and psychology. So, if you are fond of statistics and figures, a quantitative research title would be an excellent option for your research proposal or project.
How to Get a Title of Quantitative Research
How to make quantitative research title, what is the best title for quantitative research, amazing quantitative research topics for students, creative quantitative research topics, perfect quantitative research title examples, unique quantitative research titles, outstanding quantitative research title examples for students, creative example title of quantitative research samples, outstanding quantitative research problems examples, fantastic quantitative research topic examples, the best quantitative research topics, grade 12 quantitative research title for students, list of quantitative research titles for high school, easy quantitative research topics for students, trending topics for quantitative research, quantitative research proposal topics, samples of quantitative research titles, research title about business quantitative.
Finding a great title is the key to writing a great quantitative research proposal or paper. A title for quantitative research prepares you for success, failure, or mediocre grades. This post features examples of quantitative research titles for all students.
Putting together a research title and quantitative research design is not as easy as some students assume. So, an example topic of quantitative research can help you craft your own. However, even with the examples, you may need some guidelines for personalizing your research project or proposal topics.
So, here are some tips for getting a title for quantitative research:
- Consider your area of studies
- Look out for relevant subjects in the area
- Expert advice may come in handy
- Check out some sample quantitative research titles
Making a quantitative research title is easy if you know the qualities of a good title in quantitative research. Reading about how to make a quantitative research title may not help as much as looking at some samples. Looking at a quantitative research example title will give you an idea of where to start.
However, let’s look at some tips for how to make a quantitative research title:
- The title should seem interesting to readers
- Ensure that the title represents the content of the research paper
- Reflect on the tone of the writing in the title
- The title should contain important keywords in your chosen subject to help readers find your paper
- The title should not be too lengthy
- It should be grammatically correct and creative
- It must generate curiosity
An excellent quantitative title should be clear, which implies that it should effectively explain the paper and what readers can expect. A research title for quantitative research is the gateway to your article or proposal. So, it should be well thought out. Additionally, it should give you room for extensive topic research.
A sample of quantitative research titles will give you an idea of what a good title for quantitative research looks like. Here are some examples:
- What is the correlation between inflation rates and unemployment rates?
- Has climate adaptation influenced the mitigation of funds allocation?
- Job satisfaction and employee turnover: What is the link?
- A look at the relationship between poor households and the development of entrepreneurship skills
- Urbanization and economic growth: What is the link between these elements?
- Does education achievement influence people’s economic status?
- What is the impact of solar electricity on the wholesale energy market?
- Debt accumulation and retirement: What is the relationship between these concepts?
- Can people with psychiatric disorders develop independent living skills?
- Children’s nutrition and its impact on cognitive development
Quantitative research applies to various subjects in the natural and social sciences. Therefore, depending on your intended subject, you have numerous options. Below are some good quantitative research topics for students:
- The difference between the colorific intake of men and women in your country
- Top strategies used to measure customer satisfaction and how they work
- Black Friday sales: are they profitable?
- The correlation between estimated target market and practical competitive risk assignment
- Are smartphones making us brighter or dumber?
- Nuclear families Vs. Joint families: Is there a difference?
- What will society look like in the absence of organized religion?
- A comparison between carbohydrate weight loss benefits and high carbohydrate diets?
- How does emotional stability influence your overall well-being?
- The extent of the impact of technology in the communications sector
Creativity is the key to creating a good research topic in quantitative research. Find a good quantitative research topic below:
- How much exercise is good for lasting physical well-being?
- A comparison of the nutritional therapy uses and contemporary medical approaches
- Does sugar intake have a direct impact on diabetes diagnosis?
- Education attainment: Does it influence crime rates in society?
- Is there an actual link between obesity and cancer rates?
- Do kids with siblings have better social skills than those without?
- Computer games and their impact on the young generation
- Has social media marketing taken over conventional marketing strategies?
- The impact of technology development on human relationships and communication
- What is the link between drug addiction and age?
Need more quantitative research title examples to inspire you? Here are some quantitative research title examples to look at:
- Habitation fragmentation and biodiversity loss: What is the link?
- Radiation has affected biodiversity: Assessing its effects
- An assessment of the impact of the CORONA virus on global population growth
- Is the pandemic truly over, or have human bodies built resistance against the virus?
- The ozone hole and its impact on the environment
- The greenhouse gas effect: What is it and how has it impacted the atmosphere
- GMO crops: are they good or bad for your health?
- Is there a direct link between education quality and job attainment?
- How have education systems changed from traditional to modern times?
- The good and bad impacts of technology on education qualities
Your examiner will give you excellent grades if you come up with a unique title and outstanding content. Here are some quantitative research examples titles.
- Online classes: are they helpful or not?
- What changes has the global CORONA pandemic had on the population growth curve?
- Daily habits influenced by the global pandemic
- An analysis of the impact of culture on people’s personalities
- How has feminism influenced the education system’s approach to the girl child’s education?
- Academic competition: what are its benefits and downsides for students?
- Is there a link between education and student integrity?
- An analysis of how the education sector can influence a country’s economy
- An overview of the link between crime rates and concern for crime
- Is there a link between education and obesity?
Research title example quantitative topics when well-thought guarantees a paper that is a good read. Look at the examples below to get started.
- What are the impacts of online games on students?
- Sex education in schools: how important is it?
- Should schools be teaching about safe sex in their sex education classes?
- The correlation between extreme parent interference on student academic performance
- Is there a real link between academic marks and intelligence?
- Teacher feedback: How necessary is it, and how does it help students?
- An analysis of modern education systems and their impact on student performance
- An overview of the link between academic performance/marks and intelligence
- Are grading systems helpful or harmful to students?
- What was the impact of the pandemic on students?
Irrespective of the course you take, here are some titles that can fit diverse subjects pretty well. Here are some creative quantitative research title ideas:
- A look at the pre-corona and post-corona economy
- How are conventional retail businesses fairing against eCommerce sites like Amazon and Shopify?
- An evaluation of mortality rates of heart attacks
- Effective treatments for cardiovascular issues and their prevention
- A comparison of the effectiveness of home care and nursing home care
- Strategies for managing effective dissemination of information to modern students
- How does educational discrimination influence students’ futures?
- The impacts of unfavorable classroom environment and bullying on students and teachers
- An overview of the implementation of STEM education to K-12 students
- How effective is digital learning?
If your paper addresses a problem, you must present facts that solve the question or tell more about the question. Here are examples of quantitative research titles that will inspire you.
- An elaborate study of the influence of telemedicine in healthcare practices
- How has scientific innovation influenced the defense or military system?
- The link between technology and people’s mental health
- Has social media helped create awareness or worsened people’s mental health?
- How do engineers promote green technology?
- How can engineers raise sustainability in building and structural infrastructures?
- An analysis of how decision-making is dependent on someone’s sub-conscious
- A comprehensive study of ADHD and its impact on students’ capabilities
- The impact of racism on people’s mental health and overall wellbeing
- How has the current surge in social activism helped shape people’s relationships?
Are you looking for an example of a quantitative research title? These ten examples below will get you started.
- The prevalence of nonverbal communication in social control and people’s interactions
- The impacts of stress on people’s behavior in society
- A study of the connection between capital structures and corporate strategies
- How do changes in credit ratings impact equality returns?
- A quantitative analysis of the effect of bond rating changes on stock prices
- The impact of semantics on web technology
- An analysis of persuasion, propaganda, and marketing impact on individuals
- The dominant-firm model: what is it, and how does it apply to your country’s retail sector?
- The role of income inequality in economy growth
- An examination of juvenile delinquents’ treatment in your country
Excellent Topics For Quantitative Research
Here are some titles for quantitative research you should consider:
- Does studying mathematics help implement data safety for businesses
- How are art-related subjects interdependent with mathematics?
- How do eco-friendly practices in the hospitality industry influence tourism rates?
- A deep insight into how people view eco-tourisms
- Religion vs. hospitality: Details on their correlation
- Has your country’s tourist sector revived after the pandemic?
- How effective is non-verbal communication in conveying emotions?
- Are there similarities between the English and French vocabulary?
- How do politicians use persuasive language in political speeches?
- The correlation between popular culture and translation
Here are some quantitative research titles examples for your consideration:
- How do world leaders use language to change the emotional climate in their nations?
- Extensive research on how linguistics cultivate political buzzwords
- The impact of globalization on the global tourism sector
- An analysis of the effects of the pandemic on the worldwide hospitality sector
- The influence of social media platforms on people’s choice of tourism destinations
- Educational tourism: What is it and what you should know about it
- Why do college students experience math anxiety?
- Is math anxiety a phenomenon?
- A guide on effective ways to fight cultural bias in modern society
- Creative ways to solve the overpopulation issue
An example of quantitative research topics for 12 th -grade students will come in handy if you want to score a good grade. Here are some of the best ones:
- The link between global warming and climate change
- What is the greenhouse gas impact on biodiversity and the atmosphere
- Has the internet successfully influenced literacy rates in society
- The value and downsides of competition for students
- A comparison of the education system in first-world and third-world countries
- The impact of alcohol addiction on the younger generation
- How has social media influenced human relationships?
- Has education helped boost feminism among men and women?
- Are computers in classrooms beneficial or detrimental to students?
- How has social media improved bullying rates among teenagers?
High school students can apply research titles on social issues or other elements, depending on the subject. Let’s look at some quantitative topics for students:
- What is the right age to introduce sex education for students
- Can extreme punishment help reduce alcohol consumption among teenagers?
- Should the government increase the age of sexual consent?
- The link between globalization and the local economy collapses
- How are global companies influencing local economies?
There are numerous possible quantitative research topics you can write about. Here are some great quantitative research topics examples:
- The correlation between video games and crime rates
- Do college studies impact future job satisfaction?
- What can the education sector do to encourage more college enrollment?
- The impact of education on self-esteem
- The relationship between income and occupation
You can find inspiration for your research topic from trending affairs on social media or in the news. Such topics will make your research enticing. Find a trending topic for quantitative research example from the list below:
- How the country’s economy is fairing after the pandemic
- An analysis of the riots by women in Iran and what the women gain to achieve
- Is the current US government living up to the voter’s expectations?
- How is the war in Ukraine affecting the global economy?
- Can social media riots affect political decisions?
A proposal is a paper you write proposing the subject you would like to cover for your research and the research techniques you will apply. If the proposal is approved, it turns to your research topic. Here are some quantitative titles you should consider for your research proposal:
- Military support and economic development: What is the impact in developing nations?
- How does gun ownership influence crime rates in developed countries?
- How can the US government reduce gun violence without influencing people’s rights?
- What is the link between school prestige and academic standards?
- Is there a scientific link between abortion and the definition of viability?
You can never have too many sample titles. The samples allow you to find a unique title you’re your research or proposal. Find a sample quantitative research title here:
- Does weight loss indicate good or poor health?
- Should schools do away with grading systems?
- The impact of culture on student interactions and personalities
- How can parents successfully protect their kids from the dangers of the internet?
- Is the US education system better or worse than Europe’s?
If you’re a business major, then you must choose a research title quantitative about business. Let’s look at some research title examples quantitative in business:
- Creating shareholder value in business: How important is it?
- The changes in credit ratings and their impact on equity returns
- The importance of data privacy laws in business operations
- How do businesses benefit from e-waste and carbon footprint reduction?
- Organizational culture in business: what is its importance?
We Are A Call Away
Interesting, creative, unique, and easy quantitative research topics allow you to explain your paper and make research easy. Therefore, you should not take choosing a research paper or proposal topic lightly. With your topic ready, reach out to us today for excellent research paper writing services .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
200+ Experimental Quantitative Research Topics For STEM Students In 2023

STEM means Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math, which is not the only stuff we learn in school. It is like a treasure chest of skills that help students become great problem solvers, ready to tackle the real world’s challenges.
In this blog, we are here to explore the world of Research Topics for STEM Students. We will break down what STEM really means and why it is so important for students. In addition, we will give you the lowdown on how to pick a fascinating research topic. We will explain a list of 200+ Experimental Quantitative Research Topics For STEM Students.
And when it comes to writing a research title, we will guide you step by step. So, stay with us as we unlock the exciting world of STEM research – it is not just about grades; it is about growing smarter, more confident, and happier along the way.
What Is STEM?
Table of Contents
STEM is Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. It is a way of talking about things like learning, jobs, and activities related to these four important subjects. Science is about understanding the world around us, technology is about using tools and machines to solve problems, engineering is about designing and building things, and mathematics is about numbers and solving problems with them. STEM helps us explore, discover, and create cool stuff that makes our world better and more exciting.
Why STEM Research Is Important?
STEM research is important because it helps us learn new things about the world and solve problems. When scientists, engineers, and mathematicians study these subjects, they can discover cures for diseases, create new technology that makes life easier, and build things that help us live better. It is like a big puzzle where we put together pieces of knowledge to make our world safer, healthier, and more fun.
- STEM research leads to new discoveries and solutions.
- It helps find cures for diseases.
- STEM technology makes life easier.
- Engineers build things that improve our lives.
- Mathematics helps us understand and solve complex problems.
How to Choose a Topic for STEM Research Paper
Here are some steps to choose a topic for STEM Research Paper:
Step 1: Identify Your Interests
Think about what you like and what excites you in science, technology, engineering, or math. It could be something you learned in school, saw in the news, or experienced in your daily life. Choosing a topic you’re passionate about makes the research process more enjoyable.
Step 2: Research Existing Topics
Look up different STEM research areas online, in books, or at your library. See what scientists and experts are studying. This can give you ideas and help you understand what’s already known in your chosen field.
Step 3: Consider Real-World Problems
Think about the problems you see around you. Are there issues in your community or the world that STEM can help solve? Choosing a topic that addresses a real-world problem can make your research impactful.
Step 4: Talk to Teachers and Mentors
Discuss your interests with your teachers, professors, or mentors. They can offer guidance and suggest topics that align with your skills and goals. They may also provide resources and support for your research.
Step 5: Narrow Down Your Topic
Once you have some ideas, narrow them down to a specific research question or project. Make sure it’s not too broad or too narrow. You want a topic that you can explore in depth within the scope of your research paper.
Here we will discuss 200+ Experimental Quantitative Research Topics For STEM Students:
Qualitative Research Topics for STEM Students:
Qualitative research focuses on exploring and understanding phenomena through non-numerical data and subjective experiences. Here are 10 qualitative research topics for STEM students:
- Exploring the experiences of female STEM students in overcoming gender bias in academia.
- Understanding the perceptions of teachers regarding the integration of technology in STEM education.
- Investigating the motivations and challenges of STEM educators in underprivileged schools.
- Exploring the attitudes and beliefs of parents towards STEM education for their children.
- Analyzing the impact of collaborative learning on student engagement in STEM subjects.
- Investigating the experiences of STEM professionals in bridging the gap between academia and industry.
- Understanding the cultural factors influencing STEM career choices among minority students.
- Exploring the role of mentorship in the career development of STEM graduates.
- Analyzing the perceptions of students towards the ethics of emerging STEM technologies like AI and CRISPR.
- Investigating the emotional well-being and stress levels of STEM students during their academic journey.
Easy Experimental Research Topics for STEM Students:
These experimental research topics are relatively straightforward and suitable for STEM students who are new to research:
- Measuring the effect of different light wavelengths on plant growth.
- Investigating the relationship between exercise and heart rate in various age groups.
- Testing the effectiveness of different insulating materials in conserving heat.
- Examining the impact of pH levels on the rate of chemical reactions.
- Studying the behavior of magnets in different temperature conditions.
- Investigating the effect of different concentrations of a substance on bacterial growth.
- Testing the efficiency of various sunscreen brands in blocking UV radiation.
- Measuring the impact of music genres on concentration and productivity.
- Examining the correlation between the angle of a ramp and the speed of a rolling object.
- Investigating the relationship between the number of blades on a wind turbine and energy output.
Research Topics for STEM Students in the Philippines:
These research topics are tailored for STEM students in the Philippines:
- Assessing the impact of climate change on the biodiversity of coral reefs in the Philippines.
- Studying the potential of indigenous plants in the Philippines for medicinal purposes.
- Investigating the feasibility of harnessing renewable energy sources like solar and wind in rural Filipino communities.
- Analyzing the water quality and pollution levels in major rivers and lakes in the Philippines.
- Exploring sustainable agricultural practices for small-scale farmers in the Philippines.
- Assessing the prevalence and impact of dengue fever outbreaks in urban areas of the Philippines.
- Investigating the challenges and opportunities of STEM education in remote Filipino islands.
- Studying the impact of typhoons and natural disasters on infrastructure resilience in the Philippines.
- Analyzing the genetic diversity of endemic species in the Philippine rainforests.
- Assessing the effectiveness of disaster preparedness programs in Philippine communities.
Read More
- Frontend Project Ideas
- Business Intelligence Projects For Beginners
Good Research Topics for STEM Students:
These research topics are considered good because they offer interesting avenues for investigation and learning:
- Developing a low-cost and efficient water purification system for rural communities.
- Investigating the potential use of CRISPR-Cas9 for gene therapy in genetic disorders.
- Studying the applications of blockchain technology in securing medical records.
- Analyzing the impact of 3D printing on customized prosthetics for amputees.
- Exploring the use of artificial intelligence in predicting and preventing forest fires.
- Investigating the effects of microplastic pollution on aquatic ecosystems.
- Analyzing the use of drones in monitoring and managing agricultural crops.
- Studying the potential of quantum computing in solving complex optimization problems.
- Investigating the development of biodegradable materials for sustainable packaging.
- Exploring the ethical implications of gene editing in humans.
Unique Research Topics for STEM Students:
Unique research topics can provide STEM students with the opportunity to explore unconventional and innovative ideas. Here are 10 unique research topics for STEM students:
- Investigating the use of bioluminescent organisms for sustainable lighting solutions.
- Studying the potential of using spider silk proteins for advanced materials in engineering.
- Exploring the application of quantum entanglement for secure communication in the field of cryptography.
- Analyzing the feasibility of harnessing geothermal energy from underwater volcanoes.
- Investigating the use of CRISPR-Cas12 for rapid and cost-effective disease diagnostics.
- Studying the interaction between artificial intelligence and human creativity in art and music generation.
- Exploring the development of edible packaging materials to reduce plastic waste.
- Investigating the impact of microgravity on cellular behavior and tissue regeneration in space.
- Analyzing the potential of using sound waves to detect and combat invasive species in aquatic ecosystems.
- Studying the use of biotechnology in reviving extinct species, such as the woolly mammoth.
Experimental Research Topics for STEM Students in the Philippines
Research topics for STEM students in the Philippines can address specific regional challenges and opportunities. Here are 10 experimental research topics for STEM students in the Philippines:
- Assessing the effectiveness of locally sourced materials for disaster-resilient housing construction in typhoon-prone areas.
- Investigating the utilization of indigenous plants for natural remedies in Filipino traditional medicine.
- Studying the impact of volcanic soil on crop growth and agriculture in volcanic regions of the Philippines.
- Analyzing the water quality and purification methods in remote island communities.
- Exploring the feasibility of using bamboo as a sustainable construction material in the Philippines.
- Investigating the potential of using solar stills for freshwater production in water-scarce regions.
- Studying the effects of climate change on the migration patterns of bird species in the Philippines.
- Analyzing the growth and sustainability of coral reefs in marine protected areas.
- Investigating the utilization of coconut waste for biofuel production.
- Studying the biodiversity and conservation efforts in the Tubbataha Reefs Natural Park.
Capstone Research Topics for STEM Students in the Philippines:
Capstone research projects are often more comprehensive and can address real-world issues. Here are 10 capstone research topics for STEM students in the Philippines:
- Designing a low-cost and sustainable sanitation system for informal settlements in urban Manila.
- Developing a mobile app for monitoring and reporting natural disasters in the Philippines.
- Assessing the impact of climate change on the availability and quality of drinking water in Philippine cities.
- Designing an efficient traffic management system to address congestion in major Filipino cities.
- Analyzing the health implications of air pollution in densely populated urban areas of the Philippines.
- Developing a renewable energy microgrid for off-grid communities in the archipelago.
- Assessing the feasibility of using unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) for agricultural monitoring in rural Philippines.
- Designing a low-cost and sustainable aquaponics system for urban agriculture.
- Investigating the potential of vertical farming to address food security in densely populated urban areas.
- Developing a disaster-resilient housing prototype suitable for typhoon-prone regions.
Experimental Quantitative Research Topics for STEM Students:
Experimental quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to conclude. Here are 10 Experimental Quantitative Research Topics For STEM Students interested in experimental quantitative research:
- Examining the impact of different fertilizers on crop yield in agriculture.
- Investigating the relationship between exercise and heart rate among different age groups.
- Analyzing the effect of varying light intensities on photosynthesis in plants.
- Studying the efficiency of various insulation materials in reducing building heat loss.
- Investigating the relationship between pH levels and the rate of corrosion in metals.
- Analyzing the impact of different concentrations of pollutants on aquatic ecosystems.
- Examining the effectiveness of different antibiotics on bacterial growth.
- Trying to figure out how temperature affects how thick liquids are.
- Finding out if there is a link between the amount of pollution in the air and lung illnesses in cities.
- Analyzing the efficiency of solar panels in converting sunlight into electricity under varying conditions.
Descriptive Research Topics for STEM Students
Descriptive research aims to provide a detailed account or description of a phenomenon. Here are 10 topics for STEM students interested in descriptive research:
- Describing the physical characteristics and behavior of a newly discovered species of marine life.
- Documenting the geological features and formations of a particular region.
- Creating a detailed inventory of plant species in a specific ecosystem.
- Describing the properties and behavior of a new synthetic polymer.
- Documenting the daily weather patterns and climate trends in a particular area.
- Providing a comprehensive analysis of the energy consumption patterns in a city.
- Describing the structural components and functions of a newly developed medical device.
- Documenting the characteristics and usage of traditional construction materials in a region.
- Providing a detailed account of the microbiome in a specific environmental niche.
- Describing the life cycle and behavior of a rare insect species.
Research Topics for STEM Students in the Pandemic:
The COVID-19 pandemic has raised many research opportunities for STEM students. Here are 10 research topics related to pandemics:
- Analyzing the effectiveness of various personal protective equipment (PPE) in preventing the spread of respiratory viruses.
- Studying the impact of lockdown measures on air quality and pollution levels in urban areas.
- Investigating the psychological effects of quarantine and social isolation on mental health.
- Analyzing the genomic variation of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and its implications for vaccine development.
- Studying the efficacy of different disinfection methods on various surfaces.
- Investigating the role of contact tracing apps in tracking & controlling the spread of infectious diseases.
- Analyzing the economic impact of the pandemic on different industries and sectors.
- Studying the effectiveness of remote learning in STEM education during lockdowns.
- Investigating the social disparities in healthcare access during a pandemic.
- Analyzing the ethical considerations surrounding vaccine distribution and prioritization.
Research Topics for STEM Students Middle School
Research topics for middle school STEM students should be engaging and suitable for their age group. Here are 10 research topics:
- Investigating the growth patterns of different types of mold on various food items.
- Studying the negative effects of music on plant growth and development.
