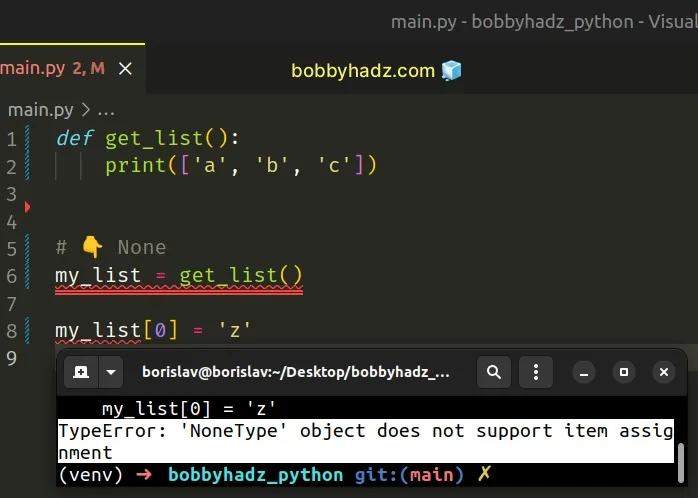
TypeError: NoneType object does not support item assignment
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 3 min

# TypeError: NoneType object does not support item assignment
The Python "TypeError: NoneType object does not support item assignment" occurs when we try to perform an item assignment on a None value.
To solve the error, figure out where the variable got assigned a None value and correct the assignment.
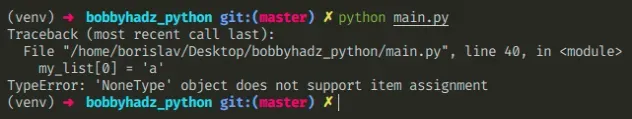
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
We tried to assign a value to a variable that stores None .
# Checking if the variable doesn't store None
Use an if statement if you need to check if a variable doesn't store a None value before the assignment.
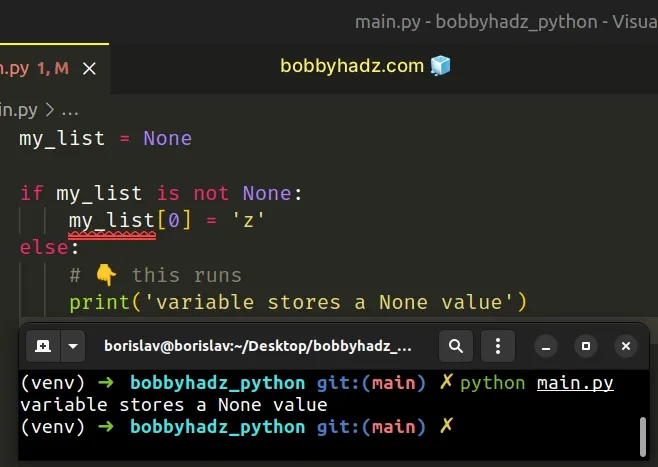
The if block is only run if the variable doesn't store a None value, otherwise, the else block runs.
# Setting a fallback value if the variable stores None
Alternatively, you can set a fallback value if the variable stores None .
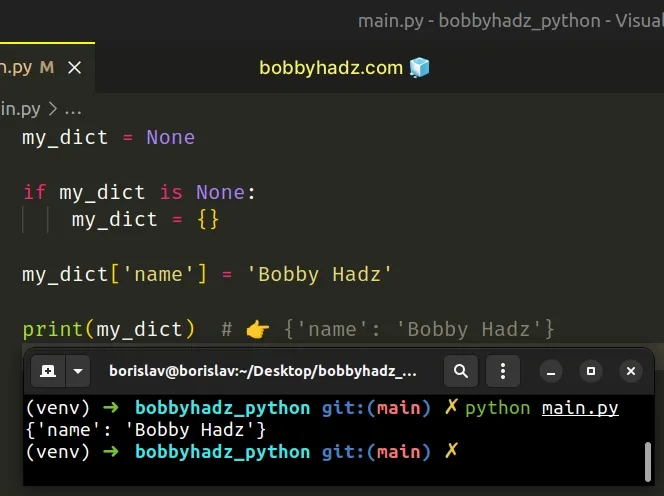
If the variable stores a None value, we set it to an empty dictionary.
# Track down where the variable got assigned a None value
You have to figure out where the variable got assigned a None value in your code and correct the assignment to a list or a dictionary.
The most common sources of None values are:
- Having a function that doesn't return anything (returns None implicitly).
- Explicitly setting a variable to None .
- Assigning a variable to the result of calling a built-in function that doesn't return anything.
- Having a function that only returns a value if a certain condition is met.
# Functions that don't return a value return None
Functions that don't explicitly return a value return None .
You can use the return statement to return a value from a function.
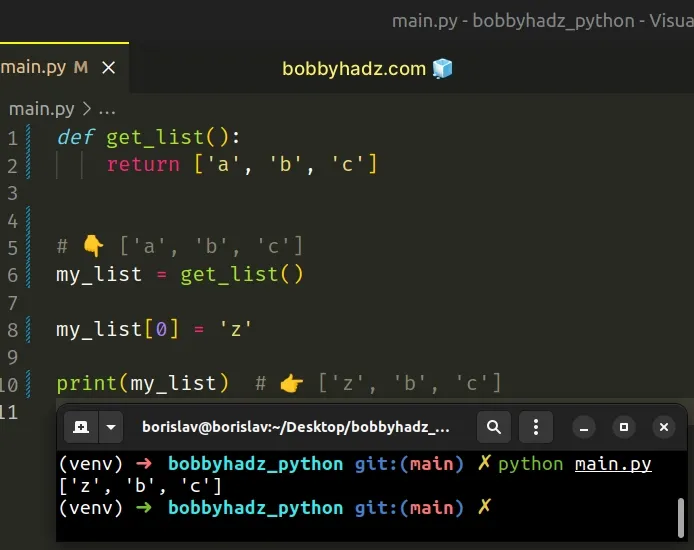
The function now returns a list, so we can safely change the value of a list element using square brackets.
# Many built-in functions return None
Note that there are many built-in functions (e.g. sort() ) that mutate the original object in place and return None .
The sort() method mutates the list in place and returns None , so we shouldn't store the result of calling it into a variable.
To solve the error, remove the assignment.
# A function that returns a value only if a condition is met
Another common cause of the error is having a function that returns a value only if a condition is met.
The if statement in the get_list function is only run if the passed-in argument has a length greater than 3 .
To solve the error, you either have to check if the function didn't return None or return a default value if the condition is not met.
Now the function is guaranteed to return a value regardless of whether the condition is met.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Return a default value if None in Python
- Why does my function print None in Python [Solved]
- Check if a Variable is or is not None in Python
- Convert None to Empty string or an Integer in Python
- How to Convert JSON NULL values to None using Python
- Join multiple Strings with possibly None values in Python
- Why does list.reverse() return None in Python

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
[Solved] TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment

In this article, we will be discussing the TypeError:’str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment exception . We will also be going through solutions to this problem with example programs.
Why is This Error Raised?
When you attempt to change a character within a string using the assignment operator, you will receive the Python error TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment.
As we know, strings are immutable. If you attempt to change the content of a string, you will receive the error TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment .
There are four other similar variations based on immutable data types :
- TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
- TypeError: 'int' object does not support item assignment
- TypeError: 'float' object does not support item assignment
- TypeError: 'bool' object does not support item assignment
Replacing String Characters using Assignment Operators
Replicate these errors yourself online to get a better idea here .
In this code, we will attempt to replace characters in a string.
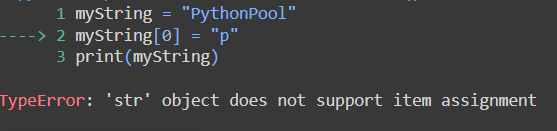
Strings are an immutable data type. However, we can change the memory to a different set of characters like so:
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in JSON
Let’s review the following code, which retrieves data from a JSON file.
In line 5, we are assigning data['sample'] to a string instead of an actual dictionary. This causes the interpreter to believe we are reassigning the value for an immutable string type.
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in PySpark
The following program reads files from a folder in a loop and creates data frames.
This occurs when a PySpark function is overwritten with a string. You can try directly importing the functions like so:
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in PyMongo
The following program writes decoded messages in a MongoDB collection. The decoded message is in a Python Dictionary.
At the 10th visible line, the variable x is converted as a string.
It’s better to use:
Please note that msg are a dictionary and NOT an object of context.
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Random Shuffle
The below implementation takes an input main and the value is shuffled. The shuffled value is placed into Second .
random.shuffle is being called on a string, which is not supported. Convert the string type into a list and back to a string as an output in Second
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Pandas Data Frame
The following program attempts to add a new column into the data frame
The iteration statement for dataset in df: loops through all the column names of “sample.csv”. To add an extra column, remove the iteration and simply pass dataset['Column'] = 1 .
![python class does not support item assignment [Solved] runtimeerror: cuda error: invalid device ordinal](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Solved-runtimeerror-cuda-error-invalid-device-ordinal-300x157.webp)
These are the causes for TypeErrors : – Incompatible operations between 2 operands: – Passing a non-callable identifier – Incorrect list index type – Iterating a non-iterable identifier.
The data types that support item assignment are: – Lists – Dictionaries – and Sets These data types are mutable and support item assignment
As we know, TypeErrors occur due to unsupported operations between operands. To avoid facing such errors, we must: – Learn Proper Python syntax for all Data Types. – Establish the mutable and immutable Data Types. – Figure how list indexing works and other data types that support indexing. – Explore how function calls work in Python and various ways to call a function. – Establish the difference between an iterable and non-iterable identifier. – Learn the properties of Python Data Types.
We have looked at various error cases in TypeError:’str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment. Solutions for these cases have been provided. We have also mentioned similar variations of this exception.
Trending Python Articles
![python class does not support item assignment [Fixed] typeerror can’t compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/typeerror-cant-compare-datetime.datetime-to-datetime.date_-300x157.webp)

