Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 03 October 2022

How COVID-19 shaped mental health: from infection to pandemic effects
- Brenda W. J. H. Penninx ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7779-9672 1 , 2 ,
- Michael E. Benros ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4939-9465 3 , 4 ,
- Robyn S. Klein 5 &
- Christiaan H. Vinkers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3698-0744 1 , 2
Nature Medicine volume 28 , pages 2027–2037 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
41k Accesses
143 Citations
492 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Epidemiology
- Infectious diseases
- Neurological manifestations
- Psychiatric disorders
The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has threatened global mental health, both indirectly via disruptive societal changes and directly via neuropsychiatric sequelae after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Despite a small increase in self-reported mental health problems, this has (so far) not translated into objectively measurable increased rates of mental disorders, self-harm or suicide rates at the population level. This could suggest effective resilience and adaptation, but there is substantial heterogeneity among subgroups, and time-lag effects may also exist. With regard to COVID-19 itself, both acute and post-acute neuropsychiatric sequelae have become apparent, with high prevalence of fatigue, cognitive impairments and anxiety and depressive symptoms, even months after infection. To understand how COVID-19 continues to shape mental health in the longer term, fine-grained, well-controlled longitudinal data at the (neuro)biological, individual and societal levels remain essential. For future pandemics, policymakers and clinicians should prioritize mental health from the outset to identify and protect those at risk and promote long-term resilience.
Similar content being viewed by others

Personalized brain circuit scores identify clinically distinct biotypes in depression and anxiety

Short- and long-term neuropsychiatric outcomes in long COVID in South Korea and Japan

