- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring

Teaching as a Profession, Essay Example
Pages: 1
Words: 353
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
A teacher is an influential person in the society because he or she contributes to imparting of knowledge to all members of the society who go to school. Therefore, teaching is a professional career that needs many skills and expertise for the process to be effective. Various factors define teaching as a professional career.
Teachings as a profession need adaptability. This is because teachers deal with a variety of abilities that students have. Teachers are required to have innovative lessons in order for their students to master their standards (McKenzie & Santiago, 2005). For example, teachers use various innovative techniques to make their lessons to be understood well by students. They employ the use of technology, music, art, physical activities and hands on activities to help students to have more understanding according to their unique learning styles. Teachers also modify their discipline plans because there are students who require extra behaviors support. Teachers also adapt to changes in teaching programs because the curriculum switches in different years. Therefore, teachers are always required to understand how to do things in new ways.
Teachers need to be motivated in order for them to be able to encounter negativity, not from students alone but, also from parents, frustrated colleagues or administration that is not supportive (Lunenburg & Ornstein, 2007). Teachers demonstrate motivation by giving encouragement to students, giving students meaningful feedback, personalized attention to help them succeed. Teachers renew their commitments daily in order to act as positive role model to the students and the larger school community.
Teachers need to be good monitors and evaluators. Teachers need to be able to make an assessment on the progress of the students (McKenzie & Santiago, 2005)Teachers in their day to day duty assess their students in order to find out if they understand the concepts taught. If the students show misunderstanding of the concepts, then teachers employs alternative teaching strategy that makes students understand the concepts taught.
Lunenburg, F. & Ornstein, A. (2007). Educational administration: concepts and practices, 2 nd edition. Belmont: Cengage Learning.
McKenzie, P. & Santiago, P. (2005). Teachers matter: attracting, developing and retaining effective teachers, 1 st edition. Paris: OECD Publishing.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Ford Motor Company and Honda Motors, Research Paper Example
Gregg vs. Georgia, Reaction Paper Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371

Blogs – Digital Class
- Online Teaching
Teaching As a Profession Essay

Teaching is a respected profession which demands consistency and patience. Educators are not only seen as knowledge distributors but also mentors and role models. This article “ Teaching as a Profession Essay” sheds light on the value of such teachers and what the world would be without them. Let’s get started with the importance of teaching profession.
Many teachers dedicate all their lives to empowering students and making them better and more successful human beings in their lives. Furthermore, they even help them financially so that they’re not left behind in life. These are those children who can never afford to be admitted to coaching classes for competitive exams. Anand Kumar teaches, guides, and motivates students to dream big and fulfil those dreams.
Table of Contents
Some Respected Teachers in History
The first Anand Kumar from Super 30 (played by Hrithik Roshan) made a record of selecting 18 students for IIT out of 30 students.
The next example in front of us is Siva Subramania Iyer. He was the teacher of Dr APJ Abdul Kalam and he was responsible for giving India its Missile Man. He taught him to fly high and inspired him to make it big. Teaching as a profession can influence and shape future leaders.
Thus, not only teaching a profession a thing to pursue but also a passion that can take you to heights.
What is a Teaching Profession?
We all know what it is teaching profession. But still, we need to be aware of the importance of teaching profession. They mentor and motivate students to perform well in their studies and be passionate about their careers.
Let’s explain concept of profession and specifically discuss teaching as a profession. Teaching is a job made to make students more capable and teach important academic and life lessons even about values like respect, sharing, ethical values, and cultures. Teachers, through the teaching profession, not only teach academics but also influence the way students live their lives.
Teachers are the ones who teach students to live life with discipline and high value and also play a crucial role in shaping the minds and lives of students, allowing them to attain knowledge, skills, and values crucial for personal and intellectual growth.
Importance of Teaching Profession
Teaching is the most desirable Profession nowadays. The importance of the Teaching Profession incorporates tomfoolery and learning together. Being in the teaching profession doesn’t mean you have to share your knowledge.
Teachers play a vital role in student’s life by assisting them with achieving their goals. Therefore, choosing the Teaching Profession offers perpetual career opportunities. However, Teaching isn’t the only Profession; in fact, it is the activity to serve education.
This is highlighted in essay about teaching profession, which discuss the ways it helps shape individuals and society. Let’s check out the reasons explaining the importance of teaching profession in this “Teaching as a Profession Essay”.
Improves Communication Abilities
Teaching is a systematic strategy to communicate with more and more people. In this manner, being in the teaching profession will improve communication abilities. Therefore, one can interact more confidently with others.
Fun and learning together
Among all careers and professions, we found teaching much better. The Importance of the Teaching Profession is that one can have fun and learn together. Other than training students, teachers can be involved in other educational program activities, reinforcing that why teaching is a profession with a dynamic and exciting environment.
Experience To Handle Various Youngsters
In the teacher profession, teachers encounter students from various backgrounds and with different mindsets. School or college is a place where various students with various mentalities reach. The teacher should have the ability to handle all youngsters normal, savvy, or physically disabled.
Brilliant Organization Abilities
The teaching profession makes one multi-tasker; notwithstanding teaching academics to students, teachers, and Organizational abilities. Being organized means one can manage time and resources proficiently and really for improved productivity.
Ethical And Restrained
One characteristic of the teaching profession involves morals and discipline. Teachers teach ethical values which make students more focused.
Setting up Role Models for Others
Being a teacher isn’t a lot of complex however being a favorite of all is what matters. Teachers should inspire students to find their secret talents and achieve their aims. An inspired teacher can make students motivated by setting up Role models.
Assemble Future Leaders
Teachers are the source of affecting tomorrow’s leaders.
Inspire and Influence
Teachers have the added responsibility of shaping the future generation and also have an opportunity to make a distinction. They will have the exceptional opportunity to guide a mass in the correct direction.
Improvement and Learning
It will associate with young, curious, personalities all day, you would actually want to propel yourself and get better consistently. At the point when you are in an environment that asks a lot of questions and is curious, you grow and develop consistently.
Work Satisfaction
Teaching provides job satisfaction that resembles no other and the joy of making a distinction and making a change in the correct direction is like no other.
Teaching is a deferential job and look up to teachers for work. They guide and direct students and also they inspire and shape future generations.
Potential for Growth
It is a clear career path with a lot of opportunities and with online teaching apps and virtual classrooms on the rise you can teach from the comfort of your home and without any geographical restrictions.
Role of a Teacher
While writing an essay on teaching as a profession, the role of a teacher must be included. Teachers should find different ways to teach students and apply them in teaching so that the maximum information and knowledge reach the students.
Teaching as profession involves not just for teaching the syllabus but also for inspiring students by exchanging thoughts, sharing a bond, and being with them in every up and down.
Teaching profession essay often highlights how teachers impact students’ overall development through their skills, knowledge, personality, and teaching methods. It helps teachers to become successful teachers and mentors for their students.
Teaching essay topics often explore the complexity of the teacher’s role, covering everything from subject mastery to emotional guidance. Many discussions around what is teaching profession emphasize that it goes beyond academics—it is about shaping minds.
Academic Path For A Teacher
To pursue teaching as a profession, you can follow some of the below-mentioned ways:
Nursery Teacher
To become a teacher of pre-primary, you should complete your 12th and pursue a Nursery Teacher Training (NTT) course of 1-year duration. You can also go for a Kindergarten Training Program or a Montessori Teacher Training program for about 9 months to 1 year. Even after completing graduation, you can opt for these courses. With the right qualifications and skills, you can try your career in teaching.
Also, by pursuing the child development program of Anganwadi Workers (AWW) – Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), you can begin your career as a teacher in Anganwadi. Many essays about teaching profession emphasize the significance of early childhood educators.
Primary School Teacher
In the primary section of teaching, you can have the chance to teach students a variety of subjects and enhance the learning experience. If you want to make your career as a teacher for primary classes, then you have the following options:
The option of a Primary Teacher Training (PTT) program of a 2-year duration is also available for pursuing.
You can also take part in the Teacher Eligibility Test (TET) to get recruited as Primary School Teachers in Government schools and Government primary schools.
Secondary and Higher Secondary School Teachers
If you want to be a teacher of higher secondary classes then you can do a Master’s degree after graduation and then pursue a B.Ed. degree.
If you want to qualify as a teacher for central government-run schools, then the Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET) will be the option for you. CTET is conducted by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) for applicants to be eligible to be a teacher at the secondary and higher secondary levels.
You can also opt for the Teacher Eligibility Test (TET) or a State Level Eligibility Test (SLET) for recruiting secondary-level and higher-secondary-level teachers. Essays like “Why I Chose Teaching as a Profession Essay” often explore the challenges and rewards of teaching at this level.
College and University Teacher
If you want to teach students in colleges or universities or want to be called a lecturer in government or private colleges and universities, then follow the available options:
How to Become a College or University Teacher?
If you want to choose teaching as a career in a college or university, you must get a degree in a Master’s program.
Once you complete a Master’s degree, you can apply for the National Eligibility Test (NET) conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA). NET requires a postgraduate degree and a certification of eligibility for entrance.
It is an essay on the teaching profession that can help you on your pathway to becoming a teacher. This is a common theme in essays discussing what is teaching profession in higher education.
Characteristics of Teaching
However, many teachers teach in schools/academies/Institutions or colleges, yet not all may prevail with regards to being great teachers for students. So, what are the characteristics of the Teaching Profession that make teachers more successful in the classroom?
Those who enjoy investing energy with youngsters and will make others educated with their abilities can choose Teaching as a Profession. Is Teaching a Profession that requires special qualities? Yes, it is! The Importance of Teaching Profession cannot be overstated, as it shapes the minds of future generations. Teaching as a profession essay often discusses how these traits are essential for a fulfilling teaching career. Moreover, 20 reasons why teaching is a profession often include factors like job satisfaction, career growth, and the opportunity to inspire future generations.
To become an exemplary teacher, one may possess relevant qualities like creating a dynamic environment, being adaptable, and kind, classroom management, a good comical inclination, an active personality, being Innovative, calm demeanor, experience, and so on.
Teachers’ unions and teachers’ associations
In most countries, there is one major teachers’ organization to which all or nearly all teachers belong and pay duty. Sometimes participation is obligatory, sometimes voluntary.
In the former Soviet Union, where a significant part of the political and social existence of the people had been organized around unions, there were three teachers’ unions — preschool teachers, primary and secondary school teachers, and teachers in advanced education. These unions provided pensions, vacation pay, and debilitated leave pay and in this way touched the welfare of teachers at many points.
England, for example, has two distinct associations for male and female secondary school teachers, two unique associations for male and female headmasters of secondary schools, and a separate Association of Teachers in Technical Institutions.
These associations are parallel to the National Union of Teachers, which is open to any qualified teacher from nursery school to college level. The National Union has no political affiliation except for being politically powerful by its own doing.
France, in contrast, has a wide variety of teachers’ organizations, with various political leanings, however, they do not manage everything well together and are politically less successful.
In this “Teaching as a Profession Essay”, we learn the importance of teaching profession and how to explain teaching as a profession. Teaching provides a way to give back to society and teachers have so much potential in the field, that they should be given every opportunity possible to use it.
Teaching is a profession of imparting knowledge and skills to students in a way that will help them achieve their full potential and such as teaching can be an incredibly rewarding career. Teaching is one of the few professions that allow you to work with children and then retire from the same occupation while still young.
- Important Principles of Teaching
- Basic Requirements Of Teaching
- Level of Teaching – Memory, Understanding & Reflective Level
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Essay Curve
Essay on Teaching As A Profession – Short & Long Essay Examples

Essay on Teaching As A Profession: Teaching is often considered one of the noblest professions, as educators play a crucial role in shaping the minds and futures of young individuals. In this essay, we will explore the various aspects of teaching as a profession, including the responsibilities, challenges, and rewards that come with the job. From inspiring students to fostering a love of learning, teaching requires dedication, patience, and a genuine passion for helping others succeed. Join us as we delve into the world of teaching as a profession.
Table of Contents
Teaching As A Profession Essay Writing Tips
1. Start by introducing the topic of teaching as a profession and why it is important in society. You can mention the impact teachers have on shaping the future generation and the role they play in educating and inspiring students.
2. Provide a brief overview of the history of teaching as a profession, highlighting how it has evolved over the years and the increasing demands and challenges that teachers face in today’s world.
3. Discuss the qualities and skills required to be an effective teacher. This can include patience, empathy, communication skills, subject knowledge, and the ability to adapt teaching methods to meet the needs of diverse learners.
4. Explain the importance of ongoing professional development for teachers. This can include attending workshops, conferences, and pursuing advanced degrees to stay current with best practices in education.
5. Discuss the impact of technology on teaching as a profession. Highlight how teachers are incorporating technology into their lessons to enhance learning and engage students in new ways.
6. Address the challenges and rewards of being a teacher. This can include long hours, low pay, and dealing with difficult students, as well as the satisfaction of seeing students succeed and making a positive impact on their lives.
7. Provide examples of successful teachers who have made a difference in their students’ lives and in the education system. This can help illustrate the importance and value of teaching as a profession.
8. Discuss the future of teaching as a profession and how it may continue to evolve in response to changing educational trends and societal needs.
9. Conclude your essay by summarizing the key points you have discussed and reiterating the importance of teaching as a profession in shaping the future of society.
10. Remember to proofread your essay for grammar and spelling errors before submitting it. Make sure your ideas are well-organized and supported with evidence and examples to make a compelling argument for teaching as a profession.
Essay on Teaching As A Profession in 10 Lines – Examples
1. Teaching is a noble profession that involves shaping the minds of future generations. 2. Teachers play a crucial role in imparting knowledge, skills, and values to students. 3. The profession requires patience, dedication, and a passion for helping others learn. 4. Teachers must continuously adapt to new teaching methods and technologies to keep up with the changing educational landscape. 5. Effective communication and interpersonal skills are essential for building relationships with students and parents. 6. Teachers must have a deep understanding of their subject matter and be able to convey complex concepts in a way that is easily understood by students. 7. The profession offers opportunities for professional growth and development through ongoing training and education. 8. Teachers have the power to inspire and motivate students to reach their full potential. 9. The impact of a good teacher can last a lifetime, influencing students long after they have left the classroom. 10. Despite the challenges and demands of the profession, teaching can be incredibly rewarding and fulfilling for those who are passionate about education.
Sample Essay on Teaching As A Profession in 100-180 Words
Teaching is a noble profession that requires dedication, passion, and a commitment to lifelong learning. Teachers play a crucial role in shaping the minds of future generations, imparting knowledge and skills that will help students succeed in their personal and professional lives.
As a profession, teaching requires continuous professional development to stay current with best practices and educational trends. Teachers must also possess strong communication skills, empathy, and the ability to connect with students on a personal level.
Despite the challenges and demands of the profession, teaching can be incredibly rewarding. The impact that teachers have on their students can be profound, shaping their beliefs, values, and aspirations for the future.
In conclusion, teaching is not just a job, but a calling that requires a deep sense of purpose and a genuine desire to make a difference in the lives of others.
Short Essay on Teaching As A Profession in 200-500 Words
Teaching is often considered one of the noblest professions in the world. It involves shaping the minds of young individuals and preparing them for the future. Teaching is not just a job, but a calling that requires dedication, passion, and a genuine desire to make a difference in the lives of students.
One of the key aspects of teaching as a profession is the impact that teachers have on their students. Teachers play a crucial role in shaping the future of their students by imparting knowledge, instilling values, and fostering critical thinking skills. They serve as mentors, role models, and guides, helping students navigate through the challenges of academic life and beyond.
Teaching is a profession that requires continuous learning and growth. Teachers are constantly updating their knowledge and skills to keep up with the latest developments in their field. They attend workshops, conferences, and seminars to enhance their teaching techniques and strategies. They also collaborate with colleagues to share best practices and learn from each other.
Another important aspect of teaching as a profession is the sense of fulfillment that comes from seeing students succeed. Teachers take pride in the achievements of their students, whether it be academic success, personal growth, or overcoming challenges. The joy of witnessing a student’s “aha” moment or seeing them reach their full potential is a rewarding experience that keeps teachers motivated and inspired.
Teaching is also a profession that requires patience, empathy, and understanding. Teachers work with students from diverse backgrounds, abilities, and learning styles. They must be able to adapt their teaching methods to meet the needs of each individual student and create a supportive and inclusive learning environment. Teachers must also be able to handle difficult situations with grace and professionalism, such as dealing with challenging behavior or supporting students through personal struggles.
Despite the many rewards of teaching, it is also a profession that comes with its own set of challenges. Teachers often face long hours, heavy workloads, and limited resources. They must juggle multiple responsibilities, from lesson planning and grading to parent meetings and extracurricular activities. Teaching can be emotionally and physically demanding, requiring resilience, perseverance, and a strong support system.
In conclusion, teaching is a profession that requires a unique combination of skills, qualities, and dedication. It is a rewarding and fulfilling career that offers the opportunity to make a positive impact on the lives of students. While teaching may have its challenges, the joy of seeing students grow and succeed makes it all worth it. Teachers are not just educators, but mentors, advocates, and inspirations who shape the future generation.
Essay on Teaching As A Profession in 1000-1500 Words
Teaching is often regarded as one of the noblest professions in the world. It is a profession that plays a crucial role in shaping the future of individuals and society as a whole. Teachers are not just educators, but also mentors, role models, and guides who have the power to inspire and empower their students. In this essay, we will explore the various aspects of teaching as a profession and why it is considered so important.
First and foremost, teaching is a profession that requires a high level of dedication, passion, and commitment. Teachers are responsible for imparting knowledge and skills to their students, and they play a key role in helping them achieve their full potential. A good teacher is not just someone who imparts information, but also someone who inspires and motivates their students to learn and grow. Teaching requires patience, empathy, and the ability to connect with students on a personal level. It is a profession that demands constant learning and self-improvement, as teachers need to stay updated with the latest developments in their field and adapt their teaching methods to meet the needs of their students.
Teaching is also a profession that requires a high level of expertise and skill. Teachers need to have a deep understanding of their subject matter, as well as the ability to communicate complex ideas in a clear and engaging manner. They need to be able to create a positive and inclusive learning environment where all students feel valued and respected. Teachers also need to be able to assess the progress of their students and provide constructive feedback to help them improve. In addition, teachers need to be able to manage their classroom effectively, handle disciplinary issues, and work collaboratively with parents, colleagues, and other stakeholders to ensure the success of their students.
One of the most rewarding aspects of teaching is the opportunity to make a positive impact on the lives of students. Teachers have the power to inspire and empower their students, to help them discover their passions and talents, and to guide them towards a successful and fulfilling future. Teachers often form close relationships with their students, and they have the privilege of witnessing their growth and development over time. The impact of a good teacher can last a lifetime, as students carry the lessons they have learned and the values they have imbibed with them into adulthood.
Teaching is also a profession that offers a great deal of personal satisfaction and fulfillment. The joy of seeing a student grasp a difficult concept, the pride of watching them succeed in their endeavors, and the gratitude of knowing that you have made a difference in someone’s life are all rewards that come with being a teacher. Teaching is a profession that allows you to use your talents and skills to make a positive impact on the world, and it provides a sense of purpose and meaning that is hard to find in other professions.
Despite the many rewards of teaching, it is also a profession that comes with its own set of challenges and difficulties. Teachers often have to deal with large class sizes, limited resources, and diverse student populations with varying needs and abilities. They have to juggle multiple responsibilities, from lesson planning and grading to parent meetings and extracurricular activities. Teaching can be physically and emotionally demanding, and it requires a great deal of resilience and perseverance to succeed in this profession.
Another challenge that teachers face is the lack of recognition and support that they often receive. Teaching is a profession that is often undervalued and underpaid, especially in comparison to other professions that require similar levels of education and expertise. Teachers are often asked to do more with less, and they are frequently subjected to criticism and scrutiny from parents, administrators, and policymakers. Despite these challenges, however, teachers continue to do their best to provide a quality education to their students and to make a positive impact on their lives.
In conclusion, teaching is a profession that is both challenging and rewarding. It requires a high level of dedication, expertise, and skill, as well as a deep commitment to the well-being and success of students. Teachers have the power to inspire, empower, and guide their students towards a brighter future, and they play a crucial role in shaping the next generation of leaders, thinkers, and innovators. Despite the challenges that they face, teachers continue to work tirelessly to make a difference in the lives of their students and to create a better world for future generations. Teaching is not just a profession, but a calling, and those who choose to answer that call have the power to change the world for the better.
Related Essays
Essay on A Visit To A Fair – 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Value of Games And Sports – Essay in 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Essay on Importance of Teacher – 100, 200, 500, 1000 Words
Essay on A Visit To A Museum – 100, 200, 500, 1000 Words
Essay on Effect of Social Media On Youth
Essay on Shri Guru Nanak Dev Ji – Short & Long Essay Examples
Essay on Nuclear Family – Short Essay & Long Essay upto 1500 Words
Essay on Anudeep Durishetty – 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Essay on Non Violence – Samples, 10 Lines to 1500 Words
Covid 19 Responsive School – Essay in 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Our Mission
Redefining the Role of the Teacher: It’s a Multifaceted Profession
A closer look at what being an educator really means.
Imagine a school where teaching is considered to be a profession rather than a trade. The role of teachers in a child's education -- and in American culture -- has fundamentally changed. Teaching differs from the old "show-and-tell" practices as much as modern medical techniques differ from practices such as applying leeches and bloodletting.
Instruction doesn't consist primarily of lecturing to students who sit in rows at desks, dutifully listening and recording what they hear, but, rather, offers every child a rich, rewarding, and unique learning experience. The educational environment isn't confined to the classroom but, instead, extends into the home and the community and around the world. Information isn't bound primarily in books; it's available everywhere in bits and bytes.
Students aren't consumers of facts. They are active creators of knowledge. Schools aren't just brick-and-mortar structures -- they're centers of lifelong learning. And, most important, teaching is recognized as one of the most challenging and respected career choices, absolutely vital to the social, cultural, and economic health of our nation.
Today, the seeds of such a dramatic transformation in education are being planted. Prompted by massive revolutions in knowledge, information technology, and public demand for better learning, schools nationwide are slowly but surely restructuring themselves.
Leading the way are thousands of teachers who are rethinking every part of their jobs -- their relationship with students, colleagues, and the community; the tools and techniques they employ; their rights and responsibilities; the form and content of curriculum; what standards to set and how to assess whether they are being met; their preparation as teachers and their ongoing professional development; and the very structure of the schools in which they work. In short, teachers are reinventing themselves and their occupation to better serve schools and students.
New Relationships and Practices
Traditionally, teaching was a combination of information-dispensing, custodial child care and sorting out academically inclined students from others. The underlying model for schools was an education factory in which adults, paid hourly or daily wages, kept like-aged youngsters sitting still for standardized lessons and tests.
Teachers were told what, when, and how to teach. They were required to educate every student in exactly the same way and were not held responsible when many failed to learn. They were expected to teach using the same methods as past generations, and any deviation from traditional practices was discouraged by supervisors or prohibited by myriad education laws and regulations. Thus, many teachers simply stood in front of the class and delivered the same lessons year after year, growing gray and weary of not being allowed to change what they were doing.
Many teachers today, however, are encouraged to adapt and adopt new practices that acknowledge both the art and science of learning. They understand that the essence of education is a close relationship between a knowledgeable, caring adult and a secure, motivated child. They grasp that their most important role is to get to know each student as an individual in order to comprehend his or her unique needs, learning style, social and cultural background, interests, and abilities.
This attention to personal qualities is all the more important as America continues to become the most pluralistic nation on Earth. Teachers have to be committed to relating to youngsters of many cultures, including those young people who, with traditional teaching, might have dropped out -- or have been forced out -- of the education system.
Their job is to counsel students as they grow and mature -- helping them integrate their social, emotional, and intellectual growth -- so the union of these sometimes separate dimensions yields the abilities to seek, understand, and use knowledge; to make better decisions in their personal lives; and to value contributing to society.
They must be prepared and permitted to intervene at any time and in any way to make sure learning occurs. Rather than see themselves solely as masters of subject matter such as history, math, or science, teachers increasingly understand that they must also inspire a love of learning.
In practice, this new relationship between teachers and students takes the form of a different concept of instruction. Tuning in to how students really learn prompts many teachers to reject teaching that is primarily lecture based in favor of instruction that challenges students to take an active role in learning.
They no longer see their primary role as being the king or queen of the classroom, a benevolent dictator deciding what's best for the powerless underlings in their care. They've found they accomplish more if they adopt the role of educational guides, facilitators, and co-learners.
The most respected teachers have discovered how to make students passionate participants in the instructional process by providing project-based, participatory, educational adventures. They know that in order to get students to truly take responsibility for their own education, the curriculum must relate to their lives, learning activities must engage their natural curiosity, and assessments must measure real accomplishments and be an integral part of learning.
Students work harder when teachers give them a role in determining the form and content of their schooling -- helping them create their own learning plans and deciding the ways in which they will demonstrate that they have, in fact, learned what they agreed to learn.
The day-to-day job of a teacher, rather than broadcasting content, is becoming one of designing and guiding students through engaging learning opportunities. An educator's most important responsibility is to search out and construct meaningful educational experiences that allow students to solve real-world problems and show they have learned the big ideas, powerful skills, and habits of mind and heart that meet agreed-on educational standards. The result is that the abstract, inert knowledge that students used to memorize from dusty textbooks comes alive as they participate in the creation and extension of new knowledge.
New Tools and Environments
One of the most powerful forces changing teachers' and students' roles in education is new technology. The old model of instruction was predicated on information scarcity. Teachers and their books were information oracles, spreading knowledge to a population with few other ways to get it.
But today's world is awash in information from a multitude of print and electronic sources. The fundamental job of teaching is no longer to distribute facts but to help children learn how to use them by developing their abilities to think critically, solve problems, make informed judgments, and create knowledge that benefits both the students and society. Freed from the responsibility of being primary information providers, teachers have more time to spend working one-on-one or with small groups of students.
Recasting the relationship between students and teachers demands that the structure of school changes as well. Though it is still the norm in many places to isolate teachers in cinderblock rooms with age-graded pupils who rotate through classes every hour throughout a semester -- or every year, in the case of elementary school -- this paradigm is being abandoned in more and more schools that want to give teachers the time, space, and support to do their jobs.
Extended instructional periods and school days, as well as reorganized yearly schedules, are all being tried as ways to avoid chopping learning into often arbitrary chunks based on limited time. Also, rather than inflexibly group students in grades by age, many schools feature mixed-aged classes in which students spend two or more years with the same teachers.
In addition, ability groups, from which those judged less talented can rarely break free, are being challenged by a recognition that current standardized tests do not measure many abilities or take into account the different ways people learn best.
One of the most important innovations in instructional organization is team teaching, in which two or more educators share responsibility for a group of students. This means that an individual teacher no longer has to be all things to all students. This approach allows teachers to apply their strengths, interests, skills, and abilities to the greatest effect, knowing that children won't suffer from their weaknesses, because there's someone with a different set of abilities to back them up.
To truly professionalize teaching, in fact, we need to further differentiate the roles a teacher might fill. Just as a good law firm has a mix of associates, junior partners, and senior partners, schools should have a greater mix of teachers who have appropriate levels of responsibility based on their abilities and experience levels. Also, just as much of a lawyer's work occurs outside the courtroom, so, too, should we recognize that much of a teacher's work is done outside the classroom.
New Professional Responsibilities
Aside from rethinking their primary responsibility as directors of student learning, teachers are also taking on other roles in schools and in their profession. They are working with colleagues, family members, politicians, academics, community members, employers, and others to set clear and obtainable standards for the knowledge, skills, and values we should expect America's children to acquire. They are participating in day-to-day decision making in schools, working side-by-side to set priorities, and dealing with organizational problems that affect their students' learning.
Many teachers also spend time researching various questions of educational effectiveness that expand the understanding of the dynamics of learning. And more teachers are spending time mentoring new members of their profession, making sure that education school graduates are truly ready for the complex challenges of today's classrooms.
Reinventing the role of teachers inside and outside the classroom can result in significantly better schools and better-educated students. But though the roots of such improvement are taking hold in today's schools, they need continued nurturing to grow and truly transform America's learning landscape. The rest of us -- politicians and parents, superintendents and school board members, employers and education school faculty -- must also be willing to rethink our roles in education to give teachers the support, freedom, and trust they need to do the essential job of educating our children.
Judith Taack Lanier is a distinguished professor of education at Michigan State University.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1: The Teaching Profession
Unlearning Box
“Those who can, do. Those who can’t, teach.”
“It’s easy to become a teacher.”
“Teaching is an 8:30-3:00 job. You have it so easy!”
You may have heard people in your own life share quotes and comments such as these. These quotes are hurtful and untrue. Teaching is a profession. Teachers are capable, intelligent, and held to extremely high professional standards. Quotes and comments like these demonstrate gross misunderstandings of what it means to be a teacher in the United States.
In this chapter, we will begin to peer behind the scenes of what it means to be a teacher in the United States. We’ll walk through a day in the life of a teacher, break down what is involved to become a teacher, and close with characteristics of effective teachers.
Chapter Outline
Elementary perspective, secondary perspective, special education perspective, profile of teachers today, undergraduate degree program, graduate degree program, accreditation of epps, provisional certification, residency programs.
- Maintaining a Teaching License
InTASC Standards
Professionalism & dispositions, teacher beliefs, a day in the life.
To get started, let’s drop into three different classrooms to get a feel for a day in the life of an elementary teacher, a secondary (high school) teacher, and a special education teacher.
The school doors open at 7 AM, and you greet children as they enter the cafeteria for breakfast. Once morning duty is over, you hurry to your classroom to await the 25 students that will come filing in momentarily. You make sure materials and directions for tasks are ready and calming music is playing. As students enter, you gather signed forms and respond to notes from families, help students with their morning activities, take attendance, and hold a morning meeting. The rest of the day, you are simultaneously teaching the content areas–English, math, science and social studies–and social skills as students navigate groupwork and friendships. Various other educators drop in throughout the day: the reading specialist to work with a group of readers who need extra support, the occupational therapist to help a student with some motor skills still developing, the speech pathologist to help students with articulation and language development, the instructional coach and sometimes the principal to give you feedback on your instruction.