HatchJS.com
Cracking the Shell of Mystery
TypeError: Type object does not support item assignment: How to fix it?
TypeError: Type object does not support item assignment
Have you ever tried to assign a value to a property of a type object and received a TypeError? If so, you’re not alone. This error is a common one, and it can be frustrating to figure out what went wrong.
In this article, we’ll take a look at what a type object is, why you can’t assign values to its properties, and how to avoid this error. We’ll also provide some examples of how to work with type objects correctly.
So, if you’re ready to learn more about TypeErrors and type objects, read on!
What is a type object?
A type object is a special kind of object that represents a data type. For example, the `int` type object represents the integer data type, and the `str` type object represents the string data type.
Type objects are created when you use the `type()` function. For example, the following code creates a type object for the integer data type:
python int_type = type(1)
Type objects have a number of properties that you can use to get information about them. For example, the `__name__` property returns the name of the type, and the `__bases__` property returns a list of the type’s base classes.
Why can’t you assign values to type objects?
Type objects are immutable, which means that their values cannot be changed. This is because type objects are used to represent the abstract concept of a data type, and their values are not meant to be changed.
If you try to assign a value to a property of a type object, you’ll receive a TypeError. For example, the following code will raise a TypeError:
python int_type.name = “New name”
How to avoid TypeErrors
To avoid TypeErrors, you should never try to assign values to properties of type objects. If you need to change the value of a property, you should create a new object with the desired value.
For example, the following code correctly changes the value of the `name` property of an integer object:
python new_int = int(1) new_int.name = “New name”
TypeErrors can be frustrating, but they can usually be avoided by understanding what type objects are and how they work. By following the tips in this article, you can avoid these errors and write more robust code.
| Header 1 | Header 2 | Header 3 | |—|—|—| | TypeError: type object does not support item assignment | Definition | Cause | | An error that occurs when you try to assign a value to an element of a type object that does not support item assignment. | The type object is immutable, which means that its values cannot be changed. | Trying to assign a value to an element of a type object will result in a TypeError. |
A TypeError is a type of error that occurs when an operation or function is applied to an object of an inappropriate type. For example, trying to assign a value to an attribute of a type object will result in a TypeError.
TypeErrors can be difficult to debug, because they can occur in a variety of situations. However, by understanding what causes a TypeError, you can be better equipped to avoid them.
What causes a TypeError?
There are a few different things that can cause a TypeError:
- Using an incompatible data type: One of the most common causes of a TypeError is using an incompatible data type. For example, trying to add a string to a number will result in a TypeError.
- Using an invalid operator: Another common cause of a TypeError is using an invalid operator. For example, trying to divide a number by zero will result in a TypeError.
- Calling a method on an object that doesn’t support it: Finally, trying to call a method on an object that doesn’t support it can also result in a TypeError. For example, trying to call the `.sort()` method on a string will result in a TypeError.
There are a few things you can do to avoid TypeErrors:
- Be careful about the data types you use: Make sure that you are using the correct data types for your operations. For example, if you are adding two numbers, make sure that both numbers are numbers.
- Use the correct operators: Make sure that you are using the correct operators for your operations. For example, if you are dividing two numbers, use the `/` operator.
- Read the documentation: If you are not sure whether a method is supported by an object, read the documentation to find out.
By following these tips, you can help to avoid TypeErrors in your code.
TypeErrors can be a frustrating experience, but they can also be a learning opportunity. By understanding what causes a TypeError, you can be better equipped to avoid them. And by following the tips in this article, you can help to reduce the number of TypeErrors in your code.
Additional resources
- [Python TypeError documentation](https://docs.python.org/3/library/exceptions.htmlTypeError)
- [Stack Overflow: TypeError questions](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/typeerror)
- [Real Python: How to avoid TypeErrors in Python](https://realpython.com/python-typeerror/)
3. How to fix a TypeError?
To fix a TypeError, you need to identify the cause of the error and then take steps to correct it. Some common fixes include:
Using the correct data type
Using the correct operator
Calling the correct method on the object
Let’s take a look at some examples of how to fix each of these types of errors.
One of the most common causes of TypeErrors is using the wrong data type. For example, if you try to add a string to an integer, you will get a TypeError because strings and integers are different data types. To fix this error, you need to convert the string to an integer or the integer to a string.
x = ‘123’ y = 456
This will raise a TypeError because you cannot add a string to an integer z = x + y
To fix this error, you can convert the string to an integer z = int(x) + y
Another common cause of TypeErrors is using the wrong operator. For example, if you try to divide an integer by a string, you will get a TypeError because you cannot divide an integer by a string. To fix this error, you need to use the correct operator.
x = 123 y = ‘456’
This will raise a TypeError because you cannot divide an integer by a string z = x / y
To fix this error, you can use the `str()` function to convert the string to an integer z = x / int(y)
Finally, another common cause of TypeErrors is calling the wrong method on an object. For example, if you try to call the `len()` method on a string, you will get a TypeError because the `len()` method is not defined for strings. To fix this error, you need to call the correct method on the object.
x = ‘hello’
This will raise a TypeError because the `len()` method is not defined for strings y = len(x)
To fix this error, you can use the `str()` function to convert the string to an integer y = len(str(x))
By following these tips, you can help to avoid TypeErrors in your Python code.
4. Examples of TypeErrors
Here are some examples of TypeErrors:
x = ‘hello’ x[0] = ‘a’
This will result in a TypeError because strings are immutable and cannot be changed.
print(int(‘123’))
This will also result in a TypeError because the string ‘123’ cannot be converted to an integer.
class MyClass: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name
my_class = MyClass(‘John’) my_class.name = ‘Jane’
This will also result in a TypeError because the method `name` is not defined on the `MyClass` object.
TypeErrors are a common problem in Python, but they can be easily avoided by following the tips in this article. By using the correct data types, operators, and methods, you can help to ensure that your Python code is free of errors.
Q: What does the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment” mean?
A: This error occurs when you try to assign a value to a property of a type object. For example, the following code will raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.name = ‘MyType’ Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in TypeError: type object does not support item assignment
The reason for this error is that type objects are immutable, which means that their properties cannot be changed after they are created. If you need to change the value of a property of a type object, you can create a new type object with the desired value.
Q: How can I fix the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment”?
A: There are two ways to fix this error. The first way is to create a new type object with the desired value. For example, the following code will fix the error in the example above:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {‘name’: ‘MyType’}) >>> type.name ‘MyType’
The second way to fix this error is to use a dictionary to store the properties of the type object. For example, the following code will also fix the error in the example above:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.__dict__[‘name’] = ‘MyType’ >>> type.name ‘MyType’
Q: What are some common causes of the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment”?
A: There are a few common causes of this error. The first is trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that does not exist. For example, the following code will raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.foo = ‘bar’ Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in AttributeError: type object has no attribute ‘foo’
The second is trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is read-only. For example, the following code will also raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.name = ‘MyType’ Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in TypeError: can’t set attribute ‘name’ of type object
The third is trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is not a valid type. For example, the following code will also raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.name = 123 Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in TypeError: can’t assign int to str object
Q: How can I avoid the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment”?
A: There are a few things you can do to avoid this error. First, make sure that you are trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that exists. Second, make sure that you are not trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is read-only. Third, make sure that you are not trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is not a valid type.
Here are some specific examples of how to avoid this error:
- Instead of trying to assign a value to the `name` property of a type object, you can create a new type object with the desired value. For example:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {‘name’: ‘MyType’})
- Instead of trying to assign a value to the `name` property of a type object, you can use a dictionary to store the properties of the type object. For example:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.__dict__[‘name’] = ‘MyType’
- Instead of trying to assign a value to the `name` property of a type object, you can use a getter and setter method to access the property. For example:
In this blog post, we discussed the TypeError: type object does not support item assignment error. We first explained what the error is and then provided several ways to fix it. We also discussed some common causes of the error and how to avoid them.
We hope that this blog post has been helpful and that you now have a better understanding of the TypeError: type object does not support item assignment error. If you have any other questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
Author Profile

Latest entries
- December 26, 2023 Error Fixing User: Anonymous is not authorized to perform: execute-api:invoke on resource: How to fix this error
- December 26, 2023 How To Guides Valid Intents Must Be Provided for the Client: Why It’s Important and How to Do It
- December 26, 2023 Error Fixing How to Fix the The Root Filesystem Requires a Manual fsck Error
- December 26, 2023 Troubleshooting How to Fix the `sed unterminated s` Command
Similar Posts
Ggplot error: discrete value supplied to continuous scale: how to fix it.
Have you ever tried to use ggplot2 to plot a data set, only to get an error message like “Discrete value supplied to continuous scale”? If so, you’re not alone. This is a common error that can be caused by a number of things, but it’s usually pretty easy to fix. In this article, we’ll…
Could not execute zipalign: How to Fix This Error
Could Not Execute Zipalign: What It Means and How to Fix It If you’re a developer, you’ve probably come across the error message “Could not execute zipalign.” This error can occur for a variety of reasons, but it typically means that your app’s APK file is not properly aligned. When an APK file is not…
Laravel 5.8 Internal Server Error – How to Fix
Laravel is Currently Unable to Handle This Request: What It Means and How to Fix It Laravel is a popular PHP framework that’s known for its speed, flexibility, and ease of use. However, even the best frameworks can sometimes encounter errors. One common error that Laravel users may encounter is “Laravel is currently unable to…
How to Fix the Conversion Failed When Converting Date and/or Time from Character String Error
Have you ever encountered the error message “Conversion failed when converting date and/or time from character string”? If so, you’re not alone. This error is a common one, and it can be caused by a variety of factors. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what this error means, what causes it, and…
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘xgboost’
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named xgboost XGBoost is a popular machine learning library for gradient boosting. It’s known for its speed, scalability, and accuracy. However, sometimes you may encounter the error “ModuleNotFoundError: No module named xgboost” when you try to import the library. This error can be caused by a number of things, such as: The…
TensorFlow 2.0: AttributeError: module ‘tensorflow.compat.v2’ has no attribute ‘__internal__’
AttributeError: module ‘tensorflow.compat.v2’ has no attribute ‘__internal__’ This error occurs when you try to access the `__internal__` attribute of the `tensorflow.compat.v2` module. This attribute is not available in TensorFlow 2.0, so you will need to use a different method to access the information you need. In this article, we will discuss what causes this error…
Typeerror: nonetype object does not support item assignment
When working with Python projects, we may come across an error that reads “Typeerror: nonetype object does not support item assignment” .
At first glance, this error message can seem cryptic and frustrating. However, it’s actually a helpful clue that points toward the root of the problem.
In this guide, we’ll explore the causes of this error as well as provide practical examples of how to resolve it.
What is Typeerror: nonetype object does not support item assignment?
The Python error TypeError: ‘NoneType’ object does not support item assignment occurs means that we are trying to assign a value to an object that has a value of None (or null in other programming languages).
Moreover, None is a special value that represents the absence of a value.
Thus it is often used as a default value for function arguments or to indicate that a variable has not been initialized.
How to reproduce Typeerror: nonetype object does not support item assignment
Here’s an example code snippet that could produce this error:
In this code, we have a variable x that has not been assigned a value. Its value will be None by default.
Therefore if we try to assign a value to x[0] , you will get a TypeError because you cannot assign a value to an index of None.
Now let’s find the possible factors why and when we can get this error. Hence you might consider in finding solutions.
When do we get this error?
These are the common possible causes when we got the TypeError: ‘NoneType’ object does not support item assignment.
How to fix nonetype object does not support item assignment
Here are the possible solutions you can try in fixing the error nonetype object does not support item assignment .
Solution 1: Verify why the variable is assigned to the value None
The first way to fix the error is to ensure why the variable is assigned to None.
Solution 2: Skip assigning the value using the index if variable is None
In this solution, we should avoid assigning the value using the index, when the variable is assigned to None.
Solution 3: Create a list with a value assigned to None
Create a list with values assigned to when a variable is assigned to None needs to store values in the variable.
Moreover, the index should be available in the list. Wherein the list assigned to the value None is changeable by adding values to the index.
Anyway, we also have a solution for Typeerror series objects are mutable thus they cannot be hashed errors, you might encounter.
I think that’s all for this guide. We hope you have learned and we helped you fix your error.

