

a blog by Sander Berkouwer
- The things that are better left unspoken
HOWTO: Add the required Hybrid Identity URLs to the Trusted Sites list of Internet Explorer and Edge

Most Microsoft-based Hybrid Identity implementations use Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) Servers, Web Application Proxies and Azure AD Connect installations. In this series, labeled Hardening Hybrid Identity , we’re looking at hardening these implementations, using recommended practices.
In this part of the series, we’ll look at the required Hybrid Identity URLs that you want to add to the Trusted Sites list in Internet Explorer.
Note: This is the second part for adding Microsoft Cloud URLs to Internet Explorer’s zone. In this part we look at the Trusted Sites zone. In the previous part we looked at the Local Intranet zone .
Note: Adding URLs to the Trusted Sites zone for Internet Explorer, also applies to Microsoft Edge.
Why look at the Trusted Sites?
Hybrid Identity enables functionality for people using on-premises user accounts, leveraging Azure Active Directory as an additional identity platform. By default, Azure AD is the identity platform for Microsoft Cloud services, like Exchange Online, SharePoint Online and Azure.
By adding the URLs for these services to the Trusted Sites list, we enable a seamless user experience without browser prompts or hick-ups to these services.
Internet Explorer offers built-in zones. Per zone, Internet Explorer is allowed specific functionality. Restricted Sites is the most restricted zone and Internet Explorer deploys the maximum safeguards and fewer secure features (like Windows Integrated Authentication) are enabled.
The Trusted Sites zone, by default, offers a medium level of security.
Possible negative impact (What could go wrong?)
Internet Explorer’s zones are defined with specific default settings to lower the security features for websites added to these zones.
When you use a Group Policy object to add websites that don’t need the functionality of the Trusted Sites zone to the zone, the systems in scope for the Group Policy object are opened up to these websites. This may result in unwanted behavior of the browser such as browser hijacks, identity theft and remote code executions, for example when you mistype the URLs or when DNS is compromised.
While this does not represent a clear and immediate danger, it is a situation to avoid.
Getting ready
The best way to manage Internet Explorer zones is to use Group Policy.
To create a Group Policy object, manage settings for the Group Policy object and link it to an Organizational Unit, Active Directory site and/or Active Directory domain, log into a system with the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) installed with an account that is either:
- A member of the Domain Admins group, or;
- The current owner of the Group Policy Object, and have the Link GPOs permission on the Organizational Unit(s), Site(s) and/or Domain(s) where the Group Policy Object is to be linked, or;
- Delegated the Edit Settings or Edit settings, delete and modify security permission on the GPO, and have the Link GPOs permission on the Organizational Unit(s), Site(s) and/or Domain(s) where the Group Policy Object is to be linked.
The URLs to add
You’ll want to add the following URLs to the Trusted Sites zone, depending on the way you’ve setup your Hybrid Identity implementation:
*.microsoft.com
*.microsoftonline.com, *.windows.net, ajax.aspnetcdn.com, microsoft.com, microsoftline.com, microsoftonline-p.net, onmicrosoft.com.
The above URLs are used in Hybrid Identity environments. While they overlap with some of the URLs for the Local Intranet Zone, these URLs allow side services to work properly, too.
*.msappproxy.net
Web applications that you integrate with Azure Active Directory through the Azure AD Application Proxy are published using https://*.msappproxy.net URLs. Add the above wildcard URL to the Trusted Sites list, when you’ve deployed or are planning to deploy Azure AD App Proxy. If you use vanity names for Azure AD App Proxied applications, add these to the Trusted Sites list, as well.
Other Office 365 services
Most Hybrid Identity implementations are used to allow access to Office 365 only. Last year, 65% of Hybrid Identity implementations are used to unlock access to one or more Office 365 services, like Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business and Teams, only. This blogpost focuses on the Hybrid Identity URLs, but you might want to add more Office 365 URLs and IP address ranges to the Trusted Sites list as you deploy, roll out and use Office 365 services. You can use this (mostly outdated) Windows PowerShell script to perform that action , if you need.
How to add the URLs to the Trusted Sites zone
To add the URLs to the Trusted Sites zone, perform these steps:
- Log into a system with the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) installed.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console ( gpmc.msc )
- In the left pane, navigate to the Group Policy objects node.
- Locate the Group Policy Object that you want to use and select it, or right-click the Group Policy Objects node and select New from the menu.
- Right-click the Group Policy object and select Edit… from the menu. The Group Policy Management Editor window appears.
- In the main pane of the Group Policy Management Editor window, expand the Computer Configuration node, then Policies , Administrative Templates , Windows Components , Internet Explorer , Internet Control Panel and then the Security Page node.
![SiteToZoneAssignmentListSettingGPO_thumb[3] SiteToZoneAssignmentListSettingGPO_thumb[3]](https://dirteam.com/sander/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2019/10/SiteToZoneAssignmentListSettingGPO_thumb3_thumb.jpg)
- In the main pane, double-click the Sites to Zone Assignment List setting.
- Enable the Group Policy setting by selecting the Enabled option in the top pane.
- Click the Show… button in the left pane. The Show Contents window appears.
- Add the above URLs to the Trusted Sites zone by entering the URL in the Value name column and the number 2 in the Value column for each of the URLs.
- Click OK when done.
- Close the Group Policy Editor window.
- In the left navigation pane of the Group Policy Management Console, navigate to the Organization Unit (OU) where you want to link the Group Policy object.