Stress-resilience impacts psychological wellbeing as evidenced by brain–gut microbiome interactions
In 2019, the COVID-19 outbreak was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO), with 590 million confirmed cases and 6.4 million deaths worldwide as of August 2022 (ref. 1 ). To contain the spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) across the globe, many national and local governments implemented often drastic restrictions as preventive health measures. Consequently, the pandemic has not only led to potential SARS-CoV-2 exposure, infection and disease but also to a wide range of policies consisting of mask requirements, quarantines, lockdowns, physical distancing and closure of non-essential services, with unprecedented societal and economic consequences.
As the world is slowly gaining control over COVID-19, it is timely and essential to ask how the pandemic has affected global mental health. Indirect effects include stress-evoking and disruptive societal changes, which may detrimentally affect mental health in the general population. Direct effects include SARS-CoV-2-mediated acute and long-lasting neuropsychiatric sequelae in affected individuals that occur during primary infection or as part of post-acute COVID syndrome (PACS) 2 —defined as symptoms lasting beyond 3–4 weeks that can involve multiple organs, including the brain. Several terminologies exist for characterizing the effects of COVID-19. PACS also includes late sequalae that constitute a clinical diagnosis of ‘long COVID’ where persistent symptoms are still present 12 weeks after initial infection and cannot be attributed to other conditions 3 .
Here we review both the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 on mental health. First, we summarize empirical findings on how the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted population mental health, through mental health symptom reports, mental disorder prevalence and suicide rates. Second, we describe mental health sequalae of SARS-CoV-2 virus infection and COVID-19 disease (for example, cognitive impairment, fatigue and affective symptoms). For this, we use the term PACS for neuropsychiatric consequences beyond the acute period, and will also describe the underlying neurobiological impact on brain structure and function. We conclude with a discussion of the lessons learned and knowledge gaps that need to be further addressed.
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on population mental health
Independent of the pandemic, mental disorders are known to be prevalent globally and cause a very high disease burden 4 , 5 , 6 . For most common mental disorders (including major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders and alcohol use disorder), environmental stressors play a major etiological role. Disruptive and unpredictable pandemic circumstances may increase distress levels in many individuals, at least temporarily. However, it should be noted that the pandemic not only resulted in negative stressors but also in positive and potentially buffering changes for some, including a better work–life balance, improved family dynamics and enhanced feelings of closeness 7 .
Awareness of the potential mental health impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is reflected in the more than 35,000 papers published on this topic. However, this rapid research output comes with a cost: conclusions from many papers are limited due to small sample sizes, convenience sampling with unclear generalizability implications and lack of a pre-COVID-19 comparison. More reliable estimates of the pandemic mental health impact come from studies with longitudinal or time-series designs that include a pre-pandemic comparison. In our description of the evidence, we, therefore, explicitly focused on findings from meta-analyses that include longitudinal studies with data before the pandemic, as recently identified through a systematic literature search by the WHO 8 .
Self-reported mental health problems
Most studies examining the pandemic impact on mental health used online data collection methods to measure self-reported common indicators, such as mood, anxiety or general psychological distress. Pooled prevalence estimates of clinically relevant high levels of depression and anxiety symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic range widely—between 20% and 35% 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 —but are difficult to interpret due to large methodological and sample heterogeneity. It also is important to note that high levels of self-reported mental health problems identify increased vulnerability and signal an increased risk for mental disorders, but they do not equal clinical caseness levels, which are generally much lower.
Three meta-analyses, pooling data from between 11 and 61 studies and involving ~50,000 individuals or more 13 , 14 , 15 , compared levels of self-reported mental health problems during the COVID-19 pandemic with those before the pandemic. Meta-analyses report on pooled effect sizes—that is, weighted averages of study-level effect sizes; these are generally considered small when they are ~0.2, moderate when ~0.5 and large when ~0.8. As shown in Table 1 , meta-analyses on mental health impact of the COVID-19 pandemic reach consistent conclusions and indicate that there has been a heterogeneous, statistically significant but small increase in self-reported mental health problems, with pooled effect sizes ranging from 0.07 to 0.27. The largest symptom increase was found when using specific mental health outcome measures assessing depression or anxiety symptoms. In addition, loneliness—a strong correlate of depression and anxiety—showed a small but significant increase during the pandemic (Table 1 ; effect size = 0.27) 16 . In contrast, self-reported general mental health and well-being indicators did not show significant change, and psychotic symptoms seemed to have decreased slightly 13 . In Europe, alcohol purchase decreased, but high-level drinking patterns solidified among those with pre-pandemic high drinking levels 17 . When compared to pre-COVID levels, no change in self-reported alcohol use (effect size = −0.01) was observed in a recent meta-analysis summarizing 128 studies from 58 (predominantly European and North American) countries 18 .
What is the time trajectory of self-reported mental health problems during the pandemic? Although findings are not uniform, various large-scale studies confirmed that the increase in mental health problems was highest during the first peak months of the pandemic and smaller—but not fully gone—in subsequent months when infection rates declined and social restrictions eased 13 , 19 , 20 . Psychological distress reports in the United Kingdom increased again during the second lockdown period 15 . Direct associations between anxiety and depression symptom levels and the average number of daily COVID-19 cases were confirmed in the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) data 21 . Studies that examined longer-term trajectories of symptoms during the first or even second year of the COVID-19 pandemic are more sparse but revealed stability of symptoms without clear evidence of recovery 15 , 22 . The exception appears to be for loneliness, as some studies confirmed further increasing trends throughout the first COVID-19 pandemic year 22 , 23 . As most published population-based studies were conducted in the early time period in which absolute numbers of SARS-CoV2-infected individuals were still low, the mental health impacts described in such studies are most likely due to indirect rather than direct effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, it is possible that, in longer-term or later studies, these direct and indirect effects may be more intertwined.
The extent to which governmental policies and communication have impacted on population mental health is a relevant question. In cross-country comparisons, the extent of social restrictions showed a dose–response relationship with mental health problems 24 , 25 . In a review of 33 studies worldwide, it was concluded that governments that enacted stringent measures to contain the spread of COVID-19 benefitted not only the physical but also the mental health of their population during the pandemic 26 , even though more stringent policies may lead to more short-term mental distress 25 . It has been suggested that effective communication of risks, choices and policy measures may reduce polarization and conspiracy theories and mitigate the mental health impact of such measures 25 , 27 , 28 .
In sum, the general pattern of results is that of an increase in mental health symptoms in the population, especially during the first pandemic months, that remained elevated throughout 2020 and early 2021. It should be emphasized that this increase has a small effect size. However, even a small upward shift in mental health problems warrants attention as it has not yet shown to be returned to pre-pandemic levels, and it may have meaningful cumulative consequences at the population level. In addition, even a small effect size may mask a substantial heterogeneity in mental health impact, which may have affected vulnerable groups disproportionally (see below).
Mental disorders, self-harm and suicide
Whether the observed increase in mental health problems during the COVID-19 pandemic has translated into more mental disorders or even suicide mortality is not easy to answer. Mental disorders, characterized by more severe, disabling and persistent symptoms than self-reported mental health problems, are usually diagnosed by a clinician based on the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (DSM-5) criteria or with validated semi-structured clinical interviews. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic, research systematically examining the population prevalence of mental disorders has been sparse. Unfortunately, we can also not strongly rely on healthcare use studies as the pandemic impacted on healthcare provision more broadly, thereby making figures of patient admissions difficult to interpret.
On a global scale and based on imputations and modeling from survey data of self-reported mental health problems, the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study 29 estimated that the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a 28% (95% uncertainty interval (UI): 25–30) increase in major depressive disorders and a 26% (95% UI: 23–28) increase in anxiety disorders. It should be noted that these estimations come with high uncertainty as the assumption that transient pandemic-related increases in mental symptoms extrapolate into incident mental disorders remains disputable. So far, only four longitudinal population-based studies have measured and compared current mental (that is, depressive and anxiety) disorder prevalence—defined using psychiatric diagnostic criteria—before and during the pandemic. Of these, two found no change 30 , 31 , one found a decrease 32 and one found an increase in prevalence of these disorders 33 . These studies were local, limited to high-income countries, often small-scale and used different modes of assessment (for example, online versus in-person) before and during the pandemic. This renders these observational results uncertain as well, but their contrast to the GBD calculations 29 is striking.
Time-series analysis of monthly suicide trends in 21 middle-income to high-income countries across the globe yielded no evidence for an increase in suicide rates in the first 4 months of the pandemic, and there was evidence of a fall in rates in 12 countries 34 . Also in the United States, there was a significant decrease in suicide mortality in the first pandemic months but a slight increase in mortality due to drug overdose and homicide 35 . A living systematic review 36 also concluded that, throughout 2020, there was no observed increase in suicide rates in 20 studies conducted in North America, Europe and Asia. Analyses of electronic health record data in the primary care setting showed reduced rates of self-harm during the first COVID-19 pandemic year 37 . In contrast, emergency department visits for self-harm behavior were unchanged 38 or increased 39 . Such inconsistent findings across healthcare settings may reflect a reluctance in healthcare-seeking behavior for mental healthcare issues. In the living systematic review, eight of 11 studies that examined service use data found a significant decrease in reported self-harm/suicide attempts after COVID lockdown, which returned to pre-lockdown levels in some studies with longer follow-up (5 months) 36 .
In sum, although calculations based on survey data predict a global increase of mental disorder prevalence, objective and consistent evidence for an increased mental disorder, self-harm or suicide prevalence or incidence during the first pandemic year remains absent. This observation, coupled with the only small increase in mental health symptom levels in the overall population, may suggest that most of the general population has demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptation. However, alternative interpretations are possible. First, there is a large degree of heterogeneity in the mental health impact of COVID-19, and increased mental health in one group (for example, due to better work–family balance and work flexibility) may have masked mental health problems in others. Various societal responses seen in many countries, such as community support activities and bolstering mental health and crisis services, may have had mitigating effects on the mental health burden. Also, the relationship between mental health symptom increases during stressful periods and its subsequent effects on the incidence of mental disorders may be non-linear or could be less visible due to resulting alternative outcomes, such as drug overdose or homicide. Finally, we cannot rule out a lag-time effect, where disorders may take more time to develop or be picked up, especially because some of the personal financial or social consequences of the COVID pandemic may only become apparent later. It should be noted that data from low-income countries and longer-term studies beyond the first pandemic year are largely absent.
Which individuals are most affected by the COVID-19 pandemic?
There is substantial heterogeneity across studies that evaluated how the COVID pandemic impacted on mental health 13 , 14 , 15 . Although our society as a whole may have the ability to adequately bounce back from pandemic effects, there are vulnerable people who have been affected more than others.
First, women have consistently reported larger increases in mental health problems in response to the COVID-19 pandemic than men 13 , 15 , 29 , 40 , with meta-analytic effect sizes being 44% 15 to 75% 13 higher. This could reflect both higher stress vulnerability or larger daily life disruptions due to, for example, increased childcare responsibilities, exposure to home violence or greater economic impact due to employment disruptions that all disproportionately fell to women 41 , thereby exacerbating the already existing pre-pandemic gender inequalities in depression and anxiety levels. In addition, adolescents and young adults have been disproportionately affected compared to younger children and older adults 12 , 15 , 29 , 40 . This may be the result of unfavorable behavioral and social changes (for example, school closure periods 42 ) during a crucial development phase where social interactions outside the family context are pivotal. Alarmingly, even though suicide rates did not seem to increase at the population level, studies in China 43 and Japan 44 indicated significant increases in suicide rates in children and adolescents.
Existing socio-cultural disparities in mental health may have further widened during the COVID pandemic. Whether the impact is larger for individuals with low socio-economic status remains unclear, with contrasting meta-analyses pointing toward this group being protected 15 or at increased risk 40 . Earlier meta-analyses did not find that the mental health impact of COVID-19 differed across Europe, North America, Asia and Oceania 13 , 14 , but data are lacking from Africa and South America. Nevertheless, a large-scale within-country comparison in the United States found that the mental health of Black, Hispanic and Asian respondents worsened relatively more during the pandemic compared to White respondents. Moreover, White respondents were more likely to receive professional mental healthcare during the pandemic, and, conversely, Black, Hispanic, and Asian respondents demonstrated higher levels of unmet mental healthcare needs during this time 45 .
People with pre-existing somatic conditions represent another vulnerable group in which the pandemic had a greater impact (pooled effect size of 0.25) 13 . This includes people with conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis or cardiometabolic disease as well as those with multiple comorbidities. The disproportionate impact may reflect this groupʼs elevated COVID-19 risk and, consequently, more perceived stress and fear of infection, but it could also reflect disruptions of regular healthcare services.
Healthcare workers faced increased workload, rapidly changing and challenging work environments and exposure to infections and death, accompanied by fear of infecting themselves and their families. High prevalences of (subthreshold) depression (13% 46 ), depressive symptoms (31% 47 ), (subthreshold) anxiety (16% 46 ), anxiety symptoms (23% 47 ) and post-traumatic stress disorder (~22% 46 , 47 ) have been reported in healthcare workers. However, a meta-analysis did not find a larger mental health impact of the pandemic as compared to the general population 40 , and another meta-analysis (of 206 studies) found that the mental health status of healthcare workers was similar to or even better than that of the general population during the first COVID year 48 . However, it is important to note that these meta-analyses could not differentiate between frontline and non-frontline healthcare workers.
Finally, individuals with pre-existing mental disorders may be at increased risk for exacerbation of mental ill-health during the pandemic, possibly due to disease history—illustrating a higher genetic and/or environmental vulnerability—but also due to discontinuity of mental healthcare. Already before the pandemic, mental health systems were under-resourced and disorganized in most countries 6 , 49 , but a third of all WHO member states reported disruptions to mental and substance use services during the first 18 months of the pandemic 50 , with reduced, shortened or postponed appointments and limited capacity for acute inpatient admissions 51 , 52 . Despite this, there is no clear evidence that individuals with pre-existing mental disorders are disproportionately affected by pandemic-related societal disruptions; the effect size for pandemic impact on self-reported mental health problems was similar in psychiatric patients and the general population 13 . In the United States, emergency visits for ten different mental disorders were generally stable during the pandemic compared to earlier periods 53 . In a large Dutch study 22 , 54 with multiple pre-pandemic and during-pandemic assessments, there was no difference in symptom increase among patients relative to controls (see Fig. 1 for illustration). In absolute terms, however, it is important to note that psychiatric patients show much higher symptom levels of depression, anxiety, loneliness and COVID-fear than healthy controls. Again, variation in mental health changes during the pandemic is large: next to psychiatric patients who showed symptom decrease due to, for example, experiencing relief from social pressures, there certainly have been many patients with symptom increases and relapses during the pandemic.
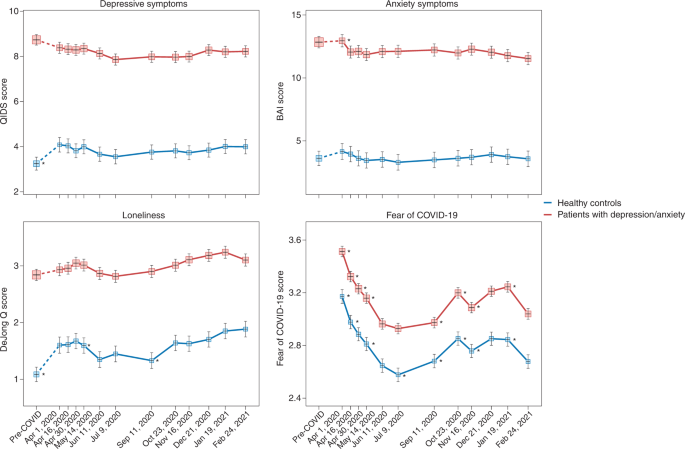
Trajectories of mean depressive symptoms (QIDS score), anxiety symptoms (BAI score), loneliness (De Jong questionnaire score) and Fear of COVID-19 score before and during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in healthy controls (blue line, n = 378) and in patients with depressive and/or anxiety disorders (red line, n = 908). The x -axis indicates time with one pre-COVID assessment (averaged over up to five earlier assessments conducted between 2006 and 2019) and 11 online assessments during April 2020 through February 2021. Symbols indicate the mean score during the assessment with 95% CIs. As compared to pre-COVID assessment scores, the figure shows a statistically significant increase of depression and loneliness symptoms during the first pandemic peak (April 2020) in healthy controls but not in patients (for more details, see refs. 22 , 54 ). Asterisks indicate where subsequent wave scores differ from the prior wave scores ( P < 0.05). The figure also illustrates the stability of depressive and anxiety symptoms during the first COVID year, a significant increase in loneliness during this period and fluctuations of Fear of COVID-19 score that positively correlate with infection rates in the Netherlands. Raw data are from the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA), which were re-analyzed for the current plots to illustrate differences between two groups (healthy controls versus patients). BAI, Beck Anxiety Inventory; QIDS, Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptoms.
Impact of COVID-19 infection and disease on mental health and the brain
Not only the pandemic but also COVID-19 itself can have severe impact on the mental health of affected individuals and, thus, of the population at large. Below we describe acute and post-acute neuropsychiatric sequelae seen in patients with COVID-19 and link these to neurobiological mechanisms.
Neuropsychiatric sequelae in individuals with COVID-19
Common symptoms associated with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection include headache, anosmia (loss of sense of smell) and dysgeusia (loss of sense of taste). The broader neuropsychiatric impact is dependent on infection severity and is very heterogeneous (Table 2 ). It ranges from no neuropsychiatric symptoms among the large group of asymptomatic COVID-19 cases to milder transient neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as fatigue, sleep disturbance and cognitive impairment, predominantly occurring among symptomatic patients with COVID-19 (ref. 55 ). Cognitive impairment consists of sustained memory impairments and executive dysfunction, including short-term memory loss, concentration problems, word-finding problems and impaired daily problem-solving, colloquially termed ‘brain fog’ by patients and clinicians. A small number of infected individuals become severely ill and require hospitalization. During hospital admission, the predominant neuropsychiatric outcome is delirium 56 . Delirium occurs among one-third of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and among over half of patients with COVID-19 who require intensive care unit (ICU) treatment. These delirium rates seem similar to those observed among individuals with severe illness hospitalized for other general medical conditions 57 . Delirium is associated with neuropsychiatric sequalae after hospitalization, as part of post-intensive care syndrome 58 , in which sepsis and inflammation are associated with cognitive dysfunction and an increased risk of a broad range of psychiatric symptoms, from anxiety to depression and psychotic symptoms with hallucinations 59 , 60 .
A subset of patients with COVID-19 develop PACS 61 , which can include neuropsychiatric symptoms. A large meta-analysis summarizes 51 studies involving 18,917 patients with a mean follow-up of 77 days (range, 14–182 days) 62 . The most prevalent neuropsychiatric symptom associated with COVID-19 was sleep disturbance, with a pooled prevalence of 27.4%, followed by fatigue (24.4%), cognitive impairment (20.2%), anxiety symptoms (19.1%), post-traumatic stress symptoms (15.7%) and depression symptoms (12.9%) (Table 2 ). Another meta-analysis that assessed patients 12 weeks or more after confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis found that 32% experienced fatigue, and 22% experienced cognitive impairment 63 . To what extent neuropsychiatric symptoms are truly unique for patients with COVID remains unclear from these meta-analyses, as hardly any study included well-matched controls with other types of respiratory infections or inflammatory conditions.
Studies based on electronic health records have examined whether higher levels of neuropsychiatric symptoms truly translate into a higher incidence of clinically overt mental disorders 64 , 65 . In a 1-year follow-up using the US Veterans Affairs database, 153,848 survivors of SARS-CoV-2 infection exhibited an increased incidence of any mental disorder with a relative risk of 1.46 and, specifically, 1.35 for anxiety disorders, 1.39 for depressive disorders and 1.38 for stress and adjustment disorders, compared to a contemporary group and a historical control group ( n = 5,859,251) 65 . In absolute numbers, the incident risk difference attributable to SARS-CoV-2 for mental disorders was 64 per 1,000 individuals. Taquet et al. 64 analyzed electronic health records from the US-based TriNetX network with over 81 million patients and 236,379 COVID-19 survivors followed for 6 months. In absolute numbers, 6-month incidence of hospital contacts related to diagnoses of anxiety, affective disorder or psychotic disorder was 7.0%, 4.5% and 0.4%, respectively. Risks of incident neurological or psychiatric diagnoses were directly correlated with COVID-19 severity and increased by 78% when compared to influenza and by 32% when compared to other respiratory tract infections. In contrast, a medical record study involving 8.3 million adults confirmed that neuropsychiatric disorders were significantly elevated among COVID-19 hospitalized individuals but to a similar extent as in hospitalized patients with other severe respiratory disease 66 . In line with this, a study using language processing of clinical notes in electronic health records did not find an increase in fatigue, mood and anxiety symptoms among COVID-19 hospitalized individuals when compared to hospitalized patients for other indications and adjusted for sociodemographic features and hospital course 67 . It is important to note that research based only on hospital records might be influenced by increased health-seeking behavior that could be differential across care settings or by increased follow-up by hospitals of patients with COVID-19 (compared to patients with other conditions).
Consequently, whether PACS symptoms form a unique pattern due to specific infection with SARS-CoV-2 remains debatable. Prospective case–control studies that do not rely on hospital records but measure the incidence of neuropsychiatric symptoms and diagnoses after COVID-19 are still scarce, but they are critical for distinguishing causation and confounding when characterizing PACS and the uniqueness of neuropsychiatric sequalae after COVID-19 (ref. 68 ). Recent studies with well-matched control groups illustrate that long-term consequences may not be so unique, as they were similar to those observed in patients with other diseases of similar severity, such as after acute myocardial infarction or in ICU patients 56 , 66 . A first prospective follow-up study of COVID-19 survivors and control patients matched on disease severity, age, sex and ICU admission found similar neuropsychiatric outcomes, regarding both new-onset psychiatric diagnosis (19% versus 20%) and neuropsychiatric symptoms (81% versus 93%). However, moderate but significantly worse cognitive outcomes 6 months after symptom onset were found among survivors of COVID-19 (ref. 69 ). In line with this, a longitudinal study of 785 participants from the UK Biobank showed small but significant cognitive impairment among individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 compared to matched controls 70 .
Numerous psychosocial mechanisms can lead to neuropsychiatric sequalae of COVID-19, including functional impairment; psychological impact due to, for example, fear of dying; stress of being infected with a novel pandemic disease; isolation as part of quarantine and lack of social support; fear/guilt of spreading COVID-19 to family or community; and socioeconomic distress by lost wages 71 . However, there is also ample evidence that neurobiological mechanisms play an important role, which is discussed below.
Neurobiological mechanisms underlying neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19
Acute neuropsychiatric symptoms among patients with severe COVID-19 have been found to correlate with the level of serum inflammatory markers 72 and coincide with neuroimaging findings of immune activation, including leukoencephalopathy, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum or cranial nerve enhancement 73 . Rare presentations, including meningitis, encephalitis, inflammatory demyelination, cerebral infarction and acute hemorrhagic necrotizing encephalopathy, have also been reported 74 . Hospitalized patients with frank encephalopathies display impaired blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity with leptomeningeal enhancement on brain magnetic resonance images 75 . Studies of postmortem specimens from patients who succumbed to acute COVID-19 reveal significant neuropathology with signs of hypoxic damage and neuroinflammation. These include evidence of BBB permeability with extravasation of fibrinogen, microglial activation, astrogliosis, leukocyte infiltration and microhemorrhages 76 , 77 . However, it is still unclear to what extent these findings differ from patients with similar illness severity due to acute non-COVID illness, as these brain effects might not be virus-specific effects but rather due to cytokine-mediated neuroinflammation and critical illness.
Post-acute neuroimaging studies in SARS-CoV-2-recovered patients, as compared to control patients without COVID-19, reveal numerous alterations in brain structure on a group level, although effect sizes are generally small. These include minor reduction in gray matter thickness in the various regions of the cortex and within the corpus collosum, diffuse edema, increases in markers of tissue damage in regions functionally connected to the olfactory cortex and reductions in overall brain size 70 , 78 . Neuroimaging studies of post-acute COVID-19 patients also report abnormalities consistent with micro-structural and functional alterations, specifically within the hippocampus 79 , 80 , a brain region critical for memory formation and regulating anxiety, mood and stress responses, but also within gray matter areas involving the olfactory system and cingulate cortex 80 . Overall, these findings are in line with ongoing anosmia, tremors, affect problems and cognitive impairment.
Interestingly, despite findings mentioned above, there is little evidence of SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion with productive replication, and viral material is rarely found in the central nervous system (CNS) of patients with COVID-19 (refs. 76 , 77 , 81 ). Thus, neurobiological mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-mediated neuropsychiatric sequelae remain unclear, especially in patients who initially present with milder forms of COVID-19. Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with hypoxia, cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and dysregulated innate and adaptive immune responses (reviewed in ref. 82 ). All these effects could contribute to neuroinflammation and endothelial cell activation (Fig. 2 ). Examination of cerebrospinal fluid in patients with neuroimaging findings revealed elevated levels of pro-inflammatory, BBB-destabilizing cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, IL-8 and mononuclear cell chemoattractants 83 , 84 . Whether these cytokines arise from the periphery, due to COVID-19-mediated CRS, or from within the CNS, is unclear. As studies generally lack control patients with other severe illnesses, the specificity of such findings to SARS-CoV-2 also remains unclear. Systemic inflammatory processes, including cytokine release, have been linked to glial activation with expression of chemoattractants that recruit immune cells, leading to neuroinflammation and injury 85 . Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of neurofilament light, a biomarker of neuronal damage, were reportedly elevated in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 regardless of whether they exhibited neurologic diseases 86 . Acute thromboembolic events leading to ischemic infarcts are also common in patients with COVID-19 due to a potentially increased pro-coagulant process secondary to CRS 87 .
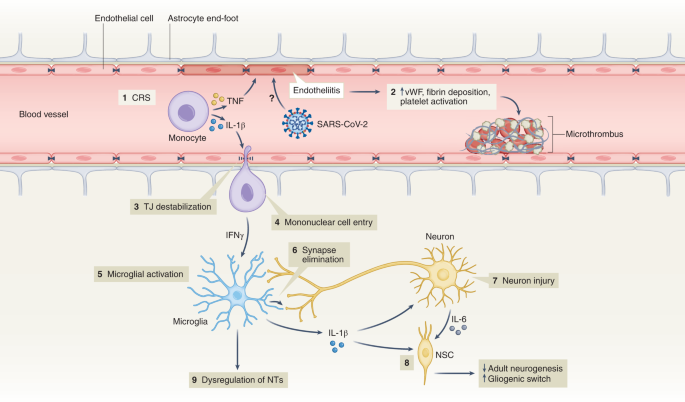
(1) Elevation of BBB-destabilizing cytokines (IL-1β and TNF) within the serum due to CRS or local interactions of mononuclear and endothelial cells. (2) Virus-induced endotheliitis increases susceptibility to microthrombus formation due to platelet activation, elevation of vWF and fibrin deposition. (3) Cytokine, mononuclear and endothelial cell interactions promote disruption of the BBB, which may allow entry of leukocytes expressing IFNg into the CNS (4), leading to microglial activation (5). (6) Activated microglia may eliminate synapses and/or express cytokines that promote neuronal injury. (7) Injured neurons express IL-6 which, together with IL-1β, promote a ‘gliogenic switch’ in NSCs (8), decreasing adult neurogenesis. (9) The combination of microglial (and possibly astrocyte) activation, neuronal injury and synapse loss may lead to dysregulation of NTs and neuronal circuitry. IFNg, interferon-g; NSC, neural stem cell; NT, neurotransmitter; TJ, tight junction; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
It is also unclear whether hospitalized patients with COVID-19 may develop brain abnormalities due to hypoxia or CRS rather than as a direct effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Hypoxia may cause neuronal dysfunction, cerebral edema, increased BBB permeability, cytokine expression and onset of neurodegenerative diseases 88 , 89 . CRS, with life-threatening levels of serum TNF-α and IL-1 (ref. 90 ) could also impact BBB function, as these cytokines destabilize microvasculature endothelial cell junctional proteins critical for BBB integrity 91 . In mild SARS-CoV-2 infection, circulating immune factors combined with mild hypoxia might impact BBB function and lead to neuroinflammation 92 , as observed during infection with other non-neuroinvasive respiratory pathogens 93 . However, multiple studies suggest that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein itself may also induce venous and arterial endothelial cell activation and endotheliitis, disrupt BBB integrity or cross the BBB via adoptive transcytosis 94 , 95 , 96 .
Reducing neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19
The increased risk of COVID-19-related neuropsychiatric sequalae was most pronounced during the first pandemic peak but reduced over the subsequent 2 years 64 , 97 . This may be due to reduced impact of newer SARS-CoV-2 strains (that is, Omicron) but also protective effects of vaccination, which limit SARS-CoV-2 spread and may, thus, prevent neuropsychiatric sequalae. Fully vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections exhibit a 50% reduction in PACS 98 , even though vaccination does not improve PACS-related neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with a prior history of COVID-19 (ref. 99 ). As patients with pre-existing mental disorders are at increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, they deserve to be among the prioritization groups for vaccination efforts 100 .
Adequate treatment strategies for neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19 are needed. As no specific evidence-based intervention yet exists, the best current treatment approach is that for neuropsychiatric sequelae arising after other severe medical conditions 101 . Stepped care—a staged approach of mental health services comprising a hierarchy of interventions, from least to most intensive, matched to the individual’s need—is efficacious with monitoring of mental health and cognitive problems. Milder symptoms likely benefit from counseling and holistic care, including physiotherapy, psychotherapy and rehabilitation. Individuals with moderate to severe symptoms fulfilling psychiatric diagnoses should receive guideline-concordant care for these disorders 61 . Patients with pre-existing mental disorders also deserve special attention when affected by COVID-19, as they have shown to have an increased risk of COVID-19-related hospitalization, complications and death 102 . This may involve interventions to address their general health, any unfavorable socioenvironmental factors, substance abuse or treatment adherence issues.
Lessons learned, knowledge gaps and future challenges
Ultimately, it is not only the millions of people who have died from COVID-19 worldwide that we remember but also the distress experienced during an unpredictable period with overstretched healthcare systems, lockdowns, school closures and changing work environments. In a world that is more and more globalized, connectivity puts us at risk for future pandemics. What can be learned from the last 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic about how to handle future and longstanding challenges related to mental health?
Give mental health equal priority to physical health
The COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated that our population seems quite resilient and adaptive. Nevertheless, even if society as a whole may bounce back, there is a large group of people whose mental health has been and will be disproportionately affected by this and future crises. Although various groups, such as the WHO 8 , the National Health Commission of China 103 , the Asia Pacific Disaster Mental Health Network 104 and a National Taskforce in India 105 , developed mental health policies early on, many countries were late in realizing that a mental health agenda deserves immediate attention in a rapidly evolving pandemic. Implementation of comprehensive and integrated mental health policies was generally inconsistent and suboptimal 106 and often in the shadow of policies directed at containing and reducing the spread of SARS-CoV-2. Leadership is needed to convey the message that mental health is as important as physical health and that we should focus specific attention and early interventions on those at the highest risk. This includes those vulnerable due to factors such as low socioeconomic status, specific developmental life phase (adolescents and young adults), pre-existing risk (poor physical or somatic health and early life trauma) or high exposure to pandemic-related (work) changes—for example, women and healthcare personnel. This means that not only should investment in youth and reducing health inequalities remain at the top of any policy agenda but also that mental health should be explicitly addressed from the start in any future global health crisis situation.
Communication and trust is crucial for mental health
Uncertainty and uncontrollability during the pandemic have challenged rational thinking. Negative news travels fast. Communication that is vague, one-sided and dishonest can negatively impact on mental health and amplify existing distress and anxiety 107 . Media reporting should not overemphasize negative mental health impact—for example, putative suicide rate increases or individual negative experiences—which could make situations worse than they actually are. Instead, communication during crises requires concrete and actionable advice that avoids polarization and strengthens vigilance, to foster resilience and help prevent escalation to severe mental health problems 108 , 109 .
Rapid research should be collaborative and high-quality
Within the scientific community, the topic of mental health during the pandemic led to a multitude of rapid studies that generally had limited methodological quality—for example, cross-sectional designs, small or selective sampling or study designs lacking valid comparison groups. These contributed rather little to our understanding of the mental health impact of the emerging crisis. In future events that have global mental health impact, where possible, collaborative and interdisciplinary efforts with well-powered and well-controlled prospective studies using standardized instruments will be crucial. Only with fine-grained determinants and outcomes can data reliably inform mental health policies and identify who is most at risk.
Do not neglect long-term mental health effects
So far, research has mainly focused on the acute and short-term effects of the pandemic on mental health, usually spanning pandemic effects over several months to 1 year. However, longer follow-up of how a pandemic impacts population mental health is essential. Can societal and economic disruptions after the pandemic increase risk of mental disorders at a later stage when the acute pandemic effects have subsided? Do increased self-reported mental health problems return to pre-pandemic levels, and which groups of individuals remain most affected in the long-term? We need to realize that certain pandemic consequences, particularly those affecting income and school/work careers, may become visible only over the course of several years. Consequently, we should maintain focus and continue to monitor and quantify the effects of the pandemic in the years to come—for example, by monitoring mental healthcare use and suicide. This should include specific at-risk populations (for example, adolescents) and understudied populations in low-income and middle-income countries.
Pay attention to mental health consequences of infectious diseases
Even though our knowledge on PACS is rapidly expanding, there are still many unanswered questions related to who is at risk, the long-term course trajectories and the best ways to intervene early. Consequently, we need to be aware of the neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19 and, for that matter, of any infectious disease. Clinical attention and research should be directed toward alleviating potential neuropsychiatric ramifications of COVID-19. Next to clinical studies, studies using human tissues and appropriate animal models are pivotal to determine the CNS region-specific and neural-cell-specific effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the induced immune activation. Indeed, absence of SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion is an opportunity to learn and discover how peripheral neuroimmune mechanisms can contribute to neuropsychiatric sequelae in susceptible individuals. This emphasizes the importance of an interdisciplinary approach where somatic and mental health efforts are combined but also the need to integrate clinical parameters after infection with biological parameters (for example, serum, cerebrospinal fluid and/or neuroimaging) to predict who is at risk for PACS and deliver more targeted treatments.
Prepare mental healthcare infrastructure for pandemic times
If we take mental health seriously, we should not only monitor it but also develop the resources and infrastructure necessary for rapid early intervention, particularly for specific vulnerable groups. For adequate mental healthcare to be ready for pandemic times, primary care, community mental health and public mental health should be prepared. In many countries, health services were not able to meet the population’s mental health needs before the pandemic, which substantially worsened during the pandemic. We should ensure rapid access to mental health services but also address the underlying drivers of poor mental health, such as mitigating risks of unemployment, sexual violence and poverty. Collaboration in early stages across disciplines and expertise is essential. Anticipating disruption to face-to-face services, mental healthcare providers should be more prepared for consultations, therapy and follow-up by telephone, video-conferencing platforms and web applications 51 , 52 . The pandemic has shown that an inadequate infrastructure, pre-existing inequalities and low levels of technological literacy hindered the use and uptake of e-health, both in healthcare providers and in patients across different care settings. The necessary investments can ensure rapid upscaling of mental health services during future pandemics for those individuals with a high mental health need due to societal changes, government measures, fear of infection or infection itself.
Even though much attention has been paid to the physical health consequences of COVID-19, mental health has unjustly received less attention. There is an urgent need to prepare our research and healthcare infrastructures not only for adequate monitoring of the long-term mental health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic but also for future crises that will shape mental health. This will require collaboration to ensure interdisciplinary and sound research and to provide attention and care at an early stage for those individuals who are most vulnerable—giving mental health equal priority to physical health from the very start.
WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard (WHO, 2022; https://covid19.who.int/
Rando, H. M. et al. Challenges in defining long COVID: striking differences across literature, electronic health records, and patient-reported information. Preprint at https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.03.20.21253896v1 (2021).
Nalbandian, A. et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat. Med. 27 , 601–615 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Abbafati, C. et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 396 , 1204–1222 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Penninx, B. W., Pine, D. S., Holmes, E. A. & Reif, A. Anxiety disorders. Lancet 397 , 914–927 (2021).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Herrman, H. et al. Time for united action on depression: a Lancet –World Psychiatric Association Commission. Lancet 399 , 957–1022 (2022).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Radka, K., Wyeth, E. H. & Derrett, S. A qualitative study of living through the first New Zealand COVID-19 lockdown: affordances, positive outcomes, and reflections. Prev. Med. Rep. 26 , 101725 (2022).
Mental Health and COVID-19: Early Evidence of the Pandemic’s Impact (WHO, 2022).
Dragioti, E. et al. A large-scale meta-analytic atlas of mental health problems prevalence during the COVID-19 early pandemic. J. Med. Virol. 94 , 1935–1949 (2022).
Zhang, S. X. et al. Mental disorder symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic in Latin America—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 31 , e23 (2022).
Zhang, S. X. et al. Meta-analytic evidence of depression and anxiety in Eastern Europe during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol . 13 , 2000132 (2022).
Racine, N. et al. Global prevalence of depressive and anxiety symptoms in children and adolescents during COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 175 , 1142–1150 (2021).
Robinson, E., Sutin, A. R., Daly, M. & Jones, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies comparing mental health before versus during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. J. Affect. Disord. 296 , 567–576 (2022).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Prati, G. & Mancini, A. D. The psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns: a review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies and natural experiments. Psychol. Med. 51 , 201–211 (2021).
Patel, K. et al. Psychological distress before and during the COVID-19 pandemic among adults in the United Kingdom based on coordinated analyses of 11 longitudinal studies. JAMA Netw. Open 5 , e227629 (2022).
Ernst, M. et al. Loneliness before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Am. Psychol . 77 , 660–677 (2022).
Kilian, C. et al. Changes in alcohol use during the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Drug Alcohol Rev . 41 , 918–931 (2022).
Acuff, S. F., Strickland, J. C., Tucker, J. A. & Murphy, J. G. Changes in alcohol use during COVID-19 and associations with contextual and individual difference variables: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 36 , 1–19 (2022).
Varga, T. V. et al. Loneliness, worries, anxiety, and precautionary behaviours in response to the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal analysis of 200,000 Western and Northern Europeans. Lancet Reg. Health Eur . 2 , 100020 (2021).
Fancourt, D., Steptoe, A. & Bu, F. Trajectories of anxiety and depressive symptoms during enforced isolation due to COVID-19 in England: a longitudinal observational study. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 141–149 (2021).
Jia, H. et al. National and state trends in anxiety and depression severity scores among adults during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, 2020–2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 70 , 1427–1432 (2021).
Kok, A. A. L. et al. Mental health and perceived impact during the first Covid-19 pandemic year: a longitudinal study in Dutch case–control cohorts of persons with and without depressive, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 305 , 85–93 (2022).
Su, Y. et al. Prevalence of loneliness and social isolation among older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Psychogeriatr. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610222000199 (2022).
Knox, L., Karantzas, G. C., Romano, D., Feeney, J. A. & Simpson, J. A. One year on: what we have learned about the psychological effects of COVID-19 social restrictions: a meta-analysis. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 46 , 101315 (2022).
Aknin, L. B. et al. Policy stringency and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal analysis of data from 15 countries. Lancet Public Health 7 , e417–e426 (2022).
Lee, Y. et al. Government response moderates the mental health impact of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of depression outcomes across countries. J. Affect. Disord. 290 , 364–377 (2021).
Wu, J. T. et al. Nowcasting epidemics of novel pathogens: lessons from COVID-19. Nat. Med. 27 , 388–395 (2021).
Brooks, S. K. et al. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence. Lancet 395 , 912–920 (2020).
Santomauro, D. F. et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 398 , 1700–1712 (2021).
Knudsen, A. K. S. et al. Prevalence of mental disorders, suicidal ideation and suicides in the general population before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Norway: a population-based repeated cross-sectional analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Eur . 4 , 100071 (2021).
Ayuso-Mateos, J. L. et al. Changes in depression and suicidal ideation under severe lockdown restrictions during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Spain: a longitudinal study in the general population. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci . 30 , e49 (2021).
Vloo, A. et al. Gender differences in the mental health impact of the COVID-19 lockdown: longitudinal evidence from the Netherlands. SSM Popul. Health 15 , 100878 (2021).
Winkler, P. et al. Prevalence of current mental disorders before and during the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic: an analysis of repeated nationwide cross-sectional surveys. J. Psychiatr. Res. 139 , 167–171 (2021).
Pirkis, J. et al. Suicide trends in the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic: an interrupted time-series analysis of preliminary data from 21 countries. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 579–588 (2021).
Faust, J. S. et al. Mortality from drug overdoses, homicides, unintentional injuries, motor vehicle crashes, and suicides during the pandemic, March–August 2020. JAMA 326 , 84–86 (2021).
John, A. et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on self-harm and suicidal behaviour: update of living systematic review. F1000Res. 9 , 1097 (2020).
Steeg, S. et al. Temporal trends in primary care-recorded self-harm during and beyond the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic: time series analysis of electronic healthcare records for 2.8 million patients in the Greater Manchester Care Record. EClinicalMedicine 41 , 101175 (2021).
Rømer, T. B. et al. Psychiatric admissions, referrals, and suicidal behavior before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Denmark: a time-trend study. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 144 , 553–562 (2021).
Holland, K. M. et al. Trends in US emergency department visits for mental health, overdose, and violence outcomes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Psychiatry 78 , 372–379 (2021).
Kunzler, A. M. et al. Mental burden and its risk and protective factors during the early phase of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: systematic review and meta-analyses. Global Health 17 , 34 (2021).
Flor, L. S. et al. Quantifying the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on gender equality on health, social, and economic indicators: a comprehensive review of data from March, 2020, to September, 2021. Lancet 399 , 2381–2397 (2022).
Viner, R. et al. School closures during social lockdown and mental health, health behaviors, and well-being among children and adolescents during the first COVID-19 wave: a systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 176 , 400–409 (2022).
Zheng, X. Y. et al. Trends of injury mortality during the COVID-19 period in Guangdong, China: a population-based retrospective analysis. BMJ Open 11 , e045317 (2021).
Tanaka, T. & Okamoto, S. Increase in suicide following an initial decline during the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5 , 229–238 (2021).
Thomeer, M. B., Moody, M. D. & Yahirun, J. Racial and ethnic disparities in mental health and mental health care during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-021-01006-7 (2022).
Hill, J. E. et al. The prevalence of mental health conditions in healthcare workers during and after a pandemic: systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 78 , 1551–1573 (2022).
Marvaldi, M., Mallet, J., Dubertret, C., Moro, M. R. & Guessoum, S. B. Anxiety, depression, trauma-related, and sleep disorders among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 126 , 252–264 (2021).
Phiri, P. et al. An evaluation of the mental health impact of SARS-CoV-2 on patients, general public and healthcare professionals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 34 , 100806 (2021).
Jorm, A. F., Patten, S. B., Brugha, T. S. & Mojtabai, R. Has increased provision of treatment reduced the prevalence of common mental disorders? Review of the evidence from four countries. World Psychiatry 16 , 90–99 (2017).
Third Round of the Global Pulse Survey on Continuity of Essential Health Services during the COVID-19 Pandemic (WHO, 2021).
Baumgart, J. G. et al. The early impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health facilities and psychiatric professionals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 , 8034 (2021).
Raphael, J., Winter, R. & Berry, K. Adapting practice in mental healthcare settings during the COVID-19 pandemic and other contagions: systematic review. BJPsych Open 7 , e62 (2021).
Anderson, K. N. et al. Changes and inequities in adult mental health-related emergency department visits during the COVID-19 pandemic in the US. JAMA Psychiatry 79 , 475–485 (2022).
Pan, K. Y. et al. The mental health impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people with and without depressive, anxiety, or obsessive-compulsive disorders: a longitudinal study of three Dutch case–control cohorts. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 121–129 (2021).
Dantzer, R., O’Connor, J. C., Freund, G. G., Johnson, R. W. & Kelley, K. W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9 , 46–56 (2008).
Nersesjan, V. et al. Central and peripheral nervous system complications of COVID-19: a prospective tertiary center cohort with 3-month follow-up. J. Neurol. 268 , 3086–3104 (2021).
Wilson, J. E. et al. Delirium. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim . 6 , 90 (2020).
Rawal, G., Yadav, S. & Kumar, R. Post-intensive care syndrome: an overview. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 5 , 90–92 (2017).
Pandharipande, P. P. et al. Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 369 , 1306–1316 (2013).
Girard, T. D. et al. Long-term cognitive impairment after hospitalization for community-acquired pneumonia: a prospective cohort study. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 33 , 929–935 (2018).
Crook, H., Raza, S., Nowell, J., Young, M. & Edison, P. Long covid—mechanisms, risk factors, and management. BMJ 374 , n1648 (2021).
Badenoch, J. B. et al. Persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms after COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Commun . 4 , fcab297 (2021).
Ceban, F. et al. Fatigue and cognitive impairment in post-COVID-19 syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 101 , 93–135 (2022).
Taquet, M., Geddes, J. R., Husain, M., Luciano, S. & Harrison, P. J. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 416–427 (2021).
Xie, Y., Xu, E. & Al-Aly, Z. Risks of mental health outcomes in people with covid-19: cohort study. BMJ 376 , e068993 (2022).
Kieran Clift, A. et al. Neuropsychiatric ramifications of severe COVID-19 and other severe acute respiratory infections. JAMA Psychiatry 79 , 690–698 (2022).
Castro, V. M., Rosand, J., Giacino, J. T., McCoy, T. H. & Perlis, R. H. Case–control study of neuropsychiatric symptoms following COVID-19 hospitalization in 2 academic health systems. Mol. Psych. (in the press).
Amin-Chowdhury, Z. & Ladhani, S. N. Causation or confounding: why controls are critical for characterizing long COVID. Nat. Med. 27 , 1129–1130 (2021).
Nersesjan, V. et al. Neuropsychiatric and cognitive outcomes in patients 6 months after COVID-19 requiring hospitalization compared with matched control patients hospitalized for non-COVID-19 illness. JAMA Psychiatry 79 , 486–497 (2022).
Douaud, G. et al. SARS-CoV-2 is associated with changes in brain structure in UK Biobank. Nature 604 , 697–707 (2022).
Zhang, H. et al. Psychological experience of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and qualitative meta-synthesis. Am. J. Infect. Control 50 , 809–819 (2022).
Mazza, M. G. et al. Anxiety and depression in COVID-19 survivors: role of inflammatory and clinical predictors. Brain Behav. Immun. 89 , 594–600 (2020).
Moonis, G. et al. The spectrum of neuroimaging findings on CT and MRI in adults With COVID-19. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 217 , 959–974 (2021).
