Climate Change Essay for Students and Children
500+ words climate change essay.
Climate change refers to the change in the environmental conditions of the earth. This happens due to many internal and external factors. The climatic change has become a global concern over the last few decades. Besides, these climatic changes affect life on the earth in various ways. These climatic changes are having various impacts on the ecosystem and ecology. Due to these changes, a number of species of plants and animals have gone extinct.


When Did it Start?
The climate started changing a long time ago due to human activities but we came to know about it in the last century. During the last century, we started noticing the climatic change and its effect on human life. We started researching on climate change and came to know that the earth temperature is rising due to a phenomenon called the greenhouse effect. The warming up of earth surface causes many ozone depletion, affect our agriculture , water supply, transportation, and several other problems.
Reason Of Climate Change
Although there are hundreds of reason for the climatic change we are only going to discuss the natural and manmade (human) reasons.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Natural Reasons
These include volcanic eruption , solar radiation, tectonic plate movement, orbital variations. Due to these activities, the geographical condition of an area become quite harmful for life to survive. Also, these activities raise the temperature of the earth to a great extent causing an imbalance in nature.
Human Reasons
Man due to his need and greed has done many activities that not only harm the environment but himself too. Many plant and animal species go extinct due to human activity. Human activities that harm the climate include deforestation, using fossil fuel , industrial waste , a different type of pollution and many more. All these things damage the climate and ecosystem very badly. And many species of animals and birds got extinct or on a verge of extinction due to hunting.
Effects Of Climatic Change
These climatic changes have a negative impact on the environment. The ocean level is rising, glaciers are melting, CO2 in the air is increasing, forest and wildlife are declining, and water life is also getting disturbed due to climatic changes. Apart from that, it is calculated that if this change keeps on going then many species of plants and animals will get extinct. And there will be a heavy loss to the environment.
What will be Future?
If we do not do anything and things continue to go on like right now then a day in future will come when humans will become extinct from the surface of the earth. But instead of neglecting these problems we start acting on then we can save the earth and our future.

Although humans mistake has caused great damage to the climate and ecosystem. But, it is not late to start again and try to undo what we have done until now to damage the environment. And if every human start contributing to the environment then we can be sure of our existence in the future.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is climate change and how it affects humans?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Climate change is a phenomenon that happens because of human and natural reasons. And it is one of the most serious problems that not only affect the environment but also human beings. It affects human in several ways but in simple language, we can say that it causes many diseases and disasters that destroy life on earth.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Can we stop these climatic changes?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Yes, we can stop these climatic changes but for that, every one of us has to come forward and has to adapt ways that can reduce and control our bad habits that affect the environment. We have to the initiative and make everyone aware of the climatic changes.” } } ] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Argumentative Essay Writing
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change

Make Your Case: A Guide to Writing an Argumentative Essay on Climate Change
Published on: Mar 2, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
Argumentative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide
Learn How to Write an Argumentative Essay Outline
Best Argumentative Essay Examples for Your Help
Basic Types of Argument and How to Use Them?
Take Your Pick – 200+ Argumentative Essay Topics
Essential Tips and Examples for Writing an Engaging Argumentative Essay about Abortion
Crafting a Winning Argumentative Essay on Social Media
Craft a Winning Argumentative Essay about Mental Health
Strategies for Writing a Winning Argumentative Essay about Technology
Crafting an Unbeatable Argumentative Essay About Gun Control
Win the Debate - Writing An Effective Argumentative Essay About Sports
Ready, Set, Argue: Craft a Convincing Argumentative Essay About Wearing Mask
Crafting a Powerful Argumentative Essay about Global Warming: A Step-by-Step Guide
Share this article
With the issue of climate change making headlines, it’s no surprise that this has become one of the most debated topics in recent years.
But what does it really take to craft an effective argumentative essay about climate change?
Writing an argumentative essay requires a student to thoroughly research and articulate their own opinion on a specific topic.
To write such an essay, you will need to be well-informed regarding global warming. By doing so, your arguments may stand firm backed by both evidence and logic.
In this blog, we will discuss some tips for crafting a factually reliable argumentative essay about climate change!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Argumentative Essay about Climate Change?
The main focus will be on trying to prove that global warming is caused by human activities. Your goal should be to convince your readers that human activity is causing climate change.
To achieve this, you will need to use a variety of research methods to collect data on the topic. You need to make an argument as to why climate change needs to be taken more seriously.
Argumentative Essay Outline about Climate Change
An argumentative essay about climate change requires a student to take an opinionated stance on the subject.
The outline of your paper should include the following sections:
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Introduction
The first step is to introduce the topic and provide an overview of the main points you will cover in the essay.
This should include a brief description of what climate change is. Furthermore, it should include current research on how humans are contributing to global warming.
An example is:
| |

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Thesis Statement For Climate Change Argumentative Essay
The thesis statement should be a clear and concise description of your opinion on the topic. It should be established early in the essay and reiterated throughout.
For example, an argumentative essay about climate change could have a thesis statement such as:
âclimate change is caused by human activity and can be addressed through policy solutions that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote cleaner energy sourcesâ. |
Climate Change Argumentative Essay Conclusion
The conclusion should restate your thesis statement and summarize the main points of the essay.
It should also provide a call to action, encouraging readers to take steps toward addressing climate change.
For example,
Climate change is an urgent issue that must be addressed now if we are to avoid catastrophic consequences in the future. We must take action to reduce our emissions and transition to cleaner energy sources. It is up to us as citizens to demand policy solutions from our governments that will ensure a safe and sustainable future. |
How To Write An Argumentative Essay On Climate Change
Writing an argumentative essay about climate change requires a student to take an opinionated stance on the subject.
Following are the steps to follow for writing an argumentative essay about climate change
Do Your Research
The first step is researching the topic and collecting evidence to back up your argument.
You should look at scientific research, articles, and data on climate change as well as current policy solutions.
Pick A Catchy Title
Once you have gathered your evidence, it is time to pick a title for your essay. It should be specific and concise.
Outline Your Essay
After selecting a title, create an outline of the main points you will include in the essay.
This should include an introduction, body paragraphs that provide evidence for your argument, and a conclusion.
Compose Your Essay
Finally, begin writing your essay. Start with an introduction that provides a brief overview of the main points you will cover and includes your thesis statement.
Then move on to the body paragraphs, providing evidence to back up your argument.
Finally, conclude the essay by restating your thesis statement and summarizing the main points.
Proofread and Revise
Once you have finished writing the essay, it is important to proofread and revise your work.
Check for any spelling or grammatical errors, and make sure the argument is clear and logical.
Finally, consider having someone else read over the essay for a fresh perspective.
By following these steps, you can create an effective argumentative essay on climate change. Good luck!
Examples Of Argumentative Essays About Climate Change
Climate Change is real and happening right now. It is one of the most urgent environmental issues that we face today.
Argumentative essays about this topic can help raise awareness that we need to protect our planet.
Below you will find some examples of argumentative essays on climate change written by CollegeEssay.orgâs expert essay writers.
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change And Global Warming
Persuasive Essay About Climate Change
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change In The Philippines
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Caused By Humans
Geography Argumentative Essay About Climate Change
Check our extensive blog on argumentative essay examples to ace your next essay!
Good Argumentative Essay Topics About Climate Change
Choosing a great topic is essential to help your readers understand and engage with the issue.
Here are some suggestions:
- Should governments fund projects that will reduce the effects of climate change?
- Is it too late to stop global warming and climate change?
- Are international treaties effective in reducing carbon dioxide emissions?
- What are the economic implications of climate change?
- Should renewable energy be mandated as a priority over traditional fossil fuels?
- How can individuals help reduce their carbon footprint and fight climate change?
- Are regulations on industry enough to reduce global warming and climate change?
- Could geoengineering be used to mitigate climate change?
- What are the social and political effects of global warming and climate change?
- Should companies be held accountable for their contribution to climate change?
Check our comprehensive blog on argumentative essay topics to get more topic ideas!
We hope these topics and resources help you write a great argumentative essay about climate change.
Now that you know how to write an argumentative essay about climate change, itâs time to put your skills to the test.
Overwhelmed with assignments and thinking, "I wish someone could write me an essay "?
Our specialized writing service is here to turn that wish into reality. With a focus on quality, originality, and timely delivery, our team of professionals is committed to crafting essays that align perfectly with your academic goals.
And for those seeking an extra edge, our essay writer , an advanced AI tool, is ready to elevate your writing to new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good introduction to climate change.
An introduction to a climate change essay can include a short description of why the topic is important and/or relevant.
It can also provide an overview of what will be discussed in the body of the essay.
The introduction should conclude with a clear, focused thesis statement that outlines the main argument in your essay.
What is a good thesis statement for climate change?
A good thesis statement for a climate change essay should state the main point or argument you will make in your essay.
You could argue that “The science behind climate change is irrefutable and must be addressed by governments, businesses, and individuals.”
Cathy A. (Medical school essay, Education)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Essay Service Examples Environment Climate Change
Climate Change Essay
What Is Climate Change?
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

The Impact Of Climate Change On Ecosystems And Human Populations
The science of climate change, potential solutions for climate change.
Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- Climate Change
- Health Promotion
Climate change is a consequential effect of humanity’s expansion. It can kill off entire species...
- Global Warming
Reporters and the majority of the population utilize the terms climate change and global warming...
- Carbon Dioxide
Global warming is highly controversial issue in this global world where each country facing...
Climate change is known as a major problem that is long term in the world with massive and...
Climate change may seem abstract and distant for many of us. However, it is one of the gravest...
- Conservation of Forest
- Conversation
It’s finally Christmas and you’re hyped to surprise your friends and family at home after so many...
- Marketing Strategy
Have you noticed that every summer is warmer than the one before? Have you noticed a change in the...
The researcher has used the most appropriate research design that enables her to take a closer...
- Fossil Fuels
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. These shifts may...
Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!
Products and services
Our innovative products and services for learners, authors and customers are based on world-class research and are relevant, exciting and inspiring.
- Academic Research
- English Language Learning
- English Language Assessment
- Educational resources for schools
- Educational Research & Network
- Assessment Research
- Cambridge Assessment International Education
- Cambridge CEM
- Cambridge Partnership for Education
- Cambridge Dictionary
- The Cambridge Mathematics Project
We unlock the potential of millions of people worldwide. Our assessments, publications and research spread knowledge, spark enquiry and aid understanding around the world.
- People and planet
- News and insights
- Accessibility
- Rights and permissions
- Annual Report
No matter who you are, what you do, or where you come from, you’ll feel proud to work here.
- Language learning materials
- Language Assessment

Climate change essay competition: A spark of change

Writing Teens
We’d like to share another chosen essay from this year’s Bahçeşehir essay competition, on the topic of climate change. There were many fantastic entries across grades 9 and 10. A huge congratulations to all finalists and every student who took the time to submit their work.
Bahçeşehir College is committed to increasing students’ awareness of the changing world we live in. This climate change essay competition saw many students submitting well thought out pieces of writing. These essays were marked on their format, creativity, organisation, clarity, unity/development of thought, and grammar/mechanics.
Asli’s essay
“A little spark you create might not be enough when on its own, but it also can turn into bright flames when combined with thousand others. What you can do is be one of those sparks.”
Please take a few minutes to read one of the five winning essays, supplied below.
A spark of change
“Most human beings have an almost infinite capacity for taking things for granted,” says Aldous Huxley in one of his books. He perfectly summarises the biggest cause of the issues the world of today struggles with, the issues that are created by humans’ tendency to ignore the consequences of their actions. Water shortages, light pollution, desertification – all problems that you are familiar with by this point. People spend their resources like there is no tomorrow, not even thinking about how much harm their behavior might cause. What they fail to remember is that they themselves live in the very world they do not seem to care what happens to. Each year, more water is gone to waste, a bigger amount of meat is consumed, and the number of trees cut down keeps increasing. Some consequences are immediately noticeable; people can see how much smaller the Amazon forests got or how much water was used needlessly. However, what some cannot or do not want to realise is that there is another big threat creeping up behind the alarming scene, maybe not as flashily, but just as steadily: climate change.
Environmental conditions are changing rapidly with the temperatures increasing, water levels rising, the glaciers melting – complications no-one had to deal with a mere two hundred years ago. [1] The human race’s means of living is not only changing the climate, but is also transforming with it. The transformation is not exactly for the better, though, but the worse. Despite what few might be thinking, nothing about this transformation is adaptation; it is demolition on a large scale, destruction of the only place we have the privilege of living in. This has to stop; humans must start adapting and stop destroying if anything is going to be different. Just as Greta Thunberg stated, climate change is not only a threat; it is, above all, an opportunity to adapt and create a greener, healthier world. People have to define what exactly causes the seemingly little, but in reality, crucial environmental changes, develop methods to ameliorate their consequences, and find ways to raise awareness. Humans forget that they are supposed to be the protectors of the world, not the ravagers. How is the Earth going to survive, if the only species it has the chance to lean on turn their back to it?
With how often the media leaves you exposed to them, all the warnings and announcements about the danger us humans are in must be playing again and again in your mind – like some sort of a malfunctioning tape. And yes, while most people know everything they say by heart, no one actually takes them to the same place, resulting in a society that is knowledgeable but deeply lacks awareness. That is the root of all the threats the world is up against; everyone knows they have to change themselves to start change on a bigger scale, but they all expect some other person or organisation to light that match. The thing is, no good is ever going to happen when people keep standing on the sidelines. No results, positive or negative, come from doing nothing. This is why someone has to act up; someone that might as well be you.
All in all, the human race’s negative impact on climate and the environment is getting out control; the quality of life on Earth is decreasing, not just for humans, but also for all sorts of species. People have to fix what they have damaged, yet they fail to do anything in the fear of wasting their resources. What they do not realise is that with each day that passes without any action, the number of natural resources available also decreases significantly. [2] Yes, there is a possibility that the efforts might be futile, but doing nothing is not going to help with anything either. Not enough people are willing to get out of their comfort zones for the sake of the world. It is not that difficult to turn off a switch, use public transportation when the opportunity arises, or eat a portion less meat than you normally would have. Those are the simple acts many thinks do not matter, but create huge differences when applied on a societal basis. A little spark you create might not be enough when on its own, but it also can turn into bright flames when combined with thousand others. What you can do is be one of those sparks. Maybe what you do will not be enough for the whole world to change, but it might as well be part of the act that leads up to it.
[1] https://reporter.anu.edu.au/global-warming-began-earlier-we-thought
[2] https://ec.europa.eu/clima/climate-change/climate-change-consequences_en
Bahçeşehir College is a global education brand, founded by Enver Y ücel in 1968. Bahçeşehir College is considered as one of the most prestigious private school chains in Turkey, with 142 campuses in 62 provinces.
If you enjoyed this essay, please take some time to read Özlem ‘ s winning essay.
You have to be logged in to save articles
- Climate Change and the Media Biases Words: 1473
- Climate Change: The Negative Effects Words: 1503
- Social Issue: Climate Change Words: 1062
- Climate Change Impacts Florida’s Biodiversity Words: 1805
- The Controversies of Climate Change Words: 1421
- “The Basics of Climate Change” Blog Words: 604
- Climate Change Factors and Impacts on Blue Crab Populations Words: 5492
- Climate Change from Different Perspectives Words: 1953
- Climate Change as a Challenge to Australia Words: 2975
- The Importance of Addressing Climate Change Words: 1144
- Climate Change Prediction for the Caribbean Words: 483
- Climate Change: The Impact on North America Words: 2798
- Security and Climate Change Words: 3018
- Climate Change and Crop Production Words: 1140
- Climate Change: Causes, Dynamics, and Effects Words: 568
- Climate Change and Related Issues in Canada Words: 680
- Water Scarcity Due to Climate Change Words: 1206
- Climate Change and Corporate Responsibility Words: 3614
- Water Scarcity as Effect of Climate Change Words: 1317
- Climate Change in Environmentally Vulnerable Countries Words: 1461
- Climate Change: Factors and Future Words: 1487
- The Health Impacts of Climate Change in China Words: 909
- Climate Change: Changing Patterns of Malaria Words: 2996
Climate Change Impacts
Explore the impacts of climate change with our effects of climate change essay. Learn more about climate change causes, effects, and solutions with the help of our sample. Keep reading to gain inspiration for your essay on climate change and its impact.
Effects of Climate Change: Essay Conclusion
Climate change, climate change impacts, managing climate change, effects of climate change: essay introduction.
It is doubtless that global change has become one the challenges, which encompasses a wide range of human life, including social and economical aspects of human life. Research has indicated that climate change will continue affecting the world as long as proper measures are not taken to protect the environment.
In this line of thought, human activities have been widely blamed for escalating effects of climate change around the world (Hillel & Rosenzweig 2010). Only time will tell whether taming climate change is possible or not.
In this regard, this assessment covers the impact of climate change in our lives today even as world leaders burn midnight oil to develop strategies, aimed at taming the scourge. This proposal topic has an array of benefits, especially in understanding the fatal nature of climate change.
It will mainly focus on the effects of climate change and make proposals on how to counteract the effects of climate together some of the preventive measures being considered by international leaders.
Through literature review, this project will compare different views as argued by different authors in order to synthesize the issue with varying view points. This will be crucial in capturing the main objective of the projects, which revolves around the analysis of the effects of climate change in the world today.
How is climate change defined? Although different environmental experts tend to have different definitions, the Australian Government defines climate change as the weather pattern observed for several years. These changes are mainly caused by human activities, which negatively impact the environment.
With reference to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report released in the year 2007, climate change is no longer a myth, but a reality, whose impact has continually escalated from 1950s, mainly due to rising levels of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
This implies that human activities have significantly contributed this environmental scourge, which continues to affect most parts of the world. The IPCC report was a representation of the world view on climate change, collected from various scientific journals published around the world (Australian Government 2012).
The Australian Department of Climate Change and Energy Efficiency affirms that there is enough evidence to support the fact that the climate system of the earth has continuously been warming. Some of the observations made include the rising level of air in the world and high ocean temperatures. Others are the rising sea level, constant melting of snow and ice in most parts of the world.
One important fact to note about climate change is that it involves the rising temperatures of the climate system holistically, including all the oceans, atmosphere and the cryosphere. These findings concluded that the climate system is in a heating mode.
Even as we review other people’s work, it is important to note that climate change is more than mere global warming as perceived by most people. From scientific revelation, the climate will be varied broadly especially if the warming continues uncontrollably (Australian Government 2012). As a result, the world is likely to experience irregular rainfall patterns, occurrence of severe climatic events like heavy currents and droughts among others.
The impact of climate change has been felt in every part of the world. According to United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), Asia, Africa and Latin America are among the regions of the world, which have severely been affected by the scourge. In a 2010 survey carried out by Climate Change Secretariat, Africa is under the pressure of climate change and remains vulnerable to these effects.
Unlike most parts of the world, Africa experiences varying climatic changes. Common occurrences in Africa are severe droughts and floods, which have had negative implications on the continent’s economy (UNFCCC 2010).
The two events are widely known to predispose famine and overall interference with the socio-well being of the society. According to the UNFCCC’s analysis, close to a third of Africa’s population inhabit drought-prone regions, while more than two million remain vulnerable to drought every year (UNFCCC 2010).
In understanding the implication of climate change in Africa, the survey found out that the issue of climate change is intertwined with several factors, which contribute to its escalation across the continent.
Some of these factors include poverty, weak institutions, illiteracy, lack of information and technology, limited infrastructure, poor accessibility to resources, poor management and conflicts. In addition, there is widespread exploitation of land, which remains a major threat to the climate.
Due to pressure on farming land, most farmers exert pressure through over-cultivation and deforestation. In addition, other factors like dunes and storms continue posing more negative threats to the environment and human beings (UNFCCC 2010).
As a result of these events, the continent experiences drought and overall scarcity of water. Due to this emerging trend, Africa is likely to face shortage of rainfall and overall scarcity of water. With Africa having several trans-boundary river basins, the continent is likely to experience conflicts over these basins. Another important aspect captured in the report is agriculture (UNFCCC 2010).
Since most subsistence farmers in Africa depend on rainfall and irrigation, the sector has been affected by insufficient supply in most Sub-Saharan regions. Besides this, UNFCCC notes that climate change has resulted into loss of agricultural land and a drop in subsistence crop production. With a good percentage of the population under the threat of starvation, climate change has undoubtedly led to escalation of insufficient food supply.
It is amazing to note that climate change has also contributed to the spread of some diseases like malaria, tuberculosis and diarrhea in most parts of Africa. As stated by the UNFCCC, there has been a shift in the distribution of disease vectors.
For instance, migration of mosquitoes to regions of higher altitude is likely to expose people in such regions to the risk of contracting malaria (UNFCCC 2010). Additionally, climate change is likely to result into negative impact on African ecosystems and habitats, which are already threatened by these changes. Due to reduced habitat and changing climatic conditions some species are likely to move to more tolerable regions.
In this line of though Robert Watson, Marufu Zinyowera and Richard Moss found out that climate change can have severe effects on human health. In a research carried out in 1998, the three reiterated that human health may be affected as a result of heat-stress mortality, urban air pollution and vector-borne diseases, which could be favored as a result of change in temperature or rainfall in a given ecosystem (Watson, Zinyowera & Moss 1998, p. 7).
Additionally, Watson, Zinyowera and Moss argued that these effects are commonly felt in developing countries, where lives are lost, communities affected and the cost in medical care rises due to high prevalence of some health complications.
With regard to the impact of climate change on biodiversity, Watson, Zinyowera and Moss, agree with UNFCCC’s findings. In their 1998 survey, the three argued that all ecosystems play a fundamental role in the society (Watson, Zinyowera & Moss 1998).
For instance, they are a source of goods and services to any society. In particular, these goods and services include provision of food, processing and storage of carbon and other nutrients, assimilation of wastes and provision of recreation and tourism opportunities among others.
As a result, they argued that climatic changes are known to alter the geographical local of various ecological systems, including the presence of certain species and their ability to remain productive to support the society. According to their findings, ecological systems are essentially dynamic and are commonly affected by climatic variations of whichever magnitude.
Nevertheless, the extreme to which the climate varies determines the changes, which occur in the ecosystem. In addition, the three authors noted the high level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere was a major contributing factor towards climate changes taking place in the world today (Watson, Zinyowera & Moss 1998).
Besides influencing the ecosystems, Watson, Zinyowera and Moss noted that climate change may also have secondary effects, say, variations in soil characteristics and interference of regimes. These include diseases, pests and diseases, which are likely to support the existence of some species favorably than others (Watson, Zinyowera & Moss 1998).
This will automatically affect the survival of some species and the overall population of organisms. Similarly, they argued that that climate change has direct impact on food production in most parts of the world. According to the 1998 survey, the type of agricultural systems in place determines the manner in which crop productivity is affected by changes in climatic conditions and patterns.
Like many other scholars, Barrie Pittock spent his life studying the environment and how it is affected by changes in climate. In his 2009, survey, Climate Change: The Science, Impacts and Solutions , Pittock outlined several reasons why there is cause for alarm, regarding climate change in the world today.
According to Pittock, the UNFCCC seeks to reduce the impact of climate change by being on the frontline in the war against global warming (Pittock 2009, p. 107). He further noted that human-induced climate change is a major security threat in the world today. This stance is mainly backed by the well-known effects of climate change described by the UNFCCC and the IPCC.
Moreover, Pittock reiterated that climate change has complex effects in the world today, citing a number of examples. In cases where there is high rainfall resulting from climate change, the world may experience direct or indirect implications.
This could be seen through high or low crop yield, depending on the type of soil or crop. On the other hand, indirect effects may refer to changes in demand and supply, emanating from either low or high yield, depending on other factors. He therefore agreed with several authors and researchers who have enumerated implications of climate change on the environment and human life at large.
For example, Pittock noted that climate change has been a major cause of water shortages in most parts of the world (Pittock 2009, p. 108). He however attributed this to a number of factors, including precipitation decrease in some regions, high rates of evaporation in the world and general loss of glaciers.
Economically, Pittock noted that climate change affects the economic progress of a nation since resources may be diverted to disease control instead of advancing developing projects.
Moreover, it is important to note that most of the countries, which suffer severely as a result of climate change, are poor nations that lack stable economic muscles. As a result, there is a likelihood of richer countries becoming stronger as developing economies weaken further. Lastly, Pittock noted that some of the threats emanating from climate change cause irreversible damages, which end up haunting human beings forever (Pittock 2009, p. 109).
With reference to a number of scholars who have done research on the impact of climate change, it is evident that human activities have a role in the escalation of these effects. In his 2010 survey, Martin Kernan noted that there is a relation between human activities and global warming.
As a result of this global relationship, the world has registered an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. In this survey, he noted that the increase in green house gases is rampant in the northern hemisphere than any other part of the world.
As a result of high temperatures, Martin underscore that the changes have impact on the composition of natural ecosystems, regarding species population and their ability to survive (Kernan 2010, p. 15). What is most evident in Martin’s research is his comparison of the current state of the climate, to what was known hundreds of years ago.
Climate change also affects the quality of water in the United States. According to a research carried out by Robert Mendelsohn and James Neumann, water plays an important role in the life of a human being. Some of these functions include but not limited to power generation, food production, recreation and ecological processes (Mendelsohn & Mendelsohn 2004, p. 133).
However, this is only possible if the water is available and of good quality. Thus, changes in spatial distribution and quality can have direct social and economic effects on the society.
This alteration may occur as a result of increased concentration in greenhouse gases. Climate change can be detected by observing variation in temperatures, frequent and intense droughts and altered precipitation patterns among other factors (Mendelsohn & Mendelsohn 2004, p. 133).
The findings on the impact of climate change on the quality of water have also been pursued by Jan Dam, who argued that natural systems are usually sensitive to changes in climate variation. Hydrological quality is mainly affected by the temperature or concentration of water (Dam 2003, p. 95).
When oceans and other water bodies overheat because of high temperatures, this may result into negative impact on aquatic animals, which adapt to certain hydrological temperatures. Similarly, the quality of water is always altered when gases like carbon dioxide are dissolved in water basins. This may affect the mix of species present in a given ecosystem.
Based on the impact of climate change, it is doubtless that management of the risks has to be effected promptly before they become fatal and irreversible. One of the ways of controlling climate change is through reduction of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
This can be achieved through several ways, which minimize the emission of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (McCarthy 2001, p. 222). According to James McCarthy, this can be realized by adopting alternative sources of energy unlike how most economies rely of oil and petroleum products as the main source of energy. Additionally, good methods of farming are important to maintain the value of the environment for sustainable support.
Use of international legislations is also necessary in ensuring that rich countries do not exploit developing nations as they are major contributors of effluents into the atmosphere (Hillel & Rosenzweig 2010). Above all, the fight against climate change calls for environmental campaign, which requires the efforts of everybody in the world.
From the above review of literature, it is clear that climate change is a major socio and environmental issue affecting the world today. Mainly caused by human activities, climate change poses a chain of challenges and threats to the environment.
For instance, there are several diseases, which affect human beings as a result of climate change (Rosenberg & Edmonds 2005). Of importance is also the alteration of the quality of the natural environment, which affects biodiversity. This has led to the extinction of some species, while others have increased exponentially in numbers.
Moreover, it is imperative to note that some of the occurrences, which are considered to be natural, are caused by climate change. Common ones include floods and draughts (Faure, Gupta & Nentjes 2003, p. 340).
Most of these calamities continue to be recognized as natural disasters yet they can be controlled using simple mitigation measures. In most cases, adoption of renewable sources of energy has always been considered to be the most important way of saving the world from climate change. Although it is a complex issue to handle, joint global efforts are important in making progress.
Australian Government 2012, Impacts of climate change .
Dam, J 2003, Impacts of Climate Change and Climate Variability on Hydrological Regimes , Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
Faure, M, Gupta, J & Nentjes, A 2003, Climate Change and the Kyoto Protocol: The Role of Institutions and Instruments to Control Global Change , Edward Elgar Publishing, United Kingdom.
Hillel, D & Rosenzweig, C 2010, Handbook of Climate Change and Agroecosystems: Impacts, Adaptation, and Mitigation , World Scientific, Singapore.
Kernan, M 2010, Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Ecosystems , John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey.
Mendelsohn, R & Neumann, J 2004, The Impact Of Climate Change On The United States Economy , Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
Pittock, B 2009, Climate Change: The Science, Impacts and Solutions , Csiro Publishing, Sydney.
Rosenberg, N, & Edmonds, J 2005, Climate Change Impacts for the Conterminous USA: An Integrated Assessment , Springer, New York.
UNFCCC 2010, Climate Change: Impacts, Vulnerabilities and Adaptation In Developing Countries.
Watson, R, Zinyowera, M & Moss, R 1998, The Regional Impacts of Climate Change: An Assessment of Vulnerability , Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, January 8). Climate Change Impacts. https://studycorgi.com/climate-change-impacts/
"Climate Change Impacts." StudyCorgi , 8 Jan. 2020, studycorgi.com/climate-change-impacts/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'Climate Change Impacts'. 8 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "Climate Change Impacts." January 8, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/climate-change-impacts/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Climate Change Impacts." January 8, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/climate-change-impacts/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "Climate Change Impacts." January 8, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/climate-change-impacts/.
This paper, “Climate Change Impacts”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: October 7, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Explore Greyhound Nation
- Loyola Today
Our Future Is Now - A Climate Change Essay by Francesca Minicozzi, '21
Francesca Minicozzi (class of 2021) is a Writing/Biology major who plans to study medicine after graduation. She wrote this essay on climate change for WR 355/Travel Writing, which she took while studying abroad in Newcastle in spring 2020. Although the coronavirus pandemic curtailed Francesca’s time abroad, her months in Newcastle prompted her to learn more about climate change. Terre Ryan Associate Professor, Writing Department
Our Future Is Now
By Francesca Minicozzi, '21 Writing and Biology Major
“If you don’t mind me asking, how is the United States preparing for climate change?” my flat mate, Zac, asked me back in March, when we were both still in Newcastle. He and I were accustomed to asking each other about the differences between our home countries; he came from Cambridge, while I originated in Long Island, New York. This was one of our numerous conversations about issues that impact our generation, which we usually discussed while cooking dinner in our communal kitchen. In the moment of our conversation, I did not have as strong an answer for him as I would have liked. Instead, I informed him of the few changes I had witnessed within my home state of New York.