- Right-click the OU and select Link an existing GPO… from the menu.
- In the Select GPO window, select the GPO.
- Click OK to link the GPO.
Repeat the last three steps to link the GPO to all OUs that require it. Take Block Inheritance into account for OUs by linking the GPO specifically to include all people in scope.
To enable functionality in a Hybrid Identity implementation, we need to open up the web browser to allow functionality for specific web addresses. By enabling the right URLs we minimize our efforts in enabling the functionality and also minimize the negative effect on browser security.
There is no need to add all the URLs to specific Internet Explorer zones, when you don’t need to functionality. However, do not forget to add the specific URLs when you enable specific functionality like the Azure AD Application Proxy and remove specific URLs when you move away from specific functionality.
Further reading
Office 365 URLs and IP address ranges Group Policy – Internet Explorer Security Zones Add Site to Local Intranet Zone Group Policy
Posted on October 17, 2019 by Sander Berkouwer in Active Directory , Entra ID , Security
2 Responses to HOWTO: Add the required Hybrid Identity URLs to the Trusted Sites list of Internet Explorer and Edge

Great Post! Thank you so much for teaching us on how to add hybrid identity urls to the trusted list of sites on browsers like internet explorer and Microsoft edge.
I want to block all websites on edge and only give access to 2 sites but using group policy can someone help on this?
leave your comment cancel
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Advertisement

Search this site
Dirteam.com / activedir.org blogs.
- Strategy and Stuff
- Dave Stork's IMHO
- The way I did it
- Sergio's Shack
- Things I do
- Tomek's DS World
Microsoft MVP (2009-2025)
Veeam vanguard (2016-2024), vmware vexpert (2019-2022).

Xcitium Security MVP (2023)

Recent Posts
- Join Raymond and me as we discuss “UnOauthorized” with Eric Woodruff
- I’m speaking at NT Konferenca 2024
- What's New in Entra ID for August 2024
- On-premises Identity-related updates and fixes for August 2024
- What's New in Veeam Backup and Replication v12.2 for Identity Admins
Recent Comments
- disa pointid on On-premises Identity-related updates and fixes for August 2024
- Frank Keough on Hardening SMB on Domain Controllers, Step 1: Reporting on SMBv1 connections , SMBv2 connections and SMB null sessions
- Sander Berkouwer on TODO: Upgrade the Certificates for your Windows Server 2016-based Domain Controllers (and up) to enable Windows Hello for Business Hybrid Scenarios
- Jeff McGowan on TODO: Upgrade the Certificates for your Windows Server 2016-based Domain Controllers (and up) to enable Windows Hello for Business Hybrid Scenarios
- Sander Berkouwer on Configuring Geo-Redundancy for AD FS on-premises with Azure Traffic Manager
The information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and the authors make no warranties, either express or implied. Information in these documents, including URL and other Internet Web site references, is subject to change without notice. The entire risk of the use or the results from the use of this document remains with the user. Active Directory, Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT, and Windows Server are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
techlauve.com – a knowledge base for IT professionals.
Inhale problems, exhale solutions..
- Nick’s Blog
- Active Directory
- Privacy Policy
« Outlook: “Sending and Receiving reported error (OX80040600)”
Terminal Server Does Not Accept Enough Client Connections »
Adding Sites to Internet Security Zones Using Group Policy
Sometimes it is useful to leverage the power of Group Policy in Active Directory to add sites to certain security zones in Internet Explorer. This can save the network admin the trouble of managing the security zone lists for each computer (or user) separately. In the following example, each user on the network needs to have a specific site added to the Trusted Sites list.
This tutorial assumes that group policy is in good working order on the domain and that all client users and computers can access the directory.
- Open the Group Policy Management MMC console.
- Right-click the organization unit (OU) that the policy should apply to, taking special care to consider whether the policy should apply to computers or users on this particular network.
- Select “Create and Link a GPO Here…” to create a new group policy object.
- In the “New GPO” window, enter a good, descriptive name for this new policy and click “OK”. (ex. “Trusted Sites Zone – Users” or something even more descriptive)
- Locate the newly created GPO in the left-side navigation pane, right-click it and select “Edit…”
- Expand “Administrative Templates” under either “Computer Configuration” or “User Configuration” depending on which type of OU the new policy was linked to in step 2.
- The path to the settings that this example will be using is: Administrative Templates -- Windows Components -- Internet Explorer -- Internet Control Panel -- Security Page
- In the right-hand pane, double-click “Site to Zone Assignment List”.
- Enable the policy and click the “Show…” button next to “Enter the zone assignments here.” This will pop up the “Show Contents” window.
- Click the “Add…” button. This will pop up the “Add Item” window.
- In the first box, labeled “Enter the name of the item to be added:”, enter the URL to the site. (ex. https://secure.ourimportantwebapp.com) . Keep in mind that wildcards can be used. (ex. https://*.ourimportantdomain.com) . Leave off any trailing slashes or sub-folders unless that type of specific control is called for.
- 1 – Intranet Zone
- 2 – Trusted Sites Zone
- 3 – Internet Zone
- 4 – Restricted Sites Zone
- Once the zone assignment has been entered, click “OK”. This will once again show the “Show Contents” window and the new entry should be present.
- Click “OK” and “OK” again to get back to the Group Policy Management Console.