Pauses throughout the day from the busy pace of classroom life include related arts, where students go to learn about music, visual art, library, P.E., and more while you meet with your grade level for team planning; and lunch and recess, which involve scarfing down your lunch while getting your students through the lunch line, figuring out who changed their lunch choice or left their lunch at home, opening mustard packets, reminding students to eat while they talk with friends, and hopefully scuttling off to check your school mailbox and take a bathroom break. After a post-recess water break, you return to classroom instruction, with a few interruptions for students leaving early for doctor’s appointments, a student needing to go to the nurse’s office, another teacher popping in to borrow a book, or sometimes even a whole-school assembly for a class play or anti-bullying program.
When it is time to pack up for the day at 2:30, you make sure all students know how they are getting home that day, have their materials packed and ready to go, and then you bid them farewell at the door with a hug, high-five, or handshake as they head to their dismissal area. Once your room is empty, you go to monitor a dismissal area to make sure everyone is safe. After school, you might have a faculty meeting, a debrief with an instructional coach based on today’s observation, or time to prepare tomorrow’s instructional materials. You marvel at how quickly yet another day has passed in the life of an elementary school teacher.
The bell rings at 8:15 AM, but you’ve already been at school for more than an hour–making copies, checking emails, and writing the plans and goals for the day on the board. As an English teacher, you’ve decided to work on writing fluency during this year, so as the students enter the classroom, they take out their journals and begin responding to the prompt on the board. Every day the class meets, the students will write for five minutes and then briefly discuss their responses with each other and as a whole group. You write alongside them to model what it looks like, and often share your own writing–at the beginning of the year, most of the students struggled to write for five straight minutes, but now nearly all of them have gotten the hang of it. The rest of the lesson involves a minilesson on figurative language, small group discussions about students’ literature circle books, and a whole group review game to prepare for the unit test on Wednesday.
The school adopted a block schedule last year, so your classes are 75 minutes long. You teach three of four blocks each day; today is an A day, so first block is 9th grade honors and the other two are 10th grade general English. Tomorrow, you will teach two blocks of 9th grade general and one block of 10th grade College Preparatory English. You hate these labels and what they do to the students in the room, and, as department chair, you have been working with your principal to remove such rigid tracking.

“Bear Block” falls between 1st and 2nd block, and ten students stream into the room to retake tests, make up missed homework, or just hang out and read. You glance at the learning management system and see that there are 45 essays waiting for you, but there won’t be time to look more closely at them until later tonight. During lunch, some of your journalism club students are in the room, partially working on stories and layouts, but mostly sharing the latest news about their friends and acquaintances.
For the Professional Learning Community (PLC) meeting during fourth block, you will meet with the other 10th grade English teachers to look at the results of a common assessment. At some schools in the district, the grade-level teachers all teach the same lessons, but luckily at this school you have more freedom in how you teach the material. There is a new teacher on the team who is struggling with classroom management, so the first 15 minutes of the meeting is spent discussing some strategies that have worked in other teachers’ rooms.
The end of the day comes at 3:15 PM, but it will be another hour or two before you head home–there are sub plans to finish for Thursday because you will be attending a district-wide training for working with English Language Learners, and you are hoping to send at least ten texts and emails to parents. The initial fear of parent contact faded quickly, and now it’s one of your strengths–you reach out early and often, connecting with families around student successes first. Later, if students begin struggling, contact is much more seamless. It’s been a long, exhausting day, but interacting with the students has made it all worth it.
You arrive early in the morning, an hour or so before teachers officially start the school day. You greet the office manager, principal, and custodian on the way to your classroom. Aside from these three, the building will be mostly empty for another half hour. You’ve found that this quiet morning time provides the best opportunity to catch up on Individualized Education Plan (IEP) paperwork, reflect on student data from the prior day, and make adjustments to instruction for the coming day. As the official start time for the school day draws close, you make a quick dash to the copy machine, fingers crossed that it isn’t broken and that there isn’t a line of teachers anxiously waiting their turn. It’s your lucky day. Your last photocopies shoot out of the machine just as the overhead announcement calls teachers to report to their morning duty stations. You quickly drop the copies off in your classroom, pick up your data binder, and dash out the door to the bus loop.
The bus loop is a flurry of activity. You greet students with high-fives, occasional hugs, and countless reminders to “use walking feet.” Amid all of these informal greetings, you are slipping in some IEP services by completing morning check-ins with several students who have behavioral or social-emotional goals on their IEPs. From an outsider’s view, these check-ins don’t look that different from your interactions with any other student. However, intermixed with those high-fives and hugs you quietly assess needs, remind students of the goals they are working on, offer supports where needed, and quickly make notes in your data binder. On this particular day, a third grader with autism reports that he is feeling like “a category 3 hurricane.” You know he needs some quiet time before joining his homeroom class, so you walk him to the computer lab where he has an open invitation to help the instructional technology specialist get the computer lab set up for the day.
The halls begin to clear as the instructional day begins. You spend the next six hours in constant motion, serving 18 students across four grade levels. You transition between co-teaching in general education classes and pulling small groups of students to your own classroom for intensive intervention in literacy, math, or social skills. When co-teaching, your job is to supplement the general education teacher’s deep knowledge of grade-level content with specialized instructional strategies that make content meaningful and accessible for students with disabilities and other learning differences. When providing intensive intervention, you implement research-based programs that target specific skills identified in your students’ IEPs. Data collection is on-going and individualized for each student, so your trusty data binder is by your side in all settings.
Normally, you would end the school day completing check-outs with the same students you saw in the morning. Today, you assign that responsibility to a teaching assistant so you can participate in a special education eligibility meeting. It is the initial eligibility meeting for this student and her family. A team of educators work with the parents to determine if the first grader has a disability and needs special education. Her parents feel overwhelmed by the process and fearful when the team concludes that their daughter has an intellectual disability. This is a moment when your job and your passion meet. You assure the parents that the future is bright for their daughter, that the educational label does not change who she is or who she will be, and that you will highlight her strengths and address her needs as you plan her education with them as equal partners. The decisions that you will make with this family are new to them, but for you they are a familiar and important part of your day as an elementary special education teacher.
Becoming a Teacher
The scenarios above describe some typical teaching days, but not all days are the same in teaching. In fact, each one will be different in some way. Deciding to become a teacher is an exciting commitment to shaping the future, and it is both demanding and rewarding. We’ll take a look at the profile of teachers today in the United States, and then discuss various routes toward earning the credentials necessary to become a classroom teacher.
The National Center for Educational Statistics (NCES) collects data on various aspects of education, one of which is the demographics of teachers and students. In the 2017-2018 school year, there were 3.5 million full- or part-time public school K-12 teachers ( NCES, 2020a ). (K-12 means the range of grades public schools serve, starting with kindergarten in elementary school and culminating with 12th grade in high school.) Of those teachers, 76% were female [1] , 79% were White, 90% held a standard teaching license (more on that below), and 58% had earned a graduate degree (at the master’s level or beyond). A majority of teachers were in the middle of their careers, with 40% having ten to twenty years of experience in the classroom. The average salary of a full-time public school teacher was $57,900, with the average first-year teacher earning $44,200. (Note that salaries vary based on years of experience, highest degree earned, and location.)
Stop & Investigate
Check out the demographics of teachers in your state or school district. How do they compare? Find the salary scale for teachers in your local school district. How does it compare?
Let’s revisit some of those demographics on racial diversity. Figure 1.1 depicts specific racial categories of public school teachers in the 2017-2018 school year, compared with the 1999-2000 school year.
Figure 1.1: Racial Demographics of U.S. Public School Teachers, 1999-2000 and 2017-2018

Note: Data for teachers who identified as Asian, Pacific Islander, and two or more races in 1999-2000 was unavailable. The 2017-2018 data for teachers who identified as Pacific Islander rounded down to 0.
The trends are clear: in the United States, we lack a racially diverse teaching force, and that trend has not changed much in the past 20 years. While the 2017-2018 school year included more Hispanic, Asian, and multi-racial teachers, teachers are still overwhelmingly White. In the same school year, however, students who attended public schools were only 44% White ( NCES, 2020b ). That means that generally, there are more White teachers and more students of color ( Geiger, 2018 ). This trend is concerning, given that research shows that having teachers of color benefits all students, not just students of color ( Wells, Fox, & Cordova-Cobo, 2016 ).

There are many reasons why teachers in the United States are not racially diverse. While the U.S. Supreme Court’s 1954 decision in Brown v. Board of Education (further explained in Chapters 3 and 5 ) demanded all schools integrate to address some of the inequalities between separate schools for White and Black students, it did have other consequences that directly impacted the diversity of teachers in the United States. This case caused 38,000 Black teachers (about one-third of the Black teachers in the country) to lose their jobs in the years following the case (Milner & Howard, 2004; Thompson, 2019 ). Even though this historical antecedent did limit access to teaching jobs for Black people, racial discrimination in the hiring process continues to compound this issue. D’Amico et al. (2017) found that despite equally-qualified candidates applying for jobs in one large school district, White teacher candidates still received a disproportionate number of job offers: of the 70% White applicants, 77% received job offers, while of the 13% Black candidates, 6% received job offers (D’Amico, Pawlewicz, Earley, & McGeehan, 2017; Klein, 2017 ). Beyond the hiring process, retention of hired teachers is lower for teachers of color than for White teachers. For example, between the 2011-2012 and 2012-2013 school years, only 15% of White teachers left their jobs, compared to 22% of Black teachers and 21% of Hispanic teachers ( U.S. Department of Education, 2016 ).
Critical Lens: Naming Races
You may have noticed in this section that races are capitalized (like White and Black). Capitalizing these names recognizes the people more than the color. In fact, the Associated Press recently changed its writing style guide [2] to capitalize Black and Indigenous when referring to racial categories.
Pathways Toward Teacher Certification
High-quality, well-prepared educators are the foundation of our educational system. Well-prepared teachers are more effective in the classroom and also tend to have higher rates of retention, meaning they choose to stay in the teaching profession (Darling-Hammond, 2010). There are several different ways that you can become a teacher, depending on where you are in your life and career. These pathways toward teacher certification fall into two general categories: traditional or alternative preparation. Traditional preparation involves an undergraduate or graduate degree program affiliated with an Educator Preparation Program (EPP) , while alternative preparation can take many forms, including provisional certification or residency programs like Teach for America. No matter how you obtain your teaching license , you will have to renew the license periodically.
Traditional Preparation: Educator Preparation Program (EPP)
The most traditional way to earn your teaching certificate is through an Educator Preparation Program (EPP). An EPP could offer a few different programs that would culminate in your teaching certificate. Two popular options are an undergraduate degree program or a graduate degree program.
In this pathway toward teacher certification, participants enter a 4-year degree program knowing that they want to become a teacher upon graduation. Exact majors vary: sometimes you might major in education, or in a specific form of education (like elementary education). If you want to teach elementary school, you are expected to be more of a generalist: you will likely teach all content areas to your students. Therefore, you will take education classes in all of these areas. If you want to teach middle or high school or become a related arts teacher (arts, language, etc.), you will major in your future area of specialization, such as history if you want to teach social studies, or music if you want to be a music teacher. Regardless of the exact structure of the specific program, participants take classes that help them learn about pedagogy (the art and science of teaching), along with specific methods of instruction (such as how to teach the structures of different disciplines like literacy, math, science, or social studies).
Completing coursework is just one part of becoming a teacher in a traditional undergraduate degree program. There are also tests that future teachers must pass to prove they are prepared to teach. Some of these tests occur early in the degree as entrance requirements to an education program to assess basic literacy and math skills; some of these tests occur at the end of the degree as a culmination of all courses. These tests, run by ETS, are called Praxis tests. Their website [3] has information about testing requirements in different states.
Critical Lens: Bias in Standardized Assessments
While standardized assessments have been associated with measuring intelligence and learning for many years, some schools are moving away from relying solely on standardized tests as a measure of aptitude. You or someone you know might not be a great test taker, and you may have experienced first-hand (or second-hand through an acquaintance) how standardized tests aren’t always a reliable measure of what you know. Beyond test anxiety, standardized tests also tend to be culturally biased. That means that some cultural norms are assumed to be shared by all test takers, but this isn’t necessarily the case. A passage in a reading assessment, for example, might assume that a test-taker can build on background knowledge of certain experiences, like going camping, that they haven’t had, or use vocabulary words that are more common in middle-class White households. Another standardized test of intelligence, the IQ test [4] , was used early on by eugenicists to argue that White test-takers scored higher because they were the smarter race, using questionable statistical analyses and overlooking that the tests were written to benefit White test-takers. However, these standardized tests were often used to choose “highly qualified” candidates for jobs such as military leaders, therefore limiting access to certain professions based on race and socioeconomic status.

One of the most important parts of preparing to become a teacher is getting practice working in actual classrooms with actual students. In a traditional undergraduate degree program, you will engage in two different types of field placements. The first types of field placements are sometimes called practicum , which are part-time placements that are often tied to specific courses (like methods classes, where you learn about how to teach specific content areas like language arts, math, science, or social studies). You attend practicum a few hours a week in between your other coursework. In these practicum placements, you get to try out what you are learning in class with actual classrooms, teachers, and students. Sometimes you are observing to learn more; other times you are actively leading instruction in one-on-one, small group, or whole group settings. Your various practicum placements typically will be in different schools and different grade levels to give you experience working with many different types of students and teachers. The second type of field placement is called student teaching or an internship . This full-time placement occurs at the very end of your degree program. You spend all day, every day at your placement, just like the classroom teacher does. As the semester progresses, you will take on more and more responsibility for planning and teaching. By the middle of the semester, you will usually be responsible for all of the planning and teaching for all content areas for several weeks. After those few weeks, you begin passing the instructional responsibilities back to the classroom teacher. Both practicum and student teaching will require you to work closely with the classroom teacher, who may be called your mentor teacher . Neither type of field placement is an official job, so you should not expect to be paid for these experiences.
After you have completed all of your undergraduate coursework, your field placement hours, and your state’s required testing, you will earn your teaching certificate and be ready to apply for your first teaching job.
The first graduate, or post-baccalaureate, degree programs were developed in the 1970s as Masters of Arts in Teaching (MAT) programs (Darling-Hammond, 2010). A post-baccalaureate degree program is designed for people who want to become teachers, but who have already completed their undergraduate coursework in a field other than education. Therefore, a post-baccalaureate degree program allows people to learn how to become teachers while earning a master’s degree. In a post-baccalaureate degree program, courses are often offered in the evenings to cater to the needs of adult students who may be working or have family commitments during the day. Even though its structure is a little different, a post-baccalaureate degree program also has the field experiences explained above (practicum and internship).
After you have completed all of your post-baccalaureate coursework, your field placement hours, and your state’s required testing, you will earn your teaching certificate and be ready to apply for your first teaching job. The master’s degree you will earn in a post-baccalaureate program can result in higher pay for teachers in some states. (Even if you earn your teaching credential in an undergraduate program, you can still earn a master’s degree in education and get a pay increase in many states.)
Research has shown that teachers who earn their teaching certificate through an educator preparation program (EPP) feel significantly more prepared to meet their students’ needs than those that pursue other routes toward licensure (i.e., Darling-Hammond, Chung, & Frelow, 2002). One reason for this finding lies in the high standards that EPPs must meet. EPPs must be accredited by either state or national agencies. Accreditation means that the programs have met specific standards of high-quality teacher preparation programs.
The first national credentialing agency was the National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE), which was founded in 1954. By 2016, NCATE was replaced by CAEP (pronounced “cape”), which stands for the Council for the Accreditation of Educator Preparation. In their mission, they state: “CAEP advances equity and excellence in educator preparation through evidence-based accreditation that assures quality and supports continuous improvement to strengthen P-12 student learning” ( CAEP, 2020b , “Mission”). To receive CAEP accreditation, EPPs have to demonstrate evidence of their success in five areas, or standards [5] : (1) content and pedagogical knowledge; (2) clinical partnerships and practice; (3) candidate quality, recruitment, and selectivity; (4) program impact; and (5) provider quality, continuous improvement, and capacity. When you enroll in an EPP with CAEP or state-level accreditation, you know you are in a high-quality program that has provided evidence of meeting rigorous standards to prepare teachers.
Alternative Preparation
Sometimes, you decide to become a teacher after you have already earned an undergraduate degree in another field. Perhaps you’ve even worked in another field for several years, and you realize that you would like to become a teacher instead. While each state has different policies and programs for preparing teachers beyond undergraduate coursework, a few common approaches include provisional certification and residency programs like Teach for America.
Some schools face shortages of teachers in certain content areas or in more urban settings, which mean they need teachers as soon as possible–even if those teachers aren’t officially certified just yet. A provisional teaching license allows an individual to become a teacher temporarily, while they work with their employer to arrange to meet the requirements of earning a teaching license (such as taking the required Praxis tests). These licenses might be valid for a period of time ranging from one to three years and typically are not renewable, meaning that if you do not meet the licensure requirements before your certificate expires, you will not be able to continue teaching. Sometimes provisional certification is also called emergency certification, since it is designed to meet an immediate need.
Residency programs are another alternative pathway to receive a teaching credential. Typical participants in a residency model already have a bachelor’s degree prior to beginning a residency program. During the residency program, future teachers work simultaneously on a master’s degree in education while being placed in a school full-time. Typically residents do not serve as the teacher of record in the classroom, meaning they are not solely responsible for all instruction. Residency programs are particularly popular in high-needs areas where there is high teacher turnover and recruitment and retainment of teachers is challenging, such as urban centers. Some critiques of residency programs center on the short-term, intense nature of the experience: while a traditional undergraduate pathway toward a teaching credential takes around four years, a residency may last only one year, with the field experience occurring concurrently with coursework ( NYU Steinhardt, 2018 ).
Teach for America (TFA) is one well-known residency program. TFA recruits from undergraduate completers, mostly from programs other than education, to complete intensive training in the summer immediately following their graduation and prior to assuming their teaching position. Teach for America places candidates in higher-needs areas, while incentivizing the program by offering candidates a free master’s degree in education while they complete two years of teaching in the program. However, fast-tracked, alternative certification programs like Teach for America do tend to have lower rates of retention ( Hegarty, 2001 ). Retention refers to how long teachers stay in the field of education. Higher retention rates lead to higher-quality teachers, since you will keep growing in your competency as a teacher the longer you stay in the profession. Therefore, some alternative certification programs like Teach for America receive critiques for their short-term placement of teachers in schools for a couple of years instead of long-term teaching careers.
Maintaining A Teaching License
Once you have earned an initial teaching license, you will be able to teach for a period of time before you have to renew it. Usually, you will have to renew your license every three or five years; each state sets their own regulations, and different licenses sometimes have different timespans. Renewing your teaching license is important because teaching and learning are constantly changing and evolving, and you will best serve your students by being up-to-date on the latest information. You can earn renewal credits in a variety of ways, including taking graduate courses, attending conferences, attending professional development opportunities offered in your district and beyond, and more. The year your license will expire, you will have to submit a request to renew your license to your state Department of Education, including evidence of how you met your continuing education requirements. You cannot be a teacher with an expired license, so it is important that you remember to keep your teaching license current.
Each state has their own policies for becoming a teacher, so what happens if you earn a teaching license in one state and then have to move to another state? Many state Departments of Education have reciprocity with other states, meaning that your license could be transferred to a new state without having to start over completely. You might have to meet a few additional requirements unique to your new state, such as Praxis tests, but you don’t have to go back to school to get another degree in education. Learn more about reciprocity from the Education Commission of the States [6] , including a state-by-state comparison of reciprocity conditions [7] .
Look up the licensure and reciprocity policies for your state. Here is Virginia’s licensure website [8] . What do you notice about your state’s policies?
Characteristics of Effective Teachers
First of all, what does it mean to be an effective teacher? Effectiveness can be hard to define. Some ways to measure effectiveness include student achievement, such as test scores; performance ratings from supervisors, like administration members observing a lesson; or informal feedback in the form of comments from students or other stakeholders. Defining effectiveness is further complicated by the reality that there are many variables that a teacher cannot control that still impact these various measures ( Stronge, 2018 ).
Pause & Ponder
Who was a teacher who positively influenced your life? What did they do that left this impact? Was it how they approached instruction, interacted with you as a person inside or outside of school, or facilitated an extracurricular club? Now, think about a teacher who negatively affected you. What did they do that caused you to have a less than desirable experience?
As you yourself have experienced as a learner, there are certain characteristics that effective teachers share. Even though all teachers have distinct personalities and instructional approaches that they bring to the classroom–since teachers, like students, are still individual people–here are some practices that effective teachers have in common.
Over the span of 15 years, Walker ( 2008 ) asked college students what made effective teachers in their own experiences and found twelve recurring characteristics.