- Analyzing the relationship between the shape of a paper airplane and its flight distance.
- Investigating the properties of different materials in making effective insulators for hot and cold beverages.
- Studying the effect of salt on the buoyancy of different objects in water.
- Analyzing the behavior of magnets when exposed to different temperatures.
- Investigating the factors that affect the rate of ice melting in different environments.
- Studying the impact of color on the absorption of heat by various surfaces.
- Analyzing the growth of crystals in different types of solutions.
- Investigating the effectiveness of different natural repellents against common pests like mosquitoes.
Technology Research Topics for STEM Students
Technology is at the forefront of STEM fields. Here are 10 research topics for STEM students interested in technology:
- Developing and optimizing algorithms for autonomous drone navigation in complex environments.
- Exploring the use of blockchain technology for enhancing the security and transparency of supply chains.
- Investigating the applications of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in medical training and surgery simulations.
- Studying the potential of 3D printing for creating personalized prosthetics and orthopedic implants.
- Analyzing the ethical and privacy implications of facial recognition technology in public spaces.
- Investigating the development of quantum computing algorithms for solving complex optimization problems.
- Explaining the use of machine learning and AI in predicting and mitigating the impact of natural disasters.
- Studying the advancement of brain-computer interfaces for assisting individuals with
- disabilities.
- Analyzing the role of wearable technology in monitoring and improving personal health and wellness.
- Investigating the use of robotics in disaster response and search and rescue operations.
Scientific Research Topics for STEM Students
Scientific research encompasses a wide range of topics. Here are 10 research topics for STEM students focusing on scientific exploration:
- Investigating the behavior of subatomic particles in high-energy particle accelerators.
- Studying the ecological impact of invasive species on native ecosystems.
- Analyzing the genetics of antibiotic resistance in bacteria and its implications for healthcare.
- Exploring the physics of gravitational waves and their detection through advanced interferometry.
- Investigating the neurobiology of memory formation and retention in the human brain.
- Studying the biodiversity and adaptation of extremophiles in harsh environments.
- Analyzing the chemistry of deep-sea hydrothermal vents and their potential for life beyond Earth.
- Exploring the properties of superconductors and their applications in technology.
- Investigating the mechanisms of stem cell differentiation for regenerative medicine.
- Studying the dynamics of climate change and its impact on global ecosystems.
Interesting Research Topics for STEM Students:
Engaging and intriguing research topics can foster a passion for STEM. Here are 10 interesting research topics for STEM students:
- Exploring the science behind the formation of auroras and their cultural significance.
- Investigating the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy in the universe.
- Studying the psychology of decision-making in high-pressure situations, such as sports or
- emergencies.
- Analyzing the impact of social media on interpersonal relationships and mental health.
- Exploring the potential for using genetic modification to create disease-resistant crops.
- Investigating the cognitive processes involved in solving complex puzzles and riddles.
- Studying the history and evolution of cryptography and encryption methods.
- Analyzing the physics of time travel and its theoretical possibilities.
- Exploring the role of Artificial Intelligence in creating art and music.
- Investigating the science of happiness and well-being, including factors contributing to life satisfaction.
Practical Research Topics for STEM Students
Practical research often leads to real-world solutions. Here are 10 practical research topics for STEM students:
- Developing an affordable and sustainable water purification system for rural communities.
- Designing a low-cost, energy-efficient home heating and cooling system.
- Investigating strategies for reducing food waste in the supply chain and households.
- Studying the effectiveness of eco-friendly pest control methods in agriculture.
- Analyzing the impact of renewable energy integration on the stability of power grids.
- Developing a smartphone app for early detection of common medical conditions.
- Investigating the feasibility of vertical farming for urban food production.
- Designing a system for recycling and upcycling electronic waste.
- Studying the environmental benefits of green roofs and their potential for urban heat island mitigation.
- Analyzing the efficiency of alternative transportation methods in reducing carbon emissions.
Experimental Research Topics for STEM Students About Plants
Plants offer a rich field for experimental research. Here are 10 experimental research topics about plants for STEM students:
- Investigating the effect of different light wavelengths on plant growth and photosynthesis.
- Studying the impact of various fertilizers and nutrient solutions on crop yield.
- Analyzing the response of plants to different types and concentrations of plant hormones.
- Investigating the role of mycorrhizal in enhancing nutrient uptake in plants.
- Studying the effects of drought stress and water scarcity on plant physiology and adaptation mechanisms.
- Analyzing the influence of soil pH on plant nutrient availability and growth.
- Investigating the chemical signaling and defense mechanisms of plants against herbivores.
- Studying the impact of environmental pollutants on plant health and genetic diversity.
- Analyzing the role of plant secondary metabolites in pharmaceutical and agricultural applications.
- Investigating the interactions between plants and beneficial microorganisms in the rhizosphere.
Qualitative Research Topics for STEM Students in the Philippines
Qualitative research in the Philippines can address local issues and cultural contexts. Here are 10 qualitative research topics for STEM students in the Philippines:
- Exploring indigenous knowledge and practices in sustainable agriculture in Filipino communities.
- Studying the perceptions and experiences of Filipino fishermen in coping with climate change impacts.
- Analyzing the cultural significance and traditional uses of medicinal plants in indigenous Filipino communities.
- Investigating the barriers and facilitators of STEM education access in remote Philippine islands.
- Exploring the role of traditional Filipino architecture in natural disaster resilience.
- Studying the impact of indigenous farming methods on soil conservation and fertility.
- Analyzing the cultural and environmental significance of mangroves in coastal Filipino regions.
- Investigating the knowledge and practices of Filipino healers in treating common ailments.
- Exploring the cultural heritage and conservation efforts of the Ifugao rice terraces.
- Studying the perceptions and practices of Filipino communities in preserving marine biodiversity.
Science Research Topics for STEM Students
Science offers a diverse range of research avenues. Here are 10 science research topics for STEM students:
- Investigating the potential of gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 in curing genetic diseases.
- Studying the ecological impacts of species reintroduction programs on local ecosystems.
- Analyzing the effects of microplastic pollution on aquatic food webs and ecosystems.
- Investigating the link between air pollution and respiratory health in urban populations.
- Studying the role of epigenetics in the inheritance of acquired traits in organisms.
- Analyzing the physiology and adaptations of extremophiles in extreme environments on Earth.
- Investigating the genetics of longevity and factors influencing human lifespan.
- Studying the behavioral ecology and communication strategies of social insects.
- Analyzing the effects of deforestation on global climate patterns and biodiversity loss.
- Investigating the potential of synthetic biology in creating bioengineered organisms for beneficial applications.
Correlational Research Topics for STEM Students
Correlational research focuses on relationships between variables. Here are 10 correlational research topics for STEM students:
- Analyzing the correlation between dietary habits and the incidence of chronic diseases.
- Studying the relationship between exercise frequency and mental health outcomes.
- Investigating the correlation between socioeconomic status and access to quality healthcare.
- Analyzing the link between social media usage and self-esteem in adolescents.
- Studying the correlation between academic performance and sleep duration among students.
- Investigating the relationship between environmental factors and the prevalence of allergies.
- Analyzing the correlation between technology use and attention span in children.
- Studying how environmental factors are related to the frequency of allergies.
- Investigating the link between parental involvement in education and student achievement.
- Analyzing the correlation between temperature fluctuations and wildlife migration patterns.
Quantitative Research Topics for STEM Students in the Philippines
Quantitative research in the Philippines can address specific regional issues. Here are 10 quantitative research topics for STEM students in the Philippines
- Analyzing the impact of typhoons on coastal erosion rates in the Philippines.
- Studying the quantitative effects of land use change on watershed hydrology in Filipino regions.
- Investigating the quantitative relationship between deforestation and habitat loss for endangered species.
- Analyzing the quantitative patterns of marine biodiversity in Philippine coral reef ecosystems.
- Studying the quantitative assessment of water quality in major Philippine rivers and lakes.
- Investigating the quantitative analysis of renewable energy potential in specific Philippine provinces.
- Analyzing the quantitative impacts of agricultural practices on soil health and fertility.
- Studying the quantitative effectiveness of mangrove restoration in coastal protection in the Philippines.
- Investigating the quantitative evaluation of indigenous agricultural practices for sustainability.
- Analyzing the quantitative patterns of air pollution and its health impacts in urban Filipino areas.
Things That Must Keep In Mind While Writing Quantitative Research Title
Here are few things that must be keep in mind while writing quantitative research tile:
1. Be Clear and Precise
Make sure your research title is clear and says exactly what your study is about. People should easily understand the topic and goals of your research by reading the title.
2. Use Important Words
Include words that are crucial to your research, like the main subjects, who you’re studying, and how you’re doing your research. This helps others find your work and understand what it’s about.
3. Avoid Confusing Words
Stay away from words that might confuse people. Your title should be easy to grasp, even if someone isn’t an expert in your field.
4. Show Your Research Approach
Tell readers what kind of research you did, like experiments or surveys. This gives them a hint about how you conducted your study.
5. Match Your Title with Your Research Questions
Make sure your title matches the questions you’re trying to answer in your research. It should give a sneak peek into what your study is all about and keep you on the right track as you work on it.
STEM students, addressing what STEM is and why research matters in this field. It offered an extensive list of research topics , including experimental, qualitative, and regional options, catering to various academic levels and interests. Whether you’re a middle school student or pursuing advanced studies, these topics offer a wealth of ideas. The key takeaway is to choose a topic that resonates with your passion and aligns with your goals, ensuring a successful journey in STEM research. Choose the best Experimental Quantitative Research Topics For Stem Students today!
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research
Introduction, general overviews.
- Survey Research Designs
- Correlational Designs
- Other Nonexperimental Designs
- Randomized Experimental Designs
- Quasi-Experimental Designs
- Single-Case Designs
- Single-Case Analyses
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
- Mixed Methods Research
- Multivariate Research Methodology
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Sampling Strategies
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Context of Postgraduate Programs
- Single-Subject Research Design
- Social Network Analysis
- Statistical Assumptions
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Black Women in Academia
- Girls' Education in the Developing World
- History of Education in Europe
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research by James H. McMillan , Richard S. Mohn , Micol V. Hammack LAST REVIEWED: 24 July 2013 LAST MODIFIED: 24 July 2013 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756810-0113
The field of education has embraced quantitative research designs since early in the 20th century. The foundation for these designs was based primarily in the psychological literature, and psychology and the social sciences more generally continued to have a strong influence on quantitative designs until the assimilation of qualitative designs in the 1970s and 1980s. More recently, a renewed emphasis on quasi-experimental and nonexperimental quantitative designs to infer causal conclusions has resulted in many newer sources specifically targeting these approaches to the field of education. This bibliography begins with a discussion of general introductions to all quantitative designs in the educational literature. The sources in this section tend to be textbooks or well-known sources written many years ago, though still very relevant and helpful. It should be noted that there are many other sources in the social sciences more generally that contain principles of quantitative designs that are applicable to education. This article then classifies quantitative designs primarily as either nonexperimental or experimental but also emphasizes the use of nonexperimental designs for making causal inferences. Among experimental designs the article distinguishes between those that include random assignment of subjects, those that are quasi-experimental (with no random assignment), and those that are single-case (single-subject) designs. Quasi-experimental and nonexperimental designs used for making causal inferences are becoming more popular in education given the practical difficulties and expense in conducting well-controlled experiments, particularly with the use of structural equation modeling (SEM). There have also been recent developments in statistical analyses that allow stronger causal inferences. Historically, quantitative designs have been tied closely to sampling, measurement, and statistics. In this bibliography there are important sources for newer statistical procedures that are needed for particular designs, especially single-case designs, but relatively little attention to sampling or measurement. The literature on quantitative designs in education is not well focused or comprehensively addressed in very many sources, except in general overview textbooks. Those sources that do include the range of designs are introductory in nature; more advanced designs and statistical analyses tend to be found in journal articles and other individual documents, with a couple exceptions. Another new trend in educational research designs is the use of mixed-method designs (both quantitative and qualitative), though this article does not emphasize these designs.
For many years there have been textbooks that present the range of quantitative research designs, both in education and the social sciences more broadly. Indeed, most of the quantitative design research principles are much the same for education, psychology, and other social sciences. These sources provide an introduction to basic designs that are used within the broader context of other educational research methodologies such as qualitative and mixed-method. Examples of these textbooks written specifically for education include Johnson and Christensen 2012 ; Mertens 2010 ; Arthur, et al. 2012 ; and Creswell 2012 . An example of a similar text written for the social sciences, including education that is dedicated only to quantitative research, is Gliner, et al. 2009 . In these texts separate chapters are devoted to different types of quantitative designs. For example, Creswell 2012 contains three quantitative design chapters—experimental, which includes both randomized and quasi-experimental designs; correlational (nonexperimental); and survey (also nonexperimental). Johnson and Christensen 2012 also includes three quantitative design chapters, with greater emphasis on quasi-experimental and single-subject research. Mertens 2010 includes a chapter on causal-comparative designs (nonexperimental). Often survey research is addressed as a distinct type of quantitative research with an emphasis on sampling and measurement (how to design surveys). Green, et al. 2006 also presents introductory chapters on different types of quantitative designs, but each of the chapters has different authors. In this book chapters extend basic designs by examining in greater detail nonexperimental methodologies structured for causal inferences and scaled-up experiments. Two additional sources are noted because they represent the types of publications for the social sciences more broadly that discuss many of the same principles of quantitative design among other types of designs. Bickman and Rog 2009 uses different chapter authors to cover topics such as statistical power for designs, sampling, randomized controlled trials, and quasi-experiments, and educational researchers will find this information helpful in designing their studies. Little 2012 provides a comprehensive coverage of topics related to quantitative methods in the social, behavioral, and education fields.
Arthur, James, Michael Waring, Robert Coe, and Larry V. Hedges, eds. 2012. Research methods & methodologies in education . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Readers will find this book more of a handbook than a textbook. Different individuals author each of the chapters, representing quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method designs. The quantitative chapters are on the treatment of advanced statistical applications, including analysis of variance, regression, and multilevel analysis.
Bickman, Leonard, and Debra J. Rog, eds. 2009. The SAGE handbook of applied social research methods . 2d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
This handbook includes quantitative design chapters that are written for the social sciences broadly. There are relatively advanced treatments of statistical power, randomized controlled trials, and sampling in quantitative designs, though the coverage of additional topics is not as complete as other sources in this section.
Creswell, John W. 2012. Educational research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research . 4th ed. Boston: Pearson.
Creswell presents an introduction to all major types of research designs. Three chapters cover quantitative designs—experimental, correlational, and survey research. Both the correlational and survey research chapters focus on nonexperimental designs. Overall the introductions are complete and helpful to those beginning their study of quantitative research designs.
Gliner, Jeffrey A., George A. Morgan, and Nancy L. Leech. 2009. Research methods in applied settings: An integrated approach to design and analysis . 2d ed. New York: Routledge.
This text, unlike others in this section, is devoted solely to quantitative research. As such, all aspects of quantitative designs are covered. There are separate chapters on experimental, nonexperimental, and single-subject designs and on internal validity, sampling, and data-collection techniques for quantitative studies. The content of the book is somewhat more advanced than others listed in this section and is unique in its quantitative focus.
Green, Judith L., Gregory Camilli, and Patricia B. Elmore, eds. 2006. Handbook of complementary methods in education research . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Green, Camilli, and Elmore edited forty-six chapters that represent many contemporary issues and topics related to quantitative designs. Written by noted researchers, the chapters cover design experiments, quasi-experimentation, randomized experiments, and survey methods. Other chapters include statistical topics that have relevance for quantitative designs.
Johnson, Burke, and Larry B. Christensen. 2012. Educational research: Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed approaches . 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
This comprehensive textbook of educational research methods includes extensive coverage of qualitative and mixed-method designs along with quantitative designs. Three of twenty chapters focus on quantitative designs (experimental, quasi-experimental, and single-case) and nonexperimental, including longitudinal and retrospective, designs. The level of material is relatively high, and there are introductory chapters on sampling and quantitative analyses.
Little, Todd D., ed. 2012. The Oxford handbook of quantitative methods . Vol. 1, Foundations . New York: Oxford Univ. Press.
This handbook is a relatively advanced treatment of quantitative design and statistical analyses. Multiple authors are used to address strengths and weaknesses of many different issues and methods, including advanced statistical tools.
Mertens, Donna M. 2010. Research and evaluation in education and psychology: Integrating diversity with quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods . 3d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
This textbook is an introduction to all types of educational designs and includes four chapters devoted to quantitative research—experimental and quasi-experimental, causal comparative and correlational, survey, and single-case research. The author’s treatment of some topics is somewhat more advanced than texts such as Creswell 2012 , with extensive attention to threats to internal validity for some of the designs.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Education »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Academic Achievement
- Academic Audit for Universities
- Academic Freedom and Tenure in the United States
- Action Research in Education
- Adjuncts in Higher Education in the United States
- Administrator Preparation
- Adolescence
- Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Courses
- Advocacy and Activism in Early Childhood
- African American Racial Identity and Learning
- Alaska Native Education
- Alternative Certification Programs for Educators
- Alternative Schools
- American Indian Education
- Animals in Environmental Education
- Art Education
- Artificial Intelligence and Learning
- Assessing School Leader Effectiveness
- Assessment, Behavioral
- Assessment, Educational
- Assessment in Early Childhood Education
- Assistive Technology
- Augmented Reality in Education
- Beginning-Teacher Induction
- Bilingual Education and Bilingualism
- Black Undergraduate Women: Critical Race and Gender Perspe...
- Blended Learning
- Case Study in Education Research
- Changing Professional and Academic Identities
- Character Education
- Children’s and Young Adult Literature
- Children's Beliefs about Intelligence
- Children's Rights in Early Childhood Education
- Citizenship Education
- Civic and Social Engagement of Higher Education
- Classroom Learning Environments: Assessing and Investigati...
- Classroom Management
- Coherent Instructional Systems at the School and School Sy...
- College Admissions in the United States
- College Athletics in the United States
- Community Relations
- Comparative Education
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning
- Computer-Based Testing
- Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Evaluating Improvement Net...
- Continuous Improvement and "High Leverage" Educational Pro...
- Counseling in Schools
- Critical Approaches to Gender in Higher Education
- Critical Perspectives on Educational Innovation and Improv...
- Critical Race Theory
- Crossborder and Transnational Higher Education
- Cross-National Research on Continuous Improvement
- Cross-Sector Research on Continuous Learning and Improveme...
- Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Culturally Responsive Leadership
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogies
- Culturally Responsive Teacher Education in the United Stat...
- Curriculum Design
- Data Collection in Educational Research
- Data-driven Decision Making in the United States
- Deaf Education
- Desegregation and Integration
- Design Thinking and the Learning Sciences: Theoretical, Pr...
- Development, Moral
- Dialogic Pedagogy
- Digital Age Teacher, The
- Digital Citizenship
- Digital Divides
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning
- Distributed Leadership
- Doctoral Education and Training
- Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) in Denmark
- Early Childhood Education and Development in Mexico
- Early Childhood Education in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Childhood Education in Australia
- Early Childhood Education in China
- Early Childhood Education in Europe
- Early Childhood Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Early Childhood Education in Sweden
- Early Childhood Education Pedagogy
- Early Childhood Education Policy
- Early Childhood Education, The Arts in
- Early Childhood Mathematics
- Early Childhood Science
- Early Childhood Teacher Education
- Early Childhood Teachers in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Years Professionalism and Professionalization Polici...
- Economics of Education
- Education For Children with Autism
- Education for Sustainable Development
- Education Leadership, Empirical Perspectives in
- Education of Native Hawaiian Students
- Education Reform and School Change
- Educational Statistics for Longitudinal Research
- Educator Partnerships with Parents and Families with a Foc...
- Emotional and Affective Issues in Environmental and Sustai...
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- English as an International Language for Academic Publishi...
- Environmental and Science Education: Overlaps and Issues
- Environmental Education
- Environmental Education in Brazil
- Epistemic Beliefs
- Equity and Improvement: Engaging Communities in Educationa...
- Equity, Ethnicity, Diversity, and Excellence in Education
- Ethical Research with Young Children
- Ethics and Education
- Ethics of Teaching
- Ethnic Studies
- Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention
- Family and Community Partnerships in Education
- Family Day Care
- Federal Government Programs and Issues
- Feminization of Labor in Academia
- Finance, Education
- Financial Aid
- Formative Assessment
- Future-Focused Education
- Gender and Achievement
- Gender and Alternative Education
- Gender, Power and Politics in the Academy
- Gender-Based Violence on University Campuses
- Gifted Education
- Global Mindedness and Global Citizenship Education
- Global University Rankings
- Governance, Education
- Grounded Theory
- Growth of Effective Mental Health Services in Schools in t...
- Higher Education and Globalization
- Higher Education and the Developing World
- Higher Education Faculty Characteristics and Trends in the...
- Higher Education Finance
- Higher Education Governance
- Higher Education Graduate Outcomes and Destinations
- Higher Education in Africa
- Higher Education in China
- Higher Education in Latin America
- Higher Education in the United States, Historical Evolutio...
- Higher Education, International Issues in
- Higher Education Management
- Higher Education Policy
- Higher Education Research
- Higher Education Student Assessment
- High-stakes Testing
- History of Early Childhood Education in the United States
- History of Education in the United States
- History of Technology Integration in Education
- Homeschooling
- Inclusion in Early Childhood: Difference, Disability, and ...
- Inclusive Education
- Indigenous Education in a Global Context
- Indigenous Learning Environments
- Indigenous Students in Higher Education in the United Stat...
- Infant and Toddler Pedagogy
- Inservice Teacher Education
- Integrating Art across the Curriculum
- Intelligence
- Intensive Interventions for Children and Adolescents with ...
- International Perspectives on Academic Freedom
- Intersectionality and Education
- Knowledge Development in Early Childhood
- Leadership Development, Coaching and Feedback for
- Leadership in Early Childhood Education
- Leadership Training with an Emphasis on the United States
- Learning Analytics in Higher Education
- Learning Difficulties
- Learning, Lifelong
- Learning, Multimedia
- Learning Strategies
- Legal Matters and Education Law
- LGBT Youth in Schools
- Linguistic Diversity
- Linguistically Inclusive Pedagogy
- Literacy Development and Language Acquisition
- Literature Reviews
- Mathematics Identity
- Mathematics Instruction and Interventions for Students wit...
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Measurement for Improvement in Education
- Measurement in Education in the United States
- Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis in Education
- Methodological Approaches for Impact Evaluation in Educati...
- Mindfulness, Learning, and Education
- Motherscholars
- Multiliteracies in Early Childhood Education
- Multiple Documents Literacy: Theory, Research, and Applica...
- Museums, Education, and Curriculum
- Music Education
- Narrative Research in Education
- Native American Studies
- Nonformal and Informal Environmental Education
- Note-Taking
- Numeracy Education
- One-to-One Technology in the K-12 Classroom
- Online Education
- Open Education
- Organizing for Continuous Improvement in Education
- Organizing Schools for the Inclusion of Students with Disa...