The new policy will take effect at the next group policy refresh interval, which is usually 15 minutes. To test immediately, run a gpupdate /force on a user/computer that falls into the scope of the new policy and go to “Tools -> Internet Options -> Security -> Trusted Sites -> Sites”. The site(s) added should be in the list. If the sites do not show up, check the event logs for any group policy processing errors.
Related content:
- How To: Time Sync Across Windows Network
- Group Policy Not Applied To Remote VPN Users
- QuickBooks Payroll Opens/Saves the Wrong W2 Form
- Microsoft Virtual Server Web Console Constantly Asks For Password
- Group Policy: Applying Different User Policies to the Same User for Workstations and Terminal Server
No comment yet
Juicer breville says:.
November 26, 2012 at 12:11 am (UTC -5)
Hurrah, that’s what I was looking for, what a information! existing here at this web site, thanks admin of this web page.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
You may use these HTML tags and attributes: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Remember Me
Connect With Us
Connect with us.
Social Connect by NewsPress
Not finding the answer that you're looking for? Need more help with a problem that is addressed in one of our articles?
techlauve.com is affiliated with Rent-A-Nerd, Inc. in New Orleans, LA.
- DFS Replication (1)
- Group Policy (1)
- Microsoft Exhange (3)
- Microsoft Outlook (11)
- Copiers (1)
- Multi Function Devices (1)
- Printers (2)
- Scanners (1)
- Blackberry (1)
- Firewalls (2)
- Wireless (2)
- Hard Drives (1)
- SAN Systems (1)
- Hyper-V (3)
- Virtual Server (1)
- WordPress (1)
- Security (7)
- QuickBooks (2)
- Quicken (1)
- Antivirus/Antimalware (4)
- Backup Exec (2)
- Internet Explorer (5)
- Microsoft SQL (1)
- Licensing (2)
- Steinberg Nuendo (1)
- Mac OS X (1)
- Server 2003 (12)
- Server 2008 (14)
- Small Business Server 2003 (7)
- Terminal Server (6)
- Updates (2)
- Windows 7 (9)
- Windows XP (11)
- Reviews (1)
- Rent-A-Nerd, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Licence .
Valid XHTML 1.0 Strict Valid CSS Level 2.1
techlauve.com - a knowledge base for IT professionals. uses Graphene theme by Syahir Hakim.
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Troubleshoot "Internet Explorer Zonemapping" failures when processing Group Policy
- 2 contributors
When you execute GPUpdate /force , you may see the following output:
When you run GPRESULT /H GPReport.html and examine the report, you see the following information under Component Status :
The System event log contains an event ID 1085 that indicates a Group Policy processing error related to "Internet Explorer ZoneMapping," like the following one:
This event can occur if you enter an invalid entry within the Site To Zone Assignment List policy in the following paths:
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Internet Explorer\Internet Control Panel\Security Page
The "Site To Zone Assignment List" policy
The format of the Site To Zone Assignment List policy is described within the policy. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone. These zone numbers have associated security settings that apply to all sites in the zone.
Internet Explorer has four security zones, which are used by this policy setting to associate sites with zones. They're numbered 1 to 4 and defined in descending order of most to least trusted:
- Local Intranet zone
- Trusted Sites zone
- Internet zone
- Restricted Sites zone
The security settings can be set for each of these zones through other policy settings, and their default settings are:
- Trusted Sites zone (Low template)
- Intranet zone (Medium-Low template)
- Internet zone (Medium template)
- Restricted Sites zone (High template)
The Local Machine zone and its locked-down equivalent have special security settings that protect your local computer.
If you enable this policy setting, you can enter a list of sites and their related zone numbers. The association of a site with a zone ensures that the security settings for the specified zone are applied to that site. For each entry that you add to the list, enter the following information:
Valuename : It's used to specify a host for an intranet site, or a fully qualified domain name for other sites. The valuename may also include a specific protocol. For example, if you enter https://www.contoso.com as the valuename , other protocols aren't affected. If you just enter www.contoso.com , all protocols for that site are affected, including http, https, ftp, and so on. The site may also be expressed as an IP address (such as 127.0.0.1) or a range (such as 127.0.0.1-10). To avoid creating conflicting policies, don't include other characters after the domain, such as a trailing slash or URL path. For example, the policy settings for www.contoso.com and www.contoso.com/mail would be treated as the same policy setting by Internet Explorer, and therefore, conflict.
Value : It's the number of the zone you want to associate the site with security settings. The Value of the above Internet Explorer zones is 1 to 4 .
When you enter data in the Group Policy Editor, there's no syntax or logical error checking available. This error checking is performed on the client when the Internet Explorer Zonemapping Group Policy Extension converts the registry into the format used by Internet Explorer. During that conversion, the same methods are implemented when you manually add a site to a specific security zone. If an entry is rejected when you add it manually, the conversion also fails if the Group Policy is used and the event 1085 is issued. For example, when you try to add a wildcard entry to a top-level domain (TLD) (like *.com or *.co.uk ) while adding a site, the wildcard entry is rejected. Now, the question is, which entries are treated as TLDs; by default, the following schemes are treated as TLDs in Internet Explorer:
- Flat domains (such as .com ).
- Two-letter domains in a two-letter TLD (such as .co.uk ).
