- How it works

How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter – A Quick Guide with Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
Dissertation discussion is the chapter where you explore the relevance, significance, and meanings of your findings – allowing you to showcase your talents in describing and analyzing the results of your study.
Here, you will be expected to demonstrate how your research findings answer the research questions established or test the hypothesis .
The arguments you assert in the dissertation analysis and discussions chapter lay the foundations of your conclusion . It is critically important to discuss the results in a precise manner.
To help you understand how to write a dissertation discussion chapter, here is the list of the main elements of this section so you stay on the right track when writing:
- Summary: Start by providing a summary of your key research findings
- Interpretations: What is the significance of your findings?
- Implications: Why are your findings important to academic and scientific communities, and what purpose would they serve?
- Limitations: When and where will your results have no implications?
- Future Recommendations : Advice for other researchers and scientists who explore the topic further in future.
The dissertation discussion chapter should be carefully drafted to ensure that the results mentioned in your research align with your research question, aims, and objectives.
Considering the importance of this chapter for all students working on their dissertations, we have comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation discussion chapter.
The discussion and conclusion chapters often overlap. Depending on your university, you may be asked to group these two sections in one chapter – Discussion and Conclusion.
In some cases, the results and discussion are put together under the Results and Discussion chapter. Here are some dissertation examples of working out the best structure for your dissertation.
Alternatively, you can look for the required dissertation structure in your handbook or consult your supervisor.
Steps of How to Write Dissertation Discussion Chapter
1. provide a summary of your findings.
Start your discussion by summarising the key findings of your research questions. Avoid repeating the information you have already stated in the previous chapters.
You will be expected to clearly express your interpretation of results to answer the research questions established initially in one or two paragraphs.
Here are some examples of how to present the summary of your findings ;
- “The data suggests that”,
- “The results confirm that”,
- “The analysis indicates that”,
- “The research shows a relationship between”, etc.
2. Interpretations of Results
Your audience will expect you to provide meanings of the results, although they might seem obvious to you. The results and their interpretations should be linked to the research questions so the reader can understand the value your research has added to the literature.
There are many ways of interpreting the data, but your chosen approach to interpreting the data will depend on the type of research involved . Some of the most common strategies employed include;
- Describing how and why you ended up with unexpected findings and explaining their importance in detail
- Relating your findings with previous studies conducted
- Explaining your position with logical arguments when/if any alternative explanations are suggested
- An in-depth discussion around whether or not the findings answered your research questions and successfully tested the hypothesis
Examples of how you can start your interpretation in the Discussion chapter are –
- “Findings of this study contradict those of Allen et al. (2014) that”,
- “Contrary to the hypothesized association,” “Confirming the hypothesis…”,
- “The findings confirm that A is….. even though Allen et al. (2014) and Michael (2012) suggested B was …..”
3. Implications of your Study
What practical and theoretical implications will your study have for other researchers and the scientific community as a whole?
It is vital to relate your results to the knowledge in the existing literature so the readers can establish how your research will contribute to the existing data.
When thinking of the possible consequences of your findings, you should ask yourself these;
- Are your findings in line with previous studies? What contribution did your research make to them?
- Why are your results entirely different from other studies on the same topic?
- Did your findings approve or contradict existing knowledge?
- What are the practical implications of your study?
Remember that as the researcher, you should aim to let your readers know why your study will contribute to the existing literature. Possible ways of starting this particular section are;
- “The findings show that A….. whereas Lee (2017) and John (2013) suggested that B”, “The results of this study completely contradict the claims made in theories”,
- “These results are not in line with the theoretical perspectives”,
- “The statistical analysis provides a new understanding of the relationship between A and B”,
- “Future studies should take into consideration the findings of this study because”
“Improve your work’s language, structure, style, and overall quality. Get help from our experienced dissertation editors to improve the quality of your paper to First Class Standard. Click here to learn more about our Dissertation, Editing, and Improvement Services .
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue, then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across various disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

4. Recognise the Limitations of your Research
Almost every academic research has some limitations. Acknowledging them will only add to your credibility as a scientific researcher.
In addition to the possible human errors, it’s important to take into account other factors that might have influenced the results of your study, including but not limited to unexpected research obstacles, specific methodological choices , and the overall research design.
Avoid mentioning any limitations that may not be relevant to your research aim, but clearly state the limitations that may have affected your results.
For example, if you used a sample size that included a tiny population, you may not generalise your results.
Similarly, obstacles faced in collecting data from the participants can influence the findings of your study. Make a note of all such research limitations , but explain to the reader why your results are still authentic.
- The small sample size limited the generalisability of the results.
- The authenticity of the findings may have been influenced by….
- The obstacles in collecting data resulted in…
- It is beyond the framework of this research…
5. Provide Recommendations for Future Research
The limitations of your research work directly result in future recommendations. However, it should be noted that your recommendations for future research work should include the areas that your own work could not report so other researchers can build on them.
Sometimes the recommendations are a part of the conclusion chapter . Some examples;
- More research is needed to be performed….
The Purpose of Dissertation Discussion Chapter
Remember that the discussion section of a dissertation is the heart of your research because a) it will indicate your stance on the topic of research, and b) it answers the research questions initially established in the Introduction chapter .
Every piece of information you present here will add value to the existing literature within your field of study. How you structured your findings in the preceding chapter will help you determine the best structure for your dissertation discussion section.
For example, it might be logical to structure your analysis/discussions by theme if you chose the pattern in your findings section.
But generally, discussion based on research questions is the more widely used structure in academia because this pattern clearly indicates how you have addressed the aim of your research.
Most UK universities require the supervisor or committee members to comment on the extent to which each research question has been answered. You will be doing them a great favour if you structure your discussion so that each research question is laid out separately.
Irrespective of whether you are writing an essay, dissertation, or chapter of a dissertation , all pieces of writing should start with an introduction .
Once your readers have read through your study results, you might want to highlight the contents of the subsequent discussion as an introduction paragraph (summary of your results – as explained above).
Likewise, the discussion chapter is expected to end with a concluding paragraph – allowing you the opportunity to summarise your interpretations.
The dissertation analysis & discussion chapter is usually very long, so it will make sense to emphasise the critical points in a concluding paragraph so the reader can grasp the essential information. This will also help to make sure the reader understands your analysis.
Also Read: Research Discussion Of Findings
Useful Tips
Presentation of graphs, tables, and figures.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, students spent days creating graphs and charts for their statistical analysis work . Thanks to technology, you can produce even more accurate graphs and figures today in a shorter period.
Using Microsoft Word, STATA, SPSS, Microsoft Excel and other statistical analysis software, we can now draw beautiful-looking figures, tables , and graphs with just a few clicks and make them appear in our document at the desired place. But there are downsides to being too dependent on technology.
Many students make the common mistake of using colours to represent variables when really they have to print their dissertation paper final copy in black and white.
Any colours on graphs and figures will eventually be viewed in the grayscale presentation. Recognizing different shades of grey on the same chart or graph can sometimes be a little confusing.
For example, green and purple appear as pretty much the same shade of grey on a line chat, meaning your chart will become unreadable to the marker.
Another trap you may fall into is the unintentional stuffing of the dissertation chapter with graphs and figures. Even though it is essential to show numbers and statistics, you don’t want to overwhelm your readers with too many.
It may not be necessary to have a graph/table under each sub-heading. Only you can best judge whether or not you need to have a graph/table under a particular sub-heading as the writer.
Relating to Previous Chapters
As a student, it can be challenging to develop your own analysis and discussion of results. One of the excellent discussion chapter requirements is to showcase your ability to relate previous research to your research results.
Avoid repeating the same information over and over. Many students fall into this trap which negatively affects the mark of their overall dissertation paper .
Concise and to-the-point information will help you effectively convey your point to the readers.
Although you must demonstrate how your findings relate to previous research, it is equally important to ensure you are not simply rewriting what has already been said in the introduction and literature review chapters.
The best strategy is to use examples from previous sections to postulate an argument.
Hyperlinks are recommended to take the reader from one section to another. This is especially important for submitting electronic documents as .word or .pdf files. Hyperlinking is tedious and time-consuming, so you should allow for this in your dissertation timeline to avoid rushing in the closing stages.
Also read: How to Write the Abstract for the Dissertation.
Using Subsections and Subheadings
You might want to reflect on the structure of the discussion in your organizstion of the dissertation discussion chapter, and for that, you will need to create sub-sections.
It is essential to keep subsections to the point and as short as possible. Use a layer of subheadings if possible.
For example
Subsection 4.1 of Chapter 4- Discussion can be further divided into sections 4.1.1 and 4.2.2. After three numerical layers (4.1.1, 4.2.2, and 4.2.3), any subheadings need not appear in the contents table.
The titles of all subsections will appear on your table of contents so choose the wordings carefully. A title too long or too short might confuse the reader. A one or two-word subheading will not give the reader enough information to understand the section.
Likewise, using a research question or long sentences in the subheading is not recommended. It might help to examine how other researchers and writers create these subheadings.
Critical Thinking
Your critical thinking skills are the crux of your dissertation discussion chapter. You will do yourself a great disservice if you fail to put the critical thinking element into the equation.
After all, this exercise aims to showcase clarity in your thoughts and arguments. Markers of the dissertation give more importance to the analysis and discussion chapter. But you could be marked negatively if this particular chapter lacks critical thinking.
Many students struggle to distinguish between fundamental descriptive analysis and critical thinking with their opinions on the research topic.
Critical thinking is a skill developed over time, and it might be daunting for you to come to terms with the idea of critical thinking and its use in your analysis. But even if you are no expert, you must try your best.

“Still unsure about how to write a dissertation discussion chapter ? Why not take advantage of our UK-based dissertation writing service ? Your dissertation is essential to your degree, so you cannot risk failing it.
With our custom writing service , you are guaranteed to have all your dissertation paper elements put into the right place. Our expert academics can help you with your full dissertation paper or a part of it. Click here to learn more about our dissertation services.
Duplication of Content
Another critical error students make reaffirming the point the graph/chart was supposed to make. Writing out the same information as presented in the graph defeats the whole purpose of having them in the first place.
You will be expected to form your opinions and arguments based on the findings (as presented by the graphs), so keep an eye on this mistake. Finally, avoid simply inserting a graph without any explanation whatsoever.
It should be noted that there is no correct or incorrect number of charts/figures one can use in the dissertation findings and discussion chapter. A balance must be struck.
Avoid Over Interpretation
This is a major no-no when writing a dissertation discussion. Do not make an argument that isn’t backed by your collected data.
The results and interpretations that cannot be supported should not be mentioned. Your research will be deemed unauthentic and will also be questioned by your supervisor if you do so. Results should be interpreted without any bias.
How to Write the Findings of a Dissertation.
Do not Speculate
Speculation in the discussion chapter of your dissertation is discouraged. Your dissertation’s discussion is based on your collected data and how it relates to your research questions. Thus, speculating here will undoubtedly undermine your research’s credibility.
Also, try not to generalise your findings. If your research is based on a specific population, do not state that the same findings might apply in every case. As indicated previously, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of your research.
On the other hand, if you think your discussion needs to address other populations as well, start your sentence like this ‘We speculate that..’ or ‘It is speculated that..’ This will keep you from getting into any trouble.
What are the elements of the Dissertation Discussion?
The list of the main elements of the discussion chapter are:
- Implications : Why are your findings important to academic and scientific communities, and what purpose would they serve?
- Future Recommendations: Advice for other researchers and scientists who explore the topic further in future.
What are the steps of writing a Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
- Write a summary of the findings
- Provide a summary of your findings
- Interpretations of Results
- Recognise the Limitations of your research
- Provide Recommendations for Future Research.
Can we use graphs and charts in the Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
Yes, using graphs to aid your statistical results and enhance presentation is essential, but do not overwhelm it with a lot of graphs in multiple colours.
You May Also Like
When writing your dissertation, an abstract serves as a deal maker or breaker. It can either motivate your readers to continue reading or discourage them.
Do dissertations scare you? Struggling with writing a flawless dissertation? Well, congratulations, you have landed in the perfect place. In this blog, we will take you through the detailed process of writing a dissertation. Sounds fun? We thought so!
Dissertation conclusion is perhaps the most underrated part of a dissertation or thesis paper. Learn how to write a dissertation conclusion.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?
Reflecting on and Comparing Your Data, Recognising the Strengths and Limitations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
359 Accesses
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with subsections and paragraphs. We also present a list of points to do and avoid when writing the discussion together with a Discussion chapter checklist.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Braun V, Clarke V (2013) Successful qualitative research: a practical guide for beginners. SAGE Publications, London
Google Scholar
McGregor SLT (2018) Understanding and evaluating research: a critical guide. SAGE Publications, Los Angeles, CA
Book Google Scholar
PLOS (2023) Author resources. How to write discussions and conclusions. Accessed Mar 3, 2023, from https://plos.org/resource/how-to-write-conclusions/ . Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Cottrell S (2017) Critical thinking skills: effective analysis, argument and reflection, 3rd edn. Palgrave, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Results and Discussion
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
- Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Study Skills
- Exam Skills
- How to Write a Research Proposal
- Ethical Issues in Research
- Dissertation: The Introduction
- Researching and Writing a Literature Review
- Writing your Methodology
- Dissertation: Results and Discussion
- Dissertation: Conclusions and Extras
Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis eBook