- Outdoor Play and Learning
- Outdoor Play and Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Pedagogical Leadership
- Pedagogy of Teacher Education, A
- Performance Objectives and Measurement
- Performance-based Research Assessment in Higher Education
- Performance-based Research Funding
- Phenomenology in Educational Research
- Philosophy of Education
- Physical Education
- Podcasts in Education
- Policy Context of United States Educational Innovation and...
- Politics of Education
- Portable Technology Use in Special Education Programs and ...
- Post-humanism and Environmental Education
- Pre-Service Teacher Education
- Problem Solving
- Productivity and Higher Education
- Professional Development
- Professional Learning Communities
- Program Evaluation
- Programs and Services for Students with Emotional or Behav...
- Psychology Learning and Teaching
- Psychometric Issues in the Assessment of English Language ...
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Samp...
- Qualitative Research Design
- Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research
- Queering the English Language Arts (ELA) Writing Classroom
- Race and Affirmative Action in Higher Education
- Reading Education
- Refugee and New Immigrant Learners
- Relational and Developmental Trauma and Schools
- Relational Pedagogies in Early Childhood Education
- Reliability in Educational Assessments
- Religion in Elementary and Secondary Education in the Unit...
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Cont...
- Research-Practice Partnerships in Education within the Uni...
- Response to Intervention
- Restorative Practices
- Risky Play in Early Childhood Education
- Scale and Sustainability of Education Innovation and Impro...
- Scaling Up Research-based Educational Practices
- School Accreditation
- School Choice
- School Culture
- School District Budgeting and Financial Management in the ...
- School Improvement through Inclusive Education
- School Reform
- Schools, Private and Independent
- School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
- Science Education
- Secondary to Postsecondary Transition Issues
- Self-Regulated Learning
- Self-Study of Teacher Education Practices
- Service-Learning
- Severe Disabilities
- Single Salary Schedule
- Single-sex Education
- Social Context of Education
- Social Justice
- Social Pedagogy
- Social Science and Education Research
- Social Studies Education
- Sociology of Education
- Standards-Based Education
- Student Access, Equity, and Diversity in Higher Education
- Student Assignment Policy
- Student Engagement in Tertiary Education
- Student Learning, Development, Engagement, and Motivation ...
- Student Participation
- Student Voice in Teacher Development
- Sustainability Education in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Higher Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Epistemologies
- Teacher Collaboration in School Improvement
- Teacher Evaluation and Teacher Effectiveness
- Teacher Preparation
- Teacher Training and Development
- Teacher Unions and Associations
- Teacher-Student Relationships
- Teaching Critical Thinking
- Technologies, Teaching, and Learning in Higher Education
- Technology Education in Early Childhood
- Technology, Educational
- Technology-based Assessment
- The Bologna Process
- The Regulation of Standards in Higher Education
- Theories of Educational Leadership
- Three Conceptions of Literacy: Media, Narrative, and Gamin...
- Tracking and Detracking
- Traditions of Quality Improvement in Education
- Transformative Learning
- Transitions in Early Childhood Education
- Tribally Controlled Colleges and Universities in the Unite...
- Understanding the Psycho-Social Dimensions of Schools and ...
- University Faculty Roles and Responsibilities in the Unite...
- Using Ethnography in Educational Research
- Value of Higher Education for Students and Other Stakehold...
- Virtual Learning Environments
- Vocational and Technical Education
- Wellness and Well-Being in Education
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Young Children and Spirituality
- Young Children's Learning Dispositions
- Young Children's Working Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.180.204]
- 81.177.180.204
Quantitative research in education : Recent e-books
- Recent e-books
- << Previous: Background information
- Next: Recent print books >>
- Background information
- Recent print books
- Connect to Stanford e-resources
- Last Updated: Jun 6, 2024 3:37 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.stanford.edu/quantitative_research_in_ed

A Quick Guide to Quantitative Research in the Social Sciences
(12 reviews)
Christine Davies, Carmarthen, Wales
Copyright Year: 2020
Last Update: 2021
Publisher: University of Wales Trinity Saint David
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Jennifer Taylor, Assistant Professor, Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi on 4/18/24
This resource is a quick guide to quantitative research in the social sciences and not a comprehensive resource. It provides a VERY general overview of quantitative research but offers a good starting place for students new to research. It... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This resource is a quick guide to quantitative research in the social sciences and not a comprehensive resource. It provides a VERY general overview of quantitative research but offers a good starting place for students new to research. It offers links and references to additional resources that are more comprehensive in nature.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The content is relatively accurate. The measurement scale section is very sparse. Not all types of research designs or statistical methods are included, but it is a guide, so details are meant to be limited.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The examples were interesting and appropriate. The content is up to date and will be useful for several years.
Clarity rating: 5
The text was clearly written. Tables and figures are not referenced in the text, which would have been nice.
Consistency rating: 5
The framework is consistent across chapters with terminology clearly highlighted and defined.
Modularity rating: 5
The chapters are subdivided into section that can be divided and assigned as reading in a course. Most chapters are brief and concise, unless elaboration is necessary, such as with the data analysis chapter. Again, this is a guide and not a comprehensive text, so sections are shorter and don't always include every subtopic that may be considered.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The guide is well organized. I appreciate that the topics are presented in a logical and clear manner. The topics are provided in an order consistent with traditional research methods.
Interface rating: 5
The interface was easy to use and navigate. The images were clear and easy to read.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
I did not notice any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The materials are not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I teach a Marketing Research course to undergraduates. I would consider using some of the chapters or topics included, especially the overview of the research designs and the analysis of data section.
Reviewed by Tiffany Kindratt, Assistant Professor, University of Texas at Arlington on 3/9/24
The text provides a brief overview of quantitative research topics that is geared towards research in the fields of education, sociology, business, and nursing. The author acknowledges that the textbook is not a comprehensive resource but offers... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text provides a brief overview of quantitative research topics that is geared towards research in the fields of education, sociology, business, and nursing. The author acknowledges that the textbook is not a comprehensive resource but offers references to other resources that can be used to deepen the knowledge. The text does not include a glossary or index. The references in the figures for each chapter are not included in the reference section. It would be helpful to include those.
Overall, the text is accurate. For example, Figure 1 on page 6 provides a clear overview of the research process. It includes general definitions of primary and secondary research. It would be helpful to include more details to explain some of the examples before they are presented. For instance, the example on page 5 was unclear how it pertains to the literature review section.
In general, the text is relevant and up-to-date. The text includes many inferences of moving from qualitative to quantitative analysis. This was surprising to me as a quantitative researcher. The author mentions that moving from a qualitative to quantitative approach should only be done when needed. As a predominantly quantitative researcher, I would not advice those interested in transitioning to using a qualitative approach that qualitative research would enhance their research—not something that should only be done if you have to.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is written in a clear manner. It would be helpful to the reader if there was a description of the tables and figures in the text before they are presented.
Consistency rating: 4
The framework for each chapter and terminology used are consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The text is clearly divided into sections within each chapter. Overall, the chapters are a similar brief length except for the chapter on data analysis, which is much more comprehensive than others.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics in the text are presented in a clear and logical order. The order of the text follows the conventional research methodology in social sciences.
I did not encounter any interface issues when reviewing this text. All links worked and there were no distortions of the images or charts that may confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 3
There are some grammatical/typographical errors throughout. Of note, for Section 5 in the table of contents. “The” should be capitalized to start the title. In the title for Table 3, the “t” in typical should be capitalized.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
The examples are culturally relevant. The text is geared towards learners in the UK, but examples are relevant for use in other countries (i.e., United States). I did not see any examples that may be considered culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I teach a course on research methods in a Bachelor of Science in Public Health program. I would consider using some of the text, particularly in the analysis chapter to supplement the current textbook in the future.
Reviewed by Finn Bell, Assistant Professor, University of Michigan, Dearborn on 1/3/24
For it being a quick guide and only 26 pages, it is very comprehensive, but it does not include an index or glossary. read more
For it being a quick guide and only 26 pages, it is very comprehensive, but it does not include an index or glossary.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, the text is accurate, error-free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
This text is up-to-date, and given the content, unlikely to become obsolete any time soon.
The text is very clear and accessible.
The text is internally consistent.
Given how short the text is, it seems unnecessary to divide it into smaller readings, nonetheless, it is clearly labelled such that an instructor could do so.
The text is well-organized and brings readers through basic quantitative methods in a logical, clear fashion.
Easy to navigate. Only one table that is split between pages, but not in a way that is confusing.
There were no noticeable grammatical errors.
The examples in this book don't give enough information to rate this effectively.
This text is truly a very quick guide at only 26 double-spaced pages. Nonetheless, Davies packs a lot of information on the basics of quantitative research methods into this text, in an engaging way with many examples of the concepts presented. This guide is more of a brief how-to that takes readers as far as how to select statistical tests. While it would be impossible to fully learn quantitative research from such a short text, of course, this resource provides a great introduction, overview, and refresher for program evaluation courses.
Reviewed by Shari Fedorowicz, Adjunct Professor, Bridgewater State University on 12/16/22
The text is indeed a quick guide for utilizing quantitative research. Appropriate and effective examples and diagrams were used throughout the text. The author clearly differentiates between use of quantitative and qualitative research providing... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text is indeed a quick guide for utilizing quantitative research. Appropriate and effective examples and diagrams were used throughout the text. The author clearly differentiates between use of quantitative and qualitative research providing the reader with the ability to distinguish two terms that frequently get confused. In addition, links and outside resources are provided to deepen the understanding as an option for the reader. The use of these links, coupled with diagrams and examples make this text comprehensive.
The content is mostly accurate. Given that it is a quick guide, the author chose a good selection of which types of research designs to include. However, some are not provided. For example, correlational or cross-correlational research is omitted and is not discussed in Section 3, but is used as a statistical example in the last section.
Examples utilized were appropriate and associated with terms adding value to the learning. The tables that included differentiation between types of statistical tests along with a parametric/nonparametric table were useful and relevant.
The purpose to the text and how to use this guide book is stated clearly and is established up front. The author is also very clear regarding the skill level of the user. Adding to the clarity are the tables with terms, definitions, and examples to help the reader unpack the concepts. The content related to the terms was succinct, direct, and clear. Many times examples or figures were used to supplement the narrative.
The text is consistent throughout from contents to references. Within each section of the text, the introductory paragraph under each section provides a clear understanding regarding what will be discussed in each section. The layout is consistent for each section and easy to follow.
The contents are visible and address each section of the text. A total of seven sections, including a reference section, is in the contents. Each section is outlined by what will be discussed in the contents. In addition, within each section, a heading is provided to direct the reader to the subtopic under each section.
The text is well-organized and segues appropriately. I would have liked to have seen an introductory section giving a narrative overview of what is in each section. This would provide the reader with the ability to get a preliminary glimpse into each upcoming sections and topics that are covered.
The book was easy to navigate and well-organized. Examples are presented in one color, links in another and last, figures and tables. The visuals supplemented the reading and placed appropriately. This provides an opportunity for the reader to unpack the reading by use of visuals and examples.
No significant grammatical errors.
The text is not offensive or culturally insensitive. Examples were inclusive of various races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This quick guide is a beneficial text to assist in unpacking the learning related to quantitative statistics. I would use this book to complement my instruction and lessons, or use this book as a main text with supplemental statistical problems and formulas. References to statistical programs were appropriate and were useful. The text did exactly what was stated up front in that it is a direct guide to quantitative statistics. It is well-written and to the point with content areas easy to locate by topic.
Reviewed by Sarah Capello, Assistant Professor, Radford University on 1/18/22
The text claims to provide "quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences," which it does. There is no index or glossary, although vocabulary words are bolded and defined throughout the text. read more
The text claims to provide "quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences," which it does. There is no index or glossary, although vocabulary words are bolded and defined throughout the text.
The content is mostly accurate. I would have preferred a few nuances to be hashed out a bit further to avoid potential reader confusion or misunderstanding of the concepts presented.
The content is current; however, some of the references cited in the text are outdated. Newer editions of those texts exist.
The text is very accessible and readable for a variety of audiences. Key terms are well-defined.
There are no content discrepancies within the text. The author even uses similarly shaped graphics for recurring purposes throughout the text (e.g., arrow call outs for further reading, rectangle call outs for examples).
The content is chunked nicely by topics and sections. If it were used for a course, it would be easy to assign different sections of the text for homework, etc. without confusing the reader if the instructor chose to present the content in a different order.
The author follows the structure of the research process. The organization of the text is easy to follow and comprehend.
All of the supplementary images (e.g., tables and figures) were beneficial to the reader and enhanced the text.
There are no significant grammatical errors.
I did not find any culturally offensive or insensitive references in the text.
This text does the difficult job of introducing the complicated concepts and processes of quantitative research in a quick and easy reference guide fairly well. I would not depend solely on this text to teach students about quantitative research, but it could be a good jumping off point for those who have no prior knowledge on this subject or those who need a gentle introduction before diving in to more advanced and complex readings of quantitative research methods.
Reviewed by J. Marlie Henry, Adjunct Faculty, University of Saint Francis on 12/9/21
Considering the length of this guide, this does a good job of addressing major areas that typically need to be addressed. There is a contents section. The guide does seem to be organized accordingly with appropriate alignment and logical flow of... read more
Considering the length of this guide, this does a good job of addressing major areas that typically need to be addressed. There is a contents section. The guide does seem to be organized accordingly with appropriate alignment and logical flow of thought. There is no glossary but, for a guide of this length, a glossary does not seem like it would enhance the guide significantly.
The content is relatively accurate. Expanding the content a bit more or explaining that the methods and designs presented are not entirely inclusive would help. As there are different schools of thought regarding what should/should not be included in terms of these designs and methods, simply bringing attention to that and explaining a bit more would help.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
This content needs to be updated. Most of the sources cited are seven or more years old. Even more, it would be helpful to see more currently relevant examples. Some of the source authors such as Andy Field provide very interesting and dynamic instruction in general, but they have much more current information available.
The language used is clear and appropriate. Unnecessary jargon is not used. The intent is clear- to communicate simply in a straightforward manner.
The guide seems to be internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework. There do not seem to be issues in this area. Terminology is internally consistent.
For a guide of this length, the author structured this logically into sections. This guide could be adopted in whole or by section with limited modifications. Courses with fewer than seven modules could also logically group some of the sections.
This guide does present with logical organization. The topics presented are conceptually sequenced in a manner that helps learners build logically on prior conceptualization. This also provides a simple conceptual framework for instructors to guide learners through the process.
Interface rating: 4
The visuals themselves are simple, but they are clear and understandable without distracting the learner. The purpose is clear- that of learning rather than visuals for the sake of visuals. Likewise, navigation is clear and without issues beyond a broken link (the last source noted in the references).
This guide seems to be free of grammatical errors.
It would be interesting to see more cultural integration in a guide of this nature, but the guide is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. The language used seems to be consistent with APA's guidelines for unbiased language.
Reviewed by Heng Yu-Ku, Professor, University of Northern Colorado on 5/13/21
The text covers all areas and ideas appropriately and provides practical tables, charts, and examples throughout the text. I would suggest the author also provides a complete research proposal at the end of Section 3 (page 10) and a comprehensive... read more
The text covers all areas and ideas appropriately and provides practical tables, charts, and examples throughout the text. I would suggest the author also provides a complete research proposal at the end of Section 3 (page 10) and a comprehensive research study as an Appendix after section 7 (page 26) to help readers comprehend information better.
For the most part, the content is accurate and unbiased. However, the author only includes four types of research designs used on the social sciences that contain quantitative elements: 1. Mixed method, 2) Case study, 3) Quasi-experiment, and 3) Action research. I wonder why the correlational research is not included as another type of quantitative research design as it has been introduced and emphasized in section 6 by the author.
I believe the content is up-to-date and that necessary updates will be relatively easy and straightforward to implement.
The text is easy to read and provides adequate context for any technical terminology used. However, the author could provide more detailed information about estimating the minimum sample size but not just refer the readers to use the online sample calculators at a different website.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework. The author provides the right amount of information with additional information or resources for the readers.
The text includes seven sections. Therefore, it is easier for the instructor to allocate or divide the content into different weeks of instruction within the course.
Yes, the topics in the text are presented in a logical and clear fashion. The author provides clear and precise terminologies, summarizes important content in Table or Figure forms, and offers examples in each section for readers to check their understanding.
The interface of the book is consistent and clear, and all the images and charts provided in the book are appropriate. However, I did encounter some navigation problems as a couple of links are not working or requires permission to access those (pages 10 and 27).
No grammatical errors were found.
No culturally incentive or offensive in its language and the examples provided were found.
As the book title stated, this book provides “A Quick Guide to Quantitative Research in Social Science. It offers easy-to-read information and introduces the readers to the research process, such as research questions, research paradigms, research process, research designs, research methods, data collection, data analysis, and data discussion. However, some links are not working or need permissions to access them (pages 10 and 27).
Reviewed by Hsiao-Chin Kuo, Assistant Professor, Northeastern Illinois University on 4/26/21, updated 4/28/21
As a quick guide, it covers basic concepts related to quantitative research. It starts with WHY quantitative research with regard to asking research questions and considering research paradigms, then provides an overview of research design and... read more
As a quick guide, it covers basic concepts related to quantitative research. It starts with WHY quantitative research with regard to asking research questions and considering research paradigms, then provides an overview of research design and process, discusses methods, data collection and analysis, and ends with writing a research report. It also identifies its target readers/users as those begins to explore quantitative research. It would be helpful to include more examples for readers/users who are new to quantitative research.
Its content is mostly accurate and no bias given its nature as a quick guide. Yet, it is also quite simplified, such as its explanations of mixed methods, case study, quasi-experimental research, and action research. It provides resources for extended reading, yet more recent works will be helpful.
The book is relevant given its nature as a quick guide. It would be helpful to provide more recent works in its resources for extended reading, such as the section for Survey Research (p. 12). It would also be helpful to include more information to introduce common tools and software for statistical analysis.
The book is written with clear and understandable language. Important terms and concepts are presented with plain explanations and examples. Figures and tables are also presented to support its clarity. For example, Table 4 (p. 20) gives an easy-to-follow overview of different statistical tests.
The framework is very consistent with key points, further explanations, examples, and resources for extended reading. The sample studies are presented following the layout of the content, such as research questions, design and methods, and analysis. These examples help reinforce readers' understanding of these common research elements.
The book is divided into seven chapters. Each chapter clearly discusses an aspect of quantitative research. It can be easily divided into modules for a class or for a theme in a research method class. Chapters are short and provides additional resources for extended reading.
The topics in the chapters are presented in a logical and clear structure. It is easy to follow to a degree. Though, it would be also helpful to include the chapter number and title in the header next to its page number.
The text is easy to navigate. Most of the figures and tables are displayed clearly. Yet, there are several sections with empty space that is a bit confusing in the beginning. Again, it can be helpful to include the chapter number/title next to its page number.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
No major grammatical errors were found.
There are no cultural insensitivities noted.
Given the nature and purpose of this book, as a quick guide, it provides readers a quick reference for important concepts and terms related to quantitative research. Because this book is quite short (27 pages), it can be used as an overview/preview about quantitative research. Teacher's facilitation/input and extended readings will be needed for a deeper learning and discussion about aspects of quantitative research.
Reviewed by Yang Cheng, Assistant Professor, North Carolina State University on 1/6/21
It covers the most important topics such as research progress, resources, measurement, and analysis of the data. read more
It covers the most important topics such as research progress, resources, measurement, and analysis of the data.
The book accurately describes the types of research methods such as mixed-method, quasi-experiment, and case study. It talks about the research proposal and key differences between statistical analyses as well.
The book pinpointed the significance of running a quantitative research method and its relevance to the field of social science.
The book clearly tells us the differences between types of quantitative methods and the steps of running quantitative research for students.
The book is consistent in terms of terminologies such as research methods or types of statistical analysis.
It addresses the headlines and subheadlines very well and each subheading should be necessary for readers.
The book was organized very well to illustrate the topic of quantitative methods in the field of social science.
The pictures within the book could be further developed to describe the key concepts vividly.
The textbook contains no grammatical errors.
It is not culturally offensive in any way.
Overall, this is a simple and quick guide for this important topic. It should be valuable for undergraduate students who would like to learn more about research methods.
Reviewed by Pierre Lu, Associate Professor, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 11/20/20
As a quick guide to quantitative research in social sciences, the text covers most ideas and areas. read more
As a quick guide to quantitative research in social sciences, the text covers most ideas and areas.
Mostly accurate content.
As a quick guide, content is highly relevant.
Succinct and clear.
Internally, the text is consistent in terms of terminology used.
The text is easily and readily divisible into smaller sections that can be used as assignments.
I like that there are examples throughout the book.
Easy to read. No interface/ navigation problems.
No grammatical errors detected.
I am not aware of the culturally insensitive description. After all, this is a methodology book.
I think the book has potential to be adopted as a foundation for quantitative research courses, or as a review in the first weeks in advanced quantitative course.
Reviewed by Sarah Fischer, Assistant Professor, Marymount University on 7/31/20
It is meant to be an overview, but it incredibly condensed and spends almost no time on key elements of statistics (such as what makes research generalizable, or what leads to research NOT being generalizable). read more
It is meant to be an overview, but it incredibly condensed and spends almost no time on key elements of statistics (such as what makes research generalizable, or what leads to research NOT being generalizable).
Content Accuracy rating: 1
Contains VERY significant errors, such as saying that one can "accept" a hypothesis. (One of the key aspect of hypothesis testing is that one either rejects or fails to reject a hypothesis, but NEVER accepts a hypothesis.)
Very relevant to those experiencing the research process for the first time. However, it is written by someone working in the natural sciences but is a text for social sciences. This does not explain the errors, but does explain why sometimes the author assumes things about the readers ("hail from more subjectivist territory") that are likely not true.
Clarity rating: 3
Some statistical terminology not explained clearly (or accurately), although the author has made attempts to do both.
Very consistently laid out.
Chapters are very short yet also point readers to outside texts for additional information. Easy to follow.
Generally logically organized.
Easy to navigate, images clear. The additional sources included need to linked to.
Minor grammatical and usage errors throughout the text.
Makes efforts to be inclusive.
The idea of this book is strong--short guides like this are needed. However, this book would likely be strengthened by a revision to reduce inaccuracies and improve the definitions and technical explanations of statistical concepts. Since the book is specifically aimed at the social sciences, it would also improve the text to have more examples that are based in the social sciences (rather than the health sciences or the arts).
Reviewed by Michelle Page, Assistant Professor, Worcester State University on 5/30/20
This text is exactly intended to be what it says: A quick guide. A basic outline of quantitative research processes, akin to cliff notes. The content provides only the essentials of a research process and contains key terms. A student or new... read more
This text is exactly intended to be what it says: A quick guide. A basic outline of quantitative research processes, akin to cliff notes. The content provides only the essentials of a research process and contains key terms. A student or new researcher would not be able to use this as a stand alone guide for quantitative pursuits without having a supplemental text that explains the steps in the process more comprehensively. The introduction does provide this caveat.
Content Accuracy rating: 3
There are no biases or errors that could be distinguished; however, it’s simplicity in content, although accurate for an outline of process, may lack a conveyance of the deeper meanings behind the specific processes explained about qualitative research.