How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment
by Suf | Programming , Python , Tips
In Python, integers are single values. You cannot access elements in integers like you can with container objects. If you try to change an integer in-place using the indexing operator [], you will raise the TypeError: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment.
This error can occur when assigning an integer to a variable with the same name as a container object like a list or dictionary.
To solve this error, check the type of the object before the item assignment to make sure it is not an integer.
This tutorial will go through how to solve this error and solve it with the help of code examples.

Table of contents
Typeerror: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment.
Let’s break up the error message to understand what the error means. TypeError occurs whenever you attempt to use an illegal operation for a specific data type.
The part 'int' object tells us that the error concerns an illegal operation for integers.
The part does not support item assignment tells us that item assignment is the illegal operation we are attempting.
Integers are single values and do not contain elements. You must use indexable container objects like lists to perform item assignments.
This error is similar to the TypeError: ‘int’ object is not subscriptable .
Let’s look at an example where we define a function that takes a string holding a phrase, splits the string into words and then stores the counts of each word in a dictionary. The code is as follows:
We will then use the input() method to take a string from the user as follows:
Let’s run the code to see what happens:
The error occurs because we set word_dict to an integer in the try code block with word_dict = value + 1 when we encounter the second occurrence of the word really . Then when the for loop moves to the next word fun which does not exist in the dictionary, we execute the except code block. But word_dict[word] = 1 expects a dictionary called word_dict , not an integer. We cannot perform item assignment on an integer.
We need to ensure that the word_dict variable remains a dictionary throughout the program lifecycle to solve this error. We need to increment the value of the dictionary by one if the word already exists in the dictionary. We can access the value of a dictionary using the subscript operator. Let’s look at the revised code:
The code runs successfully and counts the occurrences of all words in the string.
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial. The TypeError: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment occurs when you try to change the elements of an integer using indexing. Integers are single values and are not indexable.
You may encounter this error when assigning an integer to a variable with the same name as a container object like a list or dictionary.
It is good practice to check the type of objects created when debugging your program.
If you want to perform item assignments, you must use a list or a dictionary.
For further reading on TypeErrors, go to the articles:
- How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment
- How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
To learn more about Python for data science and machine learning, go to the online courses page on Python for the most comprehensive courses available.
Have fun and happy researching!

Suf is a senior advisor in data science with deep expertise in Natural Language Processing, Complex Networks, and Anomaly Detection. Formerly a postdoctoral research fellow, he applied advanced physics techniques to tackle real-world, data-heavy industry challenges. Before that, he was a particle physicist at the ATLAS Experiment of the Large Hadron Collider. Now, he’s focused on bringing more fun and curiosity to the world of science and research online.
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Flatten a List of Lists in Python
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Solve Python ModuleNotFoundError: no module named ‘jinja2’
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Solve Python TypeError: int() argument must be a string, a bytes-like object or a number, not ‘NoneType’
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Solve AttributeError: 'dict' object has no attribute 'iteritems'
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
Buy Me a Coffee
Solve Python TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment

Consider the example below:
Solution #1: Change the tuple to list first
Solution #2: create a new tuple.
This tutorial shows you two easy solutions on how to change the tuple object element(s) and avoid the TypeError.
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️

How to Solve ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment (Python)
Here’s everything about TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python.
You’ll learn:
- The specifics of the tuple data type
- The difference between immutable and mutable data types
- How to change immutable data types
So if you want to understand this error in Python and how to solve it, then you’re in the right place.
Let’s jump right in!
- IndentationError: Unexpected Unindent in Python
- How to Solve ImportError: Attempted Relative Import With No Known Parent Package (Python)
- SyntaxError: Invalid Character in Identifier: How to Solve? (Python)
- 3 Ways to Solve Series Objects Are Mutable and Cannot be Hashed (Python)
- 9 Examples of Unexpected Character After Line Continuation Character (Python)
Mutable, or Immutable? That Is the Question
Data types in Python are mutable or immutable .
All data types that are numeric , for example, are immutable .
You can write something like this:
Have you changed the variable a ?
Not really: When you write a = 1 , you put the object 1 in memory and told the name a to refer to this literal.
Next, when you write a = a + 1 , Python evaluates the expression on the right:
Python takes the object referred by a (the 1 ) and then adds 1 to it.
You get a new object, a 2 . This object goes right into the memory and a references instead of object 1 .
The value of object 1 has not changed—it would be weird if 1 would out of a sudden a 2 , for example, wouldn’t it? So instead of overwriting an object ( 1 ), a new object ( 2 ) is created and assigned to the variable ( a ).
Mutable Data Types
More complex data types in Python are sequences such as:
- Byte Arrays
Sequences contain several values, which can be accessed by index.

However, some sequences are mutable (byte arrays, lists) , while others are immutable (tuples) .
You can create a tuple and access its elements like this:
Yet if you try to change one of the elements, you get an error:
Notice that the item in the tuple at index 2 is a list. You can change the list without changing the tuple:
The object stored in the tuple remains the same, but its contents have changed. But what if you still need to change the element in the tuple?
You can do this by converting the tuple to a list. Then you change the element, and then convert the list to a tuple again:
For large amounts of data, conversion operations can take quite a long time:
As you can see, for a list of 100 million float numbers, this operation takes about a second. This is not a long time for most tasks, but it is still worth considering if you are dealing with large amounts of data.
However, there is another way to “change” a tuple element—you can rebuild a tuple using slicing and concatenation:
Note that it is necessary to put a comma in parentheses to create a tuple of one element. If you use just parentheses, then (‘uno’) is not a tuple, but a string in parentheses .
Concatenating a string with a tuple is not possible:
Interestingly, you can use shorthand operators on a tuple, like this:
Or even like this:
3 Examples of TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python
Let’s look at some practical examples of when this error can occur. The simplest is when you initially enter the sequence incorrectly:
In this example, the name list1 refers to a tuple despite the list in the name. The name does not affect the type of variable. To fix this error, simply change the parentheses to square brackets in the constructor:
Perhaps you have a list with some values, such as the student’s name and grade point average:
Alice did a poor job this semester, and her GPA dropped to 90:
Unfortunately, you cannot just change the average score in such a list. You already know that you can convert a tuple to a list, or form a new tuple. For example, like this:
However, if you need to change values regularly, it makes sense to switch from a list of tuples to a dictionary. Dictionaries are a perfect fit for such tasks. You can do this easily with the dict() constructor:
Now you can change the average by student name:
#1 Real World Example of TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python
An interesting example of a novice programmer trying to enter values in a list from the keyboard using the eval() function:
This method is not very reliable by itself.
Even if the user enters the correct sequence separated by commas—for example, 3, 2, 4, 1 —it will be evaluated in a tuple.
Naturally, an attempt to assign a new value to a tuple element in the line list[i +1] = list[i] raises a TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment .
Here, you see another mistake—which, by the way, may even be invisible during program execution.
The my_sort function uses the list data type name as the argument name. This is not only the name of the data type, but also the list constructor.
Python will not throw an error while executing this code, but if you try to create a list using the constructor inside the my_sort function, you will have big problems.

In this case, to enter elements into the list, it would be more correct to read the entire string and then split it using the split() method. If you need integer values, you can also apply the map() function, then convert the resulting map object into a list:
The construction looks a little cumbersome, but it does its job. You can also enter list items through a list comprehension:
You can choose the design that you like best.
#2 Real World Example of TypeError: ‘Tuple’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Python
Another example of when a TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment may occur is the use of various libraries.
If you have not studied the documentation well enough, you may not always clearly understand which data type will be returned in a given situation. In this example, the author tries to make the picture redder by adding 20 to the red color component:
This produces an error on the line pixel[0] = pixel[0] + 20 . How?
You are converting pixels to a list in line of code 3 . Indeed, if you check the type of the pixels variable, you get a list:
However, in the loop, you iterate over the pixels list elements, and they already have a different type. Check the type of the pixels list element with index 0 :
And this is a tuple!
So, you can solve this problem by converting lists to tuples inside a loop, for example.
However, in this case, you will need to slightly adjust the iterable value. This is because you will need the pixel color values and the index to write the new values into the original array.
For this, use the enumerate() function:
The program will work successfully with that version of a loop, and you will get a redder image at the output. It would be more correct to trim values above 255 , for example:
But if the program consists only of this transformation, then Python will already truncate the values when saving the image.
Here’s more Python support:
- 9 Examples of Unexpected Character After Line Continuation Character
- 3 Ways to Solve Series Objects Are Mutable and Cannot be Hashed
- How to Solve SyntaxError: Invalid Character in Identifier
- ImportError: Attempted Relative Import With No Known Parent Package
- IndentationError: Unexpected Unindent in Python (and 3 More)