The following blog post includes a granular explanation of domains:
Understanding Domain Names in Internet Explorer
To identify incorrect entries in the policy, download and run the IEDigest tool. After creating a report and opening it in your web browser, you'll see a Warnings section where incorrect entries are named. These entries need to be removed (or corrected) in the Group Policy. Here's an example of how it looks like when trying to add *.com to a zone:
Warnings Description Key Name Value Invalid entry in Site to Zone Assignment List. Click here for more info HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey *.com is invalid
More information
- Intranet site is identified as an Internet site when you use an FQDN or an IP address
- Security Zones in Microsoft Edge
Third-party contact disclaimer
Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find additional information about this topic. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of third-party contact information.
Additional resources
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Why is SiteToZoneAssignment GPO applying, but sites not appearing in IE
We have a Windows server 2012 R2 remote desktop farm, which we have applied a GPO to, to control site to zone assignments.
This was working fine up until recently, but just lately, we have found that this setting is not applying.
If I toggle ESC on, and then back off on the server I am on, the sites now show up in IE zone list for the currently logged in user. It does not however, seem to apply to all users. That list of sites will then follow them to other servers and that user will be ok moving forward.
We use user profile disks, so the users registry hive is not available on that server unless they are logged in, which might explain why it only occurs for the logged in test user.
EDIT : I can see the registry entries being created under HKCU ZoneMapKey and HKLM ZoneMap.
According to this article, IE should read settings from both of those locations, but they simply do not appear in the site list in IE control panel.
Is it possible that there has been an update for 2012 that has altered some ESC registry setting that causes us this issue?
- group-policy
- windows-server-2012-r2
- internet-explorer
- remote-desktop-services
- windows-update
- Check the zone assignment in the registry, IE ignore esc zone assignment if you have normal zone assignment. – yagmoth555 ♦ Commented Jul 7, 2016 at 11:59
- I have applied the settings under the computer settings in the policy. If I look in HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey, I can see all of the entries, they just don't show up in IE itself – James Edmonds Commented Jul 7, 2016 at 13:35
- But ESC is not enabled! – James Edmonds Commented Jul 7, 2016 at 13:49
- I would try HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main\FeatureControl\FEATURE_IGNORE_POLICIES_ZONEMAP_IF_ESC_ENABLED_KB918915\ to 1 anyhow, it's for fixing a bug when ZoneMap is done and ESC is on/off. – yagmoth555 ♦ Commented Jul 7, 2016 at 13:52
- It's tagged for Win2003, but the registry fix work in 2012; support.microsoft.com/en-gb/kb/918915 , they tell HKLM to fix it for all user, or it work too like you told in HCU – yagmoth555 ♦ Commented Jul 7, 2016 at 14:11
3 Answers 3
I created a new user account, and when logged on for the first time, it too experienced the same issue with sites not showing in IE, even though the GPO was applied.
I found in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap , there is a key called IEHarden (remembered the name back from my 2003 days with a similar ESC kind of issue). It looks like even though the server has ESC turned off, this key is set to 1. When either deleting, or setting this to 0, the sites immediately appear in internet control panel, and works as expected.
So while I know what is causing the problem, and have enough to fudge a workaround by deleting that key for each user on login, I still don't understand why that key is set to 1, or even exists in the first place (some users who could see the sites already, don't even have that key!). Again I can only come back to an update that has messed with IE ESC in some way.
Now have the full answer;
Two of our 8 session host created profiles with the IEHarden key, while the others did not (these two were setup by our consultants, although after asking them they are clueless).
Seems under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Terminal Server\Install\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap the IEHarden key existed, so was being given to all new profiles created on that server.
Deleted the key from both, and all now back to normal!
Thanks James for posting the info. For anyone who faces this issue the key to look for is:
- Curious about your environment. The OPs info and references solved my related issues. But the key you're describing doesn't exist in my 2012-R2 servers. – bvj Commented Feb 15, 2018 at 8:14
Besides IEHarden under HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap I had in my company also to set IsInstalled at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components\{A509B1A8-37EF-4b3f-8CFC-4F3A74704073} to dword:00000000 .
These two registry settings did fully resolve the issue for us. Before IEHarden was somehow set after a certain time back to 1.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged group-policy windows-server-2012-r2 internet-explorer remote-desktop-services windows-update ..
- The Overflow Blog
- The world’s largest open-source business has plans for enhancing LLMs
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Site maintenance - Mon, Sept 16 2024, 21:00 UTC to Tue, Sept 17 2024, 2:00...
Hot Network Questions
- What was the newest chess piece
- Recursive relation for power series coefficients
- My math professor is Chinese. Is it okay for me to speak Chinese to her in office hours?
- Rich Mental Images
- Stuck as a solo dev
- Convert base-10 to base-0.1
- Positivity for the mild solution of a heat equation on the torus
- Why is steaming food faster than boiling it?
- Explicit Examples for Unrestricted Hartree Fock Calculations
- Building rear track wheel from road wheel
- Swapping front Shimano 105 R7000 34x50t 11sp Chainset with Shimano Deore FC-M5100 chainset; 11-speed 26x36t
- Connected components both topologically and graph-theoretically
- How can we speed up the process of returning our lost luggage?
- Function with memories of its past life
- Why do the shape/fluid loaders have three levels?
- crontab schedule on Alpine Linux does not seem to run on Sundays
- What is the best way to protect from polymorphic viruses?
- Question on a polynomial
- Odorless color less , transparent fluid is leaking underneath my car
- Should I be careful about setting levels too high at one point in a track?
- ASCII 2D landscape
- What makes amplifiers so expensive?
- How to deal with coauthors who just do a lot of unnecessary work and exploration to be seen as hard-working and grab authorship?