The content is outlined in traditional format to highlight quantitative considerations for formatting research foundational pieces. The resources/references used to point the reader to literature sources can be easily updated with future editions.
The jargon in the text is simple to follow and provides adequate context for its purpose. It is simplified for its intention as a guide which is appropriate.
Each section of the text follows a consistent flow. Explanation of the research content or concept is defined and then a connection to literature is provided to expand the readers understanding of the section’s content. Terminology is consistent with the qualitative process.
As an “outline” and guide, this text can be used to quickly identify the critical parts of the quantitative process. Although each section does not provide deeper content for meaningful use as a stand alone text, it’s utility would be excellent as a reference for a course and can be used as an content guide for specific research courses.
The text’s outline and content are aligned and are in a logical flow in terms of the research considerations for quantitative research.
The only issue that the format was not able to provide was linkable articles. These would have to be cut and pasted into a browser. Functional clickable links in a text are very successful at leading the reader to the supplemental material.
No grammatical errors were noted.
This is a very good outline “guide” to help a new or student researcher to demystify the quantitative process. A successful outline of any process helps to guide work in a logical and systematic way. I think this simple guide is a great adjunct to more substantial research context.
Table of Contents
- Section 1: What will this resource do for you?
- Section 2: Why are you thinking about numbers? A discussion of the research question and paradigms.
- Section 3: An overview of the Research Process and Research Designs
- Section 4: Quantitative Research Methods
- Section 5: the data obtained from quantitative research
- Section 6: Analysis of data
- Section 7: Discussing your Results
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This resource is intended as an easy-to-use guide for anyone who needs some quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences, covering subjects such as education, sociology, business, nursing. If you area qualitative researcher who needs to venture into the world of numbers, or a student instructed to undertake a quantitative research project despite a hatred for maths, then this booklet should be a real help.
The booklet was amended in 2022 to take into account previous review comments.
About the Contributors
Christine Davies , Ph.D
Contribute to this Page
College of Education and Human Development
Department of Educational Psychology
Quantitative methods in education
Solve problems in education through research.
Students in Quantitative Methods in Education engage in the science and practice of educational measurement and statistics, primarily through the development and application of statistical and psychometric methods. All QME students will engage in coursework addressing fundamental topics related to statistics, educational measurement, research methods, and foundations in education (e.g., learning and cognition, social development). Students will also undertake additional coursework and complete a set of milestones that will specialize their knowledge and scholarship in educational measurement or statistics. Upon matriculation, graduates will be equipped to help inform educational policy, practice, and curriculum and—most importantly—help schools and students succeed.
- Test publishing firms
- Teaching and research at colleges and universities (PhD only)
- Research and evaluation centers
- Public school systems
- State departments of instruction
- Private industry
Quote from V.N. Vimal Rao, PhD '23
The strong theoretical and methodological foundation I developed in QME and EPSY supports my research and my mentoring of student researchers, while the teaching experience and knowledge of educational psychology I gained supports my teaching and mentoring of teaching assistants. V.N. Vimal Rao, PhD '23 Teaching Assistant Professor in the Department of Statistics University of Illinois Urbana Champaign
Submit your application for the fall semester following the deadlines below. Note the dates are the same for both MA and PhD applicants.
To be considered for fellowships and departmental financial assistance, application materials must be submitted to the program and the Graduate School by the December 1 deadline. (If you are requesting a waiver for the application fee, the last day to apply is 11/17/24.)
If you're not seeking a fellowship or departmental financial aid, you have until March 1 to submit your application materials. (If you are requesting a waiver for the application fee, the last day to apply is 2/15/25.)
MA curriculum (33 credits)
PhD curriculum (72 credits)
The QME program strives to provide funding opportunities to all incoming students. While we can’t typically guarantee funding, over the last five years, we have been able to fund over 95% of our students that were looking for funding (including our MA students)!
Visit the College of Education and Human Development's Finance and Funding page for information on tuition.
Fellowships and awards
Submit your application materials by the December 1 deadline, and you’ll automatically be considered for Graduate School fellowships and departmental awards based on scholastic achievement. Notification of awards will be sent in March.
Note: Spring, summer, and fall (March deadline) applicants will not qualify for fellowships.
Graduate assistantships
Get paid to work as a teaching assistant, graduate instructor or research assistant. Graduate assistantships are available through the department, College of Education and Human Development, and the University.
- John P. Yackel/Pearson Graduate Internship
- Jack Merwin Graduate Assistantship
- All University of Minnesota graduate assistantships
Note: Applicants who complete their applications by the March 1 deadline will be less likely to receive graduate assistantships than students who meet the December 1 deadline.
Additional funding
Visit the College of Education and Human Development's Finance and Funding page for more information on funding.
Financial aid
Visit OneStop Student Services for more information on available financial aid.
The Department of Educational Psychology offers a minor in educational psychology with an emphasis in quantitative methods in education.
Quote from Rik Lamm, PhD '23
My background in the QME program has equipped me with the skills necessary for my current role as a Research, Evaluation, and Assessment Scientist for Bloomington Public Schools. These include developing non-cognitive surveys such as student climate surveys and parent engagement surveys, as well as analyzing data from academic assessments such as the MCAs. Additionally, QME has equipped me with the skills to interpret complex data in order to predict longitudinal trends. This ability leads to the development of research-driven strategies that benefit both students and teachers. Rik Lamm, PhD '23 Research, Evaluation, and Assessment Scientist Bloomington Public Schools
Faculty and staff
Assistant Professor
Assistant professor
Nidhi Kohli
Royal and Virginia Anderson Professor of Quantitative Methods in Education; Program Coordinator
Chelsey Legacy
Teaching assistant professor
Suzanne Loch
Senior teaching specialist
Michael Rodriguez
CEHD Dean; Campbell Leadership Chair in Education and Human Development; co-founding director of Educational Equity Resource Center
Andrew Zieffler
Teaching professor
Adjunct faculty and program affiliates
Adjunct faculty, claudio violato.
Assistant dean, Medical School
Program affiliates
Adam rothman.
Associate professor, School of Statistics
Quote from José Palma, PhD '21
It is the combination of psychometric research and applied focus, in addition to knowledge gained from my academic journey, that makes me a competitive and atypical educational measurement researcher today. José Palma, PhD '21 ACES Faculty Fellow and Assistant Professor Texas A&M University
Andrew Zieffler receives 2023-2024 Outstanding Contributions to Graduate and Professional Education Award
Dr. Andrew Zieffler was one of the recipients of the 2024 Outstanding Contributions to Graduate and Professional Education. Zieffler was given the award for the outstanding contributions he has made to graduate and professional education.
Corissa Rohloff, PhD student in Ed Psych, awarded Russell W. Burris Memorial Fellowship
Corissa Rohloff, PhD candidate in the quantitative methods in education program, has been awarded the Russell W. Burris Memorial Fellowship.
QME recognizes students in year end celebration
Students in the Department of Educational Psychology’s quantitative methods in education (QME) program were recognized for their contributions to the program during the 2022-23 academic year.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions . This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected. It often involves the use of surveys, experiments, or other structured data collection methods to gather quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Methods

Quantitative Research Methods are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used to describe the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. This research method is used to answer the questions of what, where, when, and how. Descriptive research designs use a variety of methods such as observation, case studies, and surveys to collect data. The data is then analyzed using statistical tools to identify patterns and relationships.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to investigate the relationship between two or more variables. Researchers use correlational research to determine whether a relationship exists between variables and to what extent they are related. This research method involves collecting data from a sample and analyzing it using statistical tools such as correlation coefficients.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks full control over the independent variable. Researchers use quasi-experimental research designs when it is not feasible or ethical to manipulate the independent variable.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method involves manipulating the independent variable and observing the effects on the dependent variable. Researchers use experimental research designs to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. This research method is used to gather information on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors of individuals. Researchers use survey research to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large sample size. Survey research can be conducted through various methods such as online, phone, mail, or in-person interviews.
Quantitative Research Analysis Methods
Here are some commonly used quantitative research analysis methods:
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis is the most common quantitative research analysis method. It involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.

Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Researchers use regression analysis to identify and quantify the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical technique used to identify underlying factors that explain the correlations among a set of variables. Researchers use factor analysis to reduce a large number of variables to a smaller set of factors that capture the most important information.
Structural Equation Modeling
Structural equation modeling is a statistical technique used to test complex relationships between variables. It involves specifying a model that includes both observed and unobserved variables, and then using statistical methods to test the fit of the model to the data.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is collected over time. It involves identifying patterns and trends in the data, as well as any seasonal or cyclical variations.
Multilevel Modeling
Multilevel modeling is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels. For example, researchers might use multilevel modeling to analyze data that is collected from individuals who are nested within groups, such as students nested within schools.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has many applications across a wide range of fields. Here are some common examples:
- Market Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions.
- Health Research: Quantitative research is used in health research to study the effectiveness of medical treatments, identify risk factors for diseases, and track health outcomes over time. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from clinical trials, surveys, and other sources to inform medical practice and policy.
- Social Science Research: Quantitative research is used in social science research to study human behavior, attitudes, and social structures. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform social policies, educational programs, and community interventions.
- Education Research: Quantitative research is used in education research to study the effectiveness of teaching methods, assess student learning outcomes, and identify factors that influence student success. Researchers use experimental and quasi-experimental designs, as well as surveys and other quantitative methods, to collect and analyze data.
- Environmental Research: Quantitative research is used in environmental research to study the impact of human activities on the environment, assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies, and identify ways to reduce environmental risks. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from field studies, experiments, and other sources.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research:
- Numerical data : Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
- Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves collecting data from a large sample of individuals or groups in order to increase the reliability and generalizability of the findings.
- Objective approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and impartial in its approach, focusing on the collection and analysis of data rather than personal beliefs, opinions, or experiences.
- Control over variables: Quantitative research often involves manipulating variables to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers aim to control for extraneous variables that may impact the results.
- Replicable : Quantitative research aims to be replicable, meaning that other researchers should be able to conduct similar studies and obtain similar results using the same methods.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to produce findings that can be generalized to larger populations beyond the specific sample studied. This is achieved through the use of random sampling methods and statistical inference.
Examples of Quantitative Research
Here are some examples of quantitative research in different fields:
- Market Research: A company conducts a survey of 1000 consumers to determine their brand awareness and preferences. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns that can inform marketing strategies.
- Health Research : A researcher conducts a randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of a new drug for treating a particular medical condition. The study involves collecting data from a large sample of patients and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Social Science Research : A sociologist conducts a survey of 500 people to study attitudes toward immigration in a particular country. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify factors that influence these attitudes.
- Education Research: A researcher conducts an experiment to compare the effectiveness of two different teaching methods for improving student learning outcomes. The study involves randomly assigning students to different groups and collecting data on their performance on standardized tests.
- Environmental Research : A team of researchers conduct a study to investigate the impact of climate change on the distribution and abundance of a particular species of plant or animal. The study involves collecting data on environmental factors and population sizes over time and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Psychology : A researcher conducts a survey of 500 college students to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify correlations and potential causal relationships.
- Political Science: A team of researchers conducts a study to investigate voter behavior during an election. They use survey methods to collect data on voting patterns, demographics, and political attitudes, and analyze the results using statistical methods.
How to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here is a general overview of how to conduct quantitative research:
- Develop a research question: The first step in conducting quantitative research is to develop a clear and specific research question. This question should be based on a gap in existing knowledge, and should be answerable using quantitative methods.
- Develop a research design: Once you have a research question, you will need to develop a research design. This involves deciding on the appropriate methods to collect data, such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies. You will also need to determine the appropriate sample size, data collection instruments, and data analysis techniques.
- Collect data: The next step is to collect data. This may involve administering surveys or questionnaires, conducting experiments, or gathering data from existing sources. It is important to use standardized methods to ensure that the data is reliable and valid.
- Analyze data : Once the data has been collected, it is time to analyze it. This involves using statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables. Common statistical techniques include correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
- Interpret results: After analyzing the data, you will need to interpret the results. This involves identifying the key findings, determining their significance, and drawing conclusions based on the data.
- Communicate findings: Finally, you will need to communicate your findings. This may involve writing a research report, presenting at a conference, or publishing in a peer-reviewed journal. It is important to clearly communicate the research question, methods, results, and conclusions to ensure that others can understand and replicate your research.
When to use Quantitative Research
Here are some situations when quantitative research can be appropriate:
- To test a hypothesis: Quantitative research is often used to test a hypothesis or a theory. It involves collecting numerical data and using statistical analysis to determine if the data supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- To generalize findings: If you want to generalize the findings of your study to a larger population, quantitative research can be useful. This is because it allows you to collect numerical data from a representative sample of the population and use statistical analysis to make inferences about the population as a whole.
- To measure relationships between variables: If you want to measure the relationship between two or more variables, such as the relationship between age and income, or between education level and job satisfaction, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data on both variables and use statistical analysis to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
- To identify patterns or trends: Quantitative research can be useful for identifying patterns or trends in data. For example, you can use quantitative research to identify trends in consumer behavior or to identify patterns in stock market data.
- To quantify attitudes or opinions : If you want to measure attitudes or opinions on a particular topic, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data using surveys or questionnaires and analyze the data using statistical methods to determine the prevalence of certain attitudes or opinions.
Purpose of Quantitative Research
The purpose of quantitative research is to systematically investigate and measure the relationships between variables or phenomena using numerical data and statistical analysis. The main objectives of quantitative research include:
- Description : To provide a detailed and accurate description of a particular phenomenon or population.
- Explanation : To explain the reasons for the occurrence of a particular phenomenon, such as identifying the factors that influence a behavior or attitude.
- Prediction : To predict future trends or behaviors based on past patterns and relationships between variables.
- Control : To identify the best strategies for controlling or influencing a particular outcome or behavior.
Quantitative research is used in many different fields, including social sciences, business, engineering, and health sciences. It can be used to investigate a wide range of phenomena, from human behavior and attitudes to physical and biological processes. The purpose of quantitative research is to provide reliable and valid data that can be used to inform decision-making and improve understanding of the world around us.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
There are several advantages of quantitative research, including:
- Objectivity : Quantitative research is based on objective data and statistical analysis, which reduces the potential for bias or subjectivity in the research process.
- Reproducibility : Because quantitative research involves standardized methods and measurements, it is more likely to be reproducible and reliable.
- Generalizability : Quantitative research allows for generalizations to be made about a population based on a representative sample, which can inform decision-making and policy development.
- Precision : Quantitative research allows for precise measurement and analysis of data, which can provide a more accurate understanding of phenomena and relationships between variables.
- Efficiency : Quantitative research can be conducted relatively quickly and efficiently, especially when compared to qualitative research, which may involve lengthy data collection and analysis.
- Large sample sizes : Quantitative research can accommodate large sample sizes, which can increase the representativeness and generalizability of the results.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
There are several limitations of quantitative research, including:
- Limited understanding of context: Quantitative research typically focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, which may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the context or underlying factors that influence a phenomenon.
- Simplification of complex phenomena: Quantitative research often involves simplifying complex phenomena into measurable variables, which may not capture the full complexity of the phenomenon being studied.
- Potential for researcher bias: Although quantitative research aims to be objective, there is still the potential for researcher bias in areas such as sampling, data collection, and data analysis.
- Limited ability to explore new ideas: Quantitative research is often based on pre-determined research questions and hypotheses, which may limit the ability to explore new ideas or unexpected findings.
- Limited ability to capture subjective experiences : Quantitative research is typically focused on objective data and may not capture the subjective experiences of individuals or groups being studied.
- Ethical concerns : Quantitative research may raise ethical concerns, such as invasion of privacy or the potential for harm to participants.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Mixed Methods Research – Types & Analysis

Qualitative Research Methods

Quasi-Experimental Research Design – Types...

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...
Trends and Motivations in Critical Quantitative Educational Research: A Multimethod Examination Across Higher Education Scholarship and Author Perspectives
- Open access
- Published: 04 June 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Christa E. Winkler ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1700-5444 1 &
- Annie M. Wofford ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2246-1946 2
23 Accesses
11 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
To challenge “objective” conventions in quantitative methodology, higher education scholars have increasingly employed critical lenses (e.g., quantitative criticalism, QuantCrit). Yet, specific approaches remain opaque. We use a multimethod design to examine researchers’ use of critical approaches and explore how authors discussed embedding strategies to disrupt dominant quantitative thinking. We draw data from a systematic scoping review of critical quantitative higher education research between 2007 and 2021 ( N = 34) and semi-structured interviews with 18 manuscript authors. Findings illuminate (in)consistencies across scholars’ incorporation of critical approaches, including within study motivations, theoretical framing, and methodological choices. Additionally, interview data reveal complex layers to authors’ decision-making processes, indicating that decisions about embracing critical quantitative approaches must be asset-based and intentional. Lastly, we discuss findings in the context of their guiding frameworks (e.g., quantitative criticalism, QuantCrit) and offer implications for employing and conducting research about critical quantitative research.
Similar content being viewed by others

Ethical Considerations of Conducting Systematic Reviews in Educational Research

When Does a Researcher Choose a Quantitative, Qualitative, or Mixed Research Approach?
Systematic reviews in educational research: methodology, perspectives and application.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Across the field of higher education and within many roles—including policymakers, researchers, and administrators—key leaders and educational partners have historically relied on quantitative methods to inform system-level and student-level changes to policy and practice. This reliance is rooted, in part, on the misconception that quantitative methods depict the objective state of affairs in higher education. This perception is not only inaccurate but also dangerous, as the numbers produced from quantitative methods are “neither objective nor color-blind” (Gillborn et al., 2018 , p. 159). In fact, like all research, quantitative data collection and analysis are informed by theories and beliefs that are susceptible to bias. Further, such bias may come in multiple forms such as researcher bias and bias within the statistical methods themselves (e.g., Bierema et al., 2021 ; Torgerson & Torgerson, 2003 ). Thus, if left unexamined from a critical perspective, quantitative research may inform policies and practices that fuel the engine of cultural and social reproduction in higher education (e.g., Bourdieu, 1977 ).
Largely, critical approaches to higher education research have been dominated by qualitative methods (McCoy & Rodricks, 2015 ). While qualitative approaches are vital, some have argued that a wider conceptualization of critical inquiry may propel our understanding of processes in higher education (Stage & Wells, 2014 ) and that critical research need not be explicitly qualitative (refer to Sablan, 2019 ; Stage, 2007 ). If scholars hope to embrace multiple ways of challenging persistent inequities and structures of oppression in higher education, such as racism, advancing critical quantitative work can help higher education researchers “expose and challenge hidden assumptions that frequently encode racist perspectives beneath the façade of supposed quantitative objectivity” (Gillborn et al., 2018 , p. 158).
Across professional networks in higher education, the perspectives of association leaders (e.g., Association for the Study of Higher Education [ASHE]) have often placed qualitative and quantitative research in opposition to each other, with qualitative research being a primary way to amplify the voices of systemically minoritized students, faculty, and staff (Kimball & Friedensen, 2019 ). Yet, given the vast growth of critical higher education research (e.g., Byrd, 2019 ; Espino, 2012 ; Martínez-Alemán et al., 2015 ), recent ASHE presidents have recognized how prior leaders planted transformative seeds of critical theory and praxis (Renn, 2020 ) and advocated for critical higher education scholarship as a disrupter (Stewart, 2022 ). With this shift in discourse, many members of the higher education research community have also grown their desire to expand upon the legacy of critical research—in both qualitative and quantitative forms.
Critical quantitative approaches hold promise as one avenue for meeting recent calls to embrace equity-mindedness and transform the future of higher education research, yet current structures of training and resources for quantitative methods lack guidance on engaging such approaches. For higher education scholars to advance critical inquiry via quantitative methods, we must first understand the extent to which such approaches have been adopted. Accordingly, this study sheds light on critical quantitative approaches used in higher education literature and provides storied insights from the experiences of scholars who have engaged critical perspectives with quantitative methods. We were guided by the following research questions:
To what extent do higher education scholars incorporate critical perspectives into quantitative research?
How do higher education scholars discuss specific strategies to leverage critical perspectives in quantitative research?
Contextualizing Existing Critical Approaches to Quantitative Research
To foreground our analysis of literature employing critical quantitative lenses to studies about higher education, we first must understand the roots of such framing. Broadly, the foundations of critical quantitative approaches align with many elements of equity-mindedness. Equity-mindedness prompts individuals to question divergent patterns in educational outcomes, recognize that racism is embedded in everyday practices, and invest in un/learning the effects of racial identity and racialized expectations (Bensimon, 2018 ). Yet, researchers’ commitments to critical quantitative approaches stand out as a unique thread in the larger fabric of opportunities to embrace equity-mindedness in higher education research. Below, we discuss three significant publications that have been widely applied as frameworks to engage critical quantitative approaches in higher education. While these publications are not the only ones associated with critical inquiry in quantitative research, their evolution, commonalities, and distinctions offer a robust background of epistemological development in this area of scholarship.
Quantitative Criticalism (Stage, 2007 )
Although some higher education scholars have applied critical perspectives in their research for many years, Stage’s ( 2007 ) introduction of quantitative criticalism was a salient contribution to creating greater discourse related to such perspectives. Quantitative criticalism, as a coined paradigmatic approach for engaging critical questions using quantitative data, was among the first of several crucial publications on this topic in a 2007 edition of New Directions for Institutional Research . Collectively, this special issue advanced perspectives on how higher education scholars may challenge traditional positivist and post-positivist paradigms in quantitative inquiry. Instead, researchers could apply (what Stage referred to as) quantitative criticalism to develop research questions centering on social inequities in educational processes and outcomes as well as challenge widely accepted models, measures, and analytic practices.
Notably, Stage ( 2007 ) grounded the motivation for this new paradigmatic approach in the core concepts of critical inquiry (e.g., Kincheloe & McLaren, 1994 ). Tracing critical inquiry back to the German Frankfurt school, Stage discussed how the principles of critical theory have evolved over time and highlighted Kincheloe and McLaren’s ( 1994 ) definition of critical theory as most relevant to the principles of quantitative criticalism. Kincheloe and McLaren’s definition of critical describes how researchers applying critical paradigms in their scholarship center concepts such as socially and historically created power structures, subjectivity, privilege and oppression, and the reproduction of oppression in traditional research approaches. Perhaps most importantly, Kincheloe and McLaren urge scholars to be self-conscious in their decision making—a tall ask of quantitative scholars operating from positivist and post-positivist vantage points.