Tech entrepreneur and founder of Tech Medic, who has become a prominent advocate for the Right to Repair movement. She has testified before the US Federal Trade Commission and been featured on CBS Sunday Morning, helping influence change within the tech industry.
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Python typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment Solution
Tuples are immutable objects . “Immutable” means you cannot change the values inside a tuple. You can only remove them. If you try to assign a new value to an item in a variable, you’ll encounter the “typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error.
In this guide, we discuss what this error means and why you may experience it. We’ll walk through an example of this error so you can learn how to solve it in your code.
Find your bootcamp match
Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
While tuples and lists both store sequences of data, they have a few distinctions. Whereas you can change the values in a list, the values inside a tuple cannot be changed. Also, tuples are stored within parenthesis whereas lists are declared between square brackets.
Because you cannot change values in a tuple, item assignment does not work.
Consider the following code snippet:
This code snippet lets us change the first value in the “honor_roll” list to Holly. This works because lists are mutable. You can change their values. The same code does not work with data that is stored in a tuple.
An Example Scenario
Let’s build a program that tracks the courses offered by a high school. Students in their senior year are allowed to choose from a class but a few classes are being replaced.
Start by creating a collection of class names:
We’ve created a tuple that stores the names of each class being offered.
The science department has notified the school that psychology is no longer being offered due to a lack of numbers in the class. We’re going to replace psychology with philosophy as the philosophy class has just opened up a few spaces.
To do this, we use the assignment operator:
This code will replace the value at the index position 3 in our list of classes with “Philosophy”. Next, we print our list of classes to the console so that the user can see what classes are being actively offered:
Use a for loop to print out each class in our tuple to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
Our code returns an error.
The Solution
We’ve tried to use the assignment operator to change a subject in our list. Tuples are immutable so we cannot change their values. This is why our code returns an error.
To solve this problem, we convert our “classes” tuple into a list . This will let us change the values in our sequence of class names.
Do this using the list() method:
We use the list() method to convert the value of “classes” to a list. We assign this new list to the variable “as_list”. Now that we have our list of classes stored as a list, we can change existing classes in the list.
Let’s run our code:
Our code successfully changes the “Psychology” class to “Philosophy”. Our code then prints out the list of classes to the console.
If we need to store our data as a tuple, we can always convert our list back to a tuple once we have changed the values we want to change. We can do this using the tuple() method:
This code converts “as_list” to a tuple and prints the value of our tuple to the console:
We could use this tuple later in our code if we needed our class names stored as a tuple.
The “typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error is raised when you try to change a value in a tuple using item assignment.
To solve this error, convert a tuple to a list before you change the values in a sequence. Optionally, you can then convert the list back to a tuple.
Now you’re ready to fix this error in your code like a pro !
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Python's Assignment Operator: Write Robust Assignments
Table of Contents
The Assignment Statement Syntax
The assignment operator, assignments and variables, other assignment syntax, initializing and updating variables, making multiple variables refer to the same object, updating lists through indices and slices, adding and updating dictionary keys, doing parallel assignments, unpacking iterables, providing default argument values, augmented mathematical assignment operators, augmented assignments for concatenation and repetition, augmented bitwise assignment operators, annotated assignment statements, assignment expressions with the walrus operator, managed attribute assignments, define or call a function, work with classes, import modules and objects, use a decorator, access the control variable in a for loop or a comprehension, use the as keyword, access the _ special variable in an interactive session, built-in objects, named constants.
Python’s assignment operators allow you to define assignment statements . This type of statement lets you create, initialize, and update variables throughout your code. Variables are a fundamental cornerstone in every piece of code, and assignment statements give you complete control over variable creation and mutation.
Learning about the Python assignment operator and its use for writing assignment statements will arm you with powerful tools for writing better and more robust Python code.
In this tutorial, you’ll:
- Use Python’s assignment operator to write assignment statements
- Take advantage of augmented assignments in Python
- Explore assignment variants, like assignment expressions and managed attributes
- Become aware of illegal and dangerous assignments in Python
You’ll dive deep into Python’s assignment statements. To get the most out of this tutorial, you should be comfortable with several basic topics, including variables , built-in data types , comprehensions , functions , and Python keywords . Before diving into some of the later sections, you should also be familiar with intermediate topics, such as object-oriented programming , constants , imports , type hints , properties , descriptors , and decorators .
Free Source Code: Click here to download the free assignment operator source code that you’ll use to write assignment statements that allow you to create, initialize, and update variables in your code.
Assignment Statements and the Assignment Operator
One of the most powerful programming language features is the ability to create, access, and mutate variables . In Python, a variable is a name that refers to a concrete value or object, allowing you to reuse that value or object throughout your code.
To create a new variable or to update the value of an existing one in Python, you’ll use an assignment statement . This statement has the following three components:
- A left operand, which must be a variable
- The assignment operator ( = )
- A right operand, which can be a concrete value , an object , or an expression
Here’s how an assignment statement will generally look in Python:
Here, variable represents a generic Python variable, while expression represents any Python object that you can provide as a concrete value—also known as a literal —or an expression that evaluates to a value.
To execute an assignment statement like the above, Python runs the following steps:
- Evaluate the right-hand expression to produce a concrete value or object . This value will live at a specific memory address in your computer.
- Store the object’s memory address in the left-hand variable . This step creates a new variable if the current one doesn’t already exist or updates the value of an existing variable.
The second step shows that variables work differently in Python than in other programming languages. In Python, variables aren’t containers for objects. Python variables point to a value or object through its memory address. They store memory addresses rather than objects.
This behavior difference directly impacts how data moves around in Python, which is always by reference . In most cases, this difference is irrelevant in your day-to-day coding, but it’s still good to know.
The central component of an assignment statement is the assignment operator . This operator is represented by the = symbol, which separates two operands:
- A value or an expression that evaluates to a concrete value
Operators are special symbols that perform mathematical , logical , and bitwise operations in a programming language. The objects (or object) on which an operator operates are called operands .
Unary operators, like the not Boolean operator, operate on a single object or operand, while binary operators act on two. That means the assignment operator is a binary operator.
Note: Like C , Python uses == for equality comparisons and = for assignments. Unlike C, Python doesn’t allow you to accidentally use the assignment operator ( = ) in an equality comparison.
Equality is a symmetrical relationship, and assignment is not. For example, the expression a == 42 is equivalent to 42 == a . In contrast, the statement a = 42 is correct and legal, while 42 = a isn’t allowed. You’ll learn more about illegal assignments later on.
The right-hand operand in an assignment statement can be any Python object, such as a number , list , string , dictionary , or even a user-defined object. It can also be an expression. In the end, expressions always evaluate to concrete objects, which is their return value.
Here are a few examples of assignments in Python:
The first two sample assignments in this code snippet use concrete values, also known as literals , to create and initialize number and greeting . The third example assigns the result of a math expression to the total variable, while the last example uses a Boolean expression.
Note: You can use the built-in id() function to inspect the memory address stored in a given variable.
Here’s a short example of how this function works:
The number in your output represents the memory address stored in number . Through this address, Python can access the content of number , which is the integer 42 in this example.
If you run this code on your computer, then you’ll get a different memory address because this value varies from execution to execution and computer to computer.
Unlike expressions, assignment statements don’t have a return value because their purpose is to make the association between the variable and its value. That’s why the Python interpreter doesn’t issue any output in the above examples.
Now that you know the basics of how to write an assignment statement, it’s time to tackle why you would want to use one.
The assignment statement is the explicit way for you to associate a name with an object in Python. You can use this statement for two main purposes:
- Creating and initializing new variables
- Updating the values of existing variables
When you use a variable name as the left operand in an assignment statement for the first time, you’re creating a new variable. At the same time, you’re initializing the variable to point to the value of the right operand.
On the other hand, when you use an existing variable in a new assignment, you’re updating or mutating the variable’s value. Strictly speaking, every new assignment will make the variable refer to a new value and stop referring to the old one. Python will garbage-collect all the values that are no longer referenced by any existing variable.
Assignment statements not only assign a value to a variable but also determine the data type of the variable at hand. This additional behavior is another important detail to consider in this kind of statement.
Because Python is a dynamically typed language, successive assignments to a given variable can change the variable’s data type. Changing the data type of a variable during a program’s execution is considered bad practice and highly discouraged. It can lead to subtle bugs that can be difficult to track down.
Unlike in math equations, in Python assignments, the left operand must be a variable rather than an expression or a value. For example, the following construct is illegal, and Python flags it as invalid syntax:
In this example, you have expressions on both sides of the = sign, and this isn’t allowed in Python code. The error message suggests that you may be confusing the equality operator with the assignment one, but that’s not the case. You’re really running an invalid assignment.
To correct this construct and convert it into a valid assignment, you’ll have to do something like the following:
In this code snippet, you first import the sqrt() function from the math module. Then you isolate the hypotenuse variable in the original equation by using the sqrt() function. Now your code works correctly.
Now you know what kind of syntax is invalid. But don’t get the idea that assignment statements are rigid and inflexible. In fact, they offer lots of room for customization, as you’ll learn next.
Python’s assignment statements are pretty flexible and versatile. You can write them in several ways, depending on your specific needs and preferences. Here’s a quick summary of the main ways to write assignments in Python:
Up to this point, you’ve mostly learned about the base assignment syntax in the above code snippet. In the following sections, you’ll learn about multiple, parallel, and augmented assignments. You’ll also learn about assignments with iterable unpacking.
Read on to see the assignment statements in action!
Assignment Statements in Action
You’ll find and use assignment statements everywhere in your Python code. They’re a fundamental part of the language, providing an explicit way to create, initialize, and mutate variables.
You can use assignment statements with plain names, like number or counter . You can also use assignments in more complicated scenarios, such as with:
- Qualified attribute names , like user.name
- Indices and slices of mutable sequences, like a_list[i] and a_list[i:j]
- Dictionary keys , like a_dict[key]
This list isn’t exhaustive. However, it gives you some idea of how flexible these statements are. You can even assign multiple values to an equal number of variables in a single line, commonly known as parallel assignment . Additionally, you can simultaneously assign the values in an iterable to a comma-separated group of variables in what’s known as an iterable unpacking operation.
In the following sections, you’ll dive deeper into all these topics and a few other exciting things that you can do with assignment statements in Python.
The most elementary use case of an assignment statement is to create a new variable and initialize it using a particular value or expression:
All these statements create new variables, assigning them initial values or expressions. For an initial value, you should always use the most sensible and least surprising value that you can think of. For example, initializing a counter to something different from 0 may be confusing and unexpected because counters almost always start having counted no objects.
Updating a variable’s current value or state is another common use case of assignment statements. In Python, assigning a new value to an existing variable doesn’t modify the variable’s current value. Instead, it causes the variable to refer to a different value. The previous value will be garbage-collected if no other variable refers to it.
Consider the following examples:
These examples run two consecutive assignments on the same variable. The first one assigns the string "Hello, World!" to a new variable named greeting .
The second assignment updates the value of greeting by reassigning it the "Hi, Pythonistas!" string. In this example, the original value of greeting —the "Hello, World!" string— is lost and garbage-collected. From this point on, you can’t access the old "Hello, World!" string.
Even though running multiple assignments on the same variable during a program’s execution is common practice, you should use this feature with caution. Changing the value of a variable can make your code difficult to read, understand, and debug. To comprehend the code fully, you’ll have to remember all the places where the variable was changed and the sequential order of those changes.
Because assignments also define the data type of their target variables, it’s also possible for your code to accidentally change the type of a given variable at runtime. A change like this can lead to breaking errors, like AttributeError exceptions. Remember that strings don’t have the same methods and attributes as lists or dictionaries, for example.