Asadi-Pooya, A. A. & Simani, L. Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci . 413 , 116832 (2020).
Lersy, F. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid features in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and neurological manifestations: correlation with brain magnetic resonance imaging findings in 58 patients. J. Infect. Dis. 223 , 600–609 (2021).
Thakur, K. T. et al. COVID-19 neuropathology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center/New York Presbyterian Hospital. Brain 144 , 2696–2708 (2021).
Cosentino, G. et al. Neuropathological findings from COVID-19 patients with neurological symptoms argue against a direct brain invasion of SARS-CoV-2: a critical systematic review. Eur. J. Neurol. 28 , 3856–3865 (2021).
Tian, T. et al. Long-term follow-up of dynamic brain changes in patients recovered from COVID-19 without neurological manifestations. JCI Insight 7 , e155827 (2022).
Lu, Y. et al. Cerebral micro-structural changes in COVID-19 patients—an MRI-based 3-month follow-up study. EClinicalMedicine 25 , 100484 (2020).
Qin, Y. et al . Long-term microstructure and cerebral blood flow changes in patients recovered from COVID-19 without neurological manifestations. J. Clin. Invest . 131 , e147329 (2021).
Matschke, J. et al. Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: a post-mortem case series. Lancet Neurol. 19 , 919–929 (2020).
Shivshankar, P. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection: host response, immunity, and therapeutic targets. Inflammation 45 , 1430–1449 (2022).
Manganotti, P. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid and serum interleukins 6 and 8 during the acute and recovery phase in COVID-19 neuropathy patients. J. Med. Virol. 93 , 5432–5437 (2021).
Farhadian, S. et al. Acute encephalopathy with elevated CSF inflammatory markers as the initial presentation of COVID-19. BMC Neurol . 20 , 248 (2020).
Francistiová, L. et al. Cellular and molecular effects of SARS-CoV-2 linking lung infection to the brain. Front. Immunol . 12 , 730088 (2021).
Paterson, R. W. et al. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid biomarker profiles in acute SARS-CoV-2-associated neurological syndromes. Brain Commun . 3 , fcab099 (2021).
Cryer, M. J. et al. Prothrombotic milieu, thrombotic events and prophylactic anticoagulation in hospitalized COVID-19 positive patients: a review. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost . 28 , 10760296221074353 (2022).
Nalivaeva, N. N. & Rybnikova, E. A. Editorial: Brain hypoxia and ischemia: new insights into neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Front. Neurosci . 13 , 770 (2019).
Brownlee, N. N. M., Wilson, F. C., Curran, D. B., Lyttle, N. & McCann, J. P. Neurocognitive outcomes in adults following cerebral hypoxia: a systematic literature review. NeuroRehabilitation 47 , 83–97 (2020).
Del Valle, D. M. et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 26 , 1636–1643 (2020).
Daniels, B. P. et al. Viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns regulate blood–brain barrier integrity via competing innate cytokine signals. mBio 5 , e01476-14 (2014).
Reynolds, J. L. & Mahajan, S. D. SARS-COV2 alters blood brain barrier integrity contributing to neuro-inflammation. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 16 , 4–6 (2021).
Bohmwald, K., Gálvez, N. M. S., Ríos, M. & Kalergis, A. M. Neurologic alterations due to respiratory virus infections. Front. Cell. Neurosci . 12 , 386 (2018).
Khaddaj-Mallat, R. et al. SARS-CoV-2 deregulates the vascular and immune functions of brain pericytes via spike protein. Neurobiol. Dis . 161 , 105561 (2021).
Qian, Y. et al. Direct activation of endothelial cells by SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is blocked by simvastatin. J Virol. 95 , e0139621 (2021).
Rhea, E. M. et al. The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood–brain barrier in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 24 , 368–378 (2021).
Magnúsdóttir, I. et al. Acute COVID-19 severity and mental health morbidity trajectories in patient populations of six nations: an observational study. Lancet Public Health 7 , e406–e416 (2022).
Antonelli, M. et al. Risk factors and disease profile of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID Symptom Study app: a prospective, community-based, nested, case–control study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22 , 43–55 (2022).
Wisnivesky, J. P. et al. Association of vaccination with the persistence of post-COVID symptoms. J. Gen. Intern. Med . 37 , 1748–1753 (2022).
De Picker, L. J. et al. Severe mental illness and European COVID-19 vaccination strategies. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 356–359 (2021).
Cohen, G. H. et al. Comparison of simulated treatment and cost-effectiveness of a stepped care case-finding intervention vs usual care for posttraumatic stress disorder after a natural disaster. JAMA Psychiatry 74 , 1251–1258 (2017).
Vai, B. et al. Mental disorders and risk of COVID-19-related mortality, hospitalisation, and intensive care unit admission: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 797–812 (2021).
Xiang, Y. T. et al. Timely mental health care for the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak is urgently needed. Lancet Psychiatry 7 , 228 (2020).
Newnham, E. A. et al. The Asia Pacific Disaster Mental Health Network: setting a mental health agenda for the region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17 , 6144 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar
Dandona, R. & Sagar, R. COVID-19 offers an opportunity to reform mental health in India. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 9–11 (2021).
Qiu, D. et al. Policies to improve the mental health of people influenced by COVID-19 in China: a scoping review. Front. Psychiatry 11 , 588137 (2020).
Su, Z. et al. Mental health consequences of COVID-19 media coverage: the need for effective crisis communication practices. Global Health 17 , 4 (2021).
Petersen, M. B. COVID lesson: trust the public with hard truths. Nature 598 , 237 (2021).
van der Bles, A. M., van der Linden, S., Freeman, A. L. J. & Spiegelhalter, D. J. The effects of communicating uncertainty on public trust in facts and numbers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 7672–7683 (2020).
Titze-de-Almeida, R. et al. Persistent, new-onset symptoms and mental health complaints in Long COVID in a Brazilian cohort of non-hospitalized patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 22 , 133 (2022).
Carfì, A., Bernabei, R. & Landi, F. Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19. JAMA 324 , 603–605 (2020).
Bliddal, S. et al. Acute and persistent symptoms in non-hospitalized PCR-confirmed COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 11 , 13153 (2021).
Kim, Y. et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome in patients after 12 months from COVID-19 infection in Korea. BMC Infect. Dis . 22 , 93 (2022).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank E. Giltay for assistance on data analyses and production of Fig. 1 . B.W.J.H.P. discloses support for research and publication of this work from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme-funded RESPOND project (grant no. 101016127).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychiatry, Amsterdam UMC, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Brenda W. J. H. Penninx & Christiaan H. Vinkers
Amsterdam Public Health, Mental Health Program and Amsterdam Neuroscience, Mood, Anxiety, Psychosis, Sleep & Stress Program, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Biological and Precision Psychiatry, Copenhagen Research Center for Mental Health, Mental Health Center Copenhagen, Copenhagen University Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark
Michael E. Benros
Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
Departments of Medicine, Pathology & Immunology and Neuroscience, Center for Neuroimmunology & Neuroinfectious Diseases, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA
Robyn S. Klein
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Brenda W. J. H. Penninx .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Medicine thanks Jane Pirkis and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary handling editor: Karen O’Leary, in collaboration with the Nature Medicine team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Penninx, B.W.J.H., Benros, M.E., Klein, R.S. et al. How COVID-19 shaped mental health: from infection to pandemic effects. Nat Med 28 , 2027–2037 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-02028-2
Download citation
Received : 06 June 2022
Accepted : 26 August 2022
Published : 03 October 2022
Issue Date : October 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-02028-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Mental health disturbance in preclinical medical students and its association with screen time, sleep quality, and depression during the covid-19 pandemic.
- Tjhin Wiguna
- Valerie Josephine Dirjayanto
- Erik Kinzie
BMC Psychiatry (2024)
Protocol for a pilot cluster randomised controlled trial of a multicomponent sustainable return to work IGLOo intervention
- Oliver Davis
- Jeremy Dawson
- Fehmidah Munir
Pilot and Feasibility Studies (2024)
Impact of COVID-19 first wave on the mental health of healthcare workers in a Front-Line Spanish Tertiary Hospital: lessons learned
- Juan D. Molina
- Franco Amigo
- Gabriel Rubio
Scientific Reports (2024)
Long-term risk of psychiatric disorder and psychotropic prescription after SARS-CoV-2 infection among UK general population
- Daniel Prieto-Alhambra
Nature Human Behaviour (2024)
Changes in alcohol consumption and alcohol problems before and after the COVID-19 pandemic: a prospective study in heavy drinking young adults
- Kasey G. Creswell
- Garrett C. Hisler
- Aidan G. C. Wright
Nature Mental Health (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- COVID-19 and your mental health
Worries and anxiety about COVID-19 can be overwhelming. Learn ways to cope as COVID-19 spreads.
At the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, life for many people changed very quickly. Worry and concern were natural partners of all that change — getting used to new routines, loneliness and financial pressure, among other issues. Information overload, rumor and misinformation didn't help.
Worldwide surveys done in 2020 and 2021 found higher than typical levels of stress, insomnia, anxiety and depression. By 2022, levels had lowered but were still higher than before 2020.
Though feelings of distress about COVID-19 may come and go, they are still an issue for many people. You aren't alone if you feel distress due to COVID-19. And you're not alone if you've coped with the stress in less than healthy ways, such as substance use.
But healthier self-care choices can help you cope with COVID-19 or any other challenge you may face.
And knowing when to get help can be the most essential self-care action of all.
Recognize what's typical and what's not
Stress and worry are common during a crisis. But something like the COVID-19 pandemic can push people beyond their ability to cope.
In surveys, the most common symptoms reported were trouble sleeping and feeling anxiety or nervous. The number of people noting those symptoms went up and down in surveys given over time. Depression and loneliness were less common than nervousness or sleep problems, but more consistent across surveys given over time. Among adults, use of drugs, alcohol and other intoxicating substances has increased over time as well.
The first step is to notice how often you feel helpless, sad, angry, irritable, hopeless, anxious or afraid. Some people may feel numb.
Keep track of how often you have trouble focusing on daily tasks or doing routine chores. Are there things that you used to enjoy doing that you stopped doing because of how you feel? Note any big changes in appetite, any substance use, body aches and pains, and problems with sleep.
These feelings may come and go over time. But if these feelings don't go away or make it hard to do your daily tasks, it's time to ask for help.
Get help when you need it
If you're feeling suicidal or thinking of hurting yourself, seek help.
- Contact your healthcare professional or a mental health professional.
- Contact a suicide hotline. In the U.S., call or text 988 to reach the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline , available 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Or use the Lifeline Chat . Services are free and confidential.
If you are worried about yourself or someone else, contact your healthcare professional or mental health professional. Some may be able to see you in person or talk over the phone or online.
You also can reach out to a friend or loved one. Someone in your faith community also could help.
And you may be able to get counseling or a mental health appointment through an employer's employee assistance program.
Another option is information and treatment options from groups such as:
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI).
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
Self-care tips
Some people may use unhealthy ways to cope with anxiety around COVID-19. These unhealthy choices may include things such as misuse of medicines or legal drugs and use of illegal drugs. Unhealthy coping choices also can be things such as sleeping too much or too little, or overeating. It also can include avoiding other people and focusing on only one soothing thing, such as work, television or gaming.
Unhealthy coping methods can worsen mental and physical health. And that is particularly true if you're trying to manage or recover from COVID-19.
Self-care actions can help you restore a healthy balance in your life. They can lessen everyday stress or significant anxiety linked to events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Self-care actions give your body and mind a chance to heal from the problems long-term stress can cause.
Take care of your body
Healthy self-care tips start with the basics. Give your body what it needs and avoid what it doesn't need. Some tips are:
- Get the right amount of sleep for you. A regular sleep schedule, when you go to bed and get up at similar times each day, can help avoid sleep problems.
- Move your body. Regular physical activity and exercise can help reduce anxiety and improve mood. Any activity you can do regularly is a good choice. That may be a scheduled workout, a walk or even dancing to your favorite music.
- Choose healthy food and drinks. Foods that are high in nutrients, such as protein, vitamins and minerals are healthy choices. Avoid food or drink with added sugar, fat or salt.
- Avoid tobacco, alcohol and drugs. If you smoke tobacco or if you vape, you're already at higher risk of lung disease. Because COVID-19 affects the lungs, your risk increases even more. Using alcohol to manage how you feel can make matters worse and reduce your coping skills. Avoid taking illegal drugs or misusing prescriptions to manage your feelings.
Take care of your mind
Healthy coping actions for your brain start with deciding how much news and social media is right for you. Staying informed, especially during a pandemic, helps you make the best choices but do it carefully.
Set aside a specific amount of time to find information in the news or on social media, stay limited to that time, and choose reliable sources. For example, give yourself up to 20 or 30 minutes a day of news and social media. That amount keeps people informed but not overwhelmed.
For COVID-19, consider reliable health sources. Examples are the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Other healthy self-care tips are:
- Relax and recharge. Many people benefit from relaxation exercises such as mindfulness, deep breathing, meditation and yoga. Find an activity that helps you relax and try to do it every day at least for a short time. Fitting time in for hobbies or activities you enjoy can help manage feelings of stress too.
- Stick to your health routine. If you see a healthcare professional for mental health services, keep up with your appointments. And stay up to date with all your wellness tests and screenings.
- Stay in touch and connect with others. Family, friends and your community are part of a healthy mental outlook. Together, you form a healthy support network for concerns or challenges. Social interactions, over time, are linked to a healthier and longer life.
Avoid stigma and discrimination
Stigma can make people feel isolated and even abandoned. They may feel sad, hurt and angry when people in their community avoid them for fear of getting COVID-19. People who have experienced stigma related to COVID-19 include people of Asian descent, health care workers and people with COVID-19.
Treating people differently because of their medical condition, called medical discrimination, isn't new to the COVID-19 pandemic. Stigma has long been a problem for people with various conditions such as Hansen's disease (leprosy), HIV, diabetes and many mental illnesses.
People who experience stigma may be left out or shunned, treated differently, or denied job and school options. They also may be targets of verbal, emotional and physical abuse.
Communication can help end stigma or discrimination. You can address stigma when you:
- Get to know people as more than just an illness. Using respectful language can go a long way toward making people comfortable talking about a health issue.
- Get the facts about COVID-19 or other medical issues from reputable sources such as the CDC and WHO.
- Speak up if you hear or see myths about an illness or people with an illness.
COVID-19 and health
The virus that causes COVID-19 is still a concern for many people. By recognizing when to get help and taking time for your health, life challenges such as COVID-19 can be managed.
- Mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. National Institutes of Health. https://covid19.nih.gov/covid-19-topics/mental-health. Accessed March 12, 2024.
- Mental Health and COVID-19: Early evidence of the pandemic's impact: Scientific brief, 2 March 2022. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Sci_Brief-Mental_health-2022.1. Accessed March 12, 2024.
- Mental health and the pandemic: What U.S. surveys have found. Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/03/02/mental-health-and-the-pandemic-what-u-s-surveys-have-found/. Accessed March 12, 2024.
- Taking care of your emotional health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://emergency.cdc.gov/coping/selfcare.asp. Accessed March 12, 2024.
- #HealthyAtHome—Mental health. World Health Organization. www.who.int/campaigns/connecting-the-world-to-combat-coronavirus/healthyathome/healthyathome---mental-health. Accessed March 12, 2024.
- Coping with stress. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. www.cdc.gov/mentalhealth/stress-coping/cope-with-stress/. Accessed March 12, 2024.
- Manage stress. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://health.gov/myhealthfinder/topics/health-conditions/heart-health/manage-stress. Accessed March 20, 2020.
- COVID-19 and substance abuse. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/covid-19-substance-use#health-outcomes. Accessed March 12, 2024.
- COVID-19 resource and information guide. National Alliance on Mental Illness. https://www.nami.org/Support-Education/NAMI-HelpLine/COVID-19-Information-and-Resources/COVID-19-Resource-and-Information-Guide. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- Negative coping and PTSD. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. https://www.ptsd.va.gov/gethelp/negative_coping.asp. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- Health effects of cigarette smoking. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/fact_sheets/health_effects/effects_cig_smoking/index.htm#respiratory. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- People with certain medical conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-with-medical-conditions.html. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- Your healthiest self: Emotional wellness toolkit. National Institutes of Health. https://www.nih.gov/health-information/emotional-wellness-toolkit. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- World leprosy day: Bust the myths, learn the facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/leprosy/world-leprosy-day/. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- HIV stigma and discrimination. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/hiv-stigma/. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- Diabetes stigma: Learn about it, recognize it, reduce it. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/diabetes_stigma.html. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- Phelan SM, et al. Patient and health care professional perspectives on stigma in integrated behavioral health: Barriers and recommendations. Annals of Family Medicine. 2023; doi:10.1370/afm.2924.
- Stigma reduction. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/od2a/case-studies/stigma-reduction.html. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- Nyblade L, et al. Stigma in health facilities: Why it matters and how we can change it. BMC Medicine. 2019; doi:10.1186/s12916-019-1256-2.
- Combating bias and stigma related to COVID-19. American Psychological Association. https://www.apa.org/topics/covid-19-bias. Accessed March 15, 2024.
- Yashadhana A, et al. Pandemic-related racial discrimination and its health impact among non-Indigenous racially minoritized peoples in high-income contexts: A systematic review. Health Promotion International. 2021; doi:10.1093/heapro/daab144.
- Sawchuk CN (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. March 25, 2024.
Products and Services
- A Book: Endemic - A Post-Pandemic Playbook
- Begin Exploring Women's Health Solutions at Mayo Clinic Store
- A Book: Future Care
- Antibiotics: Are you misusing them?
- COVID-19 and vitamin D
- Convalescent plasma therapy
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- COVID-19: How can I protect myself?
- Herd immunity and respiratory illness
- COVID-19 and pets
- COVID-19 antibody testing
- COVID-19, cold, allergies and the flu
- Long-term effects of COVID-19
- COVID-19 tests
- COVID-19 drugs: Are there any that work?
- COVID-19 in babies and children
- Coronavirus infection by race
- COVID-19 travel advice
- COVID-19 vaccine: Should I reschedule my mammogram?
- COVID-19 vaccines for kids: What you need to know
- COVID-19 vaccines
- COVID-19 variant
- COVID-19 vs. flu: Similarities and differences
- COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
- Debunking coronavirus myths
- Different COVID-19 vaccines
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
- Fever: First aid
- Fever treatment: Quick guide to treating a fever
- Fight coronavirus (COVID-19) transmission at home
- Honey: An effective cough remedy?
- How do COVID-19 antibody tests differ from diagnostic tests?
- How to measure your respiratory rate
- How to take your pulse
- How to take your temperature
- How well do face masks protect against COVID-19?
- Is hydroxychloroquine a treatment for COVID-19?
- Loss of smell
- Mayo Clinic Minute: You're washing your hands all wrong
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How dirty are common surfaces?
- Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pregnancy and COVID-19
- Safe outdoor activities during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Safety tips for attending school during COVID-19
- Sex and COVID-19
- Shortness of breath
- Thermometers: Understand the options
- Treating COVID-19 at home
- Unusual symptoms of coronavirus
- Vaccine guidance from Mayo Clinic
- Watery eyes
Related information
- Mental health: What's normal, what's not - Related information Mental health: What's normal, what's not
- Mental illness - Related information Mental illness
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
- Open access
- Published: 11 April 2023
Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health, anxiety, and depression
- Ida Kupcova 1 ,
- Lubos Danisovic 1 ,
- Martin Klein 2 &
- Stefan Harsanyi 1
BMC Psychology volume 11 , Article number: 108 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
10k Accesses
21 Citations
46 Altmetric
Metrics details
The COVID-19 pandemic affected everyone around the globe. Depending on the country, there have been different restrictive epidemiologic measures and also different long-term repercussions. Morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 affected the mental state of every human being. However, social separation and isolation due to the restrictive measures considerably increased this impact. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), anxiety and depression prevalence increased by 25% globally. In this study, we aimed to examine the lasting effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the general population.
A cross-sectional study using an anonymous online-based 45-question online survey was conducted at Comenius University in Bratislava. The questionnaire comprised five general questions and two assessment tools the Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and the Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS). The results of the Self-Rating Scales were statistically examined in association with sex, age, and level of education.
A total of 205 anonymous subjects participated in this study, and no responses were excluded. In the study group, 78 (38.05%) participants were male, and 127 (61.69%) were female. A higher tendency to anxiety was exhibited by female participants (p = 0.012) and the age group under 30 years of age (p = 0.042). The level of education has been identified as a significant factor for changes in mental state, as participants with higher levels of education tended to be in a worse mental state (p = 0.006).
Conclusions
Summarizing two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, the mental state of people with higher levels of education tended to feel worse, while females and younger adults felt more anxiety.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The first mention of the novel coronavirus came in 2019, when this variant was discovered in the city of Wuhan, China, and became the first ever documented coronavirus pandemic [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. At this time there was only a sliver of fear rising all over the globe. However, in March 2020, after the declaration of a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO), the situation changed dramatically [ 4 ]. Answering this, yet an unknown threat thrust many countries into a psycho-socio-economic whirlwind [ 5 , 6 ]. Various measures taken by governments to control the spread of the virus presented the worldwide population with a series of new challenges to which it had to adjust [ 7 , 8 ]. Lockdowns, closed schools, losing employment or businesses, and rising deaths not only in nursing homes came to be a new reality [ 9 , 10 , 11 ]. Lack of scientific information on the novel coronavirus and its effects on the human body, its fast spread, the absence of effective causal treatment, and the restrictions which harmed people´s social life, financial situation and other areas of everyday life lead to long-term living conditions with increased stress levels and low predictability over which people had little control [ 12 ].
Risks of changes in the mental state of the population came mainly from external risk factors, including prolonged lockdowns, social isolation, inadequate or misinterpreted information, loss of income, and acute relationship with the rising death toll. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, anxiety and depression prevalence increased by 25% globally [ 13 ]. Unemployment specifically has been proven to be also a predictor of suicidal behavior [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. These risk factors then interact with individual psychological factors leading to psychopathologies such as threat appraisal, attentional bias to threat stimuli over neutral stimuli, avoidance, fear learning, impaired safety learning, impaired fear extinction due to habituation, intolerance of uncertainty, and psychological inflexibility. The threat responses are mediated by the limbic system and insula and mitigated by the pre-frontal cortex, which has also been reported in neuroimaging studies, with reduced insula thickness corresponding to more severe anxiety and amygdala volume correlated to anhedonia as a symptom of depression [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ]. Speaking in psychological terms, the pandemic disturbed our core belief, that we are safe in our communities, cities, countries, or even the world. The lost sense of agency and confidence regarding our future diminished the sense of worth, identity, and meaningfulness of our lives and eroded security-enhancing relationships [ 24 ].
Slovakia introduced harsh public health measures in the first wave of the pandemic, but relaxed these measures during the summer, accompanied by a failure to develop effective find, test, trace, isolate and support systems. Due to this, the country experienced a steep growth in new COVID-19 cases in September 2020, which lead to the erosion of public´s trust in the government´s management of the situation [ 25 ]. As a means to control the second wave of the pandemic, the Slovak government decided to perform nationwide antigen testing over two weekends in November 2020, which was internationally perceived as a very controversial step, moreover, it failed to prevent further lockdowns [ 26 ]. In addition, there was a sharp rise in the unemployment rate since 2020, which continued until July 2020, when it gradually eased [ 27 ]. Pre-pandemic, every 9th citizen of Slovakia suffered from a mental health disorder, according to National Statistics Office in 2017, the majority being affective and anxiety disorders. A group of authors created a web questionnaire aimed at psychiatrists, psychologists, and their patients after the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Slovakia. The results showed that 86.6% of respondents perceived the pathological effect of the pandemic on their mental status, 54.1% of whom were already treated for affective or anxiety disorders [ 28 ].
In this study, we aimed to examine the lasting effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the general population. This study aimed to assess the symptoms of anxiety and depression in the general public of Slovakia. After the end of epidemiologic restrictive measures (from March to May 2022), we introduced an anonymous online questionnaire using adapted versions of Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) [ 29 , 30 ]. We focused on the general public because only a portion of people who experience psychological distress seek professional help. We sought to establish, whether during the pandemic the population showed a tendency to adapt to the situation or whether the anxiety and depression symptoms tended to be present even after months of better epidemiologic situation, vaccine availability, and studies putting its effects under review [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ].
Materials and Methods
This study utilized a voluntary and anonymous online self-administered questionnaire, where the collected data cannot be linked to a specific respondent. This study did not process any personal data. The questionnaire consisted of 45 questions. The first three were open-ended questions about participants’ sex, age (date of birth was not recorded), and education. Followed by 2 questions aimed at mental health and changes in the will to live. Further 20 and 20 questions consisted of the Zung SAS and Zung SDS, respectively. Every question in SAS and SDS is scored from 1 to 4 points on a Likert-style scale. The scoring system is introduced in Fig. 1 . Questions were presented in the Slovak language, with emphasis on maintaining test integrity, so, if possible, literal translations were made from English to Slovak. The questionnaire was created and designed in Google Forms®. Data collection was carried out from March 2022 to May 2022. The study was aimed at the general population of Slovakia in times of difficult epidemiologic and social situations due to the high prevalence and incidence of COVID-19 cases during lockdowns and social distancing measures. Because of the character of this web-based study, the optimal distribution of respondents could not be achieved.
Categories of Zung SAS and SDS scores with clinical interpretation
During the course of this study, 205 respondents answered the anonymous questionnaire in full and were included in the study. All respondents were over 18 years of age. The data was later exported from Google Forms® as an Excel spreadsheet. Coding and analysis were carried out using IBM SPSS Statistics version 26 (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 26.0, Armonk, NY, USA). Subject groups were created based on sex, age, and education level. First, sex due to differences in emotional expression. Second, age was a risk factor due to perceived stress and fear of the disease. Last, education due to different approaches to information. In these groups four factors were studied: (1) changes in mental state; (2) affected will to live, or frequent thoughts about death; (3) result of SAS; (4) result of SDS. For SAS, no subject in the study group scored anxiety levels of “severe” or “extreme”. Similarly for SDS, no subject depression levels reached “moderate” or “severe”. Pearson’s chi-squared test(χ2) was used to analyze the association between the subject groups and studied factors. The results were considered significant if the p-value was less than 0.05.
Ethical permission was obtained from the local ethics committee (Reference number: ULBGaKG-02/2022). This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All methods were carried out following the institutional guidelines. Due to the anonymous design of the study and by the institutional requirements, written informed consent for participation was not required for this study.
In the study, out of 205 subjects in the study group, 127 (62%) were female and 78 (38%) were male. The average age in the study group was 35.78 years of age (range 19–71 years), with a median of 34 years. In the age group under 30 years of age were 34 (16.6%) subjects, while 162 (79%) were in the range from 31 to 49 and 9 (0.4%) were over 50 years old. 48 (23.4%) participants achieved an education level of lower or higher secondary and 157 (76.6%) finished university or higher. All answers of study participants were included in the study, nothing was excluded.
In Tables 1 and 2 , we can see the distribution of changes in mental state and will to live as stated in the questionnaire. In Table 1 we can see a disproportion in education level and mental state, where participants with higher education tended to feel worse much more than those with lower levels of education. Changes based on sex and age did not show any statistically significant results.
In Table 2 . we can see, that decreased will to live and frequent thoughts about death were only marginally present in the study group, which suggests that coping mechanisms play a huge role in adaptation to such events (e.g. the global pandemic). There is also a possibility that living in times of better epidemiologic situations makes people more likely to forget about the bad past.
Anxiety and depression levels as seen in Tables 3 and 4 were different, where female participants and the age group under 30 years of age tended to feel more anxiety than other groups. No significant changes in depression levels based on sex, age, and education were found.
Compared to the estimated global prevalence of depression in 2017 (3.44%), in 2021 it was approximately 7 times higher (25%) [ 14 ]. Our study did not prove an increase in depression, while anxiety levels and changes in the mental state did prove elevated. No significant changes in depression levels go in hand with the unaffected will to live and infrequent thoughts about death, which were important findings, that did not supplement our primary hypothesis that the fear of death caused by COVID-19 or accompanying infections would enhance personal distress and depression, leading to decreases in studied factors. These results are drawn from our limited sample size and uneven demographic distribution. Suicide ideations rose from 5% pre-pandemic to 10.81% during the pandemic [ 35 ]. In our study, 9.3% of participants experienced thoughts about death and since we did not specifically ask if they thought about suicide, our results only partially correlate with suicidal ideations. However, as these subjects exhibited only moderate levels of anxiety and mild levels of depression, the rise of suicide ideations seems unlikely. The rise in suicidal ideations seemed to be especially true for the general population with no pre-existing psychiatric conditions in the first months of the pandemic [ 36 ]. The policies implemented by countries to contain the pandemic also took a toll on the population´s mental health, as it was reported, that more stringent policies, mainly the social distancing and perceived government´s handling of the pandemic, were related to worse psychological outcomes [ 37 ]. The effects of lockdowns are far-fetched and the increases in mental health challenges, well-being, and quality of life will require a long time to be understood, as Onyeaka et al. conclude [ 10 ]. These effects are not unforeseen, as the global population suffered from life-altering changes in the structure and accessibility of education or healthcare, fluctuations in prices and food insecurity, as well as the inevitable depression of the global economy [ 38 ].
The loneliness associated with enforced social distancing leads to an increase in depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress in children in adolescents, with possible long-term sequelae [ 39 ]. The increase in adolescent self-injury was 27.6% during the pandemic [ 40 ]. Similar findings were described in the middle-aged and elderly population, in which both depression and anxiety prevalence rose at the beginning of the pandemic, during the pandemic, with depression persisting later in the pandemic, while the anxiety-related disorders tended to subside [ 41 ]. Medical professionals represented another specific at-risk group, with reported anxiety and depression rates of 24.94% and 24.83% respectively [ 42 ]. The dynamic of psychopathology related to the COVID-19 pandemic is not clear, with studies reporting a return to normal later in 2020, while others describe increased distress later in the pandemic [ 20 , 43 ].
Concerning the general population, authors from Spain reported that lockdowns and COVID-19 were associated with depression and anxiety [ 44 ]. In January 2022 Zhao et al., reported an elevation in hoarding behavior due to fear of COVID-19, while this process was moderated by education and income levels, however, less in the general population if compared to students [ 45 ]. Higher education levels and better access to information could improve persons’ fear of the unknown, however, this fact was not consistent with our expectations in this study, as participants with university education tended to feel worse than participants with lower education. A study on adolescents and their perceived stress in the Czech Republic concluded that girls are more affected by lockdowns. The strongest predictor was loneliness, while having someone to talk to, scored the lowest [ 46 ]. Garbóczy et al. reported elevated perceived stress levels and health anxiety in 1289 Hungarian and international students, also affected by disengagement from home and inadequate coping strategies [ 47 ]. Wathelet et al. conducted a study on French University students confined during the pandemic with alarming results of a high prevalence of mental health issues in the study group [ 48 ]. Our study indicated similar results, as participants in the age group under 30 years of age tended to feel more anxious than others.
In conclusion, we can say that this pandemic changed the lives of many. Many of us, our family members, friends, and colleagues, experienced life-altering events and complicated situations unseen for decades. Our decisions and actions fueled the progress in medicine, while they also continue to impact society on all levels. The long-term effects on adolescents are yet to be seen, while effects of pain, fear, and isolation on the general population are already presenting themselves.
The limitations of this study were numerous and as this was a web-based study, the optimal distribution of respondents could not be achieved, due to the snowball sampling strategy. The main limitation was the small sample size and uneven demographic distribution of respondents, which could impact the representativeness of the studied population and increase the margin of error. Similarly, the limited number of older participants could significantly impact the reported results, as age was an important risk factor and thus an important stressor. The questionnaire omitted the presence of COVID-19-unrelated life-changing events or stressors, and also did not account for any preexisting condition or risk factor that may have affected the outcome of the used assessment scales.
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to compliance with institutional guidelines but they are available from the corresponding author (SH) on a reasonable request.
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:727–33.
Liu Y-C, Kuo R-L, Shih S-R. COVID-19: the first documented coronavirus pandemic in history. Biomed J. 2020;43:328–33.
Advice for the public on COVID-19 – World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public . Accessed 13 Nov 2022.
Osterrieder A, Cuman G, Pan-Ngum W, Cheah PK, Cheah P-K, Peerawaranun P, et al. Economic and social impacts of COVID-19 and public health measures: results from an anonymous online survey in Thailand, Malaysia, the UK, Italy and Slovenia. BMJ Open. 2021;11:e046863.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mofijur M, Fattah IMR, Alam MA, Islam ABMS, Ong HC, Rahman SMA, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on the social, economic, environmental and energy domains: Lessons learnt from a global pandemic. Sustainable Prod Consum. 2021;26:343–59.
Article Google Scholar
Vlachos J, Hertegård E, Svaleryd B. The effects of school closures on SARS-CoV-2 among parents and teachers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118:e2020834118.
Ludvigsson JF, Engerström L, Nordenhäll C, Larsson E, Open Schools. Covid-19, and child and teacher morbidity in Sweden. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:669–71.
Miralles O, Sanchez-Rodriguez D, Marco E, Annweiler C, Baztan A, Betancor É, et al. Unmet needs, health policies, and actions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a report from six european countries. Eur Geriatr Med. 2021;12:193–204.
Onyeaka H, Anumudu CK, Al-Sharify ZT, Egele-Godswill E, Mbaegbu P. COVID-19 pandemic: a review of the global lockdown and its far-reaching effects. Sci Prog. 2021;104:368504211019854.
The Lancet null. India under COVID-19 lockdown. Lancet. 2020;395:1315.
Lo Coco G, Gentile A, Bosnar K, Milovanović I, Bianco A, Drid P, et al. A cross-country examination on the fear of COVID-19 and the sense of loneliness during the First Wave of COVID-19 outbreak. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:2586.
COVID-19 pandemic. triggers 25% increase in prevalence of anxiety and depression worldwide. https://www.who.int/news/item/02-03-2022-covid-19-pandemic-triggers-25-increase-in-prevalence-of-anxiety-and-depression-worldwide . Accessed 14 Nov 2022.
Bueno-Notivol J, Gracia-García P, Olaya B, Lasheras I, López-Antón R, Santabárbara J. Prevalence of depression during the COVID-19 outbreak: a meta-analysis of community-based studies. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2021;21:100196.
Hajek A, Sabat I, Neumann-Böhme S, Schreyögg J, Barros PP, Stargardt T, et al. Prevalence and determinants of probable depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic in seven countries: longitudinal evidence from the european COvid Survey (ECOS). J Affect Disord. 2022;299:517–24.
Piumatti G, Levati S, Amati R, Crivelli L, Albanese E. Trajectories of depression, anxiety and stress among adults during the COVID-19 pandemic in Southern Switzerland: the Corona Immunitas Ticino cohort study. Public Health. 2022;206:63–9.
Korkmaz H, Güloğlu B. The role of uncertainty tolerance and meaning in life on depression and anxiety throughout Covid-19 pandemic. Pers Indiv Differ. 2021;179:110952.
McIntyre RS, Lee Y. Projected increases in suicide in Canada as a consequence of COVID-19. Psychiatry Res. 2020;290:113104.
Funkhouser CJ, Klemballa DM, Shankman SA. Using what we know about threat reactivity models to understand mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Behav Res Ther. 2022;153:104082.
Landi G, Pakenham KI, Crocetti E, Tossani E, Grandi S. The trajectories of anxiety and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic and the protective role of psychological flexibility: a four-wave longitudinal study. J Affect Disord. 2022;307:69–78.
Holt-Gosselin B, Tozzi L, Ramirez CA, Gotlib IH, Williams LM. Coping strategies, neural structure, and depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal study in a naturalistic sample spanning clinical diagnoses and subclinical symptoms. Biol Psychiatry Global Open Sci. 2021;1:261–71.
McCracken LM, Badinlou F, Buhrman M, Brocki KC. The role of psychological flexibility in the context of COVID-19: Associations with depression, anxiety, and insomnia. J Context Behav Sci. 2021;19:28–35.
Talkovsky AM, Norton PJ. Negative affect and intolerance of uncertainty as potential mediators of change in comorbid depression in transdiagnostic CBT for anxiety. J Affect Disord. 2018;236:259–65.
Milman E, Lee SA, Neimeyer RA, Mathis AA, Jobe MC. Modeling pandemic depression and anxiety: the mediational role of core beliefs and meaning making. J Affect Disorders Rep. 2020;2:100023.
Sagan A, Bryndova L, Kowalska-Bobko I, Smatana M, Spranger A, Szerencses V, et al. A reversal of fortune: comparison of health system responses to COVID-19 in the Visegrad group during the early phases of the pandemic. Health Policy. 2022;126:446–55.
Holt E. COVID-19 testing in Slovakia. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:32.
Stalmachova K, Strenitzerova M. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on employment in transport and telecommunications sectors. Transp Res Procedia. 2021;55:87–94.
Izakova L, Breznoscakova D, Jandova K, Valkucakova V, Bezakova G, Suvada J. What mental health experts in Slovakia are learning from COVID-19 pandemic? Indian J Psychiatry. 2020;62(Suppl 3):459–66.
Rabinčák M, Tkáčová Ľ, VYUŽÍVANIE PSYCHOMETRICKÝCH KONŠTRUKTOV PRE, HODNOTENIE PORÚCH NÁLADY V OŠETROVATEĽSKEJ PRAXI. Zdravotnícke Listy. 2019;7:7.
Google Scholar
Sekot M, Gürlich R, Maruna P, Páv M, Uhlíková P. Hodnocení úzkosti a deprese u pacientů se zhoubnými nádory trávicího traktu. Čes a slov Psychiat. 2005;101:252–7.
Lipsitch M, Krammer F, Regev-Yochay G, Lustig Y, Balicer RD. SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in vaccinated individuals: measurement, causes and impact. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022;22:57–65.
Accorsi EK, Britton A, Fleming-Dutra KE, Smith ZR, Shang N, Derado G, et al. Association between 3 doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and symptomatic infection caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta Variants. JAMA. 2022;327:639–51.
Barda N, Dagan N, Cohen C, Hernán MA, Lipsitch M, Kohane IS, et al. Effectiveness of a third dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for preventing severe outcomes in Israel: an observational study. Lancet. 2021;398:2093–100.
Magen O, Waxman JG, Makov-Assif M, Vered R, Dicker D, Hernán MA, et al. Fourth dose of BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in a nationwide setting. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1603–14.
Dubé JP, Smith MM, Sherry SB, Hewitt PL, Stewart SH. Suicide behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic: a meta-analysis of 54 studies. Psychiatry Res. 2021;301:113998.
Kok AAL, Pan K-Y, Rius-Ottenheim N, Jörg F, Eikelenboom M, Horsfall M, et al. Mental health and perceived impact during the first Covid-19 pandemic year: a longitudinal study in dutch case-control cohorts of persons with and without depressive, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorders. J Affect Disord. 2022;305:85–93.
Aknin LB, Andretti B, Goldszmidt R, Helliwell JF, Petherick A, De Neve J-E, et al. Policy stringency and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal analysis of data from 15 countries. The Lancet Public Health. 2022;7:e417–26.
Prochazka J, Scheel T, Pirozek P, Kratochvil T, Civilotti C, Bollo M, et al. Data on work-related consequences of COVID-19 pandemic for employees across Europe. Data Brief. 2020;32:106174.
Loades ME, Chatburn E, Higson-Sweeney N, Reynolds S, Shafran R, Brigden A, et al. Rapid systematic review: the impact of social isolation and loneliness on the Mental Health of Children and Adolescents in the Context of COVID-19. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59:1218–1239e3.
Zetterqvist M, Jonsson LS, Landberg Ã, Svedin CG. A potential increase in adolescent nonsuicidal self-injury during covid-19: a comparison of data from three different time points during 2011–2021. Psychiatry Res. 2021;305:114208.
Mooldijk SS, Dommershuijsen LJ, de Feijter M, Luik AI. Trajectories of depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic in a population-based sample of middle-aged and older adults. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;149:274–80.
Sahebi A, Nejati-Zarnaqi B, Moayedi S, Yousefi K, Torres M, Golitaleb M. The prevalence of anxiety and depression among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021;107:110247.
Stephenson E, O’Neill B, Kalia S, Ji C, Crampton N, Butt DA, et al. Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on anxiety and depression in primary care: a retrospective cohort study. J Affect Disord. 2022;303:216–22.
Goldberg X, Castaño-Vinyals G, Espinosa A, Carreras A, Liutsko L, Sicuri E et al. Mental health and COVID-19 in a general population cohort in Spain (COVICAT study).Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022;:1–12.
Zhao Y, Yu Y, Zhao R, Cai Y, Gao S, Liu Y, et al. Association between fear of COVID-19 and hoarding behavior during the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of mental health status. Front Psychol. 2022;13:996486.
Furstova J, Kascakova N, Sigmundova D, Zidkova R, Tavel P, Badura P. Perceived stress of adolescents during the COVID-19 lockdown: bayesian multilevel modeling of the Czech HBSC lockdown survey. Front Psychol. 2022;13:964313.
Garbóczy S, Szemán-Nagy A, Ahmad MS, Harsányi S, Ocsenás D, Rekenyi V, et al. Health anxiety, perceived stress, and coping styles in the shadow of the COVID-19. BMC Psychol. 2021;9:53.
Wathelet M, Duhem S, Vaiva G, Baubet T, Habran E, Veerapa E, et al. Factors Associated with Mental Health Disorders among University students in France Confined during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e2025591.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to provide our appreciation and thanks to all the respondents in this study.
This research project received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Medical Biology, Genetics and Clinical Genetics, Faculty of Medicine, Comenius University in Bratislava, Sasinkova 4, Bratislava, 811 08, Slovakia
Ida Kupcova, Lubos Danisovic & Stefan Harsanyi
Institute of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Comenius University in Bratislava, Sasinkova 4, Bratislava, 811 08, Slovakia
Martin Klein
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
IK and SH have produced the study design. All authors contributed to the manuscript writing, revising, and editing. LD and MK have done data management and extraction, SH did the data analysis. Drafting and interpretation of the manuscript were made by all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefan Harsanyi .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical permission was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Medical Biology, Genetics and Clinical Genetics, Faculty of Medicine, Comenius University in Bratislava (Reference number: ULBGaKG-02/2022). The need for informed consent was waived by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Medical Biology, Genetics and Clinical Genetics, Faculty of Medicine, Comenius University in Bratislava due to the anonymous design of the study. This study did not process any personal data and the dataset does not contain any direct or indirect identifiers of participants. This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All methods were carried out following the institutional guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kupcova, I., Danisovic, L., Klein, M. et al. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health, anxiety, and depression. BMC Psychol 11 , 108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01130-5
Download citation
Received : 14 November 2022
Accepted : 20 March 2023
Published : 11 April 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01130-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mental health
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
How did COVID-19 affect Americans’ well-being and mental health?
Subscribe to global connection, emily dobson , emily dobson ph.d. student - university of maryland carol graham , carol graham senior fellow - economic studies @cgbrookings tim hua , and tim hua student - middlebury college, former intern - global economy and development sergio pinto sergio pinto doctoral student, university of maryland.
April 8, 2022
COVID-19 has justifiably raised widespread public concern about mental health worldwide. In the U.S., the pandemic was an unprecedented shock to society at a time when the nation was already coping with a crisis of despair and related deaths from suicides, overdoses, and alcohol poisoning. Meanwhile, COVID-19’s impact was inequitable: Deaths were concentrated among the elderly and minorities working in essential jobs, groups who up to the pandemic had been reporting better mental health. We still do not fully understand how the shock has affected society’s well-being and mental health.
In a recent paper in which we compared trends in 2019-2020 using several nationally representative datasets, we found a variety of contrasting stories. While data from the 2019 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) and the 2020 Household Pulse Survey (HPS) containing the same mental health screening questions for depression and anxiety show that both increased significantly, especially among young and low-income Americans in 2020, we found no such changes when analyzing alternative depression questions that are also asked in a consistent manner in the 2019-2020 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and the 2019-2020 NHIS. Despite the differences in trends, the basic determinants of mental health were similar in three data sets in the same two years.
Our findings raise questions about the robustness of the many studies claiming unprecedented increases in depression and anxiety among the young compared to older cohorts. Many of them, due to the urgency created by COVID-19 and a paucity of good, consistent data, matched datasets and used different questions therein in their attempt to identify changes in the trends between the two years. The inconsistency in the outcome changes over time across datasets points to the need for caution in drawing conclusions, as well as in relying too heavily on a single study; results generated from different data may differ considerably.
Given the paucity of comparable data and the usual one-year lag in the release of the final mortality data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), we also tried to get a handle on changes in patterns in mental health by examining emergency medical services (EMS) data calls related to behavior, overdoses, suicide attempts, and gun violence. The EMS data has the advantage of using the same methods and samples over the two-year period. We found an increase in gun violence and opioid overdose calls in 2020 after lockdowns, but surprisingly, a sharp decrease in behavioral health calls and no change in suicide-related EMS activations. The latter trend is a puzzle, but possible explanations include opioid overdose deaths increasing markedly and possibly substituting for suicide deaths. Alternatively, many older men—who are the demographic groups with the most suicide deaths—died of COVID-19 in that same period; another tragic “substitution” effect.
Finally, we looked at whether over the long run there is a relationship between poor mental health and later deaths of despair in micropolitan and metropolitan statistical areas (MMSAs). We found modest support for that possibility. Based on mental health reports in the BRFSS and CDC mortality data, we find that two-to-three-year-lagged bad mental health days (at the individual level) are associated with higher rates of deaths of despair (at the MMSA level), and that the two-to-four-year-lagged rates of deaths of despair are associated with a higher number of bad mental health days in later years. We cannot establish a direction of causality, but it is possible that there are vicious circles at play with individual trends in mental health contributing to broader community distress, and communities with more despair-related deaths likely to have more mental health problems later as a result.
Our analysis, based on many different datasets and indicators of despair, does not contradict other studies in that despair is an ongoing problem in the U.S., as reflected by both mental health reports and trends in EMS activations. However, we do find that the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic are mixed, and that while some trends, such as opioid overdose deaths, worsened in 2020 compared to 2019, others, such as in some mental health reports and in suicide rates, improved slightly. Our work does not speak to the longer-term mental health consequences of the pandemic, but it does suggest that there were deep pockets of both despair and resilience throughout it. It also suggests that caution is necessary in drawing policy implications from any one study.
Related Content
Emily Dobson, Carol Graham, Tim Hua, Sergio Pinto
April 4, 2022
Carol Graham, Fred Dews
January 28, 2022
Related Books
Carol Graham
March 28, 2017
August 8, 2012
Global Economy and Development
Isabel V. Sawhill, Kai Smith
May 29, 2024
Harris A. Eyre, Carol Graham
January 3, 2022