- Prepared. Effective teachers were ready to teach every day and used time efficiently.
- Positive. Effective teachers were optimistic about their jobs and their students.
- Hold high expectations. Effective teachers believe everyone can succeed and challenge students to do their best.
- Creative. Effective teachers come up with new, innovative ideas to teach content.
- Fair. Effective teachers establish clear requirements for assignments, give everyone what they need to succeed, and recognize that learners are unique.
- Display a personal touch. Effective teachers connect with students by sharing stories about themselves and participating in their students’ worlds, like going to a performance or sporting event.
- Cultivate a sense of belonging. Effective teachers make students feel welcomed and safe in the classroom.
- Compassionate. Effective teachers are sensitive and empathetic to students’ situations.
- Have a sense of humor. Effective teachers bring humor into the classroom, but never at a student’s expense (i.e., laugh with, not at, students).
- Respect students. Effective teachers maintain privacy and don’t embarrass students in front of the class.
- Forgiving. Effective teachers don’t give up on students and start each day without holding grudges about how previous days have gone.
- Admit mistakes. Effective teachers apologize when they make mistakes and make adjustments accordingly.
In addition to these personal qualities, there are specific ways to structure learning that are more effective than others. Creemers and Kryiakides (2006) called this the “dynamic model of educational effectiveness.” The dynamic model focuses more on teaching and learning than other factors that are beyond the teacher’s control in the classroom. Eight factors that tend to have an impact on student learning are explained in Table 1.1 (adapted from Muijs et al., 2014 ).
Table 1.1: Eight Factors that Impact Student Learning (Muijs et al., 2014)
| Orientation | |
| Structuring | |
| Questioning | , discussed in ) |
| Teaching modeling | |
| Application | |
| The classroom as a learning environment | |
| Management of time | |
| Assessment |
As you can see, while we all bring our own personalities to our own classrooms and instruction, there are some practices that have consistently impacted student learning. We will continue discussing those specific practices throughout the rest of this book, and you will continue honing those skills as you continue on your pathway toward becoming a teacher.
Common characteristics of effective teachers can be found in ten InTASC standards . A nonpartisan, nationwide group of public officials with leadership positions in U.S. K-12 education called the Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO) created a subgroup called the Interstate Teacher Assessment and Support Consortium (InTASC). InTASC created a list of ten standards that cover model core teaching practices that high-quality K-12 teachers should be able to demonstrate as effective teachers. These standards were originally released in 1992 to guide early-career teachers, but the group realized that these characteristics were actually applicable to all teachers. Therefore, in 2011, InTASC revised the standards and expanded them to all teachers. Table 1.2 breaks down the 10 standards into the four overarching categories.
Table 1.2: InTASC Standards by Categories
| This category recognizes that before we can teach, we must understand our learners. |
| This category focuses on the depth of knowledge teachers need to possess in their corresponding content areas in order to support students in their accurate learning of content. |
| After mastering the content knowledge itself, effective teachers need to understand how to deliver instruction by weaving together assessment, planning, and instructional strategies. |
| In this category, a teacher’s role as a life-long learner is the focus. Learning can occur through professional development (like trainings and classes), reflection, taking on leadership roles, and collaborating with various stakeholders. |
The last category of InTASC standards focuses on professionalism. Teachers are held to very high standards as professionals because of their influence on shaping students’ learning, outlook, and futures. Teachers are expected to be role models, both within and beyond the classroom. Therefore, there are certain interpersonal skills–sometimes called dispositions –that teachers are expected to demonstrate as professionals.
In your own experience as a student, what are some behaviors or actions you have observed from teachers that made you respect them or lose respect for them? How will this impact how you practice professionalism in your future classroom?
A challenge related to dispositions is that research has not yet established an exact set of non-academic qualities that teachers need to demonstrate in order to be successful ( CAEP, 2020a ). Therefore, expectations of which dispositions should be observed will vary. Overall, here are a few examples of dispositions that you should possess as a future teacher.
- Communication. You will be expected to demonstrate mastery of oral and written communication with a variety of stakeholders, including students, co-workers, administration, and families. Communication should be respectful and positive, and teachers are often expected to demonstrate mastery of conventions of standardized English.
- Professional image. Related to communication, you are expected to portray a professional image in words and actions. You will be expected to dress professionally. You will be expected to avoid documentation of overly reckless behavior, such as photos on social media of drinking to excess at a party. As a teacher, you are a representative of your school district, and you are expected to maintain that professionalism within and beyond the classroom.
- Organization. While there is no one “correct” way to be organized, you will be expected to manage your time, complete tasks by deadlines, and show up to work on time. You will also need to be able to organize student records (including assessments) and return assignments to students in a timely manner.
- Collaboration. You will be expected to collaborate with a variety of stakeholders, including students, co-workers, administration, and families. Many times, you will be interacting with people whose backgrounds differ from your own, and it is very important that you respect the contributions of others, even if you would not approach a situation in exactly the same way.
- Reflection. You will be expected to reflect on your instructional practice and adjust your next steps accordingly. Rarely does an instructional activity go perfectly, and that’s OK! Teachers must be able to reflect on what went well and what to change going forward.
Critical Lens: Linguicism
You’re heard of lots of -isms: racism, sexism, classism. What about linguicism? Fain (2008) cites Skutnabb-Kangas (1988) to define linguicism as “unequal treatment of languages based upon power structures that privilege certain languages as having legitimacy” (p. 205). People often assume that “Standard English” is right and everything else is not (Wheeler & Swords, 2006). Standardized English received this position as a “prestige dialect” (Wheeler & Swords, 2006) about 500 years ago, when the self-declared “superior” Europeans came to the Americas and began interacting with the so-called “inferior” native people. Linguistic discrimination, therefore, is a result of the “racist project of colonialism” (Otto, 2004, p. 3). Linguicism can be applied to languages, such as Spanish, or dialects, such as African American Language or Southern English. As Wheeler and Swords (2006) remind us, “while language varieties clearly differ, difference does not signal deficit” (p. 14). (Note: We use the term “Standarized English” instead of “Standard English” to highlight the artificial construction of one language as the “standard” and all others as “substandard” [Wheeler & Swords, 2006].)
Many of these dispositions and expressions of professionalism are culturally bound. For example, tattoos may need to be covered in some school districts, while others do not mind if age-appropriate tattoos are visible. It is important to know the expectations within your local context so that you can act accordingly. In Chapter 5 , we will discuss more about your legal and ethical protections and expectations as a teacher.
Explore the purple “Critical Disposition” boxes in the InTASC standards document [9] (starting on p. 12). What trends do you see? What will this mean for your future classroom?

In the teaching profession, it is also important to be aware of our beliefs. Awareness of our own beliefs can be particularly challenging because sometimes we are socialized into certain beliefs and do not even realize we hold them until we meet someone who holds different beliefs. Furthermore, in education, “Whiteness is the invisible norm” (Derman-Sparks & Ramsey, 2006, p. 35). As we established earlier in this chapter, most teachers in the United States identify as White. That means that the majority of teachers share certain aspects of mainstream cultural backgrounds and bring them into their schools and classrooms, often teaching next door to other teachers who share those same mainstream cultural backgrounds. That is how one cultural background can become the invisible norm.
We teach who we are. We bring our identities into our classrooms on a daily basis, just like our students do. Who we are involves many different facets of our identity, called intersectionality . Legal scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw ( 1989 ) invented the term “intersectionality,” and it has since been applied in varied contexts, including education. The idea behind intersectionality is that many different aspects of our identity–including characteristics such as race, economic class, gender, and more–overlap and “intersect” with one another. Our identities–and our students’ identities–are greater than any one isolated characteristic. In this short video, Kimberlé Crenshaw explains intersectionality and its impact in educational settings.
Where do some of your identities lie in this diagram of intersectionality? Which groups within each characteristic tend to have the most power? (For example, which racial groups tend to be the most empowered or disempowered?) What other characteristics would you add to this diagram?

As human beings, we have a natural desire to belong in order to survive. This drive to survive results in our grouping people–both consciously and unconsciously–based on their similarities or differences to us. Unfortunately, those same survival skills mean that we may think less of people who are different from us. We may think they aren’t as smart, or aren’t as good at what they do, or don’t do things the “right” way (the way we do them). Judging or evaluating another culture based on your own culture is called ethnocentrism . If we aren’t careful, we can let ethnocentrism interfere with our professionalism as teachers. We might think a student is less capable of success in our classrooms or beyond based on our own cultural beliefs about certain characteristics. Sometimes we assume people from certain racial, socioeconomic, ability, and other demographic groups are less capable, simply because of our own expectations or cultures. We might consciously or unconsciously believe certain stereotypes –sweeping, oversimplified generalizations about a group–and those stereotypes will filter into our interactions with our students, our expectations of our students, and our teaching in general. As Gorski (2013) reminds us, “no amount of resources or pedagogical strategies will help us to provide the best opportunity for low-income students to reach their full potential as learners if we do not attend first to the stereotypes, biases, and assumptions we have about them and their families” (p. 69).
Therefore, an important aspect of being an effective teacher is knowing yourself. Freire (1973) discussed the importance of critical consciousness, the ability to see beyond one’s own limited realm of experiences. Members of mainstream groups must be especially aware of their identities and how these identities impact their teaching (Gay, 2010; Harro, 2000).
In this chapter, we surveyed the teaching profession in the context of the United States. You learned that teachers today are mostly White females with 10-20 years of experience in the classroom. Pathways toward preparing high-quality teachers can be traditional, such as earning an undergraduate or graduate degree in education, or alternative, such as provisional certification or residency programs like Teach for America. No matter how you earn your initial teaching license, you will need to renew it periodically. Finally, the teaching profession depends on characteristics of effective teachers. InTASC standards remind us of ten common characteristics of effective teachers across four domains, and dispositions relate to our general professional demeanor as teachers. Additionally, we must be aware of our beliefs and how they consciously and unconsciously contribute to our instruction. In the rest of this book, we will continue to explore the complexities of the teaching profession.
- The demographics from NCES are only broken down by male/female. ↵
- https://apnews.com/71386b46dbff8190e71493a763e8f45a?utm_campaign=SocialFlow&utm_source=Twitter&utm_medium=AP ↵
- https://www.ets.org/praxis ↵
- https://www.businessinsider.com/iq-tests-dark-history-finally-being-used-for-good-2017-10#:~:text=The%20first%20of%20these%20tests,basis%20for%20modern%20IQ%20testing. ↵
- http://caepnet.org/standards/introduction ↵
- https://www.ecs.org/50-state-comparison-teacher-license-reciprocity/ ↵
- https://c0arw235.caspio.com/dp/b7f93000c5143bf0c78540a0bfa4 ↵
- https://www.doe.virginia.gov/teaching/licensure/index.shtml ↵
- https://ccsso.org/sites/default/files/2017-11/InTASC_Model_Core_Teaching_Standards_2011.pdf ↵
Abbreviation for kindergarten through 12th grade, the traditional span of public schools in the United States.
Landmark Supreme Court case in 1954 that declared separate educational facilities were not equal, ending segregation in schools.
One way to earn a teaching license through completing coursework at an Educator Preparation Program (EPP).
Programs offered through colleges or universities to earn teaching credentials.
Pathway toward earning teaching certification that does not involve undergraduate coursework and might involve residency programs or provisional certification.
Earned after meeting state-established requirements (such as courses and testing) in order to become a teacher. Requires periodic renewal.
Term referring to teachers in areas like music, visual arts, drama, etc.
The art and science of teaching.
How to teach the structures of different disciplines like literacy, math, science, or social studies.
Series of teacher certification tests offered by ETS.
Part-time field placements that are often tied to specific courses to give preservice teachers experience in classrooms.
Full-time practicum experience, usually situated at the end of an educator preparation program. May also be called internship.
Full-time practicum experience, usually situated at the end of an educator preparation program. May also be called student teaching.
Teacher of record in a practicum placement. Mentors preservice teachers by modeling effective instruction and sharing classroom responsibilities.
Process of formal review of an Educator Preparation Program by an outside agency, such as CAEP.
Council for the Accreditation of Educator Preparation.
Teaching license that is temporary, usually with certain stipulations or provisions attached. Sometimes called an emergency teaching license.
Alternative pathway toward teacher certification in which future teachers work simultaneously on a master’s degree in education while being placed in a school full-time.
Agreements among different states to honor teaching licenses earned in other states, sometimes with additional requirements added (like testing).
Framework designed by Benjamin Bloom and colleagues in 1956, and later revised in 2001. Divides educational goals/cognitive processes into six categories of increasing complexity: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create.
10 standards from the Interstate Teacher Assessment and Support Consortium that cover model core teaching practices for K-12 educators.
Interpersonal skills expected of teachers as professionals.
Unequal treatment of languages based upon power structures that privilege certain languages as having legitimacy.
Term coined by Crenshaw (1989) meaning many different aspects of identity--including race, economic class, gender, and more--overlap and intersect with one another.
Judging or evaluating another culture based on your own culture.
Sweeping, oversimplified generalizations about a group.
Foundations of American Education: A Critical Lens Copyright © by Melissa Wells and Courtney Clayton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Teaching as a Profession
- First Online: 01 January 2014
Cite this chapter

- A. Reis Monteiro 2
Part of the book series: SpringerBriefs in Education ((BRIEFSEDUCAT))
1998 Accesses
5 Citations
According to international and national reports and studies, the overall status of the teaching profession is not very prestigious (and indeed far from it), as already mentioned. Underlying its widely degraded status—and being decisive for its future—is the crux of grasping its very identity. Teachers should consider themselves and be considered as professionals of the right to education and of pedagogic communication, the centre of gravity of their professionalism being interpersonal relationship. At the core of the teaching profession is its unique and far-reaching ethical dimension. The improvement of its quality should therefore begin at … the beginning. The human quality of the candidates to exercising the profession should be taken into account when deciding on the criteria for entering professional education and evaluating professional performance. Besides selection, education and evaluation, improving the quality of the teaching profession should also include other aspects of its professional and social status, such as working conditions, as well as pay and career perspectives, without overlooking the relevance of school management. The future of the teaching profession is obviously tied to that of the school. Teachers should become professionals of example. Professional exemplarity should be understood as an exceptional incarnation of a blend of qualities, values and knowledge. The teaching profession should be principally responsible for attracting the best human beings. How? by means of outstanding professional self-governing bodies, composed of people holding a passionate and inspiring vision.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Teachers as Active Contributors in Quality of Education: A Special Reference to the Finnish Context

Teaching Effectiveness in Spain: Towards an Evidence–Based Approach for Informing Policymakers

Teaching and Teacher Education: The Need to Go Beyond Rhetoric
www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_dialogue/---sector/documents/meetingdocument/wcms_162259.pdf .
www.metlife.com/assets/cao/foundation/MetLife-Teacher-Survey-2012.pdf .
http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/education-philosophy .
See the database of the Center for the Study of Ethics in the Professions (CSEP, created in 1976), Illinois Institute of Technology (USA) ( http://ethics.iit.edu/codes/coe.html ).
Kindly made electronically available by OAJ (February 2013).
www.cpa.ca/cpasite/userfiles/Documents/Canadian%20Code%20of%20Ethics%20for%20Psycho.pdf .
www.acm.org/serving/se/code.htm#full .
www.socialworkers.org/pubs/code/code.asp .
The European Federation of Psychologists’ Associations refers to its Code of Ethics as a “Meta-Code” ( www.efpa.be/ethics.php ).
www.acm.org/constitution/code.html .
www.cpa.ca/publications .
http://portal.unesco.org/en/ev.php-URL_ID=13084andURL_DO=DO_TOPICandURL_SECTION=201.html .
http://portal.unesco.org/en/ev.php-URL_ID=13144andURL_DO=DO_TOPICandURL_SECTION=201.html .
www.ei-ie.org/en/websections/content_detail/3270 .
EI is a world Federation of about 400 professional organizations in the education field, representative of about 30 million professionals in more than 170 countries and territories. www.ei-ie.org/worldcongress/docs/WC04Res_DeclarationProfEthics_e.pdf .
Teachercodes.iiep.unesco.org/index.php?lang = EN.
www.iiep.unesco.org/fileadmin/user_upload/Cap_Dev_Training/Virtual_Institute/pdf/Forums/IIEP-UNESCO_Forum_Teacher_Codes_Report.pdf .
The philosopher Olivier Reboul (1925–1992) said that “every teacher is a teacher of Morals, even without his or her knowing” ( 1971 , p. 109).
www.nbpts.org/UserFiles/File/what_teachers.pdf
The NBPTS webpage reads:
National Board for Professional Teaching Standards, known simply as National Board, is an independent, nonprofit organization. It was formed in 1987 to advance the quality of teaching and learning by developing professional standards for accomplished teaching, creating a voluntary system to certify teachers who meet those standards and integrating board-certified teachers into educational reform efforts. (See more at: http://www.nbpts.org/who-we-are#sthash.EMoRVWn1.dpuf )
Other organizations for voluntary certification, at federal level, include the American Board for Certification of Teacher Excellence (ABCTE), the National Center for Alternative Certification (NCAC) and the National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE).
www.bcteacherregulation.ca/documents/AboutUs/Standards/edu_stds.pdf .
The Royal Commission on Learning was established by the Province of Ontario, in May 1993, “to present a vision and action plan to guide Ontario’s reform of elementary and secondary education” for ensuring “that Ontario youth are well prepared for the challenges of the twenty-first century” (Order in Council). The Commission released its report, entitled For the Love of Learning , in January 1995.
Lewin, K. (1951). Field theory in social science: Selected theoretical papers by Kurt Lewin . New York: Harper and Row.
The Ontario’s New Teacher Induction Program (NTIP) is a good example.
They are organized according to the rules of the European Higher Education Area (EHEA), created by the Bologna Process, and the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS, each one corresponding to 25–30 h of learning work, and each academic year consisting of 60 ECTS).
Accountability is an ancient English term whose etymology is ‘count’, but has gained a broader meaning that entered the dictionaries and encyclopedias only in the 1980s, following Dario Castiglione ( 2006 ).
An OECD ( 2011b ) Report comments: “Given the ‘teacher-bashing’ engaged in by the previous government, this show of trust in the competence and professionalism of the teaching force was an essential ingredient in repairing the rupture that had developed between the profession and the government” (p. 76).
In connexion with this, the Report of the 2013 International Summit on the Teaching Profession notes:
Jaakko Meretniemi, a teacher from Finland, struck a different note. He said that teachers in Finland are well educated – all have master’s degrees. He did not see the need for a formal teacher-evaluation system. Teachers get plenty of feedback from their students and colleagues. He worried that the Summit was going in the wrong direction, that increasing teacher inspections might kill teachers’ passion for their work. (Asia Society 2013 , p. 17).
http://core.roehampton.ac.uk/digital/froarc/comgre/ .
Translation: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0012/001202/120260e.pdf (p. 123).
Karl Marx (1818–1883) put it this way in “Theses on Feuerbach”, first published as an appendix to Ludwig Feuerbach and the End of Classical German Philosophy (1886): “The materialist doctrine concerning the changing of circumstances and upbringing forgets that circumstances are changed by men and that it is essential to educate the educator himself”. ( www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/download/Marx_Ludwig_Feurbach_and_the_End_of_German_Classical_Philosop.pdf ). This is a problem similar to the political one highlighted by Tom Campbell ( 2006 ): “The eternal problem of political philosophy is how we can guard the guardians” (p. 100).
www.oecd.org/dataoecd/53/16/46335575.pdf .
Learning to be — The world of education today and tomorrow is the title of an influential Report prepared by an International Commission appointed by UNESCO, published in 1972.
For instance, the Teachers’ Code of Ethics and Practice of the Council for the Teaching Profession in Malta, adopted in 2012, which elaborates on six “Key Principles”, refers three times to ‘role model’ (defined as “any person who serves as an example and whose behaviour is emulated by others”), namely: “A teacher shall endeavour to be a role model and shall act within the community in a manner which enhances the prestige of the profession”. Teachers should “behave in keeping with their unique position of trust and status as role models”. They shoul:
Be mindful of their position as a role models to students; and Both in their personal and professional life, be mindful of their behaviour and attitude, being that these may have an impact on the profession they represent.
( http://education.gov.mt/en/resources/documents/teachers%20resources/teachers%20code%20of%20ethics%20en.pdf ).
www.alberteinsteinsite.com/quotes/einsteinquotes.html .
www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/1200 .
Aldrich, R. (1995). John Locke (1632–1704). In UNESCO, Penseurs de l’éducation — Volume 3 (pp. 65–82). Paris: UNESCO/BIE. www.ibe.unesco.org/fileadmin/user_upload/archive/publications/ThinkersPdf/lockee.PDF .
Aristotle. (1925). The Nicomachean ethics (Translated with an Introduction by David Ross, Revised by J. L. Ackrill and J. O. Urmson). Oxford: University Press (1998).
Google Scholar
Asia Society. (2011). The international summit on the teaching profession — improving teacher quality around the world . http://asiasociety.org/files/lwtw-teachersummitreport0611.pdf .
Asia Society. (2012). The 2012 international summit on the teaching profession — teaching and leadership for the twenty-first century . http://asiasociety.org/files/2012teachingsummit.pdf .
Asia Society. (2013). The 2013 international summit on the teaching profession — teacher quality . http://asiasociety.org/files/teachingsummit2013.pdf .
Bæchler, J. (1994). Précis de la démocratie . Paris: Calman-Lévy/Éditions UNESCO.
Barber, M., Donnelly, K., & Rizvi, S. (2012). Oceans of innovation — the Atlantic, the Pacific, global leadership and the future of education . London: Institute of Public Policy Research. www.ippr.org/images/media/files/publication/2012/09/oceans-of-innovation_Aug2012_9543.pdf .
Britzman, D. P. (2009). The very thought of education: psychoanalysis and the impossible professions . New York: State University of New York.
Campbell, E. (2008). Teaching ethically as a moral condition of professionalism. In L. Nucci & D. Narvaez (Ed.), International handbook of moral and character education . New York and London: Routledge. Retrieved January 2013 from http://sitemaker.umich.edu/tei/files/campbell_teaching_ethically.pdf .
Campbell, T. (2006). Rights—A critical introduction . London: Routledge.
Castiglione, D. (2006). Accountability. In Encyclopedia of governance . California: SAGE Publications.
Darling-Hammond, L., & Rothman, R. (2011). Lessons learned from Finland, Ontario, and Singapore. In L. Darling-Hammond, & R. Rothman (Ed.), Teacher and leader effectiveness in high-performing education systems (pp. 1–11). Washington, DC: Alliance for Excellent Education and Stanford Center for Opportunity Policy in Education. www.all4ed.org/files/TeacherLeaderEffectivenessReport.pdf .
Department for Education. (2010). The importance of teaching — the schools white paper 2010. Presented to Parliament by the Secretary of State for Education by Command of Her Majesty, November 2010. www.education.gov.uk/publications/eOrderingDownload/CM-7980.pdf .
Dulot, A. et al. (2012). Refondons l’École de la République — Rapport de la concertation . www.refondonslecole.gouv.fr/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/refondons_l_ecole_de_la_republique_rapport_de_la_concertation1.pdf .
European Commission. (2012). Supporting the teaching professions for better learning outcomes . Commission Staff Working Document—Accompanying the Document: Communication from the Commission—Rethinking Education: Investing in Skills for Better Socio-Economic Outcomes (SWD (2012) 374 final). Retrieved July 2014 from http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=SWD:2012:0374:FIN:EN:PDF .
Figazzolo, L. (2013). The use and abuse of teacher appraisal — an overview of cases in the developed world . Brussels: Education International. http://download.ei-ie.org/Docs/WebDepot/TeacherAppraisal.pdf .
House of Commons. (2012). Great teachers: attracting, training and retaining the best ninth report of session 2010 – 12, volume I: Report, together with formal minutes. London: Education Committee. www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201012/cmselect/cmeduc/1515/1515.pdf .
ILO. (2012). Handbook of good human resource practices in the teaching profession . Geneva: International Labour Organization—Sectoral Activities Department. www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_dialogue/---sector/documents/publication/wcms_187793.pdf .
Immordino-Yang, M. (2009). Social neuroscience and its application to education. In S. Feifer, & G. Rattan (Eds.), Emotional disorders: A neuropsychological, psychopharmacological, and educational perspective (pp. 15–22). Middletown, MD: School Neuropsychology Press. Retrieved September 2012 from www.bcf.usc.edu/~immordin/papers/Immordino-Yang_2009_SocialNeuroscienceEdApplications.pdf .
Immordino-Yang, M. (2011). Implications of affective and social neuroscience for educational theory. Educational Philosophy and Theory, 43 (1), 98–103. Retrieved September 2012 from www.bcf.usc.edu/~immordin/papers/Immordino-Yang_EPAT_2011.pdf .
Immordino-Yang, M., & Fischer, K. (2010). Neuroscience bases of learning. In V. G. Aukrust (Ed.), International encyclopedia of education (3rd ed., pp. 310–316). Oxford: Elsevier. Retrieved September 2012 from www-bcf.usc.edu/~immordin/papers/Immordino-Yang+Fischer_2009_NeuroscienceBasesofLearning.pdf .
Jetsonen, S. (2011). Setting the scene for learning. In The best school in the world. Helsinki: Museum of Finnish Architecture. http://issuu.com/suomen-rakennustaiteen-museo/docs/bestschoolintheworld_book#download .
Johansson, E. (2011). Introduction. In The best school in the world . Helsinki: Museum of Finnish Architecture. http://issuu.com/suomen-rakennustaiteen-museo/docs/bestschoolintheworld_book#download .
Kane, R., & Mallon, M. (2006). Perceptions of teachers and teaching . New Zealand: Ministry of Education. Retrieved January 2013 from www.teacherscouncil.govt.nz/research/percept-teachersteaching.pdf .
Kant, I. (1803). On education (‘Über Pädagogik’, Translated by Annette Churton, with an Introduction by C. A. Foley Rhys Davids, M.A.). Boston, U.S.A.: D. C. Heath and Co., Publishers, 1906. http://archive.org/details/kantoneducationu00kantuoft .
Leslie, C. (Ed.). (2013). Towards a royal college of teaching — raising the status of the profession . London: The Royal College of Surgeons of England. Retrieved July 2014 from http://filestore.aqa.org.uk/news/pdf/AQA-NEWS-TOWARDS-A-ROYAL-COLLEGE.PDF .
MacBeath, J. (2012). Future of teaching profession . Education International Research Institute, University of Cambridge—Faculty of Education, Leadership for Learning—The Cambridge Network. http://download.ei-ie.org/Docs/WebDepot/EI%20Study%20on%20the%20Future%20of%20Teaching%20Profession.pdf .
McRuer, J. C. (1968–1971). Report of the royal commission inquiry into civil rights—Report number one, volume . Toronto: Queens’ Printer.
National Commission on Excellence in Education. (1983). A nation at risk: The imperative for educational reform (Washington) . http://datacenter.spps.org/uploads/SOTW_A_Nation_at_Risk_1983.pdf .
Nuikkinen, K. (2011). Learning spaces: How they meet evolving educational needs. In The best school in the world . Helsinki: Museum of Finnish Architecture. http://issuu.com/suomen-rakennustaiteen-museo/docs/bestschoolintheworld_book#download .
OECD. (2005). Teachers matter—Attracting, developing and retaining effective teachers . Paris: OECD Publishing.
OECD. (2011a). Building a high-quality teaching profession—Lessons from around the world—Background report for the international summit on the teaching profession . Paris: OECD Publishing. Retrieved January 2013 from www2.ed.gov/about/inits/ed/internationaled/background.pdf .
OECD. (2011b). Strong performers and successful reformers in education—Lessons from PISA for the United States . Paris: OECD Publishing. Retrieved June 2014 from www.oecd.org/pisa/46623978.pdf .
OECD. (2013). Teachers for the 21st century—Using evaluation to improve teaching — Background report for the 2013 international summit on the teaching profession . Paris: OECD Publishing. Retrieved April 2013 from www.oecd.org/site/eduistp13/TS2013%20Background%20Report.pdf .
OECD. (2014). Equity, excellence and inclusiveness in education—Policy lessons from around the world . Paris: OECD Publishing, by Andreas Schleicher. Retrieved June 2014 from http://teachfirstnz.org/images/uploads/Documents/OECD.pdf .
Pearson. (2012). Lessons in country performance in education—2012 report . London: The Learning Curve, Economist Intelligence Unit. http://thelearningcurve.pearson.com/the-report .
Plato. (1997). In: J. M. Cooper & D. S. Hutchinson (Eds.), Complete works . Indianapolis/Cambridge: Hackeht Publishing Company.
Ramsey, G. (2000). Quality matters—Revitalising teaching: Critical times, critical choices—Report of the review of teacher education . New South Wales. www.det.nsw.edu.au/teachrev/reports/reports.pdf .
Ravitch, D. (2012). Schools we can envy. The New York Review of Book . 8 March. Retrieved January 2013 from www.nybooks.com/articles/archives/2012/mar/08/schools-we-can-envy/?pagination=false .
Reboul, O. (1971). La philosophie de l’éducation . Paris: PUF (1981, 3è éd.).
Rousseau, J.-J. (1993a). Émile (Translated by Barbara Foxley, Introduction by P. D. Jimack). Vermont: Everyman (2004).
Rousseau, J.-J. (1993b). The social contract and discourses (Translated and introduced by G. D. H. Cole, updated by P. D. Jimack). Vermont: Everyman.
Royal Commission on Learning. (1995). For the love of learning . www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/general/abcs/rcom/full/royalcommission.pdf .
Sahlberg, P. (2010). The secret to Finland’s success: Educating teachers . Stanford University, School of Education, Stanford Center for Opportunity Policy in Education—Research brief. http://edpolicy.stanford.edu/sites/default/files/publications/secret-finland%E2%80%99s-success-educating-teachers.pdf .
Shulman, L. (2005). The signature pedagogies (Delivered at the math science partnerships (MSP) workshop: ‘Teacher education for effective teaching and learning’, hosted by the National Research Council’s Center for Education, February 6–8, 2005, Irvine, California). Retrieved January 2013 from http://hub.mspnet.org/media/data/Shulman_Signature_Pedagogies.pdf?media_000000005488.pdf .
The Holmes Group. (1986). Tomorrow’s teachers . New York. Retrieved January 2013 from www.canterbury.ac.uk/education/tf-mentors/ProfessionalDev/Documents/TomorrowsTeachers.pdf .
UNESCO. (1998). World education report—1998—Teachers and teaching in a changing world . www.unesco.org/education/information/wer/PDFeng/wholewer98.PDF .
Whitty, G. (2006). “Teacher professionalism in a new era”, text of the first General Teaching Council for Northern Ireland Annual Lecture delivered at Queen’s University, Belfast, March 14, 2006. Retrieved January 2013 from www.gtcni.org.uk/publications/uploads/document/Annual%20Lecture%20Paper.pdf .
World Bank. (2012). What matters most in teacher policies?—A framework for building a more effective teaching profession . Human Development Network, SABER: Systems Approach for Better Education Results. http://siteresources.worldbank.org/EDUCATION/Resources/278200-1290520949227/SABER-Teachers-Framework-Updated_June14.2012.pdf .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal
A. Reis Monteiro
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to A. Reis Monteiro .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Monteiro, A.R. (2015). Teaching as a Profession. In: The Teaching Profession. SpringerBriefs in Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12130-7_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12130-7_5
Published : 04 November 2014
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-12129-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-12130-7
eBook Packages : Humanities, Social Sciences and Law Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Essay on Teaching Profession & Its Benefits
Teaching is an often under-appreciated profession, but the impact of a good teacher cannot be overstated. Teachers are an essential part of society, shaping the next generation’s future.
Teaching also provides a chance for personal growth and development as well as the ability to make a difference in lives. This essay will explore some benefits of teaching profession.
Essay on Teaching Profession
A good teacher is not only knowledgeable on the topic but also has a set of relationships with the students that go beyond the classroom.
Teaching might not be an easy task but it is an important one. Teaching can change someone’s life by teaching them new skills or providing them with a more thorough understanding of something they were previously confused about.
1 – Why teaching is important?
Teachers make a real difference in the lives of people who are ill or suffering. Students learn to develop their own learning styles Students get to know one another and develop social skills and begin to know their place in the world.
Teaching is important because it makes a huge impact on development of society or a country. It is a profession that has the ability make a stronger nation.
2 – Reasons to Become a Teacher
The role of the teacher is to be a caretaker of others; responsible for bringing out the best in everyone you come into contact with. There may be a lot of reasons to become a teacher but some are listed here.
3 – Teaching is Great for Personal Growth
These lessons are crucial to a child’s life and can help mold the next generation of successful people. Teaching Makes you a better person. One of the best things about teaching is that it makes you a better person.
Children inspire teachers and, in turn, they can teach children to follow their dreams, achieve their goals, and be independent. By teaching students, you can inspire the students you once were. As a teacher, you have the opportunity to teach students the value of education and the joys of learning.
4 – Benefits of Teaching
The job satisfaction level of teaching is particularly high. Many teachers tell us that they are really able to connect with their students and share a passion for what they are learning.
In addition to developing other professional skills, teaching also allows students to learn the essential skills necessary for success in college and in life.
Research shows that children are more successful when they are taught at a younger age, and it is generally recommended that teachers serve from 6 to 18 years of age.
Teaching also provides opportunities for personal growth and development.
5 – The Need for Teachers
In fact, the vast majority of students who need teachers are not even aware that they need them.
In a culture where children learn at a faster rate, they want more hands-on learning experiences. At present, America’s children spend less time studying and doing traditional lessons and more time doing research, in comparison to their counterparts in other countries.
The teacher’s role in this situation is to provide this hands-on learning experience. Being able to instill in children an enthusiasm for learning is what teachers do best, and the best teacher in the world is one who inspires children to learn.
6 – Challenges of teaching
Teaching is a stressful job, which means that some people are discouraged and turn down the opportunity to teach. However, teachers do not have much time off, since the students usually need to meet with them on a daily basis. Therefore, they have to be at their best and available. The job also requires a lot of patience, because students can be difficult to deal with. Experience of teaching Teaching requires a high level of knowledge, and a good knowledge of the subject of study is necessary. Many teachers also need a thorough knowledge of the educational system in the country they teach in. Teachers also have to be able to read and write in multiple languages, which may be a challenge in the Philippines.
Teaching jobs come with a lot of challenges and stress. Some of these challenges are occupational and some are related to age. Regardless of the challenges you face, the biggest challenges facing teachers are the following: Overcrowding Class sizes are high, especially in public schools. In addition to the extra people in your classes, some schools have open classrooms that are designed so that students can come in and out at will. As a result, teachers spend a lot of time with their students when it is not a class period. This is important to learn about so that you can set up a classroom that will be able to function well. You can train your students in the art of teaching so that they can accomplish more on their own. Relationships Teaching is a way to be in a community.
7 – Teaching as a career
Teaching may be the most popular career option in the United States. Even though the job market has not been as favorable to young people as many may think, many remain devoted to teaching. Having a job as a teacher means that you can also be a job seeker. It is important to consider all of the factors before deciding on a career, especially if you plan on staying at one position for the rest of your life. Other careers Teaching may not be the most popular choice for young people, but it is not out of the question. Other options include becoming a police officer, a teacher in a foreign language, or a nurse.
8 – How to become a teacher
As the link between life and education, the teaching profession is not something that you can just wake up and decide to do. You must be attracted to the teaching field and have a great passion for it. In a market where many people are on the lookout for teaching jobs, you must be outstanding in what you do in order to win the position. In the last 15 years, there has been a steady increase in
9 – Conclusion
Teaching provides a way to give back to society and to help improve the lives of those who come after us. Since teachers have so much potential in the field, they should be given every opportunity possible to use it. Don’t let yourself be left out of the perfect opportunity. Be the one to bring change and be the one to inspire others. Become a teacher, and it will change your life.
Teaching is the profession of imparting knowledge and skills to students in a way that will help them achieve their full potential. As such, teaching can be an incredibly rewarding career. What’s more, teaching is one of the few professions that allow you to work with children and then retire from the same occupation while still young. Teaching gives you the chance to make a lasting impact on the world by inspiring a new generation of thinkers and leaders. Teaching is also a way for people to find meaning in their lives after struggling in other areas.
Similar Posts
Free printable chart of preposition, what is epigram in figure of speech definition, examples, sentences, essay on corruption: causes & its effects, rules for hyphen use, essay about climate change (what are causes and what we can do to avoid it), do does did sentences (50 examples), leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Teaching — Exploring the Noble Profession of Teaching
Exploring The Noble Profession of Teaching
- Categories: Dream Career Teacher Teaching
About this sample