In Python, you can make several variables reference the same object in a multiple-assignment line. This can be useful when you want to initialize several similar variables using the same initial value:
In this example, you chain two assignment operators in a single line. This way, your two variables refer to the same initial value of 0 . Note how both variables hold the same memory address, so they point to the same instance of 0 .
When it comes to integer variables, Python exhibits a curious behavior. It provides a numeric interval where multiple assignments behave the same as independent assignments. Consider the following examples:
To create n and m , you use independent assignments. Therefore, they should point to different instances of the number 42 . However, both variables hold the same object, which you confirm by comparing their corresponding memory addresses.
Now check what happens when you use a greater initial value:
Now n and m hold different memory addresses, which means they point to different instances of the integer number 300 . In contrast, when you use multiple assignments, both variables refer to the same object. This tiny difference can save you small bits of memory if you frequently initialize integer variables in your code.
The implicit behavior of making independent assignments point to the same integer number is actually an optimization called interning . It consists of globally caching the most commonly used integer values in day-to-day programming.
Under the hood, Python defines a numeric interval in which interning takes place. That’s the interning interval for integer numbers. You can determine this interval using a small script like the following:
This script helps you determine the interning interval by comparing integer numbers from -10 to 500 . If you run the script from your command line, then you’ll get an output like the following:
This output means that if you use a single number between -5 and 256 to initialize several variables in independent statements, then all these variables will point to the same object, which will help you save small bits of memory in your code.
In contrast, if you use a number that falls outside of the interning interval, then your variables will point to different objects instead. Each of these objects will occupy a different memory spot.
You can use the assignment operator to mutate the value stored at a given index in a Python list. The operator also works with list slices . The syntax to write these types of assignment statements is the following:
In the first construct, expression can return any Python object, including another list. In the second construct, expression must return a series of values as a list, tuple, or any other sequence. You’ll get a TypeError if expression returns a single value.
Note: When creating slice objects, you can use up to three arguments. These arguments are start , stop , and step . They define the number that starts the slice, the number at which the slicing must stop retrieving values, and the step between values.
Here’s an example of updating an individual value in a list:
In this example, you update the value at index 2 using an assignment statement. The original number at that index was 7 , and after the assignment, the number is 3 .
Note: Using indices and the assignment operator to update a value in a tuple or a character in a string isn’t possible because tuples and strings are immutable data types in Python.
Their immutability means that you can’t change their items in place :
You can’t use the assignment operator to change individual items in tuples or strings. These data types are immutable and don’t support item assignments.
It’s important to note that you can’t add new values to a list by using indices that don’t exist in the target list:
In this example, you try to add a new value to the end of numbers by using an index that doesn’t exist. This assignment isn’t allowed because there’s no way to guarantee that new indices will be consecutive. If you ever want to add a single value to the end of a list, then use the .append() method.
If you want to update several consecutive values in a list, then you can use slicing and an assignment statement:
In the first example, you update the letters between indices 1 and 3 without including the letter at 3 . The second example updates the letters from index 3 until the end of the list. Note that this slicing appends a new value to the list because the target slice is shorter than the assigned values.
Also note that the new values were provided through a tuple, which means that this type of assignment allows you to use other types of sequences to update your target list.
The third example updates a single value using a slice where both indices are equal. In this example, the assignment inserts a new item into your target list.
In the final example, you use a step of 2 to replace alternating letters with their lowercase counterparts. This slicing starts at index 1 and runs through the whole list, stepping by two items each time.
Updating the value of an existing key or adding new key-value pairs to a dictionary is another common use case of assignment statements. To do these operations, you can use the following syntax:
The first construct helps you update the current value of an existing key, while the second construct allows you to add a new key-value pair to the dictionary.
For example, to update an existing key, you can do something like this:
In this example, you update the current inventory of oranges in your store using an assignment. The left operand is the existing dictionary key, and the right operand is the desired new value.
While you can’t add new values to a list by assignment, dictionaries do allow you to add new key-value pairs using the assignment operator. In the example below, you add a lemon key to inventory :
In this example, you successfully add a new key-value pair to your inventory with 100 units. This addition is possible because dictionaries don’t have consecutive indices but unique keys, which are safe to add by assignment.
The assignment statement does more than assign the result of a single expression to a single variable. It can also cope nicely with assigning multiple values to multiple variables simultaneously in what’s known as a parallel assignment .
Here’s the general syntax for parallel assignments in Python:
Note that the left side of the statement can be either a tuple or a list of variables. Remember that to create a tuple, you just need a series of comma-separated elements. In this case, these elements must be variables.
The right side of the statement must be a sequence or iterable of values or expressions. In any case, the number of elements in the right operand must match the number of variables on the left. Otherwise, you’ll get a ValueError exception.
In the following example, you compute the two solutions of a quadratic equation using a parallel assignment:
In this example, you first import sqrt() from the math module. Then you initialize the equation’s coefficients in a parallel assignment.
The equation’s solution is computed in another parallel assignment. The left operand contains a tuple of two variables, x1 and x2 . The right operand consists of a tuple of expressions that compute the solutions for the equation. Note how each result is assigned to each variable by position.
A classical use case of parallel assignment is to swap values between variables:
The highlighted line does the magic and swaps the values of previous_value and next_value at the same time. Note that in a programming language that doesn’t support this kind of assignment, you’d have to use a temporary variable to produce the same effect:
In this example, instead of using parallel assignment to swap values between variables, you use a new variable to temporarily store the value of previous_value to avoid losing its reference.
For a concrete example of when you’d need to swap values between variables, say you’re learning how to implement the bubble sort algorithm , and you come up with the following function:
In the highlighted line, you use a parallel assignment to swap values in place if the current value is less than the next value in the input list. To dive deeper into the bubble sort algorithm and into sorting algorithms in general, check out Sorting Algorithms in Python .
You can use assignment statements for iterable unpacking in Python. Unpacking an iterable means assigning its values to a series of variables one by one. The iterable must be the right operand in the assignment, while the variables must be the left operand.
Like in parallel assignments, the variables must come as a tuple or list. The number of variables must match the number of values in the iterable. Alternatively, you can use the unpacking operator ( * ) to grab several values in a variable if the number of variables doesn’t match the iterable length.
Here’s the general syntax for iterable unpacking in Python:
Iterable unpacking is a powerful feature that you can use all around your code. It can help you write more readable and concise code. For example, you may find yourself doing something like this:
Whenever you do something like this in your code, go ahead and replace it with a more readable iterable unpacking using a single and elegant assignment, like in the following code snippet:
The numbers list on the right side contains four values. The assignment operator unpacks these values into the four variables on the left side of the statement. The values in numbers get assigned to variables in the same order that they appear in the iterable. The assignment is done by position.
Note: Because Python sets are also iterables, you can use them in an iterable unpacking operation. However, it won’t be clear which value goes to which variable because sets are unordered data structures.
The above example shows the most common form of iterable unpacking in Python. The main condition for the example to work is that the number of variables matches the number of values in the iterable.
What if you don’t know the iterable length upfront? Will the unpacking work? It’ll work if you use the * operator to pack several values into one of your target variables.
For example, say that you want to unpack the first and second values in numbers into two different variables. Additionally, you would like to pack the rest of the values in a single variable conveniently called rest . In this case, you can use the unpacking operator like in the following code:
In this example, first and second hold the first and second values in numbers , respectively. These values are assigned by position. The * operator packs all the remaining values in the input iterable into rest .
The unpacking operator ( * ) can appear at any position in your series of target variables. However, you can only use one instance of the operator:
The iterable unpacking operator works in any position in your list of variables. Note that you can only use one unpacking operator per assignment. Using more than one unpacking operator isn’t allowed and raises a SyntaxError .
Dropping away unwanted values from the iterable is a common use case for the iterable unpacking operator. Consider the following example:
In Python, if you want to signal that a variable won’t be used, then you use an underscore ( _ ) as the variable’s name. In this example, useful holds the only value that you need to use from the input iterable. The _ variable is a placeholder that guarantees that the unpacking works correctly. You won’t use the values that end up in this disposable variable.
Note: In the example above, if your target iterable is a sequence data type, such as a list or tuple, then it’s best to access its last item directly.
To do this, you can use the -1 index:
Using -1 gives you access to the last item of any sequence data type. In contrast, if you’re dealing with iterators , then you won’t be able to use indices. That’s when the *_ syntax comes to your rescue.
The pattern used in the above example comes in handy when you have a function that returns multiple values, and you only need a few of these values in your code. The os.walk() function may provide a good example of this situation.
This function allows you to iterate over the content of a directory recursively. The function returns a generator object that yields three-item tuples. Each tuple contains the following items:
- The path to the current directory as a string
- The names of all the immediate subdirectories as a list of strings
- The names of all the files in the current directory as a list of strings
Now say that you want to iterate over your home directory and list only the files. You can do something like this:
This code will issue a long output depending on the current content of your home directory. Note that you need to provide a string with the path to your user folder for the example to work. The _ placeholder variable will hold the unwanted data.
In contrast, the filenames variable will hold the list of files in the current directory, which is the data that you need. The code will print the list of filenames. Go ahead and give it a try!
The assignment operator also comes in handy when you need to provide default argument values in your functions and methods. Default argument values allow you to define functions that take arguments with sensible defaults. These defaults allow you to call the function with specific values or to simply rely on the defaults.
As an example, consider the following function:
This function takes one argument, called name . This argument has a sensible default value that’ll be used when you call the function without arguments. To provide this sensible default value, you use an assignment.
Note: According to PEP 8 , the style guide for Python code, you shouldn’t use spaces around the assignment operator when providing default argument values in function definitions.
Here’s how the function works:
If you don’t provide a name during the call to greet() , then the function uses the default value provided in the definition. If you provide a name, then the function uses it instead of the default one.
Up to this point, you’ve learned a lot about the Python assignment operator and how to use it for writing different types of assignment statements. In the following sections, you’ll dive into a great feature of assignment statements in Python. You’ll learn about augmented assignments .
Augmented Assignment Operators in Python
Python supports what are known as augmented assignments . An augmented assignment combines the assignment operator with another operator to make the statement more concise. Most Python math and bitwise operators have an augmented assignment variation that looks something like this:
Note that $ isn’t a valid Python operator. In this example, it’s a placeholder for a generic operator. This statement works as follows:
- Evaluate expression to produce a value.
- Run the operation defined by the operator that prefixes the = sign, using the previous value of variable and the return value of expression as operands.
- Assign the resulting value back to variable .
In practice, an augmented assignment like the above is equivalent to the following statement:
As you can conclude, augmented assignments are syntactic sugar . They provide a shorthand notation for a specific and popular kind of assignment.
For example, say that you need to define a counter variable to count some stuff in your code. You can use the += operator to increment counter by 1 using the following code:
In this example, the += operator, known as augmented addition , adds 1 to the previous value in counter each time you run the statement counter += 1 .
It’s important to note that unlike regular assignments, augmented assignments don’t create new variables. They only allow you to update existing variables. If you use an augmented assignment with an undefined variable, then you get a NameError :
Python evaluates the right side of the statement before assigning the resulting value back to the target variable. In this specific example, when Python tries to compute x + 1 , it finds that x isn’t defined.
Great! You now know that an augmented assignment consists of combining the assignment operator with another operator, like a math or bitwise operator. To continue this discussion, you’ll learn which math operators have an augmented variation in Python.
An equation like x = x + b doesn’t make sense in math. But in programming, a statement like x = x + b is perfectly valid and can be extremely useful. It adds b to x and reassigns the result back to x .