In advancing quantitative criticalism, Stage ( 2007 ) first argued that all critical scholars must center their outcomes on equity. To enact this core focus on equity in quantitative criticalism, Stage outlined two tasks for researchers. First, critical quantitative researchers must “use data to represent educational processes and outcomes on a large scale to reveal inequities and to identify social or institutional perpetuation of systematic inequities in such processes and outcomes” (p. 10). Second, Stage advocated for critical quantitative researchers to “question the models, measures, and analytic practices of quantitative research in order to offer competing models, measures, and analytic practices that better describe experiences of those who have not been adequately represented” (p. 10). Stage’s arguments and invitations for criticalism spurred crucial conversations, many of which led to the development of a two-part series on critical quantitative approaches in New Directions for Institutional Research (Stage & Wells, 2014 ; Wells & Stage, 2015 ). With nearly a decade of new perspectives to offer, manuscripts within these subsequent special issues expanded the concepts of quantitative criticalism. Specifically, these new contributions advanced the notion that quantitative criticalism should include all parts of the research process—instead of maintaining a focus on paradigm and research questions alone—and made inroads when it came to challenging the (default, dominant) process of quantitative research. While many scholars offered noteworthy perspectives in these special issues (Stage & Wells, 2014 ; Wells & Stage, 2015 ), we now turn to one specific article within these special issues that offered a conceptual model for critical quantitative inquiry.
Critical Quantitative Inquiry (Rios-Aguilar, 2014 )
Building from and guided by the work of other criticalists (namely, Estela Bensimon, Sara Goldrick-Rab, Frances Stage, and Erin Leahey), Rios-Aguilar ( 2014 ) developed a complementary framework representing the process and application of critical quantitative inquiry in higher education scholarship. At the heart of Rios-Aguilar’s conceptualization lies the acknowledgment that quantitative research is a human activity that requires careful decisions. With this foundation comes the pressing need for quantitative scholars to engage in self-reflection and transparency about the processes and outcomes of their methodological choices—actions that could potentially disrupt traditional notions and deficit assumptions that maintain systems of oppression in higher education.
Rios-Aguilar ( 2014 ) offered greater specificity to build upon many principles from other criticalists. For one, methodologically, Rios-Aguilar challenged the notion of using “fancy” statistical methods just for the sake of applying advanced methods. Instead, she argued that critical quantitative scholars should engage “in a self-reflection of the actual research practices and statistical approaches (i.e., choice of centering approach, type of model estimated, number of control variables, etc.) they use and the various influences that affect those practices” (Rios-Aguilar, 2014 , p. 98). In this purview, scholars should ensure that all methodological choices advance their ability to reveal inequities; such choices may include those that challenge the use of reference groups in coding, the interpretation of statistics in ways that move beyond p -values for statistical significance, or the application and alignment of theoretical and conceptual frameworks that focus on the assets of systemically minoritized students. Rios-Aguilar also noted, in agreement with the foundations of equity-mindedness and critical theory, that quantitative criticalists have an obligation to translate findings into tangible changes in policy and practice that can redress inequities.
Ultimately, Rios-Aguilar’s ( 2014 ) framework focused on “the interplay between research questions, theory, method/research practices, and policy/advocacy” to identify how quantitative criticalists’ scholarship can be “relevant and meaningful” (p. 96). Specifically, Rios-Aguilar called upon quantitative criticalists to ask research questions that center on equity and power, engage in self-reflection about their data sources, analyses, and disaggregation techniques, attend to interpretation with practical/policy-related significance, and expand beyond field-level silos in theory and implications. Without challenging dominant approaches in quantitative higher education research, Rios-Aguilar noted that the field will continue to inaccurately capture the experiences of systemically minoritized students. In college access and success, for example, ignoring this need for evolving approaches and models would continue what Bensimon ( 2007 ) referred to as the Tintonian Dynasty, with scholars widely applying and citing Tinto’s work but failing to acknowledge the unique experiences of systemically minoritized students. These and other concrete recommendations have served as a springboard for quantitative criticalists, prompting scholars to incorporate critical approaches in more cohesive and congruent ways.
QuantCrit (Gillborn et al., 2018 )
As an epistemologically different but related form of critical quantitative scholarship, QuantCrit—quantitative critical race theory—has emerged as a vital stream of inquiry that applies critical race theory to methodological approaches. Given that statistical methods were developed in support of the eugenics movement (Zuberi, 2001 ), QuantCrit researchers must consider how the “norms” of quantitative research support white supremacy (Zuberi & Bonilla-Silva, 2008 ). Fortunately, as Garcia et al. ( 2018 ) noted, “[t]he problems concerning the ahistorical and decontextualized ‘default’ mode and misuse of quantitative research methods are not insurmountable” (p. 154). As such, the goal of QuantCrit is to conduct quantitative research in a way that can contextualize and challenge historical, social, political, and economic power structures that uphold racism (e.g., Garcia et al., 2018 ; Gillborn et al., 2018 ).
In coining the term QuantCrit, Gillborn et al. ( 2018 ) provided five QuantCrit tenets adapted from critical race theory. First, the centrality of racism offers a methodological and political statement about how racism is complex, fluid, and rooted in social dynamics of power. Second, numbers are not neutral demonstrates an imperative for QuantCrit researchers—one that prompts scholars to understand how quantitative data have been collected and analyzed to prioritize interests rooted in white, elite worldviews. As such, QuantCrit researchers must reject numbers as “true” and as presenting a unidimensional truth. Third, categories are neither “natural” nor given prompts researchers to consider how “even the most basic decisions in research design can have fundamental consequences for the re/presentation of race inequity” (Gillborn et al., 2018 , p. 171). Notably, even when race is a focus, scholars must operationalize and interpret findings related to race in the context of racism. Fourth, prioritizing voice and insight advances the notion that data cannot “speak for itself” and numerous interpretations are possible. In QuantCrit, this tenet leverages experiential knowledge among People of Color as an interpretive tool. Finally, the fifth tenet explicates how numbers can be used for social justice but statistical research cannot be placed in a position of greater legitimacy in equity efforts relative to qualitative research. Collectively, although Gillborn et al. ( 2018 ) stated that they expect—much like all epistemological foundations—the tenets of QuantCrit to be expanded, we must first understand how these stated principles arise in critical quantitative research.
Bridging Critical Quantitative Concepts as a Guiding Framework
Guided by these framings (i.e., quantitative criticalism, critical quantitative inquiry, QuantCrit) as a specific stream of inquiry within the larger realm of equity-minded educational research, we explore the extent to which the primary elements of these critical quantitative frameworks are applied in higher education. Across the framings discussed, the commitment to equity-mindedness contributes to a shared underlying essence of critical quantitative approaches. Not only do Stage, Rios-Aguilar, and Gillborn et al. aim for researchers to center on inequities and commit to disrupting “neutral” decisions about and interpretations of statistics, but they also advocate for critical quantitative research (by any name) to serve as a tool for advocacy and praxis—creating structural changes to discriminatory policies and practices, rather than ceasing equity-based commitments with publications alone. Thus, the conceptual framework for the present study brings together alignments and distinctions in scholars’ motivations and actualizations of quantitative research through a critical lens.
Specifically, looking to Stage ( 2007 ), quantitative criticalists must center on inequity in their questions and actions to disrupt traditional models, methods, and practices. Second, extending critical inquiry through all aspects of quantitative research (Rios-Aguilar, 2014 ), researchers must interrogate how critical perspectives can be embedded in every part of research. The embedded nature of critical approaches should consider how study questions, frameworks, analytic practices, and advocacy are developed with intentionality, reflexivity, and the goal of unmasking inequities. Third, centering on the five known tenets of QuantCrit (Gillborn et al., 2018 ), QuantCrit researchers should adapt critical race theory for quantitative research. Although QuantCrit tenets are likely to be expanded in the future, the foundations of such research should continue to acknowledge the centrality of racism, advance critiques of statistical neutrality and categories that serve white racial interests, prioritize the lived experiences of People of Color, and complicate how statistics can be one—but not the lone—part of social justice endeavors.
Over many years, higher education scholars have advanced more critical research, as illustrated through publication trends of critical quantitative manuscripts in higher education (Wofford & Winkler, 2022 ). However, the application of critical quantitative approaches remains laced with tensions among paradigms and analytic strategies. Despite recent systematic examinations of critical quantitative scholarship across educational research broadly (Tabron & Thomas, 2023 ), there has yet to be a comprehensive, systematic review of higher education studies that attempt to apply principles rooted in quantitative criticalism, critical quantitative inquiry, and QuantCrit. Thus, much remains to be learned regarding whether and how higher education researchers have been able to apply the principles previously articulated. In order for researchers to fully (re)imagine possibilities for future critical approaches to quantitative higher education research, we must first understand the landscape of current approaches.
Study Aims and Role of the Researchers
Study aims and scope.
For this study, we examined the extent to which authors adopted critical quantitative approaches in higher education research and the trends in tools and strategies they employed to do so. In other words, we sought to understand to what extent, and in what ways, authors—in their own perspectives—applied critical perspectives to quantitative research. We relied on the nomenclature used by the authors of each manuscript (e.g., whether they operated from the lens of quantitative criticalism, QuantCrit, or another approach determined by the authors). Importantly, our intent was not to evaluate the quality of authors’ applications of critical approaches to quantitative research in higher education.
Researcher Positionality
As with all research, our positions and motivations shape how we conceptualized and executed the present study. We come to this work as early career higher education faculty, drawn to the study of higher education as one way to rectify educational disparities, and thus are both deeply invested in understanding how critical quantitative approaches may advance such efforts. After engaging in initial discussions during an association-sponsored workshop on critical quantitative research in higher education, we were motivated to explore these perspectives, understand trends in our field, and inform our own empirical engagement. Throughout our collaboration, we were also reflexive about the social privileges we hold in the academy and society as white, cisgender women—particularly given how quantitative criticalism and QuantCrit create inroads for systemically minoritized scholars to combat the erasure of perspectives from their communities due to small sample sizes. As we work to understand prior critical quantitative endeavors, with the goal of creating opportunity for this work to flourish in the future, we continually reflect on how we can use our positions of privilege to be co-conspirators in the advancement of quantitative research for social justice in higher education.
This study employed a qualitatively driven multimethod sequential design (Hesse-Biber et al., 2015 ) to illuminate how critical quantitative perspectives and methods have been applied in higher education contexts over 15 years. Anguera et al. ( 2018 ) noted that the hallmark feature of multimethod studies is the coexistence of different methodologies. Unlike mixed-methods studies, which integrate both quantitative and qualitative methods, multimethod studies can be exclusively qualitative, exclusively quantitative, or a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods. A multimethod research design was also appropriate given the distinct research questions in this study—each answered using a different stream of data. Specifically, we conducted a systematic scoping review of existing literature and facilitated follow-up interviews with a subset of corresponding authors from included publications, as detailed below and in Fig. 1 . We employed a systematic scoping review to examine the extent to which higher education scholars incorporated critical perspectives into quantitative research (research question one), and we then conducted follow-up interviews to elucidate how those scholars discussed specific strategies for leveraging critical perspectives in their quantitative research (research question two).

Sequential multimethod approach to data collection and analysis
Given the scope of our work—which examined the extent to which, and in what ways, authors applied critical perspectives to quantitative higher education research—we employed an exploratory approach with a constructivist lens. Using a constructivist paradigm allowed us to explore the many realities of doing critical quantitative research, with the authors themselves constructing truths from their worldviews (Magoon, 1977 ). In what follows, we contextualize both our methodological choices and the limitations of those choices in executing this study.
Data Sources
Systematic scoping review.
First, we employed a systematic scoping review of published higher education literature. Consistent with the purpose of a scoping review, we sought to “examine the extent, range, and nature” of critical quantitative approaches in higher education that integrate quantitative methods and critical inquiry (Arskey & O’Malley, 2005 , p. 6). We used a multi-stage scoping framework (Arskey & O’Malley, 2005 ; Levac et al., 2010 ) to identify studies that were (a) empirical, (b) conducted within a higher education context, and (c) guided by critical quantitative perspectives. We restricted our review to literature published in 2007 or later (i.e., since Stage’s formal introduction of quantitative criticalism in higher education). All studies considered for review were written in the English language.
The literature search spanned multiple databases, including Academic Search Premier, Scopus, ERIC, PsychINFO, Web of Science, SocINDEX , Psychological and Behavioral Sciences Collection, Sociological Abstracts, and JSTOR. To locate relevant works, we used independent and combined keywords that reflected the inclusion criteria, with the initial search resulting in 285 unique records for eligibility screening. All screening was conducted separately by both authors using the CADIMA online platform (Kohl et al., 2018). In total, 285 title/abstract records were screened for eligibility, with 40 full-text records subsequently screened for eligibility. After separately screening all records, we discussed inconsistencies in title/abstract and full-text eligibility ratings to reach consensus. This strategy led us to a sample of 34 manuscripts that met all inclusion criteria (Fig. 2 ).

Identification of systematic scoping review sample via literature search and screening
Systematic scoping reviews are particularly well-suited for initial examinations of emerging approaches in the literature (Munn et al., 2018 ), aligning with our goal to establish an initial understanding of the landscape of critical quantitative research applications in higher education. It also relies heavily on researcher-led qualitative review of the literature, which we viewed as a vital component of our study, as we sought to identify not just what researchers did (e.g., what topics they explored or in what outlets they did so), but also how they articulated their decision-making process in the literature. Alternative methods to examining the literature, such as bibliometric analysis, supervised topic modeling, and network analysis, may reveal additional insights regarding the scope and structure of critical quantitative research in higher education not addressed in the current study. As noted by Munn et al. ( 2018 ), systematic scoping reviews can serve as a useful precursor to more advanced approaches of research synthesis.
Semi-structured Interviews
To understand how scholars navigated the opportunities and tensions of critical quantitative inquiry in their research, we then conducted semi-structured interviews with authors whose work was identified in the scoping review. For each article meeting the review criteria ( N = 34), we compiled information about the corresponding author and their contact information as our sample universe (Robinson, 2014 ). Each corresponding author was contacted via email for participation in a semi-structured interview. There were 32 distinct corresponding authors for the 34 manuscripts, as two corresponding authors led two manuscripts each within our corpus of data. In the recruitment email, we provided corresponding authors with a link to a Qualtrics intake survey; this survey confirmed potential participants’ role as corresponding author on the identified manuscript, collected information about their professional roles and social identities, and provided information about informed consent in the study. Twenty-five authors responded to the Qualtrics survey, with 18 corresponding authors ultimately participating in an interview.
Individual semi-structured interviews were conducted via Zoom and lasted approximately 45–60 min. The interview protocol began with questions about corresponding authors’ backgrounds, then moving into questions regarding their motivations for engaging in critical approaches to quantitative methods, navigation of the epistemological and methodological tensions that may arise when doing quantitative research with a critical lens, approaches to research design, frameworks, and methods that challenged quantitative norms, and experiences with the publication process for their manuscript included in the scoping review. In other words, we asked that corresponding authors explicitly relay the thought processes underlying their methodological choices in the article(s) from our scoping review. Importantly, given the semi-structured nature of these interviews, conversations also reflected participants’ broader trajectory to and through critical quantitative thinking as well as their general reflections about how the field of higher education has grappled with critical approaches to quantitative scholarship. To increase consistency in our data collection and the nature of these conversations, the first author conducted all interviews. With participants’ consent, we recorded each interview, had interviews professionally transcribed, and then de-identified data for subsequent analysis. All interview participants were compensated for their time and contributions with a $50 Amazon gift card.
At the conclusion of each interview, participants were given the opportunity to select their own pseudonym. A profile of interview participants, along with their self-selected pseudonyms, is provided in Table 1 . Although we invited all corresponding authors to participate in interviews, our sample may reflect some self-selection bias, as authors had to opt in to be represented in the interview data. Further, interview insights do not represent all perspectives from participants’ co-authors, some of which may diverge based on lived experiences, history with quantitative research, or engagement with critical quantitative approaches.
Data Analysis
After identifying the sample of 34 publications, we began data analysis for the scoping review by uploading manuscripts to Dedoose. Both researchers then independently applied a priori codes (Saldaña, 2015 ) from Stage’s ( 2007 ) conceptualization of quantitative criticalism, Rios-Aguilar’s ( 2014 ) framework for quantitative critical inquiry, and Gillborn et al.’s ( 2018 ) QuantCrit tenets (Table 2 ). While we applied codes in accordance with Stage’s and Rios-Aguilar’s conceptualizations to each article, codes relevant to Gillborn et al.’s tenets of QuantCrit were only applied to manuscripts where authors self-identified as explicitly employing QuantCrit. Given the distinct epistemological origin of QuantCrit from broader forms of critical quantitative scholarship, codes representing the tenets of QuantCrit reflect its origins in critical race theory and may not be appropriate to apply to broader streams of critical quantitative scholarship that do not center on racism (e.g., scholarship related to (dis)ability, gender identity, sexual identity and orientation). After individually completing a priori coding, we met to reconcile discrepancies and engage in peer debriefing (Creswell & Miller, 2000 ). Data synthesis involved tabulating and reporting findings to explore how each manuscript component aligned with critical quantitative frameworks in higher education research to date.
We analyzed interview data through a multiphase process that engaged deductive and inductive coding strategies. After interviews were transcribed and redacted, we uploaded the transcripts to Dedoose for collaborative qualitative coding. The second author read each transcript in full to holistically understand participants’ insights about generating critical quantitative research. During this initial read, the second author noted quotes that were salient to our question regarding the strategies that scholars use to employ critical quantitative approaches.
Then, using the a priori codes drawn from Stage’s ( 2007 ), Rios-Aguilar’s ( 2014 ) and Gillborn et al.’s ( 2018 ) conceptualizations relevant to quantitative criticalism, critical quantitative inquiry, and QuantCrit, we collaboratively established a working codebook for deductive coding by defining the a priori codes in ways that could capture how participants discussed their work. Although these a priori codes had been previously applied to the manuscripts in the scoping review, definitions and applications of the same codes for interview analysis were noticeably broader (to align with the nature of conversations during interviews). For example, we originally applied the code “policy/advocacy”—established from Rios-Aguilar's work—to components from the implications section of scoping review manuscripts. When (re)developed for deductive coding of interview data, however, we expanded the definition of “policy/advocacy” to include participants’ policy- and advocacy-related actions (beyond writing) that advanced critical inquiry and equity for their educational communities.
In the final phase of analysis, each research team member engaged in inductive coding of the interview data. Specifically, we relied on open coding (Saldaña, 2015 ) to analyze excerpts pertaining to participants’ strategies for employing critical quantitative approaches that were not previously captured by deductive codes. Through open coding, we used successive analysis to work in sequence from a single case to multiple cases (Miles et al., 2014 ). Then, as suggested by Saldaña ( 2015 ), we collapsed our initial codes into broader categories that allowed us insight regarding how participants’ strategies in critical quantitative research expanded beyond those which have been previously articulated. Finally, to draw cohesive interpretations from these data, we independently drafted analytic memos for each interview participant’s transcript, later bridging examples from the scoping review that mapped onto qualitative codes as a form of establishing greater confidence and trustworthiness in our multimethod design.
In introducing study findings through a synthesized lens that heeds our multimethod design, we organize the sections below to draw from both scoping review and interview data. Specifically, we organize findings into two primary areas that address authors’ (1) articulated motivations to adopt critical approaches to quantitative higher education research, and (2) methodological choices that they perceive to align with critical approaches to quantitative higher education research. Within these sections, we discuss several coherent areas where authors collectively grappled with tensions in motivation (i.e., broad motivations, using coined names of critical approaches, conveying positionality, leveraging asset-based frameworks) and method (i.e., using data sources and choosing variables, challenging coding norms, interpreting statistical results), all of which signal authors’ efforts to embody criticality in quantitative research about higher education. Given our sequential research questions, which first examined the landscape of critical quantitative higher education research and then asked authors to elucidate their thought processes and strategies underlying their approaches to these manuscripts, our findings primarily focus on areas of convergence across data sources; we do, however, highlight challenges and tensions authors faced in conducting such work.
Articulated Motivations in Critical Approaches to Quantitative Research
To date, critical quantitative researchers in higher education have heeded Stage’s ( 2007 ) call to use data to reveal the large-scale perpetuation of inequities in educational processes and outcomes. This emerged as a defining aspect of higher education scholars’ critical quantitative work, as all manuscripts ( N = 34) in the scoping review articulated underlying motivations to identify and/or address inequities.
Often, these motivations were reflected in the articulated research questions ( n = 31; 91.2%). For example, one manuscript sought to “critically examine […] whether students were differentially impacted” by an educational policy based on intersecting race/ethnicity, gender, and income (Article 29, p. 39). Others sought to challenge notions of homogeneity across groups of systemically minoritized individuals by “explor[ing] within-group heterogeneity” of constructs such as sense of belonging among Asian American students (Article 32, p. iii) and “challenging the assumption that [economically and educationally challenged] students are a monolithic group with the same values and concerns” (Article 31, p. 5). These underlying motivations for conducting critical quantitative research emerged most clearly in the named approaches, positionality statements, and asset-based frameworks articulated in manuscripts.
Adopting the Coined Names of Quantitative Criticalism, QuantCrit, and Related Approaches
Based on the inclusion criteria applied in the scoping review, we anticipated that all manuscripts would employ approaches that were explicitly critical and quantitative in nature. Accordingly, all manuscripts ( N = 34; 100%) adopted approaches that were coined as quantitative criticalism , QuantCrit , critical policy analysis (CPA), critical quantitative intersectionality (CQI) , or some combination of those terms. Twenty-one manuscripts (61.8%) identified their approach as quantitative criticalism, nine manuscripts (26.5%) identified their approach as QuantCrit, two manuscripts (5.9%) identified their approach as CPA, and two manuscripts (5.9%) identified their approach as CQI.
One of the manuscripts that applied quantitative criticalism broadly described it as an approach that “seeks to quantitatively understand the predictors contributing to completion for a specific population of minority students” (Article 34, p. 62), noting that researchers have historically “attempted to explain the experiences of [minority] students using theories, concepts, and approaches that were initially designed for white, middle and upper class students” (Article 34, p. 62). Although this example speaks only to the limited context and outcomes of one study, it highlights a broader theme found across articles; that is, quantitative criticalism was often leveraged to challenge dominant theories, concepts, and approaches that failed to represent systemically minoritized individuals’ experiences. In challenging dominant theories, QuantCrit applications were most explicitly associated with critical race theory and issues of racism. One manuscript noted that “QuantCrit recognizes the limitations of quantitative data as it cannot fully capture individual experiences and the impact of racism” (Article 29, p. 9). However, these authors subsequently noted that “quantitative methodology can support CRT work by measuring and highlighting inequities” (Article 29, p. 9). Several scholars who employed QuantCrit explicitly identified tenets of QuantCrit that they aimed to address, with several authors making clear how they aligned decisions with two tenets establishing that categories are not given and numbers are not neutral.
Despite broadly applying several of the coined names for critical realms of quantitative research, interview data revealed that several authors felt a palpable tension in labeling. Some participants, like Nathan, questioned the surface-level engagement that may come with coined names: “I don’t know, I think it’s the thinking and the thought processes and the intentionality that matters. How invested should we be in the label?” Nathan elaborated by noting how he has shied away from labeling some of his work as quantitative criticalist , given that he did not have a clear answer about “what would set it apart from the equity-minded, inequality-focused, structurally and systematically-oriented kind of work.” Similarly, Leo stated how labels could (un)intentionally stop short of the true mission for the research, recalling that he felt “more inclined to say that I’m employing critical quantitative leanings or influences from critical quant” because a true application of critical epistemology should be apparent in each part of the research process. Although most interview participants remained comfortable with labeling, we also note that—within both interview data and the articles themselves—authors sometimes presented varied source attributions for labels and conflated some of the coined names, representing the messiness of this emerging body of research.