- XeLaTeX does not show latin extended characters with stix2
Group Policy Central
News, Tips and Tutorials for all your Group Policy needss
How to configuring IE Site Zone mapping using group policy without locking out the user

Put simply we are going to setup the IE Zone registry keys manually using Group Policy Preferences…
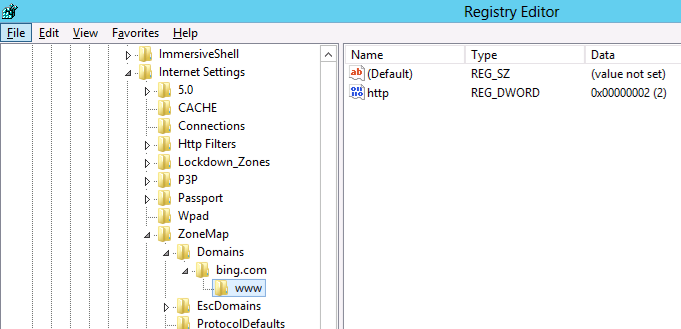
However it’s a little complicated as the URL that is in the Site to Zone mapping is actually stored as the name of the key. Finally the protocol is the registry value with a number that assigns it to the corresponding zone. In the example we use we will first look at the currently site that the users has setup in the trusted site list ( www.bing.com ). As you can see below the zone is store at HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains then the domain is stored as a key “Bing.com” then “www”. Within the “www” key the protocol (http and/or https) is the value name with the value representing what zone it should be a member.
Note: We are just using bing.com as an example as you would never add at search engine as a trusted site.
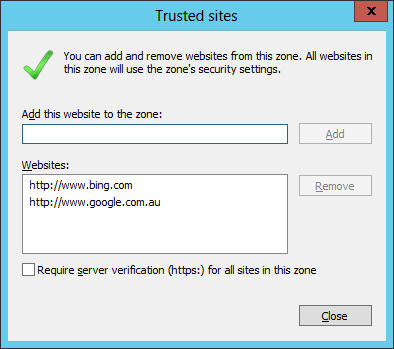
Now we will add the additional site www.google.com.au also to the trusted sites list using group policy.
Step 1 . Edit a Group Policy that is targeted to the users that you want the IE Zones applied.
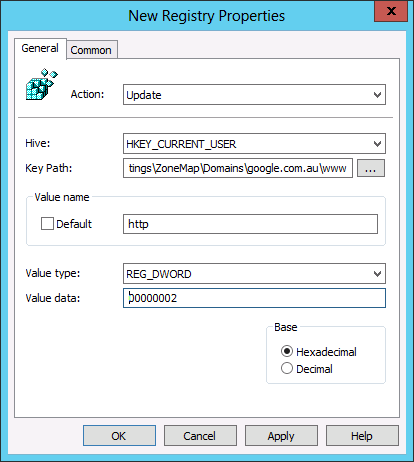
Step 2. Create a new Group Policy Preferences Registry Extension then select the “HKEY_CURRENT_USERS” Hive and then type “Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\google.com.au\www” in the Key path. Then enter the Value name of “HTTP” and selected the Value Type as “REG_DWORD” and set the value data as “00000002”.
And you’re Done…
TIP: For your reference the values and their corresponding Zones are listed below in the table.
| Value | Zone Name |
| 00000000 | My Computer |
| 00000001 | Local Intranet |
| 00000002 | Trusted Site |
| 00000003 | Internet |
| 00000004 | Restricted |
As you can see below the IE zone will push out to your users and it will be added to the trusted zone list, while still allowing them to add and remove other zones from the list.
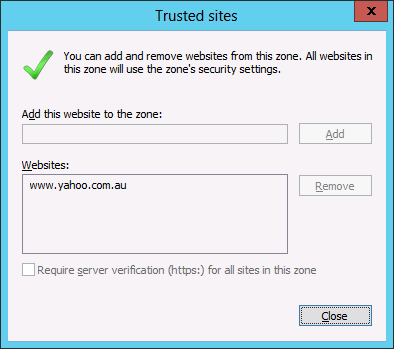
TIP: As always the native group policy settings will take precedence over Group Policy Preferences therefore if you have the “Site to Zone Assignment List” setting configured as well this will override (not merge) the above settings (See image below).
Author: Alan Burchill
Related articles.

47 thoughts on “ How to configuring IE Site Zone mapping using group policy without locking out the user ”
Group Policy Central http://t.co/Y2cVZ0TP
Where on earth did you find this little gem?
I worked this one out on my own a few years back, Should have written a blog / guide back then! I’d be a millionnaire!!
But still – this is a great way to allow the users to add their own trusts, of on site to fix a broken site without returning to GPO Editor just for a single user!
- Pingback: Security Tip: Block Internet Explorer invocation of Java with Group Policy
I wasn’t able to get this to work. I tried it on both User and Computer settings. There was no sub folder under ‘hotmail.com’. The domain I’m trying to remove.
I’m unable to get this to work. Even the group policy results test shows it is successful, but it never shows up in the IE Internet settings. I’ve added a REG entry to also “uncheck” the require https: and that doesn’t show up either. I’ve test on both WinXP with IE8 and Win7 with IE9. Same results. I’ve looked at the registry and see nothing added. Plus, there are no errors in the event log.
Strange behavior.
I just troubleshooted with the same problem that it was not working with no error message to troubleshoot anywhere.