Mental Health
On This Page: -->
Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Frequently asked questions, mental health resources.

NIH has compiled a library of resources related to COVID-19 and mental illnesses and disorders, including condition-specific and population-specific resources.

An Urgent Issue
Both SARS-CoV-2 and the COVID-19 pandemic have significantly affected the mental health of adults and children. In a 2021 study, nearly half of Americans surveyed reported recent symptoms of an anxiety or depressive disorder, and 10% of respondents felt their mental health needs were not being met. Rates of anxiety, depression, and substance use disorder have increased since the beginning of the pandemic. And people who have mental illnesses or disorders and then get COVID-19 are more likely to die than those who don’t have mental illnesses or disorders.
Mental health is a focus of NIH research during the COVID-19 pandemic. Researchers at NIH and supported by NIH are creating and studying tools and strategies to understand, diagnose, and prevent mental illnesses or disorders and improve mental health care for those in need.
How COVID-19 Can Impact Mental Health
If you get COVID-19, you may experience a number of symptoms related to brain and mental health, including:
Cognitive and attention deficits (brain fog)
Anxiety and depression
Suicidal behavior
Data suggest that people are more likely to develop mental illnesses or disorders in the months following infection, including symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). People with Long COVID may experience many symptoms related to brain function and mental health.
How the Pandemic Affects Developing Brains
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of children is not yet fully understood. NIH-supported research is investigating factors that may influence the cognitive, social, and emotional development of children during the pandemic, including:
Changes to routine
Virtual schooling
Mask wearing
Caregiver absence or loss
Financial instability
Not Everyone Is Affected Equally
While the COVID-19 pandemic can affect the mental health of anyone, some people are more likely to be affected than others. People who are more likely to experience symptoms of mental illnesses or disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic include:
People from racial and ethnic minority groups
Mothers and pregnant people
People with financial or housing insecurity
People with disabilities
People with preexisting mental illnesses or substance use problems
Health care workers
People who belong to more than one of these groups may be at an even greater risk for mental illness.
Telehealth’s Potential to Help
The pandemic has prevented many people from visiting health care professionals in person, and as a result, telehealth has been more widely adopted during this time. Telehealth visits for mental health and substance use disorders increased significantly from 2020 to 2021 and now make up nearly half of all total visits for behavioral health.
Widespread adoption of telehealth services may help people who otherwise would not be able to access mental health support, such as people in rural areas or places with few providers.

I have a preexisting mental illness. Is COVID-19 more dangerous to me?
COVID-19 can be worse for people with mental illnesses. Data suggest that people who reported symptoms of anxiety or depression had a greater chance of being hospitalized after a COVID-19 diagnosis than people without those symptoms.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that having mood disorders and schizophrenia spectrum disorders can increase a person’s chances of having severe COVID-19. People with mental illnesses who belong to minority groups are also more likely to get COVID-19. And people with schizophrenia are significantly more likely to get COVID-19 and more likely to die from it.
Despite these risks, effective treatments are available. If you have a preexisting mental illness and get COVID-19, talk to your health care professional to determine the treatment plan that’s appropriate for you.
I’m experiencing symptoms of a mental illness or disorder. What should I do?
If you are experiencing symptoms of anxiety, depression, or any other mental illness or disorder, there are ways you can get help. For immediate help:
Call or text the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 (para ayuda en español, llame al 988)
Call or text the Disaster Distress Helpline , 1-800-985-5990 (press 2 for Spanish)
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration can help you find mental health or substance use specialists.
Talk to your health care professional or mental health care professional. Together, you can work on a plan to manage or reduce your symptoms.
What research is NIH doing on the mental health impacts of COVID-19?
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and other NIH Institutes have created research initiatives to address mental health for people in general and for the most vulnerable people specifically. Examples of this research include:
NIH's Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) Initiative has launched RECOVER-NEURO , a clinical trial that will test interventions to combat cognitive problems caused by Long COVID, including brain fog, memory problems, difficulty with attention, thinking clearly, and problem solving.
NIMH launched a five-year research study called RECOUP-NY to promote the mental health of New Yorkers from communities hard-hit by COVID-19. The study will test the use of a new care model called Problem Management Plus (PM+) that can be used by non-specialists.
A study funded by NIMH is examining the use of mobile apps to address mental health disparities .
The Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) is funding research to understand the effects of mask usage for children , including any impacts on their emotional and brain development.
NIMH is funding research on the impacts of the pandemic on underserved and vulnerable populations and on the cognitive, social, and emotional development of children .
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) is funding research on how COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 affect the causes and consequences of alcohol misuse .
A collaborative study supported by NIMH and the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) enrolled more than 3,600 people from all 50 U.S. states to understand the stressors affecting people during the pandemic.