As you already learned, Python provides an operator to shorten x = x + b . Yes, the += operator allows you to write x += b instead. Python also offers augmented assignment operators for most math operators. Here’s a summary:
| Operator | Description | Example | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adds the right operand to the left operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Subtracts the right operand from the left operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Multiplies the right operand with the left operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Divides the left operand by the right operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Performs of the left operand by the right operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Finds the remainder of dividing the left operand by the right operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Raises the left operand to the power of the right operand and stores the result in the left operand |
The Example column provides generic examples of how to use the operators in actual code. Note that x must be previously defined for the operators to work correctly. On the other hand, y can be either a concrete value or an expression that returns a value.
Note: The matrix multiplication operator ( @ ) doesn’t support augmented assignments yet.
Consider the following example of matrix multiplication using NumPy arrays:
Note that the exception traceback indicates that the operation isn’t supported yet.
To illustrate how augmented assignment operators work, say that you need to create a function that takes an iterable of numeric values and returns their sum. You can write this function like in the code below:
In this function, you first initialize total to 0 . In each iteration, the loop adds a new number to total using the augmented addition operator ( += ). When the loop terminates, total holds the sum of all the input numbers. Variables like total are known as accumulators . The += operator is typically used to update accumulators.
Note: Computing the sum of a series of numeric values is a common operation in programming. Python provides the built-in sum() function for this specific computation.
Another interesting example of using an augmented assignment is when you need to implement a countdown while loop to reverse an iterable. In this case, you can use the -= operator:
In this example, custom_reversed() is a generator function because it uses yield . Calling the function creates an iterator that yields items from the input iterable in reverse order. To decrement the control variable, index , you use an augmented subtraction statement that subtracts 1 from the variable in every iteration.
Note: Similar to summing the values in an iterable, reversing an iterable is also a common requirement. Python provides the built-in reversed() function for this specific computation, so you don’t have to implement your own. The above example only intends to show the -= operator in action.
Finally, counters are a special type of accumulators that allow you to count objects. Here’s an example of a letter counter:
To create this counter, you use a Python dictionary. The keys store the letters. The values store the counts. Again, to increment the counter, you use an augmented addition.
Counters are so common in programming that Python provides a tool specially designed to facilitate the task of counting. Check out Python’s Counter: The Pythonic Way to Count Objects for a complete guide on how to use this tool.
The += and *= augmented assignment operators also work with sequences , such as lists, tuples, and strings. The += operator performs augmented concatenations , while the *= operator performs augmented repetition .
These operators behave differently with mutable and immutable data types:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Runs an augmented concatenation operation on the target sequence. Mutable sequences are updated in place. If the sequence is immutable, then a new sequence is created and assigned back to the target name. | ||
| Adds to itself times. Mutable sequences are updated in place. If the sequence is immutable, then a new sequence is created and assigned back to the target name. |
Note that the augmented concatenation operator operates on two sequences, while the augmented repetition operator works on a sequence and an integer number.
Consider the following examples and pay attention to the result of calling the id() function:
Mutable sequences like lists support the += augmented assignment operator through the .__iadd__() method, which performs an in-place addition. This method mutates the underlying list, appending new values to its end.
Note: If the left operand is mutable, then x += y may not be completely equivalent to x = x + y . For example, if you do list_1 = list_1 + list_2 instead of list_1 += list_2 above, then you’ll create a new list instead of mutating the existing one. This may be important if other variables refer to the same list.
Immutable sequences, such as tuples and strings, don’t provide an .__iadd__() method. Therefore, augmented concatenations fall back to the .__add__() method, which doesn’t modify the sequence in place but returns a new sequence.
There’s another difference between mutable and immutable sequences when you use them in an augmented concatenation. Consider the following examples:
With mutable sequences, the data to be concatenated can come as a list, tuple, string, or any other iterable. In contrast, with immutable sequences, the data can only come as objects of the same type. You can concatenate tuples to tuples and strings to strings, for example.
Again, the augmented repetition operator works with a sequence on the left side of the operator and an integer on the right side. This integer value represents the number of repetitions to get in the resulting sequence:
When the *= operator operates on a mutable sequence, it falls back to the .__imul__() method, which performs the operation in place, modifying the underlying sequence. In contrast, if *= operates on an immutable sequence, then .__mul__() is called, returning a new sequence of the same type.
Note: Values of n less than 0 are treated as 0 , which returns an empty sequence of the same data type as the target sequence on the left side of the *= operand.
Note that a_list[0] is a_list[3] returns True . This is because the *= operator doesn’t make a copy of the repeated data. It only reflects the data. This behavior can be a source of issues when you use the operator with mutable values.
For example, say that you want to create a list of lists to represent a matrix, and you need to initialize the list with n empty lists, like in the following code:
In this example, you use the *= operator to populate matrix with three empty lists. Now check out what happens when you try to populate the first sublist in matrix :
The appended values are reflected in the three sublists. This happens because the *= operator doesn’t make copies of the data that you want to repeat. It only reflects the data. Therefore, every sublist in matrix points to the same object and memory address.
If you ever need to initialize a list with a bunch of empty sublists, then use a list comprehension :
This time, when you populate the first sublist of matrix , your changes aren’t propagated to the other sublists. This is because all the sublists are different objects that live in different memory addresses.
Bitwise operators also have their augmented versions. The logic behind them is similar to that of the math operators. The following table summarizes the augmented bitwise operators that Python provides:
| Operator | Operation | Example | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Augmented bitwise AND ( ) | |||
| Augmented bitwise OR ( ) | |||
| Augmented bitwise XOR ( ) | |||
| Augmented bitwise right shift | |||
| Augmented bitwise left shift |
The augmented bitwise assignment operators perform the intended operation by taking the current value of the left operand as a starting point for the computation. Consider the following example, which uses the & and &= operators:
Programmers who work with high-level languages like Python rarely use bitwise operations in day-to-day coding. However, these types of operations can be useful in some situations.
For example, say that you’re implementing a Unix-style permission system for your users to access a given resource. In this case, you can use the characters "r" for reading, "w" for writing, and "x" for execution permissions, respectively. However, using bit-based permissions could be more memory efficient:
You can assign permissions to your users with the OR bitwise operator or the augmented OR bitwise operator. Finally, you can use the bitwise AND operator to check if a user has a certain permission, as you did in the final two examples.
You’ve learned a lot about augmented assignment operators and statements in this and the previous sections. These operators apply to math, concatenation, repetition, and bitwise operations. Now you’re ready to look at other assignment variants that you can use in your code or find in other developers’ code.
Other Assignment Variants
So far, you’ve learned that Python’s assignment statements and the assignment operator are present in many different scenarios and use cases. Those use cases include variable creation and initialization, parallel assignments, iterable unpacking, augmented assignments, and more.
In the following sections, you’ll learn about a few variants of assignment statements that can be useful in your future coding. You can also find these assignment variants in other developers’ code. So, you should be aware of them and know how they work in practice.
In short, you’ll learn about:
- Annotated assignment statements with type hints
- Assignment expressions with the walrus operator
- Managed attribute assignments with properties and descriptors
- Implicit assignments in Python
These topics will take you through several interesting and useful examples that showcase the power of Python’s assignment statements.
PEP 526 introduced a dedicated syntax for variable annotation back in Python 3.6 . The syntax consists of the variable name followed by a colon ( : ) and the variable type:
Even though these statements declare three variables with their corresponding data types, the variables aren’t actually created or initialized. So, for example, you can’t use any of these variables in an augmented assignment statement:
If you try to use one of the previously declared variables in an augmented assignment, then you get a NameError because the annotation syntax doesn’t define the variable. To actually define it, you need to use an assignment.
The good news is that you can use the variable annotation syntax in an assignment statement with the = operator:
The first statement in this example is what you can call an annotated assignment statement in Python. You may ask yourself why you should use type annotations in this type of assignment if everybody can see that counter holds an integer number. You’re right. In this example, the variable type is unambiguous.
However, imagine what would happen if you found a variable initialization like the following:
What would be the data type of each user in users ? If the initialization of users is far away from the definition of the User class, then there’s no quick way to answer this question. To clarify this ambiguity, you can provide the appropriate type hint for users :
Now you’re clearly communicating that users will hold a list of User instances. Using type hints in assignment statements that initialize variables to empty collection data types—such as lists, tuples, or dictionaries—allows you to provide more context about how your code works. This practice will make your code more explicit and less error-prone.
Up to this point, you’ve learned that regular assignment statements with the = operator don’t have a return value. They just create or update variables. Therefore, you can’t use a regular assignment to assign a value to a variable within the context of an expression.
Python 3.8 changed this by introducing a new type of assignment statement through PEP 572 . This new statement is known as an assignment expression or named expression .
Note: Expressions are a special type of statement in Python. Their distinguishing characteristic is that expressions always have a return value, which isn’t the case with all types of statements.
Unlike regular assignments, assignment expressions have a return value, which is why they’re called expressions in the first place. This return value is automatically assigned to a variable. To write an assignment expression, you must use the walrus operator ( := ), which was named for its resemblance to the eyes and tusks of a walrus lying on its side.
The general syntax of an assignment statement is as follows:
This expression looks like a regular assignment. However, instead of using the assignment operator ( = ), it uses the walrus operator ( := ). For the expression to work correctly, the enclosing parentheses are required in most use cases. However, there are certain situations in which these parentheses are superfluous. Either way, they won’t hurt you.
Assignment expressions come in handy when you want to reuse the result of an expression or part of an expression without using a dedicated assignment to grab this value beforehand.
Note: Assignment expressions with the walrus operator have several practical use cases. They also have a few restrictions. For example, they’re illegal in certain contexts, such as lambda functions, parallel assignments, and augmented assignments.
For a deep dive into this special type of assignment, check out The Walrus Operator: Python’s Assignment Expressions .
A particularly handy use case for assignment expressions is when you need to grab the result of an expression used in the context of a conditional statement. For example, say that you need to write a function to compute the mean of a sample of numeric values. Without the walrus operator, you could do something like this:
In this example, the sample size ( n ) is a value that you need to reuse in two different computations. First, you need to check whether the sample has data points or not. Then you need to use the sample size to compute the mean. To be able to reuse n , you wrote a dedicated assignment statement at the beginning of your function to grab the sample size.
You can avoid this extra step by combining it with the first use of the target value, len(sample) , using an assignment expression like the following:
The assignment expression introduced in the conditional computes the sample size and assigns it to n . This way, you guarantee that you have a reference to the sample size to use in further computations.
Because the assignment expression returns the sample size anyway, the conditional can check whether that size equals 0 or not and then take a certain course of action depending on the result of this check. The return statement computes the sample’s mean and sends the result back to the function caller.
Python provides a few tools that allow you to fine-tune the operations behind the assignment of attributes. The attributes that run implicit operations on assignments are commonly referred to as managed attributes .
Properties are the most commonly used tool for providing managed attributes in your classes. However, you can also use descriptors and, in some cases, the .__setitem__() special method.
To understand what fine-tuning the operation behind an assignment means, say that you need a Point class that only allows numeric values for its coordinates, x and y . To write this class, you must set up a validation mechanism to reject non-numeric values. You can use properties to attach the validation functionality on top of x and y .
Here’s how you can write your class:
In Point , you use properties for the .x and .y coordinates. Each property has a getter and a setter method . The getter method returns the attribute at hand. The setter method runs the input validation using a try … except block and the built-in float() function. Then the method assigns the result to the actual attribute.
Here’s how your class works in practice:
When you use a property-based attribute as the left operand in an assignment statement, Python automatically calls the property’s setter method, running any computation from it.