Part of the Skills You Need Guide for Students .
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Writing your Dissertation: Results and Discussion
When writing a dissertation or thesis, the results and discussion sections can be both the most interesting as well as the most challenging sections to write.
You may choose to write these sections separately, or combine them into a single chapter, depending on your university’s guidelines and your own preferences.
There are advantages to both approaches.
Writing the results and discussion as separate sections allows you to focus first on what results you obtained and set out clearly what happened in your experiments and/or investigations without worrying about their implications.This can focus your mind on what the results actually show and help you to sort them in your head.
However, many people find it easier to combine the results with their implications as the two are closely connected.
Check your university’s requirements carefully before combining the results and discussions sections as some specify that they must be kept separate.
Results Section
The Results section should set out your key experimental results, including any statistical analysis and whether or not the results of these are significant.
You should cover any literature supporting your interpretation of significance. It does not have to include everything you did, particularly for a doctorate dissertation. However, for an undergraduate or master's thesis, you will probably find that you need to include most of your work.
You should write your results section in the past tense: you are describing what you have done in the past.
Every result included MUST have a method set out in the methods section. Check back to make sure that you have included all the relevant methods.
Conversely, every method should also have some results given so, if you choose to exclude certain experiments from the results, make sure that you remove mention of the method as well.
If you are unsure whether to include certain results, go back to your research questions and decide whether the results are relevant to them. It doesn’t matter whether they are supportive or not, it’s about relevance. If they are relevant, you should include them.
Having decided what to include, next decide what order to use. You could choose chronological, which should follow the methods, or in order from most to least important in the answering of your research questions, or by research question and/or hypothesis.
You also need to consider how best to present your results: tables, figures, graphs, or text. Try to use a variety of different methods of presentation, and consider your reader: 20 pages of dense tables are hard to understand, as are five pages of graphs, but a single table and well-chosen graph that illustrate your overall findings will make things much clearer.
Make sure that each table and figure has a number and a title. Number tables and figures in separate lists, but consecutively by the order in which you mention them in the text. If you have more than about two or three, it’s often helpful to provide lists of tables and figures alongside the table of contents at the start of your dissertation.
Summarise your results in the text, drawing on the figures and tables to illustrate your points.
The text and figures should be complementary, not repeat the same information. You should refer to every table or figure in the text. Any that you don’t feel the need to refer to can safely be moved to an appendix, or even removed.
Make sure that you including information about the size and direction of any changes, including percentage change if appropriate. Statistical tests should include details of p values or confidence intervals and limits.
While you don’t need to include all your primary evidence in this section, you should as a matter of good practice make it available in an appendix, to which you should refer at the relevant point.
For example:
Details of all the interview participants can be found in Appendix A, with transcripts of each interview in Appendix B.
You will, almost inevitably, find that you need to include some slight discussion of your results during this section. This discussion should evaluate the quality of the results and their reliability, but not stray too far into discussion of how far your results support your hypothesis and/or answer your research questions, as that is for the discussion section.
See our pages: Analysing Qualitative Data and Simple Statistical Analysis for more information on analysing your results.
Discussion Section
This section has four purposes, it should:
- Interpret and explain your results
- Answer your research question
- Justify your approach
- Critically evaluate your study
The discussion section therefore needs to review your findings in the context of the literature and the existing knowledge about the subject.
You also need to demonstrate that you understand the limitations of your research and the implications of your findings for policy and practice. This section should be written in the present tense.
The Discussion section needs to follow from your results and relate back to your literature review . Make sure that everything you discuss is covered in the results section.
Some universities require a separate section on recommendations for policy and practice and/or for future research, while others allow you to include this in your discussion, so check the guidelines carefully.
Starting the Task
Most people are likely to write this section best by preparing an outline, setting out the broad thrust of the argument, and how your results support it.
You may find techniques like mind mapping are helpful in making a first outline; check out our page: Creative Thinking for some ideas about how to think through your ideas. You should start by referring back to your research questions, discuss your results, then set them into the context of the literature, and then into broader theory.
This is likely to be one of the longest sections of your dissertation, and it’s a good idea to break it down into chunks with sub-headings to help your reader to navigate through the detail.
Fleshing Out the Detail
Once you have your outline in front of you, you can start to map out how your results fit into the outline.
This will help you to see whether your results are over-focused in one area, which is why writing up your research as you go along can be a helpful process. For each theme or area, you should discuss how the results help to answer your research question, and whether the results are consistent with your expectations and the literature.
The Importance of Understanding Differences
If your results are controversial and/or unexpected, you should set them fully in context and explain why you think that you obtained them.
Your explanations may include issues such as a non-representative sample for convenience purposes, a response rate skewed towards those with a particular experience, or your own involvement as a participant for sociological research.
You do not need to be apologetic about these, because you made a choice about them, which you should have justified in the methodology section. However, you do need to evaluate your own results against others’ findings, especially if they are different. A full understanding of the limitations of your research is part of a good discussion section.
At this stage, you may want to revisit your literature review, unless you submitted it as a separate submission earlier, and revise it to draw out those studies which have proven more relevant.
Conclude by summarising the implications of your findings in brief, and explain why they are important for researchers and in practice, and provide some suggestions for further work.
You may also wish to make some recommendations for practice. As before, this may be a separate section, or included in your discussion.
The results and discussion, including conclusion and recommendations, are probably the most substantial sections of your dissertation. Once completed, you can begin to relax slightly: you are on to the last stages of writing!
Continue to: Dissertation: Conclusion and Extras Writing your Methodology
See also: Writing a Literature Review Writing a Research Proposal Academic Referencing What Is the Importance of Using a Plagiarism Checker to Check Your Thesis?

Writing the Dissertation - Guides for Success: The Results and Discussion
- Writing the Dissertation Homepage
- Overview and Planning
- The Literature Review
- The Methodology
- The Results and Discussion
- The Conclusion
- The Abstract
- The Difference
- What to Avoid
Overview of writing the results and discussion
The results and discussion follow on from the methods or methodology chapter of the dissertation. This creates a natural transition from how you designed your study, to what your study reveals, highlighting your own contribution to the research area.
Disciplinary differences
Please note: this guide is not specific to any one discipline. The results and discussion can vary depending on the nature of the research and the expectations of the school or department, so please adapt the following advice to meet the demands of your project and department. Consult your supervisor for further guidance; you can also peruse our Writing Across Subjects guide .
Guide contents
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common conventions of the results and discussion chapters, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows:
- The Difference - Breaks down the distinctions between the results and discussion chapters.
- Results - Provides a walk-through of common characteristics of the results chapter.
- Discussion - Provides a walk-through of how to approach writing your discussion chapter, including structure.
- What to Avoid - Covers a few frequent mistakes you'll want to...avoid!
- FAQs - Guidance on first- vs. third-person, limitations and more.
- Checklist - Includes a summary of key points and a self-evaluation checklist.
Training and tools
- The Academic Skills team has recorded a Writing the Dissertation workshop series to help you with each section of a standard dissertation, including a video on writing the results and discussion (embedded below).
- The dissertation planner tool can help you think through the timeline for planning, research, drafting and editing.
- iSolutions offers training and a Word template to help you digitally format and structure your dissertation.
Introduction
The results of your study are often followed by a separate chapter of discussion. This is certainly the case with scientific writing. Some dissertations, however, might incorporate both the results and discussion in one chapter. This depends on the nature of your dissertation and the conventions within your school or department. Always follow the guidelines given to you and ask your supervisor for further guidance.
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the essentials of writing your results and discussion, giving you the necesary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to leave a positive impression on your markers! This guide covers the results and discussion as separate – although interrelated – chapters, as you'll see in the next two tabs. However, you can easily adapt the guidance to suit one single chapter – keep an eye out for some hints on how to do this throughout the guide.
Results or discussion - what's the difference?
To understand what the results and discussion sections are about, we need to clearly define the difference between the two.
The results should provide a clear account of the findings . This is written in a dry and direct manner, simply highlighting the findings as they appear once processed. It’s expected to have tables and graphics, where relevant, to contextualise and illustrate the data.
Rather than simply stating the findings of the study, the discussion interprets the findings to offer a more nuanced understanding of the research. The discussion is similar to the second half of the conclusion because it’s where you consider and formulate a response to the question, ‘what do we now know that we didn’t before?’ (see our Writing the Conclusion guide for more). The discussion achieves this by answering the research questions and responding to any hypotheses proposed. With this in mind, the discussion should be the most insightful chapter or section of your dissertation because it provides the most original insight.
Across the next two tabs of this guide, we will look at the results and discussion chapters separately in more detail.
Writing the results
The results chapter should provide a direct and factual account of the data collected without any interpretation or interrogation of the findings. As this might suggest, the results chapter can be slightly monotonous, particularly for quantitative data. Nevertheless, it’s crucial that you present your results in a clear and direct manner as it provides the necessary detail for your subsequent discussion.
Note: If you’re writing your results and discussion as one chapter, then you can either:
1) write them as distinctly separate sections in the same chapter, with the discussion following on from the results, or...
2) integrate the two throughout by presenting a subset of the results and then discussing that subset in further detail.
Next, we'll explore some of the most important factors to consider when writing your results chapter.
How you structure your results chapter depends on the design and purpose of your study. Here are some possible options for structuring your results chapter (adapted from Glatthorn and Joyner, 2005):
- Chronological – depending on the nature of the study, it might be important to present your results in order of how you collected the data, such as a pretest-posttest design.
- Research method – if you’ve used a mixed-methods approach, you could isolate each research method and instrument employed in the study.
- Research question and/or hypotheses – you could structure your results around your research questions and/or hypotheses, providing you have more than one. However, keep in mind that the results on their own don’t necessarily answer the questions or respond to the hypotheses in a definitive manner. You need to interpret the findings in the discussion chapter to gain a more rounded understanding.
- Variable – you could isolate each variable in your study (where relevant) and specify how and whether the results changed.
Tables and figures
For your results, you are expected to convert your data into tables and figures, particularly when dealing with quantitative data. Making use of tables and figures is a way of contextualising your results within the study. It also helps to visually reinforce your written account of the data. However, make sure you’re only using tables and figures to supplement , rather than replace, your written account of the results (see the 'What to avoid' tab for more on this).
Figures and tables need to be numbered in order of when they appear in the dissertation, and they should be capitalised. You also need to make direct reference to them in the text, which you can do (with some variation) in one of the following ways:
Figure 1 shows…
The results of the test (see Figure 1) demonstrate…
The actual figures and tables themselves also need to be accompanied by a caption that briefly outlines what is displayed. For example:
Table 1. Variables of the regression model
Table captions normally appear above the table, whilst figures or other such graphical forms appear below, although it’s worth confirming this with your supervisor as the formatting can change depending on the school or discipline. The style guide used for writing in your subject area (e.g., Harvard, MLA, APA, OSCOLA) often dictates correct formatting of tables, graphs and figures, so have a look at your style guide for additional support.
Using quotations
If your qualitative data comes from interviews and focus groups, your data will largely consist of quotations from participants. When presenting this data, you should identify and group the most common and interesting responses and then quote two or three relevant examples to illustrate this point. Here’s a brief example from a qualitative study on the habits of online food shoppers:
Regardless of whether or not participants regularly engage in online food shopping, all but two respondents commented, in some form, on the convenience of online food shopping:
"It’s about convenience for me. I’m at work all week and the weekend doesn’t allow much time for food shopping, so knowing it can be ordered and then delivered in 24 hours is great for me” (Participant A).
"It fits around my schedule, which is important for me and my family” (Participant D).
"In the past, I’ve always gone food shopping after work, which has always been a hassle. Online food shopping, however, frees up some of my time” (Participant E).
As shown in this example, each quotation is attributed to a particular participant, although their anonymity is protected. The details used to identify participants can depend on the relevance of certain factors to the research. For instance, age or gender could be included.
Writing the discussion
The discussion chapter is where “you critically examine your own results in the light of the previous state of the subject as outlined in the background, and make judgments as to what has been learnt in your work” (Evans et al., 2014: 12). Whilst the results chapter is strictly factual, reporting on the data on a surface level, the discussion is rooted in analysis and interpretation , allowing you and your reader to delve beneath the surface.
Next, we will review some of the most important factors to consider when writing your discussion chapter.
Like the results, there is no single way to structure your discussion chapter. As always, it depends on the nature of your dissertation and whether you’re dealing with qualitative, quantitative or mixed-methods research. It’s good to be consistent with the results chapter, so you could structure your discussion chapter, where possible, in the same way as your results.
When it comes to structure, it’s particularly important that you guide your reader through the various points, subtopics or themes of your discussion. You should do this by structuring sections of your discussion, which might incorporate three or four paragraphs around the same theme or issue, in a three-part way that mirrors the typical three-part essay structure of introduction, main body and conclusion.