Zac’s response was consistent with his normal, diplomatic self. “I have been following the BBC news in terms of the climate crisis for the past few years. The U.K. has been working hard to transition to renewable energy sources. Similar to the United States, here in the United Kingdom we have converted over to solar panels too. My home does not have solar panels, but a lot of our neighbors have switched to solar energy in the past few years.”
“Our two countries are similar, yet so different,” I thought. Our conversation continued as we prepared our meals, with topics ranging from climate change to the upcoming presidential election to Britain’s exit from the European Union. However, I could not shake the fact that I knew so little about a topic so crucial to my generation.
After I abruptly returned home from the United Kingdom because of the global pandemic, my conversation with my flat mate lingered in my mind. Before the coronavirus surpassed climate change headlines, I had seen the number of internet postings regarding protests to protect the planet dramatically increase. Yet the idea of our planet becoming barren and unlivable in a not-so-distant future had previously upset me to the point where a part of me refused to deal with it. After I returned from studying abroad, I decided to educate myself on the climate crisis.
My quest for climate change knowledge required a thorough understanding of the difference between “climate change” and “global warming.” Climate change is defined as “a pattern of change affecting global or regional climate,” based on “average temperature and rainfall measurements” as well as the frequency of extreme weather events. 1 These varied temperature and weather events link back to both natural incidents and human activity. 2 Likewise, the term global warming was coined “to describe climate change caused by humans.” 3 Not only that, but global warming is most recently attributed to an increase in “global average temperature,” mainly due to greenhouse gas emissions produced by humans. 4
I next questioned why the term “climate change” seemed to take over the term “global warming” in the United States. According to Frank Luntz, a leading Republican consultant, the term “global warming” functions as a rather intimidating phrase. During George W. Bush’s first presidential term, Luntz argued in favor of using the less daunting phrase “climate change” in an attempt to overcome the environmental battle amongst Democrats and Republicans. 5 Since President Bush’s term, Luntz remains just one political consultant out of many politicians who has recognized the need to address climate change. In an article from 2019, Luntz proclaimed that political parties aside, the climate crisis affects everyone. Luntz argued that politicians should steer clear of trying to communicate “the complicated science of climate change,” and instead engage voters by explaining how climate change personally impacts citizens with natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and forest fires. 6 He even suggested that a shift away from words like “sustainability” would gear Americans towards what they really want: a “cleaner, safer, healthier” environment. 7
The idea of a cleaner and heathier environment remains easier said than done. The Paris Climate Agreement, introduced in 2015, began the United Nations’ “effort to combat global climate change.” 8 This agreement marked a global initiative to “limit global temperature increase in this century to 2 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels,” while simultaneously “pursuing means to limit the increase to 1.5 degrees.” 9 Every country on earth has joined together in this agreement for the common purpose of saving our planet. 10 So, what could go wrong here? As much as this sounds like a compelling step in the right direction for climate change, President Donald Trump thought otherwise. In June 2017, President Trump announced the withdrawal of the United States from the Paris Agreement with his proclamation of climate change as a “’hoax’ perpetrated by China.” 11 President Trump continued to question the scientific facts behind climate change, remaining an advocate for the expansion of domestic fossil fuel production. 12 He reversed environmental policies implemented by former President Barack Obama to reduce fossil fuel use. 13
Trump’s actions against the Paris Agreement, however, fail to represent the beliefs of Americans as a whole. The majority of American citizens feel passionate about the fight against climate change. To demonstrate their support, some have gone as far as creating initiatives including America’s Pledge and We Are Still In. 14 Although the United States officially exited the Paris Agreement on November 4, 2020, this withdrawal may not survive permanently. 15 According to experts, our new president “could rejoin in as short as a month’s time.” 16 This offers a glimmer of hope.
The Paris Agreement declares that the United States will reduce greenhouse gas emission levels by 26 to 28 percent by the year 2025. 17 As a leader in greenhouse gas emissions, the United States needs to accept the climate crisis for the serious challenge that it presents and work together with other nations. The concept of working coherently with all nations remains rather tricky; however, I remain optimistic. I think we can learn from how other countries have adapted to the increased heating of our planet. During my recent study abroad experience in the United Kingdom, I was struck by Great Britain’s commitment to combating climate change.
Since the United Kingdom joined the Paris Agreement, the country targets a “net-zero” greenhouse gas emission for 2050. 18 This substantial alteration would mark an 80% reduction of greenhouse gases from 1990, if “clear, stable, and well-designed policies are implemented without interruption.” 19 In order to stay on top of reducing emissions, the United Kingdom tracks electricity and car emissions, “size of onshore and offshore wind farms,” amount of homes and “walls insulated, and boilers upgraded,” as well as the development of government policies, including grants for electric vehicles. 20 A strong grip on this data allows the United Kingdom to target necessary modifications that keep the country on track for 2050. In my brief semester in Newcastle, I took note of these significant changes. The city of Newcastle is small enough that many students and faculty are able to walk or bike to campus and nearby essential shops. However, when driving is unavoidable, the majority of the vehicles used are electric, and many British citizens place a strong emphasis on carpooling to further reduce emissions. The United Kingdom’s determination to severely reduce greenhouse emissions is ambitious and particularly admirable, especially as the United States struggles to shy away from its dependence on fossil fuels.
So how can we, as Americans, stand together to combat global climate change? Here are five adjustments Americans can make to their homes and daily routines that can dramatically make a difference:
- Stay cautious of food waste. Studies demonstrate that “Americans throw away up to 40 percent of the food they buy.” 21 By being more mindful of the foods we purchase, opting for leftovers, composting wastes, and donating surplus food to those in need, we can make an individual difference that impacts the greater good. 22
- Insulate your home. Insulation functions as a “cost-effective and accessible” method to combat climate change. 23 Homes with modern insulation reduce energy required to heat them, leading to a reduction of emissions and an overall savings; in comparison, older homes can “lose up to 35 percent of heat through their walls.” 24
- Switch to LED Lighting. LED stands for “light-emitting diodes,” which use “90 percent less energy than incandescent bulbs and half as much as compact fluorescents.” 25 LED lights create light without producing heat, and therefore do not waste energy. Additionally, these lights have a longer duration than other bulbs, which means they offer a continuing savings. 26
- Choose transportation wisely. Choose to walk or bike whenever the option presents itself. If walking or biking is not an option, use an electric or hybrid vehicle which emits less harmful gases. Furthermore, reduce the number of car trips taken, and carpool with others when applicable.
- Finally, make your voice heard. The future of our planet remains in our hands, so we might as well use our voices to our advantage. Social media serves as a great platform for this. Moreover, using social media to share helpful hints to combat climate change within your community or to promote an upcoming protest proves beneficial in the long run. If we collectively put our voices to good use, together we can advocate for change.
As many of us are stuck at home due to the COVID-19 pandemic, these suggestions are slightly easier to put into place. With numerous “stay-at-home” orders in effect, Americans have the opportunity to make significant achievements for climate change. Personally, I have taken more precautions towards the amount of food consumed within my household during this pandemic. I have been more aware of food waste, opting for leftovers when too much food remains. Additionally, I have realized how powerful my voice is as a young college student. Now is the opportunity for Americans to share how they feel about climate change. During this unprecedented time, our voice is needed now more than ever in order to make a difference.
However, on a much larger scale, the coronavirus outbreak has shed light on reducing global energy consumption. Reductions in travel, both on the roads and in the air, have triggered a drop in emission rates. In fact, the International Energy Agency predicts a 6 percent decrease in energy consumption around the globe for this year alone. 27 This drop is “equivalent to losing the entire energy demand of India.” 28 Complete lockdowns have lowered the global demand for electricity and slashed CO2 emissions. However, in New York City, the shutdown has only decreased carbon dioxide emissions by 10 percent. 29 This proves that a shift in personal behavior is simply not enough to “fix the carbon emission problem.” 30 Climate policies aimed to reduce fossil fuel production and promote clean technology will be crucial steppingstones to ameliorating climate change effects. Our current reduction of greenhouse gas emissions serves as “the sort of reduction we need every year until net-zero emissions are reached around 2050.” 31 From the start of the coronavirus pandemic, politicians came together for the common good of protecting humanity; this demonstrates that when necessary, global leaders are capable of putting humankind above the economy. 32
After researching statistics comparing the coronavirus to climate change, I thought back to the moment the virus reached pandemic status. I knew that a greater reason underlay all of this global turmoil. Our globe is in dire need of help, and the coronavirus reminds the world of what it means to work together. This pandemic marks a turning point in global efforts to slow down climate change. The methods we enact towards not only stopping the spread of the virus, but slowing down climate change, will ultimately depict how humanity will arise once this pandemic is suppressed. The future of our home planet lies in how we treat it right now.
- “Climate Change: What Do All the Terms Mean?,” BBC News (BBC, May 1, 2019), https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-48057733 )
- Ibid.
- Kate Yoder, “Frank Luntz, the GOP's Message Master, Calls for Climate Action,” Grist (Grist, July 26, 2019), https://grist.org/article/the-gops-most-famous-messaging-strategist-calls-for-climate-action
- Melissa Denchak, “Paris Climate Agreement: Everything You Need to Know,” NRDC, April 29, 2020, https://www.nrdc.org/stories/paris-climate-agreement-everything-you-need-know)
- “Donald J. Trump's Foreign Policy Positions,” Council on Foreign Relations (Council on Foreign Relations), accessed May 7, 2020, https://www.cfr.org/election2020/candidate-tracker/donald-j.-trump?gclid=CjwKCAjw4871BRAjEiwAbxXi21cneTRft_doA5if60euC6QCL7sr-Jwwv76IkgWaUTuyJNx9EzZzRBoCdjsQAvD_BwE#climate and energy )
- David Doniger, “Paris Climate Agreement Explained: Does Congress Need to Sign Off?,” NRDC, December 15, 2016, https://www.nrdc.org/experts/david-doniger/paris-climate-agreement-explained-does-congress-need-sign )
- “How the UK Is Progressing,” Committee on Climate Change, March 9, 2020, https://www.theccc.org.uk/what-is-climate-change/reducing-carbon-emissions/how-the-uk-is-progressing/)
- Ibid.
- “Top 10 Ways You Can Fight Climate Change,” Green America, accessed May 7, 2020, https://www.greenamerica.org/your-green-life/10-ways-you-can-fight-climate-change )
- Matt McGrath, “Climate Change and Coronavirus: Five Charts about the Biggest Carbon Crash,” BBC News (BBC, May 5, 2020), https://www.bbc.com/news/amp/science-environment-52485712 )

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Global Warming

- Updated on
- Apr 27, 2024

Being able to write an essay is an integral part of mastering any language. Essays form an integral part of many academic and scholastic exams like the SAT, and UPSC amongst many others. It is a crucial evaluative part of English proficiency tests as well like IELTS, TOEFL, etc. Major essays are meant to emphasize public issues of concern that can have significant consequences on the world. To understand the concept of Global Warming and its causes and effects, we must first examine the many factors that influence the planet’s temperature and what this implies for the world’s future. Here’s an unbiased look at the essay on Global Warming and other essential related topics.
Short Essay on Global Warming and Climate Change?
Since the industrial and scientific revolutions, Earth’s resources have been gradually depleted. Furthermore, the start of the world’s population’s exponential expansion is particularly hard on the environment. Simply put, as the population’s need for consumption grows, so does the use of natural resources , as well as the waste generated by that consumption.
Climate change has been one of the most significant long-term consequences of this. Climate change is more than just the rise or fall of global temperatures; it also affects rain cycles, wind patterns, cyclone frequencies, sea levels, and other factors. It has an impact on all major life groupings on the planet.
Also Read: Essay on Yoga Day
Also Read: Speech on Yoga Day
What is Global Warming?
Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth’s average surface temperature over the past century, primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by people burning fossil fuels . The greenhouse gases consist of methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and chlorofluorocarbons. The weather prediction has been becoming more complex with every passing year, with seasons more indistinguishable, and the general temperatures hotter.
The number of hurricanes, cyclones, droughts, floods, etc., has risen steadily since the onset of the 21st century. The supervillain behind all these changes is Global Warming. The name is quite self-explanatory; it means the rise in the temperature of the Earth.
Also Read: What is a Natural Disaster?
What are the Causes of Global Warming?
According to recent studies, many scientists believe the following are the primary four causes of global warming:
- Deforestation
- Greenhouse emissions
- Carbon emissions per capita
Extreme global warming is causing natural disasters , which can be seen all around us. One of the causes of global warming is the extreme release of greenhouse gases that become trapped on the earth’s surface, causing the temperature to rise. Similarly, volcanoes contribute to global warming by spewing excessive CO2 into the atmosphere.
The increase in population is one of the major causes of Global Warming. This increase in population also leads to increased air pollution . Automobiles emit a lot of CO2, which remains in the atmosphere. This increase in population is also causing deforestation, which contributes to global warming.
The earth’s surface emits energy into the atmosphere in the form of heat, keeping the balance with the incoming energy. Global warming depletes the ozone layer, bringing about the end of the world. There is a clear indication that increased global warming will result in the extinction of all life on Earth’s surface.
Also Read: Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation, and Wildlife Resources
Solutions for Global Warming
Of course, industries and multinational conglomerates emit more carbon than the average citizen. Nonetheless, activism and community effort are the only viable ways to slow the worsening effects of global warming. Furthermore, at the state or government level, world leaders must develop concrete plans and step-by-step programmes to ensure that no further harm is done to the environment in general.
Although we are almost too late to slow the rate of global warming, finding the right solution is critical. Everyone, from individuals to governments, must work together to find a solution to Global Warming. Some of the factors to consider are pollution control, population growth, and the use of natural resources.
One very important contribution you can make is to reduce your use of plastic. Plastic is the primary cause of global warming, and recycling it takes years. Another factor to consider is deforestation, which will aid in the control of global warming. More tree planting should be encouraged to green the environment. Certain rules should also govern industrialization. Building industries in green zones that affect plants and species should be prohibited.
Also Read: Essay on Pollution
Effects of Global Warming
Global warming is a real problem that many people want to disprove to gain political advantage. However, as global citizens, we must ensure that only the truth is presented in the media.
This decade has seen a significant impact from global warming. The two most common phenomena observed are glacier retreat and arctic shrinkage. Glaciers are rapidly melting. These are clear manifestations of climate change.
Another significant effect of global warming is the rise in sea level. Flooding is occurring in low-lying areas as a result of sea-level rise. Many countries have experienced extreme weather conditions. Every year, we have unusually heavy rain, extreme heat and cold, wildfires, and other natural disasters.
Similarly, as global warming continues, marine life is being severely impacted. This is causing the extinction of marine species as well as other problems. Furthermore, changes are expected in coral reefs, which will face extinction in the coming years. These effects will intensify in the coming years, effectively halting species expansion. Furthermore, humans will eventually feel the negative effects of Global Warming.
Also Read: Concept of Sustainable Development
Sample Essays on Global Warming
Here are some sample essays on Global Warming:
Essay on Global Warming Paragraph in 100 – 150 words
Global Warming is caused by the increase of carbon dioxide levels in the earth’s atmosphere and is a result of human activities that have been causing harm to our environment for the past few centuries now. Global Warming is something that can’t be ignored and steps have to be taken to tackle the situation globally. The average temperature is constantly rising by 1.5 degrees Celsius over the last few years.
The best method to prevent future damage to the earth, cutting down more forests should be banned and Afforestation should be encouraged. Start by planting trees near your homes and offices, participate in events, and teach the importance of planting trees. It is impossible to undo the damage but it is possible to stop further harm.
Also Read: Social Forestry
Essay on Global Warming in 250 Words
Over a long period, it is observed that the temperature of the earth is increasing. This affected wildlife, animals, humans, and every living organism on earth. Glaciers have been melting, and many countries have started water shortages, flooding, and erosion and all this is because of global warming.
No one can be blamed for global warming except for humans. Human activities such as gases released from power plants, transportation, and deforestation have increased gases such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere. The main question is how can we control the current situation and build a better world for future generations. It starts with little steps by every individual.
Start using cloth bags made from sustainable materials for all shopping purposes, instead of using high-watt lights use energy-efficient bulbs, switch off the electricity, don’t waste water, abolish deforestation and encourage planting more trees. Shift the use of energy from petroleum or other fossil fuels to wind and solar energy. Instead of throwing out the old clothes donate them to someone so that it is recycled.
Donate old books, don’t waste paper. Above all, spread awareness about global warming. Every little thing a person does towards saving the earth will contribute in big or small amounts. We must learn that 1% effort is better than no effort. Pledge to take care of Mother Nature and speak up about global warming.
Also Read: Types of Water Pollution
Essay on Global Warming in 500 Words
Global warming isn’t a prediction, it is happening! A person denying it or unaware of it is in the most simple terms complicit. Do we have another planet to live on? Unfortunately, we have been bestowed with this one planet only that can sustain life yet over the years we have turned a blind eye to the plight it is in. Global warming is not an abstract concept but a global phenomenon occurring ever so slowly even at this moment. Global Warming is a phenomenon that is occurring every minute resulting in a gradual increase in the Earth’s overall climate. Brought about by greenhouse gases that trap the solar radiation in the atmosphere, global warming can change the entire map of the earth, displacing areas, flooding many countries, and destroying multiple lifeforms. Extreme weather is a direct consequence of global warming but it is not an exhaustive consequence. There are virtually limitless effects of global warming which are all harmful to life on earth. The sea level is increasing by 0.12 inches per year worldwide. This is happening because of the melting of polar ice caps because of global warming. This has increased the frequency of floods in many lowland areas and has caused damage to coral reefs. The Arctic is one of the worst-hit areas affected by global warming. Air quality has been adversely affected and the acidity of the seawater has also increased causing severe damage to marine life forms. Severe natural disasters are brought about by global warming which has had dire effects on life and property. As long as mankind produces greenhouse gases, global warming will continue to accelerate. The consequences are felt at a much smaller scale which will increase to become drastic shortly. The power to save the day lies in the hands of humans, the need is to seize the day. Energy consumption should be reduced on an individual basis. Fuel-efficient cars and other electronics should be encouraged to reduce the wastage of energy sources. This will also improve air quality and reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Global warming is an evil that can only be defeated when fought together. It is better late than never. If we all take steps today, we will have a much brighter future tomorrow. Global warming is the bane of our existence and various policies have come up worldwide to fight it but that is not enough. The actual difference is made when we work at an individual level to fight it. Understanding its import now is crucial before it becomes an irrevocable mistake. Exterminating global warming is of utmost importance and each one of us is as responsible for it as the next.
Also Read: Essay on Library: 100, 200 and 250 Words
Essay on Global Warming UPSC
Always hear about global warming everywhere, but do we know what it is? The evil of the worst form, global warming is a phenomenon that can affect life more fatally. Global warming refers to the increase in the earth’s temperature as a result of various human activities. The planet is gradually getting hotter and threatening the existence of lifeforms on it. Despite being relentlessly studied and researched, global warming for the majority of the population remains an abstract concept of science. It is this concept that over the years has culminated in making global warming a stark reality and not a concept covered in books. Global warming is not caused by one sole reason that can be curbed. Multifarious factors cause global warming most of which are a part of an individual’s daily existence. Burning of fuels for cooking, in vehicles, and for other conventional uses, a large amount of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, and methane amongst many others is produced which accelerates global warming. Rampant deforestation also results in global warming as lesser green cover results in an increased presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which is a greenhouse gas. Finding a solution to global warming is of immediate importance. Global warming is a phenomenon that has to be fought unitedly. Planting more trees can be the first step that can be taken toward warding off the severe consequences of global warming. Increasing the green cover will result in regulating the carbon cycle. There should be a shift from using nonrenewable energy to renewable energy such as wind or solar energy which causes less pollution and thereby hinder the acceleration of global warming. Reducing energy needs at an individual level and not wasting energy in any form is the most important step to be taken against global warming. The warning bells are tolling to awaken us from the deep slumber of complacency we have slipped into. Humans can fight against nature and it is high time we acknowledged that. With all our scientific progress and technological inventions, fighting off the negative effects of global warming is implausible. We have to remember that we do not inherit the earth from our ancestors but borrow it from our future generations and the responsibility lies on our shoulders to bequeath them a healthy planet for life to exist.
Also Read: Essay on Disaster Management
Climate Change and Global Warming Essay
Global Warming and Climate Change are two sides of the same coin. Both are interrelated with each other and are two issues of major concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases released such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth’s atmosphere cause Global Warming which leads to climate change. Black holes have started to form in the ozone layer that protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays.
Human activities have created climate change and global warming. Industrial waste and fumes are the major contributors to global warming.
Another factor affecting is the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation and also one of the reasons for climate change. Global warming has resulted in shrinking mountain glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic and causing climate change. Switching from the use of fossil fuels to energy sources like wind and solar.
When buying any electronic appliance buy the best quality with energy savings stars. Don’t waste water and encourage rainwater harvesting in your community.
Also Read: Essay on Air Pollution
Tips to Write an Essay
Writing an effective essay needs skills that few people possess and even fewer know how to implement. While writing an essay can be an assiduous task that can be unnerving at times, some key pointers can be inculcated to draft a successful essay. These involve focusing on the structure of the essay, planning it out well, and emphasizing crucial details.
Mentioned below are some pointers that can help you write better structure and more thoughtful essays that will get across to your readers:
- Prepare an outline for the essay to ensure continuity and relevance and no break in the structure of the essay
- Decide on a thesis statement that will form the basis of your essay. It will be the point of your essay and help readers understand your contention
- Follow the structure of an introduction, a detailed body followed by a conclusion so that the readers can comprehend the essay in a particular manner without any dissonance.
- Make your beginning catchy and include solutions in your conclusion to make the essay insightful and lucrative to read
- Reread before putting it out and add your flair to the essay to make it more personal and thereby unique and intriguing for readers
Also Read: I Love My India Essay: 100 and 500+ Words in English for School Students
Ans. Both natural and man-made factors contribute to global warming. The natural one also contains methane gas, volcanic eruptions, and greenhouse gases. Deforestation, mining, livestock raising, burning fossil fuels, and other man-made causes are next.
Ans. The government and the general public can work together to stop global warming. Trees must be planted more often, and deforestation must be prohibited. Auto usage needs to be curbed, and recycling needs to be promoted.
Ans. Switching to renewable energy sources , adopting sustainable farming, transportation, and energy methods, and conserving water and other natural resources.
Relevant Blogs
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Digvijay Singh
Having 2+ years of experience in educational content writing, withholding a Bachelor's in Physical Education and Sports Science and a strong interest in writing educational content for students enrolled in domestic and foreign study abroad programmes. I believe in offering a distinct viewpoint to the table, to help students deal with the complexities of both domestic and foreign educational systems. Through engaging storytelling and insightful analysis, I aim to inspire my readers to embark on their educational journeys, whether abroad or at home, and to make the most of every learning opportunity that comes their way.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
This was really a good essay on global warming… There has been used many unic words..and I really liked it!!!Seriously I had been looking for a essay about Global warming just like this…
Thank you for the comment!
I want to learn how to write essay writing so I joined this page.This page is very useful for everyone.
Hi, we are glad that we could help you to write essays. We have a beginner’s guide to write essays ( https://leverageedu.com/blog/essay-writing/ ) and we think this might help you.
It is not good , to have global warming in our earth .So we all have to afforestation program on all the world.
thank you so much
Very educative , helpful and it is really going to strength my English knowledge to structure my essay in future
Thank you for the comment, please follow our newsletter to get more insights on studying abroad and exams!
Global warming is the increase in 𝓽𝓱𝓮 ᴀᴠᴇʀᴀɢᴇ ᴛᴇᴍᴘᴇʀᴀᴛᴜʀᴇs ᴏғ ᴇᴀʀᴛʜ🌎 ᴀᴛᴍᴏsᴘʜᴇʀᴇ