Words: 667 |
Published: Aug 31, 2023
Words: 667 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Life Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1783 words
3 pages / 1449 words
4 pages / 1847 words
1 pages / 431 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Teaching
Should teachers be paid more? This question is at the forefront of discussions surrounding education reform and the value we place on the educators who shape the future of our society. Adequate compensation for teachers is not [...]
Teacher self-evaluation is a process in which educators reflect on their own teaching practices and assess their effectiveness in the classroom. It involves examining various areas of teaching, such as classroom management, [...]
Effective teaching is a multidimensional concept that encompasses a variety of strategies, techniques, and methodologies aimed at promoting student learning and engagement. At its core, effective teaching is about making a [...]
Effective teaching is a cornerstone of successful learning and personal development. The art of teaching involves more than delivering information; it encompasses a set of principles that guide educators in creating meaningful [...]
The purpose of this essay is to critically reflect on providing supervision and mentoring support to others within the work place through teaching, learning and assessment. Evidence will be drawn from knowledge and understanding [...]
Dictionaries play a key role in language acquisition and teaching as they enhance learners’ autonomy. In this regard, in order to avoid asking a teacher frequently, a dictionary which is chosen meticulously may well be a wise [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
the encyclopaedia of pedagogy and informal education
What is teaching? A definition and discussion
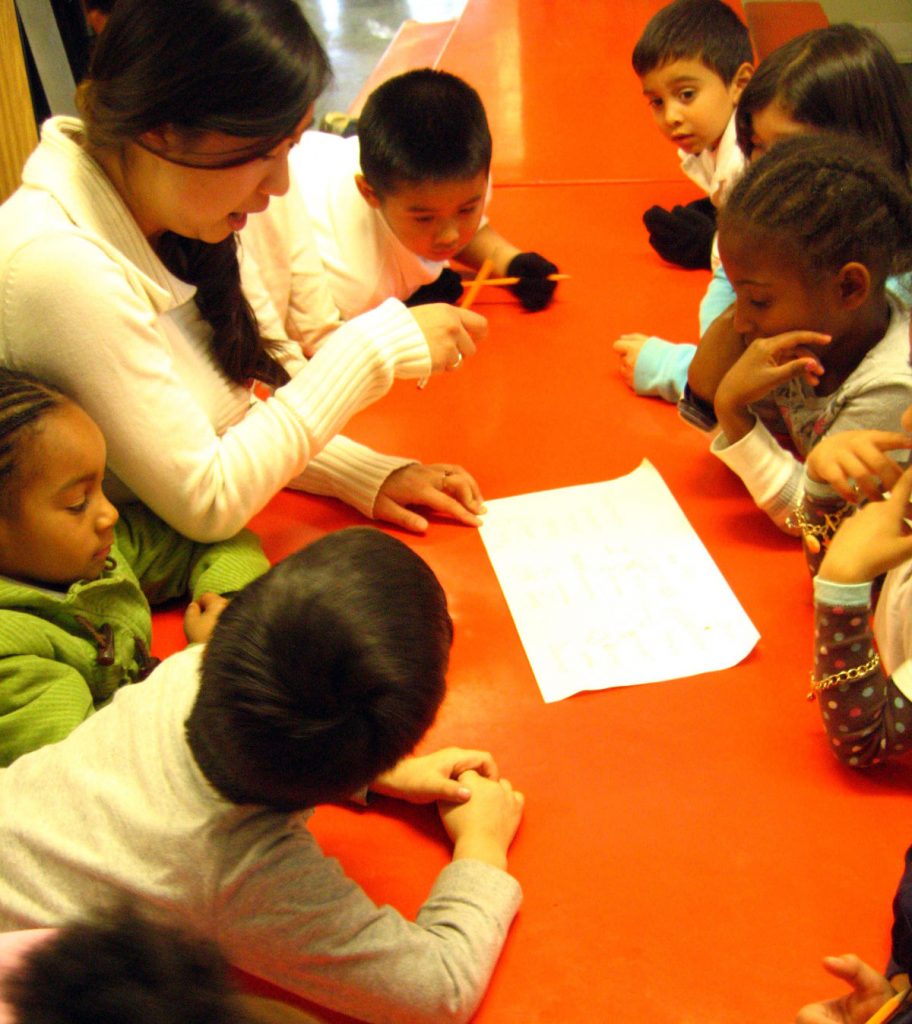

In this piece Mark K Smith explores the nature of teaching – those moments or sessions where we make specific interventions to help people learn particular things. He sets this within a discussion of pedagogy and didactics and demonstrates that we need to unhook consideration of the process of teaching from the role of ‘teacher’ in schools.
Contents : introduction • what is teaching • a definition of teaching • teaching, pedagogy and didactics • approaching teaching as a process • structuring interventions and making use of different methods • what does good teaching look like • conclusion • further reading and references • acknowledgements • how to cite this piece, linked piece: the key activities of teaching, a definition for starters : teaching is the process of attending to people’s needs, experiences and feelings, and intervening so that they learn particular things, and go beyond the given., introduction.
In teacher education programmes – and in continuing professional development – a lot of time is devoted to the ‘what’ of teaching – what areas we should we cover, what resources do we need and so on. The ‘how’ of teaching also gets a great deal of space – how to structure a lesson, manage classes, assess for learning for learning and so on. Sometimes, as Parker J. Palmer (1998: 4) comments, we may even ask the “why” question – ‘for what purposes and to what ends do we teach? ‘But seldom, if ever’, he continues: ‘do we ask the “who” question – who is the self that teaches?’
The thing about this is that the who, what, why and how of teaching cannot be answered seriously without exploring the nature of teaching itself.
What is teaching?
In much modern usage, the words ‘teaching’ and ‘teacher’ are wrapped up with schooling and schools. One way of approaching the question ‘What is teaching?’ is to look at what those called ‘teachers’ do – and then to draw out key qualities or activities that set them apart from others. The problem is that all sorts of things are bundled together in job descriptions or roles that may have little to do with what we can sensibly call teaching.
Another way is to head for dictionaries and search for both the historical meanings of the term, and how it is used in everyday language. This brings us to definitions like:
Impart knowledge to or instruct (someone) as to how to do something; or Cause (someone) to learn or understand something by example or experience.
As can be seen from these definitions we can say that we are all teachers in some way at some time.
Further insight is offered by looking at the ancestries of the words. For example, the origin of the word ‘teach’ lies in the Old English tæcan meaning ‘show, present, point out’, which is of Germanic origin; and related to ‘token’, from an Indo-European root shared by Greek deiknunai ‘show’, deigma ‘sample ( http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/teach ).
Fostering learning
To make sense of all this it is worth turning to what philosophers of education say. Interestingly, the question, ‘What is teaching?’ hasn’t been a hotbed of activity in recent years in the UK and USA. However, as Paul Hirst (1975) concluded, ‘being clear about what teaching is matters vitally because how teachers understand teaching very much affects what they actually do in the classroom’.
Hirst (1975) makes two very important points. For him teaching should involve:
- Setting out with the intention of someone learning something.
- Considering people’s feelings, experiences and needs. Teaching is only teaching if people can take on what is taught.
To this we can add Jerome Bruner’s insights around the nature of education, and the process of learning and problem solving.
To instruct someone… is not a matter of getting him to commit results to mind. Rather, it is to teach him to participate in the process that makes possible the establishment of knowledge. We teach a subject not to produce little living libraries on that subject, but rather to get a student to think mathematically for himself, to consider matters as an historian does, to take part in the process of knowledge-getting. Knowing is a process not a product. (1966: 72)
We can begin to weave these into a definition – and highlight some forms it takes.
A definition : Teaching is the process of attending to people’s needs, experiences and feelings, and intervening so that they learn particular things, and go beyond the given.
Interventions commonly take the form of questioning, listening, giving information, explaining some phenomenon, demonstrating a skill or process, testing understanding and capacity, and facilitating learning activities (such as note taking, discussion, assignment writing, simulations and practice).
Let us look at the key elements.
Attending to people’s feelings, experiences and needs
Considering what those we are supposed to be teaching need, and what might be going on for them, is one of the main things that makes ‘education’ different to indoctrination. Indoctrination involves knowingly encouraging people to believe something regardless of the evidence (see Snook 1972; Peterson 2007). It also entails a lack of respect for their human rights. Education can be described as the ‘wise, hopeful and respectful cultivation of learning undertaken in the belief that all should have the chance to share in life’ (Smith 2015). The process of education flows from a basic orientation of respect – respect for truth, others and themselves, and the world ( op. cit. ). For teachers to be educators they must, therefore:
- Consider people’s needs and wishes now and in the future.
- Reflect on what might be good for all (and the world in which we live).
- Plan their interventions accordingly.
There are a couple of issues that immediately arise from this.
First, how do we balance individual needs and wishes against what might be good for others? For most of us this is probably something that we should answer on a case-by-case basis – and it is also something that is likely to be a focus for conversation and reflection in our work with people.
Second, what do we do when people do not see the point of learning things – for example, around grammar or safety requirements? The obvious response to this question is that we must ask and listen – they may have point. However, we also must weigh this against what we know about the significance of these things in life, and any curriculum or health and safety or other requirements we have a duty to meet. In this case we have a responsibility to try to introduce them to people when the time is right, to explore their relevance and to encourage participation.
Failing to attend to people’s feelings and experiences is problematic – and not just because it reveals a basic lack of respect for them. It is also pointless and counter-productive to try to explore things when people are not ready to look at them. We need to consider their feelings and look to their experiences – both of our classroom or learning environment, and around the issues or areas we want to explore. Recent developments in brain science has underlined the significance of learning from experience from the time in the womb on (see, for example Lieberman 2013). Bringing people’s experiences around the subjects or areas we are looking to teach about into the classroom or learning situation is, thus, fundamental to the learning process.
Learning particular things
Teaching involves creating an environment and engaging with others, so that they learn particular things. This can be anything from tying a shoe lace to appreciating the structure of a three act play. I want highlight three key elements here – focus, knowledge and the ability to engage people in learning.
This may be a bit obvious – but it is probably worth saying – teaching has to have a focus. We should be clear about we are trying to do. One of the findings that shines through research on teaching is that clear learning intentions help learners to see the point of a session or intervention, keep the process on track, and, when challenging, make a difference in what people learn (Hattie 2009: location 4478).
As teachers and pedagogues there are a lot of times when we are seeking to foster learning but there may not be great clarity about the specific goals of that learning (see Jeffs and Smith 2018 Chapter 1). This is especially the case for informal educators and pedagogues. We journey with people, trying to build environments for learning and change, and, from time-to-time, creating teaching moments. It is in the teaching moments that we usually need an explicit focus.
Subject knowledge
Equally obvious, we need expertise, we need to have content. As coaches we should know about our sport; as religious educators about belief, practice and teachings; and, as pedagogues, ethics, human growth and development and social life. Good teachers ‘have deep knowledge of the subjects they teach, and when teachers’ knowledge falls below a certain level it is a significant impediment to students’ learning’ (Coe et. al. 2014: 2).
That said, there are times when we develop our understandings and capacities as we go. In the process of preparing for a session or lesson or group, we may read, listen to and watch YouTube items, look at other resources and learn. We build content and expertise as we teach. Luckily, we can draw on a range of things to support us in our efforts – video clips, web resources, textbooks, activities. Yes, it might be nice to be experts in all the areas we have to teach – but we can’t be. It is inevitable that we will be called to teach in areas where we have limited knowledge. One of the fascinating and comforting things research shows is that what appears to count most for learning is our ability as educators and pedagogues. A good understanding of, and passion for, a subject area; good resources to draw upon; and the capacity to engage people in learning yields good results. It is difficult to find evidence that great expertise in the subject matter makes a significant difference within a lot of schooling (Hattie 2009: location 2963).
Sometimes subject expertise can get in the way – it can serve to emphasize the gap between people’s knowledge and capacities and that of the teacher. On the other hand, it can be used to generate enthusiasm and interest; to make links; and inform decisions about what to teach and when. Having a concern for learning – and, in particular, seeking to create environments where people develop as and, can be, self-directed learners – is one of the key features here.

Engaging people in learning
At the centre of teaching lies enthusiasm and a commitment to, and expertise in, the process of engaging people in learning. This is how John Hattie (2009: location 2939) put it:
… it is teachers using particular teaching methods, teachers with high expectations for all students, and teachers who have created positive student-teacher relationships that are more likely to have the above average effects on student achievement.
Going beyond the given
The idea of “going beyond the information given” was central to Jerome Bruner’s explorations of cognition and education. He was part of the shift in psychology in the 1950s and early 1960s towards the study of people as active processors of knowledge, as discoverers of new understandings and possibilities. Bruner wanted people to develop their ability to ‘go beyond the data to new and possibly fruitful predictions’ (Bruner 1973: 234); to experience and know possibility. He hoped people would become as ‘autonomous and self-propelled’ thinkers as possible’ (Bruner 1961: 23). To do this, teachers and pedagogues had to, as Hirst (1975) put it, appreciate learner’s feelings, experiences and needs; to engage with their processes and view of the world.
Two key ideas became central to this process for Jerome Bruner – the ‘spiral’ and scaffolding.
The spiral . People, as they develop, must take on and build representations of their experiences and the world around them. (Representations being the way in which information and knowledge are held and encoded in our memories). An idea, or concept is generally encountered several times. At first it is likely to be in a concrete and simple way. As understanding develops, it is likely to encountered and in greater depth and complexity. To succeed, teaching, educating, and working with others must look to where in the spiral people are, and how ‘ready’ they are to explore something. Crudely, it means simplifying complex information where necessary, and then revisiting it to build understanding (David Kolb talked in a similar way about experiential learning).
Scaffolding . The idea of scaffolding (which we will come back to later) is close to what Vygotsky talked about as the zone of proximal development. Basically, it entails creating a framework, and offering structured support, that encourages and allows learners to develop particular understandings, skills and attitudes.
Intervening
The final element – making specific interventions – concerns the process of taking defined and targeted action in a situation. In other words, as well as having a clear focus, we try to work in ways that facilitate that focus.
Thinking about teaching as a process of making specific interventions is helpful, I think, because it:
Focuses on the different actions we take . As we saw in the definition, interventions commonly take the form of questioning, listening, giving information, explaining some phenomenon, demonstrating a skill or process, testing understanding and capacity, and facilitating learning activities (such as note taking, discussion, assignment writing, simulations and practice).
Makes us look at how we move from one way of working or communicating to another . Interventions often involve shifting a conversation or discussion onto a different track or changing the process or activity. It may well be accompanied by a change in mood and pace (e.g. moving from something that is quite relaxed into a period of more intense activity). The process of moving from one way of working – or way of communicating – to another is far from straightforward. It calls upon us to develop and deepen our practice.
Highlights the more formal character of teaching . Interventions are planned, focused and tied to objectives or intentions. Teaching also often entails using quizzes and tests to see whether planned outcomes have been met. The feel and character of teaching moments are different to many other processes that informal educators, pedagogues and specialist educators use. Those processes, like conversation, playing a game and walking with people are usually more free-flowing and unpredictable.
Teaching, however, is not a simple step-by-step process e.g. of attending, getting information and intervening. We may well start with an intervention which then provides us with data. In addition, things rarely go as planned – at least not if we attend to people’s feelings, experiences and needs. In addition, learners might not always get the points straightaway or see what we are trying to help them learn. They may be able to take on what is being taught – but it might take time. As a result, how well we have done is often unlikely to show up in the results of any tests or in assessments made in the session or lesson.
Teaching, pedagogy and didactics
Earlier, we saw that relatively little attention had been given to defining the essential nature of teaching in recent years in the UK and North America. This has contributed to confusion around the term and a major undervaluing of other forms of facilitating learning. The same cannot be said in a number of continental European countries where there is a much stronger appreciation of the different forms education takes. Reflecting on these traditions helps us to better understand teaching as a particular process – and to recognize that it is fundamentally concerned with didactics rather than pedagogy.
Perhaps the most helpful starting point for this discussion is the strong distinction made in ancient Greek society between the activities of pedagogues (paidagögus) and subject teachers (didáskalos or diadacts). The first pedagogues were slaves – often foreigners and the ‘spoils of war’ (Young 1987). They were trusted and sometimes learned members of rich households who accompanied the sons of their ‘masters’ in the street, oversaw their meals etc., and sat beside them when being schooled. These pedagogues were generally seen as representatives of their wards’ fathers and literally ‘tenders’ of children (pais plus agögos, a ‘child-tender’). Children were often put in their charge at around 7 years and remained with them until late adolescence. As such pedagogues played a major part in their lives – helping them to recognize what was wrong and right, learn how to behave in different situations, and to appreciate how they and those around them might flourish.
Moral supervision by the pedagogue (paidagogos) was also significant in terms of status.
He was more important than the schoolmaster, because the latter only taught a boy his letters, but the paidagogos taught him how to behave, a much more important matter in the eyes of his parents. He was, moreover, even if a slave, a member of the household, in touch with its ways and with the father’s authority and views. The schoolmaster had no such close contact with his pupils. (Castle 1961: 63-4)
The distinction between teachers and pedagogues, instruction and guidance, and education for school or life was a feature of discussions around education for many centuries. It was still around when Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) explored education. In On Pedagogy (Über Pädagogik) first published in 1803, he talked as follows:
Education includes the nurture of the child and, as it grows, its culture. The latter is firstly negative, consisting of discipline; that is, merely the correcting of faults. Secondly, culture is positive, consisting of instruction and guidance (and thus forming part of education). Guidance means directing the pupil in putting into practice what he has been taught. Hence the difference between a private teacher who merely instructs, and a tutor or governor who guides and directs his pupil. The one trains for school only, the other for life. (Kant 1900: 23-4)
It was later – and particularly associated with the work of Herbart (see, for example, Allgemeine pädagogik – General Pedagogics, 1806 and Umriss Pädagogischer Vorlesungen , 1835 – Plan of Lectures on Pedagogy and included in Herbart 1908) – that teaching came to be seen, wrongly, as the central activity of education (see Hamilton 1999).
Didactics – certainly within German traditions – can be approached as Allgemeine Didaktik (general didactics) or as Fachdidaktik (subject didactics). Probably, the most helpful ways of translating didaktik is as the study of the teaching-learning process. It involves researching and theorizing the process and developing practice (see Kansanen 1999). The overwhelming focus within the didaktik tradition is upon the teaching-learning process in schools, colleges and university.
To approach education and learning in other settings it is necessary to turn to the pädagogik tradition . Within this tradition fields like informal education, youth work, community development, art therapy, playwork and child care are approached as forms of pedagogy. Indeed, in countries like Germany and Denmark, a relatively large number of people are employed as pedagogues or social pedagogues. While these pedagogues teach, much of their activity is conversationally, rather than curriculum, -based. Within this what comes to the fore is a focus on flourishing and of the significance of the person of the pedagogue (Smith and Smith 2008). In addition, three elements stand out about the processes of the current generation of specialist pedagogues. First, they are heirs to the ancient Greek process of accompanying and fostering learning. Second, their pedagogy involves a significant amount of helping and caring for. Indeed, for many of those concerned with social pedagogy it is a place where care and education meet – one is not somehow less than the other (Cameron and Moss 2011). Third, they are engaged in what we can call ‘bringing situations to life’ or ‘sparking’ change (animation). In other words, they animate, care and educate (ACE). Woven into those processes are theories and beliefs that we also need to attend to (see Alexander 2000: 541).