Figure 1: The three-part cycle that embodies a typical essay structure and reflects how you structure themes or subtopics in your discussion.
This is your topic sentence where you clearly state the focus of this paragraph/section. It’s often a fairly short, declarative statement in order to grab the reader’s attention, and it should be clearly related to your research purpose, such as responding to a research question.
This constitutes your analysis where you explore the theme or focus, outlined in the topic sentence, in further detail by interrogating why this particular theme or finding emerged and the significance of this data. This is also where you bring in the relevant secondary literature.
This is the evaluative stage of the cycle where you explicitly return back to the topic sentence and tell the reader what this means in terms of answering the relevant research question and establishing new knowledge. It could be a single sentence, or a short paragraph, and it doesn’t strictly need to appear at the end of every section or theme. Instead, some prefer to bring the main themes together towards the end of the discussion in a single paragraph or two. Either way, it’s imperative that you evaluate the significance of your discussion and tell the reader what this means.
A note on the three-part structure
This is often how you’re taught to construct a paragraph, but the themes and ideas you engage with at dissertation level are going to extend beyond the confines of a short paragraph. Therefore, this is a structure to guide how you write about particular themes or patterns in your discussion. Think of this structure like a cycle that you can engage in its smallest form to shape a paragraph; in a slightly larger form to shape a subsection of a chapter; and in its largest form to shape the entire chapter. You can 'level up' the same basic structure to accommodate a deeper breadth of thinking and critical engagement.
Using secondary literature
Your discussion chapter should return to the relevant literature (previously identified in your literature review ) in order to contextualise and deepen your reader’s understanding of the findings. This might help to strengthen your findings, or you might find contradictory evidence that serves to counter your results. In the case of the latter, it’s important that you consider why this might be and the implications for this. It’s through your incorporation of secondary literature that you can consider the question, ‘What do we now know that we didn’t before?’
Limitations
You may have included a limitations section in your methodology chapter (see our Writing the Methodology guide ), but it’s also common to have one in your discussion chapter. The difference here is that your limitations are directly associated with your results and the capacity to interpret and analyse those results.
Think of it this way: the limitations in your methodology refer to the issues identified before conducting the research, whilst the limitations in your discussion refer to the issues that emerged after conducting the research. For example, you might only be able to identify a limitation about the external validity or generalisability of your research once you have processed and analysed the data. Try not to overstress the limitations of your work – doing so can undermine the work you’ve done – and try to contextualise them, perhaps by relating them to certain limitations of other studies.
Recommendations
It’s often good to follow your limitations with some recommendations for future research. This creates a neat linearity from what didn’t work, or what could be improved, to how other researchers could address these issues in the future. This helps to reposition your limitations in a positive way by offering an action-oriented response. Try to limit the amount of recommendations you discuss – too many can bring the end of your discussion to a rather negative end as you’re ultimately focusing on what should be done, rather than what you have done. You also don’t need to repeat the recommendations in your conclusion if you’ve included them here.
What to avoid
This portion of the guide will cover some common missteps you should try to avoid in writing your results and discussion.
Over-reliance on tables and figures
It’s very common to produce visual representations of data, such as graphs and tables, and to use these representations in your results chapter. However, the use of these figures should not entirely replace your written account of the data. You don’t need to specify every detail in the data set, but you should provide some written account of what the data shows, drawing your reader’s attention to the most important elements of the data. The figures should support your account and help to contextualise your results. Simply stating, ‘look at Table 1’, without any further detail is not sufficient. Writers often try to do this as a way of saving words, but your markers will know!
Ignoring unexpected or contradictory data
Research can be a complex process with ups and downs, surprises and anomalies. Don’t be tempted to ignore any data that doesn’t meet your expectations, or that perhaps you’re struggling to explain. Failing to report on data for these, and other such reasons, is a problem because it undermines your credibility as a researcher, which inevitably undermines your research in the process. You have to do your best to provide some reason to such data. For instance, there might be some methodological reason behind a particular trend in the data.
Including raw data
You don’t need to include any raw data in your results chapter – raw data meaning unprocessed data that hasn’t undergone any calculations or other such refinement. This can overwhelm your reader and obscure the clarity of the research. You can include raw data in an appendix, providing you feel it’s necessary.
Presenting new results in the discussion
You shouldn’t be stating original findings for the first time in the discussion chapter. The findings of your study should first appear in your results before elaborating on them in the discussion.
Overstressing the significance of your research
It’s important that you clarify what your research demonstrates so you can highlight your own contribution to the research field. However, don’t overstress or inflate the significance of your results. It’s always difficult to provide definitive answers in academic research, especially with qualitative data. You should be confident and authoritative where possible, but don’t claim to reach the absolute truth when perhaps other conclusions could be reached. Where necessary, you should use hedging (see definition) to slightly soften the tone and register of your language.
Definition: Hedging refers to 'the act of expressing your attitude or ideas in tentative or cautious ways' (Singh and Lukkarila, 2017: 101). It’s mostly achieved through a number of verbs or adverbs, such as ‘suggest’ or ‘seemingly.’
Q: What’s the difference between the results and discussion?
A: The results chapter is a factual account of the data collected, whilst the discussion considers the implications of these findings by relating them to relevant literature and answering your research question(s). See the tab 'The Differences' in this guide for more detail.
Q: Should the discussion include recommendations for future research?
A: Your dissertation should include some recommendations for future research, but it can vary where it appears. Recommendations are often featured towards the end of the discussion chapter, but they also regularly appear in the conclusion chapter (see our Writing the Conclusion guide for more). It simply depends on your dissertation and the conventions of your school or department. It’s worth consulting any specific guidance that you’ve been given, or asking your supervisor directly.
Q: Should the discussion include the limitations of the study?
A: Like the answer above, you should engage with the limitations of your study, but it might appear in the discussion of some dissertations, or the conclusion of others. Consider the narrative flow and whether it makes sense to include the limitations in your discussion chapter, or your conclusion. You should also consult any discipline-specific guidance you’ve been given, or ask your supervisor for more. Be mindful that this is slightly different to the limitations outlined in the methodology or methods chapter (see our Writing the Methodology guide vs. the 'Discussion' tab of this guide).
Q: Should the results and discussion be in the first-person or third?
A: It’s important to be consistent , so you should use whatever you’ve been using throughout your dissertation. Third-person is more commonly accepted, but certain disciplines are happy with the use of first-person. Just remember that the first-person pronoun can be a distracting, but powerful device, so use it sparingly. Consult your lecturer for discipline-specific guidance.
Q: Is there a difference between the discussion and the conclusion of a dissertation?
A: Yes, there is a difference. The discussion chapter is a detailed consideration of how your findings answer your research questions. This includes the use of secondary literature to help contextualise your discussion. Rather than considering the findings in detail, the conclusion briefly summarises and synthesises the main findings of your study before bringing the dissertation to a close. Both are similar, particularly in the way they ‘broaden out’ to consider the wider implications of the research. They are, however, their own distinct chapters, unless otherwise stated by your supervisor.
The results and discussion chapters (or chapter) constitute a large part of your dissertation as it’s here where your original contribution is foregrounded and discussed in detail. Remember, the results chapter simply reports on the data collected, whilst the discussion is where you consider your research questions and/or hypothesis in more detail by interpreting and interrogating the data. You can integrate both into a single chapter and weave the interpretation of your findings throughout the chapter, although it’s common for both the results and discussion to appear as separate chapters. Consult your supervisor for further guidance.
Here’s a final checklist for writing your results and discussion. Remember that not all of these points will be relevant for you, so make sure you cover whatever’s appropriate for your dissertation. The asterisk (*) indicates any content that might not be relevant for your dissertation. To download a copy of the checklist to save and edit, please use the Word document, below.
- Results and discussion self-evaluation checklist