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Climate Change Essays
Van gogh’s paintings attacked by climate activists 🔥 trending.
Van Gogh’s sunflowers painting was recently a subject of discussion following the environmental protests by individuals from the Just Stop Oil organization. Two women donned…
The layers of the Atmosphere
The layers of the atmosphere entail the various envelopes of gas surrounding the earth from the ground upwards. The atmosphere has got five different layers…
Environmental management for a changing world
Summary The purpose of this essay is to show the proposed updated approaches for global sustainability through the definition of the planetary boundary within which…
Global Warming Evaluation Essay
In the past one decade, the world has been struggling with the problem of global warming. Different organizations have come together to deal with the…
Accident prevention and safety promotion initiative for parents and caregivers…
Environmental factors causing a threat to children Infants are very susceptible to environmental pollution especially if it is indoors. The indoor air contamination can be…

Sustainability and technology forecasting
Sustainability evaluation is a critical aspect of technology forecasting. Technology forecasting just as the name suggests is the process of projecting the future of a…
Difference between science and faith
Scientists are annoyed when it is mentioned that there is no difference between science and faith. For instance, Ben Carson argued that Darwin was propelled…
Rising carbon dioxide levels on puffer fish sensory receptors
Introduction Most studies on the effect of CO2 level in the oceans has suggested that there is increased hypercapnic acid-base disturbance among marine animals (Heuer…
Our personal responsibility toward the natural world
We rely on the natural world as humans. However, our effect has become largely unsustainable. Thus, we ought to change our direction and base our…
Facts and fiction in climate change debates
Which newspaper article did you select and why Out of roughly 800 articles found in Lexis-Nexis academic database, on issues pertaining climate change, I decided…
How has climate change played a big role in the…
Introduction The devastating civil war in Syria is attributed to a variety of complex interrelated factors ranging from religious and social political factors to climate…
Climatic change in Australia and its effect
Australia like any other country in the world have been hit my noticeable climatic changes over the last few years. Climatic change is associated with…
Global warming: causes and mitigation
It is important to appreciate the fact that climate change can be defined as a change in the global climate patterns with particular focus from…
Wicked problem essay
In this essay, the Urban Heat Island effect will be viewed especially in the con text of Phoenix, Arizona. As a phenomenon, urban heat island…
Climate change a human rights issue
Climate change is as important matter just as people human rights are concerned. Some of the serious issues concerning climate change are the extreme weather…
Water Pollution in America: Lead Poisoning
Abstract Issues concerning water quality are a primary challenge facing the human race in contemporary society. American water systems are constructed using lead and iron…
Evidence for Global Climate Change
In such an apparent state that the world is in concerning climate change, it is not surprising to still hear people saying it is a…
Sustainable Agriculture and Climate Change
Abstract Agricultural sector of an economy is the most crucial one in terms of providing food to the individuals of the nations as well as…
Isotopes in Carbon Dating
Introduction Carbon-14 is a weakly radioactive isotope of Carbon also called radiocarbon. Radiocarbon dating was developed as a technique to measure radioactivity (Andreev, 2007). C-14…
International Environmental Agreements
The environmental conservation has been one of the most debated topics in the 20th and the 21st century. The increasing human population has led to…
What is the best site for researching quality climate change paper samples?
Samples is a website filled with sample essays and papers on the subject of climate change, as well as all related topics on this and many others.
How to use climate change essay examples to create my paper?
The examples are intended to help find primary sources for studying climate-related materials, help to get acquainted with the expertise and structure of writing from our writers and assist in getting acquainted with the features of writing different types of essays.
Is it allowed to submit your climate change essay samples as mine?
It is possible but be prepared that the professor or commission may not accept them since they are all in the public domain and are intended primarily for finding the necessary information, examples of text structuring, etc.
What college paper and essay examples can students find on our site?
The catalogue contains various topics and different types of works (essays, papers, etc.). Consequently, the number of examples in each category can exceed several dozen.
If you have a chance to look inside our climate change essay examples, it may turn out to be your winning ticket to the fascinating world of writing. Here, you may find research papers compiled by professionals. In addition, the range of topics related to climate and human impact on the environment can be used to create persuasive essays of the highest quality.
Climate Change Essay Examples: Problems & Solutions
When writing an essay about climate change, we consider it a distant problem as far as it is not real or visible to the naked eye. However, the suffering of our planet due to human intervention and a long-lasting bad influence on nature resulted in atmosphere changes, the greenhouse effect, and global warming.
The temperature will rise by 1.5 ℃ during the next 20 years. The problem might not seem urgent, but the results may be harmful, hazardous, and irreversible. Students may find it dull to write about the environment. Moreover, they need deep knowledge of geography and have developed analytical skills to predict consequences. Teachers try to guide students in the precise analysis of their effect on the Earth in essays about climate change.
Sample Essay on Climate Change: Ideal to Follow
In writing an argumentative essay, it may be challenging to figure out the main principles of writing and follow a logical outline. You may use any sample essay on climate change from our database to read and follow in such a situation.
Our Essays Inspire and Provoke Thinking
Reading piles of books can overload your mind and mess up your ideas. Sometimes, you need a short but logical and informative paper to grasp concepts for perfect argumentative essay writing. However, reading our samples of climate change essays, you will be excited with certain and understandable content that provides inspiration and food for thinking.
Right Structure and Topic: Crucial Moments
When you write a climate change opinion essay, you may pay attention more to your ideas, scientific facts, and results of further development of climate change. But your teacher considers correspondence of topic to the content and proper structure. Therefore, in our templates of essays on climate change, our writers adhere to all academic writing requirements.
Moreover, on the list of topics, you may find the most interesting and develop your ideas using additional resources. Finally, remember catchy phrases that draw attention from the first sight, as our samples do.
Expert Writers Work Hard on Result
The team of professionals provides writing services to support beginners or guide amateurs. Each global climate change essay is unique and reveals all the issues of every subject and topic. There must be enough experience to write a highly-graded essay, and our authors, with good practice, may teach any willing student the subtleties of perfect writing.
Essays on Climate Change to Any Taste
Not all the students have time to write papers. Many of them have no desire to spend hours in front of the laptop screen. Few of them have enough writing experience. If you are one of those students who have not found a required sample to follow and are ready to pay for an excellent project, you are in the right place. We can cope with climate change college essays of any difficulty level. Be sure of on-time delivery and quality.
Your grades are our reputation!
- ♻️ Recycling
- Air Pollution
- Animal Rights
- Animal Testing
- Climate Change
- Deforestation
- Endangered Species
- Environmental Issues
- Global Warming

Climate Change Essay
500+ words essay on climate change.
Climate change is a major global challenge today, and the world is becoming more vulnerable to this change. Climate change refers to the changes in Earth’s climate condition. It describes the changes in the atmosphere which have taken place over a period ranging from decades to millions of years. A recent report from the United Nations predicted that the average global temperature could increase by 6˚ Celsius at the end of the century. Climate change has an adverse effect on the environment and ecosystem. With the help of this essay, students will get to know the causes and effects of climate change and possible solutions. Also, they will be able to write essays on similar topics and can boost their writing skills.
What Causes Climate Change?
The Earth’s climate has always changed and evolved. Some of these changes have been due to natural causes such as volcanic eruptions, floods, forest fires etc., but quite a few of them are due to human activities. Human activities such as deforestation, burning fossil fuels, farming livestock etc., generate an enormous amount of greenhouse gases. This results in the greenhouse effect and global warming which are the major causes of climate change.
Effects of Climate Change
If the current situation of climate change continues in a similar manner, then it will impact all forms of life on the earth. The earth’s temperature will rise, the monsoon patterns will change, sea levels will rise, and storms, volcanic eruptions and natural disasters will occur frequently. The biological and ecological balance of the earth will get disturbed. The environment will get polluted and humans will not be able to get fresh air to breathe and fresh water to drink. Life on earth will come to an end.
Steps to be Taken to Reduce Climate Change
The Government of India has taken many measures to improve the dire situation of Climate Change. The Ministry of Environment and Forests is the nodal agency for climate change issues in India. It has initiated several climate-friendly measures, particularly in the area of renewable energy. India took several steps and policy initiatives to create awareness about climate change and help capacity building for adaptation measures. It has initiated a “Green India” programme under which various trees are planted to make the forest land more green and fertile.
We need to follow the path of sustainable development to effectively address the concerns of climate change. We need to minimise the use of fossil fuels, which is the major cause of global warming. We must adopt alternative sources of energy, such as hydropower, solar and wind energy to make a progressive transition to clean energy. Mahatma Gandhi said that “Earth provides enough to satisfy every man’s need, but not any man’s greed”. With this view, we must remodel our outlook and achieve the goal of sustainable development. By adopting clean technologies, equitable distribution of resources and addressing the issues of equity and justice, we can make our developmental process more harmonious with nature.
We hope students liked this essay on Climate Change and gathered useful information on this topic so that they can write essays in their own words. To get more study material related to the CBSE, ICSE, State Board and Competitive exams, keep visiting the BYJU’S website.
Frequently Asked Questions on climate change Essay
What are the reasons for climate change.
1. Deforestation 2. Excessive usage of fossil fuels 3. Water, Soil pollution 4. Plastic and other non-biodegradable waste 5. Wildlife and nature extinction