SOLUTION: I fired up regedit and navigated to “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\” There I saw the site I wanted to add as a sub-key to “ZoneMap” and not as a subkey to “Domains” as it is supposed to be. The “Domains” subkey was empty. I deleted the site from “ZoneMap” and then did a gpupdate. When I then refreshed regedit the site was created no the correct location and everything was working. 🙂
Thanks for the info, but this isn’t my experience at all.
I’ve checked the registry for this same error and see nothing. I’ve even searched the entire registry for the domain name, and it finds nothing…
I’ve got a computer policy that is applied to the OU where the computer lives. All items in the policy are updating successfully, except for the registry entries. I’ve run the group policy results and see no errors. I’ve even created the policy by using the registry wizard and importing the items from my local registry. When I check the local registry on my test machines, I see nothing change. If I add the entries via IE, then they show up in the correct places. I’m stumped why this isn’t working…
Tough one. I often had typos in the GP preferences mess things up for me in the past, also the correct amount of \ signs in the key path is important. Personally I have never used it in computer policy, but I’ve always used user policy, perhaps that is worth a try? Also I always use “Replace” and not “update” in the GP Preference.
What do you mean by, “the correct amount of signs in the key path”? What is a sign?
I had the same thought about user policy yesterday and tried that as well. No luck. I haven’t tried the “Replace” option. I’ll test that next.
A bit clumsy explained, sorry about that. But I meant where you put the (slash) \ in the path. “Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\*.contoso.com” is the correct path, but if you write “\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\*.contoso.com” or “Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\*.contoso.com\” then it will fail.
Not sure why but I can’t make this work at all. The GPP does not write the reg entries at all. I tried changing the action to create and also update, but no difference. Any suggestions?
well John, you don’t really tell me much of your setup so there is not much for me to go on here. But in general my checklist would be something like this:
1. It’s a GPP setting under the user (not computer) and it writes to the HKCU hive? 2. Use “replace” 3. Trippe-check that the path is written correctly. For example: “Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\*.contoso.com” 4. Use “gpresult -r” on the client computer to check that the user gets the GPP 5. If the user gets the GPP, check the application log on the computer. If a GPP fails you will see it in the application log at the time the user logs in and it usually tells you why.
That’s my suggestions at the moment.
You nailed the problem – I was using a computer policy, not a user policy. As soon as a rebuilt it as a user policy, everything fell into place perfectly. Thanks for posting this, it was a huge timesaver!
You’re welcome, I’m glad I could help. 🙂
Excellent post. I was just trying to figure out the exact registry keys to modify when I found this page. Nice work !
For the same case.. My user wants to add site to their trusted site list.. Please help…
Mahfuj: I’m not sure what you mean. If you use GPP to configure the IE zones then the users are allowed to add sites to them. Do you want ot prevernt them from adding sites to the trusted site list? Or do you want to allow them to add sites to the trusted site list?
Yes.. I want my user will add sites to trusted site list….. But “Add this website to the zone” field and “Add” button is gray out.. for all users.
Yes.. I want to allow my users to add sites to trusted site list….. But “Add this website to the zone†field and “Add†button is gray out.. for all users.
This means you have the administrative template still configured for the user so it will prevent them from editing their zone list. You have to be sure that you ONLY configure IE site zones via Group Policy Preferences…
I agree with Alan, it is most likely another GPO that contains settings for the IE zones, either in computer or user settings.
Thanks… I’ve figureout the issue.. Site to zone assignments list should be Not Configured for both Computer and user configuration settings….
You have a typo in the third paragraph that starts with “Hoever it’s a little complicted. Typo: “As you can see below the zone is store at HKCU\Software\Microsoft\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains…” should be “As you can see below the zone is store at HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains…” The “Windows” part of the path is missing 😉
@KJS thanks.. I have corrected…
What versions of IE does this method support?
I have not tested it… but I think will work with all versions.
I am really loathing the decision by MS to go down the GPP route without replacing existing functionality with something equally simple. With this Zone mapping and the amount of work with getting favourites working it is a nightmare trying to replace existing simple easily updated GPOs with GPPs, I am not looking forward to doing it for Office.
Helpful. Thanks
Worked perfectly; delivering the following record helped the annoying windows security prompts for executing VBS/HTA files off network shares: file://privateDomainName.FQDN 1 file://privateDomainName 1
Many thanks,
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find a lot of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content for you personally? I wouldn’t mind producing a post or elaborating on some of the subjects you write concerning here. Again, awesome weblog!
That brings us to quite possibly the most intriguing match-up to that point of the season when Oregon comes to Rice-Eccles. Alabama will try to rebound from their loss to the Sooners and rank fourth in the Sporting News college football preseason rankings. Ole Miss and Mississippi State moving the Egg Bowl away from Jackson, Miss.
What’s up, always i used to check web site posts here in the early hours in the morning, because i like to find out more and more.
Alan, great post. I’m having this issue my question is would this solution work for widows 7?
Yes it will
Very helpful posting, many thanks.
Has anyone had trouble getting this to work with Windows XP? It works well with all my Win& PC’s but is hit and miss on the XP.
Had a similar Issue, however a little different. This article may help you… http://www.grishbi.com/2015/03/unable-to-change-ie-zone-security-settings/
Excellent work Alan.
I know it is mentioned, but I would re-emphasize http or https as required.
As Per-Torben Sørensen suggested, use Replace. I’ve had issues with update instead of replace so I always use replace. It seems update doesn’t add something if it is missing, but replace does.