- << Previous: The Methodology
- Next: The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://library.soton.ac.uk/writing_the_dissertation
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
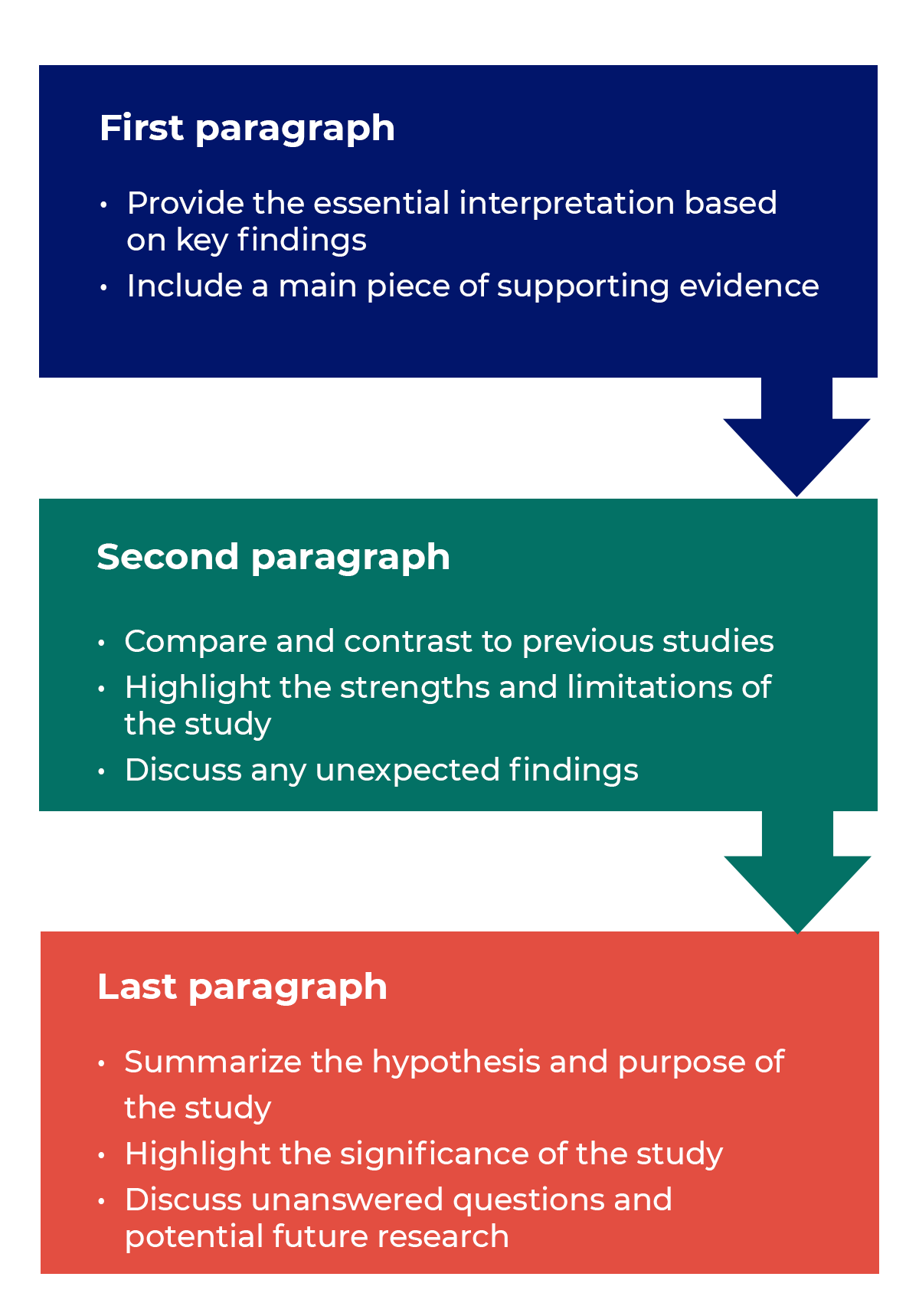
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter: Guide & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter: Guide & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Dissertation discussion section is a chapter that interprets the results obtained from research and offers an in-depth analysis of findings. In this section, students need to analyze the outcomes, evaluate their significance, and compare them to previous research. The discussion section may also explore the limitations of the study and suggest further research perspectives.
If you are stuck with your thesis or dissertation discussion chapter, you are in the right place to complete this section successfully. This article will outline our best solutions and methods on how to write the discussion of a dissertation or thesis. We also will share advanced dissertation discussion examples to help you finalize your PhD work. Feel like academic writing gives you hassles? Remember that you can always rely on academic experts qualified in your field to get professional dissertation help online .
What Is a Dissertation Discussion?
First and foremost, students need to have a clear understanding of what dissertation discussion is. This is not the same as your results section , where you share data from your research. You are going deeper into the explanation of the existing data in your thesis or dissertation discussion section. In other words, you illustrate practical implications of your research and how the data can be used, researched further, or limited. What will make your discussion section of a dissertation excellent:
- clear structure
- practical implication
- elaboration on future work on this topic.
This section should go after research methodology and before the dissertation conclusion . It should be directly relevant to questions posed in your introduction. The biggest mistake you can make is to rewrite your result chapter with other words and add some limitations and recommendation paragraphs. However, this is an entirely different type of writing you need to complete.
Purpose of a Dissertation Discussion Chapter
A dissertation discussion section is critical to explaining students’ findings and the application of data to real-life cases. As we mentioned before, this section will often be read right after the dissertation methods . It evaluates and elaborates on findings and helps to understand the importance of your performed thesis research. A dissertation discussion opens a new perspective on further research on the same field or topic. It also outlines critical data to consider in subsequent studies. In a nutshell, this is the section where you explain your work to a broad audience.
Structure of a Dissertation Discussion Section
Let’s start your writing journey of this research part with a clear delineation of what it should include and then briefly discuss each component. Here are some basic things you need to consider for an excellent discussion chapter of dissertation :
- Brief summary It does not mean copying an introduction section. However, the first few paragraphs will make an overview of your findings and topic.
- Interpretations This is a critical component of your work — elaborate on your results and explain possible ways of using them.
- Implication Research work is not just 100+ pages of text. Students should explain and illustrate how it could be used for solving practical problems.
- Constraints This is where you outline your limitations. For instance, your research was done only on students, and it may have different results with elderly people.
- Recommendations You can also define possible ways of future research on the exact topic when writing a discussion for your thesis or dissertation. Tell readers, for example, that it would be helpful to run similar research in other specific circumstances.
How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
One of the most commonly asked questions for our experts is how to write the discussion section of a dissertation or thesis. We understand why it can be complicated to get a clear answer. Students often think that this section is similar to the result chapter and just retells it in other words. But it is not so. Let’s go through all steps to writing a discussion in a dissertation, and share our best examples from academic papers.

1. Remind Your Research Questions & Objectives
Writing the discussion chapter of a dissertation is not a big deal if you understand its aim and each component in a text structure. First of all, you need to evaluate how your results help to answer research questions you defined in the beginning. It is not about repeating the result, you did it in previous paragraphs. However, dissertation or thesis discussion should underline how your findings help to answer the research problem. Start writing from a brief intro by recalling research questions or hypotheses . Then, show how your results answer them or support a hypothesis in your work.
2. Sum Up Key Findings
Next part of your discussion for dissertation is to provide a short summary of previous data. But do not respite the same summary paragraphs from results or introduction of a dissertation . Here researchers should be more thoughtful and go deeper into the work’s aims. Try to explain in a few sentences what you get from running research. For instance, starters usually write the statement that “our data proves that…” or “survey results illustrate a clear correlation between a and b that is critical for proving our working hypothesis…”. A discussion chapter of your dissertation is not just a fixation on results but a more profound summary connected to research goals and purpose. Here is an example: Summary of Findings Example
3. Interpret the Results
The most critical part of a discussion section is to explain and enact the results you’ve got. It is the most significant part of any text. Students should be clear about what to include in these paragraphs. Here is some advice to make this elaboration structured:
- Identify correlations or patterns in the data for dissertation discussion.
- Underline how results can answer research questions or prove your hypothesis.
- Emphasize how your findings are connected to the previous topic studies.
- Point out essential statements you can use in future research.
- Evaluate the significance of your results and any unexpected data you have.
- What others can learn from your research and how this work contributes to the field.
- Consider any possible additional or unique explanation of your findings.
- Go deeper with options of how results can be applied in practice.
Writing a dissertation discussion chapter can be tough, but here is a great sample to learn from. Example of Interpretations in Disssertation Discussion
4. Discuss How Your Findings Relate to the Literature
Here we came to the implications of your findings for the dissertation discussion. In other words, this is a few sentences on how your work is connected to other studies on the same research topic or what literature gap you are going to fill with the data and research you launched. Remember to mention how your study address the limitations you have discovered while writing a literature review . First, outline how your hypothesis relates to theories or previous works in the field. Maybe, you challenged some theories or tried to define your own. Be specific in this section. Second, define a practical implementation of your work. Maybe, it can support recommendations or change legislation. Discussion chapter of a thesis is a place where you explain your work, make it valuable, and incorporate additional meaning for some specific data. Example of Implications in Disssertation Discussion
5. Mention Possible Limitations
It is pretty tricky to conduct research without limitations. You will always have some, which does not mean that your work is not good. When you write a discussion chapter in a thesis or dissertation, focus on what may influence your results and how changing independent variables can affect your data collection methods and final outcomes. Here are some points to consider when you structure your dissertation discussion limitation part:
- If results can change in case you change the reference group?
- What will happen with data if it changes circumstances?
- What could influence results?
Critical thinking and analysis can help you to outline possible limitations. It can be the age of the reference group, change of questionnaire in a survey, or specific use of data extraction equipment. Be transparent about what could affect your results. Example of Complications
6. Provide Recommendations for Further Research
Writing a dissertation discussion also makes a connection to possible future research. So, other scientists may complete that. While elaborating on possible implementations of your study, you may also estimate future approaches in topic research. Here are some points to consider while your discussion in thesis writing:
- Outline questions related to your topic that you did not answer in defined study or did not outline as research questions. There are other possible gaps to research.
- Suggest future research based on limitations. For example, if you define surveyed people’s age as a limitation, recommend running another survey for older or younger recipients.
Example of Recommendations
7. Conclude Your Thesis/ Dissertation Discussion
You are almost done, the last step is to provide a brief summary of a section. It is not the same as a conclusion for whole research. However, you need to briefly outline key points from the dissertation discussion. To finalize writing the discussion section of a dissertation, go through the text and check if there is no unimportant information. Do not overload the text with relevant data you did not present in the result section. Be specific in your summary paragraphs. It is a holistic view of everything you pointed out. Provide a few sentences to systemize all you outlined in the text. Example of a Concluding Summary in a Dissertation Discussion Section
Dissertation Discussion Example
If we need to share one piece of practical advice, it would be to use thesis or dissertation discussion examples when writing your own copy. StudyCrumb provides the best samples from real students' work to help you understand the stylistic and possible structure of this part. It does not mean you need to copy and paste them into your work. However, you can use a dissertation discussion example for inspiration and brainstorming ideas for breaking writing blocks. Here’s a doctoral thesis discussion chapter example.
Dissertation Discussion Writing Tips
Before reading this blog, you should already know how to write a thesis discussion. However, we would share some essential tips you need to have in mind while working on the document.
- Be consistent Your dissertation discussion chapter is a part of bigger research, and it should be in line with your whole work.
- Understand your reader You are writing an academic text that will be analyzed by professionals and experts in the same field. Be sure that you are not trying to simplify your discussion.
- Be logical Do not jump into a new line of discussion if you did not delineate it as a research question at the beginning.
- Be clear Do not include any data that was not presented in the result section.
- Consider word choice Use such terms as “our data indicate…” or “our data suggests…” instead of “the data proves.”
- Use proper format Follow the formatting rules specified by a specific paper style (e.g., APA style format , MLA format , or Chicago format ) or provided by your instructor.
Bottom Line on Writing a Dissertation Discussion Chapter
At this stage, it should not be a question for you on how to write a discussion chapter in a PhD thesis or dissertation. Let’s make it clear. It is not a result section but still a place to elaborate on data and go deeper with explanations. Dissertation discussion section includes some intro, result interpretations, limitations, and recommendations for future research. Our team encourages you to use examples before starting your own piece of writing. It will help you to realize the purpose and structure of this chapter and inspire better texts! If you have other questions regarding the PhD writing process, check our blog for more insights. From detailed instruction on how to write a dissertation or guide on formatting a dissertation appendix , we’ve got you covered.
Order dissertation discussion from our proficient writers. They will take a significant burden off of you. Instead, they will carry out high-level academic work in a short time.
FAQ About Dissertation Discussion Chapter
1. where does a discussion section go in a dissertation.
Dissertation discussion section is used to go right after the result chapter. The logic is simple — you share your data and then go to the elaboration and explanation of it. Check the sample thesis we provide to students for details on structure.
2. How long should a dissertation discussion chapter be?
It is not a surprise that dissertation discussion chapter is extremely significant for the research. Here you will go into the details of your study and interpret results to prove or not your hypothesis. It should take almost 25% of your work.
3. What tense should I use in a dissertation discussion?
Thesis or dissertation discussion used to have some rules on using tenses. You need to use the present tense when referring to established facts and use the past tense when referring to previous studies. And check your text before submission to ensure that you did not miss something.
4. What not to include in a dissertation discussion section?
The answer is easy. Discussion section of a dissertation should not include any new findings or describe some unsupported claims. Also, do not try to feel all possible gaps with one research. It may be better to outline your ideas for future studies in recommendations.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