How can we save this climate change situation?
1. Avoid over usage of natural resources 2. Do not use or buy items made from animals 3. Avoid plastic usage and pollution
Are there any natural causes for climate change?
Yes, some of the natural causes for climate change are: 1. Solar variations 2. Volcanic eruption and tsunamis 3. Earth’s orbital changes
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples
You will notice that there are many climate change research topics you can discuss. Our team has prepared this compilation of 185 ideas that you can use in your work.
📝 Key Points to Use to Write an Outstanding Climate Change Essay
🏆 best climate change title ideas & essay examples, 🥇 most interesting climate change topics to write about, 🎓 simple & easy research titles about climate change, 👍 good research topics about climate change, 🔍 interesting topics to write about climate change, ⭐ good essay topics on climate change, ❓ climate change essay questions.
A climate change essay is familiar to most students who learn biology, ecology, and politics. In order to write a great essay on climate change, you need to explore the topic in great detail and show your understanding of it.
This article will provide you with some key points that you could use in your paper to make it engaging and compelling.
First of all, explore the factors contributing to climate change. Most people know that climate change is associated with pollution, but it is essential to examine the bigger picture. Consider the following questions:
- What is the mechanism by which climate change occurs?
- How do the activities of large corporations contribute to climate change?
- Why is the issue of deforestation essential to climate change?
- How do people’s daily activities promote climate change?
Secondly, you can focus on solutions to the problems outlined above.
Climate change essay topics often provide recommendations on how individuals and corporations could reduce their environmental impact. These questions may help to guide you through this section:
- How can large corporations decrease the influence of their operations on the environment?
- Can you think of any examples of corporations who have successfully decreased their environmental footprint?
- What steps can people take to reduce pollution and waste as part of their daily routine?
- Do you believe that trends such as reforestation and renewable energy will help to stop climate change? Why or why not?
- Can climate change be reversed at all, or is it an inescapable trend?
In connection with these topics, you could also discuss various government policies to address climate change. Over the past decades, many countries enacted laws to reduce environmental damage. There are plenty of ideas that you could address here:
- What are some famous national policies for environmental protection?
- Are laws and regulations effective in protecting the environment? Why or why not?
- How do environmentally-friendly policies affect individuals and businesses?
- Are there any climate change graphs that show the effectiveness of national policies for reducing environmental damage?
- How could government policies on climate change be improved?
Despite the fact that there is definite proof of climate change, the concept is opposed by certain politicians, business persons, and even scientists.
You could address the opposition to climate change in your essay and consider the following:
- Why do some people think that climate change is not real?
- What is the ultimate proof of climate change?
- Why is it beneficial for politicians and business persons to argue against climate change?
- Do you think that climate change is a real issue? Why or why not?
The impact of ecological damage on people, animals, and plants is the focus of most essay titles on global warming and climate change. Indeed, describing climate change effects in detail could earn you some extra marks. Use scholarly resources to research these climate change essay questions:
- How has climate change impacted wildlife already?
- If climate change advances at the same pace, what will be the consequences for people?
- Besides climate change, what are the impacts of water and air pollution? What does the recent United Nations’ report on climate change say about its effects?
- In your opinion, could climate change lead to the end of life on Earth? Why or why not?
Covering at least some of the points discussed in this post will help you write an excellent climate change paper! Don’t forget to search our website for more useful materials, including a climate change essay outline, sample papers, and much more!
- Climate Change – Problems and Solutions It is important to avoid cutting trees and reduce the utilization of energy to protect the environment. Many organizations have been developed to enhance innovation and technology in the innovation of eco-friendly machines.
- Causes and Effects of Climate Changes Climate change is the transformation in the distribution patterns of weather or changes in average weather conditions of a place or the whole world over long periods.
- Global Warming as Serious Threat to Humanity One of the most critical aspects of global warming is the inability of populations to predict, manage, and decrease natural disruptions due to their inconsistency and poor cooperation between available resources.
- Is Climate Change a Real Threat? Climate change is a threat, but its impact is not as critical as wrong political decisions, poor social support, and unstable economics.
- Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions The agreement across the board is that human activities such as emissions of the greenhouse gases have contributed to global warming.
- Climate Change – Global Warming For instance, in the last one century, scientists have directly linked the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere with the increase in temperature of the earth.
- Climate Change Causes and Predictions These changes are as a result of the changes in the factors which determine the amount of sunlight that gets to the earth surface.
- The Role of Technology in Climate Change The latter is people’s addiction, obsession, and ingenuity when it comes to technology, which was the main cause of climate change and will be the primary solution to it as well.
- Climate Change and Its Impacts on the UAE Currently, the rise in temperature in the Arctic is contributing to the melting of the ice sheets. The long-range weather forecast indicates that the majority of the coastal areas in the UAE are at the […]
- Climate Change: Human Impact on the Environment This paper is an in-depth exploration of the effects that human activities have had on the environment, and the way the same is captured in the movie, The Eleventh Hour.
- Transportation Impact on Climate Change It is apparent that the number of motor vehicles in the world is increasing by the day, and this translates to an increase in the amount of pollutants produced by the transportation industry annually.
- The Impact of Climate Change on Food Security Currently, the world is beginning to encounter the effects of the continuous warming of the Earth. Some of the heat must be reflected in space to ensure that there is a temperature balance in the […]
- Climate Change Impacts on Ocean Life The destruction of the ozone layer has led to the exposure of the earth to harmful radiation from the sun. The rising temperatures in the oceans hinder the upward flow of nutrients from the seabed […]
- Global Warming and Human Impact: Pros and Cons These points include the movement of gases in the atmosphere as a result of certain human activities, the increase of the temperature because of greenhouse gas emissions, and the rise of the oceans’ level that […]
- Climate Change and Role of Government He considers that the forest’s preservation is vital, as it is the wellspring of our human well-being. As such, the legislature can pass policies that would contribute to safeguarding our nation’s well-being, but they do […]
- Climate Change Definition and Description The wind patterns, the temperature and the amount of rainfall are used to determine the changes in temperature. Usually, the atmosphere changes in a way that the energy of the sun absorbed by the atmosphere […]
- Research Driven Critique: Steven Maher and Climate Change The ravaging effects of Covid-19 must not distract the world from the impending ramifications of severe environmental and climatic events that shaped the lives of a significant portion of the population in the past year.
- How Aviation Impacts Climate Change A measurement of the earth’s radiation budget imbalance brought on by changes in the quantities of gases and aerosols or cloudiness is known as radiative forcing.
- Tourism and Climate Change Problem There are a number of factors that propelled the growth of tourism and these factors include the improvement of the standards of living in many developed nations, good work polices allowing more time for vacations […]
- Climate Change’s Impact on Crop Production I will address the inefficiencies of water use in our food production systems, food waste, and the impact of temperature on crop yield.
- Climate Change: The Day After Tomorrow In the beginning of the film “The Day After Tomorrow”, the main character, Professor Jack Hall, is trying to warn the world of the drastic consequences of a changing climate being caused by the polluting […]
- Climate Change: Causes, Impact on People and the Environment Climate change is the alteration of the normal climatic conditions in the earth, and it occurs over some time. In as much as there are arguments based around the subject, it is mainly caused by […]
- Maize Production and Climate Change in South Africa Maize farming covers 58% of the crop area in South Africa and 60% of this is in drier areas of the country.
- Neolithic Revolution and Climate Change At the primary stage of the evolution of human civilization, the rise of agriculture in the later part of stone age, also known as the Neolithic Revolution, was ultimately necessary to keep pace with the […]
- “Climate Change: Turning Up the Heat” by Barrie Pittock The researcher stresses that people should try to minimize the negative effects of climate change in order to enable humanity to adapt to the changing environment in a more effective way.
- Global Perspectives in the Climate Change Strategy It is required to provide an overview of those programs and schemes of actions that were used in the local, federal and global policies of the countries of the world to combat air pollution.
- Climate Change as a Global Security Threat It is important to stress that agriculture problems can become real for the USA as well since numerous draughts and natural disasters negatively affect this branch of the US economy.
- Climate Change, Development and Disaster Risk Reduction However, the increased cases of droughts, storms, and very high rainfalls in different places are indicative of the culmination of the effects of climate change, and major disasters are yet to follow in the future.
- Anthropogenic Climate Change Since anthropogenic climate change occurs due to the cumulative effect of greenhouse gases, it is imperative that climatologists focus on both immediate and long term interventions to avert future crises of global warming that seem […]
- Wildfires and Impact of Climate Change Climate change has played a significant role in raise the likelihood and size of wildfires around the world. Climate change causes more moisture to evaporate from the earth, drying up the soil and making vegetation […]
- Rainforests of Victoria: Potential Effects of Climate Change The results of the research by Brooke in the year 2005 was examined to establish the actual impacts of climate change on the East Gippsland forest, especially for the fern specie.
- Climate Change and Renewable Energy Options The existence of various classes of world economies in the rural setting and the rise of the middle class economies has put more pressure on environmental services that are highly demanded and the use of […]
- Saving the Forest and Climate Changes The greenhouse gases from such emissions play a key role in the depletion of the most essential ozone layer, thereby increasing the solar heating effect on the adjacent Earth’s surface as well as the rate […]
- Climate Change: Mitigation Strategies To address the latter views, the current essay will show that the temperature issue exists and poses a serious threat to the planet.
- Global Warming and Effects Within 50 Years Global warming by few Scientists is often known as “climate change” the reason being is that according to the global warming is not the warming of earth it basically is the misbalance in climate.
- Energy Conservation for Solving Climate Change Problem The United States Environmental Protection Agency reports that of all the ways energy is used in America, about 39% is used to generate electricity.
- The Three Myths of Climate Change In the video, Linda Mortsch debunks three fundamental misconceptions people have regarding climate change and sets the record straight that the phenomenon is happening now, affects everyone, and is not easy to adapt.
- The Climate Change Articles Comparison In a broader sense, both articles address the concept of sustainability and the means of reinforcing its significance in the context of modern global society to prevent further deterioration of the environment from happening.
- Climate Change: The Key Issues An analysis of world literature indicates the emergence in recent years of a number of scientific publications on the medical and environmental consequences of global climate change.
- Global Warming: Causes and Consequences Other definitions of global warming are “the increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s near-surface air and oceans since the mid-twentieth century and its projected continuation”.
- Technological and Policy Solutions to Prevent Climate Change Scientists and researchers across the globe are talking about the alarming rates of temperature increase, which threaten the integrity of the polar ice caps.
- The Key Drivers of Climate Change The use of fossil fuel in building cooling and heating, transportation, and in the manufacture of goods leads to an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere.
- Ways to Reduce Global Warming The objectives of this report are to identify the causes of global warming, to highlight the expected effects of global warming and to identify ways of reducing global warming.
- The Straw Man Fallacy in the Topic of Climate Change The straw man fallacy is a type of logical fallacy whereby one person misrepresents their opponent’s question or argument to make it easier to respond.
- Desert, Glaciers, and Climate Change When the wind blows in a relatively flat area with no vegetation, this wind moves loose and fine particles to erode a vast area of the landscape continuously in a process called deflation.
- Evidence of Climate Change The primary reason for the matter is the melting of ice sheets, which adds water to the ocean. The Republic of Maldives is already starting to feel the effects of global sea-level rise now.
- Weather Abnormalities and Climate Change One of the crucial signs of climate change is the rise of the sea level. Thus, the problem of climate change is a threat to water security and needs resolution.
- Technology Influence on Climate Change Undoubtedly, global warming is a portrayal of climate change in the modern world and hence the need for appropriate interventions to foster the sustainability of the environment.
- Climate Change’s Negative Impact on Biodiversity This essay’s primary objective is to trace and evaluate the impact of climate change on biological diversity through the lens of transformations in the marine and forest ecosystems and evaluation of the agricultural sector both […]
- Climate Change Impact on Bangladesh Today, there are a lot of scientists from the fields of ecology and meteorology who are monitoring the changes of climate in various regions of the world.
- The Role of Science and Technology in International Relations Regarding Climate Change This paper examines the role of science and technology as it has been used to address the challenge of climate change, which is one of the major issues affecting the global societies today.
- Climate Change: Is Capitalism the Problem or the Solution? This means that capitalism, which is the ability to produce wealth lies in the solution and also the causes of the current global climatic governance.
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Tourism in Coastal Areas It is hereby recommended that governments have a huge role to play in mitigating the negative effects of climate change on coastal towns.
- The Negative Effects of Climate Change in Cities This is exemplified by the seasonal hurricanes in the USA and the surrounding regions, the hurricanes of which have destroyed houses and roads in the past.
- Biology of Climate Change There is sufficient evidence that recent climate change is a result of human activities.”Warming of the climate system is unequivocal; as is now evident from observations of increases in global average air and ocean temperatures, […]
- Impact of Food Waste on Climate Change In conclusion, I believe that some of the measures that can be taken to prevent food waste are calculating the population and their needs.
- Climate Change and Resource Sustainability in Balkan: How Quickly the Impact is Happening In addition, regarding the relief of the Balkans, their territory is dominated by a large number of mountains and hills, especially in the west, among which the northern boundary extends to the Julian Alps and […]
- Climate Change: Renewable Energy Sources Climate change is the biggest threat to humanity, and deforestation and “oil dependency” only exacerbate the situation and rapidly kill people. Therefore it is important to invest in the development of renewable energy sources.
- Climate Change and the Allegory of the Cave Plato’s allegory of the cave reflects well our current relationship with the environment and ways to find a better way to live in the world and live with it.
- Climate Change, Economy, and Environment Central to the sociological approach to climate change is studying the relationship between the economy and the environment. Another critical area of sociologists ‘ attention is the relationship between inequality and the environment.
- Terrorism, Corruption, and Climate Change as Threats Therefore, threats affecting countries around the globe include terrorism, corruption, and climate change that can be mitigated through integrated counter-terror mechanisms, severe punishment for dishonest practices, and creating awareness of safe practices.
- Climate Change’s Impact on Hendra Virus Transmission to humans occurs once people are exposed to an infected horse’s body fluids, excretions, and tissues. Land clearing in giant fruit bats’ habitats has exacerbated food shortages due to climate change, which has led […]
- Global Climate Change and Environmental Conservation There may be a significantly lesser possibility that skeptics will acknowledge the facts and implications of climate change, which may result in a lower desire on their part to adopt adaptation. The climate of Minnesota […]
- Beef Production’s Impact on Climate Change This industry is detrimental to the state of the planet and, in the long term, can lead to irreversible consequences. It is important to monitor the possible consequences and reduce the consumption of beef.
- Cities and Climate Change: Articles Summary The exponential population growth in the United States of America and the energy demands put the nation in a dilemma. Climate change challenges are experienced as a result of an increase in greenhouse gas emissions […]
- The Impact of Climate Change on Vulnerable Human Populations The fact that the rise in temperatures caused by the greenhouse effect is a threat to humans development has focused global attention on the “emissions generated from the combustion” of fossil fuels.
- Food Waste Management: Impact on Sustainability and Climate Change How effective is composting food waste in enhancing sustainability and reducing the effects of climate change? The following key terms are used to identify and scrutinize references and study materials.”Food waste” and sustain* “Food waste” […]
- Protecting the Environment Against Climate Change The destruction of the ozone layer, which helps in filtering the excessive ray of light and heat from the sun, expose people to some skin cancer and causes drought.
- The Global Warming Problem and Solution Therefore, it is essential to make radical decisions, first of all, to reduce the use of fossil fuels such as oil, carbon, and natural gas. One of the ways of struggle is to protest in […]
- Climate Change and Immigration Issues Due to its extensive coverage of the aspects of climate migration, the article will be significant to the research process in acquiring a better understanding of the effects of climate change on different people from […]
- Global Warming: Speculation and Biased Information For example, people or organizations that deny the extent or existence of global warming may finance the creation and dissemination of incorrect information.
- Impacts of Climate Change on Ocean The development of phytoplankton is sensitive to the temperature of the ocean. Some marine life is leaving the ocean due to the rising water temperature.
- Impact of Climate Change on the Mining Sector After studying the necessary information on the topic of sustainability and Sustainability reports, the organization was allocated one of the activities that it performs to maintain it.
- Climate Change: Historical Background and Social Values The Presidential and Congress elections in the US were usually accompanied by the increased interest in the issue of climate change in the 2010s.
- Communities and Climate Change Article by Kehoe In the article, he describes the stringent living conditions of the First Nations communities and estimates the dangers of climate change for these remote areas.
- Discussion: Reverting Climate Change Undertaking some of these activities requires a lot of finances that have seen governments setting aside funds to help in the budgeting and planning of the institutions.
- Was Climate Change Affecting Species? It was used because it helps establish the significance of the research topic and describes the specific effects of climate change on species.
- Climate Change Attitudes and Counteractions The argument is constructed around the assumption that the deteriorating conditions of climate will soon become one of the main reasons why many people decide to migrate to other places.
- How Climate Change Could Impact the Global Economy In “This is How Climate Change Could Affect the World Economy,” Natalie Marchand draws attention to the fact that over the next 30 years, global GDP will shrink by up to 18% if global temperatures […]
- Effective Policy Sets to Curb Climate Change A low population and economic growth significantly reduce climate change while reducing deforestation and methane gas, further slowing climate change. The world should adopt this model and effectively increase renewable use to fight climate change.
- Climate Change: Social-Ecological Systems Framework One of the ways to understand and assess the technogenic impact on various ecological systems is to apply the Social-Ecological Systems Framework.
- The Climate Change Mitigation Issues Indeed, from the utilitarian perspective, the current state of affairs is beneficial only for the small percentage of the world population that mostly resides in developed countries.
- The Dangers of Global Warming: Environmental and Economic Collapse Global warming is caused by the so-called ‘Greenhouse effect’, when gases in Earth’s atmosphere, such as water vapor or methane, let the Sun’s light enter the planet but keep some of its heat in.
- Aviation, Climate Change, and Better Engine Designs: Reducing CO2 Emissions The presence of increasing levels of CO2 and other oxides led to the deterioration of the ozone layer. More clients and partners in the industry were becoming aware and willing to pursue the issue of […]
- Climate Change as a Problem for Businesses and How to Manage It Additionally, some businesses are directly contributing to climate change due to a lack of measures that will minimise the emission of carbon.
- Climate Change and Disease-Carrying Insects In order to prevent the spreading of the viruses through insects, the governments should implement policies against the emissions which contribute to the growth of the insects’ populations.
- Aspects of Global Warming Global warming refers to the steadily increasing temperature of the Earth, while climate change is how global warming changes the weather and climate of the planet.
- David Lammy on Climate Change and Racial Justice However, Lammy argues that people of color living in the global south and urban areas are the ones who are most affected by the climate emergency.
- Moral Aspects of Climate Change Addresses However, these approaches are anthropocentric because they intend to alleviate the level of human destruction to the environment, but place human beings and their economic development at the center of all initiatives.
- Feminism: A Road Map to Overcoming COVID-19 and Climate Change By exposing how individuals relate to one another as humans, institutions, and organizations, feminism aids in the identification of these frequent dimensions of suffering.
- Global Warming: Moral and Political Challenge That is, if the politicians were to advocate the preservation of the environment, they would encourage businesses completely to adopt alternative methods and careful usage of resources.
- Climate Change: Inconsistencies in Reporting An alternative route that may be taken is to engage in honest debates about the issue, which will reduce alarmism and defeatism.
- Climate Change: The Chornobyl Nuclear Accident Also, I want to investigate the reasons behind the decision of the USSR government to conceal the truth and not let people save their lives.
- “World on the Edge”: Managing the Causes of Climate Change Brown’s main idea is to show the possibility of an extremely unfortunate outcome in the future as a result of the development of local agricultural problems – China, Iran, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, and others – […]
- Gendering Climate Change: Geographical Insights In the given article, the author discusses the implications of climate change on gender and social relations and encourages scholars and activists to think critically and engage in debates on a global scale.
- Climate Change and Its Consequences for Oklahoma This concept can be defined as a rise in the Earth’s temperature due to anthropogenic activity, resulting in alteration of usual weather in various parts of the planet.
- Climate Change Impacts in Sub-Saharan Africa This is why I believe it is necessary to conduct careful, thorough research on why climate change is a threat to our planet and how to stop it.
- Climate Change: Global Warming Intensity Average temperatures on Earth are rising faster than at any time in the past 2,000 years, and the last five of them have been the hottest in the history of meteorological observations since 1850.
- The Negative Results of Climate Change Climate change refers to the rise of the sea due to hot oceans expanding and the melting of ice sheets and glaciers.
- Addressing Climate Change: The Collective Action Problem While all the nations agree that climate change is a source of substantial harm to the economy, the environment, and public health, not all countries have similar incentives for addressing the problem. Addressing the problem […]
- Health Issues on the Climate Change However, the mortality rate of air pollution in the United States is relatively low compared to the rest of the world.
- Collective Climate Change Responsibility The fact is that individuals are not the most critical contributors to the climate crisis, and while ditching the plastic straw might feel good on a personal level, it will not solve the situation.
- Climate Change and Challenges in Miami, Florida The issue of poor environment maintenance in Miami, Florida, has led to climate change, resulting in sea-level rise, an increase of flood levels, and droughts, and warmer temperatures in the area.
- Global Warming and Climate Change The author shows the tragedy of the situation with climate change by the example of birds that arrived too early from the South, as the buds begin to bloom, although it is still icy.
- Climate Change as Systemic Risk of Globalization However, the integration became more complex and rapid over the years, making it systemic due to the higher number of internal connections.
- Impact of Climate Change on Increased Wildfires Over the past decades, America has experienced the most severe fires in its history regarding the coverage of affected areas and the cost of damage.
- Creating a Policy Briefing Book: Climate Change in China After that, a necessary step included the evaluation of the data gathered and the development of a summary that perfectly demonstrated the crucial points of this complication.
- Natural Climate Solutions for Climate Change in China The social system and its response to climate change are directly related to the well-being, economic status, and quality of life of the population.
- Climate Change and Limiting the Fuel-Powered Transportation When considering the options for limiting the extent of the usage of fuel-powered vehicles, one should pay attention to the use of personal vehicles and the propensity among most citizens to prefer diesel cars as […]
- Climate Change Laboratory Report To determine the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causing global warming in the next ten decades, if the estimated rate of deforestation is maintained.
- Climate Change and Stabilization Wages The more the annual road activity indicates that more cars traversed throughout a fiscal year, the higher the size of the annual fuel consumption. The Carbon Capture and Storage technology can also reduce carbon emissions […]
- UK Climate Change Act 2008 The aim of the UK is to balance the levels of greenhouse gases to circumvent the perilous issue of climate change, as well as make it probable for people to acclimatize to an inevitable climate […]
- Sustainability, Climate Change Impact on Supply Chains & Circular Economy With recycling, reusing of materials, and collecting waste, industries help to fight ecological issues, which are the cause of climate change by saving nature’s integrity.
- Climate Change Indicators and Media Interference There is no certainty in the bright future for the Earth in the long-term perspective considering the devastating aftereffects that the phenomenon might bring. The indicators are essential to evaluate the scale of the growing […]
- Climate Change: Sustainability Development and Environmental Law The media significantly contributes to the creation of awareness, thus the importance of integrating the role of the news press with sustainability practices.
- How Climate Change Affects Conflict and Peace The review looks at various works from different years on the environment, connections to conflict, and the impact of climate change.
- Toyota Corporation: The Effects of Climate Change on the Word’s Automobile Sector Considering the broad nature of the sector, the study has taken into account the case of Toyota Motor Corporation which is one of the firms operating within the sector.
- The Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture However, the move to introduce foreign species of grass such as Bermuda grass in the region while maintaining the native grass has been faced by challenges related to the fiscal importance of the production.
- Health and Climate Change Climate change, which is a universal problem, is thought to have devastating effects on human and animal health. However, the precise health effects are not known.
- The Issue of Climate Change The only confirmed facts are the impact of one’s culture and community on willingness to participate in environmental projects, and some people can refuse to join, thereby demonstrating their individuality.
- Climate Change as a Battle of Generation Z These issues have attracted the attention of the generation who they have identified climate change as the most challenging problem the world is facing today.
- Climate Change and Health in Nunavut, Canada Then, the authors tend to use strict and formal language while delivering their findings and ideas, which, again, is due to the scholarly character of the article. Thus, the article seems to have a good […]
- Climate Change: Anticipating Drastic Consequences Modern scientists focus on the problem of the climate change because of expecting the dramatic consequences of the process in the future.
- The Analysis of Process of Climate Change Dietz is the head of the Division of Nutrition and Physical Activity at the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.
- The Way Climate Change Affects the Planet It can help analyze past events such as the Pleistocene ice ages, but the current climate change does not fit the criteria. It demonstrates how slower the change was when compared to the current climate […]
- Polar Bear Decline: Climate Change From Pole to Pole In comparison to 2005 where five of the populations were stable, it shows that there was a decline in stability of polar bear population.
- Preparing for the Impacts of Climate Change The three areas of interest that this report discusses are the impacts of climate change on social, economic and environmental fronts which are the key areas that have created a lot of debate and discussion […]
- Climate Change and Threat to Animals In the coming years, the increase in the global temperatures will make many living populations less able to adapt to the emergent conditions or to migrate to other regions that are suitable for their survival.
- Strategy for Garnering Effective Action on Climate Change Mitigation The approach should be participatory in that every member of the community is aware of ways that leads to climate change in order to take the necessary precaution measures. Many member nations have failed to […]
- Impact of Global Climate Change on Malaria There will be a comparison of the intensity of the changes to the magnitude of the impacts on malaria endemicity proposed within the future scenarios of the climate.
- Climate Change Economics: A Review of Greenstone and Oliver’s Analysis The article by Greenstone and Oliver indicates that the problem of global warming is one of the most perilous disasters whose effects are seen in low agricultural output, poor economic wellbeing of people, and high […]
- Pygmy-Possum Burramys Parvus: The Effects of Climate Change The study will be guided by the following research question: In what ways will the predicted loss of snow cover due to climate change influence the density and habitat use of the mountain pygmy-possum populations […]
- Climate Change and the Occurrence of Infectious Diseases This paper seeks to explore the nature of two vector-borne diseases, malaria, and dengue fever, in regards to the characteristics that would make them prone to effects of climate change, and to highlight some of […]
- Links Between Methane, Plants, and Climate Change According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, it is the anthropogenic activities that has increased the load of greenhouse gases since the mid-20th century that has resulted in global warming. It is only the […]
- United Nations Climate Change Conference In the Kyoto protocol, members agreed that nations needed to reduce the carbon emissions to levels that could not threaten the planet’s livelihoods.
- The Involve of Black People in the Seeking of Climate Change Whereas some researchers use the magnitude of pollution release as opposed to closeness to a hazardous site to define exposure, others utilize the dispersion of pollutants model to comprehend the link between exposure and population.
- Climate Change Dynamics: Are We Ready for the Future? One of the critical challenges of preparedness for future environmental changes is the uncertainty of how the climate system will change in several decades.
- How Climate Change Impacts Ocean Temperature and Marine Life The ocean’s surface consumes the excess heat from the air, which leads to significant issues in all of the planet’s ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Plan for Abu Dhabi City, UAE Abu Dhabi is the capital city of the UAE and the Abu Dhabi Emirate and is located on a triangular island in the Persian Gulf.
- Climate Change in Communication Moreover, environmental reporting is not accurate and useful since profits influence and political interference affect the attainment of truthful, objective, and fair facts that would promote efficiency in newsrooms on environmental reporting.
- Global Pollution and Climate Change Both of these works address the topic of Global pollution, Global warming, and Climate change, which are relevant to the current situation in the world.
- Climate Change Is a Scientific Fallacy Even in the worst-case scenario whereby the earth gives in and fails to support human activities, there can always be a way out.
- Climate Change: Change Up Your Approach People are becoming aware of the relevance of things and different aspects of their life, which is a positive trend. However, the share of this kind of energy will be reduced dramatically which is favorable […]
- Climate Change: The Broken Ozone Layer It explains the effects of climate change and the adaptation methods used. Vulnerability is basically the level of exposure and weakness of an aspect with regard to climate change.
- Climate Change and Economic Growth The graph displays the levels of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and the years before our time with the number 0 being the year 1950.
- Tropic of Chaos: Climate Change and the New Geography of Violence The point of confluence in the cattle raids in East Africa and the planting of opium in the poor communities is the struggle to beat the effects of climatic changes.
- Personal Insight: Climate Change To my mind, economic implications are one of the most concerning because the economy is one of the pillars of modern society.
- A Shift From Climate Change Awareness Under New President Such statements raised concerns among American journalists and general population about the future of the organization as one of the main forces who advocated for the safe and healthy environment of Americans and the global […]
- Human Influence on Climate Change Climate changes are dangerous because they influence all the living creatures in the world. Thus, it is hard to overestimate the threat for humankind the climate changes represent.
- Environmental Studies: Climate Changes Ozone hole is related to forest loss in that the hole is caused by reaction of different chemicals that are found in the atmosphere and some of these gases, for example, the carbon dioxide gas […]
- Global Warming: Negative Effects to the Environment The effect was the greening of the environment and its transformation into habitable zones for humans The second system has been a consequence of the first, storage.
- Global Warming Problem Overview: Significantly Changing the Climate Patterns The government is not in a position to come up with specific costs that are attached to the extent of environmental pollution neither are the polluters aware about the costs that are attached to the […]
- Global Change Biology in Terms of Global Warming A risk assessment method showed that the current population could persist for at least 2000 years at hatchling sex ratios of up to 75% male.
- The Politics of Climate Change, Saving the Environment In the first article, the author expresses his concern with the problem of data utilization on climate change and negative consequences arising from this.
- Global Warming Issues Review and Environmental Sustainability Whether it is the melt down of Arctic ice, the damage of the Ozone layer, extra pollution in developing countries; all sums up to one thing in common and that is global warming.
- Starbucks: Corporate Social Responsibility and Global Climate Change Then in the 90s and onwards to the 21st century, Starbucks coffee can be seen almost anywhere and in places where one least expects to see a Starbucks store.
- Global Warming: Ways to Help End Global Warming An innovative understanding of global warming has included it in the agenda of firms and governments. 5 trillion dollars are shouldering the responsibility of collecting and distributing information on the firms’ exposure to carbon emission-related […]
- Biofuels and Climate Change Developed countries are in the forefront to promote biofuels as a solution to the oil crisis and to a broader sense, the food crisis.
- The Influence of Global Warming and Pollution on the Environment This essay is going to address global warming from a psychological point of view with an emphasis on the psychological and social reasons that make it important to tackle this problem which is threatening the […]
- How Global Warming Has an Effect on Wildlife? According to one of the most detailed ecological studies of climate change, global warming is already directly affecting the lives of animals and plants living in various habitats across the world.
- Climate Change Risks in South Eastern Australia
- The Politics and Economics of International Action on Climate Change
- Climate Change: Influence on Lifestyle in the Future
- Climate Change During Socialism and Capitalistic Epochs
- Climate Change and Public Health Policies
- Climate Changes: Cause and Effect
- World Trade as the Adjustment Mechanism of Agriculture to Climate Change by Julia & Duchin
- Chad Frischmann: The Young Minds Solving Climate Change
- Public Health Education on Climate Change Effects
- Research Plan “Climate Change”
- Diets and Climate Change
- The Role of Human Activities on the Climate Change
- Climate Change Factors and Countermeasures
- Climate Change Effects on Population Health
- Climate Change: Who Is at Fault?
- Climate Change: Reducing Industrial Air Pollution
- Global Climate Change and Biological Implications
- Global Warming, Its Consequences and Prevention
- Climate Change and Risks for Business in Australia
- Climate Change Solutions for Australia
- Climate Change, Industrial Ecology and Environmental Chemistry
- “Climate Change May Destroy Alaskan Towns” Video
- Climate Change Effects on Kenya’s Tea Industry
- Environmental Perils: Climate Change Issue
- Technologically Produced Emissions Impact on Climate Change
- Climate Change and American National Security
- Climate Change, Air Pollution, Soil Degradation
- Climate Change in Canada
- International Climate Change Agreements
- Polar Transformations as a Global Warming Issue
- Moral Obligations to Climate Change and Animal Life
- Technology’s Impact on Climate Change
- Climate Change in Abu Dhabi
- Global Warming and Climate Change: Fighting and Solutions
- Climate Change Debates and Scientific Opinion
- Earth’s Geologic History and Global Climate Change
- CO2 Emission and Climate Change Misconceptions
- Geoengineering as a Possible Response to Climate Change
- Global Warming: People Impact on the Environment
- Climate Change Probability and Predictions
- Climate Changes and Human Population Distribution
- Climate Change as International Issue
- Climate Change for Australian Magpie-Lark Birds
- Climate Change Effects on Ocean Acidification
- Climate Change Governance: Concepts and Theories
- Climate Change Impacts on the Aviation Industry
- Climate Change Management and Risk Governance
- United Nation and Climate Change
- Human Rights and Climate Change Policy-Making
- Climate Change: Anthropological Concepts and Perspectives
- Climate Change Impacts on Business in Bangladesh
- Pollution & Climate Change as Environmental Risks
- Climate Change: Nicholas Stern and Ross Garnaut Views
- Challenges Facing Humanity: Technology and Climate Change
- Climate Change Potential Consequences
- Climate Change in United Kingdom
- Climate Change From International Relations Perspective
- Climate Change and International Collaboration
- International Security and Climate Change
- Climate Change Effects on World Economy
- Global Warming and Climate Change
- Responsible Factors for Climate Change
- Organisational Sustainability and Climate Change Strategy
- The Effect of Science on Climate Change
- Vulnerability of World Countries to Climate Change
- Anthropogenic Climate Change
- The Implementation of MOOCs on Climate Change
- The Climate Change and the Asset-Based Community Development
- Global Warming and Its Effects on the Environment
- Climate Change Research Studies
- Environmental Issue – Climate Change
- Climate Change Negative Health Impacts
- Early Climate Change Science
- Climate Change and Corporate World
- Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) in Reducing the Effects of Climate Change
- Climate Change Affecting Coral Triangle Turtles
- Introduction to Climate Change: Major Threats and the Means to Avoid Them
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Indigenous Peoples
- Asian Drivers of Global Change
- The Causes and Effects of Climate Change in the US
- Metholdogy for Economic Discourse Analysis in Climate Change
- The Impact of Climate Change on New Hampshire Business
- Climate Change Effects on an Individual’s Life in the Future
- The Role of Behavioural Economics in Energy and Climate Policy
- The Economic Cost of Climate Change Effects
- Climate Change: Floods in Queensland Australia
- Impact of Climate Change and Solutions
- Climate Change and Its Global Implications in Hospitality and Tourism
- Climate Change Needs Human Behavior Change
- Negative Impacts of Climate Change in the Urban Areas and Possible Strategies to Address Them
- Climate Changes: Snowpack
- The United Nation’s Response to Climate Change
- Critical Review: “Food’s Footprint: Agriculture and Climate Change” by Jennifer Burney
- Global Warming: Justing Gillis Discussing Studies on Climate Change
- Economics and Human Induced Climate Change
- Business & Climate Change
- Global Warming Causes and Unfavorable Climatic Changes
- Spin, Science and Climate Change
- Climate Change, Coming Home: Global Warming’s Effects on Populations
- Social Concepts and Climate Change
- Climate Change and Human Health
- Climate Change: The Complex Issue of Global Warming
- Climate Changes: Human Activities and Global Warming
- Public Awareness of Climate Changes and Carbon Footprints
- Climate Change: Impact of Carbon Emissions to the Atmosphere
- Problems of Climate Change
- Solving the Climate Change Crisis Through Development of Renewable Energy
- Climate Change Is the Biggest Challenge in the World That Affects the Flexibility of Individual Specie
- Climate Changes
- Climate Change Definition and Causes
- Climate Change: Nearing a Mini Ice Age
- Global Warming Outcomes and Sea-Level Changes
- Climate Change: Causes and Effects
- China Climate Change
- Protecting Forests to Prevent Climate Change
- Climate Change in Saudi Arabia and Miami
- Effects of Global Warming on the Environment
- Threat to Biodiversity Is Just as Important as Climate Change
- Does Climate Change Affect Entrepreneurs?
- Does Climate Change Information Affect Stated Risks of Pine Beetle Impacts on Forests
- Does Energy Consumption Contribute to Climate Change?
- Does Forced Solidarity Hinder Adaptation to Climate Change?
- Does Risk Communication Really Decrease Cooperation in Climate Change Mitigation?
- Does Risk Perception Limit the Climate Change Mitigation Behaviors?
- What Are the Differences Between Climate Change and Global Warming?
- What Are the Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture in North East Central Europe?
- What Are the Policy Challenges That National Governments Face in Addressing Climate Change?
- What Are the Primary Causes of Climate Change?
- What Are the Risks of Climate Change and Global Warming?
- What Does Climate Change Mean for Agriculture in Developing Countries?
- What Drives the International Transfer of Climate Change Mitigation Technologies?
- What Economic Impacts Are Expected to Result From Climate Change?
- What Motivates Farmers’ Adaptation to Climate Change?
- What Natural Forces Have Caused Climate Change?
- What Problems Are Involved With Establishing an International Climate Change?
- What Role Has Human Activity Played in Causing Climate Change?
- Which Incentives Does Regulation Give to Adapt Network Infrastructure to Climate Change?
- Why Climate Change Affects Us?
- Why Does Climate Change Present Potential Dangers for the African Continent?
- Why Economic Analysis Supports Strong Action on Climate Change?
- Why Should People Care For the Perceived Event of Climate Change?
- Why the Climate Change Debate Has Not Created More Cleantech Funds in Sweden?
- Why Worry About Climate Change?
- Will African Agriculture Survive Climate Change?
- Will Carbon Tax Mitigate the Effects of Climate Change?
- Will Climate Change Affect Agriculture?
- Will Climate Change Cause Enormous Social Costs for Poor Asian Cities?
- Will Religion and Faith Be the Answer to Climate Change?
- Flood Essay Topics
- Ecosystem Essay Topics
- Atmosphere Questions
- Extinction Research Topics
- Desert Research Ideas
- Greenhouse Gases Research Ideas
- Recycling Research Ideas
- Water Issues Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/
"337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "337 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
What Are the Effects of Climate Change?
A rapidly warming planet poses an existential threat to all life on earth. Just how bad it gets depends on how quickly we act.

An area flooded by Super Typhoon Noru in the Bulacan Province of the Philippines, September 26, 2022
Rouelle Umali/Xinhua via Getty Images

- Share this page block
Climate change is our planet’s greatest existential threat . If we don’t limit greenhouse gas emissions from the burning of fossil fuels, the consequences of rising global temperatures include massive crop and fishery collapse, the disappearance of hundreds of thousands of species, and entire communities becoming uninhabitable. While these outcomes may still be avoidable, climate change is already causing suffering and death. From raging wildfires and supercharged storms, its compounding effects can be felt today, outside our own windows.
Understanding these impacts can help us prepare for what’s here, what’s avoidable, and what’s yet to come, and to better prepare and protect all communities. Even though everyone is or will be affected by climate change, those living in the world’s poorest countries—which have contributed least to the problem—are the most climate-vulnerable. They have the fewest financial resources to respond to crises or adapt, and they’re closely dependent on a healthy, thriving natural world for food and income. Similarly, in the United States, it is most often low-income communities and communities of color that are on the frontlines of climate impacts. And because climate change and rising inequality are interconnected crises, decision makers must take action to combat both—and all of us must fight for climate justice. Here’s what you need to know about what we’re up against.
Effects of climate change on weather
Effects of climate change on the environment, effects of climate change on agriculture, effects of climate change on animals, effects of climate change on humans, future effects of climate change.
As global temperatures climb, widespread shifts in weather systems occur, making events like droughts , hurricanes , and floods more intense and unpredictable. Extreme weather events that may have hit just once in our grandparents’ lifetimes are becoming more common in ours. However, not every place will experience the same effects: Climate change may cause severe drought in one region while making floods more likely in another.
Already, the planet has warmed 1.1 degrees Celsius (1.9 degrees Fahrenheit) since the preindustrial era began 250 years ago, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) . And scientists warn it could reach a worst-case scenario of 4 degrees Celsius (7.2 degrees Fahrenheit) by 2100 if we fail to tackle the causes of climate change —namely, the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and gas) .