Remember rsop.msc is your friend. It doesn’t show the registry changes, but does show if an additional policy is applied that overrides the registry settings. With these specific settings, you can do a C:\>gpupdate /force, close and re-open the browser or re-run rsop.msc to see if the changes took place. All without logging out and back in, or rebooting.
Best, David
Much appreciated. Need to retain as much of the admin aspects for people doing programming while still giving them the tools needed for internal sites.
I am able to get the GP to work fine, however the site I am adding still doesn’t come up under the Intranet Zone as I have set. I am trying to add the internal IP of the site – 192.0.0.25. When I add this manually in IE, it works fine. When done through GP, it shows in IE under the Intranet zone, but doesn’t get treated like an intranet zone (File > properties, shows it as Internet). Is there a way to use the IP address instead of the domain name?
We needed to add a list of no less than 10 sites to the trusted list. Rather than doing it individually as you have shown, I exported the “Domains” key to a shared drive and then created a logon script that copies it to the local machine and then imports it to the registry. Now, whenever we need to add more trusted sites, I can just update the reg key in the shared location.
Question on using Wild Cards in the URL. I just found your post yesterday and am very excited about testing out using preferences in place of policies for our list of trusted sites.
I have several URLs that I am using wildcards in. If I enter the wildcard in the key path (Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\*.contoso.com) I end up with this listed in trusted sites in IE: http://*.contoso.com .
Will this function properly for all domains that add a prefix to .contoso.com? Also, is there anyway to use a wildcard to it would work with either http or https sites? We have several of those.
Excellent article…..working for me. One thing I want to mention that If you want to add just e.g., http://google.com it is working fine. but if you want to add http://google.com/xyz then you should add google.com/xyz after \Domains\ e.g. Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\Domains\google.com/xyz
Thanks for posting.
Is this applicable for HKLM registry location via GPP?
Since we need to implement for machine level.
Brilliant, thanks for this blog, works like a treat. thanks for your effort putting this up 5 years later and people are still coming across these things 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Site sponsor, featured post.
Popular Posts

- Best Practice (40)
- Group Policy FAQ (3)
- KB Focus (5)
- Other Site Links (15)
- Podcast (2)
- ScreenCast (4)
- Security (33)
- Setting of the Week (41)
- Site News (19)
- TechEd (35)
- Tutorials (117)
- Uncategorized (6)
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How to view all IE Trusted Sites when security settings are managed?
If the Security Zones for Internet Explorer are managed by my system administrator, the list of Trusted Sites is disabled and I cannot scroll through the list. Is there a way I can view the full list of Trusted Sites?

- internet-explorer
- security-policy
- Not a duplicate, but somewhat related: serverfault.com/questions/612903/… - "IE11: How to check into which zone a URL falls?" – T S Commented Apr 23 at 9:21
11 Answers 11
In the registry , perform a search for a URL that is known to be trusted. This should get you to the relevant key where you can see all of the others.
On my Windows 7 installation, the path appears to be HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey , which is slightly different from this answer .
The key should contain several string values with a name indicating the URL and numeric data indicating the zone, one of the following by default.
- 0 = My Computer
- 1 = Local Intranet Zone
- 2 = Trusted sites Zone
- 3 = Internet Zone
- 4 = Restricted Sites Zone
- 8 Mine are all under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE – Richard Collette Commented Sep 26, 2014 at 18:03
Depends upon your firm whether the list is under HKLM or HKCU. Here's a quick Powershell command to get the list
- 3 +1: This is the only solution which worked for me! Thanks! – Kidburla Commented Mar 18, 2015 at 15:41
- 3 Remove the ".property" on the end of each line to see which zone the site is configured for: 1 = Local Intranet, 2 = Trusted Sites, 3 = Restricted Sites – BateTech Commented Jul 10, 2019 at 12:25
From powershell:
- 1 Can you explain this answer/flesh it out a bit more for those who don't know PS as well? – studiohack Commented Feb 10, 2015 at 16:13
- Start -> type gpedit.msc -> hit Enter
- navigate to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security Page
- in the right-hand panel, double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List option, then click Show...
- trusted sites are the ones with 2 in the Value column (1 = Intranet, 3 = Internet, 4 = Restricted)
If that doesn't work (that option is set to "Not Configured" or the list is empty), try the same, except instead of Computer Configuration, start with User Configuration.
- 3 Both of these settings are "Not Configured" and the lists are empty. – JustinStolle Commented Apr 18, 2012 at 22:33
- "You do not have permission to perform this action" - gpedit also locked down – LJT Commented Apr 13, 2016 at 0:10
I came up with the following solution, I hope others will find it useful as well.
I have limited rights, only local, not enough to open and view GPEDIT on AD level.
So, what I did, and works, is to open a command prompt (as Admin) and run the command:
C:\WINDOWS\system32>GPResult /V /SCOPE Computer /H c:\temp\stuff.txt
Then perform a search e.g. for the "ZoneMapKey"
C:\WINDOWS\system32>find "ZoneMapKey" c:\temp\stuff.txt >> c:\temp\sites.txt
Keep in mind there are other keys that might require your attention, like the "approvedactivexinstalsites"...
You will have an output like:
KeyName: Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey\https://www.wesayso.com
Clean it up (I use Excel, use the \ as seperator and be done with it) and you will have a great list.