Mental Health Resources by Topic
A library of resources related to COVID-19 and mental illnesses and disorders
Page last updated: September 28, 2023
- High Contrast
- Increase Font
- Decrease Font
- Default Font
- Turn Off Animations
- News and Features
- Conferences
- Clinical Tools
- Special Collections
Position Paper: The Impact of COVID-19 on Mental Health

In a position paper published in The Lancet Psychiatry , a group of mental health experts and other individuals from around the world came together to discuss the influence coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) poses to mental health care. The study authors noted that the pandemic reveals both system failings and opportunities for improving mental health delivery.
Potential Consequences of COVID-19
The COVID-19 public health crisis has led to a spike in known risk factors for mental health conditions, including everything from social isolation to unemployment to overall feelings of insecurity and instability. In light of these risk factors, as well as potential long-term mental health impacts, the researchers advocate for both short-term and ongoing responses.
Most general public surveys link COVID-19 to increased symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. Panic buying, binge-watching TV, and other unhealthy behaviors have been reported. Increased social media use, which is also reported, ups the odds of anxiety (odds ratio 1.72 [95% CI, 1.31–2.26]) and combined depression with anxiety (1.91 [1.52–2.41]). Quarantine can contribute to stress and anger and may also prompt behaviors such as online gambling.
People with COVID-19 face post-traumatic symptoms, psychological instability, depression, and anxiety. “The possibility that SARS-CoV-2 is neurotropic emphasizes the need for evaluation of potential short-term and long-term effects on the nervous system,” the study authors stated
People with pre-existing mental health conditions generally have an increased risk of infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Not only are older adults at a higher risk of severe COVID-19 illness, they also face a heightened risk of mental health issues due to possible cognitive decline. People with pre-existing mental health conditions and disorders are also especially sensitive to quarantine, physical distancing, food availability, and general disruption of their routine.
Mental Health Service Responses
The authors of the study suggest rethinking conventional mental health approaches in order to improve the cost and scale of treatment. The public health response to COVID-19 should include clear, up-to-date information about infection rates and distancing measures (to reduce uncertainty), as well as information on education, self-care, family support, and collaboration across agencies. Study authors also identified and supported steps already being taken to control infection and to promote wellness among special populations, such as healthcare workers.
Mental Health Care Adaptations
The study authors recommend an ethics- and rights-driven approach to care. They acknowledge potential discrimination “in adjudicating access to insufficiently available health interventions and applying and weighing the added risk of SARS-CoV-2 exposure in decisions about involuntary institutionalization.” Potential future service cuts, disproportionate additional illness burden, reduced service access, inadequate financial support, exacerbation of inequalities in access to health care, and the need for greater family and caregiver support are also valid concerns.
With access to care often limited, and in-person contact either limited or unavailable, patients and caregivers need to feel empowered to take ownership of their care to ensure the best outcomes, the study authors stated. Relative risks and benefits of treatment changes should be considered, especially with patients receiving clozapine, injectable medications, or electroconvulsive therapy.
“Treatment plans might need to be rapidly renegotiated, and should be based on best practices,” the researchers stated. “There is thus a need to enhance and create robust resources to support shared decision making.”
The benefit of person-centered care is noted and should not be ignored when there’s a need for rapid decision-making. Care design and delivery can be strengthened by “increased peer worker involvement in the co-design of adapted services and by increasing the number of peer workers, especially in countries with limited resources,” researchers stated.
Long-Term Needs
Moving forward, the study authors suggest community monitoring and mental health screening to mitigate the potential long-term mental health effects of COVID-19. Digital health and digital phenotyping are 2 possibilities. With local needs clarified, community stakeholder groups can design interventions.
Community support services can help people experiencing acute distress, as well as those who don’t trust mainstream mental health care. Healthcare systems should thereby anticipate an increase in “unmet mental health needs” among vulnerable groups and prepare for them. Telemedicine is one way to fill gaps in care during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Provision of Mental Health Care
The authors of the study list the following indicators that should be assessed regularly during and after the pandemic, and compared with pre-pandemic data, to determine changes in delivery:
- The proportion of all mental health services provided in inpatient, emergency, institutional (eg, prisons), outpatient, community, and home-based settings
- Rates of face-to-face, video, and telephone contact with different types of mental health providers
- Rates of prescription and use of psychiatric medication
- Access to, and use of, different mental health services both by people with pre-existing mental health disorders and those with new incident cases of mental illness, and the sociodemographic characteristics of these users
- Quality of care of different mental health services (including acceptability and satisfaction with healthcare providers), with a focus on user expectations and satisfaction and on functional, vocational, and clinical outcomes (including the views of families or caregivers)
- Disparities in mental health care, with socioeconomic, race, and ethnicity data linked to quality measures
- Integration of mental health services with general health services, social welfare, and other institutions (eg, schools, prisons), and community associations
- Governmental and non-governmental financial support for mental health and social care services, and healthcare leaders should regularly monitor the use and effectiveness of mental health care. Certain indicators should be assessed regularly during and after the pandemic, and then compared with pre-pandemic data to determine changes in delivery.
“There is an opportunity to replace the old way of managing the gap between the supply of and demand for mental health care (ie, rationing) with a system that prioritizes high-quality and equitable care rather than focusing only on how much work is done,” the study authors concluded.
Several study authors declared affiliations with the pharmaceutical industry. Please see the original reference for a full list of authors’ disclosures.
Moreno C, Wykes T, Galderisi S, et al. How mental health care should change as a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic . Lancet Psychiatry . 2020;7(9):813-824.
Picked For You
Latest News

Spotlight Course
Want to read more.
Please login or register first to view this content.
Login Register
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Volume 76, Issue 2
- COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on social relationships and health
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1512-4471 Emily Long 1 ,
- Susan Patterson 1 ,
- Karen Maxwell 1 ,
- Carolyn Blake 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7342-4566 Raquel Bosó Pérez 1 ,
- Ruth Lewis 1 ,
- Mark McCann 1 ,
- Julie Riddell 1 ,
- Kathryn Skivington 1 ,
- Rachel Wilson-Lowe 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4409-6601 Kirstin R Mitchell 2
- 1 MRC/CSO Social and Public Health Sciences Unit , University of Glasgow , Glasgow , UK
- 2 MRC/CSO Social and Public Health Sciences Unit, Institute of Health & Wellbeing , University of Glasgow , Glasgow , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Emily Long, MRC/CSO Social and Public Health Sciences Unit, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G3 7HR, UK; emily.long{at}glasgow.ac.uk
This essay examines key aspects of social relationships that were disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. It focuses explicitly on relational mechanisms of health and brings together theory and emerging evidence on the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic to make recommendations for future public health policy and recovery. We first provide an overview of the pandemic in the UK context, outlining the nature of the public health response. We then introduce four distinct domains of social relationships: social networks, social support, social interaction and intimacy, highlighting the mechanisms through which the pandemic and associated public health response drastically altered social interactions in each domain. Throughout the essay, the lens of health inequalities, and perspective of relationships as interconnecting elements in a broader system, is used to explore the varying impact of these disruptions. The essay concludes by providing recommendations for longer term recovery ensuring that the social relational cost of COVID-19 is adequately considered in efforts to rebuild.
- inequalities
Data availability statement
Data sharing not applicable as no data sets generated and/or analysed for this study. Data sharing not applicable as no data sets generated or analysed for this essay.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to copy, redistribute, remix, transform and build upon this work for any purpose, provided the original work is properly cited, a link to the licence is given, and indication of whether changes were made. See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2021-216690
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Infectious disease pandemics, including SARS and COVID-19, demand intrapersonal behaviour change and present highly complex challenges for public health. 1 A pandemic of an airborne infection, spread easily through social contact, assails human relationships by drastically altering the ways through which humans interact. In this essay, we draw on theories of social relationships to examine specific ways in which relational mechanisms key to health and well-being were disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Relational mechanisms refer to the processes between people that lead to change in health outcomes.
At the time of writing, the future surrounding COVID-19 was uncertain. Vaccine programmes were being rolled out in countries that could afford them, but new and more contagious variants of the virus were also being discovered. The recovery journey looked long, with continued disruption to social relationships. The social cost of COVID-19 was only just beginning to emerge, but the mental health impact was already considerable, 2 3 and the inequality of the health burden stark. 4 Knowledge of the epidemiology of COVID-19 accrued rapidly, but evidence of the most effective policy responses remained uncertain.
The initial response to COVID-19 in the UK was reactive and aimed at reducing mortality, with little time to consider the social implications, including for interpersonal and community relationships. The terminology of ‘social distancing’ quickly became entrenched both in public and policy discourse. This equation of physical distance with social distance was regrettable, since only physical proximity causes viral transmission, whereas many forms of social proximity (eg, conversations while walking outdoors) are minimal risk, and are crucial to maintaining relationships supportive of health and well-being.
The aim of this essay is to explore four key relational mechanisms that were impacted by the pandemic and associated restrictions: social networks, social support, social interaction and intimacy. We use relational theories and emerging research on the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic response to make three key recommendations: one regarding public health responses; and two regarding social recovery. Our understanding of these mechanisms stems from a ‘systems’ perspective which casts social relationships as interdependent elements within a connected whole. 5
Social networks
Social networks characterise the individuals and social connections that compose a system (such as a workplace, community or society). Social relationships range from spouses and partners, to coworkers, friends and acquaintances. They vary across many dimensions, including, for example, frequency of contact and emotional closeness. Social networks can be understood both in terms of the individuals and relationships that compose the network, as well as the overall network structure (eg, how many of your friends know each other).
Social networks show a tendency towards homophily, or a phenomenon of associating with individuals who are similar to self. 6 This is particularly true for ‘core’ network ties (eg, close friends), while more distant, sometimes called ‘weak’ ties tend to show more diversity. During the height of COVID-19 restrictions, face-to-face interactions were often reduced to core network members, such as partners, family members or, potentially, live-in roommates; some ‘weak’ ties were lost, and interactions became more limited to those closest. Given that peripheral, weaker social ties provide a diversity of resources, opinions and support, 7 COVID-19 likely resulted in networks that were smaller and more homogenous.
Such changes were not inevitable nor necessarily enduring, since social networks are also adaptive and responsive to change, in that a disruption to usual ways of interacting can be replaced by new ways of engaging (eg, Zoom). Yet, important inequalities exist, wherein networks and individual relationships within networks are not equally able to adapt to such changes. For example, individuals with a large number of newly established relationships (eg, university students) may have struggled to transfer these relationships online, resulting in lost contacts and a heightened risk of social isolation. This is consistent with research suggesting that young adults were the most likely to report a worsening of relationships during COVID-19, whereas older adults were the least likely to report a change. 8
Lastly, social connections give rise to emergent properties of social systems, 9 where a community-level phenomenon develops that cannot be attributed to any one member or portion of the network. For example, local area-based networks emerged due to geographic restrictions (eg, stay-at-home orders), resulting in increases in neighbourly support and local volunteering. 10 In fact, research suggests that relationships with neighbours displayed the largest net gain in ratings of relationship quality compared with a range of relationship types (eg, partner, colleague, friend). 8 Much of this was built from spontaneous individual interactions within local communities, which together contributed to the ‘community spirit’ that many experienced. 11 COVID-19 restrictions thus impacted the personal social networks and the structure of the larger networks within the society.
Social support
Social support, referring to the psychological and material resources provided through social interaction, is a critical mechanism through which social relationships benefit health. In fact, social support has been shown to be one of the most important resilience factors in the aftermath of stressful events. 12 In the context of COVID-19, the usual ways in which individuals interact and obtain social support have been severely disrupted.
One such disruption has been to opportunities for spontaneous social interactions. For example, conversations with colleagues in a break room offer an opportunity for socialising beyond one’s core social network, and these peripheral conversations can provide a form of social support. 13 14 A chance conversation may lead to advice helpful to coping with situations or seeking formal help. Thus, the absence of these spontaneous interactions may mean the reduction of indirect support-seeking opportunities. While direct support-seeking behaviour is more effective at eliciting support, it also requires significantly more effort and may be perceived as forceful and burdensome. 15 The shift to homeworking and closure of community venues reduced the number of opportunities for these spontaneous interactions to occur, and has, second, focused them locally. Consequently, individuals whose core networks are located elsewhere, or who live in communities where spontaneous interaction is less likely, have less opportunity to benefit from spontaneous in-person supportive interactions.
However, alongside this disruption, new opportunities to interact and obtain social support have arisen. The surge in community social support during the initial lockdown mirrored that often seen in response to adverse events (eg, natural disasters 16 ). COVID-19 restrictions that confined individuals to their local area also compelled them to focus their in-person efforts locally. Commentators on the initial lockdown in the UK remarked on extraordinary acts of generosity between individuals who belonged to the same community but were unknown to each other. However, research on adverse events also tells us that such community support is not necessarily maintained in the longer term. 16
Meanwhile, online forms of social support are not bound by geography, thus enabling interactions and social support to be received from a wider network of people. Formal online social support spaces (eg, support groups) existed well before COVID-19, but have vastly increased since. While online interactions can increase perceived social support, it is unclear whether remote communication technologies provide an effective substitute from in-person interaction during periods of social distancing. 17 18 It makes intuitive sense that the usefulness of online social support will vary by the type of support offered, degree of social interaction and ‘online communication skills’ of those taking part. Youth workers, for instance, have struggled to keep vulnerable youth engaged in online youth clubs, 19 despite others finding a positive association between amount of digital technology used by individuals during lockdown and perceived social support. 20 Other research has found that more frequent face-to-face contact and phone/video contact both related to lower levels of depression during the time period of March to August 2020, but the negative effect of a lack of contact was greater for those with higher levels of usual sociability. 21 Relatedly, important inequalities in social support exist, such that individuals who occupy more socially disadvantaged positions in society (eg, low socioeconomic status, older people) tend to have less access to social support, 22 potentially exacerbated by COVID-19.
Social and interactional norms
Interactional norms are key relational mechanisms which build trust, belonging and identity within and across groups in a system. Individuals in groups and societies apply meaning by ‘approving, arranging and redefining’ symbols of interaction. 23 A handshake, for instance, is a powerful symbol of trust and equality. Depending on context, not shaking hands may symbolise a failure to extend friendship, or a failure to reach agreement. The norms governing these symbols represent shared values and identity; and mutual understanding of these symbols enables individuals to achieve orderly interactions, establish supportive relationship accountability and connect socially. 24 25
Physical distancing measures to contain the spread of COVID-19 radically altered these norms of interaction, particularly those used to convey trust, affinity, empathy and respect (eg, hugging, physical comforting). 26 As epidemic waves rose and fell, the work to negotiate these norms required intense cognitive effort; previously taken-for-granted interactions were re-examined, factoring in current restriction levels, own and (assumed) others’ vulnerability and tolerance of risk. This created awkwardness, and uncertainty, for example, around how to bring closure to an in-person interaction or convey warmth. The instability in scripted ways of interacting created particular strain for individuals who already struggled to encode and decode interactions with others (eg, those who are deaf or have autism spectrum disorder); difficulties often intensified by mask wearing. 27
Large social gatherings—for example, weddings, school assemblies, sporting events—also present key opportunities for affirming and assimilating interactional norms, building cohesion and shared identity and facilitating cooperation across social groups. 28 Online ‘equivalents’ do not easily support ‘social-bonding’ activities such as singing and dancing, and rarely enable chance/spontaneous one-on-one conversations with peripheral/weaker network ties (see the Social networks section) which can help strengthen bonds across a larger network. The loss of large gatherings to celebrate rites of passage (eg, bar mitzvah, weddings) has additional relational costs since these events are performed by and for communities to reinforce belonging, and to assist in transitioning to new phases of life. 29 The loss of interaction with diverse others via community and large group gatherings also reduces intergroup contact, which may then tend towards more prejudiced outgroup attitudes. While online interaction can go some way to mimicking these interaction norms, there are key differences. A sense of anonymity, and lack of in-person emotional cues, tends to support norms of polarisation and aggression in expressing differences of opinion online. And while online platforms have potential to provide intergroup contact, the tendency of much social media to form homogeneous ‘echo chambers’ can serve to further reduce intergroup contact. 30 31
Intimacy relates to the feeling of emotional connection and closeness with other human beings. Emotional connection, through romantic, friendship or familial relationships, fulfils a basic human need 32 and strongly benefits health, including reduced stress levels, improved mental health, lowered blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease. 32 33 Intimacy can be fostered through familiarity, feeling understood and feeling accepted by close others. 34
Intimacy via companionship and closeness is fundamental to mental well-being. Positively, the COVID-19 pandemic has offered opportunities for individuals to (re)connect and (re)strengthen close relationships within their household via quality time together, following closure of many usual external social activities. Research suggests that the first full UK lockdown period led to a net gain in the quality of steady relationships at a population level, 35 but amplified existing inequalities in relationship quality. 35 36 For some in single-person households, the absence of a companion became more conspicuous, leading to feelings of loneliness and lower mental well-being. 37 38 Additional pandemic-related relational strain 39 40 resulted, for some, in the initiation or intensification of domestic abuse. 41 42
Physical touch is another key aspect of intimacy, a fundamental human need crucial in maintaining and developing intimacy within close relationships. 34 Restrictions on social interactions severely restricted the number and range of people with whom physical affection was possible. The reduction in opportunity to give and receive affectionate physical touch was not experienced equally. Many of those living alone found themselves completely without physical contact for extended periods. The deprivation of physical touch is evidenced to take a heavy emotional toll. 43 Even in future, once physical expressions of affection can resume, new levels of anxiety over germs may introduce hesitancy into previously fluent blending of physical and verbal intimate social connections. 44
The pandemic also led to shifts in practices and norms around sexual relationship building and maintenance, as individuals adapted and sought alternative ways of enacting sexual intimacy. This too is important, given that intimate sexual activity has known benefits for health. 45 46 Given that social restrictions hinged on reducing household mixing, possibilities for partnered sexual activity were primarily guided by living arrangements. While those in cohabiting relationships could potentially continue as before, those who were single or in non-cohabiting relationships generally had restricted opportunities to maintain their sexual relationships. Pornography consumption and digital partners were reported to increase since lockdown. 47 However, online interactions are qualitatively different from in-person interactions and do not provide the same opportunities for physical intimacy.
Recommendations and conclusions
In the sections above we have outlined the ways in which COVID-19 has impacted social relationships, showing how relational mechanisms key to health have been undermined. While some of the damage might well self-repair after the pandemic, there are opportunities inherent in deliberative efforts to build back in ways that facilitate greater resilience in social and community relationships. We conclude by making three recommendations: one regarding public health responses to the pandemic; and two regarding social recovery.
Recommendation 1: explicitly count the relational cost of public health policies to control the pandemic
Effective handling of a pandemic recognises that social, economic and health concerns are intricately interwoven. It is clear that future research and policy attention must focus on the social consequences. As described above, policies which restrict physical mixing across households carry heavy and unequal relational costs. These include for individuals (eg, loss of intimate touch), dyads (eg, loss of warmth, comfort), networks (eg, restricted access to support) and communities (eg, loss of cohesion and identity). Such costs—and their unequal impact—should not be ignored in short-term efforts to control an epidemic. Some public health responses—restrictions on international holiday travel and highly efficient test and trace systems—have relatively small relational costs and should be prioritised. At a national level, an earlier move to proportionate restrictions, and investment in effective test and trace systems, may help prevent escalation of spread to the point where a national lockdown or tight restrictions became an inevitability. Where policies with relational costs are unavoidable, close attention should be paid to the unequal relational impact for those whose personal circumstances differ from normative assumptions of two adult families. This includes consideration of whether expectations are fair (eg, for those who live alone), whether restrictions on social events are equitable across age group, religious/ethnic groupings and social class, and also to ensure that the language promoted by such policies (eg, households; families) is not exclusionary. 48 49 Forethought to unequal impacts on social relationships should thus be integral to the work of epidemic preparedness teams.
Recommendation 2: intelligently balance online and offline ways of relating
A key ingredient for well-being is ‘getting together’ in a physical sense. This is fundamental to a human need for intimate touch, physical comfort, reinforcing interactional norms and providing practical support. Emerging evidence suggests that online ways of relating cannot simply replace physical interactions. But online interaction has many benefits and for some it offers connections that did not exist previously. In particular, online platforms provide new forms of support for those unable to access offline services because of mobility issues (eg, older people) or because they are geographically isolated from their support community (eg, lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) youth). Ultimately, multiple forms of online and offline social interactions are required to meet the needs of varying groups of people (eg, LGBTQ, older people). Future research and practice should aim to establish ways of using offline and online support in complementary and even synergistic ways, rather than veering between them as social restrictions expand and contract. Intelligent balancing of online and offline ways of relating also pertains to future policies on home and flexible working. A decision to switch to wholesale or obligatory homeworking should consider the risk to relational ‘group properties’ of the workplace community and their impact on employees’ well-being, focusing in particular on unequal impacts (eg, new vs established employees). Intelligent blending of online and in-person working is required to achieve flexibility while also nurturing supportive networks at work. Intelligent balance also implies strategies to build digital literacy and minimise digital exclusion, as well as coproducing solutions with intended beneficiaries.
Recommendation 3: build stronger and sustainable localised communities
In balancing offline and online ways of interacting, there is opportunity to capitalise on the potential for more localised, coherent communities due to scaled-down travel, homeworking and local focus that will ideally continue after restrictions end. There are potential economic benefits after the pandemic, such as increased trade as home workers use local resources (eg, coffee shops), but also relational benefits from stronger relationships around the orbit of the home and neighbourhood. Experience from previous crises shows that community volunteer efforts generated early on will wane over time in the absence of deliberate work to maintain them. Adequately funded partnerships between local government, third sector and community groups are required to sustain community assets that began as a direct response to the pandemic. Such partnerships could work to secure green spaces and indoor (non-commercial) meeting spaces that promote community interaction. Green spaces in particular provide a triple benefit in encouraging physical activity and mental health, as well as facilitating social bonding. 50 In building local communities, small community networks—that allow for diversity and break down ingroup/outgroup views—may be more helpful than the concept of ‘support bubbles’, which are exclusionary and less sustainable in the longer term. Rigorously designed intervention and evaluation—taking a systems approach—will be crucial in ensuring scale-up and sustainability.
The dramatic change to social interaction necessitated by efforts to control the spread of COVID-19 created stark challenges but also opportunities. Our essay highlights opportunities for learning, both to ensure the equity and humanity of physical restrictions, and to sustain the salutogenic effects of social relationships going forward. The starting point for capitalising on this learning is recognition of the disruption to relational mechanisms as a key part of the socioeconomic and health impact of the pandemic. In recovery planning, a general rule is that what is good for decreasing health inequalities (such as expanding social protection and public services and pursuing green inclusive growth strategies) 4 will also benefit relationships and safeguard relational mechanisms for future generations. Putting this into action will require political will.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not required.
- Office for National Statistics (ONS)
- Ford T , et al
- Riordan R ,
- Ford J , et al
- Glonti K , et al
- McPherson JM ,
- Smith-Lovin L
- Granovetter MS
- Fancourt D et al
- Stadtfeld C
- Office for Civil Society
- Cook J et al
- Rodriguez-Llanes JM ,
- Guha-Sapir D
- Patulny R et al
- Granovetter M
- Winkeler M ,
- Filipp S-H ,
- Kaniasty K ,
- de Terte I ,
- Guilaran J , et al
- Wright KB ,
- Martin J et al
- Gabbiadini A ,
- Baldissarri C ,
- Durante F , et al
- Sommerlad A ,
- Marston L ,
- Huntley J , et al
- Turner RJ ,
- Bicchieri C
- Brennan G et al
- Watson-Jones RE ,
- Amichai-Hamburger Y ,
- McKenna KYA
- Page-Gould E ,
- Aron A , et al
- Pietromonaco PR ,
- Timmerman GM
- Bradbury-Jones C ,
- Mikocka-Walus A ,
- Klas A , et al
- Marshall L ,
- Steptoe A ,
- Stanley SM ,
- Campbell AM
- ↵ (ONS), O.f.N.S., Domestic abuse during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, England and Wales . Available: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/crimeandjustice/articles/domesticabuseduringthecoronaviruscovid19pandemicenglandandwales/november2020
- Rosenberg M ,
- Hensel D , et al
- Banerjee D ,
- Bruner DW , et al
- Bavel JJV ,
- Baicker K ,
- Boggio PS , et al
- van Barneveld K ,
- Quinlan M ,
- Kriesler P , et al
- Mitchell R ,
- de Vries S , et al
Twitter @karenmaxSPHSU, @Mark_McCann, @Rwilsonlowe, @KMitchinGlasgow
Contributors EL and KM led on the manuscript conceptualisation, review and editing. SP, KM, CB, RBP, RL, MM, JR, KS and RW-L contributed to drafting and revising the article. All authors assisted in revising the final draft.
Funding The research reported in this publication was supported by the Medical Research Council (MC_UU_00022/1, MC_UU_00022/3) and the Chief Scientist Office (SPHSU11, SPHSU14). EL is also supported by MRC Skills Development Fellowship Award (MR/S015078/1). KS and MM are also supported by a Medical Research Council Strategic Award (MC_PC_13027).
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Last updated 27/06/24: Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website: https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > Journals
- > Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine
- > Volume 37 Issue 4: Themed Issue: COVID-19 and Ment...
- > Mental health and the COVID-19 pandemic: looking back...