Tokyo during a record-breaking heat wave, August 13, 2020
The Yomiuri Shimbun via AP Images
Higher average temperatures
This change in global average temperature—seemingly small but consequential and climbing—means that, each summer, we are likely to experience increasingly sweltering heat waves. Even local news meteorologists are starting to connect strings of record-breaking days to new long-term trends, which are especially problematic in regions where infrastructure and housing have not been built with intensifying heat in mind. And heat waves aren’t just uncomfortable—they’re the leading cause of weather-related fatalities in the United States.
Longer-lasting droughts
Hotter temperatures increase the rate at which water evaporates from the air, leading to more severe and pervasive droughts . Already, climate change has pushed the American West into a severe “megadrought”—the driest 22-year stretch recorded in at least 1,200 years—shrinking drinking water supplies, withering crops , and making forests more susceptible to insect infestations. Drought can also create a positive feedback loop in which drier soil and less plant cover cause even faster evaporation.
More intense wildfires
This drier, hotter climate also creates conditions that fuel more vicious wildfire seasons—with fires that spread faster and burn longer—putting millions of additional lives and homes at risk. The number of large wildfires doubled between 1984 and 2015 in the western United States. And in California alone, the annual area burned by wildfires increased 500 percent between 1972 and 2018.
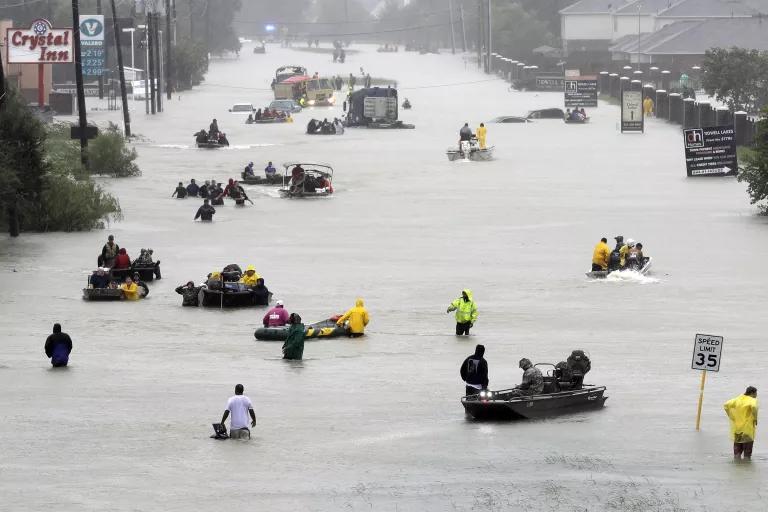

Evacuation after Hurricane Harvey in Houston, August 28, 2017
David J. Phillip/AP Photo
Stronger storms
Warmer air also holds more moisture, making tropical cyclones wetter, stronger, and more capable of rapidly intensifying. In the latest report from the IPCC , scientists found that daily rainfall during extreme precipitation events would increase by about 7 percent for each degree Celsius of global warming, increasing the dangers of flooding . The frequency of severe Category 4 and 5 hurricanes is also expected to increase. In 2017, Hurricane Harvey, a devastating Category 4 storm, dumped a record 275 trillion pounds of rain and resulted in dozens of deaths in the Houston area.
From the poles to the tropics, climate change is disrupting ecosystems. Even a seemingly slight shift in temperature can cause dramatic changes that ripple through food webs and the environment.
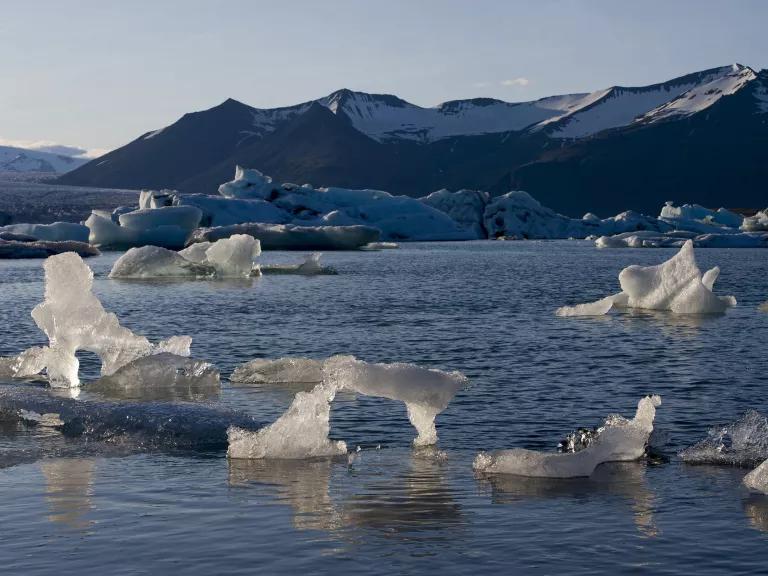

The lake at Jökulsárlón, a glacial lagoon in Iceland, which has grown because of continued glacial melting
Eskinder Debebe/UN Photo
Melting sea ice
The effects of climate change are most apparent in the world’s coldest regions—the poles. The Arctic is heating up twice as fast as anywhere else on earth, leading to the rapid melting of glaciers and polar ice sheets, where a massive amount of water is stored. As sea ice melts, darker ocean waters that absorb more sunlight become exposed, creating a positive feedback loop that speeds up the melting process. In just 15 years, the Arctic could be entirely ice-free in the summer.
Sea level rise
Scientists predict that melting sea ice and glaciers, as well as the fact that warmer water expands in volume, could cause sea levels to rise as much as 6.6 feet by the end of the century, should we fail to curb emissions. The extent (and pace) of this change would devastate low-lying regions, including island nations and densely populated coastal cities like New York City and Mumbai.
But sea level rise at far lower levels is still costly, dangerous, and disruptive. According to the 2022 Sea Level Rise Technical Report from the National Ocean Service, the United States will see a foot of sea level rise by 2050, which will regularly damage infrastructure, like roads, sewage treatment plants, and even power plants . Beaches that families have grown up visiting may be gone by the end of the century. Sea level rise also harms the environment, as encroaching seawater can both erode coastal ecosystems and invade freshwater inland aquifers, which we rely on for agriculture and drinking water. Saltwater incursion is already reshaping life in nations like Bangladesh , where one-quarter of the lands lie less than 7 feet above sea level.
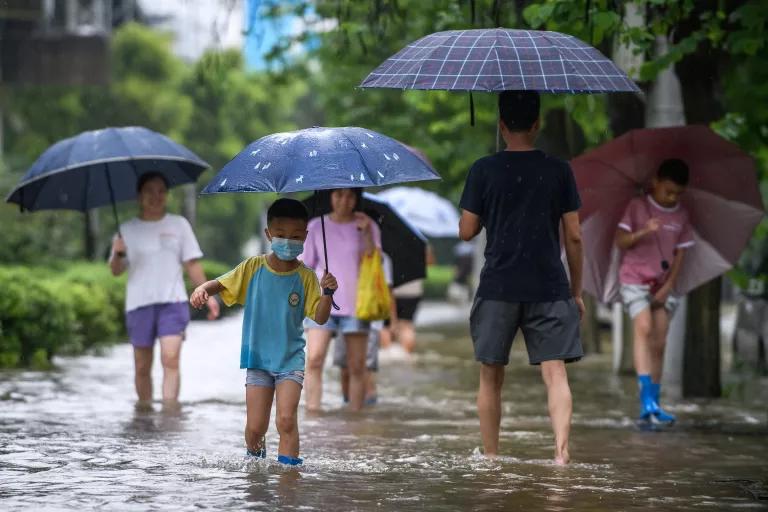

A waterlogged road, caused by rainstorm and upstream flood discharge, in the Shaoguan, Guangdong Province of China, June 21, 2022
Stringer/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images
In addition to coastal flooding caused by sea level rise, climate change influences the factors that result in inland and urban flooding: snowmelt and heavy rain. As global warming continues to both exacerbate sea level rise and extreme weather, our nation’s floodplains are expected to grow by approximately 45 percent by 2100. In 2022, deadly flooding in Pakistan—which inundated as much as a third of the country—resulted from torrential rains mixed with melting glaciers and snow.
Warmer ocean waters and marine heat waves
Oceans are taking the brunt of our climate crisis. Covering more than 70 percent of the planet’s surface, oceans absorb 93 percent of all the heat that’s trapped by greenhouse gases and up to 30 percent of all the carbon dioxide emitted from burning fossil fuels.
Temperature-sensitive fish and other marine life are already changing migration patterns toward cooler and deeper waters to survive, sending food webs and important commercial fisheries into disarray. And the frequency of marine heat waves has increased by more than a third . These spikes have led to mass die-offs of plankton and marine mammals.
To make matters worse, the elevated absorption of carbon dioxide by the ocean leads to its gradual acidification , which alters the fundamental chemical makeup of the water and threatens marine life that has evolved to live in a narrow pH band. Animals like corals, oysters, and mussels will likely feel these effects first, as acidification disrupts the calcification process required to build their shells.
Ecosystem stressors
Land-based ecosystems—from old-growth forests to savannahs to tropical rainforests—are faring no better. Climate change is likely to increase outbreaks of pests, invasive species, and pathogen infections in forests. It’s changing the kinds of vegetation that can thrive in a given region and disrupting the life cycles of wildlife, all of which is changing the composition of ecosystems and making them less resilient to stressors. While ecosystems have the capacity to adapt, many are reaching the hard limits of that natural capacity . More repercussions will follow as temperatures rise.
Climate change appears to be triggering a series of cascading ecological changes that we can neither fully predict nor, once they have enough momentum, fully stop. This ecosystem destabilization may be most apparent when it comes to keystone species that have an outsize- role in holding up an ecosystem’s structure.

Coffee plants destroyed by frost due to extremely low temperatures near Caconde in the São Paulo state of Brazil, August 25, 2021
Jonne Roriz/Bloomberg via Getty Images
Less predictable growing seasons
In a warming world, farming crops is more unpredictable—and livestock, which are sensitive to extreme weather, become harder to raise. Climate change shifts precipitation patterns, causing unpredictable floods and longer-lasting droughts. More frequent and severe hurricanes can devastate an entire season’s worth of crops. Meanwhile, the dynamics of pests, pathogens, and invasive species—all of which are costly for farmers to manage—are also expected to become harder to predict. This is bad news, given that most of the world’s farms are small and family-run. One bad drought or flood could decimate an entire season’s crop or herd. For example, in June 2022, a triple-digit heat wave in Kansas wiped out thousands of cows. While the regenerative agriculture movement is empowering rural communities to make their lands more resilient to climate change, unfortunately, not all communities can equitably access the support services that can help them embrace these more sustainable farming tactics.
Reduced soil health
Healthy soil has good moisture and mineral content and is teeming with bugs, bacteria, fungi, and microbes that in turn contribute to healthy crops. But climate change, particularly extreme heat and changes in precipitation, can degrade soil quality. These impacts are exacerbated in areas where industrial, chemical-dependent monoculture farming has made soil and crops less able to withstand environmental changes.
Food shortages
Ultimately, impacts to our agricultural systems pose a direct threat to the global food supply. And food shortages and price hikes driven by climate change will not affect everyone equally: Wealthier people will continue to have more options for accessing food, while potentially billions of others will be plummeted into food insecurity—adding to the billions that already have moderate or severe difficulty getting enough to eat.

The poison dart frog’s survival is currently threatened by habitat loss and climate change.
Chris Mattison/Minden Pictures
It’s about far more than just the polar bears: Half of all animal species in the world’s most biodiverse places, like the Amazon rainforest and the Galapagos Islands, are at risk of extinction from climate change. And climate change is threatening species that are already suffering from the biodiversity crisis, which is driven primarily by changes in land and ocean use (like converting wild places to farmland) and direct exploitation of species (like overfishing and wildlife trade). With species already in rough shape—more than 500,000 species have insufficient habitat for long-term survival—unchecked climate change is poised to push millions over the edge.
Climate change rapidly and fundamentally alters (or in some cases, destroys) the habitat that wildlife have incrementally adapted to over millennia. This is especially harmful for species’ habitats that are currently under threat from other causes. Ice-dependent mammals like walruses and penguins, for example, won’t fare well as ice sheets shrink. Rapid shifts in ocean temperatures stress the algae that nourishes coral reefs, causing reefs to starve—an increasingly common phenomenon known as coral bleaching . Disappearing wetlands in the Midwest’s Prairie Pothole Region means the loss of watering holes and breeding grounds for millions of migratory birds. (Many species are now struggling to survive, as more than 85 percent of wetlands have been lost since 1700). And sea level rise will inundate or erode away many coastal habitats, where hundreds of species of birds, invertebrates, and other marine species live.
Many species’ behaviors—mating, feeding, migration—are closely tied to subtle seasonal shifts, as in temperature , precipitation level, and foliage. In some cases, changes to the environment are happening quicker than species are able to adapt. When the types and quantity of plant life change across a region, or when certain species bloom or hatch earlier or later than in the past, it impacts food and water supplies and reverberates up food chains.

Wildfire smoke–filled air in Multnomah County, Oregon, September 16, 2020
Motoya Nakamura/Multnomah County Communications, CC BY NC-ND 4.0
Ultimately, the way climate change impacts weather, the environment, animals, and agriculture affects humanity as well. But there’s more. Around the world, our ways of life—from how we get our food to the industries around which our economies are based—have all developed in the context of relatively stable climates. As global warming shakes this foundation, it promises to alter the very fabric of society. At worst, this could lead to widespread famine, disease, war, displacement , injury, and death. For many around the world, this grim forecast is already their reality. In this way, climate change poses an existential threat to all human life.
Human health
Climate change worsens air quality . It increases exposure to hazardous wildfire smoke and ozone smog triggered by warmer conditions, both of which harm our health, particularly for those with pre-existing illnesses like asthma or heart disease.
Insect-borne diseases like malaria and Zika become more prevalent in a warming world as their carriers are able to exist in more regions or thrive for longer seasons. In the past 30 years, the incidence of Lyme disease from ticks has nearly doubled in the United States, according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Thousands of people face injury, illness , and death every year from more frequent or more intense extreme weather events. At a 2-degree Celsius rise in global average temperature, an estimated one billion people will face heat stress risk. In the summer of 2022 alone, thousands died in record-shattering heat waves across Europe. Weeks later, dozens were killed by record-breaking urban flooding in the United States and South Korea—and more than 1,500 people perished in the flooding in Pakistan , where resulting stagnant water and unsanitary conditions threaten even more.
The effects of climate change—and the looming threat of what’s yet to come—take a significant toll on mental health too. One 2021 study on climate anxiety, published in the journal Nature , surveyed 10,000 young people from 10 different countries. Forty-five percent of respondents said that their feelings about climate change, varying from anxiety to powerlessness to anger, impacted their daily lives.
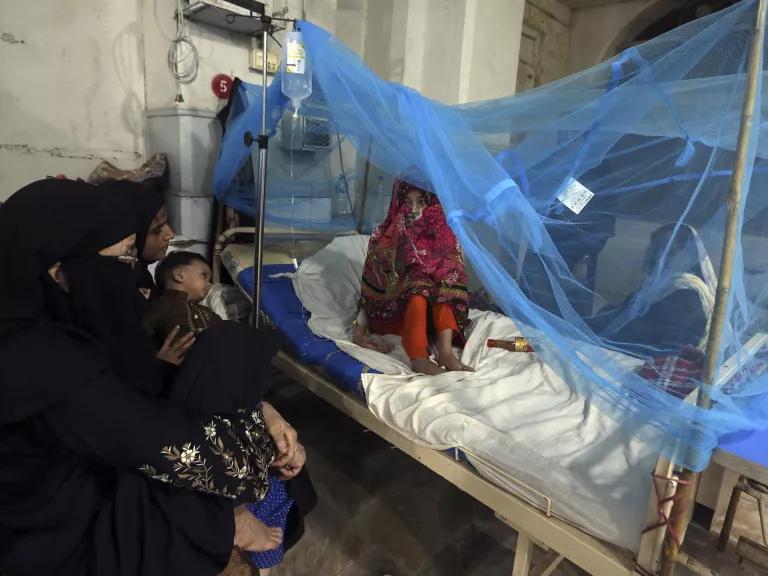
A patient with dengue fever, a mosquito-borne disease, in Karachi, Pakistan, where the spread of diseases worsened due to flooding, September 2022
Fareed Khan/AP Photo
Worsening inequity
The climate crisis exacerbates existing inequities. Though wealthy nations, such as the United States, have emitted the lion’s share of historical greenhouse gas emissions, it’s developing countries that may lack the resources to adapt and will now bear the brunt of the climate crisis. In some cases, low-lying island nations—like many in the Pacific —may cease to exist before developed economies make meaningful reductions to their carbon emissions.
Even within wealthier nations, disparities will continue to grow between those rich enough to shield themselves from the realities of climate change and those who cannot. Those with ample resources will not be displaced from their homes by wars over food or water—at least not right away. They will have homes with cool air during heat waves and be able to easily evacuate when a hurricane is headed their way. They will be able to buy increasingly expensive food and access treatment for respiratory illness caused by wildfire smoke. Billions of others can’t—and are paying the highest price for climate pollution they did not produce.
Hurricane Katrina, for example, displaced more than one million people around the Gulf Coast. But in New Orleans , where redlining practices promoted racial and economic segregation, the city’s more affluent areas tended to be located on higher ground—and those residents were able to return and rebuild much faster than others.
Displacement
Climate change will drive displacement due to impacts like food and water scarcities, sea level rise, and economic instability. It’s already happening. The United Nations Global Compact on Refugees recognizes that “climate, environmental degradation and disasters increasingly interact with the drivers of refugee movements.” Again, communities with the fewest resources—including those facing political instability and poverty—will feel the effects first and most devastatingly.

A flood-damaged home in Queens, New York, December 1, 2021
K.C. Wilsey/FEMA
Economic impacts
According to the 2018 National Climate Assessment, unless action is taken, climate change will cost the U.S. economy as much as $500 billion per year by the end of the century. And that doesn’t even include its enormous impacts on human health . Entire local industries—from commercial fishing to tourism to husbandry—are at risk of collapsing, along with the economic support they provide.
Recovering from the destruction wrought by extreme weather like hurricanes, flash floods, and wildfires is also getting more expensive every year. In 2021, the price tag of weather disasters in the United States totaled $145 billion —the third-costliest year on record, including a number of billion-dollar weather events.
The first wave of impacts can already be felt in our communities and seen on the nightly news. The World Health Organization says that in the near future, between 2030 and 2050, climate change is expected to cause an additional 250,000 deaths per year from things like malnutrition, insect-borne diseases, and heat stress. And the World Bank estimates that climate change could displace more than 140 million people within their home countries in sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Latin America by 2050.
But the degree to which the climate crisis upends our lives depends on whether global leaders decide to chart a different course. If we fail to curb greenhouse gas emissions, scientists predict a catastrophic 4.3 degrees Celsius , (or around 8 degrees Fahrenheit) of warming by the end of the century. What would a world that warm look like? Wars over water. Crowded hospitals to contend with spreading disease. Collapsed fisheries. Dead coral reefs. Even more lethal heat waves. These are just some of the impacts predicted by climate scientists .

Solar panel installation at a floating photovoltaic plant on a lake in Haltern am See, Germany, April 2022
Martin Meissner/AP Photo
Climate mitigation, or our ability to reverse climate change and undo its widespread effects, hinges on the successful enactment of policies that yield deep cuts to carbon pollution, end our dependence on dangerous fossil fuels and the deadly air pollution they generate, and prioritize the people and ecosystems on the frontlines. And these actions must be taken quickly in order to ensure a healthier present day and future. In one of its latest reports, the IPCC presented its most optimistic emissions scenario, in which the world only briefly surpasses 1.5 degrees of warming but sequestration measures cause it to dip back below by 2100. Climate adaptation , a term that refers to coping with climate impacts, is no longer optional ; it’s necessary, particularly for the world’s most vulnerable populations.
By following the urgent warnings of the IPCC and limiting warming, we may be able to avoid passing some of the critical thresholds that, once crossed, can lead to potentially irreversible, catastrophic impacts for the planet, including more warming. These thresholds are known as climate tipping points and refer to when a natural system "tips" into an entirely different state. One example would be Arctic permafrost, which stores carbon like a freezer: As the permafrost melts from warming temperatures, it releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Importantly, climate action is not a binary pass-fail test. Every fraction of a degree of warming that we prevent will reduce human suffering and death, and keep more of the planet’s natural systems intact. The good news is that a wide range of solutions exist to sharply reduce emissions, slow the pace of warming, and protect communities on the frontlines of climate impacts. Climate leaders the world over—those on major political stages as well as grassroots community activists—are offering up alternative models to systems that prioritize polluters over people. Many of these solutions are rooted in ancestral and Indigenous understandings of the natural world and have existed for millennia. Some solutions require major investments into clean, renewable energy and sustainable technologies. To be successful, climate solutions must also address intersecting crises—like poverty, racism, and gender inequality —that compound and drive the causes and impacts of the climate crisis. A combination of human ingenuity and immense political will can help us get there.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
We need climate action to be a top priority in Washington.
Tell President Biden and Congress to slash climate pollution and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
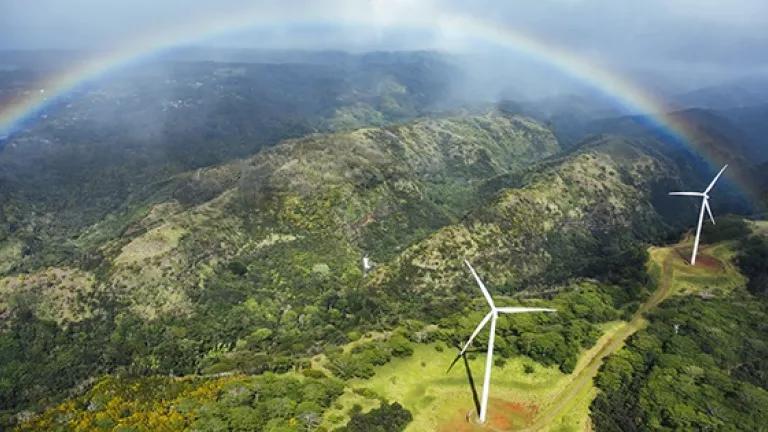

Urge President Biden and Congress to make equitable climate action a top priority
2023 was the hottest year on record, underscoring the urgency of shifting to clean energy and curbing the carbon pollution that is driving the climate crisis. President Biden and Congress have the tools to get the job done.
Related Stories

When Customers and Investors Demand Corporate Sustainability
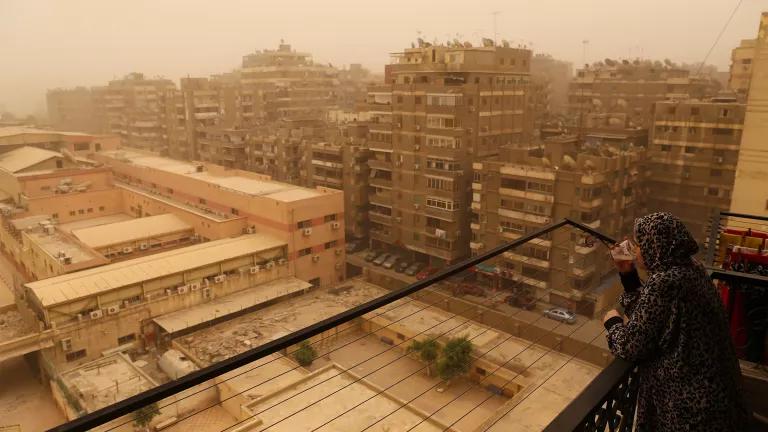

COP27: The Issues, the Tensions, and the Urgent Need for Unity on Climate

Mutual Aid and Disaster Justice: “We Keep Us Safe”
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
- Share full article

The Science of Climate Change Explained: Facts, Evidence and Proof
Definitive answers to the big questions.
Credit... Photo Illustration by Andrea D'Aquino
Supported by
By Julia Rosen
Ms. Rosen is a journalist with a Ph.D. in geology. Her research involved studying ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica to understand past climate changes.
- Published April 19, 2021 Updated Nov. 6, 2021
The science of climate change is more solid and widely agreed upon than you might think. But the scope of the topic, as well as rampant disinformation, can make it hard to separate fact from fiction. Here, we’ve done our best to present you with not only the most accurate scientific information, but also an explanation of how we know it.
How do we know climate change is really happening?
- How much agreement is there among scientists about climate change?
- Do we really only have 150 years of climate data? How is that enough to tell us about centuries of change?
- How do we know climate change is caused by humans?
- Since greenhouse gases occur naturally, how do we know they’re causing Earth’s temperature to rise?
- Why should we be worried that the planet has warmed 2°F since the 1800s?
- Is climate change a part of the planet’s natural warming and cooling cycles?
- How do we know global warming is not because of the sun or volcanoes?
- How can winters and certain places be getting colder if the planet is warming?
- Wildfires and bad weather have always happened. How do we know there’s a connection to climate change?
- How bad are the effects of climate change going to be?
- What will it cost to do something about climate change, versus doing nothing?
Climate change is often cast as a prediction made by complicated computer models. But the scientific basis for climate change is much broader, and models are actually only one part of it (and, for what it’s worth, they’re surprisingly accurate ).
For more than a century , scientists have understood the basic physics behind why greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide cause warming. These gases make up just a small fraction of the atmosphere but exert outsized control on Earth’s climate by trapping some of the planet’s heat before it escapes into space. This greenhouse effect is important: It’s why a planet so far from the sun has liquid water and life!
However, during the Industrial Revolution, people started burning coal and other fossil fuels to power factories, smelters and steam engines, which added more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Ever since, human activities have been heating the planet.