Challenging Objectivity by Conveying Researcher Positionality
Positionality statements acknowledge the influence of scholars’ identities and social positions on research decisions. Quantitative research has historically been viewed as an objective, value-neutral endeavor, with some researchers deeming positionality statements as unnecessary and inconsistent with the positivist paradigm from which such work is often conducted. Several interviewed authors noted that positivist or post-positivist roots of quantitative research characterized their doctoral training, which often meant that their “original thinking around statistics and research was very post-positivist” (Carter) or that “there really wasn’t much of a discussion, as far as I can remember as a doc student, about epistemology or ontology” (Randall). Although positionality statements have been generally rare in quantitative research studies, half of the manuscripts in our sample ( n = 17; 50.0%) included statements of researcher positionality. One interview participant, Gabrielle, discussed the importance of positionality statements as one way to challenge norms of quantitative research in saying:
It’s not objective, right? I think having more space to say, “This is why I chose the measures I chose. This is how I’m coming to this work. This is why it matters to me. This is my positioning, right?” I think that’s really important in quantitative work…that raises that level of consciousness to say these are not just passive, like every decision you make in your research is an active decision.
While Gabrielle, as well as Carter and Randall, all came to be advocates of positionality statements in quantitative scholarship through different pathways, it became clear through these and other interviews that positionality statements were one way to bring greater transparency to a traditionally value-neutral space.
As an additional source of contextual data, we reviewed submission guidelines for the peer-reviewed journals in which manuscripts were published. Not one of the 15 peer-reviewed outlets represented in our scoping review sample required that authors include positionality statements. One outlet, Journal of Diversity in Higher Education (where two scoping review articles were printed), offered “inclusive reporting standards” where they recommended that authors include reflexivity and positionality statements in their submitted manuscripts (American Psychological Association, 2024 ). Another outlet, Teachers College Record (where one scoping review article was printed), mentioned positionality statements in their author instructions. Yet, Teachers College Record did not require nor recommend the inclusion of author positionality statements; rather, they offered recommendations if authors chose to include them. Specifically, they suggested that if authors chose to include a positionality statement, it should be “more than demographic information or abstract statements” (Sage Journals, 2024 ). The remaining 13 peer-reviewed outlets from the scoping review data made no mention of author reflexivity or positionality in their author guidelines.
When present, the scoping review revealed that positionality statements varied in form and content. Some positionality statements were embedded in manuscript narratives, while others existed as separate tables with each author’s positionality represented as a separate row. In content, it was most common for authors to identify how their identities and experiences motivated their work. For example, one author noted their shared identity with their research participants as a low-income, first-generation Latina college student (Article 2, p. 25). Another author discussed the identity that they and their co-author shared as AAPI faculty, making the research “personally relevant for [them]” (Article 11, p. 344),
In interviews, participants recalled how the relationship between their identities, lived experiences, and motivations for critical approaches to quantitative research were all intertwined. Leo mentioned, “naming who we are in a study helps us be very forthright with the pieces that we’re more likely to attend to.” Yet, Leo went on to say that “one of the most cosmetic choices that people see in critically oriented quantitative research is our positionality statements,” which other participants noted about how information in positionality statements is presented. In several interviews, authors’ reflections on whether these statements should appear as lists of identities or deeper statements about reflexivity presented a clear tension. For some, positionality statements were places to “identify ourselves and our social locations” (David) or “brand yourself” as a critical quantitative scholar to meet “trendy” writing standards in this area (Michelle). Yet, others felt such statements fall short in revealing “how this study was shaped by their background identities and perspectives” (Junco) or appear to “be written in response to the context of the research or people participating” (Ginger). Ultimately, many participants felt that shaping honest positionality statements that better convey “the assumptions, and the biases and experiences we’ve all had” (Randall) was one area where quantitative higher education scholars could significantly improve their writing to reflect a critical lens.
Some manuscripts also clarified how authors’ identities and social positions reshaped the research process and product. For instance, authors of one manuscript reported being “guided by [their] cultural intuition” throughout the research (Article 17, p. 218). Alternatively, another author described the narrative style of their manuscript as intentionally “autobiographical and personally reflexive” in order “to represent the connections [they] made between [their] own experiences and findings that emerged” from their work (Article 28, p. 56). Taken together, among the manuscripts that explicitly included positionality statements, these remarks make clear that authors had widely varying approaches to their reflexivity and writing processes.
Actualizing Asset-Based Frameworks
Notably, conceptual and theoretical frameworks emerged as a common way for critical quantitative scholars to pursue equitable educational processes and outcomes in higher education research. Nearly all ( n = 32; 94.1%) manuscripts explicitly challenged dominant conceptual and theoretical models. Some authors enacted this challenge by countering canonical constructs and theories in the framing of their study. For example, several manuscripts addressed critiques of theoretical concepts such as integration and sense of belonging in building the conceptual framework for their own studies. Other manuscripts were constructed with the underlying goal to problematize and redefine frameworks, such as engagement for Latina/e/o/x students or the “leaky pipeline” discourse related to broadening participation in the sciences.
Across interviews, participants challenged deficit framings or “traditional” theoretical and conceptual approaches in many ways. Some frameworks are taken as a “truism in higher ed” (Leo), such as sense of belonging and Astin’s ( 1984 ) I-E-O model, and these frameworks were sometimes purposefully used to disrupt their normative assumptions. Randall, for one, recalled using a more normative higher education framework but opted to think about this framework “as more culturalized” than had previously been done. Further, Carter noted that “thinking about the findings in an anti-deficit lens” comprised a large portion of critical quantitative approaches. Using frameworks for asset-based interpretation was further exemplified by Caroline stating, “We found that Black students don’t do as well, but it’s not the fault of Black students.” Instead, Caroline challenged deficit understandings through the selected framework and implications for institutional policy. Collectively, challenging normative theoretical underpinnings in higher education was widely favored among participants, and Jackie hoped that “the field continues to turn a critical lens onto itself, to grow and incorporate new knowledges and even older forms of knowledge that maybe it hasn’t yet.”
Alternatively, some participants discussed rejecting widely used frameworks in higher education research in favor of adapting frameworks from other disciplines. For example, QuantCrit researchers drew from critical race theory (and related frameworks, such as intersectionality) to quantitatively examine higher education topics in ways that value the knowledge of People of Color. In using these frameworks, which have origins in critical legal and Black feminist theorization, interview participants noted how important it was “to put yourself out there with talking about race and racism” (Isabel) and connect the statistics “back to systems related to power, privilege, and oppression [because] it’s about connecting [results] to these systemic factors that shape experience, opportunities, barriers, all of that kind of stuff” (Jackie). Further, several authors related pulling theoretical lenses from sociology, gender studies, feminist studies, and queer studies to explore asset-based theorization in higher education contexts and potentially (re)build culturally relevant concepts for quantitative measurement in higher education.
Embodying Criticality in Methodological Sources, Approaches, and Interpretations
Moving beyond underlying motivations of critical quantitative higher education research, scoping review authors also frequently actualized the task of questioning and reconstructing “models, measures, and analytic practices [to] better describe experiences of those who have not been adequately represented” (Stage, 2007 , p. 10). Common across all manuscripts ( N = 34) was the discussion of specific ways in which authors’ critical quantitative approaches informed their analytic decisions. In fact, “analytic practices” was by far the most prevalent code applied to the manuscripts in our dataset, with 342 total references across the 34 manuscripts. This amounted to 20.8% of the excerpts in the scoping review dataset being coded as reflecting critical quantitative approaches to analytic practices, specifically.
Interestingly, many analytic approaches reflected what some would consider “standard” quantitative methodological tools. For example, manuscripts employed factor analysis to assess measures, t-tests to examine differences between groups, and hierarchical linear regression to examine relationships in specific contexts. Some more advanced, though less commonly applied, methods included measurement invariance testing and latent class analysis. Thus, applying a critical quantitative lens tended not to involve applying a separate set of analytic tools; rather, the critical lens was reflected in authors’ selection of data sources and variables, approaches to data coding and (dis)aggregation, and interpretation of statistical results.
Selecting Data Sources and Variables
Although scholars were explicit in their underlying motivations and approaches to critical quantitative research, this did not often translate into explicitly critical data collection endeavors. Most manuscripts ( n = 29; 85.3%) leveraged existing measures and data sources for quantitative analysis. Existing data sources included many national, large-scale datasets including the Educational Longitudinal Study (NCES), National Survey of Recent College Graduates (NSF), and the Current Population Survey (U.S. Census Bureau). Other large-scale data sources reflecting specific higher education contexts and populations included the HEDS Diversity and Equity Campus Climate Survey, Learning About STEM Student Outcomes (LASSO) platform, and National Longitudinal Survey of Freshmen. Only five manuscripts (14.7%) conducted analysis using original data collected and/or with newly designed measures.
It was apparent, however, that many authors grappled with challenges related to using existing data and measures. Interview participants’ stories crystallized the strengths and limitations of secondary data. Over half of the interview participants in our study spoke about their choices regarding quantitative data sources. Some participants noted that surveys “weren’t really designed to ask critical questions” (Sarah) and discussed the issues with survey data collected around sex and gender (Jessica). Still, Sarah and Jessica drew from existing survey data to complicate the higher education experiences they aimed to understand and tried to leverage critical framing to question “traditional” definitions of social constructs. In another discussion about data sources and the design of such sources, Carter expanded by saying:
I came in without [being] able to think through the sampling or data collection portion, but rather “this is what I have, how do I use it in a way that is applying critical frameworks but also staying true to the data themselves.” That is something that looks different for each study.
In discussing quantitative data source design, more broadly, Tyler added: “In a lot of ways, all quantitative methods are mixed methods. All of our measures should be developed with a qualitative component to them.” In the scoping review articles, one example of this qualitative component is evident within the cognitive interviews that Sablan ( 2019 ) employed to validate survey items. Finally, several participants noted how crucial it is to “just be honest and acknowledge the [limitations of secondary data] in the paper” (Caroline) and “not try to hide [the limitations]” (Alexis), illustrating the value of increased transparency when it comes to the selection and use of existing quantitative data in manuscripts advancing critical perspectives.
Regardless of data source, attention to power, oppression, and systemic inequities was apparent in the selection of variables across manuscripts. Many variables, and thus the associated models, captured institutional contexts and conditions. The multilevel nature of variables, which extended beyond individual experiences, aligned with authors’ articulated motivations to disrupt inequitable educational processes and outcomes, which are often systemic and institutionalized in nature. For one, David explained key motivations behind his analytic process: “We could have controlled for various effects, but we really wanted to see how are [the outcomes] differing by these different life experiences?” David’s focus on moving past “controlling” for different effects shows a deep level of intentionality that was reflected among many participants. Carter expanded on this notion by recalling how variable selection required, “thinking through how I can account for systemic oppression in my model even though it’s not included in the survey…I’ve never seen it measured.” Further, Leo discussed how reflexivity shaped variable selection and shared: “Ultimately, it’s thinking about how do these environments not function in value-neutral ways, right? It’s not just selecting X, Y, and Z variable to include. It’s being able to interrogate [how] these variables represent environments that are not power neutral.” The process of selecting quantitative data sources and variables was perhaps best summed up by Nick, who concisely shared, “it’s been very iterative.” Indeed, most participants recalled how their methodological processes necessitated reflexivity—an iterative process of continually revisiting assumptions one brings to the quantitative research process (Jamieson et al., 2023 )—and a willingness to lean into innovative ways of operationalizing data for critical purposes.
Challenging the Norms of Coding
An especially common way of enacting critical principles in quantitative research was to challenge traditional norms of coding. This emerged in three primary ways: (1) disaggregation of categories to reflect heterogeneity in individuals’ experiences, (2) alternative approaches to identifying reference groups, and (3) efforts to capture individuals’ intersecting identities. Across manuscripts, authors often intentionally disaggregated identity subgroups (e.g., race/ethnicity, gender) and ran distinct analytical models for each subgroup separately. In interviews, Junco expressed that running separate models was one way that analyses could cultivate a different way of thinking about racial equity. Specifically, Junco challenged colleagues’ analytic processes by asking whether their research questions “really need to focus on racial comparison?” Junco then pushed her colleagues by asking, “can we make a different story when we look at just the Black groups? Or when we look at only Asian groups, can we make a different story that people have not really heard?” Isabel added that focusing on measurement for People of Color allowed for them (Isabel and her research collaborators) to “apply our knowledge and understanding about minoritized students to understand what the nuances were.” In nearly one third of the manuscripts ( n = 11; 32.4%), focusing on single group analyses emerged as one way that QuantCrit scholars disrupted the perceived neutrality of numbers and how categories have previously been established to serve white, elite interests. Five of those manuscripts (14.7%) explicitly focused on understanding heterogeneity within systemically minoritized subpopulations, including Asian American, Latina/e/o/x, and Black students.
It was not the case, however, that authors avoided group comparisons altogether. For example, one team of authors used separate principal components analysis (PCA) models for Indigenous and non-Indigenous students with the explicit intent of comparing models between groups. The authors noted that “[t]ypically, monolithic comparisons between racial groups perpetuate deficit thinking and marginalization.” However, they sought to “highlight the nuance in belonging for Indigenous community college students as it differs from the White-centric or normative standards” by comparing groups from an asset-driven perspective (Article 5, p. 7). Thus, in cases where critical quantitative scholars included group comparisons, the intentionality underlying those choices as a mechanism to highlight inequities and/or contribute to asset-based narratives was apparent.
Four manuscripts (11.8%) were explicit in their efforts to identify alternative analytic methods to normative reference groups. Reference groups are often required when building quantitative models with categorical variables such as racial/ethnic and gender identity. Often, dominant identities (e.g., respondents who are white and/or men) comprise the largest portion of a research sample and are selected as the comparison group, typifying experiences of individuals with those dominant identities. To counter the traditional practice of reference groups, some manuscript authors stated using effect coding, often referencing the work of Mayhew and Simonoff ( 2015 ), and dynamic centering as two alternatives. Effect coding (used in three manuscripts) removes the need for a reference group; instead, all groups are compared to the overall sample mean. Dynamic centering (used in one manuscript), on the other hand, uses a reference group but one that is intentionally selected based on the construct in question, as opposed to relying on sample size or dominant identities.
Interview participants also discussed navigating alternative coding practices, with several authors raising key points about their exposure to and capacity building for effect coding. As Angela described, effect coding necessitates that “you don’t choose a specific group as your benchmark to do the comparison. And you instead compare to the group.” Angela then stated that this approach made more sense than choosing benchmarks, as she felt uncomfortable identifying one group as a comparison group. Junco, however, noted that “effect coding was much more complicated than what I thought,” as she reflected on unlearning positivist strategies in favor of equity-focused approaches that could elucidate greater nuance. Importantly, using alternative coding practices was not universal among manuscripts or interview participants. One manuscript utilized traditional dummy coding for race in regression models, with white students as the reference group to which all other groups were compared. The authors explicated that “using white students as the reference [was] not a result of ‘privileging’ them or maintaining the patterns of power related to racial categorizations” (Article 8, p. 1282). Instead, they argued that the comparison was a deliberate choice to “reveal patterns of racial or ethnic educational inequality compared to the privileged racial group” (Article 8, p. 1282). Another author maintained the use of reference groups purely for ease of interpretation. David shared, “it’s easier for the person to just look at it and compare magnitudes.” However, by prioritizing the benefit of easy interpretation with traditional reference groups, authors may incur other costs (such as sustaining unnecessary comparisons to white students). Additionally, several manuscripts ( n = 13; 38.2%) employed analytic coding practices that aimed to account for intersectionality. While authors identified these practices by various names (e.g., interaction terms, mediating variables, conditional effects) they all afforded similar opportunities. The most common practice among authors in our sample ( n = 8; 23.5%) was computing interaction terms to account for intersecting identities, such as race and gender. Specifically pertaining to intersectionality, Alexis summarized many researchers’ tensions well in sharing, “I know what Kimberlé Crenshaw says. But how do I operationalize that mathematically into something that’s relevant?” In offering one way that intersectionality could be realized with quantitative data, Tyler stated that “being able to keep in these variables that are interacting [via interaction terms] and showing differences” may align with the core ideas of intersectionality. Yet, participants also recognized that statistics would inherently always fall short of representing respondents’ lived experiences, as discussed by Nick: “We disaggregate as far as we can, but you could only go so far, and like, how do we deal with tension.” Several other participants reflected on bringing in open-text response data about individuals’ social identities, categorizing racial and ethnic groups according to continent (while also recognizing that this did not necessarily attend to the complexities of diasporas), or making decisions about groups that qualify as “minoritized” based on disciplinary and social movements. Collectively, the disparate approaches that authors used and discussed directly speak to critical higher education scholars’ movement away from normative comparisons that did not meaningfully answer questions related to (in)equity and/or intersectionality in higher education.
Interpreting Statistical Results
One notable, albeit less common, way higher education scholars enacted critical quantitative approaches through analytic methods was by challenging traditional ways of reporting and interpreting statistical results. The dominant approach to statistical methods aligns with a null hypothesis significance testing (NHST) approach, whereby p -values—used as indicators of statistically significant effects—serve to identify meaningful results. NHST practices were prevalent in nearly all scoping review manuscripts; yet, there were some exceptions. For example, three manuscripts (8.8%) cautioned against reliance on statistical significance due to its dependence on large sample size (i.e., statistical power), which is often at odds with centering research on systemically minoritized populations. One of those manuscripts (2.9%) even chose to interpret nonsignificant results from their quantitative analyses. In a similar vein, two manuscripts (5.9%) also questioned and adapted common statistical practices related to model selection (e.g., using corrected Akaike information criteria (AIC) instead of p -values) and variable selection (e.g., avoiding use of variance explained so as not to “[exclude] marginalized students from groups with small representations in the data” (Article 23, p. 7). Meanwhile, others attended to raw numeric data and uncertainty associated with quantitative results. The resources to enact these alternative methodological practices were briefly discussed by Tyler through his interview, in which he shared: “The use of p -values is so poorly done that the American Statistical Association has released a statement on p -values, an entire special collection [and people in my field] don’t know those things exist.” Tyler went on to share that this knowledge barrier was tied to the siloed nature of academia, and that such siloes may inhibit the generation of critical quantitative research that draws from different disciplinary origins.
Among interviewed authors, many also viewed interpretation as a stage of quantitative research that required a high level of responsibility and awareness of worldview. Nick related that using a QuantCrit approach changed how he was interpreting results, in “talking about educational debts instead of gaps, talking about racism instead of race.” As demonstrated by Nick, critical interpretations of statistics necessitate congruence with theoretical or conceptual framing, as well, given the explicit call to interrogate structures of inequity and power in research adopting a critical lens. Leo described this responsibility as a necessary challenge:
It’s very easy to look at results and interpret them—I don’t wanna say ‘as is’ because I don’t think that there is an ‘as is’—but interpret them in ways that they’re traditionally interpreted and to keep them there. But, if we’re truly trying to accomplish these critical quantitative themes, then we need to be able to reference these larger structures to make meaning of the results that are put in front of us.
Nick, Leo, and several other participants all emphasized how crucial interpretation is in critical quantitative research in ways that expanded beyond statistical practices; ultimately, the perspective that “behind every number is a human” served as a primary motivation for many authors in fulfilling the call toward ethical and intentional interpretation of statistics.
Leveraging a multimethod approach with 15 years of published manuscripts ( N = 34) and 18 semi-structured interviews with corresponding authors, this study identifies the extent to which principles of quantitative criticalism, critical quantitative inquiry, and QuantCrit have been applied in higher education research. While scholars are continuing to develop strategies to enact a critical quantitative lens in their studies—a path we hope will continue, as continued questioning, creativity, and exploration of new possibilities underscore the foundations of critical theory (Bronner, 2017 )—our findings do suggest that higher education researchers may benefit from intentional conversations regarding specific analytic practices they use to advance critical quantitative research (e.g., confidence intervals versus p -values, finite mixture models versus homogeneous distribution models).
Our interviews with higher education scholars who produced such work also fills a need for guidance on strategies to enact critical perspectives in quantitative research, addressing an absence of such from most quantitative training and resources. By drawing on the work and insights of higher education researchers engaging critical quantitative approaches, we provide a foundation on which future scholars can imagine and implement a fuller range of possibilities for critical inquiry via quantitative methods in higher education. In what follows, we discuss the findings of this study alongside the frameworks from which they drew inspiration. Then, we offer implications for research and practice to catalyze continued exploration and application of critical quantitative approaches in higher education scholarship.
Synthesizing Key Takeaways
First, scoping review data revealed several commonalities across manuscripts regarding authors’ underlying motivations to identify and/or address inequities for systemically minoritized populations—speaking to how critical quantitative approaches can fall within the larger umbrella of equity-mindedness in higher education research. Such motivations were reflected in authors’ research questions and frameworks (consistent with Stage’s ( 2007 ) initial guidance). Most manuscripts identified their approach as quantitative criticalism broadly, although there were sometimes blurred boundaries between approaches termed quantitative criticalism, QuantCrit, critical policy analysis, and critical quantitative intersectionality. Notably, authors’ decisions about which framing their work invoked also determined how scholars enacted a specified critical quantitative approach. For example, the tenets of QuantCrit, offered by Gillborn et al. ( 2018 ), were specifically heeded by researchers seeking to take up a QuantCrit lens. Scholars who noted inspiration from Rios-Aguilar ( 2014 ) often drew specifically from the framework for critical quantitative inquiry. While the key ingredients of these critical quantitative approaches were offered in the foundational framings we introduced, the field has lacked understanding on how scholars take up these considerations. Thus, the present findings create inroads to a conversation about applying and extending the articulated components associated with critical quantitative higher education research.
Second, our multimethod approach illuminated general agreement (in manuscripts and interviews) that quantitative research in higher education—whether explicitly critical or not—is not neutral nor objective. However, despite positionality being a key part of Rios-Aguilar’s ( 2014 ) critical quantitative inquiry framework, only half of the manuscripts included researcher positionality. Thus, while educational researchers may agree that, without challenging objectivity, quantitative methods serve to uphold inequity (e.g., Arellano, 2022 ; Castillo & Babb, 2024 ), higher education scholars may not have yet established consensus on how these principles materialize. To be clear, consensus need not be the goal of critical quantitative approaches, given that critical theory demands constant questioning for new ways of thinking and being (Bronner, 2017 ); yet, greater solidarity among critical quantitative higher education researchers may be beneficial, so that community-based discussions can drive the actualization of equity-minded motivations. Interview data also revealed complications in how scholars choose if, and how, to define and label critical quantitative approaches. Some participants struggled with whether their work was “critical enough” to be labeled as such. Those conversations raise concerns that critical quantitative research in higher education could—or potentially has—become an exclusionary space where level of criticality is measured by an arbitrary barometer (refer to Garvey & Huynh, 2024 ). Meanwhile, other participants worried that attaching such a label to their work was irrelevant (i.e., that it was the motivations and intentionality underlying the work that mattered, not the label). Although the field remains in disagreement regarding if/how labeling should be implemented for critical quantitative approaches, “it is the naming of experience and ideologies of power that initiates the process [of transformation] in its critical form” (Hanley, 2004 , p. 55). As such, we argue that naming critical quantitative approaches can serve as a lever for transforming quantitative higher education research and create power in related dialogue.