- 4 I tried this but got an error "ERROR: Invalid Syntax. Options /U, /P, /R, /V, /Z cannot be specified along with /X, /H." – Kidburla Commented Mar 18, 2015 at 15:39
- C:\WINDOWS\system32>GPResult /V /SCOPE COMPUTER >> c:\temp\stuff.txt generate the file for me. "COMPUTER" in caps per the help file. Use >> to write to file instead of /H – MrChrister Commented Feb 4, 2019 at 22:58
This one works on my Windows 7 machine. It was set by my company's domain controller.
Here is an enhanced version of the script that translates the zone type number in the registry to its name as seen in the IE explorer settings dialog box.
Above we see how to gather the registry value names in a registry key and then get the data of each of those values. As each enter separates the value name and the value data with a comma, it could be further enhanced to output to a file with the csv extension and then opened in Excel. Many more possibilities if you want an actual report. But if just need to know what is the site list this will show most of them.
on windows 10 The URL are saved in Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMapKey
to get the values you can brows to the above key or via PowerShell
My key was located here (in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, not HKEY_CURRENT_USER)
I could right-click "ZoneMapKey" and choose "Export"
This .reg file can be opened in Notepad to view (and search) the text contents.
This PowerShell script provides a list from both registry keys if they are populated and uses the out-gridview cmdlet to provide a search capability using the out-gridview filter field.
Stick this in Powershell for a list of the trusted sites:
1 = Intranet zone – sites on your local network. 2 = Trusted Sites zone – sites that have been added to your trusted sites. 3 = Internet zone – sites that are on the Internet. 4 = Restricted Sites zone – sites that have been specifically added to your restricted sites.
Answer taken from: https://blogs.sulross.edu/gfreidline/2017/06/20/show-ie-trusted-sites-from-powershell/
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged internet-explorer security-policy managed ..
- The Overflow Blog
- The world’s largest open-source business has plans for enhancing LLMs
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Site maintenance - Mon, Sept 16 2024, 21:00 UTC to Tue, Sept 17 2024, 2:00...
Hot Network Questions
- Why is the center of a meniscus completely flat?
- Doesn't nonlocality follow from nonrealism in the EPR thought experiment and Bell tests?
- If one is arrested, but has a baby/pet in their house, what are they supposed to do?
- Do carbon fiber wings need a wing spar?
- Odorless color less , transparent fluid is leaking underneath my car
- Python script to renumber slide ids inside a pptx presentation
- Swapping front Shimano 105 R7000 34x50t 11sp Chainset with Shimano Deore FC-M5100 chainset; 11-speed 26x36t
- The walk radical in Traditional Chinese
- What is the action-cost of grabbing spell components?
- How do I annotate a molecule on Chemfig?
- Question on a polynomial
- How frequently is random number generated when plotting function containing RandomReal?
- Place with signs in Chinese & Arabic
- What makes amplifiers so expensive?
- Convert base-10 to base-0.1
- Whom did Jesus' followers accompany -- a soldier or a civilian?
- Why does a capacitor act as an open circuit under a DC circuit?
- A word like "science/scientific" that can be used for ALL academic fields?
- Why is the Liar a problem?
- What is the best way to protect from polymorphic viruses?
- Arduino Uno Serial.write() how many bits are actually transmitted at once by UART and effect of baudrate on other interrupts
- What's the strongest material known to humanity that we could use to make Powered Armor Plates?
- Should I be careful about setting levels too high at one point in a track?
- How should I email HR after an unpleasant / annoying interview?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This article describes how and where Internet Explorer security zones and privacy settings are stored and managed in the registry. You can use Group Policy or the Microsoft Internet Explorer Administration Kit (IEAK) to set security zones and privacy settings.
This Microsoft created software will allow you to enter a URL and display not only the zone that falls into (including the local computer zone - there are actually four IE zones) but it will show the specific IE settings that would be applied. It's a great tool for diagnosing policy issues: https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/fdcc/2011/09/22 ...
In this part of the series, we’ll look at the required Hybrid Identity URLs that you want to add to the Trusted Sites list in Internet Explorer. Note: This is the second part for adding Microsoft Cloud URLs to Internet Explorer’s zone.
There is a native Group Policy that allows you to control Internet Explorer site zone list is called “Site to Zone Assignment List†which I will go thought below how to use. Step 1. Edit the Group Policy Object that is targeted to the users you whish this setting to be applied. Step 2. Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative ...
Users can use the Internet Control Panel to assign specific sites to Zones and to configure the permission results for each zone. In managed environments, administrators can use Group Policy to assign specific sites to Zones (via "Site to Zone Assignment List" policy) and specify the settings for URLActions on a per-zone basis.
Sometimes it is useful to leverage the power of Group Policy in Active Directory to add sites to certain security zones in Internet Explorer. This can save the network admin the trouble of managing the security zone lists for each computer (or user) separately.
The format of the Site To Zone Assignment List policy is described within the policy. This policy setting allows you to manage a list of sites that you want to associate with a particular security zone.
According to this article, IE should read settings from both of those locations, but they simply do not appear in the site list in IE control panel. Is it possible that there has been an update for 2012 that has altered some ESC registry setting that causes us this issue?
Unfortunately this means that you can now longer natively configured the IE Site to Zone mapping using native group policy setting without still allowing the user to customise the URL list. So below I will show you how you can still use Group Policy to configure the IE Zone via group policy while still allowing the user the ability to add ...
navigate to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security Page in the right-hand panel, double-click on the Site to Zone Assignment List option, then click Show...