According to the data, implementing the co-orientation theory was successful and can be used for the same circumstances in the future. As we found, most participants agreed with the importance of those theses on the five fundamental reforms. It means that the results identified a successful government work in choosing the messages to communicate about examined reforms. At the same time, the situation is not so favorable with implementing the principles of two-way symmetrical communications. According to the results, people did not feel that the government had a mutual, open, and equal dialogue with the public about the reforms.
Our study underlines the importance of future research on using TikTok for political communication. As discussed above, TikTok is the most commonly used social media platform for many young voters. This means that political discussion will also move to this platform. Our research and typology of political communication content can be used in the future planning of effective political campaigns. For example, we can assume that “play videos” have enormous potential to facilitate complicated topics and provide specific agenda settings. We also identified additional affordances of TikTok used for political communication, such as built-in video editors, playlists for specific topics, a green screen for news explainers, and duets for reflection on news and discussion. It means that these features make TikTok suitable for efficient political communications.
As we pointed out in the literature review, there are few works on using TikTok affordances for political communications, and this topic can be expanded in the future. Government institutions have already understood the importance of this platform for efficient communication with younger audiences, and we will see more political projects on TikTok. That is why expanding research on using TikTok for political communication will be enormous in the following years. Our work is one of the first research on the role of emerging media in war communication and can be used as a practical guide for government's strategic planning in times of emergencies.
Although this study has provided critical first insights into the effects of multimodal disinformation and rebuttals, there are some limitations. First and most importantly, the effects of multimodal disinformation and rebuttals partially depend on the topic of the message. Although fact-checkers reduce credibility of disinformation in both settings, and attitudinal congruence plays a consistent role in conditioning responses to multimodal disinformation, visuals do not have the same impact on affecting the credibility of news on school shootings and refugees.
As we mentioned before, our study has some limitations, as the research was conducted based on data from United State citizens. However, for a better understanding of government communication practices, it would be productive to implement the same research in other countries. Some cultural differences can influence the communication strategies the government uses in times of emergency. Another possible way to examine this topic is to conduct research using a specific period of time. For future studies, it will be beneficial to expand the number of survey recipients.
To summarize, Airbnb has expertise in communicating CSR and CSA campaigns. We defined their communication strategy about the program for Ukrainian refugees as quite successful. They applied all the principles of CSR communication best practices, used dialogic theory to engage with the public on social media, and created clear messaging on applying for the program. Airbnb examples of CSR communication can be used by other businesses to create a communication strategy for unplanned CSR campaigns. Moreover, it can be further researched how Airbnb's CSR campaign influenced the organizational reputation in the future.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 8. The Discussion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The purpose of the discussion section is to interpret and describe the significance of your findings in relation to what was already known about the research problem being investigated and to explain any new understanding or insights that emerged as a result of your research. The discussion will always connect to the introduction by way of the research questions or hypotheses you posed and the literature you reviewed, but the discussion does not simply repeat or rearrange the first parts of your paper; the discussion clearly explains how your study advanced the reader's understanding of the research problem from where you left them at the end of your review of prior research.
Annesley, Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Peacock, Matthew. “Communicative Moves in the Discussion Section of Research Articles.” System 30 (December 2002): 479-497.
Importance of a Good Discussion
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it:
- Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
- Presents the underlying meaning of your research, notes possible implications in other areas of study, and explores possible improvements that can be made in order to further develop the concerns of your research;
- Highlights the importance of your study and how it can contribute to understanding the research problem within the field of study;
- Presents how the findings from your study revealed and helped fill gaps in the literature that had not been previously exposed or adequately described; and,
- Engages the reader in thinking critically about issues based on an evidence-based interpretation of findings; it is not governed strictly by objective reporting of information.
Annesley Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Bitchener, John and Helen Basturkmen. “Perceptions of the Difficulties of Postgraduate L2 Thesis Students Writing the Discussion Section.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 5 (January 2006): 4-18; Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
These are the general rules you should adopt when composing your discussion of the results :
- Do not be verbose or repetitive; be concise and make your points clearly
- Avoid the use of jargon or undefined technical language
- Follow a logical stream of thought; in general, interpret and discuss the significance of your findings in the same sequence you described them in your results section [a notable exception is to begin by highlighting an unexpected result or a finding that can grab the reader's attention]
- Use the present verb tense, especially for established facts; however, refer to specific works or prior studies in the past tense
- If needed, use subheadings to help organize your discussion or to categorize your interpretations into themes
II. The Content
The content of the discussion section of your paper most often includes :
- Explanation of results : Comment on whether or not the results were expected for each set of findings; go into greater depth to explain findings that were unexpected or especially profound. If appropriate, note any unusual or unanticipated patterns or trends that emerged from your results and explain their meaning in relation to the research problem.
- References to previous research : Either compare your results with the findings from other studies or use the studies to support a claim. This can include re-visiting key sources already cited in your literature review section, or, save them to cite later in the discussion section if they are more important to compare with your results instead of being a part of the general literature review of prior research used to provide context and background information. Note that you can make this decision to highlight specific studies after you have begun writing the discussion section.
- Deduction : A claim for how the results can be applied more generally. For example, describing lessons learned, proposing recommendations that can help improve a situation, or highlighting best practices.
- Hypothesis : A more general claim or possible conclusion arising from the results [which may be proved or disproved in subsequent research]. This can be framed as new research questions that emerged as a consequence of your analysis.
III. Organization and Structure
Keep the following sequential points in mind as you organize and write the discussion section of your paper:
- Think of your discussion as an inverted pyramid. Organize the discussion from the general to the specific, linking your findings to the literature, then to theory, then to practice [if appropriate].
- Use the same key terms, narrative style, and verb tense [present] that you used when describing the research problem in your introduction.
- Begin by briefly re-stating the research problem you were investigating and answer all of the research questions underpinning the problem that you posed in the introduction.
- Describe the patterns, principles, and relationships shown by each major findings and place them in proper perspective. The sequence of this information is important; first state the answer, then the relevant results, then cite the work of others. If appropriate, refer the reader to a figure or table to help enhance the interpretation of the data [either within the text or as an appendix].
- Regardless of where it's mentioned, a good discussion section includes analysis of any unexpected findings. This part of the discussion should begin with a description of the unanticipated finding, followed by a brief interpretation as to why you believe it appeared and, if necessary, its possible significance in relation to the overall study. If more than one unexpected finding emerged during the study, describe each of them in the order they appeared as you gathered or analyzed the data. As noted, the exception to discussing findings in the same order you described them in the results section would be to begin by highlighting the implications of a particularly unexpected or significant finding that emerged from the study, followed by a discussion of the remaining findings.
- Before concluding the discussion, identify potential limitations and weaknesses if you do not plan to do so in the conclusion of the paper. Comment on their relative importance in relation to your overall interpretation of the results and, if necessary, note how they may affect the validity of your findings. Avoid using an apologetic tone; however, be honest and self-critical [e.g., in retrospect, had you included a particular question in a survey instrument, additional data could have been revealed].
- The discussion section should end with a concise summary of the principal implications of the findings regardless of their significance. Give a brief explanation about why you believe the findings and conclusions of your study are important and how they support broader knowledge or understanding of the research problem. This can be followed by any recommendations for further research. However, do not offer recommendations which could have been easily addressed within the study. This would demonstrate to the reader that you have inadequately examined and interpreted the data.
IV. Overall Objectives
The objectives of your discussion section should include the following: I. Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings
Briefly reiterate the research problem or problems you are investigating and the methods you used to investigate them, then move quickly to describe the major findings of the study. You should write a direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results, usually in one paragraph.
II. Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important
No one has thought as long and hard about your study as you have. Systematically explain the underlying meaning of your findings and state why you believe they are significant. After reading the discussion section, you want the reader to think critically about the results and why they are important. You don’t want to force the reader to go through the paper multiple times to figure out what it all means. If applicable, begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most significant or unanticipated finding first, then systematically review each finding. Otherwise, follow the general order you reported the findings presented in the results section.
III. Relate the Findings to Similar Studies
No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for your research. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your study differs from other research about the topic. Note that any significant or unanticipated finding is often because there was no prior research to indicate the finding could occur. If there is prior research to indicate this, you need to explain why it was significant or unanticipated. IV. Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings
It is important to remember that the purpose of research in the social sciences is to discover and not to prove . When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. This is especially important when describing the discovery of significant or unanticipated findings.
V. Acknowledge the Study’s Limitations
It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor! Note any unanswered questions or issues your study could not address and describe the generalizability of your results to other situations. If a limitation is applicable to the method chosen to gather information, then describe in detail the problems you encountered and why. VI. Make Suggestions for Further Research
You may choose to conclude the discussion section by making suggestions for further research [as opposed to offering suggestions in the conclusion of your paper]. Although your study can offer important insights about the research problem, this is where you can address other questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or highlight hidden issues that were revealed as a result of conducting your research. You should frame your suggestions by linking the need for further research to the limitations of your study [e.g., in future studies, the survey instrument should include more questions that ask..."] or linking to critical issues revealed from the data that were not considered initially in your research.
NOTE: Besides the literature review section, the preponderance of references to sources is usually found in the discussion section . A few historical references may be helpful for perspective, but most of the references should be relatively recent and included to aid in the interpretation of your results, to support the significance of a finding, and/or to place a finding within a particular context. If a study that you cited does not support your findings, don't ignore it--clearly explain why your research findings differ from theirs.
V. Problems to Avoid
- Do not waste time restating your results . Should you need to remind the reader of a finding to be discussed, use "bridge sentences" that relate the result to the interpretation. An example would be: “In the case of determining available housing to single women with children in rural areas of Texas, the findings suggest that access to good schools is important...," then move on to further explaining this finding and its implications.
- As noted, recommendations for further research can be included in either the discussion or conclusion of your paper, but do not repeat your recommendations in the both sections. Think about the overall narrative flow of your paper to determine where best to locate this information. However, if your findings raise a lot of new questions or issues, consider including suggestions for further research in the discussion section.
- Do not introduce new results in the discussion section. Be wary of mistaking the reiteration of a specific finding for an interpretation because it may confuse the reader. The description of findings [results section] and the interpretation of their significance [discussion section] should be distinct parts of your paper. If you choose to combine the results section and the discussion section into a single narrative, you must be clear in how you report the information discovered and your own interpretation of each finding. This approach is not recommended if you lack experience writing college-level research papers.
- Use of the first person pronoun is generally acceptable. Using first person singular pronouns can help emphasize a point or illustrate a contrasting finding. However, keep in mind that too much use of the first person can actually distract the reader from the main points [i.e., I know you're telling me this--just tell me!].
Analyzing vs. Summarizing. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Discussion. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Hess, Dean R. "How to Write an Effective Discussion." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004); Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sauaia, A. et al. "The Anatomy of an Article: The Discussion Section: "How Does the Article I Read Today Change What I Will Recommend to my Patients Tomorrow?” The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 74 (June 2013): 1599-1602; Research Limitations & Future Research . Lund Research Ltd., 2012; Summary: Using it Wisely. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Discussion. Writing in Psychology course syllabus. University of Florida; Yellin, Linda L. A Sociology Writer's Guide . Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, 2009.
Writing Tip
Don’t Over-Interpret the Results!
Interpretation is a subjective exercise. As such, you should always approach the selection and interpretation of your findings introspectively and to think critically about the possibility of judgmental biases unintentionally entering into discussions about the significance of your work. With this in mind, be careful that you do not read more into the findings than can be supported by the evidence you have gathered. Remember that the data are the data: nothing more, nothing less.
MacCoun, Robert J. "Biases in the Interpretation and Use of Research Results." Annual Review of Psychology 49 (February 1998): 259-287; Ward, Paulet al, editors. The Oxford Handbook of Expertise . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2018.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Write Two Results Sections!
One of the most common mistakes that you can make when discussing the results of your study is to present a superficial interpretation of the findings that more or less re-states the results section of your paper. Obviously, you must refer to your results when discussing them, but focus on the interpretation of those results and their significance in relation to the research problem, not the data itself.
Azar, Beth. "Discussing Your Findings." American Psychological Association gradPSYCH Magazine (January 2006).
Yet Another Writing Tip
Avoid Unwarranted Speculation!
The discussion section should remain focused on the findings of your study. For example, if the purpose of your research was to measure the impact of foreign aid on increasing access to education among disadvantaged children in Bangladesh, it would not be appropriate to speculate about how your findings might apply to populations in other countries without drawing from existing studies to support your claim or if analysis of other countries was not a part of your original research design. If you feel compelled to speculate, do so in the form of describing possible implications or explaining possible impacts. Be certain that you clearly identify your comments as speculation or as a suggestion for where further research is needed. Sometimes your professor will encourage you to expand your discussion of the results in this way, while others don’t care what your opinion is beyond your effort to interpret the data in relation to the research problem.
- << Previous: Using Non-Textual Elements
- Next: Limitations of the Study >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Library Guides
Dissertations 5: findings, analysis and discussion: home.
- Results/Findings
Alternative Structures
The time has come to show and discuss the findings of your research. How to structure this part of your dissertation?
Dissertations can have different structures, as you can see in the dissertation structure guide.
Dissertations organised by sections
Many dissertations are organised by sections. In this case, we suggest three options. Note that, if within your course you have been instructed to use a specific structure, you should do that. Also note that sometimes there is considerable freedom on the structure, so you can come up with other structures too.
A) More common for scientific dissertations and quantitative methods:
- Results chapter
- Discussion chapter
Example:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
- (Recommendations)
if you write a scientific dissertation, or anyway using quantitative methods, you will have some objective results that you will present in the Results chapter. You will then interpret the results in the Discussion chapter.
B) More common for qualitative methods
- Analysis chapter. This can have more descriptive/thematic subheadings.
- Discussion chapter. This can have more descriptive/thematic subheadings.
- Case study of Company X (fashion brand) environmental strategies
- Successful elements
- Lessons learnt
- Criticisms of Company X environmental strategies
- Possible alternatives
C) More common for qualitative methods
- Analysis and discussion chapter. This can have more descriptive/thematic titles.
- Case study of Company X (fashion brand) environmental strategies
If your dissertation uses qualitative methods, it is harder to identify and report objective data. Instead, it may be more productive and meaningful to present the findings in the same sections where you also analyse, and possibly discuss, them. You will probably have different sections dealing with different themes. The different themes can be subheadings of the Analysis and Discussion (together or separate) chapter(s).
Thematic dissertations
If the structure of your dissertation is thematic , you will have several chapters analysing and discussing the issues raised by your research. The chapters will have descriptive/thematic titles.
- Background on the conflict in Yemen (2004-present day)
- Classification of the conflict in international law
- International law violations
- Options for enforcement of international law
- Next: Results/Findings >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 2:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/c.php?g=696975
CONNECT WITH US
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 21 August 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 25 October 2022.