Implications for Future Studies on Critical Quantitative Higher Education Research
As with any empirical approach, and especially those that are gaining traction (as critical quantitative approaches are in higher education; Wofford & Winkler, 2022 ), there is utility in conducting research about the research . First, in the context of higher education as a broad field of applied research, there is a need to illustrate what critical quantitative scholars focus on when they conceptualize higher education in the first place. For example, is higher education viewed as a possibility for social mobility? Or are critical quantitative scholars viewing postsecondary institutions as engines of inequity? Second, it was notable that—among the manuscripts including positionality statements—it was common for such statements to read as biographies (i.e., lists of social identities) rather than as reflexive accounts about the roles/commitments of the researcher(s). Future research would benefit from a deeper understanding of the enactment of positionality in critical quantitative higher education research. Third, given the productive tensions associated with naming and understanding the (dis)agreed upon ingredients between quantitative criticalism, critical quantitative inquiry, QuantCrit, as well as additional known and unknown conceptualizations, further research regarding how higher education scholars grapple with definitions, distinctions, and adaptations of these related approaches will clarify how scholars can advance their critical commitments with quantitative postsecondary data.
Implications for Employing Critical Quantitative Higher Education Research
Emerging analytical tools for critical quantitative research.
In terms of employing critical quantitative approaches in higher education research, there is significant room for scholars to explore emerging quantitative methodological tools. We agree with López et al.’s ( 2018 ) assessment that critical quantitative work tends to remain demographic and/or descriptive in its methodological nature, and there is great potential for more advanced inferential quantitative methods to serve critical aims. While there are some examples in the literature—for example, Sablan’s ( 2019 ) work in the realm of quantitative measurement and Malcom-Piqueux’s (2015) work related to latent class analysis and other person-centered modeling approaches—additional examples of advanced and innovative analytical tools were limited in our findings. Thus, integrating more advanced quantitative methodological tools into critical quantitative higher education research, such as finite mixture modeling (as noted by Malcom-Piqueux, 2015), measurement invariance testing, and multi-group structural equation modeling, may advance the ways in which scholars address questions related to heterogeneity in the experiences and outcomes of college students, faculty, and staff.
Traditional quantitative analytical tools have historically highlighted between-group differences that perpetuate deficit narratives for systemically minoritized students, faculty, and staff on college campuses; for example, comparing the educational outcomes of Black students to white students. Emerging approaches such as finite mixture modeling hold promise in unearthing more nuanced understandings. Of growing interest to many critical quantitative scholars is heterogeneity within minoritized populations; finite mixture modeling approaches such as growth mixture modeling, latent class analysis, and latent profile analysis are particularly well suited to reveal within-group differences that are otherwise obfuscated in most quantitative analyses. Although we found a few examples in our scoping review of authors who leveraged more traditional group comparisons for equity-minded aims, these emerging analytical approaches may be better suited for the questions asked by future critical quantitative scholars.
One Size Does Not Fit All
Many emerging analytical tools demonstrate promise in advancing conversations about inequity, particularly related to heterogeneity in subpopulations on college and university campuses. As noted previously, however, Rios-Aguilar ( 2014 ) noted that critical quantitative research need not rely solely on “fancy” or advanced analytical tools; in fact, our findings did not lead us to conclude that higher education scholars have established a set of analytical approaches that are explicitly critical in nature. Rather, our results revealed a common theme: that critical quantitative scholarship in higher education necessitates an elevated degree of intentionality in selection, application, and interpretation of whichever analytical approaches—advanced or not—scholars choose.
As noted, there were several instances in our data where commonly critiqued analytical approaches were still applied in the critical quantitative literature. For example, we found manuscripts that conducted a monolithic comparison of Indigenous and non-Indigenous students and the utilization of traditional dummy coding with white students as a normative reference group. What made these manuscripts distinct from more non-critical quantitative research was the thoughtfulness and intentionality with which those approaches were selected to serve equity-minded goals—an intentionality that was explicitly communicated to readers in the methods section of manuscripts. Just as the inclusion of positionality statements in half of the manuscripts suggests that researcher objectivity was generally not assumed by higher education scholars conducting critical quantitative scholarship, choices that often otherwise go unquestioned were interrogated and discussed in manuscripts.
Cokley and Awad ( 2013 ) share several recommendations for advancing social justice research via quantitative methods. One of their recommendations addresses the utilization of racial group comparisons in quantitative analyses. They do not suggest that researchers avoid comparisons between groups altogether, but rather they avoid “unnecessary” comparisons between groups (p. 35). They elaborate that, “[t]here should be a clear research questions that necessitates the use of the comparison” if utilized in quantitative research with critical aims (Cokley & Awad, 2013 , p. 35). Our findings suggested that—in the current state of critical quantitate scholarship in higher education—it is not so much about a specific set of approaches deeming scholarship as critical (or not), but rather about asking critical questions (as Stage initially called us to do in 2007) and then selecting methods that align with those goals.
Opportunities for Training and Collaboration
Notably, many of the emerging analytical approaches mentioned require a significant degree of methodological training. The limited use of such tools, which are otherwise well-suited for critical quantitative applications, points to a potential disconnect in training of higher education scholars. Some structured opportunities for partnership between disciplinary and methodological scholars have emerged via training programs such as the Quantitative Research Methods (QRM) for STEM Education Scholars Program (funded by the National Science Foundation Award 1937745) and the Institute on Mixture Modeling for Equity-Oriented Researchers, Scholars and Educators (IMMERSE) fellowship (funded by the Institute for Education Sciences Award R305B220021). These grant-funded training opportunities connect quantitative methodological experts with applied researchers across educational contexts.
We must consider additional ways, both formal and informal, to expand training opportunities for higher education scholars with interest in both advanced quantitative methods and equity-focused research; until then, expertise in quantitative methods and critical frameworks will likely inhabit two distinct communities of scholars. For higher education scholars to fully embrace the potential of critical quantitative research, we will be well served by intentional partnerships across methodological (e.g., quantitative and qualitative) and disciplinary (e.g., higher education scholars and methodologists) boundaries. In addition to expanding applied researchers’ analytical skillsets, training and collaboration opportunities also prepare potential critical quantitative scholars in higher education to select methodological approaches, whether introductory or advanced, that most closely align with their research aims.
Historically, critical inquiry has been viewed primarily as an endeavor for qualitative research. Recently, educational scholars have begun considering the possibilities for quantitative research to be leveraged in support of critical inquiry. However, there remains limited work evaluating whether and to what extent principles from quantitative criticalism, critical quantitative inquiry, and QuantCrit have been applied in higher education research. By drawing on the work and insights of scholars engaging in critical quantitative work, we provide a foundation on which future scholars can imagine and implement a vast range of possibilities for critical inquiry via quantitative methods in higher education. Ultimately, this work will allow scholars to realize the potential for research methodologies to directly support critical aims.
Data Availability
The list of manuscripts generated from the scoping review analysis is available via the Online Supplemental Materials Information link. Given the nature of our sample and topics discussed, interview data will not be shared publicly to protect participant anonymity.
American Psychological Association. (2024). Journal of Diversity in Higher Education. https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/dhe
Anguera, M. T., Blanco-Villaseñor, A., Losada, J. L., Sánchez-Algarra, P., & Onwuegbuzie, A. J. (2018). Revisiting the difference between mixed methods and multimethods: Is it all in the name? Quality & Quantity, 52 , 2757–2770.
Article Google Scholar
Arellano, L. (2022). Questioning the science: How quantitative methodologies perpetuate inequity in higher education. Education Sciences, 12 (2), 116.
Arskey, H., & O’Malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8 (1), 19–32.
Astin, A. W. (1984). Student involvement: A developmental theory for higher education. Journal of College Student Personnel, 25 , 297–308.
Google Scholar
Bensimon, E. M. (2007). The underestimated significance of practitioner knowledge in the scholarship on student success. The Review of Higher Education, 30 (4), 441–469.
Bensimon, E. M. (2018). Reclaiming racial justice in equity. Change: The Magazine of Higher Learning, 50 (3–4), 95–98.
Bierema, A., Hoskinson, A. M., Moscarella, R., Lyford, A., Haudek, K., Merrill, J., & Urban-Lurain, M. (2021). Quantifying cognitive bias in educational researchers. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 44 (4), 395–413.
Bourdieu, P. (1977). Cultural reproduction and social reproduction. In J. Karabel & A. H. Halsey (Eds.), Power and ideology in education (pp. 487–511). Oxford University Press.
Bronner, S. E. (2017). Critical theory: A very short introduction (Vol. 263). Oxford University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Byrd, D. (2019). The diversity distraction: A critical comparative analysis of discourse in higher education scholarship. Review of Higher Education, 42 , 135–172.
Castillo, W., & Babb, N. (2024). Transforming the future of quantitative educational research: A systematic review of enacting QuantCrit. Race Ethnicity and Education, 27 (1), 1–21.
Cokley, A., & Awad, G. H. (2013). In defense of quantitative methods: Using the “master’s tools” to promote social justice. Journal for Social Action in Counseling and Psychology, 5 (2), 26–41.
Creswell, J. W., & Miller, D. L. (2000). Determining validity in qualitative inquiry. Theory into Practice, 39 (3), 124–130.
Espino, M. M. (2012). Seeking the “truth” in the stories we tell: The role of critical race epistemology in higher education research. The Review of Higher Education, 36 (1), 31–67.
Garcia, N. M., López, N., & Vélez, V. N. (2018). Race, ethnicity, and education: Vol 21, No 2. QuantCrit: Rectifying quantitative methods through critical race theory . Routledge.
Garvey, J. C., & Huynh, J. (2024). Quantitative criticalism in education research. Critical Education, 15 (1), 74–90.
Gillborn, D., Warmington, P., & Demack, S. (2018). QuantCrit: Education, policy, ‘Big Data’ and principles for a critical race theory of statistics. Race Ethnicity and Education, 21 (2), 158–179.
Hanley, M. S. (2004). The name game: Naming in culture, critical theory, and the arts. Journal of Thought, 39 (4), 53–74.
Hesse-Biber, S., Rodriguez, D., & Frost, N. A. (2015). A qualitatively driven approach to multimethod and mixed methods research. In S. Hesse-Biber & R. B. Johnson (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of multimethod and mixed methods research inquiry. Oxford University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Jamieson, M. K., Govaart, G. H., & Pownall, M. (2023). Reflexivity in quantitative research: A rationale and beginner’s guide. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 17 (4), 1–15.
Kimball, E., & Friedensen, R. E. (2019). The search for meaning in higher education research: A discourse analysis of ASHE presidential addresses. The Review of Higher Education, 42 (4), 1549–1574.
Kincheloe, J. L., & McLaren, P. L. (1994). Rethinking critical theory and qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (pp. 138–157). Sage Publications Inc.
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science, 5 , 69.
López, N., Erwin, C., Binder, M., & Javier Chavez, M. (2018). Making the invisible visible: Advancing quantitative methods in higher education using critical race theory and intersectionality. Race Ethnicity and Education, 21 (2), 180–207.
Magoon, A. J. (1977). Constructivist approaches in educational research. Review of Educational Research, 47 (4), 651–693.
Martínez-Alemán, A. M., Pusser, B., & Bensimon, E. M. (Eds.). (2015). Critical approaches to the study of higher education: A practical introduction . Johns Hopkins University Press.
Mayhew, M. J., & Simonoff, J. S. (2015). Non-White, no more: Effect coding as an alternative to dummy coding with implications for higher education researchers. Journal of College Student Development, 56 (2), 170–175.
McCoy, D. L., & Rodricks, D. J. (2015). Critical race theory in higher education: 20 years of theoretical and research innovations. ASHE Higher Education Report, 41 (3), 1.
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., & Saldaña, J. (2014). Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook . Sage.
Munn, Z., Peters, M. D. J., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review of scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 18 , 1–7.
Renn, K. A. (2020). Reimagining the study of higher education: Generous thinking, chaos, and order in a low consensus field. The Review of Higher Education, 43 (4), 917–934.
Rios-Aguilar, C. (2014). The changing context of critical quantitative inquiry. New Directions for Institutional Research, 158 , 95–107.
Robinson, O. C. (2014). Sampling in interview-based qualitative research: A theoretical and practical guide. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 11 (1), 25–41.
Sablan, J. R. (2019). Can you really measure that? Combining critical race theory and quantitative methods. American Educational Research Journal, 56 (1), 178–203.
Sage Journals. (2024). Teachers college record: The voice of scholarship in education. https://journals.sagepub.com/author-instructions/TCZ
Saldaña, J. (2015). The coding manual for qualitative researchers . Sage Publications.
Stage, F. K. (Ed.). (2007). New directions for institutional research: No. 133. Using quantitative data to answer critical questions . Jossey-Bass.
Stage, F. K., & Wells, R. S. (Eds.). (2014). New directions for institutional research: No. 158. New scholarship in critical quantitative research—Part 1: Studying institutions and people in context . Jossey-Bass.
Stewart, D. L. (2022). Spanning and unsettling the borders of critical scholarship in higher education. The Review of Higher Education, 45 (4), 549–563.
Tabron, L. A., & Thomas, A. K. (2023). Deeper than wordplay: A systematic review of critical quantitative approaches in education research (2007–2021). Review of Educational Research, 93 , 756. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543221130017
Torgerson, D. J., & Torgerson, C. J. (2003). Avoiding bias in randomised controlled trials in educational research. British Journal of Educational Studies, 51 (1), 36–45.
Wells, R. S., & Stage, F. K. (Eds.). (2015). New directions for institutional research: No. 163. New scholarship in critical quantitative research—Part 2: New populations, approaches, and challenges . Jossey-Bass.
Wofford, A. M., & Winkler, C. E. (2022). Publication patterns of higher education research using quantitative criticalism and QuantCrit perspectives. Innovative Higher Education, 47 (6), 967–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10755-022-09628-3
Zuberi, T. (2001). Thicker than blood: How racial statistics lie . University of Minnesota Press.
Zuberi, T., & Bonilla-Silva, E. (2008). White logic, White methods: Racism and methodology . Lanham.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the American Educational Research Association, Division D. The authors gratefully thank Dr. Jason (Jay) Garvey for his support as an early thought partner with regard to this project, and Dr. Christopher Sewell for his helpful feedback on an earlier version of this manuscript, which was presented at the 2022 Association for the Study of Higher Education meeting.
This research was supported by a grant from the American Educational Research Association, Division D.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Counseling, Higher Education Leadership, Educational Psychology, & Foundations, Mississippi State University, 175 President’s Circle, 536 Allen Hall, Mississippi State, MS, 39762, USA
Christa E. Winkler
Department of Educational Leadership & Policy Studies, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA
Annie M. Wofford
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christa E. Winkler .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 26 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Winkler, C.E., Wofford, A.M. Trends and Motivations in Critical Quantitative Educational Research: A Multimethod Examination Across Higher Education Scholarship and Author Perspectives. Res High Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-024-09802-w
Download citation
Received : 25 June 2023
Accepted : 14 May 2024
Published : 04 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-024-09802-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Critical quantitative
- Quantitative criticalism
- Scoping review
- Multimethod study
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research: Comparing the Methods and Strategies for Education Research

No matter the field of study, all research can be divided into two distinct methodologies: qualitative and quantitative research. Both methodologies offer education researchers important insights.
Education research assesses problems in policy, practices, and curriculum design, and it helps administrators identify solutions. Researchers can conduct small-scale studies to learn more about topics related to instruction or larger-scale ones to gain insight into school systems and investigate how to improve student outcomes.
Education research often relies on the quantitative methodology. Quantitative research in education provides numerical data that can prove or disprove a theory, and administrators can easily share the number-based results with other schools and districts. And while the research may speak to a relatively small sample size, educators and researchers can scale the results from quantifiable data to predict outcomes in larger student populations and groups.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research in Education: Definitions
Although there are many overlaps in the objectives of qualitative and quantitative research in education, researchers must understand the fundamental functions of each methodology in order to design and carry out an impactful research study. In addition, they must understand the differences that set qualitative and quantitative research apart in order to determine which methodology is better suited to specific education research topics.
Generate Hypotheses with Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on thoughts, concepts, or experiences. The data collected often comes in narrative form and concentrates on unearthing insights that can lead to testable hypotheses. Educators use qualitative research in a study’s exploratory stages to uncover patterns or new angles.
Form Strong Conclusions with Quantitative Research
Quantitative research in education and other fields of inquiry is expressed in numbers and measurements. This type of research aims to find data to confirm or test a hypothesis.
Differences in Data Collection Methods
Keeping in mind the main distinction in qualitative vs. quantitative research—gathering descriptive information as opposed to numerical data—it stands to reason that there are different ways to acquire data for each research methodology. While certain approaches do overlap, the way researchers apply these collection techniques depends on their goal.
Interviews, for example, are common in both modes of research. An interview with students that features open-ended questions intended to reveal ideas and beliefs around attendance will provide qualitative data. This data may reveal a problem among students, such as a lack of access to transportation, that schools can help address.
An interview can also include questions posed to receive numerical answers. A case in point: how many days a week do students have trouble getting to school, and of those days, how often is a transportation-related issue the cause? In this example, qualitative and quantitative methodologies can lead to similar conclusions, but the research will differ in intent, design, and form.
Taking a look at behavioral observation, another common method used for both qualitative and quantitative research, qualitative data may consider a variety of factors, such as facial expressions, verbal responses, and body language.
On the other hand, a quantitative approach will create a coding scheme for certain predetermined behaviors and observe these in a quantifiable manner.
Qualitative Research Methods
- Case Studies : Researchers conduct in-depth investigations into an individual, group, event, or community, typically gathering data through observation and interviews.
- Focus Groups : A moderator (or researcher) guides conversation around a specific topic among a group of participants.
- Ethnography : Researchers interact with and observe a specific societal or ethnic group in their real-life environment.
- Interviews : Researchers ask participants questions to learn about their perspectives on a particular subject.
Quantitative Research Methods
- Questionnaires and Surveys : Participants receive a list of questions, either closed-ended or multiple choice, which are directed around a particular topic.
- Experiments : Researchers control and test variables to demonstrate cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations : Researchers look at quantifiable patterns and behavior.
- Structured Interviews : Using a predetermined structure, researchers ask participants a fixed set of questions to acquire numerical data.
Choosing a Research Strategy
When choosing which research strategy to employ for a project or study, a number of considerations apply. One key piece of information to help determine whether to use a qualitative vs. quantitative research method is which phase of development the study is in.
For example, if a project is in its early stages and requires more research to find a testable hypothesis, qualitative research methods might prove most helpful. On the other hand, if the research team has already established a hypothesis or theory, quantitative research methods will provide data that can validate the theory or refine it for further testing.
It’s also important to understand a project’s research goals. For instance, do researchers aim to produce findings that reveal how to best encourage student engagement in math? Or is the goal to determine how many students are passing geometry? These two scenarios require distinct sets of data, which will determine the best methodology to employ.
In some situations, studies will benefit from a mixed-methods approach. Using the goals in the above example, one set of data could find the percentage of students passing geometry, which would be quantitative. The research team could also lead a focus group with the students achieving success to discuss which techniques and teaching practices they find most helpful, which would produce qualitative data.
Learn How to Put Education Research into Action
Those with an interest in learning how to harness research to develop innovative ideas to improve education systems may want to consider pursuing a doctoral degree. American University’s School of Education online offers a Doctor of Education (EdD) in Education Policy and Leadership that prepares future educators, school administrators, and other education professionals to become leaders who effect positive changes in schools. Courses such as Applied Research Methods I: Enacting Critical Research provides students with the techniques and research skills needed to begin conducting research exploring new ways to enhance education. Learn more about American’ University’s EdD in Education Policy and Leadership .
What’s the Difference Between Educational Equity and Equality?
EdD vs. PhD in Education: Requirements, Career Outlook, and Salary
Top Education Technology Jobs for Doctorate in Education Graduates
American University, EdD in Education Policy and Leadership
Edutopia, “2019 Education Research Highlights”
Formplus, “Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data: 15 Key Differences and Similarities”
iMotion, “Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research: What Is What?”
Scribbr, “Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research”
Simply Psychology, “What’s the Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Research?”
Typeform, “A Simple Guide to Qualitative and Quantitative Research”
Request Information
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
Elementary Education Research Paper Topics

This comprehensive guide to elementary education research paper topics is designed to assist students and researchers in the field of education. The guide provides a wide array of topics divided into ten categories, each with ten unique topics, offering a diverse range of areas to explore in the field of elementary education. Additionally, the guide offers expert advice on how to choose a research topic and how to write an elementary education research paper. The final sections of the guide introduce iResearchNet’s professional writing services and encourage students to take advantage of these services for their research needs.
100 Elementary Education Research Paper Topics
Elementary education is a broad field with numerous areas to explore. Whether you’re interested in teaching methods, curriculum development, educational technology, or the social aspects of elementary education, there’s a research topic for you. Here, we present a comprehensive list of elementary education research paper topics, divided into ten categories. Each category contains ten unique topics, offering a diverse range of areas to explore in your research.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
1. Teaching Methods and Strategies
- The effectiveness of Montessori methods in elementary education.
- The role of play in learning in the early years.
- The impact of differentiated instruction on student achievement.
- The benefits and challenges of cooperative learning in the elementary classroom.
- The role of feedback in promoting student learning.
- The impact of teaching strategies on students’ motivation.
- The effectiveness of inquiry-based learning in science education.
- The role of storytelling in teaching literacy skills.
- The impact of technology on teaching and learning in the elementary classroom.
- The role of creativity in teaching and learning.
2. Curriculum and Instruction
- The impact of curriculum design on student learning.
- The role of interdisciplinary teaching in elementary education.
- The effectiveness of project-based learning in teaching science.
- The role of cultural relevance in curriculum design.
- The impact of standardized testing on curriculum and instruction.
- The role of critical thinking in the elementary curriculum.
- The effectiveness of integrating arts in the curriculum.
- The impact of curriculum alignment on student achievement.
- The role of experiential learning in the elementary curriculum.
- The challenges of teaching social studies in the elementary classroom.
3. Educational Technology
- The impact of digital technology on student learning.
- The role of educational games in teaching math.
- The effectiveness of using iPads in the classroom.
- The role of virtual reality in teaching science.
- The impact of technology on student engagement.
- The challenges of integrating technology in the classroom.
- The role of technology in promoting collaborative learning.
- The effectiveness of using technology in teaching reading skills.
- The impact of technology on teacher-student communication.
- The role of technology in personalized learning.
4. Social Aspects of Elementary Education
- The impact of classroom climate on student learning.
- The role of social-emotional learning in elementary education.
- The effectiveness of character education programs.