Where it was cooler or warmer in 2020 compared with the middle of the 20th century

Global average temperature compared with the middle of the 20th century
+0.75°C
–0.25°

30 billion metric tons
Carbon dioxide emitted worldwide 1850-2017
Rest of world
Other developed
European Union
Developed economies
Other countries
United States

E.U. and U.K.

We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
- Climatic variation since the last glaciation
- The greenhouse effect
- Radiative forcing
- Water vapour
- Carbon dioxide
- Surface-level ozone and other compounds
- Nitrous oxides and fluorinated gases
- Land-use change
- Stratospheric ozone depletion
- Volcanic aerosols
- Variations in solar output
- Variations in Earth’s orbit
- Water vapour feedback
- Cloud feedbacks
- Ice albedo feedback
- Carbon cycle feedbacks
- Modern observations
- Prehistorical climate records
- Theoretical climate models
- Patterns of warming
- Precipitation patterns
- Regional predictions
- Ice melt and sea level rise
- Ocean circulation changes
- Tropical cyclones
- Environmental consequences of global warming
- Socioeconomic consequences of global warming

How does global warming work?
Where does global warming occur in the atmosphere, why is global warming a social problem, where does global warming affect polar bears.

global warming
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- U.S. Department of Transportation - Global Warming: A Science Overview
- NOAA Climate.gov - Climate Change: Global Temperature
- Natural Resources Defense Council - Global Warming 101
- American Institute of Physics - The discovery of global warming
- LiveScience - Causes of Global Warming
- global warming - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- global warming - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

Human activity affects global surface temperatures by changing Earth ’s radiative balance—the “give and take” between what comes in during the day and what Earth emits at night. Increases in greenhouse gases —i.e., trace gases such as carbon dioxide and methane that absorb heat energy emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiate it back—generated by industry and transportation cause the atmosphere to retain more heat, which increases temperatures and alters precipitation patterns.
Global warming, the phenomenon of increasing average air temperatures near Earth’s surface over the past one to two centuries, happens mostly in the troposphere , the lowest level of the atmosphere, which extends from Earth’s surface up to a height of 6–11 miles. This layer contains most of Earth’s clouds and is where living things and their habitats and weather primarily occur.
Continued global warming is expected to impact everything from energy use to water availability to crop productivity throughout the world. Poor countries and communities with limited abilities to adapt to these changes are expected to suffer disproportionately. Global warming is already being associated with increases in the incidence of severe and extreme weather, heavy flooding , and wildfires —phenomena that threaten homes, dams, transportation networks, and other facets of human infrastructure. Learn more about how the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report, released in 2021, describes the social impacts of global warming.
Polar bears live in the Arctic , where they use the region’s ice floes as they hunt seals and other marine mammals . Temperature increases related to global warming have been the most pronounced at the poles, where they often make the difference between frozen and melted ice. Polar bears rely on small gaps in the ice to hunt their prey. As these gaps widen because of continued melting, prey capture has become more challenging for these animals.
Recent News
global warming , the phenomenon of increasing average air temperatures near the surface of Earth over the past one to two centuries. Climate scientists have since the mid-20th century gathered detailed observations of various weather phenomena (such as temperatures, precipitation , and storms) and of related influences on climate (such as ocean currents and the atmosphere’s chemical composition). These data indicate that Earth’s climate has changed over almost every conceivable timescale since the beginning of geologic time and that human activities since at least the beginning of the Industrial Revolution have a growing influence over the pace and extent of present-day climate change .
Giving voice to a growing conviction of most of the scientific community , the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was formed in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). The IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), published in 2021, noted that the best estimate of the increase in global average surface temperature between 1850 and 2019 was 1.07 °C (1.9 °F). An IPCC special report produced in 2018 noted that human beings and their activities have been responsible for a worldwide average temperature increase between 0.8 and 1.2 °C (1.4 and 2.2 °F) since preindustrial times, and most of the warming over the second half of the 20th century could be attributed to human activities.
AR6 produced a series of global climate predictions based on modeling five greenhouse gas emission scenarios that accounted for future emissions, mitigation (severity reduction) measures, and uncertainties in the model projections. Some of the main uncertainties include the precise role of feedback processes and the impacts of industrial pollutants known as aerosols , which may offset some warming. The lowest-emissions scenario, which assumed steep cuts in greenhouse gas emissions beginning in 2015, predicted that the global mean surface temperature would increase between 1.0 and 1.8 °C (1.8 and 3.2 °F) by 2100 relative to the 1850–1900 average. This range stood in stark contrast to the highest-emissions scenario, which predicted that the mean surface temperature would rise between 3.3 and 5.7 °C (5.9 and 10.2 °F) by 2100 based on the assumption that greenhouse gas emissions would continue to increase throughout the 21st century. The intermediate-emissions scenario, which assumed that emissions would stabilize by 2050 before declining gradually, projected an increase of between 2.1 and 3.5 °C (3.8 and 6.3 °F) by 2100.
Many climate scientists agree that significant societal, economic, and ecological damage would result if the global average temperature rose by more than 2 °C (3.6 °F) in such a short time. Such damage would include increased extinction of many plant and animal species, shifts in patterns of agriculture , and rising sea levels. By 2015 all but a few national governments had begun the process of instituting carbon reduction plans as part of the Paris Agreement , a treaty designed to help countries keep global warming to 1.5 °C (2.7 °F) above preindustrial levels in order to avoid the worst of the predicted effects. Whereas authors of the 2018 special report noted that should carbon emissions continue at their present rate, the increase in average near-surface air temperature would reach 1.5 °C sometime between 2030 and 2052, authors of the AR6 report suggested that this threshold would be reached by 2041 at the latest.

The AR6 report also noted that the global average sea level had risen by some 20 cm (7.9 inches) between 1901 and 2018 and that sea level rose faster in the second half of the 20th century than in the first half. It also predicted, again depending on a wide range of scenarios, that the global average sea level would rise by different amounts by 2100 relative to the 1995–2014 average. Under the report’s lowest-emission scenario, sea level would rise by 28–55 cm (11–21.7 inches), whereas, under the intermediate emissions scenario, sea level would rise by 44–76 cm (17.3–29.9 inches). The highest-emissions scenario suggested that sea level would rise by 63–101 cm (24.8–39.8 inches) by 2100.

The scenarios referred to above depend mainly on future concentrations of certain trace gases, called greenhouse gases , that have been injected into the lower atmosphere in increasing amounts through the burning of fossil fuels for industry, transportation , and residential uses. Modern global warming is the result of an increase in magnitude of the so-called greenhouse effect , a warming of Earth’s surface and lower atmosphere caused by the presence of water vapour , carbon dioxide , methane , nitrous oxides , and other greenhouse gases. In 2014 the IPCC first reported that concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides in the atmosphere surpassed those found in ice cores dating back 800,000 years.

Of all these gases, carbon dioxide is the most important, both for its role in the greenhouse effect and for its role in the human economy. It has been estimated that, at the beginning of the industrial age in the mid-18th century, carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere were roughly 280 parts per million (ppm). By the end of 2022 they had risen to 419 ppm, and, if fossil fuels continue to be burned at current rates, they are projected to reach 550 ppm by the mid-21st century—essentially, a doubling of carbon dioxide concentrations in 300 years.

A vigorous debate is in progress over the extent and seriousness of rising surface temperatures, the effects of past and future warming on human life, and the need for action to reduce future warming and deal with its consequences. This article provides an overview of the scientific background related to the subject of global warming. It considers the causes of rising near-surface air temperatures, the influencing factors, the process of climate research and forecasting, and the possible ecological and social impacts of rising temperatures. For an overview of the public policy developments related to global warming occurring since the mid-20th century, see global warming policy . For a detailed description of Earth’s climate, its processes, and the responses of living things to its changing nature, see climate . For additional background on how Earth’s climate has changed throughout geologic time , see climatic variation and change . For a full description of Earth’s gaseous envelope, within which climate change and global warming occur, see atmosphere .
Essay: To fix climate anxiety (and also climate change), we first have to fix individualism

- Copy Link URL Copied!

How do you cope? I feel the sorrow, the quiet plea for guidance every time someone asks me this question. As an environmental reporter dedicated to helping people make sense of climate change, I know I should have answers. But the truth is, it took me until now to face my own grief.
My heart keeps breaking whenever I meet yet another child struggling with asthma amid orange, smoke-filled skies. I, too, am reeling from the whiplash of extreme drought and extreme rain , and I’m still haunted by the thought of a mother having to call each of her daughters to say goodbye as the homes around her cave to fire.
Each year, as I reflect on my own reporting on the floods that keep getting worse and the toxic pollution building up in all forms of life , I find myself questioning whether I could ever justify bringing my own children into this world. I agonize over the amount of plastic we can’t avoid using and mourn the monarch butterflies that have vanished. With each new heat record shattered, and each new report declaring a code red for humanity , I can’t help but feel like we’re just counting down the days to our own extinction.
In the face of sea level rise, can we reimagine California’s vanishing coastline?
“Climate anxiety” is the term we now use to describe these feelings, but I must confess, I was perplexed when I first heard these words a few years ago. Anger, frustration, helplessness, exhaustion — these are the emotions I come across more often when getting to know the communities bracing for, or recovering from, the devastation of what they’ve long considered home.
Then a college student asked me about climate anxiety. It came up again on social media, and again in personal essays and polls. This paralyzing dread was suddenly the talk of the town — but it has also, very noticeably, remained absent in some circles.
All this has led me to wonder: What, exactly, is climate anxiety? And how should we cope? At first blush, this anxiety seems rooted in a fear that we’ll never go back to normal, that the future we were once promised is now gone. But who this “normal” is even for (and what we’re actually afraid of losing) speaks to a much more complicated question:
Is this anxiety pointing to a deeper responsibility that we all must face — and ultimately, is this anxiety something we can transcend?
For Jade Sasser, whose research on climate emotions has been grounded by her own experiences as a Black woman, these questions sharpened into focus during a research-methods seminar that she was teaching early last year at UC Riverside.
The class — all female, many from low-income immigrant communities — had been a fairly quiet group all quarter, so Sasser was surprised when the room completely erupted after she broached what she thought would be an academic, somewhat dispassionate discussion about climate change and the future.
Every student was suddenly talking, even yelling, over one another. Thought after thought tumbled out as they shared that not only does the future feel bleak when it comes to the job market, the housing crisis and whether their generation will ever be able to “settle down with kids” — but all this is many times worse when you’re not white, not documented and not born into a college-educated family.
How can they feel hopeful about the future, they asked, when, on top of everything already stacked against them, they also have to worry about wildfires, extreme heat and air pollution getting out of control?
‘It’s almost shameful to want to have children’
‘Climate Anxiety and the Kid Question’ asks: With American society feeling more socially and politically polarized than ever, is it right to bring another person into the world?
“It was literally a collective meltdown unlike anything I had ever experienced,” said Sasser, whose podcast and book, “ Climate Anxiety and the Kid Question, ” were largely inspired by her students that day. “I understood in that moment that you cannot assume someone does not also experience anxiety simply because their way of talking about it may not be the same as yours.”
It doesn’t help, she added, that many people don’t realize what they’re feeling is climate anxiety because the way we talk about it tends to center the experiences of white and more privileged people — people who have been insulated from oppression and have rarely (until now) had to worry about the safety of their own future.
“For a lot of people, climate anxiety looks a certain way: It looks very scared, it looks very sad, and it looks like a person who is ready, willing and able to talk about it,” Sasser said. “But for those who are experiencing many compounding forms of vulnerability at the same time, you can’t just pick out one part of it and say, ‘Oh, this is what’s causing me to feel this way.’”
A brave first step is to acknowledge privilege — and to support, and perhaps even learn, from those who have had to be resilient long before climate change became so overwhelming.
“For me, this work is a matter of survival,” said Kevin J. Patel, who grew up in South L.A. and has been fighting for climate justice since he was 11. He was contemplative, nodding, when I shared what I learned from Sasser, and he gently added that one privilege many communities don’t have is the ability to turn it off. Not everyone can go on a vacation or take a day to recharge, he said. Even having the time to talk about your sadness can be a luxury.
Feeling climate anxiety? These books offer glimmers of hope — and much-needed wisdom
Patel learned at a young age that not all communities get the same level of care. Growing up with hazy air, in a neighborhood hemmed in by the 10 and 110 freeways, Patel almost collapsed one day in front of his sixth-grade class when his heart suddenly started pounding at more than 300 beats per minute.
His parents, farmers from Gujarat, India, rushed Patel to the emergency room and held his hand while everyone around him thought he was dying. After months of hospital visits and procedures, doctors determined that he had developed a severe heart condition in large part due to the smog.
‘For me, this work is a matter of survival.’
— Kevin J. Patel
As he learned to live with an irregular heartbeat, he found joy in his family’s tiny garden and marveled at all the ladybugs that gathered on the tulsi, a special type of basil. He taught his classmates that food came from the ground, not the grocery store, and together, they went on to form an environmental club.
Today, Patel speaks with the hardened wisdom of someone who has experienced much more than the typical 23-year-old. He’s constantly doing something — whether it’s supporting a neighbor, getting water bottle refill stations installed at his school, or turning the idea of a Los Angeles County Youth Climate Commission into reality. For years, he has guided other marginalized youth through OneUpAction , a grassroots environmental group that he built from the ground up.
Even if he doesn’t call it anxiety, he admits he sometimes has trouble focusing, and there’s a tenseness in his body that can be hard to shake off. But he’s usually able to turn it around by talking to his friends or elders, or by reciting his favorite proverb:
They tried to bury us, but they didn’t know we were seeds.
“It’s not about what I need, it’s about what my community needs,” he said. “There is joy in caring for one another. There is joy in coming together to fight for a future that we believe in.”
When talking about climate anxiety, it’s important to differentiate whether you’re assessing these emotions as a mental health condition, or as a cultural phenomenon.
Let’s start with mental health: Polls show climate anxiety is on the rise and that people all around the world are losing sleep over climate change. Organizations like the Climate-Aware Therapist Directory and the American Psychiatric Assn. have put together an increasing number of guides and resources to help more people understand how climate change has affected our emotional well-being.
Poll shows Californians’ climate anxiety is on the rise
Just knowing that climate change is getting worse can trigger serious psychological responses. And the shock and trauma are all the more great if you’ve already had to live through the kinds of disasters that keep the rest of us up at night.
It’s also important to note that social media has magnified our sense of doom. What you see on social media tends to be a particularly intense and cherry-picked version of reality, but studies show that’s exactly how the vast majority of young people are getting their information about climate change: online rather than in school.
But you can’t treat climate anxiety like other forms of anxiety, and here’s where the cultural politics come in: The only way to make climate anxiety go away is to make climate change go away, and given the fraught and deeply systemic underpinnings of climate change, we must also consider this context when it comes to our climate emotions. How we feel is just as much a product of the narratives that have shaped the way we perceive and respond to the world.
“Climate anxiety can’t be limited to just a clinical setting — we have to take it out of the therapy room and look at it through a lens of privilege, and power, and the economic, historical and social structures that are at the root of the problem,” said Sarah Jaquette Ray, whose book “ A Field Guide to Climate Anxiety ” is a call to arms to think more expansively about our despair. “Treating a person’s climate anxiety without challenging these systems only addresses the symptoms, not the causes... and if white or more privileged emotions get the most airtime, and if we don’t see how climate is intersecting with all these other problems, that can result in a greater silencing of the people most impacted.”

Ray, an environmental humanist who chairs the environmental studies program at Cal Poly Humboldt, also emphasized that our distress can actually be a catalyst for much-needed change. These emotions are meant to shake us out of complacency, to sound the alarm to the very real crisis before us. But if we don’t openly talk about climate anxiety as something that is not only normal but also expected, we run the risk of further individualizing the problem. We already have a tendency to shut down and feel alone in our sorrows, which traps us into thinking only about ourselves.
“One huge reason why climate anxiety feels so awful is this feeling of not being able to do anything about it,” Ray said. “But if you actually saw yourself as part of a collective, as interconnected with all these other movements doing meaningful things, you wouldn’t be feeling this despair and loneliness.”
The trick to fixing climate anxiety is to fix individualism, she said. Start small, tap into what you’re already good at, join something bigger than yourself.
And by fixing individualism, as many young activists like Patel have already figured out, we just might have a better shot at fixing climate change.
Let us consider, for a moment, how the words that we use can also limit the way we think about our vulnerability and despair.
Something as simple as the “climate” in “climate anxiety” and how we define “environment” can unintentionally reinforce who we center in the conversation.
“In Nigeria, what we call our environment — it’s not just trees and mountains — it’s also about our food, our jobs, the biodiversity that gives us the life support that we need to thrive every day. That’s what we call our environment; it’s about our people,” said Jennifer Uchendu, who founded SustyVibes , a youth-led sustainability group based in her home country, as well as the Eco-Anxiety in Africa Project , which seeks to validate the emotions and experiences of communities often overlooked in climate conversations. “So if people are being oppressed by the system, it is still linked to our idea of the environment.”
Many of Uchendu’s elders have expressed a lifetime of feeling frustrated and powerless, for example, but she said they didn’t immediately connect these feelings to climate change because “climate anxiety” sounded to them like a new and elite phenomenon.
Editorial: California can make climate polluters pay for the mess they have made of Earth
We hear so often today that climate change is the existential crisis of our time, but that dismisses the trauma and violence to all the people who have been fighting to survive for centuries. Colonization, greed and exploitation are inseparable from climate change, Uchendu said, but we miss these connections when we consider our emotions only through a Western lens.
For Jessa Calderon, a Chumash and Tongva songwriter, these disconnects are ever-present in the concrete-hardened rivers snaking through Los Angeles, and the sour taste of industrialization often singeing the air. In her darkest moments, her heart hurts wondering if her son, Honor, will grow up to know clean water.
Her voice cracked as she recalled a brown bear that had been struck dead on the freeway near the Cajon Pass. As she watched strangers gawk at the limp body and share videos online, she wished she had been able to put the bear to rest and sing him into the spirit world.
“If we don’t see them as our people, then we have no hope for ourselves as a people, because we’re showing that we care about nothing more than ourselves,” she said. “And if we care about nothing more than ourselves, then we’re going to continue to devastate each other and the land.”
It is not too late to turn your climate anxiety into climate empathy. Acknowledging the emotional toll on people beyond yourself can be an opportunity to listen and support one another. Embracing our feelings — and then finding others who also want to turn their fear into action — can be the missing spark to much-needed social and environmental healing.
There is also wisdom to be learned in the songs and traditions of past movements, when people banded together — for civil rights, for women’s suffrage — and found ways to keep hope alive against all odds. And the more we look to the young people still caring for their elders in Nigeria, and to our Indigenous neighbors who continue to sing and love and tend to every living being, the better we might also comprehend the resilience required of all of us in the warming years ahead.
Opinion: Here are the places that could become too hot for humans due to climate change
So how should we cope? For Patel, living with his irregular but unwavering heartbeat, he finds strength in the words of adrienne maree brown, who famously wrote in “ Emergent Strategy ” that in the same way our lives are shaped today by our ancestors, we ourselves are future ancestors. Calderon, who similarly taught her son to leave this Earth better with every passing generation, confided to me that on the days when the sorrow feels too great, she sneaks off to plant native manzanita seeds in neighborhoods stripped of plants and trees.
As I’m reminded of all the love we can still sow for the future, I think of Phoenix Armenta, a longtime climate justice organizer in Oakland who has inspired numerous people, including myself, to take heart in all the times we actually got it right. (Remember acid rain? It was a huge problem, but collective action inspired multiple countries to join forces in the 1980s, and we did what needed to be done.)
“Imagine what kind of world you actually want to live in and start working to make that happen,” said Armenta, who recently made the switch to government planning to help more communities find their voice and determine their own visions for the future.
To grieve the world as we know it is to miss out on opportunities to transform our world for the better. To believe we have nothing left to hope for is a self-fulfilling void. We must find the courage to care, to change, to reimagine the systems that got us into such a devastating crisis in the first place — and we must allow ourselves to dream.
“But it can’t just be my dream, or your dream. It has to be our collective dream,” Armenta said. “I’ve known for a very long time that I can’t save the world, but we can save the world together.”
More to Read

Climate disasters can elicit despair when they go viral. These activists found inspiration
Sept. 12, 2024

Comic: Emerging from environmental dissociation
Sept. 11, 2024

Rosanna Xia is an environment reporter for the Los Angeles Times, where she specializes in stories about the coast and ocean. She was a Pulitzer Prize finalist in 2020 for explanatory reporting, and her award-winning book, “ California Against the Sea ,” has been praised as a poetic and mind-expanding exploration of what we stand to lose in the face of rising water.
More From the Los Angeles Times
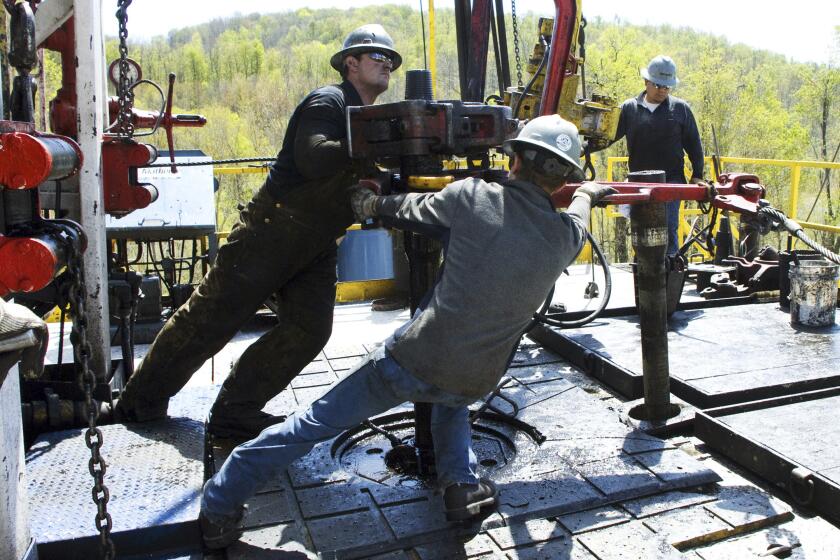

World & Nation
Harris supported the Green New Deal. Now she’s promoting domestic oil drilling
Sept. 13, 2024
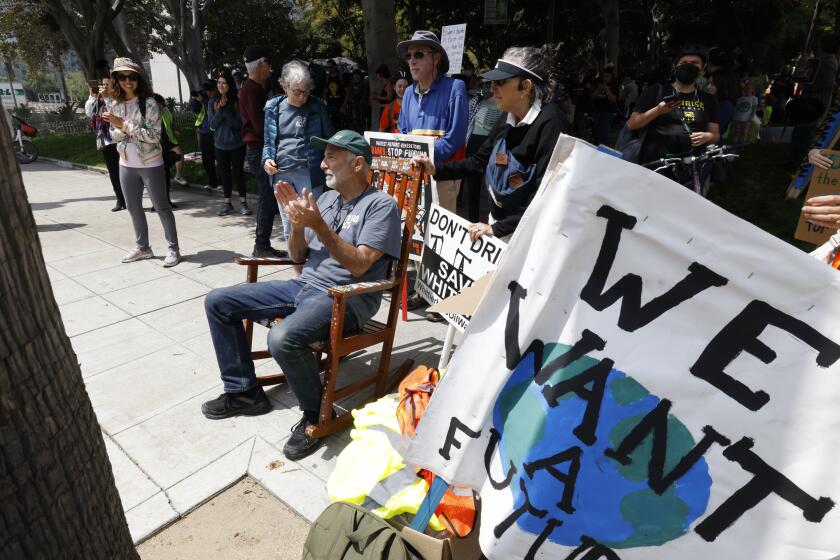

Climate & Environment
A key ally in the battle against climate change? People over 60

Gen Z: Will they finally solve the plastic crisis?