Article contents
Introduction, mental health effects of covid-19, research priorities, financial support, conflict of interest, ethical standards, mental health and the covid-19 pandemic: looking back and moving forward.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 December 2020
COVID-19 continues to exert unprecedented challenges for society and it is now well recognised that mental health is a key healthcare issue related to the pandemic. The current edition of the Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine focusses on the impact of COVID-19 on mental illness by combining historical review papers, current perspectives and original research. It is important that psychiatrists leading mental health services in Ireland continue to advocate for mental health supports for healthcare workers and their patients, while aiming to deliver services flexibly. As the pandemic evolves, it remains to be seen whether the necessary funding to deliver effective mental healthcare will be allocated to psychiatric services. Ongoing service evaluation and research is needed as the myriad impacts of the pandemic continue to evolve. In a time of severe budgetary constraints, ensuring optimum use of scare resources becomes an imperative.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to present the greatest global health challenge in modern history. While emerging data is improving our understanding of the virus and its impact on health, societal cohesion and world economies, the situation globally continues to evolve. As such, findings and learnings that emerge at one point of the pandemic can appear to have relatively limited utility at another point. Arguably, never in living memory has there been a global phenomenon impacting population mental health in such a dynamic fashion. The challenge for mental health science is to capture and report these dynamic trends in a timely manner to inform and support psychiatrists implementing evidence-based care in this uniquely challenging environment. A parallel requirement is that such services are adequately resourced to meet the needs of both service user and provider.
This COVID-19-themed issue of the Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine aims to provide a more nuanced understanding of the multifaceted mental health impact of the pandemic to date. In so doing, we sincerely hope that this issue will provide colleagues with a timely and useful resource in these uncertain times.
A number of commentators in the popular media have noted that one potential silver-lining of this pandemic has been a mainstreaming of mental health within the broader considerations of the health impact of the pandemic. It is has been noted that mental health needs have never been as central to public discourse as during recent media discussions about the impact of the various restrictions implemented due to the pandemic. The assumption that this increased consideration of mental health will indeed represent a true and meaningful shift in public policy towards psychiatric services and, by extension, increased funding, is yet to be borne out. Indeed, there remains a very real risk that this discourse will merely serve to enhance the already considerable societal focus on psychological well-being and continue to marginalise the moderate to severe end of the mental illness spectrum. It is particularly noteworthy that certain high-risk groups with pre-existing mental illness might remain most vulnerable to the potentially deleterious psychological impact of the pandemic, notwithstanding that many patients within these groups may display significant resilience. An ambiguous focus on mental health , which fails to take account of the urgent needs of overextended and under-resourced psychiatric services, represents a clear and pressing concern. Within this exceptional set of circumstances, the compelling need for effective advocacy emanating from psychiatrists to constructively inform and shape public discourse has been brought sharply into focus.
As predicted at the outset of the first wave of the pandemic, psychiatric morbidity is peaking later than the physical health consequences of the pandemic (Gunnell et al. Reference Gunnell, Appleby, Arensman, Hawton, John and Kapur 2020 ), and current trends suggest that this peak will indeed endure for longer than the impact on physical health. Emerging data from services nationwide indicates increasing referrals to psychiatric services following the initial pandemic lockdown, and ongoing evaluation of referrals to psychiatric services is now needed.
A further strategy which can help to determine the effects of the current pandemic is a reflection on historical events and the retrospective lessons that may be learned from them. Two historical papers in this issue focus on previous pandemics and other global events to evaluate how mental illness was impacted at the time. The multifaceted impact of COVID-19 on population mental health may not be realised for some time and it is important to start planning now for ongoing consequences such as the potential severe economic consequences in the months and years ahead.
Another somewhat double-edged silver-lining of the pandemic is the increased acknowledgement of the psychological burden associated with frontline healthcare service provision (Behrman et al. Reference Behrman, Baruch and Stegen 2020 ; Faderani et al. Reference Faderani, Monks, Peprah, Colori, Allen, Amphlett and Edwards 2020 ). Pre-pandemic data indicated a high-level of stress and burnout among doctors in Ireland (McNicholas et al. Reference McNicholas, Sharma, Oconnor and Barrett 2020 ; Humphries et al. Reference Humphries, McDermott, Creese, Matthews, Conway and Byrne 2020 ). Calls have been consistently made since the outset of the pandemic to enshrine the well-being of healthcare staff as a central tenet of the overall model of healthcare service response (Unadkat and Farquhar, Reference Unadkat and Farquhar 2020 ). This pro-active approach was advocated not only because protecting staff was recognised as the right thing to do but also to buffer against the predictable psychological consequences of providing healthcare within extremely challenging and rapidly-changing circumstances (Maunder et al. Reference Maunder, Leszcz, Savage, Adam, Peladeau and Romano 2008 ).
This Special Issue highlights some of the array of tools which have been proposed as helpful to clinicians to off-set stress and enhance resilience. To this end, there are considerations of mindfulness and story-telling which are proffered as possible means to pause and reflect and indeed the somewhat unique (for this journal) inclusion of poetry and prose represents an attempt to support and highlight the importance of enacting such strategies. Undoubtedly, however, research into what are described as psychological preparedness tools for healthcare workers is at a nascent stage and considerable further research is required prior to widespread implementation.
It is unsurprising, therefore, that while comprehensive Pandemic Preparedness Tools (Adelaja et al. Reference Adelaja, Sayma, Walton, McLachlan, de Boisanger and Bartlett-Pestell 2020 ) all incorporate specific elements designed to support the psychological well-being of healthcare staff, it appears reasonable to assert that additional support structures or tools have not been the experience of clinicians working throughout the pandemic. Indeed, a recent survey by the British Medical Association reported that 40% of the 6650 respondents indicated a worsening in their mental health status compared to pre-pandemic (Rimmer, Reference Rimmer 2020 ), with 10% describing their mental health as much worse . This is broadly in keeping with data from previous pandemics which suggest that, of those who experience negative psychological sequelae, the majority of healthcare staff will experience transient psychological distress rather than diagnosable moderate–severe conditions (Greenberg et al. Reference Greenberg, Docherty, Gnanapragasam and Wessely 2020 ; Maunder et al. Reference Maunder, Hunter, Vincent, Bennett, Peladeau and Leszcz 2003 , Reference Maunder, Lancee, Balderson, Bennett, Borgundvaag and Evans 2006 , Reference Maunder, Leszcz, Savage, Adam, Peladeau and Romano 2008 ).
These figures remain concerning however, and while Irish data does not exist, if the medical population in Ireland experiences similar trends to our international colleagues, the overall prevalence rates and service need for doctors as psychiatric patients will rise significantly. As psychiatrists, we have a particular duty to highlight these risks; effective advocacy within this context is paramount. Moreover, this underscores a recognised pressing but under-considered need to develop doctor specific psychiatry services within the psychiatric service framework in Ireland. This model, already piloted in England and extended in the context of the pandemic, has seen an exponential rise in referrals over the latter stages of the pandemic (Conference Proceedings for Occupational Health and Burnout among Healthcare Workers: https://www.ucd.ie/medicine/capsych/summerschool2020/ ).
As outlined above, the constantly evolving nature of the pandemic presents an unprecedented challenge to researchers aiming to identify strategies for addressing the mental health issues arising in the current pandemic. Risk factors for mental illness may coalesce in different ways at different time points of the pandemic waves. By extension, the particulars of service need and delivery will also shift against this backdrop and it is important that psychiatric services remain flexible in service delivery at this time. Despite these challenges, it is crucial to prioritise an integrated approach to psychiatric translational research in Ireland which can inform service innovation and development. The efforts of colleagues to continue to innovate and examine outcomes despite the aforementioned complexities and myriad pressures is indeed laudable and worthwhile as our efforts to transform and remodel services can have real impact for our service users.
As with the first edition dedicated to COVID-19, we sincerely hope that this themed issue provides a useful resource to colleagues as we continue to grapple with unprecedented demands. There is currently no road map to inform how the situation will evolve and what will be the ultimate extent of service need. Once again, we are most grateful to all contributors who, despite unparalleled service pressures, have taken the time to reflect and share perspectives on their experiences, innovations and clinical practice. This issue highlights the extraordinary demands on psychiatric services and the likely enduring nature of this need in the years to come as longer-term impacts of the pandemic, particularly potential economic contraction, exert their toll on population mental illness. Effective advocacy for our patients, ourselves and our colleagues remains paramount.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Authors have no conflict of interest to disclore.
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committee on human experimentation with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.

This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref .
- Google Scholar
View all Google Scholar citations for this article.
Save article to Kindle
To save this article to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service.
- Volume 37, Issue 4
- B. Gavin (a1) , J. Lyne (a2) (a3) and F. McNicholas (a4) (a5)
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/ipm.2020.128
Save article to Dropbox
To save this article to your Dropbox account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Dropbox account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save article to Google Drive
To save this article to your Google Drive account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Google Drive account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .
Reply to: Submit a response
- No HTML tags allowed - Web page URLs will display as text only - Lines and paragraphs break automatically - Attachments, images or tables are not permitted
Your details
Your email address will be used in order to notify you when your comment has been reviewed by the moderator and in case the author(s) of the article or the moderator need to contact you directly.
You have entered the maximum number of contributors
Conflicting interests.
Please list any fees and grants from, employment by, consultancy for, shared ownership in or any close relationship with, at any time over the preceding 36 months, any organisation whose interests may be affected by the publication of the response. Please also list any non-financial associations or interests (personal, professional, political, institutional, religious or other) that a reasonable reader would want to know about in relation to the submitted work. This pertains to all the authors of the piece, their spouses or partners.
- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
- Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- HIV and AIDS
- Hypertension
- Mental disorders
- Top 10 causes of death
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- Data collection tools
- Global Health Observatory
- Insights and visualizations
- COVID excess deaths
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment in WHO
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
- Publications /
Mental health and psychosocial considerations during the COVID-19 outbreak
Interim guidance

WHO and public health authorities around the world are acting to contain the COVID-19 outbreak. However, this time of crisis is generating stress throughout the population. The considerations presented in this document have been developed by the WHO Department of Mental Health and Substance Use as a series of messages that can be used in communications to support mental and psychosocial well-being in different target groups during the outbreak.
Arabic | French | Russian | Spanish
Other languages
Polish | Portuguese
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Mental health after...
Mental health after covid-19
Linked research.
Risks of mental health outcomes in people with covid-19
- Related content
- Peer review
- Scott Weich , professor of mental health
- Mental Health Research Unit, School of Health and Related Research, University of Sheffield, Sheffield S1 4DA, UK
- s.weich{at}sheffield.ac.uk
The risks are clear, it’s now time to learn and respond
A clear picture has emerged of the mental health impacts of the early waves of the covid-19 pandemic in England—when hospital admissions and mortality were common and lockdowns particularly restrictive. 1 Longitudinal population based studies show that symptoms of anxiety and depression were marked but often transient, increasing during lockdowns and subsiding afterwards to pre-pandemic levels. 2 3 4 5 Nevertheless, around 10% of the population experienced persistent distress, 4 6 with women, 18-30 years olds, people with pre-existing mental or physical health problems, those living in deprived areas, and ethnic minority communities most affected. 1
The psychiatric sequelae of infection with early SARS-CoV-2 variants are most clearly shown in three large studies based on two US healthcare databases. In their linked paper, Xie and colleagues (doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-068993 ) 7 considered outcomes over 12 months in a large cohort of adults who survived the acute phase of covid-19—longer than the 90 day and six month follow-up periods in two previous studies by Taquet and colleagues. 8 9
Xie and colleagues analysed healthcare data from the US Department of Veterans Affairs on 153 848 patients who survived at least 30 days after a positive polymerase chain reaction test result (start of follow-up) between March 2020 and January 2021. Outcomes were compared with two control groups without covid-19, matched on start of follow-up and survival 30 days after that date: 5 637 840 contemporary controls and 5 859 251 historical controls who had not experienced the pandemic (data from 2018). Additional comparisons were made with people who had seasonal influenza and with those admitted to hospital for influenza and other reasons. Study outcomes included non-psychotic psychiatric disorders and prescriptions of antidepressants and anxiolytics, and survival analyses adjusted for confounders selected algorithmically from hundreds of candidate variables.
Estimated hazards ratios for anxiety and depressive disorders among people with covid-19 (compared with contemporary controls) were 1.35 (95% confidence interval 1.30 to 1.39) and 1.39 (1.34 to 1.43), respectively, corresponding to risk differences per 1000 individuals at one year of 11.06 (9.64 to 12.53) and 15.12 (13.38 to 16.91). Hazard ratios were increased for antidepressant (1.55, 1.50 to 1.60) and benzodiazepine prescribing (1.65, 1.58 to 1.72). All associations were smaller compared with historical controls. When people with covid-19 were compared with patients who had influenza before the pandemic, hazard ratios for anxiety and depressive disorders were slightly smaller (1.44 (1.22 to 1.71) and 1.32 (1.12 to 1.56), respectively) than those previously reported by Taquet and colleagues over six months. 9
What do these studies tell us? Both report significant and consistent but modest associations between SARS-CoV-2 infection and increased rates of psychiatric disorders. Although between group differences persist for at least 12 months, 7 the absolute risk of experiencing a psychiatric disorder decreases sharply after the first month. 9 Both studies were susceptible to residual confounding and potential misclassification of recurrent versus first onset infections, limiting causal inference and interpretation. Importantly, mental healthcare might have been more accessible to those known to have had covid-19 than contemporaries without this condition or among historical cohorts, further biasing estimates away from the null. 10
What have we learnt? Time, money, and scarce research expertise have been devoted to showing, again and on a societal scale, that threat makes people anxious but diminishes for most people when the danger passes. 1 Further confirmation has shown that those who are most disadvantaged experience the worst (mental) health outcomes, particularly after the harms caused by a decade of austerity in the UK and many other countries. 11 12 Health inequalities have widened, particularly for people with serious mental illness who have experienced even more exclusion and premature mortality during the pandemic. 12 13
The worst of the pandemic might be behind us in terms of mortality and social restrictions. Taking stock, it could be argued that much of the research concerned with the mental health impacts of covid-19 represents more hindsight than insight. Looking back at what happened is arguably less important than reflecting on what we have learnt, what we need to do next, and what we still do not know. Our attachment to syndromal phenotypes 14 means that we have learnt remarkably little about the causes of mental ill health—in this case psychopathology associated with a viral pandemic. We continue to generate more heat than light as we reflect on the usual biopsychosocial suspects 10 without cutting through to conclusive insights or effective interventions.
We do not yet know the true incidence and consequences of long covid, 15 and we are still witnessing the unfolding toll of the pandemic on healthcare staff. 16 Also, we do not have an effective response to the devastating disruption to health, social care, and voluntary sector services on the lives of people with serious mental illness. 17 And while epidemiological research has flourished—at least in terms of scientific publications—we are guilty of failing to prioritise evaluations of mental healthcare interventions, including clinical trials, just when these are most needed. 18
Competing interests: The BMJ has judged that there are no disqualifying financial ties to commercial companies.
Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; not externally peer reviewed.
This article is made freely available for personal use in accordance with BMJ's website terms and conditions for the duration of the covid-19 pandemic or until otherwise determined by BMJ. You may download and print the article for any lawful, non-commercial purpose (including text and data mining) provided that all copyright notices and trade marks are retained.
- ↵ Network NMHI. COVID-19 mental health and wellbeing surveillance: report London: Office for Health Improvement and Disparities; 2021 [updated 18/11/21]. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-mental-health-and-wellbeing-surveillance-report .
- Chandola T ,
- Booker CL ,
- McManus S ,
- Fancourt D ,
- Steptoe A ,
- Niedzwiedz CL ,
- Benzeval M ,
- Leyland AH ,
- Katikireddi SV
- Luciano S ,
- Geddes JR ,
- Harrison PJ
- Rogers JP ,
- Goldblatt P ,
- Etchecopar-Etchart D ,
- Johnstone M ,
- Greenberg N ,
- ↵ Farmer P. Investing in Community Services Manchester: National Health Executive; 2022. https://mag.nationalhealthexecutive.com/publication/?i=729893&ver=html5&p=44 .
- Gilbody S ,
- Littlewood E ,
- Gascoyne S ,
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Online-Delivered Group and Personal Exercise Programs to Support Low Active Older Adults' Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Randomized Controlled Trial
Affiliations.
- 1 School of Kinesiology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
- 2 School of Kinesiology, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, United States.
- 3 School of Exercise Science, Physical and Health Education, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada.
- 4 Department of Human Nutrition, Foods, and Exercise, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, United States.
- PMID: 34328433
- PMCID: PMC8330630
- DOI: 10.2196/30709
Background: In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, experts in mental health science emphasized the importance of developing and evaluating approaches to support and maintain the mental health of older adults.
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess whether a group-based exercise program relative to a personal exercise program (both delivered online) and waitlist control (WLC) can improve the psychological health of previously low active older adults during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: The Seniors COVID-19 Pandemic and Exercise (SCOPE) trial was a 3-arm, parallel randomized controlled trial conducted between May and September 2020 in which low active older adults (aged ≥65 years) were recruited via media outlets and social media. After baseline assessments, consented participants were randomized to one of two 12-week exercise programs (delivered online by older adult instructors) or a WLC condition. A total of 241 older adults (n=187 women) provided baseline measures (via online questionnaires), were randomized (n group =80, n personal =82, n control =79), and completed measures every 2 weeks for the duration of the trial. The trial's primary outcome was psychological flourishing. Secondary outcomes included global measures of mental and physical health, life satisfaction, and depression symptoms.
Results: The results of latent growth modeling revealed no intervention effects for flourishing, life satisfaction, or depression symptoms (P>.05 for all). Participants in the group condition displayed improved mental health relative to WLC participants over the first 10 weeks (effect size [ES]=0.288-0.601), and although the week 12 effect (ES=0.375) was in the same direction the difference was not statistically significant (P=.089). Participants in the personal condition displayed improved mental health, when compared with WLC participants, in the same medium ES range (ES=0.293-0.565) over the first 8 weeks, and while the effects were of a similar magnitude at weeks 10 (ES=0.455, P=.069) and 12 (ES=0.258, P=.353), they were not statistically significant. In addition, participants in the group condition displayed improvements in physical health when compared with the WLC (ES=0.079-0.496) across all 12 weeks of the study following baseline. No differences were observed between the personal exercise condition and WLC for physical health (slope P=.271).
Conclusions: There were no intervention effects for the trial's primary outcome (ie, psychological flourishing). It is possible that the high levels of psychological flourishing at baseline may have limited the extent to which those indicators could continue to improve further through intervention (ie, potential ceiling effects). However, the intervention effects for mental and physical health point to the potential capacity of low-cost and scalable at-home programs to support the mental and physical health of previously inactive adults in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04412343 ; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04412343.
Keywords: COVID-19; mental health; physical activity; randomized trial.
©Mark R Beauchamp, Ryan M Hulteen, Geralyn R Ruissen, Yan Liu, Ryan E Rhodes, Colin M Wierts, Katrina J Waldhauser, Samantha H Harden, Eli Puterman. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 30.07.2021.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
CONSORT flow diagram.
Program attendance in the two…
Program attendance in the two experimental conditions across the 12-week trial.
Trajectories for mental health outcomes…
Trajectories for mental health outcomes over the course of the trial.
Similar articles
- Effects of older adults' social identification on psychological flourishing and exercise program adherence. Reis NA, Waldhauser KJ, Hives BA, Hulteen RM, Ruissen GR, Wierts CM, Puterman E, Liu Y, Rhodes RE, Beauchamp MR. Reis NA, et al. Psychol Health. 2023 May 25:1-13. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2023.2215804. Online ahead of print. Psychol Health. 2023. PMID: 37231641
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
- Efficacy of a Single-Session "Empowered Relief" Zoom-Delivered Group Intervention for Chronic Pain: Randomized Controlled Trial Conducted During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ziadni MS, Gonzalez-Castro L, Anderson S, Krishnamurthy P, Darnall BD. Ziadni MS, et al. J Med Internet Res. 2021 Sep 10;23(9):e29672. doi: 10.2196/29672. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34505832 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
- Older Adults' Mental Health Through Leisure Activities During COVID-19: A Scoping Review. Rivera-Torres S, Mpofu E, Jean Keller M, Ingman S. Rivera-Torres S, et al. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2021 Aug 9;7:23337214211036776. doi: 10.1177/23337214211036776. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2021. PMID: 34395816 Free PMC article. Review.
- Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression. Martiny K. Martiny K. Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
- Comparative effects of three different physical education teaching modes on college students' physical fitness during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal study. Tao Z, Zhu E, Sun X, Sun J. Tao Z, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Mar 27;10(7):e28305. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28305. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38601624 Free PMC article.
- "If I want to be able to keep going, I must be active." Exploring older adults' perspectives of remote physical activity supports: a mixed-methods study. Mehrabi S, Drisdelle S, Dutt HR, Middleton LE. Mehrabi S, et al. Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 24;12:1328492. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1328492. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38327585 Free PMC article.
- Global landscape of COVID-19 research: a visualization analysis of randomized clinical trials. Zyoud SH. Zyoud SH. Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jan 22;24(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01254-3. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38252392 Free PMC article.
- Enhancing Minds in Motion® as a virtual program delivery model for people living with dementia and their care partners. Neudorf B, Dinh C, Barnes V, Stergiou-Dayment C, Middleton L. Neudorf B, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Jan 19;19(1):e0291166. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291166. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38241269 Free PMC article.
- The effects of psychosocial and behavioral interventions on depressive and anxiety symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. He J, Lin J, Sun W, Cheung T, Cao Y, Fu E, Chan SHW, Tsang HWH. He J, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 4;13(1):19094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45839-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37925535 Free PMC article.
- Jowell A, Carstensen LL, Barry M. A life-course model for healthier ageing: lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2020 Oct;1(1):e9–e10. doi: 10.1016/s2666-7568(20)30008-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Holmes EA, O'Connor RC, Perry VH, Tracey I, Wessely S, Arseneault L, Ballard C, Christensen H, Cohen Silver R, Everall I, Ford T, John A, Kabir T, King K, Madan I, Michie S, Przybylski AK, Shafran R, Sweeney A, Worthman CM, Yardley L, Cowan K, Cope C, Hotopf M, Bullmore E. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Jun;7(6):547–560. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30168-1. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32304649 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Banerjee D. The impact of Covid-19 pandemic on elderly mental health. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2020 Dec;35(12):1466–1467. doi: 10.1002/gps.5320. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32364283 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- World Health Organization . #HealthyAtHome - Physical Activity. World Health Organization; [2021-06-21]. https://www.who.int/news-room/campaigns/connecting-the-world-to-combat-c... .
- Jacob L, Tully MA, Barnett Y, Lopez-Sanchez GF, Butler L, Schuch F, López-Bueno R, McDermott D, Firth J, Grabovac I, Yakkundi A, Armstrong N, Young T, Smith L. The relationship between physical activity and mental health in a sample of the UK public: A cross-sectional study during the implementation of COVID-19 social distancing measures. Ment Health Phys Act. 2020 Oct;19:100345. doi: 10.1016/j.mhpa.2020.100345. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32834833 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
Associated data
- Search in ClinicalTrials.gov
Related information
Linkout - more resources, full text sources.
- Europe PubMed Central
- JMIR Publications
- PubMed Central
- MedlinePlus Health Information
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
- Higher Education Today
- American Council On Education
- Carnegie Classifications
- Race and Ethnicity In Higher Education
Limiting the Growing Need for Treatment: Digital Mental Health Supports on Campus
July 1, 2024
Title Digital Mental Health Interventions at Colleges & Universities
Authors: Sara Abelson, Daniel Eisenberg, Ashley Johnston, Sarah Ketchen Lipson, Michelle Liu, Shannon N. Ogden, and Stephen M. Schueller
Source: Ruderman Family Foundation
In the last decade, the number of college students reporting clinically significant mental health symptoms has doubled, causing higher education leadership to consider the role of digital mental health interventions (DMHIs).
Digital mental health interventions provide behavioral and psychological support through technology such as websites, mobile apps, and other online platforms. Many DMHIs are preventative resources that can support students with less acute needs. Some forms of digital intervention can reduce the need for treatment and allow students to self-manage, while others increase engagement with interventions or provide additional interventions through human support.
The Ruderman Family Foundation commissioned research into popular DMHIs offered at many colleges and universities. The researchers concluded that though they can be effective at improving mental health, most widely used DMHIs in college settings have limited direct evidence of effectiveness. There is a clear need for additional research into the effectiveness and disbursement of DMHIs, but there is also reason for optimism about the role of technology in mental health support.
The report states that each institution wanting to include DMHIs in its mental health strategies should consider how digital interventions fit with its existing system of resources and its specific population’s needs. Higher education leaders should view DMHIs as part of a holistic, public health approach to student mental health. The authors determined the following areas of research and evaluation to guide decision-making regarding the use of DMHIs for college students.
- More rigorous evaluation of commonly used programs: How effective are commonly used campus programs for students?
- Evaluation of user engagement: How many students on campus are actively using digital intervention tools?
- Real-world evidence and post-deployment evaluation: What benefits do DMHIs continue to offer when used in off-campus conditions by students?
Across these areas for future research, the needs and inclusion of diverse student populations should be a top priority. Underrepresented students, such as first-generation, low-income, and students of color, are at a higher risk for adverse mental health. In looking to implement digital mental health intervention tools, students at a higher risk should be at the center of research.
To learn more about digital mental health interventions, click here .
—Eliza Gonzalez
If you have any questions or comments about this blog post, please contact us .
Keep Reading

Why We Should Partner with Students to Address Campus Mental Health
Students know students, says Laura Horne, director of programs for Active Minds. Engaging them as equal partners in improving mental health on campus can make all the difference.