- The role of peer relationships in student learning.
- The impact of school culture on student achievement.
- The challenges of teaching diversity and inclusion in the elementary classroom.
- The role of student-teacher relationships in student learning.
- The effectiveness of anti-bullying programs in elementary schools.
- The impact of parental involvement on student achievement.
- The role of community partnerships in promoting student learning.
5. Special Education
- The effectiveness of inclusive education in the elementary classroom.
- The role of individualized education programs in supporting students with special needs.
- The impact of teacher training on the success of inclusive education.
- The challenges of teaching students with learning disabilities.
- The role of assistive technology in supporting students with special needs.
- The effectiveness of earlyintervention programs for students with special needs.
- The impact of classroom accommodations on the academic success of students with special needs.
- The role of collaboration between general and special education teachers.
- The effectiveness of behavior management strategies for students with emotional and behavioral disorders.
- The impact of special education policies on student outcomes.
6. Early Childhood Education
- The impact of early childhood education on academic success.
- The role of play in early childhood education.
- The effectiveness of early literacy programs.
- The role of parental involvement in early childhood education.
- The impact of early childhood education on social skills development.
- The challenges of teaching math in early childhood education.
- The role of creativity in early childhood education.
- The effectiveness of early intervention programs.
- The impact of early childhood education on cognitive development.
- The role of teacher-child relationships in early childhood education.
7. Educational Policies and Reforms
- The impact of No Child Left Behind on elementary education.
- The role of Common Core State Standards in curriculum development.
- The effectiveness of school choice policies.
- The role of educational policies in promoting equity in education.
- The impact of teacher evaluation policies on teaching and learning.
- The challenges of implementing educational reforms in elementary schools.
- The role of educational policies in promoting teacher quality.
- The effectiveness of policies aimed at reducing the achievement gap.
- The impact of educational funding policies on student achievement.
- The role of educational policies in promoting parental involvement.
8. Teacher Education and Professional Development
- The impact of teacher education programs on teacher effectiveness.
- The role of ongoing professional development in promoting teacher quality.
- The effectiveness of mentorship programs for novice teachers.
- The role of reflective practice in teacher professional development.
- The impact of teacher beliefs on teaching practices.
- The challenges of teaching in high-needs schools.
- The role of teacher collaboration in professional development.
- The effectiveness of teacher induction programs.
- The impact of teacher leadership on school improvement.
- The role of teacher autonomy in promoting job satisfaction.
9. Classroom Management
- The impact of classroom management strategies on student behavior.
- The role of positive reinforcement in promoting appropriate behavior.
- The effectiveness of classroom rules and procedures.
- The role of teacher-student relationships in classroom management.
- The impact of classroom environment on student learning.
- The challenges of managing disruptive behavior.
- The role of behavior management strategies in promoting a positive classroom climate.
- The effectiveness of conflict resolution strategies in the classroom.
- The impact of classroom management on student engagement.
- The role of classroom routines in promoting student responsibility.
10. Assessment and Evaluation
- The impact of formative assessment on student learning.
- The role of feedback in student assessment.
- The effectiveness of performance-based assessment.
- The role of self-assessment in promoting student learning.
- The impact of standardized testing on teaching and learning.
- The challenges of assessing student learning in diverse classrooms.
- The role of assessment in curriculum planning.
- The effectiveness of portfolio assessment.
- The impact of grading policies on student motivation.
- The role of assessment in identifying students at risk of academic failure.
This comprehensive list of elementary education research paper topics provides a wide range of areas to explore. Whether you’re interested in teaching methods, curriculum development, educational technology, or the social aspects of elementary education, there’s a research topic for you. Remember, the best research topic is one that you’re genuinely interested in and passionate about.
Elementary Education Research Guide
Elementary education, also known as primary education, is a crucial stage in the educational journey of a child. It is during these formative years that children acquire foundational skills in areas such as reading, writing, mathematics, science, and social studies. Additionally, they develop critical thinking skills, creativity, and social competencies that are essential for their overall growth and development.
Elementary education serves as the building block for all future learning. The experiences and knowledge gained during these years can significantly influence a child’s attitude towards learning, their academic success, and their lifelong learning habits. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that children receive quality education during these years.
Research in elementary education is of paramount importance. It helps educators, policymakers, and stakeholders understand the best practices, methodologies, and strategies to enhance learning outcomes in primary education. It also provides insights into the challenges faced in elementary education and how to address them effectively.
Elementary education research paper topics can span a wide range of areas, including teaching methods, learning styles, the impact of technology on learning, educational policies, classroom management, and many more. Choosing a research topic in this field requires careful consideration of various factors, including your interests, the relevance of the topic, and the availability of resources.
In the following sections, we provide a comprehensive list of elementary education research paper topics, expert advice on choosing a topic and writing a research paper, and information about iResearchNet’s professional writing services. Whether you are a student embarking on your first research project or a seasoned researcher looking for new areas to explore, this guide is designed to assist you in your research journey.
Choosing Elementary Education Research Paper Topics
Choosing a research topic is a critical step in the research process. The topic you select will guide your study, influence the complexity and relevance of your work, and determine how engaged you are throughout the process. In the field of elementary education, there are numerous intriguing topics that can be explored. Here are some expert tips to assist you in this process:
- Understanding Your Interests: The first step in choosing a research topic is to understand your interests. What areas of elementary education fascinate you the most? Are you interested in how teaching methods influence student learning, or are you more intrigued by the role of technology in the classroom? Reflecting on these questions can help you narrow down your options and choose a topic that truly engages you. Remember, research is a time-consuming process, and your interest in the topic will keep you motivated.
- Evaluating the Scope of the Topic: Once you have identified your areas of interest, the next step is to evaluate the scope of potential elementary education research paper topics. A good research topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow. If it’s too broad, you may struggle to cover all aspects of the topic effectively. If it’s too narrow, you may have difficulty finding enough information to support your research. Try to choose a topic that is specific enough to be manageable but broad enough to have sufficient resources.
- Assessing Available Resources and Data: Before finalizing a topic, it’s important to assess the available resources and data. Are there enough academic sources, such as books, journal articles, and reports, that you can use for your research? Is there accessible data that you can analyze if your research requires it? A preliminary review of literature and data can save you from choosing a topic with limited resources.
- Considering the Relevance and Applicability of the Topic: Another important factor to consider is the relevance and applicability of the topic. Is the topic relevant to current issues in elementary education? Can the findings of your research be applied in real-world settings? Choosing a relevant and applicable topic can increase the impact of your research and make it more interesting for your audience.
- Seeking Advice: Don’t hesitate to seek advice from your professors, peers, or other experts in the field. They can provide valuable insights, suggest resources, and help you refine your topic. Discussing your ideas with others can also help you see different perspectives and identify potential issues that you may not have considered.
- Flexibility: Finally, be flexible. Research is a dynamic process, and it’s okay to modify your topic as you delve deeper into your study. You may discover new aspects of the topic that are more interesting or find that some aspects are too challenging to explore due to constraints. Being flexible allows you to adapt your research to these changes and ensure that your study is both feasible and engaging.
Remember, choosing a research topic is not a decision to be taken lightly. It requires careful consideration and planning. However, with these expert tips, you can navigate this process more effectively and choose an elementary education research paper topic that not only meets your academic requirements but also fuels your passion for learning.
How to Write an Elementary Education Research Paper
Writing a research paper is a significant academic task that requires careful planning, thorough research, and meticulous writing. In the field of elementary education, this process can be particularly challenging due to the complexity and diversity of the field. However, with the right approach and strategies, you can write a compelling and insightful research paper. Here are some expert tips to guide you through this process:
- Understanding the Structure of a Research Paper: A typical research paper includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. The introduction presents your research question and its significance. The literature review provides an overview of existing research related to your topic. The methodology explains how you conducted your research. The results section presents your findings, and the discussion interprets these findings in the context of your research question. Finally, the conclusion summarizes your research and suggests areas for future research.
- Developing a Strong Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement is the central argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise, and debatable. A strong thesis statement guides your research and helps your readers understand the purpose of your paper.
- Conducting Thorough Research: Before you start writing, conduct a thorough review of the literature related to your topic. This will help you understand the current state of research in your area, identify gaps in the literature, and position your research within this context. Use academic databases to find relevant books, journal articles, and other resources. Remember to evaluate the credibility of your sources and take detailed notes to help you when writing.
- Writing and Revising Drafts: Start writing your research paper by creating an outline based on the structure of a research paper. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure that you cover all necessary sections. Write a first draft without worrying too much about perfection. Focus on getting your ideas down first. Then, revise your draft to improve clarity, coherence, and argumentation. Make sure each paragraph has a clear topic sentence and supports your thesis statement.
- Proper Citation and Avoiding Plagiarism: Always cite your sources properly to give credit to the authors whose work you are building upon and to avoid plagiarism. Familiarize yourself with the citation style required by your institution or discipline, such as APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, or Harvard. There are many citation tools available online that can help you with this.
- Seeking Feedback: Don’t hesitate to seek feedback on your drafts from your professors, peers, or writing centers at your institution. They can provide valuable insights and help you improve your paper.
- Proofreading: Finally, proofread your paper to check for any grammatical errors, typos, or inconsistencies in formatting. A well-written, error-free paper makes a good impression on your readers and enhances the credibility of your research.
- Incorporating Elementary Education Concepts: When writing an elementary education research paper, it’s crucial to accurately incorporate elementary education concepts. Make sure you understand these concepts thoroughly and can explain them clearly in your paper. Use examples where appropriate to illustrate these concepts.
- Analyzing and Interpreting Data: If your research involves data analysis, be sure to explain your analysis process and interpret the results in a way that is understandable to your readers. Discuss the implications of your findings for the broader field of elementary education.
- Discussing Real-World Applications: Elementary education is a practical field with many real-world applications. Discuss how your research relates to these applications. This can make your research more interesting and relevant to your readers.
Remember, writing a research paper is a process that requires time, effort, and patience. Don’t rush through it.Take the time to plan your research, conduct thorough research, write carefully, and revise your work. With these expert tips, you can write an elementary education research paper that is insightful, well-structured, and contributes to the field of elementary education.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
Writing a research paper is a significant undertaking that requires a deep understanding of the topic, strong writing skills, and the ability to conduct thorough research. At iResearchNet, we understand the challenges that students face when writing a research paper, and we are here to help. We offer a range of professional writing services designed to support students in their academic journey.
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers: Our team of writers are not just experts in their respective fields, but they also hold advanced degrees. They understand the intricacies of academic writing and are adept at writing research papers in various fields, including education.
- Custom Written Works: Every research paper is unique, and we treat it as such. Our writers work closely with you to understand your specific requirements and expectations. They then craft a research paper that meets these requirements and reflects your understanding and perspective.
- In-Depth Research: A good research paper is underpinned by thorough research. Our writers conduct in-depth research using reliable and relevant sources to ensure that your paper is informative and credible.
- Custom Formatting: Formatting is an essential aspect of academic writing. Our writers are familiar with various formatting styles, including APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard, and can format your paper according to your preferred style.
- Top Quality: We are committed to delivering top-quality research papers. Our writers adhere to high writing standards, and our quality assurance team reviews each paper to ensure it meets these standards.
- Customized Solutions: We understand that every student has unique needs. Whether you need a research paper on a complex topic in elementary education, assistance with a specific section of your paper, or editing and proofreading services, we can provide a solution that fits your needs.
- Flexible Pricing: We believe that professional writing services should be accessible to all students. That’s why we offer flexible pricing options that cater to different budgets. We are transparent about our pricing, and there are no hidden charges.
- Short Deadlines up to 3 hours: We understand that time is of the essence when it comes to academic assignments. Our writers are skilled at working under pressure and can deliver high-quality papers within short deadlines.
- Timely Delivery: We respect your deadlines and are committed to delivering your paper on time. Our writers start working on your paper as soon as your order is confirmed, and we keep you updated on the progress of your paper.
- 24/7 Support: We believe in providing continuous support to our clients. Our customer support team is available 24/7 to answer your questions, address your concerns, and assist you with your order.
- Absolute Privacy: We respect your privacy and are committed to protecting your personal and financial information. We have robust privacy policies and security measures in place to ensure that your information is safe.
- Easy Order Tracking: We provide an easy and transparent order tracking system that allows you to monitor the progress of your paper and communicate with your writer.
- Money Back Guarantee: Your satisfaction is our top priority. If you are not satisfied with our service, we offer a money-back guarantee.
At iResearchNet, we are committed to helping you succeed in your academic journey. We understand the challenges of writing a research paper and are here to support you every step of the way. Whether you need help choosing a topic, conducting research, writing your paper, or editing and proofreading your work, our expert writers are ready to assist you. With our professional writing services, you can focus on learning and leave the stress of writing to us.
Order Your Custom Research Paper Today!
Embarking on the journey of writing a research paper can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to complex fields like elementary education. But remember, you don’t have to face this challenge alone. iResearchNet is here to provide you with the support you need to produce a high-quality, insightful, and impactful research paper.
Our team of expert degree-holding writers is ready to assist you in creating a custom-written research paper that not only meets but exceeds academic standards. Whether you’re struggling with topic selection, research, writing, or formatting, we’ve got you covered. Our comprehensive services are designed to cater to your unique needs and ensure your academic success.
Don’t let the stress of writing a research paper hinder your learning experience. Take advantage of our professional writing services and focus on what truly matters – your learning and growth. With iResearchNet, you can be confident that you’re submitting a top-quality research paper that reflects your understanding and hard work.
So, are you ready to unleash your academic potential? Order a custom education research paper on any topic from iResearchNet today. Let us help you navigate your academic journey and secure your success. Remember, your academic achievement is our top priority, and we’re committed to helping you reach your goals. Order now and experience the iResearchNet difference!
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Internet & Technology
6 facts about americans and tiktok.
62% of U.S. adults under 30 say they use TikTok, compared with 39% of those ages 30 to 49, 24% of those 50 to 64, and 10% of those 65 and older.
Many Americans think generative AI programs should credit the sources they rely on
Americans’ use of chatgpt is ticking up, but few trust its election information, whatsapp and facebook dominate the social media landscape in middle-income nations, sign up for our internet, science, and tech newsletter.
New findings, delivered monthly
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure in the U.S.
64% of Americans live within 2 miles of a public electric vehicle charging station, and those who live closest to chargers view EVs more positively.
When Online Content Disappears
A quarter of all webpages that existed at one point between 2013 and 2023 are no longer accessible.
A quarter of U.S. teachers say AI tools do more harm than good in K-12 education
High school teachers are more likely than elementary and middle school teachers to hold negative views about AI tools in education.
Teens and Video Games Today
85% of U.S. teens say they play video games. They see both positive and negative sides, from making friends to harassment and sleep loss.
Americans’ Views of Technology Companies
Most Americans are wary of social media’s role in politics and its overall impact on the country, and these concerns are ticking up among Democrats. Still, Republicans stand out on several measures, with a majority believing major technology companies are biased toward liberals.
22% of Americans say they interact with artificial intelligence almost constantly or several times a day. 27% say they do this about once a day or several times a week.
About one-in-five U.S. adults have used ChatGPT to learn something new (17%) or for entertainment (17%).
Across eight countries surveyed in Latin America, Africa and South Asia, a median of 73% of adults say they use WhatsApp and 62% say they use Facebook.
5 facts about Americans and sports
About half of Americans (48%) say they took part in organized, competitive sports in high school or college.
REFINE YOUR SELECTION
Research teams, signature reports.
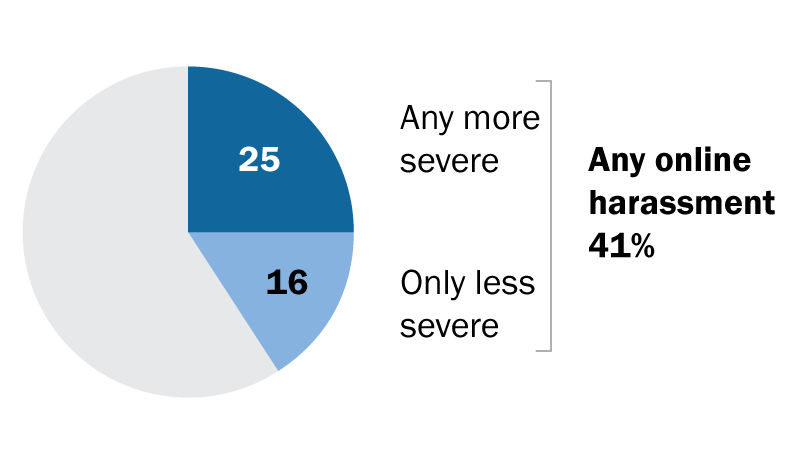
The State of Online Harassment
Roughly four-in-ten Americans have experienced online harassment, with half of this group citing politics as the reason they think they were targeted. Growing shares face more severe online abuse such as sexual harassment or stalking
Parenting Children in the Age of Screens
Two-thirds of parents in the U.S. say parenting is harder today than it was 20 years ago, with many citing technologies – like social media or smartphones – as a reason.
Dating and Relationships in the Digital Age
From distractions to jealousy, how Americans navigate cellphones and social media in their romantic relationships.
Americans and Privacy: Concerned, Confused and Feeling Lack of Control Over Their Personal Information
Majorities of U.S. adults believe their personal data is less secure now, that data collection poses more risks than benefits, and that it is not possible to go through daily life without being tracked.
Americans and ‘Cancel Culture’: Where Some See Calls for Accountability, Others See Censorship, Punishment
Social media fact sheet, digital knowledge quiz, video: how do americans define online harassment.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The impact of poverty on education. The use of student data to inform instruction. The role of parental involvement in education. The effects of mindfulness practices in the classroom. The use of technology in the classroom. The role of critical thinking in education.
Table of Contents. 🔝 Top-15 Research Titles about Education. #️⃣ Quantitative Research Topics. ️📋 Qualitative Research Topics. 🎒 Titles about School Issues in 2024. 🦼 Research Topics on Special Education. 👶 Early Childhood Education. 🧠 Educational Psychology. 🧸 Child Development Topics.
Here are some elementary education title research ideas. Assessing quick computer literacy among elementary school pupils. The role of video games in childhood brain development. Male vs female role models in early education periods. The advantages of digital textbooks in elementary schools.
An example of quantitative research topics for 12 th -grade students will come in handy if you want to score a good grade. Here are some of the best ones: The link between global warming and climate change. What is the greenhouse gas impact on biodiversity and the atmosphere.
Quantitative Research Topics. Quantitative Research Topics are as follows: The effects of social media on self-esteem among teenagers. A comparative study of academic achievement among students of single-sex and co-educational schools. The impact of gender on leadership styles in the workplace.
Here are 10 practical research topics for STEM students: Developing an affordable and sustainable water purification system for rural communities. Designing a low-cost, energy-efficient home heating and cooling system. Investigating strategies for reducing food waste in the supply chain and households.
Introduction. The field of education has embraced quantitative research designs since early in the 20th century. The foundation for these designs was based primarily in the psychological literature, and psychology and the social sciences more generally continued to have a strong influence on quantitative designs until the assimilation of qualitative designs in the 1970s and 1980s.
The. quantitative research methods in education emphasise basic group designs. for research and evaluation, analytic metho ds for exploring re lationships. between categorical and continuous ...
Educational research has a strong tradition of employing state-of-the-art statistical and psychometric (psychological measurement) techniques. Commonly referred to as quantitative methods, these techniques cover a range of statistical tests and tools. The Sage encyclopedia of educational research, measurement, and evaluation by Bruce B. Frey (Ed.)
David Gibson (Ed.) Publication Date: 2020. The book aims to advance global knowledge and practice in applying data science to transform higher education learning and teaching to improve personalization, access and effectiveness of education for all. Currently, higher education institutions and involved stakeholders can derive multiple benefits ...
This book presents a clear and straightforward guide for all those seeking to conduct quantitative research in the field of education, using primary research data samples. It provides educational researchers with the tools they can work with to achieve results efficiently. ... Topics: Management Education, Big Data/Analytics, Statistics for ...
For applied quantitative research in education to become more critical, learners of quantitative methodology must be made aware of its historical and modern misuses. ... are known to skew responses to survey questions pertaining to sensitive topics (Grimm, 2010). The insight of CQL is to recognize that numbers are not generated in a vacuum.
This resource is intended as an easy-to-use guide for anyone who needs some quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences, covering subjects such as education, sociology, business, nursing. If you area qualitative researcher who needs to venture into the world of numbers, or a student instructed to undertake a quantitative research project despite a hatred for ...
Mixed-methods research is a flexible approach, where the research design is determined by what we want to find out rather than by any predetermined epistemological position. In mixed-methods research, qualitative or quantitative components can predominate, or both can have equal status. 1.4. Units and variables.
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
Research trends in mathematics education: A quantitative content analysis of major journals 2017-2021 . Katibe Gizem Yığ. 1. Burdur Mehmet Akif Ersoy University, Turkey (ORCID: 0000-0001-5783-3861) This research aims to uncover current trends and key issues by examining the research in mathematics education during the period 2017-2021.
Students in Quantitative Methods in Education engage in the science and practice of educational measurement and statistics, primarily through the development and application of statistical and psychometric methods. All QME students will engage in coursework addressing fundamental topics related to statistics, educational measurement, research ...
Education Research: Quantitative research is used in education research to study the effectiveness of teaching methods, assess student learning outcomes, and identify factors that influence student success. Researchers use experimental and quasi-experimental designs, as well as surveys and other quantitative methods, to collect and analyze data.
Across professional networks in higher education, the perspectives of association leaders (e.g., Association for the Study of Higher Education [ASHE]) have often placed qualitative and quantitative research in opposition to each other, with qualitative research being a primary way to amplify the voices of systemically minoritized students, faculty, and staff (Kimball & Friedensen, 2019).
Learn quantitative research principles, methods, and analysis. ... Choose the Quantitative Research Course That Aligns Best With Your Educational Goals. C. University of California, Davis. ... Other topics to explore. Arts and Humanities. 338 courses. Business. 1095 courses. Computer Science. 668 courses.
Education research often relies on the quantitative methodology. Quantitative research in education provides numerical data that can prove or disprove a theory, and administrators can easily share the number-based results with other schools and districts. And while the research may speak to a relatively small sample size, educators and ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Elementary education is a broad field with numerous areas to explore. Whether you're interested in teaching methods, curriculum development, educational technology, or the social aspects of elementary education, there's a research topic for you. Here, we present a comprehensive list of elementary education research paper topics, divided ...
Quantitative research Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions. This type of research can be used to establish generalizable facts. about a topic. Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions.
Americans' Views of Technology Companies. Most Americans are wary of social media's role in politics and its overall impact on the country, and these concerns are ticking up among Democrats. Still, Republicans stand out on several measures, with a majority believing major technology companies are biased toward liberals. short readsApr 3, 2024.
Guaranteed income programs have been successful in low-income countries. Now, researchers hope to test their effectiveness in the U.S. May 30, 2024. AAMCNews. Women are changing the face of medicine in America. Data from the past 18 years show how women have driven growth in the supply of physicians and expanded their presence in some of the ...