A huge deposit of marine fossils found under San Pedro High School

Climate Change: Evidence and Causes: Update 2020 (2020)
Chapter: conclusion, c onclusion.
This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of the recent change is almost certainly due to emissions of greenhouse gases caused by human activities. Further climate change is inevitable; if emissions of greenhouse gases continue unabated, future changes will substantially exceed those that have occurred so far. There remains a range of estimates of the magnitude and regional expression of future change, but increases in the extremes of climate that can adversely affect natural ecosystems and human activities and infrastructure are expected.
Citizens and governments can choose among several options (or a mixture of those options) in response to this information: they can change their pattern of energy production and usage in order to limit emissions of greenhouse gases and hence the magnitude of climate changes; they can wait for changes to occur and accept the losses, damage, and suffering that arise; they can adapt to actual and expected changes as much as possible; or they can seek as yet unproven “geoengineering” solutions to counteract some of the climate changes that would otherwise occur. Each of these options has risks, attractions and costs, and what is actually done may be a mixture of these different options. Different nations and communities will vary in their vulnerability and their capacity to adapt. There is an important debate to be had about choices among these options, to decide what is best for each group or nation, and most importantly for the global population as a whole. The options have to be discussed at a global scale because in many cases those communities that are most vulnerable control few of the emissions, either past or future. Our description of the science of climate change, with both its facts and its uncertainties, is offered as a basis to inform that policy debate.
A CKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The following individuals served as the primary writing team for the 2014 and 2020 editions of this document:
- Eric Wolff FRS, (UK lead), University of Cambridge
- Inez Fung (NAS, US lead), University of California, Berkeley
- Brian Hoskins FRS, Grantham Institute for Climate Change
- John F.B. Mitchell FRS, UK Met Office
- Tim Palmer FRS, University of Oxford
- Benjamin Santer (NAS), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- John Shepherd FRS, University of Southampton
- Keith Shine FRS, University of Reading.
- Susan Solomon (NAS), Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Kevin Trenberth, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Walsh, University of Alaska, Fairbanks
- Don Wuebbles, University of Illinois
Staff support for the 2020 revision was provided by Richard Walker, Amanda Purcell, Nancy Huddleston, and Michael Hudson. We offer special thanks to Rebecca Lindsey and NOAA Climate.gov for providing data and figure updates.
The following individuals served as reviewers of the 2014 document in accordance with procedures approved by the Royal Society and the National Academy of Sciences:
- Richard Alley (NAS), Department of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University
- Alec Broers FRS, Former President of the Royal Academy of Engineering
- Harry Elderfield FRS, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Cambridge
- Joanna Haigh FRS, Professor of Atmospheric Physics, Imperial College London
- Isaac Held (NAS), NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
- John Kutzbach (NAS), Center for Climatic Research, University of Wisconsin
- Jerry Meehl, Senior Scientist, National Center for Atmospheric Research
- John Pendry FRS, Imperial College London
- John Pyle FRS, Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge
- Gavin Schmidt, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
- Emily Shuckburgh, British Antarctic Survey
- Gabrielle Walker, Journalist
- Andrew Watson FRS, University of East Anglia
The Support for the 2014 Edition was provided by NAS Endowment Funds. We offer sincere thanks to the Ralph J. and Carol M. Cicerone Endowment for NAS Missions for supporting the production of this 2020 Edition.
F OR FURTHER READING
For more detailed discussion of the topics addressed in this document (including references to the underlying original research), see:
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2019: Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [ https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc ]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), 2019: Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration: A Research Agenda [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/25259 ]
- Royal Society, 2018: Greenhouse gas removal [ https://raeng.org.uk/greenhousegasremoval ]
- U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP), 2018: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume II: Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States [ https://nca2018.globalchange.gov ]
- IPCC, 2018: Global Warming of 1.5°C [ https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15 ]
- USGCRP, 2017: Fourth National Climate Assessment Volume I: Climate Science Special Reports [ https://science2017.globalchange.gov ]
- NASEM, 2016: Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/21852 ]
- IPCC, 2013: Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Working Group 1. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis [ https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1 ]
- NRC, 2013: Abrupt Impacts of Climate Change: Anticipating Surprises [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/18373 ]
- NRC, 2011: Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts Over Decades to Millennia [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12877 ]
- Royal Society 2010: Climate Change: A Summary of the Science [ https://royalsociety.org/topics-policy/publications/2010/climate-change-summary-science ]
- NRC, 2010: America’s Climate Choices: Advancing the Science of Climate Change [ https://www.nap.edu/catalog/12782 ]
Much of the original data underlying the scientific findings discussed here are available at:
- https://data.ucar.edu/
- https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu
- https://iridl.ldeo.columbia.edu
- https://ess-dive.lbl.gov/
- https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/
- https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
- http://scrippsco2.ucsd.edu
- http://hahana.soest.hawaii.edu/hot/
| was established to advise the United States on scientific and technical issues when President Lincoln signed a Congressional charter in 1863. The National Research Council, the operating arm of the National Academy of Sciences and the National Academy of Engineering, has issued numerous reports on the causes of and potential responses to climate change. Climate change resources from the National Research Council are available at . | |
| is a self-governing Fellowship of many of the world’s most distinguished scientists. Its members are drawn from all areas of science, engineering, and medicine. It is the national academy of science in the UK. The Society’s fundamental purpose, reflected in its founding Charters of the 1660s, is to recognise, promote, and support excellence in science, and to encourage the development and use of science for the benefit of humanity. More information on the Society’s climate change work is available at |

Climate change is one of the defining issues of our time. It is now more certain than ever, based on many lines of evidence, that humans are changing Earth's climate. The Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, with their similar missions to promote the use of science to benefit society and to inform critical policy debates, produced the original Climate Change: Evidence and Causes in 2014. It was written and reviewed by a UK-US team of leading climate scientists. This new edition, prepared by the same author team, has been updated with the most recent climate data and scientific analyses, all of which reinforce our understanding of human-caused climate change.
Scientific information is a vital component for society to make informed decisions about how to reduce the magnitude of climate change and how to adapt to its impacts. This booklet serves as a key reference document for decision makers, policy makers, educators, and others seeking authoritative answers about the current state of climate-change science.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Special Collections
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access Options
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Reason to Submit
- ESA Call for Papers
- Benefits of Publishing Open Access
- About Journal of Medical Entomology
- About the Entomological Society of America
- Editorial Board
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Impact of climate change on the geographical distribution of ticks of public health significance in Colombia: Amblyomma ovale (Ixodida: Ixodidae), the Amblyomma maculatum (Ixodida: Ixodidae) complex and the Amblyomma cajennense (Ixodida: Ixodidae) complex
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Gina Polo, Jorge Gamarra, Laura Natalia Robayo-Sánchez, Jesús A Cortés-Vecino, Alejandro Ramírez-Hernández, Impact of climate change on the geographical distribution of ticks of public health significance in Colombia: Amblyomma ovale (Ixodida: Ixodidae), the Amblyomma maculatum (Ixodida: Ixodidae) complex and the Amblyomma cajennense (Ixodida: Ixodidae) complex, Journal of Medical Entomology , 2024;, tjae100, https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjae100
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Ticks of the Amblyomma maculatum (Ixodida Ixodidae) complex, the Amblyomma cajennense (Ixodida Ixodidae) complex and Amblyomma ovale (Ixodida Ixodidae) are known to transmit various Rickettsia species in Colombia, but their exact distribution is unknown. We built several models based on current climate and projected future climate changes using a maximum entropy approach. A total of 314 records of the A. cajennense complex (65.9%; n = 207), A. ovale (22.9%; n = 72), and the A. maculatum complex (11.1%; n = 35) were obtained. Amblyomma ovale has a current distribution in the Pacific, Caribbean and Andean regions and could be potentially found in the Amazon. Amblyomma maculatum has a current distribution in the Andean and could potentially be found in the Caribbean and Orinoco regions. Amblyomma mixtum can be found near the Caribbean Sea and in the Pacific region, and A. patinoi is likely to be found in the Andean region and the Caribbean. In 2070, it will be possible to find an expansion of A. ovale and A. maculatum and a decrease of A. mixtum and A. patinoi . The variables that best predict the distribution of these species are isothermality (small fluctuations in temperature) and annual precipitation. Amblyomma cajennense s.l and A. ovale , A. cajennese s.l and A. patinoi , as well as A. maculatum and A. patinoi , have an important environmental sympatry. Epidemiological and acarological surveillance is crucial to investigate rickettsiosis caused by R. parkeri in A. ovale regions, by R. rickettsii in A. patinoi and A. mixtum areas, and by R. parkeri s.s in A. maculatum regions.
Entomological Society of America members
Personal account.
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Short-term Access
To purchase short-term access, please sign in to your personal account above.
Don't already have a personal account? Register
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| September 2024 | 23 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Entomology Today
- Recommend to Your Librarian
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1938-2928
- Print ISSN 0022-2585
- Copyright © 2024 Entomological Society of America
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Standing To Enforce The Future: Citizen Suits And Climate Change
Boston College Law Review (Forthcoming 2025).
74 Pages Posted: 9 Sep 2024
Margaret Sova McCabe
University of Arkansas - School of Law
Jordan C. Budd
University of New Hampshire School of Law
Date Written: August 01, 2024
Climate change poses an incalculable threat to human civilization. To forestall or perhaps avert its most devastating consequences, “[d]eep, rapid and sustained” reductions must be made in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that are fueling the climate crisis. Despite recently enacting the first significant federal legislation to address this threat, the United States – which generates more GHG emissions than any nation but China – continues to fall far short of the requisite reductions. Notwithstanding a political environment that likely precludes further legislative action in the immediate future, this Article takes as its starting point the premise that these circumstances might change, and that Congress might choose to use its lawmaking powers to significantly expand federal efforts to reduce the nation’s GHG emissions. Were Congress to do so, and if its response included direct restrictions on GHG emission activities in addition to incentive and subsidy arrangements, federal policy would require powerful accompanying enforcement mechanisms to reach the vast number of GHG sources subject to regulation. Among the most far-reaching enforcement tools at the disposal of Congress is its authorization of private suits to restrain or penalize prohibited conduct. Such actions, referred to as citizen suits, are an integral part of most federal regulatory programs and would likely play an important role in any federal effort to broadly regulate GHG emissions. This central enforcement mechanism, however, likely faces an insurmountable hurdle in the context climate-change policy: the increasingly restrictive standing doctrine of the current Supreme Court. To establish standing to sue, a private enforcer must meet the Court’s highly restrictive test for Article III standing, including proof of a causal association between the requested relief and the substantial remediation of the litigant’s injury. For the Justices who now control the Court, litigation that makes incremental progress toward the future resolution of a vast and ongoing injury is not enough to justify the exercise of federal jurisdiction. The injuries caused by climate change result from the collective activity of an incalculably vast number of GHG emitters across the world. Any effort to fully remediate climate-related injuries will necessarily require a similarly vast and collective global intervention – including, potentially, citizen suits that individually target just a small proportion of overall global GHG emissions. Such suits thus must rest on the principle that Article III permits incremental relief that, in the aggregate, helps turn the tide against climate change. As this Article explains, it is highly likely that a majority of the current Court will repudiate that proposition. In view of this impediment to private enforcement, the Article proposes that Congress consider pairing, whenever possible, direct regulatory restrictions on emissions activities with parallel restrictions on associated prerequisite activities. GHG emissions arise from economic arrangements that often involve activities that inflict harms unrelated to climate change – for example, localized environmental and health injuries arising from the processing, transportation, and distribution of methane-emitting cattle. Litigants separately harmed by such prerequisite activity will meet the requirements of Article III standing, since the relief they seek will directly – not incrementally – remedy their separate injuries. Accordingly, legal restrictions on those prerequisite activities would be subject to citizen suits based on the injuries they directly inflict, with the consequence of restricting dependent but otherwise nonjusticiable emission activities as well. The Article illustrates how this approach might work in the context of regulating the cattle industry, which accounts for a significant proportion of GHG emissions in the United States. In addition to direct regulation, which would not support standing for private enforcement, the Article describes how separate regulatory restrictions on concentrated animal feed operations (CAFOs) would effectively reduce methane emissions associated with cattle by constraining the industry’s prerequisite production and distribution channels. Since CAFOs inflict a variety of localized environmental and health injuries as a consequence of their massive scale, individuals subject to such harms would have standing to bring citizen suits to challenge their operation – with the collateral effect of restricting a primary source of GHG emissions.
Keywords: "greenhouse gasses", cafo, cafos, emissions, citizen suits, climate change, climate change policy, emissions regulations, standing, greenhouse emissions
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Margaret Sova McCabe (Contact Author)
University of arkansas - school of law ( email ).
1 University ADMN 305 Fayetteville, AR 72701 United States
University of New Hampshire School of Law ( email )
Two White Street Concord, NH 03301 United States
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, european economics: agriculture, natural resources & environmental studies ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Environmental Economics eJournal
Climate change law & policy ejournal, environmental law & policy ejournal, environmental law, policy & governance ejournal, international institutions: transnational networks ejournal, comparative political economy: regulation ejournal.
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Global Warming — Persuasive Speech On Climate Change
Persuasive Speech on Climate Change
- Categories: Global Warming
About this sample

Words: 523 |
Published: Mar 13, 2024
Words: 523 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Evidence of climate change, consequences of climate change, challenges and denial.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 745 words
3 pages / 1370 words
2 pages / 958 words
2 pages / 801 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Global Warming
Oceans play a very important role in moderating climate change by helping in the regulation of both heat and carbon dioxide levels. It is therefore very important to understand the interrelationship between the oceans and [...]
Global warming is a phenomenon that has been affecting the planet for decades, and its impact on biodiversity and ecosystems has become increasingly concerning. The purpose of this essay is to analyze current research on the [...]
Global warming is a pressing issue that affects every living being on this planet. As temperatures rise and extreme weather events become more frequent, it is crucial that we take action to mitigate the effects of climate [...]
Polar bears (Ursus maritimus), the iconic arctic predators, have long captured the imagination and concern of people worldwide. Residing primarily within the circumpolar Arctic, these majestic animals are perfectly adapted to [...]
It is a melancholy object to those who have been unfortunate enough to inhabit this once great planet. These individuals, instead of searching for cooler, healthier planets, are forced to employ all of their resources and [...]
Preventing global warming requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, protecting and restoring natural [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Green industrial policy for climate action in the basic materials industry
- Open access
- Published: 11 September 2024
- Volume 177 , article number 147 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Åsa Löfgren ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4528-1753 1 ,
- Lassi Ahlvik 2 ,
- Inge van den Bijgaart 3 ,
- Jessica Coria 4 ,
- Jūratė Jaraitė 5 ,
- Filip Johnsson 6 &
- Johan Rootzén 7
66 Accesses
11 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Historically, the basic materials industry has had relatively low R&D expenditure levels, raising concerns about meeting 2050 climate targets given the crucial need for innovation and technology advancement in this industry. Decisive government intervention and active support for key technological pathways are required to address significant market failures and catalyse industrial decarbonisation. This Essay lays out the economic justification for an active green industrial policy and proposes key policy design principles, with the aim of striking a balance between facilitating the green industrial transition and maintaining cost efficiency in meeting climate targets.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Despite ongoing climate mitigation efforts, the realisation of net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emission targets represents a daunting task. Emissions associated with industrial processes, which amount to approximately one-third of the total global CO 2 emissions, pose a particularly significant challenge. In recent decades, these emissions have grown, both in sheer volume and as a proportion of total emissions (Lamb et al. 2021 ; Bashmakov et al. 2022 ). The basic materials industry, here encompassing iron and steel, cement, and chemicals, is responsible for roughly 60 percent of these industrial emissions (Bashmakov et al. 2022 ). These industries are characterised by high resource and emissions intensities, large production units, long turnover times in capital stock, high investment costs and non-standardised process designs (Rissman et al. 2020 ; Bataille 2020 ). Production is primarily directed towards upstream markets and combined with other inputs before it reaches end consumers (Rootzén and Johnsson 2017 ). In addition, traditionally, the basic materials industry has invested relatively little in research and development (R&D) (Galindo-Rueda and Verger 2016 ). Figure 1 illustrates that this trend of relatively low R&D spending, compared with other industrial sectors, has continued in recent years and is present even in several of the most innovative countries. This pattern raises serious concerns, given the pivotal role of innovation and the advancement of technologies currently at the demonstration level in achieving the 2050 climate targets (IEA 2021 ). While there are a few near-zero carbon emissions industrial projects close to final investment decision or under construction, there exist, to date, no full-scale, fully built and operating near-zero emissions iron and steel, cement, or chemicals plants anywhere in the world (Bataille et al. 2024 ). Transforming the basic materials industry to net zero GHG emissions will require concurrent efforts towards improving resource efficiency, promoting circular flows and practices across value chains for basic materials, phasing out existing emission-intensive capital, and phasing-in new net-zero emission production capacity (Vogl et al. 2021 ; Bataille et al. 2018, Bataille et al. 2023 ). The objective of this Essay is to present the economic rationale for implementing green industrial policies in the basic materials industry, and to suggest strategies for designing policies that balance promoting the industrial transition with the achievement of climate goals in a cost-effective manner.

Enterprise expenditure on R&D as a share of gross value added. Focus of this essay is on the basic materials industry here encompassing iron and steel, cement, and chemicals (included in the basic metals (iron and steel), other non-metallic minerals (cement) and chemicals and chemical product (chemicals) categories). Note: The ratio of R&D enterprise expenditure and value added is calculated by dividing R&D enterprise expenditure in millions of national currency by value added in millions of national currency. Data on R&D enterprise expenditure by manufacturing sector are obtained from Eurostat’s ‘Science, technology, digital society’ database. Data on value added were obtained from the OECD’s ‘Value added and its components by activity, ISIC rev4’ dataset. Observations are for the year 2018 for all countries except France and Sweden, whose data are for 2017
The need to accelerate the green transition in industry has been recognised by policy makers across the globe. This is exemplified by initiatives like the EU Innovation Fund, the EU Net-Zero Industry Act, the US Inflation Reduction Act, Japan’s Green Innovation Fund, and China’s 14th Five-Year Plan, which will together make billions of dollars available to stimulate innovation, demonstration, and investments in enabling technologies such as direct or indirect (via hydrogen) electrification processes, carbon capture and storage (CCS), and zero-emissions electricity supply (IEA 2023 ). On the surface, these types of policy interventions appear to run counter to conventional policy recommendations, which generally caution against favoring specific technological solutions for achieving decarbonisation goals (Jaffe et al. 2005 ; Juhász et al. 2023 ). However, such recommendations are based on models that disregard the specific market failures relevant to sectors such as the basic materials industry, which become particularly prevalent as more radical emission reductions are required. Acknowledging these market failures, this Essay commences with laying out the economic rationale for green industrial policy targeting the basic materials industry. Similar to the broader concept of industrial policy, there is no commonly accepted definition of what green industrial policy entails (Altenburg and Rodrik 2017 ). Here, we define green industrial policy as a policy that actively steers the transformation of the structure of domestic economic activity, and hence the technological pathways, of selected sectors or industries with the goal of achieving net-zero GHG emissions. Footnote 1 The targeted nature of green industrial policy distinguishes it from broad-based decarbonisation policies, such as carbon pricing, while the goal of net-zero GHG emissions differentiates it from traditional growth-oriented industrial policy.
The question whether or not governments should engage in active green industrial policy, has been the subject of extensive debate in the academic literature. For instance, Nilsson et al. ( 2021 ) argue for the pursuit of multiple policy strategies to support industry decarbonisation, Mazzucato et al. ( 2020 ) advocate for a mission-oriented approach in favor of desired societal goals, with a proactive role for the government in shaping markets, while Karlson et al. ( 2021 ) argue against such an ‘entrepreneurial state’, pointing at the limited empirical support for effective industrial and innovation policies. While the necessity of green industrial policy is increasingly recognised, many scholars remain hesitant due to the risks of rent-seeking, corruption, and misallocation of resources that can arise when governments attempt to steer economic development through targeted policies (see, e.g., Nahm and Urpelainen 2021 and Wen et al. 2021 ). In response, we seek to contribute by elaborating on the rationale for green industrial policy from an economics perspective, akin to Hallegatte et al. ( 2013 ) and Rodrik ( 2014 ). Next, acknowledging the reservations of many scholars, our analysis turns to the crucial question of how to effectively shape a green industrial policy in the coming decades, a key aspect highlighted in Aiginger and Rodrik ( 2020 ). We provide important considerations for policy design, articulated through three principles detailed in Section 3, which aim at balancing the enabling of a green industrial transition with cost efficiency. These principles could be relevant beyond the basic materials industries, and more broadly provide important insights into the debate on the appropriate equilibrium between government intervention and market forces.
2 Effective green industrial policy implies abandoning technology domain neutrality
The superiority of a policy approach that relies on multiple instruments to simultaneously address environmental and innovation market failures is well-established (e.g., Aldy et al. 2010 ; Acemoglu et al. 2012 ; Aghion et al. 2016 ). A critical decision policymakers subsequently face is whether to adopt technology-neutral or technology-specific strategies to accelerate the development and deployment of green technologies (Fabra and Montero 2023 ). Technology-neutral policies include broad-based policies, such as pricing environmental externalities through emissions taxes or emissions trading schemes, as well as general subsidies for R&D or technology deployment (Lehmann and Soderholm 2018 ).
Beyond creating the right incentives, technology-neutral policies allow markets to select technological pathways to achieve climate targets, promoting the development and deployment of the least costly technologies first. In contrast, technology-specific policies promote particular technological fields, sectors, or even individual projects through tailored support mechanisms, such as feed-in tariffs or targeted R&D subsidies.
Technology-neutral policies avoid several pitfalls of technology-specific policies. These include concerns that public support might crowd out private investments, that information asymmetries and lack of relevant expertise may lead policymakers to endorse mitigation strategies that either underperform or prove costlier than expected, and concerns about the risk of regulatory capture and increased lobbying by industry leaders. Yet, the promotion of technology-neutral policies rests on the assumption that market failures associated with the development and diffusion of technologies are absent or are properly addressed by other policies. However, such market failures are particularly prevalent in the basic materials industry, posing considerable barriers to the innovation and deployment of green technologies (Löfgren and Rootzén 2021 ).
First, innovation in the basic materials industry is highly path-dependent and can be expected to generate spillover effects (Aghion et al. 2016 ; Popp et al. 2019 ; Noll et al. 2023 ).For example, advancements in low-carbon steel production techniques, such as hydrogen-based direct reduction, build upon decades of research in metallurgical processes (Pei et al. 2020 ). Policy interventions to encourage investments in hydrogen-based direct reduction within one country can create first-mover advantages for national industry, while also contributing to reducing future costs and risks across the globe.
Second, investments in innovative low-carbon technologies within the basic materials industry depend on coordination among actors within the industries as well as along supply chains. Network effects — where the value of a technology increases as more market participants adopt it (Greaker and Midttømme 2016 ; Heijmans 2023 ) — can lead to technology lock-in, thereby hindering the adoption of new technologies. This is illustrated by the case of CCS, where a cement factory investing in carbon capture relies on other actors to invest in energy, transport, and storage infrastructure (Golombek et al. 2023 ). According to the International Energy Agency, attaining the necessary adoption of hydrogen and CCS mandates a significant increase in investments in supporting infrastructures (IEA 2021 ). The importance of supply chain coordination is further emphasised by Dugoua and Dumas ( 2021 ), who demonstrate that green innovation in industrial networks requires producers to coordinate with suppliers. Without such coordination, shared suppliers can become bottlenecks to green innovation. Importantly, Dugoua and Dumas ( 2021 ) show that when innovation is complementary across firms, price-based policies, such as carbon taxes, may not be sufficient to achieve deep industrial decarbonisation at the lowest cost.
Third, substantial financial barriers exist for investments in both existing and novel green technological pathways, as markets may be overly myopic and lack complete information about which technology will ultimately prevail (Nemet 2009 ; Armitage et al. 2024 ). For the basic materials industry, where capital intensity is high, project lead times are long, and where commodity and policy risks are significant, this means that private investors and lenders, in the absence of policy interventions, tend to be particularly hesitant. Cordonnier and Saygin ( 2023 ) describe how there is a general lack of tailored financing instruments to de-risk and improve the economic viability of industrial decarbonisation projects. They also describe how annual investments in new production plants compatible with net-zero pathways for chemicals, steel, cement and aluminium production is much too low to be consistent with net-zero pathways. They estimate that investments in such near zero production plants need to increase from USD 15 billion globally today to USD 70 billion by 2030 and USD 125 billion by 2050.
Overcoming these market failures requires targeted policies that involve selecting specific technologies. This implies that, contrary to the principles of technology-neutral policy, which advocates for policy that does not favor certain technologies, full technology neutrality will not be attainable, or even preferred. In this approach, carbon pricing would address the emissions externality, while targeted policies—such as targeted investment support and targeted R&D subsidies—would tackle the specific market failures that hinder innovation and the deployment of green technologies in the basic materials industry. These targeted interventions are crucial because market failures related to technology path-dependence, coordination, and financial barriers arise not only from insufficient market incentives, but also from uncertainties surrounding technological pathways. This underscores the need for government involvement in technology selection, making a strong case for a proactive and targeted green industrial policy.
But how should an active targeted green industrial policy be designed? We argue that such policy should identify and commit to what we term as ‘technology domains’. A technology domain, as we define it, is a broad technological pathway that enables a collection of specific technologies or, as we call them, ‘technology families’. To decarbonise the basic materials industry, there are a limited number of technology domains available to choose from. These domains include direct electrification, indirect electrifica tion (via hydrogen), biogenic carbon as a fuel and feedstock, carbon capture and storage, among others. These technology domains are not mutually exclusive, and may be combined. The successful implementation of these technologies requires parallel development of various interconnected technological systems and business models, along with corresponding modifications to regulatory frameworks and support systems. Figure 2 depicts several principal domains and corresponding examples of technology families pertinent to the decarbonisation of the basic materials industry. While green industrial policy can be designed to target specific technology domains, the development of certain markets and infrastructure, such as those that expand the supply of clean electricity, may benefit multiple domains. This interconnection is represented by the dotted arrows between the technology domains in Figure 2 .