We can see from this discussion that when English language commentators talk of pedagogy as the art and science of teaching they are mistaken. As Hamilton (1999) has pointed out teaching in schools is properly approached in the main as didactics – the study of teaching-learning processes. Pedagogy is something very different. It may include didactic elements but for the most part it is concerned with animation, caring and education (see what is education? ). It’s focus is upon flourishing and well-being. Within schools there may be specialist educators and practitioners that do this but they are usually not qualified school teachers. Instead they hold other professional qualifications, for example in pedagogy, social work, youth work and community education. To really understand teaching as a process we need to unhook it from school teaching and recognize that it is an activity that is both part of daily life and is an element of other practitioner’s repertoires. Pedagogues teach, for example, but from within a worldview or haltung that is often radically different to school teachers.
Approaching teaching as a process
Some of the teaching we do can be planned in advance because the people involved know that they will be attending a session, event or lesson where learning particular skills, topics or feelings is the focus. Some teaching arises as a response to a question, issue or situation. However, both are dependent on us:
Recognizing and cultivating teachable moments. Cultivating relationships for learning. Scaffolding learning – providing people with temporary support so that they deepen and develop their understanding and skills and grow as independent learners. Differentiating learning – adjusting the way we teach and approach subjects so that we can meet the needs of diverse learners. Accessing resources for learning. Adopting a growth mindset.
We are going to look briefly at each of these in turn.
Recognizing and cultivating teachable moments
Teachers – certainly those in most formal settings like schools – have to follow a curriculum. They have to teach specified areas in a particular sequence. As a result, there are always going to be individuals who are not ready for that learning. As teachers in these situations we need to look out for moments when students may be open to learning about different things; where we can, in the language of Quakers, ‘speak to their condition’. Having a sense of their needs and capacities we can respond with the right things at the right time.
Informal educators, animators and pedagogues work differently for a lot of the time. The direction they take is often not set by a syllabus or curriculum. Instead, they listen for, and observe what might be going on for the people they are working with. They have an idea of what might make for well-being and development and can apply it to the experiences and situations that are being revealed. They look out for moments when they can intervene to highlight an issue, give information, and encourage reflection and learning.
In other words, all teaching involves recognizing and cultivating ‘learning moments’ or ‘teaching moments’.
It was Robert J Havinghurst who coined the term ‘teachable moment’. One of his interests as an educationalist was the way in which certain things have to be learned in order for people to develop.
When the timing is right, the ability to learn a particular task will be possible. This is referred to as a ‘teachable moment’. It is important to keep in mind that unless the time is right, learning will not occur. Hence, it is important to repeat important points whenever possible so that when a student’s teachable moment occurs, s/he can benefit from the knowledge. (Havinghurst 1953)
There are times of special sensitivity when learning is possible. We have to look out for them, to help create environments that can create or stimulate such moments, be ready to respond, and draw on the right resources.
Cultivating collaborative relationships for learning
The main thing here is that teaching, like other parts of our work, is about relationship. We have to think about our relationships with those we are supposed to be teaching and about the relationships they have with each other. Creating an environment where people can work with each other, cooperate and learning is essential. One of the things that has been confirmed by recent research in neuroscience is that ‘our brains are wired to connect’, we are wired to be social (Lieberman 2013). It is not surprising then, that on the whole cooperative learning is more effective that either competitive learning (where students compete to meet a goal) or individualistic learning (Hattie 2011: 4733).
As teachers, we need to be appreciated as someone who can draw out learning; cares about what people are feeling, experiencing and need; and breathe life to situations. This entails what Carl Rogers (in Kirschenbaum and Henderson 1990: 304-311) talked about as the core conditions or personal qualities that allow us to facilitate learning in others:
Realness or genuineness . Rogers argued that when we are experienced as real people -entering into relationships with learners ‘without presenting a front or a façade’, we more likely to be effective. Prizing, acceptance, trust . This involves caring for learners, but in a non-possessive way and recognizing they have worth in their own right. It entails trusting in capacity of others to learn, make judgements and change. Empathic understanding . ‘When the teacher has the ability to understand the student’s reactions from the inside, has a sensitive awareness of the way the process of education and learning seems to the student, then again the likelihood of significant learning is increased’.
In practical terms this means we talk to people, not at them. We listen. We seek to connect and understand. We trust in their capacity to learn and change. We know that how we say things is often more important than what we say.
Scaffolding
Scaffolding entails providing people with temporary support so that they deepen and develop their understanding and skills – and develop as independent learners.
Like physical scaffolding, the supportive strategies are incrementally removed when they are no longer needed, and the teacher gradually shifts more responsibility over the learning process to the student. (Great Schools Partnership 2015)
To do this well, educators and workers need to be doing what we have explored above – cultivating collaborative relationships for learning, and building on what people know and do and then working just beyond it. The term used for latter of these is taken from the work of Lev Vygotsky – is working in the learner’s zone of proximal development .
A third key aspect of scaffolding is that the support around the particular subject or skill is gradually removed as people develop their expertise and commitment to learning.
Scaffolding can take different forms. It might simply involve ‘showing learners what to do while talking them through the activity and linking new learning to old through questions, resources, activities and language’ (Zwozdiak-Myers and Capel, S. 2013 location 4568). (For a quick overview of some different scaffolding strategies see Alber 2014 ).
The educational use of the term ‘scaffolding’ is linked to the work of Jerome Bruner –who believed that children (and adults) were active learners. They constructed their own knowledge. Scaffolding was originally used to describe how pedagogues interacted with pre-school children in a nursery (Woods et. al . 1976). Bruner defined scaffolding as ‘the steps taken to reduce the degrees of freedom in carrying out some task so that the child can concentrate on the difficult skill she is in the process of acquiring’ (Bruner 1978: 19).
Differentiation
Differentiation involves adjusting the way we teach and approach subjects so that we can meet the needs of diverse learners. It entails changing content, processes and products so that people can better understand what is being taught and develop appropriate skills and the capacity to act.
The basic idea is that the primary educational objectives—making sure all students master essential knowledge, concepts, and skills—remain the same for every student, but teachers may use different instructional methods to help students meet those expectations. (Great Schools Partnership 2013)
It is often used when working with groups that have within them people with different needs and starting knowledge and skills. (For a quick guide to differentiation see BBC Active ).
Accessing resources for learning
One of the key elements we require is the ability to access and make available resources for learning. The two obvious and central resources we have are our own knowledge, feelings and skills; and those of the people we are working with. Harnessing the experience, knowledge and feelings of learners is usually a good starting point. It focuses attention on the issue or subject; shares material; and can encourage joint working. When it is an area that we need to respond to immediately, it can also give us a little space gather our thoughts and access the material we need.
The third key resource is the internet – which we can either make a whole group activity by using search via a whiteboard or screen, or an individual or small group activity via phones and other devices. One of the good things about this is that it also gives us an opportunity not just to reflect on the subject of the search but also on the process. We can examine, for example, the validity of the source or the terms we are using to search for something.
The fourth great resource is activities. Teachers need to build up a repertoire of different activities that can be used to explore issues and areas (see the section below).
Last, and certainly not least, there are the standard classroom resources – textbooks, handouts and study materials.
As teachers we need to have a range of resources at our fingertips. This can be as simple as carrying around a file of activities, leaflets and handouts or having materials, relevant sites and ebooks on our phones and devices.
Adopting a growth mindset
Last, we need to encourage people to adopt what Carol Dweck (2012) calls a growth mindset. Through researching the characteristics of children who succeed in education (and more generally flourish in life), Dweck found that some people have a fixed mindset and some a growth mindset.
Believing that your qualities are carved in stone— the fixed mindset —creates an urgency to prove yourself over and over. If you have only a certain amount of intelligence, a certain personality, and a certain moral character—well, then you’d better prove that you have a healthy dose of them. It simply wouldn’t do to look or feel deficient in these most basic characteristics…. There’s another mindset in which these traits are not simply a hand you’re dealt and have to live with, always trying to convince yourself and others that you have a royal flush when you’re secretly worried it’s a pair of tens. In this mindset, the hand you’re dealt is just the starting point for development. This growth mindset is based on the belief that your basic qualities are things you can cultivate through your efforts. Although people may differ in every which way—in their initial talents and aptitudes, interests, or temperaments—everyone can change and grow through application and experience. (Dweck 2012: 6-7)
The fixed mindset is concerned with outcomes and performance; the growth mindset with getting better at the task.
In her research she found, for example, that students with a fixed mindset when making the transition from elementary school to junior high in the United States, declined – their grades immediately dropped and over the next two years continued to decline. Students with a growth mindset showed an increase in their grades ( op. cit. : 57). The significance of this for teaching is profound. Praising and valuing achievement tends to strengthen the fixed mindset; praising and valuing effort helps to strengthen a growth mindset.
While it is possible to question elements of Dweck’s research and the either/or way in which prescriptions are presented (see Didau 2015), there is particular merit when teaching of adopting a growth mindset (and encouraging it in others). It looks to change and development rather than proving outselves.
Structuring interventions and making use of different methods
One of the key things that research into the processes of teaching and educating tells us is that learners tend to like structure; they want to know the shape of a session or intervention and what it is about. They also seem to like variety, and changes in the pace of the work (e.g. moving from something quite intense to something free flowing).
It is also worth going back to the dictionary definitions – and the origins of the word ‘teach’. What we find here are some hints of what Geoff Petty (2009) has talked about as ‘teacher-centred’ methods (as against active methods and student-centred methods).
If we ask learners about their experiences and judgements, one of things that comes strongly through the research in this area is that students overwhelming prefer group discussion, games and simulations and activities like drama, artwork and experiments. At the bottom of this list come analysis, theories, essays and lectures (see Petty 2009: 139-141). However, there is not necessarily a connection between what people enjoy doing and what produces learning.
Schoolteachers may use all of these methods – but so might sports workers and instructors, youth ministers, community development workers and social pedagogues. Unlike schoolteachers, informal educators like these are not having to follow a curriculum for much of their time, nor teach content to pass exams. As such they are able to think more holistically and to think of themselves as facilitators of learning. This means:
Focusing on the active methods in the central column; Caring about people’s needs, experiences and feeling; Looking for teachable moments when then can make inputs often along the lines of the first column (teacher-centred methods); and Encouraging people to learn for themselves i.e. take on projects, to read and study, and to learn independently and be self-directed (student-centred methods).
In an appendix to this piece we look at some key activities of teaching and provide practical guidance. [See key teaching activities ]
What does good teaching look like?
What one person sees as good teaching can easily be seen as bad by another. Here we are going to look at what the Ofsted (2015) framework for inspection says. However, before we go there it is worth going back to what Paul Hirst argued back in 1975 and how we are defining teaching here. Our definition was:
Teaching is the process of attending to people’s needs, experiences and feelings, and making specific interventions to help them learn particular things.
We are looking at teaching as a specific process – part of what we do as educators, animators and pedagogues. Ofsted is looking at something rather different. They are grouping together teaching, learning and assessment – and adding in some other things around the sort of outcomes they want to see. That said, it is well worth looking at this list as the thinking behind it does impact on a lot of the work we do.
Inspectors will make a judgement on the effectiveness of teaching, learning and assessment by evaluating the extent to which: teachers, practitioners and other staff have consistently high expectations of what each child or learner can achieve, including the most able and the most disadvantaged teachers, practitioners and other staff have a secure understanding of the age group they are working with and have relevant subject knowledge that is detailed and communicated well to children and learners assessment information is gathered from looking at what children and learners already know, understand and can do and is informed by their parents/previous providers as appropriate assessment information is used to plan appropriate teaching and learning strategies, including to identify children and learners who are falling behind in their learning or who need additional support, enabling children and learners to make good progress and achieve well except in the case of the very young, children and learners understand how to improve as a result of useful feedback from staff and, where relevant, parents, carers and employers understand how learners should improve and how they can contribute to this engagement with parents, carers and employers helps them to understand how children and learners are doing in relation to the standards expected and what they need to do to improve equality of opportunity and recognition of diversity are promoted through teaching and learning where relevant, English, mathematics and other skills necessary to function as an economically active member of British society and globally are promoted through teaching and learning.
We see some things that many will not disagree with like having high expectations of learners, knowing what the needs of the group may be, having expertise in the area being taught; recogniting diversity and having a concern for equality of opportunity; and so on. We may also see the role that assessment plays in reinforcing learning and helping to shape future learning. However, there are things we may disagree with. Perhaps more importantly there are all sorts of things missing here. For example, why is there an emphasis on economic activity as against social, religious and political participation? Another issue, for many of you reading this, is possibly the way in which little account is made of the extent to which learners take responsibility for their own learning. They are encouraged to contribute to learning but not own it.
Good teaching is rather more than technique according to Parker J. Palmer . Good teaching, he says, ‘comes from the identity and integrity of the teacher’ (Palmer 1998: 11). It is the way we are experienced, our enthusiasm, our care, our knowledge, our interest in, and concern for, people that is the key to whether we are felt to be good teachers. As Jackie Beere (2012) and others have argued we need to be present as people in the classroom or learning environment.
This is not to say that technique isn’t important. It is. We need to be skilled at scaffolding learning; creating relationships and environments for learning; and catching teaching moments. It is just that these skills need to be employed by someone who can be respected, is experienced as real and is wise.
In this piece we have made a plea to explore teaching as a process rather than something that is usually approached as the thinking and activity associated with a particular role – the school teacher. As has been argued elsewhere a significant amount of what those called school teachers do is difficult to classify as education (see What is education? ). Even the most informal of educators will find themselves teaching. They may well work hard at building and facilitating environments where people can explore, relate and learn. However, extending or deepening that exploration often leads to short, or not so short bursts of teaching or instructing. For example, as sports coaches or outdoor educators we may be both trying to develop teamwork and build particular skills or capacities. As a specialist or religious educators we might be seeking to give information, or introduce ideas that need some explanation. These involve moments of teaching or instructing. Once we accept this then we can hopefully begin to recognize that school teachers have a lot to learn from other teachers – and vice versa.
We also need to unhook ‘pedagogy’ from school teaching within English language discussions – and to connect it with the tradition of didactics. One of the problems with the false link of school teaching to pedagogy is that it is impairing a proper discussion of pedagogy. However, that may change a little in the UK at least with the development of professional standards for social pedagogy and the emergence of graduate and post-graduate study in the area.
Further reading and references
Check out the Teaching and Learning Toolkit . The Educational Endowment Foundation has produced a very accessible review of the evidence concerning different things that schools do. Many of the things that schools do have little or no evidence to support them e.g. streaming and setting, insisting on school uniform, using performance related pay. Some things are very productive like giving feedback; teaching specific strategies to set goals, and monitor and evaluate academic development; peer tutoring; and early years’ intervention.
Key teaching activities . This infed page outlines 9 key activities and why they are central to the process of teaching.
Alber, R. (2014). 6 Scaffolding Strategies to Use With Your Students, Eductopia . [ http://www.edutopia.org/blog/scaffolding-lessons-six-strategies-rebecca-alber . Retrieved February 9, 2016].
BBC Active (2010). Methods of Differentiation in the Classroom . London: Pearson Education . [ http://www.bbcactive.com/BBCActiveIdeasandResources/MethodsofDifferentiationintheClassroom.aspx . Retrieved: January 31, 2016]
Beere, J. (2012). The Perfect Ofsted Lesson Bancyfelin: Independent Thinking Press.
Bruner, J. S. (1960). The Process of Education . Cambridge MA.: Harvard University Press.
Bruner, J. S. (1961). The act of discovery. Harvard Educational Review , 31, 21-32.
Bruner, J. S. (1966). Toward a Theory of Instruction , Cambridge, MA.: Belkapp Press.
Bruner, J. (1973) Going Beyond the Information Given , New York: Norton.
Bruner, J. S. (1978). The role of dialogue in language acquisition. In A. Sinclair, R., J. Jarvelle, and W. J.M. Levelt (eds.) The Child’s Concept of Language. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Bruner, J. S. (1996). The Culture of Education . Cambridge, MA.: Harvard University Press.
Capel, S., Leask, M. and Turner T. (eds.) (2013). Learning to teach in the secondary school. A companion to school experience . 6e. Abingdon: Routledge.
Castle, E. B. (1961). Ancient Education and Today . Harmondsworth: Pelican.
Coe, R. et. al. (2014). What makes great teaching. Review of the underpinning research. London: The Sutton Trust. [ http://www.suttontrust.com/researcharchive/great-teaching/ . Retrieved December 20, 2014].
Covington, M. V. (2000). ‘Goal theory, motivation and school achievement: An integrative review’, Annual Review of Psychology , 51:171-200.
Cowley, S. (2011). Teaching for Dummies . Chichester: John Wiley.
Davey, A. G. (1972) ‘Education or indoctrination’, Journal of Moral Education 2 (1):5-15.
Department for Education and Skills. (2004a). Pedagogy and Practice: Teaching and Learning in the Secondary School, Unit 6 Modelling . London: Department for Education and Skills. [ http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110809101133/http://wsassets.s3.amazonaws.com/ws/nso/pdf/c60e7378e118be7f7d22d7660f85e2d8.pdf . Retrieved: February 25, 2016]
Department for Education and Skills. (2004b). Pedagogy and Practice: Teaching and Learning in the Secondary School, Unit 7 Questioning . London: Department for Education and Skills. [ http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110809101133/http://wsassets.s3.amazonaws.com/ws/nso/pdf/027c076de06e59ae10aeb9689a8a1c04.pdf . Retrieved: February 25, 2016]
Department for Education and Skills. (2004c). Pedagogy and Practice: Teaching and Learning in the Secondary School, Unit 8 Explaining . London: Department for Education and Skills. [ http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110809101133/http://nsonline.org.uk/node/96982?uc=force_uj . Retrieved: February 25, 2016].
Department for Education and Skills. (2004d). Pedagogy and Practice: Teaching and Learning in the Secondary School, Unit 10 Group work . London: Department for Education and Skills. [ http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110809101133/http://nsonline.org.uk/downloader/100963eebbb37c81ada6214ed97be548.pdf . Retrieved: February 25, 2016]
Department for Education and Skills. (2004e). Pedagogy and Practice: Teaching and Learning in the Secondary School, Unit 11 Active engagement techniques . London: Department for Education and Skills. [ http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110809101133/http://nsonline.org.uk/node/96205?uc=force_uj . Retrieved: February 25, 2016].
Department for Education and Skills. (2004f). Pedagogy and Practice: Teaching and Learning in the Secondary School, Unit 12 Assessment for learning . London: Department for Education and Skills. [ http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110809101133/http://nsonline.org.uk/downloader/2deff878cffd2cdcd59a61df29e73105.pdf . Retrieved: February 25, 2016].
Didau, D. (2015). What if everything you knew about education was wrong? Bancyfelin: Crown House Publishing.
Dweck, C. S. (2012). Mindset . London: Robinson.
Gervis and Capel (2013). ‘Motivating pupils’ in S. Capel e t. al. (eds.) Learning to teach in the secondary school. A companion to school experience . 6e. Abingdon: Routledge.
Great Schools Partnership (2013). ‘Differentiation’, S. Abbott (ed.) The Glossary of Education Reform . [ http://edglossary.org/differentiation/ . Retrieved February 10, 2016].
Great Schools Partnership (2015). ‘Scaffolding’, S. Abbott (ed.) The Glossary of Education Reform . [ http://edglossary.org/scaffolding/ . Retrieved February 10, 2016].
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible Learning: A Synthesis of Over 800 Meta-Analyses Relating to Achievement . Abingdon: Routledge.
Hamilton, D. (1999). ‘The pedagogic paradox (or why no didactics in England?)’, Pedagogy, Culture & Society , 7:1, 135-152. [ http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/14681369900200048 . Retrieved: February 10, 2012].
Havinghurst, R. J. (1953). Human Development and Education . London: Longman, Green.
Herbart, J. F (1892). The Science of Education: its general principles deduced from its aim and the aesthetic revelation of the world , translated by H. M. & E. Felkin. London: Swann Sonnenschein.
Herbart, J. F., Felkin, H. M., & Felkin, E. (1908). Letter and lectures on education: By Johann Friedrich Herbart ; Translated from the German, and edited with an introduction by Henry M. and Emmie Felkin and a preface by Oscar Browning. London: Sonnenschein.
Hirst, P. (1975). What is teaching? In R. S. Peters (ed.) The Philosophy of Education . London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
Jeffs, T. and Smith, M. K. (2018) Informal Education .London: Educational Heretics.
Kant, I. (1900). Kant on education (Ueber pa?dagogik) . Translated by A. Churton. Boston: D.C. Heath. [ http://files.libertyfund.org/files/356/0235_Bk.pdf . Accessed October 10, 2012].
Kansanen, P. (1999). ‘The “Deutsche Didadtik” and the American research on teaching’ in B. Hudson et. al. (eds.) Didadtik-Fachdidadtik as science(s) of the teaching profession ? Umeå Sweden: TNTEE Publications. [ tntee.umu.se/publications/v2n1/pdf/2_1complete.pdf . Retrieved: February 26, 2016].
Kirschenbaum, H. and Henderson, V. L. (eds.) (1990). The Carl Rogers Reader . London: Constable.
Lieberman, M. D. (2013). Social. Why Our Brains Are Wired to Connect . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Nuthall, G. A. (2007). The hidden lives of learners . Wellington, New Zealand: New Zealand Council for Educational Research.
Ofsted (2015). The common inspection framework: education, skills and early years. London: Ofsted. [ https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/461767/The_common_inspection_framework_education_skills_and_early_years.pdf . Retrieved May 28, 2018]
Palmer, P. J. (1998). The Courage to Teach. Exploring the inner landscape of a teacher’s life . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Petty, G. (2009). Teaching Today. A practical guide . Cheltenham: Nelson Thornes.
Smith, M. K. (2012). ‘What is pedagogy?’, The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education. [ https://infed.org/mobi/what-is-pedagogy/ . Retrieved: February 25, 2012].
Smith, M. K. (2015). What is education? A definition and discussion. The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education . [ https://infed.org/mobi/what-is-education-a-definition-and-discussion/ . Retrieved: February 25, 2016].
Snook, I. (1972). Concepts of Indoctrination: Philosophical Essays . London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
Wilson, L. (2009) Practical Teaching. A guide to PTLLS and DTLLS . Andover: Cengage.
Wood, D. J., Bruner, J. S., & Ross, G. (1976). The role of tutoring in problem solving. Journal of Child Psychiatry and Psychology , 17(2), 89-100.
Wragg, E. C. and Brown, G. (2001). Questioning in the Secondary School . London: RoutledgeFalmer.
Young, N. H. (1987). ‘Paidagogos: The Social Setting of a Pauline Metaphor’, Novum Testamentum 29: 150.
Zwozdiak-Myers, P. and Capel, S. (2013). Communicating with Pupils in Capel, S., Leask, M. and Turner T. (eds.) Learning to teach in the secondary school. A companion to school experience . 6e. Abingdon: Routledge.
Acknowledgements
The section ‘teaching, pedagogy and didactics’ draws heavily on another piece written by Mark K Smith for infed.org ( see Smith 2012 ).
The ACE diagram is taken from Smith, M. K. (forthcoming). Working with young people in difficult times (Chapter 1). https://infed.org/mobi/working-with-young-people-in-difficult-times/
Picture: Group project by Brande Jackson . Flickr | ccbyncnd2 licence
How to cite this piece : Smith, M. K. (2018). ‘What is teaching?’ in The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education . [ https://infed.org/mobi/what-is-teaching/ . Retrieved: insert date].
© Mark K Smith 2016, 2018.
Professionalism in the Teaching Profession Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Professionalism in Teachers
Code of conduct for teachers, reference list.
Professionalism is a very important factor and it should be present in any professional worker. In this paper, the teaching profession has been discussed and the importance of professionalism in the teaching profession has been studied in detail. Moreover, the basic requirements which every professional teacher should have to include a code of conduct, a relationship with other staff members, skills for maintaining discipline in a classroom, and usage of the internet.
Professionalism is very important in the education sector as it has a very deep impact on the role of a teacher, which in response influences the aptitude of students to learn successfully. A teacher’s professionalism can be defined as the talent to reach students substantially, increasing inventive approaches to motivate students, appealing, and stimulating immature minds to train them for growing technology (Hilferty, 2008).
The code of conduct is designed by the school administrator, professional organization/union representatives, school board members, and parent/community members. They said that code of professional conduct for teachers has some requirements which include
- Regular presence
It means that teacher should be present at school, and he/she should act very seriously against the requirements for reporting absence from school.
- Punctuality
A teacher should be very punctual as it is one of the foremost requirements for the professional teacher, and she should also fulfill the number of lectures, lessons, and workshops, etc assigned to him/her for each class. The presence of teachers is mandatory in the assembly and at the end of the day or school timings.
It means that a teacher should have respect for all staff members, admin people, students, and parents within his/her heart. These consist of penal measures, an equal number of chances, anti-biased and anti-discriminatory policies.
- Internet usage
Nowadays, it has become a requirement for teachers to know how to operate and use the internet as it is required, as it is one of the basic requirements of educational bodies.
- Positive behavior
Teachers are the symbol of inspiration for students, so they should behave properly in the class and other than class timings. She should be kind towards all children and their parents, whenever she meets them in formal or informal settings.
- Skills to actively listen and work on criticism and suggestions
Sometimes teachers have to face harsh responses from parents, senior teachers, and other staff members in schools, but she should develop an aptitude to react very softly against such issues.
- Should follow a proper standard of dress code
Whenever a teacher enters into the school environment, she should keep this thing in mind that she is acting as a role model for students, and for that, she has to maintain a proper standard of dress code, which should be decent and reasonable for school settings.
- Performing duties as per the requirements of the school administration
She should perform her duties well while she is in classrooms, gathering with and working with a teacher, in the development, education, and evaluation of students and other required professional needs.
Ethical and legal issues are considered to be the supreme priority in the educational sector. Professionals avoid discussing issues regarding other coworkers, the place where they work, and any strange situations. Teachers should act as professionals while they are in school. If teachers face any problem regarding the above-mentioned requirements, then they should speak to their mentor or administrator truthfully in a professional manner.
Hilferty, F. (2008). Teacher professionalism defined and enacted – A comparative case study of two Subject teaching associations . Australlia: VDM Verlag Dr. Mueller e.K.
- Teacher Tenure: Reasons and Oppositions
- Reluctant Disciplinarian by Gary Rubenstein
- Supply Chain Disruptions and Forecasting Failure
- Ba Ba Lu Bar's Workplace Decision-Making
- Aspects of Structured Observation in Learning
- Teacher`s Rights and Responsibilities
- School Principal: Successful Time Management
- Quality and Improvement in Education: The Role of the Educational Practitioner
- Sustain Neophytes in Teaching Profession
- Classes With Mixed Academic Performance
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, November 14). Professionalism in the Teaching Profession. https://ivypanda.com/essays/professionalism-in-the-teaching-profession/
"Professionalism in the Teaching Profession." IvyPanda , 14 Nov. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/professionalism-in-the-teaching-profession/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Professionalism in the Teaching Profession'. 14 November.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Professionalism in the Teaching Profession." November 14, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/professionalism-in-the-teaching-profession/.
1. IvyPanda . "Professionalism in the Teaching Profession." November 14, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/professionalism-in-the-teaching-profession/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Professionalism in the Teaching Profession." November 14, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/professionalism-in-the-teaching-profession/.
10 Ways the Teaching Profession Has Changed Over the Past 10 Years