The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results .
It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review , and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion . It should not be a second results section .
There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your writing around these key elements:
- Summary: A brief recap of your key results
- Interpretations: What do your results mean?
- Implications: Why do your results matter?
- Limitations: What can’t your results tell us?
- Recommendations: Avenues for further studies or analyses
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What not to include in your discussion section, step 1: summarise your key findings, step 2: give your interpretations, step 3: discuss the implications, step 4: acknowledge the limitations, step 5: share your recommendations, discussion section example.
There are a few common mistakes to avoid when writing the discussion section of your paper.
- Don’t introduce new results: You should only discuss the data that you have already reported in your results section .
- Don’t make inflated claims: Avoid overinterpretation and speculation that isn’t directly supported by your data.
- Don’t undermine your research: The discussion of limitations should aim to strengthen your credibility, not emphasise weaknesses or failures.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarising your major findings. Don’t just repeat all the data you have already reported – aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research question . This should be no more than one paragraph.
Many students struggle with the differences between a discussion section and a results section . The crux of the matter is that your results sections should present your results, and your discussion section should subjectively evaluate them. Try not to blend elements of these two sections, in order to keep your paper sharp.
- The results indicate that …
- The study demonstrates a correlation between …
- This analysis supports the theory that …
- The data suggest that …
The meaning of your results may seem obvious to you, but it’s important to spell out their significance for your reader, showing exactly how they answer your research question.
The form of your interpretations will depend on the type of research, but some typical approaches to interpreting the data include:
- Identifying correlations , patterns, and relationships among the data
- Discussing whether the results met your expectations or supported your hypotheses
- Contextualising your findings within previous research and theory
- Explaining unexpected results and evaluating their significance
- Considering possible alternative explanations and making an argument for your position
You can organise your discussion around key themes, hypotheses, or research questions, following the same structure as your results section. Alternatively, you can also begin by highlighting the most significant or unexpected results.
- In line with the hypothesis …
- Contrary to the hypothesised association …
- The results contradict the claims of Smith (2007) that …
- The results might suggest that x . However, based on the findings of similar studies, a more plausible explanation is x .
As well as giving your own interpretations, make sure to relate your results back to the scholarly work that you surveyed in the literature review . The discussion should show how your findings fit with existing knowledge, what new insights they contribute, and what consequences they have for theory or practice.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support existing theories, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge existing theories, why do you think that is?
- Are there any practical implications?
Your overall aim is to show the reader exactly what your research has contributed, and why they should care.
- These results build on existing evidence of …
- The results do not fit with the theory that …
- The experiment provides a new insight into the relationship between …
- These results should be taken into account when considering how to …
- The data contribute a clearer understanding of …
- While previous research has focused on x , these results demonstrate that y .
Even the best research has its limitations. Acknowledging these is important to demonstrate your credibility. Limitations aren’t about listing your errors, but about providing an accurate picture of what can and cannot be concluded from your study.
Limitations might be due to your overall research design, specific methodological choices , or unanticipated obstacles that emerged during your research process.
Here are a few common possibilities:
- If your sample size was small or limited to a specific group of people, explain how generalisability is limited.
- If you encountered problems when gathering or analysing data, explain how these influenced the results.
- If there are potential confounding variables that you were unable to control, acknowledge the effect these may have had.
After noting the limitations, you can reiterate why the results are nonetheless valid for the purpose of answering your research question.
- The generalisability of the results is limited by …
- The reliability of these data is impacted by …
- Due to the lack of data on x , the results cannot confirm …
- The methodological choices were constrained by …
- It is beyond the scope of this study to …
Based on the discussion of your results, you can make recommendations for practical implementation or further research. Sometimes, the recommendations are saved for the conclusion .
Suggestions for further research can lead directly from the limitations. Don’t just state that more studies should be done – give concrete ideas for how future work can build on areas that your own research was unable to address.
- Further research is needed to establish …
- Future studies should take into account …
- Avenues for future research include …

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/discussion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a results section | tips & examples, research paper appendix | example & templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
How To Write The Conclusion Chapter
The what, why & how explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD Cand). Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | September 2021
So, you’ve wrapped up your results and discussion chapters, and you’re finally on the home stretch – the conclusion chapter . In this post, we’ll discuss everything you need to know to craft a high-quality conclusion chapter for your dissertation or thesis project.
Overview: Dissertation Conclusion Chapter
- What the thesis/dissertation conclusion chapter is
- What to include in your conclusion chapter
- How to structure and write up your conclusion chapter
- A few tips to help you ace the chapter
What exactly is the conclusion chapter?
The conclusion chapter is typically the final major chapter of a dissertation or thesis. As such, it serves as a concluding summary of your research findings and wraps up the document. While some publications such as journal articles and research reports combine the discussion and conclusion sections, these are typically separate chapters in a dissertation or thesis. As always, be sure to check what your university’s structural preference is before you start writing up these chapters.
So, what’s the difference between the discussion and the conclusion chapter?
Well, the two chapters are quite similar , as they both discuss the key findings of the study. However, the conclusion chapter is typically more general and high-level in nature. In your discussion chapter, you’ll typically discuss the intricate details of your study, but in your conclusion chapter, you’ll take a broader perspective, reporting on the main research outcomes and how these addressed your research aim (or aims) .
A core function of the conclusion chapter is to synthesise all major points covered in your study and to tell the reader what they should take away from your work. Basically, you need to tell them what you found , why it’s valuable , how it can be applied , and what further research can be done.
Whatever you do, don’t just copy and paste what you’ve written in your discussion chapter! The conclusion chapter should not be a simple rehash of the discussion chapter. While the two chapters are similar, they have distinctly different functions.