Taxonomy. Key technology domains and examples of technology families with relevance for the decarbonisation of the basic materials industry
3 Technology family neutrality and market incentives remain key
As described above, green industrial policy must move away from technological neutrality as a guiding principle at the level of technology domains and instead actively support key technological pathways to achieve climate targets. Yet, the main pitfalls of industrial policy – failure to pick winners, influence of interest groups and potential crowding out of private investments – remain. While abstaining from active government intervention could circumvent these pitfalls, it could also risk a second type of error — underinvestment in technologies with the potential to substantially contribute to industrial decarbonisation.
We formulate three key principles that can guide policymakers in the design of effective green industrial policy for the basic materials industry, aimed at mitigating the pitfalls mentioned above:
Principle 1. Use experts to systematically and transparently identify pertinent market failures and select technology domains.
Requiring governments to provide documentation regarding the rationale for intervention enhances the likelihood of accurately selecting the right technology domains to support. Key market failures in the decarbonisation of the basic materials industry that justify targeted subsidies or regulatory interventions include technological spillovers, path-dependence in technology development, network effects, as well as financial and informational barriers. Targeted policies that focus on promoting specific technology domains are necessary to address these market failures. However, since selective support can be vulnerable to regulatory capture, ensuring transparency is essential to minimise the influence of special interest groups.
Principle 2. Maintain neutrality across technology families within supported technology domains.
Market actors hold more information than policy makers concerning effective solutions for emission reductions and their costs. To harness this information and keep the door open for possible future innovations, the government should maintain a level playing field within technology domains, avoiding support for specific technology families or tailored to individual firms. For instance, the government could steer its green industrial policy to specific technology domains (e.g. electrification) but make sure that selection processes treats competing firms and technology families within that domain equally.
Principle 3. Maintain and strengthen market-based climate policy instruments, such as carbon taxes and emissions trading, as the cornerstone of climate policy.
Market-based climate policy instruments are critical tools to leverage the private information held by firms and industries. They sustain incentives for cost-effective emission reductions (Lewis 1996 ; Ahlvik and Liski 2022 ), promote innovation in the most promising technological solutions and accelerate the uptake of such new technologies within technology domains (Ahlvik and Bijgaart 2024 ). Therefore, green industrial policy should supplement broad market-based climate policies, not replace them.
4 Reflections on U.S. and EU green industrial policy in light of the three principles
In recent years, green industrial policies have been increasingly debated and adopted in the world’s major economies (Juhász et al. 2022 ; Criscuolo et al. 2023 ). Below we offer some brief reflections on two of the most prominent green industrial policy packages implemented in recent years — the Inflation Reduction Act in the United States and the European Green Deal Industrial Plan — through the lens of our three principles. To provide context, we start with a concise description of the main elements of these green industrial policies.
Both the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the Green Deal Industrial Plan are complex policy packages consisting of a broad range of climate provisions. The climate provisions of the IRA are primarily a combination of tax credits, grants, and loan programs with the aim of incentivising deployment of clean energy, innovation, and domestic manufacturing. The main focus of IRA is on promoting the energy transition through clean energy tax credits (either production-based credits or investment tax credits). Notably, by 2025 the credits will be technology neutral, creating a level playing field for technologies such as solar, wind, storage, hydrogen, carbon capture, and direct air capture (Bistline et al. 2023b ). Compared to the subsidies to the power and transportation sector, the direct subsidies for innovation and the adoption of technologies specific to the industrial sector are still relatively scarce. The IRA earmarks only USD 5 billion out of a total of USD 392 billion for industrial decarbonisation (Bistline et al. 2023a ). However, given the anticipated importance of both hydrogen and carbon capture technologies for the industrial sector, the overall subsidies to industry are likely larger, as these technologies are eligible for tax credits. In addition, there exist other programs that provide investment support and incentives that are complementary to the IRA tax credits. One example is the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), which supports hydrogen initiatives through USD 8 billion of support for hydrogen hubs (Krupnick and Bergman 2022 ). Finally, to encourage the domestic development of green industries, the IRA includes significant benefits for domestic production. This feature is internationally contentious, and has raised concerns about increased protectionism, which could negatively impact international trade and trigger global subsidy races (Kleimann et al. 2023 ). In March 2024, a first round of support targeting a range of industry decarbonisation projects was announced. The Industrial Demonstrations Program received USD 6.3 billion, combining funding from IIJA and the IRA, to support the advancement of transformational technologies across several basic material industries (e.g. steel, cement and petrochemicals) and across various technological families (U.S., Department of Energy 2024 ).
The Net-Zero Industry Act (NZIA) - a central pillar of the European Green Deal Industrial Plan - was adopted by the EU Council on 27 May, 2024. Often seen as the EU’s response to the IRA, the NZIA marks a shift from the EU’s previous focus on extensively subsidising early-stage innovation to supporting green technologies closer to commercialisation and accelerating the market penetration of strategic net-zero technologies. This shift makes EU industrial policy more similar to the IRA that has a strong emphasis on technology deployment. Kleimann et al. ( 2023 ) compare the extent of subsidies and find that, aside from renewable energy production where EU subsidies are higher, EU subsidies were generally comparable to those under the IRA.
The NZIA aims to accelerate the green transition and deplyoment of green technologies by simplifying approval processes, improving market access for strategic technologies, enhancing workforce skills, and coordinating member states’ efforts through the Net-Zero Europe Platform. The NZIA does not provide direct funding for strategic technologies at the EU level; rather, such support is anticipated to come from national policies implemented by member states and from sources like the EU Innovation Fund. The EU Innovation Fund is funded through sales of the EU Emission Trading Systems’ (EU ETS) emission allowances and the total funding thus depends on the development of the carbon price. At the current carbon price of EUR 75/tCO 2 , the 530 million allowances earmarked for the fund would make EUR 40 billion available from 2020 to 2030. The funding covers five areas: (i) energy intensive industries, (ii) renewable-energy technologies, (iii) CCS, (iv) energy storage, and (v) net-zero mobility and buildings (EC 2023 ). To date 124 projects have been rewarded EUR 6.7 billion. Almost half of the funding (EUR 3.2 billion) has so far been allocated to support investments in commercial demonstration of innovative zero-carbon and low-carbon technologies in the steel, cement and petrochemicals industries (EC 2024 ).
In relation to our Principles, it appears that, while not always explicitly framed in terms of market failures, several elements of both the IRA, along with complementary acts like the IIJA, and the NZIA are consistent with our first and second principles. While the direct support dedicated specifically for decarbonisation of basic materials industries is a smaller component of the IRA, industry actors can benefit also from tax credits for domain technologies such as CCS and hydrogen. In addition, there is an acknowledgement of coordination failures as important impediments to industrial decarbonisation, and provisions to overcome these coordination failures, such as in the case of hydrogen hubs in the IIJA. In the EU, the NZIA targets market failures beyond emission and knowledge externalities, such as the need for coordinated zero-emissions electricity supply, expanded grids, and a skilled labor force. Furthermore, NZIA defines strategic net-zero technologies and the EU Innovation Fund supports investments in strategic net-zero technology ecosystems. Interestingly, these technologies translate to technology domains in the case of the basic materials industry, and hence is generally aligned with our Principles 1 and 2. The NZIA also permits the granting of state aid to strategic net-zero technologies, thereby relaxing state-aid rules. This aims to make it easier for individual member states to subsidise these technologies, accelerate the green transition, and reduce investment uncertainty through clear objectives and monitoring mechanisms.
Regarding Principle 3, it can be noted that while the EU has implemented carbon pricing to incentivise industrial decarbonisation through the EU EU ETS since 2005, carbon pricing plays a more limited role in U.S. climate policy. Footnote 2 In the U.S., carbon pricing is primarily evident through cap-and-trade programs in a limited number of states, including California’s cap-and-trade program (since 2012), Washington’s cap-and-invest program (since 2023), and the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) covering 11 states and only the power sector (since 2009). An additional cap-and-invest initiative is expected to launch in New York State in 2025. However, it is important to note that the carbon prices in these programs are much lower than the social cost of carbon, which recent studies estimate to average well over 100 USD per tonne of CO 2 (Hänsel et al. 2020 ; Rennert et al. 2022 ; Moore et al. 2024 ). As pointed out in Principle 3, policy makers should work to strengthen these broad market-based policy instruments.
5 Conclusions
This Essay lays out the economic rationale for an active green industrial policy targeting the basic materials industry. It puts forth three key policy design principles, with the aim of striking a balance between facilitating timely green industrial transition and maintaining cost efficiency. We advocate for the adoption of a green industrial policy that addresses pertinent market failures and actively supports crucial technological pathways (domains). This policy should ensure a level playing field within selected technology domains, while also employing market-based climate policy instruments to incentivise cost-effective GHG emissions reductions. As laid out above, active governmental involvement in the transition of the basic materials industry definitively comes with its potential pitfalls. However, inaction risk a second type of error — underinvestment in technologies with the potential to substantially contribute to industrial decarbonisation. Such policy error may be less visible, but not less costly. Decarbonising the global basic materials industry will be a complex task, therefore experimentation and continuous evaluation should be key components of policy implementation. Insights from economics, in conjunction with a broadened recognition of relevant barriers and market failures in the industrial sector, offer a strong foundation for successful and timely green industrial policy aimed at achieving carbon neutrality.
Data availability
Data underlying Fig. 1 are from publicly available databases as described in the figure caption.
This definition, which stresses targeted, structural transformation and a decarbonisation goal, is similar to the definition of green industrial policy outlined in Hallegatte et al. ( 2013 ) and Juhász et al. ( 2023 ).
However, it is important to note that the IRA include the first price on greenhouse gases at the federal level in the US: a charge on methane emissions that exceed specific thresholds at selected facilities in the oil and gas industry. The charge starts at USD 900 per metric ton of methane, increasing to USD 1,500 after two years (corresponding to USD 36 and USD 60 per metric ton of carbon dioxide equivalent, respectively).
Acemoglu D, Aghion P, Bursztyn L, Hemous D (2012) The environment and directed technical change. Am Econ Rev 102(1):131–166
Article Google Scholar
Aghion P, Dechezleprêtre A, Hemous D, Martin R, Van Reenen J (2016) Carbon taxes, path dependency, and directed technical change: evidence from the auto industry. J Polit Econ 124(1):1–51
Ahlvik L, Liski M (2022) Global externalities, local policies, and firm selection. J Eur Econ Assoc 20(3):1231–1275
Ahlvik L, van den Bijgaart I (2024) Screening green innovation through carbon pricing. J Environ Econ Manag 124:102932
Aiginger K, Rodrik D (2020) Rebirth of industrial policy and an agenda for the twenty-first century. J Ind Compet Trade 20:189–207
Aldy JE, Krupnick AJ, Newell RG, Parry IWH, Pizer WA (2010) Designing climate mitigation policy. J Econ Lit 48(4):903–934
Altenburg T, Rodrik D (2017) Green industrial policy: Accelerating structural change towards wealthy green economies. In: Altenburg T, Assmann C (eds) Green Industrial Policy: Concept, Policies, Country Experiences, pp 1–20
Armitage S, Bakhtian N, Jaffe A (2024) Innovation market failures and the design of new climate policy instruments. Environ Energy Policy Econ 5(1):4–48
Google Scholar
Bashmakov I, Nilsson L, Acquaye A, Bataille C, de la Cullen JS, du Can Rue, Fischedick M, Geng Y, Tanaka K (2022) Industry. Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA
Bataille C (2020) Physical and policy pathways to net-zero emissions industry. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Clim Change 11(2):e633
Bataille C, Stiebert S, Algers J, Li F, Alfare M (2024) Triggering investment in first-of-a-kind and early near-zero emissions industrial facilities. Report, Center on Global Energy Policy at Columbia University
Bataille C, Stiebert S, Hebeda O, Trollip H, McCall B, Vishwanathan SS (2023) Towards net-zero emissions concrete and steel in India, Brazil and South Africa. Climate Policy, pp 1–16
Bistline J, Mehrotra N, Wolfram C (2023a) Economic implications of the climate provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act. Working Paper 31267, National Bureau of Economic Research
Bistline JE, Brown M, Domeshek M, Marcy C, Roy N, Blanford G, Burtraw D, Farbes J, Fawcett A, Hamilton A et al (2023b) Power sector impacts of the inflation reduction act of 2022. Environ Res Lett 19(1):014013
Cordonnier J, Saygin D (2023) Financing solutions to foster industrial decarbonisation in emerging and developing economies. OECD Environment Working Papers, vol 226. pp 97
Criscuolo C, Díaz L, Lalanne G, Guillouet L, van de Put C-É, Weder C, Deutsch HZ (2023) Quantifying industrial strategies across nine oecd countries
Dugoua E, Dumas M (2021) Green product innovation in industrial networks: A theoretical model. J Environ Econ Manag 107:102420
EC (2023) Innovation Fund Progress Report 2022
EC (2024) Innovation Fund - Portfolio of signed projects
Fabra N, Montero J-P (2023) Technology-neutral versus technology-specific procurement. Econ J 133(650):669–705
Galindo-Rueda F, Verger F (2016) OECD taxonomy of economic activities based on R&D intensity. OECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Papers 4:24
Golombek R, Greaker M, Kverndokk S, Ma L (2023) Policies to promote carbon capture and storage technologies. Environ Resource Econ 85(1):267–302
Greaker M, Midttømme K (2016) Network effects and environmental externalities: Do clean technologies suffer from excess inertia? J Public Econ 143:27–38
Hallegatte S, Fay M, Vogt-Schilb A (2013) Green Industrial Policies: When and How. Policy Research Working Paper 6677
Hänsel MC, Drupp MA, Johansson DJ, Nesje F, Azar C, Freeman MC, Groom B, Sterner T (2020) Climate economics support for the un climate targets. Nat Clim Chang 10(8):781–789
Heijmans RJ (2023) Unraveling coordination problems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.08557
IEA (2021) Net Zero by 2050 - A Roadmap for the Global Energy Sector. https://www.iea.org/reports/net-zero-by-2050
IEA (2023) Energy Technology Perspectives 2023. License: CC BY 4.0
Jaffe AB, Newell RG, Stavins RN (2005) A tale of two market failures: Technology and environmental policy. Ecol Econ 54(2–3):164–174
Juhász R, Lane N, Oehlsen E, Pérez VC (2022) The who, what, when, and how of industrial policy: a text-based approach. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/uyxh9
Juhász R, Lane NJ, Rodrik D (2023) The new economics of industrial policy. Working Paper 31538, National Bureau of Economic Research
Karlson N, Sandström C, Wennberg K (2021) Bureaucrats or markets in innovation policy?–a critique of the entrepreneurial state. Rev Austrian Economics 34:81–95
Kleimann D, Poitiers N, Sapir A, Tagliapietra S, Véron N, Veugelers R, Zettelmeyer J (2023) Green tech race? the us inflation reduction act and the eu net zero industry act. The World Economy 46(12):3420–3434
Krupnick A, Bergman A (2022) Incentives for clean hydrogen production in the inflation reduction act. Resources for the Future
Lamb WF, Wiedmann T, Pongratz J, Andrew R, Crippa M, Olivier JG, Wiedenhofer D, Mattioli G, Al Khourdajie A, House J et al (2021) A review of trends and drivers of greenhouse gas emissions by sector from 1990 to 2018. Environ-Mental Research Letters 16(7):073005
Article CAS Google Scholar
Lehmann P, Soderholm P (2018) Can technology-specific deployment policies be cost-effective? the case of renewable energy support schemes. Environ Resource Econ 71:475–505
Lewis TR (1996) Protecting the environment when costs and benefits are privately known. The RAND J Economics, pp 819–847
Löfgren A, Rootzén J (2021) Brick by brick: governing industry decarbonization in the face of uncertainty and risk. Environ Innov Soc Trans 40:189–202
Mazzucato M, Kattel R, Ryan-Collins J (2020) Challenge-driven innovation policy: towards a new policy toolkit. J Ind Compet Trade 20:421–437
Moore FC, Drupp MA, Rising J, Dietz S, Rudik I, Wagner G (2024) Synthesis of evidence yields high social cost of carbon due to structural model variation and uncertainties. Working Paper 32544, National Bureau of Economic Research
Nahm J, Urpelainen J (2021) The enemy within? green industrial policy and stranded assets in china’s power sector. Glob Environ Politics 21(4):88–109
Nemet GF (2009) Demand-pull, technology-push, and government-led incentives for non-incremental technical change. Res Policy 38(5):700–709
Nilsson LJ, Bauer F, Åhman M, Andersson FN, Bataille C, de la Rue du Can S, Ericsson K, Hansen T, Johansson B, Lechtenböhmer S et al (2021) An industrial policy framework for transforming energy and emissions intensive industries towards zero emissions. Climate Policy 21(8):1053–1065
Noll B, Steffen B, Schmidt TS (2023) The effects of local interventions on global technological change through spillovers: A modeling framework and application to the road-freight sector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120:e2215684120
Pei M, Petäjäniemi M, Regnell A, Wijk O (2020) Toward a fossil free future with hybrit: Development of iron and steelmaking technology in sweden and finland. Metals 10:972
Popp D et al (2019) Environmental policy and innovation: A decade of research. Int Rev Environ Resour Econ 13(3–4):265–337
Rennert K, Errickson F, Prest BC, Rennels L, Newell RG, Pizer W, Kingdon C, Wingenroth J, Cooke R, Parthum B et al (2022) Comprehensive evidence implies a higher social cost of CO2. Nature 610(7933):687–692
Rissman J, Bataille C, Masanet E, Aden N, Morrow WR, Zhou N, Elliott N, Dell R, Heeren N, Huckestein B, Cresko J, Miller SA, Roy J, Fennell P, Cremmins B, Koch Blank T, Hone D, Williams ED, de la Rue du Can S, Sisson B, Williams M, Katzenberger J, Burtraw D, Sethi G, Ping H, Danielson D, Lu H, Lorber T, Dinkel J, Helseth J (2020) Technologies and policies to decarbonize global industry: Review and assessment of mitigation drivers through 2070. Appl Energy 266:114848
Rodrik D (2014) Green industrial policy. Oxf Rev Econ Policy 30(3):469–491
Rootzén J, Johnsson F (2017) Managing the costs of CO2 abatement in the cement industry. Climate Policy 17(6):781–800
U.S. Department of Energy (2024). Industrial demonstrations program
Vogl V, Olsson O, Nykvist B (2021) Phasing out the blast furnace to meet global climate targets. Joule 5(10):2646–2662
Wen H, Lee C-C, Zhou F (2021) Green credit policy, credit allocation efficiency and upgrade of energy-intensive enterprises. Energy Econ 94:105099
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from Formas, a Swedish Research Council for Sustainable Development [Dnr: 2020-00174] and the Mistra Carbon Exit Research Program.
Open access funding provided by University of Gothenburg. The authors acknowledge financial support from Formas, a Swedish Research Council for Sustainable Development [Dnr: 2020–00174] and the Mistra Carbon Exit Research Program.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, University of Gothenburg and Luleå University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden
Åsa Löfgren
Department of Economics and Management, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
Lassi Ahlvik
Utrecht University School of Economics, Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands
Inge van den Bijgaart
Department of Economics, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Jessica Coria
Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden and Vilnius University, Vilnius, Lithuania
Jūratė Jaraitė
Department of Space, Earth and Environment, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden
Filip Johnsson
IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Johan Rootzén
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Åsa Löfgren: contributed to the conceptualization of the Essay, the drafting and writing of the manuscript, and the creation and analysis of the content, Lassi Ahlvik: contributed to the conceptualization of the Essay, the drafting and writing of the manuscript, and the creation and analysis of the content, Inge van den Bijgaart: contributed to the conceptualization of the Essay, the drafting and writing of the manuscript, and the creation and analysis of the content, Jessica Coria: contributed to the conceptualization of the Essay, the drafting and writing of the manuscript, and the creation and analysis of the content, Jūratė Jaraitė: contributed to the conceptualization of the Essay, the drafting and writing of the manuscript, and the creation and analysis of the content, Filip Johnsson: contributed to the conceptualization of the Essay, the drafting of the manuscript, and the creation and analysis of the content and Johan Rootzén: contributed to the conceptualization of the Essay, the drafting and writing of the manuscript, and the creation and analysis of the content.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Åsa Löfgren .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All authors have reviewed the final version of the manuscript and consent to its publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests or personal relationships that could appear to have influenced the work reported in this Essay.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Löfgren, Å., Ahlvik, L., van den Bijgaart, I. et al. Green industrial policy for climate action in the basic materials industry. Climatic Change 177 , 147 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-024-03801-7
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2024
Accepted : 28 August 2024
Published : 11 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-024-03801-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Green industrial policy
- Basic materials industry
- Industrial decarbonisation
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Good. 3 pages / 1352 words. Introduction Climate change, driven predominantly by the excessive emission of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels, is undeniably one of the most pressing global issues of the world today. This essay delves into the multifaceted nature of climate change in the 21 century,...
Climate Change Sample Essay 250 Words. Climate change represents a pressing global challenge that demands immediate attention and concerted efforts. Human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This results in a greenhouse effect ...
Climate change refers to the change in the environmental conditions of the earth. This happens due to many internal and external factors. The climatic change has become a global concern over the last few decades. In this climate change essay, we have discussed its causes. so click the link and read the whole essay.
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Introduction. The first step is to introduce the topic and provide an overview of the main points you will cover in the essay. This should include a brief description of what climate change is. Furthermore, it should include current research on how humans are contributing to global warming.
1. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite this essay. Download. Climate change is a global phenomenon that affects us all. It can be challenging to wrap your head around such a complex issue, but understanding climate change is an ...
Introduction. Climate change refers to long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, often resulting from human activities such as deforestation, industrial processes, and fossil fuel consumption. The primary cause of climate change is the increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere ...
Bahçeşehir College is committed to increasing students' awareness of the changing world we live in. This climate change essay competition saw many students submitting well thought out pieces of writing. These essays were marked on their format, creativity, organisation, clarity, unity/development of thought, and grammar/mechanics.
For example, Pittock noted that climate change has been a major cause of water shortages in most parts of the world (Pittock 2009, p. 108). He however attributed this to a number of factors, including precipitation decrease in some regions, high rates of evaporation in the world and general loss of glaciers.
Climate change is defined as "a pattern of change affecting global or regional climate," based on "average temperature and rainfall measurements" as well as the frequency of extreme weather events. 1 These varied temperature and weather events link back to both natural incidents and human activity. 2 Likewise, the term global warming ...
Here are some sample essays on Global Warming: ... Climate Change and Global Warming Essay. Global Warming and Climate Change are two sides of the same coin. Both are interrelated with each other and are two issues of major concern worldwide. Greenhouse gases released such as carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants in the earth's ...
Climate Change Informative Speech. As we stand on the precipice of a changing world, it becomes increasingly important for us to understand the gravity of the situation we face. Climate change, a phenomenon that has been the subject of much debate and controversy, is no longer a distant threat, but a harsh reality that demands our attention.
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
Climate Change Essay Examples: Problems & Solutions. When writing an essay about climate change, we consider it a distant problem as far as it is not real or visible to the naked eye. However, the suffering of our planet due to human intervention and a long-lasting bad influence on nature resulted in atmosphere changes, the greenhouse effect ...
200 Words Essay on Climate Change. The climate of the Earth has changed significantly over time. While some of these changes were brought on by natural events like volcanic eruptions, floods, forest fires, etc., many of the changes were brought on by human activity. The burning of fossil fuels, domesticating livestock, and other human ...
Pages: 4 Words: 1247. Climate change, divorced from the political rhetoric, is a concrete phenomenon affecting multiple systems. The economic and social ramifications of climate change are ancillary to its measurable physical effects. However, the measurable physical effects vary depending on geographic factors.
Climate Explained is a collection of short primers that answer diverse climate change questions, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security. Image 1. Example Climate Explained essays on the Yale Climate ...
Climate Change Essay: Go through the 500+ Words Essay on Climate Change and get ideas on how to write an effective essay on issues related to the environment. Boost your essay writing skills to score high marks in the English exam and also participate in various essay writing competitions.
🏆 Best Climate Change Title Ideas & Essay Examples. Get your 100% original paper on any topic done in as little as 1 hour. Learn More . Climate Change - Problems and Solutions. It is important to avoid cutting trees and reduce the utilization of energy to protect the environment. Many organizations have been developed to enhance innovation ...
Courtney Lindwall. Climate change is our planet's greatest existential threat. If we don't limit greenhouse gas emissions from the burning of fossil fuels, the consequences of rising global ...
1,000 Word Climate Change Essay. Climate change in the world can be caused by various activities. When climate change occurs; temperatures can increase a dramatically. When temperature rises, many different changes can occur on Earth. For example, it can result in more floods, droughts, or intense rain, as well as more frequent and severe heat ...
The science of climate change is more solid and widely agreed upon than you might think. But the scope of the topic, as well as rampant disinformation, can make it hard to separate fact from ...
Global warming, the phenomenon of rising average air temperatures near Earth's surface over the past 100 to 200 years. Although Earth's climate has been evolving since the dawn of geologic time, human activities since the Industrial Revolution have a growing influence over the pace and extent of climate change.
Climate change is a long-term shift in global or regional climate patterns. Often climate change refers specifically to the rise in global temperatures from the mid-20th century to present. ... Different places have different climates. A desert, for example, is referred to as an arid climate because little water falls, as rain or snow, during ...
Then a college student asked me about climate anxiety. It came up again on social media, and again in personal essays and polls. This paralyzing dread was suddenly the talk of the town — but it ...
C ONCLUSION. This document explains that there are well-understood physical mechanisms by which changes in the amounts of greenhouse gases cause climate changes. It discusses the evidence that the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and are still increasing rapidly, that climate change is occurring, and that most of ...
Climate policy at the subnational level is sometimes framed as being counterproductive, because climate change is considered a collective action problem that can be best addressed in a coalition that should be as large as possible. Using comprehensive data from US states on climate policy and policy outcomes, we show that state-level policy is effective in accelerating the adoption of solar ...
Introduction. Species distribution models, also known as ecological niche models, are widely used in the context of climate change to model vector-borne diseases and predict future areas of potential transmission risk (Polo et al. 2015, Baak-Baak et al. 2017, Lippi et al. 2021).This spatial modeling is achieved by associating locations where a species of interest is known to be present with ...
The injuries caused by climate change result from the collective activity of an incalculably vast number of GHG emitters across the world. Any effort to fully remediate climate-related injuries will necessarily require a similarly vast and collective global intervention - including, potentially, citizen suits that individually target just a ...
Persuasive Speech on Climate Change. Climate change is a pressing issue that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. As the Earth's climate continues to warm at an alarming rate, the consequences of this phenomenon are becoming more apparent and threatening. It is crucial that we take action to address this issue and mitigate its ...
Historically, the basic materials industry has had relatively low R&D expenditure levels, raising concerns about meeting 2050 climate targets given the crucial need for innovation and technology advancement in this industry. Decisive government intervention and active support for key technological pathways are required to address significant market failures and catalyse industrial ...