- Share article

These past 10 years have been a whirlwind for the teaching profession. The policy pendulum has swung back and forth, and there has been a growing number of demands put on teachers’ plates.
“There’s an increasing amount of responsibility and accountability,” said Freeda Pirillis, a long-time teacher who is now the coordinator for an International Baccalaureate program in Chicago. “It’s almost become so burdensome and distracting to doing the job that’s important.”
As the 2010s draw to a close, Education Week spoke to teachers about some of the biggest shifts in the teaching profession over the past decade . Teachers said they’re hopeful about what’s next for the profession in the decade ahead, but their plates have never been more full.
See also : Teaching in 2020 vs. 2010: A Look Back at the Decade
From an increase in teacher activism to a decline in the number of people who want to be teachers, here are 10 of the biggest shifts in the profession.
1. States have adopted tougher academic standards. The Common Core State Standards were released in 2010, and the Next Generation Science Standards were released in 2013. With the rigorous standards came new curricula and new teaching methods. But implementation was rife with political and logistical challenges, and in the early days, many teachers were left scrambling to put together their own curriculum. There was also more of an emphasis on math and reading tests associated with the standards, teachers said, often at the expense of other subjects.
Originally, 46 states adopted the common core. Since then, more than 20 states have revised or renamed the standards to back away from some of the controversy.
Some teachers say that teaching now feels more prescriptive, and there’s less room for creativity.
2. Teacher-evaluation systems began incorporating student-test scores. Thanks to federal incentives at the beginning of the decade, most states toughened the way they grade their teachers, incorporating student test scores into educators’ ratings. Under some systems, a bad rating put teachers at risk for dismissal.
These efforts were unpopular among many teachers and their unions, and in some cases, failed to make a difference in student achievement. (In other cases, like in the District of Columbia , the high-stakes evaluation system has led to gains in student learning.)
Since the federal incentives have ended, many states walked back one or more of their evaluation refoms . Even so, teachers still say they feel an increased pressure to make sure their students are growing from year to year.
“I think the change came for teaching when we made the success of the students the teachers’ responsibility instead of helping the students simply succeed,” said Frances Spielhagen, a professor of education at Mount Saint Mary College in Newburgh, N.Y. “Once you make a person’s livelihood dependent on the success of someone she’s trying to help succeed, it changes the focus of what you’re trying to do.”
3. The influx of new technology and social media has transformed teaching. Sarah Brown Wessling, the 2010 National Teacher of the Year, said the technology has opened up new doors in her classroom. Her students have immediate access to research, and can connect with people on the other side of the country or even the world.
But there are downsides. A recent national survey found that 15 percent of students aged 12-18 were bullied online or through text messages during the 2016-17 school year. That’s higher than in past years. And the internet can be a distraction for students.
“It’s created a call to action for me,” Wessling said. “It’s really forced me to think more carefully about what engagement actually looks like in the classroom.”
4. Teen depression and suicide is on the rise. Federal data show that suicide rates for teens between the ages of 15 and 19 increased by 76 percent between 2007 and 2017 . And the suicide rate for 10- to 14-year-olds nearly tripled over that same time period.
Depression has also become increasingly common among teenagers, especially girls. Researchers are considering the rise of smartphone and social media use, as well as the prevalence of bullying, as possible reasons for increasing mental health issues.
“I’m sure teachers bare the brunt of this, and they may or may not be qualified to respond to this, but they are to whom this falls,” said Jonna Perrillo, an education historian and an associate professor of English education at the University of Texas at El Paso.
5. The increasingly divisive rhetoric in politics has made its way into classrooms. The 2016 presidential campaign was notable for how it inflamed racial and ethnic tensions. Many teachers said they have never before had such a difficult time remaining neutral, since many felt like they had to condemn some of President Donald Trump’s more controversial remarks.
Education Week examined nearly 500 incidents of hate that took place in schools between January 2015 and December 2017, and found that most targeted black and Latino students, as well as those who are Jewish or Muslim.
And the impact of some of Trump’s policies as president can also be felt in classrooms. Justin Minkel, a 2nd grade teacher in an Arkansas elementary school with high numbers of Latino students, said the crackdown on immigration has “created some negative, psychological stress” among his young students.
See also : Timeline: How Teaching Has Changed Over the Decade
6. Two horrific school shootings made safety a top-of-mind issue for teachers, students, and policymakers. The deadliest school shootings, at Sandy Hook Elementary School in Newtown, Conn., and Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Parkland, Fla., both happened this decade, leading to intense debates on how to make schools feel safer.
School shootings are still rare—Education Week has counted 24 school shootings this year , with seven deaths (five of whom were children). There are more than 132,000 schools across the United States, with about 50 million students. Even so, active-shooter drills have become ubiquitous in schools , and teachers have said lockdown drills increasingly feel more real .
“We have a heightened sense of the real threats that exist,” said Pirillis of Chicago.
In response to these threats, some policymakers (including Trump and Education Secretary Betsy DeVos) have advocated for allowing teachers to carry guns at work. This idea is often met with resistance from educators, but a handful of states allow educators to carry guns on school grounds .
7. Fewer people are enrolling in teacher-preparation programs. Across the country, enrollment in teacher-preparation programs has dropped by one-third over the past decade. Program completion has declined as well.
Enrollment numbers can be a “proxy for interest in the teaching profession,” said Lisette Partelow, the senior director of K-12 strategic initiatives at the Center for American Progress, who analyzed this data. Some of these declines, she added, are “quite worrying.”
In fact, in 2018, less than half of Americans said they wanted their child to become a public school teacher —that’s down from 70 percent in 2009.
8. States and school districts have increasingly formalized teacher-leadership roles. Teachers have called for professional opportunities that let them be involved in decision making without leaving the classroom. And this decade has seen a surge of interest in the concept. In 2014, the Education Department launched a national teacher-leadership initiative, and a recent analysis from the NCTQ found that 35 states now have formal teacher-leadership policies.
Even so, only 21 of them give teacher-leaders extra pay or other incentives, like a reduction in course load. Those incentives make teacher leadership sustainable, researchers say.
A 2017 study found that students who go to schools where their teachers have a leadership role in decision making perform significantly better on state tests .
9. Teachers across the country began protesting and leading work stoppages to demand higher pay and more money for schools. In February 2018, West Virginia teachers shut down schools across the state as they went on strike to protest changes to the statewide health insurance plan and to demand a pay raise. They were largely successful, and have been credited with lighting the match for the teacher activism that has spread across the nation like wildfire over the past two years.
The public has been largely supportive of teachers , who have positioned themselves as fighting for what students need . Over the past decade, the public and media have become more sympathetic to teachers .
“If you would have asked me 10 years ago, I never would have expected to see the Red for Ed movement in this context,” said Michelle Pearson, a middle school social studies teacher near Denver. “It wasn’t the time. ... [Now], it’s come to a precipice. It’s a situation where it’s all or nothing. We either move in that direction and bring our voices to the table, or the changes don’t get made.”
10. The conversation on teacher pay has changed. In the first part of the decade, policymakers wanted to pay high-performing teachers more. Several states and districts implemented pay-for-performance policies, and the U.S. Department of Education gave out $437 million in grants to districts that committed to implementing a performance-based pay system for teachers.
But those policies have since largely fallen out of favor. A 2017 evaluation of the Department Education’s grant program found that fewer than half of the districts planned to continue performance-based bonuses. And teachers in Denver went on strike earlier this year over a dispute centered on the district’s once-revolutionary performance-pay model.
Now, policymakers and teachers themselves are mostly advocating for across-the-board pay raises. Many teachers are dissatisfied with their pay , which is less than other similarly educated professionals .
Image via Getty
A version of this news article first appeared in the Teaching Now blog.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Essay Service Examples Education Teacher/Teaching
Essay on Teaching as a Profession
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- Stakeholders
- Teacher/Teaching
The teaching-learning process has gained all time importance in the changing educational scenario,...
The relational part of educating might just be its most underestimated angle. At the point when...
- STEM Education
- Technology in Education
STEM is a curriculum based on the idea of educating students in four specific disciplines —...
Epilepsy is considered one of the most important chronic neurological disorder (1,2),...
- Spanish Language
Sánchez, (2005) claims: 'The concern to improve language teaching is a common denominator in the...
“I covered the kitchen table with books. They had to be bang up to date. If there was a week’s...
- Natural Environment
Encouraging as many students to study botany is becoming a major priority for universities across...
This report will be about producing a critical analysis of skills, knowledge, personal...
The lecture of college teaching is very significant for me. I got the great idea and knowledge in...
Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!
Home / Essay Samples / Education / Teacher / Unveiling the Roles and Challenges of Teaching Profession
Unveiling the Roles and Challenges of Teaching Profession
- Category: Life , Education
- Topic: Career , Career Goals , Teacher
Pages: 2 (1014 words)
- Downloads: -->
--> ⚠️ Remember: This essay was written and uploaded by an--> click here.
Found a great essay sample but want a unique one?
are ready to help you with your essay
You won’t be charged yet!
Illiteracy Essays
Critical Thinking Essays
Reading Essays
Online Classes Essays
Coaching Essays
Importance of Teaching Profession | Characteristics of Teaching
- Post author: edmonger
- Post published: July 29, 2021
- Post category: Trends and Insights
- Post comments: 3 Comments
“TEACHER” the world itself includes “Teach” which means “GURU” who shares the experience, knowledge, and skills to others for a better-educated world. Apart from lavishing career, there are numerous of Importance of Teaching Profession.
In India, Teachers are treated as nation builders as teachers play the role of substitute parents. Only Teachers can facilitate student’s growth, skills, and creativity. Someone has well said that –
We all are much aware that the art of teaching is the art of assisting discovery. The teaching profession refers to providing knowledge and making a better individual with all normal forms of discipline.
The teaching Profession is strengthening career opportunities that contribute to in-country growth. To know more Importance of the Teaching Profession and the Characteristics of teachers, must read out all details described below.
What Is Teaching Profession?
Well, we all know that what it is Teaching Profession? But still, we need to be aware of more significance of the Teaching Profession. Through the Teaching Profession, one can earn a better pay scale. Teachers encourage students to be dedicated to studies and passionate about their careers.
Teaching is a profession and a mode to make students have more potential and learn important lessons even about life like respect, sharing, ethical values, and cultures.
Also Check – 20 Techniques to Supercharge Your Online Teaching
Importance of Teaching Profession
Teaching is the most desirable Profession nowadays. The importance of the Teaching Profession includes fun and learning together. Being in the teaching profession doesn’t mean you have to share your knowledge. Sometimes teachers themselves learn something new with teaching experience.
Teachers play a vital role in student’s life by helping them achieve their goals. Therefore, choosing the Teaching Profession offers endless career opportunities. However, Teaching is not the only Profession; in fact, it is the activity to serve education.
Here we have enlisted some Importance of Teaching Profession. So those who are interested in being teachers must go through the following points-
Improves Communication Skills
Teaching is a systematic technique to communicate with more and more people. Thus, being in the teaching profession will improve communication skills. As a result, one can interact more confidently with others.
Increase knowledge and skills
Teachers are only one who passes on their knowledge and skills to the young generation. Through this profession, teachers motivate and inspire students to focus and develop their natural abilities.
A learner itself
As learning has no boundaries, one can never stop learning. In the teaching profession also, the teacher can learn at any stage and age too. Even R.N. Tagore has said that
“Lamp can never light another lamp unless if continues to burn its own flame same as a teacher can never teach unless he/ she is a learner”.
Fun and learning together
Among all careers and professions, I found teaching much better. The Importance of the Teaching Profession is that one can experience fun and learn together. Besides instructing students, teachers can involve in other curriculum activities.
Experience To Handle Different Children
School or college is a place where different students with different mindsets reach. The teacher must have the ability to handle all children normal, intelligent, or physically disabled.
Excellent Organization Skills
The teaching profession makes one multi-tasker; in spite of teaching academics to students, teachers, and Organizational skills. Being organized means one can manage time and resources efficiently and effectively for better productivity.
Ethical And Disciplined
One characteristic of the teaching profession involves ethics and discipline. Teachers teach ethical values which make students more disciplined. Ethical behavior encourages students to know what is bad or good for them.
Setting up Role Model For Others
Being a teacher isn’t much complex but being a favorite of all is what matters. Teachers should inspire students to found their hidden talents and achieve their aim. An inspired teacher can make students motivated by setting up Role models.
Build Future Leaders
Teachers are the source of influencing tomorrow’s leaders. Teachers create classroom space and enable students to be educated and future responsible leaders.
Characteristics of Teaching
However, many teachers teach in schools/academies/Institutions or universities, but not all may succeed in being great teachers for students. So, what are the characteristics of the Teaching Profession that make teachers more effective in the classroom?
Those who enjoy spending time with children and are willing to make others educated with their skills can choose Teaching as a Profession. A good teacher has the power to change lives with their education. To become an exemplary teacher, one may possess relevant qualities like creating a dynamic environment, being flexible, kind, classroom management, a good sense of humor, an active personality, Innovative, a calm demeanor, experience, etc.
Final Words… In the end, we can say that the teaching profession is not just a job. The teaching profession is all about shaping the future of our country. So to guide our youth in the right direction and making their dream come true teaching professional plays a vital role.
Also Check: Is India Ready for Virtual Schools?
You Might Also Like

Revolutionizing Edtech: The Impact Of ChatGPT on the Edtech Industry
Are you a friday person in a monday world.

Embracing Ai: How Schools Can Thrive Amidst Technological Change?
This post has 3 comments.
Pingback: Importance of Teacher Training Institute in Modern Era - Edmonger
Pingback: Why Do You Want To Become Better As A Teacher? – GoGreenva.org
Pingback: How Should You Choose The TEFL Certification Courses? - ClassyNewspaper
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
How to Set Boundaries as an Overworked Educator
Consider Ms. McDaniels.
She’s a dedicated high school teacher who arrives early each day to prepare for her lessons and often stays late to offer extra help to students. Sarah McDaniels also takes work home, spending her evenings grading papers and planning future classes. Despite her passion, she feels exhausted and disconnected from her family and friends. Maybe you can relate to Sarah.
But there is a solution to Sarah’s problem: boundaries.

Boundary-setting is a form of self-compassion, a concept extensively researched by Kristin Neff. Self-compassion involves treating oneself with the same kindness and understanding that one would offer to a friend. It consists of three main components:
- Self-kindness: Being warm and understanding toward oneself rather than self-critical.
- Common humanity: Recognizing that suffering and personal inadequacy are part of the shared human experience.
- Mindfulness: Holding one’s painful thoughts and feelings in balanced awareness rather than overidentifying.
When educators set boundaries, they practice self-kindness by acknowledging their needs and limits. They recognize the common humanity in needing rest and personal time, understanding that these needs are universal and legitimate. Mindfulness helps educators stay aware of their stress levels and emotional states, allowing them to take proactive steps to care for themselves.
Boundary setting can lead to numerous positive outcomes, including reduced stress, increased job satisfaction, and better overall well-being. By establishing clear limits, educators can create a sustainable balance between their professional duties and personal lives, essential for long-term career fulfilment.
Of course, setting boundaries isn’t always easy—and students, parents, colleagues, and administrators may not be pleased when they encounter them.
However, boundary setting is essential for maintaining well-being and fostering healthy relationships. When we establish clear boundaries, we communicate our values, needs, and limits, which helps others understand where we stand. By respecting boundaries, we create an environment of mutual respect and trust where everyone knows what to expect and how to interact to honor each other’s space and emotions. It’s an invitation to engage with one another more authentically and respectfully, where everyone’s well-being is prioritized. And when we model and respect boundaries, we empower others to do the same, contributing to a culture of understanding and compassion.
Getting fierce about boundaries
Neff and her colleague Christopher Germer have explored the concept of “ fierce self-compassion .” This form of self-compassion emphasizes protective and empowering actions individuals can take to care for themselves and others. For educators, fierce self-compassion involves taking assertive steps to set and maintain boundaries, ensuring that their needs are met alongside their professional responsibilities. That can include:
- Protecting: Defending oneself from harm, including emotional and physical exhaustion. For educators, this might mean limiting the time spent on work-related tasks outside school hours.
- Providing: Ensuring that one’s own needs are met, such as scheduling time for rest, hobbies, and family. This proactive approach helps prevent burnout and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
- Motivating: Encouraging oneself to strive for a balanced and fulfilling life. Setting realistic goals and acknowledging achievements can boost morale and sustain the long-term passion for teaching.
Imagine our teacher, Ms. McDaniels, finishing up a long day of teaching and heading home…and then a colleague asks for help with a last-minute project. Sarah feels the pressure to say yes, fearing that declining might come across as uncooperative or unsupportive. However, she is already exhausted and has plans for much-needed rest. At this moment, her boundary is being threatened. She knows that if she agrees, it will push her past her limits, compromising her well-being.
To support herself, Sarah can tap into her fierce self-compassion. She can acknowledge her fatigue and the importance of her own needs over those of her colleagues. With a firm yet kind tone, Sarah can respond by saying, “I understand this project is important, but I’m unable to assist right now because I need to rest. Perhaps we can find another solution or connect tomorrow.”

Greater Good Educators Program (Winter/Spring): Bridging for Belonging
Explore the science of empathy, humility, forgiveness, and hope to develop skills for bridging differences in schools
Standing up for herself protects her energy and models healthy boundary-setting, demonstrating that self-care is valid and necessary for sustained effectiveness as an educator.
Practical strategies for setting boundaries
So, how do we practice boundary-setting with fierce self-compassion?
To integrate boundary-setting into their lives, educators can adopt the following strategies:
- Prioritize self-care: Make time for activities that nourish your body and mind. Schedule regular exercise, maintain a healthy diet, and ensure you get adequate sleep. Engaging in hobbies and spending time with loved ones can provide a much-needed break from work-related stress.
- Set clear work hours: Define specific times for work and personal life. For example, decide not to check emails after a particular hour in the evening or on weekends. Communicate these boundaries to colleagues, students, and parents to manage expectations.
- Learn to say no: Recognize limits and avoid overcommitting. Decreasing additional responsibilities or extracurricular activities can help keep your workload manageable.
- Seek support: Build a positive support network among colleagues, friends, and family. Sharing your experiences and challenges with others can provide valuable insights and encouragement. Consider joining professional learning communities or seeking mentorship for additional guidance. Check out Greater Good Educators Program .
Recognizing and respecting other people’s boundaries is also crucial in creating a psychologically safe and supportive school environment. Boundaries are personal limits that protect our emotional, mental, and physical well-being. When we honor these limits in others and ourselves, we contribute to a culture of respect and trust.
That means understanding that students, colleagues, and parents have different needs, stressors, and capacities in a school setting. Respecting someone’s boundary might involve accepting a student’s request for extra time on an assignment, recognizing when a colleague needs uninterrupted planning time, or understanding when a parent needs a break from school-related communications.
In honoring those boundaries, we validate the other person’s experience and create a space where they feel seen and respected. This, in turn, fosters open communication, reduces stress, and builds stronger, more trusting relationships within the school community.
However, creating a culture of boundaries and fierce self-compassion in schools goes beyond individual interactions; it requires systemic support and intentional practices that reinforce these values. Educators can lead by example by openly discussing the importance of boundaries and practicing self-compassion in their daily lives.
For instance, when teachers set clear limits on their availability, such as not answering emails after a certain hour, they model the importance of work-life balance for students and colleagues. When educators practice self-compassion, they experience less burnout and gain greater emotional resilience, positively impacting their teaching and student interactions. This practice can create a ripple; encouraging students to set their boundaries and respect those of others also helps them develop critical social-emotional skills. In a classroom where the educator models and values boundaries, students learn it’s OK to say no, ask for help, or request space when needed—skills essential for their well-being and future success. By integrating these practices into the fabric of school life, we create an environment where everyone can thrive, supported by a culture that values respect, empathy, and self-care.
So, as educators return to the classroom this fall, let’s embrace boundary-setting and fierce self-compassion as vital practices for well-being and positive cultures. By understanding the science behind boundary-setting and implementing practical strategies, educators can create a healthy balance between their professional and personal lives.
About the Author
Lisa Baylis
Lisa Baylis has been sharing well-being strategies for the last 20 years. A natural-born connector with an innate ability to make people feel valued and heard, she is a teacher, a counselor, a speaker, and a mother.
You May Also Enjoy

How Self-Compassion Can Help Prevent Teacher Burnout

Are Boundaries Overrated?

Dear Christine: How Can I Set Boundaries for the Holidays?