Because both .x and .y are properties, the input validation runs whenever you assign a value to either attribute. In the first example, the input values are valid numbers and the validation passes. In the final example, "one" isn’t a valid numeric value, so the validation fails.
If you look at your Point class, you’ll note that it follows a repetitive pattern, with the getter and setter methods looking quite similar. To avoid this repetition, you can use a descriptor instead of a property.
A descriptor is a class that implements the descriptor protocol , which consists of four special methods :
- .__get__() runs when you access the attribute represented by the descriptor.
- .__set__() runs when you use the attribute in an assignment statement.
- .__delete__() runs when you use the attribute in a del statement.
- .__set_name__() sets the attribute’s name, creating a name-aware attribute.
Here’s how your code may look if you use a descriptor to represent the coordinates of your Point class:
You’ve removed repetitive code by defining Coordinate as a descriptor that manages the input validation in a single place. Go ahead and run the following code to try out the new implementation of Point :
Great! The class works as expected. Thanks to the Coordinate descriptor, you now have a more concise and non-repetitive version of your original code.
Another way to fine-tune the operations behind an assignment statement is to provide a custom implementation of .__setitem__() in your class. You’ll use this method in classes representing mutable data collections, such as custom list-like or dictionary-like classes.
As an example, say that you need to create a dictionary-like class that stores its keys in lowercase letters:
In this example, you create a dictionary-like class by subclassing UserDict from collections . Your class implements a .__setitem__() method, which takes key and value as arguments. The method uses str.lower() to convert key into lowercase letters before storing it in the underlying dictionary.
Python implicitly calls .__setitem__() every time you use a key as the left operand in an assignment statement. This behavior allows you to tweak how you process the assignment of keys in your custom dictionary.
Implicit Assignments in Python
Python implicitly runs assignments in many different contexts. In most cases, these implicit assignments are part of the language syntax. In other cases, they support specific behaviors.
Whenever you complete an action in the following list, Python runs an implicit assignment for you:
- Define or call a function
- Define or instantiate a class
- Use the current instance , self
- Import modules and objects
- Use a decorator
- Use the control variable in a for loop or a comprehension
- Use the as qualifier in with statements , imports, and try … except blocks
- Access the _ special variable in an interactive session
Behind the scenes, Python performs an assignment in every one of the above situations. In the following subsections, you’ll take a tour of all these situations.
When you define a function, the def keyword implicitly assigns a function object to your function’s name. Here’s an example:
From this point on, the name greet refers to a function object that lives at a given memory address in your computer. You can call the function using its name and a pair of parentheses with appropriate arguments. This way, you can reuse greet() wherever you need it.
If you call your greet() function with fellow as an argument, then Python implicitly assigns the input argument value to the name parameter on the function’s definition. The parameter will hold a reference to the input arguments.
When you define a class with the class keyword, you’re assigning a specific name to a class object . You can later use this name to create instances of that class. Consider the following example:
In this example, the name User holds a reference to a class object, which was defined in __main__.User . Like with a function, when you call the class’s constructor with the appropriate arguments to create an instance, Python assigns the arguments to the parameters defined in the class initializer .
Another example of implicit assignments is the current instance of a class, which in Python is called self by convention. This name implicitly gets a reference to the current object whenever you instantiate a class. Thanks to this implicit assignment, you can access .name and .job from within the class without getting a NameError in your code.
Import statements are another variant of implicit assignments in Python. Through an import statement, you assign a name to a module object, class, function, or any other imported object. This name is then created in your current namespace so that you can access it later in your code:
In this example, you import the sys module object from the standard library and assign it to the sys name, which is now available in your namespace, as you can conclude from the second call to the built-in dir() function.
You also run an implicit assignment when you use a decorator in your code. The decorator syntax is just a shortcut for a formal assignment like the following:
Here, you call decorator() with a function object as an argument. This call will typically add functionality on top of the existing function, func() , and return a function object, which is then reassigned to the func name.
The decorator syntax is syntactic sugar for replacing the previous assignment, which you can now write as follows:
Even though this new code looks pretty different from the above assignment, the code implicitly runs the same steps.
Another situation in which Python automatically runs an implicit assignment is when you use a for loop or a comprehension. In both cases, you can have one or more control variables that you then use in the loop or comprehension body:
The memory address of control_variable changes on each iteration of the loop. This is because Python internally reassigns a new value from the loop iterable to the loop control variable on each cycle.
The same behavior appears in comprehensions:
In the end, comprehensions work like for loops but use a more concise syntax. This comprehension creates a new list of strings that mimic the output from the previous example.
The as keyword in with statements, except clauses, and import statements is another example of an implicit assignment in Python. This time, the assignment isn’t completely implicit because the as keyword provides an explicit way to define the target variable.
In a with statement, the target variable that follows the as keyword will hold a reference to the context manager that you’re working with. As an example, say that you have a hello.txt file with the following content:
You want to open this file and print each of its lines on your screen. In this case, you can use the with statement to open the file using the built-in open() function.
In the example below, you accomplish this. You also add some calls to print() that display information about the target variable defined by the as keyword:
This with statement uses the open() function to open hello.txt . The open() function is a context manager that returns a text file object represented by an io.TextIOWrapper instance.
Since you’ve defined a hello target variable with the as keyword, now that variable holds a reference to the file object itself. You confirm this by printing the object and its memory address. Finally, the for loop iterates over the lines and prints this content to the screen.
When it comes to using the as keyword in the context of an except clause, the target variable will contain an exception object if any exception occurs:
In this example, you run a division that raises a ZeroDivisionError . The as keyword assigns the raised exception to error . Note that when you print the exception object, you get only the message because exceptions have a custom .__str__() method that supports this behavior.
There’s a final detail to remember when using the as specifier in a try … except block like the one in the above example. Once you leave the except block, the target variable goes out of scope , and you can’t use it anymore.
Finally, Python’s import statements also support the as keyword. In this context, you can use as to import objects with a different name:
In these examples, you use the as keyword to import the numpy package with the np name and pandas with the name pd . If you call dir() , then you’ll realize that np and pd are now in your namespace. However, the numpy and pandas names are not.
Using the as keyword in your imports comes in handy when you want to use shorter names for your objects or when you need to use different objects that originally had the same name in your code. It’s also useful when you want to make your imported names non-public using a leading underscore, like in import sys as _sys .
The final implicit assignment that you’ll learn about in this tutorial only occurs when you’re using Python in an interactive session. Every time you run a statement that returns a value, the interpreter stores the result in a special variable denoted by a single underscore character ( _ ).
You can access this special variable as you’d access any other variable:
These examples cover several situations in which Python internally uses the _ variable. The first two examples evaluate expressions. Expressions always have a return value, which is automatically assigned to the _ variable every time.
When it comes to function calls, note that if your function returns a fruitful value, then _ will hold it. In contrast, if your function returns None , then the _ variable will remain untouched.
The next example consists of a regular assignment statement. As you already know, regular assignments don’t return any value, so the _ variable isn’t updated after these statements run. Finally, note that accessing a variable in an interactive session returns the value stored in the target variable. This value is then assigned to the _ variable.
Note that since _ is a regular variable, you can use it in other expressions:
In this example, you first create a list of values. Then you call len() to get the number of values in the list. Python automatically stores this value in the _ variable. Finally, you use _ to compute the mean of your list of values.
Now that you’ve learned about some of the implicit assignments that Python runs under the hood, it’s time to dig into a final assignment-related topic. In the following few sections, you’ll learn about some illegal and dangerous assignments that you should be aware of and avoid in your code.
Illegal and Dangerous Assignments in Python
In Python, you’ll find a few situations in which using assignments is either forbidden or dangerous. You must be aware of these special situations and try to avoid them in your code.
In the following sections, you’ll learn when using assignment statements isn’t allowed in Python. You’ll also learn about some situations in which using assignments should be avoided if you want to keep your code consistent and robust.
You can’t use Python keywords as variable names in assignment statements. This kind of assignment is explicitly forbidden. If you try to use a keyword as a variable name in an assignment, then you get a SyntaxError :
Whenever you try to use a keyword as the left operand in an assignment statement, you get a SyntaxError . Keywords are an intrinsic part of the language and can’t be overridden.
If you ever feel the need to name one of your variables using a Python keyword, then you can append an underscore to the name of your variable:
In this example, you’re using the desired name for your variables. Because you added a final underscore to the names, Python doesn’t recognize them as keywords, so it doesn’t raise an error.
Note: Even though adding an underscore at the end of a name is an officially recommended practice , it can be confusing sometimes. Therefore, try to find an alternative name or use a synonym whenever you find yourself using this convention.
For example, you can write something like this:
In this example, using the name booking_class for your variable is way clearer and more descriptive than using class_ .
You’ll also find that you can use only a few keywords as part of the right operand in an assignment statement. Those keywords will generally define simple statements that return a value or object. These include lambda , and , or , not , True , False , None , in , and is . You can also use the for keyword when it’s part of a comprehension and the if keyword when it’s used as part of a ternary operator .
In an assignment, you can never use a compound statement as the right operand. Compound statements are those that require an indented block, such as for and while loops, conditionals, with statements, try … except blocks, and class or function definitions.
Sometimes, you need to name variables, but the desired or ideal name is already taken and used as a built-in name. If this is your case, think harder and find another name. Don’t shadow the built-in.
Shadowing built-in names can cause hard-to-identify problems in your code. A common example of this issue is using list or dict to name user-defined variables. In this case, you override the corresponding built-in names, which won’t work as expected if you use them later in your code.
Consider the following example:
The exception in this example may sound surprising. How come you can’t use list() to build a list from a call to map() that returns a generator of square numbers?
By using the name list to identify your list of numbers, you shadowed the built-in list name. Now that name points to a list object rather than the built-in class. List objects aren’t callable, so your code no longer works.
In Python, you’ll have nothing that warns against using built-in, standard-library, or even relevant third-party names to identify your own variables. Therefore, you should keep an eye out for this practice. It can be a source of hard-to-debug errors.
In programming, a constant refers to a name associated with a value that never changes during a program’s execution. Unlike other programming languages, Python doesn’t have a dedicated syntax for defining constants. This fact implies that Python doesn’t have constants in the strict sense of the word.
Python only has variables. If you need a constant in Python, then you’ll have to define a variable and guarantee that it won’t change during your code’s execution. To do that, you must avoid using that variable as the left operand in an assignment statement.
To tell other Python programmers that a given variable should be treated as a constant, you must write your variable’s name in capital letters with underscores separating the words. This naming convention has been adopted by the Python community and is a recommendation that you’ll find in the Constants section of PEP 8 .
In the following examples, you define some constants in Python:
The problem with these constants is that they’re actually variables. Nothing prevents you from changing their value during your code’s execution. So, at any time, you can do something like the following:
These assignments modify the value of two of your original constants. Python doesn’t complain about these changes, which can cause issues later in your code. As a Python developer, you must guarantee that named constants in your code remain constant.
The only way to do that is never to use named constants in an assignment statement other than the constant definition.
You’ve learned a lot about Python’s assignment operators and how to use them for writing assignment statements . With this type of statement, you can create, initialize, and update variables according to your needs. Now you have the required skills to fully manage the creation and mutation of variables in your Python code.
In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to:
- Write assignment statements using Python’s assignment operators
- Work with augmented assignments in Python
- Explore assignment variants, like assignment expression and managed attributes
- Identify illegal and dangerous assignments in Python
Learning about the Python assignment operator and how to use it in assignment statements is a fundamental skill in Python. It empowers you to write reliable and effective Python code.
🐍 Python Tricks 💌
Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. No spam ever. Unsubscribe any time. Curated by the Real Python team.