What Campus Data Tell Us About Student Mental Health and COVID-19
Recent stories have warned of a “mental health tsunami” and a “mental health crisis on campuses” as over the past two years, students and campus communities worked to master the new normal of masking, vaccines, and social distancing in a global pandemic. As we look toward the future, what should campuses do about the mental health of students?

Mental Health and Post-traditional Learners
Post-traditional learners are often expected to adjust their own lives and schedules to campus life and services, including in the area of mental health. But it is equally important that campus services and culture are adjusted to better serve this growing group of students and their unique needs.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Public Health
Mental Health Research During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Focuses and Trends
Yaodong liang.
1 Law School, Changsha University, Changsha, China
2 Department of Psychology, University of Toronto St. George, Toronto, ON, Canada
3 Centre for Mental Health and Education, Central South University, Changsha, China
Associated Data
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly influenced the world. In wave after wave, many countries suffered from the pandemic, which caused social instability, hindered global growth, and harmed mental health. Although research has been published on various mental health issues during the pandemic, some profound effects on mental health are difficult to observe and study thoroughly in the short term. The impact of the pandemic on mental health is still at a nascent stage of research. Based on the existing literature, we used bibliometric tools to conduct an overall analysis of mental health research during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Researchers from universities, hospitals, communities, and medical institutions around the world used questionnaire surveys, telephone-based surveys, online surveys, cross-sectional surveys, systematic reviews and meta-analyses, and systematic umbrella reviews as their research methods. Papers from the three academic databases, Web of Science (WOS), ProQuest Academic Database (ProQuest), and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), were included. Their previous research results were systematically collected, sorted, and translated and CiteSpace 5.1 and VOSviewers 1.6.13 were used to conduct a bibliometric analysis of them.
Authors with papers in this field are generally from the USA, the People's Republic of China, the UK, South Korea, Singapore, and Australia. Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University are the top three institutions in terms of the production of research papers on the subject. The University of Toronto, Columbia University, and the University of Melbourne played an important role in the research of mental health problems during the COVID-19 pandemic. The numbers of related research papers in the USA and China are significantly larger than those in the other countries, while co-occurrence centrality indexes in Germany, Italy, England, and Canada may be higher.
We found that the most mentioned keywords in the study of mental health research during the COVID-19 pandemic can be divided into three categories: keywords that represent specific groups of people, that describe influences and symptoms, and that are related to public health policies. The most-cited issues were about medical staff, isolation, psychological symptoms, telehealth, social media, and loneliness. Protection of the youth and health workers and telemedicine research are expected to gain importance in the future.
Introduction
Although the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic will be recorded in human medical history and in socio-economic history, various psychological consequences regarding mental health among populations cannot be ignored, including stress, anxiety, depression, frustration, insomnia, and so on. Researchers from universities, hospitals, communities, and medical institutions worldwide have been focusing on mental health problems during the pandemic. They have used questionnaire surveys, telephone-based surveys, online surveys, cross-sectional surveys, systematic reviews and meta-analysis, and systematic umbrella reviews to investigate mental health problems during the pandemic. Two years after the outbreak of the COVID-19, the pandemic has gradually subsided in some countries, while others have adopted a strategy of coexisting with the virus. If more deadly mutant strains do not appear in the future, it is very likely that the pandemic will not climax again. It is pertinent to summarize and study mental health research during the pandemic, because many psychological problems have arisen as a result, and there has been significant interest in research on such issues in the previous two years.
As an effective quantitative analysis method, bibliometrics can be used not only to assess the quality and quantity of published papers, but also to explore research focuses and trends, the distribution of authors and institutions, the impact of publications, journals, and different countries regarding research contributions to the theme. Due to the rapid growth in research in this area, there are now over 1,000 academic papers, and accordingly, it would appear necessary to investigate important, valid, and meaningful information from large databases to guide scientific research. The authors used CiteSpace and VOSviewers to determine the focuses and trends in this regard.
Data Analysis and Visualization
The authors searched the Web of Science (WOS), ProQuest Academic Database (ProQuest), and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) to extract publications related to mental health and COVID-19. Their previous research results were systematically collected, sorted, and translated, and CiteSpace 5.1 and VOSviewers 1.6.13 were used to conduct a bibliometric analysis of them.
Data Source and Search Strategy
Our team selected 1,226 papers from 2019 to 2022 using three combinations of keywords, mental health and COVID-19, mental health and new coronavirus, and mental health and novel coronavirus, from the three academic paper databases, WOS, ProQuest, and CNKI. Two explanations are necessary here, the first is about the keywords and the second is about the databases. (1) The reason we used new or novel coronavirus as keywords was that the name COVID-19 has not been determined about 2 years ago. In order not to miss relevant research results, we also included these synonyms as keywords for the search. (2) Among the three databases, WOS and ProQuest, in which most of the English-language papers were published, are well-known to scholars all around the world. However, the CNKI database is not as popular as WOS or ProQuest given that most of the papers in CNKI were published in Chinese. We chose to use the CNKI data for the following three reasons: first, China was the most affected country during the COVID-19 outbreak and Chinese academic journals published significant research on mental health. Second, CNKI is the largest Chinese academic database. Third, after the outbreak, the Chinese government's virus clearance policy has been implemented and continues to date. Strict control has helped suppress the spread of the virus, but has also likely had mental health implications, given the severe reduction in social interactions. Therefore, we think that the Chinese database is appropriate and useful in this study.
About 50% of the articles were from the WOS, about 10% of the articles from ProQuest, and about 40% from CNKI. Basic information such as title, author, institution, country, abstract, keywords, methods, results, and conclusions of all articles, if not in English, are translated into English and analyzed using SiteSpaceII and VOSviewers. Since the keywords include COVID-19 and mental health, synonyms such as novel coronavirus and psychological distress spontaneously appeared while searching. Words that are closely related to the subject, such as public health, quarantine, and insomnia, were most frequently mentioned.
Most articles were published during the period from February 2020 to July 2022, including those pre-published online from April to July, and only one article that had been published in 2019 was included. Judging from the line chart above, since the volume of COVID-19 and mental health-related articles had already risen two times in June 2020 and June 2021 and then remained low until now, it is high time to conclude a previous study on COVID-19 and mental health, to sort out the foci of those studies, and to analyze and predict future trends ( Figure 1 ).

The volume of COVID-19 and mental health-related articles in 2020–2022.
Scholars from around the world have contributed to the study of mental health issues during the COVID-19 pandemic. The top 10 countries with the largest quantum of publications related to mental health during COVID-19 are the USA, People's Republic of China, England, Canada, Australia, India, Italy, Japan, Iran, and Germany. Wide and active participation of several countries has laid a solid foundation for its future development. Universities, hospitals, communities, and medical institutions around the world have conducted sample surveys of patients, students, community residents, medical workers, and other sample populations of considerable sample sizes since the outbreak. Survey and research methods include questionnaire survey, telephone-based survey, online survey, cross-sectional survey, systematic review and meta-analyses, and systematic umbrella review ( Table 1 ).
Top 20 countries.
| 1 | 280 | USA | 11 | 27 | Spain |
| 2 | 223 | China | 12 | 26 | Brazil |
| 3 | 85 | England | 13 | 22 | Saudi Arabia |
| 4 | 69 | Canada | 14 | 19 | Pakistan |
| 5 | 68 | Australia | 15 | 18 | Turkey |
| 6 | 54 | India | 16 | 12 | Bangladesh |
| 7 | 50 | Italy | 17 | 11 | Sweden |
| 8 | 41 | Japan | 18 | 10 | Singapore |
| 9 | 37 | Iran | 18 | 10 | Poland |
| 10 | 27 | Germany | 20 | 9 | Malaysia |
Most papers are from the USA, the People's Republic of China, England, Australia, Canada, India, Italy, Iran, Japan, and Germany. Judging from the country or region co-occurrence graph, England and Canada are in the center of this graph, with India, Poland, Denmark, Spain, South Korea, Portugal, Italy, and Canada around them. England, Australia, Canada, Japan, Brazil, India, Iran, and Germany have done significant research work in this field. In addition, the number of related research papers in the USA and China is significantly larger than that in all other countries ( Figure 2 ).

Country or region co-occurrence.
In Table 2 , we can see that most names of the top 20 authors are Asian names, and they are mainly from China. Six of them published more than 10 articles by the end of 2021. In the extended ranking, we find that the authors who have published a large number of papers are generally from the USA, China, the UK, South Korea, Singapore, and Australia. The authors Griffiths MD, Cheung T, Xiang Y, Lin C, Wang Y, and Zhang L were very active in this field of study.
Top 20 authors.
| 1 | 14 | Xiang YT | 7 | 7 | Zvolensky MJ |
| 2 | 13 | Zhang L | 12 | 6 | Ng CH |
| 2 | 13 | Wang Y | 12 | 6 | Pakpour AH |
| 2 | 13 | Cheung T | 14 | 5 | Li W |
| 5 | 11 | Li Y | 14 | 5 | Li X |
| 5 | 11 | Griffiths MD | 14 | 5 | Garey L |
| 7 | 7 | Li L | 14 | 5 | Zhong BL |
| 7 | 7 | Zhang Y | 14 | 5 | Wang W |
| 7 | 7 | Zhang Q | 14 | 5 | Yang Y |
| 7 | 7 | Lin CY | 20 | 4 | Hu SH |
In the abovementioned graphs, we can see six groups of related authors. The VOSviewer was used to describe the partnership between them. Though six colors were used to separate these groups, there were still lines connecting the groups to represent the partnership between them. We can take Cheung T and Xiang Y as the center of the largest group. Another group with Griffiths MD and Lin C as its center was also significant ( Figures 3 , ,4 4 ).

Author co-occurrence.

Author co-occurrence groups.
The top five institutions are Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Columbia University, and the University of Toronto. Meanwhile, the top five institutions in centrality are the University of Macau, the University of Melbourne, Columbia University, Wuhan University, and the University of Toronto. It is worth mentioning that Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Wuhan University are located in the city of Wuhan, one of the areas most affected by the virus through the outbreak. The society and economy of the city temporarily stagnated at the time, and its medical system was once paralyzed. Eventually, Wuhan City's medical system was fully recovered. The University of Toronto, Columbia University, and the University of Melbourne have played an important role in the research of mental health problems during the COVID-19 pandemic ( Table 3 and Figure 5 ).
Top 20 institutions.
| 1 | 25 | 0.18 | Huazhong University of Science and Technology |
| 2 | 25 | 0.14 | Hong Kong Polytechnic University |
| 3 | 21 | 0.12 | Shanghai Jiao Tong University |
| 4 | 19 | 0.56 | Columbia University |
| 5 | 18 | 0.44 | The University of Toronto |
| 6 | 16 | 0.61 | The University of Melbourne |
| 7 | 16 | 0.35 | Harvard Medical School |
| 8 | 14 | 0.78 | The University of Macau |
| 9 | 14 | 0.50 | Wuhan University |
| 10 | 13 | 0.12 | Kings College London |
| 11 | 13 | 0.01 | Capital Medical University |
| 12 | 12 | 0 | Nottingham Trent University |
| 13 | 11 | 0 | Peking University |
| 14 | 11 | 0.22 | New York University |
| 15 | 10 | 0.12 | Zhejiang University |
| 16 | 10 | 0 | The University of California Los Angeles |
| 16 | 10 | 0 | Sichuan University |
| 18 | 9 | 0.21 | Dalhousie University |
| 19 | 9 | 0 | Xi An Jiao Tong University |
| 20 | 8 | 0 | The University of Calgary |

Institutions' co-occurrence.
As can be seen in Figure 6 , Huazhong University of Science and Technology has led Chinese universities and research institutions, such as Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Peking University, in conducting research on COVID-19 and mental health. Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Fudan University, and the University of Melbourne acted as bridges, connecting famous universities and research institutions in Europe, America, and other countries in the world, such as Kings College London and Harvard Medical School, to jointly study issues in this field. In particular, they conduct joint research, directly or indirectly, through Hong Kong Polytechnic University, which display the important communication and joint role of Hong Kong Polytechnic University.

Keyword clustering.
Judging from Table 4 , the most mentioned keywords, in addition to COVID-19 and mental health, can be roughly divided into three categories: (1) keywords representing specific groups of people, such as adolescents, young adults, doctors, nurses, medical staff, and healthcare workers; (2) keywords describing influences and symptoms, such as isolation, loneliness, anxiety, depression, stress, and insomnia; and (3) keywords related to public health policies, such as lockdown, social distancing, telehealth, telemedicine, and quarantine.
Keyword clustering I.
| 227 | 0.54 | Mental health | 2020 | 0 |
| 16 | 0.1 | Psychological distress | 2020 | 0 |
| 16 | 0.41 | Fear | 2020 | 0 |
| 14 | 0 | Lockdown | 2020 | 0 |
| 13 | 0.1 | Healthcare worker | 2020 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | Psychological impact | 2020 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | Adolescent | 2021 | 0 |
| 7 | 0.06 | Social distancing | 2020 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | Burnout | 2021 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | Distress | 2021 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | Stigma | 2020 | 0 |
| 4 | 0.05 | Social media | 2020 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | Trauma | 2020 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | COVID-19 | 2020 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | Spirituality | 2022 | 0 |
| 20 | 0.05 | Nurse | 2020 | 1 |
| 15 | 0.24 | Insomnia | 2020 | 1 |
| 14 | 0.46 | Medical staff | 2020 | 1 |
| 11 | 0.05 | Resilience | 2020 | 1 |
| 8 | 0.1 | Sleep | 2021 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 | Qualitative research | 2021 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 | Coping | 2021 | 1 |
| 5 | 0.1 | Coping strategy | 2021 | 1 |
| 4 | 0.15 | Perceived stress | 2021 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | Prevalence | 2021 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | Physician | 2021 | 1 |
| 13 | 0.16 | Telehealth | 2020 | 2 |
| 10 | 0.17 | Children | 2021 | 2 |
| 10 | 0.27 | Telemedicine | 2020 | 2 |
| 8 | 0.21 | Mental health service | 2020 | 2 |
| 7 | 0 | Quality of life | 2021 | 2 |
| 6 | 0 | COVID | 2020 | 2 |
| 6 | 0 | College student | 2021 | 2 |
| 5 | 0.21 | Coronavirus disease 2019 | 2020 | 2 |
| 4 | 0.05 | COVID19 | 2020 | 2 |
| 3 | 0 | Viral infection | 2020 | 2 |
| 31 | 0.21 | Novel coronavirus | 2020 | 3 |
| 18 | 0.41 | Public health | 2020 | 3 |
| 9 | 0.03 | Infectious disease | 2020 | 3 |
| 8 | 0.12 | Mentalhealth | 2020 | 3 |
| 7 | 0.07 | Psychiatry | 2020 | 3 |
| 7 | 0 | Pandemics | 2020 | 3 |
| 3 | 0.03 | Young adult | 2020 | 3 |
| 3 | 0 | Risk communication | 2020 | 3 |
| 3 | 0 | COVID-19 outbreak | 2020 | 3 |
| 3 | 0.12 | Psychotherapy | 2020 | 3 |
| 112 | 0.95 | Coronavirus | 2020 | 4 |
| 14 | 0.22 | Physical activity | 2020 | 4 |
| 9 | 0 | Meta-analysis | 2020 | 4 |
| 7 | 0.05 | University student | 2021 | 4 |
| 6 | 0.23 | Exercise | 2021 | 4 |
| 5 | 0.15 | Health | 2021 | 4 |
| 4 | 0 | Depressive symptom | 2021 | 4 |
| 4 | 0 | Attitude | 2021 | 4 |
| 3 | 0.05 | Health care worker | 2020 | 4 |
| 537 | 1.08 | COVID-19 | 2020 | 5 |
| 98 | 0.6 | Pandemic | 2020 | 5 |
| 19 | 0.15 | China | 2020 | 5 |
| 13 | 0.66 | Epidemic | 2020 | 5 |
| 11 | 0 | Social support | 2020 | 5 |
| 4 | 0 | Knowledge | 2020 | 5 |
| 3 | 0.05 | Psychological stress | 2020 | 5 |
| 3 | 0 | Psychological intervention | 2020 | 5 |
| 2 | 0.19 | Qualitative study | 2022 | 5 |
| 106 | 0.72 | Anxiety | 2020 | 6 |
| 95 | 0.66 | Depression | 2020 | 6 |
| 57 | 0 | SARS-CoV-2 | 2020 | 6 |
| 54 | 0.61 | Stress | 2020 | 6 |
| 10 | 0 | Ptsd | 2021 | 6 |
| 6 | 0 | Outbreak | 2020 | 6 |
| 4 | 0 | Sleep quality | 2020 | 6 |
| 3 | 0.1 | Isolation | 2020 | 6 |
| 25 | 0 | Quarantine | 2020 | 7 |
| 21 | 0.1 | COVID-19 pandemic | 2020 | 7 |
| 13 | 0.78 | Loneliness | 2021 | 7 |
| 10 | 0 | Wellbeing | 2021 | 7 |
| 7 | 0.78 | Worry | 2021 | 7 |
| 2 | 0.2 | Youth | 2022 | 7 |
| 2 | 0 | Suicidal ideation | 2022 | 7 |
| 2 | 0.34 | Longitudinal | 2022 | 7 |
In Graph 7, we can judge that COVID-19, mental health, pandemic, and coronavirus are represented by larger red dots as their centrality indexes are naturally higher. In this bibliometric network map, other keywords emerged next to them and together formed this visualization bibliometric network. Occupational and sociodemographic characteristics are clustered together, while symptoms of mental health problems are clustered next to them. Specific groups of people and their typical symptoms and causes occupy certain areas on the map. For example, typical symptoms of university students and the possible causes of these symptoms are grouped together on the map. Similarly, quarantine policy and its influence are also classified in certain areas. In addition, research methods and solutions appeared sporadically on this map.
Table 5 shows eight groups of core keywords separated from keyword clustering I. Each of these groups contains three keywords, which proves that these keywords appear at the same time in a considerable part of the research, and are more closely related. Keyword ClusteringII cannot only present the outline of existing mental health research in academia, but also highlights the focus of research. In addition, SiteSpaceII and VOSviewers also gave us some clues about the research trends and further development.
Keyword clustering II.
| 0 | 13 | 0.918 | 2020 | Quarantine | COVID-19 pandemic | Psychological distress |
| 1 | 10 | 0.936 | 2020 | Epidemic | Telehealth | Telemedicine |
| 2 | 10 | 0.925 | 2020 | Nurse | Insomnia | Medical staff |
| 3 | 9 | 0.737 | 2020 | Coronavirus | Lockdown | Physical activity |
| 4 | 9 | 0.863 | 2020 | COVID-19 | Mental health | Pandemic |
| 5 | 8 | 0.949 | 2020 | Novel coronavirus | Public health | Mental health |
| 6 | 7 | 0.827 | 2020 | Anxiety | Depression | Stress |
| 7 | 6 | 0.887 | 2021 | Loneliness | Health | University student |
Research Focuses
Medical staff.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated mental health problems among populations, especially medical staff, patients with COVID-19, chronic disease patients, and isolated people. Doctors, nurses, and other medical staff have significantly higher rates of insomnia than other populations ( 1 ). The researchers obtained the relevant demographic data through the WeChat questionnaire survey. Questions in the questionnaire are related to insomnia, depression, anxiety, and stress-related symptoms during the pandemic. Their research found that, since the outbreak, more than one-third of the medical staff suffered from symptoms of insomnia. Psychological intervention measures were necessary for those people ( 2 ). Research within medical institutions shows that the psychological pressure of medical staff in isolation wards was greater, but had also attracted greater attention from hospital administrators. The concern of hospital managers alleviated the pressure of medical staff to a certain extent. Further, concern for the public also reduced their psychological burden. In terms of anxiety about infection and fatigue factors, the research results showed that the psychological burden of nurses was heavier than that of doctors. Healthcare workers who lived with their own children showed more obvious fatigue and anxiety, which might be due to the fear of their children becoming infected. In terms of workload and work motivation, medical staff who have been working for more than 20 years have a heavier workload, but they can still maintain their enthusiasm to fight against the pandemic ( 3 ). Another survey showed that 73.4% of healthcare workers, mainly physicians, nurses, and auxiliary staff, reported post-traumatic stress symptoms during outbreaks, with symptoms persisting for up to 3 years in 10–40% of the cases. Depressive symptoms were reported in 27.5–50.7%, insomnia symptoms in 34–36.1%, and severe anxiety symptoms in 45% ( 4 ). A subgroup analysis revealed gender and occupational differences, with female health care practitioners and nurses exhibiting higher rates of affective symptoms compared to men and medical staff, respectively ( 5 ).
As a result, depressive symptoms (21%) and anxiety symptoms (19%) are higher during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to previous epidemiological data. About 16% of the subjects suffered from severe clinical insomnia during the lockdown. The pandemic and lockdown seemed to be particularly stressful for younger adults who were under 35 years old, women, people out of work, or those with low incomes ( 6 ). In the fight against the pandemic, China adopted measures to restrict population aggregation, such as the blockade of pandemic areas, individual patient isolation, and restrictions on the movement of people in non-pandemic areas. These measures effectively prevented the spread of the pandemic. At the same time, the use of health codes, grid-like community management, and the operational efficiency of infectious disease information networks have greatly improved. However, quarantine has also brought with it a number of problems, such as increasing psychological pressure on the population, affecting the daily lives of families, and hindering social and economic development ( 7 ). A large sample size study with wide coverage published in 2021 showed that young people quarantined at home in different provinces had different rates of anxiety and depression due to different severity of pandemic situations in different regions. The risk of anxiety and depression was statistically significantly higher in girls than in boys. The rate of anxiety and depression was affected by factors, such as gender, age, and area, as well as the existence of COVID-19 cases in the surrounding area ( 8 ).
Psychological Symptoms
The impact of the aforementioned isolation measures on mental health is only part of the impact of the COVID-19 on mental health. Psychological symptoms brought about by the pandemic have also been systematically sorted out by scholars. These studies show two clues. First, certain people have special psychological symptoms; second, psychological symptoms in different countries of the world are roughly the same. Several factors were associated with a higher risk of psychiatric symptoms or low psychological wellbeing, including female gender and poor self-related health ( 9 ). Relatively, severe symptoms of anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, psychological distress, and stress were reported in the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic in China, Spain, Italy, Iran, the USA, Turkey, Nepal, and Denmark. Risk factors associated with measures of distress include female gender, younger age group, the presence of chronic or psychiatric illnesses, unemployment, student status, and frequent exposure to social media or news concerning COVID-19. The pandemic is associated with significant levels of psychological distress that, in many cases, will meet the threshold for clinical relevance. Mitigating the hazardous effects of COVID-19 on mental health is an international public health priority ( 1 ). Infectious disease pandemics often cause some people to act irrationally. The results of a survey based on psychological symptoms and irrational behaviors have drawn some conclusions. First, the vast majority of people remain in good physical and mental health, but some exhibit irrational behaviors. Second, women, elderly people, and those with confirmed cases showed more physical and mental symptoms and irrational behaviors. Finally, paradoxically, people with high education levels showed more mental symptoms, but fewer irrational behaviors ( 10 ).
Telemedicine
Just as the pandemic has enabled the rapid development of online education, the prospects of telemedicine are also favored by experts, observers, and investors. However, there are two restrictive aspects, namely, telemedicine equipment and telemedicine human resources. The application of 5G communication technology, telemedicine equipment, remote monitoring equipment, remote physical sign monitoring equipment, and medical artificial intelligence triage equipment all need to be urgently developed and improved. Jiangsu, a province in China, is a model province of the national project called “Internet + Medical and Health.” During the pandemic, the telemedicine by public hospitals in Jiangsu Province helped improve the efficiency of diagnosis and treatment, alleviating the pressure of offline diagnosis and treatment, and reducing the risk of cross-infection. Subsequently, medical staff were fully supportive of telemedicine. However, there was a shortage of medical staff in fever clinics, obstetrics and gynecology, pediatrics, and psychiatrists that provided telemedicine services, and they lacked corresponding incentive mechanisms ( 11 ). Effective mitigation strategies to improve mental health were developed by public health management experts. To control the rapid spread of COVID-19 and manage the crisis better, both developed and developing countries have been improving the efficiency of their health system by replacing a proportion of face-to-face clinical encounters with telemedicine solutions ( 12 ).
Social Media
There were rumors in various kinds of media during the COVID-19 pandemic. Although we can regard rumors as a disturbing error for psychological measurement, if they are not strictly controlled, their impact on people's mental health and behavior cannot be ignored. A study focusing on the spread of WeChat rumors has explored the psychological perception mechanism of audiences affected by rumor spreading in emergency situations. The study has significant results in the following terms: the form characteristics of the rumors in COVID-19, the ranking of susceptible age groups, the degree of dependence of the test subject on certain media and its psychological impact, and the follow-up behavior of the test subjects related to psychological variables ( 2 ). In 2021, another interesting study based on the data of TikTok videos released by three mainstream media in China showed that they inevitably caused some psychological trauma to the public. However, from the perspective of overall emotional orientation, short-format videos with positive reporting emotional tendencies had an advantage in attracting likes from TikTok users. Positive government responses to pandemic information were very important, and those responses could be recognized and praised by most social media users. Some of the TikTok videos, such as The Plasma of a Recovered Patient Cured 11 Other ICU Patients, The First COVID-19 Test Kit Passed Inspection, and A Frenchman Named Fred gave up Returning to Home to Join China's Anti-COVID-19 Battle, are extremely popular among social media users. Most social media users have been providing spiritual sustenance for people in the pandemic ( 13 ). When a public health crisis occurs, social media plays an important role in increasing public vigilance, helping the public identify rumors, and boosting public morale.
University Students and Loneliness
A study that assessed the adverse impact on the mental health of university students has drawn some conclusions. First, the severity of the outbreak has an indirect effect on negative emotions by affecting sleep quality. Second, a possible mitigation strategy to improve mental health includes ensuring suitable amounts of daily physical activity and deep sleep. Third, the pandemic has reduced people's aggressiveness, probably by making people realize the fragility and preciousness of life ( 14 ). Another research focused on social networks and mental health compared two cohorts of Swiss undergraduate students who were experiencing the crisis, and made an additional comparison with an earlier cohort who did not experience the pandemic. The researchers found that interaction and co-study networks had become sparser, and more students were studying alone. Stressors shifted from fear of missing out on social life to concern about health, family, friends, and their future ( 15 ). Young adults, women, people with lower education or lower income, the economically inactive, people living alone, and urban residents were at greater risk of being lonely during the pandemic. Being a student emerged as a higher than usual risk factor for loneliness during the lockdown ( 16 ). A study to explore the relationship between loneliness and stress among undergraduates in North America showed that the loneliness and stress among college students increased. On one hand, stress plays a key role in the deterioration of college students' mental health; on the other hand, reducing the loneliness of college students is expected to reduce the negative impact of stress on college students' mental health ( 17 ).
Research Trends
Due to the limited training sample of academic papers at present, it is difficult to predict the outcomes accurately. Though we cannot exactly predict the hot issues in the future, we can sort out some possible research trends in this field by analyzing existing research approaches. Psychological symptoms that affected people's mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic will be discovered further, especially those that probably continued to affect people's mental health even after the pandemic is controlled.
Studies on mild psychological symptoms, such as mild insomnia and anxiety, tend to decrease slowly, and in the case of severe problems caused by the pandemic, or severe psychological symptoms, such as clinical insomnia, depression, bipolar disorder, the corresponding in-depth research will continue. The impact of a global pandemic on the mental health of the global population must be profound and worthy of study. Due to the rapid development of COVID-19, many famous universities and research institutions have not had enough time to collect sufficient data and relevant research materials. The different effects on populations in different countries with different pandemic prevention policies are not yet fully displayed.
Regardless of how research on mental health develops, the COVID-19 pandemic has indeed brought us some new insights. As mentioned in many articles on mental health interventions for adolescents and college students, the mental health of specific populations and the development of telemedicine all deserve continued academic attention. Mental health intervention for adolescents and college students is a means to consider and prepare for the future. To ensure responsible and accountable behavior for future generations, we should all pay attention to the research and application of this method. Caring for specific groups of people, such as doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers, and studying how to protect them in a global pandemic is a topic that global academia must study in the future, or we will lose protection the next time the virus sweeps the world. In addition, telemedicine is the trend in the future, and face-to-face diagnosis and treatment will undoubtedly increase the risk of cross-infection during the pandemic. Therefore, the development of telemedicine is an important way to avoid contact between the patients. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the research and development of telemedicine.
Limitations
(1) Though we have selected three databases for analysis, there are still some databases that may be related to this field that are not covered in this study. (2) Since COVID-19-related research was started just 2 years ago, the results of the bibliometric analysis may vary after adding new data. (3) The citation frequency of articles is influenced by the time of publication, thus previously published articles should be cited more frequently than new ones. (4) Bibliometric data change over time, and different conclusions may be drawn over time. Therefore, this study should be updated in the future.
Conclusions
The most mentioned keywords, in addition to COVID-19 and mental health, can be roughly divided into three categories: keywords representing specific groups of people, keywords describing influences and symptoms, and keywords related to public health policies. The most mentioned issues were about medical staff, quarantine, psychological symptoms, telemedicine, social media, and loneliness. Mild psychological symptoms, such as insomnia, depression, and anxiety, tend to decrease slowly, while severe ones, such as severe clinical insomnia, depression, and bipolar disorder, are yet to be discovered. The importance of studies on the protection of youth medical staff and telemedicine studies will become even more significant in the future. While physical health is threatened by the pandemic, human mental health also suffers. Judging from the current situation of pandemic prevention and control, if severe prevention and control measures are taken, the impact of COVID-19 on the health of the social population is controllable; if a strategy of coexistence with the virus is adopted, as long as a new deadly mutation of COVID-19 does not emerge, the outcomes can be controllable. However, the impact of the pandemic on human mental health is not easy to predict. In addition to the abovementioned papers on mental health, the author also noted that some papers focused on neuromedicine pointed out that the virus might have some damage to the normal working mechanism of the human nervous system, but these studies are outside the scope of mental health research, at least for now. This study aims to summarize the observations, analysis, and research of scholars on mental health during the pandemic from 2020 to early 2022, with a view to provide more clues for future researchers. We hope that more researchers will build on our research to discover new research areas and new questions to help more countries, groups, and individuals affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Data Availability Statement
Author contributions.
YL was responsible for the concept and design, drafting this article, and bibliometric analysis. YL, LS, and XT were responsible for the revision and data collection. All authors contributed to this article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the study participants for their time and effort.
- Health Tech
- Health Insurance
- Medical Devices
- Gene Therapy
- Neuroscience
- H5N1 Bird Flu
- Health Disparities
- Infectious Disease
- Mental Health
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Chronic Disease
- Alzheimer's
- Coercive Care
- The Obesity Revolution
- The War on Recovery
- Adam Feuerstein
- Matthew Herper
- Jennifer Adaeze Okwerekwu
- Ed Silverman
- CRISPR Tracker
- Breakthrough Device Tracker
- Generative AI Tracker
- Obesity Drug Tracker
- 2024 STAT Summit
- Wunderkinds Nomination
- STAT Madness
- STAT Brand Studio
Don't miss out
Subscribe to STAT+ today, for the best life sciences journalism in the industry
Readers respond to essays on long Covid, hypochondria, and more
By Patrick Skerrett June 22, 2024