What should I include in the conclusion chapter?
To understand what needs to go into your conclusion chapter, it’s useful to understand what the chapter needs to achieve. In general, a good dissertation conclusion chapter should achieve the following:
- Summarise the key findings of the study
- Explicitly answer the research question(s) and address the research aims
- Inform the reader of the study’s main contributions
- Discuss any limitations or weaknesses of the study
- Present recommendations for future research
Therefore, your conclusion chapter needs to cover these core components. Importantly, you need to be careful not to include any new findings or data points. Your conclusion chapter should be based purely on data and analysis findings that you’ve already presented in the earlier chapters. If there’s a new point you want to introduce, you’ll need to go back to your results and discussion chapters to weave the foundation in there.
In many cases, readers will jump from the introduction chapter directly to the conclusions chapter to get a quick overview of the study’s purpose and key findings. Therefore, when you write up your conclusion chapter, it’s useful to assume that the reader hasn’t consumed the inner chapters of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, craft your conclusion chapter such that there’s a strong connection and smooth flow between the introduction and conclusion chapters, even though they’re on opposite ends of your document.
Need a helping hand?
How to write the conclusion chapter
Now that you have a clearer view of what the conclusion chapter is about, let’s break down the structure of this chapter so that you can get writing. Keep in mind that this is merely a typical structure – it’s not set in stone or universal. Some universities will prefer that you cover some of these points in the discussion chapter , or that you cover the points at different levels in different chapters.
Step 1: Craft a brief introduction section
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the conclusions chapter needs to start with a brief introduction. In this introductory section, you’ll want to tell the reader what they can expect to find in the chapter, and in what order . Here’s an example of what this might look like:
This chapter will conclude the study by summarising the key research findings in relation to the research aims and questions and discussing the value and contribution thereof. It will also review the limitations of the study and propose opportunities for future research.
Importantly, the objective here is just to give the reader a taste of what’s to come (a roadmap of sorts), not a summary of the chapter. So, keep it short and sweet – a paragraph or two should be ample.
Step 2: Discuss the overall findings in relation to the research aims
The next step in writing your conclusions chapter is to discuss the overall findings of your study , as they relate to the research aims and research questions . You would have likely covered similar ground in the discussion chapter, so it’s important to zoom out a little bit here and focus on the broader findings – specifically, how these help address the research aims .
In practical terms, it’s useful to start this section by reminding your reader of your research aims and research questions, so that the findings are well contextualised. In this section, phrases such as, “This study aimed to…” and “the results indicate that…” will likely come in handy. For example, you could say something like the following:
This study aimed to investigate the feeding habits of the naked mole-rat. The results indicate that naked mole rats feed on underground roots and tubers. Further findings show that these creatures eat only a part of the plant, leaving essential parts to ensure long-term food stability.
Be careful not to make overly bold claims here. Avoid claims such as “this study proves that” or “the findings disprove existing the existing theory”. It’s seldom the case that a single study can prove or disprove something. Typically, this is achieved by a broader body of research, not a single study – especially not a dissertation or thesis which will inherently have significant limitations . We’ll discuss those limitations a little later.

Step 3: Discuss how your study contributes to the field
Next, you’ll need to discuss how your research has contributed to the field – both in terms of theory and practice . This involves talking about what you achieved in your study, highlighting why this is important and valuable, and how it can be used or applied.
In this section you’ll want to:
- Mention any research outputs created as a result of your study (e.g., articles, publications, etc.)
- Inform the reader on just how your research solves your research problem , and why that matters
- Reflect on gaps in the existing research and discuss how your study contributes towards addressing these gaps
- Discuss your study in relation to relevant theories . For example, does it confirm these theories or constructively challenge them?
- Discuss how your research findings can be applied in the real world . For example, what specific actions can practitioners take, based on your findings?
Be careful to strike a careful balance between being firm but humble in your arguments here. It’s unlikely that your one study will fundamentally change paradigms or shake up the discipline, so making claims to this effect will be frowned upon . At the same time though, you need to present your arguments with confidence, firmly asserting the contribution your research has made, however small that contribution may be. Simply put, you need to keep it balanced .
Step 4: Reflect on the limitations of your study
Now that you’ve pumped your research up, the next step is to critically reflect on the limitations and potential shortcomings of your study. You may have already covered this in the discussion chapter, depending on your university’s structural preferences, so be careful not to repeat yourself unnecessarily.
There are many potential limitations that can apply to any given study. Some common ones include:
- Sampling issues that reduce the generalisability of the findings (e.g., non-probability sampling )
- Insufficient sample size (e.g., not getting enough survey responses ) or limited data access
- Low-resolution data collection or analysis techniques
- Researcher bias or lack of experience
- Lack of access to research equipment
- Time constraints that limit the methodology (e.g. cross-sectional vs longitudinal time horizon)
- Budget constraints that limit various aspects of the study
Discussing the limitations of your research may feel self-defeating (no one wants to highlight their weaknesses, right), but it’s a critical component of high-quality research. It’s important to appreciate that all studies have limitations (even well-funded studies by expert researchers) – therefore acknowledging these limitations adds credibility to your research by showing that you understand the limitations of your research design .
That being said, keep an eye on your wording and make sure that you don’t undermine your research . It’s important to strike a balance between recognising the limitations, but also highlighting the value of your research despite those limitations. Show the reader that you understand the limitations, that these were justified given your constraints, and that you know how they can be improved upon – this will get you marks.

Next, you’ll need to make recommendations for future studies. This will largely be built on the limitations you just discussed. For example, if one of your study’s weaknesses was related to a specific data collection or analysis method, you can make a recommendation that future researchers undertake similar research using a more sophisticated method.
Another potential source of future research recommendations is any data points or analysis findings that were interesting or surprising , but not directly related to your study’s research aims and research questions. So, if you observed anything that “stood out” in your analysis, but you didn’t explore it in your discussion (due to a lack of relevance to your research aims), you can earmark that for further exploration in this section.
Essentially, this section is an opportunity to outline how other researchers can build on your study to take the research further and help develop the body of knowledge. So, think carefully about the new questions that your study has raised, and clearly outline these for future researchers to pick up on.
Step 6: Wrap up with a closing summary
Quick tips for a top-notch conclusion chapter
Now that we’ve covered the what , why and how of the conclusion chapter, here are some quick tips and suggestions to help you craft a rock-solid conclusion.
- Don’t ramble . The conclusion chapter usually consumes 5-7% of the total word count (although this will vary between universities), so you need to be concise. Edit this chapter thoroughly with a focus on brevity and clarity.
- Be very careful about the claims you make in terms of your study’s contribution. Nothing will make the marker’s eyes roll back faster than exaggerated or unfounded claims. Be humble but firm in your claim-making.
- Use clear and simple language that can be easily understood by an intelligent layman. Remember that not every reader will be an expert in your field, so it’s important to make your writing accessible. Bear in mind that no one knows your research better than you do, so it’s important to spell things out clearly for readers.
Hopefully, this post has given you some direction and confidence to take on the conclusion chapter of your dissertation or thesis with confidence. If you’re still feeling a little shaky and need a helping hand, consider booking a free initial consultation with a friendly Grad Coach to discuss how we can help you with hands-on, private coaching.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

17 Comments
Really you team are doing great!
Your guide on writing the concluding chapter of a research is really informative especially to the beginners who really do not know where to start. Im now ready to start. Keep it up guys
Really your team are doing great!
Very helpful guidelines, timely saved. Thanks so much for the tips.
This post was very helpful and informative. Thank you team.
A very enjoyable, understandable and crisp presentation on how to write a conclusion chapter. I thoroughly enjoyed it. Thanks Jenna.
This was a very helpful article which really gave me practical pointers for my concluding chapter. Keep doing what you are doing! It meant a lot to me to be able to have this guide. Thank you so much.
Nice content dealing with the conclusion chapter, it’s a relief after the streneous task of completing discussion part.Thanks for valuable guidance
Thanks for your guidance
I get all my doubts clarified regarding the conclusion chapter. It’s really amazing. Many thanks.
Very helpful tips. Thanks so much for the guidance
Thank you very much for this piece. It offers a very helpful starting point in writing the conclusion chapter of my thesis.
It’s awesome! Most useful and timely too. Thanks a million times
Bundle of thanks for your guidance. It was greatly helpful.
Wonderful, clear, practical guidance. So grateful to read this as I conclude my research. Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Training videos | Faqs

Academic Phrases for Writing Results & Discussion Sections of a Research Paper
Overview | Abstract | Introduction | Literature Review | Materials & Methods | Results & Discussion | Conclusion & Future Work | Acknowledgements & Appendix
The results and discussion sections are one of the challenging sections to write. It is important to plan this section carefully as it may contain a large amount of scientific data that needs to be presented in a clear and concise fashion. The purpose of a Results section is to present the key results of your research. Results and discussions can either be combined into one section or organized as separate sections depending on the requirements of the journal to which you are submitting your research paper. Use subsections and subheadings to improve readability and clarity. Number all tables and figures with descriptive titles. Present your results as figures and tables and point the reader to relevant items while discussing the results. This section should highlight significant or interesting findings along with P values for statistical tests. Be sure to include negative results and highlight potential limitations of the paper. You will be criticised by the reviewers if you don’t discuss the shortcomings of your research. This often makes up for a great discussion section, so do not be afraid to highlight them.
The results and discussion section of your research paper should include the following:
- Comparison with prior studies
- Limitations of your work
- Casual arguments
- Speculations
- Deductive arguments
1. Findings
From the short review above, key findings emerge: __ We describe the results of __, which show __ This suggests that __ We showed that __ Our findings on __ at least hint that __ This is an important finding in the understanding of the __ The present study confirmed the findings about __ Another promising finding was that __ Our results demonstrated that __ This result highlights that little is known about the __ A further novel finding is that __ Together, the present findings confirm __ The implications of these findings are discussed in __ The results demonstrate two things. First, __. Second, __ The results of the experiment found clear support for the __ This analysis found evidence for __ Planned comparisons revealed that __ Our results casts a new light on __ This section summarises the findings and contributions made. It performs well, giving good results. This gives clearly better results than __ The results confirm that this a good choice for __ From the results, it is clear that __ In this section, we will illustrate some experimental results. This delivers significantly better results due to __ The result now provides evidence to __ It leads to good results, even if the improvement is negligible. This yields increasingly good results on data. The result of this analysis is then compared with the __ The applicability of these new results are then tested on __ This is important to correctly interpret the results. The results are substantially better than __ The results lead to similar conclusion where __ Superior results are seen for __ From these results it is clear that __ Extensive results carried out show that this method improves __ We obtain good results with this simple method. However, even better results are achieved when using our algorithm. It is worth discussing these interesting facts revealed by the results of __ Overall, our method was the one that obtained the most robust results. Slightly superior results are achieved with our algorithm. The result is equal to or better than a result that is currently accepted.
2. Comparison with prior studies
The results demonstrated in this chapter match state of the art methods. Here we compare the results of the proposed method with those of the traditional methods. These results go beyond previous reports, showing that __ In line with previous studies __ This result ties well with previous studies wherein __ Contrary to the findings of __ we did not find __ They have demonstrated that __ Others have shown that __ improves __ By comparing the results from __, we hope to determine __ However, in line with the ideas of __, it can be concluded that __ When comparing our results to those of older studies, it must be pointed out that __ We have verified that using __ produces similar results Overall these findings are in accordance with findings reported by __ Even though we did not replicate the previously reported __, our results suggest that __ A similar conclusion was reached by __ However, when comparing our results to those of older studies, it must be pointed out __ This is consistent with what has been found in previous __ A similar pattern of results was obtained in __ The findings are directly in line with previous findings These basic findings are consistent with research showing that __ Other results were broadly in line with __
3. Limitations of your work
Because of the lack of __ we decided to not investigate __ One concern about the findings of __ was that __ Because of this potential limitation, we treat __ The limitations of the present studies naturally include __ Regarding the limitations of __, it could be argued that __ Another limitation of this __ This limitation is apparent in many __ Another limitation in __ involves the issue of __ The main limitation is the lack of __ One limitation is found in this case. One limitation of these methods however is that they __ It presents some limitations such as __ Although widely accepted, it suffers from some limitations due to __ An apparent limitation of the method is __ There are several limitations to this approach. One limitation of our implementation is that it is __ A major source of limitation is due to __ The approach utilised suffers from the limitation that __ The limitations are becoming clear __ It suffers from the same limitations associated with a __
4. Casual arguments
A popular explanation of __ is that __ It is by now generally accepted that __ A popular explanation is that __ As it is not generally agreed that __ These are very small and difficult to observe. It is important to highlight the fact that __ It is notable that __ An important question associated with __ is __ This did not impair the __ This is important because there is __ This implies that __ is associated with __ This is indicative for lack of __ This will not be biased by __ There were also some important differences in __ It is interesting to note that, __ It is unlikely that __ This may alter or improve aspects of __ In contrast, this makes it possible to __ This is particularly important when investigating __ This has been used to successfully account for __ This introduces a possible confound in __ This was included to verify that __
5. Speculations
However, we acknowledge that there are considerable discussions among researchers as to __ We speculate that this might be due to __ There are reasons to doubt this explanation of __ It remains unclear to which degree __ are attributed to __ However, __ does seem to improve __ This does seem to depend on __ It is important to note, that the present evidence relies on __ The results show that __ does not seem to impact the __ However, the extent to which it is possible to __ is unknown Alternatively, it could simply mean that __ It is difficult to explain such results within the context of __ It is unclear whether this is a suitable for __ This appears to be a case of __ From this standpoint, __ can be considered as __ To date, __remain unknown Under certain assumptions, this can be construed as __ Because of this potential limitation, we treat __ In addition, several questions remain unanswered. At this stage of understanding, we believe__ Therefore, it remains unclear whether __ This may explain why __
6. Deductive arguments
A difference between these __ can only be attributable to __ Nonetheless, we believe that it is well justified to __ This may raise concerns about __ which can be addressed by __ As discussed, this is due to the fact that __ Results demonstrate that this is not necessarily true. These findings support the notion that __ is not influenced by __ This may be the reason why we did not find __ In order to test whether this is equivalent across __, we __ Therefore, __ can be considered to be equivalent for __
Similar Posts