What Teachers Really Need to Thrive

How to Bring Self-Compassion to Work with You

How to Set Boundaries When You’ve Never Been Taught How
- DOI: 10.1080/09620214.2022.2138940
- Corpus ID: 253628756
The COVID-19 pandemic and the reconstitution of education
- Laura C. Engel , C. Maxwell , Miri Yemini
- Published in International Studies in… 2 October 2022
Related Papers
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Comprehensive TOK Essay Guide for 2025 Titles
Subject: Philosophy and ethics
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Other
Last updated
3 September 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This document offers an in-depth analysis of the 2025 IB Theory of Knowledge (TOK) essay titles. Ideal for students aiming for a high pass grade, it breaks down each title thoroughly, providing:
Detailed Unpacking of Key Concepts: Clear explanations of each title, ensuring you understand exactly what’s being asked.
Expert Analysis of Areas of Knowledge (AOKs): Insightful connections between the essay titles and various AOKs, such as History, Natural Sciences, Mathematics, and the Arts.
Real-World Examples: Concrete examples tailored to each essay question, which can be directly used or adapted in your writing.
Critical Argumentation Tips: Guidance on how to craft balanced, coherent arguments, including how to integrate counterarguments.
Conclusion Strategies: Learn how to effectively conclude your essay with clarity and depth.
This guide provides everything you need to confidently tackle the TOK essay titles for 2025, making it a valuable resource for IB students looking to maximize their scores.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- Humanities & Social Sciences
- Health & Social Welfare
- Cancer & Palliative Care
The Reality of Assisted Dying: Understanding the Issues

- Provides up-to-date data, evidence and reflections from professionals from countries where assisted dying has been legalized;
- Takes a fresh look at the arguments around legalization of assisted dying;
- Shows how a change in the law must take account of all those who will be affected, including families and those who will feel compelled to participate by assisting suicides or performing euthanasia;
- Shows the problems and dangers of embedding assisted dying within healthcare, and explores how alternative socio-legal procedures would improve legitimacy and monitoring for patients and their families.
Purchase Options
We're committed to providing you with high-value course solutions backed by great service and a team that cares about your success.
Receive via shipping:
- Colour, print bound version of the complete text
ISBN10: 0335253172 | ISBN13: 9780335253173
- Access the eBook anytime, anywhere: online or offline
- Create notes, flashcards and make annotations while you study
- Full searchable content: quickly find the answers you are looking for
ISBN10: 0335253199 | ISBN13: 9780335253197
ISBN10: 0335253180 | ISBN13: 9780335253180
- Education news
CBSE Sample Papers 2025: Class 10, 12 Sample Question Papers Issued at cbseacademic.nic.in
Cbse has released the 10th and 12th sample papers for the cbse 2025 board exams. download the subject-wise sample question paper pdf here. .

CBSE 10th 12th Sample Papers 2025: The Central Board of Secondary Education has released the CBSE 2025 sample papers for class 10 and class 12. Earlier, the sample papers for Skill Education were issued by the board. Candidates preparing to appear for their CBSE 2025 board exams in February 2025 can visit the academic website of CBSE to download the sample paper pdf.
CBSE 2025 sample papers help students to better prepare themselves for their upcoming board exam. The sample paper PDFs will contain questions according to the exam pattern set for each subject and the marks allotted for each section. It must be noted that the sample papers are nothing but an example of the type of questions students can expect in their CBSE 2025 board exams.
CBSE 2025 sample papers for class 10 and class 12 are available on the official website - cbseacademic.nic.in. A direct link for class 10 and class 12 CBSE sample papers is also provided below.
CBSE 12th sample papers 2024-25 - Click Here
S teps to Download CBSE 10th, 12th Sample Paper PDF
The link for students to download the subject-wise CBSE sample papers is available on the official academic website. Follow the steps provided below to download the pdf
Step 1: Visit the official website of CBSE
Step 2: Click on an academic website
Step 3: Click on Sample Paper and navigate to class 10/class 12 section
Step 4: Click on the subject of choice and download the question paper pdf
CBSE 2025 Exam Dates
The next session of CBSE board exams is scheduled to be held in February 2025. The subject-wise timetable for the CBSE 10th and 12th exams 2025 will be issued by the board by December 2024. It is expected that just like the previous year the exams will begin in February and continue until April 2025. Students preparing to appear for the CBSE board exams must check their timetable and other related details at cbse.gov.in.
- West Bengal NEET UG 2024
- NIOS Practical Date Sheet 2024
- IIT JAM 2025
- AP PGECET Counselling 2024
- PUMDET Counselling 2024
- COMEDK Counselling 2024
- Rajasthan NEET UG 2024
- Tamil Nadu NEET UG Counselling 2024
- Tripura NEET UG 2024
- AIMA UGAT Admit Card 2024
- West Bengal Board
- Manipur Board
- Odisha Board
- Maharashtra Board
- Rajasthan Board
- Bihar Board
- Jharkhand Board
- Uttarakhand Board
Latest Education News
भारत में कहां से निकलती है हिंडन नदी, जानें
TNPSC Group 2 Important Questions 2024 for General Studies, English and Mental Ability
SBI SCO Recruitment 2024: Apply for 58 Specialist Cadre Officer Posts at sbi.co.in; Check Salary & Steps to Apply
September 2024 School Holidays: Educational Institutions to Remain Closed in These States, Check Complete List Here
International Literacy Day Drawings Ideas for Poster, Painting and Banner
(Updated) Paris Paralympics Medal Tally 2024, Day 9: Who is leading the Total Medal Count? Check Here
SSC Full Form with Complete Details
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Deleted Syllabus for 2025 Exams: Check Chapter-Wise Topics, And Exercises Removed
JSSC Lady Supervisor Admit Card Link 2024 OUT: जेएसएससी लेडी सुपरवाइज़ के एडमिट कार्ड जारी, ये रहा डाउनलोड लिंक
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Spot the Word 'Jeep' in 8 Seconds and Prove Your Brainpower!
KPSC Hall Ticket 2024 Out at kpsc.kar.nic.in: Check Admit Card Download Link and exam schedule
Punjab Board PSEB Class 8 Computer Science Sample Paper 2024-25: Download The Free PDF!
Brain Teaser: Which Glass Will Fill First? Only Top 1% Geniuses Pass This IQ Test in 5 Seconds!
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter-Wise Competency-Based Questions With Answer Key 2024-25: Free PDF Download
Unified Pension Scheme: लाभ, पात्रता, न्यूनतम पेंशन राशि, पेंशन कैलकुलेटर सहित सभी डिटेल्स यहां देखें
VTU Results 2024 OUT at vtu.ac.in, Download UG Semester Marksheet PDF
NExT Exam for Ayush Courses from 2021-22 Batch, Check Details Here
Is Kumar Sangakkara Set to Replace Gautam Gambhir as KKR's New Mentor?
CBSE Class 12 Physics Competency-Based Questions With Answer Key 2024-25: FREE PDF Download
AWES Army School TGT PGT PRT Recruitment 2024: जल्द जारी होगी आर्मी स्कूलटीचर भर्ती की अधिसूचना, यहाँ चेक करें डिटेल्स
- Open access
- Published: 03 September 2024
Reliability of ChatGPT in automated essay scoring for dental undergraduate examinations
- Bernadette Quah 1 , 2 ,
- Lei Zheng 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Timothy Jie Han Sng 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Chee Weng Yong 1 , 2 na1 &
- Intekhab Islam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7754-0609 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 962 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
This study aimed to answer the research question: How reliable is ChatGPT in automated essay scoring (AES) for oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMS) examinations for dental undergraduate students compared to human assessors?
Sixty-nine undergraduate dental students participated in a closed-book examination comprising two essays at the National University of Singapore. Using pre-created assessment rubrics, three assessors independently performed manual essay scoring, while one separate assessor performed AES using ChatGPT (GPT-4). Data analyses were performed using the intraclass correlation coefficient and Cronbach's α to evaluate the reliability and inter-rater agreement of the test scores among all assessors. The mean scores of manual versus automated scoring were evaluated for similarity and correlations.
A strong correlation was observed for Question 1 ( r = 0.752–0.848, p < 0.001) and a moderate correlation was observed between AES and all manual scorers for Question 2 ( r = 0.527–0.571, p < 0.001). Intraclass correlation coefficients of 0.794–0.858 indicated excellent inter-rater agreement, and Cronbach’s α of 0.881–0.932 indicated high reliability. For Question 1, the mean AES scores were similar to those for manual scoring ( p > 0.05), and there was a strong correlation between AES and manual scores ( r = 0.829, p < 0.001). For Question 2, AES scores were significantly lower than manual scores ( p < 0.001), and there was a moderate correlation between AES and manual scores ( r = 0.599, p < 0.001).
This study shows the potential of ChatGPT for essay marking. However, an appropriate rubric design is essential for optimal reliability. With further validation, the ChatGPT has the potential to aid students in self-assessment or large-scale marking automated processes.
Peer Review reports
Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, LLaMA by META, and Google’s LaMDA (Language Models for Dialogue Applications), have demonstrated tremendous potential in generating outputs based on user-specified instructions or prompts. These models are trained using large amounts of data and are capable of natural language processing tasks. Owing to their ability to comprehend, interpret, and generate natural language text, LLMs allow human-like conversations with coherent contextual responses to prompts. The capability of LLMs to summarize and generate texts that resemble human language allows the creation of task-focused systems that can ease the demands of human labor and improve efficiency.
OpenAI uses a closed application programming interface (API) to process data. Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (OpenAI Inc., California, USA, https://chat.openai.com/ ) was introduced globally in 2020 as ChatGPT3, a generative language model with 175 billion parameters [ 1 ]. It is based on a generative AI model that can generate new content based on the data on which they have been trained. The latest version, ChatGPT-4, was introduced in 2023 and has demonstrated improved creativity, reasoning, and the ability to process even more complicated tasks [ 2 ].
Since its release in the public domain, ChatGPT has been actively explored by both healthcare professionals and educators in an effort to attain human-like performance in the form of clinical reasoning, image recognition, diagnosis, and learning from medical databases. ChatGPT has proven to be a powerful tool with immense potential to provide students with an interactive platform to deepen their understanding of any given topic [ 3 ]. In addition, it is also capable of aiding in both lesson planning and student assessments [ 4 , 5 ].
The potential of ChatGPT for assessments
Automated Essay Scoring (AES) is not a new concept, and interest in AES has been increasing since the advent of AI. Three main categories of AES programs have been described, utilizing regression, classification, or neural network models [ 6 ]. A known problem of current AES systems is their unreliability in evaluating the content relevance and coherence of essays [ 6 ]. Newer language models such as ChatGPT, however, are potential game changers; they are simpler to learn than current deep learning programs and can therefore improve the accessibility of AES to educators. Mizumoto and Eguchi recently pioneered the potential use of ChatGPT (GPT-3.5 and 4) for AES in the field of linguistics and reported an accuracy level sufficient for use as a supportive tool even when fine-tuning of the model was not performed [ 7 ].
The use of these AI-powered tools may potentially ease the burden on educators in marking large numbers of essay scripts, while providing personalized feedback to students [ 8 , 9 ]. This is especially crucial with larger class sizes and increasing student-to-teacher ratios, where it can be more difficult for educators to actively engage individual students. Additionally, manual scoring by humans can be subjective and susceptible to fatigue, which may put the scoring at risk of being unreliable [ 7 , 10 ]. The use of AI for essay scoring may thus help reduce intra- and inter-rater variability associated with manual scoring by providing a more standardized and reliable scoring process that eases the time- and labor-intensive scoring workload of human assessors [ 10 , 11 ].
The current role of AI in healthcare education
Generative AI has permeated the healthcare industry and provided a diverse range of health enhancements. An example is how AI facilitates radiographic evaluation and clinical diagnosis to improve the quality of patient care [ 12 , 13 ]. In medical and dental education, virtual or augmented reality and haptic simulations are some of the exciting technological tools already implemented to improve student competence and confidence in patient assessment and execution of procedures [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. The incorporation of ChatGPT into the dental curriculum would thus be the next step in enhancing student learning. The performance of ChatGPT in the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) was recently validated, with ChatGPT achieving a score equivalent to that of a third-year medical student [ 17 ]. However, no data are available on the performance of ChatGPT in the field of dentistry or oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMS). Furthermore, the reliability of AI-powered language models for the grading of essays in the medical field has not yet been evaluated; in addition to essay structure and language, the evaluation of essay scripts in the field of OMS would require a level of understanding of dentistry, medicine and surgery.
Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the reliability of ChatGPT for AES in OMS examinations for final-year dental undergraduate students compared to human assessors. Our null hypothesis was that there would be no difference in the scores between the ChatGPT and human assessors. The research question for the study was as follows: How reliable is ChatGPT when used for AES in OMS examinations compared to human assessors?
Materials and methods
This study was conducted in the Faculty of Dentistry, National University of Singapore, under the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. The study received ethical approval from the university’s Institutional Review Board (REF: IRB-2023–1051) and was conducted and drafted with guidance from the education interventions critical appraisal worksheet introduced by BestBETs [ 18 ].
Sample size calculation for this study was based on the formula provided by Viechtbauer et al.: n = ln (1-γ) / ln(1-π), where n, γ and π represent the sample size, significance level and level of confidence respectively [ 19 ]. Based on a 5% margin of error, a 95% confidence level and a 50% outcome response, it was calculated that a minimum sample size of 59 subjects was required. Ultimately, the study recruited 69 participants, all of whom were final-year undergraduate dental students. A closed-book OMS examination was conducted on the Examplify platform (ExamSoft Worldwide Inc., Texas, USA) as a part of the end-of-module assessment. The examination comprised two open-ended essay questions based on the topics taught in the module (Table 1 ).
Creation of standardized assessment
An assessment rubric was created for each question through discussion and collaboration of a workgroup comprising four assessors involved in the study. All members of the work group were academic staff from the faculty (I.I., B.Q., L.Z., T.J.H.S.) (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2) [ 20 ]. An analytic rubric was generated using the strategy outlined by Popham [ 21 ]. The process involved a discussion within the workgroup to agree on the learning outcomes of the essay questions. Two authors (I. I. and B. Q) independently generated the rubric criteria and descriptions for Question 1 (Infection). Similarly, for Question 2 (Trauma), the rubric criteria and descriptions were generated independently by two authors (I.I. and T.J.H.S.). The rubrics were revised until a consensus was reached between each pair. In the event of any disagreement, a third author (L.Z.) provided their opinion to aid in decision making.
Marking categories of Poor (0 marks), Satisfactory (2 marks), Good (3 marks), and Outstanding (4 marks) were allocated to each criterion, with a maximum of 4 marks attainable from each criterion. A criterion for overall essay structure and language was also included, with a maximum attainable 5 marks from this criterion. The highest score for each question was 40.
Model answers to the essays were prepared by another author (C.W.Y.), who did not participate in the creation of the rubrics. Using the rubrics as a reference, the author modified the model answer to create 5 variants of the answers such that each variant fell within different score ranges of 0–10, 11–20, 21–30, 31–40, 41–50. Subsequently, three authors (B. Q., L. Z., and T.J.H.S) graded the essays using the prepared rubrics. Revisions to the rubrics were made with consensus by all three authors, a process that also helped calibrate these three authors for manual essay scoring.
AES with ChatGPT
Essay scoring was performed using ChatGPT (GPT-4, released March 14, 2023) by one assessor who did not participate in the manual essay scoring exercise (I.I.). Prompts were generated based on a guideline by Giray, and the components of Instruction, Context, Input Data and Output Indication as discussed in the guideline were included in each prompt (Supplementary Tables 3 and 4) [ 22 ]. A prompt template was generated for each question by one assessor (I.I.) with advice from two experts in prompt engineering, based on the marking rubric. The criterion and point allocation were clearly written in prose and point forms. For the fine-tuning process, the prompts were input into ChatGPT using variants of the model answers provided by C.W.Y. Minor adjustments were made to the wording of certain parts of the prompts as necessary to correct any potential misinterpretations of the prompts by the ChatGPT. Each time, the prompt was entered into a new chat in the ChatGPT in a browser where the browser history and cookies were cleared. Subsequently, finalized prompts (Supplementary Tables 3 and 4) were used to score the student essays. AES scores were not used to calculate students’ actual essay scores.
Manual essay scoring
Manual essay scoring was completed independently by three assessors (B.Q., L.Z., and T.J.H.S.) using the assessment rubrics (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2). Calibration was performed during the rubric creation stage. The essays were anonymized to prevent bias during the marking process. The assessors recorded the marks allocated to each criterion, as well as the overall score of each essay, on a pre-prepared Excel spreadsheet. Scoring was performed separately and independently by all assessors before the final collation by a research team member (I.I.) for statistical analyses. The student was considered ‘able to briefly mention’ a criterion if they did not mention any of the keywords of the points within the criterion. The student was considered ‘able to elaborate on’ a point within the criterion if they were able to mention the keywords of that point as stated in the rubric, and were thus awarded higher marks in accordance with the rubric (e.g. the student was given a higher mark if they were able to mention the need to check for dyspnea and dysphagia, instead of simply mentioning a need to check the patient’s airway). Grading was performed with only whole marks as specified in the rubrics, and assessors were not allowed to give half marks or subscores.
Data synthesis
The scores given out of 40 per essay by each assessor were compiled. Data analyses were subsequently performed using SPSS® version 29.0.1.0(171) (IBM Corporation, New York, United States). For each essay question, correlations between the essay scores given by each assessor were analyzed and displayed using the inter-item correlation matrix. A correlation coefficient value ( r ) of 0.90–1.00 was indicative of a very strong, 0.70–0.89 indicative of strong, 0.40–0.69 moderate, 0.10–0.39 weak and < 0.10 negligible positive correlation between the scorers [ 23 ]. The cutoff p -value for the significance level was set at p < 0.05. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Cronbach's α were then calculated between all assessors to assess the inter-rater agreement and reliability, respectively [ 24 ]. The ICC was interpreted on a scale of 0 to 1.00, with a higher value indicating a higher level of agreement in scores given by the scorers to each student. A value less than 0.40 was indicative of poor, 0.40–0.59 fair, 0.60–0.74 good, and 0.75–1.00 excellent agreement [ 25 ]. Using Cronbach’s α, reliability was expressed on a range from 0 to 1.00, with a higher number indicating a higher level of consistency between the scorers in their scores given across the students. The reliability was considered ‘Less Reliable’ if the score was less 0.20, ‘Rather Reliable’ if the score was 0.20–0.40, ‘Quite Reliable’ if 0.40–0.60, ‘Reliable’ if 0.60–0.80 and ‘Very Reliable’ if 0.80–1.00 [ 26 ].
Similarly, the mean scores of the three manual scorers were calculated for each question. The mean manual scores were then analyzed for correlations with AES scores by using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Student’s t-test was also used to analyze any significant differences in mean scores between manual scoring and AES. A p -value of < 0.05 was required to conclude the presence of a statistically different score between the groups.
All final-year dental undergraduate students (69/69, 100%) had their essays graded by all manual scorers and AES as part of the study. Table 2 shows the mean scores for each individual assessor as well as the mean scores for the three manual scorers (Scorers 1, 2, and 3).
Analysis of correlation and agreement between all scorers
The inter-item correlation matrices and their respective p -values are listed in Table 3 . For Question 1, there was a strong positive correlation between the scores provided by each assessor (Scorers 1, 2, 3, and AES), with r -values ranging from 0.752–0.848. All p -values were < 0.001, indicating a significant positive correlation between all assessors. For Question 2, there was a strong positive correlation between Scorers 1 and 2 ( r = 0.829) and Scorers 1 and 3 ( r = 0.756). There was a moderate positive correlation between Scorers 2 and 3 ( r = 0.655), as well as between AES and all manual scores ( r -values ranging from 0.527 to 0.571). Similarly, all p -values were < 0.001, indicative of a significant positive correlation between all scorers.
For the analysis of inter-rater agreement, ICC values of 0.858 (95% CI 0.628 – 0.933) and 0.794 (95% CI 0.563 – 0.892) were obtained for Questions 1 and 2, respectively, both of which were indicative of excellent inter-rater agreement. Cronbach’s α was 0.932 for Question 1 and 0.881 for Question 2, both of which were ‘Very Reliable’.
Analysis of correlation between manual scoring versus AES
The results of the Student’s t-test comparing the test score values from manual scoring and AES are shown in Table 2 . For Question 1, the mean manual scores (14.85 ± 4.988) were slightly higher than those of the AES (14.54 ± 5.490). However, these differences were not statistically significant ( p > 0.05). For Question 2, the mean manual scores (23.11 ± 4.241) were also higher than those of the AES (18.62 ± 4.044); this difference was statistically significant ( p < 0.001).
The results of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient calculations are shown in Table 4 . For Question 1, there was a strong and significant positive correlation between manual scoring and AES ( r = 0.829, p < 0.001). For Question 2, there was a moderate and statistically significant positive correlation between the two groups ( r = 0.599, p < 0.001).
Qualitative feedback from AES
Figures 1 , 2 and 3 show three examples of essay feedback and scoring provided by ChatGPT. ChatGPT provided feedback in a concise and systematic manner. Scores were clearly provided for each of the criteria listed in the assessment rubric. This was followed by in-depth feedback on the points within the criterion that the student had discussed and failed to mention. ChatGPT was able to differentiate between a student who briefly mentioned a key point and a student who provided better elaboration on the same point by allocating them two or three marks, respectively.