F irst Opinion is STAT’s platform for interesting, illuminating, and maybe even provocative articles about the life sciences writ large, written by biotech insiders, health care workers, researchers, and others.
To encourage robust, good-faith discussion about issues raised in First Opinion essays, STAT publishes selected Letters to the Editor received in response to them. You can submit a Letter to the Editor here , or find the submission form at the end of any First Opinion essay.
advertisement
“Long Covid feels like a gun to my head,” by Rachel Hall-Clifford
Thank you for this. I’m a 65-year-old woman who’s Covid cautious and wears a mask in public places (yes, in 2024). I’ve never had Covid as far as I know, and I try to keep up with the research. I feel like everybody would be more cautious if they read this article on long Covid, because it helps to really understand the horrible ways that a mild case of Covid can affect your life in ways that are unimaginable.
— Hildy Hogate
“I’m a hypochondriac. Here’s how the health care system needs to deal with people like me,” by Hal Rosenbluth
Health anxiety is the less biased term, rather than hypochondria with all its comic baggage.
Though the writer likes full body scans for himself and they suit his particular fears, many, many people with health anxiety, including me, wouldn’t get within 10 feet of a full body scan. It would be the opposite of reassuring.
Even if it did reassure for the moment, anyone with health anxiety knows reassurance is short-lived. A scan done in, say, January, might reassure a non-anxious person for the next six months. But it would be the rare person with health anxiety who would feel reassured for more than a couple of weeks.
And why on earth would you want to create a separate billing code for this, which would, without question, be used to pick out, stigmatize, and limit access to medical care? That doesn’t help patients, it soothes and enriches insurers, who would undoubtedly limit access to care based on a scan. How long would it take before you called to make an appointment with your doctor and were told sorry, your insurance won’t cover an office visit — your scan said you have no problems?
The writer’s personal experience, psychology, and taste for scans are just that, personal. They don’t generalize to most, or even many, of those who suffer from health anxiety.
— Maria Perry
“NIH needs reform and restructuring, key Republicans committee chairs say,” by Cathy McMorris Rodgers and Robert B. Aderholt
I agree with the authors that NIH needs reform. I was an athletic, otherwise healthy person who was struck down and disabled by long Covid in January 2022. For over two years, I’ve watched life pass me by as NIH has fumbled the $1.15 billion allocated to it by Congress to study and treat long Covid. This initiative, known as RECOVER, has failed to publish any research that furthers our understanding of the underlying cause of long Covid and the vast majority of clinical trials they’ve launched are for drugs that people have already tried and found unhelpful.
Perhaps NIH would not have bungled the long Covid funding had it not completely ignored other post viral diseases, namely myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) for the past 40 years. ME receives only $15 million a year — the most underfunded disease per patient burden at the NIH.
NIH should reevaluate how it allocates funding to diseases and base allocations on objective patient burdens. HIV, a disease with treatments that allow people with it to live mostly normal lives, receives $3.3 billion annually through NIH. Meanwhile, ME patients are disabled, have no approved treatments, and suffer a higher patient burden. Covid long haulers are suffering the same fate, many struck down as first wavers in March of 2020 are still disabled and sick as ever over four years later. Despite this, there is still no yearly allocation for long Covid in NIH’s baseline budget, as funding has only ever come from one time appropriations. NIH should right-size funding for ME and long Covid and start taking these diseases seriously.
— John Bolecek, long Covid patient
“Addressing health care workers’ trauma can help fight burnout,” by Sadie Elisseou
Thank you for writing this essay on the trauma and burnout that are all too common among today’s health care workforce. I applaud you for underscoring the importance of trauma-informed organizations and the critical value of workplaces that are safe, supportive, and flexible.
As a nurse educator and researcher, I have come to understand the important role of resilience in the work that nurses do. Considering two-thirds of nurses (65%) experience burnout, resilience-building skills are critical to mitigating nurse exhaustion and preserving our nation’s nursing pipeline. If actions are not taken to better protect the physical and mental health of our healthcare workforce, patient care will suffer. Lawmakers must take notice.
Some efforts in Congress have been successful. Congress has introduced legislation to reauthorize the Dr. Lorna Breen Provider Protection Act , bipartisan legislation that recognizes the need for mental health resources and support programs for healthcare professionals. Since its original enactment, this act has been instrumental in funding grant programs for mental health training, education, peer support, and crisis intervention services.
The reauthorization of this measure would expand grants to more than 200,000 other types of health care settings as well as renew the focus on reducing administrative burden for health care workers. While this bill is not a perfect solution, it does provide needed to support for a workforce that is understaffed, overworked, and in need to relief.
I urge Congress to finish the job and fully reauthorize the Dr. Lorna Breen Provider Protection Act this year.
— Stephanie Turner, R.N., Ed.D., M.S.N., ATI Nursing Education
About the Author Reprints
Patrick skerrett.
Acting First Opinion Editor
Patrick Skerrett is filling in as editor of First Opinion , STAT's platform for perspective and opinion on the life sciences writ large, and host of the First Opinion Podcast .
STAT encourages you to share your voice. We welcome your commentary, criticism, and expertise on our subscriber-only platform, STAT+ Connect
To submit a correction request, please visit our Contact Us page .

Recommended

Recommended Stories

Congress called for an ALS moonshot. The plan for it doesn’t leave Earth

What readers have to say about long Covid, FDA and diversity, and more

STAT Plus: Grail, aiming to market a blood test for cancer, faces host of challenges as it debuts on Nasdaq

STAT Plus: Top FDA official Peter Marks overruled staff, review team to approve Sarepta gene therapy

STAT Plus: Ateev Mehrotra, the researcher the telehealth lobby loves to hate, isn’t backing down
- DOI: 10.53841/bpsopo.2024.3.1.36
- Corpus ID: 270757749
Mental health and wellbeing of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) staff: An occupational psychology perspective
- Raul Szekely , Ciprian Ciobanu
- Published in Occupational Psychology… 7 May 2024
- Psychology, Medicine
- Occupational Psychology Outlook
16 References
Critical care nursing workforce in crisis: a discussion paper examining contributing factors, the impact of the covid-19 pandemic and potential solutions., what are the solutions for well-being and burn-out for healthcare professionals an umbrella realist review of learnings of individual-focused interventions for critical care, a systematic review of temporal person–environment fit research: trends, developments, obstacles, and opportunities for future research, the mental health of staff working on intensive care units over the covid-19 winter surge of 2020 in england: a cross sectional survey, mental health outcomes of icu and non-icu healthcare workers during the covid-19 outbreak: a cross-sectional study, a model for occupational stress amongst paediatric and adult critical care staff during covid-19 pandemic, mental health of staff working in intensive care during covid-19., post-traumatic stress disorder in intensive care unit nurses: a concept analysis, staff wellbeing in times of covid-19, symptoms of burnout in intensive care unit specialists facing the covid-19 outbreak, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

How is the loneliness epidemic affecting society?
Gen Z faces severe loneliness, worsened by social media and the pandemic. What are the solutions to this growing mental health crisis?
The loneliness epidemic profoundly affects Gen Z.
Despite being hyperconnected through social media, they experience high levels of isolation, worsened by the pandemic.
The consequences are severe, leading to mental health crises, increased rates of depression and anxiety, and a sense of disconnection from community and purpose.
A study by Cigna found Gen Z (ages 18-22) is the loneliest generation, with nearly half feeling lonely. What can be done to address this growing mental health crisis?
Presenter: Anelise Borges
Guests: Annie Ji – Sociocultural YouTuber Esther Fernandez – Copywriter Simone Heng – Human connection specialist
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Surgeon General: Why I’m Calling for a Warning Label on Social Media Platforms

By Vivek H. Murthy
Dr. Murthy is the surgeon general.
One of the most important lessons I learned in medical school was that in an emergency, you don’t have the luxury to wait for perfect information. You assess the available facts, you use your best judgment, and you act quickly.
The mental health crisis among young people is an emergency — and social media has emerged as an important contributor. Adolescents who spend more than three hours a day on social media face double the risk of anxiety and depression symptoms, and the average daily use in this age group, as of the summer of 2023, was 4.8 hours . Additionally, nearly half of adolescents say social media makes them feel worse about their bodies.
It is time to require a surgeon general’s warning label on social media platforms, stating that social media is associated with significant mental health harms for adolescents. A surgeon general’s warning label, which requires congressional action, would regularly remind parents and adolescents that social media has not been proved safe. Evidence from tobacco studies show that warning labels can increase awareness and change behavior. When asked if a warning from the surgeon general would prompt them to limit or monitor their children’s social media use, 76 percent of people in one recent survey of Latino parents said yes.
To be clear, a warning label would not, on its own, make social media safe for young people. The advisory I issued a year ago about social media and young people’s mental health included specific recommendations for policymakers, platforms and the public to make social media safer for kids. Such measures, which already have strong bipartisan support, remain the priority.
Legislation from Congress should shield young people from online harassment, abuse and exploitation and from exposure to extreme violence and sexual content that too often appears in algorithm-driven feeds. The measures should prevent platforms from collecting sensitive data from children and should restrict the use of features like push notifications, autoplay and infinite scroll, which prey on developing brains and contribute to excessive use.
Additionally, companies must be required to share all of their data on health effects with independent scientists and the public — currently they do not — and allow independent safety audits. While the platforms claim they are making their products safer, Americans need more than words. We need proof.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Outagamie County nonprofits receive ARPA funds for mental health and housing
by Ashley Kaster, FOX 11 News

APPLETON (WLUK) -- Two nonprofits in Outagamie County received their American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) fund checks Monday.
The county awarded $1,500,000 to Pillars Inc. and $750,000 to NEW Mental Health Connection to ensure operations of vital behavioral health initiatives in our community.
“This money is really a miracle for our coalition. It’s an opportunity to replenish lost reserves from the COVID pandemic. It’s also meant to stabilize our operations over the next several years which, for an organization like ours, what that does is that stability allows us to move from a place of strategy and problem-solving, instead of being in existential crisis, we can really work to solve problems instead of manage them," said NEW Mental Health Connection executive director, Beth Clay.
The grants stem from Outagamie County’s strategic decision to allocate $2.75 million of ARPA funds towards housing and mental health services.
Both Pillars Inc. and NEW Mental Health Connection play crucial roles in addressing those needs in Outagamie County.
Other areas of focus for the county's ARPA funds have been directed toward businesses, job creation, childcare and tourism programs.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Physical distancing due to the COVID‐19 outbreak can have drastic negative effects on the mental health of the elderly and disabled individuals. Physical isolation at home among family members can put the elderly and disabled person at serious mental health risk. It can cause anxiety, distress, and induce a traumatic situation for them.
On a global scale and based on imputations and modeling from survey data of self-reported mental health problems, the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study 29 estimated that the COVID-19 pandemic has led to a 28% (95% uncertainty interval (UI): 25-30) increase in major depressive disorders and a 26% (95% UI: 23-28) increase in anxiety disorders.
On a global scale and based on imputations and modeling from survey data of self-reported mental health problems, the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study 29 estimated that the COVID-19 pandemic ...
Investigating the Prevalence of COVID-19-Related Sleep Disorders Among Individuals Recovering from COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Analytical Study, Jundishapur Journal of Health Sciences, 15, 4 ...
Worldwide surveys done in 2020 and 2021 found higher than typical levels of stress, insomnia, anxiety and depression. By 2022, levels had lowered but were still higher than before 2020. Though feelings of distress about COVID-19 may come and go, they are still an issue for many people. You aren't alone if you feel distress due to COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic affected everyone around the globe. Depending on the country, there have been different restrictive epidemiologic measures and also different long-term repercussions. Morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 affected the mental state of every human being. However, social separation and isolation due to the restrictive measures considerably increased this impact.
To minimize the mental health consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic, WHO also recommends that countries: Apply a whole of society approach to promote, protect and care for mental health, including through social and financial protection to safeguard people from domestic violence or impoverishment, and by communicating widely about COVID-19 to ...
COVID-19 has justifiably raised widespread public concern about mental health worldwide. In the U.S., the pandemic was an unprecedented shock to society at a time when the nation was already ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a severe impact on the mental health and wellbeing of people around the world while also raising concerns of increased suicidal behaviour. In addition access to mental health services has been severely impeded. However, no comprehensive summary of the current data on these impacts has until now been made widely ...
Eligible papers were quality assessed according to AMSTAR-2 (14). In total, 480 reviews were excluded for key question one assessing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health, retaining 97 systematic reviews ... COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population, 32 in healthcare workers and 26 in other specific populations
The good news is that by October, 2020, mental health was top of the charts in terms of published papers and preprints on the effects of COVID-19. The bad news is that the quantity of papers is not matched by quality. In March, 2020, Holmes and colleagues outlined the priorities for mental health research during the pandemic. How much have we ...
By merging public health with mental health, the ways that COVID-19 are changing the world could be for better rather than worse (Table 1) . Table 1. ... Many of the research papers about COVID-19 in international journals were written by researchers in China, which led to great concerns because these findings cannot directly benefit frontline ...
NIMH launched a five-year research study called RECOUP-NY to promote the mental health of New Yorkers from communities hard-hit by COVID-19. The study will test the use of a new care model called Problem Management Plus (PM+) that can be used by non-specialists. A study funded by NIMH is examining the use of mobile apps to address mental health ...
Most general public surveys link COVID-19 to increased symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. Panic buying, binge-watching TV, and other unhealthy behaviors have been reported. Increased ...
This essay examines key aspects of social relationships that were disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. It focuses explicitly on relational mechanisms of health and brings together theory and emerging evidence on the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic to make recommendations for future public health policy and recovery. We first provide an overview of the pandemic in the UK context, outlining the ...
COVID-19 continues to exert unprecedented challenges for society and it is now well recognised that mental health is a key healthcare issue related to the pandemic. The current edition of the Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine focusses on the impact of COVID-19 on mental illness by combining historical review papers, current perspectives ...
WHO and public health authorities around the world are acting to contain the COVID-19 outbreak. However, this time of crisis is generating stress throughout the population. The considerations presented in this document have been developed by the WHO Department of Mental Health and Substance Use as a series of messages that can be used in ...
The COVID-19 pandemic is having a major impact on the mental health of populations in the Americas. Studies show high rates of depression and anxiety, among other psychological symptoms, particularly among women, young people, those with pre-existing mental health conditions, health workers, and persons living in vulnerable conditions. Mental health systems and services have also been severely ...
A clear picture has emerged of the mental health impacts of the early waves of the covid-19 pandemic in England—when hospital admissions and mortality were common and lockdowns particularly restrictive. 1 Longitudinal population based studies show that symptoms of anxiety and depression were marked but often transient, increasing during ...
I felt like I was suffocating.". Adolfo's school building closed for a few weeks recently because of reported cases of Covid. "There's nothing to look forward to," said Ayden Hufford, 15 ...
Background: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Oxford Precision Psychiatry Lab (OxPPL) developed open-access web-based summaries of mental health care guidelines (OxPPL guidance) in key areas such as digital approaches and telepsychiatry, suicide and self-harm, domestic violence and abuse, perinatal care, and vaccine hesitancy and prioritization in the context of mental illness, to inform ...
PubMed
What Campus Data Tell Us About Student Mental Health and COVID-19. Recent stories have warned of a "mental health tsunami" and a "mental health crisis on campuses" as over the past two years, students and campus communities worked to master the new normal of masking, vaccines, and social distancing in a global pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly influenced the world. In wave after wave, many countries suffered from the pandemic, which caused social instability, hindered global growth, and harmed mental health. Although research has been published on various mental health issues during the pandemic, some profound effects on mental health are ...
F irst Opinion is STAT's platform for interesting, illuminating, and maybe even provocative articles about the life sciences writ large, written by biotech insiders, health care workers ...
The article begins by discussing the work-related challenges encountered by ICU staff, including emotional burdens and poor working conditions, and the potential implications on mental health and patient care, and delves into the specific effects of the Covid-19 pandemic on the mental health of ICU staff. Through the lens of occupational psychology, this article sheds light on the mental ...
Social media has become an integral part of daily life in the digital age, especially for the younger generation. Platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, TikTok, and Facebook provide endless content streams, encouraging connectivity and creativity, but they also present significant mental health challenges, especially for their younger users.
The consequences are severe, leading to mental health crises, increased rates of depression and anxiety, and a sense of disconnection from community and purpose.
The advisory I issued a year ago about social media and young people's mental health included specific recommendations for policymakers, platforms and the public to make social media safer for ...
The county awarded $1,500,000 to Pillars Inc. and $750,000 to NEW Mental Health Connection to ensure operations of vital behavioral health initiatives in our community. "This money is really a ...