About Leodanis Pozo Ramos

Leodanis is an industrial engineer who loves Python and software development. He's a self-taught Python developer with 6+ years of experience. He's an avid technical writer with a growing number of articles published on Real Python and other sites.
Each tutorial at Real Python is created by a team of developers so that it meets our high quality standards. The team members who worked on this tutorial are:

Master Real-World Python Skills With Unlimited Access to Real Python
Join us and get access to thousands of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
Join us and get access to thousands of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
What Do You Think?
What’s your #1 takeaway or favorite thing you learned? How are you going to put your newfound skills to use? Leave a comment below and let us know.
Commenting Tips: The most useful comments are those written with the goal of learning from or helping out other students. Get tips for asking good questions and get answers to common questions in our support portal . Looking for a real-time conversation? Visit the Real Python Community Chat or join the next “Office Hours” Live Q&A Session . Happy Pythoning!
Keep Learning
Related Topics: intermediate best-practices python
Related Tutorials:
- Operators and Expressions in Python
- The Walrus Operator: Python's Assignment Expressions
- Iterators and Iterables in Python: Run Efficient Iterations
- Python args and kwargs: Demystified
- Basic Data Types in Python: A Quick Exploration
Keep reading Real Python by creating a free account or signing in:
Already have an account? Sign-In
Almost there! Complete this form and click the button below to gain instant access:
Python's Assignment Operator: Write Robust Assignments (Source Code)
🔒 No spam. We take your privacy seriously.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
EagerTensor object does not support item assignment
I'm trying to assign a new Value to a TF-Array. Here's my Code:
The error message:
What am I doing wrong?
4 Answers 4
You can't do this in Tensorflow.
For reference see: https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/33131
In order to change the value of a TF-Array, you need to set it Variable:
It's 2022 and it still isn't supported. A potential workaround is to convert it to numpy:
It is not ideal but there aren't a lot of options
- $\begingroup$ Tensors are immutable by design. In graph mode, Python code only provides control structure, which is captured into computation graph. This is just how Tensorflow works. Eager mode, when computations are performed, is the default, but eventually you'll use graph. The best is to use NumPy arrays, but this is not what you can compile into efficient computations later. Also, if you take Tensor.numpy() , Variable is entirely unrequired. For traceable efficient mutable arrays use TensorArray but keep in mind the ta = ta.update(...) pattern: each array mutation returns new TensorArray . $\endgroup$ – kkm mistrusts SE Commented Nov 11, 2023 at 23:58
Actually you can do this with with the use of tf.stack and tf.unstack
Your Answer
Sign up or log in, post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged python tensorflow or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Where developers feel AI coding tools are working—and where they’re missing...
- He sold his first company for billions. Now he’s building a better developer...
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Preventing unauthorized automated access to the network
Hot Network Questions
- Complexity of computing minimum unsatisfiable core
- What are these Ports on Multimeter PCB & What Protocol are they Using?
- Were Soviet doctors and nurses actually as callous as "Voices from Chernobyl" portrays in the prolog?
- Is a private third party allowed to take things to court?
- Can a floppy disk be wiped securely using the Windows format command with the passes-parameter?
- The meaning(s) of 'She couldn't buy a car yesterday.'
- Tic-tac-toe encode them all
- Why would an escrow/title company not accept ACH payments?
- How is the universe able to run physics so smoothly?
- Want a different order than permutation
- Tikz template for organization chart
- Can ATmega328P microcontroller work at 3.3 V with 8 MHz oscillator
- How do I link a heading containing spaces in Markdown?
- Using car seat in a plane
- If I was ever deported, would it only be to my country of citizenship? Or can I arrange something else?
- Expected value of a matrix = matrix of expected value?
- Is there a faster way to find the positions of specific elements in a very large list?
- Undamaged tire repeatedly deflating
- How can I grep to include the surrounding lines?
- I want to find a smooth section of the map from the Stiefel manifold to the Grassmanian manifold
- Is there any language which distinguishes between “un” as in “not” and “un” as in “inverse”?
- What made scientists think that chemistry is reducible to physics and when did that happen?
- What causes, and how to avoid, finger numbness?
- cURL in bash script reads $HOME as /root/
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
Python: making make_class TypeError: object does not support item assignment
I have this problem while making my simple make_class. Here is my code:
Running the program -
I tried to set the value in the def set(name, value): function but then it says
Traceback (most recent call last): File "main.py", line 276, in Test = make_user() File "main.py", line 265, in make_user return make_class('TAccount', {'interest': 0.202}) File "main.py", line 259, in make_class cls['set']('class_name', class_name) File "main.py", line 232, in set attrs[name] = value TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
- 2 Your code is indented incorrectly. Please edit your question. Also see minimal reproducible example . – DapperDuck Commented Jan 5, 2021 at 12:47
- 1 can you make a minimal reproducible example of your error? also, post the whole error message – oskros Commented Jan 5, 2021 at 12:47
- 1 @oskros Indeed, I just don't want to edit the question, if that is what the mistake is. – DapperDuck Commented Jan 5, 2021 at 12:48
- 2 What is supposed to be the purpose of this code? – zvone Commented Jan 5, 2021 at 12:51
- 1 Also, please edit your question to provide the full error traceback, the current output, and the expected output. – DapperDuck Commented Jan 5, 2021 at 12:55
Here is the signature you used to define make_class :
When you call make_class , the positional arguments need to be in the correct order:
Note that having make_user_class refer to a predefined global Test probably isn't a great idea. make_user_class itself should probably take the desired base class as an argument itself:
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged python or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Where developers feel AI coding tools are working—and where they’re missing...
- He sold his first company for billions. Now he’s building a better developer...
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Preventing unauthorized automated access to the network
- Should low-scoring meta questions no longer be hidden on the Meta.SO home...
- Announcing the new Staging Ground Reviewer Stats Widget
Hot Network Questions
- What are these Ports on Multimeter PCB & What Protocol are they Using?
- Can I breed fish in Minecraft?
- How do I avoid getting depressed after receiving edits?
- Does a ball fit in a pipe if they are exactly the same diameter?
- How do I link a heading containing spaces in Markdown?
- Is there a way to have my iPhone register my car which doesn't have carplay, only for the "Car is parked at"-feature?
- Short story about a space traveller on a planet of people, each immensely talented
- Is BitLocker susceptible to any known attacks other than bruteforcing when used with a very strong passphrase and no TPM?
- Did Gauss really call Archimedes an idiot?
- What is an ellipse in infinite-dimensional spaces?
- Using car seat in a plane
- Tic-tac-toe encode them all
- "Chrisma" and "Him"
- If I was ever deported, would it only be to my country of citizenship? Or can I arrange something else?
- What is the legal situation with payments authorised but not collected?
- What made scientists think that chemistry is reducible to physics and when did that happen?
- A military space Saga with a woman who is a brilliant tactician and strategist
- An everyday expression for "to dilute something with two/three/four/etc. times its volume of water"
- Why did the Apollo 13 tank #2 have a heater and a vacuum?
- What evidence exists for the historical name of Kuwohi Mountain (formerly Clingmans Dome)?
- How can the doctor measure out a dose (dissolved in water) of exactly 10% of a tablet?
- What is the mechanical equivalent of an electronic AND gate?
- I want to find a smooth section of the map from the Stiefel manifold to the Grassmanian manifold
- Why does Voyager use consumable hydrazine instead of reaction wheels that only rotate when moving the spacecraft?

COMMENTS
To avoid inheritance from dict, you can make a class inherit from MutableMapping, and then provide methods for __setitem__ and __getitem__. Additionally, the class will need to support methods for __delitem__, __iter__, __len__, and (optionally) other inherited mixin methods, like pop. The documentation has more info on the details.
Lot of issues here, I'll try to go through them one by one. The data structure dict = {} Not only is this overwriting python's dict, (see mgilson's comment) but this is the wrong data structure for the project.You should use a list instead (or a set if you have unique unordered values)
The isinstance() function returns True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in class. # 'numpy.float64' object does not support item assignment. The Python "TypeError: 'numpy.float64' object does not support item assignment" occurs when we try to assign a value to a NumPy float using square brackets.
greet[0] = 'J'. TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment. To fix this error, you can create a new string with the desired modifications, instead of trying to modify the original string. This can be done by calling the replace() method from the string. See the example below: old_str = 'Hello, world!'.
Once we have a list, we can update the item at the specified index and optionally convert the result back to a tuple. Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a tuple has an index of 0, and the last item has an index of -1 or len(my_tuple) - 1. # Constructing a new tuple with the updated element Alternatively, you can construct a new tuple that contains the updated element at the ...
If the variable stores a None value, we set it to an empty dictionary. # Track down where the variable got assigned a None value You have to figure out where the variable got assigned a None value in your code and correct the assignment to a list or a dictionary.. The most common sources of None values are:. Having a function that doesn't return anything (returns None implicitly).
TypeError: 'str' Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Pandas Data Frame The following program attempts to add a new column into the data frame import numpy as np import pandas as pd import random as rnd df = pd.read_csv('sample.csv') for dataset in df: dataset['Column'] = 1
This code replaces the character at name[c] with an empty string. We have created a separate variable called "final_username". This variable is initially an empty string.
The TypeError: 'set' object does not support item assignment occurs when you try to change the elements of a set using indexing. The set data type is not indexable. To perform item assignment you should convert the set to a list, perform the item assignment then convert the list back to a set.
3. You don't have any code in the class that allows for item assignment. For an object to allow item assignment, it needs to implement __setitem__. You would need something like: class MyList: def __init__(self,list): self.list=list. def __setitem__(self, i, elem): self.list[i] = elem.
Marcus Greenwood Hatch, established in 2011 by Marcus Greenwood, has evolved significantly over the years. Marcus, a seasoned developer, brought a rich background in developing both B2B and consumer software for a diverse range of organizations, including hedge funds and web agencies.
To conclude, Typeerror: nonetype object does not support item assignment occurs when we are trying to assign a value to an object which has a value of None. To fix this error, we need to make sure that the variable we are trying to access has a valid value before trying to assign an item to it. I think that's all for this guide.
How to Solve Python TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment; How to Solve Python TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment; To learn more about Python for data science and machine learning, go to the online courses page on Python for the most comprehensive courses available. Have fun and happy researching!
The Python TypeError: tuple object does not support item assignment issue occurs when you try to modify a tuple using the square brackets (i.e., []) and the assignment operator (i.e., =). A tuple is immutable, so you need a creative way to change, add, or remove its elements.
Naturally, an attempt to assign a new value to a tuple element in the line list [i +1] = list [i] raises a TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. Here, you see another mistake—which, by the way, may even be invisible during program execution. The my_sort function uses the list data type name as the argument name.
typeerror: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment While tuples and lists both store sequences of data, they have a few distinctions. Whereas you can change the values in a list, the values inside a tuple cannot be changed.
Here, variable represents a generic Python variable, while expression represents any Python object that you can provide as a concrete value—also known as a literal—or an expression that evaluates to a value. To execute an assignment statement like the above, Python runs the following steps: Evaluate the right-hand expression to produce a concrete value or object.
This is the line that's causing the error, at any rate. dict is a type. You have to create a dictionary before you set keys on it, you can't just set keys on the type's class. Don't use "dict" as var_name. Then you can use it.
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment when swapping values. Ask Question Asked 12 years, 11 months ago. Modified 2 years, ... How to fix 'Tuple' object does not support item assignment problem in Python. 1. iterating over tuples inside a tuple and using string inside tuples as a variable-1
In graph mode, Python code only provides control structure, which is captured into computation graph. This is just how Tensorflow works. Eager mode, when computations are performed, is the default, but eventually you'll use graph. The best is to use NumPy arrays, but this is not what you can compile into efficient computations later.
Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers; Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand; OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams; OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs; Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing; About the company Visit the blog