Example #1 of a marked essay with feedback from ChatGPT for Question 1

Example #2 of a marked essay with feedback from ChatGPT for Question 1

Example #3 of a marked essay with feedback from ChatGPT for Question 1
One limitation of ChatGPT that was identified during the scoring process was its inability to identify content that was not relevant to the essay or that was factually incorrect. This was despite the assessment rubric specifying that incorrect statements should be given 0 marks for that criterion. For example, a student who included points about incision and drainage also incorrectly stated that bone scraping to induce bleeding and packing of local hemostatic agents should be performed. Although these statements were factually incorrect, ChatGPT was unable to identify this and still awarded student marks for the point. Manual assessors were able to spot this and subsequently penalized the student for the mistake.
Since its recent rise in popularity, many people have been eager to tap into the potential of large language models, such as ChatGPT. In their review, Khan et al. discussed the growing role of ChatGPT in medical education, with promising uses for the creation of case studies and content such as quizzes and flashcards for self-directed practice [ 9 ]. As an LLM, the ability of ChatGPT to thoroughly evaluate sentence structure and clarity may allow it to confront the task of automated essay marking.
Advantages of ChatGPT in AES
This study found significant correlations and excellent inter-rater agreement between ChatGPT and manual scorers, and the mean scores between both groups showed strong to moderate correlations for both essay questions. This suggests that AES has the potential to provide a level of essay marking similar to that of the educators in our faculty. Similar positive findings were reflected in previous studies that compared manual and automated essay scoring ( r = 0.532–0.766) [ 6 ]. However, there is still a need to further fine-tune the scoring system such that the score provided by AES deviates as little as possible from human scoring. For instance, the mean AES score was lower than that of manual scoring by 5 marks for Question 2. Although the difference may not seem large, it may potentially increase or decrease the final performance grade of students.
Apart from a decent level of reliability in manual essay scoring, there are many other benefits to using ChatGPT for AES. Compared to humans, the response time to prompts is much faster and can thus increase productivity and reduce the burden of a large workload on educational assessors [ 27 ]. In addition, ChatGPT can provide individualized feedback for each essay (Figs. 1 , 2 and 3 ). This helps provide students with comments specific to their essays, a feat that is difficult to achieve for a single educator teaching a large class size.
Similar to previous systems designed for AES, machine scoring is beneficial for removing human inconsistencies that can result from fatigue, mood swings, or bias [ 10 ]. ChatGPT is no exception. Furthermore, ChatGPT is more widely accessible than the conventional AES systems. Its software runs online instead of requiring downloads on a computer, and its user interface is simple to use. With GPT-3.5 being free to use and GPT-4 being 20 USD per month, it is also relatively inexpensive.
Marking the essay is only part of the equation, and the next step is to allow the students to know what went wrong and why. Nicol and Macfarlane described seven principles for good feedback. ChatGPT can fulfil most of these principles, namely, facilitating self-assessment, encouraging teacher and peer dialogue, clarifying what good performance is, providing opportunities to close the gap between current and desired performance, and delivering high-quality information to students [ 28 ]. In this study, the feedback given by ChatGPT was categorized based on the rubric, and elaboration was provided for each criterion on the points the student mentioned and did not mention. By highlighting the ideal answer and where the student can improve, ChatGPT can clarify performance goals and provide opportunities to close the gap between the student’s current and desired performance. This creates opportunities for selfdirected learning and the utilization of blended learning environments. Students can use ChatGPT to review their preparation on topics, self-grade their essays, and receive instant feedback. Furthermore, the simple and interactive nature of the software encourages dialogue, as it can readily respond to any clarification the student wants to make. The importance of effective feedback has been demonstrated to be an essential component in medical education, in terms of enhancing the knowledge of the student without developing negative emotions [ 29 , 30 ].
These potential advantages of engaging ChatGPT for student assessments play well into the humanistic learning theory of medical education [ 31 , 32 ]. Self-directed learning allows students the freedom to learn at their own pace, with educators simply providing a conducive environment and the goals that the student should achieve. ChatGPT has the potential to supplement the role of the educator in self-directed learning, as it can be readily available to provide constructive and tailored feedback for assignments whenever the student is ready for it. This removes the burden that assignment deadlines place on students, which can allow them a greater sense of independence and control over their learning, and lead to greater self-motivation and self-fulfillment.
Potential pitfalls of ChatGPT
Potential pitfalls associated with the use of ChatGPT were identified. First, the ability to achieve reliable scores relies heavily on a well-created marking rubric with clearly defined terms. In this study, the correlations between scorers were stronger for Question 1 compared to Question 2, and the mean scores between the AES and manual scorers were also significantly different for Question 2, but not for Question 1. The lower reliability of the AES for Question 2 may be attributed to its broader nature, use of more complex medical terms, and lengthier scoring rubrics. The broad nature of the question left more room for individual interpretation and variation between humans and AES. The ability of ChatGPT to provide accurate answers may be reduced with lengthier prompts and conversations [ 27 ]. Furthermore, with less specific instructions or complex medical jargon, both automated systems and human scorers may interpret rubrics differently, resulting in varied scores across the board [ 10 , 33 , 34 ]. The authors thus recommend that to circumvent this, the use of ChatGPT for essay scoring should be restricted to questions that are less broad (e.g. shorter essays), or by breaking the task into multiple prompts for each individual criterion to reduce variations in interpretation [ 27 , 35 ]. Furthermore, the rubrics should contain concise and explicit instructions with appropriate grammar and vocabulary to avoid misinterpretation by both ChatGPT and human scorers, and provide a brief explanation to specify what certain medical terms mean (e.g. writing ‘pulse oximetry (SpO2) monitoring’ instead of only ‘SpO2’) for better contextualization [ 35 , 36 ].
Second, prompt engineering is a critical step in producing the desired outcome from ChatGPT [ 27 ]. A prompt that is too ambiguous or lacks context can lead to a response that is incomplete, generic, or irrelevant, and a prompt that exhibits bias runs the risk of bias reinforcement in the given reply [ 22 , 34 ]. Phrasing the prompt must also be carefully checked for spelling, grammatical mistakes, or inconsistencies, since ChatGPT uses the prompt’s phrasing literally. For example, a prompt that reads ‘give 3 marks if the student covers one or more coverage points’ will result in ChatGPT only giving the marks if multiple points are covered, because of the plural nature of the word ‘points’.
Third, irrelevant content may not be penalized during the essay-marking process. Students may ‘trick’ the AES by producing a lengthier essay to hit more relevant points and increase their score. This may result in essays of lower quality with multiple incorrect or nonsensical statements still rewarded with higher scores [ 10 ]. Our assessment rubric attempts to penalize the student with 0 marks if incorrect statements on the criterion are made; however, none of the students were penalized. This issue may be resolved as ChatGPT rapidly and continuously gains more medical and dental knowledge. Although data to support the competence of AI in medical education are sparse, the quality of the medical knowledge that ChatGPT already has is sufficient to achieve a passing mark at the USMLE [ 5 , 37 ]. In dentistry, when used to disseminate information on endodontics to patients, ChatGPT was found to provide detailed answers with an overall validity of 95% [ 38 ]. Over time, LLMs such as ChatGPT may be able to identify when students are not factually correct.
Other comments
The lack of human emotion in machine scoring can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. AES can provide feedback that is entirely factual and less biased than humans, and grades are objective and final [ 39 ]. However, human empathy is an essential quality that ChatGPT does not possess. One principle of good feedback is to encourage and motivate students to provide positive learning experiences and build self-esteem [ 28 ]. While ChatGPT can provide constructive feedback, it will not be able to replace the compassion, empathy, or emotional intelligence possessed by a quality educator possesses [ 40 ]. In our study, ChatGPT awarded lower mean scores of 14.54/40 (36.4%) and 18.62/40 (46.5%) compared to manual scoring for both questions. Although objective, some may view automated scoring as harsh because it provided failing grades to an average student.
This study demonstrates the ability of GPT-4 to evaluate essays without any specialized training or prompting. One long prompt was used to score each essay. Although more technical prompting methods, such as chain of thought, could be deployed, our single prompt method makes the method scalable and easier to adopt. As discussed earlier, ChatGPT is the most reliable when prompts are short and specific [ 34 ]. Hence, each prompt should ideally task ChatGPT to score only one or two criteria, rather than the entire rubric of the 10 criteria. However, in a class of 70, the assessors are required to run 700 prompts per question, which is impractical and unnecessary. With only one prompt, a good correlation was still found between the AES and manual scoring. It is likely that further exploration and experimentation with prompting techniques can improve the output.
While LLMs have the potential to revolutionize education in healthcare, some precautions must be taken. Artificial Hallucination is a widely described phenomenon; ChatGPT may generate seemingly genuine but inaccurate information [ 41 , 42 , 43 ]. Hallucinations have been attributed to biases and limitations of training data as well as algorithmic limitations [ 2 ]. Similarly, randomness of the generated responses has been observed; while it is useful for generating creative content, this may be an issue when ChatGPT is employed for topics requiring scientific or factual content [ 44 ]. Thus, LLMs are not infallible and still require human subject matter experts to validate the generated content. Finally, it is essential that educators play an active role in driving the development of dedicated training models to ensure consistency, continuity, and accountability, as overreliance on a corporate-controlled model may place educators at the mercy of algorithm changes.
The ethical implications of using ChatGPT in medical and dental education also need to be explored. As much as LLMs can provide convenience to both students and educators, privacy and data security remain a concern [ 45 ]. Robust university privacy policies and informed consent procedures should be in place for the protection of student data prior to the use of ChatGPT as part of student assessment. Furthermore, if LLMs like ChatGPT were to be used for grading examinations in the future, issues revolving around fairness and transparency of the grading process need to be resolved [ 46 ]. GPT-4 may have provided harsh scores in this study, possibly due to some shortfall in understanding certain phrases the students have written; models used in assessments will thus require sufficient training in the field of healthcare to properly acquire the relevant medical knowledge and hence understand and grade essays fairly.
As AI continues to develop, ChatGPT may eventually replace human assessors in essay scoring for dental undergraduate examinations. However, given its current limitations and dependence on a well-formed assessment rubric, relying solely on ChatGPT for exam grading may be inappropriate when the scores can affect the student’s overall module scores, career success, and mental health [ 47 ]. While this study primarily demonstrates the use of ChatGPT to grade essays, it also points to great potential in using it as an interactive learning tool. A good start for its use is essay assignments on pre-set topics, where students can direct their learning on their own and receive objective feedback on essay structure and content that does not count towards their final scores. Students can use rubrics to practice and gain effective feedback from LLMs in an engaging and stress-free environment. This reduces the burden on educators by easing the time-consuming task of grading essay assignments and allows students the flexibility to complete and grade their assignments whenever they are ready. Furthermore, assignments repeated with new class cohorts can enable more robust feedback from ChatGPT through machine learning.
Study limitations
The limitations of this study lie in part of its methodology. The study recruited 69 dental undergraduate students; while this is above the minimum calculated sample size of 59, a larger sample size would help to increase the generalizability of the study findings to larger populations of students and a wide scope of topics. The unique field of OMS also requires knowledge of both medical and dental subjects, and hence the results obtained from the use of ChatGPT for essay marking in other medical or dental specialties may differ slightly.
The use of rubrics for manual scoring could also be a potential source of bias. While the rubrics provide a framework for objective assessment, they cannot eliminate the subjectiveness of manual scoring. Variations in the interpretation of the students’ answers, leniency errors (whereby one scorer marks more leniently than another) or rater drift (fatigue from assessing many essays may affect leniency of marking and judgment) may still occur. To minimize bias resulting from these errors, multiple assessors were recruited for the manual scoring process and the average scores were used for comparison with AES.
This study investigated the reliability of ChatGPT in essay scoring for OMS examinations, and found positive correlations between ChatGPT and manual essay scoring. However, ChatGPT tended towards stricter scoring and was not capable of penalizing irrelevant or incorrect content. In its present state, GPT-4 should not be used as a standalone tool for teaching or assessment in the field of medical and dental education but can serve as an adjunct to aid students in self-assessment. The importance of proper rubric design to achieve optimal reliability when employing ChatGPT in student assessment cannot be overemphasized.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Floridi L, Chiriatti M. GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Mind Mach. 2020;30(4):681–94.
Article Google Scholar
Abd-Alrazaq A, AlSaad R, Alhuwail D, Ahmed A, Healy PM, Latifi S, Aziz S, Damseh R, Alabed Alrazak S, Sheikh J. Large language models in medical education: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9:e48291.
Kasneci E, Sessler K, Küchemann S, Bannert M, Dementieva D, Fischer F, Gasser U, Groh G, Günnemann S, Hüllermeier E, et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn Individ Differ. 2023;103:102274.
Javaid M, Haleem A, Singh RP, Khan S, Khan IH. Unlocking the opportunities through ChatGPT Tool towards ameliorating the education system. BenchCouncil Transact Benchmarks Standards Eval. 2023;3(2): 100115.
Kung TH, Cheatham M, Medenilla A, Sillos C, De Leon L, Elepaño C, Madriaga M, Aggabao R, Diaz-Candido G, Maningo J, et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLOS Digit Health. 2023;2(2):e0000198.
Ramesh D, Sanampudi SK. An automated essay scoring systems: a systematic literature review. Artif Intell Rev. 2022;55(3):2495–527.
Mizumoto A, Eguchi M. Exploring the potential of using an AI language model for automated essay scoring. Res Methods Appl Linguist. 2023;2(2): 100050.
Erturk S, Tilburg W, Igou E: Off the mark: Repetitive marking undermines essay evaluations due to boredom. Motiv Emotion 2022;46.
Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT - Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci. 2023;39(2):605–7.
Hussein MA, Hassan H, Nassef M. Automated language essay scoring systems: a literature review. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2019;5:e208.
Blood I: Automated essay scoring: a literature review. Studies in Applied Linguistics and TESOL 2011, 11(2).
Menezes LDS, Silva TP, Lima Dos Santos MA, Hughes MM, Mariano Souza SDR, Leite Ribeiro PM, Freitas PHL, Takeshita WM: Assessment of landmark detection in cephalometric radiographs with different conditions of brightness and contrast using the an artificial intelligence software. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2023:20230065.
Bennani S, Regnard NE, Ventre J, Lassalle L, Nguyen T, Ducarouge A, Dargent L, Guillo E, Gouhier E, Zaimi SH, et al. Using AI to improve radiologist performance in detection of abnormalities on chest radiographs. Radiology. 2023;309(3): e230860.
Moussa R, Alghazaly A, Althagafi N, Eshky R, Borzangy S. Effectiveness of virtual reality and interactive simulators on dental education outcomes: systematic review. Eur J Dent. 2022;16(1):14–31.
Fanizzi C, Carone G, Rocca A, Ayadi R, Petrenko V, Casali C, Rani M, Giachino M, Falsitta LV, Gambatesa E, et al. Simulation to become a better neurosurgeon An international prospective controlled trial: The Passion study. Brain Spine. 2024;4:102829.
Lovett M, Ahanonu E, Molzahn A, Biffar D, Hamilton A. Optimizing individual wound closure practice using augmented reality: a randomized controlled study. Cureus. 2024;16(4):e59296.
Google Scholar
Gilson A, Safranek CW, Huang T, Socrates V, Chi L, Taylor RA, Chartash D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical licensing examination? the implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9:e45312.
Educational Intervention Worksheet, BestBets, Accessed 31/03/2024. https://bestbets.org/ca/pdf/educational_intervention.pdf .
Viechtbauer W, Smits L, Kotz D, Budé L, Spigt M, Serroyen J, Crutzen R. A simple formula for the calculation of sample size in pilot studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68(11):1375–9.
Cox G, Morrison J, Brathwaite B: The Rubric: An Assessment Tool to Guide Students and Markers; 2015.
Popham J. W: “What’s Wrong—And What’s Right—With Rubrics.” Educ Leadersh. 1997;55(2):72–5.
Giray L. Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT: A Guide for Academic Writers. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023;51:3.
Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(5):1763–8.
Liao SC, Hunt EA, Chen W. Comparison between inter-rater reliability and inter-rater agreement in performance assessment. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2010;39(8):613–8.
Cicchetti DV. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol Assess. 1994;6(4):284–90.
Hair J, Black W, Babin B, Anderson R: Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective; 2010.
Nazir A, Wang Z: A Comprehensive Survey of ChatGPT: Advancements, Applications, Prospects, and Challenges. Meta Radiol 2023;1(2).
Nicol D, Macfarlane D: Rethinking Formative Assessment in HE: a theoretical model and seven principles of good feedback practice. IEEE Personal Communications - IEEE Pers Commun 2004;31.
Spooner M, Larkin J, Liew SC, Jaafar MH, McConkey S, Pawlikowska T. “Tell me what is ‘better’!” How medical students experience feedback, through the lens of self-regulatory learning. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):895.
Kornegay JG, Kraut A, Manthey D, Omron R, Caretta-Weyer H, Kuhn G, Martin S, Yarris LM. Feedback in medical education: a critical appraisal. AEM Educ Train. 2017;1(2):98–109.
Mukhalalati BA, Taylor A. Adult learning theories in context: a quick guide for healthcare professional educators. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2019;6:2382120519840332.
Taylor DC, Hamdy H. Adult learning theories: implications for learning and teaching in medical education: AMEE Guide No. 83. Med Teach. 2013;35(11):e1561-1572.
Chakraborty S, Dann C, Mandal A, Dann B, Paul M, Hafeez-Baig A: Effects of Rubric Quality on Marker Variation in Higher Education. Studies In Educational Evaluation 2021;70.
Heston T, Khun C. Prompt engineering in medical education. Int Med Educ. 2023;2:198–205.
Sun GH: Prompt Engineering for Nurse Educators. Nurse Educ 2024.
Meskó B. Prompt engineering as an important emerging skill for medical professionals: tutorial. J Med Internet Res. 2023;25:e50638.
Sun L, Yin C, Xu Q, Zhao W. Artificial intelligence for healthcare and medical education: a systematic review. Am J Transl Res. 2023;15(7):4820–8.
Mohammad-Rahimi H, Ourang SA, Pourhoseingholi MA, Dianat O, Dummer PMH, Nosrat A: Validity and reliability of artificial intelligence chatbots as public sources of information on endodontics. Int Endodontic J 2023, n/a(n/a).
Peng X, Ke D, Xu B: Automated essay scoring based on finite state transducer: towards ASR transcription of oral English speech. In: Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Long Papers - Volume 1. Jeju Island, Korea: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2012:50–59.
Grassini S. Shaping the future of education: Exploring the Potential and Consequences of AI and ChatGPT in Educational Settings. Educ Sci. 2023;13(7):692.
Limitations. https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt .
Sallam M, Salim NA, Barakat M, Al-Tammemi AB. ChatGPT applications in medical, dental, pharmacy, and public health education: A descriptive study highlighting the advantages and limitations. Narra J. 2023;3(1):e103.
Deng J, Lin Y. The Benefits and Challenges of ChatGPT: An Overview. Front Comput Intell Syst. 2023;2:81–3.
Choi W. Assessment of the capacity of ChatGPT as a self-learning tool in medical pharmacology: a study using MCQs. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23(1):864.
Medina-Romero MÁ, Jinchuña Huallpa J, Flores-Arocutipa J, Panduro W, Chauca Huete L, Flores Limo F, Herrera E, Callacna R, Ariza Flores V, Quispe I, et al. Exploring the ethical considerations of using Chat GPT in university education. Period Eng Nat Sci (PEN). 2023;11:105–15.
Lee H. The rise of ChatGPT: Exploring its potential in medical education. Anat Sci Educ. 2024;17(5):926–31.
Steare T, Gutiérrez Muñoz C, Sullivan A, Lewis G. The association between academic pressure and adolescent mental health problems: A systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2023;339:302–17.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to extend our gratitude to Mr Paul Timothy Tan Bee Xian and Mr Jonathan Sim for their invaluable advice on the process of prompt engineering for the effective execution of this study.
Author information
Lei Zheng, Timothy Jie Han Sng and Chee Weng Yong contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Faculty of Dentistry, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
Bernadette Quah, Lei Zheng, Timothy Jie Han Sng, Chee Weng Yong & Intekhab Islam
Discipline of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, National University Centre for Oral Health, 9 Lower Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
B.Q. contributed in the stages of conceptualization, methodology, study execution, validation, formal analysis and manuscript writing (original draft and review and editing). L.Z., T.J.H.S. and C.W.Y. contributed in the stages of methodology, study execution, and manuscript writing (review and editing). I.I. contributed in the stages of conceptualization, methodology, study execution, validation, formal analysis, manuscript writing (review and editing) and supervision. All authors provided substantial contributions to this manuscript in the following form:
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Intekhab Islam .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the university (REF: IRB-2023–1051). The waiver of consent from students was approved by the University’s Institutional Review Board, as the scores by ChatGPT were not used as the students’ actual grades, and all essay manuscripts were anonymized.
Consent for publication
All the authors reviewed the content of this manuscript and provided consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Quah, B., Zheng, L., Sng, T.J.H. et al. Reliability of ChatGPT in automated essay scoring for dental undergraduate examinations. BMC Med Educ 24 , 962 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05881-6
Download citation
Received : 04 February 2024
Accepted : 09 August 2024
Published : 03 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05881-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial intelligence
- Academic performance
- Educational
- Educational needs assessment
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]
BANKING PARTNER
Cbse board exam 2025 sample papers released for classes 10, 12; check marking scheme.
Published By : Suramya Sunilraj
Trending Desk
Last Updated: September 06, 2024, 12:18 IST
New Delhi, India

The CBSE board exams 2025 for Classes 10, and 12 are scheduled to begin on February 15 and continue till April (Representational/ PTI Photo)
The Classes 10 and 12 sample papers offer a glimpse into the exam format, important topics and frequently asked questions to help students in exam preparation
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has published the sample papers and marking scheme for classes 10 and 12 for the academic session 2024-25. Students appearing for the upcoming board exam can access and download the CBSE sample question paper by visiting the official website of CBSE Academic, which is cbseacademic.nic.in. No login credentials will be required to access the subject-wise CBSE sample papers 2025 for both Classes 10 and 12. The sample papers offer a glimpse into the exam format, important topics and frequently asked questions to help students in exam preparation.
Students must note that the board has published the Class 10 sample paper 2025 for various subjects including English, Hindi, Mathematics, Social Science, Home Science and more. Similarly, the sample papers are available for all streams and subjects for class 12, including computer science, biology, chemistry and accountancy. In addition to the CBSE 2024-25 sample papers, the board has announced the subject-wise marking scheme in detail.
According to the official notification, the Board has issued Sample Question Papers (SQPs) and Marking Schemes (MS) for classes X and XII to help in understanding the marking scheme and time management, enabling students to practice under exam conditions. This move will also provide several benefits, including familiarising students with the exam format and question types, which lessens exam anxiety and builds confidence.
CBSE Class 10, 12 Sample Papers 2025: Steps to download
Step 1: Go to the official CBSE Academic website at cbseacademic.nic.in.
Step 2: Locate and click on the ‘CBSE Class 10, 12 Sample Papers 2025’ link available on the webpage.
Step 3: Upon clicking, a new PDF file will open where the Classes 10 and 12 sample papers links are attached.
Step 4: Click on the link and the sample paper will be presented on the screen.
Step 5: Now, select the subject you want to check the sample paper for.
Step 6: Once done, save a copy of the sample paper and print a hard copy of the same for further need.
The CBSE board exams 2025 for Classes 10, and 12 are scheduled to begin on February 15 and continue till April. The official CBSE exam date sheet for 2024-25 is expected to be published in November or December on the official website, cbse.nic.in. Moreover, the results for CBSE 2025 are expected to be declared in May.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Various factors define teaching as a professional career. Teachings as a profession need adaptability. This is because teachers deal with a variety of abilities that students have. Teachers are required to have innovative lessons in order for their students to master their standards (McKenzie & Santiago, 2005).
Teaching Profession Essay. Teaching profession as it has been described by some people is a noble career. I sometimes believe that it is more of a calling than a profession because it really involves transforming the lives of people. This is not an easy task but rather a feat that calls for commitment and willingness to offer the best so that ...
Teaching as a profession essay often discusses how these traits are essential for a fulfilling teaching career. Moreover, 20 reasons why teaching is a profession often include factors like job satisfaction, career growth, and the opportunity to inspire future generations.
8. Discuss the future of teaching as a profession and how it may continue to evolve in response to changing educational trends and societal needs. 9. Conclude your essay by summarizing the key points you have discussed and reiterating the importance of teaching as a profession in shaping the future of society. 10.
advance teaching as a profession. Professionalism is a complex and elusive concept; it is dynamic and fluid. Six generally accepted criteria are used to define a profession. The teaching profession in Alberta fulfills those criteria in the following ways: 1. Its members have an organized body of knowledge that separates the group from all others.
Redefining the Role of the Teacher: It's a Multifaceted Profession. A closer look at what being an educator really means. By Judith Taack Lanier. July 1, 1997. Credit: Mark Ulriksen. Imagine a school where teaching is considered to be a profession rather than a trade. The role of teachers in a child's education -- and in American culture ...
Chapter 1: The Teaching Profession. Unlearning Box. "Those who can, do. Those who can't, teach.". "It's easy to become a teacher.". "Teaching is an 8:30-3:00 job. You have it so easy!". You may have heard people in your own life share quotes and comments such as these. These quotes are hurtful and untrue.
Policy on the teaching professions has in many Member States been a case of incremental, piecemeal changes. […] But if the teaching professions are to meet the significant challenges, a systemic response is needed with coherent and consistent policies and programmes for their recruitment, selection, initial education, induction, professional development and working conditions.
Teacher professionalism encompasses specialised knowledge developed through the integration of theory and practice, ethical responsibilities balancing student needs and societal interests, the ...
To summarize, this essay has analyzed teaching as a profession and the strategies important for the teachers to function effectively and improve their professional efficiency. These strategies of reflection that a teacher incorporates can be called the cognitive strategies. These cognitive strategies need to be taught and practiced during the ...
Essay on Teaching Profession: Teaching is an often under-appreciated profession, but the impact of a good teacher cannot be overstated. Teachers are an essential part of society, shaping the next generation's future.
Teaching is a noble profession that shapes the minds, values, and futures of generations. Educators hold the responsibility of imparting knowledge, fostering critical thinking, and nurturing personal growth in their students. This essay delves into the multifaceted nature of teaching as a noble profession, highlighting the profound impact teachers have on individuals, communities, and society ...
ABSTRACT. In this article, I discuss the status of teaching as a profession using Gardner and Shulman's framework emerging from their empirical examination of the professions in America and use Bernstein's sociology of knowledge to help explain how recontextualizing agents struggle to dominate the construction and interpretation of professionalism in teaching.
This essay focuses on teaching at the post-secondary level, for "the way we think of teaching has an influence on the way in which we teach" (Hare, ... think of teaching as a profession or think of it as a vocation does make a dif-Catholic Education: A Journal of Inquiry and Practice,Vol. 8, ...
sense of profession alism, a teacher must focus on the critical elements of attitude, behavior, and communication. E. very teacher must develop the characteristics of a professional and model professionalism every day. In fact, among the standards of the Na tional Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE) is a re
A definition: Teaching is the process of attending to people's needs, experiences and feelings, and intervening so that they learn particular things, and go beyond the given.. Interventions commonly take the form of questioning, listening, giving information, explaining some phenomenon, demonstrating a skill or process, testing understanding and capacity, and facilitating learning activities ...
Teaching is hope for better, more successful futures. Learning is hope for becoming better individuals, for gaining intelligence, and for implementing practical experiences in our future. Since we always tell our children that they should plan for their futures and work to realize those goals, the teaching profession should "practice what it ...
Professionalism is very important in the education sector as it has a very deep impact on the role of a teacher, which in response influences the aptitude of students to learn successfully. A teacher's professionalism can be defined as the talent to reach students substantially, increasing inventive approaches to motivate students, appealing ...
See also: Teaching in 2020 vs. 2010: A Look Back at the Decade. From an increase in teacher activism to a decline in the number of people who want to be teachers, here are 10 of the biggest shifts ...
Essay on Teaching as a Profession. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. In this 21st century, a teacher should adopt a new approach toward the students so that they are updated with today's tools and technology.
To conclude essay about teaching profession, to become effective teachers, it is really important for every teacher to embody all these skills apart from their expert knowledge. The achievement of all these soft skills can make a huge difference in the quality of teaching and effective learning. Quality of teaching is a very crucial part of ...
Teaching as a Profession: An Essay in the Philosophy of Education Glenn Langford Snippet view - 1978. Common terms and phrases. accepted achieve action activities apple glut argued attitude become educated beliefs and intentions bodily movements C. K. Ogden Chimborazo code of professional complete existent concerned consequence considered ...
The importance of the Teaching Profession includes fun and learning together. Being in the teaching profession doesn't mean you have to share your knowledge. Sometimes teachers themselves learn something new with teaching experience. Teachers play a vital role in student's life by helping them achieve their goals.
She's a dedicated high school teacher who arrives early each day to prepare for her lessons and often stays late to offer extra help to students. Sarah McDaniels also takes work home, spending her evenings grading papers and planning future classes. Despite her passion, she feels exhausted and disconnected from her family and friends.
The global COVID-19 pandemic has reconstituted every aspect of education. It reconfigured the most basic assumptions and practices of the delivery of learning. It altered the relationships between school, work, and home. It brought about new understandings of the role of schooling in society. It reconfigured relationships between parents, students, and teachers. It grew human uses of, and ...
This document offers an in-depth analysis of the 2025 IB Theory of Knowledge (TOK) essay titles. Ideal for students aiming for a high pass grade, it breaks down each title thoroughly, providing: Detailed Unpacking of Key Concepts: Clear explanations of each title, ensuring you understand exactly what's being asked.
"This is a book to be read by all involved in either side of this heated debate." Dr C Fourcade, President of the French Association for Palliative Care, France "This powerful collection of essays brilliantly unpacks the legal, ethical and practical issues around the assisted dying debate." Jonathan Herring, Professor of Law, University of Oxford, UK "This is an essential exploration ...
CBSE 10th 12th Sample Papers 2025: The Central Board of Secondary Education has released the CBSE 2025 sample papers for class 10 and class 12. Earlier, the sample papers for Skill Education were ...
Background This study aimed to answer the research question: How reliable is ChatGPT in automated essay scoring (AES) for oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMS) examinations for dental undergraduate students compared to human assessors? Methods Sixty-nine undergraduate dental students participated in a closed-book examination comprising two essays at the National University of Singapore. Using ...
CBSE Class 10, 12 Sample Papers 2025: Steps to download. Step 1: Go to the official CBSE Academic website at cbseacademic.nic.in. Step 2: Locate and click on the 'CBSE Class 10, 12 Sample Papers 2025' link available on the webpage. Step 3: Upon clicking, a new PDF file will open where the Classes 10 and 12 sample papers links are attached.