How to Write a Research Paper? A Beginners Guide with Useful Academic Phrases
This blog explains how to write a research paper and provides writing ideas in the form of academic phrases.

Academic Phrases for Writing Abstract Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to the abstract section. An abstract is a self-contained and short synopsis that describes a larger work.

Useful Phrases and Sentences for Academic & Research Paper Writing
In this blog, we explain various sections of a research paper and give you an overview of what these sections should contain.

Academic Phrases for Writing Literature Review Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to literature review such as summary of previous literature, research gap and research questions.

Academic Phrases for Writing Methods Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to materials and methods such as experimental setup, data collection & analysis, and statistical testing.

Academic Phrases for Writing Acknowledgements & Appendix Sections of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to thanking colleagues, acknowledging funders and writing the appendix section.
32 Comments
Awesome vocab given, I am really thankful. keep it up!
Why didn’t I find this earlier? Thank you very much! Bless your soul!
thank you!! very useful!!!
Thank you, thank you thank you!!
I’m currently writing up my PhD thesis and as a non-native English speaker, I find this site extremely useful. Thanks for making it!
Very ve4y resourceful..well done Sam
Plesse add me to your mailing list Email: [email protected]
Hi, would like to clarify if that is “casual” or “causal”? Thanks!
Hi there, it should read “causal.”
Thanx for this. so helpful!
Very helpful. Thanks
thank you so much
- Pingback: Scholarly Paraphrasing Tool and Essay Rewriter for Rewording Academic Papers - Ref-N-Write: Scientific Research Paper Writing Software Tool - Improve Academic English Writing Skills
thankyouuuuuu
thank you very much
wow thanks for the help!!
Quite interesting! Thanks a lot!
This is ammmaazzinggg, too bad im in my last year of university this is very handy!!!
Extremely Useful. Thank-you so much.
This is an excellent collection of phrases for effective writing
Thank you so much, it has been helpful.
I found it extremely important!!!
It is a precise, brief and important guides;
It is a very important which gives a guide;
It is a very important guiding explanation for writing result and discussion;
It is a very important guiding academic phrases for writing;
thank you so much.I was in need of this.
- Pingback: Research Paper Structure – Main Sections and Parts of a Research Paper
Thank you so much!!! They are so helpful!
thank its very important.
This is timely, I needed it. Thanks
This is very helpful. Thanks.
You saved my Bachoelor thesis! Huge thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 91 Share Facebook
- 68 Share Twitter
- 53 Share LinkedIn
- 0.1K Share Email
Dissertation surveys: Questions, examples, and best practices
Collect data for your dissertation with little effort and great results.
Dissertation surveys are one of the most powerful tools to get valuable insights and data for the culmination of your research. However, it’s one of the most stressful and time-consuming tasks you need to do. You want useful data from a representative sample that you can analyze and present as part of your dissertation. At SurveyPlanet, we’re committed to making it as easy and stress-free as possible to get the most out of your study.
With an intuitive and user-friendly design, our templates and premade questions can be your allies while creating a survey for your dissertation. Explore all the options we offer by simply signing up for an account—and leave the stress behind.
How to write dissertation survey questions
The first thing to do is to figure out which group of people is relevant for your study. When you know that, you’ll also be able to adjust the survey and write questions that will get the best results.
The next step is to write down the goal of your research and define it properly. Online surveys are one of the best and most inexpensive ways to reach respondents and achieve your goal.
Before writing any questions, think about how you’ll analyze the results. You don’t want to write and distribute a survey without keeping how to report your findings in mind. When your thesis questionnaire is out in the real world, it’s too late to conclude that the data you’re collecting might not be any good for assessment. Because of that, you need to create questions with analysis in mind.
You may find our five survey analysis tips for better insights helpful. We recommend reading it before analyzing your results.
Once you understand the parameters of your representative sample, goals, and analysis methodology, then it’s time to think about distribution. Survey distribution may feel like a headache, but you’ll find that many people will gladly participate.
Find communities where your targeted group hangs out and share the link to your survey with them. If you’re not sure how large your research sample should be, gauge it easily with the survey sample size calculator.
Need help with writing survey questions? Read our guide on well-written examples of good survey questions .
Dissertation survey examples
Whatever field you’re studying, we’re sure the following questions will prove useful when crafting your own.
At the beginning of every questionnaire, inform respondents of your topic and provide a consent form. After that, start with questions like:
- Please select your gender:
- What is the highest educational level you’ve completed?
- High school
- Bachelor degree
- Master’s degree
- On a scale of 1-7, how satisfied are you with your current job?
- Please rate the following statements:
- I always wait for people to text me first.
- Strongly Disagree
- Neither agree nor disagree
- Strongly agree
- My friends always complain that I never invite them anywhere.
- I prefer spending time alone.
- Rank which personality traits are most important when choosing a partner. Rank 1 - 7, where 1 is the most and 7 is the least important.
- Flexibility
- Independence
- How openly do you share feelings with your partner?
- Almost never
- Almost always
- In the last two weeks, how often did you experience headaches?
Dissertation survey best practices
There are a lot of DOs and DON’Ts you should keep in mind when conducting any survey, especially for your dissertation. To get valuable data from your targeted sample, follow these best practices:
Use the consent form.
The consent form is a must when distributing a research questionnaire. A respondent has to know how you’ll use their answers and that the survey is anonymous.
Avoid leading and double-barreled questions
Leading and double-barreled questions will produce inconclusive results—and you don’t want that. A question such as: “Do you like to watch TV and play video games?” is double-barreled because it has two variables.
On the other hand, leading questions such as “On a scale from 1-10 how would you rate the amazing experience with our customer support?” influence respondents to answer in a certain way, which produces biased results.
Use easy and straightforward language and questions
Don’t use terms and professional jargon that respondents won’t understand. Take into consideration their educational level and demographic traits and use easy-to-understand language when writing questions.
Mix close-ended and open-ended questions
Too many open-ended questions will annoy respondents. Also, analyzing the responses is harder. Use more close-ended questions for the best results and only a few open-ended ones.
Strategically use different types of responses
Likert scale, multiple-choice, and ranking are all types of responses you can use to collect data. But some response types suit some questions better. Make sure to strategically fit questions with response types.
Ensure that data privacy is a priority
Make sure to use an online survey tool that has SSL encryption and secure data processing. You don’t want to risk all your hard work going to waste because of poorly managed data security. Ensure that you only collect data that’s relevant to your dissertation survey and leave out any questions (such as name) that can identify the respondents.
Create dissertation questionnaires with SurveyPlanet
Overall, survey methodology is a great way to find research participants for your research study. You have all the tools required for creating a survey for a dissertation with SurveyPlanet—you only need to sign up . With powerful features like question branching, custom formatting, multiple languages, image choice questions, and easy export you will find everything needed to create, distribute, and analyze a dissertation survey.
Happy data gathering!
Sign up now
Free unlimited surveys, questions and responses.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example. Other interesting articles.
Step 1: Restate your research problem and research questions. The first step in writing up your discussion chapter is to remind your reader of your research problem, as well as your research aim (s) and research questions. If you have hypotheses, you can also briefly mention these.
Here are some examples of how to present the summary of your findings; "The data suggests that", "The results confirm that", "The analysis indicates that", "The research shows a relationship between", etc. 2. Interpretations of Results. Your audience will expect you to provide meanings of the results, although they might seem ...
In other words, the results chapter presents and describes the data, while the discussion chapter interprets the data. Let's look at an example. In your results chapter, you may have a plot that shows how respondents to a survey responded: the numbers of respondents per category, for instance. You may also state whether this supports a ...
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with ...
This template covers all the core components required in the discussion/analysis chapter of a typical dissertation or thesis, including: The purpose of each section is explained in plain language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. The template also includes practical examples to help you understand exactly what ...
Summarise your results in the text, drawing on the figures and tables to illustrate your points. The text and figures should be complementary, not repeat the same information. You should refer to every table or figure in the text. Any that you don't feel the need to refer to can safely be moved to an appendix, or even removed.
Here are a few best practices: Your results should always be written in the past tense. While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analysed, it should be written as concisely as possible. Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions.
Guide contents. As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common conventions of the results and discussion chapters, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows: The Difference - Breaks down the distinctions between the results and discussion chapters.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
A master's dissertation is typically 12,000-50,000 words; A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000-100,000 words; However, none of these are strict guidelines - your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation ...
Let's go through all steps to writing a discussion in a dissertation, and share our best examples from academic papers. 1. Remind Your Research Questions & Objectives. Writing the discussion chapter of a dissertation is not a big deal if you understand its aim and each component in a text structure.
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it: Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods ). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and ...
if you write a scientific dissertation, or anyway using quantitative methods, you will have some objective results that you will present in the Results chapter. You will then interpret the results in the Discussion chapter. B) More common for qualitative methods. - Analysis chapter. This can have more descriptive/thematic subheadings.
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarise your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout.
1. Begin by discussing the research question and talking about whether it was answered in the research paper based on the results. 2. Highlight any unexpected and/or exciting results and link them to the research question. 3. Point out some previous studies and draw comparisons on how your study is different. 4.
In general, a good dissertation conclusion chapter should achieve the following: Summarise the key findings of the study. Explicitly answer the research question (s) and address the research aims. Inform the reader of the study's main contributions. Discuss any limitations or weaknesses of the study.
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to results and discussion sections such as findings, limitations, arguments, and comparison to previous studies. The results and discussion sections are one of the challenging sections to write. It is important to plan this section carefully as it may contain a large amount of scientific data that needs to be presented in a clear and concise fashion.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Dissertation survey examples. Whatever field you're studying, we're sure the following questions will prove useful when crafting your own. At the beginning of every questionnaire, inform respondents of your topic and provide a consent form. After that, start with questions like: